MATH/STAT 3360, Probability
|
|
|
- Nigel James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATH/STAT 3360, Probability Sample Final Examination This Sample examination has more questions than the actual final, in order to cover a wider range of questions. Estimated times are provided after each question to help your preparation. 1. On average, in a certain course, 0% of students get an A and 15% students get a B. There are 5 students taking the course one year. What is the probability that 5 students get an A and 5 students get a B? [5. (R, Θ) have joint density function f (R,Θ) (r, θ) = 1 π e r. Let X = R cos Θ and Y = R sin Θ. (a) What is the joint density function of (X, Y )? [15 (b) Are X and Y independent? [5 3. (R, Θ) have joint density function f (R,Θ) (r, θ) = 1 π re r. Let X = R cos Θ and Y = R sin Θ. (a) What is the joint density function of (X, Y )? [15 (b) Are X and Y independent? [5 4. Random variables X and Y have joint density function f X,Y (x, y) = 5x +5y 6xy 5π e 10. (a) What is the joint density function of Z = X + Y and W = X Y? [15 (b) Are W and Z independent? [5 (c) What is Cov(X, Y )? [Hint: consider Var(Z) Var(W ).] 5. Let X and Y are independent normal random variables with mean 0 and variances σ 1 and σ respectively. (a) What is the joint density function of X and Y? [5 (b) If (R, Θ) are the polar coordinates of (X, Y ) (that is, R = X + Y and Θ is the solution to R cos Θ = X and R sin Θ = Y ) then what is the joint density function of R and Θ? [15 (c) Calculate the marginal density function of Θ. 6. X is normally distributed with mean 0 and variance 1. Y is independent of X and has probability density functions f Y (y) = 1 π(1 + y ) (a) Find the joint density function of Z = X + Y and W = X + Y. [15 (b) Are Z and W independent? [5 1
2 7. Let X have an exponential distribution with parameter λ. Suppose that given X = x, Y is normally distributed with mean x and variance σ. (a) What is the joint density function of X and Y? [5 (b) What is the covariance of X and Y? (c) Conditional on Y = 3, what is the density function of X? [You do not need to calculate the constant factor.] [5 8. X is normally distributed with mean 0 and variance 1. Y is independent of X and has probability density functions f Y (y) = λ e λ y for some constant λ > 0. Find the joint density function of Z = X + Y and W = X + 3Y. 9. Let X have a Poisson distribution with parameter λ, and given that X = n, let Y have a binomial distribution with parameters n and p. (a) What is the joint probability mass function of X and Y? [5 (b) Show that the marginal distribution of Y is a Poisson distribution with parameter λp. (c) What is the conditional distribution of X conditional on Y = i? [ Let X have a normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1. Suppose that given X = x, Y is normally distributed with mean x 3 and variance σ x. (a) What is the joint density function of X and Y? [5 (b) What is the covariance of X and Y? 11. X is normally distributed with mean and standard deviation 3. Y is normally distributed with mean 4 and standard deviation 4. What is P (Y > X)? (a) If X and Y are independent? [5 (b) If X, Y have a multivariate normal distribution, and Cov(X, Y ) =? 1. X is normally distributed with mean 5 and standard deviation 1. Y is independent and normally distributed with mean and standard deviation 3. What is P (Y > X)? [5 13. X is normally distributed with mean 3 and standard deviation 5. Y is normally distributed with mean 7 and standard deviation 1. What is P (Y > X)? (a) If X and Y are independent? [5
3 (b) If X, Y have a multivariate normal distribution, and Cov(X, Y ) = 4? 14. Let X and Y be independent uniform random variables on intervals [, 4] and [3, 4] respectively. Calculate the probability density function of X +Y. 15. Let X and Y be independent exponential random variables with parameters and 3. What is the probability that X + Y > If X is exponentially distributed with parameter λ 1 and Y is independent of X and exponentially distributed with parameter λ, what is the probability density function of X + Y? [Assume λ 1 λ.] 17. In a class of 100 students, the professor wants to determine what proportion of the students can answer a simple calculus question. The professor decides to test a random sample of 10 students. In fact 35 of the students could answer the question. (a) What is the expected number of students sampled who answer the question correctly? [5 (b) What is the variance of the number of correct answers if the students are sampled with replacement, i.e. one student could be tested more than once? (c) What is the variance of the number of correct answers if the 10 students sampled must be 10 different students? 18. An ecologist is collecting butterflies. She collects a total of 50 butterflies. There are a total of 4 species of butterfly, and each butterfly is equally likely to be any of the species. (a) What is the expected number of species of butterflies she collects? [10 (b) What is the variance of the number of species of butterflies she collects? (c) Using the one-sided Chebyshev inequality, find a bound on the probability that she collects all 4 species. [Hint: The Chebyshev inequality will give the probability of collecting at least 4 species.] 19. An ecologist is collecting snails. She collects a total of 40 snails. There are a total of 18 species of snail, and each snail is equally likely to be any of the species. (a) What is the expected number of species of snails she collects? [10 (b) What is the variance of the number of species of snails she collects? 3
4 (c) Using the one-sided Chebyshev inequality, find a bound on the probability that she collects all 18 species. [Hint: The Chebyshev inequality will give the probability of collecting at least 18 species.] 0. An ecologist is collecting beetles. She collects a total of 16 beetles. There are a total of 15 species of beetle, and each beetle is equally likely to be any of the species. (a) What is the expected number of species of beetles she collects? [10 (b) What is the variance of the number of species of beetles she collects? (c) Using the (two-sided) Chebyshev inequality, find a lower bound on the probability that the number of species she collects is between 8 and 1 inclusive. [Hint: If it is not between 8 and 1, it must be either at least 13, or at most 7.] 1. Consider the following experiment: Toss 14 fair coins. For each toss that results in a head, roll a fair (6-sided) die. Take the sum of the numbers rolled on all these dice. What is the expected outcome? [5. Consider the following experiment: Roll 100 fair (6-sided) dice. For each 3 rolled, toss a fair coin, and for each 6 rolled, toss fair coins. Count the number of heads on all coins tossed. What is the expected outcome? [5 3. Consider the following experiment: Roll a fair (6-sided) die. If the result n is odd, roll n fair dice and take the sum of the numbers. If n is even, toss n n fair coins and count the number of heads. What is the expected outcome? [5 4. The point (X, Y ) is uniformly distributed on the set. {(x, y) x + y < 3, y > 1, x > } (a) What is the conditional expectation of X given that Y =? [5 (b) What is Cov(X, Y )? 5. An insurance company finds that of its home insurance policies, only 0.5% result in a claim. Of the policies that result in a claim, the expected amount claimed is $40,000, and the standard deviation of the amount claimed is $100,000. (a) What are the expected amount claimed, and the variance of the amount claimed for any policy? [If a policy does not result in a claim, the amount claimed is $0. Hint: for the variance, try to work out E(X ).] 4
5 (b) If the company sets its premium to $430, but has administrative costs of $00 for each policy, and the company sells 500,000 policies, what is the approximate probability that the company is unable to pay out all the claims from the premiums collected? 6. A car insurance company finds that of its claims, 70% are for accidents, and 30% are for thefts. The theft claims are all for $0,000, while for the accident claims claim, the expected amount claimed is $15,000, and the standard deviation of the amount claimed is $30,000. (a) What are the expected amount claimed, and the standard deviation of the amount claimed for any claim? (b) If the company has $16,700,000 available to cover claims, and receives 1000 claims, what is the probability that it is unable to cover the claims made? 7. A truncated standard normal random variable has probability density function e x f X (x) = b if a x b x e a 0 otherwise That is, it is a normal distribution conditional on lying in the interval [a, b]. The expectation of a truncated standard normal is given by E(X) = e a e b π(φ(b) Φ(a)) An investment advisor tells you that the amount by which the market will increase next year is normally distributed with mean 10% and standard deviation 10%. The bank offers an investment product which pays the value of the market, minus a % fee if the market increases by between % and 3%. If the market rises by less than %, then it pays out your original investment; if the market rises by more than 3%, it pays out your original investment plus 30%. What is the expected value of this investment? [Hint: divide into the three cases where the market increases by less than %, the market increases by between % and 3%, and the market increases by over 3%.] [15 8. You are considering an investment. You would originally invest $1,000, and every year, the investment will either increase by 50% with probability 0.6 or decrease by 30% with probability 0.4. You plan to use the investment after 15 years. What is the expected value of the investment after 15 years? 9. If X is exponentially distributed with parameter λ 1 and Y is independent of X and normally distributed with mean µ and variance σ. 5
6 (a) find the moment generating function of X Y. (b) Use the Chernoff bound with t = µ σ to obtain a lower bound on the probability that X > Y. 30. Let X be exponentially distributed with parameter λ 1 and Y be independent of X and exponentially distributed with parameter λ, where λ 1 > λ. (a) find the moment generating function of X Y. (b) Use the Chernoff bound with t = λ1 λ to obtain an upper bound on the probability that X > Y. 31. If X is exponentially distributed with parameter λ 1 and Y is exponentially distributed with parameter λ, where λ > λ 1 : (a) find the moment generating function of X Y. (b) Use the Chernoff bound with t = λ1 λ to obtain a lower bound on the probability that X > Y. 3. If X is uniformly distributed on [-1,4], and Y is uniformly distributed on the interval [0, 3], find the moment generating function of X Y. 33. A company is planning to run an advertising campaign. It estimates that the number of customers it gains from the advertising campain will be approximately normally distributed with mean 3,000 and standard deviation 300. It also estimates that the amount spent by each customer has expected value $50 and standard deviation $30. (a) Assuming the number of customers is large enough, what is the approximate distribution of the average amount spent per customer, conditional on the number of new customers being n. [5 (b) What is the joint density function for the number of new customers and the average amount spent per customer? 34. A gambler is playing a slot machine in a casino. The gambler continues to bet $1 each time. The machine has the following payouts: Payout Probability $1 0.4 $ $ $ How many times does the gambler have to play before the probability of his having more money than he started with is less than 1%? 35. An investor s annual profit has an expectation of $,000 and a variance of 100,000,000. (Profits in different years are independent and identically distributed.) 6
7 (a) After n years, for large n, what is the approximate distribution of the investors average annual profit? [5 (b) After how many years is the probability that the investor has made an overall loss during those years less than 0.001? (c) If at any point, the investor has made a total loss of over $100,000, he must pay a fine. After how many years is the danger that he will have to pay this fine greatest, and what is the danger after this many years [assuming the approximation from (a) is valid]? 36. The number of visitors to a particular website on a given day is approximately normally distributed with mean 1000 and variance 000. A company is considering placing an advertisement on this website. It predicts that each visitor to the website will order its product with probability 0.0, and that all visitors to the website act independently. (a) What is the expectation and variance of the number of orders the company receives? (b) Using a normal approximation, what is the probability that the number of orders the company receives is more than 300? [5 7
MATH/STAT 3360, Probability Sample Final Examination Model Solutions
 MATH/STAT 3360, Probability Sample Final Examination Model Solutions This Sample examination has more questions than the actual final, in order to cover a wider range of questions. Estimated times are
MATH/STAT 3360, Probability Sample Final Examination Model Solutions This Sample examination has more questions than the actual final, in order to cover a wider range of questions. Estimated times are
Math 493 Final Exam December 01
 Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
MATH/STAT 3360, Probability FALL 2018 Hong Gu
 MATH/STAT 3360, Probability FALL 2018 Hong Gu Lecture Notes and In Class Examples August 19, 2018 1 / 142 Basic Principal of Counting Question 1 A statistics textbook has 8 chapters. Each chapter has 50
MATH/STAT 3360, Probability FALL 2018 Hong Gu Lecture Notes and In Class Examples August 19, 2018 1 / 142 Basic Principal of Counting Question 1 A statistics textbook has 8 chapters. Each chapter has 50
Problem Points S C O R E Total: 120
 PSTAT 160 A Final Exam December 10, 2015 Name Student ID # Problem Points S C O R E 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 11 10 12 10 Total: 120 1. (10 points) Take a Markov chain with the
PSTAT 160 A Final Exam December 10, 2015 Name Student ID # Problem Points S C O R E 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 11 10 12 10 Total: 120 1. (10 points) Take a Markov chain with the
STAT 418: Probability and Stochastic Processes
 STAT 418: Probability and Stochastic Processes Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical
STAT 418: Probability and Stochastic Processes Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical
1 Basic continuous random variable problems
 Name M362K Final Here are problems concerning material from Chapters 5 and 6. To review the other chapters, look over previous practice sheets for the two exams, previous quizzes, previous homeworks and
Name M362K Final Here are problems concerning material from Chapters 5 and 6. To review the other chapters, look over previous practice sheets for the two exams, previous quizzes, previous homeworks and
STAT 414: Introduction to Probability Theory
 STAT 414: Introduction to Probability Theory Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical Exercises
STAT 414: Introduction to Probability Theory Spring 2016; Homework Assignments Latest updated on April 29, 2016 HW1 (Due on Jan. 21) Chapter 1 Problems 1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 18, 19, 26, 28, 30 Theoretical Exercises
1 Basic continuous random variable problems
 Name M362K Final Here are problems concerning material from Chapters 5 and 6. To review the other chapters, look over previous practice sheets for the two exams, previous quizzes, previous homeworks and
Name M362K Final Here are problems concerning material from Chapters 5 and 6. To review the other chapters, look over previous practice sheets for the two exams, previous quizzes, previous homeworks and
Notes for Math 324, Part 19
 48 Notes for Math 324, Part 9 Chapter 9 Multivariate distributions, covariance Often, we need to consider several random variables at the same time. We have a sample space S and r.v. s X, Y,..., which
48 Notes for Math 324, Part 9 Chapter 9 Multivariate distributions, covariance Often, we need to consider several random variables at the same time. We have a sample space S and r.v. s X, Y,..., which
CME 106: Review Probability theory
 : Probability theory Sven Schmit April 3, 2015 1 Overview In the first half of the course, we covered topics from probability theory. The difference between statistics and probability theory is the following:
: Probability theory Sven Schmit April 3, 2015 1 Overview In the first half of the course, we covered topics from probability theory. The difference between statistics and probability theory is the following:
EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, Statistical Theory and Methods I. Time Allowed: Three Hours
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 008 Statistical Theory and Methods I Time Allowed: Three Hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 008 Statistical Theory and Methods I Time Allowed: Three Hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
Course: ESO-209 Home Work: 1 Instructor: Debasis Kundu
 Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Chapter IV: Random Variables - Exercises
 Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING 2010-2011 The time to repair a machine expressed in hour is a random variable with distribution function
Bernardo D Auria Statistics Department Universidad Carlos III de Madrid GROUP 89 - COMPUTER ENGINEERING 2010-2011 The time to repair a machine expressed in hour is a random variable with distribution function
1. If X has density. cx 3 e x ), 0 x < 0, otherwise. Find the value of c that makes f a probability density. f(x) =
 1. If X has density f(x) = { cx 3 e x ), 0 x < 0, otherwise. Find the value of c that makes f a probability density. 2. Let X have density f(x) = { xe x, 0 < x < 0, otherwise. (a) Find P (X > 2). (b) Find
1. If X has density f(x) = { cx 3 e x ), 0 x < 0, otherwise. Find the value of c that makes f a probability density. 2. Let X have density f(x) = { xe x, 0 < x < 0, otherwise. (a) Find P (X > 2). (b) Find
CH5 CH6(Sections 1 through 5) Homework Problems
 550.40 CH5 CH6(Sections 1 through 5) Homework Problems 1. Part of HW #6: CH 5 P1. Let X be a random variable with probability density function f(x) = c(1 x ) 1 < x < 1 (a) What is the value of c? (b) What
550.40 CH5 CH6(Sections 1 through 5) Homework Problems 1. Part of HW #6: CH 5 P1. Let X be a random variable with probability density function f(x) = c(1 x ) 1 < x < 1 (a) What is the value of c? (b) What
Notes for Math 324, Part 20
 7 Notes for Math 34, Part Chapter Conditional epectations, variances, etc.. Conditional probability Given two events, the conditional probability of A given B is defined by P[A B] = P[A B]. P[B] P[A B]
7 Notes for Math 34, Part Chapter Conditional epectations, variances, etc.. Conditional probability Given two events, the conditional probability of A given B is defined by P[A B] = P[A B]. P[B] P[A B]
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models. Professor Whitt. SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2
 IEOR 316: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2 More Probability Review: In the Ross textbook, Introduction to Probability Models, read
IEOR 316: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2 More Probability Review: In the Ross textbook, Introduction to Probability Models, read
Course 1 Solutions November 2001 Exams
 Course Solutions November Exams . A For i =,, let R = event that a red ball is drawn form urn i i B = event that a blue ball is drawn from urn i. i Then if x is the number of blue balls in urn, ( R R)
Course Solutions November Exams . A For i =,, let R = event that a red ball is drawn form urn i i B = event that a blue ball is drawn from urn i. i Then if x is the number of blue balls in urn, ( R R)
Problem Points S C O R E Total: 120
 PSTAT 160 A Final Exam Solution December 10, 2015 Name Student ID # Problem Points S C O R E 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 11 10 12 10 Total: 120 1. (10 points) Take a Markov chain
PSTAT 160 A Final Exam Solution December 10, 2015 Name Student ID # Problem Points S C O R E 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 11 10 12 10 Total: 120 1. (10 points) Take a Markov chain
This exam contains 13 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided with the exam.
 Probability and Statistics FS 2017 Session Exam 22.08.2017 Time Limit: 180 Minutes Name: Student ID: This exam contains 13 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided
Probability and Statistics FS 2017 Session Exam 22.08.2017 Time Limit: 180 Minutes Name: Student ID: This exam contains 13 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided
CS 246 Review of Proof Techniques and Probability 01/14/19
 Note: This document has been adapted from a similar review session for CS224W (Autumn 2018). It was originally compiled by Jessica Su, with minor edits by Jayadev Bhaskaran. 1 Proof techniques Here we
Note: This document has been adapted from a similar review session for CS224W (Autumn 2018). It was originally compiled by Jessica Su, with minor edits by Jayadev Bhaskaran. 1 Proof techniques Here we
ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172.
 ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172. 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided on this page, NOW! 2. This is a closed book exam.
ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172. 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided on this page, NOW! 2. This is a closed book exam.
The mean, variance and covariance. (Chs 3.4.1, 3.4.2)
 4 The mean, variance and covariance (Chs 3.4.1, 3.4.2) Mean (Expected Value) of X Consider a university having 15,000 students and let X equal the number of courses for which a randomly selected student
4 The mean, variance and covariance (Chs 3.4.1, 3.4.2) Mean (Expected Value) of X Consider a university having 15,000 students and let X equal the number of courses for which a randomly selected student
Homework 10 (due December 2, 2009)
 Homework (due December, 9) Problem. Let X and Y be independent binomial random variables with parameters (n, p) and (n, p) respectively. Prove that X + Y is a binomial random variable with parameters (n
Homework (due December, 9) Problem. Let X and Y be independent binomial random variables with parameters (n, p) and (n, p) respectively. Prove that X + Y is a binomial random variable with parameters (n
. Find E(V ) and var(v ).
 Math 6382/6383: Probability Models and Mathematical Statistics Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. A person tosses a fair coin until she obtains 2 heads in a row. She then tosses a fair die the same number
Math 6382/6383: Probability Models and Mathematical Statistics Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. A person tosses a fair coin until she obtains 2 heads in a row. She then tosses a fair die the same number
STAT 516 Midterm Exam 3 Friday, April 18, 2008
 STAT 56 Midterm Exam 3 Friday, April 8, 2008 Name Purdue student ID (0 digits). The testing booklet contains 8 questions. 2. Permitted Texas Instruments calculators: BA-35 BA II Plus BA II Plus Professional
STAT 56 Midterm Exam 3 Friday, April 8, 2008 Name Purdue student ID (0 digits). The testing booklet contains 8 questions. 2. Permitted Texas Instruments calculators: BA-35 BA II Plus BA II Plus Professional
Math 365 Final Exam Review Sheet. The final exam is Wednesday March 18 from 10am - 12 noon in MNB 110.
 Math 365 Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam is Wednesday March 18 from 10am - 12 noon in MNB 110. The final is comprehensive and will cover Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4.1, 4.2, 5.2, and 5.3. You may use your
Math 365 Final Exam Review Sheet The final exam is Wednesday March 18 from 10am - 12 noon in MNB 110. The final is comprehensive and will cover Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4.1, 4.2, 5.2, and 5.3. You may use your
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. Exam 1 21 October 2011
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 00A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Exam 2 October 20 Name: Problem (20 points) a. Let X follow the Poisson distribution with parameter
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 00A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Exam 2 October 20 Name: Problem (20 points) a. Let X follow the Poisson distribution with parameter
Chapter (4) Discrete Probability Distributions Examples
 Chapter (4) Discrete Probability Distributions Examples Example () Two balanced dice are rolled. Let X be the sum of the two dice. Obtain the probability distribution of X. Solution When the two balanced
Chapter (4) Discrete Probability Distributions Examples Example () Two balanced dice are rolled. Let X be the sum of the two dice. Obtain the probability distribution of X. Solution When the two balanced
DISCRETE VARIABLE PROBLEMS ONLY
 DISCRETE VARIABLE PROBLEMS ONLY. A biased die with four faces is used in a game. A player pays 0 counters to roll the die. The table below shows the possible scores on the die, the probability of each
DISCRETE VARIABLE PROBLEMS ONLY. A biased die with four faces is used in a game. A player pays 0 counters to roll the die. The table below shows the possible scores on the die, the probability of each
X = X X n, + X 2
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2003 Wagner Lecture 22 Variance Question: At each time step, I flip a fair coin. If it comes up Heads, I walk one step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2003 Wagner Lecture 22 Variance Question: At each time step, I flip a fair coin. If it comes up Heads, I walk one step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk
Expectation is linear. So far we saw that E(X + Y ) = E(X) + E(Y ). Let α R. Then,
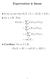 Expectation is linear So far we saw that E(X + Y ) = E(X) + E(Y ). Let α R. Then, E(αX) = ω = ω (αx)(ω) Pr(ω) αx(ω) Pr(ω) = α ω X(ω) Pr(ω) = αe(x). Corollary. For α, β R, E(αX + βy ) = αe(x) + βe(y ).
Expectation is linear So far we saw that E(X + Y ) = E(X) + E(Y ). Let α R. Then, E(αX) = ω = ω (αx)(ω) Pr(ω) αx(ω) Pr(ω) = α ω X(ω) Pr(ω) = αe(x). Corollary. For α, β R, E(αX + βy ) = αe(x) + βe(y ).
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals
 Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
MAT 271E Probability and Statistics
 MAT 271E Probability and Statistics Spring 2011 Instructor : Class Meets : Office Hours : Textbook : Supp. Text : İlker Bayram EEB 1103 ibayram@itu.edu.tr 13.30 16.30, Wednesday EEB? 10.00 12.00, Wednesday
MAT 271E Probability and Statistics Spring 2011 Instructor : Class Meets : Office Hours : Textbook : Supp. Text : İlker Bayram EEB 1103 ibayram@itu.edu.tr 13.30 16.30, Wednesday EEB? 10.00 12.00, Wednesday
Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics. https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf
 Part 1: Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
Part 1: Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
Solution: By Markov inequality: P (X > 100) 0.8. By Chebyshev s inequality: P (X > 100) P ( X 80 > 20) 100/20 2 = The second estimate is better.
 MA 485-1E, Probability (Dr Chernov) Final Exam Wed, Dec 12, 2001 Student s name Be sure to show all your work. Each problem is 4 points. Full credit will be given for 9 problems (36 points). You are welcome
MA 485-1E, Probability (Dr Chernov) Final Exam Wed, Dec 12, 2001 Student s name Be sure to show all your work. Each problem is 4 points. Full credit will be given for 9 problems (36 points). You are welcome
2. Suppose (X, Y ) is a pair of random variables uniformly distributed over the triangle with vertices (0, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1).
 Name M362K Final Exam Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. There is a table of formulae on the last page. 1. Suppose X 1,..., X 1 are independent
Name M362K Final Exam Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. There is a table of formulae on the last page. 1. Suppose X 1,..., X 1 are independent
Twelfth Problem Assignment
 EECS 401 Not Graded PROBLEM 1 Let X 1, X 2,... be a sequence of independent random variables that are uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. Consider a sequence defined by (a) Y n = max(x 1, X 2,..., X
EECS 401 Not Graded PROBLEM 1 Let X 1, X 2,... be a sequence of independent random variables that are uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. Consider a sequence defined by (a) Y n = max(x 1, X 2,..., X
Homework 4 Solution, due July 23
 Homework 4 Solution, due July 23 Random Variables Problem 1. Let X be the random number on a die: from 1 to. (i) What is the distribution of X? (ii) Calculate EX. (iii) Calculate EX 2. (iv) Calculate Var
Homework 4 Solution, due July 23 Random Variables Problem 1. Let X be the random number on a die: from 1 to. (i) What is the distribution of X? (ii) Calculate EX. (iii) Calculate EX 2. (iv) Calculate Var
MATH 1301, Practice problems
 MATH 1301, Practice problems 1. For each of the following, denote Ann s age by x, choose the equation(s) (may be more than one) that describes the statement, and find x. (a) In three years, Ann will be
MATH 1301, Practice problems 1. For each of the following, denote Ann s age by x, choose the equation(s) (may be more than one) that describes the statement, and find x. (a) In three years, Ann will be
Practice Exam 1: Long List 18.05, Spring 2014
 Practice Eam : Long List 8.05, Spring 204 Counting and Probability. A full house in poker is a hand where three cards share one rank and two cards share another rank. How many ways are there to get a full-house?
Practice Eam : Long List 8.05, Spring 204 Counting and Probability. A full house in poker is a hand where three cards share one rank and two cards share another rank. How many ways are there to get a full-house?
MTH U481 : SPRING 2009: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL
 MTH U481 : SPRING 2009: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL 1). Two urns are provided as follows: urn 1 contains 2 white chips and 4 red chips, while urn 2 contains 5 white chips and 3 red chips. One chip is chosen
MTH U481 : SPRING 2009: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL 1). Two urns are provided as follows: urn 1 contains 2 white chips and 4 red chips, while urn 2 contains 5 white chips and 3 red chips. One chip is chosen
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2016 MODULE 1 : Probability distributions Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2016 MODULE 1 : Probability distributions Time allowed: Three hours Candidates should answer FIVE questions. All questions carry equal marks.
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 2 Discrete Random Variables
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 2 Discrete Random Variables Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Random Variable Discrete Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 2 Discrete Random Variables Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Random Variable Discrete Random
Introduction and Overview STAT 421, SP Course Instructor
 Introduction and Overview STAT 421, SP 212 Prof. Prem K. Goel Mon, Wed, Fri 3:3PM 4:48PM Postle Hall 118 Course Instructor Prof. Goel, Prem E mail: goel.1@osu.edu Office: CH 24C (Cockins Hall) Phone: 614
Introduction and Overview STAT 421, SP 212 Prof. Prem K. Goel Mon, Wed, Fri 3:3PM 4:48PM Postle Hall 118 Course Instructor Prof. Goel, Prem E mail: goel.1@osu.edu Office: CH 24C (Cockins Hall) Phone: 614
Machine Learning: Homework Assignment 2 Solutions
 10-601 Machine Learning: Homework Assignment 2 Solutions Professor Tom Mitchell Carnegie Mellon University January 21, 2009 The assignment is due at 1:30pm (beginning of class) on Monday, February 2, 2009.
10-601 Machine Learning: Homework Assignment 2 Solutions Professor Tom Mitchell Carnegie Mellon University January 21, 2009 The assignment is due at 1:30pm (beginning of class) on Monday, February 2, 2009.
STA 247 Solutions to Assignment #1
 STA 247 Solutions to Assignment #1 Question 1: Suppose you throw three six-sided dice (coloured red, green, and blue) repeatedly, until the three dice all show different numbers. Assuming that these dice
STA 247 Solutions to Assignment #1 Question 1: Suppose you throw three six-sided dice (coloured red, green, and blue) repeatedly, until the three dice all show different numbers. Assuming that these dice
2. Variance and Covariance: We will now derive some classic properties of variance and covariance. Assume real-valued random variables X and Y.
 CS450 Final Review Problems Fall 08 Solutions or worked answers provided Problems -6 are based on the midterm review Identical problems are marked recap] Please consult previous recitations and textbook
CS450 Final Review Problems Fall 08 Solutions or worked answers provided Problems -6 are based on the midterm review Identical problems are marked recap] Please consult previous recitations and textbook
University of Chicago Graduate School of Business. Business 41901: Probability Final Exam Solutions
 Name: University of Chicago Graduate School of Business Business 490: Probability Final Exam Solutions Special Notes:. This is a closed-book exam. You may use an 8 piece of paper for the formulas.. Throughout
Name: University of Chicago Graduate School of Business Business 490: Probability Final Exam Solutions Special Notes:. This is a closed-book exam. You may use an 8 piece of paper for the formulas.. Throughout
Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability
 Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability Refer to Text Book: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms By Wayne L. Winston,Ch. 12 Operations Research: An Introduction By Hamdi Taha, Ch. 12 OR441-Dr.Khalid
Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability Refer to Text Book: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms By Wayne L. Winston,Ch. 12 Operations Research: An Introduction By Hamdi Taha, Ch. 12 OR441-Dr.Khalid
Week 04 Discussion. a) What is the probability that of those selected for the in-depth interview 4 liked the new flavor and 1 did not?
 STAT Wee Discussion Fall 7. A new flavor of toothpaste has been developed. It was tested by a group of people. Nine of the group said they lied the new flavor, and the remaining 6 indicated they did not.
STAT Wee Discussion Fall 7. A new flavor of toothpaste has been developed. It was tested by a group of people. Nine of the group said they lied the new flavor, and the remaining 6 indicated they did not.
Lecture 13 (Part 2): Deviation from mean: Markov s inequality, variance and its properties, Chebyshev s inequality
 Lecture 13 (Part 2): Deviation from mean: Markov s inequality, variance and its properties, Chebyshev s inequality Discrete Structures II (Summer 2018) Rutgers University Instructor: Abhishek Bhrushundi
Lecture 13 (Part 2): Deviation from mean: Markov s inequality, variance and its properties, Chebyshev s inequality Discrete Structures II (Summer 2018) Rutgers University Instructor: Abhishek Bhrushundi
Exercises with solutions (Set D)
 Exercises with solutions Set D. A fair die is rolled at the same time as a fair coin is tossed. Let A be the number on the upper surface of the die and let B describe the outcome of the coin toss, where
Exercises with solutions Set D. A fair die is rolled at the same time as a fair coin is tossed. Let A be the number on the upper surface of the die and let B describe the outcome of the coin toss, where
Probability & Statistics - FALL 2008 FINAL EXAM
 550.3 Probability & Statistics - FALL 008 FINAL EXAM NAME. An urn contains white marbles and 8 red marbles. A marble is drawn at random from the urn 00 times with replacement. Which of the following is
550.3 Probability & Statistics - FALL 008 FINAL EXAM NAME. An urn contains white marbles and 8 red marbles. A marble is drawn at random from the urn 00 times with replacement. Which of the following is
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]
![Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]](/thumbs/93/111285649.jpg) Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
Math Fall 2010 Some Old Math 302 Exams There is always a danger when distributing old exams for a class that students will rely on them
 Math 302.102 Fall 2010 Some Old Math 302 Exams There is always a danger when distributing old exams for a class that students will rely on them solely for their final exam preparations. The final exam
Math 302.102 Fall 2010 Some Old Math 302 Exams There is always a danger when distributing old exams for a class that students will rely on them solely for their final exam preparations. The final exam
for valid PSD. PART B (Answer all five units, 5 X 10 = 50 Marks) UNIT I
 Code: 15A04304 R15 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R15) Regular Examinations November/December 016 PROBABILITY THEY & STOCHASTIC PROCESSES (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
Code: 15A04304 R15 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R15) Regular Examinations November/December 016 PROBABILITY THEY & STOCHASTIC PROCESSES (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks:
1 Presessional Probability
 1 Presessional Probability Probability theory is essential for the development of mathematical models in finance, because of the randomness nature of price fluctuations in the markets. This presessional
1 Presessional Probability Probability theory is essential for the development of mathematical models in finance, because of the randomness nature of price fluctuations in the markets. This presessional
Review of Probability. CS1538: Introduction to Simulations
 Review of Probability CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Probability and Statistics in Simulation Why do we need probability and statistics in simulation? Needed to validate the simulation model Needed
Review of Probability CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Probability and Statistics in Simulation Why do we need probability and statistics in simulation? Needed to validate the simulation model Needed
STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes. Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed.
 STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed. Chapter 1: Combinatorial Analysis Demonstrate the ability to solve combinatorial
STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed. Chapter 1: Combinatorial Analysis Demonstrate the ability to solve combinatorial
18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures Review
 18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures 18-27 Review Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Outline It s the coins, stupid Much of what we have done in this course can be motivated by the i.i.d. sequence X i where each X i is
18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures 18-27 Review Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Outline It s the coins, stupid Much of what we have done in this course can be motivated by the i.i.d. sequence X i where each X i is
Math489/889 Stochastic Processes and Advanced Mathematical Finance Solutions for Homework 7
 Math489/889 Stochastic Processes and Advanced Mathematical Finance Solutions for Homework 7 Steve Dunbar Due Mon, November 2, 2009. Time to review all of the information we have about coin-tossing fortunes
Math489/889 Stochastic Processes and Advanced Mathematical Finance Solutions for Homework 7 Steve Dunbar Due Mon, November 2, 2009. Time to review all of the information we have about coin-tossing fortunes
S.R.S Varadhan by Professor Tom Louis Lindstrøm
 S.R.S Varadhan by Professor Tom Louis Lindstrøm Srinivasa S. R. Varadhan was born in Madras (Chennai), India in 1940. He got his B. Sc. from Presidency College in 1959 and his Ph.D. from the Indian Statistical
S.R.S Varadhan by Professor Tom Louis Lindstrøm Srinivasa S. R. Varadhan was born in Madras (Chennai), India in 1940. He got his B. Sc. from Presidency College in 1959 and his Ph.D. from the Indian Statistical
Lecture #13 Tuesday, October 4, 2016 Textbook: Sections 7.3, 7.4, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3
 STATISTICS 200 Lecture #13 Tuesday, October 4, 2016 Textbook: Sections 7.3, 7.4, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 Objectives: Identify, and resist the temptation to fall for, the gambler s fallacy Define random variable
STATISTICS 200 Lecture #13 Tuesday, October 4, 2016 Textbook: Sections 7.3, 7.4, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 Objectives: Identify, and resist the temptation to fall for, the gambler s fallacy Define random variable
Probability Theory: Homework problems
 June 22, 2018 Homework 1. Probability Theory: Homework problems 1. A traditional three-digit telephone area code is constructed as follows. The first digit is from the set {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, the
June 22, 2018 Homework 1. Probability Theory: Homework problems 1. A traditional three-digit telephone area code is constructed as follows. The first digit is from the set {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, the
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel/SPSS Chapter 4 Basic Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions
 Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel/SPSS Chapter 4 Basic Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions 1999 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap. 4-1 Chapter Topics Basic Probability Concepts: Sample
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel/SPSS Chapter 4 Basic Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions 1999 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap. 4-1 Chapter Topics Basic Probability Concepts: Sample
CS 1538: Introduction to Simulation Homework 1
 CS 1538: Introduction to Simulation Homework 1 1. A fair six-sided die is rolled three times. Let X be a random variable that represents the number of unique outcomes in the three tosses. For example,
CS 1538: Introduction to Simulation Homework 1 1. A fair six-sided die is rolled three times. Let X be a random variable that represents the number of unique outcomes in the three tosses. For example,
Random Variables and Expectations
 Inside ECOOMICS Random Variables Introduction to Econometrics Random Variables and Expectations A random variable has an outcome that is determined by an experiment and takes on a numerical value. A procedure
Inside ECOOMICS Random Variables Introduction to Econometrics Random Variables and Expectations A random variable has an outcome that is determined by an experiment and takes on a numerical value. A procedure
Random Variable. Discrete Random Variable. Continuous Random Variable. Discrete Random Variable. Discrete Probability Distribution
 Random Variable Theoretical Probability Distribution Random Variable Discrete Probability Distributions A variable that assumes a numerical description for the outcome of a random eperiment (by chance).
Random Variable Theoretical Probability Distribution Random Variable Discrete Probability Distributions A variable that assumes a numerical description for the outcome of a random eperiment (by chance).
Probability and Statistics Notes
 Probability and Statistics Notes Chapter Five Jesse Crawford Department of Mathematics Tarleton State University Spring 2011 (Tarleton State University) Chapter Five Notes Spring 2011 1 / 37 Outline 1
Probability and Statistics Notes Chapter Five Jesse Crawford Department of Mathematics Tarleton State University Spring 2011 (Tarleton State University) Chapter Five Notes Spring 2011 1 / 37 Outline 1
Discussion 03 Solutions
 STAT Discussion Solutions Spring 8. A new flavor of toothpaste has been developed. It was tested by a group of people. Nine of the group said they liked the new flavor, and the remaining indicated they
STAT Discussion Solutions Spring 8. A new flavor of toothpaste has been developed. It was tested by a group of people. Nine of the group said they liked the new flavor, and the remaining indicated they
MATH 250 / SPRING 2011 SAMPLE QUESTIONS / SET 3
 MATH 250 / SPRING 2011 SAMPLE QUESTIONS / SET 3 1. A four engine plane can fly if at least two engines work. a) If the engines operate independently and each malfunctions with probability q, what is the
MATH 250 / SPRING 2011 SAMPLE QUESTIONS / SET 3 1. A four engine plane can fly if at least two engines work. a) If the engines operate independently and each malfunctions with probability q, what is the
1 Proof techniques. CS 224W Linear Algebra, Probability, and Proof Techniques
 1 Proof techniques Here we will learn to prove universal mathematical statements, like the square of any odd number is odd. It s easy enough to show that this is true in specific cases for example, 3 2
1 Proof techniques Here we will learn to prove universal mathematical statements, like the square of any odd number is odd. It s easy enough to show that this is true in specific cases for example, 3 2
Class 26: review for final exam 18.05, Spring 2014
 Probability Class 26: review for final eam 8.05, Spring 204 Counting Sets Inclusion-eclusion principle Rule of product (multiplication rule) Permutation and combinations Basics Outcome, sample space, event
Probability Class 26: review for final eam 8.05, Spring 204 Counting Sets Inclusion-eclusion principle Rule of product (multiplication rule) Permutation and combinations Basics Outcome, sample space, event
Engineering Mathematics : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 2262 X find the minimum value of c.
 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 2262 MATERIAL NAME : University Questions MATERIAL CODE : SKMA104 UPDATED ON : May June 2013 Name of the Student: Branch: Unit I (Random Variables)
SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 2262 MATERIAL NAME : University Questions MATERIAL CODE : SKMA104 UPDATED ON : May June 2013 Name of the Student: Branch: Unit I (Random Variables)
ECEn 370 Introduction to Probability
 RED- You can write on this exam. ECEn 370 Introduction to Probability Section 00 Final Winter, 2009 Instructor Professor Brian Mazzeo Closed Book Non-graphing Calculator Allowed No Time Limit IMPORTANT!
RED- You can write on this exam. ECEn 370 Introduction to Probability Section 00 Final Winter, 2009 Instructor Professor Brian Mazzeo Closed Book Non-graphing Calculator Allowed No Time Limit IMPORTANT!
Discrete Distributions
 A simplest example of random experiment is a coin-tossing, formally called Bernoulli trial. It happens to be the case that many useful distributions are built upon this simplest form of experiment, whose
A simplest example of random experiment is a coin-tossing, formally called Bernoulli trial. It happens to be the case that many useful distributions are built upon this simplest form of experiment, whose
CS 361: Probability & Statistics
 February 19, 2018 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Random variables Markov s inequality This theorem says that for any random variable X and any value a, we have A random variable is unlikely to have an
February 19, 2018 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Random variables Markov s inequality This theorem says that for any random variable X and any value a, we have A random variable is unlikely to have an
Find the value of n in order for the player to get an expected return of 9 counters per roll.
 . A biased die with four faces is used in a game. A player pays 0 counters to roll the die. The table below shows the possible scores on the die, the probability of each score and the number of counters
. A biased die with four faces is used in a game. A player pays 0 counters to roll the die. The table below shows the possible scores on the die, the probability of each score and the number of counters
Chi-Squared Tests. Semester 1. Chi-Squared Tests
 Semester 1 Goodness of Fit Up to now, we have tested hypotheses concerning the values of population parameters such as the population mean or proportion. We have not considered testing hypotheses about
Semester 1 Goodness of Fit Up to now, we have tested hypotheses concerning the values of population parameters such as the population mean or proportion. We have not considered testing hypotheses about
Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics.
 Part 1: Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
Part 1: Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
Master s Written Examination - Solution
 Master s Written Examination - Solution Spring 204 Problem Stat 40 Suppose X and X 2 have the joint pdf f X,X 2 (x, x 2 ) = 2e (x +x 2 ), 0 < x < x 2
Master s Written Examination - Solution Spring 204 Problem Stat 40 Suppose X and X 2 have the joint pdf f X,X 2 (x, x 2 ) = 2e (x +x 2 ), 0 < x < x 2
STAT 345 Spring 2018 Homework 4 - Discrete Probability Distributions
 STAT 345 Spring 2018 Homework 4 - Discrete Probability Distributions Name: Please adhere to the homework rules as given in the Syllabus. 1. Coin Flipping. Timothy and Jimothy are playing a betting game.
STAT 345 Spring 2018 Homework 4 - Discrete Probability Distributions Name: Please adhere to the homework rules as given in the Syllabus. 1. Coin Flipping. Timothy and Jimothy are playing a betting game.
Math st Homework. First part of Chapter 2. Due Friday, September 17, 1999.
 Math 447. 1st Homework. First part of Chapter 2. Due Friday, September 17, 1999. 1. How many different seven place license plates are possible if the first 3 places are to be occupied by letters and the
Math 447. 1st Homework. First part of Chapter 2. Due Friday, September 17, 1999. 1. How many different seven place license plates are possible if the first 3 places are to be occupied by letters and the
MATHEMATICS 154, SPRING 2009 PROBABILITY THEORY Outline #11 (Tail-Sum Theorem, Conditional distribution and expectation)
 MATHEMATICS 154, SPRING 2009 PROBABILITY THEORY Outline #11 (Tail-Sum Theorem, Conditional distribution and expectation) Last modified: March 7, 2009 Reference: PRP, Sections 3.6 and 3.7. 1. Tail-Sum Theorem
MATHEMATICS 154, SPRING 2009 PROBABILITY THEORY Outline #11 (Tail-Sum Theorem, Conditional distribution and expectation) Last modified: March 7, 2009 Reference: PRP, Sections 3.6 and 3.7. 1. Tail-Sum Theorem
Multiple Random Variables
 Multiple Random Variables Joint Probability Density Let X and Y be two random variables. Their joint distribution function is F ( XY x, y) P X x Y y. F XY ( ) 1, < x
Multiple Random Variables Joint Probability Density Let X and Y be two random variables. Their joint distribution function is F ( XY x, y) P X x Y y. F XY ( ) 1, < x
South Pacific Form Seven Certificate
 141/1 South Pacific Form Seven Certificate INSTRUCTIONS MATHEMATICS WITH STATISTICS 2015 QUESTION and ANSWER BOOKLET Time allowed: Two and a half hours Write your Student Personal Identification Number
141/1 South Pacific Form Seven Certificate INSTRUCTIONS MATHEMATICS WITH STATISTICS 2015 QUESTION and ANSWER BOOKLET Time allowed: Two and a half hours Write your Student Personal Identification Number
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2007 Luca Trevisan Lecture 20
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2007 Luca Trevisan Lecture 20 Today we shall discuss a measure of how close a random variable tends to be to its expectation. But first we need to see how to compute
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2007 Luca Trevisan Lecture 20 Today we shall discuss a measure of how close a random variable tends to be to its expectation. But first we need to see how to compute
by Dimitri P. Bertsekas and John N. Tsitsiklis
 INTRODUCTION TO PROBABILITY by Dimitri P. Bertsekas and John N. Tsitsiklis CHAPTER 2: ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS SECTION 2.2. Probability Mass Functions Problem 1. The probability of a royal flush in poker is
INTRODUCTION TO PROBABILITY by Dimitri P. Bertsekas and John N. Tsitsiklis CHAPTER 2: ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS SECTION 2.2. Probability Mass Functions Problem 1. The probability of a royal flush in poker is
Math Spring Practice for the final Exam.
 Math 4 - Spring 8 - Practice for the final Exam.. Let X, Y, Z be three independnet random variables uniformly distributed on [, ]. Let W := X + Y. Compute P(W t) for t. Honors: Compute the CDF function
Math 4 - Spring 8 - Practice for the final Exam.. Let X, Y, Z be three independnet random variables uniformly distributed on [, ]. Let W := X + Y. Compute P(W t) for t. Honors: Compute the CDF function
Exercises in Probability Theory Paul Jung MA 485/585-1C Fall 2015 based on material of Nikolai Chernov
 Exercises in Probability Theory Paul Jung MA 485/585-1C Fall 2015 based on material of Nikolai Chernov Many of the exercises are taken from two books: R. Durrett, The Essentials of Probability, Duxbury
Exercises in Probability Theory Paul Jung MA 485/585-1C Fall 2015 based on material of Nikolai Chernov Many of the exercises are taken from two books: R. Durrett, The Essentials of Probability, Duxbury
Name of the Student:
 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: ECONOMICS
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: ECONOMICS COURSE: CBS 221 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the undergraduate
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: ECONOMICS COURSE: CBS 221 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the undergraduate
MAT 111 Final Exam Fall 2013 Name: If solving graphically, sketch a graph and label the solution.
 MAT 111 Final Exam Fall 2013 Name: Show all work on test to receive credit. Draw a box around your answer. If solving algebraically, show all steps. If solving graphically, sketch a graph and label the
MAT 111 Final Exam Fall 2013 Name: Show all work on test to receive credit. Draw a box around your answer. If solving algebraically, show all steps. If solving graphically, sketch a graph and label the
Random Variables and Their Distributions
 Chapter 3 Random Variables and Their Distributions A random variable (r.v.) is a function that assigns one and only one numerical value to each simple event in an experiment. We will denote r.vs by capital
Chapter 3 Random Variables and Their Distributions A random variable (r.v.) is a function that assigns one and only one numerical value to each simple event in an experiment. We will denote r.vs by capital
Joint Distribution of Two or More Random Variables
 Joint Distribution of Two or More Random Variables Sometimes more than one measurement in the form of random variable is taken on each member of the sample space. In cases like this there will be a few
Joint Distribution of Two or More Random Variables Sometimes more than one measurement in the form of random variable is taken on each member of the sample space. In cases like this there will be a few
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 This is for your practice. DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS Ma162 Samples from old Final Exams 1. Fred Foy has $100, 000 to invest in stocks, bonds and a money market account. The stocks have an expected return
This is for your practice. DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS Ma162 Samples from old Final Exams 1. Fred Foy has $100, 000 to invest in stocks, bonds and a money market account. The stocks have an expected return
Summary of basic probability theory Math 218, Mathematical Statistics D Joyce, Spring 2016
 8. For any two events E and F, P (E) = P (E F ) + P (E F c ). Summary of basic probability theory Math 218, Mathematical Statistics D Joyce, Spring 2016 Sample space. A sample space consists of a underlying
8. For any two events E and F, P (E) = P (E F ) + P (E F c ). Summary of basic probability theory Math 218, Mathematical Statistics D Joyce, Spring 2016 Sample space. A sample space consists of a underlying
Question Paper Code : AEC11T03
 Hall Ticket No Question Paper Code : AEC11T03 VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Affiliated to JNTUH, Hyderabad Four Year B Tech III Semester Tutorial Question Bank 2013-14 (Regulations: VCE-R11)
Hall Ticket No Question Paper Code : AEC11T03 VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Affiliated to JNTUH, Hyderabad Four Year B Tech III Semester Tutorial Question Bank 2013-14 (Regulations: VCE-R11)
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW
 AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to write complete solutions for all of the problems listed in this packet. It is important that you have mastered the concepts covered
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to write complete solutions for all of the problems listed in this packet. It is important that you have mastered the concepts covered
