Max-min Fair Beamforming for SWIPT Systems with Non-linear EH Model
|
|
|
- Bernard Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Max-min Fair Beamforming for SWIPT Systems with Non-linear EH Model Invited Paper Elena Boshkovska, Xiaoming Chen, Linglong Dai, Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, and Robert Schober arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 14 May 017 Abstract We study the beamforming design for multiuser systems with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer SWIPT. Employing a practical non-linear energy harvesting EH model, the design is formulated as a non-convex optimization problem for the maximization of the minimum harvested power across several energy harvesting receivers. The proposed problem formulation takes into account imperfect channel state information CSI and a minimum required signalto-interference-plus-noise ratio SINR. The globally optimal solution of the design problem is obtained via the semidefinite programming SDP relaxation approach. Interestingly, we can show that at most one dedicated energy beam is needed to achieve optimality. Numerical results demonstrate that with the proposed design a significant performance gain and improved fairness can be provided to the users compared to two baseline schemes. I. INTRODUCTION In the past decades, the increasing interest in data hungry applications and heterogenous services has triggered the consumption of tremendous amounts of energy in wireless communication systems. In practice, mobile devices are usually powered by batteries with limited energy storage capacity which becomes a bottleneck in perpetuating the lifetime of networks. To address this issue, energy harvesting EH- based communication technology has been proposed. In particular, this technology enables self-sustainability of powerconstrained communication devices. Communication systems may be equipped with energy harvesters [1] [3] to scavenge energy from renewable natural energy sources such as solar and wind. Yet, these conventional energy sources are only available at specific locations which limits the mobility of portable devices. Besides, the intermittent and uncontrollable nature of these natural energy sources is a concern for wireless communications, where uninterrupted and stable quality of service QoS are of paramount importance. Recently, radio frequency RF-based wireless power transfer WPT has received considerable interest from both industry and academia [4] [7]. For example, industrial companies such as Samsung Electronics and Huawei Technology, have begun to launch research and study groups to facilitate the development and standardization of WPT [4]. In fact, E. Boshkovska and R. Schober are with Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg FAU, Germany. X. Chen is with Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China. L. Dai is with Tsinghua University, Beijing, China. D. W. K. Ng is with The University of New South Wales, Australia. L. Dai is supported by the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China Grant No. 015DFG1760 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No R. Schober is supported by the AvH Professorship Program of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. D. W. K. Ng is supported under Australian Research Council s Discovery Early Career Researcher Award funding scheme project number DE the introduction of WPT avoids the high potential costs of planning, installing, displacing, and maintaining power cables in buildings and infrastructure. Specifically, for RF-based communication networks, energy from ambient propagating electromagnetic EM waves in radio frequency RF can be harvested by energy-limited communication transceivers for prolonging their lifetimes and supporting the energy consumption required for future information transmission. This technology eliminates the need for power cords and manual recharging. Moreover, the broadcast nature of wireless channels facilitates one-to-many wireless charging and the possibility of simultaneous wireless information and power transfer SWIPT [5] [7]. Compared to conventional EH, RF-based EH technology can provide on-demand energy replenishment which makes it suitable for smart wireless communication devices having strict QoS and energy requirements. In practice, wireless power has to be transferred via a signal with high carrier frequency such that antennas with small size can be used for harvesting the power. However, the associated path loss severely attenuates the signal leading to a small harvested power at the receiver. Hence, multiple antenna beamforming has been proposed to facilitate efficient WPT [8] [1]. In [8], the concept of energy beamforming was first proposed to maximize the efficiency of WPT. In [9] [11], energy beamforming was advocated to provide secure SWIPT in multiple-antenna systems. The authors of [1] investigated the impact of a massive number of antennas on the energy efficiency of SWIPT systems. However, most of the beamforming designs for SWIPT systems were based on an over-simplified linear EH model. In fact, this model was recently shown to be incapable of capturing the non-linear characteristics of practical RF EH circuits [13]. Besides, the results obtained in [8] [1] were based on the assumption of perfect knowledge of the channel state information CSI of information receivers which is not realistic in practice. Furthermore, resource allocation fairness was not considered in [8] [1] which may lead to an unsatisfactory performance for some users. In this paper, we address these problems. In particular, we formulate the beamforming design as an optimization problem to provide max-min fairness in WPT to energy harvesting receivers equipped with practical non-linear energy harvesting circuits. The optimization problem is solved by a semidefinite programming SDP based resource allocation algorithm. Simulation results illustrate an interesting trade-off between user fairness in energy harvesting and individual user data rate. Notation: We use boldface capital and lower case letters to denote matrices and vectors, respectively. A H, TrA, and
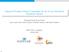
2 RF wave RF energy harvesting receiver Information receiver 1 Information receiver Passive band pass filter Rectifying circuit Output to load Transmitter Energy harvesting receiver Energy harvesting receiver 1 RF-to-DC power conversion Fig.. Block diagram of an ER. Fig. 1. A system model of a SWIPT system with K = IRs and J = ERs. RankA represent the Hermitian transpose, trace, and rank of matrix A, respectively; A 0 and A 0 indicate that A is a positive definite and a positive semidefinite matrix, respectively;i N is then N identity matrix;[b] a:b,c:d returns the a-th to the b-th rows and the c-th to the d-th column block submatrix of B; C N M denotes the set of all N M matrices with complex entries; H N denotes the set of all N N Hermitian matrices. The circularly symmetric complex Gaussian CSCG distribution is denoted by CNm, Σ with mean vector m and covariance matrix Σ; means distributed as ; E{ } denotes statistical expectation; represents the absolute value of a complex scalar. [x] + stands for max{0,x}, and [ ] T represents the transpose operation. II. SYSTEM MODEL In this section, we present the channel model for downlink SWIPT systems. A. Channel Model We consider a frequency flat and slowly time varying downlink communication channel. In the SWIPT system, there are one transmitter, K information receivers IRs, and J EH receivers ER, cf. Figure 1. The transmitter is equipped with N T 1 antennas and serves both the IRs and the ERs simultaneously in the same frequency band. We assume that each IR is a single-antenna device and each ER is equipped with N R 1 receive antennas. The received signals at IR k {1,...,K} and ER j {1,...,J} are given by K y k = h H k w k s k +w E +n, and 1 K y ERj = G H j w k s k +w E +n ERj, j {1,...,J}, respectively, where w k C NT 1 and s k C are the information beamforming vector and the associated information symbol for IR k, respectively. Without loss of generality, we assume that E{ s k } = 1, k. The vector channel of the transmitter-to-ir k link is denoted by h k C NT 1 and the channel matrix of the transmitter-to-er j link is denoted by G j C NT NR. Variables n CN0,σ s and n ERj CN0,σ si NR denote the additive white Gaussian noises AWGN at IR k and ER j, respectively, where σ s denotes the noise power at the receiver. w E C NT 1 is a Gaussian pseudo-random sequence generated by the transmitter to facilitate efficient WPT. In particular, w E is modeled as a complex Gaussian random vector with w E CN0,W E, 3 where W E H NT,W E 0, is the covariance matrix of the pseudo-random energy signal. B. Achievable Rate Since the energy signal w E is a Gaussian pseudo-random sequence which is known to all transceivers, IR k can remove it via successive interference cancellation SIC. Then, the achievable rate bit/s/hz between the transmitter and IR k is given by wk R k = log 1+ HH kw k i k wh i H, 4 kw i +σs where the interference caused by the energy signal, i.e., Trh H k W Eh k has been removed via SIC. C. Non-linear EH Model Figure shows a general block diagram of an ER consisting of a passive filter and a rectifying circuit. In practice, the implementation of an ER depends on the adopted circuit components which vary for different designs. To isolate the EH model from a specific circuit design, two general tractable models, i.e., the linear model and the non-linear model, have been proposed in the literature for characterizing the RF EH process. Mathematically, the total received RF power 1 at ER j is given by P ERj = Tr w k wk H +W E G j G H j. 5 For the linear EH model which as adopted e.g. in [8] [1], the total harvested power at ER j, Φ Linear ER j, is typically modelled by the following linear equation: Φ Linear ER j = η j P ERj, 6 where 0 η j 1 is the constant power conversion efficiency of ER j. 1 In this paper, the unit of Joule-per-second is used for measuring energy. Thus, the terms power and energy are interchangeable.
3 Yet, practical RF-based EH circuits are inherently non-linear and the conventional linear model fails to capture this important characteristic, as shown experimentally in [14] [16]. Motivated by this, a parametric non-linear EH model was proposed in [13], [17] which has been shown to be in excellent agreement closely with practical measurement results. In this paper, we adopt the more realistic non-linear EH model and the total harvested power at ER j, Φ ERj, is modelled as: Φ ERj = [Ψ ER j M j Ω j ] 1 Ω j, Ω j = where Ψ ERj = M j 1 1+expa j b j,7 8 1+exp a j P ERj b j is a sigmoidal function which has the received RF power, P ERj, as the input. Three parameters, namely, M j, a j, and b j, are introduced to describe the shape of the logistic function which depends on the physical properties of the RF EH circuit. Specifically, M j, a j, and b j are constants which determine the maximum harvestable power, the charging rate with respect to the input power, and the minimum required voltage to turn on the EH circuit, respectively. D. Channel State Information We take into account the imperfection of the channel state information CSI for beamforming design. To this end, we adopt a deterministic model [11], [18]. In particular, we model the CSI of the links as: h k = ĥk + h k, 9 { } h k C NT 1 : h k ρ k, 10 Υ k G j = Ĝj + G j, j {1,...,J}, and 11 { } Ξ j G j C NT NR : G j F υ j, j, 1 respectively, where ĥk and Ĝj are the estimates of channel vector h k and channel matrix G j, respectively. The channel estimation errors of h k and G j are denoted by h k and G j, respectively. SetsΥ k andξ j collect all possible channel estimation errors. Constants ρ k and υ j denote the maximum values of the norms of the CSI estimation error vector h k and the CSI estimation error matrix G j, respectively. III. PROBLEM FORMULATION AND SOLUTION The system objective is to maximize the minimum harvested power among all the ERs, i.e., to provide max-min fairness [19], while guaranteeing the QoS of information communication. To this end, we formulate the resource allocation We note that these parameters can be determined for any given EH circuit. algorithm design as the following non-convex optimization problem: maximize W E H N T,w k s.t. C1 : min Ψ ERj 13 G j Ξ j j {1,...,J} w k +TrW E P max, C : min h k Υ k C3 : W E 0. w k HH kw k i k wh i H kw i +σs Γ reqk, The objective function in 13 takes into account the CSI uncertainty set Ξ j to provide robustness against CSI imperfection. Constants P max and Γ reqk in constraints C1 and C denote the maximum transmit power allowance and the QoS requirement on the minimum received signal-to-interferenceplus-noise ratio SINR at IR k, respectively. Constraint C3 and W E H NT constrain matrix W E to be a positive semidefinite Hermitian matrix. It can be observed that constraint C is non-convex. Besides, there are infinitely many possibilities in both the objective function and constraint C, due to the CSI uncertainties. In order to design a computationally efficient resource allocation algorithm, we first define W k = w k w H k and transform the considered problem into the following equivalent rankconstrained semidefinite program SDP: maximize τ W E,W k H N T, β,τ s.t. C1 : TrW k +TrW E P max, TrW k H k C : min TrW i H k +σ h k Υ k Γ s, reqk i k C3 : W E 0, M j C4 : 1+exp a j β j b j τ1 Ω j+m j Ω j, j, C5 : min Tr G j Ξ j W k +W E G j G H j β j, j, C6 : RankW k 1, C7 : W k 0, 14 where H k = h k h H k. Vector β = {β 1,...,β j,...,β J } and τ are auxiliary optimization variables. We note that C7 and RankW k 1 in 14 are imposed such that W k = w k w H k. Now, the transformed problem in 14 involves infinitely many constraints only in C and C5. Besides, the rank constraint in C6 is combinatorial.we first handle constraints C and C5 by transforming them into linear matrix inequalities LMIs using the following lemma: Lemma 1 S-Procedure [0]: Let a function f m x,m {1,},x C N 1, be defined as f m x = x H A m x+re{b H m x}+c m, 15
4 where A m H N, b m C N 1, and c m R. Then, the implication f 1 x 0 f x 0 holds if and only if there exists a δ 0 such that δ [ ] A1 b 1 b H 1 c 1 [ ] A b b H 0, 16 c provided that there exists a point ˆx such that f m ˆx < 0. Applying Lemma 1, the original constraint C holds if and only if there exists a δ k 0, such that the following LMI constraint holds: [ ] δk I C: S Ck W k,δ k = NT 0 0 δ k ρ 17 k σ s + U H Wk W ĥ i 0, k Uĥk Γ reqk i k ] where Uĥk = [I NT ĥ k. Similarly, constraint C5 can be equivalently written as C5: S C5j W k,w E,ν,β 18 [ ] νj I = NTN R 0 0 β j ν j υj { K } + U H g j W k +W E U gj 0, j, where ν = {ν 1,...,ν j,...,ν J }, ν j 0, W k = I NR W k, W E = I NR W E, U gj = [I NTN R g j ], and g j = vecĝ j. Then, the considered optimization problem can be rewritten as maximize W E,W k H N T, β,τ τ 19 s.t. C1,C3,C4,C7, C : S Ck W k,δ k 0, k, C5 : S C5j W k,w E,ν,β 0, j, C6 : RankW k 1, where δ k 0 and ν 0 are the auxiliary optimization variables introduced in Lemma 1 for handling constraints C and C5, respectively. We note that C and C5 are now LMIs with finite numbers of constraints which are relatively easier to handle compared to the infinite numbers of constraints in the original problem formulation. However, the rank constraint in C6 is still an obstacle to solving the considered optimization problem due to its combinatorial nature. As a result, we adopt SDP relaxation by removing constraint C6 from the problem formulation which yields: maximize W E,W k H N T, β,τ τ 0 s.t. C1,C3,C4,C7, C : S Ck W k,δ k 0, k, C5 : S C5j W k,w E,ν,β 0, j, C6 : RankW k 1. TABLE I SIMULATION PARAMETERS. Carrier center frequency 915 MHz Bandwidth 00 khz Transceiver antenna gain 10 dbi Number of receive antennas N R Noise power σ 95 dbm Maximum transmit power P max 36 dbm Transmitter-to-ER fading distribution Rician with Rician factor 3 db Transmitter-to-IR fading distribution Rayleigh The problem in 0 is a standard convex optimization problem and can be solved numerically with computationally efficient off-the-shelf convex programs solvers such as CVX [1]. However, it is unclear if the obtained solution satisfies RankW k 1, k. Therefore, we introduce the following theorem to reveal the structure of the solution of 0. Theorem 1: Let the optimal beamforming matrix and energy covariance matrix of 0 be W k and W E, respectively. Assuming the considered problem is feasible forp max > 0 and Γ reqk > 0, k, then RankW k = 1, k, and RankW E 1. Proof: Please refer to the Appendix. Thus, the globally optimal solution of 0 can be obtained. In particular, employing information beamforming for each IR and at most one energy beam is optimal for the considered problem, despite the imperfection of the CSI and the nonlinearity of the RF EH circuits. IV. SIMULATION In this section, the performance of the proposed optimal beamforming design is evaluated via simulations. The important simulation parameters are summarized in Table I. Unless specified otherwise, we assume that there are K = IRs and J = 4 ERs which are located 100 meters and 5 meters from the transmitter, respectively. Furthermore, we choose the normalized maximum channel estimation errors of ER j and IRk as σest Gj = 1% υ j G j, j, andσ est hk = 1% ρ F h k, respectively. Besides, we assume that all IRs require the same minimum data rate, i.e., Γ reqk = Γ req. For the non-linear EH circuits, we set the maximum harvested power per wireless powered device to M j = 4 mw. Besides, we adopt a j = 150 and b j = We solve the optimization problem in 13 and obtain the average system performance by averaging over different channel realizations. In Figure 3, we show the average minimum harvested power per ER in the considered SWIPT systems for the optimal robust beamforming design. As can be observed, there is a nontrivial trade-off between the minimum harvested power per ER and the minimum required data rate per IR. In particular, the achievable data rate per user and the minimum harvested power per ER cannot be maximized simultaneously. Besides, for the optimal resource allocation, the trade-off region of the minimum achievable rate and the harvested energy is enlarged significantly for larger N T and N R. This is due to the fact that the extra degrees of freedom offered by multiple transmit antennas can be used to focus both the information and energy beams which improves the beamforming efficiency. On the
5 1 Average minimum harvested power per ER dbm = 10, N R = 3 = 10, N R = 5 = 1, N R = 3 = 1, N R = 5 Baseline scheme 1, N T = 1, N R = 3 Baseline scheme 1, N T = 1, N R = 5 Average minmum harvested power per ER dbm Proposed scheme, σ est = 1% Proposed scheme, σ est = 10% Baseline scheme, σ est = 1% Baseline scheme, σ est = 10% Minimum required data rate per IR bit/s/hz Number of ERs Fig. 3. Average minimum harvested power per ER dbm versus the minimum required data rate per IR bit/s/hz for different numbers of antennas. other hand, increasing the number of receive antennas N R at the ER can significantly improve the minimum harvested energy per ER. In fact, the additional receive antennas act as additional energy collectors which enable a more efficient energy transfer. Furthermore, we verified by simulation that RankW k = 1 can be obtained for all considered channel realizations which confirms the correctness of Theorem 1. On the other hand, we also show the performance of a baseline scheme for comparison in Figure 3. For baseline scheme 1, an existing linear EH model with η j = 1, cf. 6, is adopted for resource allocation algorithm design. Specifically, we optimize w k and W E to maximize the minimum harvested power per ER subject to the constraints in 13. Then, the resource allocation designed by baseline scheme 1 is applied in the considered system with non-linear ERs. We observe from Figure 4 that a substantial gain in harvested power is achieved by the proposed optimal resource allocation algorithm compared to baseline scheme 1. This is because baseline scheme 1 does not take into account the non-linearity of practical EH circuits leading to mismatches in resource allocation. In Figure 4, we study the average minimum harvested power per ER versus the number of ERs for different maximum normalized channel estimation error variances and beamforming schemes. The minimum required SINR is set to Γ reqk = 10 db and there are N R = 3 and N T = 10 antennas equipped at each ER and the transmitter, respectively. Besides, the maximum normalized channel estimation error variance of the transmitter-to-ir links and the transmitter-to-er links are set to be identical, i.e., σ est Gj = σ est hk = σ est. As can be observed, the average minimum harvested power per ER in the system decreases with an increasing number of ERs. In fact, the more ERs are in the system, the more difficult it is for the transmitter to provide fair resource allocation for all ERs. In particular, for a large number of ERs in the system, it is more likely that there are some ERs with poor channel qualities. Thus, the transmitter is forced to steer the information and Fig. 4. Average minimum harvested power per ER dbm versus the number of ERs for N T = 10 and N R = 3. energy signals toward ERs with weak channel conditions which reduces the minimum harvested power per ER. On the other hand, the average minimum harvested power per ER decreases with increasing σest, since the CSI quality degrades with increasing σest. In particular, for a larger value of σ est, it becomes more difficult for the transmitter to accurately focus the transmitter energy as would be necessary for achieving a high efficiency in SWIPT. For comparison, we also show the performance of baseline scheme which adopts an isotropic radiation pattern for W E. Then, we maximize the minimum harvested power per ER by optimizing W k and the power of W E subject to the same constraints as in 14 via SDP relaxation. It can be seen that the performance of the baseline scheme is unsatisfactory compared to the proposed scheme. In fact, baseline scheme cannot fully exploit the available degrees of freedom for efficient WPT as the beamforming direction of W E is fixed. V. CONCLUSIONS We studied the beamforming design for multiuser SWIPT systems with the objective of ensuring max-min fairness in WPT. The design was formulated as a non-convex optimization problem which took into account the non-linearity of practical EH circuits and the imperfection of the CSI. The optimization problem was solved by applying SDP relaxation. Simulation results demonstrated that the proposed optimal beamforming design offers significant performance gains compared to two baseline schemes. APPENDIX-PROOF OF THEOREM 1 We follow a similar approach as in [] to prove Theorem 1. We note that the relaxed problem in 0 is jointly convex with respect to the optimization variables. Besides, it can be verified that the problem satisfies the Slater s constraint qualification and thus has a zero duality gap. Therefore, to reveal the
6 structure of W k and W E, we consider the Lagrangian of problem 0 which is given by: K L=τ λ TrW k +TrW E P max + + J j=1 TrS Ck W k,δ k D Ck + TrW k Y k 1 TrS C5j W k,w E,ν,β D C5j +TrW E Z+, where λ 0, D Ck 0, Z 0, D C5j 0, j {1,...,J}, and Y k 0 are the dual variables for constraints C1, C, C3, C5, and C7, respectively. Besides, we denote as a collection of variables and constants that are not relevant to the proof. For notational convenience, we denote the optimal primal and dual variables of the SDP relaxed version of 0 by the corresponding variables with an asterisk superscript in the following. Now, we focus on those Karush-Kuhn-Tucker KKT conditions which are needed for the proof. Y k,z,d C 3k,D C 5j 0, λ 0, YkW k = 0, Z WE = 0, Yk = λ I NT, = Uĥk D C k Γ reqk U H ĥ k i kuĥi D C i U H ĥ i + J N R ] [U gj D C5j U H gj j=1 l=1 Z = λ I NT a:b,c:d, J N R ] [U gj D U H gj C5j j=1 l=1 a b c d a:b,c:d,e where a = l 1N T +1,b = ln T,c = l 1N T +1, and d = ln T. From b, we know that the columns of Wk lie in the null space of Yk. In order to reveal the rank of W k, we investigate the structure of Yk. First, it can be shown that λ > 0 since constraint C1 is active at the optimal solution. Then, we show that in c is a positive semidefinite matrix by contradiction. Suppose is a negative definite matrix, then from c, Yk becomes a full-rank and positive definite matrix. By b, Wk is forced to be the zero matrix which is not an optimal solution for P max > 0 and Γ reqk > 0. Thus, in the following, we focus on the case 0. Since matrix Yk = λ I NT is positive semidefinite, the following inequality holds: λ λ max 0, 3 where λ max is the maximum eigenvalue of matrix. From c, if λ > λ max, matrixyk will become a positive definite matrix with full rank. However, this will again yield the solution Wk = 0 which is not optimal since Γ req > 0. Thus, at the optimal solution, λ = λ max must holds. Besides, in order to have a bounded optimal dual solution, it follows that the null space of Yk is spanned by vector u,max C NT 1, which is the unit-norm eigenvector of associated with eigenvalue λ max. As a result, the optimal beamforming matrix has to be a rank-one matrix and is given by W k W k = ψu Ξk,maxu H,max. 4 where ψ is a parameter such that the power consumption satisfies constraint C. On the other hand, for revealing the structure of Z, we J j=1 NR l=1 a:b,c:d focus on e. Define an] auxiliary variable matrix B = [U gj D U H gj 0 and the correspond- C5j ing maximum eigenvalue λ max B. Since Z 0, we have λ λ max B 0. If λ = λ max B, then RankZ = N T 1 and RankWE = 1. If λ > λ max B, then RankZ = N T and RankWE = 0. Therefore, RankW E 1 and at most one energy beam is required to achieve optimality. REFERENCES [1] V. W. S. Wong, R. Schober, D. W. K. Ng, and L.-C. Wang, Key Technologies for 5G Wireless Systems. Cambridge university press, 017. [] I. Ahmed, A. Ikhlef, D. W. K. Ng, and R. Schober, Power Allocation for an Energy Harvesting Transmitter with Hybrid Energy Sources, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 1, pp , Dec [3] D. W. K. Ng, E. S. Lo, and R. Schober, Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation in OFDMA Systems with Hybrid Energy Harvesting Base Station, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 1, pp , Jul [4] AirFuel Alliance. [Online]. Available: [5] X. Chen, Z. Zhang, H.-H. Chen, and H. Zhang, Enhancing Wireless Information and Power Transfer by Exploiting Multi-Antenna Techniques, IEEE Commun. Mag., no. 4, pp , Apr [6] I. Krikidis, S. Timotheou, S. Nikolaou, G. Zheng, D. W. K. Ng, and R. Schober, Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer in Modern Communication Systems, IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 5, no. 11, pp , Nov [7] Z. Ding, C. Zhong, D. W. K. Ng, M. Peng, H. A. Suraweera, R. Schober, and H. V. Poor, Application of Smart Antenna Technologies in Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer, IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 53, no. 4, pp , Apr [8] R. Zhang and C. K. Ho, MIMO Broadcasting for Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 1, pp , May 013. [9] L. Liu, R. Zhang, and K.-C. Chua, Secrecy Wireless Information and Power Transfer with MISO Beamforming, IEEE Trans. Signal Process., vol. 6, pp , Apr [10] D. W. K. Ng, E. S. Lo, and R. Schober, Robust Beamforming for Secure Communication in Systems with Wireless Information and Power Transfer, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 13, pp , Aug [11] D. W. K. Ng and R. Schober, Secure and Green SWIPT in Distributed Antenna Networks with Limited Backhaul Capacity, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 14, no. 9, pp , Sep [1] X. Chen, X. Wang, and X. Chen, Energy-Efficient Optimization for Wireless Information and Power Transfer in Large-Scale MIMO Systems Employing Energy Beamforming, IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., vol., no. 6, pp , Dec [13] E. Boshkovska, D. Ng, N. Zlatanov, and R. Schober, Practical Non- Linear Energy Harvesting Model and Resource Allocation for SWIPT Systems, IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 19, pp , Dec [14] J. Guo and X. Zhu, An Improved Analytical Model for RF-DC Conversion Efficiency in Microwave Rectifiers, in IEEE MTT-S Int. Microw. Symp. Dig., Jun. 01, pp [15] C. Valenta and G. Durgin, Harvesting Wireless Power: Survey of Energy-Harvester Conversion Efficiency in Far-Field, Wireless Power Transfer Systems, IEEE Microw. Mag., vol. 15, pp , Jun [16] T. Le, K. Mayaram, and T. Fiez, Efficient Far-Field Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting for Passively Powered Sensor Networks, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 43, pp , May 008.
7 [17] E. Boshkovska, N. Zlatanov, L. Dai, D. W. K. Ng, and R. Schober, Secure swipt networks based on a non-linear energy harvesting model, in Proc. IEEE Wireless Commun. and Netw. Conf., Mar. 017, pp [18] J. Wang and D. Palomar, Worst-Case Robust MIMO Transmission with Imperfect Channel Knowledge, IEEE Trans. Signal Process., vol. 57, pp , Aug [19] D. Ng and R. Schober, Max-Min Fair Wireless Energy Transfer for Secure Multiuser Communication Systems, in IEEE Inf. Theory Workshop ITW, Nov. 014, pp [0] S. Boyd and L. Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, 004. [1] M. Grant and S. Boyd, CVX: Matlab Software for Disciplined Convex Programming, version.0 Beta, [Online] Sep [] E. Boshkovska, D. W. K. Ng, N. Zlatanov, A. Koelpin, and R. Schober, Robust Resource Allocation for MIMO Wireless Powered Communication Networks Based on a Non-linear EH Model, 017, accepted for publication, IEEE Trans. Commun.
Multi-Objective Beamforming for Energy-Efficient SWIPT Systems
 Multi-Objective Beamforming for Energy-Efficient SWIPT Systems Shiyang Leng, Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, Nikola Zlatanov, and Robert Schober The Pennsylvania State University, USA The University of New South
Multi-Objective Beamforming for Energy-Efficient SWIPT Systems Shiyang Leng, Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, Nikola Zlatanov, and Robert Schober The Pennsylvania State University, USA The University of New South
On the Optimality of Multiuser Zero-Forcing Precoding in MIMO Broadcast Channels
 On the Optimality of Multiuser Zero-Forcing Precoding in MIMO Broadcast Channels Saeed Kaviani and Witold A. Krzymień University of Alberta / TRLabs, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2V4 E-mail: {saeed,wa}@ece.ualberta.ca
On the Optimality of Multiuser Zero-Forcing Precoding in MIMO Broadcast Channels Saeed Kaviani and Witold A. Krzymień University of Alberta / TRLabs, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2V4 E-mail: {saeed,wa}@ece.ualberta.ca
Spectral and Energy Efficient Wireless Powered IoT Networks: NOMA or TDMA?
 1 Spectral and Energy Efficient Wireless Powered IoT Networs: NOMA or TDMA? Qingqing Wu, Wen Chen, Derric Wing wan Ng, and Robert Schober Abstract Wireless powered communication networs WPCNs, where multiple
1 Spectral and Energy Efficient Wireless Powered IoT Networs: NOMA or TDMA? Qingqing Wu, Wen Chen, Derric Wing wan Ng, and Robert Schober Abstract Wireless powered communication networs WPCNs, where multiple
Tutorial on Convex Optimization: Part II
 Tutorial on Convex Optimization: Part II Dr. Khaled Ardah Communications Research Laboratory TU Ilmenau Dec. 18, 2018 Outline Convex Optimization Review Lagrangian Duality Applications Optimal Power Allocation
Tutorial on Convex Optimization: Part II Dr. Khaled Ardah Communications Research Laboratory TU Ilmenau Dec. 18, 2018 Outline Convex Optimization Review Lagrangian Duality Applications Optimal Power Allocation
DOWNLINK transmit beamforming has recently received
 4254 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 58, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 A Dual Perspective on Separable Semidefinite Programming With Applications to Optimal Downlink Beamforming Yongwei Huang, Member,
4254 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 58, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 A Dual Perspective on Separable Semidefinite Programming With Applications to Optimal Downlink Beamforming Yongwei Huang, Member,
Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for
 Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for 1 Wireless Powered Communication Networks Qingqing Wu, Student Member, IEEE, Meixia Tao, Senior Member, IEEE, arxiv:1511.05539v1 [cs.it] 17 Nov 2015 Derrick Wing
Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for 1 Wireless Powered Communication Networks Qingqing Wu, Student Member, IEEE, Meixia Tao, Senior Member, IEEE, arxiv:1511.05539v1 [cs.it] 17 Nov 2015 Derrick Wing
Robust Transceiver Design for MISO Interference Channel with Energy Harvesting
 Robust Transceiver Design for MISO Interference Channel with Energy Harvesting Ming-Min Zhao # Yunlong Cai #2 Qingjiang Shi 3 Benoit Champagne &4 and Min-Jian Zhao #5 # College of Information Science and
Robust Transceiver Design for MISO Interference Channel with Energy Harvesting Ming-Min Zhao # Yunlong Cai #2 Qingjiang Shi 3 Benoit Champagne &4 and Min-Jian Zhao #5 # College of Information Science and
Applications of Robust Optimization in Signal Processing: Beamforming and Power Control Fall 2012
 Applications of Robust Optimization in Signal Processing: Beamforg and Power Control Fall 2012 Instructor: Farid Alizadeh Scribe: Shunqiao Sun 12/09/2012 1 Overview In this presentation, we study the applications
Applications of Robust Optimization in Signal Processing: Beamforg and Power Control Fall 2012 Instructor: Farid Alizadeh Scribe: Shunqiao Sun 12/09/2012 1 Overview In this presentation, we study the applications
Under sum power constraint, the capacity of MIMO channels
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 6, NO 9, SEPTEMBER 22 242 Iterative Mode-Dropping for the Sum Capacity of MIMO-MAC with Per-Antenna Power Constraint Yang Zhu and Mai Vu Abstract We propose an
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 6, NO 9, SEPTEMBER 22 242 Iterative Mode-Dropping for the Sum Capacity of MIMO-MAC with Per-Antenna Power Constraint Yang Zhu and Mai Vu Abstract We propose an
Robust Energy Efficient Beamforming in MISOME-SWIPT Systems With Proportional Secrecy Rate
 1 Robust Energy Efficient Beamforming in MISOME-SWIPT Systems With Proportional Secrecy Rate Yanjie Dong, Student Member, IEEE, Md. Jahangir Hossain, Senior Member, IEEE, Julian Cheng, Senior Member, IEEE,
1 Robust Energy Efficient Beamforming in MISOME-SWIPT Systems With Proportional Secrecy Rate Yanjie Dong, Student Member, IEEE, Md. Jahangir Hossain, Senior Member, IEEE, Julian Cheng, Senior Member, IEEE,
Effective Rate Analysis of MISO Systems over α-µ Fading Channels
 Effective Rate Analysis of MISO Systems over α-µ Fading Channels Jiayi Zhang 1,2, Linglong Dai 1, Zhaocheng Wang 1 Derrick Wing Kwan Ng 2,3 and Wolfgang H. Gerstacker 2 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for
Effective Rate Analysis of MISO Systems over α-µ Fading Channels Jiayi Zhang 1,2, Linglong Dai 1, Zhaocheng Wang 1 Derrick Wing Kwan Ng 2,3 and Wolfgang H. Gerstacker 2 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS. Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu
 PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
MULTI-INPUT multi-output (MIMO) channels, usually
 3086 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 57, NO. 8, AUGUST 2009 Worst-Case Robust MIMO Transmission With Imperfect Channel Knowledge Jiaheng Wang, Student Member, IEEE, and Daniel P. Palomar,
3086 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 57, NO. 8, AUGUST 2009 Worst-Case Robust MIMO Transmission With Imperfect Channel Knowledge Jiaheng Wang, Student Member, IEEE, and Daniel P. Palomar,
Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation
 Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation Chongbin Xu, Peng Wang, Zhonghao Zhang, and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Outline Background Mutual Information
Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation Chongbin Xu, Peng Wang, Zhonghao Zhang, and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Outline Background Mutual Information
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 52, NO. 2, FEBRUARY Uplink Downlink Duality Via Minimax Duality. Wei Yu, Member, IEEE (1) (2)
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 52, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 361 Uplink Downlink Duality Via Minimax Duality Wei Yu, Member, IEEE Abstract The sum capacity of a Gaussian vector broadcast channel
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 52, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 361 Uplink Downlink Duality Via Minimax Duality Wei Yu, Member, IEEE Abstract The sum capacity of a Gaussian vector broadcast channel
A Low-Complexity Algorithm for Worst-Case Utility Maximization in Multiuser MISO Downlink
 A Low-Complexity Algorithm for Worst-Case Utility Maximization in Multiuser MISO Downlin Kun-Yu Wang, Haining Wang, Zhi Ding, and Chong-Yung Chi Institute of Communications Engineering Department of Electrical
A Low-Complexity Algorithm for Worst-Case Utility Maximization in Multiuser MISO Downlin Kun-Yu Wang, Haining Wang, Zhi Ding, and Chong-Yung Chi Institute of Communications Engineering Department of Electrical
Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming
 Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming Authors: Christian Lameiro, Alfredo Nazábal, Fouad Gholam, Javier Vía and Ignacio Santamaría University of Cantabria,
Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming Authors: Christian Lameiro, Alfredo Nazábal, Fouad Gholam, Javier Vía and Ignacio Santamaría University of Cantabria,
A Proof of the Converse for the Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels
 A Proof of the Converse for the Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels Mehdi Mohseni Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, USA Email: mmohseni@stanford.edu
A Proof of the Converse for the Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels Mehdi Mohseni Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, USA Email: mmohseni@stanford.edu
Optimal Transmit Strategies in MIMO Ricean Channels with MMSE Receiver
 Optimal Transmit Strategies in MIMO Ricean Channels with MMSE Receiver E. A. Jorswieck 1, A. Sezgin 1, H. Boche 1 and E. Costa 2 1 Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich-Hertz-Institut 2
Optimal Transmit Strategies in MIMO Ricean Channels with MMSE Receiver E. A. Jorswieck 1, A. Sezgin 1, H. Boche 1 and E. Costa 2 1 Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich-Hertz-Institut 2
Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems
 Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems Xiaofang Sun, Shihao Yan, Nan Yang, Zhiguo Ding, Chao Shen, and Zhangdui Zhong State Key Lab of Rail Traffic Control and Safety, Beijing
Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems Xiaofang Sun, Shihao Yan, Nan Yang, Zhiguo Ding, Chao Shen, and Zhangdui Zhong State Key Lab of Rail Traffic Control and Safety, Beijing
Multiuser Downlink Beamforming: Rank-Constrained SDP
 Multiuser Downlink Beamforming: Rank-Constrained SDP Daniel P. Palomar Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) ELEC5470 - Convex Optimization Fall 2018-19, HKUST, Hong Kong Outline of Lecture
Multiuser Downlink Beamforming: Rank-Constrained SDP Daniel P. Palomar Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) ELEC5470 - Convex Optimization Fall 2018-19, HKUST, Hong Kong Outline of Lecture
Robust Designs of Beamforming and Power Splitting for Distributed Antenna Systems with Wireless Energy Harvesting
 Robust Designs of Beamforming and Power Splitting for Distributed Antenna Systems with Wireless Energy Harvesting Zhengyu Zhu, Sai Huang, Zheng Chu, Fuhui Zhou, Di Zhang and Inyu Lee, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:80.00v
Robust Designs of Beamforming and Power Splitting for Distributed Antenna Systems with Wireless Energy Harvesting Zhengyu Zhu, Sai Huang, Zheng Chu, Fuhui Zhou, Di Zhang and Inyu Lee, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:80.00v
A Two-Phase Power Allocation Scheme for CRNs Employing NOMA
 A Two-Phase Power Allocation Scheme for CRNs Employing NOMA Ming Zeng, Georgios I. Tsiropoulos, Animesh Yadav, Octavia A. Dobre, and Mohamed H. Ahmed Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial
A Two-Phase Power Allocation Scheme for CRNs Employing NOMA Ming Zeng, Georgios I. Tsiropoulos, Animesh Yadav, Octavia A. Dobre, and Mohamed H. Ahmed Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial
NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective
 NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective Peng Xu, Zhiguo Ding, Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:54.775v2 cs.it] 2 May 25 Abstract In this letter, the performance of non-orthogonal
NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective Peng Xu, Zhiguo Ding, Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:54.775v2 cs.it] 2 May 25 Abstract In this letter, the performance of non-orthogonal
Minimum Mean Squared Error Interference Alignment
 Minimum Mean Squared Error Interference Alignment David A. Schmidt, Changxin Shi, Randall A. Berry, Michael L. Honig and Wolfgang Utschick Associate Institute for Signal Processing Technische Universität
Minimum Mean Squared Error Interference Alignment David A. Schmidt, Changxin Shi, Randall A. Berry, Michael L. Honig and Wolfgang Utschick Associate Institute for Signal Processing Technische Universität
Transmit Beamforming Techniques for Wireless Information and Power Transfer in MISO Interference Channels
 Transmit Beamforming Techniques for Wireless Information and Power Transfer in MISO Interference Channels Hoon Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Sang-Rim Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Kyoung-Jae Lee, Member, IEEE,
Transmit Beamforming Techniques for Wireless Information and Power Transfer in MISO Interference Channels Hoon Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Sang-Rim Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Kyoung-Jae Lee, Member, IEEE,
User Cooperation in Wireless Powered Communication Networks
 User Cooperation in Wireless Powered Communication Networks Hyungsik Ju and Rui Zhang Abstract arxiv:403.723v2 [cs.it] 7 Apr 204 This paper studies user cooperation in the emerging wireless powered communication
User Cooperation in Wireless Powered Communication Networks Hyungsik Ju and Rui Zhang Abstract arxiv:403.723v2 [cs.it] 7 Apr 204 This paper studies user cooperation in the emerging wireless powered communication
On Design of Reduced-Order H Filters for Discrete-Time Systems from Incomplete Measurements
 Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Cancun, Mexico, Dec. 9-11, 2008 On Design of Reduced-Order H Filters for Discrete-Time Systems from Incomplete Measurements Shaosheng Zhou
Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Cancun, Mexico, Dec. 9-11, 2008 On Design of Reduced-Order H Filters for Discrete-Time Systems from Incomplete Measurements Shaosheng Zhou
An Uplink-Downlink Duality for Cloud Radio Access Network
 An Uplin-Downlin Duality for Cloud Radio Access Networ Liang Liu, Prati Patil, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, 5S 3G4, Canada Emails: lianguotliu@utorontoca,
An Uplin-Downlin Duality for Cloud Radio Access Networ Liang Liu, Prati Patil, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, 5S 3G4, Canada Emails: lianguotliu@utorontoca,
SINR Balancing in the Downlink of Cognitive Radio Networks with Imperfect Channel Knowledge
 SINR Balancing in the Downlink of Cognitive Radio Networks with Imperfect Channel Knowledge Muhammad Fainan Hanif, Peter J. Smith and Mohamed-Slim Alouini Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
SINR Balancing in the Downlink of Cognitive Radio Networks with Imperfect Channel Knowledge Muhammad Fainan Hanif, Peter J. Smith and Mohamed-Slim Alouini Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Lagrange Duality. Daniel P. Palomar. Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)
 Lagrange Duality Daniel P. Palomar Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) ELEC5470 - Convex Optimization Fall 2017-18, HKUST, Hong Kong Outline of Lecture Lagrangian Dual function Dual
Lagrange Duality Daniel P. Palomar Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) ELEC5470 - Convex Optimization Fall 2017-18, HKUST, Hong Kong Outline of Lecture Lagrangian Dual function Dual
THE next generation wireless communication systems call
 1 Artificial Noise Aided Secure Cognitive Beamforming for Cooperative MISO-NOMA Using SWIPT Fuhui Zhou, Member, IEEE, Zheng Chu, Member, IEEE, Haijian Sun, Student Member, IEEE, Rose Qingyang Hu, Senior
1 Artificial Noise Aided Secure Cognitive Beamforming for Cooperative MISO-NOMA Using SWIPT Fuhui Zhou, Member, IEEE, Zheng Chu, Member, IEEE, Haijian Sun, Student Member, IEEE, Rose Qingyang Hu, Senior
Adaptive beamforming for uniform linear arrays with unknown mutual coupling. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters.
 Title Adaptive beamforming for uniform linear arrays with unknown mutual coupling Author(s) Liao, B; Chan, SC Citation IEEE Antennas And Wireless Propagation Letters, 2012, v. 11, p. 464-467 Issued Date
Title Adaptive beamforming for uniform linear arrays with unknown mutual coupling Author(s) Liao, B; Chan, SC Citation IEEE Antennas And Wireless Propagation Letters, 2012, v. 11, p. 464-467 Issued Date
Optimization in Wireless Communication
 Zhi-Quan (Tom) Luo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Minnesota 200 Union Street SE Minneapolis, MN 55455 2007 NSF Workshop Challenges Optimization problems from wireless applications
Zhi-Quan (Tom) Luo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Minnesota 200 Union Street SE Minneapolis, MN 55455 2007 NSF Workshop Challenges Optimization problems from wireless applications
Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback
 IEEE INFOCOM Workshop On Cognitive & Cooperative Networks Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback Chao Wang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuen Chau. Dept.of
IEEE INFOCOM Workshop On Cognitive & Cooperative Networks Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback Chao Wang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuen Chau. Dept.of
2318 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE Mai Vu, Student Member, IEEE, and Arogyaswami Paulraj, Fellow, IEEE
 2318 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE 2006 Optimal Linear Precoders for MIMO Wireless Correlated Channels With Nonzero Mean in Space Time Coded Systems Mai Vu, Student Member,
2318 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 6, JUNE 2006 Optimal Linear Precoders for MIMO Wireless Correlated Channels With Nonzero Mean in Space Time Coded Systems Mai Vu, Student Member,
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results
 NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS, GIST Email: jchoi114@gist.ac.kr Invited Paper arxiv:176.885v1 [cs.it] 27 Jun 217 Abstract Although non-orthogonal multiple access NOMA is
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS, GIST Email: jchoi114@gist.ac.kr Invited Paper arxiv:176.885v1 [cs.it] 27 Jun 217 Abstract Although non-orthogonal multiple access NOMA is
Optimum Power Allocation in Fading MIMO Multiple Access Channels with Partial CSI at the Transmitters
 Optimum Power Allocation in Fading MIMO Multiple Access Channels with Partial CSI at the Transmitters Alkan Soysal Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Optimum Power Allocation in Fading MIMO Multiple Access Channels with Partial CSI at the Transmitters Alkan Soysal Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
2 Since these problems are restrictions of the original problem, the transmission /$ IEEE
 714 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 1, NO. 4, DECEMBER 2007 Convex Conic Formulations of Robust Downlink Precoder Designs With Quality of Service Constraints Michael Botros Shenouda,
714 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 1, NO. 4, DECEMBER 2007 Convex Conic Formulations of Robust Downlink Precoder Designs With Quality of Service Constraints Michael Botros Shenouda,
Proportional Fairness in ALOHA Networks. with RF Energy Harvesting
 Proportional Fairness in ALOHA Networks 1 with RF Energy Harvesting Zoran Hadzi-Velkov, Slavche Pejoski, Nikola Zlatanov, and Robert Schober arxiv:1806.00241v2 [cs.it] 10 Sep 2018 Abstract In this paper,
Proportional Fairness in ALOHA Networks 1 with RF Energy Harvesting Zoran Hadzi-Velkov, Slavche Pejoski, Nikola Zlatanov, and Robert Schober arxiv:1806.00241v2 [cs.it] 10 Sep 2018 Abstract In this paper,
Optimal Power Allocation for Cognitive Radio under Primary User s Outage Loss Constraint
 This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the IEEE ICC 29 proceedings Optimal Power Allocation for Cognitive Radio
This full text paper was peer reviewed at the direction of IEEE Communications Society subject matter experts for publication in the IEEE ICC 29 proceedings Optimal Power Allocation for Cognitive Radio
Lecture 8: MIMO Architectures (II) Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1. Overview. Ragnar Thobaben CommTh/EES/KTH
 MIMO : MIMO Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Wednesday, May 25, 2016 09:15-12:00, SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 20 Overview MIMO
MIMO : MIMO Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Wednesday, May 25, 2016 09:15-12:00, SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 20 Overview MIMO
Call Completion Probability in Heterogeneous Networks with Energy Harvesting Base Stations
 Call Completion Probability in Heterogeneous Networks with Energy Harvesting Base Stations Craig Wang, Salman Durrani, Jing Guo and Xiangyun (Sean) Zhou Research School of Engineering, The Australian National
Call Completion Probability in Heterogeneous Networks with Energy Harvesting Base Stations Craig Wang, Salman Durrani, Jing Guo and Xiangyun (Sean) Zhou Research School of Engineering, The Australian National
The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View
 The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697-2625 Email: sudhirs@uciedu,
The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697-2625 Email: sudhirs@uciedu,
Optimal Power Allocation for Energy Recycling Assisted Cooperative Communications
 Optimal Power llocation for Energy Recycling ssisted Cooperative Communications George. Ropokis, M. Majid Butt, Nicola Marchetti and Luiz. DaSilva CONNECT Centre, Trinity College, University of Dublin,
Optimal Power llocation for Energy Recycling ssisted Cooperative Communications George. Ropokis, M. Majid Butt, Nicola Marchetti and Luiz. DaSilva CONNECT Centre, Trinity College, University of Dublin,
A SEMIDEFINITE RELAXATION BASED CONSERVATIVE APPROACH TO ROBUST TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING WITH PROBABILISTIC SINR CONSTRAINTS
 th European Signal Processing Conference EUSIPCO-1 Aalborg, Denmark, August 3-7, 1 A SEMIDEFINITE RELAXATION BASED CONSERVATIVE APPROACH TO ROBUST TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING WITH PROBABILISTIC SINR CONSTRAINTS
th European Signal Processing Conference EUSIPCO-1 Aalborg, Denmark, August 3-7, 1 A SEMIDEFINITE RELAXATION BASED CONSERVATIVE APPROACH TO ROBUST TRANSMIT BEAMFORMING WITH PROBABILISTIC SINR CONSTRAINTS
Cognitive Wireless Powered Network: Spectrum Sharing Models and Throughput Maximization. User terminals
 Cognitive Wireless Powered Network: Spectrum Sharing Models and Throughput Maximization Seunghyun Lee Student Member IEEE and Rui Zhang Senior Member IEEE arxiv:56.595v [cs.it] Dec 5 Abstract The recent
Cognitive Wireless Powered Network: Spectrum Sharing Models and Throughput Maximization Seunghyun Lee Student Member IEEE and Rui Zhang Senior Member IEEE arxiv:56.595v [cs.it] Dec 5 Abstract The recent
Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems
 1 Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale and Long Bao Le Institute National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS) Université de Québec, Montréal,
1 Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale and Long Bao Le Institute National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS) Université de Québec, Montréal,
MULTIPLE-INPUT multiple-output (MIMO) systems
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 56, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2010 4793 Maximum Mutual Information Design for MIMO Systems With Imperfect Channel Knowledge Minhua Ding, Member, IEEE, and Steven D.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 56, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2010 4793 Maximum Mutual Information Design for MIMO Systems With Imperfect Channel Knowledge Minhua Ding, Member, IEEE, and Steven D.
Duality, Achievable Rates, and Sum-Rate Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels
 2658 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 49, NO 10, OCTOBER 2003 Duality, Achievable Rates, and Sum-Rate Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels Sriram Vishwanath, Student Member, IEEE, Nihar
2658 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 49, NO 10, OCTOBER 2003 Duality, Achievable Rates, and Sum-Rate Capacity of Gaussian MIMO Broadcast Channels Sriram Vishwanath, Student Member, IEEE, Nihar
Title. Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information. Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels
 Title Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 29 : Asia-Pacific Signal Citationand Conference: 688-691 Issue Date 29-1-4 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39789
Title Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 29 : Asia-Pacific Signal Citationand Conference: 688-691 Issue Date 29-1-4 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39789
Sum-Power Iterative Watefilling Algorithm
 Sum-Power Iterative Watefilling Algorithm Daniel P. Palomar Hong Kong University of Science and Technolgy (HKUST) ELEC547 - Convex Optimization Fall 2009-10, HKUST, Hong Kong November 11, 2009 Outline
Sum-Power Iterative Watefilling Algorithm Daniel P. Palomar Hong Kong University of Science and Technolgy (HKUST) ELEC547 - Convex Optimization Fall 2009-10, HKUST, Hong Kong November 11, 2009 Outline
Robust Adaptive Beamforming via Estimating Steering Vector Based on Semidefinite Relaxation
 Robust Adaptive Beamforg via Estimating Steering Vector Based on Semidefinite Relaxation Arash Khabbazibasmenj, Sergiy A. Vorobyov, and Aboulnasr Hassanien Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Robust Adaptive Beamforg via Estimating Steering Vector Based on Semidefinite Relaxation Arash Khabbazibasmenj, Sergiy A. Vorobyov, and Aboulnasr Hassanien Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Efficient Computation of the Pareto Boundary for the Two-User MISO Interference Channel with Multi-User Decoding Capable Receivers
 Efficient Computation of the Pareto Boundary for the Two-User MISO Interference Channel with Multi-User Decoding Capable Receivers Johannes Lindblom, Eleftherios Karipidis and Erik G. Larsson Linköping
Efficient Computation of the Pareto Boundary for the Two-User MISO Interference Channel with Multi-User Decoding Capable Receivers Johannes Lindblom, Eleftherios Karipidis and Erik G. Larsson Linköping
Trust Degree Based Beamforming for Multi-Antenna Cooperative Communication Systems
 Introduction Main Results Simulation Conclusions Trust Degree Based Beamforming for Multi-Antenna Cooperative Communication Systems Mojtaba Vaezi joint work with H. Inaltekin, W. Shin, H. V. Poor, and
Introduction Main Results Simulation Conclusions Trust Degree Based Beamforming for Multi-Antenna Cooperative Communication Systems Mojtaba Vaezi joint work with H. Inaltekin, W. Shin, H. V. Poor, and
Optimal Harvest-or-Transmit Strategy for Energy Harvesting Underlay Cognitive Radio Network
 Optimal Harvest-or-Transmit Strategy for Energy Harvesting Underlay Cognitive Radio Network Kalpant Pathak and Adrish Banerjee Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur,
Optimal Harvest-or-Transmit Strategy for Energy Harvesting Underlay Cognitive Radio Network Kalpant Pathak and Adrish Banerjee Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur,
I. Introduction. Index Terms Multiuser MIMO, feedback, precoding, beamforming, codebook, quantization, OFDM, OFDMA.
 Zero-Forcing Beamforming Codebook Design for MU- MIMO OFDM Systems Erdem Bala, Member, IEEE, yle Jung-Lin Pan, Member, IEEE, Robert Olesen, Member, IEEE, Donald Grieco, Senior Member, IEEE InterDigital
Zero-Forcing Beamforming Codebook Design for MU- MIMO OFDM Systems Erdem Bala, Member, IEEE, yle Jung-Lin Pan, Member, IEEE, Robert Olesen, Member, IEEE, Donald Grieco, Senior Member, IEEE InterDigital
USING multiple antennas has been shown to increase the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 11 A Comparison of Time-Sharing, DPC, and Beamforming for MIMO Broadcast Channels With Many Users Masoud Sharif, Member, IEEE, and Babak
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 11 A Comparison of Time-Sharing, DPC, and Beamforming for MIMO Broadcast Channels With Many Users Masoud Sharif, Member, IEEE, and Babak
Secure Degrees of Freedom of the MIMO Multiple Access Wiretap Channel
 Secure Degrees of Freedom of the MIMO Multiple Access Wiretap Channel Pritam Mukherjee Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park, MD 074 pritamm@umd.edu
Secure Degrees of Freedom of the MIMO Multiple Access Wiretap Channel Pritam Mukherjee Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park, MD 074 pritamm@umd.edu
Upper Bounds on MIMO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints
 Upper Bounds on IO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints Zukang Shen, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking Communications Group Department of Electrical Computer Engineering
Upper Bounds on IO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints Zukang Shen, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking Communications Group Department of Electrical Computer Engineering
Transmit Directions and Optimality of Beamforming in MIMO-MAC with Partial CSI at the Transmitters 1
 2005 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 6 8, 2005 Transmit Directions and Optimality of Beamforming in MIMO-MAC with Partial CSI at the Transmitters Alkan
2005 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 6 8, 2005 Transmit Directions and Optimality of Beamforming in MIMO-MAC with Partial CSI at the Transmitters Alkan
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results
 NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS GIST September 2017 (VTC-Fall 2017) 1 / 46 Abstract: Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) becomes a key technology in 5G as it can improve
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS GIST September 2017 (VTC-Fall 2017) 1 / 46 Abstract: Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) becomes a key technology in 5G as it can improve
Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels
 Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels Gill November 22, 2011 Gill (University of Delaware) November 22, 2011 1 / 25 Part I Mode Selection for MISO BC with Perfect/Imperfect CSI [1]-[3] Gill
Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels Gill November 22, 2011 Gill (University of Delaware) November 22, 2011 1 / 25 Part I Mode Selection for MISO BC with Perfect/Imperfect CSI [1]-[3] Gill
New Rank-One Matrix Decomposition Techniques and Applications to Signal Processing
 New Rank-One Matrix Decomposition Techniques and Applications to Signal Processing Yongwei Huang Hong Kong Baptist University SPOC 2012 Hefei China July 1, 2012 Outline Trust-region subproblems in nonlinear
New Rank-One Matrix Decomposition Techniques and Applications to Signal Processing Yongwei Huang Hong Kong Baptist University SPOC 2012 Hefei China July 1, 2012 Outline Trust-region subproblems in nonlinear
Average Throughput Analysis of Downlink Cellular Networks with Multi-Antenna Base Stations
 Average Throughput Analysis of Downlink Cellular Networks with Multi-Antenna Base Stations Rui Wang, Jun Zhang, S.H. Song and K. B. Letaief, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of ECE, The Hong Kong University of Science
Average Throughput Analysis of Downlink Cellular Networks with Multi-Antenna Base Stations Rui Wang, Jun Zhang, S.H. Song and K. B. Letaief, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of ECE, The Hong Kong University of Science
A robust transmit CSI framework with applications in MIMO wireless precoding
 A robust transmit CSI framework with applications in MIMO wireless precoding Mai Vu, and Arogyaswami Paulraj Information Systems Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, Stanford,
A robust transmit CSI framework with applications in MIMO wireless precoding Mai Vu, and Arogyaswami Paulraj Information Systems Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, Stanford,
A Mathematical Proof of the Superiority of NOMA Compared to Conventional OMA
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. XX, NO. X, OCT. 2016 1 A Mathematical Proof of the Superiority of NOMA Compared to Conventional OMA Zhiyong Chen, Zhiguo Ding, Senior Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. XX, NO. X, OCT. 2016 1 A Mathematical Proof of the Superiority of NOMA Compared to Conventional OMA Zhiyong Chen, Zhiguo Ding, Senior Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai,
On Power Minimization for Non-orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA)
 On Power Minimization for Non-orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) Lei Lei, Di Yuan and Peter Värbrand Journal Article N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 2016 IEEE. Personal use of this
On Power Minimization for Non-orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) Lei Lei, Di Yuan and Peter Värbrand Journal Article N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 2016 IEEE. Personal use of this
4888 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2016
 4888 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2016 Online Power Control Optimization for Wireless Transmission With Energy Harvesting and Storage Fatemeh Amirnavaei, Student Member,
4888 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2016 Online Power Control Optimization for Wireless Transmission With Energy Harvesting and Storage Fatemeh Amirnavaei, Student Member,
ITERATIVE OPTIMIZATION FOR MAX-MIN SINR IN DENSE SMALL-CELL MULTIUSER MISO SWIPT SYSTEM
 ITERATIVE OPTIMIZATION FOR MAX-MIN SINR IN DENSE SMALL-CELL MULTIUSER MISO SWIPT SYSTEM Ali Arshad Nasir, Duy Trong Ngo, Hoang Duong Tuan and Salman Durrani Research School of Engineering, Australian National
ITERATIVE OPTIMIZATION FOR MAX-MIN SINR IN DENSE SMALL-CELL MULTIUSER MISO SWIPT SYSTEM Ali Arshad Nasir, Duy Trong Ngo, Hoang Duong Tuan and Salman Durrani Research School of Engineering, Australian National
664 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 58, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2010
 664 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 58, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2010 Rank-Constrained Separable Semidefinite Programming With Applications to Optimal Beamforming Yongwei Huang, Member, IEEE, Daniel
664 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 58, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2010 Rank-Constrained Separable Semidefinite Programming With Applications to Optimal Beamforming Yongwei Huang, Member, IEEE, Daniel
Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDMA for MIMO Broadcast Channels
 TO APPEAR IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COUNICATIONS, JUNE 004 1 Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDA for IO Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal & Andrea Goldsmith Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University
TO APPEAR IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COUNICATIONS, JUNE 004 1 Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDA for IO Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal & Andrea Goldsmith Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University
INVERSE EIGENVALUE STATISTICS FOR RAYLEIGH AND RICIAN MIMO CHANNELS
 INVERSE EIGENVALUE STATISTICS FOR RAYLEIGH AND RICIAN MIMO CHANNELS E. Jorswieck, G. Wunder, V. Jungnickel, T. Haustein Abstract Recently reclaimed importance of the empirical distribution function of
INVERSE EIGENVALUE STATISTICS FOR RAYLEIGH AND RICIAN MIMO CHANNELS E. Jorswieck, G. Wunder, V. Jungnickel, T. Haustein Abstract Recently reclaimed importance of the empirical distribution function of
Morning Session Capacity-based Power Control. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland
 Morning Session Capacity-based Power Control Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland So Far, We Learned... Power control with SIR-based QoS guarantees Suitable
Morning Session Capacity-based Power Control Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland So Far, We Learned... Power control with SIR-based QoS guarantees Suitable
DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection
 1 DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection Yu Han, Shi Jin, Jun Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, and Kai-Kit Wong National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast
1 DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection Yu Han, Shi Jin, Jun Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, and Kai-Kit Wong National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast
Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Multi-User Mobile Edge Computing
 Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Multi-User Mobile Edge Computing Junfeng Guo, Zhaozhe Song, Ying Cui Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, P. R. China
Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Multi-User Mobile Edge Computing Junfeng Guo, Zhaozhe Song, Ying Cui Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, P. R. China
Optimum Transmission Scheme for a MISO Wireless System with Partial Channel Knowledge and Infinite K factor
 Optimum Transmission Scheme for a MISO Wireless System with Partial Channel Knowledge and Infinite K factor Mai Vu, Arogyaswami Paulraj Information Systems Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering
Optimum Transmission Scheme for a MISO Wireless System with Partial Channel Knowledge and Infinite K factor Mai Vu, Arogyaswami Paulraj Information Systems Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering
On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming
 On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming Namjeong Lee, Chan-Byoung Chae, Osvaldo Simeone, Joonhyuk Kang Information and Communications Engineering ICE, KAIST, Korea Email:
On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming Namjeong Lee, Chan-Byoung Chae, Osvaldo Simeone, Joonhyuk Kang Information and Communications Engineering ICE, KAIST, Korea Email:
Optimal Data and Training Symbol Ratio for Communication over Uncertain Channels
 Optimal Data and Training Symbol Ratio for Communication over Uncertain Channels Ather Gattami Ericsson Research Stockholm, Sweden Email: athergattami@ericssoncom arxiv:50502997v [csit] 2 May 205 Abstract
Optimal Data and Training Symbol Ratio for Communication over Uncertain Channels Ather Gattami Ericsson Research Stockholm, Sweden Email: athergattami@ericssoncom arxiv:50502997v [csit] 2 May 205 Abstract
A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for. Downlink Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems
 A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for 1 Downlin Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems arxiv:1008.0730v1 [cs.it] 4 Aug 2010 Peng Cheng, Meixia Tao and Wenjun Zhang Abstract Signal-to-leaage-and-noise ratio
A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for 1 Downlin Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems arxiv:1008.0730v1 [cs.it] 4 Aug 2010 Peng Cheng, Meixia Tao and Wenjun Zhang Abstract Signal-to-leaage-and-noise ratio
Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems
 1 Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems Wenqian Shen, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong Dai, Senior Member, IEEE, Yang Yang, Member, IEEE, Yue Li, Member,
1 Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems Wenqian Shen, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong Dai, Senior Member, IEEE, Yang Yang, Member, IEEE, Yue Li, Member,
Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy
 Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy Hyun-Suk Lee Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Eng., Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea Jang-Won Lee Dept. of Electrical
Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy Hyun-Suk Lee Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Eng., Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea Jang-Won Lee Dept. of Electrical
Multi-User Gain Maximum Eigenmode Beamforming, and IDMA. Peng Wang and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong
 Multi-User Gain Maximum Eigenmode Beamforming, and IDMA Peng Wang and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Contents Introduction Multi-user gain (MUG) Maximum eigenmode beamforming (MEB) MEB performance
Multi-User Gain Maximum Eigenmode Beamforming, and IDMA Peng Wang and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Contents Introduction Multi-user gain (MUG) Maximum eigenmode beamforming (MEB) MEB performance
CSI Overhead Reduction with Stochastic Beamforming for Cloud Radio Access Networks
 1 CSI Overhead Reduction with Stochastic Beamforming for Cloud Radio Access Networks Yuanming Shi, Jun Zhang, and Khaled B. Letaief, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of ECE, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
1 CSI Overhead Reduction with Stochastic Beamforming for Cloud Radio Access Networks Yuanming Shi, Jun Zhang, and Khaled B. Letaief, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of ECE, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels
 Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels Jung Hoon Lee and Huaiyu Dai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University,
Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels Jung Hoon Lee and Huaiyu Dai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University,
Heterogeneous Cellular Networks Using
 Heterogeneous Cellular Networks Using 1 Wireless Backhaul: Fast Admission Control and Large System Analysis arxiv:1501.06988v2 [cs.it] 13 Apr 2015 Jian Zhao, Member, IEEE, Tony Q. S. Quek, Senior Member,
Heterogeneous Cellular Networks Using 1 Wireless Backhaul: Fast Admission Control and Large System Analysis arxiv:1501.06988v2 [cs.it] 13 Apr 2015 Jian Zhao, Member, IEEE, Tony Q. S. Quek, Senior Member,
Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel
 /33 Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel Presented by Paul de Kerret Joint work with Antonio Bazco, Nicolas Gresset, and David Gesbert ESIT 2017 in Madrid,
/33 Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel Presented by Paul de Kerret Joint work with Antonio Bazco, Nicolas Gresset, and David Gesbert ESIT 2017 in Madrid,
536 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 63, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2015
 536 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 63, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2015 Optimized Training Design for Wireless Energy Transfer Yong Zeng, Member, IEEE, and Rui Zhang, Member, IEEE Abstract Radio-frequency
536 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 63, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2015 Optimized Training Design for Wireless Energy Transfer Yong Zeng, Member, IEEE, and Rui Zhang, Member, IEEE Abstract Radio-frequency
POWER ALLOCATION AND OPTIMAL TX/RX STRUCTURES FOR MIMO SYSTEMS
 POWER ALLOCATION AND OPTIMAL TX/RX STRUCTURES FOR MIMO SYSTEMS R. Cendrillon, O. Rousseaux and M. Moonen SCD/ESAT, Katholiee Universiteit Leuven, Belgium {raphael.cendrillon, olivier.rousseaux, marc.moonen}@esat.uleuven.ac.be
POWER ALLOCATION AND OPTIMAL TX/RX STRUCTURES FOR MIMO SYSTEMS R. Cendrillon, O. Rousseaux and M. Moonen SCD/ESAT, Katholiee Universiteit Leuven, Belgium {raphael.cendrillon, olivier.rousseaux, marc.moonen}@esat.uleuven.ac.be
12.4 Known Channel (Water-Filling Solution)
 ECEn 665: Antennas and Propagation for Wireless Communications 54 2.4 Known Channel (Water-Filling Solution) The channel scenarios we have looed at above represent special cases for which the capacity
ECEn 665: Antennas and Propagation for Wireless Communications 54 2.4 Known Channel (Water-Filling Solution) The channel scenarios we have looed at above represent special cases for which the capacity
Multiuser Capacity in Block Fading Channel
 Multiuser Capacity in Block Fading Channel April 2003 1 Introduction and Model We use a block-fading model, with coherence interval T where M independent users simultaneously transmit to a single receiver
Multiuser Capacity in Block Fading Channel April 2003 1 Introduction and Model We use a block-fading model, with coherence interval T where M independent users simultaneously transmit to a single receiver
Wireless Transmission with Energy Harvesting and Storage. Fatemeh Amirnavaei
 Wireless Transmission with Energy Harvesting and Storage by Fatemeh Amirnavaei A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in The Faculty of Engineering
Wireless Transmission with Energy Harvesting and Storage by Fatemeh Amirnavaei A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in The Faculty of Engineering
Robust MISO Beamforming Under the Deterministic Model in Two-Tier Heterogeneous Networks
 Received July 5, 017, accepted July 0, 017, date of publication July 4, 017, date of current version August 14, 017. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.017.73143 Robust MISO Beamforming Under the
Received July 5, 017, accepted July 0, 017, date of publication July 4, 017, date of current version August 14, 017. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.017.73143 Robust MISO Beamforming Under the
Handout 8: Dealing with Data Uncertainty
 MFE 5100: Optimization 2015 16 First Term Handout 8: Dealing with Data Uncertainty Instructor: Anthony Man Cho So December 1, 2015 1 Introduction Conic linear programming CLP, and in particular, semidefinite
MFE 5100: Optimization 2015 16 First Term Handout 8: Dealing with Data Uncertainty Instructor: Anthony Man Cho So December 1, 2015 1 Introduction Conic linear programming CLP, and in particular, semidefinite
J. Liang School of Automation & Information Engineering Xi an University of Technology, China
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 18, 245 255, 211 A NOVEL DIAGONAL LOADING METHOD FOR ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING W. Wang and R. Wu Tianjin Key Lab for Advanced Signal Processing Civil Aviation
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 18, 245 255, 211 A NOVEL DIAGONAL LOADING METHOD FOR ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING W. Wang and R. Wu Tianjin Key Lab for Advanced Signal Processing Civil Aviation
Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback
 Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 9697-65 Email: syed@ece.uci.edu,
Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 9697-65 Email: syed@ece.uci.edu,
Characterization of Convex and Concave Resource Allocation Problems in Interference Coupled Wireless Systems
 2382 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL 59, NO 5, MAY 2011 Characterization of Convex and Concave Resource Allocation Problems in Interference Coupled Wireless Systems Holger Boche, Fellow, IEEE,
2382 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL 59, NO 5, MAY 2011 Characterization of Convex and Concave Resource Allocation Problems in Interference Coupled Wireless Systems Holger Boche, Fellow, IEEE,
Resource and Task Scheduling for SWIPT IoT Systems with Renewable Energy Sources
 This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of this journal, but has not been fully edited. Content may change prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI 1.119/JIOT.218.2873658,
This article has been accepted for publication in a future issue of this journal, but has not been fully edited. Content may change prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI 1.119/JIOT.218.2873658,
Resource Management and Interference Control in Distributed Multi-Tier and D2D Systems. Ali Ramezani-Kebrya
 Resource Management and Interference Control in Distributed Multi-Tier and D2D Systems by Ali Ramezani-Kebrya A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Resource Management and Interference Control in Distributed Multi-Tier and D2D Systems by Ali Ramezani-Kebrya A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Optimized Training for Net Energy Maximization in Multi-Antenna Wireless Energy Transfer over Frequency-Selective Channel
 Optimized Training for Net Energy Maximization in Multi-Antenna Wireless Energy Transfer over Frequency-Selective Channel Yong Zeng and Rui Zhang 1 arxiv:1501.01728v2 [cs.it] 14 Apr 2015 Abstract This
Optimized Training for Net Energy Maximization in Multi-Antenna Wireless Energy Transfer over Frequency-Selective Channel Yong Zeng and Rui Zhang 1 arxiv:1501.01728v2 [cs.it] 14 Apr 2015 Abstract This
