Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems
|
|
|
- Phoebe Atkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Codebook Design for Channel Feedback in Lens-Based Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems Wenqian Shen, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong Dai, Senior Member, IEEE, Yang Yang, Member, IEEE, Yue Li, Member, IEEE, and Zhaocheng Wang, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 1 Mar 2017 Abstract The number of radio frequency RF) chains can be reduced through beam selection in lens-based millimeter-wave mmwave) massive MIMO systems, where the equivalent channel between RF chains and multiple users is required at the BS to achieve the multi-user multiplexing gain. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no dedicated codebook for the equivalent channel feedback in such systems. In this paper, we propose the dimension-reduced subspace codebook, which achieves a significant reduction of the feedback overhead and codebook size. Specifically, we firstly utilize the limited scattering property of mmwave channels to generate the high-dimensional vectors in the channel subspace. Then, according to the function of lens and beam selector, we propose the dimension-reduced subspace codebook to quantize the equivalent channel vector. Moreover, the performance analysis of the proposed codebook is also provided. Finally, simulation results show the superior performance of the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook compared with conventional codebooks. Index Terms Massive MIMO, mmwave, channel feedback, codebook. lens, equivalent I. INTRODUCTION MILLIMETER-Wave MmWave) massive MIMO has been regarded as a promising key technique for 5G due to the large available bandwidth and high spectrum efficiency [1]. One key challenge for practical mmwave massive MIMO systems, where each antenna is usually equipped with a radio frequency RF) chain, is the unaffordable hardware cost and energy consumption caused by a large number of RF chains. To reduce the number of RF chains, the new concept of lensbased mmwave massive MIMO has been recently proposed [2] [5]. By utilizing the energy focusing property of lens, mmwave signals from different directions are concentrated on different antennas, so that the traditional spatial channel is transformed into beamspace channel. Due to the severe path loss of mmwave signals, the number of effective channel paths is limited [6]. As a result, the beamspace channel is sparse. Then, using a beam selector, the number of RF chains can be significantly reduced, so the dimensions of equivalent channels can be also reduced. All authors are with the Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing , China s: swq13@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn; {daill, yy0553, lyee, zcwang}@tsinghua.edu.cn). This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China Grant No. 2013CB329203), the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Nos and ), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation Grant No ), and the Foundation of Shenzhen government. The dimension-reduced channel state information CSI) between RF chains and users, which is called as equivalent CSI, is required at the BS to perform channel adaptive techniques such as precoding and power allocation. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no dedicated codebook to realize the equivalent CSI feedback in the emerging lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems. The classical Grassmannian codebook [7] and random vector quantization RVQ)- based codebook [8] are not directly applicable here, since the dimension-reduced equivalent CSI in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems is not Rayleigh distributed. In this paper, to fill in this gap, we propose the dimensionreduced subspace codebook for equivalent CSI feedback in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems 1. Firstly, we utilize the limited scattering property of mmwave channels to generate the high-dimensional vectors in the channel subspace, which depends on the angle-of-departure AoD) of channel path. Then, according to the function of lens and beam selector, we propose the dimension-reduced subspace codebook to quantize the equivalent channel vector using less bits than traditional codebooks. Moreover, we provide the performance analysis of the proposed codebook, which is verified by simulation results. Notation: Lower-case and upper-case boldface letters denote vectors and matrices, respectively; ) T, ) H and ) 1 denote the transpose, conjugate transpose, and inverse of a matrix, respectively;φ = ΦΦ H Φ) 1 is the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse; E[ ] denotes the expectation operator; I P denotes the identity matrix of size P P. II. SYSTEM MODEL In this section, we briefly introduce the typical mmwave massive MIMO channel model at first. Then, we present the equivalent channel in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems. A. MmWave Massive MIMO Channel Model We consider a mmwave massive MIMO system with M antennas at the base station BS) and K single-antenna users M K) in this paper. We adopt the widely used ray-based mmwave channel model [1], where the downlink channel 1 Simulation codes are provided to reproduce the results presented in this paper:
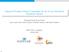
2 2 x d Precod ing V RF chains Beam selector S Lens Fig. 1. Lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems. U User1 User2 UserK vector h k C M 1 between the BS and the k-th user can be described as P k h k = g k,i aψ k,i ), 1) i where P k is the number of resolvable paths from the BS to the k-th user, g k,i is the complex gain of the i-th path of the k-th user, which is identically and independently distributed i.i.d.) with zero mean and unit variance, and aψ k,i ) C M 1 is the BS antenna response of the i-th path of the k-th user. We consider the widely used uniform linear array ULA) at the BS [1], so aψ k,i ) can be expressed as aψ k,i ) = 1 M [1,e j2πψ k,i,,e j2πψ k,im 1) ] T, 2) where ψ k,i = d λ sinθ k,i) with θ k,i denoting the AoD of the i-th path of the k-th user, d denoting the distance between BS antennas, and λ denoting the wavelength of the carrier frequency. Note that 1) can be also expressed in the matrixvector form as h k = A k g k, 3) where g k = [g k,1,g k,2,,g k,pk ] T C P k 1, and A k = [aψ k,1 ),aψ k,2 ),,aψ k,pk )] C M P k. B. Equivalent Channel in Lens-Based MmWave Massive MIMO The spatial channel h k in 3) can be transformed into the beamspace channel through a carefully designed lens which performs as a phase shifter [2]. Specifically, as shown in Fig. 1, such lens can be characterized as a spatial discrete fourier transform DFT) matrix U C M M, which is composed of the array steering vectors of M uniformly distributed orthogonal directions beams) as U = [1,aδ),,aδM 1))] H with δ = 1 M [1], [2]. Therefore, the received signal y k at the k-th user can be expressed as K hh k UH SVx d +n k = K hb k )H SVx d +n k, where γ is the transmit power,x d = [x d,1,x d,2,,x d,k ] T C K 1 is the data vector intended for K users with normalized 4) power E[ x d x H d 2 ] = I K, and the beamspace channel vector h b k CM 1 can be expressed as h b k = Uh k, 5) where the elements of h b k are channel coefficients associated with M orthogonal beams. Note that h b k is sparse due to the limited scattering of mmwave channel [2]. S C M NRF is the beam selector with N RF denoting the number of RF chains at the BS. Each column of S has and only has one nonzero element 1, and the location of this non-zero element in one column of S should be different from that in another column.n k is the complex Gaussian noise at thek-th user with zero mean and unit variance. We define the dimension-reduced equivalent channel h e k CNRF 1 as thus we have h e k = SH h b k, 6) K he k )H Vx d +n k, 7) where V = [v 1,v 2,,v K ] C NRF K is the zero-forcing ZF) precoding matrix consisting of K different unit-norm precoding vectors v i C NRF 1, which can be described as the normalized i-th column of H e ), i.e., v i = He ) :,i) H e ) :,i), where H e = [h e 1,he 2,,he K ] CNRF K. Note that the equivalent channel 6) is not Rayleigh distributed, and no dedicated codebook has been designed to quantize equivalent channel in the literature. This gap can be filled by the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook in the next section. III. PROPOSED DIMENSION-REDUCED SUBSPACE CODEBOOK In this section, we briefly review the equivalent channel feedback in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems based on the classical codebook at first. Then, we propose the dimension-reduced subspace codebook to quantize the equivalent channel vector better. Finally, we provide the performance analysis of the proposed codebook by quantifying the required number of feedback bits. A. Equivalent Channel Feedback We assume that each user knows its equivalent channel vector h e k through channel estimation [9]. Then, the k- th user quantizes h e k to B bits using a codebook D k = {d k,1,d k,2,,d k,2 B}. Considering the classical RVQ-based codebook, the quantization vector d k,i C NRF 1 is randomly generated by selecting vectors independently from the uniform distribution on the complex N RF -dimensional unit sphere [8]. The number of required feedback bits B should scale linearly withn RF to limit the system capacity loss within an acceptable level. To realize channel feedback, the k-th user will find d k,fk that is the closest to h e k, where closeness is measured by the angle between two vectors. That is, the index F k is computed according to F k = argmin i {1,2,,2 B } sin 2 h e k,d k,i)) = argmax i {1,2,,2 B } d H k,i h e k 2, 8)
3 3 where h e k = he k h e k denotes the equivalent channel direction. Since the equivalent channel magnitude h e k is just a scalar, we follow the widely used assumption that the channel magnitude h e k can be fed back to the BS perfectly [7], [8]. The index F k can be fed back through B bits, then the BS can obtain the feedback equivalent channel vector ĥe k = h e k d k,f k. However, since the equivalent channel vector h e k is not Rayleigh distributed, the classical RVQ-based codebook is not optimal in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems. In the next subsection, we will propose the dimension-reduced subspace codebook to quantize this equivalent channel better. B. Proposed Dimension-Reduced Subspace Codebook Considering h k = A k g k in 3), we can find that the channel vector h k is actually distributed on the column space of A k C M P k, which is formed by linear combination of A k s column vectors. Due to the severe propagation loss of mmwave signals [10], the number of paths is much smaller than the number of BS antenna, i.e. P k M. Therefore, P k column vectors of A k only form a subspace of the full M- dimensional space, which depends on P k different AoDs. This subspace is called as channel subspace in the rest of this paper. Therefore, we firstly propose to generate high-dimensional vectors in the channel subspace. Since the AoDs vary slower than path gains, we assume that AoDs are slow varying [11] and can be accurately estimated through beamspace channel estimation [12]. Then, we can generate the high-dimensional vector c k,i C M 1 as c k,i = A k w k,i, 9) where w k,i C P k 1 is isotropically distributed on the complex P k -dimensional unit sphere. The high-dimensional vector c k,i is distributed on the column space of A k, i.e., the channel subspace. Then, based on the high-dimensional vector c k,i, we propose the dimension-reduced subspace codebook D k = {d k,1,d k,2,,d k,2 B} to quantize the equivalent channel vector h e k, where the quantization vector d k,i C NRF 1 can be expressed as d k,i = S H Uc k,i, 10) where U and S are used to reflect the function of lens and beam selector in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems, respectively. Note that to ensure the unit-norm vector requirement of d k,i, d k,i should be normalized as d k,i = d k,i d k,i. 11) Considering 5) and 6), we can find that the quantization vector d k,i in the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook D k has the same distribution as the equivalent channel vector h e k. Thus, the proposed codebook is expected to enjoy better quantization performance than the classical RVQ-based codebook without considering the special channel characteristics of lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems. Such intuitive conclusion will be verified by the theoretical analysis of the proposed codebook in terms of the required number of feedback bits in the next subsection. C. Performance Analysis of The Proposed Codebook After the channel feedback based on the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook, the BS can perform downlink precoding based on the feedback equivalent channel matrix Ĥ e = [ĥ e 1,ĥe 2,,ĥe K ] CNRF K. We can rewrite 7) as γ K K he k )H v k x d,k + h e k K )H v i x d,i +n k, i=1,i k 12) where the second term denotes the multi-user interference. Thus, the per user rate R with limited channel feedback based on the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook is γ R = E [log 2 1+ K he k )Hv k )] 2 K. 13) i=1,i k he k )H v i 2 1+ γ K For the ideal case of perfect CSI at the BS, i.e., Ĥ e = H e, the ZF precoding vector v ideal,i is obtained as the normalized i-th column of H e ). Thus, v ideal,i is orthogonal to the k- th user s equivalent channel vector h e k for any i k, which means that we can obtain the ideal per user rate as R ideal = E [log 2 1+ γ K he k) H v ideal,k 2)]. 14) We define the rate gap Rγ) as the difference between the per user rate with ideal CSI and that with limited channel feedback: Rγ) = R ideal R. 15) Following the results from [8], the rate gap Rγ) can be upper bounded as Rγ) log 2 1+ γk 1) [ ] ) K E[ h e k 2] E sin 2 h e k,ĥe k )). 16) We can observe from 16) that the rate gap Rγ) depends on the equivalent channel norm h e k and the quantization error sin 2 h e k,ĥe k )). In the rest of this paper, we can omit the subscript k without loss of generality, where h e, A, and P denote the equivalent channel, steering matrix, and number of resolvable paths, [ respectively. Next, ] we will discuss the quantization error E sin 2 h e,ĥe )) in 16). Before that, we will prove Lemma 1 and Lemma 2 below which will be useful for the analysis of the quantization error. Lemma 1: Denoting T = S H UA, we have T H T = I P. Proof: Since thei-th row vectoraδj 1)) H ofuand the j-th column vector aψ i ) of A is asymptotically orthogonal if ψ i δj 1) when M, UA has and only has one non-zero element 1 in each column, and the location of this non-zero element in one column is different from that in another column. Generally, the beam selector S is designed to choose N RF rows of UA which includes non-zero elements [13]. Note that for the multi-user scenario, N RF is usually larger than P. Thus, T C NRF P has and only has one nonzero element 1 in each column, and the locations of nonzero elements are different for different columns. Therefore, we have T H T = I P.
4 4 Lemma 2: h e = S H UAg = g. Proof: Combining 3), 5) and 6), we have h e = S H UAg. 17) By denoting S H UA = T = [t 1,t 2,,t P ], we have h e = Tg = Σ P p=1 t pg p 18) a) = Σ P p=1 t p g p b) = Σ P p=1 g p = g, where a) is true due to the orthogonality among column vectorst p oftsee Lemma 1), and b) is true due to t p = 1 see Lemma 1). Now, we will provide an upper bound of the quantization error in 16) in the following Lemma 3. [ ] Lemma 3: The quantization error E sin 2 h e,ĥe )) of equivalent channel vector can be upper bounded as [ ] E sin 2 h e,ĥe )) < 2 B P 1. 19) Proof: Since h e = 1, ĥe = h e d F, and d F = 1, we have [ ] [ ] E sin 2 h e,ĥe )) = 1 E cos 2 h e,ĥe )) 20) [ = 1 E d H F h e 2]. By denoting g = g g and using Lemma 2, we can get h e = Tg h e = T g. Considering 10) and using w F = 1, we have d F = Tw F. Therefore, [ E d H F h e 2] = E [ wf H TH T g 2] a) = E [ w F g 2] H, 21) where a) follows from the results T H T = I P in Lemma 1. Since w F and g are isotropically distributed P -dimensional vectors, E [ w H F g 2] can be lower bounded as [8]: E [ w H F g 2] > 1 2 B P 1. 22) Combine 20), 21), and 22), we can obtain 19). Substituting 19) into 16), we have Rγ) log 2 1+ γk 1) E [ h e 2] 2 B P 1 K ). 23) Let the rate gap Rγ) 1 bps/hz [8], then the number of feedback bits B should scale according to B P 1 SNR+P 1)log 3 2 K 1), 24) where SNR = 10log 10 γ K E[ h e 2] is the signal-to-noiseratio SNR) at the receiver. We can observe from 24) that the slope of the required number of feedback bits B is P 1 when SNR increases. In other words, the required number of feedback bits B only scales linearly with P 1 to maintain a constant rate gap. Since P N RF, the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook require much less feedback overhead than the classical RVQ-based codebook where the number of feedback bits scales linearly with N RF. In next section, we will verify our analysis through simulations. R/user bps) Perfect CSI at the BS Proposed dimension reduced subspace codebook Classical RVQ based codebook [8] SNR db) Fig. 2. Per user rate of the ideal case of perfect CSI and the practical case of limited channel feedback. IV. SIMULATION RESULTS A simulation study was carried out to verify the performance of the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems. The key system parameters are set as: 1) the number of BS antennas, the number of RF chains, the number of users and the number of resolvable paths are M,N RF,K,P) = 128,24,8,3); 2) the AoDs are randomly chosen from uniform distribution U[ 1 2 π, 1 P 1 2π]; 3) the number of feedback bits B = 3 SNR+ P 1)log 2 K 1) for all considered codebooks for fair comparison. Fig. 2 shows per user rate of the ideal case of perfect CSI at the BS and the practical case of limited channel feedback, where the proposed codebook and the classical RVQ-based codebook are compared. We can observe that the rate gap between the ideal case of perfect CSI at the BS and the practical case of limited channel feedback using the proposed codebook remains constant when SNR increases, which is consistent with our theoretical analysis in Section III-C. On the contrary, for the classical RVQ-based codebook, the rate gap increases with the SNR. We can also find that the proposed codebook outperforms the classical RVQ-based codebook. V. CONCLUSIONS In this paper, we have investigated the problem of codebook design for equivalent channel feedback in lens-based mmwave massive MIMO systems for the first time. Specifically, we firstly proposed to utilize the limited scattering property of mmwave channels to generate the high-dimensional vectors in the channel subspace. After that, we further proposed the dimension-reduced subspace codebook to quantize the equivalent channel vector according to the function of lens and beam selector. We also provided the performance analysis of the proposed dimension-reduced subspace codebook. Simulation results verified that the proposed codebook has better performance than the traditional codebook.
5 5 REFERENCES [1] R. W. Heath, N. Gonzalez-Prelcic, S. Rangan, W. Roh, and A. Sayeed, An overview of signal processing techniques for millimeter wave MIMO systems, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process., vol. 10, no. 3, pp , Apr [2] J. Brady, N. Behdad, and A. M. Sayeed, Beamspace MIMO for millimeter-wave communications: System architecture, modeling, analysis, and measurements, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat., vol. 61, no. 7, pp , Jul [3] G. H. Song, J. Brady, and A. M. Sayeed, Beamspace MIMO transceivers for low-complexity and near-optimal communication at mmwave frequencies. in Proc. ICASSP, Apr. 2013, pp [4] Y. Zeng, R. Zhang, and Z. N. Chen, Electromagnetic lens-focusing antenna enabled massive MIMO: Performance improvement and cost reduction, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 32, no. 6, pp , Jun [5] Y. Zeng and R. Zhang, Millimeter wave MIMO with lens antenna array: A new path division multiplexing paradigm, IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 64, no. 4, pp , Apr [6] T. S. Rappaport, S. Sun, R. Mayzus, H. Zhao, Y. Azar, K. Wang, G. N. Wong, J. K. Schulz, M. Samimi, and F. Gutierrez, Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: It will work! IEEE Access, vol. 1, pp , May [7] D. J. Love, R. W. Heath, and T. Strohmer, Grassmannian beamforming for multiple-input multiple-output wireless systems, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 49, no. 10, pp , Oct [8] N. Jindal, MIMO broadcast channels with finite-rate feedback, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. 52, no. 11, pp , Nov [9] L. Yang, Y. Zeng, and R. Zhang, Efficient channel estimation for millimeter wave MIMO with limited RF chains, in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Communications ICC 16), May 2016, pp [10] A. Alkhateeb, O. El Ayach, G. Leus, and R. W. Heath, Channel estimation and hybrid precoding for millimeter wave cellular systems, IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process., vol. 8, no. 5, pp , Oct [11] H. Xie, F. Gao, S. Zhang, and S. Jin, A unified transmission strategy for TDD/FDD massive MIMO systems with spatial basis expansion model, to appear in IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., [12] X. Gao, L. Dai, S. Han, C.-L. I, and X. Wang, Reliable beamspace channel estimation for millimeter-wave massive MIMO systems with lens antenna array, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., under major revision, [13] X. Gao, L. Dai, Z. Chen, Z. Wang, and Z. Zhang, Near-optimal beam selection for beamspace mmwave massive MIMO systems, IEEE Commun. Lett., vol. 20, no. 5, pp , May 2016.
MASSIVE multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) can
 IEEE ICC 017 Signal Processing for Communications Symposium AoD-Adaptive Subspace Codebook for Channel Feedback in FDD assive IO Systems Wenqian Shen, Linglong Dai, Guan Gui, Zhaocheng Wang, Robert W.
IEEE ICC 017 Signal Processing for Communications Symposium AoD-Adaptive Subspace Codebook for Channel Feedback in FDD assive IO Systems Wenqian Shen, Linglong Dai, Guan Gui, Zhaocheng Wang, Robert W.
Achievable Rates of Multi-User Millimeter Wave Systems with Hybrid Precoding
 Achievable Rates of Multi-ser Millimeter Wave Systems with Hybrid Precoding Ahmed Alkhateeb, Robert W. Heath Jr. Wireless Networking and Communications Group The niversity of Texas at Austin Email: {aalkhateeb,
Achievable Rates of Multi-ser Millimeter Wave Systems with Hybrid Precoding Ahmed Alkhateeb, Robert W. Heath Jr. Wireless Networking and Communications Group The niversity of Texas at Austin Email: {aalkhateeb,
Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for. Multi-User Millimeter Wave Systems
 Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for 1 Multi-ser Millimeter Wave Systems Ahmed Alkhateeb, Geert Leus, and Robert W. Heath Jr. arxiv:1409.5162v2 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2015 Abstract Antenna arrays will be an important
Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for 1 Multi-ser Millimeter Wave Systems Ahmed Alkhateeb, Geert Leus, and Robert W. Heath Jr. arxiv:1409.5162v2 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2015 Abstract Antenna arrays will be an important
A High-Accuracy Adaptive Beam Training Algorithm for MmWave Communication
 A High-Accuracy Adaptive Beam Training Algorithm for MmWave Communication Zihan Tang, Jun Wang, Jintao Wang, and Jian Song Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology BNRist),
A High-Accuracy Adaptive Beam Training Algorithm for MmWave Communication Zihan Tang, Jun Wang, Jintao Wang, and Jian Song Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology BNRist),
Weighted DFT Codebook for Multiuser MIMO in Spatially Correlated Channels
 Weighted DFT Codebook for Multiuser MIMO in Spatially Correlated Channels Fang Yuan, Shengqian Han, Chenyang Yang Beihang University, Beijing, China Email: weiming8@gmail.com, sqhan@ee.buaa.edu.cn, cyyang@buaa.edu.cn
Weighted DFT Codebook for Multiuser MIMO in Spatially Correlated Channels Fang Yuan, Shengqian Han, Chenyang Yang Beihang University, Beijing, China Email: weiming8@gmail.com, sqhan@ee.buaa.edu.cn, cyyang@buaa.edu.cn
User Scheduling for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communications with Low-Resolution ADCs
 User Scheduling for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communications with Low-Resolution ADCs Jinseok Choi and Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking and Communication Group, The University of Texas at Austin E-mail: jinseokchoi89@utexas.edu,
User Scheduling for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communications with Low-Resolution ADCs Jinseok Choi and Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking and Communication Group, The University of Texas at Austin E-mail: jinseokchoi89@utexas.edu,
Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels
 Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels Jung Hoon Lee and Huaiyu Dai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University,
Nash Bargaining in Beamforming Games with Quantized CSI in Two-user Interference Channels Jung Hoon Lee and Huaiyu Dai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University,
Title. Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information. Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels
 Title Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 29 : Asia-Pacific Signal Citationand Conference: 688-691 Issue Date 29-1-4 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39789
Title Equal Gain Beamforming in Rayleigh Fading Channels Author(s)Tsai, Shang-Ho Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 29 : Asia-Pacific Signal Citationand Conference: 688-691 Issue Date 29-1-4 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39789
arxiv: v2 [cs.it] 24 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v2 [cs.it] 24 Feb 2017 arxiv: v2 [cs.it] 24 Feb 2017](/thumbs/86/93640841.jpg) ADC BIT ALLOCATION UNDER A POWER CONSTRAINT FOR MMWAVE MASSIVE MIMO COMMUNICATION RECEIVERS Jinseok Choi and Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking and Communications Group The University of Texas at Austin,
ADC BIT ALLOCATION UNDER A POWER CONSTRAINT FOR MMWAVE MASSIVE MIMO COMMUNICATION RECEIVERS Jinseok Choi and Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking and Communications Group The University of Texas at Austin,
I. Introduction. Index Terms Multiuser MIMO, feedback, precoding, beamforming, codebook, quantization, OFDM, OFDMA.
 Zero-Forcing Beamforming Codebook Design for MU- MIMO OFDM Systems Erdem Bala, Member, IEEE, yle Jung-Lin Pan, Member, IEEE, Robert Olesen, Member, IEEE, Donald Grieco, Senior Member, IEEE InterDigital
Zero-Forcing Beamforming Codebook Design for MU- MIMO OFDM Systems Erdem Bala, Member, IEEE, yle Jung-Lin Pan, Member, IEEE, Robert Olesen, Member, IEEE, Donald Grieco, Senior Member, IEEE InterDigital
Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels
 Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels Gill November 22, 2011 Gill (University of Delaware) November 22, 2011 1 / 25 Part I Mode Selection for MISO BC with Perfect/Imperfect CSI [1]-[3] Gill
Mode Selection for Multi-Antenna Broadcast Channels Gill November 22, 2011 Gill (University of Delaware) November 22, 2011 1 / 25 Part I Mode Selection for MISO BC with Perfect/Imperfect CSI [1]-[3] Gill
On the Design of Scalar Feedback Techniques for MIMO Broadcast Scheduling
 On the Design of Scalar Feedback Techniques for MIMO Broadcast Scheduling Ruben de Francisco and Dirk T.M. Slock Eurecom Institute Sophia-Antipolis, France Email: {defranci, slock}@eurecom.fr Abstract
On the Design of Scalar Feedback Techniques for MIMO Broadcast Scheduling Ruben de Francisco and Dirk T.M. Slock Eurecom Institute Sophia-Antipolis, France Email: {defranci, slock}@eurecom.fr Abstract
Low Resolution Adaptive Compressed Sensing for mmwave MIMO receivers
 Low Resolution Adaptive Compressed Sensing for mmwave MIMO receivers Cristian Rusu, Nuria González-Prelcic and Robert W. Heath Motivation 2 Power consumption at mmwave in a MIMO receiver Power at 60 GHz
Low Resolution Adaptive Compressed Sensing for mmwave MIMO receivers Cristian Rusu, Nuria González-Prelcic and Robert W. Heath Motivation 2 Power consumption at mmwave in a MIMO receiver Power at 60 GHz
Beam Selection for Performance-Complexity Optimization in High-Dimensional MIMO Systems
 Beam Selection for Performance-Complexity Optimization in High-Dimensional MIMO Systems John Hogan and Akbar Sayeed Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison,
Beam Selection for Performance-Complexity Optimization in High-Dimensional MIMO Systems John Hogan and Akbar Sayeed Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison,
The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View
 The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697-2625 Email: sudhirs@uciedu,
The Optimality of Beamforming: A Unified View Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697-2625 Email: sudhirs@uciedu,
Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation
 Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation Chongbin Xu, Peng Wang, Zhonghao Zhang, and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Outline Background Mutual Information
Joint FEC Encoder and Linear Precoder Design for MIMO Systems with Antenna Correlation Chongbin Xu, Peng Wang, Zhonghao Zhang, and Li Ping City University of Hong Kong 1 Outline Background Mutual Information
Two-Stage Channel Feedback for Beamforming and Scheduling in Network MIMO Systems
 Two-Stage Channel Feedback for Beamforming and Scheduling in Network MIMO Systems Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
Two-Stage Channel Feedback for Beamforming and Scheduling in Network MIMO Systems Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
USING multiple antennas has been shown to increase the
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 11 A Comparison of Time-Sharing, DPC, and Beamforming for MIMO Broadcast Channels With Many Users Masoud Sharif, Member, IEEE, and Babak
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 55, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 11 A Comparison of Time-Sharing, DPC, and Beamforming for MIMO Broadcast Channels With Many Users Masoud Sharif, Member, IEEE, and Babak
SWISS: Spectrum Weighted Identification of Signal Sources for mmwave Systems
 SWISS: Spectrum Weighted Identification of Signal Sources for mmwave Systems Ziming Cheng, Jingyue Huang, Meixia Tao, and Pooi-Yuen Kam Dept. of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai,
SWISS: Spectrum Weighted Identification of Signal Sources for mmwave Systems Ziming Cheng, Jingyue Huang, Meixia Tao, and Pooi-Yuen Kam Dept. of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai,
DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection
 1 DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection Yu Han, Shi Jin, Jun Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, and Kai-Kit Wong National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast
1 DFT-Based Hybrid Beamforming Multiuser Systems: Rate Analysis and Beam Selection Yu Han, Shi Jin, Jun Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, and Kai-Kit Wong National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast
Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback
 Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 9697-65 Email: syed@ece.uci.edu,
Vector Channel Capacity with Quantized Feedback Sudhir Srinivasa and Syed Ali Jafar Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 9697-65 Email: syed@ece.uci.edu,
Hybrid Analog and Digital Precoding: From Practical RF System Models to Information Theoretic Bounds
 Hybrid Analog and Digital Precoding: From Practical RF System Models to Information Theoretic Bounds Vijay Venkateswaran, Rajet Krishnan Huawei Technologies, Sweden, {vijayvenkateswaran, rajetkrishnan}@huaweicom
Hybrid Analog and Digital Precoding: From Practical RF System Models to Information Theoretic Bounds Vijay Venkateswaran, Rajet Krishnan Huawei Technologies, Sweden, {vijayvenkateswaran, rajetkrishnan}@huaweicom
Limited Feedback-based Unitary Precoder Design in Rician MIMO Channel via Trellis Exploration Algorithm
 Limited Feedback-based Unitary Precoder Design in Rician MIMO Channel via Trellis Exploration Algorithm Dalin Zhu Department of Wireless Communications NEC Laboratories China NLC) 11F Bld.A Innovation
Limited Feedback-based Unitary Precoder Design in Rician MIMO Channel via Trellis Exploration Algorithm Dalin Zhu Department of Wireless Communications NEC Laboratories China NLC) 11F Bld.A Innovation
On the Impact of Quantized Channel Feedback in Guaranteeing Secrecy with Artificial Noise
 On the Impact of Quantized Channel Feedback in Guaranteeing Secrecy with Artificial Noise Ya-Lan Liang, Yung-Shun Wang, Tsung-Hui Chang, Y.-W. Peter Hong, and Chong-Yung Chi Institute of Communications
On the Impact of Quantized Channel Feedback in Guaranteeing Secrecy with Artificial Noise Ya-Lan Liang, Yung-Shun Wang, Tsung-Hui Chang, Y.-W. Peter Hong, and Chong-Yung Chi Institute of Communications
Average Throughput Analysis of Downlink Cellular Networks with Multi-Antenna Base Stations
 Average Throughput Analysis of Downlink Cellular Networks with Multi-Antenna Base Stations Rui Wang, Jun Zhang, S.H. Song and K. B. Letaief, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of ECE, The Hong Kong University of Science
Average Throughput Analysis of Downlink Cellular Networks with Multi-Antenna Base Stations Rui Wang, Jun Zhang, S.H. Song and K. B. Letaief, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of ECE, The Hong Kong University of Science
ADC Bit Optimization for Spectrum- and Energy-Efficient Millimeter Wave Communications
 ADC Bit Optimization for Spectrum- and Energy-Efficient Millimeter Wave Communications Jinseok Choi, Junmo Sung, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer Wireless Networking and Communications Group, The University
ADC Bit Optimization for Spectrum- and Energy-Efficient Millimeter Wave Communications Jinseok Choi, Junmo Sung, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer Wireless Networking and Communications Group, The University
Generalized Spatial Modulation Aided MmWave MIMO with Sub-Connected Hybrid Precoding Scheme
 Generalized Spatial Modulation Aided MmWave MIMO with Sub-Connected Hybrid Precoding Scheme Longzhuang He, Jintao Wang, and Jian Song Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing,
Generalized Spatial Modulation Aided MmWave MIMO with Sub-Connected Hybrid Precoding Scheme Longzhuang He, Jintao Wang, and Jian Song Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing,
Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems
 Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems Umer Salim, David Gesbert, Dirk Slock, Zafer Beyaztas Mobile Communications Department Eurecom, France Abstract The communication between
Hybrid Pilot/Quantization based Feedback in Multi-Antenna TDD Systems Umer Salim, David Gesbert, Dirk Slock, Zafer Beyaztas Mobile Communications Department Eurecom, France Abstract The communication between
Massive MU-MIMO Downlink TDD Systems with Linear Precoding and Downlink Pilots
 Massive MU-MIMO Downlink TDD Systems with Linear Precoding and Downlink Pilots Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, and Thomas L. Marzetta Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY) Linköping University, 58
Massive MU-MIMO Downlink TDD Systems with Linear Precoding and Downlink Pilots Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, and Thomas L. Marzetta Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY) Linköping University, 58
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results
 NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS GIST September 2017 (VTC-Fall 2017) 1 / 46 Abstract: Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) becomes a key technology in 5G as it can improve
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS GIST September 2017 (VTC-Fall 2017) 1 / 46 Abstract: Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) becomes a key technology in 5G as it can improve
Hybrid Beamforming with Finite-Resolution Phase Shifters for Large-Scale MIMO Systems
 Hybrid Beamforming with Finite-Resolution Phase Shifters for Large-Scale MIMO Systems Foad Sohrabi and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario MS
Hybrid Beamforming with Finite-Resolution Phase Shifters for Large-Scale MIMO Systems Foad Sohrabi and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario MS
CHANNEL FEEDBACK QUANTIZATION METHODS FOR MISO AND MIMO SYSTEMS
 CHANNEL FEEDBACK QUANTIZATION METHODS FOR MISO AND MIMO SYSTEMS June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9293 47,
CHANNEL FEEDBACK QUANTIZATION METHODS FOR MISO AND MIMO SYSTEMS June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 9293 47,
Hybrid Precoding based on Tensor Decomposition for mmwave 3D-MIMO Systems
 Hybrid Precoding based on Tensor Decomposition for mmwave 3D-MIMO Systems Lu Liu and Yafei Tian School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China Email: {luliu, ytian}@buaa.edu.cn
Hybrid Precoding based on Tensor Decomposition for mmwave 3D-MIMO Systems Lu Liu and Yafei Tian School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China Email: {luliu, ytian}@buaa.edu.cn
Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems
 1 Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale and Long Bao Le Institute National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS) Université de Québec, Montréal,
1 Pilot Optimization and Channel Estimation for Multiuser Massive MIMO Systems Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale and Long Bao Le Institute National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS) Université de Québec, Montréal,
On the Required Accuracy of Transmitter Channel State Information in Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels
 On the Required Accuracy of Transmitter Channel State Information in Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels Giuseppe Caire University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA, USA Email: caire@usc.edu Nihar
On the Required Accuracy of Transmitter Channel State Information in Multiple Antenna Broadcast Channels Giuseppe Caire University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA, USA Email: caire@usc.edu Nihar
Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems
 Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems Xiaofang Sun, Shihao Yan, Nan Yang, Zhiguo Ding, Chao Shen, and Zhangdui Zhong State Key Lab of Rail Traffic Control and Safety, Beijing
Short-Packet Communications in Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Systems Xiaofang Sun, Shihao Yan, Nan Yang, Zhiguo Ding, Chao Shen, and Zhangdui Zhong State Key Lab of Rail Traffic Control and Safety, Beijing
Low-High SNR Transition in Multiuser MIMO
 Low-High SNR Transition in Multiuser MIMO Malcolm Egan 1 1 Agent Technology Center, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic. 1 Abstract arxiv:1409.4393v1
Low-High SNR Transition in Multiuser MIMO Malcolm Egan 1 1 Agent Technology Center, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic. 1 Abstract arxiv:1409.4393v1
Joint Power Control and Beamforming Codebook Design for MISO Channels with Limited Feedback
 Joint Power Control and Beamforming Codebook Design for MISO Channels with Limited Feedback Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto,
Joint Power Control and Beamforming Codebook Design for MISO Channels with Limited Feedback Behrouz Khoshnevis and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto,
VECTOR QUANTIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR MULTIPLE-ANTENNA CHANNEL INFORMATION FEEDBACK
 VECTOR QUANTIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR MULTIPLE-ANTENNA CHANNEL INFORMATION FEEDBACK June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La
VECTOR QUANTIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR MULTIPLE-ANTENNA CHANNEL INFORMATION FEEDBACK June Chul Roh and Bhaskar D. Rao Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego La
NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective
 NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective Peng Xu, Zhiguo Ding, Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:54.775v2 cs.it] 2 May 25 Abstract In this letter, the performance of non-orthogonal
NOMA: An Information Theoretic Perspective Peng Xu, Zhiguo Ding, Member, IEEE, Xuchu Dai and H. Vincent Poor, Fellow, IEEE arxiv:54.775v2 cs.it] 2 May 25 Abstract In this letter, the performance of non-orthogonal
Massive MIMO: Signal Structure, Efficient Processing, and Open Problems II
 Massive MIMO: Signal Structure, Efficient Processing, and Open Problems II Mahdi Barzegar Communications and Information Theory Group (CommIT) Technische Universität Berlin Heisenberg Communications and
Massive MIMO: Signal Structure, Efficient Processing, and Open Problems II Mahdi Barzegar Communications and Information Theory Group (CommIT) Technische Universität Berlin Heisenberg Communications and
Mehdi M. Molu, Pei Xiao, Rahim Tafazolli 22 nd Feb, 2017
 , Pei Xiao, Rahim Tafazolli 22 nd Feb, 2017 1 Outline Introduction and Problem Statement State of the Art Hybrid Beamformers Massive MIMO Millimetre Wave Proposed Solution (and Motivation) Sketch of the
, Pei Xiao, Rahim Tafazolli 22 nd Feb, 2017 1 Outline Introduction and Problem Statement State of the Art Hybrid Beamformers Massive MIMO Millimetre Wave Proposed Solution (and Motivation) Sketch of the
Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel
 /33 Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel Presented by Paul de Kerret Joint work with Antonio Bazco, Nicolas Gresset, and David Gesbert ESIT 2017 in Madrid,
/33 Degrees-of-Freedom Robust Transmission for the K-user Distributed Broadcast Channel Presented by Paul de Kerret Joint work with Antonio Bazco, Nicolas Gresset, and David Gesbert ESIT 2017 in Madrid,
(Article begins on next page)
 Chalmers Publication Library Copyright Notice 2010 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for
Chalmers Publication Library Copyright Notice 2010 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for
Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming
 Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming Authors: Christian Lameiro, Alfredo Nazábal, Fouad Gholam, Javier Vía and Ignacio Santamaría University of Cantabria,
Capacity Region of the Two-Way Multi-Antenna Relay Channel with Analog Tx-Rx Beamforming Authors: Christian Lameiro, Alfredo Nazábal, Fouad Gholam, Javier Vía and Ignacio Santamaría University of Cantabria,
Beamspace MIMO-NOMA for Millimeter-Wave Communications Using Lens Antenna Arrays
 Beamsace MIMO-NOMA for Millimeter-Wave Communications Using Lens Antenna Arrays Bichai Wang 1, Linglong Dai 1,XiqiGao, and Lajos anzo 3 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology
Beamsace MIMO-NOMA for Millimeter-Wave Communications Using Lens Antenna Arrays Bichai Wang 1, Linglong Dai 1,XiqiGao, and Lajos anzo 3 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology
Secure Multiuser MISO Communication Systems with Quantized Feedback
 Secure Multiuser MISO Communication Systems with Quantized Feedback Berna Özbek*, Özgecan Özdoğan*, Güneş Karabulut Kurt** *Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology,Turkey
Secure Multiuser MISO Communication Systems with Quantized Feedback Berna Özbek*, Özgecan Özdoğan*, Güneş Karabulut Kurt** *Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology,Turkey
MIMO Broadcast Channels with Finite Rate Feedback
 IO Broadcast Channels with Finite Rate Feedbac Nihar Jindal, ember, IEEE Abstract ultiple transmit antennas in a downlin channel can provide tremendous capacity ie multiplexing gains, even when receivers
IO Broadcast Channels with Finite Rate Feedbac Nihar Jindal, ember, IEEE Abstract ultiple transmit antennas in a downlin channel can provide tremendous capacity ie multiplexing gains, even when receivers
A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for. Downlink Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems
 A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for 1 Downlin Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems arxiv:1008.0730v1 [cs.it] 4 Aug 2010 Peng Cheng, Meixia Tao and Wenjun Zhang Abstract Signal-to-leaage-and-noise ratio
A New SLNR-based Linear Precoding for 1 Downlin Multi-User Multi-Stream MIMO Systems arxiv:1008.0730v1 [cs.it] 4 Aug 2010 Peng Cheng, Meixia Tao and Wenjun Zhang Abstract Signal-to-leaage-and-noise ratio
Lecture 7 MIMO Communica2ons
 Wireless Communications Lecture 7 MIMO Communica2ons Prof. Chun-Hung Liu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Chiao Tung University Fall 2014 1 Outline MIMO Communications (Chapter 10
Wireless Communications Lecture 7 MIMO Communica2ons Prof. Chun-Hung Liu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Chiao Tung University Fall 2014 1 Outline MIMO Communications (Chapter 10
Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDMA for MIMO Broadcast Channels
 TO APPEAR IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COUNICATIONS, JUNE 004 1 Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDA for IO Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal & Andrea Goldsmith Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University
TO APPEAR IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COUNICATIONS, JUNE 004 1 Dirty Paper Coding vs. TDA for IO Broadcast Channels Nihar Jindal & Andrea Goldsmith Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS. Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu
 PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF DATA-SHARING AND COMPRESSION STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD RADIO ACCESS NETWORKS Pratik Patil, Binbin Dai, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
ASPECTS OF FAVORABLE PROPAGATION IN MASSIVE MIMO Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, Thomas L. Marzetta
 ASPECTS OF FAVORABLE PROPAGATION IN MASSIVE MIMO ien Quoc Ngo, Eri G. Larsson, Thomas L. Marzetta Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY), Linöping University, 58 83 Linöping, Sweden Bell Laboratories,
ASPECTS OF FAVORABLE PROPAGATION IN MASSIVE MIMO ien Quoc Ngo, Eri G. Larsson, Thomas L. Marzetta Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY), Linöping University, 58 83 Linöping, Sweden Bell Laboratories,
Beam Based Stochastic Model of the Coverage Probability in 5G Millimeter Wave Systems
 Beam Based Stochastic Model of the Coverage Probability in 5G Millimeter Wave Systems Cristian Tatino, Ilaria Malanchini, Danish Aziz, Di Yuan Department of Science and Technology, Linköping University,
Beam Based Stochastic Model of the Coverage Probability in 5G Millimeter Wave Systems Cristian Tatino, Ilaria Malanchini, Danish Aziz, Di Yuan Department of Science and Technology, Linköping University,
Exploiting Quantized Channel Norm Feedback Through Conditional Statistics in Arbitrarily Correlated MIMO Systems
 Exploiting Quantized Channel Norm Feedback Through Conditional Statistics in Arbitrarily Correlated MIMO Systems IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING Volume 57, Issue 10, Pages 4027-4041, October 2009.
Exploiting Quantized Channel Norm Feedback Through Conditional Statistics in Arbitrarily Correlated MIMO Systems IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING Volume 57, Issue 10, Pages 4027-4041, October 2009.
Hybrid Analog-Digital Channel Estimation and. Beamforming: Training-Throughput Tradeoff. (Draft with more Results and Details)
 Hybrid Analog-Digital Channel Estimation and 1 Beamforming: Training-Throughput Tradeoff (Draft with more Results and Details) arxiv:1509.05091v2 [cs.it] 9 Oct 2015 Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale, Member, IEEE,
Hybrid Analog-Digital Channel Estimation and 1 Beamforming: Training-Throughput Tradeoff (Draft with more Results and Details) arxiv:1509.05091v2 [cs.it] 9 Oct 2015 Tadilo Endeshaw Bogale, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 64, NO. 2, FEBRUARY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 64, NO. 2, EBRUARY 2016 601 Structured Compressive Sensing-Based Spatio-Temporal Joint Channel Estimation for DD Massive MIMO Zhen Gao, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 64, NO. 2, EBRUARY 2016 601 Structured Compressive Sensing-Based Spatio-Temporal Joint Channel Estimation for DD Massive MIMO Zhen Gao, Student Member, IEEE, Linglong
Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback
 IEEE INFOCOM Workshop On Cognitive & Cooperative Networks Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback Chao Wang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuen Chau. Dept.of
IEEE INFOCOM Workshop On Cognitive & Cooperative Networks Transmitter-Receiver Cooperative Sensing in MIMO Cognitive Network with Limited Feedback Chao Wang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuen Chau. Dept.of
Approximate Ergodic Capacity of a Class of Fading Networks
 Approximate Ergodic Capacity of a Class of Fading Networks Sang-Woon Jeon, Chien-Yi Wang, and Michael Gastpar School of Computer and Communication Sciences EPFL Lausanne, Switzerland {sangwoon.jeon, chien-yi.wang,
Approximate Ergodic Capacity of a Class of Fading Networks Sang-Woon Jeon, Chien-Yi Wang, and Michael Gastpar School of Computer and Communication Sciences EPFL Lausanne, Switzerland {sangwoon.jeon, chien-yi.wang,
Quantifying the Performance Gain of Direction Feedback in a MISO System
 Quantifying the Performance Gain of Direction Feedback in a ISO System Shengli Zhou, Jinhong Wu, Zhengdao Wang 3, and ilos Doroslovacki Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Connecticut
Quantifying the Performance Gain of Direction Feedback in a ISO System Shengli Zhou, Jinhong Wu, Zhengdao Wang 3, and ilos Doroslovacki Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Connecticut
2D Unitary ESPRIT Based Super-Resolution Channel Estimation for Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO with Hybrid Precoding
 1 2D Unitary ESPRI Based Super-Resolution Channel Estimation for Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO with Hybrid Precoding Anwen Liao Zhen Gao Member IEEE Yongpeng Wu Senior Member IEEE Hua Wang Member IEEE and
1 2D Unitary ESPRI Based Super-Resolution Channel Estimation for Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO with Hybrid Precoding Anwen Liao Zhen Gao Member IEEE Yongpeng Wu Senior Member IEEE Hua Wang Member IEEE and
Tranceiver Design using Linear Precoding in a Multiuser MIMO System with Limited Feedback
 IET Communications Tranceiver Design using Linear Precoding in a Multiuser MIMO System with Limited Feedback Journal: IET Communications Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted
IET Communications Tranceiver Design using Linear Precoding in a Multiuser MIMO System with Limited Feedback Journal: IET Communications Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted
Low-Complexity Spatial Channel Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Millimeter Wave Links
 Low-Complexity Spatial Channel Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Millimeter Wave Links Hsiao-Lan Chiang Tobias Kadur Wolfgang Rave and Gerhard Fettweis Technische Universität Dresden Email: {hsiao-lanchiang
Low-Complexity Spatial Channel Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Millimeter Wave Links Hsiao-Lan Chiang Tobias Kadur Wolfgang Rave and Gerhard Fettweis Technische Universität Dresden Email: {hsiao-lanchiang
Secure Degrees of Freedom of the MIMO Multiple Access Wiretap Channel
 Secure Degrees of Freedom of the MIMO Multiple Access Wiretap Channel Pritam Mukherjee Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park, MD 074 pritamm@umd.edu
Secure Degrees of Freedom of the MIMO Multiple Access Wiretap Channel Pritam Mukherjee Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park, MD 074 pritamm@umd.edu
ITERATIVE BEAM ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS FOR TDD MIMO SYSTEMS
 ITERATIVE BEAM ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS FOR TDD MIMO SYSTEMS Dennis Ogbe, David J Love Purdue University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering West Lafayette, IN 4797, USA Vasanthan Raghavan Qualcomm,
ITERATIVE BEAM ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS FOR TDD MIMO SYSTEMS Dennis Ogbe, David J Love Purdue University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering West Lafayette, IN 4797, USA Vasanthan Raghavan Qualcomm,
On the Throughput of Proportional Fair Scheduling with Opportunistic Beamforming for Continuous Fading States
 On the hroughput of Proportional Fair Scheduling with Opportunistic Beamforming for Continuous Fading States Andreas Senst, Peter Schulz-Rittich, Gerd Ascheid, and Heinrich Meyr Institute for Integrated
On the hroughput of Proportional Fair Scheduling with Opportunistic Beamforming for Continuous Fading States Andreas Senst, Peter Schulz-Rittich, Gerd Ascheid, and Heinrich Meyr Institute for Integrated
Le Liang B.Eng., Southeast University, A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF APPLIED SCIENCE
 Practical Precoding Design for Modern Multiuser MIMO Communications by Le Liang B.Eng., Southeast University, 2012 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER
Practical Precoding Design for Modern Multiuser MIMO Communications by Le Liang B.Eng., Southeast University, 2012 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER
Statistical MIMO beam codebook design for mmwave transmissions
 Khormuji and Pitaval EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 8) 8:9 https://doi.org/.8/s338-8-9-z RESEARCH Open Access Statistical MIMO beam codebook design for mmwave transmissions Majid
Khormuji and Pitaval EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 8) 8:9 https://doi.org/.8/s338-8-9-z RESEARCH Open Access Statistical MIMO beam codebook design for mmwave transmissions Majid
How Much Training and Feedback are Needed in MIMO Broadcast Channels?
 How uch raining and Feedback are Needed in IO Broadcast Channels? ari Kobayashi, SUPELEC Gif-sur-Yvette, France Giuseppe Caire, University of Southern California Los Angeles CA, 989 USA Nihar Jindal University
How uch raining and Feedback are Needed in IO Broadcast Channels? ari Kobayashi, SUPELEC Gif-sur-Yvette, France Giuseppe Caire, University of Southern California Los Angeles CA, 989 USA Nihar Jindal University
How Much Do Downlink Pilots Improve Cell-Free Massive MIMO?
 How Much Do Downlink Pilots Improve Cell-Free Massive MIMO? Giovanni Interdonato, Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, Pål Frenger Ericsson Research, Wireless Access Networks, 581 1 Linköping, Sweden Department
How Much Do Downlink Pilots Improve Cell-Free Massive MIMO? Giovanni Interdonato, Hien Quoc Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, Pål Frenger Ericsson Research, Wireless Access Networks, 581 1 Linköping, Sweden Department
Upper Bounds on MIMO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints
 Upper Bounds on IO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints Zukang Shen, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking Communications Group Department of Electrical Computer Engineering
Upper Bounds on IO Channel Capacity with Channel Frobenius Norm Constraints Zukang Shen, Jeffrey G. Andrews, Brian L. Evans Wireless Networking Communications Group Department of Electrical Computer Engineering
Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems
 Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems - Summary of An Overview of Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems Gwanmo Ku May 14, 17, and 21, 2013 Outline Transmitter Ant. 1 Channel N
Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems - Summary of An Overview of Limited Feedback in Wireless Communication Systems Gwanmo Ku May 14, 17, and 21, 2013 Outline Transmitter Ant. 1 Channel N
Spectrum Sharing in RF-Powered Cognitive Radio Networks using Game Theory
 Spectrum Sharing in RF-owered Cognitive Radio Networks using Theory Yuanye Ma, He Henry Chen, Zihuai Lin, Branka Vucetic, Xu Li The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, Email: yuanye.ma, he.chen, zihuai.lin,
Spectrum Sharing in RF-owered Cognitive Radio Networks using Theory Yuanye Ma, He Henry Chen, Zihuai Lin, Branka Vucetic, Xu Li The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, Email: yuanye.ma, he.chen, zihuai.lin,
Coordinated Regularized Zero-Forcing Precoding for Multicell MISO Systems with Limited Feedback
 DRAFT 1 Coordinated Regularized Zero-Forcing Precoding for Multicell MISO Systems with Limited Feedbac Jawad Mirza, Student Member, IEEE, Peter J. Smith, Fellow, IEEE, Pawel A. Dmochowsi, Senior Member,
DRAFT 1 Coordinated Regularized Zero-Forcing Precoding for Multicell MISO Systems with Limited Feedbac Jawad Mirza, Student Member, IEEE, Peter J. Smith, Fellow, IEEE, Pawel A. Dmochowsi, Senior Member,
Comparisons of Performance of Various Transmission Schemes of MIMO System Operating under Rician Channel Conditions
 Comparisons of Performance of Various ransmission Schemes of MIMO System Operating under ician Channel Conditions Peerapong Uthansakul and Marek E. Bialkowski School of Information echnology and Electrical
Comparisons of Performance of Various ransmission Schemes of MIMO System Operating under ician Channel Conditions Peerapong Uthansakul and Marek E. Bialkowski School of Information echnology and Electrical
Massive MIMO As Enabler for Communications with Drone Swarms
 Massive MIMO As Enabler for Communications with Drone Swarms Prabhu Chandhar, Danyo Danev, and Erik G. Larsson Division of Communication Systems Dept. of Electrical Engineering Linköping University, Sweden
Massive MIMO As Enabler for Communications with Drone Swarms Prabhu Chandhar, Danyo Danev, and Erik G. Larsson Division of Communication Systems Dept. of Electrical Engineering Linköping University, Sweden
Robust Learning-Based ML Detection for Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit Quantized Signals
 Robust Learning-Based ML Detection for Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit Quantized Signals Jinseok Choi, Yunseong Cho, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer Wireless Networking and Communications Group, The
Robust Learning-Based ML Detection for Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit Quantized Signals Jinseok Choi, Yunseong Cho, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer Wireless Networking and Communications Group, The
AS the fifth generation (5G) wireless mobile communication
 Joint Power Allocation and Beamforming for on-orthogonal Multiple Access (OMA) in 5G Millimeter-Wave Communications Zhenyu Xiao, Senior Member, IEEE, Lipeng Zhu, Jinho Choi, Senior Member, IEEE, Pengfei
Joint Power Allocation and Beamforming for on-orthogonal Multiple Access (OMA) in 5G Millimeter-Wave Communications Zhenyu Xiao, Senior Member, IEEE, Lipeng Zhu, Jinho Choi, Senior Member, IEEE, Pengfei
A Precoding Method for Multiple Antenna System on the Riemannian Manifold
 Journal of Communications Vol. 9, No. 2, February 2014 A Precoding Method for Multiple Antenna System on the Riemannian Manifold Lin Zhang1 and S. H. Leung2 1 Department of Electronic Engineering, City
Journal of Communications Vol. 9, No. 2, February 2014 A Precoding Method for Multiple Antenna System on the Riemannian Manifold Lin Zhang1 and S. H. Leung2 1 Department of Electronic Engineering, City
Lattice Reduction Aided Precoding for Multiuser MIMO using Seysen s Algorithm
 Lattice Reduction Aided Precoding for Multiuser MIMO using Seysen s Algorithm HongSun An Student Member IEEE he Graduate School of I & Incheon Korea ahs3179@gmail.com Manar Mohaisen Student Member IEEE
Lattice Reduction Aided Precoding for Multiuser MIMO using Seysen s Algorithm HongSun An Student Member IEEE he Graduate School of I & Incheon Korea ahs3179@gmail.com Manar Mohaisen Student Member IEEE
Resolution-Adaptive Hybrid MIMO Architectures for Millimeter Wave Communications
 1 Resolution-Adaptive Hybrid MIMO Architectures for Millimeter Wave Communications Jinseok Choi, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer arxiv:1704.03137v3 cs.it] 16 Aug 2017 Abstract In this paper, we propose
1 Resolution-Adaptive Hybrid MIMO Architectures for Millimeter Wave Communications Jinseok Choi, Brian L. Evans, and Alan Gatherer arxiv:1704.03137v3 cs.it] 16 Aug 2017 Abstract In this paper, we propose
POKEMON: A NON-LINEAR BEAMFORMING ALGORITHM FOR 1-BIT MASSIVE MIMO
 POKEMON: A NON-LINEAR BEAMFORMING ALGORITHM FOR 1-BIT MASSIVE MIMO Oscar Castañeda 1, Tom Goldstein 2, and Christoph Studer 1 1 School of ECE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY; e-mail: oc66@cornell.edu,
POKEMON: A NON-LINEAR BEAMFORMING ALGORITHM FOR 1-BIT MASSIVE MIMO Oscar Castañeda 1, Tom Goldstein 2, and Christoph Studer 1 1 School of ECE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY; e-mail: oc66@cornell.edu,
Pilot Beam Sequence Design for Channel Estimation in Millimeter-Wave MIMO Systems: A POMDP Framework
 Pilot Beam Sequence Design for Channel Estimation in Millimeter-Wave MIMO Systems: A POMDP Framework Junyeong Seo, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchul Sung, Senior Member, IEEE Gilwon Lee, and Donggun Kim,
Pilot Beam Sequence Design for Channel Estimation in Millimeter-Wave MIMO Systems: A POMDP Framework Junyeong Seo, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchul Sung, Senior Member, IEEE Gilwon Lee, and Donggun Kim,
Non Orthogonal Multiple Access for 5G and beyond
 Non Orthogonal Multiple Access for 5G and beyond DIET- Sapienza University of Rome mai.le.it@ieee.org November 23, 2018 Outline 1 5G Era Concept of NOMA Classification of NOMA CDM-NOMA in 5G-NR Low-density
Non Orthogonal Multiple Access for 5G and beyond DIET- Sapienza University of Rome mai.le.it@ieee.org November 23, 2018 Outline 1 5G Era Concept of NOMA Classification of NOMA CDM-NOMA in 5G-NR Low-density
arxiv: v2 [cs.it] 9 Jun 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cs.it] 9 Jun 2015 arxiv: v2 [cs.it] 9 Jun 2015](/thumbs/82/86657110.jpg) SUBMITTED TO IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, Randomly-Directional Beamforming in Millimeter-Wave Multi-User MISO Downlink Gilwon Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchul Sung, Senior Member,
SUBMITTED TO IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, Randomly-Directional Beamforming in Millimeter-Wave Multi-User MISO Downlink Gilwon Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchul Sung, Senior Member,
OVER the past ten years, research (see the references in
 766 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Duplex Distortion Models for Limited Feedback MIMO Communication David J. Love, Member, IEEE Abstract The use of limited feedback
766 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Duplex Distortion Models for Limited Feedback MIMO Communication David J. Love, Member, IEEE Abstract The use of limited feedback
DEVICE-TO-DEVICE COMMUNICATIONS: THE PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY ADVANTAGE
 DEVICE-TO-DEVICE COMMUNICATIONS: THE PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY ADVANTAGE Daohua Zhu, A. Lee Swindlehurst, S. Ali A. Fakoorian, Wei Xu, Chunming Zhao National Mobile Communications Research Lab, Southeast
DEVICE-TO-DEVICE COMMUNICATIONS: THE PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY ADVANTAGE Daohua Zhu, A. Lee Swindlehurst, S. Ali A. Fakoorian, Wei Xu, Chunming Zhao National Mobile Communications Research Lab, Southeast
Rate-Optimum Beamforming Transmission in MIMO Rician Fading Channels
 Rate-Optimum Beamforming Transmission in MIMO Rician Fading Channels Dimitrios E. Kontaxis National and Kapodistrian University of Athens Department of Informatics and telecommunications Abstract In this
Rate-Optimum Beamforming Transmission in MIMO Rician Fading Channels Dimitrios E. Kontaxis National and Kapodistrian University of Athens Department of Informatics and telecommunications Abstract In this
Capacity of Memoryless Channels and Block-Fading Channels With Designable Cardinality-Constrained Channel State Feedback
 2038 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 50, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 Capacity of Memoryless Channels and Block-Fading Channels With Designable Cardinality-Constrained Channel State Feedback Vincent
2038 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 50, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 Capacity of Memoryless Channels and Block-Fading Channels With Designable Cardinality-Constrained Channel State Feedback Vincent
Effective Rate Analysis of MISO Systems over α-µ Fading Channels
 Effective Rate Analysis of MISO Systems over α-µ Fading Channels Jiayi Zhang 1,2, Linglong Dai 1, Zhaocheng Wang 1 Derrick Wing Kwan Ng 2,3 and Wolfgang H. Gerstacker 2 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for
Effective Rate Analysis of MISO Systems over α-µ Fading Channels Jiayi Zhang 1,2, Linglong Dai 1, Zhaocheng Wang 1 Derrick Wing Kwan Ng 2,3 and Wolfgang H. Gerstacker 2 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for
An Uplink-Downlink Duality for Cloud Radio Access Network
 An Uplin-Downlin Duality for Cloud Radio Access Networ Liang Liu, Prati Patil, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, 5S 3G4, Canada Emails: lianguotliu@utorontoca,
An Uplin-Downlin Duality for Cloud Radio Access Networ Liang Liu, Prati Patil, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, 5S 3G4, Canada Emails: lianguotliu@utorontoca,
Sparse Sensing in Colocated MIMO Radar: A Matrix Completion Approach
 Sparse Sensing in Colocated MIMO Radar: A Matrix Completion Approach Athina P. Petropulu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Acknowledgments Shunqiao
Sparse Sensing in Colocated MIMO Radar: A Matrix Completion Approach Athina P. Petropulu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Acknowledgments Shunqiao
User Selection and Power Allocation for MmWave-NOMA Networks
 User Selection and Power Allocation for MmWave-NOMA Networks Jingjing Cui, Yuanwei Liu, Zhiguo Ding, Pingzhi Fan and Arumugam Nallanathan Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, P. R. China Queen Mary
User Selection and Power Allocation for MmWave-NOMA Networks Jingjing Cui, Yuanwei Liu, Zhiguo Ding, Pingzhi Fan and Arumugam Nallanathan Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, P. R. China Queen Mary
On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming
 On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming Namjeong Lee, Chan-Byoung Chae, Osvaldo Simeone, Joonhyuk Kang Information and Communications Engineering ICE, KAIST, Korea Email:
On the Optimization of Two-way AF MIMO Relay Channel with Beamforming Namjeong Lee, Chan-Byoung Chae, Osvaldo Simeone, Joonhyuk Kang Information and Communications Engineering ICE, KAIST, Korea Email:
Massive MIMO mmwave Channel Estimation Using Approximate Message Passing and Laplacian Prior
 Massive MIMO mmwave Channel Estimation Using Approximate Message Passing and Laplacian Prior Faouzi Bellili, Foad Sohrabi, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
Massive MIMO mmwave Channel Estimation Using Approximate Message Passing and Laplacian Prior Faouzi Bellili, Foad Sohrabi, and Wei Yu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto,
Correspondence. MIMO Broadcast Channels With Finite-Rate Feedback
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORATION THEORY, VO. 5, NO., NOVEBER 6 545 Correspondence IO Broadcast Channels With Finite-Rate Feedbac Nihar Jindal, ember, IEEE Abstract ultiple transmit antennas in a downlin
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORATION THEORY, VO. 5, NO., NOVEBER 6 545 Correspondence IO Broadcast Channels With Finite-Rate Feedbac Nihar Jindal, ember, IEEE Abstract ultiple transmit antennas in a downlin
Single-User MIMO systems: Introduction, capacity results, and MIMO beamforming
 Single-User MIMO systems: Introduction, capacity results, and MIMO beamforming Master Universitario en Ingeniería de Telecomunicación I. Santamaría Universidad de Cantabria Contents Introduction Multiplexing,
Single-User MIMO systems: Introduction, capacity results, and MIMO beamforming Master Universitario en Ingeniería de Telecomunicación I. Santamaría Universidad de Cantabria Contents Introduction Multiplexing,
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results
 NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS, GIST Email: jchoi114@gist.ac.kr Invited Paper arxiv:176.885v1 [cs.it] 27 Jun 217 Abstract Although non-orthogonal multiple access NOMA is
NOMA: Principles and Recent Results Jinho Choi School of EECS, GIST Email: jchoi114@gist.ac.kr Invited Paper arxiv:176.885v1 [cs.it] 27 Jun 217 Abstract Although non-orthogonal multiple access NOMA is
Ergodic and Outage Capacity of Narrowband MIMO Gaussian Channels
 Ergodic and Outage Capacity of Narrowband MIMO Gaussian Channels Yang Wen Liang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia April 19th, 005 Outline of Presentation
Ergodic and Outage Capacity of Narrowband MIMO Gaussian Channels Yang Wen Liang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia April 19th, 005 Outline of Presentation
arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 4 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 4 Dec 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 4 Dec 2014](/thumbs/74/70461037.jpg) SUBMITTED TO IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, DECEMBER 5, 04 Randomly-Directional Beamforming in Millimeter-Wave Multi-User MIMO Downlink Gilwon Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchul Sung,
SUBMITTED TO IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, DECEMBER 5, 04 Randomly-Directional Beamforming in Millimeter-Wave Multi-User MIMO Downlink Gilwon Lee, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchul Sung,
