DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME OR STUDENT NUMBER ON ANY SHEET!
|
|
|
- Harvey Brendan Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 tatistical Mechanics ubject Exam, Wednesday, May 3, 2017 DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME OR TUDENT NUMBER ON ANY HEET! a ( b c) = b( a c) c( a b), a ( b c) = b ( c a) = c ( a b), ( a b) ( c d) = ( a c)( b d) ( a d)( b c), ( ψ) = 0, ( a) = 0, ( a) = ( a) 2 a, (ψ a) = a ψ + ψ a, (ψ a) = ψ a + ψ a, ( a b) = ( a ) b + ( b ) a + a ( b) + b ( a), ( a b) = b ( a) a ( b), ( a b) = a( b) b( a) + ( b ) a ( a ) b, r = 3, r = 0, ˆr = 2/r, ˆr = 0, ( a )ˆr = 1 r [ a ˆr( a ˆr)] = a r. V d 3 r A = V d 3 r ψ = V d 3 r A = V d 3 r (ϕ 2 ψ + ϕ ψ) = d 3 r (ϕ 2 ψ ψ 2 ϕ) = V ( A) d = d ψ = C 2 = 2 r + 2 r r d A, ψ d, d A, ϕ d ψ, (ϕ ψ ψ ϕ) d, d l A, d l ψ. 2 = ρ ρ ρ m2 r 2, ( ) 1 2 = δ( r). r l(l + 1) r 2,
2 L α β = γv γ 0 0 γ γv Fαβ = 0 Ex Ey Ez Ex 0 Bz By Ey Bz 0 Bx Ez By Bx 0, F αβ = 0 Ex Ey Ez Ex 0 Bz By Ey Bz 0 Bx Ez By Bx 0. m d dτ uα = ef αβ uβ, d p dt = e E + e v B, ωc = eb γm, E = J 0, ( B) t E = J, B = 0, t B + E = 0, αf αβ = J β, α F αβ = 0, e 2 = ħc , T αβ = π α β ϕ g αβ L, π α L ( αϕ), T 00 = 1 8π (E2 + B 2 ), T 0i = 1 ϵ ijkejbk, T ij = T i j = 1 8π (δ ij(e 2 + B 2 ) 2EiEj 2BiBj), E = A 0 t A = Φ t A, B = A. Pl(cos θ) = Y0,0 = Y1,±1 = Y2,±1 = 2l + 1 Y lm=0(θ), 1, Y1,0 = 3 cos θ, 3 8π sin θei±ϕ, Y2,0 = 15 8π sin θ cos θe±iϕ, Y2,±2 = 5 16π (3 cos2 θ 1), 15 32π sin2 θe ±2iϕ, Yl m(θ, ϕ) = ( 1) m Y lm(θ, ϕ), δll δ mm = dω Yl,m(θ, ϕ)yl,m (θ, ϕ), P0(x) = 1, P1(x) = x, P2(x) = 1 2 (3x2 1), P3(x) = 1 2 (5x3 3x), Pl(x = 1) = 1, (3D) Φ = lm 1 (2D) Φ = A0 ln(ρ) + m Φ = A0J0 = m Φ = q r E 1 = r Φ(r, θ, ϕ) = lm q22 = q21 = q20 = Qij dx Pl(x)Pl (x) = 2 1 2l + 1 δ ll, ( A lmr l + Blmr l 1) Ylm(θ, ϕ)e imϕ, p r + r 3 + m 15 32π 3 p + 3 p r 15 8π 5 16π e imϕ ( Amρ m + Bmρ m), e imϕ (AmJm(kρ) + BmNm(kρ)) e ±kz, 5r 3 q 2m(r)Y2m(θ, ϕ), r 5 r +, (2l + 1)r l+1 q lm(r)ylm(θ, ϕ), d 3 r ρ( r)(x iy) 2 = d 3 r ρ( r)(x iy)z = 5 d 3 r ρ( r)(3z 2 r 2 ) = 16π Q 33, d 3 r (3rirj r 2 δij)ρ( r), π (Q 11 2iQ12 Q22), 15 72π (Q 13 iq23), U = qφ0 p E 1 6 Q ij iej,
3 2 A α = J α, m = 1 d 3 r r J 2 = I 2 B m = r r ( m r), r 5 eħ µe = ge 2me, r d l, U = ( µ N µe) r 3 3( µ N r)( µe r) r 5 8π 3 ( µ N µe)δ 3 ( r) e ( µ N L) mr 3, T00 = 1 ( E 8π 2 + B 2) = a2 i + b2 i 8π T0i = ϵijk = ˆki EjBk = a 2 cos2 ( k r ωt), a 2 cos2 ( k r ωt), T ij = T i j = 1 8π (δ ij(e 2 + B 2 ) 2EiEj 2BiBj). = 1 { } a 2 δ ij aiaj bibj cos 2 ( k r ωt), 1 v ωs = ω 1 + v, (T M) Ez = ψ(x, y)e iωt+ikzz, 2 t ψ = (ω 2 k 2 z)ψ, Ψ = 0, E t(x, y) = B t(x, y) = ikz (ω 2 k z) 2 e iωt+ikzz tψ(x, y), ( ) ω ẑ Et, kz (T E) Bz = ψ(x, y)e iωt+ikzz, (ˆn t)ψ(x, y) = 0, B t(x, y) = E t(x, y) = ikz (ω 2 k z) 2 e iωt+ikzz tψ(x, y), ( ) ω kz ẑ Bt. A α (x) = E = e { B = ˆn E. d 4 x 1 x x J α (x )δ(x0 x 0 x x ), ˆn [(ˆn β) β] (1 β ˆn) 3 x }, P = 2e2 3c β 2 (Non.Rel.), dp dω = e 2 (1 β ˆn) 6 (ˆn β) β) 2, P = 2 3c e2 γ 6 [ β2 β β 2 ], dp dω = e 2 (1 β cos θ) 5 β 2 sin 2 θ (linear), dp P = 2e2 β 2 3c γ 6 (linear), dω = e 2 (1 βnβ) 5 β 2 ( (1 βnβ) 2 (1 β 2 )n 2 r ) (circular), P = 2 3c e2 β2 γ 4 (circular). dp dω = 1 8π ω4 ˆn p 2, P = ω4 3 p 2, (Thomson) σ = 8πe4 3m 2, λ = ħω λ m (1 cos θ s). electron ± muon ± proton ± neutron ±
4 LONG ANWER ECTION 1. (15 pts) Consider an infinitely long thin cylindrical shell of radius R oriented along the z axis. The shell has a surface charge density, σ = σ 0 cos ϕ. Find the electric potential at all positions as a function of the transverse radius r = x 2 + y 2 and the azimuthal angleϕ = tan 1 (y/x).
5 Extra workspace for #1
6 -Q a +Q a -Q +Q 2. Consider a set of four charges: +Q at x = a, y = a, z = 0, +Q at x = a, y = a, z = 0, Q at x = a, y = a, z = 0, Q at x = a, y = a, z = 0. (a) (5 pts) For large distances r, the electric potential can be written as Φ( r) = F (θ, ϕ)/r n. What is n? (b) (10 pts) Find F (θ, ϕ), where θ and ϕ are spherical coordinates (defined around the z axis).
7 Extra workspace for #2
8 3. An antenna is designed by circulating a current around a circular loop of radius R with its axis along the z direction. The current has the form I(ϕ, t) = I 0 cos(ωt ϕ), where ϕ denotes is the azimuthal angle of a point on the loop. (a) (5 pts) Find the charge per unit length, λ(ϕ, t). (b) (10 pts) Find the radiated power. (Use dipole approximation)
9 Extra work space for #3
10 4. A rectangular wave guide has transverse dimensions, 0 < x < a and 0 < y < a. For a transverse electric (TE) wave moving along the z axis with wave number k z. (a) (5 pts) Find the frequency of the propagating wave. Choose the solutions with the fewest nodes in the transverse wave function. (b) (10 pts) Find the magnetic field B(x, y, z, t) for this solution. (c) (5 pts) What is the group velocity of the wave?
11 Extra work space for #4
12 HORT ANWER ECTION 5. (3 pts each) Light is emitted from a distant source from early in the universe. Choose >, < or = for each answer than the frequency of the light mea- (a) The initial frequency of the source is sured by a present-day observer. (b) If an observer moves toward the source, the observed frequency will be the frequency measured by a static observer. than 6. (4 pts) In terms of M p /m e (mass of proton to mass of electron) calculate the ratio of the radiative powers P e /P p emitted for a very high-energy circular accelerator of a given radius R that features either electron or proton beams of the same energy and same currents. Note: Magnetic fields would be quite different to hold particles to the same energy and radius. 7. (3 pts each) ally lowpoke measures two events that both occur right in front of her nose separated by a time τ = 1.0 second. Roberto Rapido travels by in his space ship at some speed v. (Circle the correct answers) (a) The difference in the times of the two events Roberto measures, t, will always be positive may be positive or negative depending on v. (b) The distance between the two events measured by Robert will be always < c τ greater or less than c τ depending on v. 8. You wish to solve the following problem using the method of images: A point charge Q is placed far outside a grounded conducting spherical shell of radius R. The position of the charge is x = 0, y = 0, z = A >> R. You are solving for the potential outside the shell. True or false: (4 pts) (a) The image charge is inside the sphere. (b) The potential inside the sphere is constant. (c) The magnitude of the image charge must be less than Q. 9. (5 pts) Which of the following are odd under parity? Circle the answers. (a) A (the vector potential) (b) A 0 (the electric potential) (c) E (the electric field) (d) B (the magnetic field) (e) E B (f) B 2 E 2 (g) E 2 + B 2 (h) E B (i) J A (J is the electric current density)
13 10. Consider a system with non-zero electric and magnetic fields, B = B z ẑ, E = Exˆx, E x > 0, B z > 0, E x > B z. A charged particle is placed at the origin, initially with zero momentum. For each question answer True or False. (6 pts) (a) There exists a reference frame where B = 0. (b) At large times the coordinate x ±. (c) At large times the coordinate y ±. (d) At some parts of the trajectory the particle s momentum p x would be negative. a) R b) c) r 11. (4 pts) Consider the three charge configurations shown above: (a) two point charges +Q separated by R (b) two spheres of radius r < R/2, each with charge +Q uniformly spread throughout the volume, with the centers separated by R (c) two spherical shells of radius r < R/2, each with charge +Q uniformly spread throughout the surface, with the centers separated by R. The work required to move the spheres (or points) from infinity to the separation R is labeled W a, W b and W c for each configuration. Label each statement as true or false. (a) W a > W b (b) W a > W c (c) W b > W c
Electrodynamics Subject Exam Prep Quiz, Tuesday, May 2, 2017
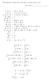 Electodynamics ubject Exam Pep Quiz, Tuesday, May, 017 a ( b c ) b( a c ) c ( a b), a ( b c ) b ( c a ) c ( a b), ( a b) ( c d) ( a c )( b d) ( a d)( b c ), ( ψ) 0, ( a ) 0, ( a ) ( a ) a, (ψ a) a ψ +
Electodynamics ubject Exam Pep Quiz, Tuesday, May, 017 a ( b c ) b( a c ) c ( a b), a ( b c ) b ( c a ) c ( a b), ( a b) ( c d) ( a c )( b d) ( a d)( b c ), ( ψ) 0, ( a ) 0, ( a ) ( a ) a, (ψ a) a ψ +
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electromagnetism Qualifying Examination January 4, 2017 9.00 am - 12.00 pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
FORMULA SHEET FOR QUIZ 2 Exam Date: November 8, 2017
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II November 5, 207 Prof. Alan Guth FORMULA SHEET FOR QUIZ 2 Exam Date: November 8, 207 A few items below are marked
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.07: Electromagnetism II November 5, 207 Prof. Alan Guth FORMULA SHEET FOR QUIZ 2 Exam Date: November 8, 207 A few items below are marked
PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Spring Final Exam Wednesday, 6 May 2009
 Name: PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Spring 2009 Final Exam Wednesday, 6 May 2009 This exam has two parts. Part I has 20 multiple choice questions, worth two points each. Part II consists of six relatively
Name: PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Spring 2009 Final Exam Wednesday, 6 May 2009 This exam has two parts. Part I has 20 multiple choice questions, worth two points each. Part II consists of six relatively
Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics
 Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics April 27, 2010 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 1-5 Electrostatics The behavior of an electrostatic field can be described
Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics April 27, 2010 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 1-5 Electrostatics The behavior of an electrostatic field can be described
Physics 214 Final Exam Solutions Winter 2017
 Physics 14 Final Exam Solutions Winter 017 1 An electron of charge e and mass m moves in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B If the energy loss by radiation is neglected, the orbit is a
Physics 14 Final Exam Solutions Winter 017 1 An electron of charge e and mass m moves in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B If the energy loss by radiation is neglected, the orbit is a
Electrodynamics Exam Solutions
 Electrodynamics Exam Solutions Name: FS 215 Prof. C. Anastasiou Student number: Exercise 1 2 3 4 Total Max. points 15 15 15 15 6 Points Visum 1 Visum 2 The exam lasts 18 minutes. Start every new exercise
Electrodynamics Exam Solutions Name: FS 215 Prof. C. Anastasiou Student number: Exercise 1 2 3 4 Total Max. points 15 15 15 15 6 Points Visum 1 Visum 2 The exam lasts 18 minutes. Start every new exercise
2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice
 2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice These are sample questions of the type of question that will be set in the exam. They haven t been checked the way exam questions are checked so there may
2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice These are sample questions of the type of question that will be set in the exam. They haven t been checked the way exam questions are checked so there may
Problem Set #4: 4.1,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 25th)
 Chapter 4 Multipoles, Dielectrics Problem Set #4: 4.,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 5th 4. Multipole expansion Consider a localized distribution of charges described by ρ(x contained entirely in a sphere of
Chapter 4 Multipoles, Dielectrics Problem Set #4: 4.,4.7,4.9 (Due Monday, March 5th 4. Multipole expansion Consider a localized distribution of charges described by ρ(x contained entirely in a sphere of
r,t r R Z j ³ 0 1 4π² 0 r,t) = 4π
 5.4 Lienard-Wiechert Potential and Consequent Fields 5.4.1 Potential and Fields (chapter 10) Lienard-Wiechert potential In the previous section, we studied the radiation from an electric dipole, a λ/2
5.4 Lienard-Wiechert Potential and Consequent Fields 5.4.1 Potential and Fields (chapter 10) Lienard-Wiechert potential In the previous section, we studied the radiation from an electric dipole, a λ/2
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Solutions Winter 2017
 Physics 14 Midterm Exam Solutions Winter 017 1. A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave, polarized in the ˆx direction, is traveling in the ẑ-direction in a dielectric medium of refractive index n 1.
Physics 14 Midterm Exam Solutions Winter 017 1. A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave, polarized in the ˆx direction, is traveling in the ẑ-direction in a dielectric medium of refractive index n 1.
E & M Qualifier. January 11, To insure that the your work is graded correctly you MUST:
 E & M Qualifier 1 January 11, 2017 To insure that the your work is graded correctly you MUST: 1. use only the blank answer paper provided, 2. use only the reference material supplied (Schaum s Guides),
E & M Qualifier 1 January 11, 2017 To insure that the your work is graded correctly you MUST: 1. use only the blank answer paper provided, 2. use only the reference material supplied (Schaum s Guides),
PHYS 3327 PRELIM 1. Prof. Itai Cohen, Fall 2010 Friday, 10/15/10. Name: Read all of the following information before starting the exam:
 PHYS 3327 PRELIM 1 Prof. Itai Cohen, Fall 2010 Friday, 10/15/10 Name: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Put your name on the exam now. Show all work, clearly and in order,
PHYS 3327 PRELIM 1 Prof. Itai Cohen, Fall 2010 Friday, 10/15/10 Name: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Put your name on the exam now. Show all work, clearly and in order,
Field Theory exam II Solutions
 Field Theory exam II Solutions Problem 1 (a) Consider point charges, one with charge q located at x 1 = (1, 0, 1), and the other one with charge q at x = (1, 0, 1). Compute the multipole moments q lm in
Field Theory exam II Solutions Problem 1 (a) Consider point charges, one with charge q located at x 1 = (1, 0, 1), and the other one with charge q at x = (1, 0, 1). Compute the multipole moments q lm in
NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2018 (8/21/2018) Electricity and Magnetism
 NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2018 (8/21/2018) Electricity and Magnetism You may solve ALL FOUR problems if you choose. The points of the best three problems will be counted towards your final score
NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2018 (8/21/2018) Electricity and Magnetism You may solve ALL FOUR problems if you choose. The points of the best three problems will be counted towards your final score
Electromagnetic Theory I
 Electromagnetic Theory I Final Examination 18 December 2009, 12:30-2:30 pm Instructions: Answer the following 10 questions, each of which is worth 10 points. Explain your reasoning in each case. Use SI
Electromagnetic Theory I Final Examination 18 December 2009, 12:30-2:30 pm Instructions: Answer the following 10 questions, each of which is worth 10 points. Explain your reasoning in each case. Use SI
(a) Write down the total Hamiltonian of this system, including the spin degree of freedom of the electron, but neglecting spin-orbit interactions.
 1. Quantum Mechanics (Spring 2007) Consider a hydrogen atom in a weak uniform magnetic field B = Bê z. (a) Write down the total Hamiltonian of this system, including the spin degree of freedom of the electron,
1. Quantum Mechanics (Spring 2007) Consider a hydrogen atom in a weak uniform magnetic field B = Bê z. (a) Write down the total Hamiltonian of this system, including the spin degree of freedom of the electron,
Formula Sheet. ( γ. 0 : X(t) = (A 1 + A 2 t) e 2 )t. + X p (t) (3) 2 γ Γ +t Γ 0 : X(t) = A 1 e + A 2 e + X p (t) (4) 2
 Formula Sheet The differential equation Has the general solutions; with ẍ + γẋ + ω 0 x = f cos(ωt + φ) (1) γ ( γ )t < ω 0 : X(t) = A 1 e cos(ω 0 t + β) + X p (t) () γ = ω ( γ 0 : X(t) = (A 1 + A t) e )t
Formula Sheet The differential equation Has the general solutions; with ẍ + γẋ + ω 0 x = f cos(ωt + φ) (1) γ ( γ )t < ω 0 : X(t) = A 1 e cos(ω 0 t + β) + X p (t) () γ = ω ( γ 0 : X(t) = (A 1 + A t) e )t
NYU Physics Preliminary Examination in Electricity & Magnetism Fall 2011
 This is a closed-book exam. No reference materials of any sort are permitted. Full credit will be given for complete solutions to the following five questions. 1. An impenetrable sphere of radius a carries
This is a closed-book exam. No reference materials of any sort are permitted. Full credit will be given for complete solutions to the following five questions. 1. An impenetrable sphere of radius a carries
Queen s University at Kingston. Faculty of Arts and Science. Department of Physics PHYSICS 106. Final Examination.
 Page 1 of 5 Queen s University at Kingston Faculty of Arts and Science Department of Physics PHYSICS 106 Final Examination April 16th, 2009 Professor: A. B. McLean Time allowed: 3 HOURS Instructions This
Page 1 of 5 Queen s University at Kingston Faculty of Arts and Science Department of Physics PHYSICS 106 Final Examination April 16th, 2009 Professor: A. B. McLean Time allowed: 3 HOURS Instructions This
A half submerged metal sphere (UIC comprehensive
 Problem 1. exam) A half submerged metal sphere (UIC comprehensive A very light neutral hollow metal spherical shell of mass m and radius a is slightly submerged by a distance b a below the surface of a
Problem 1. exam) A half submerged metal sphere (UIC comprehensive A very light neutral hollow metal spherical shell of mass m and radius a is slightly submerged by a distance b a below the surface of a
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam
 Name: Student ID: Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Spring 2018 You may use any intermediate results in the textbook. No electronic devices (calculator, computer, cell phone etc) are allowed. For
Name: Student ID: Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Spring 2018 You may use any intermediate results in the textbook. No electronic devices (calculator, computer, cell phone etc) are allowed. For
EM radiation - Lecture 14
 EM radiation - Lecture 14 1 Review Begin with a review of the potentials, fields, and Poynting vector for a point charge in accelerated motion. The retarded potential forms are given below. The source
EM radiation - Lecture 14 1 Review Begin with a review of the potentials, fields, and Poynting vector for a point charge in accelerated motion. The retarded potential forms are given below. The source
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination January 8, 216 (Friday) 9: am - 12: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination January 8, 216 (Friday) 9: am - 12: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct
Figure 1: Grad, Div, Curl, Laplacian in Cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Here ψ is a scalar function and A is a vector field.
 Figure 1: Grad, Div, Curl, Laplacian in Cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Here ψ is a scalar function and A is a vector field. Figure 2: Vector and integral identities. Here ψ is a scalar
Figure 1: Grad, Div, Curl, Laplacian in Cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Here ψ is a scalar function and A is a vector field. Figure 2: Vector and integral identities. Here ψ is a scalar
Introduction to Polarization
 Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
Angular Momentum - set 1
 Angular Momentum - set PH0 - QM II August 6, 07 First of all, let us practise evaluating commutators. Consider these as warm up problems. Problem : Show the following commutation relations ˆx, ˆL x ] =
Angular Momentum - set PH0 - QM II August 6, 07 First of all, let us practise evaluating commutators. Consider these as warm up problems. Problem : Show the following commutation relations ˆx, ˆL x ] =
- 5 - TEST 2. This test is on the final sections of this session's syllabus and. should be attempted by all students.
 - 5 - TEST 2 This test is on the final sections of this session's syllabus and should be attempted by all students. QUESTION 1 [Marks 23] A thin non-conducting rod is bent to form the arc of a circle of
- 5 - TEST 2 This test is on the final sections of this session's syllabus and should be attempted by all students. QUESTION 1 [Marks 23] A thin non-conducting rod is bent to form the arc of a circle of
McGill University. Department of Physics. Ph.D. Preliminary Examination. Long Questions
 McGill University Department of Physics Ph.D. Preliminary Examination Long Questions Examiners: Date: Tuesday May 27, 2003 Time: 2:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m. C. Burgess (Chairman) S. Das Gupta V. Kaspi J. Strom
McGill University Department of Physics Ph.D. Preliminary Examination Long Questions Examiners: Date: Tuesday May 27, 2003 Time: 2:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m. C. Burgess (Chairman) S. Das Gupta V. Kaspi J. Strom
Power Loss. dp loss = 1 = 1. Method 2, Ohmic heating, power lost per unit volume. Agrees with method 1. c = 2 loss per unit area is dp loss da
 How much power is dissipated (per unit area?). 2 ways: 1) Flow of energy into conductor: Energy flow given by S = E H, for real fields E H. so 1 S ( ) = 1 2 Re E H, dp loss /da = ˆn S, so dp loss = 1 µc
How much power is dissipated (per unit area?). 2 ways: 1) Flow of energy into conductor: Energy flow given by S = E H, for real fields E H. so 1 S ( ) = 1 2 Re E H, dp loss /da = ˆn S, so dp loss = 1 µc
Quantization of the E-M field
 April 6, 20 Lecture XXVI Quantization of the E-M field 2.0. Electric quadrupole transition If E transitions are forbidden by selection rules, then we consider the next term in the expansion of the spatial
April 6, 20 Lecture XXVI Quantization of the E-M field 2.0. Electric quadrupole transition If E transitions are forbidden by selection rules, then we consider the next term in the expansion of the spatial
A cylinder in a magnetic field (Jackson)
 Problem 1. A cylinder in a magnetic field (Jackson) A very long hollow cylinder of inner radius a and outer radius b of permeability µ is placed in an initially uniform magnetic field B o at right angles
Problem 1. A cylinder in a magnetic field (Jackson) A very long hollow cylinder of inner radius a and outer radius b of permeability µ is placed in an initially uniform magnetic field B o at right angles
2. Waves with higher frequencies travel faster than waves with lower frequencies (True/False)
 PHY 2049C Final Exam. Summer 2015. Name: Remember, you know this stuff Answer each questions to the best of your ability. Show ALL of your work (even for multiple choice questions), you may receive partial
PHY 2049C Final Exam. Summer 2015. Name: Remember, you know this stuff Answer each questions to the best of your ability. Show ALL of your work (even for multiple choice questions), you may receive partial
l=0 The expansion coefficients can be determined, for example, by finding the potential on the z-axis and expanding that result in z.
 Electrodynamics I Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 15/11/6 Name Electrodynamic Score = 14 / 14 points Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try
Electrodynamics I Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 15/11/6 Name Electrodynamic Score = 14 / 14 points Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try
does not change the dynamics of the system, i.e. that it leaves the Schrödinger equation invariant,
 FYST5 Quantum Mechanics II 9..212 1. intermediate eam (1. välikoe): 4 problems, 4 hours 1. As you remember, the Hamilton operator for a charged particle interacting with an electromagentic field can be
FYST5 Quantum Mechanics II 9..212 1. intermediate eam (1. välikoe): 4 problems, 4 hours 1. As you remember, the Hamilton operator for a charged particle interacting with an electromagentic field can be
Module I: Electromagnetic waves
 Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lecture 9: EM radiation Amol Dighe Outline 1 Electric and magnetic fields: radiation components 2 Energy carried by radiation 3 Radiation from antennas Coming up... 1 Electric
Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lecture 9: EM radiation Amol Dighe Outline 1 Electric and magnetic fields: radiation components 2 Energy carried by radiation 3 Radiation from antennas Coming up... 1 Electric
J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2)
 Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q.
 1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q. (a) Compute the electric part of the Maxwell stress tensor T ij (r) = 1 {E i E j 12 } 4π E2 δ ij both inside
1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q. (a) Compute the electric part of the Maxwell stress tensor T ij (r) = 1 {E i E j 12 } 4π E2 δ ij both inside
Lecture 21 April 15, 2010
 Lecture 21 April 15, 2010 We found that the power radiated by a relativistic particle is given by Liénard, P = 2 q 2 [ 3 c γ6 β ) 2 β ] β ) 2. This is an issue for high-energy accelerators. There are two
Lecture 21 April 15, 2010 We found that the power radiated by a relativistic particle is given by Liénard, P = 2 q 2 [ 3 c γ6 β ) 2 β ] β ) 2. This is an issue for high-energy accelerators. There are two
Physics 227 Final Exam Wednesday, May 9, Code: 000
 Physics 227 Final Exam Wednesday, May 9, 2018 Physics 227, Section RUID: Code: 000 Your name with exam code Your signature Turn off and put away LL electronic devices NOW. NO cell phones, NO smart watches,
Physics 227 Final Exam Wednesday, May 9, 2018 Physics 227, Section RUID: Code: 000 Your name with exam code Your signature Turn off and put away LL electronic devices NOW. NO cell phones, NO smart watches,
from which follow by application of chain rule relations y = y (4) ˆL z = i h by constructing θ , find also ˆL x ˆL y and
 9 Scattering Theory II 9.1 Partial wave analysis Expand ψ in spherical harmonics Y lm (θ, φ), derive 1D differential equations for expansion coefficients. Spherical coordinates: x = r sin θ cos φ (1) y
9 Scattering Theory II 9.1 Partial wave analysis Expand ψ in spherical harmonics Y lm (θ, φ), derive 1D differential equations for expansion coefficients. Spherical coordinates: x = r sin θ cos φ (1) y
E&M. 1 Capacitors. January 2009
 E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
Final Exam: Physics Spring, 2017 May 8, 2017 Version 01
 Final Exam: Physics2331 - Spring, 2017 May 8, 2017 Version 01 NAME (Please Print) Your exam should have 11 pages. This exam consists of 18 multiple-choice questions (2 points each, worth 36 points), and
Final Exam: Physics2331 - Spring, 2017 May 8, 2017 Version 01 NAME (Please Print) Your exam should have 11 pages. This exam consists of 18 multiple-choice questions (2 points each, worth 36 points), and
Joel A. Shapiro January 21, 2010
 Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 21, 20 rmation Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Joel A. shapiro@physics.rutgers.edu January 21, 20 rmation Instructor: Joel Serin 325 5-5500 X 3886, shapiro@physics Book: Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Ed.) Web home page: www.physics.rutgers.edu/grad/504
Boundary-Value Problems: Part II
 Chapter 3 Boundary-Value Problems: Part II Problem Set #3: 3., 3.3, 3.7 Due Monday March. th 3. Spherical Coordinates Spherical coordinates are used when boundary conditions have spherical symmetry. The
Chapter 3 Boundary-Value Problems: Part II Problem Set #3: 3., 3.3, 3.7 Due Monday March. th 3. Spherical Coordinates Spherical coordinates are used when boundary conditions have spherical symmetry. The
PHYSICS 7B, Section 1 Fall 2013 Midterm 2, C. Bordel Monday, November 4, pm-9pm. Make sure you show your work!
 PHYSICS 7B, Section 1 Fall 2013 Midterm 2, C. Bordel Monday, November 4, 2013 7pm-9pm Make sure you show your work! Problem 1 - Current and Resistivity (20 pts) a) A cable of diameter d carries a current
PHYSICS 7B, Section 1 Fall 2013 Midterm 2, C. Bordel Monday, November 4, 2013 7pm-9pm Make sure you show your work! Problem 1 - Current and Resistivity (20 pts) a) A cable of diameter d carries a current
Scattering. 1 Classical scattering of a charged particle (Rutherford Scattering)
 Scattering 1 Classical scattering of a charged particle (Rutherford Scattering) Begin by considering radiation when charged particles collide. The classical scattering equation for this process is called
Scattering 1 Classical scattering of a charged particle (Rutherford Scattering) Begin by considering radiation when charged particles collide. The classical scattering equation for this process is called
Physics 7B Final Exam: Monday December 14th, 2015 Instructors: Prof. R.J. Birgeneau/Dr. A. Frano
 Physics 7B Final Exam: Monday December 14th, 15 Instructors: Prof. R.J. Birgeneau/Dr. A. Frano Total points: 1 (7 problems) Show all your work and take particular care to explain what you are doing. Partial
Physics 7B Final Exam: Monday December 14th, 15 Instructors: Prof. R.J. Birgeneau/Dr. A. Frano Total points: 1 (7 problems) Show all your work and take particular care to explain what you are doing. Partial
DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME OR STUDENT NUMBER ON ANY SHEET!
 Electodynamics Subject Exam Pep Quiz Fiday Apil 29 2017 DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME OR STUDENT NUMBER ON ANY SHEET! E&MStudyGuide Ch 1 Special Relativity Pime 1.1 Gamma Factos and Such tlab γt0 Llab L0 γ 1.2
Electodynamics Subject Exam Pep Quiz Fiday Apil 29 2017 DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME OR STUDENT NUMBER ON ANY SHEET! E&MStudyGuide Ch 1 Special Relativity Pime 1.1 Gamma Factos and Such tlab γt0 Llab L0 γ 1.2
Phys 622 Problems Chapter 6
 1 Problem 1 Elastic scattering Phys 622 Problems Chapter 6 A heavy scatterer interacts with a fast electron with a potential V (r) = V e r/r. (a) Find the differential cross section dσ dω = f(θ) 2 in the
1 Problem 1 Elastic scattering Phys 622 Problems Chapter 6 A heavy scatterer interacts with a fast electron with a potential V (r) = V e r/r. (a) Find the differential cross section dσ dω = f(θ) 2 in the
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION
 Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Monday, January 8, 2018 2:00PM to 4:00PM Classical Physics Section 2. Electricity, Magnetism & Electrodynamics Two hours are permitted for
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Monday, January 8, 2018 2:00PM to 4:00PM Classical Physics Section 2. Electricity, Magnetism & Electrodynamics Two hours are permitted for
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017
 Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
EUF. Joint Entrance Examination for Postgraduate Courses in Physics
 EUF Joint Entrance Examination for Postgraduate Courses in Physics For the second semester of 06 April 06, 06 Part Instructions Do not write your name on the test. It should be identified only by your
EUF Joint Entrance Examination for Postgraduate Courses in Physics For the second semester of 06 April 06, 06 Part Instructions Do not write your name on the test. It should be identified only by your
Spring /2/ pts 1 point per minute
 Physics 519 MIDTERM Name: Spring 014 6//14 80 pts 1 point per minute Exam procedures. Please write your name above. Please sit away from other students. If you have a question about the exam, please ask.
Physics 519 MIDTERM Name: Spring 014 6//14 80 pts 1 point per minute Exam procedures. Please write your name above. Please sit away from other students. If you have a question about the exam, please ask.
Physics 228 Today: Ch 41: 1-3: 3D quantum mechanics, hydrogen atom
 Physics 228 Today: Ch 41: 1-3: 3D quantum mechanics, hydrogen atom Website: Sakai 01:750:228 or www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/228 Happy April Fools Day Example / Worked Problems What is the ratio of the
Physics 228 Today: Ch 41: 1-3: 3D quantum mechanics, hydrogen atom Website: Sakai 01:750:228 or www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/228 Happy April Fools Day Example / Worked Problems What is the ratio of the
Preliminary Exam: Electromagnetism, Thursday January 12, :00-12:00
 1 Preliminary Exam: Electromagnetism, Thursday January 12, 2017. 9:00-12:00 Answer a total of any THREE out of the four questions. For your answers you can use either the blue books or individual sheets
1 Preliminary Exam: Electromagnetism, Thursday January 12, 2017. 9:00-12:00 Answer a total of any THREE out of the four questions. For your answers you can use either the blue books or individual sheets
Phys. 506 Electricity and Magnetism Winter 2004 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 5 Total 40 Points. 1. Problem Points
 Phys. 56 Electricity and Magnetism Winter 4 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 5 Total 4 Points. Problem. Points The partial-wave analysis presented in Chapter.4 applied to the case of a perfectly conducting
Phys. 56 Electricity and Magnetism Winter 4 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 5 Total 4 Points. Problem. Points The partial-wave analysis presented in Chapter.4 applied to the case of a perfectly conducting
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2007 FINAL EXAMINATION Monday May 21, 9:00 am You have 3 hours.
 Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2007 FINAL EXAMINATION Monday May 21, 9:00 am You have 3 hours. There are 10 problems, totalling 180 points. Do all problems. Answer all problems in the white books provided.
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2007 FINAL EXAMINATION Monday May 21, 9:00 am You have 3 hours. There are 10 problems, totalling 180 points. Do all problems. Answer all problems in the white books provided.
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 12 Orbital Angular Momentum and Spherical Harmonics
 Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 12 Orbital Angular Momentum and Spherical Harmonics We now consider the spatial degrees of freedom of a particle moving in 3-dimensional space, which of course is an important
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 12 Orbital Angular Momentum and Spherical Harmonics We now consider the spatial degrees of freedom of a particle moving in 3-dimensional space, which of course is an important
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Spring 2014 Final Exam Equation Sheet. B( r) = µ o 4π
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Final Exam Equation Sheet Force Law: F q = q( E ext + v q B ext ) Poynting Vector: S = ( E B) / µ 0 Force on Current Carrying
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Final Exam Equation Sheet Force Law: F q = q( E ext + v q B ext ) Poynting Vector: S = ( E B) / µ 0 Force on Current Carrying
Set 5: Classical E&M and Plasma Processes
 Set 5: Classical E&M and Plasma Processes Maxwell Equations Classical E&M defined by the Maxwell Equations (fields sourced by matter) and the Lorentz force (matter moved by fields) In cgs (gaussian) units
Set 5: Classical E&M and Plasma Processes Maxwell Equations Classical E&M defined by the Maxwell Equations (fields sourced by matter) and the Lorentz force (matter moved by fields) In cgs (gaussian) units
Angular Momentum - set 1
 Angular Momentum - set PH0 - QM II August 6, 07 First of all, let us practise evaluating commutators. Consider these as warm up problems. Problem : Show the following commutation relations ˆx, ˆL x = 0,
Angular Momentum - set PH0 - QM II August 6, 07 First of all, let us practise evaluating commutators. Consider these as warm up problems. Problem : Show the following commutation relations ˆx, ˆL x = 0,
in Electromagnetics Numerical Method Introduction to Electromagnetics I Lecturer: Charusluk Viphavakit, PhD
 2141418 Numerical Method in Electromagnetics Introduction to Electromagnetics I Lecturer: Charusluk Viphavakit, PhD ISE, Chulalongkorn University, 2 nd /2018 Email: charusluk.v@chula.ac.th Website: Light
2141418 Numerical Method in Electromagnetics Introduction to Electromagnetics I Lecturer: Charusluk Viphavakit, PhD ISE, Chulalongkorn University, 2 nd /2018 Email: charusluk.v@chula.ac.th Website: Light
Physics 506 Winter 2008 Homework Assignment #4 Solutions. Textbook problems: Ch. 9: 9.6, 9.11, 9.16, 9.17
 Physics 56 Winter 28 Homework Assignment #4 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 9: 9.6, 9., 9.6, 9.7 9.6 a) Starting from the general expression (9.2) for A and the corresponding expression for Φ, expand
Physics 56 Winter 28 Homework Assignment #4 Solutions Textbook problems: Ch. 9: 9.6, 9., 9.6, 9.7 9.6 a) Starting from the general expression (9.2) for A and the corresponding expression for Φ, expand
Department of Physics PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2015 Part II. Long Questions
 Department of Physics PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2015 Part II. Long Questions Friday May 15th, 2014, 14-17h Examiners: Prof. J. Cline, Prof. H. Guo, Prof. G. Gervais (Chair), and Prof. D. Hanna INSTRUCTIONS
Department of Physics PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2015 Part II. Long Questions Friday May 15th, 2014, 14-17h Examiners: Prof. J. Cline, Prof. H. Guo, Prof. G. Gervais (Chair), and Prof. D. Hanna INSTRUCTIONS
Module I: Electromagnetic waves
 Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lectures 10-11: Multipole radiation Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation
Module I: Electromagnetic waves Lectures 10-11: Multipole radiation Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation
Second Year Electromagnetism Summer 2018 Caroline Terquem. Vacation work: Problem set 0. Revisions
 Second Year Electromagnetism Summer 2018 Caroline Terquem Vacation work: Problem set 0 Revisions At the start of the second year, you will receive the second part of the Electromagnetism course. This vacation
Second Year Electromagnetism Summer 2018 Caroline Terquem Vacation work: Problem set 0 Revisions At the start of the second year, you will receive the second part of the Electromagnetism course. This vacation
St Hugh s 2 nd Year: Quantum Mechanics II. Reading. Topics. The following sources are recommended for this tutorial:
 St Hugh s 2 nd Year: Quantum Mechanics II Reading The following sources are recommended for this tutorial: The key text (especially here in Oxford) is Molecular Quantum Mechanics, P. W. Atkins and R. S.
St Hugh s 2 nd Year: Quantum Mechanics II Reading The following sources are recommended for this tutorial: The key text (especially here in Oxford) is Molecular Quantum Mechanics, P. W. Atkins and R. S.
Physics 208, Spring 2016 Exam #3
 Physics 208, Spring 206 Exam #3 A Name (Last, First): ID #: Section #: You have 75 minutes to complete the exam. Formulae are provided on an attached sheet. You may NOT use any other formula sheet. You
Physics 208, Spring 206 Exam #3 A Name (Last, First): ID #: Section #: You have 75 minutes to complete the exam. Formulae are provided on an attached sheet. You may NOT use any other formula sheet. You
A GENERAL APPROACH FOR CALCULATING COUPLING IMPEDANCES OF SMALL DISCONTINUITIES
 Presented at 16th IEEE Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC 95) and Int l Conference on on High Energy Accelerators, 5/1/1995-5/5/1995, Dallas, TX, USA SLAC-PUB-9963 acc-phys/9504001 A GENERAL APPROACH
Presented at 16th IEEE Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC 95) and Int l Conference on on High Energy Accelerators, 5/1/1995-5/5/1995, Dallas, TX, USA SLAC-PUB-9963 acc-phys/9504001 A GENERAL APPROACH
Electromagnetism Answers to Problem Set 9 Spring 2006
 Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
Physics 420 Fall 2004 Quiz 1 Wednesday This quiz is worth 6 points. Be sure to show your work and label your final answers.
 Quiz 1 Wednesday This quiz is worth 6 points. Be sure to show your work and label your final answers. 1. A charge q 1 = +5.0 nc is located on the y-axis, 15 µm above the origin, while another charge q
Quiz 1 Wednesday This quiz is worth 6 points. Be sure to show your work and label your final answers. 1. A charge q 1 = +5.0 nc is located on the y-axis, 15 µm above the origin, while another charge q
Chapter 6. Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom
 Chapter 6 Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 1 6.1 Schrodinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom Symmetry suggests spherical polar coordinates Fig. 6.1 (a) Spherical polar coordinates. (b) A line of constant
Chapter 6 Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 1 6.1 Schrodinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom Symmetry suggests spherical polar coordinates Fig. 6.1 (a) Spherical polar coordinates. (b) A line of constant
PH 253 Exam I Solutions
 PH 253 Exam I Solutions. An electron and a proton are each accelerated starting from rest through a potential difference of 0.0 million volts (0 7 V). Find the momentum (in MeV/c) and kinetic energy (in
PH 253 Exam I Solutions. An electron and a proton are each accelerated starting from rest through a potential difference of 0.0 million volts (0 7 V). Find the momentum (in MeV/c) and kinetic energy (in
Mathematical Tripos Part IA Lent Term Example Sheet 1. Calculate its tangent vector dr/du at each point and hence find its total length.
 Mathematical Tripos Part IA Lent Term 205 ector Calculus Prof B C Allanach Example Sheet Sketch the curve in the plane given parametrically by r(u) = ( x(u), y(u) ) = ( a cos 3 u, a sin 3 u ) with 0 u
Mathematical Tripos Part IA Lent Term 205 ector Calculus Prof B C Allanach Example Sheet Sketch the curve in the plane given parametrically by r(u) = ( x(u), y(u) ) = ( a cos 3 u, a sin 3 u ) with 0 u
Electrodynamics II: Lecture 9
 Electrodynamics II: Lecture 9 Multipole radiation Amol Dighe Sep 14, 2011 Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation Outline 1 Multipole
Electrodynamics II: Lecture 9 Multipole radiation Amol Dighe Sep 14, 2011 Outline 1 Multipole expansion 2 Electric dipole radiation 3 Magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole radiation Outline 1 Multipole
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Section Number:
 Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly
Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 2, 3, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap. 2. 2π nx i a. ( ) = G n.
 Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
PHY4604 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Fall 2004 Final Exam SOLUTIONS December 17, 2004, 7:30 a.m.- 9:30 a.m.
 PHY464 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Fall 4 Final Eam SOLUTIONS December 7, 4, 7:3 a.m.- 9:3 a.m. No other materials allowed. If you can t do one part of a problem, solve subsequent parts in terms
PHY464 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Fall 4 Final Eam SOLUTIONS December 7, 4, 7:3 a.m.- 9:3 a.m. No other materials allowed. If you can t do one part of a problem, solve subsequent parts in terms
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON. SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2018
 ENG018 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING MODULE NO: EEE6002 Date: 17 January 2018 Time: 2.00 4.00 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are six questions.
ENG018 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING MODULE NO: EEE6002 Date: 17 January 2018 Time: 2.00 4.00 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are six questions.
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution
 Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution January 31, 011, 1:00 pm 5:pm Solve the following six problems. In the following problems, e x, e y, and e z are unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions,
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution January 31, 011, 1:00 pm 5:pm Solve the following six problems. In the following problems, e x, e y, and e z are unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions,
B(r) = µ 0a 2 J r 2ρ 2
 28 S8 Covariant Electromagnetism: Problems Questions marked with an asterisk are more difficult.. Eliminate B instead of H from the standard Maxwell equations. Show that the effective source terms are
28 S8 Covariant Electromagnetism: Problems Questions marked with an asterisk are more difficult.. Eliminate B instead of H from the standard Maxwell equations. Show that the effective source terms are
Ph304 Final Examination Electrodynamics
 Princeton University Ph304 Final Examination Electrodynamics Prof: Kirk T. McDonald (1:30-4:30 pm, May, 00) Do all work you wish graded in the exam booklets provided. mcdonald@puphep.princeton.edu http://puhep1.princeton.edu/
Princeton University Ph304 Final Examination Electrodynamics Prof: Kirk T. McDonald (1:30-4:30 pm, May, 00) Do all work you wish graded in the exam booklets provided. mcdonald@puphep.princeton.edu http://puhep1.princeton.edu/
PHZ 6607 Fall 2004 Homework #4, Due Friday, October 22, 2004
 Read Chapters 9, 10 and 20. PHZ 6607 Fall 2004 Homework #4, Due Friday, October 22, 2004 1. The usual metric of four-dimensional flat Minkowski-space in spherical-polar coordinates is ds 2 = dt 2 + dr
Read Chapters 9, 10 and 20. PHZ 6607 Fall 2004 Homework #4, Due Friday, October 22, 2004 1. The usual metric of four-dimensional flat Minkowski-space in spherical-polar coordinates is ds 2 = dt 2 + dr
 Physics Qual - Statistical Mechanics ( Fall 2016) I. Describe what is meant by: (a) A quasi-static process (b) The second law of thermodynamics (c) A throttling process and the function that is conserved
Physics Qual - Statistical Mechanics ( Fall 2016) I. Describe what is meant by: (a) A quasi-static process (b) The second law of thermodynamics (c) A throttling process and the function that is conserved
Physics 7B, Speliotopoulos Final Exam, Fall 2014 Berkeley, CA
 Physics 7B, Speliotopoulos Final Exam, Fall 4 Berkeley, CA Rules: This final exam is closed book and closed notes. In particular, calculators are not allowed during this exam. Cell phones must be turned
Physics 7B, Speliotopoulos Final Exam, Fall 4 Berkeley, CA Rules: This final exam is closed book and closed notes. In particular, calculators are not allowed during this exam. Cell phones must be turned
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION
 Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Wednesday, January 13, 2016 3:10PM to 5:10PM Modern Physics Section 4. Relativity and Applied Quantum Mechanics Two hours are permitted
Columbia University Department of Physics QUALIFYING EXAMINATION Wednesday, January 13, 2016 3:10PM to 5:10PM Modern Physics Section 4. Relativity and Applied Quantum Mechanics Two hours are permitted
We have seen how to calculate forces and potentials from the smoothed density ρ.
 9. Orbits in stationary Potentials We have seen how to calculate forces and potentials from the smoothed density ρ. Now we can analyse how stars move in this potential. Because two body interactions can
9. Orbits in stationary Potentials We have seen how to calculate forces and potentials from the smoothed density ρ. Now we can analyse how stars move in this potential. Because two body interactions can
charges q r p = q 2mc 2mc L (1.4) ptles µ e = g e
 APAS 5110. Atomic and Molecular Processes. Fall 2013. 1. Magnetic Moment Classically, the magnetic moment µ of a system of charges q at positions r moving with velocities v is µ = 1 qr v. (1.1) 2c charges
APAS 5110. Atomic and Molecular Processes. Fall 2013. 1. Magnetic Moment Classically, the magnetic moment µ of a system of charges q at positions r moving with velocities v is µ = 1 qr v. (1.1) 2c charges
Suggested solutions, FYS 500 Classical Mechanics and Field Theory 2015 fall
 UNIVERSITETET I STAVANGER Institutt for matematikk og naturvitenskap Suggested solutions, FYS 500 Classical Mecanics and Field Teory 015 fall Set 1 for 16/17. November 015 Problem 68: Te Lagrangian for
UNIVERSITETET I STAVANGER Institutt for matematikk og naturvitenskap Suggested solutions, FYS 500 Classical Mecanics and Field Teory 015 fall Set 1 for 16/17. November 015 Problem 68: Te Lagrangian for
Electromagnetic Waves Retarded potentials 2. Energy and the Poynting vector 3. Wave equations for E and B 4. Plane EM waves in free space
 Electromagnetic Waves 1 1. Retarded potentials 2. Energy and the Poynting vector 3. Wave equations for E and B 4. Plane EM waves in free space 1 Retarded Potentials For volume charge & current = 1 4πε
Electromagnetic Waves 1 1. Retarded potentials 2. Energy and the Poynting vector 3. Wave equations for E and B 4. Plane EM waves in free space 1 Retarded Potentials For volume charge & current = 1 4πε
Physics 208 Final Exam December 15, 2008
 Page 1 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Final Exam December 15, 2008 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must
Page 1 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Final Exam December 15, 2008 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must
Math Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
 Math 213 - Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky October 22, 2018 Homework Re-read section 15.3 Begin work on 1-4, 5-31 (odd), 35, 37 from 15.3 Read section 15.4 for
Math 213 - Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky October 22, 2018 Homework Re-read section 15.3 Begin work on 1-4, 5-31 (odd), 35, 37 from 15.3 Read section 15.4 for
Problems in Magnetostatics
 Problems in Magnetostatics 8th February 27 Some of the later problems are quite challenging. This is characteristic of problems in magnetism. There are trivial problems and there are tough problems. Very
Problems in Magnetostatics 8th February 27 Some of the later problems are quite challenging. This is characteristic of problems in magnetism. There are trivial problems and there are tough problems. Very
NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2017 (8/22/2017) Electricity and Magnetism
 NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2017 (8/22/2017) Electricity and Magnetism You may solve ALL FOUR problems if you choose. The points of the best three problems will be counted towards your final score
NIU Ph.D. Candidacy Examination Fall 2017 (8/22/2017) Electricity and Magnetism You may solve ALL FOUR problems if you choose. The points of the best three problems will be counted towards your final score
Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress
 1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic mass unit ) = 1 1.66
1 year 3.16 10 7 s Physics 8, Fall 2011, equation sheet work in progress circumference of earth 40 10 6 m speed of light c = 2.9979 10 8 m/s mass of proton or neutron 1 amu ( atomic mass unit ) = 1 1.66
Relativistic Transformations
 Relativistic Transformations Lecture 7 1 The Lorentz transformation In the last lecture we obtained the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames. These transformations follow
Relativistic Transformations Lecture 7 1 The Lorentz transformation In the last lecture we obtained the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames. These transformations follow
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
Chapter 11. Radiation. How accelerating charges and changing currents produce electromagnetic waves, how they radiate.
 Chapter 11. Radiation How accelerating charges and changing currents produce electromagnetic waves, how they radiate. 11.1.1 What is Radiation? Assume a radiation source is localized near the origin. Total
Chapter 11. Radiation How accelerating charges and changing currents produce electromagnetic waves, how they radiate. 11.1.1 What is Radiation? Assume a radiation source is localized near the origin. Total
Schrödinger equation for the nuclear potential
 Schrödinger equation for the nuclear potential Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 January 24, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 4) January 24, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 One-dimensional
Schrödinger equation for the nuclear potential Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 January 24, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 4) January 24, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 One-dimensional
