1 Binary Classification
|
|
|
- Jasper Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS6501: Advanced Machine Learning 017 Problem Set 1 Handed Out: Feb 11, 017 Due: Feb 18, 017 Feel free to talk to other members of the class in doing the homework. You should, however, write down your solution yourself. Please try to keep the solution brief and clear. Please use Piazza first if you have questions about the homework. Also feel free to come to office hours. Please, no handwritten solutions. You will submit your solution manuscript as a single pdf file. Please use L A TEXto typeset your solutions. The homework is due at 11:59 PM on the due date. We will be using Collab for collecting the homework assignments. Please submit your solution manuscript as a pdf file and your code as a zip file. Please do NOT hand in a hard copy of your write-up. Contact the TAs if you are having technical difficulties in submitting the assignment. 1 Binary Classification A linear program can be stated as follows: Definition 1 Let A be an m n real-valued matrix, b R m, and c R n. Find a t R n, that imizes the linear function subject to z t = c T t A t b In the linear programg terology, c is often referred to as the cost vector and z t is referred to as the objective function. 1 We can use this framework to define the problem of learning a linear discriant function. 1 Note that you don t need to really know how to solve a linear program since you can use Matlab or Scipy to obtain the solution although you may wish to brush up on Linear Algebra. This discussion closely parallels the linear programg representation found in Pattern Classification, by Duda, Hart, and Stork. 1
2 The Learning Problem: 3 Let x 1, x,..., x m represent m samples, where each sample x i R n is an n-dimensional vector, and y { 1, 1} m is an m 1 vector representing the respective labels of each of the m samples. Let w R n be an n 1 vector representing the weights of the linear discriant function, and θ be the threshold value. We predict x i to be a positive example if w T x i + θ 0. On the other hand, we predict x i to be a negative example if w T x i + θ < 0. We hope that the learned linear function can separate the data set. That is, for the true labels we hope { 1 if w T x i + θ 0 y i = 1 1 if w T x i + θ < 0. In order to find a good linear separator, we propose the following linear program: w,θ,δ δ subject to y i w T x i + θ 1 δ, x i, y i D 3 where D is the data set of all training examples. δ 0 4 a. [10 points] A data set D = { x i, y i } m i=1 that satisfies condition 1 above is called linearly separable. Show that the data set D is linearly separable if and only if there exists a hyperplane w, θ that satisfies condition 3 with δ = 0 Need a hint? 4. Conclude that D is linearly separable iff the optimal solution to the linear program [ to 4] attains δ = 0. What can we say about the linear separability of the data set if there exists a hyperplane that satisfies condition 3 with δ > 0? The solution to a. contains three parts. i Linear Separability δ = 0: The separability property implies that there exists a hyperplane v T x + ρ such that y=1 v T x + ρ 0 > y= 1 v T x + ρ 3 Note that the notation used in the Learning Problem is unrelated to the one used in the Linear Program definition. You may want to figure out the correspondence. 4 Hint: Assume that D is linearly separable. D is a finite set, so it has a positive example that is closest to the hyperplane among all positive examples. Similarly, there is a negative example that is closest to the hyperplane among negative examples. Consider their distances and use them to show that condition 3 holds. Then show the other direction.
3 Let x i to be the positive sample that is closest to the hyperplane v T x + ρ, and p + = y=1 v T x + ρ = v T x i + ρ Similarly, let x j to be the negative sample that is closest to the hyperplane v T x + ρ, and p = v T x + ρ = v T x j + ρ y= 1 Note that from the definition of separability, we know that p + and p exist and p + 0 > p. Step 1: Shifting the hyperplane. Since p + 0 > p, there exist η 0 such that p + η 0 > p η. Hence, for some values of η, the hyperplane v T x + ρ η = 0 also separates D. We will find the value of η for which the hyperplane v T x + ρ η = 0 is equi-distant from x i and x j and separates D. The value of η can be obtained as follows: v T x i + ρ η v = vt x j + ρ η, v v T x i + ρ η = v T x j + ρ η, p + η = p + η. 5 This implies that η = p+ +p. We can easily verify that for such η, p + η 0 > p η, and hence the resulting hyperplane v T x + ρ η = 0 separates D. Step : Normalizing the hyperplane. With the new hyperplane v T x + ρ η = 0, and y=1 y= 1 v T x + ρ η = p+ p v T x + ρ η = p p + y v T x + ρ η p+ p x, y D Given that p + > p and η = p+ +p, by setting w = v, θ = ρ η, and δ = 0, η η y w T x + θ 1 δ, x, y D ii Linear Separability δ = 0: If there exists a hyperplane w T x + θ such that y w T x + θ 1, x, y D 3
4 It is trivial to show that iii When δ > 0: w T x + θ 1 0, x, y D, y = 1 and w T x + θ 1 < 0, x, y D, y = 1 Now consider the value of δ. Note that if 1 δ > 0, we can apply similar argument and show that the data set is linear separable. If δ 1, we are not sure if the data set is separable or not. If the imal δ 1, then the data set is not separable. b. [5 points] Show that there is a trivial optimal solution for the following linear program: w,θ,δ δ subject to y i w T x i + θ δ, x i, y i D δ 0 Show the optimal solution and use it to very briefly explain why we chose to formulate the linear program as [ to 4] instead. The trivial solution is w = 0, θ = 0, δ = 0. This solution is optimal because 1 the constraints are satisfied, and zero is the best value we can get for δ. We do not use this formulation because the solver might give us this optimal solution which does not give us a hyperplane at all. Note that there exists other optimal solutions for this formulation. c. [10 points] Let x 1 R n, x 1 T = [ ] and y 1 = 1. Let x R n, x T = [ ] and y = 1. The data set D is defined as D = { x 1, y 1, x, y }. Consider the formulation in [ to 4] applied to D. Show the set of all possible optimal solutions solve this problem by hand. Given that there are only two samples in the data set, the data set is separable. Therefore, the optimal δ is 0. Now our job becomes finding w and θ that satisfy the following constraints: w 1 + w... + w n + θ 1 w 1 w... w n + θ 1 w 1 + w w n 1 + θ Hence, w, θ, δ is the optimal solution if δ = 0 and w 1 + w w n 1 + θ. 4
5 Multiclass Classification In this problem set, we will derive, implement, and test an SGD method for a multi-class SVM classification model, and then we will compare it with the one-vs-all approach. Given a data set D = {x i, y i } N i=1 with K classes, the multi-class SVM can be written as the following unconstrained optimization problem: w={w k } 1 K wk T w k + C k=1 N i=1 k=1...k yi, k + w T k x i w T yi x i, 6 where w k is the weight vector for class k, x i, y i is the i th instance and { 1 if y k, y, k = 0 otherwise. To derive the SGD algorithm, we first need to rewrite the objective function in Eq. 6 into the form of i g iw: w={w k } N 1 N i=1 K wk T w k + C k=1 k=1...k yi, k + w T k x i w T yi x i, so that 1 g i w = N K wk T w k + C k=1 k=1...k yi, k + w T k x i w T yi x i. Now let s derive the sub-gradient of g i w. Consider g i w/ w k, the partial sub-gradient of the first term of g i w is w k /N. Regarding the second term, we have to consider several cases. Let ỹ = arg yi, k + wk T x i k. If ỹ = k and y i = k, the partial sub-gradient of the second term is Cx x = 0. Therefore, g i w/ w k = w k /N when ỹ = k and y i = k. How about other cases? 5
6 a. [15 points] Please complete the following formulation w k /N if ỹ = k and y i = k g i w w k = w k /N Cx i w k /N + Cx i w k /N b. [15 points] The SGD algorithm runs as follows: if ỹ k and y i = k if ỹ = k and y i k if ỹ k and y i k 7 for epoch = 0... T do for x i, y i in D do for k= 1... K do w k w k η g i w k / w k η is the step size. The step size is a user specified parameter. Here, we can set it with a default value Plug Eq. 7 in, we have: for epoch = 0... T do for x i, y i in D do ỹ = arg k yi, k + wk T x i for k= 1... K do w k w k ηw k /N if ỹ y i then w yi w yi η Cx i wỹ wỹ η+cx i end if Please, complete the above algorithm. c. [0points] Let s implement a baseline one-vs-all multiclass algorithm and conduct experiments on MNIST dataset 5. We provide a basic code framework at https: 5 6
7 //github.com/uvanlp/hw1 to facilitate the implementation. However, you re welcomed to write your own code. If you want to use the code we provided, implement the one-vs-all algorithm in the main function of one vs all with data reader.py. Then, conduct cross-validation to find the best C for all underlying binary classifier assume the same C is used for all the binary classifiers. Note: You can use the LinearSVC class at Scikit-Learn, svm.linearsvc.html, to implement the underlying classifiers. Report the best C and the final accuracy. d. [5points] Implement the SGD algorithm for multi-class SVM. We provide multiclass svm.py as the code framework. However, you have to implement the update rules. Conduct cross-validation to find the best C and report the result on the test set. 6 e. [0-10 points] We will give bonus points for additional experiments. 6 To test if your algorithm implementation is correct, you can check if the objective function value of the SGD algorithm matches with the score from liblinear cjlin/liblinear. Use the following command line to train a multi-class SVM model./train -s 4 -B -1 -e C 1 train.data with C=1. There is a function in the sample code allows you to print data in liblinear format. Check if the objective function values of your implementation is the same as that of liblinear on a small subset e.g., run on only the first 100 samples. 7
CS446: Machine Learning Spring Problem Set 4
 CS446: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Problem Set 4 Handed Out: February 27 th, 2017 Due: March 11 th, 2017 Feel free to talk to other members of the class in doing the homework. I am more concerned that
CS446: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Problem Set 4 Handed Out: February 27 th, 2017 Due: March 11 th, 2017 Feel free to talk to other members of the class in doing the homework. I am more concerned that
CIS519: Applied Machine Learning Fall Homework 5. Due: December 10 th, 2018, 11:59 PM
 CIS59: Applied Machine Learning Fall 208 Homework 5 Handed Out: December 5 th, 208 Due: December 0 th, 208, :59 PM Feel free to talk to other members of the class in doing the homework. I am more concerned
CIS59: Applied Machine Learning Fall 208 Homework 5 Handed Out: December 5 th, 208 Due: December 0 th, 208, :59 PM Feel free to talk to other members of the class in doing the homework. I am more concerned
HOMEWORK 4: SVMS AND KERNELS
 HOMEWORK 4: SVMS AND KERNELS CMU 060: MACHINE LEARNING (FALL 206) OUT: Sep. 26, 206 DUE: 5:30 pm, Oct. 05, 206 TAs: Simon Shaolei Du, Tianshu Ren, Hsiao-Yu Fish Tung Instructions Homework Submission: Submit
HOMEWORK 4: SVMS AND KERNELS CMU 060: MACHINE LEARNING (FALL 206) OUT: Sep. 26, 206 DUE: 5:30 pm, Oct. 05, 206 TAs: Simon Shaolei Du, Tianshu Ren, Hsiao-Yu Fish Tung Instructions Homework Submission: Submit
DS-GA 1003: Machine Learning and Computational Statistics Homework 6: Generalized Hinge Loss and Multiclass SVM
 DS-GA 1003: Machine Learning and Computational Statistics Homework 6: Generalized Hinge Loss and Multiclass SVM Due: Monday, April 11, 2016, at 6pm (Submit via NYU Classes) Instructions: Your answers to
DS-GA 1003: Machine Learning and Computational Statistics Homework 6: Generalized Hinge Loss and Multiclass SVM Due: Monday, April 11, 2016, at 6pm (Submit via NYU Classes) Instructions: Your answers to
Machine Learning & Data Mining Caltech CS/CNS/EE 155 Set 2 January 12 th, 2018
 Policies Due 9 PM, January 9 th, via Moodle. You are free to collaborate on all of the problems, subject to the collaboration policy stated in the syllabus. You should submit all code used in the homework.
Policies Due 9 PM, January 9 th, via Moodle. You are free to collaborate on all of the problems, subject to the collaboration policy stated in the syllabus. You should submit all code used in the homework.
Classification with Perceptrons. Reading:
 Classification with Perceptrons Reading: Chapters 1-3 of Michael Nielsen's online book on neural networks covers the basics of perceptrons and multilayer neural networks We will cover material in Chapters
Classification with Perceptrons Reading: Chapters 1-3 of Michael Nielsen's online book on neural networks covers the basics of perceptrons and multilayer neural networks We will cover material in Chapters
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression
 Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
COMP 652: Machine Learning. Lecture 12. COMP Lecture 12 1 / 37
 COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification
 Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Machine Learning and Computational Statistics, Spring 2017 Homework 2: Lasso Regression
 Machine Learning and Computational Statistics, Spring 2017 Homework 2: Lasso Regression Due: Monday, February 13, 2017, at 10pm (Submit via Gradescope) Instructions: Your answers to the questions below,
Machine Learning and Computational Statistics, Spring 2017 Homework 2: Lasso Regression Due: Monday, February 13, 2017, at 10pm (Submit via Gradescope) Instructions: Your answers to the questions below,
COMS F18 Homework 3 (due October 29, 2018)
 COMS 477-2 F8 Homework 3 (due October 29, 208) Instructions Submit your write-up on Gradescope as a neatly typeset (not scanned nor handwritten) PDF document by :59 PM of the due date. On Gradescope, be
COMS 477-2 F8 Homework 3 (due October 29, 208) Instructions Submit your write-up on Gradescope as a neatly typeset (not scanned nor handwritten) PDF document by :59 PM of the due date. On Gradescope, be
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Introduction to Machine Learning
 10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning Homework 2, version 1.0 Due Oct 16, 11:59 am Rules: 1. Homework submission is done via CMU Autolab system. Please package your writeup and code into a zip or tar
10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning Homework 2, version 1.0 Due Oct 16, 11:59 am Rules: 1. Homework submission is done via CMU Autolab system. Please package your writeup and code into a zip or tar
Machine Learning. Support Vector Machines. Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression. 1 Linearly Separable Data: Hard Margin SVMs
 E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
Name (NetID): (1 Point)
 CS446: Machine Learning (D) Spring 2017 March 16 th, 2017 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
CS446: Machine Learning (D) Spring 2017 March 16 th, 2017 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
Programming Assignment 4: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis
 Programming Assignment 4: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis Deadline: Tuesday, April 4, at 11:59pm TA: Renie Liao (csc321ta@cs.toronto.edu) Submission: You must submit two files through MarkUs
Programming Assignment 4: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis Deadline: Tuesday, April 4, at 11:59pm TA: Renie Liao (csc321ta@cs.toronto.edu) Submission: You must submit two files through MarkUs
1 A Support Vector Machine without Support Vectors
 CS/CNS/EE 53 Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Problem Set 1 Handed out: 15 Jan 010 Due: 01 Feb 010 1 A Support Vector Machine without Support Vectors In this question, you ll be implementing an online
CS/CNS/EE 53 Advanced Topics in Machine Learning Problem Set 1 Handed out: 15 Jan 010 Due: 01 Feb 010 1 A Support Vector Machine without Support Vectors In this question, you ll be implementing an online
HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
 HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION Probabilistic Learning: Theory and Algorithms CS 274A, Winter 2018 Due: Friday, February 23rd, 2018, 11:55 PM Submit code and report via EEE Dropbox You should submit a
HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION Probabilistic Learning: Theory and Algorithms CS 274A, Winter 2018 Due: Friday, February 23rd, 2018, 11:55 PM Submit code and report via EEE Dropbox You should submit a
ECE521: Inference Algorithms and Machine Learning University of Toronto. Assignment 1: k-nn and Linear Regression
 ECE521: Inference Algorithms and Machine Learning University of Toronto Assignment 1: k-nn and Linear Regression TA: Use Piazza for Q&A Due date: Feb 7 midnight, 2017 Electronic submission to: ece521ta@gmailcom
ECE521: Inference Algorithms and Machine Learning University of Toronto Assignment 1: k-nn and Linear Regression TA: Use Piazza for Q&A Due date: Feb 7 midnight, 2017 Electronic submission to: ece521ta@gmailcom
Multiclass Classification-1
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
Warm up. Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not instructors.
 Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
HW3. All layers except the first will simply pass through the previous layer: W (t+1) . (The last layer will pass the first neuron).
 HW3 Inbal Joffe Aran Carmon Theory Questions 1. Let s look at the inputs set S = x 1,..., x d R d such that (x i ) j = δ ij (that is, 1 if i = j, and 0 otherwise). The size of the set is d. And for every
HW3 Inbal Joffe Aran Carmon Theory Questions 1. Let s look at the inputs set S = x 1,..., x d R d such that (x i ) j = δ ij (that is, 1 if i = j, and 0 otherwise). The size of the set is d. And for every
CSE546 Machine Learning, Autumn 2016: Homework 1
 CSE546 Machine Learning, Autumn 2016: Homework 1 Due: Friday, October 14 th, 5pm 0 Policies Writing: Please submit your HW as a typed pdf document (not handwritten). It is encouraged you latex all your
CSE546 Machine Learning, Autumn 2016: Homework 1 Due: Friday, October 14 th, 5pm 0 Policies Writing: Please submit your HW as a typed pdf document (not handwritten). It is encouraged you latex all your
1 Machine Learning Concepts (16 points)
 CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression
 CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 04, 207 Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may
CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 04, 207 Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning
 10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning Homework Due Oct 15, 10.30 am Rules Please follow these guidelines. Failure to do so, will result in loss of credit. 1. Homework is due on the due date
10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning Homework Due Oct 15, 10.30 am Rules Please follow these guidelines. Failure to do so, will result in loss of credit. 1. Homework is due on the due date
Homework 6: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis
 Homework 6: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis Deadline: Wednesday, Nov. 21, at 11:59pm Submission: You must submit two files through MarkUs 1 : 1. a PDF file containing your writeup, titled
Homework 6: Image Completion using Mixture of Bernoullis Deadline: Wednesday, Nov. 21, at 11:59pm Submission: You must submit two files through MarkUs 1 : 1. a PDF file containing your writeup, titled
Introduction to Machine Learning HW6
 CS 189 Spring 2018 Introduction to Machine Learning HW6 Your self-grade URL is http://eecs189.org/self_grade?question_ids=1_1,1_ 2,2_1,2_2,3_1,3_2,3_3,4_1,4_2,4_3,4_4,4_5,4_6,5_1,5_2,6. This homework is
CS 189 Spring 2018 Introduction to Machine Learning HW6 Your self-grade URL is http://eecs189.org/self_grade?question_ids=1_1,1_ 2,2_1,2_2,3_1,3_2,3_3,4_1,4_2,4_3,4_4,4_5,4_6,5_1,5_2,6. This homework is
Machine Learning, Fall 2011: Homework 5
 0-60 Machine Learning, Fall 0: Homework 5 Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University Due:??? Instructions There are 3 questions on this assignment. Please submit your completed homework to
0-60 Machine Learning, Fall 0: Homework 5 Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University Due:??? Instructions There are 3 questions on this assignment. Please submit your completed homework to
MIRA, SVM, k-nn. Lirong Xia
 MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter
 Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
 HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION Probabilistic Learning: Theory and Algorithms CS 274A, Winter 2019 Due: 11am Monday, February 25th, 2019 Submit scan of plots/written responses to Gradebook; submit your
HOMEWORK #4: LOGISTIC REGRESSION Probabilistic Learning: Theory and Algorithms CS 274A, Winter 2019 Due: 11am Monday, February 25th, 2019 Submit scan of plots/written responses to Gradebook; submit your
Lecture Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers
 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Amir Globerson Lecture 6 Fall Semester Scribe: Yishay Mansour 6.1 Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers Classification is one of the most important tasks in
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Amir Globerson Lecture 6 Fall Semester Scribe: Yishay Mansour 6.1 Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers Classification is one of the most important tasks in
Convex Optimization / Homework 1, due September 19
 Convex Optimization 1-725/36-725 Homework 1, due September 19 Instructions: You must complete Problems 1 3 and either Problem 4 or Problem 5 (your choice between the two). When you submit the homework,
Convex Optimization 1-725/36-725 Homework 1, due September 19 Instructions: You must complete Problems 1 3 and either Problem 4 or Problem 5 (your choice between the two). When you submit the homework,
Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized
 Evaluation Basic concepts Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain (generalization error) approximation
Evaluation Basic concepts Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain (generalization error) approximation
The Perceptron Algorithm 1
 CS 64: Machine Learning Spring 5 College of Computer and Information Science Northeastern University Lecture 5 March, 6 Instructor: Bilal Ahmed Scribe: Bilal Ahmed & Virgil Pavlu Introduction The Perceptron
CS 64: Machine Learning Spring 5 College of Computer and Information Science Northeastern University Lecture 5 March, 6 Instructor: Bilal Ahmed Scribe: Bilal Ahmed & Virgil Pavlu Introduction The Perceptron
Machine Learning Lecture 6 Note
 Machine Learning Lecture 6 Note Compiled by Abhi Ashutosh, Daniel Chen, and Yijun Xiao February 16, 2016 1 Pegasos Algorithm The Pegasos Algorithm looks very similar to the Perceptron Algorithm. In fact,
Machine Learning Lecture 6 Note Compiled by Abhi Ashutosh, Daniel Chen, and Yijun Xiao February 16, 2016 1 Pegasos Algorithm The Pegasos Algorithm looks very similar to the Perceptron Algorithm. In fact,
Logistic Regression. Will Monroe CS 109. Lecture Notes #22 August 14, 2017
 1 Will Monroe CS 109 Logistic Regression Lecture Notes #22 August 14, 2017 Based on a chapter by Chris Piech Logistic regression is a classification algorithm1 that works by trying to learn a function
1 Will Monroe CS 109 Logistic Regression Lecture Notes #22 August 14, 2017 Based on a chapter by Chris Piech Logistic regression is a classification algorithm1 that works by trying to learn a function
Linear, threshold units. Linear Discriminant Functions and Support Vector Machines. Biometrics CSE 190 Lecture 11. X i : inputs W i : weights
 Linear Discriminant Functions and Support Vector Machines Linear, threshold units CSE19, Winter 11 Biometrics CSE 19 Lecture 11 1 X i : inputs W i : weights θ : threshold 3 4 5 1 6 7 Courtesy of University
Linear Discriminant Functions and Support Vector Machines Linear, threshold units CSE19, Winter 11 Biometrics CSE 19 Lecture 11 1 X i : inputs W i : weights θ : threshold 3 4 5 1 6 7 Courtesy of University
LEC1: Instance-based classifiers
 LEC1: Instance-based classifiers Dr. Guangliang Chen February 2, 2016 Outline Having data ready knn kmeans Summary Downloading data Save all the scripts (from course webpage) and raw files (from LeCun
LEC1: Instance-based classifiers Dr. Guangliang Chen February 2, 2016 Outline Having data ready knn kmeans Summary Downloading data Save all the scripts (from course webpage) and raw files (from LeCun
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Introduction to Support Vector Machines
 Introduction to Support Vector Machines Hsuan-Tien Lin Learning Systems Group, California Institute of Technology Talk in NTU EE/CS Speech Lab, November 16, 2005 H.-T. Lin (Learning Systems Group) Introduction
Introduction to Support Vector Machines Hsuan-Tien Lin Learning Systems Group, California Institute of Technology Talk in NTU EE/CS Speech Lab, November 16, 2005 H.-T. Lin (Learning Systems Group) Introduction
Support Vector Machines
 Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Homework 4, Part B: Structured perceptron
 Homework 4, Part B: Structured perceptron CS 585, UMass Amherst, Fall 2016 Overview Due Friday, Oct 28. Get starter code/data from the course website s schedule page. You should submit a zipped directory
Homework 4, Part B: Structured perceptron CS 585, UMass Amherst, Fall 2016 Overview Due Friday, Oct 28. Get starter code/data from the course website s schedule page. You should submit a zipped directory
Announcements - Homework
 Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued. Richard Johansson
 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Logistic Regression Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 3:
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 3:
CS , Fall 2011 Assignment 2 Solutions
 CS 94-0, Fall 20 Assignment 2 Solutions (8 pts) In this question we briefly review the expressiveness of kernels (a) Construct a support vector machine that computes the XOR function Use values of + and
CS 94-0, Fall 20 Assignment 2 Solutions (8 pts) In this question we briefly review the expressiveness of kernels (a) Construct a support vector machine that computes the XOR function Use values of + and
CSE 151 Machine Learning. Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri
 CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
MATH 680 Fall November 27, Homework 3
 MATH 680 Fall 208 November 27, 208 Homework 3 This homework is due on December 9 at :59pm. Provide both pdf, R files. Make an individual R file with proper comments for each sub-problem. Subgradients and
MATH 680 Fall 208 November 27, 208 Homework 3 This homework is due on December 9 at :59pm. Provide both pdf, R files. Make an individual R file with proper comments for each sub-problem. Subgradients and
Qualifying Exam in Machine Learning
 Qualifying Exam in Machine Learning October 20, 2009 Instructions: Answer two out of the three questions in Part 1. In addition, answer two out of three questions in two additional parts (choose two parts
Qualifying Exam in Machine Learning October 20, 2009 Instructions: Answer two out of the three questions in Part 1. In addition, answer two out of three questions in two additional parts (choose two parts
Machine Learning Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13
 Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Linear Models in Machine Learning
 CS540 Intro to AI Linear Models in Machine Learning Lecturer: Xiaojin Zhu jerryzhu@cs.wisc.edu We briefly go over two linear models frequently used in machine learning: linear regression for, well, regression,
CS540 Intro to AI Linear Models in Machine Learning Lecturer: Xiaojin Zhu jerryzhu@cs.wisc.edu We briefly go over two linear models frequently used in machine learning: linear regression for, well, regression,
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Evaluation. Andrea Passerini Machine Learning. Evaluation
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Basic concepts requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Basic concepts requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain
CSE 331 Winter 2018 Homework 1
 Directions: - Due Wednesday, January 10 by 11 pm. - Turn in your work online using gradescope. You should turn in a single pdf file. You can have more than one answer per page, but please try to avoid
Directions: - Due Wednesday, January 10 by 11 pm. - Turn in your work online using gradescope. You should turn in a single pdf file. You can have more than one answer per page, but please try to avoid
Logistic Regression. Jia-Bin Huang. Virginia Tech Spring 2019 ECE-5424G / CS-5824
 Logistic Regression Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please start HW 1 early! Questions are welcome! Two principles for estimating parameters Maximum Likelihood
Logistic Regression Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please start HW 1 early! Questions are welcome! Two principles for estimating parameters Maximum Likelihood
CS 231A Section 1: Linear Algebra & Probability Review
 CS 231A Section 1: Linear Algebra & Probability Review 1 Topics Support Vector Machines Boosting Viola-Jones face detector Linear Algebra Review Notation Operations & Properties Matrix Calculus Probability
CS 231A Section 1: Linear Algebra & Probability Review 1 Topics Support Vector Machines Boosting Viola-Jones face detector Linear Algebra Review Notation Operations & Properties Matrix Calculus Probability
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions
 Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
CS 231A Section 1: Linear Algebra & Probability Review. Kevin Tang
 CS 231A Section 1: Linear Algebra & Probability Review Kevin Tang Kevin Tang Section 1-1 9/30/2011 Topics Support Vector Machines Boosting Viola Jones face detector Linear Algebra Review Notation Operations
CS 231A Section 1: Linear Algebra & Probability Review Kevin Tang Kevin Tang Section 1-1 9/30/2011 Topics Support Vector Machines Boosting Viola Jones face detector Linear Algebra Review Notation Operations
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab.
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
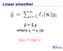 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines
 Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Experiment 1: Linear Regression
 Experiment 1: Linear Regression August 27, 2018 1 Description This first exercise will give you practice with linear regression. These exercises have been extensively tested with Matlab, but they should
Experiment 1: Linear Regression August 27, 2018 1 Description This first exercise will give you practice with linear regression. These exercises have been extensively tested with Matlab, but they should
Midterm Exam, Spring 2005
 10-701 Midterm Exam, Spring 2005 1. Write your name and your email address below. Name: Email address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. Write your name
10-701 Midterm Exam, Spring 2005 1. Write your name and your email address below. Name: Email address: 2. There should be 15 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. Write your name
CSE 546 Final Exam, Autumn 2013
 CSE 546 Final Exam, Autumn 0. Personal info: Name: Student ID: E-mail address:. There should be 5 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet).. You can use any material you brought: any book,
CSE 546 Final Exam, Autumn 0. Personal info: Name: Student ID: E-mail address:. There should be 5 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet).. You can use any material you brought: any book,
COMP 875 Announcements
 Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Machine Learning Basics
 Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Exercise 1. In the lecture you have used logistic regression as a binary classifier to assign a label y i { 1, 1} for a sample X i R D by
 Exercise 1 Deadline: 04.05.2016, 2:00 pm Procedure for the exercises: You will work on the exercises in groups of 2-3 people (due to your large group size I will unfortunately not be able to correct single
Exercise 1 Deadline: 04.05.2016, 2:00 pm Procedure for the exercises: You will work on the exercises in groups of 2-3 people (due to your large group size I will unfortunately not be able to correct single
Support Vector Machines. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Logistic Regression Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 8 Feb. 12, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 8 Feb. 12, 2018 1 10-601 Introduction
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 8 Feb. 12, 2018 1 10-601 Introduction
Stat 406: Algorithms for classification and prediction. Lecture 1: Introduction. Kevin Murphy. Mon 7 January,
 1 Stat 406: Algorithms for classification and prediction Lecture 1: Introduction Kevin Murphy Mon 7 January, 2008 1 1 Slides last updated on January 7, 2008 Outline 2 Administrivia Some basic definitions.
1 Stat 406: Algorithms for classification and prediction Lecture 1: Introduction Kevin Murphy Mon 7 January, 2008 1 1 Slides last updated on January 7, 2008 Outline 2 Administrivia Some basic definitions.
10701/15781 Machine Learning, Spring 2007: Homework 2
 070/578 Machine Learning, Spring 2007: Homework 2 Due: Wednesday, February 2, beginning of the class Instructions There are 4 questions on this assignment The second question involves coding Do not attach
070/578 Machine Learning, Spring 2007: Homework 2 Due: Wednesday, February 2, beginning of the class Instructions There are 4 questions on this assignment The second question involves coding Do not attach
Machine Learning: Assignment 1
 10-701 Machine Learning: Assignment 1 Due on Februrary 0, 014 at 1 noon Barnabas Poczos, Aarti Singh Instructions: Failure to follow these directions may result in loss of points. Your solutions for this
10-701 Machine Learning: Assignment 1 Due on Februrary 0, 014 at 1 noon Barnabas Poczos, Aarti Singh Instructions: Failure to follow these directions may result in loss of points. Your solutions for this
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Linear classification. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 10-708 Probabilistic Graphical Models Homework 3 (v1.1.0) Due Apr 14, 7:00 PM Rules: 1. Homework is due on the due date at 7:00 PM. The homework should be submitted via Gradescope. Solution to each problem
10-708 Probabilistic Graphical Models Homework 3 (v1.1.0) Due Apr 14, 7:00 PM Rules: 1. Homework is due on the due date at 7:00 PM. The homework should be submitted via Gradescope. Solution to each problem
Statistical Machine Learning Theory. From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction. Hisashi Kashima.
 http://goo.gl/jv7vj9 Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
http://goo.gl/jv7vj9 Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
Homework 3. Convex Optimization /36-725
 Homework 3 Convex Optimization 10-725/36-725 Due Friday October 14 at 5:30pm submitted to Christoph Dann in Gates 8013 (Remember to a submit separate writeup for each problem, with your name at the top)
Homework 3 Convex Optimization 10-725/36-725 Due Friday October 14 at 5:30pm submitted to Christoph Dann in Gates 8013 (Remember to a submit separate writeup for each problem, with your name at the top)
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Multi-Class Classification; Kernel Methods
 Machine Learning (CSE 446): Multi-Class Classification; Kernel Methods Sham M Kakade c 2018 University of Washington cse446-staff@cs.washington.edu 1 / 12 Announcements HW3 due date as posted. make sure
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Multi-Class Classification; Kernel Methods Sham M Kakade c 2018 University of Washington cse446-staff@cs.washington.edu 1 / 12 Announcements HW3 due date as posted. make sure
Problem 1 (10 points)
 y x CHEN 1703 - HOMEWORK 4 Submit your MATLAB solutions via the course web site. Be sure to include your name and UNID in your m-file. Submit each solution seperately. Also be sure to document your solutions
y x CHEN 1703 - HOMEWORK 4 Submit your MATLAB solutions via the course web site. Be sure to include your name and UNID in your m-file. Submit each solution seperately. Also be sure to document your solutions
Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms
 Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms George Papamakarios December 214 Abstract Gradient-based optimization methods are popular in machine learning applications. In large-scale problems,
Comparison of Modern Stochastic Optimization Algorithms George Papamakarios December 214 Abstract Gradient-based optimization methods are popular in machine learning applications. In large-scale problems,
Statistical Machine Learning Theory. From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction. Hisashi Kashima.
 http://goo.gl/xilnmn Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
http://goo.gl/xilnmn Course website KYOTO UNIVERSITY Statistical Machine Learning Theory From Multi-class Classification to Structured Output Prediction Hisashi Kashima kashima@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp DEPARTMENT
Real Estate Price Prediction with Regression and Classification CS 229 Autumn 2016 Project Final Report
 Real Estate Price Prediction with Regression and Classification CS 229 Autumn 2016 Project Final Report Hujia Yu, Jiafu Wu [hujiay, jiafuwu]@stanford.edu 1. Introduction Housing prices are an important
Real Estate Price Prediction with Regression and Classification CS 229 Autumn 2016 Project Final Report Hujia Yu, Jiafu Wu [hujiay, jiafuwu]@stanford.edu 1. Introduction Housing prices are an important
10-701/15-781, Machine Learning: Homework 4
 10-701/15-781, Machine Learning: Homewor 4 Aarti Singh Carnegie Mellon University ˆ The assignment is due at 10:30 am beginning of class on Mon, Nov 15, 2010. ˆ Separate you answers into five parts, one
10-701/15-781, Machine Learning: Homewor 4 Aarti Singh Carnegie Mellon University ˆ The assignment is due at 10:30 am beginning of class on Mon, Nov 15, 2010. ˆ Separate you answers into five parts, one
Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP
 CS546: Machine Learning in NLP (Spring 2018) http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs546/ Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu 3324 Siebel Center Office hours: Tue/Thu 2pm-3pm
CS546: Machine Learning in NLP (Spring 2018) http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs546/ Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu 3324 Siebel Center Office hours: Tue/Thu 2pm-3pm
Perceptron (Theory) + Linear Regression
 10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING
 CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING 5: Vector Data: Support Vector Machine Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu October 18, 2017 Homework 1 Announcements Due end of the day of this Thursday (11:59pm)
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING 5: Vector Data: Support Vector Machine Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu October 18, 2017 Homework 1 Announcements Due end of the day of this Thursday (11:59pm)
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
1. Kernel ridge regression In contrast to ordinary least squares which has a cost function. m (θ T x (i) y (i) ) 2, J(θ) = 1 2.
 CS229 Problem Set #2 Solutions 1 CS 229, Public Course Problem Set #2 Solutions: Theory Kernels, SVMs, and 1. Kernel ridge regression In contrast to ordinary least squares which has a cost function J(θ)
CS229 Problem Set #2 Solutions 1 CS 229, Public Course Problem Set #2 Solutions: Theory Kernels, SVMs, and 1. Kernel ridge regression In contrast to ordinary least squares which has a cost function J(θ)
Mathematical Tools for Neuroscience (NEU 314) Princeton University, Spring 2016 Jonathan Pillow. Homework 8: Logistic Regression & Information Theory
 Mathematical Tools for Neuroscience (NEU 34) Princeton University, Spring 206 Jonathan Pillow Homework 8: Logistic Regression & Information Theory Due: Tuesday, April 26, 9:59am Optimization Toolbox One
Mathematical Tools for Neuroscience (NEU 34) Princeton University, Spring 206 Jonathan Pillow Homework 8: Logistic Regression & Information Theory Due: Tuesday, April 26, 9:59am Optimization Toolbox One
Machine Learning (CS 567) Lecture 3
 Machine Learning (CS 567) Lecture 3 Time: T-Th 5:00pm - 6:20pm Location: GFS 118 Instructor: Sofus A. Macskassy (macskass@usc.edu) Office: SAL 216 Office hours: by appointment Teaching assistant: Cheol
Machine Learning (CS 567) Lecture 3 Time: T-Th 5:00pm - 6:20pm Location: GFS 118 Instructor: Sofus A. Macskassy (macskass@usc.edu) Office: SAL 216 Office hours: by appointment Teaching assistant: Cheol
Optimization and Gradient Descent
 Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Machine Learning 4771
 Machine Learning 477 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 5 Generalization Guarantees VC-Dimension Nearest Neighbor Classification (infinite VC dimension) Structural Risk Minimization Support Vector Machines
Machine Learning 477 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 5 Generalization Guarantees VC-Dimension Nearest Neighbor Classification (infinite VC dimension) Structural Risk Minimization Support Vector Machines
CS60021: Scalable Data Mining. Large Scale Machine Learning
 J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
J. Leskovec, A. Rajaraman, J. Ullman: Mining of Massive Datasets, http://www.mmds.org 1 CS60021: Scalable Data Mining Large Scale Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Example: Spam filtering Instance
INTRODUCTION TO DATA SCIENCE
 INTRODUCTION TO DATA SCIENCE JOHN P DICKERSON Lecture #13 3/9/2017 CMSC320 Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30pm 4:45pm ANNOUNCEMENTS Mini-Project #1 is due Saturday night (3/11): Seems like people are able to do
INTRODUCTION TO DATA SCIENCE JOHN P DICKERSON Lecture #13 3/9/2017 CMSC320 Tuesdays & Thursdays 3:30pm 4:45pm ANNOUNCEMENTS Mini-Project #1 is due Saturday night (3/11): Seems like people are able to do
