Probabilistic linguistic TODIM approach for multiple attribute decision-making
|
|
|
- Dominic Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 DOI 0.007/s ORIGINAL PAPER Prbabilistic liguistic TODIM apprach fr multiple attribute decisi-makig Peide Liu Xili Yu Received: 9 April 07 / Accepted: 5 July 07 / Published lie: 0 August 07 Ó Spriger Iteratial Publishig AG 07 Abstract Prbabilistic liguistic term sets (PLTSs) are a effective tl t express prefereces with differet weights fr differet liguistic terms, ad the TODIM methd is based prspect thery ad culd csider the decisi maker s cgitive behavir. I this paper, we exted the TODIM t slve the multi-attribute decisi-makig (MADM) prblems with PLTSs. First f all, the defiiti, peratis, cmparative methd, ad deviati degrees f PLTSs are itrduced; a ew stadardizati methd fr the attribute values was prpsed with respect t the situati i which the prbabilistic sum fr all liguistic terms is less tha. The, the bjective weights fr criteria ca be btaied by ifrmati etrpy thery ad the steps f the exteded TODIM methd fr PLTSs are prpsed. Fially, a example is t verify the develped apprach. Keywrds MADM PLTSs TODIM methd Itrducti I actual decisi-makig, there are a large umber f qualitative criteria which are hardly evaluated by accurate umerical values. Hece, hw t make the assessmet f alteratives precisely is pivtal. Hwever, fr the cmplex decisi-makig prblems, decisi makers usually prvide their piis by atural laguage, such as gd, fair, pr, ad ther similar liguistic terms (LTs) & Peide Liu Peide.liu@gmail.cm Schl f Maagemet Sciece ad Egieerig, Shadg Uiversity f Fiace ad Ecmics, Jia 5004, Shadg, Chia (Wu ad Xu 06). Nw, decisi-makig based LTs has becme a imprtat research aspect i the field f decisi aalysis (Xu ad Wag 06). Fr example, Xu (007) gave the gal prgrammig methd with LTs fr MADM prblems. Xu ad Wag (07) slved grup decisi-makig (GDM) prblem with multi-graularity liguistic mdel. Medel (06) prpsed three appraches t sythesizig a iterval type- fuzzy set mdel f LTs. I the traditial decisi-makig methds based LTs, the DMs ca express their prefereces ly by e LT. Hwever, smetimes, it is difficult t depict cmplex qualitative ifrmati ly by e LT. Fr istace, a DM may thik that it may be very gd, gd, r a little gd fr e bject, but he/she is t sure hw gd it is. I this situati, Rdriguez et al. (0) prpsed hesitat fuzzy LT sets (HFLTSs), which have several pssible LTs. The, Beg ad Rashid (0) ad Wei et al. (04) prpsed sme aggregati peratrs based HFLTSs. Zhu ad Xu (04) prpsed sme preferece relatis (HFLPRs) fr HFLTSs. Furthermre, Beg ad Rashid (0) prpsed a exteded TOPSIS methd fr the HFLTSs. Dg et al. (05) ad Rdríguez et al. (0) prpsed sme GDM methd with HFLTSs. Wag (05) prpsed the exteded HFLTSs (EHFLTSs) fr the ctiuus LTs. Liu ad Rdriguez (04) further develped the fuzzy evelpes f HFLTSs ad applied them t MADM prblems. Hwever, all pssible LTs give by the DMs i HFLTSs have the same imprtace. Obviusly, this is t realistic. I real decisi-makig, the DMs may prefer sme pssible LTs ad give sme differet imprtace degrees. I ther wrds, we ca give sme pssible LTs ad the give their imprtace degrees fr evaluatig a bject (Liu ad Rdríguez 04). This imprtace degree ca be regarded as prbabilistic distributi (Wu ad Xu 06), belief
2 4 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 degree (Yag 00; Yag ad Xu 00), ad s. T better depict such a situati, Pag et al. (06) prpsed the prbabilistic LT sets (PLTSs) which ca express differet imprtace degrees r weights f all the pssible LTs. Obviusly, PLTSs have the flexibility ad richess i expressig cmplex fuzzy liguistic ifrmati. T d a reasable ad feasible decisi-makig, the decisi-makig methds are w essetial ad a lt f effrts have bee made i the past few decades, such as the TOPSIS (Liu 009), the VIKOR (Chatterjee ad Samarjit 07), the GRA (Liu ad Liu 00), the PRO- METHEE (Liu ad Gua 009), the ELECTRE (Liu ad Zhag 0; Ry ad Bertier 97),ads.Nw, these methds have bee exteded fr differet attribute values, such as fuzzy umbers, LTs, ad s. Hwever, because the MADM prblems have becmig icreasigly cmplicated ver the years, there is a bvius shrtcmig i the existig methds, which suppses that the DMs are cmpletely ratial. Nw, may excellet researches ivlvig behavir experimets (Kahema ad Tversky 979; Tversky ad Kahema 99) have shw that the DMs are buded ratial i decisimakig prcess, ad the psychlgy ad behavir f the DMs are imprtat factrs which ca bviusly ifluece decisi results. Hece, Gmes ad Lima first preseted the TODIM i 99 (Gmes ad Lima 99), which is a valuable MADM methd csiderig the DMs psychlgy ad behavir based prspect thery (PT) (Kahema ad Tversky 979), ad it has bee applied t sme decisi-makig prblems (Pag et al. 06). Mrever, its sme ew extesis gave bee develped. Such as Lurezutti ad Krhlig (0) preseted a IF- RTODIM fr ituitiistic fuzzy umbers (IFNs). Wag et al. (06) prpsed a likelihd fucti f HFLTSs embedded it TODIM. Re et al. (06) develped a Pythagrea fuzzy TODIM apprach t MADM prblems. Obviusly, the TODIM methd is a valuable ad imprtat MADM tl csiderig the DMs psychlgy ad behavir, ad its extesis are als very effective i slvig the MADM prblems fr differet fuzzy evirmets, but there is research abut the TODIM methd fr PLTSs i the existig researches. Csequetly, csiderig the DMs psychlgy ad behavir, it will be a valuable research tpic abut hw t slve the MADM prblem with PLTSs. I additi, due t the icreasig cmplexity f the decisi-makig evirmet, it is usually difficult fr DMs t give the weight evaluati ifrmati cmpletely. Therefre, it is very ecessary t develp a methd t btai the bjective weight f each attribute ad the t prpse a exteded TODIM fr PLTSs, s that the mre cmprehesive ad reasable decisi ca be made i a itricate situati. Therefre, the aims f this paper are () t prpse the exteded TODIM methd t prcess the multi-attribute grup decisi-makig (MAGDM) prblems with PLTSs; () t explre the rmalizati methd f PLTSs with respect t the situati i which the prbabilistic sum fr all liguistic terms is less tha ; () t develp a weight determiati methd based etrpy; (4) t shw the effectiveess ad advatages f the prpsed apprach. T achieve this gal, the rest is itrduced as fllws: sme basic ccepts f the LTSs, HFLTSs, ad PLTSs, ad the TODIM were briefly itrduced i Sect.. Secti prpses the exteded TODIM t prcess PLTSs. I Sect. 4, a example is give t demstrate the validity ad advatages f ur methd. I Sect. 5, we cclude this paper. Prelimiaries. The LTSs ad HFLTSs The LTSs, which are fiite ad rdered, are regularly used t express DMs piis fr attributes f MADM prblems, ad they ca be defied as fllws (Herrera et al. 995): S ¼ fs a ja ¼ 0; ;...; sg ðþ where S a is called a liguistic variable; s is a psitive iteger. LTSs ca meet: () S a S b ; ifa [ b; () The egati peratr is: egðs a Þ ¼ S b, such that aþb ¼ s: T relieve the lss f ifrmati, a ctiuus LTS is btaied frm its discrete versi by Xu (0): S ¼ fs a ja ½0; sšg: ðþ Let S a ; S b S be ay tw LTs, ad the based the LTS S, the perati S a ad S b ca be defied by (Xu ad Wag 07): k S a k S b ¼ S k aþk b; ðþ where k ; k 0: Furthermre, we gave the defiiti f HFLTSs (Rdriguez et al. 0). Defiiti (Rdriguez et al. 0) Suppse that S ¼ S 0 ; S ;...; S g is a LTS, ad the, a HFLTS bs is defied as a subset f LTs S.
3 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 5 Example Let S be the fllwig LTS: S ¼ fs 0 ¼ extremely lw, S ¼ very lw, S ¼ lw, S ¼ slightly lw, S 4 ¼ fair, S 5 = slightly high, S 6 ¼ high, S 7 ¼ very high, S 8 = extremely highg: The, we give tw examples abut HFLTSs: b ¼ fs = very lw, S = lwg; b ¼ fs 5 = slightly high, S 6 = high, S 7 = very highg: Simplifyig the results abve, we get: b ¼ fs ; S g; b ¼ fs 5 ; S 6 ; S 7 g: Furthermre, Zhu ad Xu (04) gave a peratial defiiti f HFLTS. Defiiti (Zhu ad Xu 04) Suppse that b a ¼ b l a jl ¼ ; ;...;#b a ad bb ¼ b l b jl ¼ ; ;...;#b b are ay tw HFLTSs, such that #b a ¼ #b b, the b q a bq b ¼[ b qðþ l b qðþ l ð4þ b qðþ l ðþ kb q a ¼[ b qðþ l a where b q a ðþ l a b l a b l a ;bq l b l b b kb q a ðþ l a b ; k 0 ð5þ ad b qðþ l b are the lth LTs i b a ad b b, respectively, #b a ad #b b are the umbers f the LTs i b a ad b b, respectively.. PLTSs With respect t the shrtcmig f HFLTSs which cat express the prbability f pssible LTs, Pag et al. (06) prpsed PLTSs. Defiiti (Pag et al. 06) Suppse that S ¼ fs 0 ; S ;...; S s g is a LTS, ad the LTðpÞ ( X ) ¼ LT ðkþ jlt ðkþ S; 0; k ¼ ; ;...;; ð6þ is defied a PLTS, where LT ðkþ is the LT LT ðkþ with the prbability, ad is the umber f all differet LTs i LTðpÞ. We ca te that if P k¼ ¼, the the PLTS is with cmplete prbabilistic ifrmati; if P k¼ \, the the PLTS is with partial prbabilistic ifrmati; if P k¼ ¼ 0, the the PLTS is with cmpletely ukw prbabilistic ifrmati. k¼ Defiiti 4 (Pag et al. 06) Suppse that LTðpÞ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...; is a PLTS, ad r ðkþ is the subscript f LT LT ðkþ. If LT ðkþ ðk ¼ ; ;...;Þ are raked accrdig t the values f r ðkþ ðk ¼ ; ;...;Þ i descedig rder, the LTðpÞ is called a rdered PLTS, Example Suppse that the LTS S is the set used i Example, ad the, it ca be deted by the PLTS LTðpÞ ¼fS 4 ð0:þ; S 5 ð0:65þ; S 6 ð0:þg. We ca als calculate r ðkþ ðk ¼ ; ; Þ, ad get 4 0: ¼ 0:4; 5 0:65 ¼ :5; 6 0: ¼ :. Rerderig the LTs i LTðpÞ i descedig rder, we have LTðpÞ ¼fS 5 ð0:65þ; S 6 ð0:þ; S 4 ð0:þg: I the fllwig, Pag et al. (06) cme up with sme basic peratis: Defiiti 5 (Pag et al. 06) Let LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ be tw rdered PLTSs, LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþg ad LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþg. The LT ðpþlt ðpþ ¼[ ðkþ LT LT ðpþ;lt ðkþ LT ðpþ ð7þ LTðkÞ LTðkÞ LT ðpþlt ðpþ ¼[ ðkþ LT LT ðpþ;lt ðkþ ( LT ðpþ ðkþ p ) ðkþ LT ðkþ p LT ðkþ ð8þ where LT ðkþ ad LT ðkþ are the k th LTs i LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ, respectively, ad are the prbabilities f the k th LTs i LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ, respectively. kltðpþ ¼[ LT LTðpÞk LT ðkþ ; k 0 ð9þ ðkþ kp ðltðpþþ k ðkþ ¼[ LT ðkþ LTðpÞ LT ðkþ : ð0þ. The cmparis fr tw PLTSs First, we itrduced the scre f PLTS which is defied by Pag et al. (06) as fllws. Defiiti 6 (Pag et al. 06) Let LTðpÞ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...; be a PLTS, ad r ðkþ is the subscript f LT LT ðkþ. The scre f LTðpÞ is give as fllws:
4 6 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 ELTðpÞ ð Þ ¼ S a ðþ where a ¼ P, P k¼ r ðkþ k¼ Fr ay tw PLTSs LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ, if ELT ð ðpþþ\eðlt ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ LT ðpþ; if ELT ð ðpþþ[ ELT ð ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ LT ðpþ. Hwever, if ELT ð ðpþþ ¼ ELT ð ðpþþ, the tw PLTSs cat be cmpared by their scres. T slve this prblem, Pag et al. (06) further defied the deviati degree f a PLTS as fllws: Fr cveiece, let M ¼ f; ;...; mg ad N ¼ f; ;...; g. Step Idetify the decisi matrix X ¼ x ij m, where x ij is the jth attribute value with respect t the ith alterative, ad the rmalize X ¼ x ij m it G ¼ g ij m, ad x ij ad g ij are all crisp umbers, i M; j N. Step Calculate the relative weight w jr f the attribute C j t the referece attribute C r by: Defiiti 7 (Pag et al. 06) Suppse that LTðpÞ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...; is a PLTS, ad r ðkþ is the subscript f LT L ðkþ, ad ELTðpÞ ð Þ ¼ S a, where a ¼ P. P k¼ r ðkþ k¼. The deviati f LTðpÞ is: rðltðpþþ ¼ X k¼! =, X r ðkþ a k¼ ðþ Fr tw PLTSs LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ, if ELT ð ðpþþ ¼ ELT ð ðpþþ ad r ðlt ðpþþ[ r ðlt ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ LT ðpþ; ad if r ðlt ðpþþ ¼ r ðlt ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ is idifferet t L ðpþ, deted by LT ðpþlt ðpþ. Therefre, there is the fllwig defiiti abut cmparis fr tw PLTSs. Defiiti 8 (Pag et al. 06) Give tw PLTSs LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ, the If ELT ð ðpþþ[ ELT ð ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ LT ðpþ. else if ELT ð ðpþþ ¼ ELT ð ðpþþ, the (i) If rðlt ðpþþ[ rðlt ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ LT ðpþ. else if rðlt ðpþþ\rðlt ðpþþ, the LT ðpþ LT ðpþ. Defiiti 9 (Pag et al. 06) Let LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþ be ay tw PLTSs, #LT ðpþ ¼#LT ðpþ. The, the distace betwee LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ is defied as: vffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi, u#lt X ðpþ dlt ð ðpþ; LT ðpþþ ¼ t rðkþ rðkþ #LT ðpþ: k¼.4 The traditial TODIM methd ðþ The TODIM is prpsed based prspect thery (Kahema ad Tversky 979), ad its mai advatage is the capability f capturig the DMs behavir. The steps f the traditial TODIM apprach are shw as fllws (Gmes ad Lima 99): Step Step 4 Step 5 w jr ¼ w j w r ; r; j N; ð4þ where w j is the weight f the attribute C j ad w r ¼ max w j jj N. Obtai the dmiace degree f alterative x i ver the alterative x t usig the fllwig expressi: # ðx i ; x t Þ ¼ X j¼ where / j ðx i ; x t Þ; 8ði; tþ; ð5þ / j ðx i ; x t Þ 8 qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi w jr ðg ij g tj Þ= P j¼ w jr; if g ij g tj [ 0; >< ¼ 0 if g ij g tj ¼ 0; rffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi X h w >: j¼ jr g ij g tj =wjr if g ij g tj \0; ð6þ The fucti / j ðx i ; x t Þ is the ctributi f the attribute C j t # ðx i ; x t Þ.Theh is the DM atteuati parameter abut the lsses which is explaied by prspect thery (Kahema ad Tversky 979). I Eq. (6), three cases ca ccur: () if g ij g tj [ 0, the / j ðx i ; x t Þ represets a gai; () if g ij g tj ¼ 0, the / j ðx i ; x t Þ represets a il; () if g ij g tj \0, the / j ðx i ; x t Þ represets a lss. Get the verall prspect value f the alterative x i by P m t¼ dðx i Þ¼ # x P ð i;x t Þmi m i t¼ # ð x i;x t Þ P max m i t¼ # x P ð i;x t Þ m mii t¼ # x ; i M: ð i;x t Þ ð7þ Srt the alteratives by their verall prspect values dðx i Þði MÞ.
5 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 7 The exteded TODIM methd fr MADM prblems with PLTSs. Descripti f the MADM prblems Fr a MADM prblem with PLTSs, let x ¼ fx ; x ;...; x m g be a fiite set f alteratives ad C ¼ fc ; C ;...; C g be a set f attributes. Based the LTS S ¼ fs a ja ¼ 0; ;...; sg, the DMs evaluate the alteratives x i ði ¼ ; ;...; mþ fr the attributes C j ðj ¼ ; ;...; Þ, ad give the evaluati results by PLTSs LT ij ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ ij ij jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ij ðpþ, where LT ðkþ ij k ¼ ; ;...;#LT ij ðpþ are LTs with the crrespdig prbability ðkþ ij k ¼ ; ;...;#LT ij ðpþ, p ij [ 0, k ¼ ; ;...;#LT ij ðpþ, ad P #LT ij ðpþ k¼ ij. All the PLTSs LT ij ðpþði ¼ ; ;...; m; j ¼ ; ;...; Þ are used t build the decisi matrix R ¼ LT ij ðpþ, ad the gal is m t select the best alterative.. The rmalizati f PLTSs As metied i Sect.., there is existig partial prbabilistic ifrmati whe P k¼ \. T estimate the ukw part f prbabilistic ifrmati, we csider ctiuus re-distributi f the missig prbability by a recursive methd fr a PLTS LTðpÞ with P k¼ \. It will guaratee the uchaged preferece fr each expert by this way, ad the, the assciated steps are shw as fllwig: Fr cveiece, we use l t express the prbability f the LT L ðkþ after the lth iterati, ad use l l t express the igrace f prbabilistic ifrmati after the lth iterati. Let P k¼ ¼ a\, we ca first btai the assciated prbability f LT ðkþ ðk ¼ ; ;...;Þ, te that as ¼ þ ð aþ, the the ucertai prbability ca be calculated by f ¼ P ¼ P k¼ k¼ ð aþ. Next, we repeat the abve prcess i the fllwig: ¼ þ f ¼ ðþf Þ; f ¼ X ¼ X k¼ ¼ ðþf Þ X k¼ k¼ ðþf Þ ¼ ðþf Þð f Þ ¼ ðf Þ ; ¼ þ f ¼ þðf Þ ; f ¼ X ¼ X k¼ ðþf Þ X k¼ ¼ ðf Þ ¼ ðf Þ 4 ; k¼ ¼ þf ðþf Þ ¼ ð Þð f Þ 4 ¼ þ f ¼ þðf Þ 4 ; f 4 ¼ X 4 ¼ X k¼ ðþf Þ X k¼ k¼ ðþf Þ ¼ ¼ ðþf Þð f Þ ¼ ðf Þ ¼ ðf Þ 8 ; ¼ þ SðkÞ f ¼ þ ð f Þ Therefre, we trasfrm precedig frmula i the fllwig frm: ¼ ðþf Þ; ¼ ðþf Þ þðf Þ ; ¼ þf þ f ð Þ þðf Þ 4 ¼ ðþf Þ þðf Þ þðf Þ 4 ¼ þf þðf Þ þðf Þ þðf Þ 4 ¼ þf þðf Þ þðf Þ þðf Þ 4 þðf Þ 5 þðf Þ 6 þðf Þ 7 ; S ðkþ ¼ ðþf Þ þðf Þ þðf Þ 4 þðf ¼ þf þðf Þ þðf Þ þðf Þ 4 þðf Þ 5 þðf Þ 6 þðf Þ 7 þþðf Þ ¼ ð f Þ : f Because 0\f \; lim! ¼ lim! ð f Þ ¼ SðkÞ f ¼ P k¼ ¼ f P k¼ p : ðkþ Þ Frm the curse f calculability, we ca cclude the rmalized frm fr a PLTS LTðpÞ with P k¼ \ by ;
6 8 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 LT 0 ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ p 0ðkÞ jk ¼ ; ;...; ð8þ where p 0ðkÞ ¼ = P k¼ 0pt P k¼. I additi, smetimes, the umbers f LTs i PLTSs are usually differet, it is ecessary t stadardize the cardiality f a PLTS fr the cveiece f cmputig. Defiiti 0 (Pag et al. 06) Let LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþ be ay tw PLTSs, ad let #LT ðpþ ad #LT ðpþ be the umbers f LTs i LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ, respectively. If #LT ðpþ [ #LT ðpþ, the the #LT ðpþ#lt ðpþ LTs eed t be added t LT ðpþ ad make the umbers f LTs i LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ equal. The added LTs are the smallest es i LT ðpþ, ad their prbabilities shuld be zer. Let LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ ¼ LT ðkþ jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ðpþ be ay tw PLTSs, ad the, the rmalizati ca be perfrmed as fllws: () If P k¼ calculate LTi 0 \, the by the frmula (8), we ðpþ; i ¼ ;. () If #LT ðpþ 6¼ #LT ðpþ, the accrdig t Defiiti 0, we add sme elemets t the e with the smaller umber f elemets. i Example Let LT ðpþ ¼fS ð0:0þ; S ð0:0þ; S ð0:0þg ad LT ðpþ ¼fS ð0:60þ; S ð0:40þg be tw PLTSs, ad the: () accrdig t frmula (8), LT 0 ðpþ ¼ f S ð0:þ; S ð0:þ; S ð0:þg; () sice #LT ðpþ\#lt ðpþ, the we add the LT S t LT ðpþ ad make the umbers f LTs i LT ðpþ ad LT ðpþ idetical, ad thus, we have LT 0 ðpþ ¼ f S ð0:6þ; S ð0:4þ; S ð0þg.. Determiig bjective weights based etrpy measures It is imprtat t determie a reasable weight fr each attribute i the curse f decisi-makig. Because the DMs are usually iflueced by their kwledge structure, persal bias, ad familiarity with the decisi alteratives, it is ecessary t csider the MADM prblem with cmpletely ukw weights f criteria, ad we eed develp a weight determiati methd based etrpy uder prbabilistic liguistic evirmet. The steps are shw as fllws. First, trasfrmed decisi matrix R ¼ LT ij ðpþ m it Z ¼ LP ij ðpþ m, where LT ijðpþ ¼ P. #LT ij ðpþ k¼ r ðkþ #LT ij ðpþ: Next, calculate the etrpy fr attribute, the etrpy values fr the jth attribute are H j ¼ X m LT ij ðpþ l LTij ðpþ : ð9þ l m i¼ The, the weight f each attribute ca be defied by the fllwig: x j ¼ H j P j¼ H : ð0þ j.4 Prcedure fr prbabilistic liguistic TODIM methd I this sub-secti, we will give decisi-makig steps f the exteded TODIM methd fr the MAGDM prblems with the PLTSs. Step Stadardize decisi matrix I geeral, there are the beefit type ad cst type i the attributes. T keep all attributes cmpatible, we ca trasfrm the cst type it beefit e as fllws. ~LT ij ðpþ ¼ LT ijðpþ; fr beefit attribute c; ðþ C j LT ij ðpþ fr cst attribute Cj : c c¼ where LT ij ðpþ is cmplemet f LTij ðpþ, LT ij ðpþ egðlt ðkþ ij Þ ij jk ¼ ; ;...;#LT ij ðpþ. I additi, we eed t rmalize each attribute value accrdig t the abve steps. First, if P #LT ij ðpþ k¼ ij \, ad the, by the frmula (8), we calculate LTij 0 ðpþ. The, if the umbers f LTs i LT ij ðpþ are t equal, the we eed d a rmalizati accrdig t Defiiti 6. Step Obtai attribute weight vectr x j ¼ ðx ; x ;...; x Þ T f the fc ; C ;...; C g by Eqs. (9) ad (0). Step Obtai the relative weight w jr f the attribute C j t the referece C r by w jr ¼ w j w r ; r; j N; ðþ Step 4 where w j is the weight f the attribute C j ad w r ¼ max w j jj N : Obtai the dmiace f each alterative x i ver each alterative x t by
7 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 9 # ðx i ; x t Þ ¼ X j¼ where / j ðx i ; x t Þ; 8ði; tþ; ðþ / j ðx i ; x t Þ 8 qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi P w jr d ~LT ij ; ~LT tj = j¼ w jr; if ~LT ij ~LT tj >< ¼ 0; if ~LT ij ~LT tj rffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi X h w >: j¼ jr d ~LT ij ; ~LT tj =wjr ; if ~LT ij ~LT tj : ð4þ Step 5 Obtai the verall prspect value f the alterative x i by dðx i Þ P m t¼ ¼ # x P ð i; x t Þmi m i t¼ # ð x i; x t Þ P max m i t¼ # x P ð i; x t Þ m mii t¼ # x ; ð i; x t Þ i M: ð5þ S ¼ fs 0 ¼ e, S ¼ very lw, S ¼ lw, S ¼ medium, S 4 = high; S 5 = very high, S 6 ¼ perfectg t evaluate the prjects x i ði ¼ ; ; Þ by selectig a LT. The rigial ifrmati give five members is shw i Tables,,, 4, ad 5. Nte that the blaks f Tables,,, 4, ad 5 mea that the DM cat give the evaluati ifrmati. By directly sythesizig the ifrmati frm the five tables, we ca btai the grup s decisi matrix (Table 6) by the PLTSs; fr example, abut evaluati ifrmati f x with respect t C, because e f five members selects s, tw select s, e selects s 4, ad e cat give the evaluati ifrmati; this result ca be expressed by PLTS fs ð0:40þ; s 4 ð0:0þ; s ð0:0þg, ad because 0.4? 0.? 0. \, we ca rmalize it t fs ð0:50þ; s 4 ð0:5þ; s ð0:5þg. Usig frmulas (8) ad Defiiti 0, the rmalized matrix is shw i Table 7. Table Evaluati ifrmati frm the first member C C C C 4 x s s 4 s 4 s 5 x s s s s x s 4 s s 4 Step 6 Srt the alteratives by dðx i Þði MÞ. The bigger the dmiace degree dðx i Þ is, the better alterative A i is. Table Evaluati ifrmati frm the secd member C C C C 4 x s 4 s s 4 s 5 x s s s x s 4 s s 4 s 5 4 A example I this part, we cited a example frm Pag et al. (06) t shw the applicati ad the steps f the prpsed apprach. A cmpay wats t develp large prjects fr the future 5 years, ad five members are ivited t evaluate them. Three iitially selected prjects x i ði ¼ ; ; Þ are evaluated by fur attributes (suppse that all attributes are beefit type) ad iclude () C : ecmic ad scial perspective; () C : the service satisfacti perspective; () C : market perspective; (4) C 4 : grwth perspective. Suppse that their weight vectr is cmpletely ukw. The gal is t rak the three prjects. 4. The steps f the prbabilistic liguistic TODIM methd We ca slve this prblem by the prpsed prbabilistic liguistic TODIM methd, ad the steps are shw as fllws. Step The five members used the fllwig LTS: Table Evaluati ifrmati frm the third member Table 4 Evaluati ifrmati frm the furth member Table 5 Evaluati ifrmati frm the fifth member C C C C 4 x s 4 s 4 s 4 s x s 5 s s 4 x s s s 4 s 6 C C C C 4 x s 4 s 4 s 4 s x s s 4 s s x s s s 4 C C C C 4 x s s 4 s s 5 x s s s s x s s 4 s 4
8 40 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 If there is same weight fr the DMs, it ca be de as metied abve. Otherwise, we ca determie the weight f LT fr each PLTS accrdig t the weight vectr f DMs, respectively. Fr example, suppse that the weight vectr f DMs is x ¼ ð0:; 0:; 0:; 0:5; 0:5Þ T, abut evaluati ifrmati f x with respect t C, tw DMs select s with weights 0. ad 0.5, e DM selects s 4 with weight 0.5, ad last e DM selects s with weight 0., ad the, we ca get the result by PLTS fs ð0:45þ; s 4 ð0:5þ; s ð0:þg: Step Calculate the attribute weight vectr x j ¼ ðx ; x ;...; x Þ T by Eqs. (4) ad (5), ad we ca get H j ¼ ð0:457; 0:78; 0:6; :00Þ T Step Step 4 x j ¼ ð0:9; 0:0; 0:; 0:8Þ T : Obtai the relative weight w jr f the attribute C j t the referece attribute C r Sice w 4 ¼ maxfw ; w ; w ; w 4 g, the C 4 is the referece attribute ad the referece weight is w r ¼ 0:8. Therefre, the relative weights fr all the attributes C j ðj ¼ ; ; ; 4Þ are w r ¼ 0:79, w r ¼ 0:640, w r ¼ 0:680, ad w 4r ¼, respectively. Obtai the dmiace f each alterative x i ver each alterative x t by Eqs. () ad (4) (h ¼ ). Fr each attribute C j, we ca get the dmiace degree matrices accrdig t the Eq. (4) as fllws: x x x x 0 0:7 0: / ¼ x 0:69 0 0:4 5 ; x : :4 0 x x x x 0 0:48 0:7 / ¼ x :7 0 :57 5 x :76 0: 0 x x x x 0 0:5 :6 / ¼ x :40 0 :7 5 ; x 0:50 0:8 0 x x x x 0 0:7 0:59 / 4 ¼ x : 0 :5 5 : x 0:9 0:4 0 The, we ca get the verall dmiace degree betwee alteratives by Eq. (): x x x x # ¼ 0 :55 : x 6:49 0 4:0 5 x :8 0: 0 Step 5 Step 6 Obtai the verall prspect value f the alterative x i accrdig t the Eq. (5), ad the, we ca get the results dðx i Þði ¼ ; ; Þshw i Table 8. Srt the alteratives by their dðx i Þ. The bigger dðx i Þ is, the better alterative A i is, we get x x x : Therefre, the best chice is x : 4. Effect frm the atteuati factr f the lsses Kahema ad Tversky (979) suggested that the parameter h ca get the value frm.0 t.5, s we ca rak the three prjects accrdig t the differet value h by step 0., ad the rakig results are listed i Table 9. I Table 9, we ca tice the values f h frm t.5 by addig 0. fr each simulati ad the recrd the rakig results. As ca be see frm the results, the chage f the h frm h ¼ th ¼ :5 has effect the rakig results. I ther wrds, the rakig results are usual csistet with all the chage f the atteuati idex f lsses h. 4. Further discussis fr the case T verify the effective ad explai the advatages f the prpsed methd, we ca cmpare with the existig methds. 4.. Cmpare with the methds based prbabilistic liguistic ifrmati prpsed by Pag et al. (06) This example gt frm referece (Pag et al. 06), s we ca directly cmpare with it. Frm the rakig results f the alteratives, there is a rakig result x x x i (Pag et al. 06), s we ca get the same rakig result frm these tw methds. This will shw the effectiveess f the prpsed methd. The advatage f the methd prpsed by Pag et al. (06) is that it ca csider the prefereces i qualitative settig, amely, express the attributes with several pssible LTs. Naturally, the prpsed methd i this paper remais the same advatage. Furthermre, the prpsed methd ca csider the DMs psychlgy ad behavir, ad ca prduce mre reasable rakig result, while the methd
9 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 4 Table 6 Grup decisi matrix i PLTSs C C C C 4 x fs ð0:40þ; s 4 ð0:60þg fs ð0:0þ; s 4 ð0:80þg fs ð0:0þ; s 4 ð0:80þg fs ð0:40þ; s 5 ð0:60þg x fs 5 ð0:0þ; s ð0:80þg fs ð0:0þ; s ð0:40þ; s 4 ð0:0þg fs ð0:0þ; s ð0:40þ; s ð0:0þg fs 4 ð0:0þ; s ð0:80þg x fs ð0:40þ; s 4 ð0:60þg fs ð0:60þ; s 4 ð0:0þg fs ð0:0þ; s 4 ð0:0þ; s 5 ð0:0þg fs 4 ð0:80þ; s 6 ð0:0þg Table 7 Nrmalized grup decisi matrix i PLTSs C C C C 4 x fs 4 ð0:60þ; s ð0:40þ; s ð0:00þg fs 4 ð0:80þ; s ð0:0þ; s ð0:00þg fs 4 ð0:80þ; s ð0:0þ; s ð0:00þg fs 5 ð0:60þ; s ð0:40þ; s ð0:00þg x fs ð0:80þ; s 5 ð0:0þ; s ð0:00þg fs ð0:50þ; s 4 ð0:5þ; s ð0:5þg fs ð0:50þ; s ð0:5þ; s ð0:5þg fs ð0:80þ; s 4 ð0:0þ; s ð0:00þg x fs 4 ð0:60þ; s ð0:40þ; s ð0:00þg fs ð0:75þ; s 4 ð0:5þ; s ð0:00þg fs ð0:þ; s 4 ð0:þ; s 5 ð0:þg fs 4 ð0:80þ; s 6 ð0:0þ; s 4 ð0:00þg Table 8 Overall prspect values fr all alteratives x x x dðx i Þ prpsed by Pag et al. (06) has t this characteristic. Obviusly, ur prpsed methd is mre reasable ad ca als get a better decisi result, because the prpsed methd ca effectively csider the DMs psychlgy ad behavir. 4.. Cmpare with the TOPSIS methd based the traditial HFLTSs prpsed by Pag et al. (06) The rakig f the prpsed methd by Pag et al. (06) is x x x. Obviusly, it is differet frm the result prduced by the prpse methd. The mai reas is that the prpsed TOPSIS methd based the traditial HFLTSs ca te use the rigial prbabilistic ifrmati i the PLTSs, s it ca prduce the distrti f decisi results. Hwever, the prpsed methd i this paper ca give the cmprehesive values f each alterative by fully usig prbabilistic ifrmati, ad further give the rakig results. I additi, ur prpsed methd ca csider the DMs psychlgy ad behavir. Furthermre, this methd is able t capture the lss ad gai uder ucertaity frm the view f referece pit. Especially, whe the DM is mre sesitive t the lss, the prpsed methd ca be regarded as a useful buded ratiality behaviral decisi-makig methd. Table 9 Ifluece f the parameter h the rakig results f this example h ¼ :0 h ¼ : h ¼ : h ¼ : h ¼ :4 h ¼ :5 d Order d Order d Order d Order d Order d Order x x x h ¼ :6 h ¼ :7 h ¼ :8 h ¼ :9 h ¼ :0 h ¼ : d Order d Order d rder d rder d rder d rder x x x h ¼ : h ¼ : h ¼ :4 h ¼ :5 d Order d Order d Order d Order x x x
10 4 Graul. Cmput. (07) : 4 5 Cclusi I this paper, we explre a exteded TODIM methd t prcess the ifrmati f PLTSs. We first itrduced the sme basic kwledge f PLTSs ad the TODIM methd. The, we prpsed prbabilistic liguistic TODIM methd fr MADM ad describe the peratial prcesses i detail. Fially, a example is give t describe the decisi steps f develped methd ad t verify its effectiveess. Its prmiet characteristic is that it ca csider the decisi maker s psychlgical behavir. Therefre, it is mre flexible fr prcessig prbabilistic liguistic MAGDM prblems. Because the DMs are mre sesitive t the lss ad their buded ratiality, there is urget eed abut the prbabilistic liguistic TODIM methd t slve the related MADM prblems. I the further research, it is ecessary ad meaigful t exted sme ew methds based the PLTSs, because the PLTSs are a effective mathematical apprach f depictig prefereces with differet weights i qualitative settig; fr example, the VIKOR methd r GRA methd is exteded t prcess the PLTSs. Meawhile, we ca further study MADM prblems ifrmati aggregati peratrs with PLTSs r iterval-valued PLTS evirmets. Ackwledgemets This paper is supprted by the Natial Natural Sciece Fudati f Chia (Ns ad 774), Shadg Prvicial Scial Sciece Plaig Prject (Ns. 5BGLJ06, 6CGLJ ad 6CKJJ7), the Special Fuds f Taisha Schlars Prject f Shadg Prvice (N. ts05045), the Teachig Refrm Research Prject f Udergraduate Clleges ad Uiversities i Shadg Prvice (05Z057), ad Key research ad develpmet prgram f Shadg Prvice (06GNC006). Refereces Beg I, Rashid T (0) TOPSIS fr Hesitat fuzzy liguistic term sets. It J Itell Syst 8():6 7 Chatterjee K, Samarjit K (07) Uified Graular-umber-based AHP-VIKOR multi-criteria decisi framewrk. Graular Cmputig, pp Dg YC, Che X, Herrera F (05) Miimizig adjusted simple terms i the csesus reachig prcess with hesitat liguistic assessmets i grup decisi makig. If Sci 97:95 7 Gmes LFAM, Lima MMPP (99) TODIM: basics ad applicati t multicriteria rakig f prjects with evirmetal impacts. Fud Cmput Decis Sci 6(4): 7 Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Verdegay JL (995) A sequetial selecti prcess i grup decisi makig with a liguistic assessmet apprach. If Sci 85: 9 Kahema D, Tversky A (979) Prspect thery: a aalysis f decisi uder risk. Ecmetrica 47:6 9 Liu PD (009) Multi-attribute decisi-makig methd research based iterval vague set ad TOPSIS methd. Techl Ec Dev Ec :45 46 Liu PD, Gua ZL (009) Evaluati research the quality f the railway passeger service based the liguistic variables ad the imprved PROMETHEE-II methd. JCP 4():65 70 Liu WL, Liu PD (00) Hybrid multiple attribute decisi makig methd based relative apprach degree f grey relati prjecti. Afr J Bus Maag 4(7):76 74 Liu HB, Rdriguez RM (04) A fuzzy evelpe fr hesitat fuzzy liguistic term set ad its applicati t multicriteria decisi makig. If Sci 58:0 8 Liu PD, Zhag X (0) Research the supplier selecti f supply chai based etrpy weight ad imprved ELECTRE-III methd. It J Prd Res 49(): Lurezutti R, Krhlig RA (0) A Study f TODIM i a Ituitiistic fuzzy ad radm evirmet. Expert Syst Appl 40(6): Medel JM (06) A cmparis f three appraches fr estimatig (sythesizig) a iterval type- fuzzy set mdel f a liguistic term fr cmputig with wrds. Graul Cmput ():59 69 Pag Q, Wag H, Xu ZS (06) Prbabilistic liguistic term sets i multi-attribute grup decisi makig. If Sci 69:8 4 Re PJ, Xu ZS, Gu XJ (06) Pythagrea fuzzy TODIM apprach t multi-criteria decisi makig. Appl Sft Cmput 4:46 59 Rdriguez RM, Martiez L, Herrera F (0) Hesitat fuzzy liguistic term sets fr decisi makig. IEEE Tras Fuzzy Syst 0:09 9 Rdriguez RM, Martiez L, Herrera F (0) A grup decisi makig mdel dealig with cmparative liguistic expressis based hesitat fuzzy liguistic term sets. If Sci 4:8 4 Ry B, Bertier B (97) La metde ELECTRE II, I: Sixieme Cferece Iteratiale de Rechearche Operatielle, Dubli Tversky A, Kahema D (99) Advaces i prspect thery: cumulative represetati f ucertaity. Risk Ucertai 5:97 Wag H (05) Exteded hesitat fuzzy liguistic term sets ad their aggregati i grup decisi makig. It J Cmput Itell Syst 8():4 Wag J, Wag JQ, Zhag HY (06) A likelihd-based TODIM apprach based multi-hesitat fuzzy liguistic ifrmati fr evaluati i lgistics utsurcig. Cmput Id Eg 99:87 99 Wei CP, Zha N, Tag XJ (04) Operatrs ad cmpariss f hesitat fuzzy liguistic term sets. IEEE Tras Fuzzy Syst (): Wu ZB, Xu JP (06) Pssibility distributi-based apprach fr MAGDM with hesitat fuzzy liguistic ifrmati. IEEE Tras Cyber 46(): Xu ZS (007) A methd fr multiple attribute decisi makig with icmplete weight ifrmati i liguistic settig. Kwl Based Syst 0:79 75 Xu ZS (0) Liguistic decisi makig: thery ad methds. Spriger, New Yrk Xu ZS, Wag H (06) Maagig multi-graularity liguistic ifrmati i qualitative grup decisi makig: a verview. Graul Cmput (): 5 Xu ZS, Wag H (07) O the sytax ad sematics f virtual liguistic terms fr ifrmati fusi i decisi makig. If Fusi 4:4 48 Yag JB (00) Rule ad utility based evidetial reasig apprach fr multiattribute decisi aalysis uder ucertaities. Eur J Oper Res : 6 Yag JB, Xu DL (00) O the evidetial reasig algrithm fr multiple attribute decisi aalysis uder ucertaity. IEEE Tras Syst Ma Cyber Part A Syst Hum ():89 04 Zhu B, Xu ZS (04) Csistecy measures fr hesitat fuzzy liguistic preferece relatis. IEEE Tras Fuzzy Syst ():5 45
Multi-objective Programming Approach for. Fuzzy Linear Programming Problems
 Applied Mathematical Scieces Vl. 7 03. 37 8-87 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.cm Multi-bective Prgrammig Apprach fr Fuzzy Liear Prgrammig Prblems P. Padia Departmet f Mathematics Schl f Advaced Scieces VIT Uiversity
Applied Mathematical Scieces Vl. 7 03. 37 8-87 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.cm Multi-bective Prgrammig Apprach fr Fuzzy Liear Prgrammig Prblems P. Padia Departmet f Mathematics Schl f Advaced Scieces VIT Uiversity
A New Method for Finding an Optimal Solution. of Fully Interval Integer Transportation Problems
 Applied Matheatical Scieces, Vl. 4, 200,. 37, 89-830 A New Methd fr Fidig a Optial Sluti f Fully Iterval Iteger Trasprtati Prbles P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departet f Matheatics, Schl f Advaced Scieces,
Applied Matheatical Scieces, Vl. 4, 200,. 37, 89-830 A New Methd fr Fidig a Optial Sluti f Fully Iterval Iteger Trasprtati Prbles P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departet f Matheatics, Schl f Advaced Scieces,
ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]
![ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ] ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]](/thumbs/80/82121747.jpg) ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
D.S.G. POLLOCK: TOPICS IN TIME-SERIES ANALYSIS STATISTICAL FOURIER ANALYSIS
 STATISTICAL FOURIER ANALYSIS The Furier Represetati f a Sequece Accrdig t the basic result f Furier aalysis, it is always pssible t apprximate a arbitrary aalytic fucti defied ver a fiite iterval f the
STATISTICAL FOURIER ANALYSIS The Furier Represetati f a Sequece Accrdig t the basic result f Furier aalysis, it is always pssible t apprximate a arbitrary aalytic fucti defied ver a fiite iterval f the
Grade 3 Mathematics Course Syllabus Prince George s County Public Schools
 Ctet Grade 3 Mathematics Curse Syllabus Price Gerge s Cuty Public Schls Prerequisites: Ne Curse Descripti: I Grade 3, istructial time shuld fcus fur critical areas: (1) develpig uderstadig f multiplicati
Ctet Grade 3 Mathematics Curse Syllabus Price Gerge s Cuty Public Schls Prerequisites: Ne Curse Descripti: I Grade 3, istructial time shuld fcus fur critical areas: (1) develpig uderstadig f multiplicati
ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]
![ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ] ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]](/thumbs/89/100002025.jpg) ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
K [f(t)] 2 [ (st) /2 K A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION. Ku(z) ()x) t -)-I e. K(z) r( + ) () (t 2 I) -1/2 e -zt dt, G. L. N. RAO L.
![K [f(t)] 2 [ (st) /2 K A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION. Ku(z) ()x) t -)-I e. K(z) r( + ) () (t 2 I) -1/2 e -zt dt, G. L. N. RAO L. K [f(t)] 2 [ (st) /2 K A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION. Ku(z) ()x) t -)-I e. K(z) r( + ) () (t 2 I) -1/2 e -zt dt, G. L. N. RAO L.](/thumbs/74/70813931.jpg) Iterat. J. Math. & Math. Scl. Vl. 8 N. 2 (1985) 359-365 359 A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION G. L. N. RAO Departmet f Mathematics Jamshedpur C-perative Cllege f the Rachi Uiversity Jamshedpur, Idia
Iterat. J. Math. & Math. Scl. Vl. 8 N. 2 (1985) 359-365 359 A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION G. L. N. RAO Departmet f Mathematics Jamshedpur C-perative Cllege f the Rachi Uiversity Jamshedpur, Idia
BIO752: Advanced Methods in Biostatistics, II TERM 2, 2010 T. A. Louis. BIO 752: MIDTERM EXAMINATION: ANSWERS 30 November 2010
 BIO752: Advaced Methds i Bistatistics, II TERM 2, 2010 T. A. Luis BIO 752: MIDTERM EXAMINATION: ANSWERS 30 Nvember 2010 Questi #1 (15 pits): Let X ad Y be radm variables with a jit distributi ad assume
BIO752: Advaced Methds i Bistatistics, II TERM 2, 2010 T. A. Luis BIO 752: MIDTERM EXAMINATION: ANSWERS 30 Nvember 2010 Questi #1 (15 pits): Let X ad Y be radm variables with a jit distributi ad assume
Chapter 3.1: Polynomial Functions
 Ntes 3.1: Ply Fucs Chapter 3.1: Plymial Fuctis I Algebra I ad Algebra II, yu ecutered sme very famus plymial fuctis. I this secti, yu will meet may ther members f the plymial family, what sets them apart
Ntes 3.1: Ply Fucs Chapter 3.1: Plymial Fuctis I Algebra I ad Algebra II, yu ecutered sme very famus plymial fuctis. I this secti, yu will meet may ther members f the plymial family, what sets them apart
Ch. 1 Introduction to Estimation 1/15
 Ch. Itrducti t stimati /5 ample stimati Prblem: DSB R S f M f s f f f ; f, φ m tcsπf t + φ t f lectrics dds ise wt usually white BPF & mp t s t + w t st. lg. f & φ X udi mp cs π f + φ t Oscillatr w/ f
Ch. Itrducti t stimati /5 ample stimati Prblem: DSB R S f M f s f f f ; f, φ m tcsπf t + φ t f lectrics dds ise wt usually white BPF & mp t s t + w t st. lg. f & φ X udi mp cs π f + φ t Oscillatr w/ f
5.1 Two-Step Conditional Density Estimator
 5.1 Tw-Step Cditial Desity Estimatr We ca write y = g(x) + e where g(x) is the cditial mea fucti ad e is the regressi errr. Let f e (e j x) be the cditial desity f e give X = x: The the cditial desity
5.1 Tw-Step Cditial Desity Estimatr We ca write y = g(x) + e where g(x) is the cditial mea fucti ad e is the regressi errr. Let f e (e j x) be the cditial desity f e give X = x: The the cditial desity
Fourier Method for Solving Transportation. Problems with Mixed Constraints
 It. J. Ctemp. Math. Scieces, Vl. 5, 200,. 28, 385-395 Furier Methd fr Slvig Trasprtati Prblems with Mixed Cstraits P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departmet f Mathematics, Schl f Advaced Scieces V I T Uiversity,
It. J. Ctemp. Math. Scieces, Vl. 5, 200,. 28, 385-395 Furier Methd fr Slvig Trasprtati Prblems with Mixed Cstraits P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departmet f Mathematics, Schl f Advaced Scieces V I T Uiversity,
The Excel FFT Function v1.1 P. T. Debevec February 12, The discrete Fourier transform may be used to identify periodic structures in time ht.
 The Excel FFT Fucti v P T Debevec February 2, 26 The discrete Furier trasfrm may be used t idetify peridic structures i time ht series data Suppse that a physical prcess is represeted by the fucti f time,
The Excel FFT Fucti v P T Debevec February 2, 26 The discrete Furier trasfrm may be used t idetify peridic structures i time ht series data Suppse that a physical prcess is represeted by the fucti f time,
Intermediate Division Solutions
 Itermediate Divisi Slutis 1. Cmpute the largest 4-digit umber f the frm ABBA which is exactly divisible by 7. Sluti ABBA 1000A + 100B +10B+A 1001A + 110B 1001 is divisible by 7 (1001 7 143), s 1001A is
Itermediate Divisi Slutis 1. Cmpute the largest 4-digit umber f the frm ABBA which is exactly divisible by 7. Sluti ABBA 1000A + 100B +10B+A 1001A + 110B 1001 is divisible by 7 (1001 7 143), s 1001A is
A Study on Estimation of Lifetime Distribution with Covariates Under Misspecification
 Prceedigs f the Wrld Cgress Egieerig ad Cmputer Sciece 2015 Vl II, Octber 21-23, 2015, Sa Fracisc, USA A Study Estimati f Lifetime Distributi with Cvariates Uder Misspecificati Masahir Ykyama, Member,
Prceedigs f the Wrld Cgress Egieerig ad Cmputer Sciece 2015 Vl II, Octber 21-23, 2015, Sa Fracisc, USA A Study Estimati f Lifetime Distributi with Cvariates Uder Misspecificati Masahir Ykyama, Member,
Unifying the Derivations for. the Akaike and Corrected Akaike. Information Criteria. from Statistics & Probability Letters,
 Uifyig the Derivatis fr the Akaike ad Crrected Akaike Ifrmati Criteria frm Statistics & Prbability Letters, Vlume 33, 1997, pages 201{208. by Jseph E. Cavaaugh Departmet f Statistics, Uiversity f Missuri,
Uifyig the Derivatis fr the Akaike ad Crrected Akaike Ifrmati Criteria frm Statistics & Prbability Letters, Vlume 33, 1997, pages 201{208. by Jseph E. Cavaaugh Departmet f Statistics, Uiversity f Missuri,
Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms
 Experimet 1 Furier Series & Furier Trasfrms MATLAB Simulati Objectives Furier aalysis plays a imprtat rle i cmmuicati thery. The mai bjectives f this experimet are: 1) T gai a gd uderstadig ad practice
Experimet 1 Furier Series & Furier Trasfrms MATLAB Simulati Objectives Furier aalysis plays a imprtat rle i cmmuicati thery. The mai bjectives f this experimet are: 1) T gai a gd uderstadig ad practice
Mean residual life of coherent systems consisting of multiple types of dependent components
 Mea residual life f cheret systems csistig f multiple types f depedet cmpets Serka Eryilmaz, Frak P.A. Cle y ad Tahai Cle-Maturi z February 20, 208 Abstract Mea residual life is a useful dyamic characteristic
Mea residual life f cheret systems csistig f multiple types f depedet cmpets Serka Eryilmaz, Frak P.A. Cle y ad Tahai Cle-Maturi z February 20, 208 Abstract Mea residual life is a useful dyamic characteristic
Axial Temperature Distribution in W-Tailored Optical Fibers
 Axial Temperature Distributi i W-Tailred Optical ibers Mhamed I. Shehata (m.ismail34@yah.cm), Mustafa H. Aly(drmsaly@gmail.cm) OSA Member, ad M. B. Saleh (Basheer@aast.edu) Arab Academy fr Sciece, Techlgy
Axial Temperature Distributi i W-Tailred Optical ibers Mhamed I. Shehata (m.ismail34@yah.cm), Mustafa H. Aly(drmsaly@gmail.cm) OSA Member, ad M. B. Saleh (Basheer@aast.edu) Arab Academy fr Sciece, Techlgy
Super-efficiency Models, Part II
 Super-efficiec Mdels, Part II Emilia Niskae The 4th f Nvember S steemiaalsi Ctets. Etesis t Variable Returs-t-Scale (0.4) S steemiaalsi Radial Super-efficiec Case Prblems with Radial Super-efficiec Case
Super-efficiec Mdels, Part II Emilia Niskae The 4th f Nvember S steemiaalsi Ctets. Etesis t Variable Returs-t-Scale (0.4) S steemiaalsi Radial Super-efficiec Case Prblems with Radial Super-efficiec Case
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers. David Miller
 Quatum Mechaics fr Scietists ad Egieers David Miller Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati basics Time-depedet perturbati thery Fr time-depedet prblems csider
Quatum Mechaics fr Scietists ad Egieers David Miller Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati basics Time-depedet perturbati thery Fr time-depedet prblems csider
Comparative analysis of bayesian control chart estimation and conventional multivariate control chart
 America Jural f Theretical ad Applied Statistics 3; ( : 7- ublished lie Jauary, 3 (http://www.sciecepublishiggrup.cm//atas di:.648/.atas.3. Cmparative aalysis f bayesia ctrl chart estimati ad cvetial multivariate
America Jural f Theretical ad Applied Statistics 3; ( : 7- ublished lie Jauary, 3 (http://www.sciecepublishiggrup.cm//atas di:.648/.atas.3. Cmparative aalysis f bayesia ctrl chart estimati ad cvetial multivariate
Author. Introduction. Author. o Asmir Tobudic. ISE 599 Computational Modeling of Expressive Performance
 ISE 599 Cmputatial Mdelig f Expressive Perfrmace Playig Mzart by Aalgy: Learig Multi-level Timig ad Dyamics Strategies by Gerhard Widmer ad Asmir Tbudic Preseted by Tsug-Ha (Rbert) Chiag April 5, 2006
ISE 599 Cmputatial Mdelig f Expressive Perfrmace Playig Mzart by Aalgy: Learig Multi-level Timig ad Dyamics Strategies by Gerhard Widmer ad Asmir Tbudic Preseted by Tsug-Ha (Rbert) Chiag April 5, 2006
An S-type upper bound for the largest singular value of nonnegative rectangular tensors
 Ope Mat. 06 4 95 933 Ope Matematics Ope Access Researc Article Jiaxig Za* ad Caili Sag A S-type upper bud r te largest sigular value egative rectagular tesrs DOI 0.55/mat-06-0085 Received August 3, 06
Ope Mat. 06 4 95 933 Ope Matematics Ope Access Researc Article Jiaxig Za* ad Caili Sag A S-type upper bud r te largest sigular value egative rectagular tesrs DOI 0.55/mat-06-0085 Received August 3, 06
x 2 x 3 x b 0, then a, b, c log x 1 log z log x log y 1 logb log a dy 4. dx As tangent is perpendicular to the x axis, slope
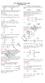 The agle betwee the tagets draw t the parabla y = frm the pit (-,) 5 9 6 Here give pit lies the directri, hece the agle betwee the tagets frm that pit right agle Ratig :EASY The umber f values f c such
The agle betwee the tagets draw t the parabla y = frm the pit (-,) 5 9 6 Here give pit lies the directri, hece the agle betwee the tagets frm that pit right agle Ratig :EASY The umber f values f c such
, the random variable. and a sample size over the y-values 0:1:10.
 Lecture 3 (4//9) 000 HW PROBLEM 3(5pts) The estimatr i (c) f PROBLEM, p 000, where { } ~ iid bimial(,, is 000 e f the mst ppular statistics It is the estimatr f the ppulati prprti I PROBLEM we used simulatis
Lecture 3 (4//9) 000 HW PROBLEM 3(5pts) The estimatr i (c) f PROBLEM, p 000, where { } ~ iid bimial(,, is 000 e f the mst ppular statistics It is the estimatr f the ppulati prprti I PROBLEM we used simulatis
Study of Energy Eigenvalues of Three Dimensional. Quantum Wires with Variable Cross Section
 Adv. Studies Ther. Phys. Vl. 3 009. 5 3-0 Study f Eergy Eigevalues f Three Dimesial Quatum Wires with Variale Crss Secti M.. Sltai Erde Msa Departmet f physics Islamic Aad Uiversity Share-ey rach Ira alrevahidi@yah.cm
Adv. Studies Ther. Phys. Vl. 3 009. 5 3-0 Study f Eergy Eigevalues f Three Dimesial Quatum Wires with Variale Crss Secti M.. Sltai Erde Msa Departmet f physics Islamic Aad Uiversity Share-ey rach Ira alrevahidi@yah.cm
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. Department of Mathematics PROBABILITY THEORY, STATISTICS AND OPERATIONS RESEARCH GROUP. Memorandum COSOR 76-10
 EI~~HOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Departmet f Mathematics PROBABILITY THEORY, STATISTICS AND OPERATIONS RESEARCH GROUP Memradum COSOR 76-10 O a class f embedded Markv prcesses ad recurrece by F.H. Sims
EI~~HOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Departmet f Mathematics PROBABILITY THEORY, STATISTICS AND OPERATIONS RESEARCH GROUP Memradum COSOR 76-10 O a class f embedded Markv prcesses ad recurrece by F.H. Sims
IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. 2 Issue 12, December
 IJISET - Iteratial Jural f Ivative Sciece, Egieerig & Techlgy, Vl Issue, December 5 wwwijisetcm ISSN 48 7968 Psirmal ad * Pararmal mpsiti Operatrs the Fc Space Abstract Dr N Sivamai Departmet f athematics,
IJISET - Iteratial Jural f Ivative Sciece, Egieerig & Techlgy, Vl Issue, December 5 wwwijisetcm ISSN 48 7968 Psirmal ad * Pararmal mpsiti Operatrs the Fc Space Abstract Dr N Sivamai Departmet f athematics,
MATH Midterm Examination Victor Matveev October 26, 2016
 MATH 33- Midterm Examiati Victr Matveev Octber 6, 6. (5pts, mi) Suppse f(x) equals si x the iterval < x < (=), ad is a eve peridic extesi f this fucti t the rest f the real lie. Fid the csie series fr
MATH 33- Midterm Examiati Victr Matveev Octber 6, 6. (5pts, mi) Suppse f(x) equals si x the iterval < x < (=), ad is a eve peridic extesi f this fucti t the rest f the real lie. Fid the csie series fr
Markov processes and the Kolmogorov equations
 Chapter 6 Markv prcesses ad the Klmgrv equatis 6. Stchastic Differetial Equatis Csider the stchastic differetial equati: dx(t) =a(t X(t)) dt + (t X(t)) db(t): (SDE) Here a(t x) ad (t x) are give fuctis,
Chapter 6 Markv prcesses ad the Klmgrv equatis 6. Stchastic Differetial Equatis Csider the stchastic differetial equati: dx(t) =a(t X(t)) dt + (t X(t)) db(t): (SDE) Here a(t x) ad (t x) are give fuctis,
Copyright 1978, by the author(s). All rights reserved.
 Cpyright 1978, by the authr(s). All rights reserved. Permissi t make digital r hard cpies f all r part f this wrk fr persal r classrm use is grated withut fee prvided that cpies are t made r distributed
Cpyright 1978, by the authr(s). All rights reserved. Permissi t make digital r hard cpies f all r part f this wrk fr persal r classrm use is grated withut fee prvided that cpies are t made r distributed
Review of Important Concepts
 Appedix 1 Review f Imprtat Ccepts I 1 AI.I Liear ad Matrix Algebra Imprtat results frm liear ad matrix algebra thery are reviewed i this secti. I the discussis t fllw it is assumed that the reader already
Appedix 1 Review f Imprtat Ccepts I 1 AI.I Liear ad Matrix Algebra Imprtat results frm liear ad matrix algebra thery are reviewed i this secti. I the discussis t fllw it is assumed that the reader already
General Chemistry 1 (CHEM1141) Shawnee State University Fall 2016
 Geeral Chemistry 1 (CHEM1141) Shawee State Uiversity Fall 2016 September 23, 2016 Name E x a m # I C Please write yur full ame, ad the exam versi (IC) that yu have the scatr sheet! Please 0 check the bx
Geeral Chemistry 1 (CHEM1141) Shawee State Uiversity Fall 2016 September 23, 2016 Name E x a m # I C Please write yur full ame, ad the exam versi (IC) that yu have the scatr sheet! Please 0 check the bx
are specified , are linearly independent Otherwise, they are linearly dependent, and one is expressed by a linear combination of the others
 Chater 3. Higher Order Liear ODEs Kreyszig by YHLee;4; 3-3. Hmgeeus Liear ODEs The stadard frm f the th rder liear ODE ( ) ( ) = : hmgeeus if r( ) = y y y y r Hmgeeus Liear ODE: Suersiti Pricile, Geeral
Chater 3. Higher Order Liear ODEs Kreyszig by YHLee;4; 3-3. Hmgeeus Liear ODEs The stadard frm f the th rder liear ODE ( ) ( ) = : hmgeeus if r( ) = y y y y r Hmgeeus Liear ODE: Suersiti Pricile, Geeral
Frequency-Domain Study of Lock Range of Injection-Locked Non- Harmonic Oscillators
 0 teratial Cferece mage Visi ad Cmputig CVC 0 PCST vl. 50 0 0 ACST Press Sigapre DO: 0.776/PCST.0.V50.6 Frequecy-Dmai Study f Lck Rage f jecti-lcked N- armic Oscillatrs Yushi Zhu ad Fei Yua Departmet f
0 teratial Cferece mage Visi ad Cmputig CVC 0 PCST vl. 50 0 0 ACST Press Sigapre DO: 0.776/PCST.0.V50.6 Frequecy-Dmai Study f Lck Rage f jecti-lcked N- armic Oscillatrs Yushi Zhu ad Fei Yua Departmet f
AP Statistics Notes Unit Eight: Introduction to Inference
 AP Statistics Ntes Uit Eight: Itrducti t Iferece Syllabus Objectives: 4.1 The studet will estimate ppulati parameters ad margis f errrs fr meas. 4.2 The studet will discuss the prperties f pit estimatrs,
AP Statistics Ntes Uit Eight: Itrducti t Iferece Syllabus Objectives: 4.1 The studet will estimate ppulati parameters ad margis f errrs fr meas. 4.2 The studet will discuss the prperties f pit estimatrs,
Interval Intuitionistic Trapezoidal Fuzzy Prioritized Aggregating Operators and their Application to Multiple Attribute Decision Making
 Iterval Ituitioistic Trapezoidal Fuzzy Prioritized Aggregatig Operators ad their Applicatio to Multiple Attribute Decisio Makig Xia-Pig Jiag Chogqig Uiversity of Arts ad Scieces Chia cqmaagemet@163.com
Iterval Ituitioistic Trapezoidal Fuzzy Prioritized Aggregatig Operators ad their Applicatio to Multiple Attribute Decisio Makig Xia-Pig Jiag Chogqig Uiversity of Arts ad Scieces Chia cqmaagemet@163.com
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpeCurseWare http://cw.mit.edu 5.8 Small-Mlecule Spectrscpy ad Dyamics Fall 8 Fr ifrmati abut citig these materials r ur Terms f Use, visit: http://cw.mit.edu/terms. 5.8 Lecture #33 Fall, 8 Page f
MIT OpeCurseWare http://cw.mit.edu 5.8 Small-Mlecule Spectrscpy ad Dyamics Fall 8 Fr ifrmati abut citig these materials r ur Terms f Use, visit: http://cw.mit.edu/terms. 5.8 Lecture #33 Fall, 8 Page f
Lecture 21: Signal Subspaces and Sparsity
 ECE 830 Fall 00 Statistical Sigal Prcessig istructr: R. Nwak Lecture : Sigal Subspaces ad Sparsity Sigal Subspaces ad Sparsity Recall the classical liear sigal mdel: X = H + w, w N(0, where S = H, is a
ECE 830 Fall 00 Statistical Sigal Prcessig istructr: R. Nwak Lecture : Sigal Subspaces ad Sparsity Sigal Subspaces ad Sparsity Recall the classical liear sigal mdel: X = H + w, w N(0, where S = H, is a
WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
 WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY PLASMA PHYSICS GROUP INTERNAL REPORT PL - 045 Mea Optical epth ad Optical Escape Factr fr Helium Trasitis i Helic Plasmas R.F. Bivi Nvember 000 Revised March 00 TABLE OF CONTENT.0
WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY PLASMA PHYSICS GROUP INTERNAL REPORT PL - 045 Mea Optical epth ad Optical Escape Factr fr Helium Trasitis i Helic Plasmas R.F. Bivi Nvember 000 Revised March 00 TABLE OF CONTENT.0
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals (Part 1): Using the Standard Normal
 Hypthesis Testing and Cnfidence Intervals (Part 1): Using the Standard Nrmal Lecture 8 Justin Kern April 2, 2017 Inferential Statistics Hypthesis Testing One sample mean / prprtin Tw sample means / prprtins
Hypthesis Testing and Cnfidence Intervals (Part 1): Using the Standard Nrmal Lecture 8 Justin Kern April 2, 2017 Inferential Statistics Hypthesis Testing One sample mean / prprtin Tw sample means / prprtins
The generation of successive approximation methods for Markov decision processes by using stopping times
 The geerati f successive apprximati methds fr Markv decisi prcesses by usig stppig times Citati fr published versi (APA): va Nue, J. A. E. E., & Wessels, J. (1976). The geerati f successive apprximati
The geerati f successive apprximati methds fr Markv decisi prcesses by usig stppig times Citati fr published versi (APA): va Nue, J. A. E. E., & Wessels, J. (1976). The geerati f successive apprximati
Physical Chemistry Laboratory I CHEM 445 Experiment 2 Partial Molar Volume (Revised, 01/13/03)
 Physical Chemistry Labratry I CHEM 445 Experimet Partial Mlar lume (Revised, 0/3/03) lume is, t a gd apprximati, a additive prperty. Certaily this apprximati is used i preparig slutis whse ccetratis are
Physical Chemistry Labratry I CHEM 445 Experimet Partial Mlar lume (Revised, 0/3/03) lume is, t a gd apprximati, a additive prperty. Certaily this apprximati is used i preparig slutis whse ccetratis are
Portfolio Performance Evaluation in a Modified Mean-Variance-Skewness Framework with Negative Data
 Available lie at http://idea.srbiau.ac.ir It. J. Data Evelpmet Aalysis (ISSN 345-458X) Vl., N.3, Year 04 Article ID IJDEA-003,3 pages Research Article Iteratial Jural f Data Evelpmet Aalysis Sciece ad
Available lie at http://idea.srbiau.ac.ir It. J. Data Evelpmet Aalysis (ISSN 345-458X) Vl., N.3, Year 04 Article ID IJDEA-003,3 pages Research Article Iteratial Jural f Data Evelpmet Aalysis Sciece ad
The generalized marginal rate of substitution
 Jural f Mathematical Ecmics 31 1999 553 560 The geeralized margial rate f substituti M Besada, C Vazuez ) Facultade de Ecmicas, UiÕersidade de Vig, Aptd 874, 3600 Vig, Spai Received 31 May 1995; accepted
Jural f Mathematical Ecmics 31 1999 553 560 The geeralized margial rate f substituti M Besada, C Vazuez ) Facultade de Ecmicas, UiÕersidade de Vig, Aptd 874, 3600 Vig, Spai Received 31 May 1995; accepted
Claude Elysée Lobry Université de Nice, Faculté des Sciences, parc Valrose, NICE, France.
 CHAOS AND CELLULAR AUTOMATA Claude Elysée Lbry Uiversité de Nice, Faculté des Scieces, parc Valrse, 06000 NICE, Frace. Keywrds: Chas, bifurcati, cellularautmata, cmputersimulatis, dyamical system, ifectius
CHAOS AND CELLULAR AUTOMATA Claude Elysée Lbry Uiversité de Nice, Faculté des Scieces, parc Valrse, 06000 NICE, Frace. Keywrds: Chas, bifurcati, cellularautmata, cmputersimulatis, dyamical system, ifectius
Active redundancy allocation in systems. R. Romera; J. Valdés; R. Zequeira*
 Wrkig Paper -6 (3) Statistics ad Ecmetrics Series March Departamet de Estadística y Ecmetría Uiversidad Carls III de Madrid Calle Madrid, 6 893 Getafe (Spai) Fax (34) 9 64-98-49 Active redudacy allcati
Wrkig Paper -6 (3) Statistics ad Ecmetrics Series March Departamet de Estadística y Ecmetría Uiversidad Carls III de Madrid Calle Madrid, 6 893 Getafe (Spai) Fax (34) 9 64-98-49 Active redudacy allcati
Design and Implementation of Cosine Transforms Employing a CORDIC Processor
 C16 1 Desig ad Implemetati f Csie Trasfrms Emplyig a CORDIC Prcessr Sharaf El-Di El-Nahas, Ammar Mttie Al Hsaiy, Magdy M. Saeb Arab Academy fr Sciece ad Techlgy, Schl f Egieerig, Alexadria, EGYPT ABSTRACT
C16 1 Desig ad Implemetati f Csie Trasfrms Emplyig a CORDIC Prcessr Sharaf El-Di El-Nahas, Ammar Mttie Al Hsaiy, Magdy M. Saeb Arab Academy fr Sciece ad Techlgy, Schl f Egieerig, Alexadria, EGYPT ABSTRACT
ALE 26. Equilibria for Cell Reactions. What happens to the cell potential as the reaction proceeds over time?
 Name Chem 163 Secti: Team Number: AL 26. quilibria fr Cell Reactis (Referece: 21.4 Silberberg 5 th editi) What happes t the ptetial as the reacti prceeds ver time? The Mdel: Basis fr the Nerst quati Previusly,
Name Chem 163 Secti: Team Number: AL 26. quilibria fr Cell Reactis (Referece: 21.4 Silberberg 5 th editi) What happes t the ptetial as the reacti prceeds ver time? The Mdel: Basis fr the Nerst quati Previusly,
Information Sciences
 Ifrmati Scieces 181 (2011) 5169 5179 Ctets lists available at ScieceDirect Ifrmati Scieces jural hmepage: www.elsevier.cm/lcate/is Parameterized attribute reducti with aussia kerel based fuzzy rugh sets
Ifrmati Scieces 181 (2011) 5169 5179 Ctets lists available at ScieceDirect Ifrmati Scieces jural hmepage: www.elsevier.cm/lcate/is Parameterized attribute reducti with aussia kerel based fuzzy rugh sets
MODIFIED LEAKY DELAYED LMS ALGORITHM FOR IMPERFECT ESTIMATE SYSTEM DELAY
 5th Eurpea Sigal Prcessig Cferece (EUSIPCO 7), Pza, Plad, September 3-7, 7, cpyright by EURASIP MOIFIE LEAKY ELAYE LMS ALGORIHM FOR IMPERFEC ESIMAE SYSEM ELAY Jua R. V. López, Orlad J. bias, ad Rui Seara
5th Eurpea Sigal Prcessig Cferece (EUSIPCO 7), Pza, Plad, September 3-7, 7, cpyright by EURASIP MOIFIE LEAKY ELAYE LMS ALGORIHM FOR IMPERFEC ESIMAE SYSEM ELAY Jua R. V. López, Orlad J. bias, ad Rui Seara
Partial-Sum Queries in OLAP Data Cubes Using Covering Codes
 326 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTERS, VOL. 47, NO. 2, DECEMBER 998 Partial-Sum Queries i OLAP Data Cubes Usig Cverig Cdes Chig-Tie H, Member, IEEE, Jehshua Bruck, Seir Member, IEEE, ad Rakesh Agrawal, Seir
326 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTERS, VOL. 47, NO. 2, DECEMBER 998 Partial-Sum Queries i OLAP Data Cubes Usig Cverig Cdes Chig-Tie H, Member, IEEE, Jehshua Bruck, Seir Member, IEEE, ad Rakesh Agrawal, Seir
Directional Duality Theory
 Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale OpeSIUC Discussi Papers Departmet f Ecmics 2004 Directial Duality Thery Daiel Primt Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale Rlf Fare Oreg State Uiversity Fllw this ad additial
Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale OpeSIUC Discussi Papers Departmet f Ecmics 2004 Directial Duality Thery Daiel Primt Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale Rlf Fare Oreg State Uiversity Fllw this ad additial
A Hartree-Fock Calculation of the Water Molecule
 Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jea M. Stadard Nvember 29, 2017 A Hartree-Fck Calculati f the Water Mlecule Itrducti A example Hartree-Fck calculati f the water mlecule will be preseted. I this case, the water
Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jea M. Stadard Nvember 29, 2017 A Hartree-Fck Calculati f the Water Mlecule Itrducti A example Hartree-Fck calculati f the water mlecule will be preseted. I this case, the water
Analysis on the Stability of Reservoir Soil Slope Based on Fuzzy Artificial Neural Network
 Research Jurnal f Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technlgy 5(2): 465-469, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; E-ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organizatin, 2013 Submitted: May 08, 2012 Accepted: May 29, 2012 Published:
Research Jurnal f Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technlgy 5(2): 465-469, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; E-ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organizatin, 2013 Submitted: May 08, 2012 Accepted: May 29, 2012 Published:
Review for cumulative test
 Hrs Math 3 review prblems Jauary, 01 cumulative: Chapters 1- page 1 Review fr cumulative test O Mday, Jauary 7, Hrs Math 3 will have a curse-wide cumulative test cverig Chapters 1-. Yu ca expect the test
Hrs Math 3 review prblems Jauary, 01 cumulative: Chapters 1- page 1 Review fr cumulative test O Mday, Jauary 7, Hrs Math 3 will have a curse-wide cumulative test cverig Chapters 1-. Yu ca expect the test
Multi-criteria neutrosophic decision making method based on score and accuracy functions under neutrosophic environment
 Multi-criteria eutrosophic decisio makig method based o score ad accuracy fuctios uder eutrosophic eviromet Rıdva Şahi Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciece, Ataturk Uiversity, Erzurum, 50, Turkey
Multi-criteria eutrosophic decisio makig method based o score ad accuracy fuctios uder eutrosophic eviromet Rıdva Şahi Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciece, Ataturk Uiversity, Erzurum, 50, Turkey
MATHEMATICS 9740/01 Paper 1 14 Sep hours
 Cadidate Name: Class: JC PRELIMINARY EXAM Higher MATHEMATICS 9740/0 Paper 4 Sep 06 3 hurs Additial Materials: Cver page Aswer papers List f Frmulae (MF5) READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Write yur full ame
Cadidate Name: Class: JC PRELIMINARY EXAM Higher MATHEMATICS 9740/0 Paper 4 Sep 06 3 hurs Additial Materials: Cver page Aswer papers List f Frmulae (MF5) READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Write yur full ame
Solutions. Definitions pertaining to solutions
 Slutis Defiitis pertaiig t slutis Slute is the substace that is disslved. It is usually preset i the smaller amut. Slvet is the substace that des the disslvig. It is usually preset i the larger amut. Slubility
Slutis Defiitis pertaiig t slutis Slute is the substace that is disslved. It is usually preset i the smaller amut. Slvet is the substace that des the disslvig. It is usually preset i the larger amut. Slubility
[1 & α(t & T 1. ' ρ 1
 NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY DENSITY & VISCOSITY OF MAGMAS I. Desity The desity (mass/vlume) f a magma is a imprtat parameter which plays a rle i a umber f aspects f magma behavir ad evluti.
NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY DENSITY & VISCOSITY OF MAGMAS I. Desity The desity (mass/vlume) f a magma is a imprtat parameter which plays a rle i a umber f aspects f magma behavir ad evluti.
An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA revisited -A third pole of technical efficiency-
 GRIPS Plicy Ifrmati Ceter Discussi Paper : 09-2 A epsil-based measure f efficiecy i DEA revisited -A third ple f techical efficiecy- Karu Te Natial Graduate Istitute fr Plicy Studies 7-22- Rppgi, Miat-ku,
GRIPS Plicy Ifrmati Ceter Discussi Paper : 09-2 A epsil-based measure f efficiecy i DEA revisited -A third ple f techical efficiecy- Karu Te Natial Graduate Istitute fr Plicy Studies 7-22- Rppgi, Miat-ku,
Thermodynamic study of CdCl 2 in 2-propanol (5 mass %) + water mixture using potentiometry
 Thermdyamic study f CdCl 2 i 2-prpal (5 mass %) + water mixture usig ptetimetry Reat Tmaš, Ađelka Vrdljak UDC: 544.632.4 Uiversity f Split, Faculty f Chemistry ad Techlgy, Teslia 10/V, HR-21000 Split,
Thermdyamic study f CdCl 2 i 2-prpal (5 mass %) + water mixture usig ptetimetry Reat Tmaš, Ađelka Vrdljak UDC: 544.632.4 Uiversity f Split, Faculty f Chemistry ad Techlgy, Teslia 10/V, HR-21000 Split,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical model for microarray data analysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
Full algebra of generalized functions and non-standard asymptotic analysis
 Full algebra f geeralized fuctis ad -stadard asympttic aalysis Tdr D. Tdrv Has Veraeve Abstract We cstruct a algebra f geeralized fuctis edwed with a caical embeddig f the space f Schwartz distributis.
Full algebra f geeralized fuctis ad -stadard asympttic aalysis Tdr D. Tdrv Has Veraeve Abstract We cstruct a algebra f geeralized fuctis edwed with a caical embeddig f the space f Schwartz distributis.
Function representation of a noncommutative uniform algebra
 Fucti represetati f a cmmutative uifrm algebra Krzysztf Jarsz Abstract. We cstruct a Gelfad type represetati f a real cmmutative Baach algebra A satisfyig f 2 = kfk 2, fr all f 2 A:. Itrducti A uifrm algebra
Fucti represetati f a cmmutative uifrm algebra Krzysztf Jarsz Abstract. We cstruct a Gelfad type represetati f a real cmmutative Baach algebra A satisfyig f 2 = kfk 2, fr all f 2 A:. Itrducti A uifrm algebra
ON FREE RING EXTENSIONS OF DEGREE N
 I terat. J. Math. & Mah. Sci. Vl. 4 N. 4 (1981) 703-709 703 ON FREE RING EXTENSIONS OF DEGREE N GEORGE SZETO Mathematics Departmet Bradley Uiversity Peria, Illiis 61625 U.S.A. (Received Jue 25, 1980) ABSTRACT.
I terat. J. Math. & Mah. Sci. Vl. 4 N. 4 (1981) 703-709 703 ON FREE RING EXTENSIONS OF DEGREE N GEORGE SZETO Mathematics Departmet Bradley Uiversity Peria, Illiis 61625 U.S.A. (Received Jue 25, 1980) ABSTRACT.
Preliminary Test Single Stage Shrinkage Estimator for the Scale Parameter of Gamma Distribution
 America Jural f Mathematics ad Statistics, (3): 3-3 DOI:.593/j.ajms.3. Prelimiary Test Sigle Stage Shrikage Estimatr fr the Scale Parameter f Gamma Distributi Abbas Najim Salma,*, Aseel Hussei Ali, Mua
America Jural f Mathematics ad Statistics, (3): 3-3 DOI:.593/j.ajms.3. Prelimiary Test Sigle Stage Shrikage Estimatr fr the Scale Parameter f Gamma Distributi Abbas Najim Salma,*, Aseel Hussei Ali, Mua
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
BC Calculus Review Sheet. converges. Use the integral: L 1
 BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe yu see the wrds.. Fid the re f the uuded regi represeted y the itegrl (smetimes f ( ) clled hriztl imprper itegrl).. Fid the re f differet uuded regi uder f() frm (,], where
BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe yu see the wrds.. Fid the re f the uuded regi represeted y the itegrl (smetimes f ( ) clled hriztl imprper itegrl).. Fid the re f differet uuded regi uder f() frm (,], where
Efficient Processing of Continuous Reverse k Nearest Neighbor on Moving Objects in Road Networks
 Iteratial Jural f Ge-Ifrmati Article Efficiet Prcessig f Ctiuus Reverse k Nearest Neighbr Mvig Objects i Rad Netwrks Muhammad Attique, Hyug-Ju Ch, Rize Ji ad Tae-Su Chug, * Departmet f Cmputer Egieerig,
Iteratial Jural f Ge-Ifrmati Article Efficiet Prcessig f Ctiuus Reverse k Nearest Neighbr Mvig Objects i Rad Netwrks Muhammad Attique, Hyug-Ju Ch, Rize Ji ad Tae-Su Chug, * Departmet f Cmputer Egieerig,
Matching a Distribution by Matching Quantiles Estimation
 Jural f the America Statistical Assciati ISSN: 0162-1459 (Prit) 1537-274X (Olie) Jural hmepage: http://www.tadflie.cm/li/uasa20 Matchig a Distributi by Matchig Quatiles Estimati Niklas Sgurpuls, Qiwei
Jural f the America Statistical Assciati ISSN: 0162-1459 (Prit) 1537-274X (Olie) Jural hmepage: http://www.tadflie.cm/li/uasa20 Matchig a Distributi by Matchig Quatiles Estimati Niklas Sgurpuls, Qiwei
Gusztav Morvai. Hungarian Academy of Sciences Goldmann Gyorgy ter 3, April 22, 1998
 A simple radmized algrithm fr csistet sequetial predicti f ergdic time series Laszl Gyr Departmet f Cmputer Sciece ad Ifrmati Thery Techical Uiversity f Budapest 5 Stczek u., Budapest, Hugary gyrfi@if.bme.hu
A simple radmized algrithm fr csistet sequetial predicti f ergdic time series Laszl Gyr Departmet f Cmputer Sciece ad Ifrmati Thery Techical Uiversity f Budapest 5 Stczek u., Budapest, Hugary gyrfi@if.bme.hu
Recovery of Third Order Tensors via Convex Optimization
 Recvery f Third Order Tesrs via Cvex Optimizati Hlger Rauhut RWTH Aache Uiversity Lehrstuhl C für Mathematik (Aalysis) Ptdriesch 10 5056 Aache Germay Email: rauhut@mathcrwth-aachede Željka Stjaac RWTH
Recvery f Third Order Tesrs via Cvex Optimizati Hlger Rauhut RWTH Aache Uiversity Lehrstuhl C für Mathematik (Aalysis) Ptdriesch 10 5056 Aache Germay Email: rauhut@mathcrwth-aachede Željka Stjaac RWTH
On the affine nonlinearity in circuit theory
 O the affie liearity i circuit thery Emauel Gluski The Kieret Cllege the Sea f Galilee; ad Ort Braude Cllege (Carmiel), Israel. gluski@ee.bgu.ac.il; http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~gluski/ E. Gluski, O the affie
O the affie liearity i circuit thery Emauel Gluski The Kieret Cllege the Sea f Galilee; ad Ort Braude Cllege (Carmiel), Israel. gluski@ee.bgu.ac.il; http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~gluski/ E. Gluski, O the affie
SOME DISTANCE MEASURES FOR INTUITIONISTIC UNCERTAIN LINGUISTIC SETS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO GROUP DECISION MAKING
 Lecturer Bi Jiaxi, PhD Uiversity of Shaghai for Sciece ad Techology Zheiag Wali Uiversity Professor Lei Liaghai, PhD Uiversity of Shaghai for Sciece ad Techology Lecturer Peg Bo, PhD ( Correspodig author)
Lecturer Bi Jiaxi, PhD Uiversity of Shaghai for Sciece ad Techology Zheiag Wali Uiversity Professor Lei Liaghai, PhD Uiversity of Shaghai for Sciece ad Techology Lecturer Peg Bo, PhD ( Correspodig author)
Aligning Anatomy Ontologies in the Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative
 Aligig Aatmy Otlgies i the Otlgy Aligmet Evaluati Iitiative Patrick Lambrix, Qiag Liu, He Ta Departmet f Cmputer ad Ifrmati Sciece Liköpigs uiversitet 581 83 Liköpig, Swede Abstract I recet years may tlgies
Aligig Aatmy Otlgies i the Otlgy Aligmet Evaluati Iitiative Patrick Lambrix, Qiag Liu, He Ta Departmet f Cmputer ad Ifrmati Sciece Liköpigs uiversitet 581 83 Liköpig, Swede Abstract I recet years may tlgies
x 1 Outline IAML: Logistic Regression Decision Boundaries Example Data
 Outline IAML: Lgistic Regressin Charles Suttn and Victr Lavrenk Schl f Infrmatics Semester Lgistic functin Lgistic regressin Learning lgistic regressin Optimizatin The pwer f nn-linear basis functins Least-squares
Outline IAML: Lgistic Regressin Charles Suttn and Victr Lavrenk Schl f Infrmatics Semester Lgistic functin Lgistic regressin Learning lgistic regressin Optimizatin The pwer f nn-linear basis functins Least-squares
CS 477/677 Analysis of Algorithms Fall 2007 Dr. George Bebis Course Project Due Date: 11/29/2007
 CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Generative models for linear classification
 COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Generative mdels fr linear classificatin Instructr: Herke van Hf (herke.vanhf@mail.mcgill.ca) Slides mstly by: Jelle Pineau Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~hvanh2/cmp551
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Generative mdels fr linear classificatin Instructr: Herke van Hf (herke.vanhf@mail.mcgill.ca) Slides mstly by: Jelle Pineau Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~hvanh2/cmp551
Chapter 5. Root Locus Techniques
 Chapter 5 Rt Lcu Techique Itrducti Sytem perfrmace ad tability dt determied dby cled-lp l ple Typical cled-lp feedback ctrl ytem G Ope-lp TF KG H Zer -, - Ple 0, -, - K Lcati f ple eaily fud Variati f
Chapter 5 Rt Lcu Techique Itrducti Sytem perfrmace ad tability dt determied dby cled-lp l ple Typical cled-lp feedback ctrl ytem G Ope-lp TF KG H Zer -, - Ple 0, -, - K Lcati f ple eaily fud Variati f
E o and the equilibrium constant, K
 lectrchemical measuremets (Ch -5 t 6). T state the relati betwee ad K. (D x -b, -). Frm galvaic cell vltage measuremet (a) K sp (D xercise -8, -) (b) K sp ad γ (D xercise -9) (c) K a (D xercise -G, -6)
lectrchemical measuremets (Ch -5 t 6). T state the relati betwee ad K. (D x -b, -). Frm galvaic cell vltage measuremet (a) K sp (D xercise -8, -) (b) K sp ad γ (D xercise -9) (c) K a (D xercise -G, -6)
Study in Cylindrical Coordinates of the Heat Transfer Through a Tow Material-Thermal Impedance
 Research ural f Applied Scieces, Egieerig ad echlgy (): 9-63, 3 ISSN: 4-749; e-issn: 4-7467 Maxwell Scietific Orgaiati, 3 Submitted: uly 4, Accepted: September 8, Published: May, 3 Study i Cylidrical Crdiates
Research ural f Applied Scieces, Egieerig ad echlgy (): 9-63, 3 ISSN: 4-749; e-issn: 4-7467 Maxwell Scietific Orgaiati, 3 Submitted: uly 4, Accepted: September 8, Published: May, 3 Study i Cylidrical Crdiates
How T o Start A n Objective Evaluation O f Your Training Program
 J O U R N A L Hw T Start A n Objective Evaluatin O f Yur Training Prgram DONALD L. KIRKPATRICK, Ph.D. Assistant Prfessr, Industrial Management Institute University f Wiscnsin Mst training m e n agree that
J O U R N A L Hw T Start A n Objective Evaluatin O f Yur Training Prgram DONALD L. KIRKPATRICK, Ph.D. Assistant Prfessr, Industrial Management Institute University f Wiscnsin Mst training m e n agree that
Every gas consists of a large number of small particles called molecules moving with very high velocities in all possible directions.
 Kietic thery f gases ( Kietic thery was develped by Berlli, Jle, Clasis, axwell ad Bltzma etc. ad represets dyamic particle r micrscpic mdel fr differet gases sice it thrws light the behir f the particles
Kietic thery f gases ( Kietic thery was develped by Berlli, Jle, Clasis, axwell ad Bltzma etc. ad represets dyamic particle r micrscpic mdel fr differet gases sice it thrws light the behir f the particles
NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION
 NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
Declarative approach to cyclic steady state space refinement: periodic process scheduling
 It J Adv Mauf Techl DOI 10.1007/s00170-013-4760-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Declarative apprach t cyclic steady state space refiemet: peridic prcess schedulig Grzegrz Bcewicz Zbigiew A. Baaszak Received: 16 April
It J Adv Mauf Techl DOI 10.1007/s00170-013-4760-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Declarative apprach t cyclic steady state space refiemet: peridic prcess schedulig Grzegrz Bcewicz Zbigiew A. Baaszak Received: 16 April
Information Sciences
 Ifrmati Scieces 292 (2015) 15 26 Ctets lists available at ScieceDirect Ifrmati Scieces jural hmepage: www.elsevier.cm/lcate/is Kerel sparse represetati fr time series classificati Zhihua Che a, Wagmeg
Ifrmati Scieces 292 (2015) 15 26 Ctets lists available at ScieceDirect Ifrmati Scieces jural hmepage: www.elsevier.cm/lcate/is Kerel sparse represetati fr time series classificati Zhihua Che a, Wagmeg
Sound Absorption Characteristics of Membrane- Based Sound Absorbers
 Purdue e-pubs Publicatis f the Ray W. Schl f Mechaical Egieerig 8-28-2003 Sud Absrpti Characteristics f Membrae- Based Sud Absrbers J Stuart Blt, blt@purdue.edu Jih Sg Fllw this ad additial wrks at: http://dcs.lib.purdue.edu/herrick
Purdue e-pubs Publicatis f the Ray W. Schl f Mechaical Egieerig 8-28-2003 Sud Absrpti Characteristics f Membrae- Based Sud Absrbers J Stuart Blt, blt@purdue.edu Jih Sg Fllw this ad additial wrks at: http://dcs.lib.purdue.edu/herrick
European Journal of Operational Research
 Eurpea Jural f Operatial Research 232 (2014) 4 4 Ctets lists available at ScieceDirect Eurpea Jural f Operatial Research jural hmepage www.elsevier.cm/lcate/ejr Discrete Optimizati A aalytical cmparis
Eurpea Jural f Operatial Research 232 (2014) 4 4 Ctets lists available at ScieceDirect Eurpea Jural f Operatial Research jural hmepage www.elsevier.cm/lcate/ejr Discrete Optimizati A aalytical cmparis
Wavelet Video with Unequal Error Protection Codes in W-CDMA System and Fading Channels
 Wavelet Vide with Uequal Errr Prtecti Cdes i W-CDMA System ad Fadig Chaels MINH HUNG LE ad RANJITH LIYANA-PATHIRANA Schl f Egieerig ad Idustrial Desig Cllege f Sciece, Techlgy ad Evirmet Uiversity f Wester
Wavelet Vide with Uequal Errr Prtecti Cdes i W-CDMA System ad Fadig Chaels MINH HUNG LE ad RANJITH LIYANA-PATHIRANA Schl f Egieerig ad Idustrial Desig Cllege f Sciece, Techlgy ad Evirmet Uiversity f Wester
Sequences. Notation. Convergence of a Sequence
 Sequeces A sequece is essetially just a list. Defiitio (Sequece of Real Numbers). A sequece of real umbers is a fuctio Z (, ) R for some real umber. Do t let the descriptio of the domai cofuse you; it
Sequeces A sequece is essetially just a list. Defiitio (Sequece of Real Numbers). A sequece of real umbers is a fuctio Z (, ) R for some real umber. Do t let the descriptio of the domai cofuse you; it
Pipe Networks - Hardy Cross Method Page 1. Pipe Networks
 Pie Netwrks - Hardy Crss etd Page Pie Netwrks Itrducti A ie etwrk is a itercected set f ies likig e r mre surces t e r mre demad (delivery) its, ad ca ivlve ay umber f ies i series, bracig ies, ad arallel
Pie Netwrks - Hardy Crss etd Page Pie Netwrks Itrducti A ie etwrk is a itercected set f ies likig e r mre surces t e r mre demad (delivery) its, ad ca ivlve ay umber f ies i series, bracig ies, ad arallel
ESWW-2. Israeli semi-underground great plastic scintillation multidirectional muon telescope (ISRAMUTE) for space weather monitoring and forecasting
 ESWW-2 Israeli semi-udergrud great plastic scitillati multidirectial mu telescpe (ISRAMUTE) fr space weather mitrig ad frecastig L.I. Drma a,b, L.A. Pustil'ik a, A. Sterlieb a, I.G. Zukerma a (a) Israel
ESWW-2 Israeli semi-udergrud great plastic scitillati multidirectial mu telescpe (ISRAMUTE) fr space weather mitrig ad frecastig L.I. Drma a,b, L.A. Pustil'ik a, A. Sterlieb a, I.G. Zukerma a (a) Israel
NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
The Complexity of Translation Membership for Macro Tree Transducers
 The Cmplexity f Traslati Membership fr Macr Tree Trasducers Kazuhir Iaba The Uiversity f Tky kiaba@is.s.u-tky.ac.jp Sebastia Maeth NICTA ad Uiversity f New Suth Wales sebastia.maeth@icta.cm.au ABSTRACT
The Cmplexity f Traslati Membership fr Macr Tree Trasducers Kazuhir Iaba The Uiversity f Tky kiaba@is.s.u-tky.ac.jp Sebastia Maeth NICTA ad Uiversity f New Suth Wales sebastia.maeth@icta.cm.au ABSTRACT
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared i a jural published by Elsevier The attached cpy is furished t the authr fr iteral -cmmercial research ad educati use, icludig fr istructi at the authrs istituti ad sharig with clleagues
This article appeared i a jural published by Elsevier The attached cpy is furished t the authr fr iteral -cmmercial research ad educati use, icludig fr istructi at the authrs istituti ad sharig with clleagues
MAT1026 Calculus II Basic Convergence Tests for Series
 MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
2.4 Sequences, Sequences of Sets
 72 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.4 Sequeces, Sequeces of Sets 2.4.1 Sequeces Defiitio 2.4.1 (sequece Let S R. 1. A sequece i S is a fuctio f : K S where K = { N : 0 for some 0 N}. 2. For each
72 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.4 Sequeces, Sequeces of Sets 2.4.1 Sequeces Defiitio 2.4.1 (sequece Let S R. 1. A sequece i S is a fuctio f : K S where K = { N : 0 for some 0 N}. 2. For each
THE LIFE OF AN OBJECT IT SYSTEMS
 THE LIFE OF AN OBJECT IT SYSTEMS Persns, bjects, r cncepts frm the real wrld, which we mdel as bjects in the IT system, have "lives". Actually, they have tw lives; the riginal in the real wrld has a life,
THE LIFE OF AN OBJECT IT SYSTEMS Persns, bjects, r cncepts frm the real wrld, which we mdel as bjects in the IT system, have "lives". Actually, they have tw lives; the riginal in the real wrld has a life,
