ОбЪВАИНВННЫИ. АУ б На. El ИССJ18АОВ8НИИ. A.M.Baldin, L.A.Didenko, V.G.Grishin, A.A.Kuznetsov, z. V.Metreveli
|
|
|
- Leon Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ОбЪВАИНВННЫИ ИНСТИТУТ RАВРНЫХ ИССJ8АОВ8НИИ АУ б На El A.M.Baldin, L.A.Didenko, V.G.Grishin, A.A.Kuznetsov, z. V.Metreveli HADRON JETS IN CUMULATIVE PROCESSES FOR п-с INTERACTIONS - А Т Р = 40 Ge V /с Subrnitted to the XXII International Conference on High Energy Physics (Leipzig, 984) *rер, Tbilisi State University, USSR 9.84
2 . INTRODUCTION The analysis of multiple hadron production in different processes, such as е+е- annihilation, deep-inelastic lepton-hadron collisions and soft hadron-hadron interactions, -ьаs shown that the production of hadron jets, which have а number of universal properties, is observed in these interactions / 0. Collective characteristics of the jets, "sphericity", "thrust" and others, the multiplicity of hadrons and their momentum distributions in the jets coincide for these processes at equal energies in the c.m.s. The observed similarity of the properties of hadron jets is probaьly due to the existence.of single mechanism of quark hadronization for soft and hard interactions. It is of interest to study the properties of hadron jets produced in hadron-nucleus collisions which can give information on the influence of nuclear matter on their formation and will allow one to estaьlish more general regularities of quark hadronization for different types of interactions. Cumulative processes are of principal interest / 4/, In this case quark-parton structure functions determined due to multiquark states in nuclei, are obtained from data on limiting nuclear fragmentation (Е > 3+4 GeV). Quark hadronization fro-m multiquark nuclear states is practically unstudied. Therefore it is particularly interesting to select jets in the region of nuclear fragmentatio and to compare them with the properties of hadron jets in е+е- and hadron-hadron interactions. This paper is devoted to the study of jet production in cumulative "-С interactions at 40 GeV/c. The results obtained are comparf'd with е+е- and "-Р data at Р = 40 GeV/c. Figure presents possiьle diagrams of the fragmentation production of hadron jets for "- р, е+е- and cumulative "-с interac tions, The analysis carried out in / 8 0 has shown that the production of two hadron jets in "-Р interactions, collimated towards an incident pion and in an opposite direction, can Ье mainly coцsidered as а result of the fragmentation of noninteracting u(d) quarks (forward hemisphere in the c.m.s.) and uu(ud) diquarks (backward hemisphere in the c.m.s.) from primary particles. Similarly, the production of secondary particle jets in the c.m.s. of "-с interactions can Ье presented as а result of the fragmentation of noninteracting ii(d) quarks from incident "- -rneson in the forward hemisphere and -t,--. - tl'т}'т i U!litНWX,,,:oюsd
3 rre nnr jttt/ - meson ('J) <>Н JUU!.-' nucteon (q.) s'f : д -----/6-;.--- ". 2 EXPERIМENT -Гр \ С'"С cumulative as а result of quark fragmentation from multiquark states of carbon nucleus in the backward hemisphere (region of targetnucleus fragmentation)., In this paper we study the fragmentation of quarks and diquarks into charged pions, neutral strange К 0 -mesons and Л - hyperons and collective characteristics of jets. Fig.. Schemes of rr р, cumulative "-с and е+е- interac - tions. Experimental data have been obtained using the 2m propane bubьle chamber exposed to а beam of 40 GeV /с "- -mesons at the Serpukhov accelerator. The work was done on statistics of 6480 rr -с interac tions * in which charged pions and protons were measured (the latter were identified over а momentum range of ' 200_$ Plab S 800 MeV/c), 550 K 0 -mesons (К 0 "+"] and 294Л - hyperons (Л prr-) were also usd in the a'halysis. 688 inelastic "-р interactions with '753 К 0 -mesons and 345 Л -hyperons 8 were used to compare wth the "-с data. The method of selection of "-р and "-с interactions, the identification of neutral strange particles and а further processing of the events are described in detail in papers /lб. 2О/. Multinucleon "-с interactions with the total charge of secondary particles Q"' N+- N_ = +, +2, +3, +4, where N+ and N_ are the numbers of secondary positive and negative particles per interaction, were selected for the analysis. In this case the protons having Р ь s 300 MeV /с were excluded as in this region the fraction oi spectator protons from th target-nucleus is large. For each group of mul tinucleon rr -с interactions with charge Q the analysis was performed in the c.m.s. of incident "- -meson and the corresponding number of nucleons (v ) involved in the interaction. In the events with Q = + the:e were two interacting protons, with Q = +2 three protons and 2 *Pion interactions with quasi-free nucleons were excluded. ', Туре of interaction Eventв Vli th cumulative jets j30.0 Eventв with cumulative jetв у..5 Statistics of events Average Energy Number of Q number events of inter- Ec.m.s. with given acting (Gs ') Q and nucleons nl Multinucleon interactionв all all all ТаЬlе Praction of events in % with ven Q from all / '"С interactions б so on. As neutrons also participate in these collisions, their number was estimated Ьу the momentum conservation law for the events with given Q in the collision c.m.s. 2. The energy of collision is defined Ьу the formula Ec,m.s.=' VS = "J2v 0 mnerr () with mn the nucleon mass and Е" the energy of incident pion. Such an approach makes it possiьle to observe the change of the properties of hadron jets, produced on nuclei, with increasing the number of' nucleons involved in the interaction what is somewhat similar to an investigation of the properties of hadron jets versus the atomic number of target-nucleus. ТаЬlе presents the number of events selected with charge Q = +, +2, +3, +4 and their fraction (in %) of the total cross section of "-с interactions. The cumulative events were selected using variaьle = Е- р =, where Е and Р are the energy and longi tudinal mome!um of secondary particles in the lab.system. According to the estaьlished selection criteria/ 22/ an event was assumed to Ье cumulative if а "±-meson with or а proton with 2. 3
4 was registrated in it. However, the hadronization of quarks from multiquark nuclear states can occur so that none of the particles has the value of outside the kinemaical limit of pion-nucleon collision whereas the sum of all in а jet, produced in quark hadronization, is larger than. (2) = I. >,. i As is shown/2, the events with cumulative particles incompletely reflect all cumulative processes and their configuration in momentum space. Thus, cumulative interactions were selected according to the condition (2): the events were selected in which the value of for а group (jet) of particles, moving backward in the c.m.s.(тr-vn),. was larger than.а group.of particles satisfying the condition (2) was assumed to Ье а cumulative jet. ТаЬlе presents the number of cumulative events thus selected and their fraction of all "-с interactions. The fraction of cumula ti ve j ets wi th К n -mesons and Л -hyperons was respectively -8% and 0% of all cumulative jets. 3. JET STRUCTURE The study of jet particle production in тr -с interactions has been performed using the standard variaьles: sphericity S and thrust Т. Sphericity S is defined as follows: S=!min(I.P 2 /I.\P*\ 2 ) (3) 2 i l.i with Р; the momenta of secondary particles in the collision c.m.s. and Pl.i the transverse moclenta of particle relative to some axi s : The ахз.s, for whз.ch Pl. has а mз.nз.mum value, з.s assumed to Ье а jet axis. Thrust Т is found according to the formula: T=max(I.\P;\ /I.\P.*\). (4).. Here Р is tbe projection of the momenta of secondary particles on some direction. The jet axis is defined as an axis which maximizes the sum I \Р \. These variaьles are described in detail in paper/28. It should Ье noted that variaьles S and determine the jet cone opening angle. Figure 2 shows the dependence of average values of sphericity <S> on collision energy Е for е+е- annihilation An average value of S c.mfr "-Р interactions at Ec.m.s. = 8. 7 GeV is also shown Ьу an arrow. In the same figure are presented average values of < S> versus Ес.m.в. for the j ets 4 ' il Fig.2. Average values of sphericity <S> for different types of interactions with n+?. 4 versus energy in the c.m.s. of colliding particles: V, а for е+е- annihilations; 8 - for cumulative tт-с interactions with >.0; i - for noncumulative тr -с collisions; а) for jets of secondary particles with х?. 0.05; Ь) for jets of secondary particles with х : (6)',,_"Gt\lo!: ft-ofi J._ Ц) I)AICI. Н f- :: : ::: l f- t t f ";il ";# f- Лl * t t +' + + 'J t' Q< '! s ю s ю е т of secondary particles collimated towards а primary pion and in an opposit direction in the cumulative ( >.О) and noncumulative ( <.0) events. The particles, having Jx J 2\Р \ = > refer to the jets. For comparison with the Е - е+е- c;fa'fa the j ets were selected in which the multiplici ty of charged particles, n± was 4. As seen from the figure, the value of <S> for both jets in cumulative тr-с interactions agrees with the е+е- data at equal energies in the c.m.s. For the noncumulative events one can see а disagreement with similar data on е+е- interactions for the hadron jets produced in the fragmentation region of target-nucleus. An analogous picture is observed when comparing the values of variaьle Т. In order to rule out а possiьle influence of such nuclcar effects as Fermi-motion and pion absorption in the nucleus which can lead to the production of particles and grops of particles with the value of 0 outside the kinematical limit of pion-nucleon collision, we have selected jets with?..5. In ТаЬlе are presented the number of events satisfying this condition and their fraction of all "-С interactions with n± 4. For the cumulative jets thus selected the dependence of average values of <8> on energy Е с.m.в. does not differ from that presented in fig ШLTIPLICITY OF SECONDARY PARTICLES. Hultiplicity of Charged Particles It is known that in various types of hadron-hadron interactions and in е+е- annihilation the multiplicity of charged particles is different: e.g., in рр collisions the average va- Е. s f""'l 5
5 '' л J' т--.--т-тт----т--т-- ю v 5 AOONE SPEAR МARtC. DASP.to PWTO TASSO JADE l'oanty-:t /.,;/,."" "' ; -' / /.-"". / Fig. 3. Aver_age multiplicity of charged particles, <n+>, versus energy in the c.m.s. for e+eand cumulative "-С interactions (Е). Solid curve - QCD prediction for е+е- annihilation. Туре of interaction Multiplicities of К n -mesons and А -hyperons in "-р and cumulative "-с interactions rr"p "-с, Q=+,+2 <v > = 3.3 n ТаЫе 2 6. o,l-l23&5uuiol-5-ioio Vs (GeV) ues of <n+> are smaer than in е+е- annihiation at the same energies in the c.m.s. (fig.з), and in "-Р and к-р interactions the vaues of <n+> coincide with the е+е- data at y's ::; 2 GeV 8 5 It is of i"nterest to compare the mutiplicity <n+> in е+- annihilation and in cumuative processes. -Figure 3 depicts the average mutipicity of charged partices versus y's in е+е- and cumulative "-с colisions. It is seen that in cumulative processes the vaue of <n+> increases with increasing Е 0 m, 8 and, within exerimentaf errors, it coincides with the values of <n+> for е е- annihiation at equa Ec.m.s.' However, the anaysis has shown that this increase of <n+> in cumulative processes is greaty due to increasing the number of protons in the fina state/2. 2. Mutipicities of Neutra Strange Partices ТаЬlе 2 shows the average mutipicities of Kn -mesons and А -hyperons in "-р and cumuative "-с interactions with charge Q = +, +2. As is seen from the taьle, the mutipicities of Kn -mesons and А -hyperons in cumuative interactions are larger than in pion-proton colisions. Nevertheess in "-с events the mutipicity of neutra kaons increases proportionally to the average mutipicity of rr 0 -mesons, <n>, in these events* so that within the experimenta errors,"the <nкn> ' f h с rato s sm ar or t ese nteractons. onsequent у, <n > in cumutive processes no additiona sources of strange meson production are observed as compared to neutra pions. In comparison with the mutiplicity of А -hyperons in pionnuceon collisions, the mutiplicity of А -hyperons in cumu- ative events increases approximatey in proportion to the number of nucleons invoved in the interaction. It is produced <ny>. supposed that y-quanta in the events are mainly from the decays of rr 0 -mesons, therefore <n> = Туре of partices <nк,а > <nк,а > <n"o> <nк,а> <vn > кn А кn. А h. h. h. < n А 5... Wt n t е expermenta errors, t е rato s sm ar for "-р and "-с interactions. <vn> 5. CНARACTERISTICS OF CНARGED PARTICLES IN JETS Besides the anaysis of the coective characteristics of the jets, sphericity and thrust, it is interesting to compare one-partice momentum distributions of secondary particles in the jets for cumuative "-с and е+е- interactions. In fig.4 is shown the transverse momentum squared distribution of а secondary particles in cumulative interactions with Q = + reative to the jet axis. The Р{ di.stributions of partices are simiar, within the experimenta errors, for the jets produced in the forward and backward hemisphere in the c.m.s. of (rr-vn) collisions. So figure 4 presents the sununed distribution for both hemispheres. The transverse squared distribution of charged partices relative to the jet axis in е+е- annihilation for approximatey close energies (y's: = = 3+7 GeV) is given in the same figure for comparison. As seen, these distributions are similar for both types of the interactions considered. 2Р Figure 5 illustrates the х = Е distributions of sec.m.s. condary partices in the forward and backward hemispheres in the c.m.s. of "-с interactions with Q= +, where Р is the longitudinal momentum of particles reative to the jet axis. The data are come!red with а similar distribution for е+ е- ennihilation at y's = 7.4 Gev 28 The distribution is normalized so tht the area under it in the range lx > 0. is the same as in rr С events. - 7
6 ? ml- - 'f l\ - -j,f 4';_, ч + 0, - t t t t - t- 0,0 fi 0,5,5 20 /f(wv/c)' Fig.4. Transverse momentum squared distribution of charged particles relative to the jet axis in cumulative "-С collisions at JS = 5. 3 GeV (8) and in е+ е- annihilation at vs = 3+ 7 GeV. «-.kl ).{ =. АА 6 ' ; t./ ttt+ t o,d Ц5 \0 \() -!,5 ж, Fig.5. х distribution of charged particles relative to the jet axis in cumulative rт-с interactions atvs: = 5.3 GeV and in е+е- annihilation at vsi = 7.4 GeV; а) distribution of particles in jets flying in the c.m.s.; Ь) distribution of particles in jets flying backward in the c.m.s. From the figure one can see that in cumulative rт-с collisions the distribution of particles in the jets, collimated towards an incident тг -meson, is in agreement with а similar distribution in е+е- interactions. For particles, produced in the fragmentation nuclear region in these events (both for pions and for protons),the х distribution relative to the jet axis differs from а similar distribution of charged particles in е+е- annihilation. This difference can Ье due to variations of initial states of interacting objects which leads to various compositions of secondary particles in the f inal state and to distributions in their phase space distribufions (in cumulative rт-с interactions with Q = + the average numьer of nucleons, <vn >, is 3.3 whereas in е+ е- annihilations at ys = 7.4 GeV the mean mul tiplicity of рр" pairs per event <npp > is <О. ). Therefore it would Ье more correct to compare identical systems of secondary particles in the final state (in this case meson ones) in their rest frame. With this aim the events with two i dentified protons were sel ected from cumulative rт- С interactions wit h Q = +. The protons were excluded from the analysis; the energy of the remaining ineson system, <М >, was 0 GeV The value of < М 0 > was decreased Ьу 6% if the fraction of neutrons i n the final state was accounted for Е"Т---.--т !="" * ++ r --lz \ j 0, Е- Q0 LL--' :. 0,5,0 s 2Р 5 -м. Fig. 7. у distribution of pions for cumulative "-С interactions at <М 0 > = 0 GeV and е+ е- annihilation atjs= 3 GeV J and 7.4 GeV. Fig. б. х distribution of pions in cumulative rт-с collisions for < м 0 > = 0 -GeV and in е+ е- annihilation for ys = 7. 4 GeV. ц+.\,,.. -. ) \,, :z, \ 'tl't! \ li 0,0:: ГС, <М.>=ЮGеv,. } er I[S Gev --- (S?.4Gev \j 0,00 r.! -2 'f". -'t. s The х: = and у distributions of charged pions calculated in the est frame of mesons (М 0 ), were analyzed. In this case ps is the total momentum of pions in their rest frame м 0 and у the rapidity determined relative to the jet axis in the same system (the jet axis was reconstructed Ьу variaьle Т). In such an approach the production of pion jets in the fragmentation region of target-nucleus can Ье interpreted as а result of the fragmentation of quarks from multiquark states of carbon nucleus. Figures б and 7 compare the dn and dn distributions dxs dy в of charged pions, produced in thernuclear fragmentation region for cumu.lative rт-с events at <М > = 0 GeV, with the xr and у distributions of pions in е+е- annihilation for approximately equal energies ys. As seen from the figures, these distributions of pions are similar for both types of interaction. 9
7 \ б. QUARК AND DIQUARК FRAGМENTATION INTO STRANGE PARTICLES,. Fragшentation Functions Comparing the processes of quark and diquark fragmentation into neutral К n -mesons and Л-hyperons for various types of interaction, we use the scaling function in terms of + -. fj dx'- whch the е е data are analyzed. Here хе"' 2E*/v'S; fj Р*/Е*; Р* and Е* are the moщentum and energy of the considered hadron in the coll ision c.m. s. According to quark-parton model predictions, for quark fragmentation this function depends only on variaьle хе: annihilation, we analyze the function Jl J M-6~ El - 8794 A.Mih ul ', T.Angelescu STRANGENESS EXCHANGE IN HIGH ENERGY INTERACTIONS 1975 El - 8794 A.Mihul, T.Angelescu STRANGENESS EXCHANGE IN HIGH ENERGY INTERACTIONS Submitted to Physics Letters
M-6~ El - 8794 A.Mih ul ', T.Angelescu STRANGENESS EXCHANGE IN HIGH ENERGY INTERACTIONS 1975 El - 8794 A.Mihul, T.Angelescu STRANGENESS EXCHANGE IN HIGH ENERGY INTERACTIONS Submitted to Physics Letters
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5564/pmas.v54i4.619 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES Ts.Baatar, R.Togoo, G.Sharkhuu, B.Otgongerel Institute
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5564/pmas.v54i4.619 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES Ts.Baatar, R.Togoo, G.Sharkhuu, B.Otgongerel Institute
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)072
 Cumulative protons in hadron-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus interactions E-mail: yuldashev@jinr.ru E.Kh. Bazarov S.L. Lutpullaev K. Olimov E-mail: olimov@uzsci.net V.I. Petrov New experimental data on the
Cumulative protons in hadron-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus interactions E-mail: yuldashev@jinr.ru E.Kh. Bazarov S.L. Lutpullaev K. Olimov E-mail: olimov@uzsci.net V.I. Petrov New experimental data on the
[Published in Russian: V.V.Ammosov et al. Yadernaya Fizika I Inzhiniring 4 (2013) ] Received:
![[Published in Russian: V.V.Ammosov et al. Yadernaya Fizika I Inzhiniring 4 (2013) ] Received: [Published in Russian: V.V.Ammosov et al. Yadernaya Fizika I Inzhiniring 4 (2013) ] Received:](/thumbs/88/115132660.jpg) [Published in Russian: V.V.Ammosov et al. Yadernaya Fizika I Inzhiniring 4 (01)77 778] Received:.09.01 PRODUCION OF HIGH-P CUMULAIVE PARICLES IN PROON- NUCLEUS INERACIONS A 50 GeV. V.V.Ammosov 1, N.N.Antonov
[Published in Russian: V.V.Ammosov et al. Yadernaya Fizika I Inzhiniring 4 (01)77 778] Received:.09.01 PRODUCION OF HIGH-P CUMULAIVE PARICLES IN PROON- NUCLEUS INERACIONS A 50 GeV. V.V.Ammosov 1, N.N.Antonov
'tч о/ч /J4 1984" , АУбна. ( 3 Не, t) ОбЪ8АМН8ННЫI. м с с Jl е А.о в а н м й. El INVESTIGATION OF ТНЕ CHARGE-EXCHANGE REACTION
 ОбЪ8АМН8ННЫI ИНСТИТУТ RАВРНЫХ с с Jl е А а н й, АУбна 'tч /Ч /J El-8-38 ' IVESTIGATIO OF ТНЕ CHARGE-EXCHAGE REACTIO ( 3 Не, t) АТ 37, 678, AD 78 GeV /с WITH! -ISOBAR EXCITATIO I CARBO Submitte to"pis'ma
ОбЪ8АМН8ННЫI ИНСТИТУТ RАВРНЫХ с с Jl е А а н й, АУбна 'tч /Ч /J El-8-38 ' IVESTIGATIO OF ТНЕ CHARGE-EXCHAGE REACTIO ( 3 Не, t) АТ 37, 678, AD 78 GeV /с WITH! -ISOBAR EXCITATIO I CARBO Submitte to"pis'ma
Storm Open Library 3.0
 S 50% off! 3 O L Storm Open Library 3.0 Amor Sans, Amor Serif, Andulka, Baskerville, John Sans, Metron, Ozdoby,, Regent, Sebastian, Serapion, Splendid Quartett, Vida & Walbaum. d 50% f summer j sale n
S 50% off! 3 O L Storm Open Library 3.0 Amor Sans, Amor Serif, Andulka, Baskerville, John Sans, Metron, Ozdoby,, Regent, Sebastian, Serapion, Splendid Quartett, Vida & Walbaum. d 50% f summer j sale n
MOMENTUM AND ANGULAR DISTRIBUTIONS OF CHARGED SECONDARI'ES IN 40 GeV jc
 ОбЪ8АИН8ННЫИ ИНСТИТУТ ядерных исседваним дуби а El84442 MOMETUM AD AGULAR DISTRIBUTIOS OF CHARGED SECODARIES I 40 GeV jc я А ITERACTIOS WITH SIGLE PARTICLE HIGH pj TRIGGER Berl inbudapesdubnapraguesofiatbilisi
ОбЪ8АИН8ННЫИ ИНСТИТУТ ядерных исседваним дуби а El84442 MOMETUM AD AGULAR DISTRIBUTIOS OF CHARGED SECODARIES I 40 GeV jc я А ITERACTIOS WITH SIGLE PARTICLE HIGH pj TRIGGER Berl inbudapesdubnapraguesofiatbilisi
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007](/thumbs/74/69624022.jpg) Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
3 /,,,:;. c E THE LEVEL DENSITY OF NUCLEI IN THE REGION 230 ~ A < 254. A.L.Komov, L.A.Malov, V.G.Soloviev, V.V.Voronov.
 ~ - t-1 'I I 3 /,,,:;. c E4-9236 A.L.Komov, L.A.Malov, V.G.Soloviev, V.V.Voronov THE LEVEL DENSITY OF NUCLEI IN THE REGION 230 ~ A < 254 1975 E4-9236 AX.Komov, L.A.Malov, V.G.SoIoviev, V.V.Voronov THE
~ - t-1 'I I 3 /,,,:;. c E4-9236 A.L.Komov, L.A.Malov, V.G.Soloviev, V.V.Voronov THE LEVEL DENSITY OF NUCLEI IN THE REGION 230 ~ A < 254 1975 E4-9236 AX.Komov, L.A.Malov, V.G.SoIoviev, V.V.Voronov THE
On the determination of the longitudinal. component of the fragmentation function of the. N.B.Skachkov, O.G.Smirnova, L.G.Tkatchev.
 DELPHI Collaboration DELPHI 95- PHYS 472 30 January, 995 On the determination of the longitudinal component of the fragmentation function of the process e + e??! h + X from DELPHI data N.B.Skachkov, O.G.Smirnova,
DELPHI Collaboration DELPHI 95- PHYS 472 30 January, 995 On the determination of the longitudinal component of the fragmentation function of the process e + e??! h + X from DELPHI data N.B.Skachkov, O.G.Smirnova,
IS.Akh«b.ki»n, J.Bartke, V.G.Griihin, M.Kowahki
 М^.Ш:й*;п II, 1Д1 Н1Х ЯвШДЮМ* i ПГиГ- ii i) и ii in ill i El-83-670 IS.Akh«b.ki»n, J.Bartke, V.G.Griihin, M.Kowahki SMALL ANGLE CORRELATIONS OF IDENTICAL PARTICLES IN CARBON-CARBON INTERACTIONS AT P *
М^.Ш:й*;п II, 1Д1 Н1Х ЯвШДЮМ* i ПГиГ- ii i) и ii in ill i El-83-670 IS.Akh«b.ki»n, J.Bartke, V.G.Griihin, M.Kowahki SMALL ANGLE CORRELATIONS OF IDENTICAL PARTICLES IN CARBON-CARBON INTERACTIONS AT P *
J. Ranft* CERN, Geneva. s. Ritter. Sektion Physik Karl-Marx-Universitit Leipzig, DDR A B S T R A C T
 ~UROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH TIS-RP/128/PP 27 April 1984 RAPIDITY RATIOS. FEYNMAN-X DISTRIBUTIONS AND FORWARD-BACKWARD CORRELATIONS IN HADRON-NUCLEUS COLLISIONS IN A DUAL MONTE-CARLO MULTI-CHAIN
~UROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH TIS-RP/128/PP 27 April 1984 RAPIDITY RATIOS. FEYNMAN-X DISTRIBUTIONS AND FORWARD-BACKWARD CORRELATIONS IN HADRON-NUCLEUS COLLISIONS IN A DUAL MONTE-CARLO MULTI-CHAIN
Exotic in dense and cold nuclear matter.
 Exotic in dense and cold nuclear matter. К.Мikhailov,А.Stavinskiy,G.Sharkov,V.Stolin(ITEP) Abstract The way to create and to investigate a dense cold matter droplets in the laboratory is proposed. The
Exotic in dense and cold nuclear matter. К.Мikhailov,А.Stavinskiy,G.Sharkov,V.Stolin(ITEP) Abstract The way to create and to investigate a dense cold matter droplets in the laboratory is proposed. The
PoS(IHEP-LHC-2011)008
 in pp collisions at the LHC Sergei Lobanov Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russian Federation E-mail: Sergey.Lobanov@cern.ch Artem Maevskiy M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russian
in pp collisions at the LHC Sergei Lobanov Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russian Federation E-mail: Sergey.Lobanov@cern.ch Artem Maevskiy M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russian
Slowing-down of Charged Particles in a Plasma
 P/2532 France Slowing-down of Charged Particles in a Plasma By G. Boulègue, P. Chanson, R. Combe, M. Félix and P. Strasman We shall investigate the case in which the slowingdown of an incident particle
P/2532 France Slowing-down of Charged Particles in a Plasma By G. Boulègue, P. Chanson, R. Combe, M. Félix and P. Strasman We shall investigate the case in which the slowingdown of an incident particle
STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI
 STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI M. Ajaz 1, 2, M. K. Suleymanov 2, 3, K. H. Khan 2, A. Zaman 2, H. Younis 2, A. Rahman 4 1 Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan
STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI M. Ajaz 1, 2, M. K. Suleymanov 2, 3, K. H. Khan 2, A. Zaman 2, H. Younis 2, A. Rahman 4 1 Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan
About One way of Encoding Alphanumeric and Symbolic Information
 Int. J. Open Problems Compt. Math., Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2010 ISSN 1998-6262; Copyright ICSRS Publication, 2010 www.i-csrs.org About One way of Encoding Alphanumeric and Symbolic Information Mohammed
Int. J. Open Problems Compt. Math., Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2010 ISSN 1998-6262; Copyright ICSRS Publication, 2010 www.i-csrs.org About One way of Encoding Alphanumeric and Symbolic Information Mohammed
String Parton Models in Geant4
 String Parton Models in Geant4 G.Folger, J.P.Wellisch CERN, CH-2 Geneva, Switzerland Dual parton or quark gluon string model are the by now almost standard theoretical techniques by which one can arrive
String Parton Models in Geant4 G.Folger, J.P.Wellisch CERN, CH-2 Geneva, Switzerland Dual parton or quark gluon string model are the by now almost standard theoretical techniques by which one can arrive
A TEST OF THE FLAVOR INDEPENDENCE OF STRONG INTERACTIONS *
 A TEST OF THE FLAVOR INDEPENDENCE OF STRONG INTERACTIONS * SLAC-PUB- 6659 September 1994 (N) Thomas W. Markiewicz a, representing The SLD Collaboration a Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University,
A TEST OF THE FLAVOR INDEPENDENCE OF STRONG INTERACTIONS * SLAC-PUB- 6659 September 1994 (N) Thomas W. Markiewicz a, representing The SLD Collaboration a Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University,
Fall Quarter 2010 UCSB Physics 225A & UCSD Physics 214 Homework 1
 Fall Quarter 2010 UCSB Physics 225A & UCSD Physics 214 Homework 1 Problem 2 has nothing to do with what we have done in class. It introduces somewhat strange coordinates called rapidity and pseudorapidity
Fall Quarter 2010 UCSB Physics 225A & UCSD Physics 214 Homework 1 Problem 2 has nothing to do with what we have done in class. It introduces somewhat strange coordinates called rapidity and pseudorapidity
\ / I N S T I T U T E FOR HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS И Ф В Э
 \ / I N S T I T U T E FOR HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS И Ф В Э 80-179 ОЭФ SERP-E-134 R.I.Dzhelyadin, S.V.Golovkin, A.S.Konstantinov, V.F.Konstantinov, V.P.Kubarovski, L.G.Landsberg, V.A.Mukhin, V.F.Obrastsov, Yu.D.Prokoshkin,
\ / I N S T I T U T E FOR HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS И Ф В Э 80-179 ОЭФ SERP-E-134 R.I.Dzhelyadin, S.V.Golovkin, A.S.Konstantinov, V.F.Konstantinov, V.P.Kubarovski, L.G.Landsberg, V.A.Mukhin, V.F.Obrastsov, Yu.D.Prokoshkin,
~ ~3 )~\f. (_3Уь~. El OBSERVATION AND STUDY OF А NARROW STATE IN А I -(1385)К + SYSTEM А -Ъ~ " ОбЬ8АИН8ННЫМ. АУ б На. И С CJI ВАОВ.
 ОбЬ8АИН8ННЫМ ИНСТИТУТ RАВРНЫХ И С CJI ВАОВ.аН ИМ (_3Уь. А -Ъ " 3 )f OBSERVATIO AD STUDY OF А ARROW STATE I А I -(385)К + SYSTEM АУ б На El-84-25 Berlin-Budapest-Dubna Moscow-Prague-Sofia-Tbllisi-Collaboration
ОбЬ8АИН8ННЫМ ИНСТИТУТ RАВРНЫХ И С CJI ВАОВ.аН ИМ (_3Уь. А -Ъ " 3 )f OBSERVATIO AD STUDY OF А ARROW STATE I А I -(385)К + SYSTEM АУ б На El-84-25 Berlin-Budapest-Dubna Moscow-Prague-Sofia-Tbllisi-Collaboration
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
SPIN STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEON AND POLARIZATION. Charles Y. Prescott Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford CA 94309
 SLAC-PUB-662 September 1994 (TE) SPIN STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEON AND POLARIZATION Charles Y. Prescott Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford CA 9439 Work supported by Department
SLAC-PUB-662 September 1994 (TE) SPIN STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEON AND POLARIZATION Charles Y. Prescott Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford CA 9439 Work supported by Department
E S.Drenska, S.Cht.Mavrodiev ON MODELLING OF HADRON INTERACTIONS
 E2 12844 S.Drenska, S.Cht.Mavrodiev ON MODELLING OF HADRON INTERACTIONS Дренска С, Мавродиев С.Щ. Е2-12844 О моделировании адронных взаимодействии На основе понятия об эффективном радиусе взаимодействия
E2 12844 S.Drenska, S.Cht.Mavrodiev ON MODELLING OF HADRON INTERACTIONS Дренска С, Мавродиев С.Щ. Е2-12844 О моделировании адронных взаимодействии На основе понятия об эффективном радиусе взаимодействия
arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015](/thumbs/94/118739665.jpg) ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and
 Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and 12 C+ 181 Ta Collisions at 4.2 GeV/c per Nucleon* Kh. K. Olimov 1),2) **, Sayyed A. Hadi 3) 1) *** and Mahnaz Q. Haseeb Abstract
Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and 12 C+ 181 Ta Collisions at 4.2 GeV/c per Nucleon* Kh. K. Olimov 1),2) **, Sayyed A. Hadi 3) 1) *** and Mahnaz Q. Haseeb Abstract
67. W.M. Snow et al. (M. Sarsour), NSR collaboration, Parity violating neutron spin rotation in He-4 and H., Nuovo Cim. C035N04, (2012).
 68. A. Adare et al. (M. Sarsour), PHENIX collaboration, J/ψ suppression at forward rapidity in Au + Au collisions at s NN =39 and 62.4 GeV, Phys. Rev. C 86, 064901 (2012). 67. W.M. Snow et al. (M. Sarsour),
68. A. Adare et al. (M. Sarsour), PHENIX collaboration, J/ψ suppression at forward rapidity in Au + Au collisions at s NN =39 and 62.4 GeV, Phys. Rev. C 86, 064901 (2012). 67. W.M. Snow et al. (M. Sarsour),
COMPASS Drell-Yan. Michela Chiosso, University of Torino and INFN. TMD ECT* Workshop April 2016
 COMPASS Drell-Yan Michela Chiosso, University of Torino and INFN TMD ECT* Workshop 11-15 April 2016 Outline Single polarized Drell-Yan at COMPASS DY vs SIDIS at COMPASS Experimental setup Spin-dependent
COMPASS Drell-Yan Michela Chiosso, University of Torino and INFN TMD ECT* Workshop 11-15 April 2016 Outline Single polarized Drell-Yan at COMPASS DY vs SIDIS at COMPASS Experimental setup Spin-dependent
Energy-energy and transversal energy-energy correlations in e + e and pp collisions
 Energy-energy and transversal energy-energy correlations in e + e and pp collisions A. Ali, 1, E. A. Kuraev, 2, 1 DESY, Hamburg, Germany 2 JINR, BLTP, Dubna, Moscow region, Russia July 14, 2013 A. Ali,
Energy-energy and transversal energy-energy correlations in e + e and pp collisions A. Ali, 1, E. A. Kuraev, 2, 1 DESY, Hamburg, Germany 2 JINR, BLTP, Dubna, Moscow region, Russia July 14, 2013 A. Ali,
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
Part II Particle and Nuclear Physics Examples Sheet 1
 T. Potter Lent/Easter Terms 2017 Part II Particle and Nuclear Physics Examples Sheet 1 Matter and Forces 1. (A) Explain the meaning of the terms quark, lepton, hadron, nucleus and boson as used in the
T. Potter Lent/Easter Terms 2017 Part II Particle and Nuclear Physics Examples Sheet 1 Matter and Forces 1. (A) Explain the meaning of the terms quark, lepton, hadron, nucleus and boson as used in the
2. HEAVY QUARK PRODUCTION
 2. HEAVY QUARK PRODUCTION In this chapter a brief overview of the theoretical and experimental knowledge of heavy quark production is given. In particular the production of open beauty and J/ψ in hadronic
2. HEAVY QUARK PRODUCTION In this chapter a brief overview of the theoretical and experimental knowledge of heavy quark production is given. In particular the production of open beauty and J/ψ in hadronic
J.Bell, C.T.Coffin, B.P.Roe, A.A.Seidl, D.Sinclair, E.Wang (University of Michigan,Ann Arbon, Michigan USA)
 I N S T I T U T E FOR HIGH ENERGY P H Y S I C S И В Э 81-в5 Н V.V.Ammosov, A.G.Denisov, P.F.Ermolov, G.S.Gapienko, V.A.Gapienko, V.I.Klyukhin, V.I.Koreshev, P.V.Pitukhin, V.I.Sirotenko, E.A.Slobodyuk,
I N S T I T U T E FOR HIGH ENERGY P H Y S I C S И В Э 81-в5 Н V.V.Ammosov, A.G.Denisov, P.F.Ermolov, G.S.Gapienko, V.A.Gapienko, V.I.Klyukhin, V.I.Koreshev, P.V.Pitukhin, V.I.Sirotenko, E.A.Slobodyuk,
STRUCTURE FUNCTIONS AND CHARGE RATIOS IN MUON NUCLEON SCATTERING" University of California Santa Cruz, California
 SLACPUB1965 U. C. S. C. 7663 June 1977 (T/E) STRUCTURE FUNCTIONS AND CHARGE RATIOS IN MUON NUCLEON SCATTERING" C. de1 Papa,? D. Dorfan, S.M. Flat&, C.A. Heusch B. Lieberman, + H. IYIeyer,ttt L. Moss, T.
SLACPUB1965 U. C. S. C. 7663 June 1977 (T/E) STRUCTURE FUNCTIONS AND CHARGE RATIOS IN MUON NUCLEON SCATTERING" C. de1 Papa,? D. Dorfan, S.M. Flat&, C.A. Heusch B. Lieberman, + H. IYIeyer,ttt L. Moss, T.
A brief history of accelerators, detectors and experiments: (See Chapter 14 and Appendix H in Rolnick.)
 Physics 557 Lecture 7 A brief history of accelerators, detectors and experiments: (See Chapter 14 and Appendix H in Rolnick.) First came the study of the debris from cosmic rays (the God-given particle
Physics 557 Lecture 7 A brief history of accelerators, detectors and experiments: (See Chapter 14 and Appendix H in Rolnick.) First came the study of the debris from cosmic rays (the God-given particle
Quark model. Jan 30, 2006 Lecture 8 1
 Quark model Jan 30, 2006 Lecture 8 1 Quark model of hadrons!!!! Developed long before QCD was recognized as the appropriate quantum field theory of the strong interactions Postulate that 1.! All baryons
Quark model Jan 30, 2006 Lecture 8 1 Quark model of hadrons!!!! Developed long before QCD was recognized as the appropriate quantum field theory of the strong interactions Postulate that 1.! All baryons
Nucleon Valence Quark Structure
 Nucleon Valence Quark Structure Z.-E. Meziani, S. Kuhn, O. Rondon, W. Melnitchouk Physics Motivation Nucleon spin and flavor structure High-x quark distributions Spin-flavor separation Moments of structure
Nucleon Valence Quark Structure Z.-E. Meziani, S. Kuhn, O. Rondon, W. Melnitchouk Physics Motivation Nucleon spin and flavor structure High-x quark distributions Spin-flavor separation Moments of structure
Math-Net.Ru All Russian mathematical portal
 Math-Net.Ru All Russian mathematical portal U. V. Linnik, On the representation of large numbers as sums of seven cubes, Rec. Math. [Mat. Sbornik] N.S., 1943, Volume 12(54), Number 2, 218 224 Use of the
Math-Net.Ru All Russian mathematical portal U. V. Linnik, On the representation of large numbers as sums of seven cubes, Rec. Math. [Mat. Sbornik] N.S., 1943, Volume 12(54), Number 2, 218 224 Use of the
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 10 Nov 1997
 E2 97 325 November 1997 Charmed sea contribution to the inclusive hadroproduction of the mesons with open charm in the Quark Gluon String Model G.H.Arakelyan 1 arxiv:hep-ph/9711276v1 10 Nov 1997 Joint
E2 97 325 November 1997 Charmed sea contribution to the inclusive hadroproduction of the mesons with open charm in the Quark Gluon String Model G.H.Arakelyan 1 arxiv:hep-ph/9711276v1 10 Nov 1997 Joint
High Energy Physics. Lecture 9. Deep Inelastic Scattering Scaling Violation. HEP Lecture 9 1
 High Energy Physics Lecture 9 Deep Inelastic Scattering Scaling Violation HEP Lecture 9 1 Deep Inelastic Scattering: The reaction equation of DIS is written e+ p e+ X where X is a system of outgoing hadrons
High Energy Physics Lecture 9 Deep Inelastic Scattering Scaling Violation HEP Lecture 9 1 Deep Inelastic Scattering: The reaction equation of DIS is written e+ p e+ X where X is a system of outgoing hadrons
Comparison of experimental and theoretical results to define centrality of heavy ion collisions. 1. Introduction.
 Oral talk for the 24 th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids (ICNTS) Bologna, Italy, 0-05 September 2008 and submitted in Radiation Measurements with Manuscript Number: RADMEAS-D-08-00227R
Oral talk for the 24 th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids (ICNTS) Bologna, Italy, 0-05 September 2008 and submitted in Radiation Measurements with Manuscript Number: RADMEAS-D-08-00227R
Review of collective flow at RHIC and LHC
 Review of collective flow at RHIC and LHC Jaap Onderwaater 29 November 2012 J. Onderwaater (EMMI,GSI) Collective flow 29 November 2012 1 / 37 Heavy ion collision stages Outline Heavy ion collisions and
Review of collective flow at RHIC and LHC Jaap Onderwaater 29 November 2012 J. Onderwaater (EMMI,GSI) Collective flow 29 November 2012 1 / 37 Heavy ion collision stages Outline Heavy ion collisions and
CUMULATIVE PARTICLE PRODUCTION IN FERMILAB EXPERIMENT E665*
 SLAC-PUB-5291 June 1990 E CUMULATIVE PARTICLE PRODUCTION IN FERMILAB EXPERIMENT E665* S. Shuvalov Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford, California 94309 and Institute of Theoretical
SLAC-PUB-5291 June 1990 E CUMULATIVE PARTICLE PRODUCTION IN FERMILAB EXPERIMENT E665* S. Shuvalov Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford, California 94309 and Institute of Theoretical
QCD at hadron colliders
 QCD at hadron colliders This will be a brief experimentalist s view, with a concentration on the two hadron-hadron colliders mentioned in the previous talk If you want a good reference book for graduate
QCD at hadron colliders This will be a brief experimentalist s view, with a concentration on the two hadron-hadron colliders mentioned in the previous talk If you want a good reference book for graduate
Heavy quark production in e + e - & pp collisions
 Heavy quark production in e + e - & pp collisions Seminar talk by Bernhard Maaß 12. Dezember 2013 IKP TU Darmstadt Bernhard Maaß 1 Outline I. Introduction to heavy quark production II. Producing quarks
Heavy quark production in e + e - & pp collisions Seminar talk by Bernhard Maaß 12. Dezember 2013 IKP TU Darmstadt Bernhard Maaß 1 Outline I. Introduction to heavy quark production II. Producing quarks
Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector
 Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector Martin Spousta for the ATLAS Collaboration Charles University in Prague DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3204/desy-proc-2014-04/275 Measurements of soft and hard
Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector Martin Spousta for the ATLAS Collaboration Charles University in Prague DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3204/desy-proc-2014-04/275 Measurements of soft and hard
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 Q1. (a) The K meson has strangeness 1. State the quark composition of a meson... State the baryon number of the K meson... (iii) What is the quark composition of the K meson?.... The figure below shows
Q1. (a) The K meson has strangeness 1. State the quark composition of a meson... State the baryon number of the K meson... (iii) What is the quark composition of the K meson?.... The figure below shows
Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions
 Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Universita di Torino and INFN Torino * The selection criteria of the results presented here are (to some
Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Universita di Torino and INFN Torino * The selection criteria of the results presented here are (to some
E THE PION FORM FACTOR WITH GENERALIZED p -DOMINANCE
 E2 7508 S.Dubnicka, V.A.Meshcheryakov THE PION FORM FACTOR WITH GENERALIZED p -DOMINANCE 1973 г Е2-7508 S.Dubnifcka,* V.A.Meshcheryakov THE PION FORM FACTOR WITH GENERALIZED p -DOMINANCE Submitted! to
E2 7508 S.Dubnicka, V.A.Meshcheryakov THE PION FORM FACTOR WITH GENERALIZED p -DOMINANCE 1973 г Е2-7508 S.Dubnifcka,* V.A.Meshcheryakov THE PION FORM FACTOR WITH GENERALIZED p -DOMINANCE Submitted! to
& Λ Production in ALICE
 Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
Journal of Physics: Conference eries OPEN ACCE Related content K & Λ Production in ALICE - trangeness production in ALICE Domenico Elia and the ALICE Collaboration o cite this article: Luke Hanratty and
COALESCENCE MODEL PAULI QUENCHING IN HIGH-ENERGY HEAVY-ION COLLISIONS
 сообщенин объеаин е. нноrо ИНСТИТУТа RА8РНЫХ ИСС18АОВ8ИИI АУбна /f.j,.--!' E-8-IOI K.K.Gudima J, G.Ropke, H.Schulz з, V.D.Toneev ТНЕ AND ТНЕ COALESCENCE MODEL PAULI QUENCHING IN HIGH-ENERGY HEAVY-ION COLLISIONS
сообщенин объеаин е. нноrо ИНСТИТУТа RА8РНЫХ ИСС18АОВ8ИИI АУбна /f.j,.--!' E-8-IOI K.K.Gudima J, G.Ropke, H.Schulz з, V.D.Toneev ТНЕ AND ТНЕ COALESCENCE MODEL PAULI QUENCHING IN HIGH-ENERGY HEAVY-ION COLLISIONS
Measurement of light mesons at RHIC by the PHENIX experiment
 Eur. Phys. J. C (2009) 61: 835 840 DOI 10.1140/epjc/s10052-009-0879-4 Regular Article - Experimental Physics Measurement of light mesons at RHIC by the PHENIX experiment M. Naglis a for the PHENIX Collaboration
Eur. Phys. J. C (2009) 61: 835 840 DOI 10.1140/epjc/s10052-009-0879-4 Regular Article - Experimental Physics Measurement of light mesons at RHIC by the PHENIX experiment M. Naglis a for the PHENIX Collaboration
Collider overview and kinematics
 1 Collider overview and kinematics QCD studies at colliders 2 ee - ep - pp QCD collider studies Short Long distance Q: large momentum scale PEP, PETRA, Cornell, LEP, SLD, NLC SLAC, FNAL, CERN, HERA, erhic
1 Collider overview and kinematics QCD studies at colliders 2 ee - ep - pp QCD collider studies Short Long distance Q: large momentum scale PEP, PETRA, Cornell, LEP, SLD, NLC SLAC, FNAL, CERN, HERA, erhic
Physics at Hadron Colliders
 Physics at Hadron Colliders Part 2 Standard Model Physics Test of Quantum Chromodynamics - Jet production - W/Z production - Production of Top quarks Precision measurements -W mass - Top-quark mass QCD
Physics at Hadron Colliders Part 2 Standard Model Physics Test of Quantum Chromodynamics - Jet production - W/Z production - Production of Top quarks Precision measurements -W mass - Top-quark mass QCD
Lecture 9. Isospin The quark model
 Lecture 9 Isospin The quark model There is one more symmetry that applies to strong interactions. isospin or isotopic spin It was useful in formulation of the quark picture of known particles. We can consider
Lecture 9 Isospin The quark model There is one more symmetry that applies to strong interactions. isospin or isotopic spin It was useful in formulation of the quark picture of known particles. We can consider
LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI SIS-Pubblicazioni
 LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI SIS-Pubblicazioni LNF-06/22 (P) 29 August 2006 HADRON PROPERTIES IN THE NUCLEAR MEDIUM THE PANDA PROGRAM WITH pa REACTIONS Olaf N. Hartmann INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di
LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI SIS-Pubblicazioni LNF-06/22 (P) 29 August 2006 HADRON PROPERTIES IN THE NUCLEAR MEDIUM THE PANDA PROGRAM WITH pa REACTIONS Olaf N. Hartmann INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di
ISR physics at BABAR
 SLAC-PUB-499 ISR physics at BABAR S.Serednyakov, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract A method of measuring e+e- annihilation cross sections at low energy s < 5 GeV, using
SLAC-PUB-499 ISR physics at BABAR S.Serednyakov, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract A method of measuring e+e- annihilation cross sections at low energy s < 5 GeV, using
Nucleon polarised parton distribution functions
 Nucleon polarised parton distribution functions Gerhard K. Mallot CERN, 111 Geneva 3, Switzerland Abstract An introduction to the present status of spin-dependent parton distribution functions is given.
Nucleon polarised parton distribution functions Gerhard K. Mallot CERN, 111 Geneva 3, Switzerland Abstract An introduction to the present status of spin-dependent parton distribution functions is given.
FUTURE SPIN EXPERIMENTS AT SLAC
 SLAC-PUB-9658 February 2003 FUTURE SPIN EXPERIMENTS AT SLAC Stephen Rock for the Real Photon Collaboration University of Mass, Amherst MA 01003 Abstract. A series of three photo-production experiments
SLAC-PUB-9658 February 2003 FUTURE SPIN EXPERIMENTS AT SLAC Stephen Rock for the Real Photon Collaboration University of Mass, Amherst MA 01003 Abstract. A series of three photo-production experiments
Inclusive distributions at the LHC as predicted from the DPMJET-III model with chain fusion
 Inclusive distributions at the LHC as predicted from the DPMJET-III model with chain fusion F.Bopp, R.Engel, J.Ranft and S.Roesler () DPMJET III () Chain fusion in DPMJET III (3) dn/dη cm distributions
Inclusive distributions at the LHC as predicted from the DPMJET-III model with chain fusion F.Bopp, R.Engel, J.Ranft and S.Roesler () DPMJET III () Chain fusion in DPMJET III (3) dn/dη cm distributions
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics
 An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics W. N. COTTINGHAM and D. A. GREENWOOD Ж CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface. page xiii Notation xv 1 The particle physicist's view of Nature
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics W. N. COTTINGHAM and D. A. GREENWOOD Ж CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface. page xiii Notation xv 1 The particle physicist's view of Nature
Puzzles of multiplicity
 Puzzles of multiplicity Elena Kokoulina, Vladimir Nikitin LHEP JINR, Dubna, Russia Introduction High energy physics began with registration of usual charged hadrons: protons and pions. Later the number
Puzzles of multiplicity Elena Kokoulina, Vladimir Nikitin LHEP JINR, Dubna, Russia Introduction High energy physics began with registration of usual charged hadrons: protons and pions. Later the number
Elementary Particle Physics Glossary. Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016
 Elementary Particle Physics Glossary Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016 1 Contents 1 Terms A-C 5 1.1 Accelerator.............................. 5 1.2 Annihilation..............................
Elementary Particle Physics Glossary Course organiser: Dr Marcella Bona February 9, 2016 1 Contents 1 Terms A-C 5 1.1 Accelerator.............................. 5 1.2 Annihilation..............................
The Development of Particle Physics. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.:
 The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 4531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk The structure of the nucleon Electron - nucleon elastic scattering Rutherford, Mott cross-sections
The Development of Particle Physics Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev E45, Tel.: 0114 4531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk The structure of the nucleon Electron - nucleon elastic scattering Rutherford, Mott cross-sections
Dynamics of Anti-Proton Protons and Anti-Proton Nucleus Reactions
 NUCLEA THEO, Vol. 35 (06) eds. M. Gaidarov, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Dynamics of Anti-Proton Protons and Anti-Proton Nucleus eactions A. Galoyan, A. ibon, V. Uzhinsky 3 VBLHEP, JIN, Dubna 4980, ussia
NUCLEA THEO, Vol. 35 (06) eds. M. Gaidarov, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Dynamics of Anti-Proton Protons and Anti-Proton Nucleus eactions A. Galoyan, A. ibon, V. Uzhinsky 3 VBLHEP, JIN, Dubna 4980, ussia
At this time the quark model consisted of three particles, the properties of which are given in the table.
 *1 In 1961 Murray Gell-Mann predicted the existence of a new particle called an omega (Ω) minus. It was subsequently discovered in 1964. At this time the quark model consisted of three particles, the properties
*1 In 1961 Murray Gell-Mann predicted the existence of a new particle called an omega (Ω) minus. It was subsequently discovered in 1964. At this time the quark model consisted of three particles, the properties
St anfo rd L in ear A ccele rat o r Cent e r
 SLAC-PUB-7212 July 1996 NUCLEAR EFFECTS AT HERA STANLEY J. BRODSKY St anfo rd L in ear A ccele rat o r Cent e r St anfo rd University, St anfo rd, California 94 309 To appear in the Proceedings of the
SLAC-PUB-7212 July 1996 NUCLEAR EFFECTS AT HERA STANLEY J. BRODSKY St anfo rd L in ear A ccele rat o r Cent e r St anfo rd University, St anfo rd, California 94 309 To appear in the Proceedings of the
Particle Physics Outline the concepts of particle production and annihilation and apply the conservation laws to these processes.
 Particle Physics 12.3.1 Outline the concept of antiparticles and give examples 12.3.2 Outline the concepts of particle production and annihilation and apply the conservation laws to these processes. Every
Particle Physics 12.3.1 Outline the concept of antiparticles and give examples 12.3.2 Outline the concepts of particle production and annihilation and apply the conservation laws to these processes. Every
Analysis of a Multi-Muon Signal at Collider and Fixed-Target Experiments
 Analysis of a Multi-Muon Signal at Collider and Fixed-Target Experiments In Collaboration with Manuel Drees August 23rd, 2010 SUSY10 1 Introduction 2 Ghost Events 3 Simulation 4 Outlook and Summary Introduction
Analysis of a Multi-Muon Signal at Collider and Fixed-Target Experiments In Collaboration with Manuel Drees August 23rd, 2010 SUSY10 1 Introduction 2 Ghost Events 3 Simulation 4 Outlook and Summary Introduction
Flavour Physics and CP Violation (FPCP) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA May 16, 2002
 NEW RESULTS ON MIXING FROM LEP STEPHEN ARMSTRONG European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) EP Division Geneva, Switzerland Flavour Physics and CP Violation (FPCP) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
NEW RESULTS ON MIXING FROM LEP STEPHEN ARMSTRONG European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) EP Division Geneva, Switzerland Flavour Physics and CP Violation (FPCP) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
Overview of recent HERMES results
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Overview of recent HERMES results To cite this article: Hrachya Marukyan and 216 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 1238 View the article online for updates
1 The pion bump in the gamma reay flux
 1 The pion bump in the gamma reay flux Calculation of the gamma ray spectrum generated by an hadronic mechanism (that is by π decay). A pion of energy E π generated a flat spectrum between kinematical
1 The pion bump in the gamma reay flux Calculation of the gamma ray spectrum generated by an hadronic mechanism (that is by π decay). A pion of energy E π generated a flat spectrum between kinematical
Lecture 2: The First Second origin of neutrons and protons
 Lecture 2: The First Second origin of neutrons and protons Hot Big Bang Expanding and cooling Soup of free particles + anti-particles Symmetry breaking Soup of free quarks Quarks confined into neutrons
Lecture 2: The First Second origin of neutrons and protons Hot Big Bang Expanding and cooling Soup of free particles + anti-particles Symmetry breaking Soup of free quarks Quarks confined into neutrons
HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT. Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF
 98 7 HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT J. J. VAN HUNEN (for the HERMES collaboration) Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF Postbus 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
98 7 HADRONIZATION IN A NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT J. J. VAN HUNEN (for the HERMES collaboration) Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-Energiefysica, NIKHEF Postbus 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam, The Netherlands
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Neutrino Energy Reconstruction Methods Using Electron Scattering Data. Afroditi Papadopoulou Pre-conference, EINN /29/17
 Neutrino Energy Reconstruction Methods Using Electron Scattering Data Afroditi Papadopoulou Pre-conference, EINN 2017 10/29/17 Outline Nuclear Physics and Neutrino Oscillations. Outstanding Challenges
Neutrino Energy Reconstruction Methods Using Electron Scattering Data Afroditi Papadopoulou Pre-conference, EINN 2017 10/29/17 Outline Nuclear Physics and Neutrino Oscillations. Outstanding Challenges
The Detector Design of the Jefferson Lab EIC
 The Detector Design of the Jefferson Lab EIC Jefferson Lab E-mail: mdiefent@jlab.org The Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) is envisioned as the next-generation U.S. facility to study quarks and gluons in strongly
The Detector Design of the Jefferson Lab EIC Jefferson Lab E-mail: mdiefent@jlab.org The Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) is envisioned as the next-generation U.S. facility to study quarks and gluons in strongly
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W
 A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
Studying Evolution with Jets at STAR. Renee Fatemi University of Kentucky May 28 th, 2015
 Studying Evolution with Jets at STAR Renee Fatemi University of Kentucky May 28 th, 2015 Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider Absolute Polarimeter (H jet) RHIC pc Polarimeters Siberian Snakes PHOBOS PHENIX
Studying Evolution with Jets at STAR Renee Fatemi University of Kentucky May 28 th, 2015 Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider Absolute Polarimeter (H jet) RHIC pc Polarimeters Siberian Snakes PHOBOS PHENIX
Decay rates and Cross section. Ashfaq Ahmad National Centre for Physics
 Decay rates and Cross section Ashfaq Ahmad National Centre for Physics 11/17/2014 Ashfaq Ahmad 2 Outlines Introduction Basics variables used in Exp. HEP Analysis Decay rates and Cross section calculations
Decay rates and Cross section Ashfaq Ahmad National Centre for Physics 11/17/2014 Ashfaq Ahmad 2 Outlines Introduction Basics variables used in Exp. HEP Analysis Decay rates and Cross section calculations
176 5 t h Fl oo r. 337 P o ly me r Ma te ri al s
 A g la di ou s F. L. 462 E l ec tr on ic D ev el op me nt A i ng er A.W.S. 371 C. A. M. A l ex an de r 236 A d mi ni st ra ti on R. H. (M rs ) A n dr ew s P. V. 326 O p ti ca l Tr an sm is si on A p ps
A g la di ou s F. L. 462 E l ec tr on ic D ev el op me nt A i ng er A.W.S. 371 C. A. M. A l ex an de r 236 A d mi ni st ra ti on R. H. (M rs ) A n dr ew s P. V. 326 O p ti ca l Tr an sm is si on A p ps
Study of the MPD detector performance in pp collisions at NICA
 Study of the MPD detector performance in pp collisions at NICA Katherin Shtejer Díaz On behalf of the MPD Collaboration VBLHEP, JINR, Russia NICA Days 2017, November 6-10 Introduction Phase diagram of
Study of the MPD detector performance in pp collisions at NICA Katherin Shtejer Díaz On behalf of the MPD Collaboration VBLHEP, JINR, Russia NICA Days 2017, November 6-10 Introduction Phase diagram of
The Quark Parton Model
 The Quark Parton Model Quark Model Pseudoscalar J P = 0 Mesons Vector J P = 1 Mesons Meson Masses J P = 3 /2 + Baryons J P = ½ + Baryons Resonances Resonance Detection Discovery of the ω meson Dalitz Plots
The Quark Parton Model Quark Model Pseudoscalar J P = 0 Mesons Vector J P = 1 Mesons Meson Masses J P = 3 /2 + Baryons J P = ½ + Baryons Resonances Resonance Detection Discovery of the ω meson Dalitz Plots
High-p T Neutral Pion Production in Heavy Ion Collisions at SPS and RHIC
 High- Neutral Pion Production in Heavy Ion Collisions at SPS and RHIC K. Reygers for the WA98 and the PHENIX collaboration Institut für Kernphysik der Universität Münster Wilhelm-Klemm-Str. 9, D-4849 Münster,
High- Neutral Pion Production in Heavy Ion Collisions at SPS and RHIC K. Reygers for the WA98 and the PHENIX collaboration Institut für Kernphysik der Universität Münster Wilhelm-Klemm-Str. 9, D-4849 Münster,
Study of charm fragmentation in e + e annihilation and ep scattering
 Study of charm fragmentation in e + e annihilation and ep scattering - Summer Student Report - by Thomas Lübbert H1 Collaboration at DESY Advisor: Co-Advisor: Dr. Günter Grindhammer Andrej Liptaj September
Study of charm fragmentation in e + e annihilation and ep scattering - Summer Student Report - by Thomas Lübbert H1 Collaboration at DESY Advisor: Co-Advisor: Dr. Günter Grindhammer Andrej Liptaj September
Measurements of charm and beauty proton structure functions F2 c c and F2 b b at HERA
 Measurements of charm and beauty proton structure functions F c c and F b b at HERA Vladimir Chekelian MPI for Physics, Germany E-mail: shekeln@mail.desy.de Inclusive charm and beauty production is studied
Measurements of charm and beauty proton structure functions F c c and F b b at HERA Vladimir Chekelian MPI for Physics, Germany E-mail: shekeln@mail.desy.de Inclusive charm and beauty production is studied
NUCLEON FORM FACTORS IN A RELATIVISTIC QUARK MODEL* Abstract We demonstrate that a relativistic constituent-quark
 SLAC-PUB-5968 November1992 CT).-. NUCLEON FORM FACTORS IN A RELATIVISTIC QUARK MODEL* Felix Schlumpf StanfonE Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94309 Abstract We demonstrate
SLAC-PUB-5968 November1992 CT).-. NUCLEON FORM FACTORS IN A RELATIVISTIC QUARK MODEL* Felix Schlumpf StanfonE Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94309 Abstract We demonstrate
On the Distribution o f Vertex-Degrees in a Strata o f a Random Recursive Tree. Marian D O N D A J E W S K I and Jerzy S Z Y M A N S K I
 BULLETIN DE L ACADÉMIE POLONAISE DES SCIENCES Série des sciences mathématiques Vol. XXX, No. 5-6, 982 COMBINATORICS On the Distribution o f Vertex-Degrees in a Strata o f a Rom Recursive Tree by Marian
BULLETIN DE L ACADÉMIE POLONAISE DES SCIENCES Série des sciences mathématiques Vol. XXX, No. 5-6, 982 COMBINATORICS On the Distribution o f Vertex-Degrees in a Strata o f a Rom Recursive Tree by Marian
Nucleon Spin. Tyler Corbett
 Nucleon Spin Tyler Corbett Abstract: In 1988 the European Muon Collaboration showed that the quark contribution to spin only accounts for 20-30 percent of the nucleon spin; The "naive quark parton model
Nucleon Spin Tyler Corbett Abstract: In 1988 the European Muon Collaboration showed that the quark contribution to spin only accounts for 20-30 percent of the nucleon spin; The "naive quark parton model
Measurement of Collins Asymmetries in the inclusive production of hadron pairs
 Measurement of Collins Asymmetries in the inclusive production of hadron pairs INFN-University of Ferrara For the BaBar Collaboration SIF-Società Italiana di Fisica XCVI Congresso Nazionale Bologna, 20-24
Measurement of Collins Asymmetries in the inclusive production of hadron pairs INFN-University of Ferrara For the BaBar Collaboration SIF-Società Italiana di Fisica XCVI Congresso Nazionale Bologna, 20-24
Physique des Particules Avancées 2
 Physique des Particules Avancées Interactions Fortes et Interactions Faibles Leçon 6 Les collisions p p (http://dpnc.unige.ch/~bravar/ppa/l6) enseignant Alessandro Bravar Alessandro.Bravar@unige.ch tél.:
Physique des Particules Avancées Interactions Fortes et Interactions Faibles Leçon 6 Les collisions p p (http://dpnc.unige.ch/~bravar/ppa/l6) enseignant Alessandro Bravar Alessandro.Bravar@unige.ch tél.:
Flavor Asymmetry of the Nucleon Sea and W-Boson Production*
 Flavor Asymmetry of the Nucleon Sea and W-Boson Production* Department of Physics University of Illinois 7 December 2012 *R. Yang, J.C. Peng, M. Grosse-Perdekamp, Phys. Lett. B 680 (2009) 231-234 What
Flavor Asymmetry of the Nucleon Sea and W-Boson Production* Department of Physics University of Illinois 7 December 2012 *R. Yang, J.C. Peng, M. Grosse-Perdekamp, Phys. Lett. B 680 (2009) 231-234 What
Noncentral collisions
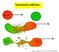 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Analysis of fixed target collisions with the STAR detector
 Analysis of fixed target collisions with the STAR detector Brooke Haag for the STAR Collaboration Hartnell College / University of California, Davis Presented at the Meeting of the California Section of
Analysis of fixed target collisions with the STAR detector Brooke Haag for the STAR Collaboration Hartnell College / University of California, Davis Presented at the Meeting of the California Section of
Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR
 Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR Katarzyna Kowalik for the STAR Collaboration Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720 Abstract. This contribution
Longitudinal Double Spin Asymmetry in Inclusive Jet Production at STAR Katarzyna Kowalik for the STAR Collaboration Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720 Abstract. This contribution
Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV
 Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV Samantha G Brovko June 14, 2011 1 INTRODUCTION In ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions a partonic state of
Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV Samantha G Brovko June 14, 2011 1 INTRODUCTION In ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions a partonic state of
The estimation of production rates of π + K, π K + and π + π atoms in proton-nucleus interactions at 450 GeV/c
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH DIRAC Note 55 December 6, 5 The estimation of production rates of π + K, π K + and π + π atoms in protonnucleus interactions at 5 GeV/c O.Gorchakov, L.Nemenov
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH DIRAC Note 55 December 6, 5 The estimation of production rates of π + K, π K + and π + π atoms in protonnucleus interactions at 5 GeV/c O.Gorchakov, L.Nemenov
Structure of Hadrons and the parton model
 Structure of Hadrons and the parton model Ben Kilminster University of Zürich - Physik Institut Phenomenology of Particle Physics - PPP2 Lecture: 10/3/2015 Topics in this lecture How do we study the structure
Structure of Hadrons and the parton model Ben Kilminster University of Zürich - Physik Institut Phenomenology of Particle Physics - PPP2 Lecture: 10/3/2015 Topics in this lecture How do we study the structure

 ;
;