Modeling differences in itemposition effects in the PISA 2009 reading assessment within and between schools
|
|
|
- Allan Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modeling differences in itemposition effects in the PISA 2009 reading assessment within and between schools Dries Debeer & Rianne Janssen (University of Leuven) Johannes Hartig & Janine Buchholz (DIPF)
2 Content A. Position Effects? 1. First Two traditions 3. Combined B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment 1. Introduction 2. Model 3. Results 4. Discussion 2
3 First... Educational measurement: Common assumption: item characteristics constant regardless ability of examinee, administration conditions Common practice: alternate test forms with different item orders Common psychometric models do not take the order / positions of items into account 3
4 However Effects of item order / item position have been found repeatedly. 4
5 Item Order PERSON 1 Position K Item A B C D E F Z Different Item Orders PERSON 2 Position K Item E Z F D B A C 5
6 Item Position PERSON 1 Position K Item A B C D E F Z Different Item Positions PERSON 2 Position K Item E Z F D B A C 6
7 However Effects of item order / item position have been found repeatedly. item order: Monk and Stallings (1970); MacNicol (1956); Mollenkopf (1950); Moses, Yang & Wilson (2007). item position (IRT) Whitely and Dawis (1976); Yen (1980); Knowles (1988); Meyers, Miller and Way (2009); Debeer and Janssen (2013) 7
8 A. Position effects? 1. Introduction 2. Methods: two traditions Test side / item side Person side 3. Combined approach 8
9 Test side / item side IRT Response (correct/incorrect) Person (ability) Item (difficulty) Position effect 9
10 Item-side Two step approach: Meyers, Miller and Way (2009) Estimate item difficulties within each test form Relate differences in item difficulty to differences in item position 10
11 Person side IRT Position effect Response (correct/incorrect) Person (ability) Item (difficulty) 11
12 Person-side Tradition Measurement of change Dynamic Rasch of Verguts & De Boeck (2000) log it P X pi 1 p t pi i t pi is the number of correct answers for person p up to item i 1. is the learning parameter 12
13 A. Position effects? 1. Introduction 2. Methods: two traditions Test side / item side Person side 3. Combined approach 13
14 Combined approach Combination of test-side and person side. Within an IRT-framework 14
15 IRT-framework Position effect: item side: logit Y pik = 1 = θ p β i + δ ik β Position effect across items: logit Y pik = 1 = θ p β i + δ k β 15
16 IRT-framework Ability θ p Difficulty β i Position effect Test 16
17 IRT-framework Position effect across items: Trend Position as a property Functional form (linear effect on difficulty) logit Y pik = 1 = θ p β i + γ k 1 γ < 0 : a fatigue effect γ > 0 : a learning effect 17
18 IRT-framework Incongruence between modeling and interpretation Modeled at item side, interpretation at person side. Person side: individual differences/position dimension persistence? 18
19 IRT-framework Individual differences (Person side) logit Y pik = 1 = θ p β i + γ p k 1 Interpretation! 19
20 Individual differences Position dimension persistence? Latent trait Item difficulty Test 20
21 Individual differences Position dimension persistence? Latent trait Item difficulty Position dimension Test 21
22 Content A. Modeling 1. Introduction 2. Two traditions 3. Combined B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment 1. Introduction 2. Model 3. Results 4. Discussion 22
23 B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment Analysis of the data form international PISA 2009 study In collaboration with Johannes Hartig & Janine Buchholz (DIPF) 23
24 B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment 1. Introduction PISA Multilevel decomposition Research questions 2. Model 3. Results 4. Discussion 24
25 Introduction PISA Program for International Student Assessment of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) International assessment among 15-year-olds Reading (R) Math (M) Science (S) Rotated cluster design => Analysis of item position effect (on difficulty) 25
26 PISA data Published reading assessment data from the PISA 2009 study (OECD, 2010). Data from students from schools in 65 countries was analysed. Responses to 125 reading test items were used in the analysis, responses on 7 partial credit items were dichotomized. 26
27 Booklet Design Rotated cluster design PISA 2009 Booklet Cluster 1 Cluster 2 Cluster 3 Cluster 4 1 M1 R1 R3 M3 2 R1 S1 R4 R7 3 S1 R3 M2 S3 4 R3 R4 S2 R2 5 R4 M2 R5 M1 6 R5 R6 R7 R3 7 R6 M3 S3 R4 8 R2 M1 S1 R6 9 M2 S2 R6 R1 10 S2 R5 M3 S1 11 M3 R7 R2 M2 12 R7 S3 M1 S5 13 S3 R2 R1 R5 27
28 Cluster Position PISA 2009 Booklet Design The cluster (coded 0 to 3) position was used as proxy for the item position in the analyses. Booklet M1 R1 S1 R3 R4 R5 R6 R2 M2 S2 M3 R7 S3 1 R1 S1 R3 R4 M2 R6 M3 M1 S2 R5 R7 S3 R2 2 R3 R4 M2 S2 R5 R7 S3 S1 R6 M3 R2 M1 R1 3 M3 R7 S3 R2 M1 R3 R4 R6 R1 S1 M2 S2 R5 R: Reading, M: Mathematics, S: Science 28
29 Multilevel Decomposition In hierarchical sample structures (e.g. students within schools), the variation of measured variables can be decomposed in variance within and between groups. When individual differences in item position effects are modeled for hierarchical samples, these effects can also be decomposed by introducing the group level into the model. 29
30 Multilevel Decomposition Individual Differences in Persistence Between schools Within schools 30
31 Multilevel Decomposition Decomposing item position effects in educational assessments within and between schools might provide insights in the nature of these effects as well as in the structure of the school and student population. Proportions of variance between schools can be estimated for the ability measured as well as for item position effects. 31
32 Multilevel Decomposition Latent trait Average positon effect Individual differences between & within schools Test 32
33 Research Questions Question 1: Is there a general item position effect, how large is it, and is it consistent across countries with different national performance levels? Question 2: Is there individual variance in item position effects (i.e. variation in persistence) in different countries? Question 3: How large is the proportion of variance (ICC) in persistence between schools? 33
34 Research Questions Question 4: How are students performance levels and persistence related within schools in different countries? Question 5: How are performance levels and persistence related on school level in different countries? Question 6: How are country-level results related to the countries performance level? 34
35 B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment 1. Introduction PISA Multilevel decomposition Research questions 2. Model 3. Results 4. Discussion 35
36 Model Multilevel Model: logit Y ips = θ p W + θ s B β i + k pi γ + γ p W + γ s B Person p (1,..., P) School s (1,..., S) Item i (1,..., I) θ p W = ability level of student p (within-school) θ s B = ability level of school s (between schools) β i = difficulty of item i k pi = cluster position k (0,..., 3) at which item i is presented to person p γ = average position effect across students and schools γ p W = position effect for student p (within school) γ s B = position effect for school s (between schools) 36
37 Model Level 1 (Response) logit Y ips = θ ps β i + k pi γ ps Level 2 (Student) θ ps = θ p W + θ s B γ ps = γ p W + γ s B Level 3 (School) θ p W 2 W γ p W ~ N 0 0, σ θp θ s B γ s B ~ N 0 γ, σ θp W,γ p W σ θp W,γ p W σ 2 γp W σ 2 θs B σ θs B,γB s σ θs B,γ s B σ 2 γp B 37
38 Estimation All models were estimated with HLM, Student weights provided in the database were used as level 2 (student level) weighting variable. 38
39 B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment 1. Introduction PISA Multilevel decomposition Research questions 2. Model 3. Results 4. Discussion 39
40 Main Position Effects Fixed Effects of Item Cluster Position in 65 Countries There is a negative effect of the cluster position in all countries, but the size varies substantially. 40
41 Main Position Effects Standardized persistence γ Change in cluster positions + 1 cluster positions + 3 cluster positions (Greece) (Average) (Finland)
42 Random Position Effects Overall individual differences in persistence There are significant individual differences in persistence. 42
43 Random Position Effects ICC in reading vs. ICC in Persistence A moderate amount of variance in persistence is located at the school level (less pronounced than for reading ability). 43
44 Correlation Between Ability Level and Persistence Correlations within schools Within schools, ability and persistence are correlated (slightly) negatively in most countries. 44
45 Correlation Between Ability Level and Persistence Correlations between schools Ability level and persistence level on school level are correlated positively in most countries. 45
46 Country Level Correlations with Performance Level Country level correlations between national reading scores and the model based results (N=65) Reading Score Cluster position effect γ.36 Variance in persistence within schools σ 2 γp W -.54 Variance in persistence between schools σ 2 γp B -.06 Within-school correlation r θ p W, γ p W.56 Between-school correlation r θ s B, γ s B.55 46
47 Position Effects and National Performance Level The strength of the position effect is related to the national performance level (r =.36) 47
48 Position Effects and National Performance Level The variance of persistence on student level is negatively related to the national performance level (r = -.54) 48
49 Position Effects and National Performance Level The correlation of ability and persistence within schools is related to the national performance level (r =.56) 49
50 Position Effects and National Performance Level The correlation of ability and persistence on school level is related to the national performance level (r =.55) 50
51 Country Level Correlations with Performance Level The negative cluster position effect is less pronounced in higher performing countries. The variance in persistence between students and between schools is lower in higher performing countries. The correlation of ability and persistence within and between schools is higher in higher performing countries. 51
52 B. PISA 2009 Reading assessment 1. Introduction PISA Multilevel decomposition Research questions 2. Model 3. Results 4. Discussion 52
53 Discussion Results vary between countries, the only consistent finding is that the cluster position effect is negative. Include student level covariates (motivation) Include school level covariates We modeled a linear trend of cluster position, the appropriateness of this should be inspected on country level. 53
54 Discussion Different response process variables (omission, no credit, full credit) are modeled in one variable. Maybe there are differences in the omitting process and accuracy process across students/schools/countries. Maybe there is an interaction between the item format (open ended/multiple choice) and the item position effect. Still far from understanding the mechanisms. 54
55 your Thank attention for you! Position does matter!
Polytomous Item Explanatory IRT Models with Random Item Effects: An Application to Carbon Cycle Assessment Data
 Polytomous Item Explanatory IRT Models with Random Item Effects: An Application to Carbon Cycle Assessment Data Jinho Kim and Mark Wilson University of California, Berkeley Presented on April 11, 2018
Polytomous Item Explanatory IRT Models with Random Item Effects: An Application to Carbon Cycle Assessment Data Jinho Kim and Mark Wilson University of California, Berkeley Presented on April 11, 2018
Basic IRT Concepts, Models, and Assumptions
 Basic IRT Concepts, Models, and Assumptions Lecture #2 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #2: 1of 64 Lecture #2 Overview Background of IRT and how it differs from CFA Creating a scale An introduction
Basic IRT Concepts, Models, and Assumptions Lecture #2 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #2: 1of 64 Lecture #2 Overview Background of IRT and how it differs from CFA Creating a scale An introduction
Fitting Multidimensional Latent Variable Models using an Efficient Laplace Approximation
 Fitting Multidimensional Latent Variable Models using an Efficient Laplace Approximation Dimitris Rizopoulos Department of Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical Center, the Netherlands d.rizopoulos@erasmusmc.nl
Fitting Multidimensional Latent Variable Models using an Efficient Laplace Approximation Dimitris Rizopoulos Department of Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical Center, the Netherlands d.rizopoulos@erasmusmc.nl
A multivariate multilevel model for the analysis of TIMMS & PIRLS data
 A multivariate multilevel model for the analysis of TIMMS & PIRLS data European Congress of Methodology July 23-25, 2014 - Utrecht Leonardo Grilli 1, Fulvia Pennoni 2, Carla Rampichini 1, Isabella Romeo
A multivariate multilevel model for the analysis of TIMMS & PIRLS data European Congress of Methodology July 23-25, 2014 - Utrecht Leonardo Grilli 1, Fulvia Pennoni 2, Carla Rampichini 1, Isabella Romeo
Statistical and psychometric methods for measurement: Scale development and validation
 Statistical and psychometric methods for measurement: Scale development and validation Andrew Ho, Harvard Graduate School of Education The World Bank, Psychometrics Mini Course Washington, DC. June 11,
Statistical and psychometric methods for measurement: Scale development and validation Andrew Ho, Harvard Graduate School of Education The World Bank, Psychometrics Mini Course Washington, DC. June 11,
Ensemble Rasch Models
 Ensemble Rasch Models Steven M. Lattanzio II Metamatrics Inc., Durham, NC 27713 email: slattanzio@lexile.com Donald S. Burdick Metamatrics Inc., Durham, NC 27713 email: dburdick@lexile.com A. Jackson Stenner
Ensemble Rasch Models Steven M. Lattanzio II Metamatrics Inc., Durham, NC 27713 email: slattanzio@lexile.com Donald S. Burdick Metamatrics Inc., Durham, NC 27713 email: dburdick@lexile.com A. Jackson Stenner
What Rasch did: the mathematical underpinnings of the Rasch model. Alex McKee, PhD. 9th Annual UK Rasch User Group Meeting, 20/03/2015
 What Rasch did: the mathematical underpinnings of the Rasch model. Alex McKee, PhD. 9th Annual UK Rasch User Group Meeting, 20/03/2015 Our course Initial conceptualisation Separation of parameters Specific
What Rasch did: the mathematical underpinnings of the Rasch model. Alex McKee, PhD. 9th Annual UK Rasch User Group Meeting, 20/03/2015 Our course Initial conceptualisation Separation of parameters Specific
Item Response Theory and Computerized Adaptive Testing
 Item Response Theory and Computerized Adaptive Testing Richard C. Gershon, PhD Department of Medical Social Sciences Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University gershon@northwestern.edu May 20,
Item Response Theory and Computerized Adaptive Testing Richard C. Gershon, PhD Department of Medical Social Sciences Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University gershon@northwestern.edu May 20,
Lesson 7: Item response theory models (part 2)
 Lesson 7: Item response theory models (part 2) Patrícia Martinková Department of Statistical Modelling Institute of Computer Science, Czech Academy of Sciences Institute for Research and Development of
Lesson 7: Item response theory models (part 2) Patrícia Martinková Department of Statistical Modelling Institute of Computer Science, Czech Academy of Sciences Institute for Research and Development of
Overview. Multidimensional Item Response Theory. Lecture #12 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop. Basics of MIRT Assumptions Models Applications
 Multidimensional Item Response Theory Lecture #12 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #12: 1of 33 Overview Basics of MIRT Assumptions Models Applications Guidance about estimating MIRT Lecture
Multidimensional Item Response Theory Lecture #12 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #12: 1of 33 Overview Basics of MIRT Assumptions Models Applications Guidance about estimating MIRT Lecture
Exploiting TIMSS and PIRLS combined data: multivariate multilevel modelling of student achievement
 Exploiting TIMSS and PIRLS combined data: multivariate multilevel modelling of student achievement Second meeting of the FIRB 2012 project Mixture and latent variable models for causal-inference and analysis
Exploiting TIMSS and PIRLS combined data: multivariate multilevel modelling of student achievement Second meeting of the FIRB 2012 project Mixture and latent variable models for causal-inference and analysis
Monte Carlo Simulations for Rasch Model Tests
 Monte Carlo Simulations for Rasch Model Tests Patrick Mair Vienna University of Economics Thomas Ledl University of Vienna Abstract: Sources of deviation from model fit in Rasch models can be lack of unidimensionality,
Monte Carlo Simulations for Rasch Model Tests Patrick Mair Vienna University of Economics Thomas Ledl University of Vienna Abstract: Sources of deviation from model fit in Rasch models can be lack of unidimensionality,
Assessment of fit of item response theory models used in large scale educational survey assessments
 DOI 10.1186/s40536-016-0025-3 RESEARCH Open Access Assessment of fit of item response theory models used in large scale educational survey assessments Peter W. van Rijn 1, Sandip Sinharay 2*, Shelby J.
DOI 10.1186/s40536-016-0025-3 RESEARCH Open Access Assessment of fit of item response theory models used in large scale educational survey assessments Peter W. van Rijn 1, Sandip Sinharay 2*, Shelby J.
Dimensionality Assessment: Additional Methods
 Dimensionality Assessment: Additional Methods In Chapter 3 we use a nonlinear factor analytic model for assessing dimensionality. In this appendix two additional approaches are presented. The first strategy
Dimensionality Assessment: Additional Methods In Chapter 3 we use a nonlinear factor analytic model for assessing dimensionality. In this appendix two additional approaches are presented. The first strategy
8. AN EVALUATION OF THE URBAN SYSTEMIC INITIATIVE AND OTHER ACADEMIC REFORMS IN TEXAS: STATISTICAL MODELS FOR ANALYZING LARGE-SCALE DATA SETS
 8. AN EVALUATION OF THE URBAN SYSTEMIC INITIATIVE AND OTHER ACADEMIC REFORMS IN TEXAS: STATISTICAL MODELS FOR ANALYZING LARGE-SCALE DATA SETS Robert H. Meyer Executive Summary A multidisciplinary team
8. AN EVALUATION OF THE URBAN SYSTEMIC INITIATIVE AND OTHER ACADEMIC REFORMS IN TEXAS: STATISTICAL MODELS FOR ANALYZING LARGE-SCALE DATA SETS Robert H. Meyer Executive Summary A multidisciplinary team
Anders Skrondal. Norwegian Institute of Public Health London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. Based on joint work with Sophia Rabe-Hesketh
 Constructing Latent Variable Models using Composite Links Anders Skrondal Norwegian Institute of Public Health London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Based on joint work with Sophia Rabe-Hesketh
Constructing Latent Variable Models using Composite Links Anders Skrondal Norwegian Institute of Public Health London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Based on joint work with Sophia Rabe-Hesketh
Psychometric Issues in Formative Assessment: Measuring Student Learning Throughout the Academic Year Using Interim Assessments
 Psychometric Issues in Formative Assessment: Measuring Student Learning Throughout the Academic Year Using Interim Assessments Jonathan Templin The University of Georgia Neal Kingston and Wenhao Wang University
Psychometric Issues in Formative Assessment: Measuring Student Learning Throughout the Academic Year Using Interim Assessments Jonathan Templin The University of Georgia Neal Kingston and Wenhao Wang University
IRT models and mixed models: Theory and lmer practice
 IRT models and mixed models: Theory and lmer practice Paul De Boeck Sun-Joo Cho U. Amsterdam Peabody College & K.U.Leuven Vanderbilt U. NCME, April 8 2011, New Orleans 1. explanatory item response models
IRT models and mixed models: Theory and lmer practice Paul De Boeck Sun-Joo Cho U. Amsterdam Peabody College & K.U.Leuven Vanderbilt U. NCME, April 8 2011, New Orleans 1. explanatory item response models
APPENDICES TO Protest Movements and Citizen Discontent. Appendix A: Question Wordings
 APPENDICES TO Protest Movements and Citizen Discontent Appendix A: Question Wordings IDEOLOGY: How would you describe your views on most political matters? Generally do you think of yourself as liberal,
APPENDICES TO Protest Movements and Citizen Discontent Appendix A: Question Wordings IDEOLOGY: How would you describe your views on most political matters? Generally do you think of yourself as liberal,
Item Response Theory (IRT) Analysis of Item Sets
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn NERA Conference Proceedings 2011 Northeastern Educational Research Association (NERA) Annual Conference Fall 10-21-2011 Item Response Theory (IRT) Analysis
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn NERA Conference Proceedings 2011 Northeastern Educational Research Association (NERA) Annual Conference Fall 10-21-2011 Item Response Theory (IRT) Analysis
Modeling rater effects using a combination of Generalizability Theory and IRT
 Psychological Test and Assessment Modeling, Volume 60, 2018 (1), 53-80 Modeling rater effects using a combination of Generalizability Theory and IRT Jinnie Choi 1 & Mark R. Wilson 2 Abstract Motivated
Psychological Test and Assessment Modeling, Volume 60, 2018 (1), 53-80 Modeling rater effects using a combination of Generalizability Theory and IRT Jinnie Choi 1 & Mark R. Wilson 2 Abstract Motivated
An Overview of Item Response Theory. Michael C. Edwards, PhD
 An Overview of Item Response Theory Michael C. Edwards, PhD Overview General overview of psychometrics Reliability and validity Different models and approaches Item response theory (IRT) Conceptual framework
An Overview of Item Response Theory Michael C. Edwards, PhD Overview General overview of psychometrics Reliability and validity Different models and approaches Item response theory (IRT) Conceptual framework
Measurement Invariance (MI) in CFA and Differential Item Functioning (DIF) in IRT/IFA
 Topics: Measurement Invariance (MI) in CFA and Differential Item Functioning (DIF) in IRT/IFA What are MI and DIF? Testing measurement invariance in CFA Testing differential item functioning in IRT/IFA
Topics: Measurement Invariance (MI) in CFA and Differential Item Functioning (DIF) in IRT/IFA What are MI and DIF? Testing measurement invariance in CFA Testing differential item functioning in IRT/IFA
Hierarchical Generalized Linear Models. ERSH 8990 REMS Seminar on HLM Last Lecture!
 Hierarchical Generalized Linear Models ERSH 8990 REMS Seminar on HLM Last Lecture! Hierarchical Generalized Linear Models Introduction to generalized models Models for binary outcomes Interpreting parameter
Hierarchical Generalized Linear Models ERSH 8990 REMS Seminar on HLM Last Lecture! Hierarchical Generalized Linear Models Introduction to generalized models Models for binary outcomes Interpreting parameter
ESTIMATION OF IRT PARAMETERS OVER A SMALL SAMPLE. BOOTSTRAPPING OF THE ITEM RESPONSES. Dimitar Atanasov
 Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 19 (2009), 59 68 STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA ESTIMATION OF IRT PARAMETERS OVER A SMALL SAMPLE. BOOTSTRAPPING OF THE ITEM RESPONSES Dimitar Atanasov Estimation of the parameters
Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 19 (2009), 59 68 STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA ESTIMATION OF IRT PARAMETERS OVER A SMALL SAMPLE. BOOTSTRAPPING OF THE ITEM RESPONSES Dimitar Atanasov Estimation of the parameters
Extensions and Applications of Item Explanatory Models to Polytomous Data in Item Response Theory. Jinho Kim
 Extensions and Applications of Item Explanatory Models to Polytomous Data in Item Response Theory by Jinho Kim A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Extensions and Applications of Item Explanatory Models to Polytomous Data in Item Response Theory by Jinho Kim A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Logistic Regression and Item Response Theory: Estimation Item and Ability Parameters by Using Logistic Regression in IRT.
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1998 Logistic Regression and Item Response Theory: Estimation Item and Ability Parameters by Using
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1998 Logistic Regression and Item Response Theory: Estimation Item and Ability Parameters by Using
Comparing IRT with Other Models
 Comparing IRT with Other Models Lecture #14 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #14: 1of 45 Lecture Overview The final set of slides will describe a parallel between IRT and another commonly used
Comparing IRT with Other Models Lecture #14 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #14: 1of 45 Lecture Overview The final set of slides will describe a parallel between IRT and another commonly used
Summer School in Applied Psychometric Principles. Peterhouse College 13 th to 17 th September 2010
 Summer School in Applied Psychometric Principles Peterhouse College 13 th to 17 th September 2010 1 Two- and three-parameter IRT models. Introducing models for polytomous data. Test information in IRT
Summer School in Applied Psychometric Principles Peterhouse College 13 th to 17 th September 2010 1 Two- and three-parameter IRT models. Introducing models for polytomous data. Test information in IRT
On the Use of Nonparametric ICC Estimation Techniques For Checking Parametric Model Fit
 On the Use of Nonparametric ICC Estimation Techniques For Checking Parametric Model Fit March 27, 2004 Young-Sun Lee Teachers College, Columbia University James A.Wollack University of Wisconsin Madison
On the Use of Nonparametric ICC Estimation Techniques For Checking Parametric Model Fit March 27, 2004 Young-Sun Lee Teachers College, Columbia University James A.Wollack University of Wisconsin Madison
PIRLS 2016 Achievement Scaling Methodology 1
 CHAPTER 11 PIRLS 2016 Achievement Scaling Methodology 1 The PIRLS approach to scaling the achievement data, based on item response theory (IRT) scaling with marginal estimation, was developed originally
CHAPTER 11 PIRLS 2016 Achievement Scaling Methodology 1 The PIRLS approach to scaling the achievement data, based on item response theory (IRT) scaling with marginal estimation, was developed originally
1 if response to item i is in category j 0 otherwise (1)
 7 Scaling Methodology and Procedures for the Mathematics and Science Literacy, Advanced Mathematics, and Physics Scales Greg Macaskill Raymond J. Adams Margaret L. Wu Australian Council for Educational
7 Scaling Methodology and Procedures for the Mathematics and Science Literacy, Advanced Mathematics, and Physics Scales Greg Macaskill Raymond J. Adams Margaret L. Wu Australian Council for Educational
Statistical and psychometric methods for measurement: G Theory, DIF, & Linking
 Statistical and psychometric methods for measurement: G Theory, DIF, & Linking Andrew Ho, Harvard Graduate School of Education The World Bank, Psychometrics Mini Course 2 Washington, DC. June 27, 2018
Statistical and psychometric methods for measurement: G Theory, DIF, & Linking Andrew Ho, Harvard Graduate School of Education The World Bank, Psychometrics Mini Course 2 Washington, DC. June 27, 2018
A Marginal Maximum Likelihood Procedure for an IRT Model with Single-Peaked Response Functions
 A Marginal Maximum Likelihood Procedure for an IRT Model with Single-Peaked Response Functions Cees A.W. Glas Oksana B. Korobko University of Twente, the Netherlands OMD Progress Report 07-01. Cees A.W.
A Marginal Maximum Likelihood Procedure for an IRT Model with Single-Peaked Response Functions Cees A.W. Glas Oksana B. Korobko University of Twente, the Netherlands OMD Progress Report 07-01. Cees A.W.
SCORING TESTS WITH DICHOTOMOUS AND POLYTOMOUS ITEMS CIGDEM ALAGOZ. (Under the Direction of Seock-Ho Kim) ABSTRACT
 SCORING TESTS WITH DICHOTOMOUS AND POLYTOMOUS ITEMS by CIGDEM ALAGOZ (Under the Direction of Seock-Ho Kim) ABSTRACT This study applies item response theory methods to the tests combining multiple-choice
SCORING TESTS WITH DICHOTOMOUS AND POLYTOMOUS ITEMS by CIGDEM ALAGOZ (Under the Direction of Seock-Ho Kim) ABSTRACT This study applies item response theory methods to the tests combining multiple-choice
Stochastic Approximation Methods for Latent Regression Item Response Models
 Research Report Stochastic Approximation Methods for Latent Regression Item Response Models Matthias von Davier Sandip Sinharay March 2009 ETS RR-09-09 Listening. Learning. Leading. Stochastic Approximation
Research Report Stochastic Approximation Methods for Latent Regression Item Response Models Matthias von Davier Sandip Sinharay March 2009 ETS RR-09-09 Listening. Learning. Leading. Stochastic Approximation
Florida State University Libraries
 Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2005 Modeling Differential Item Functioning (DIF) Using Multilevel Logistic Regression Models: A Bayesian
Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2005 Modeling Differential Item Functioning (DIF) Using Multilevel Logistic Regression Models: A Bayesian
An Equivalency Test for Model Fit. Craig S. Wells. University of Massachusetts Amherst. James. A. Wollack. Ronald C. Serlin
 Equivalency Test for Model Fit 1 Running head: EQUIVALENCY TEST FOR MODEL FIT An Equivalency Test for Model Fit Craig S. Wells University of Massachusetts Amherst James. A. Wollack Ronald C. Serlin University
Equivalency Test for Model Fit 1 Running head: EQUIVALENCY TEST FOR MODEL FIT An Equivalency Test for Model Fit Craig S. Wells University of Massachusetts Amherst James. A. Wollack Ronald C. Serlin University
The application and empirical comparison of item. parameters of Classical Test Theory and Partial Credit. Model of Rasch in performance assessments
 The application and empirical comparison of item parameters of Classical Test Theory and Partial Credit Model of Rasch in performance assessments by Paul Moloantoa Mokilane Student no: 31388248 Dissertation
The application and empirical comparison of item parameters of Classical Test Theory and Partial Credit Model of Rasch in performance assessments by Paul Moloantoa Mokilane Student no: 31388248 Dissertation
A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY. Yu-Feng Chang
 A Restricted Bi-factor Model of Subdomain Relative Strengths and Weaknesses A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Yu-Feng Chang IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
A Restricted Bi-factor Model of Subdomain Relative Strengths and Weaknesses A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Yu-Feng Chang IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Application of Item Response Theory Models for Intensive Longitudinal Data
 Application of Item Response Theory Models for Intensive Longitudinal Data Don Hedeker, Robin Mermelstein, & Brian Flay University of Illinois at Chicago hedeker@uic.edu Models for Intensive Longitudinal
Application of Item Response Theory Models for Intensive Longitudinal Data Don Hedeker, Robin Mermelstein, & Brian Flay University of Illinois at Chicago hedeker@uic.edu Models for Intensive Longitudinal
Bayesian and frequentist cross-validation methods for explanatory item response models. Daniel C. Furr
 Bayesian and frequentist cross-validation methods for explanatory item response models by Daniel C. Furr A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
Bayesian and frequentist cross-validation methods for explanatory item response models by Daniel C. Furr A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
Classical Test Theory. Basics of Classical Test Theory. Cal State Northridge Psy 320 Andrew Ainsworth, PhD
 Cal State Northridge Psy 30 Andrew Ainsworth, PhD Basics of Classical Test Theory Theory and Assumptions Types of Reliability Example Classical Test Theory Classical Test Theory (CTT) often called the
Cal State Northridge Psy 30 Andrew Ainsworth, PhD Basics of Classical Test Theory Theory and Assumptions Types of Reliability Example Classical Test Theory Classical Test Theory (CTT) often called the
Methods for the Comparison of DIF across Assessments W. Holmes Finch Maria Hernandez Finch Brian F. French David E. McIntosh
 Methods for the Comparison of DIF across Assessments W. Holmes Finch Maria Hernandez Finch Brian F. French David E. McIntosh Impact of DIF on Assessments Individuals administrating assessments must select
Methods for the Comparison of DIF across Assessments W. Holmes Finch Maria Hernandez Finch Brian F. French David E. McIntosh Impact of DIF on Assessments Individuals administrating assessments must select
Introduction To Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Item Response Theory
 Introduction To Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Item Response Theory Lecture 23 May 3, 2005 Applied Regression Analysis Lecture #23-5/3/2005 Slide 1 of 21 Today s Lecture Confirmatory Factor Analysis.
Introduction To Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Item Response Theory Lecture 23 May 3, 2005 Applied Regression Analysis Lecture #23-5/3/2005 Slide 1 of 21 Today s Lecture Confirmatory Factor Analysis.
Measurement Theory. Reliability. Error Sources. = XY r XX. r XY. r YY
 Y -3 - -1 0 1 3 X Y -10-5 0 5 10 X Measurement Theory t & X 1 X X 3 X k Reliability e 1 e e 3 e k 1 The Big Picture Measurement error makes it difficult to identify the true patterns of relationships between
Y -3 - -1 0 1 3 X Y -10-5 0 5 10 X Measurement Theory t & X 1 X X 3 X k Reliability e 1 e e 3 e k 1 The Big Picture Measurement error makes it difficult to identify the true patterns of relationships between
Presented by. Philip Holmes-Smith School Research Evaluation and Measurement Services
 The Statistical Analysis of Student Performance Data Presented by Philip Holmes-Smith School Research Evaluation and Measurement Services Outline of session This session will address four topics, namely:.
The Statistical Analysis of Student Performance Data Presented by Philip Holmes-Smith School Research Evaluation and Measurement Services Outline of session This session will address four topics, namely:.
Estimation of item location effects by means of the generalized logistic regression model: a simulation study and an application
 Psychology Science Quarterly, Volume 50, 2008 (1), p. 64-74 Estimation of item location effects by means of the generalized logistic regression model: a simulation study and an application RAINER ALEXANDROWICZ
Psychology Science Quarterly, Volume 50, 2008 (1), p. 64-74 Estimation of item location effects by means of the generalized logistic regression model: a simulation study and an application RAINER ALEXANDROWICZ
36-309/749 Experimental Design for Behavioral and Social Sciences. Dec 1, 2015 Lecture 11: Mixed Models (HLMs)
 36-309/749 Experimental Design for Behavioral and Social Sciences Dec 1, 2015 Lecture 11: Mixed Models (HLMs) Independent Errors Assumption An error is the deviation of an individual observed outcome (DV)
36-309/749 Experimental Design for Behavioral and Social Sciences Dec 1, 2015 Lecture 11: Mixed Models (HLMs) Independent Errors Assumption An error is the deviation of an individual observed outcome (DV)
Estimating Multilevel Linear Models as Structural Equation Models
 Bauer & Curran, Psychometric Society Paper Presentation, 6/2/02 Estimating Multilevel Linear Models as Structural Equation Models Daniel J. Bauer North Carolina State University Patrick J. Curran University
Bauer & Curran, Psychometric Society Paper Presentation, 6/2/02 Estimating Multilevel Linear Models as Structural Equation Models Daniel J. Bauer North Carolina State University Patrick J. Curran University
Estimating the Hausman test for multilevel Rasch model. Kingsley E. Agho School of Public health Faculty of Medicine The University of Sydney
 Estimating the Hausman test for multilevel Rasch model Kingsley E. Agho School of Public health Faculty of Medicine The University of Sydney James A. Athanasou Faculty of Education University of Technology,
Estimating the Hausman test for multilevel Rasch model Kingsley E. Agho School of Public health Faculty of Medicine The University of Sydney James A. Athanasou Faculty of Education University of Technology,
A Nonlinear Mixed Model Framework for Item Response Theory
 Psychological Methods Copyright 2003 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2003, Vol. 8, No. 2, 185 205 1082-989X/03/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/1082-989X.8.2.185 A Nonlinear Mixed Model Framework for
Psychological Methods Copyright 2003 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2003, Vol. 8, No. 2, 185 205 1082-989X/03/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/1082-989X.8.2.185 A Nonlinear Mixed Model Framework for
Multidimensional Linking for Tests with Mixed Item Types
 Journal of Educational Measurement Summer 2009, Vol. 46, No. 2, pp. 177 197 Multidimensional Linking for Tests with Mixed Item Types Lihua Yao 1 Defense Manpower Data Center Keith Boughton CTB/McGraw-Hill
Journal of Educational Measurement Summer 2009, Vol. 46, No. 2, pp. 177 197 Multidimensional Linking for Tests with Mixed Item Types Lihua Yao 1 Defense Manpower Data Center Keith Boughton CTB/McGraw-Hill
On the Construction of Adjacent Categories Latent Trait Models from Binary Variables, Motivating Processes and the Interpretation of Parameters
 Gerhard Tutz On the Construction of Adjacent Categories Latent Trait Models from Binary Variables, Motivating Processes and the Interpretation of Parameters Technical Report Number 218, 2018 Department
Gerhard Tutz On the Construction of Adjacent Categories Latent Trait Models from Binary Variables, Motivating Processes and the Interpretation of Parameters Technical Report Number 218, 2018 Department
LSAC RESEARCH REPORT SERIES. Law School Admission Council Research Report March 2008
 LSAC RESEARCH REPORT SERIES Structural Modeling Using Two-Step MML Procedures Cees A. W. Glas University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands Law School Admission Council Research Report 08-07 March 2008
LSAC RESEARCH REPORT SERIES Structural Modeling Using Two-Step MML Procedures Cees A. W. Glas University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands Law School Admission Council Research Report 08-07 March 2008
A Study of Statistical Power and Type I Errors in Testing a Factor Analytic. Model for Group Differences in Regression Intercepts
 A Study of Statistical Power and Type I Errors in Testing a Factor Analytic Model for Group Differences in Regression Intercepts by Margarita Olivera Aguilar A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of
A Study of Statistical Power and Type I Errors in Testing a Factor Analytic Model for Group Differences in Regression Intercepts by Margarita Olivera Aguilar A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of
A comparison of two estimation algorithms for Samejima s continuous IRT model
 Behav Res (2013) 45:54 64 DOI 10.3758/s13428-012-0229-6 A comparison of two estimation algorithms for Samejima s continuous IRT model Cengiz Zopluoglu Published online: 26 June 2012 # Psychonomic Society,
Behav Res (2013) 45:54 64 DOI 10.3758/s13428-012-0229-6 A comparison of two estimation algorithms for Samejima s continuous IRT model Cengiz Zopluoglu Published online: 26 June 2012 # Psychonomic Society,
18. SEPARATION STATISTICS
 18. SEPARATION STATISTICS The person and item separation statistics used in Rasch measurement are still unfamiliar to some practitioners (Wright, Mead and Bell, 1979 ; Wright and Stone, 1979 ; and Wrightand
18. SEPARATION STATISTICS The person and item separation statistics used in Rasch measurement are still unfamiliar to some practitioners (Wright, Mead and Bell, 1979 ; Wright and Stone, 1979 ; and Wrightand
Studies on the effect of violations of local independence on scale in Rasch models: The Dichotomous Rasch model
 Studies on the effect of violations of local independence on scale in Rasch models Studies on the effect of violations of local independence on scale in Rasch models: The Dichotomous Rasch model Ida Marais
Studies on the effect of violations of local independence on scale in Rasch models Studies on the effect of violations of local independence on scale in Rasch models: The Dichotomous Rasch model Ida Marais
36-720: The Rasch Model
 36-720: The Rasch Model Brian Junker October 15, 2007 Multivariate Binary Response Data Rasch Model Rasch Marginal Likelihood as a GLMM Rasch Marginal Likelihood as a Log-Linear Model Example For more
36-720: The Rasch Model Brian Junker October 15, 2007 Multivariate Binary Response Data Rasch Model Rasch Marginal Likelihood as a GLMM Rasch Marginal Likelihood as a Log-Linear Model Example For more
arxiv: v1 [stat.ap] 11 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v1 [stat.ap] 11 Aug 2014 arxiv: v1 [stat.ap] 11 Aug 2014](/thumbs/88/115143289.jpg) Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) A multilevel finite mixture item response model to cluster examinees and schools Michela Gnaldi Silvia Bacci Francesco Bartolucci arxiv:1408.2319v1
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) A multilevel finite mixture item response model to cluster examinees and schools Michela Gnaldi Silvia Bacci Francesco Bartolucci arxiv:1408.2319v1
Contributions to latent variable modeling in educational measurement Zwitser, R.J.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Contributions to latent variable modeling in educational measurement Zwitser, R.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Zwitser, R. J. (2015).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Contributions to latent variable modeling in educational measurement Zwitser, R.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Zwitser, R. J. (2015).
UCLA Department of Statistics Papers
 UCLA Department of Statistics Papers Title Can Interval-level Scores be Obtained from Binary Responses? Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/6vg0z0m0 Author Peter M. Bentler Publication Date 2011-10-25
UCLA Department of Statistics Papers Title Can Interval-level Scores be Obtained from Binary Responses? Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/6vg0z0m0 Author Peter M. Bentler Publication Date 2011-10-25
Detection of Uniform and Non-Uniform Differential Item Functioning by Item Focussed Trees
 arxiv:1511.07178v1 [stat.me] 23 Nov 2015 Detection of Uniform and Non-Uniform Differential Functioning by Focussed Trees Moritz Berger & Gerhard Tutz Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Akademiestraße
arxiv:1511.07178v1 [stat.me] 23 Nov 2015 Detection of Uniform and Non-Uniform Differential Functioning by Focussed Trees Moritz Berger & Gerhard Tutz Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Akademiestraße
BAYESIAN MODEL CHECKING STRATEGIES FOR DICHOTOMOUS ITEM RESPONSE THEORY MODELS. Sherwin G. Toribio. A Dissertation
 BAYESIAN MODEL CHECKING STRATEGIES FOR DICHOTOMOUS ITEM RESPONSE THEORY MODELS Sherwin G. Toribio A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate College of Bowling Green State University in partial fulfillment
BAYESIAN MODEL CHECKING STRATEGIES FOR DICHOTOMOUS ITEM RESPONSE THEORY MODELS Sherwin G. Toribio A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate College of Bowling Green State University in partial fulfillment
Multidimensional item response theory observed score equating methods for mixed-format tests
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Summer 2014 Multidimensional item response theory observed score equating methods for mixed-format tests Jaime Leigh Peterson University
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Summer 2014 Multidimensional item response theory observed score equating methods for mixed-format tests Jaime Leigh Peterson University
Longitudinal Data Analysis of Health Outcomes
 Longitudinal Data Analysis of Health Outcomes Longitudinal Data Analysis Workshop Running Example: Days 2 and 3 University of Georgia: Institute for Interdisciplinary Research in Education and Human Development
Longitudinal Data Analysis of Health Outcomes Longitudinal Data Analysis Workshop Running Example: Days 2 and 3 University of Georgia: Institute for Interdisciplinary Research in Education and Human Development
Testing and Interpreting Interaction Effects in Multilevel Models
 Testing and Interpreting Interaction Effects in Multilevel Models Joseph J. Stevens University of Oregon and Ann C. Schulte Arizona State University Presented at the annual AERA conference, Washington,
Testing and Interpreting Interaction Effects in Multilevel Models Joseph J. Stevens University of Oregon and Ann C. Schulte Arizona State University Presented at the annual AERA conference, Washington,
The Application and Promise of Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) in Studying First-Year Student Programs
 The Application and Promise of Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) in Studying First-Year Student Programs Chad S. Briggs, Kathie Lorentz & Eric Davis Education & Outreach University Housing Southern Illinois
The Application and Promise of Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) in Studying First-Year Student Programs Chad S. Briggs, Kathie Lorentz & Eric Davis Education & Outreach University Housing Southern Illinois
USING BAYESIAN TECHNIQUES WITH ITEM RESPONSE THEORY TO ANALYZE MATHEMATICS TESTS. by MARY MAXWELL
 USING BAYESIAN TECHNIQUES WITH ITEM RESPONSE THEORY TO ANALYZE MATHEMATICS TESTS by MARY MAXWELL JIM GLEASON, COMMITTEE CHAIR STAVROS BELBAS ROBERT MOORE SARA TOMEK ZHIJIAN WU A DISSERTATION Submitted
USING BAYESIAN TECHNIQUES WITH ITEM RESPONSE THEORY TO ANALYZE MATHEMATICS TESTS by MARY MAXWELL JIM GLEASON, COMMITTEE CHAIR STAVROS BELBAS ROBERT MOORE SARA TOMEK ZHIJIAN WU A DISSERTATION Submitted
How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018
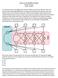 How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018 The random intercept cross lagged panel model (RI CLPM) as proposed by Hamaker, Kuiper and Grasman (2015, Psychological Methods) is a model
How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018 The random intercept cross lagged panel model (RI CLPM) as proposed by Hamaker, Kuiper and Grasman (2015, Psychological Methods) is a model
ABSTRACT. Yunyun Dai, Doctor of Philosophy, Mixtures of item response theory models have been proposed as a technique to explore
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: A MIXTURE RASCH MODEL WITH A COVARIATE: A SIMULATION STUDY VIA BAYESIAN MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO ESTIMATION Yunyun Dai, Doctor of Philosophy, 2009 Directed By: Professor, Robert
ABSTRACT Title of Document: A MIXTURE RASCH MODEL WITH A COVARIATE: A SIMULATION STUDY VIA BAYESIAN MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO ESTIMATION Yunyun Dai, Doctor of Philosophy, 2009 Directed By: Professor, Robert
Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment. CASMA Research Report
 Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment CASMA Research Report Number 24 in Relation to Measurement Error for Mixed Format Tests Jae-Chun Ban Won-Chan Lee February 2007 The authors are
Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment CASMA Research Report Number 24 in Relation to Measurement Error for Mixed Format Tests Jae-Chun Ban Won-Chan Lee February 2007 The authors are
Chapter 11. Scaling the PIRLS 2006 Reading Assessment Data Overview
 Chapter 11 Scaling the PIRLS 2006 Reading Assessment Data Pierre Foy, Joseph Galia, and Isaac Li 11.1 Overview PIRLS 2006 had ambitious goals for broad coverage of the reading purposes and processes as
Chapter 11 Scaling the PIRLS 2006 Reading Assessment Data Pierre Foy, Joseph Galia, and Isaac Li 11.1 Overview PIRLS 2006 had ambitious goals for broad coverage of the reading purposes and processes as
M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY Final Year STATISTICS. Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 (DMSTT21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY - 2013 Final Year STATISTICS Paper - I : Statistical Quality Control Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 Answer any Five questions All questions carry equal
(DMSTT21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY - 2013 Final Year STATISTICS Paper - I : Statistical Quality Control Time : 03 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 Answer any Five questions All questions carry equal
PREDICTING THE DISTRIBUTION OF A GOODNESS-OF-FIT STATISTIC APPROPRIATE FOR USE WITH PERFORMANCE-BASED ASSESSMENTS. Mary A. Hansen
 PREDICTING THE DISTRIBUTION OF A GOODNESS-OF-FIT STATISTIC APPROPRIATE FOR USE WITH PERFORMANCE-BASED ASSESSMENTS by Mary A. Hansen B.S., Mathematics and Computer Science, California University of PA,
PREDICTING THE DISTRIBUTION OF A GOODNESS-OF-FIT STATISTIC APPROPRIATE FOR USE WITH PERFORMANCE-BASED ASSESSMENTS by Mary A. Hansen B.S., Mathematics and Computer Science, California University of PA,
Whats beyond Concerto: An introduction to the R package catr. Session 4: Overview of polytomous IRT models
 Whats beyond Concerto: An introduction to the R package catr Session 4: Overview of polytomous IRT models The Psychometrics Centre, Cambridge, June 10th, 2014 2 Outline: 1. Introduction 2. General notations
Whats beyond Concerto: An introduction to the R package catr Session 4: Overview of polytomous IRT models The Psychometrics Centre, Cambridge, June 10th, 2014 2 Outline: 1. Introduction 2. General notations
Covariates of the Rating Process in Hierarchical Models for Multiple Ratings of Test Items
 Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics March XXXX, Vol. XX, No. issue;, pp. 1 28 DOI: 10.3102/1076998606298033 Ó AERA and ASA. http://jebs.aera.net Covariates of the Rating Process in Hierarchical
Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics March XXXX, Vol. XX, No. issue;, pp. 1 28 DOI: 10.3102/1076998606298033 Ó AERA and ASA. http://jebs.aera.net Covariates of the Rating Process in Hierarchical
A Bivariate Generalized Linear Item Response Theory Modeling Framework to the Analysis of Responses and Response Times
 Multivariate Behavioral Research ISSN: 0027-3171 (Print 1532-7906 (Online Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/hmbr20 A Bivariate Generalized Linear Item Response Theory Modeling Framework
Multivariate Behavioral Research ISSN: 0027-3171 (Print 1532-7906 (Online Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/hmbr20 A Bivariate Generalized Linear Item Response Theory Modeling Framework
Item-Focussed Trees for the Detection of Differential Item Functioning in Partial Credit Models
 arxiv:1609.08970v1 [stat.me] 8 Sep 016 Item-Focussed Trees for the Detection of Differential Item Functioning in Partial Credit Models Stella Bollmann, Moritz Berger & Gerhard Tutz Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität
arxiv:1609.08970v1 [stat.me] 8 Sep 016 Item-Focussed Trees for the Detection of Differential Item Functioning in Partial Credit Models Stella Bollmann, Moritz Berger & Gerhard Tutz Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität
A Markov chain Monte Carlo approach to confirmatory item factor analysis. Michael C. Edwards The Ohio State University
 A Markov chain Monte Carlo approach to confirmatory item factor analysis Michael C. Edwards The Ohio State University An MCMC approach to CIFA Overview Motivating examples Intro to Item Response Theory
A Markov chain Monte Carlo approach to confirmatory item factor analysis Michael C. Edwards The Ohio State University An MCMC approach to CIFA Overview Motivating examples Intro to Item Response Theory
The Discriminating Power of Items That Measure More Than One Dimension
 The Discriminating Power of Items That Measure More Than One Dimension Mark D. Reckase, American College Testing Robert L. McKinley, Educational Testing Service Determining a correct response to many test
The Discriminating Power of Items That Measure More Than One Dimension Mark D. Reckase, American College Testing Robert L. McKinley, Educational Testing Service Determining a correct response to many test
Utilizing Hierarchical Linear Modeling in Evaluation: Concepts and Applications
 Utilizing Hierarchical Linear Modeling in Evaluation: Concepts and Applications C.J. McKinney, M.A. Antonio Olmos, Ph.D. Kate DeRoche, M.A. Mental Health Center of Denver Evaluation 2007: Evaluation and
Utilizing Hierarchical Linear Modeling in Evaluation: Concepts and Applications C.J. McKinney, M.A. Antonio Olmos, Ph.D. Kate DeRoche, M.A. Mental Health Center of Denver Evaluation 2007: Evaluation and
Creating and Interpreting the TIMSS Advanced 2015 Context Questionnaire Scales
 CHAPTER 15 Creating and Interpreting the TIMSS Advanced 2015 Context Questionnaire Scales Michael O. Martin Ina V.S. Mullis Martin Hooper Liqun Yin Pierre Foy Lauren Palazzo Overview As described in Chapter
CHAPTER 15 Creating and Interpreting the TIMSS Advanced 2015 Context Questionnaire Scales Michael O. Martin Ina V.S. Mullis Martin Hooper Liqun Yin Pierre Foy Lauren Palazzo Overview As described in Chapter
New Developments for Extended Rasch Modeling in R
 New Developments for Extended Rasch Modeling in R Patrick Mair, Reinhold Hatzinger Institute for Statistics and Mathematics WU Vienna University of Economics and Business Content Rasch models: Theory,
New Developments for Extended Rasch Modeling in R Patrick Mair, Reinhold Hatzinger Institute for Statistics and Mathematics WU Vienna University of Economics and Business Content Rasch models: Theory,
Estimation and Centering
 Estimation and Centering PSYED 3486 Feifei Ye University of Pittsburgh Main Topics Estimating the level-1 coefficients for a particular unit Reading: R&B, Chapter 3 (p85-94) Centering-Location of X Reading
Estimation and Centering PSYED 3486 Feifei Ye University of Pittsburgh Main Topics Estimating the level-1 coefficients for a particular unit Reading: R&B, Chapter 3 (p85-94) Centering-Location of X Reading
Designing Multilevel Models Using SPSS 11.5 Mixed Model. John Painter, Ph.D.
 Designing Multilevel Models Using SPSS 11.5 Mixed Model John Painter, Ph.D. Jordan Institute for Families School of Social Work University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 1 Creating Multilevel Models
Designing Multilevel Models Using SPSS 11.5 Mixed Model John Painter, Ph.D. Jordan Institute for Families School of Social Work University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill 1 Creating Multilevel Models
Chapter 4: Factor Analysis
 Chapter 4: Factor Analysis In many studies, we may not be able to measure directly the variables of interest. We can merely collect data on other variables which may be related to the variables of interest.
Chapter 4: Factor Analysis In many studies, we may not be able to measure directly the variables of interest. We can merely collect data on other variables which may be related to the variables of interest.
Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment. CASMA Research Report
 Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment CASMA Research Report Number 31 Assessing Equating Results Based on First-order and Second-order Equity Eunjung Lee, Won-Chan Lee, Robert L. Brennan
Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment CASMA Research Report Number 31 Assessing Equating Results Based on First-order and Second-order Equity Eunjung Lee, Won-Chan Lee, Robert L. Brennan
Modelling heterogeneous variance-covariance components in two-level multilevel models with application to school effects educational research
 Modelling heterogeneous variance-covariance components in two-level multilevel models with application to school effects educational research Research Methods Festival Oxford 9 th July 014 George Leckie
Modelling heterogeneous variance-covariance components in two-level multilevel models with application to school effects educational research Research Methods Festival Oxford 9 th July 014 George Leckie
Use of Robust z in Detecting Unstable Items in Item Response Theory Models
 A peer-reviewed electronic journal. Copyright is retained by the first or sole author, who grants right of first publication to the Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation. Permission is granted to
A peer-reviewed electronic journal. Copyright is retained by the first or sole author, who grants right of first publication to the Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation. Permission is granted to
Comparison between conditional and marginal maximum likelihood for a class of item response models
 (1/24) Comparison between conditional and marginal maximum likelihood for a class of item response models Francesco Bartolucci, University of Perugia (IT) Silvia Bacci, University of Perugia (IT) Claudia
(1/24) Comparison between conditional and marginal maximum likelihood for a class of item response models Francesco Bartolucci, University of Perugia (IT) Silvia Bacci, University of Perugia (IT) Claudia
Making the Most of What We Have: A Practical Application of Multidimensional Item Response Theory in Test Scoring
 Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics Fall 2005, Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 295 311 Making the Most of What We Have: A Practical Application of Multidimensional Item Response Theory in Test Scoring
Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics Fall 2005, Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 295 311 Making the Most of What We Have: A Practical Application of Multidimensional Item Response Theory in Test Scoring
Overview of Talk. Motivating Example: Antisocial Behavior (AB) Raw Data
 An Evaluative Comparison of Random Coefficient Growth Models for Individual Development May 6, 7 Association for Psychological Science Overview of Talk Motivating example Definition of Random Coefficient
An Evaluative Comparison of Random Coefficient Growth Models for Individual Development May 6, 7 Association for Psychological Science Overview of Talk Motivating example Definition of Random Coefficient
Validation of Cognitive Structures: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
 Multivariate Behavioral Research, 38 (1), 1-23 Copyright 2003, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. Validation of Cognitive Structures: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach Dimiter M. Dimitrov Kent State
Multivariate Behavioral Research, 38 (1), 1-23 Copyright 2003, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. Validation of Cognitive Structures: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach Dimiter M. Dimitrov Kent State
Development and Calibration of an Item Response Model. that Incorporates Response Time
 Development and Calibration of an Item Response Model that Incorporates Response Time Tianyou Wang and Bradley A. Hanson ACT, Inc. Send correspondence to: Tianyou Wang ACT, Inc P.O. Box 168 Iowa City,
Development and Calibration of an Item Response Model that Incorporates Response Time Tianyou Wang and Bradley A. Hanson ACT, Inc. Send correspondence to: Tianyou Wang ACT, Inc P.O. Box 168 Iowa City,
Introduction to GSEM in Stata
 Introduction to GSEM in Stata Christopher F Baum ECON 8823: Applied Econometrics Boston College, Spring 2016 Christopher F Baum (BC / DIW) Introduction to GSEM in Stata Boston College, Spring 2016 1 /
Introduction to GSEM in Stata Christopher F Baum ECON 8823: Applied Econometrics Boston College, Spring 2016 Christopher F Baum (BC / DIW) Introduction to GSEM in Stata Boston College, Spring 2016 1 /
Generalized Linear Models for Non-Normal Data
 Generalized Linear Models for Non-Normal Data Today s Class: 3 parts of a generalized model Models for binary outcomes Complications for generalized multivariate or multilevel models SPLH 861: Lecture
Generalized Linear Models for Non-Normal Data Today s Class: 3 parts of a generalized model Models for binary outcomes Complications for generalized multivariate or multilevel models SPLH 861: Lecture
IEOR E4570: Machine Learning for OR&FE Spring 2015 c 2015 by Martin Haugh. The EM Algorithm
 IEOR E4570: Machine Learning for OR&FE Spring 205 c 205 by Martin Haugh The EM Algorithm The EM algorithm is used for obtaining maximum likelihood estimates of parameters when some of the data is missing.
IEOR E4570: Machine Learning for OR&FE Spring 205 c 205 by Martin Haugh The EM Algorithm The EM algorithm is used for obtaining maximum likelihood estimates of parameters when some of the data is missing.
Class Notes: Week 8. Probit versus Logit Link Functions and Count Data
 Ronald Heck Class Notes: Week 8 1 Class Notes: Week 8 Probit versus Logit Link Functions and Count Data This week we ll take up a couple of issues. The first is working with a probit link function. While
Ronald Heck Class Notes: Week 8 1 Class Notes: Week 8 Probit versus Logit Link Functions and Count Data This week we ll take up a couple of issues. The first is working with a probit link function. While
