A Detailed Derivation of the Distribution of Class Identification in a Chance Society :
|
|
|
- Morris Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 March 22 A Detailed Derivation of the Distribution of Class Identification in a Chance Society : A Note on the Fararo-Kosaka Model Atsushi ISHIDA Purpose Kenji Kosaka and Thomas J. Fararo (99) proposed a model, hereafter referred to as the Fararo- Kosaka model, to explain the generalization of images of stratification and distribution of class identification. Because the Fararo-Kosaka model is mathematically simple and has a number of meaningful derivations, the model has attracted many followers. In particular, in Japan, the Fararo-Kosaka model has been considered a plausible theoretical framework for explaining the middle classification phenomenon, which has been empirically observed in the last three decades. This note presents a detailed derivation of the distribution of class identification in order to help learners, especially beginners in mathematical sociology, to gain a deeper understanding of the model. 2 Axioms of the Model The complete axioms of the Fararo-Kosaka model are described in detail in Kosaka and Fararo (99), Fararo and Kosaka (23), and Kosaka (26). Here, we briefly introduce the essence of the model axioms. Axiom. There exists a multidimensional stratification system S that is composed of a Cartesian product of s characteristics C, C2,, Cs and each Ci is ordered linearly. Each s-tuple representing a social class in C C2 Cs is ordered lexicographically. In a word, S is mathematically defined as a linearly ordered set (C C2 Cs,!l) with a lexicographic order!l. We call each of C, C2,, Cs a dimension and each component of Ci a rank. In the following analysis, we assume that each dimension has an identical number of ranks more than (i.e., the rank homogeneity assumption). The number of dimensions is denoted by s and the number of ranks in Ci is denoted by r. At this stage, we call S the s r stratification system. The ranks in Ci are denoted by integers from as the lowest up to r as the highest as follows: Key Words: class identification, Fararo-Kosaka model, convolution of sequences This note is partly based on the lecture notes for Mathematical Sociology at School of Sociology, Kwansei Gakuin University in 29 and 2. This work was supported by the JSPS Grant-in-Aid Scientific Research on Theoretical and Empirical Studies of Relative Deprivation in Unequal Societies in a Time of Globalization (2 23). Associate Professor, School of Sociology, Kwansei Gakuin University
2 4 Ci {,,2,, r 2, r }. An s-tuple representing a class in the stratification system is generally denoted by (k, k2,, ks), ki Ci. Axiom 2. Each actor in the society has an initial image of the stratification system, and this image consists only of one social class to which the actor belongs. The images of the stratification system change through interaction with others. Axiom 3. In each interaction among actors, each actor s image is transformed according to the following postulated process: The actor searches for information as to the class location of the other actor (termed an alter) in an order corresponding to the lexicographic ordering and the search continues until a class distinction is made or all dimensions have been exhausted, whichever comes first. Axiom 4. The following postulated process transforms the state of the image of any actor as a consequence of any interaction. Let cl (a) be the sampled part of the class location of alter a, when the information search process has been completed in that interaction. Then the following four transition rules determine the transformation of the image state:. If cl (a) is represented in the image that is already held by the actor, no change occurs. 2. If cl (a) is above the highest class in the image, then cl (a) becomes the new highest class. 3. If cl (a) is lower than the lowest class in the image, then cl (a) becomes the new lowest class. 4. If cl (a) is between some pair of classes in the image, then it is inserted between them in the new image. Given that there is at least one actor in each class and each actor randomly encounters each other actor in the society, then sooner or later every actor will have a stable image of the system, which will remain unchanged by any further encounters. The last axiom is about the determination of class identification that is also called as self-location in the stratification system in Fararo and Kosaka s terminology. Axiom 5. An actor expresses his/her class identification on the basis of the relative location of his/her affiliation class on his/her own stable image of the stratification system. 3 Derivations of the Model Findings of the Fararo-Kosaka model derived from the model axioms are examined in detail in a series of articles and books by Fararo and Kosaka. Here, I only state the propositions relevant to the distribution of class identification. Proposition. The number of classes in any stable image is the same for all actors and is given by
3 March 22 n s(r ). () Proof. In the i-th dimension, an actor belonging to (k, k2,, ks) recognizes r ki classes of higher rank and ki classes of lower rank. Therefore, the number of classes recognized by an actor is r ki ki r. Because this applies to all dimensions, we have s(r ) classes. By adding, which is the number of the affiliation class of the actor, we arrive at Equation (). Here, let us label the ranks on a stable class image from the top to the bottom as s(r ), s(r ),, 2,,. Proposition 2. For an actor who belongs to (k, k2,, ks), a rank of the affiliation class on a stable class image, which is assumed to be actor s class identification, denoted by ρ, is given by ρ ki. (2) s!i Proof. The rank ρ is given by the total number of classes recognized to be of lower rank by the actor. As the total number of classes recognized to be of lower rank in the i-th dimension is ki, thesummation of all dimensions yields Equation (2). According to Fararo and Kosaka (99), we now introduce the term chance society to denote a society in which an equal number of people are assigned to each logically possible class in a stratification system. In addition, to simplify the following description, we assume that one person is assigned to each class. Then, the last proposition is about the distribution of class identification in a chance society. Proposition 3. In a chance society, the distribution of class identification ρ is given by a function f (ρ ) such that s f r s.2 s s 4 s 3 s Figure : Distribution of class identification in a chance society (r 3) s
4 4 f (ρ)!k ( )k ρ rk s k s ρ rk (3)!k s s ρ rk ( )k k s (4) where [a] denotes the integer part of a, and k s denotes a binomial coefficient. Kosaka and Fararo (99), Fararo and Kosaka (23), and Kosaka (26) present this distribution function in the form of Equation (4) from a textbook on combinatorial mathematics by Niven (965). On the other hand, Yosano (996) and Kosaka and Yosano (998) present this proposition in the form of Equation (3) from the proposition of the convolution of independent discrete uniform distributions (Feller 957). Given that each dimension of stratification system is independently uniformly distributed over Ci, we get the probability function of class identification by dividing the above equation by r s. Furthermore, apart from the chance society assumption, according to the central limit theorem, it is concluded that relative class identification ρ /s is asymptotically normally distributed on N (μ, σ 2 /s) if s given that each dimension is independently and identically distributed with mean μ and variance σ 2 (Yosano 996; Kosaka and Yosano 998). Finally, Hamada (22) proves by using the Lyapounov s central limit theorem that relative class identification is asymptotically normally distributed no matter how each dimension is distributed, as long as each independent distribution of dimension has finite μ, σ 2 and the maximum value of ranks. These propositions are mathematically true and there are no words to be added to the propositions in terms of mathematics. However, it is worth noting the detailed derivation of Proposition 3, especially for undergraduate students who have a strong desire to learn mathematical sociology and want to completely understand the derivation. Therefore, in the next section, we present the derivation of Proposition 3 in terms of the convolution of sequences. 4 Detailed Derivation of Proposition 3 Let us consider the distribution of class identification in a chance society where one person is assigned to each class. 4. A Case with r 2 First, we shall consider the case in which each dimension of the stratification system consists of two ranks Ci {, }.We want to determine the number of s-tuples (k, k2,, ks), ki {, } that satisfy the constraint condition ρ!s i ki. In this case, if ρ of the s dimensions are and the rest are, then the condition is satisfied. This leads to the combination of s objects taken ρ at a time. Hence, the number of actors whose class identification is ρ, denoted by f (ρ ), is given by From the binomial theorem, f (ρ ) s s! scρ ρ ρ!(s ρ )!. (5) ( x) s s!ρ s ρ x ρ. (6)
5 March 22 Table The number of dimensions s and Pascal s triangle (r 2) s generating function ( x) ( x) 2 ( x) ( x) ( x) ( x) ( x) This identity indicates that f (ρ ) coincides with a coefficient of x ρ in the binomial theorem. Furthermore, ( x) s is the generating function of each row in Pascal s triangle. Hence, the distribution of class identification under the condition of s dimensions is shown in Pascal s triangle (Table ) Generalization By analogy with the above analysis using the binomial theorem, it can be predicted that if all dimensions have the same rank r, the number of actors of rank ρ is given by the function f (ρ ), which determines the coefficient of x ρ in a expansion of power of a single-variable polynomial, such that r!k xk s s(r )!ρ f (ρ )x ρ. (7) Indeed, this is right. To prove this equation, we introduce the concept of generating functions of sequences and their convolution ). In general, we denote any infinite sequence as an a, a,, an,. Let us now introduce a function a(x) in which the coefficient of x ρ corresponds one to one with the k-th element of the sequence an, thatis a(x) ak x!k k a x ax an x n. This function a(x) is called the generating function of the sequence an. Let us introduce another infinite sequence as bn b, b,, bn,. The generating function of this sequence bn is b(x) bk x!k k. A detailed explanation on the binomial coefficient, generating function of sequence and convolution is given in Ch.5 of Graham et. al. (989).
6 4 Now, we introduce the specific mathematical operation on sequences called convolution of sequences which produces another sequence. Strictly, the convolution of an and bn, denoted by an bn, is defined as an bn ak bn k n!k (a b), (a b a b), (a b2 a b a2 b),, ak bn k,. n!k (8) Furthermore, the product of the generating functions a(x) and b(x) is a(x) b(x)!n ( n!k ) ak bn k x n. (9)! From Equations (8) and (9), we can see that the convolution of sequences corresponds to the product of the generating functions of these sequences. Generally, the convolution of s infinite sequences an, a2n,, asn is defined as an a2n asn a2k2 k k s n asks. () ak We now introduce a specific infinite sequence Ur whose first r elements are and the remaining are, that is Ur u, u,, ur, ur,,,,,,,!! r objects where uk (k!r ) (k r ) We denote the generating function of Ur as Ur(x), that is r Ur(x) x!k k.! For example, U2,,,, and its generating function is ( x). From the definition of convolution, the ρ th element of the convolution of s objects of Ur is uk2 uks. () uk k k s ρ If at least one ki exceeds r, then the term uk uk2 uks is zero. Therefore, Equation () yields the number of patterns of s-tuples (k,, ks) satisfying the following conditions: i {,, s}, ki {,,...,r 2, r }, ρ ki, s!i
7 March 22 and this is equal to the number of actors whose rank is ρ in his/her image of the stratification system in a chance society in the framework of the Fararo-Kosaka model. Table 2 Outcome of convolution of three objects of U3 k U3 U3 U3 U3 U3 U Until now, it is shown that the distribution of class identification in the s r stratification system in a chance society is uniquely given by the convolution of s objects of Ur, thatis Ur Ur Ur.!!!! s objects Next, we derive the explicit expression of the sequence. To this end, we use the finding that the convolution of sequences corresponds to the product of the generating functions. The generating function that corresponds to convolution of s objects of Ur is given by (Ur(x)) r s x!k k s. We derive the explicit form of f (ρ ) by expanding this equation: r!k xk s ( x x 2 x 3 x r ) s xr x s ( x r ) s ( x) s!k k s ( )k x rk s!j j ( ) j x j (2) As for the last form of the right-hand side of the equation, both left and right terms are derived by the generalized binomial theorem. Let us introduce the notations ark, bj defined as ark s k ( )k, bj s j ( ) j. Furthermore, bj can be transformed into the following form: bj s j ( ) j s j j s Hj where shj is known as the repeated combination of s objects taken j with duplication allowed. By using the notations ark and bj, Equation (2) can be transformed into the following:
8 4 r!k xk s!k ark x rk!j bj xj. (3) Equation (3) consists of the product of two different generating functions. Comparing with Equation (9), let us examine the coefficient of x ρ in the expansion of Equation (3). The coefficient of x ρ is the sum of ark bj which satisfies ρ rk j. Because j ρ rk and j!, k moves in the range between and. Hence, the function f (ρ ), which is equal to the coefficient of x ρ,is f (ρ )!k ark bρ rk!k s ( )k k!k ( ) k ρ rk s k s ρ rk ρ rk!k s s ρ rk ( )k k s. ρ s rk Therefore, Equations (3) and (4) in Proposition 3 are derived. The generating function of the distribution of class identification is the following: 5Conclusion r!k xk s!k ark xrk!j bj xj s(r )!ρ s(r )!ρ!k ark bρ rk x ρ!k ( )k ρ rk s k s ρ rk x ρ. We presented a detailed derivation of the distribution of class identification in a chance society. We hope that this will aid learners in gaining a deeper understanding of the Fararo-Kosaka model. There are a number of works which apply or extend the model in terms of, for example, images of shape of the stratification (Fararo and Kosaka 992), social mobility (Watanabe and Doba 995), cognitive efficientcy (Ishida 23), reference group (Maeda 2), as well as theoretical works revisiting the model s derivations by Yosano (996) and Hamada (22). Learners interested in this model are advised to review these works next. References Fararo, T. J., and K. Kosaka Generating Images of the Shape of a Class System. Journal of Mathematical Sociology 7(2 3): Fararo, T. J., and K. Kosaka. 23. Generating Images of Stratification: A Formal Theory. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publisher. Feller, W An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications. New York: Wiley. Graham, R. L., D. E. Knuth, and O. Patashnik Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science. Boston: Addison-Wesley. Hamada, H. 22. A Model of Class Identification: Generalization of Fararo-Kosaka Model with Lyapounov s Central Limit Theorem. Kwansei Gakuin University School of Sociology Journal 4: Ishida, A. 23. Cognitive Efficiency and Images of Stratification: FK Model Revisited under Condition of Truncation of Scanning Process FK Sociological
9 March 22 Theory and Methods 8(2): [in Japanese] Kosaka, K., and T. J. Fararo. 99. Self-location in a Class System: A Formal-Theoretical Analysis. Pp in Advances in Group Processes Volume 8 edited by Edward J. Lawler, Barry Markovsky, Cecilia Ridgeway and Henry A. Walker. Greenwich: JAI Press. Kosaka, K. 26. A Formal Theory in Sociology: FK Model Relevant to Images of Stratification System FK Tokyo: Harvest-sha. [in Japanese] Kosaka, K., and A. Yosano The Methods in Sociology Pp in Course in Sociology : Theories and Methods edited by K. Kosaka and Y. Koto.Tokyo: Tokyo University Press. [in Japanese] Maeda, Y. 2 Mathematical Model of Class Identification Reflecting Discrimination Process: FK Model with Comparative Reference Group FK Sociological Theory and Methods 26(2): [in Japanese] Niven, I Mathematics of Choice: or, How to Count without Counting. New York: Random House. Watanabe, T., and G. Doba Images of Stratification and Social Mobility Sociological Theory and Methods (): [in Japanese] Yosano, A Prolification of Class Identifying Factors and Self Identification Sociological Theory and Methods (): [in Japanese]
10 4 A Detailed Derivation of the Distribution of Class Identification in a Chance Society : A Note on the Fararo-Kosaka Model ABSTRACT Kosaka and Fararo (99) proposed a model to explain the generalization of images of stratification and distribution of class identification. This note presents a detailed derivation of the distribution of class identification in order to help learners, especially beginners in mathematical sociology, to gain a deeper understanding of the model. Key Words: class identification, Fararo-Kosaka model, convolution of sequences
CURRENT RESEARCH IN SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
 CURRENT RESEARCH IN SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Volume 4, Number 2 Submitted: February 7, 1999 Resubmitted: February 10, 1999 Accepted: February 16, 1999 Publication date: February 17, 1999 A PROGRAM FOR CALCULATING
CURRENT RESEARCH IN SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Volume 4, Number 2 Submitted: February 7, 1999 Resubmitted: February 10, 1999 Accepted: February 16, 1999 Publication date: February 17, 1999 A PROGRAM FOR CALCULATING
Permutations with Inversions
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 4 2001, Article 01.2.4 Permutations with Inversions Barbara H. Margolius Cleveland State University Cleveland, Ohio 44115 Email address: b.margolius@csuohio.edu
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 4 2001, Article 01.2.4 Permutations with Inversions Barbara H. Margolius Cleveland State University Cleveland, Ohio 44115 Email address: b.margolius@csuohio.edu
SERIES
 SERIES.... This chapter revisits sequences arithmetic then geometric to see how these ideas can be extended, and how they occur in other contexts. A sequence is a list of ordered numbers, whereas a series
SERIES.... This chapter revisits sequences arithmetic then geometric to see how these ideas can be extended, and how they occur in other contexts. A sequence is a list of ordered numbers, whereas a series
Application of Logic to Generating Functions. Holonomic (P-recursive) Sequences
 Application of Logic to Generating Functions Holonomic (P-recursive) Sequences Johann A. Makowsky Faculty of Computer Science, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel http://www.cs.technion.ac.il/
Application of Logic to Generating Functions Holonomic (P-recursive) Sequences Johann A. Makowsky Faculty of Computer Science, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel http://www.cs.technion.ac.il/
HS Algebra IIB Mathematics CC
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) Unit 1: Linear and Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Unit
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) Unit 1: Linear and Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Unit
ON DIVISIBILITY OF SOME POWER SUMS. Tamás Lengyel Department of Mathematics, Occidental College, 1600 Campus Road, Los Angeles, USA.
 INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (007, #A4 ON DIVISIBILITY OF SOME POWER SUMS Tamás Lengyel Department of Mathematics, Occidental College, 600 Campus Road, Los Angeles, USA
INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (007, #A4 ON DIVISIBILITY OF SOME POWER SUMS Tamás Lengyel Department of Mathematics, Occidental College, 600 Campus Road, Los Angeles, USA
Generative Techniques: Bayes Rule and the Axioms of Probability
 Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 2 / MoSIG M1 Second Semester 2016/2017 Lesson 8 3 March 2017 Generative Techniques: Bayes Rule and the Axioms of Probability Generative
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 2 / MoSIG M1 Second Semester 2016/2017 Lesson 8 3 March 2017 Generative Techniques: Bayes Rule and the Axioms of Probability Generative
EVALUATION OF A FAMILY OF BINOMIAL DETERMINANTS
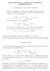 EVALUATION OF A FAMILY OF BINOMIAL DETERMINANTS CHARLES HELOU AND JAMES A SELLERS Abstract Motivated by a recent work about finite sequences where the n-th term is bounded by n, we evaluate some classes
EVALUATION OF A FAMILY OF BINOMIAL DETERMINANTS CHARLES HELOU AND JAMES A SELLERS Abstract Motivated by a recent work about finite sequences where the n-th term is bounded by n, we evaluate some classes
Last Update: March 1 2, 201 0
 M ath 2 0 1 E S 1 W inter 2 0 1 0 Last Update: March 1 2, 201 0 S eries S olutions of Differential Equations Disclaimer: This lecture note tries to provide an alternative approach to the material in Sections
M ath 2 0 1 E S 1 W inter 2 0 1 0 Last Update: March 1 2, 201 0 S eries S olutions of Differential Equations Disclaimer: This lecture note tries to provide an alternative approach to the material in Sections
Using Markov Chains To Model Human Migration in a Network Equilibrium Framework
 Using Markov Chains To Model Human Migration in a Network Equilibrium Framework Jie Pan Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Saint Joseph s University Philadelphia, PA 19131 Anna Nagurney School
Using Markov Chains To Model Human Migration in a Network Equilibrium Framework Jie Pan Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Saint Joseph s University Philadelphia, PA 19131 Anna Nagurney School
CS 237: Probability in Computing
 CS 237: Probability in Computing Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University Lecture 13: Normal Distribution Exponential Distribution Recall that the Normal Distribution is given by an explicit
CS 237: Probability in Computing Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University Lecture 13: Normal Distribution Exponential Distribution Recall that the Normal Distribution is given by an explicit
HAMMING DISTANCE FROM IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER F Introduction and Motivation
 HAMMING DISTANCE FROM IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER F 2 GILBERT LEE, FRANK RUSKEY, AND AARON WILLIAMS Abstract. We study the Hamming distance from polynomials to classes of polynomials that share certain
HAMMING DISTANCE FROM IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER F 2 GILBERT LEE, FRANK RUSKEY, AND AARON WILLIAMS Abstract. We study the Hamming distance from polynomials to classes of polynomials that share certain
Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums of binomial coefficients
 Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums of binomial coefficients Tamás Mathematics Department Occidental College 29th Journées Arithmétiques JA2015, July 6-10, 2015 Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums
Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums of binomial coefficients Tamás Mathematics Department Occidental College 29th Journées Arithmétiques JA2015, July 6-10, 2015 Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums
Analysis of Multinomial Response Data: a Measure for Evaluating Knowledge Structures
 Analysis of Multinomial Response Data: a Measure for Evaluating Knowledge Structures Department of Psychology University of Graz Universitätsplatz 2/III A-8010 Graz, Austria (e-mail: ali.uenlue@uni-graz.at)
Analysis of Multinomial Response Data: a Measure for Evaluating Knowledge Structures Department of Psychology University of Graz Universitätsplatz 2/III A-8010 Graz, Austria (e-mail: ali.uenlue@uni-graz.at)
PROBLEMS OF CAUSAL ANALYSIS IN THE SOCIAL SCIENCES
 Patrick Suppes PROBLEMS OF CAUSAL ANALYSIS IN THE SOCIAL SCIENCES This article is concerned with the prospects and problems of causal analysis in the social sciences. On the one hand, over the past 40
Patrick Suppes PROBLEMS OF CAUSAL ANALYSIS IN THE SOCIAL SCIENCES This article is concerned with the prospects and problems of causal analysis in the social sciences. On the one hand, over the past 40
On the Impossibility of Certain Ranking Functions
 On the Impossibility of Certain Ranking Functions Jin-Yi Cai Abstract Suppose all the individuals in a field are linearly ordered. Groups of individuals form teams. Is there a perfect ranking function
On the Impossibility of Certain Ranking Functions Jin-Yi Cai Abstract Suppose all the individuals in a field are linearly ordered. Groups of individuals form teams. Is there a perfect ranking function
Links Between Sums Over Paths in Bernoulli s Triangles and the Fibonacci Numbers
 Links Between Sums Over Paths in Bernoulli s Triangles and the Fibonacci Numbers arxiv:1611.09181v1 [math.co] 28 Nov 2016 Denis Neiter and Amsha Proag Ecole Polytechnique Route de Saclay 91128 Palaiseau
Links Between Sums Over Paths in Bernoulli s Triangles and the Fibonacci Numbers arxiv:1611.09181v1 [math.co] 28 Nov 2016 Denis Neiter and Amsha Proag Ecole Polytechnique Route de Saclay 91128 Palaiseau
Running Modulus Recursions
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 13 (2010), Article 10.1.6 Running Modulus Recursions Bruce Dearden and Jerry Metzger University of North Dakota Department of Mathematics Witmer Hall
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 13 (2010), Article 10.1.6 Running Modulus Recursions Bruce Dearden and Jerry Metzger University of North Dakota Department of Mathematics Witmer Hall
ALL TEXTS BELONG TO OWNERS. Candidate code: glt090 TAKEN FROM
 How are Generating Functions used in finding the closed form of sequences involving recurrence relations and in the analysis of probability distributions? Mathematics Extended Essay Word count: 3865 Abstract
How are Generating Functions used in finding the closed form of sequences involving recurrence relations and in the analysis of probability distributions? Mathematics Extended Essay Word count: 3865 Abstract
Finite vector spaces and certain lattices
 Finite vector spaces and certain lattices Thomas W. Cusick 106 Diefendorf Hall, Department of Mathematics, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY 14214-3093 E-mail: cusick@acsu.buffalo.edu
Finite vector spaces and certain lattices Thomas W. Cusick 106 Diefendorf Hall, Department of Mathematics, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY 14214-3093 E-mail: cusick@acsu.buffalo.edu
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE ALGEBRA II
 CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE ALGEBRA II Course Number 5116 Department Mathematics Qualification Guidelines Successful completion of both semesters of Algebra 1 or Algebra 1
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE ALGEBRA II Course Number 5116 Department Mathematics Qualification Guidelines Successful completion of both semesters of Algebra 1 or Algebra 1
SUMS OF POWERS AND BERNOULLI NUMBERS
 SUMS OF POWERS AND BERNOULLI NUMBERS TOM RIKE OAKLAND HIGH SCHOOL Fermat and Pascal On September 22, 636 Fermat claimed in a letter that he could find the area under any higher parabola and Roberval wrote
SUMS OF POWERS AND BERNOULLI NUMBERS TOM RIKE OAKLAND HIGH SCHOOL Fermat and Pascal On September 22, 636 Fermat claimed in a letter that he could find the area under any higher parabola and Roberval wrote
The Sum n. Introduction. Proof I: By Induction. Caleb McWhorter
 The Sum 1 + + + n Caleb McWhorter Introduction Mathematicians study patterns, logic, and the relationships between objects. Though this definition is so vague it could be describing any field not just
The Sum 1 + + + n Caleb McWhorter Introduction Mathematicians study patterns, logic, and the relationships between objects. Though this definition is so vague it could be describing any field not just
Postulate 2 [Order Axioms] in WRW the usual rules for inequalities
![Postulate 2 [Order Axioms] in WRW the usual rules for inequalities Postulate 2 [Order Axioms] in WRW the usual rules for inequalities](/thumbs/95/123582190.jpg) Number Systems N 1,2,3,... the positive integers Z 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3,... the integers Q p q : p,q Z with q 0 the rational numbers R {numbers expressible by finite or unending decimal expansions} makes sense
Number Systems N 1,2,3,... the positive integers Z 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3,... the integers Q p q : p,q Z with q 0 the rational numbers R {numbers expressible by finite or unending decimal expansions} makes sense
4. List of program goals/learning outcomes to be met. Goal-1: Students will have the ability to analyze and graph polynomial functions.
 Course of Study Advanced Algebra 1. Introduction: Common Core Advanced Algebra, Mathematics Department, Grade 9-12, 2 semester course. 2. Course Description Common Core Advanced Algebra is a one year advanced
Course of Study Advanced Algebra 1. Introduction: Common Core Advanced Algebra, Mathematics Department, Grade 9-12, 2 semester course. 2. Course Description Common Core Advanced Algebra is a one year advanced
Quadratics and Other Polynomials
 Algebra 2, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Quadratics and Other Polynomials Overview Number of instructional days: 15 (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Content to be learned Know and apply the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Algebra 2, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Quadratics and Other Polynomials Overview Number of instructional days: 15 (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Content to be learned Know and apply the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
What you learned in Math 28. Rosa C. Orellana
 What you learned in Math 28 Rosa C. Orellana Chapter 1 - Basic Counting Techniques Sum Principle If we have a partition of a finite set S, then the size of S is the sum of the sizes of the blocks of the
What you learned in Math 28 Rosa C. Orellana Chapter 1 - Basic Counting Techniques Sum Principle If we have a partition of a finite set S, then the size of S is the sum of the sizes of the blocks of the
Columbus State Community College Mathematics Department Public Syllabus
 Columbus State Community College Mathematics Department Public Syllabus Course and Number: MATH 2568 Elementary Linear Algebra Credits: 4 Class Hours Per Week: 4 Prerequisites: MATH 2153 with a C or higher
Columbus State Community College Mathematics Department Public Syllabus Course and Number: MATH 2568 Elementary Linear Algebra Credits: 4 Class Hours Per Week: 4 Prerequisites: MATH 2153 with a C or higher
- 1 - Items related to expected use of technology appear in bold italics.
 - 1 - Items related to expected use of technology appear in bold italics. Operating with Geometric and Cartesian Vectors Determining Intersections of Lines and Planes in Three- Space Similar content as
- 1 - Items related to expected use of technology appear in bold italics. Operating with Geometric and Cartesian Vectors Determining Intersections of Lines and Planes in Three- Space Similar content as
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY. MATH 3120 INTRO DO PDES The Schrödinger equation
 VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 31 INTRO DO PDES The Schrödinger equation 1. Introduction Our goal is to investigate solutions to the Schrödinger equation, i Ψ t = Ψ + V Ψ, 1.1 µ where i is the imaginary number
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MATH 31 INTRO DO PDES The Schrödinger equation 1. Introduction Our goal is to investigate solutions to the Schrödinger equation, i Ψ t = Ψ + V Ψ, 1.1 µ where i is the imaginary number
Algorithmic Approach to Counting of Certain Types m-ary Partitions
 Algorithmic Approach to Counting of Certain Types m-ary Partitions Valentin P. Bakoev Abstract Partitions of integers of the type m n as a sum of powers of m (the so called m-ary partitions) and their
Algorithmic Approach to Counting of Certain Types m-ary Partitions Valentin P. Bakoev Abstract Partitions of integers of the type m n as a sum of powers of m (the so called m-ary partitions) and their
THE GROUP OF UNITS OF SOME FINITE LOCAL RINGS I
 J Korean Math Soc 46 (009), No, pp 95 311 THE GROUP OF UNITS OF SOME FINITE LOCAL RINGS I Sung Sik Woo Abstract The purpose of this paper is to identify the group of units of finite local rings of the
J Korean Math Soc 46 (009), No, pp 95 311 THE GROUP OF UNITS OF SOME FINITE LOCAL RINGS I Sung Sik Woo Abstract The purpose of this paper is to identify the group of units of finite local rings of the
A SUMMARY OF RECURSION SOLVING TECHNIQUES
 A SUMMARY OF RECURSION SOLVING TECHNIQUES KIMMO ERIKSSON, KTH These notes are meant to be a complement to the material on recursion solving techniques in the textbook Discrete Mathematics by Biggs. In
A SUMMARY OF RECURSION SOLVING TECHNIQUES KIMMO ERIKSSON, KTH These notes are meant to be a complement to the material on recursion solving techniques in the textbook Discrete Mathematics by Biggs. In
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 18 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 18 Oct 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 18 Oct 2016](/thumbs/73/69166755.jpg) ON SOME CLASS OF SUMS ANDREI K. SVININ Abstract. We consider some class of the sums which naturally include the sums of powers of integers. We suggest a number of conjectures concerning a representation
ON SOME CLASS OF SUMS ANDREI K. SVININ Abstract. We consider some class of the sums which naturally include the sums of powers of integers. We suggest a number of conjectures concerning a representation
On reaching head-to-tail ratios for balanced and unbalanced coins
 Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 0 (00) 0 0 www.elsevier.com/locate/jspi On reaching head-to-tail ratios for balanced and unbalanced coins Tamas Lengyel Department of Mathematics, Occidental
Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 0 (00) 0 0 www.elsevier.com/locate/jspi On reaching head-to-tail ratios for balanced and unbalanced coins Tamas Lengyel Department of Mathematics, Occidental
Multi-objective Quadratic Assignment Problem instances generator with a known optimum solution
 Multi-objective Quadratic Assignment Problem instances generator with a known optimum solution Mădălina M. Drugan Artificial Intelligence lab, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussels,
Multi-objective Quadratic Assignment Problem instances generator with a known optimum solution Mădălina M. Drugan Artificial Intelligence lab, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussels,
A Note about the Pochhammer Symbol
 Mathematica Moravica Vol. 12-1 (2008), 37 42 A Note about the Pochhammer Symbol Aleksandar Petoević Abstract. In this paper we give elementary proofs of the generating functions for the Pochhammer symbol
Mathematica Moravica Vol. 12-1 (2008), 37 42 A Note about the Pochhammer Symbol Aleksandar Petoević Abstract. In this paper we give elementary proofs of the generating functions for the Pochhammer symbol
MATHEMATICS (IX-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session
 MATHEMATICS (IX-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2018-19 The Syllabus in the subject of Mathematics has undergone changes from time to time in accordance with growth of the subject and emerging needs of the society.
MATHEMATICS (IX-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2018-19 The Syllabus in the subject of Mathematics has undergone changes from time to time in accordance with growth of the subject and emerging needs of the society.
TEACHER NOTES FOR ADVANCED MATHEMATICS 1 FOR AS AND A LEVEL
 April 2017 TEACHER NOTES FOR ADVANCED MATHEMATICS 1 FOR AS AND A LEVEL This book is designed both as a complete AS Mathematics course, and as the first year of the full A level Mathematics. The content
April 2017 TEACHER NOTES FOR ADVANCED MATHEMATICS 1 FOR AS AND A LEVEL This book is designed both as a complete AS Mathematics course, and as the first year of the full A level Mathematics. The content
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 A Correlation of Pearson to the Standards for Mathematics Appendix A, Integrated Pathway High School A Correlation of Pearson, Appendix A Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson,, meets the
A Correlation of Pearson to the Standards for Mathematics Appendix A, Integrated Pathway High School A Correlation of Pearson, Appendix A Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson,, meets the
12.1 Arithmetic Progression Geometric Progression General things about sequences
 ENGR11 Engineering Mathematics Lecture Notes SMS, Victoria University of Wellington Week Five. 1.1 Arithmetic Progression An arithmetic progression is a sequence where each term is found by adding a fixed
ENGR11 Engineering Mathematics Lecture Notes SMS, Victoria University of Wellington Week Five. 1.1 Arithmetic Progression An arithmetic progression is a sequence where each term is found by adding a fixed
A Probabilistic Algorithm for -SAT Based on Limited Local Search and Restart
 A Probabilistic Algorithm for -SAT Based on Limited Local Search and Restart Uwe Schöning Universität Ulm, Abteilung Theoretische Informatik James-Franck-Ring, D-89069 Ulm, Germany e-mail: schoenin@informatik.uni-ulm.de
A Probabilistic Algorithm for -SAT Based on Limited Local Search and Restart Uwe Schöning Universität Ulm, Abteilung Theoretische Informatik James-Franck-Ring, D-89069 Ulm, Germany e-mail: schoenin@informatik.uni-ulm.de
Algebra 2 Secondary Mathematics Instructional Guide
 Algebra 2 Secondary Mathematics Instructional Guide 2009-2010 ALGEBRA 2AB (Grade 9, 10 or 11) Prerequisite: Algebra 1AB or Geometry AB 310303 Algebra 2A 310304 Algebra 2B COURSE DESCRIPTION Los Angeles
Algebra 2 Secondary Mathematics Instructional Guide 2009-2010 ALGEBRA 2AB (Grade 9, 10 or 11) Prerequisite: Algebra 1AB or Geometry AB 310303 Algebra 2A 310304 Algebra 2B COURSE DESCRIPTION Los Angeles
The Generating Functions for Pochhammer
 The Generating Functions for Pochhammer Symbol { }, n N Aleksandar Petoević University of Novi Sad Teacher Training Faculty, Department of Mathematics Podgorička 4, 25000 Sombor SERBIA and MONTENEGRO Email
The Generating Functions for Pochhammer Symbol { }, n N Aleksandar Petoević University of Novi Sad Teacher Training Faculty, Department of Mathematics Podgorička 4, 25000 Sombor SERBIA and MONTENEGRO Email
For all For every For each For any There exists at least one There exists There is Some
 Section 1.3 Predicates and Quantifiers Assume universe of discourse is all the people who are participating in this course. Also let us assume that we know each person in the course. Consider the following
Section 1.3 Predicates and Quantifiers Assume universe of discourse is all the people who are participating in this course. Also let us assume that we know each person in the course. Consider the following
A Note on Multiplicity Weight of Nodes of Two Point Taylor Expansion
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol, 207, no 6, 307-3032 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom https://doiorg/02988/ams2077302 A Note on Multiplicity Weight of Nodes of Two Point Taylor Expansion Koichiro Shimada
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol, 207, no 6, 307-3032 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom https://doiorg/02988/ams2077302 A Note on Multiplicity Weight of Nodes of Two Point Taylor Expansion Koichiro Shimada
Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics. Editors J. H. Ewing F. W. Gehring P. R. Halmos
 Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics Editors J. H. Ewing F. W. Gehring P. R. Halmos Springer Books on Elemeritary Mathematics by Serge Lang MATH! Encounters with High School Students 1985, ISBN 96129-1 The
Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics Editors J. H. Ewing F. W. Gehring P. R. Halmos Springer Books on Elemeritary Mathematics by Serge Lang MATH! Encounters with High School Students 1985, ISBN 96129-1 The
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
 Academic Council 25/05/2011 Item No. 4.25 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI SYLLABUS for the F.Y.B.A/B.Sc. Programme:B.A./B.Sc. Course: (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic year 2011
Academic Council 25/05/2011 Item No. 4.25 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI SYLLABUS for the F.Y.B.A/B.Sc. Programme:B.A./B.Sc. Course: (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic year 2011
MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS
 MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS JI YOUNG CHOI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SHIPPENSBURG UNIVERSITY SHIPPENSBURG, PA 17257, U.S.A. Abstract. Given positive integers n, k, and m, the (n, k)-th m- restrained
MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS JI YOUNG CHOI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SHIPPENSBURG UNIVERSITY SHIPPENSBURG, PA 17257, U.S.A. Abstract. Given positive integers n, k, and m, the (n, k)-th m- restrained
An example for the L A TEX package ORiONeng.sty
 Operations Research Society of South Africa Submitted for publication in ORiON Operasionele Navorsingsvereniging van Suid-Afrika An example for the L A TEX package ORiONeng.sty Authors identities suppressed:
Operations Research Society of South Africa Submitted for publication in ORiON Operasionele Navorsingsvereniging van Suid-Afrika An example for the L A TEX package ORiONeng.sty Authors identities suppressed:
Senior Math Circles November 19, 2008 Probability II
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 9, 2008 Probability II Probability Counting There are many situations where
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 9, 2008 Probability II Probability Counting There are many situations where
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: Targeted Review
 College Algebra with Corequisite Support: Targeted Review 978-1-63545-056-9 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: Targeted Review 978-1-63545-056-9 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
A class of trees and its Wiener index.
 A class of trees and its Wiener index. Stephan G. Wagner Department of Mathematics Graz University of Technology Steyrergasse 3, A-81 Graz, Austria wagner@finanz.math.tu-graz.ac.at Abstract In this paper,
A class of trees and its Wiener index. Stephan G. Wagner Department of Mathematics Graz University of Technology Steyrergasse 3, A-81 Graz, Austria wagner@finanz.math.tu-graz.ac.at Abstract In this paper,
and Transitional Comprehensive Curriculum. Algebra I Part 2 Unit 7: Polynomials and Factoring
 Algebra I Part Unit 7: Polynomials and Factoring Time Frame: Approximately four weeks Unit Description This unit focuses on the arithmetic operations on polynomial expressions as well as on basic factoring
Algebra I Part Unit 7: Polynomials and Factoring Time Frame: Approximately four weeks Unit Description This unit focuses on the arithmetic operations on polynomial expressions as well as on basic factoring
Enumerating split-pair arrangements
 Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 115 (28 293 33 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcta Enumerating split-pair arrangements Ron Graham 1, Nan Zang Department of Computer Science, University of California
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 115 (28 293 33 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcta Enumerating split-pair arrangements Ron Graham 1, Nan Zang Department of Computer Science, University of California
Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 03 notes Summer
 Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 03 notes Summer 01 1 Lines and quadratics 1. Polynomials, functions in which each term is a positive integer power of the independent variable include
Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 03 notes Summer 01 1 Lines and quadratics 1. Polynomials, functions in which each term is a positive integer power of the independent variable include
Algebra 2 and Trigonometry
 Page 1 Algebra 2 and Trigonometry In implementing the Algebra 2 and Trigonometry process and content performance indicators, it is expected that students will identify and justify mathematical relationships,
Page 1 Algebra 2 and Trigonometry In implementing the Algebra 2 and Trigonometry process and content performance indicators, it is expected that students will identify and justify mathematical relationships,
IB Mathematics HL Year 2 Unit 11: Completion of Algebra (Core Topic 1)
 IB Mathematics HL Year Unit : Completion of Algebra (Core Topic ) Homewor for Unit Ex C:, 3, 4, 7; Ex D: 5, 8, 4; Ex E.: 4, 5, 9, 0, Ex E.3: (a), (b), 3, 7. Now consider these: Lesson 73 Sequences and
IB Mathematics HL Year Unit : Completion of Algebra (Core Topic ) Homewor for Unit Ex C:, 3, 4, 7; Ex D: 5, 8, 4; Ex E.: 4, 5, 9, 0, Ex E.3: (a), (b), 3, 7. Now consider these: Lesson 73 Sequences and
1 ** The performance objectives highlighted in italics have been identified as core to an Algebra II course.
 Strand One: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and skills from the pervious grade levels. The standards are designed so that new learning builds on preceding
Strand One: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and skills from the pervious grade levels. The standards are designed so that new learning builds on preceding
1 Introduction. 2 A regression model
 Regression Analysis of Compositional Data When Both the Dependent Variable and Independent Variable Are Components LA van der Ark 1 1 Tilburg University, The Netherlands; avdark@uvtnl Abstract It is well
Regression Analysis of Compositional Data When Both the Dependent Variable and Independent Variable Are Components LA van der Ark 1 1 Tilburg University, The Netherlands; avdark@uvtnl Abstract It is well
Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Media Update 7th Edition 2010, (Demana, et al)
 A Correlation of Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Media Update To the Virginia Standards of Learning for Mathematical Analysis February 2009 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how, meets
A Correlation of Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Media Update To the Virginia Standards of Learning for Mathematical Analysis February 2009 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how, meets
Survey of Smoking Behavior. Survey of Smoking Behavior. Survey of Smoking Behavior
 Sample HH from Frame HH One-Stage Cluster Survey Population Frame Sample Elements N =, N =, n = population smokes Sample HH from Frame HH Elementary units are different from sampling units Sampled HH but
Sample HH from Frame HH One-Stage Cluster Survey Population Frame Sample Elements N =, N =, n = population smokes Sample HH from Frame HH Elementary units are different from sampling units Sampled HH but
IDENTITIES INVOLVING BERNOULLI NUMBERS RELATED TO SUMS OF POWERS OF INTEGERS
 IDENTITIES INVOLVING ERNOULLI NUMERS RELATED TO SUMS OF POWERS OF INTEGERS PIERLUIGI MAGLI Abstract. Pointing out the relations between integer power s sums and ernoulli and Genocchi polynomials, several
IDENTITIES INVOLVING ERNOULLI NUMERS RELATED TO SUMS OF POWERS OF INTEGERS PIERLUIGI MAGLI Abstract. Pointing out the relations between integer power s sums and ernoulli and Genocchi polynomials, several
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11
 Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11 Andrew Nobel October 24, 2017 Basics of Counting Product Rule Product Rule: Suppose that the elements of a collection S can be specified by a sequence of k
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11 Andrew Nobel October 24, 2017 Basics of Counting Product Rule Product Rule: Suppose that the elements of a collection S can be specified by a sequence of k
How do we analyze, evaluate, solve, and graph quadratic functions?
 Topic: 4. Quadratic Functions and Factoring Days: 18 Key Learning: Students will be able to analyze, evaluate, solve and graph quadratic functions. Unit Essential Question(s): How do we analyze, evaluate,
Topic: 4. Quadratic Functions and Factoring Days: 18 Key Learning: Students will be able to analyze, evaluate, solve and graph quadratic functions. Unit Essential Question(s): How do we analyze, evaluate,
Common Core State Standards. Clusters and Instructional Notes Perform arithmetic operations with complex numbers. 5.6
 Algebra II Unit 1: Polynomial, Rational, and Radical Relationships This unit develops the structural similarities between the system of polynomials and the system of integers. Students draw on analogies
Algebra II Unit 1: Polynomial, Rational, and Radical Relationships This unit develops the structural similarities between the system of polynomials and the system of integers. Students draw on analogies
Jaegug Bae and Sungjin Choi
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 40 (2003), No. 5, pp. 757 768 A GENERALIZATION OF A SUBSET-SUM-DISTINCT SEQUENCE Jaegug Bae and Sungjin Choi Abstract. In 1967, as an answer to the question of P. Erdös on a set of
J. Korean Math. Soc. 40 (2003), No. 5, pp. 757 768 A GENERALIZATION OF A SUBSET-SUM-DISTINCT SEQUENCE Jaegug Bae and Sungjin Choi Abstract. In 1967, as an answer to the question of P. Erdös on a set of
CBSE OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE. Published by : 1/11, Sahitya Kunj, M.G. Road, Agra , UP (India) Ph.: ,
 OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE CBSE SOLVED PAPER 2018 MATHEMATICS CLASS 9 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS 1/11, Sahitya Kunj, M.G. Road, Agra - 282002, UP (India) Ph.: 0562 2857671, 2527781 email: contact@oswaalbooks.com
OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE CBSE SOLVED PAPER 2018 MATHEMATICS CLASS 9 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS 1/11, Sahitya Kunj, M.G. Road, Agra - 282002, UP (India) Ph.: 0562 2857671, 2527781 email: contact@oswaalbooks.com
Unit 2, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties
 Unit 2, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Unit 2 - Polynomial Equations & Inequalities 2.1 Laws of Exponents - record the rules for
Unit 2, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Unit 2 - Polynomial Equations & Inequalities 2.1 Laws of Exponents - record the rules for
Situation: Summing the Natural Numbers
 Situation: Summing the Natural Numbers Prepared at Penn State University Mid-Atlantic Center for Mathematics Teaching and Learning 14 July 005 Shari and Anna Edited at University of Georgia Center for
Situation: Summing the Natural Numbers Prepared at Penn State University Mid-Atlantic Center for Mathematics Teaching and Learning 14 July 005 Shari and Anna Edited at University of Georgia Center for
Fast Sorting and Selection. A Lower Bound for Worst Case
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Fast Sorting and Selection USGS NEIC. Public domain government image. A Lower Bound
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Fast Sorting and Selection USGS NEIC. Public domain government image. A Lower Bound
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Blended Approach
 College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Blended Approach 978-1-63545-058-3 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Blended Approach 978-1-63545-058-3 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
Linear Algebra. The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems of equations.
 POLI 7 - Mathematical and Statistical Foundations Prof S Saiegh Fall Lecture Notes - Class 4 October 4, Linear Algebra The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems
POLI 7 - Mathematical and Statistical Foundations Prof S Saiegh Fall Lecture Notes - Class 4 October 4, Linear Algebra The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems
SET THEORY IN LINEAR ALGEBRA
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol.,, no. 5, 7-7 SET THEORY IN LINEAR ALGEBRA HAMIDE DOGAN University of Teas at El Paso, Department of Mathematical Sciences El Paso, TX 79968 hdogan@utep.edu Abstract Set theory
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol.,, no. 5, 7-7 SET THEORY IN LINEAR ALGEBRA HAMIDE DOGAN University of Teas at El Paso, Department of Mathematical Sciences El Paso, TX 79968 hdogan@utep.edu Abstract Set theory
Introduction to Quantitative Techniques for MSc Programmes SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS, MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MALET STREET LONDON WC1E 7HX
 Introduction to Quantitative Techniques for MSc Programmes SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS, MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MALET STREET LONDON WC1E 7HX September 2007 MSc Sep Intro QT 1 Who are these course for? The September
Introduction to Quantitative Techniques for MSc Programmes SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS, MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MALET STREET LONDON WC1E 7HX September 2007 MSc Sep Intro QT 1 Who are these course for? The September
CONVOLUTION TREES AND PASCAL-T TRIANGLES. JOHN C. TURNER University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand (Submitted December 1986) 1.
 JOHN C. TURNER University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand (Submitted December 986). INTRODUCTION Pascal (6-66) made extensive use of the famous arithmetical triangle which now bears his name. He wrote
JOHN C. TURNER University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand (Submitted December 986). INTRODUCTION Pascal (6-66) made extensive use of the famous arithmetical triangle which now bears his name. He wrote
Applications. More Counting Problems. Complexity of Algorithms
 Recurrences Applications More Counting Problems Complexity of Algorithms Part I Recurrences and Binomial Coefficients Paths in a Triangle P(0, 0) P(1, 0) P(1,1) P(2, 0) P(2,1) P(2, 2) P(3, 0) P(3,1) P(3,
Recurrences Applications More Counting Problems Complexity of Algorithms Part I Recurrences and Binomial Coefficients Paths in a Triangle P(0, 0) P(1, 0) P(1,1) P(2, 0) P(2,1) P(2, 2) P(3, 0) P(3,1) P(3,
Congruence Classes of 2-adic Valuations of Stirling Numbers of the Second Kind
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 16 (2013), Article 13.3.6 Congruence Classes of 2-adic Valuations of Stirling Numbers of the Second Kind Curtis Bennett and Edward Mosteig Department
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 16 (2013), Article 13.3.6 Congruence Classes of 2-adic Valuations of Stirling Numbers of the Second Kind Curtis Bennett and Edward Mosteig Department
MTH Linear Algebra. Study Guide. Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
1 Counting Collections of Functions and of Subsets.
 1 Counting Collections of Functions and of Subsets See p144 All page references are to PJEccles book unless otherwise stated Let X and Y be sets Definition 11 F un (X, Y will be the set of all functions
1 Counting Collections of Functions and of Subsets See p144 All page references are to PJEccles book unless otherwise stated Let X and Y be sets Definition 11 F un (X, Y will be the set of all functions
CS 170 Algorithms Fall 2014 David Wagner MT2
 CS 170 Algorithms Fall 2014 David Wagner MT2 PRINT your name:, (last) SIGN your name: (first) Your Student ID number: Your Unix account login: cs170- The room you are sitting in right now: Name of the
CS 170 Algorithms Fall 2014 David Wagner MT2 PRINT your name:, (last) SIGN your name: (first) Your Student ID number: Your Unix account login: cs170- The room you are sitting in right now: Name of the
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 21 No , THE VARIANCE OF SAMPLE VARIANCE FROM A FINITE POPULATION
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 21 No. 3 2005, 387-394 THE VARIANCE OF SAMPLE VARIANCE FROM A FINITE POPULATION Eungchun Cho 1, Moon Jung Cho 2, John Eltinge 3 1 Department
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 21 No. 3 2005, 387-394 THE VARIANCE OF SAMPLE VARIANCE FROM A FINITE POPULATION Eungchun Cho 1, Moon Jung Cho 2, John Eltinge 3 1 Department
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Compressed Approach
 College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Compressed Approach 978-1-63545-059-0 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
College Algebra with Corequisite Support: A Compressed Approach 978-1-63545-059-0 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable)
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework 7
 MATH22 Linear Algebra B Homework 7 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra and its Applications Pearson, 26 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
MATH22 Linear Algebra B Homework 7 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra and its Applications Pearson, 26 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
CHAPTER 10 Comparing Two Populations or Groups
 CHAPTER 10 Comparing Two Populations or Groups 10.1 Comparing Two Proportions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Comparing Two Proportions
CHAPTER 10 Comparing Two Populations or Groups 10.1 Comparing Two Proportions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Comparing Two Proportions
arxiv: v1 [stat.ot] 6 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v1 [stat.ot] 6 Apr 2017 arxiv: v1 [stat.ot] 6 Apr 2017](/thumbs/89/98354253.jpg) A Mathematically Sensible Explanation of the Concept of Statistical Population Yiping Cheng Beijing Jiaotong University, China ypcheng@bjtu.edu.cn arxiv:1704.01732v1 [stat.ot] 6 Apr 2017 Abstract In statistics
A Mathematically Sensible Explanation of the Concept of Statistical Population Yiping Cheng Beijing Jiaotong University, China ypcheng@bjtu.edu.cn arxiv:1704.01732v1 [stat.ot] 6 Apr 2017 Abstract In statistics
On the Sylvester Denumerants for General Restricted Partitions
 On the Sylvester Denumerants for General Restricted Partitions Geir Agnarsson Abstract Let n be a nonnegative integer and let ã = (a 1... a k be a k-tuple of positive integers. The term denumerant introduced
On the Sylvester Denumerants for General Restricted Partitions Geir Agnarsson Abstract Let n be a nonnegative integer and let ã = (a 1... a k be a k-tuple of positive integers. The term denumerant introduced
An Application of Catalan Numbers on Cayley Tree of Order 2: Single Polygon Counting
 BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://math.usm.my/bulletin Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. (2) 31(2) (2008), 175 183 An Application of Catalan Numbers on Cayley Tree of Order 2:
BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://math.usm.my/bulletin Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. (2) 31(2) (2008), 175 183 An Application of Catalan Numbers on Cayley Tree of Order 2:
Sequences that satisfy a(n a(n)) = 0
 Sequences that satisfy a(n a(n)) = 0 Nate Kube Frank Ruskey October 13, 2005 Abstract We explore the properties of some sequences for which a(n a(n)) = 0. Under the natural restriction that a(n) < n the
Sequences that satisfy a(n a(n)) = 0 Nate Kube Frank Ruskey October 13, 2005 Abstract We explore the properties of some sequences for which a(n a(n)) = 0. Under the natural restriction that a(n) < n the
ACE 562 Fall Lecture 2: Probability, Random Variables and Distributions. by Professor Scott H. Irwin
 ACE 562 Fall 2005 Lecture 2: Probability, Random Variables and Distributions Required Readings: by Professor Scott H. Irwin Griffiths, Hill and Judge. Some Basic Ideas: Statistical Concepts for Economists,
ACE 562 Fall 2005 Lecture 2: Probability, Random Variables and Distributions Required Readings: by Professor Scott H. Irwin Griffiths, Hill and Judge. Some Basic Ideas: Statistical Concepts for Economists,
Lesson 8: Why Stay with Whole Numbers?
 Student Outcomes Students use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context. Students create functions that
Student Outcomes Students use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context. Students create functions that
LAKELAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE FORM
 LAKELAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE FORM ORIGINATION DATE: 8/2/99 APPROVAL DATE: 3/22/12 LAST MODIFICATION DATE: 3/28/12 EFFECTIVE TERM/YEAR: FALL/ 12 COURSE ID: COURSE TITLE: MATH2800 Linear Algebra
LAKELAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE FORM ORIGINATION DATE: 8/2/99 APPROVAL DATE: 3/22/12 LAST MODIFICATION DATE: 3/28/12 EFFECTIVE TERM/YEAR: FALL/ 12 COURSE ID: COURSE TITLE: MATH2800 Linear Algebra
Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 653914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/653914 Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 653914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/653914 Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
CS 468: Computational Topology Group Theory Fall b c b a b a c b a c b c c b a
 Q: What s purple and commutes? A: An abelian grape! Anonymous Group Theory Last lecture, we learned about a combinatorial method for characterizing spaces: using simplicial complexes as triangulations
Q: What s purple and commutes? A: An abelian grape! Anonymous Group Theory Last lecture, we learned about a combinatorial method for characterizing spaces: using simplicial complexes as triangulations
MINIMAL POLYNOMIALS AND CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIALS OVER RINGS
 JP Journal of Algebra, Number Theory and Applications Volume 0, Number 1, 011, Pages 49-60 Published Online: March, 011 This paper is available online at http://pphmj.com/journals/jpanta.htm 011 Pushpa
JP Journal of Algebra, Number Theory and Applications Volume 0, Number 1, 011, Pages 49-60 Published Online: March, 011 This paper is available online at http://pphmj.com/journals/jpanta.htm 011 Pushpa
GENERALIZATION OF UNIVERSAL PARTITION AND BIPARTITION THEOREMS. Hacène Belbachir 1
 #A59 INTEGERS 3 (23) GENERALIZATION OF UNIVERSAL PARTITION AND BIPARTITION THEOREMS Hacène Belbachir USTHB, Faculty of Mathematics, RECITS Laboratory, Algiers, Algeria hbelbachir@usthb.dz, hacenebelbachir@gmail.com
#A59 INTEGERS 3 (23) GENERALIZATION OF UNIVERSAL PARTITION AND BIPARTITION THEOREMS Hacène Belbachir USTHB, Faculty of Mathematics, RECITS Laboratory, Algiers, Algeria hbelbachir@usthb.dz, hacenebelbachir@gmail.com
ON THE TAYLOR COEFFICIENTS OF THE HURWITZ ZETA FUNCTION
 ON THE TAYLOR COEFFICIENTS OF THE HURWITZ ZETA FUNCTION Khristo N. Boyadzhiev Department of Mathematics, Ohio Northern University, Ada, Ohio, 45810 k-boyadzhiev@onu.edu Abstract. We find a representation
ON THE TAYLOR COEFFICIENTS OF THE HURWITZ ZETA FUNCTION Khristo N. Boyadzhiev Department of Mathematics, Ohio Northern University, Ada, Ohio, 45810 k-boyadzhiev@onu.edu Abstract. We find a representation
Traditional Pathway: Algebra II
 Traditional Pathway: Algebra II Building on their work with linear, quadratic, and exponential functions, students extend their repertoire of functions to include polynomial, rational, and radical functions.
Traditional Pathway: Algebra II Building on their work with linear, quadratic, and exponential functions, students extend their repertoire of functions to include polynomial, rational, and radical functions.
MULTISECTION METHOD AND FURTHER FORMULAE FOR π. De-Yin Zheng
 Indian J. pure appl. Math., 39(: 37-55, April 008 c Printed in India. MULTISECTION METHOD AND FURTHER FORMULAE FOR π De-Yin Zheng Department of Mathematics, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 30036,
Indian J. pure appl. Math., 39(: 37-55, April 008 c Printed in India. MULTISECTION METHOD AND FURTHER FORMULAE FOR π De-Yin Zheng Department of Mathematics, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 30036,
Chapter 1 A Survey of Divisibility 14
 Chapter 1 A Survey of Divisibility 14 SECTION C Euclidean Algorithm By the end of this section you will be able to use properties of the greatest common divisor (gcd) obtain the gcd using the Euclidean
Chapter 1 A Survey of Divisibility 14 SECTION C Euclidean Algorithm By the end of this section you will be able to use properties of the greatest common divisor (gcd) obtain the gcd using the Euclidean
