Calibration and Comparison of Chlorine Decay Models for a Test Water Distribution System
|
|
|
- Samantha Bonnie Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Calibration and Comparison of Chlorine Decay Models for a Test Water Distribution System Stefan H. Maier, Roger S. Powell and Clive A. Woodward, Water Operational Research Centre, Department of Manufacturing and Engineering Systems, Brunel University, Uxbridge, UB8 3PH, U.K.; Thames Water Utilities Ltd., Group Research & Technology, Spencer House, Manor Farm Road, Reading, RG2 0JN, U.K. All correspondence to be sent to: Dr Roger Powell, Water Operational Research Centre, Department of Manufacturing and Engineering Systems, Brunel University, Uxbridge, UB8 3PH, U.K. Tel /203296, Fax /812556, roger.powell@brunel.ac.uk. Short Title: Comparison of Chlorine Decay Models Keywords: water distribution system, water quality, chlorine decay coefficients, network calibration, parameter estimation, EPANET Abstract This paper investigates the kinetics of monochloramine as disinfectant in a 1.3 km water pipe. A novel procedure for the correction of chlorine meter errors is introduced and applied. Parameter estimation using nonlinear optimisation procedures is used to identify decay coefficients for monochloramine models with a single coefficient or two coefficients as used in EPANET. Important difficulties in fitting these parameters which come about because of the model structure are highlighted. Finally, results of decay coefficients are presented and investigated for flow, inlet chlorine concentration and temperature dependence. 1 Introduction Free chlorine and monochloramine are widely used as disinfectants in water distribution systems. Knowledge of the dynamic behaviour of this disinfectant is important when designing new systems and when determining the effects of operational changes. 1
2 The aim of this paper is to investigate and compare two commonly used chlorine decay models in detail, i.e. a single decay coefficient model and the combined bulk and wall demand model as used in EPANET (?), using data obtained from physical measurements. The models are adapted for the use of monochloramine as disinfectant. In addition, data from bottled samples are presented and compared with results obtained from the chlorine transducers. 2 Review of Chlorine Kinetics Most work on disinfection kinetics is concerned with free chlorine (Cl 2 or HOCl). It is frequently assumed that free chlorine decays according to first order reaction kinetics (?;?): c(x 2, t 2 ) = c(x 1, t 1 ) e K(t 2 t 1 ) (1) with x 2 x 1 = v (t 2 t 1 ), (2) where t 1, t 2 represent time, x 1, x 2 represent distance along the pipe and v is the constant velocity of water in the pipe. Therefore, the decay of free chlorine is characterised by just one (constant) decay coefficient K. The travel time between points x 1 and x 2 is τ = x = t v 2 t 1. A variation of the decay coefficient K may be required, since in recent years more evidence has been published that shows that simple first order kinetics do not fully match the behaviour of free chlorine in a distribution system. Lungwitz et al. (?) investigated booster (impulse) chlorination and found that they had to 2
3 postulate several decay coefficients depending on the chlorine gradient. Schneider et al. (?) concluded that the decay coefficient (and possibly other parameters) are flow dependent. Woodward et al. (?) found experimentally that the monochloramine decay coefficient changes with flow rate. Heraud et al. (?) used different decay coefficients depending on pipe materials and diameter to fit their model to the data. Simulation packages reflect these findings to some extent. In Piccolo (?) it is possible to use a chlorine decay coefficient, K H2 0, which depends on total organic carbon and temperature or to use diameter dependent decay coefficients within the distribution system. EPANET (?;?) includes a wall demand and a flow dependent mass transfer coefficient. Thus, it replaces the constant decay coefficient K with K = k b + k f k w R H (k f + k w ) (3) where k f is a flow dependent mass transfer coefficient, k b, k w are parameters representing bulk and wall demand respectively and R H is the hydraulic radius. The mass-transfer coefficient k f is calculated as given in Rossman (?) or Edwards et al. (?). In the present study, monochloramine is investigated since it is used in the London distribution system and it also finds application in other water networks world-wide, e.g. (?). Monochloramine (NH 2 Cl) is generally believed to behave in the same fashion as free chlorine, except that it reacts more slowly (?); also it was suggested that monochloramine is more efficient against biofilms than free chlorine (?;?). 3
4 Total chlorine, which includes free chlorine, monochloramine and organic chloramines, is measured using online meters. Organic chloramines are relatively stable and have a very low bacterial action (?) and thus are considered as a constant fraction of total chlorine in this work. Thus, first order kinetics as in Fig.?? are obtained, which can be described as c(x 2, t 2 ) = (c(x 1, t 1 ) c ) e K(t 2 t 1 ) + c. (4) where c(x, t) is the total chlorine concentration at position x and time t. Monochloramine is the reactive fraction of total chlorine, or {c(x, t) c }, while c is the non-reactive fraction of total chlorine, i.e. the organic chloramines. Starting from the beginning of the pipe (the chlorination point) we have x 1 = 0, t 1 = t 0, τ = t 2 t 1 and we can drop the index from x 2, t 2. Giving c(x, t) = (c(0, t 0 ) c ) e Kτ + c. (5) 3 Experimental Work 3.1 Torus Pipe Rig All experiments discussed in this paper were performed on the TORUS pipe rig or with pipe rig water. The pipe rig consists of a 1.3 km, 110 mm inside diameter pipe distribution system built of approved construction material. It is mainly made of medium density polyethylene (MDPE) and is divided into three sections of approximate length 500 m, 400 m and 400 m, respectively, which are 4
5 buried m underground. Measurements were taken at the inlet and at the three sample points along the rig. The amperometric total chlorine meters use a range of 0 to 2 mg/l of free or total chlorine and have an accuracy of ±0.05 mg/l at full scale deflection. They were recalibrated, both in zero position and span, at regular intervals. Chlorine titrations allow a full speciation of chlorine. Replicate titrations were performed (i.e. 3 to 5 titrations of the same water sample) in order to minimise errors. After discarding outliers, the averages of the remaining titration values are used for the following considerations. 3.2 Pipe Rig Experiments A series of step flow and step chlorine experiments was devised in order to obtain the relationship between chlorine concentration within the pipe, the initial conditions and flow rate. The experimental schedule is depicted in Fig.??. Apart from the step chlorine trials, the total chlorine residual at the pipe rig inlet was about mg/l. Step changes in flow were from 0.08 l/s to 0.3 l/s, 0.45 l/s, 0.6 l/s or 0.9 l/s. Typically, a step change in chlorine was from 0.4 mg/l to 0.65 mg/l. For bottle trials samples of the pipe rig inlet water were taken in bottles of volume 500ml or 1000ml and analysed by titrations. 5
6 4 Chlorine Meter Preprocessing Chlorine meters exhibit their own dynamics, and consequently preprocessing techniques are necessary to eliminate the unwanted signal. Let us assume that the (averaged) titration values are normally more accurate than the chlorine meters and, further, that the error in the meter readings is due to a relatively slow meter drift. The aim of the correction procedure is to find this error signal by using titration results and then to adjust the meter reading values as appropriate. Since a titration is a bench analysis, titration values are unequally spaced and relatively sparse. However, if the error signal is only varying slowly, the Nyquist theorem is still satisfied (i.e. there are at least two samples per period of the error signal). Evidence for the validity of this assumption of slow variation is given in Maier (?). The error function is calculated as the ratio between the titration data c b (x 0, t i ) and the chlorine meter data c m (x 0, t). Here t i denotes the unequally spaced time instants of the titrations; t represents, for brevity, the equally and closely spaced time instants of the meter readings, and x 0 is the distance of the point of investigation from the inlet. Since we are, in this context, only concerned with data specific to each sampling point, the dependence on the distance is irrelevant and we will omit x 0 in this section. Thus, we obtain the error function ɛ M (t i ) (subscript M for multiplicative) as ɛ M (t i ) = c b(t i ), (6) c m (t) t=ti 6
7 To reconstruct the error function between the time instants t i, ɛ M (t i ) is at first reverse-calibrated and then interpolated. Let w recalibration windows W j be of the form W j = [ t r j + δ, t r j+1 δ ], (7) where t r j is the jth time of recalibration and δ is a small positive perturbation. Following eq. (7), the reverse-calibration factors are j c m (t) r(t i ) = c m (t) k=1 t=t r k δ t=t r k +δ for t i W j. (8) Thus, the reverse-calibrated error signal ɛ R M (t i) is ɛ R M(t i ) = ɛ M (t i ) r(t i ) (9) Finally, this error function is interpolated m 1 ɛ IR M (t) = ɛ R M(t i ) l i (t), (10) i=1 where l i (t) denotes the linear interpolation function that is non-zero between t i and t i+1 and m is the number of titration times t i in the considered data. The superscript I indicates that ɛ IR M (t) is an interpolated signal, the superscript R refers to the reverse-calibration of eq. (9). The reverse-calibration is intended to inverse the effect of the recalibrations such that the chlorine reading directly after recalibration (at t = t r k + δ) is the same as the reading just before recalibration 7
8 (at t = t r k δ). Since the recalibrations guarantee that the meter is within the linear region of its scale the resulting error function ɛ R M (t i) should adhere to the low frequency assumption made above. Finally the error function ɛ IR M (t) is filtered, in accordance with the assumption of slow varying error, to remove any high frequency noise and smooth the signal. Thus, we obtain ɛ IRF M (t) = ɛ IR M (t) b 5 (t), (11) where denotes the convolution sum of the discrete Fourier transform and b 5 (t) is the impulse response of a fifth order low pass (Butterworth) filter. The cut-off frequency of day was chosen for a remaining absolute value of the Fourier transform of approximately 1 2 % of its maximum value (cf. Fig.??). The corrected chlorine data c c (t) is then obtained by multiplication of the meter data c m (t) with the final error function ɛ IRF M (t) c c (t) = c m (t) ɛ IRF M (t) (12) Typical examples of the correction obtained with this procedure are given in figs.?? and??. These figures show original meter data (dotted line), corrected data (dark line) and titration results (asterisks). In the total investigated time period the maximal absolute error is reduced from 0.28 mg/l to 0.13 mg/l, the maximal mean square error from mg/l to mg/l. Other preprocessing methods were tested and are reported elsewhere (?). The method described in this paper has the best performance of those tested. 8
9 5 Determination of Decay Coefficients Two possible descriptions of monochloramine decay as in eq. (5) were studied. 1) K = constant, 2) K = k b + k f k w R H (k f +k w, as used in EPANET. ) To calibrate both models the unknown parameters K and c (case 1) or k b, k w and c (case 2) have to be found such that the data fits a model according to eq. (5). 5.1 Parameter Estimation for the Single Decay Coefficient Model To find the single decay coefficient K as given in case 1, the solution of a nonlinear optimisation problem is necessary. The problem is to find the minimum over K and c of n 1 n 2 J 1 = (c c (x j, t i ) g 1 (j, i; K, c )) 2, (13) j=1 i=1 with g 1 (j, i; K, c ) = (c c (0, t 0,i ) c ) exp( Kτ(i, j) ) + c, (14) where c c (x j, t i ) is the corrected chlorine meter reading at time t i and distance x j, and τ(i, j) is the travel time between x j and x = 0 determined for the aliquot of water that is at time t i at x j. The measurement c c (0, t 0,i ) is the corrected meter reading at the inlet for the time when the aliquot of water that reaches x j at time 9
Paper 4.3. Introduction
 Paper 4.3 Removal of free and combined chlorine at GAC surfaces and impact on pool water quality Bertram Skibinski, PhD student, Susanne Müller, PhD student and Wolfgang Uhl, Chairholder, Water Supply
Paper 4.3 Removal of free and combined chlorine at GAC surfaces and impact on pool water quality Bertram Skibinski, PhD student, Susanne Müller, PhD student and Wolfgang Uhl, Chairholder, Water Supply
Analysis of Free Ammonia in Chloramination Applications Using Lab Method and the APA6000
 Analysis of Free Ammonia in Chloramination Applications Using Lab Method 10200 and the APA6000 Chloramination Chemistry Knowledge of chloramination chemistry is required to understand the rationale behind
Analysis of Free Ammonia in Chloramination Applications Using Lab Method 10200 and the APA6000 Chloramination Chemistry Knowledge of chloramination chemistry is required to understand the rationale behind
DBP Control: Chloramine Chemistry. Chris Griffin Hach Company
 DBP Control: Chloramine Chemistry Chris Griffin Hach Company 1 BEFORE WE BEGIN 2 Who currently Uses Chlorine only? Before we begin. Uses Chloramination at their water plant or in distribution? Uses Chloramination
DBP Control: Chloramine Chemistry Chris Griffin Hach Company 1 BEFORE WE BEGIN 2 Who currently Uses Chlorine only? Before we begin. Uses Chloramination at their water plant or in distribution? Uses Chloramination
ChemScan PROCESS ANALYZERS
 ChemScan PROCESS ANALYZERS, Applied Spectrometry Associates, Inc. www.chemscan.com ChemScan Application Summary #54 Peak Point Chloramination Control Rev. 9/ Over the past few years the EPA has tightened
ChemScan PROCESS ANALYZERS, Applied Spectrometry Associates, Inc. www.chemscan.com ChemScan Application Summary #54 Peak Point Chloramination Control Rev. 9/ Over the past few years the EPA has tightened
Chapter 5. Coupled Simulation - Optimization Model for Chlorine Management in Drinking Water Distribution Systems
 Chapter 5 Coupled Simulation - Optimization Model for Chlorine Management in Drinking Water Distribution Systems 5.1 Introduction Optimization is the act of obtaining the best result under given circumstances.
Chapter 5 Coupled Simulation - Optimization Model for Chlorine Management in Drinking Water Distribution Systems 5.1 Introduction Optimization is the act of obtaining the best result under given circumstances.
Science of Chloramination. Maine Water Utilities Association June 8, 2010
 Science of Chloramination June 8, 2010 What is chloramination? Chloramination is the process of disinfecting water using chloramines, compounds of chlorine and ammonia. The use of chloramines in the United
Science of Chloramination June 8, 2010 What is chloramination? Chloramination is the process of disinfecting water using chloramines, compounds of chlorine and ammonia. The use of chloramines in the United
A Study on Linear and Nonlinear Stiff Problems. Using Single-Term Haar Wavelet Series Technique
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 3, no. 53, 65-636 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.988/ijma.3.3894 A Study on Linear and Nonlinear Stiff Problems Using Single-Term Haar Wavelet Series
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 3, no. 53, 65-636 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.988/ijma.3.3894 A Study on Linear and Nonlinear Stiff Problems Using Single-Term Haar Wavelet Series
Understanding Chlorine Measurement. Rebecca Luedee Environmental Sales
 Understanding Chlorine Measurement Rebecca Luedee Environmental Sales Introduction to Chlorine Reaction with Water Forms hydrochloric (HCl) and hypochlorous (HOCl) acids: Cl 2 + H 2 O HOCl + HCl HOCl dissociates
Understanding Chlorine Measurement Rebecca Luedee Environmental Sales Introduction to Chlorine Reaction with Water Forms hydrochloric (HCl) and hypochlorous (HOCl) acids: Cl 2 + H 2 O HOCl + HCl HOCl dissociates
Disinfection Overview. Learning Objectives. Topics to be Covered. Be able to discuss the purpose and types of disinfection
 Disinfection Overview Workshop developed by RCAP/AWWA and funded by the USEPA Learning Objectives Be able to discuss the purpose and types of disinfection Be able to discuss the basics of chlorination
Disinfection Overview Workshop developed by RCAP/AWWA and funded by the USEPA Learning Objectives Be able to discuss the purpose and types of disinfection Be able to discuss the basics of chlorination
CEE 684 (697K) Dichloropropanone Lab
 CEE 684 (697K) Dichloropropanone Lab Laboratory Project Work in groups of three to investigate the kinetics of reaction between aqueous chlorine and 1,1-dichloropropanone (DCP). Use the paper by Guthrie
CEE 684 (697K) Dichloropropanone Lab Laboratory Project Work in groups of three to investigate the kinetics of reaction between aqueous chlorine and 1,1-dichloropropanone (DCP). Use the paper by Guthrie
Mathematical models for prediction of trihalomethanes in drinking water
 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 Mathematical models for prediction of trihalomethanes in drinking water J.
19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 Mathematical models for prediction of trihalomethanes in drinking water J.
technical reprint R/P098 fast timing with slow scintillators
 technical reprint R/P98 fast timing with slow scintillators fast timing with slow scintillators Q(t) = 1 (1 - exp (-t/ ô )) A G Wright, Electron Tubes Ltd., Bury Street, Ruislip, HA4 7TA, UK Q(t) note
technical reprint R/P98 fast timing with slow scintillators fast timing with slow scintillators Q(t) = 1 (1 - exp (-t/ ô )) A G Wright, Electron Tubes Ltd., Bury Street, Ruislip, HA4 7TA, UK Q(t) note
Effects of water quality characters on chlorine decay in water distribution networks
 Effects of water quality characters on chlorine decay in water distribution networks Theses of the PhD Dissertation by AL Heboos Sonia Department of Sanitary and Environmental Engineering Faculty of Civil
Effects of water quality characters on chlorine decay in water distribution networks Theses of the PhD Dissertation by AL Heboos Sonia Department of Sanitary and Environmental Engineering Faculty of Civil
TCEQ Directed Assistance Module (DAM) No. 5: Understanding and Controlling the Chloramination Process
 TCEQ Directed Assistance Module (DAM) No. 5: Understanding and Controlling the Chloramination Process Presented at the West Harris County Regional Water Authority Chloramines 101 Workshop July 10, 2008
TCEQ Directed Assistance Module (DAM) No. 5: Understanding and Controlling the Chloramination Process Presented at the West Harris County Regional Water Authority Chloramines 101 Workshop July 10, 2008
CEL 795- Water and Wastewater Treatment Unit Processes 1 st -Semester Disinfection Dr. Arun Kumar
 CEL 795- Water and Wastewater Treatment Unit Processes 1 st -Semester 2011-2012 Disinfection Dr. Arun Kumar (arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in) Courtesy: Dr. Irene Xagoraraki (MSU, USA) Disinfection Water is often
CEL 795- Water and Wastewater Treatment Unit Processes 1 st -Semester 2011-2012 Disinfection Dr. Arun Kumar (arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in) Courtesy: Dr. Irene Xagoraraki (MSU, USA) Disinfection Water is often
CEE 371 Water and Wastewater Systems
 Updated: 21 November 2009 CEE 371 Water and Wastewater Systems Print version Lecture #14 Drinking Water Treatment: Chlorination Reading: Chapter 7, pp.233-238, 259-262 David Reckhow CEE 371 L#14 1 Forms
Updated: 21 November 2009 CEE 371 Water and Wastewater Systems Print version Lecture #14 Drinking Water Treatment: Chlorination Reading: Chapter 7, pp.233-238, 259-262 David Reckhow CEE 371 L#14 1 Forms
CHLORAMINATION AND CHLORAMINE ANALYSIS SW AWWA 2014
 CHLORAMINATION AND CHLORAMINE ANALYSIS SW AWWA 2014 COMBINED CHLORINE - CHLORAMINATION Chlorine (HOCl and OCl - ) reacts with ammonia to form chloramines, commonly referred to as combined chlorine The
CHLORAMINATION AND CHLORAMINE ANALYSIS SW AWWA 2014 COMBINED CHLORINE - CHLORAMINATION Chlorine (HOCl and OCl - ) reacts with ammonia to form chloramines, commonly referred to as combined chlorine The
IB Paper 6: Signal and Data Analysis
 IB Paper 6: Signal and Data Analysis Handout 5: Sampling Theory S Godsill Signal Processing and Communications Group, Engineering Department, Cambridge, UK Lent 2015 1 / 85 Sampling and Aliasing All of
IB Paper 6: Signal and Data Analysis Handout 5: Sampling Theory S Godsill Signal Processing and Communications Group, Engineering Department, Cambridge, UK Lent 2015 1 / 85 Sampling and Aliasing All of
Application Your benefits
 Technical Information CCS140 and CCS141 Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 flow assembly Application Oxidizing agents such as chlorine or anorganic
Technical Information CCS140 and CCS141 Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 flow assembly Application Oxidizing agents such as chlorine or anorganic
Chloramine (Mono) and Nitrogen, Free Ammonia
 Chloramine (Mono) and Nitrogen, Free Ammonia DOC316.53.01016 Indophenol Method 1 Method 10200 0.04 to 4.50 mg/l Cl 2 0.01 to 0.50 mg/l NH 3 N Powder Pillows Scope and application: For the determination
Chloramine (Mono) and Nitrogen, Free Ammonia DOC316.53.01016 Indophenol Method 1 Method 10200 0.04 to 4.50 mg/l Cl 2 0.01 to 0.50 mg/l NH 3 N Powder Pillows Scope and application: For the determination
Disinfection. What is disinfection? Why to disinfect?
 Disinfection What is disinfection? Why to disinfect? Disinfection is a process which inactivate or remove the pathogenic microorganisms in system. Treated (including disinfection) water should ensure the
Disinfection What is disinfection? Why to disinfect? Disinfection is a process which inactivate or remove the pathogenic microorganisms in system. Treated (including disinfection) water should ensure the
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Residual Chlorine & Chlorine Demand. Chlorine and its uses. It ain t chloride!
 Slide 1 Residual Chlorine & Chlorine Demand Slide 2 It ain t chloride! It is important to keep in mind that there is a distinct difference between chloride ion and chlorine. They are chemically distinct
Slide 1 Residual Chlorine & Chlorine Demand Slide 2 It ain t chloride! It is important to keep in mind that there is a distinct difference between chloride ion and chlorine. They are chemically distinct
Parameter Method Range # of Tests Code Page. Acidity (as % Oleic acid) titration % acidity 6 HI
 Single Parameter Test Kits Parameter # of Tests Code Page Acidity Acidity (as % Oleic acid) 0.00-1.00 % acidity 6 HI387.8 Acidity (as CaCO₃) Methyl/Orange and Total 0-100 mg/l (ppm); 0-500 mg/l (ppm) 110
Single Parameter Test Kits Parameter # of Tests Code Page Acidity Acidity (as % Oleic acid) 0.00-1.00 % acidity 6 HI387.8 Acidity (as CaCO₃) Methyl/Orange and Total 0-100 mg/l (ppm); 0-500 mg/l (ppm) 110
CCS140 and CCS141. Technical Information. Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 assembly
 Technical Information CCS140 and CCS141 Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 assembly Application Oxidising agents such as chlorine or anorganic
Technical Information CCS140 and CCS141 Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 assembly Application Oxidising agents such as chlorine or anorganic
Disinfection. Disinfection is used to treat both domestic water and wastewater.
 Disinfection Disinfection is the selective destruction of disease causing organisms (viruses, bacteria, protozoans). It destroys most recognized pathogenic microorganisms, but not necessarily all microbial
Disinfection Disinfection is the selective destruction of disease causing organisms (viruses, bacteria, protozoans). It destroys most recognized pathogenic microorganisms, but not necessarily all microbial
CHLORINE THEORY & MEASUREMENT
 CHLORINE THEORY & MEASUREMENT Introduction Chlorine, dissolved in liquid, is one of the most effective and economical germ-killers for the treatment of water to make it potable or safe to drink. Chlorine's
CHLORINE THEORY & MEASUREMENT Introduction Chlorine, dissolved in liquid, is one of the most effective and economical germ-killers for the treatment of water to make it potable or safe to drink. Chlorine's
CCS140 and CCS141. Technical Information. Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 assembly
 Technical Information CCS140 and CCS141 Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 assembly Application Oxidising agents such as chlorine or anorganic
Technical Information CCS140 and CCS141 Sensors for free chlorine Amperometric, membrane-covered sensors for installation in the CCA250 assembly Application Oxidising agents such as chlorine or anorganic
Design Data 17. Partial Flow Conditions of Box Culverts
 Design Data 17 Partial Flow Conditions of Box Culverts Sewers, both sanitary and storm, are designed to carry a peak flow based on anticipated land development. The hydraulic capacity of sewers or culverts
Design Data 17 Partial Flow Conditions of Box Culverts Sewers, both sanitary and storm, are designed to carry a peak flow based on anticipated land development. The hydraulic capacity of sewers or culverts
DPD Test N Tube Method *
 CHLORINE, FREE (0 to 5.00 mg/l) DPD Test N Tube Method * Method 10102 For water, wastewater, and seawater 1. Enter the stored program number for Test N Tube free chlorine (Cl 2 ). Press: PRGM The display
CHLORINE, FREE (0 to 5.00 mg/l) DPD Test N Tube Method * Method 10102 For water, wastewater, and seawater 1. Enter the stored program number for Test N Tube free chlorine (Cl 2 ). Press: PRGM The display
FOURIER TRANSFORMS. f n = 1 N. ie. cyclic. dw = F k 2 = N 1. See Brault & White 1971, A&A, , for a tutorial introduction.
 FOURIER TRANSFORMS F(w) = T 0 f(t) e iwt dt f(t) = 1 2π wn w N F(w) e iwt dw F k = N 1 n=0 f n e 2πikn/N f n = 1 N N 1 k=0 F k e 2πikn/N Properties 1. Shift origin by t F F e iw t F invariant F 2 = power
FOURIER TRANSFORMS F(w) = T 0 f(t) e iwt dt f(t) = 1 2π wn w N F(w) e iwt dw F k = N 1 n=0 f n e 2πikn/N f n = 1 N N 1 k=0 F k e 2πikn/N Properties 1. Shift origin by t F F e iw t F invariant F 2 = power
Tailoring activated carbon for enhanced adsorption of disinfection byproduct precursors
 Tailoring activated carbon for enhanced adsorption of disinfection byproduct precursors Thien D. Do, M.S. Julian L. Fairey, Ph.D., P.E. Southwest AWWA Annual Conference October 12-14, 2014, Tulsa, OK DBP
Tailoring activated carbon for enhanced adsorption of disinfection byproduct precursors Thien D. Do, M.S. Julian L. Fairey, Ph.D., P.E. Southwest AWWA Annual Conference October 12-14, 2014, Tulsa, OK DBP
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 254 Part V
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 254 Part V
Ultrasonic Thickness Inspection of Oil Pipeline Based on Marginal Spectrum. of Hilbert-Huang Transform
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Ultrasonic Thickness Inspection of Oil Pipeline Based on Marginal Spectrum of Hilbert-Huang Transform Yimei MAO, Peiwen
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Ultrasonic Thickness Inspection of Oil Pipeline Based on Marginal Spectrum of Hilbert-Huang Transform Yimei MAO, Peiwen
Time Series Analysis: 4. Linear filters. P. F. Góra
 Time Series Analysis: 4. Linear filters P. F. Góra http://th-www.if.uj.edu.pl/zfs/gora/ 2012 Linear filters in the Fourier domain Filtering: Multiplying the transform by a transfer function. g n DFT G
Time Series Analysis: 4. Linear filters P. F. Góra http://th-www.if.uj.edu.pl/zfs/gora/ 2012 Linear filters in the Fourier domain Filtering: Multiplying the transform by a transfer function. g n DFT G
On the Early Development of Dispersion in Flow through a Tube with Wall Reactions
 World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 9 7 On the Early Development of Dispersion in Flow through a Tube with Wall Reactions M. W. Lau, and C. O. Ng Abstract This is a study on numerical
World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 9 7 On the Early Development of Dispersion in Flow through a Tube with Wall Reactions M. W. Lau, and C. O. Ng Abstract This is a study on numerical
Digital Baseband Systems. Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proakis
 Digital Baseband Systems Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proais Baseband Pulse Transmission Baseband digital signals - signals whose spectrum extend down to or near zero frequency. Model of the
Digital Baseband Systems Reference: Digital Communications John G. Proais Baseband Pulse Transmission Baseband digital signals - signals whose spectrum extend down to or near zero frequency. Model of the
Time Series Analysis: 4. Digital Linear Filters. P. F. Góra
 Time Series Analysis: 4. Digital Linear Filters P. F. Góra http://th-www.if.uj.edu.pl/zfs/gora/ 2018 Linear filters Filtering in Fourier domain is very easy: multiply the DFT of the input by a transfer
Time Series Analysis: 4. Digital Linear Filters P. F. Góra http://th-www.if.uj.edu.pl/zfs/gora/ 2018 Linear filters Filtering in Fourier domain is very easy: multiply the DFT of the input by a transfer
Science of Chloramination. Maine Water Utilities Association Michael Koza, Portland Water District June 2010
 Science of Chloramination Michael Koza, Portland Water District June 2010 Chloramination The process of combining chlorine and ammonia to create a combined form of chlorine for drinking water disinfection
Science of Chloramination Michael Koza, Portland Water District June 2010 Chloramination The process of combining chlorine and ammonia to create a combined form of chlorine for drinking water disinfection
7.7 The Schottky Formula for Shot Noise
 110CHAPTER 7. THE WIENER-KHINCHIN THEOREM AND APPLICATIONS 7.7 The Schottky Formula for Shot Noise On p. 51, we found that if one averages τ seconds of steady electron flow of constant current then the
110CHAPTER 7. THE WIENER-KHINCHIN THEOREM AND APPLICATIONS 7.7 The Schottky Formula for Shot Noise On p. 51, we found that if one averages τ seconds of steady electron flow of constant current then the
Edge Detection. Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003
 Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
ECE 301 Fall 2010 Division 2 Homework 10 Solutions. { 1, if 2n t < 2n + 1, for any integer n, x(t) = 0, if 2n 1 t < 2n, for any integer n.
 ECE 3 Fall Division Homework Solutions Problem. Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal from its samples. Consider the following periodic signal, depicted below: {, if n t < n +, for any integer n,
ECE 3 Fall Division Homework Solutions Problem. Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal from its samples. Consider the following periodic signal, depicted below: {, if n t < n +, for any integer n,
A New On-line Cyanide Analyzer for Measurement of Cyanide in Hydrometallurgical Processing of Precious Metal Ores
 Application Note 37890312 A New On-line Cyanide Analyzer for Measurement of Cyanide in Hydrometallurgical Processing of Precious Metal Ores Keywords CNSolution 9310 On-line Cyanide Analyzer Cyanidation
Application Note 37890312 A New On-line Cyanide Analyzer for Measurement of Cyanide in Hydrometallurgical Processing of Precious Metal Ores Keywords CNSolution 9310 On-line Cyanide Analyzer Cyanidation
Chlorine, Free and Total, High Range
 Chlorine, Free and Total, High Range DOC316.53.01490 USEPA DPD Method 1 Method 10069 (free) 10070 (total) 0.1 to 10.0 mg/l Cl 2 (HR) Powder Pillows Scope and application: For testing higher levels of free
Chlorine, Free and Total, High Range DOC316.53.01490 USEPA DPD Method 1 Method 10069 (free) 10070 (total) 0.1 to 10.0 mg/l Cl 2 (HR) Powder Pillows Scope and application: For testing higher levels of free
Chlorine, Free and Total, High Range
 Chlorine, Free and Total, High Range DOC316.53.01449 USEPA DPD Method 1 Method DPD 0.1 to 8.0 mg/l Cl 2 Powder Pillows Scope and application: For testing residual chlorine and chloramines in water, wastewater,
Chlorine, Free and Total, High Range DOC316.53.01449 USEPA DPD Method 1 Method DPD 0.1 to 8.0 mg/l Cl 2 Powder Pillows Scope and application: For testing residual chlorine and chloramines in water, wastewater,
ANALYSIS OF CHLORINATED BY-PRODUCTS IN SWIMMING POOL WATER BY MEMBRANE INTRODUCTION MASS SPECTROMETRY- INFLUENCE OF WATER PHYSICOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS
 ANALYSIS OF CHLORINATED BY-PRODUCTS IN SWIMMING POOL WATER BY MEMBRANE INTRODUCTION MASS SPECTROMETRY- INFLUENCE OF WATER PHYSICOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS N. CIMETIERE. N. GARANDEL, P. HUMEAU INTRODUCTION Chlorine
ANALYSIS OF CHLORINATED BY-PRODUCTS IN SWIMMING POOL WATER BY MEMBRANE INTRODUCTION MASS SPECTROMETRY- INFLUENCE OF WATER PHYSICOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS N. CIMETIERE. N. GARANDEL, P. HUMEAU INTRODUCTION Chlorine
Pakistan of Information Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan.
 Transient plane source (tps) sensors for simultaneous measurements of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of insulators, fluids and conductors Asghari Maqsood 1, M Anis-ur-Rehman 2 1 Centre for
Transient plane source (tps) sensors for simultaneous measurements of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of insulators, fluids and conductors Asghari Maqsood 1, M Anis-ur-Rehman 2 1 Centre for
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005
 Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS
 Attom High Resolution ICP-MS PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS Nu Plasma II Multi-Collector ICP-MS Panorama HR Stable Isotope Ratio MS Astrum Glow Discharge MS Nu Plasma 1700 Multi-Collector ICP-MS Horizon
Attom High Resolution ICP-MS PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS Nu Plasma II Multi-Collector ICP-MS Panorama HR Stable Isotope Ratio MS Astrum Glow Discharge MS Nu Plasma 1700 Multi-Collector ICP-MS Horizon
MAGNETIC NOZZLE PLASMA EXHAUST SIMULATION FOR THE VASIMR ADVANCED PROPULSION CONCEPT
 MAGNETIC NOZZLE PLASMA EXHAUST SIMULATION FOR THE VASIMR ADVANCED PROPULSION CONCEPT ABSTRACT A. G. Tarditi and J. V. Shebalin Advanced Space Propulsion Laboratory NASA Johnson Space Center Houston, TX
MAGNETIC NOZZLE PLASMA EXHAUST SIMULATION FOR THE VASIMR ADVANCED PROPULSION CONCEPT ABSTRACT A. G. Tarditi and J. V. Shebalin Advanced Space Propulsion Laboratory NASA Johnson Space Center Houston, TX
Reservoir Oscillations with Through Flow
 American Journal of Environmental Sciences 3 (): 37-42, 27 ISSN 553-345X 27 Science Publications Reservoir Oscillations with Through Flow A. A. Khan 28 Lowry Hall, epartment of Civil Engineering, Clemson
American Journal of Environmental Sciences 3 (): 37-42, 27 ISSN 553-345X 27 Science Publications Reservoir Oscillations with Through Flow A. A. Khan 28 Lowry Hall, epartment of Civil Engineering, Clemson
RELAY CONTROL WITH PARALLEL COMPENSATOR FOR NONMINIMUM PHASE PLANTS. Ryszard Gessing
 RELAY CONTROL WITH PARALLEL COMPENSATOR FOR NONMINIMUM PHASE PLANTS Ryszard Gessing Politechnika Śl aska Instytut Automatyki, ul. Akademicka 16, 44-101 Gliwice, Poland, fax: +4832 372127, email: gessing@ia.gliwice.edu.pl
RELAY CONTROL WITH PARALLEL COMPENSATOR FOR NONMINIMUM PHASE PLANTS Ryszard Gessing Politechnika Śl aska Instytut Automatyki, ul. Akademicka 16, 44-101 Gliwice, Poland, fax: +4832 372127, email: gessing@ia.gliwice.edu.pl
Available online at ScienceDirect
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 70 ( 2014 ) 934 942 12th International Conference on Computing and Control for the Water Industry, CCWI2013 Prediction of chlorine
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 70 ( 2014 ) 934 942 12th International Conference on Computing and Control for the Water Industry, CCWI2013 Prediction of chlorine
Land at Larchwood Farm, Whitehorse Lane Finchampstead, Berkshire
 Land at Larchwood Farm, Whitehorse Lane Finchampstead, Berkshire An Archaeological Evaluation for Mr. John Westbrook by James McNicoll-Norbury Thames Valley Archaeological Services Ltd Site Code LFF08/103
Land at Larchwood Farm, Whitehorse Lane Finchampstead, Berkshire An Archaeological Evaluation for Mr. John Westbrook by James McNicoll-Norbury Thames Valley Archaeological Services Ltd Site Code LFF08/103
2A1H Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to HT 2011 For hints and answers visit dwm/courses/2tf
 Time-Frequency Analysis II (HT 20) 2AH 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 20 For hints and answers visit www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf David Murray. A periodic
Time-Frequency Analysis II (HT 20) 2AH 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 20 For hints and answers visit www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf David Murray. A periodic
Basic Structure of the High-energy Observations. Preparation of the Data for the Analysis. Methods to Examine the Periodic Signal
 Timing Analysis of the Fermi Observations Basic Structure of the High-energy Observations Preparation of the Data for the Analysis Methods to Examine the Periodic Signal The related commands to perform
Timing Analysis of the Fermi Observations Basic Structure of the High-energy Observations Preparation of the Data for the Analysis Methods to Examine the Periodic Signal The related commands to perform
Charlmont Road, Tooting, London Borough of Wandsworth
 123-125 Charlmont Road, Tooting, London Borough of Wandsworth An Archaeological Evaluation For Eramo Developments Limited by Andrew Weale and Andrew Taylor Thames Valley Archaeological Services Ltd Site
123-125 Charlmont Road, Tooting, London Borough of Wandsworth An Archaeological Evaluation For Eramo Developments Limited by Andrew Weale and Andrew Taylor Thames Valley Archaeological Services Ltd Site
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
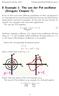 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Three Axis Magnetic Field Transducer x-h3x-xx_e3d-2.5khz-1-0.2t
 DESCRIPTION: TYPICAL APPLICATIONS: The is a high accuracy magnetic flux density-toanalogue-voltage transducer with a highlevel and temperature compensated output signal for each of the three components
DESCRIPTION: TYPICAL APPLICATIONS: The is a high accuracy magnetic flux density-toanalogue-voltage transducer with a highlevel and temperature compensated output signal for each of the three components
Elec4621 Advanced Digital Signal Processing Chapter 11: Time-Frequency Analysis
 Elec461 Advanced Digital Signal Processing Chapter 11: Time-Frequency Analysis Dr. D. S. Taubman May 3, 011 In this last chapter of your notes, we are interested in the problem of nding the instantaneous
Elec461 Advanced Digital Signal Processing Chapter 11: Time-Frequency Analysis Dr. D. S. Taubman May 3, 011 In this last chapter of your notes, we are interested in the problem of nding the instantaneous
EXPERIMENT 3 THE IODINE CLOCK
 EXPERIMENT 3 THE IODINE CLOCK Introduction The Rates of Chemical Reactions Broadly defined, chemical kinetics is the study of the rates at which chemical reactions proceed. Oftentimes, reaction rate data
EXPERIMENT 3 THE IODINE CLOCK Introduction The Rates of Chemical Reactions Broadly defined, chemical kinetics is the study of the rates at which chemical reactions proceed. Oftentimes, reaction rate data
Study of the impact of natural organic matter on the variation of the overall reaction coefficient in a simulated water distribution network
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 8, August 2017 320 Study of the impact of natural organic matter on the variation of the overall reaction coefficient in a
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 8, August 2017 320 Study of the impact of natural organic matter on the variation of the overall reaction coefficient in a
FC80 Free Chlorine Analyzer ELECTRO-CHEMICAL DEVICES
 FC80 Free Chlorine Analyzer ELECTRO-CHEMICAL DEVICES FC80 System Configuration Free Chlorine Analyzer 1) Constant Head Flow Controller 2) S80- ph with Temperature Sensor 3) Free Chlorine Sensor (FCS) 4)
FC80 Free Chlorine Analyzer ELECTRO-CHEMICAL DEVICES FC80 System Configuration Free Chlorine Analyzer 1) Constant Head Flow Controller 2) S80- ph with Temperature Sensor 3) Free Chlorine Sensor (FCS) 4)
Chlorine Disinfection. Sidney Innerebner, PhD, PE, CWP Indigo Water Group Littleton, Colorado
 Chlorine Disinfection Sidney Innerebner, PhD, PE, CWP Indigo Water Group Littleton, Colorado Wastewater Exam Cram Disinfection is Awesome! Source: http://www.impatientoptimists.org/posts/2013/04/ltyphoidletsactnowtoprotectchildrenfromthis19thcenturydisease
Chlorine Disinfection Sidney Innerebner, PhD, PE, CWP Indigo Water Group Littleton, Colorado Wastewater Exam Cram Disinfection is Awesome! Source: http://www.impatientoptimists.org/posts/2013/04/ltyphoidletsactnowtoprotectchildrenfromthis19thcenturydisease
CE 370. Disinfection. Location in the Treatment Plant. After the water has been filtered, it is disinfected. Disinfection follows filtration.
 CE 70 Disinfection 1 Location in the Treatment Plant After the water has been filtered, it is disinfected. Disinfection follows filtration. 1 Overview of the Process The purpose of disinfecting drinking
CE 70 Disinfection 1 Location in the Treatment Plant After the water has been filtered, it is disinfected. Disinfection follows filtration. 1 Overview of the Process The purpose of disinfecting drinking
a monte carlo simulation of photomultiplier resolution
 technical reprint R/P080 a monte carlo simulation of photomultiplier resolution a Monte Carlo simulation of photomultiplier resolution A G Wright, Electron Tubes Limited, Bury Street, Ruislip, Middlesex
technical reprint R/P080 a monte carlo simulation of photomultiplier resolution a Monte Carlo simulation of photomultiplier resolution A G Wright, Electron Tubes Limited, Bury Street, Ruislip, Middlesex
Machine Learning. A Bayesian and Optimization Perspective. Academic Press, Sergios Theodoridis 1. of Athens, Athens, Greece.
 Machine Learning A Bayesian and Optimization Perspective Academic Press, 2015 Sergios Theodoridis 1 1 Dept. of Informatics and Telecommunications, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens,
Machine Learning A Bayesian and Optimization Perspective Academic Press, 2015 Sergios Theodoridis 1 1 Dept. of Informatics and Telecommunications, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens,
PoS(idm2008)010. The PICASSO Dark Matter Search Project. A. Davour for the PICASSO collaboration Queen s University
 The PICASSO Dark Matter Search Project A. Davour for the PICASSO collaboration Queen s University E-mail: adavour@owl.phy.queensu.ca PICASSO is an array of bubble detectors constructed to search for spin
The PICASSO Dark Matter Search Project A. Davour for the PICASSO collaboration Queen s University E-mail: adavour@owl.phy.queensu.ca PICASSO is an array of bubble detectors constructed to search for spin
2A1H Time-Frequency Analysis II
 2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 209 For any corrections see the course page DW Murray at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf. (a) A signal g(t) with period
2AH Time-Frequency Analysis II Bugs/queries to david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk HT 209 For any corrections see the course page DW Murray at www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf. (a) A signal g(t) with period
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 78 (2015 ) th International Building Physics Conference, IBPC 2015
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 78 (2015 ) 537 542 6th International Building Physics Conference, IBPC 2015 Characterization of fibrous insulating materials in their
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 78 (2015 ) 537 542 6th International Building Physics Conference, IBPC 2015 Characterization of fibrous insulating materials in their
UNCERTAINTIES FOR PRESSURE-TIME EFFICIENCY MEASUREMENTS
 UNCERTAINTIES FOR PRESSURE-TIME EFFICIENCY MEASUREMENTS ABSTRACT Jørgen Ramdal Norwegian University of Science and Technology Pontus P. Jonsson Luleå University of Technology Ole Gunnar Dahlhaug Norwegian
UNCERTAINTIES FOR PRESSURE-TIME EFFICIENCY MEASUREMENTS ABSTRACT Jørgen Ramdal Norwegian University of Science and Technology Pontus P. Jonsson Luleå University of Technology Ole Gunnar Dahlhaug Norwegian
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Antimicrobial activity of chlorinated amino acids and peptides
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Antimicrobial activity of chlorinated amino acids and peptides Melanie S. A. Coker*, Wan-Ping Hu, Senti T Senthilmohan and Anthony J. Kettle Free Radical Research Group, University
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Antimicrobial activity of chlorinated amino acids and peptides Melanie S. A. Coker*, Wan-Ping Hu, Senti T Senthilmohan and Anthony J. Kettle Free Radical Research Group, University
Application of an ultrasonic velocity profile monitor in a hydraulic laboratory
 Application of an ultrasonic velocity profile monitor in a hydraulic laboratory Abstract Helmut Knoblauch 1, Roman Klasinc 1, Thomas Geisler 1 Velocity profile measurement using the ultrasound-pulse-doppler
Application of an ultrasonic velocity profile monitor in a hydraulic laboratory Abstract Helmut Knoblauch 1, Roman Klasinc 1, Thomas Geisler 1 Velocity profile measurement using the ultrasound-pulse-doppler
CHLORINE, FREE, Ultra-high Range ( mg/l Cl 2 ) Method 10069
 CHLORINE, FREE, Ultra-high Range (0.0 10.0 mg/l Cl 2 ) Method 10069 DPD Method USEPA accepted for reporting drinking water analyses * For testing higher levels of free chlorine (hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite)
CHLORINE, FREE, Ultra-high Range (0.0 10.0 mg/l Cl 2 ) Method 10069 DPD Method USEPA accepted for reporting drinking water analyses * For testing higher levels of free chlorine (hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite)
Thursday 29 June 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA A Level Physics A H556/03 Unified physics Thursday 29 June 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes *6830056239* You must have: The Data, Formulae and Relationship Booklet
Oxford Cambridge and RSA A Level Physics A H556/03 Unified physics Thursday 29 June 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes *6830056239* You must have: The Data, Formulae and Relationship Booklet
Filtering and Edge Detection
 Filtering and Edge Detection Local Neighborhoods Hard to tell anything from a single pixel Example: you see a reddish pixel. Is this the object s color? Illumination? Noise? The next step in order of complexity
Filtering and Edge Detection Local Neighborhoods Hard to tell anything from a single pixel Example: you see a reddish pixel. Is this the object s color? Illumination? Noise? The next step in order of complexity
3 Chemical exchange and the McConnell Equations
 3 Chemical exchange and the McConnell Equations NMR is a technique which is well suited to study dynamic processes, such as the rates of chemical reactions. The time window which can be investigated in
3 Chemical exchange and the McConnell Equations NMR is a technique which is well suited to study dynamic processes, such as the rates of chemical reactions. The time window which can be investigated in
NEW EUMETSAT POLAR SYSTEM ATTITUDE MONITORING SOFTWARE
 NEW EUMETSAT POLAR SYSTEM ATTITUDE MONITORING SOFTWARE Pablo García Sánchez (1), Antonio Pérez Cambriles (2), Jorge Eufrásio (3), Pier Luigi Righetti (4) (1) GMV Aerospace and Defence, S.A.U., Email: pgarcia@gmv.com,
NEW EUMETSAT POLAR SYSTEM ATTITUDE MONITORING SOFTWARE Pablo García Sánchez (1), Antonio Pérez Cambriles (2), Jorge Eufrásio (3), Pier Luigi Righetti (4) (1) GMV Aerospace and Defence, S.A.U., Email: pgarcia@gmv.com,
Sodium Chloride - Analytical Standard
 Sodium Chloride - Analytical Standard Determination of Total Mercury Former numbering: ECSS/CN 312-1982 & ESPA/CN-E-106-1994 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The present EuSalt Analytical Standard describes
Sodium Chloride - Analytical Standard Determination of Total Mercury Former numbering: ECSS/CN 312-1982 & ESPA/CN-E-106-1994 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The present EuSalt Analytical Standard describes
Chlorine disinfectant in the water industry
 Chlorine disinfectant in the water industry Based on its chemical characteristics and its reactivity response, chlorine is very well suited for disinfection of water and to prevent contamination with bacteria
Chlorine disinfectant in the water industry Based on its chemical characteristics and its reactivity response, chlorine is very well suited for disinfection of water and to prevent contamination with bacteria
Metropolis, 2D Ising model
 Metropolis, 2D Ising model You can get visual understanding from the java applets available, like: http://physics.ucsc.edu/~peter/ising/ising.html Average value of spin is magnetization. Abs of this as
Metropolis, 2D Ising model You can get visual understanding from the java applets available, like: http://physics.ucsc.edu/~peter/ising/ising.html Average value of spin is magnetization. Abs of this as
Assessing Post-Treatment Aeration Variables to Reduce Disinfection Byproducts(THMs) for Small Systems
 Assessing Post-Treatment Aeration Variables to Reduce Disinfection Byproducts(THMs) for Small Systems Ethan S. Brooke & M.R. Collins Water Treatment Technology Assistance Center Civil Engineering University
Assessing Post-Treatment Aeration Variables to Reduce Disinfection Byproducts(THMs) for Small Systems Ethan S. Brooke & M.R. Collins Water Treatment Technology Assistance Center Civil Engineering University
Effects of water quality characters on chlorine decay in water distribution networks
 Effects of water quality characters on chlorine decay in water distribution networks A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by AL Heboos Sonia Department of Sanitary and Environmental
Effects of water quality characters on chlorine decay in water distribution networks A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by AL Heboos Sonia Department of Sanitary and Environmental
PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS
 Nu Plasma II Multi-Collector ICP-MS Aspect HR Stable Isotope Ratio MS PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS Astrum Glow Discharge MS Nu Plasma 1700 Multi-Collector ICP-MS Panorama HR Stable Isotope Ratio
Nu Plasma II Multi-Collector ICP-MS Aspect HR Stable Isotope Ratio MS PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS Astrum Glow Discharge MS Nu Plasma 1700 Multi-Collector ICP-MS Panorama HR Stable Isotope Ratio
Project PAJ2 Dynamic Performance of Adhesively Bonded Joints. Report No. 3 August Proposed Draft for the Revision of ISO
 NPL Report CMMT(A)81 Project PAJ2 Dynamic Performance of Adhesively Bonded Joints Report No. 3 August 1997 Proposed Draft for the Revision of ISO 11003-2 Adhesives - Determination of Shear Behaviour of
NPL Report CMMT(A)81 Project PAJ2 Dynamic Performance of Adhesively Bonded Joints Report No. 3 August 1997 Proposed Draft for the Revision of ISO 11003-2 Adhesives - Determination of Shear Behaviour of
A METHOD OF ADAPTATION BETWEEN STEEPEST- DESCENT AND NEWTON S ALGORITHM FOR MULTI- CHANNEL ACTIVE CONTROL OF TONAL NOISE AND VIBRATION
 A METHOD OF ADAPTATION BETWEEN STEEPEST- DESCENT AND NEWTON S ALGORITHM FOR MULTI- CHANNEL ACTIVE CONTROL OF TONAL NOISE AND VIBRATION Jordan Cheer and Stephen Daley Institute of Sound and Vibration Research,
A METHOD OF ADAPTATION BETWEEN STEEPEST- DESCENT AND NEWTON S ALGORITHM FOR MULTI- CHANNEL ACTIVE CONTROL OF TONAL NOISE AND VIBRATION Jordan Cheer and Stephen Daley Institute of Sound and Vibration Research,
Laplacian Filters. Sobel Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters
 Sobel Filters Note that smoothing the image before applying a Sobel filter typically gives better results. Even thresholding the Sobel filtered image cannot usually create precise, i.e., -pixel wide, edges.
Sobel Filters Note that smoothing the image before applying a Sobel filter typically gives better results. Even thresholding the Sobel filtered image cannot usually create precise, i.e., -pixel wide, edges.
Exercises. Chapter 1. of τ approx that produces the most accurate estimate for this firing pattern.
 1 Exercises Chapter 1 1. Generate spike sequences with a constant firing rate r 0 using a Poisson spike generator. Then, add a refractory period to the model by allowing the firing rate r(t) to depend
1 Exercises Chapter 1 1. Generate spike sequences with a constant firing rate r 0 using a Poisson spike generator. Then, add a refractory period to the model by allowing the firing rate r(t) to depend
Method (0.04 to 4.50 mg/l Cl 2 ) Powder Pillows
 Chlorine Free, Indophenol, 10241 Indophenol 1 1 Patent pending. DOC316.53.01256 Method 10241 (0.04 to 4.50 mg/l Cl 2 ) Powder Pillows Scope and Application: For determining residual free chlorine levels
Chlorine Free, Indophenol, 10241 Indophenol 1 1 Patent pending. DOC316.53.01256 Method 10241 (0.04 to 4.50 mg/l Cl 2 ) Powder Pillows Scope and Application: For determining residual free chlorine levels
University, Tempe, Arizona, USA b Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of New. Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA
 This article was downloaded by: [University of New Mexico] On: 27 September 2012, At: 22:13 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered
This article was downloaded by: [University of New Mexico] On: 27 September 2012, At: 22:13 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered
Nonlinear acoustic imaging via reduced order model backprojection
 Nonlinear acoustic imaging via reduced order model backprojection Alexander V. Mamonov 1, Vladimir Druskin 2, Andrew Thaler 3 and Mikhail Zaslavsky 2 1 University of Houston, 2 Schlumberger-Doll Research
Nonlinear acoustic imaging via reduced order model backprojection Alexander V. Mamonov 1, Vladimir Druskin 2, Andrew Thaler 3 and Mikhail Zaslavsky 2 1 University of Houston, 2 Schlumberger-Doll Research
Department of Physics PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2016 Part I. Short Questions
 Department of Physics PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2016 Part I. Short Questions Thursday May 19th, 2016, 14-17h Examiners: Prof. J. Cline, Prof. H. Guo, Prof. G. Gervais (Chair), and Prof. D. Hanna INSTRUCTIONS
Department of Physics PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2016 Part I. Short Questions Thursday May 19th, 2016, 14-17h Examiners: Prof. J. Cline, Prof. H. Guo, Prof. G. Gervais (Chair), and Prof. D. Hanna INSTRUCTIONS
Geophysical Survey Report
 Report Lost Mansion of Nydfwch, Penllergare, Swansea for January 2008 J2449 John Cook BSc. (Hons) Document Title: Client: Stratascan Job No: Techniques: Report Lost Mansion of Nydfwch, Penllergare, Swansea
Report Lost Mansion of Nydfwch, Penllergare, Swansea for January 2008 J2449 John Cook BSc. (Hons) Document Title: Client: Stratascan Job No: Techniques: Report Lost Mansion of Nydfwch, Penllergare, Swansea
MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL OF WATER QUALITY IN DRINKING WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS CONSIDERING DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS
 MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL OF WATER QUALITY IN DRINKING WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS CONSIDERING DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS by MINGYU XIE A thesis submitted to The University of Birmingham for the degree of
MODEL PREDICTIVE CONTROL OF WATER QUALITY IN DRINKING WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS CONSIDERING DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS by MINGYU XIE A thesis submitted to The University of Birmingham for the degree of
CONTRIBUTION TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF THE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOUR OF FLOATING HARBOUR SYSTEMS USING FREQUENCY DOMAIN DECOMPOSITION
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF THE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOUR OF FLOATING HARBOUR SYSTEMS USING FREQUENCY DOMAIN DECOMPOSITION S. Uhlenbrock, University of Rostock, Germany G. Schlottmann, University of
CONTRIBUTION TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF THE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOUR OF FLOATING HARBOUR SYSTEMS USING FREQUENCY DOMAIN DECOMPOSITION S. Uhlenbrock, University of Rostock, Germany G. Schlottmann, University of
Quantitative application of pulse phase thermography to determine material parameters
 Quantitative application of pulse phase thermography to determine material parameters by B. Stotter, K.H. Gresslehner, G. Mayr, G. Hendorfer and J. Sekelja University of Applied Sciences Upper Austria,
Quantitative application of pulse phase thermography to determine material parameters by B. Stotter, K.H. Gresslehner, G. Mayr, G. Hendorfer and J. Sekelja University of Applied Sciences Upper Austria,
EXPERIMENT 5. The Franck-Hertz Experiment (Critical Potentials) Introduction
 EXPERIMENT 5 The Franck-Hertz Experiment (Critical Potentials) Introduction In the early part of the twentieth century the structure of the atom was studied in depth. In the process of developing and refining
EXPERIMENT 5 The Franck-Hertz Experiment (Critical Potentials) Introduction In the early part of the twentieth century the structure of the atom was studied in depth. In the process of developing and refining
Review: Continuous Fourier Transform
 Review: Continuous Fourier Transform Review: convolution x t h t = x τ h(t τ)dτ Convolution in time domain Derivation Convolution Property Interchange the order of integrals Let Convolution Property By
Review: Continuous Fourier Transform Review: convolution x t h t = x τ h(t τ)dτ Convolution in time domain Derivation Convolution Property Interchange the order of integrals Let Convolution Property By
Supplementary Information for cryosparc: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-em structure determination
 Supplementary Information for cryosparc: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-em structure determination Supplementary Note : Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) SGD iteratively optimizes an objective
Supplementary Information for cryosparc: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-em structure determination Supplementary Note : Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) SGD iteratively optimizes an objective
Lesson 04. KAZE, Non-linear diffusion filtering, ORB, MSER. Ing. Marek Hrúz, Ph.D.
 Lesson 04 KAZE, Non-linear diffusion filtering, ORB, MSER Ing. Marek Hrúz, Ph.D. Katedra Kybernetiky Fakulta aplikovaných věd Západočeská univerzita v Plzni Lesson 04 KAZE ORB: an efficient alternative
Lesson 04 KAZE, Non-linear diffusion filtering, ORB, MSER Ing. Marek Hrúz, Ph.D. Katedra Kybernetiky Fakulta aplikovaných věd Západočeská univerzita v Plzni Lesson 04 KAZE ORB: an efficient alternative
7/06 Electric Fields and Energy
 Part ASome standard electric field and potential configurations About this lab: Electric fields are created by electric charges and exert force on charges. Electric potential gives an alternative description.
Part ASome standard electric field and potential configurations About this lab: Electric fields are created by electric charges and exert force on charges. Electric potential gives an alternative description.
