ASYMPTOTIC THEORY FOR WEAKLY NON-LINEAR WAVE EQUATIONS IN SEMI-INFINITE DOMAINS
|
|
|
- Cecil Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 004(004), No. 07, pp. 8. ISSN: URL: or ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) ASYMPTOTIC THEORY FOR WEAKLY NON-LINEAR WAVE EQUATIONS IN SEMI-INFINITE DOMAINS CHIRAKKAL V. EASWARAN Abstract. We prove the existence and uniqueness of solutions of a class of weakly non-linear wave equations in a semi-infinite region 0 x, t < L/ ɛ under arbitrary initial and boundary conditions. We also establish the asymptotic validity of formal perturbation approximations of the solutions in this region.. Introduction Many physical phenomena involve the action of weak non-linear perturbations acting over long periods of space and time. Some of these phenomena can be mathematically modeled by partial differential equations containing small non-linear terms. These non-linear effects, characterized by a small parameter ɛ, could accumulate over time and space to significantly impact the space and time evolution of the systems. Some examples of physical models involving such weakly non-linear equations are: (i) The wave equation with a cubic non-linearity governing the slow oscillations of overhead power lines [7]. (ii) The non-linear Schroedinger equation with slowly varying coefficients with applications in water waves and non-linear optics [, ]. (iii) The shallow water wave equations with small initial displacement, and the weakly non-linear acoustics equations [5, 8]. (iv) The equations describing the motion of a slightly viscoelastic column with viscous damping [6]. The traditional tool to study the effect of small non-linearities is perturbation expansion in terms of the small parameter ɛ. Straight forward perturbation expansion of solutions usually become unbounded at large times (or lengths) because of unbounded growth in the wave amplitude. Averaging, matched asymptotic expansions and multiple-scale techniques are the standard techniques used to develop approximations of solutions of these non-linear perturbation problems that remain bounded at large times and distances. A review of these tools can be found in [5], and a number of examples and related approaches can be found in [8]. 000 Mathematics Subject Classification. 35C0, 35L0. Key words and phrases. Multiple scale, perturbation, non-linear, waves, asymptotic. c 004 Texas State University - San Marcos. Submitted November 9, 003. Published January, 004.
2 CHIRAKKAL V. EASWARAN EJDE-004/07 Generally, multiple scale expansions of solutions of wave equations anticipate in advance the dependence of solutions on different time scales in order to construct solutions which are explicit functions of time. Prior to 99, most studies of weakly nonlinear wave equations dealt with initial value problems on the infinite line < x < or initial-boundary value problems on a finite space interval x with fixed end conditions. The latter problem could be transformed into an initialvalue problem on the infinite space interval. For such problems, a fast time scale t and a slow time scale T = ɛt are introduced to develop asymptotic solutions. In [], the existence, uniqueness and continuous dependence of solutions on initial data as well as the asymptotic validity of formal expansions of solutions were proved for these types of problems. This was accomplished using Green s functions and transformation of the initial-boundary value problem to an initial value problem on the infinite interval < x <, using an odd π-periodic extension. For signaling problems in which the initial conditions are zero and boundary data at x = 0 propagate in the region x > 0, a perturbation scheme based on a slow spatial scale X = ɛx can be used [4]. In [], a multi-scale method was developed for weakly nonlinear wave equations in the region x > 0 with arbitrary initial and boundary data. These problems can not be transformed into initial value problems on the infinite interval < x <, since such a transformation leads to coupled, second-order, non-linear, non-homogeneous partial differential equations that are difficult to solve. In [], we introduced a long time scale T = ɛt and a long space scale X = ɛx, in addition to the fast variables x and t, to develop asymptotic solutions. The necessity of both scaled time and space variables is an essential characteristic of such problems. The main purpose of this paper is to establish the existence, uniqueness and continuous dependence of classical solutions on initial data for a class of initialboundary value problems for the weakly non-linear wave equations in a rectangular region 0 x, t < L/ ɛ, where ɛ is a small parameter and L is an arbitrary positive number. In addition, we establish the asymptotic validity of formal expansions of solutions for such problems. We use an integral representation of the solution to accomplish this.. Existence, uniqueness and continuous dependence of solutions on initial data In this section we prove the existence and uniqueness in the classical sense of the solution to the hyperbolic system u tt u xx + ɛh(u, u t, u x ) = 0, t, x > 0, 0 < ɛ u(x, 0) = a(x); u t (x, 0) = b(x); u(0, t) = ρ(t), t, x > 0 (.) Let us assume that the initial and boundary data as well as the non-linear function h satisfy the following conditions: (A) a(x), ρ(t) are twice continuously differentiable for x 0, t 0. b(x)is continuously differentiable for x 0, the function h and its derivatives are analytic and uniformly bounded in its arguments. a(0) = ρ(0), b(0) = ρ (0), ρ(0) = 0, a (0) = 0, ρ (0) = 0, a (0) + ɛh(a(0), b(0), a (0)) = 0 Theorem.. Suppose h, a(x), b(x), ρ(t) satisfy the conditions (A). Then for any ɛ with 0 < ɛ ɛ 0, the non-linear initial-boundary value problem (.) has
3 EJDE-004/07 ASYMPTOTIC THEORY 3 a unique, twice continuously differentiable solution in a region of the x t plane, 0 x, t L/ ɛ, where L is a sufficiently small positive constant independent of ɛ. Moreover, this solution depends continuously on the initial-boundary data. The conditions on the initial values of various functions in (A) ensure that the solution u and its first and second partial derivatives are continuous across x = t. The proof of this theorem depends crucially on the integral representation of the solution to the hyperbolic system (.)- (see [0]): [a(x + t) + a(x t)] + x+t b(λ) dλ x t + ɛ t 0 u(x, t) = dτ x+(t τ) x (t τ) h(u, u τ (λ, τ), u λ (λ, τ))dλ, if 0 t x, ρ(t x) + [a(t + x) + a(t x)] + t+x t x b(λ)dλ (.) + ɛ t 0 dτ x+(t τ) x (t τ) h(u, u τ (λ, τ), u λ (λ, τ))dλ, if t x 0, By direct differentiation, one can show the equivalence of the system (.) to (.) whenever C solutions of (.) exist. τ t x-(t-τ) x+(t-τ) x-t x x+t λ Figure. Region of integration for the first case in (.). This region has area t Using the above representation of solutions, and the assumptions on the regularity of initial and boundary conditions, one can show that a twice continuously differentiable solution u(x, t; ɛ) of the hyperbolic system exists in a rectangle 0 t, x O(/ ɛ). This solution depends continuously on the initial-boundary data, and formal perturbation series expansions asymptotically converge to the solution in this rectangle. Let T : S S denote the integral operator defined by (.), where S = {(x, t) 0 x, t L ɛ } We represent the integral equations (.) in the form u = T u. The proof consists of showing that T is a contraction on a space of twice continuously differentiable functions defined on S, and therefore by Banach s Fixed Point Theorem, a unique solution u exists. Let CM (S) be the space of twice continuously differentiable functions on S with norm f = max (x,t) S i,j=0 i+j i+j f(x, t) x i t j M
4 4 CHIRAKKAL V. EASWARAN EJDE-004/07 t τ t-x λ= x-(t-τ) λ=x+t-τ x t-x t+x λ Figure. Region of integration for the second case in (.). This region has area tx x Let us write T u = u I + T ɛ u (.3) where { u I (x, t) = [a(x + t) + a(x t)] + x+t x t b(λ)dλ, if 0 t x ρ(t x) + [a(t + x) + a(t x)] + t+x (.4) b(λ)dλ, if t x 0 t x and T ɛ u = ɛ t 0 dτ x+(t τ) x (t τ) h(u, u τ (λ, τ), u λ (λ, τ))dλ, if 0 t x t 0 dτ x+(t τ) x (t τ) h(u, u τ (λ, τ), u λ (λ, τ))dλ, if t x 0 = ɛ From (.3) we get (.5) T u u I + T ɛ u (.6) Because of the boundedness conditions on ρ, a and b, there exists a nonnegative constant M, independent of ɛ, such that u I M (.7) From Figures and 3, it follows that there exist constants M and M such that { M ɛt, if t x T ɛ u M ɛ(tx x ), if t x Thus for t and x in the region S, one can find an ɛ-independent constant M such that T ɛ u M L Combining this inequality with (.7) and (.6), T u M + M L M for sufficiently small L. This shows that T : C M (S) C M (S).
5 EJDE-004/07 ASYMPTOTIC THEORY 5 We next show that T is a contraction on C M (S). Using the Lipschitz property of h, there exists a constant M : h(u, u t, u x ) h(v, v t, v x ) M u v for all (x, t) S. It follows from (.5) that one can find constants K and K satisfying { T ɛ u T ɛ v ɛt K u v, if t x ɛ(tx x )K u v, if t x Thus there is a nonnegative constant K such that T u T v = T ɛ u T ɛ v KL u v for all (x, t) S. Then for sufficiently small L, independent of ɛ, T u T v k u v (.8) for all u, v CM (S) and 0 k <. This shows that T is a contraction of CM (S) into itself for sufficiently small L. By applying Banach fixed point theorem, it follows that T has a unique fixed point in CM (S). Since solutions of the integral equation (.) are also solutions of the hyperbolic system (.), we have proved that (.) has a unique solution in the space S. We next prove that the solutions of the hyperbolic system (.) depends continuously on the initial-boundary values, in the sense that small changes in these values result in small changes in the solution within the region S in which existenceuniqueness of solutions have been proved. Let ũ be the solution of the hyperbolic system (.) corresponding to the initial boundary conditions u(x, 0) = ã(x); u t (x, 0) = b(x); u(0, t) = ρ(t), t, x > 0 (.9) Assume that the initial-boundary data in (4) satisfy conditions similar to (A). Following (.3), we let T ũ = ũ I + T ɛ ũ. Then the following estimate can be made: u ũ u I ũ I + T ɛ u T ɛ ũ From an argument similar to (.8), there exists a k, 0 k <, such that so that and T ɛ u T ɛ ũ k u ũ u ũ u I ũ I + k u ũ u ũ k u I ũ I whenever u, ũ are in C M (S). This proves that small changes in initial data lead to small changes in the solutions.
6 6 CHIRAKKAL V. EASWARAN EJDE-004/07 3. Asymptotic validity of formal expansions Next we prove that perturbation series expansions of solutions of (.) are asymptotically convergent to the exact solutions. Let v(x, t) be defined on S satisfying v tt v xx + ɛh(v, v t, v x ) = ɛ n r (x, t) v(x, 0) = a(x) + ɛ n r (x) v t (x, 0) = b(x) + ɛ n r 3 (x) v(0, t) = ρ(t) + ɛ n r 4 (t) (3.) The motivation to study this system is that they satisfy the original partial differential equation and initial/boundary conditions to O(ɛ n ) and O(ɛ n ) respectively, where usually n =. (A) Assume that h, r, r, r 3, r 4 satisfy boundary conditions as in (A), and that r 3, r 4 are in C Theorem 3.. Let v satisfy (3.) and the r i( i 4) satisfy (A). Then for n >, u v = O(ɛ n ) for all t, x S. Thus in the limit of small ɛ, the formal approximation v converges to the solution u. Proof. Note that a formal integral representation of (3.) can be written in the form where T ɛ r = ɛ n ɛ n v = ṽ I + T ɛ v + T ɛ r (3.) t 0 dτ x+(t τ) x (t τ) r (λ, τ)dλ, if 0 t x t 0 dτ x+(t τ) x (t τ) r (λ, τ)dλ, if t x 0 and v I is analogous to (.4). From the geometry of Figures and, it follows that there exists constants M3 and M3 such that { T M3 ɛ n t, if t x ɛ r M3 ɛ n (tx x ), if t x. Thus for t and x in the region S, one can find a constant M 3 such that T ɛ r ɛ n M 3 L. In addition, there exists a non-negative constant M 4 such that, From (.3) and (3.) it follows that u I ṽ I ɛ n M 4. u v T ɛ u T ɛ v + u I ṽ I + T ɛ r k u v + ɛ n (M 3 L + M 4 ) so that u v ɛn k (M 3L + M 4 ) showing that u v = O(ɛ n ) for x, t S. This establishes Theorem 3..
7 EJDE-004/07 ASYMPTOTIC THEORY 7 4. Applications of the asymptotic theory The results obtained above give formal theoretical support to a multiple-scale solution technique for weakly non-linear wave equations developed in []. It is shown there that the solution of (.) involves two scaled (or slow) variables, X = ɛx and T = ɛt, in addition to the regular (or fast) variables x and t. The perturbation solution then defines two regions, t > x and t x. For t x, the first order solution has the form u 0 (x, t, T ) = f(σ, T ) + g(ξ, T ) where σ = x t and ξ = x + t are the forward and backward going characteristics of the wave equation. It is shown in [] that f and g are governed by: f σt lim M M g ξt + lim M M M 0 M 0 h(f + g, g ξ f σ, g ξ + f σ ) dξ = 0, h(f + g, g ξ f σ, g ξ + f σ ) dσ = 0 with appropriate initial-boundary conditions. For the region t > x, the first order solution takes the form u 0 (x, t, X, T ) = p(µ, X, T ) + q(ξ, X, T ) where µ = t x and ξ = t+x. In general the PDEs governing p and q are complicated coupled nonlinear equations; but for special cases, they are considerably simplified. For example, when h involves only the first derivatives of u, h = h(u t, u x ), it can be shown that p µt + p µx + lim M q ξt q ξx + lim M M M M 0 M 0 h(p µ + q ξ, q ξ p µ )dξ = 0, h(p µ + q ξ, q ξ p µ )dµ = 0. The important point here is that the two equations governing the interaction of backward and forward propagating waves form a pair of coupled, nonlinear firstorder PDEs whose theory is well-developed. This is a considerable simplification from the original second order nonlinear equation. We refer to [] for details of solutions of these equations as well as explicit solutions for the cases h = u t + u(u t u x ) and h = u t. Concluding remarks. For weakly non-linear hyperbolic partial differential equations in the region t > 0, x > 0, we established the existence, uniqueness and continuous dependence of solutions on initial data within a rectangle 0 x, t < L/ ɛ. Although it appears from numerical evidence that the existence-uniqueness theorems could hold in much longer space and time intervals, it is not clear how to establish that. We also proved the asymptotic validity of formal perturbation expansions of solutions within this rectangle. References [] Ablowitz, M. J. and Segur, H. On the evolution of packets of water waves J. Fluid. Mech. 9, pp , 979. [] S. C. Chikwendu and C. V. Easwaran Multiple-scale solution of initial-boundary value problems for weakly nonlinear wave equations on the semi-infinite line. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 5, pp (99).
8 8 CHIRAKKAL V. EASWARAN EJDE-004/07 [3] C. V. Easwaran. A Scaled Characteristics method for the asymptotic solution of weakly nonlinear wave equations Electronic J. Diff. Equations 998, pp. -0 (998) [4] C. V. Easwaran and S. C. Chikwendu A Laplace-Transform Multiple Scale procedure for the asymptotic solution of weakly non-linear partial differential equations. Int. J. Non-linear Mechanics, 34, pp. 7-, 998. [5] J. Kevorkian and J. D. Cole. Multiple Scale and Singular Perturbation Methods. Springer Verlag, New York, 996. [6] R. W. Lardner, Second order solution of a non linear wave equation. Quart. Appl. Math. 39 pp. 5 38, 98. [7] C. J. Myerscough. A simple model for the growth of wind-induced oscillations in overhead lines. J. Sound and Vibration 39, pp (975). [8] A. H. Nayfeh, A comparison of perturbation methods for nonlinear hyperbolic waves. In Singular Perturbations and Asymptotics, R.E. Mayer and S.U.Parter, Eds, Academic Press, NY 980, pp [9] J. A. Sanders and Verhulst, Averaging methods in nonlinear dynamical systems Springer Verlag, New york, 985 [0] A. N. Tychonov and A. A. Samarski. Partial Differential Equations of Mathematical Physics. Holden-Day, San Francisco, 964. [] W. T. van Horssen, An asymptotic theory for a class of initial-boundary value problems for weakly nonlinear wave equations. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 48, pp (988). [] G. B. Whitham. Linear and Non-Linear Waves. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 974. Department of Computer Science, State University of New York, New Paltz, NY 56, USA address: easwaran@newpaltz.edu
ANALYSIS OF A NONLINEAR SURFACE WIND WAVES MODEL VIA LIE GROUP METHOD
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 206 (206), No. 228, pp. 8. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ANALYSIS OF A NONLINEAR SURFACE WIND WAVES MODEL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 206 (206), No. 228, pp. 8. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ANALYSIS OF A NONLINEAR SURFACE WIND WAVES MODEL
EXISTENCE AND APPROXIMATION OF SOLUTIONS OF SECOND ORDER NONLINEAR NEUMANN PROBLEMS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No. 03, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) EXISTENCE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No. 03, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) EXISTENCE
BLOW-UP OF SOLUTIONS FOR A NONLINEAR WAVE EQUATION WITH NONNEGATIVE INITIAL ENERGY
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 213 (213, No. 115, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu BLOW-UP OF SOLUTIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 213 (213, No. 115, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu BLOW-UP OF SOLUTIONS
SIMULTANEOUS AND NON-SIMULTANEOUS BLOW-UP AND UNIFORM BLOW-UP PROFILES FOR REACTION-DIFFUSION SYSTEM
 Electronic Journal of Differential Euations, Vol. 22 (22), No. 26, pp. 9. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SIMULTANEOUS AND NON-SIMULTANEOUS
Electronic Journal of Differential Euations, Vol. 22 (22), No. 26, pp. 9. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SIMULTANEOUS AND NON-SIMULTANEOUS
FUNCTIONAL COMPRESSION-EXPANSION FIXED POINT THEOREM
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 28(28), No. 22, pp. 1 12. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) FUNCTIONAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 28(28), No. 22, pp. 1 12. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) FUNCTIONAL
NON-EXTINCTION OF SOLUTIONS TO A FAST DIFFUSION SYSTEM WITH NONLOCAL SOURCES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016, No. 45, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu NON-EXTINCTION OF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016, No. 45, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu NON-EXTINCTION OF
ENERGY DECAY ESTIMATES FOR LIENARD S EQUATION WITH QUADRATIC VISCOUS FEEDBACK
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 00(00, No. 70, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp ENERGY DECAY ESTIMATES
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 00(00, No. 70, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp ENERGY DECAY ESTIMATES
UNIFORM DECAY OF SOLUTIONS FOR COUPLED VISCOELASTIC WAVE EQUATIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 16 16, No. 7, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu UNIFORM DECAY OF SOLUTIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 16 16, No. 7, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu UNIFORM DECAY OF SOLUTIONS
CONVERGENCE BEHAVIOUR OF SOLUTIONS TO DELAY CELLULAR NEURAL NETWORKS WITH NON-PERIODIC COEFFICIENTS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2007(2007), No. 46, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) CONVERGENCE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2007(2007), No. 46, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) CONVERGENCE
MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS FOR THE p-laplace EQUATION WITH NONLINEAR BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2006(2006), No. 37, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) MULTIPLE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2006(2006), No. 37, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) MULTIPLE
EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR A RESONANT PROBLEM UNDER LANDESMAN-LAZER CONDITIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2008(2008), No. 98, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) EXISTENCE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2008(2008), No. 98, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) EXISTENCE
Asymptotic Behavior of Waves in a Nonuniform Medium
 Available at http://pvamuedu/aam Appl Appl Math ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol 12, Issue 1 June 217, pp 217 229 Applications Applied Mathematics: An International Journal AAM Asymptotic Behavior of Waves in a Nonuniform
Available at http://pvamuedu/aam Appl Appl Math ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol 12, Issue 1 June 217, pp 217 229 Applications Applied Mathematics: An International Journal AAM Asymptotic Behavior of Waves in a Nonuniform
EXISTENCE OF NONTRIVIAL SOLUTIONS FOR A QUASILINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS WITH SIGN-CHANGING POTENTIAL
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2014 (2014), No. 05, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTENCE OF NONTRIVIAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2014 (2014), No. 05, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTENCE OF NONTRIVIAL
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
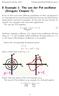 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Dissipative quasi-geostrophic equations with L p data
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. (), No. 56, pp. 3. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Dissipative quasi-geostrophic
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. (), No. 56, pp. 3. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Dissipative quasi-geostrophic
L 1 stability of conservation laws for a traffic flow model
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 14, pp. 1 18. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu ftp ejde.math.unt.edu (login:
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 14, pp. 1 18. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu ftp ejde.math.unt.edu (login:
SELF-ADJOINTNESS OF SCHRÖDINGER-TYPE OPERATORS WITH SINGULAR POTENTIALS ON MANIFOLDS OF BOUNDED GEOMETRY
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2003(2003), No.??, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) SELF-ADJOINTNESS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2003(2003), No.??, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) SELF-ADJOINTNESS
WEAK ASYMPTOTIC SOLUTION FOR A NON-STRICTLY HYPERBOLIC SYSTEM OF CONSERVATION LAWS-II
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 94, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu WEAK ASYMPTOTIC
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 94, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu WEAK ASYMPTOTIC
SOLUTION OF AN INITIAL-VALUE PROBLEM FOR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS VIA MONOTONE OPERATOR METHODS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 214 (214), No. 225, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SOLUTION OF AN INITIAL-VALUE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 214 (214), No. 225, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SOLUTION OF AN INITIAL-VALUE
A non-local problem with integral conditions for hyperbolic equations
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1999(1999), No. 45, pp. 1 6. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu ftp ejde.math.unt.edu (login:
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1999(1999), No. 45, pp. 1 6. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu ftp ejde.math.unt.edu (login:
SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS WITH DEPENDENCE ON THE GRADIENT
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2012 (2012), No. 139, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2012 (2012), No. 139, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC
OBSERVABILITY INEQUALITY AND DECAY RATE FOR WAVE EQUATIONS WITH NONLINEAR BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 27 (27, No. 6, pp. 2. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu OBSERVABILITY INEQUALITY AND DECAY RATE FOR WAVE EQUATIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 27 (27, No. 6, pp. 2. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu OBSERVABILITY INEQUALITY AND DECAY RATE FOR WAVE EQUATIONS
GLOBAL ATTRACTIVITY IN A NONLINEAR DIFFERENCE EQUATION
 Sixth Mississippi State Conference on ifferential Equations and Computational Simulations, Electronic Journal of ifferential Equations, Conference 15 (2007), pp. 229 238. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.mathmississippi
Sixth Mississippi State Conference on ifferential Equations and Computational Simulations, Electronic Journal of ifferential Equations, Conference 15 (2007), pp. 229 238. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.mathmississippi
A PROPERTY OF SOBOLEV SPACES ON COMPLETE RIEMANNIAN MANIFOLDS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No.??, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) A PROPERTY
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No.??, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) A PROPERTY
MULTIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF PROBLEMS WITH SIGN-CHANGING POTENTIAL
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 015 015), No. 0, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MULTIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 015 015), No. 0, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MULTIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS
A COMPUTATIONAL TECHNIQUE FOR SOLVING BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM WITH TWO SMALL PARAMETERS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2013 (2013), No. 30, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu A COMPUTATIONAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2013 (2013), No. 30, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu A COMPUTATIONAL
NONSTANDARD NUMERICAL METHODS FOR A CLASS OF PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH PREDATOR INTERFERENCE
 Sixth Mississippi State Conference on Differential Equations and Computational Simulations, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 15 (2007), pp. 67 75. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu
Sixth Mississippi State Conference on Differential Equations and Computational Simulations, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 15 (2007), pp. 67 75. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu
POTENTIAL LANDESMAN-LAZER TYPE CONDITIONS AND. 1. Introduction We investigate the existence of solutions for the nonlinear boundary-value problem
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 25(25), No. 94, pp. 1 12. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) POTENTIAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 25(25), No. 94, pp. 1 12. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) POTENTIAL
ON THE OSCILLATION OF THE SOLUTIONS TO LINEAR DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS WITH VARIABLE DELAY
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 008(008, No. 50, pp. 1 15. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp ON THE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 008(008, No. 50, pp. 1 15. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp ON THE
BOUNDEDNESS AND EXPONENTIAL STABILITY OF SOLUTIONS TO DYNAMIC EQUATIONS ON TIME SCALES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20062006, No. 12, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu login: ftp BOUNDEDNESS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20062006, No. 12, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu login: ftp BOUNDEDNESS
GORDON TYPE THEOREM FOR MEASURE PERTURBATION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 211 211, No. 111, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GODON TYPE THEOEM FO
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 211 211, No. 111, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GODON TYPE THEOEM FO
Partial differential equation for temperature u(x, t) in a heat conducting insulated rod along the x-axis is given by the Heat equation:
 Chapter 7 Heat Equation Partial differential equation for temperature u(x, t) in a heat conducting insulated rod along the x-axis is given by the Heat equation: u t = ku x x, x, t > (7.1) Here k is a constant
Chapter 7 Heat Equation Partial differential equation for temperature u(x, t) in a heat conducting insulated rod along the x-axis is given by the Heat equation: u t = ku x x, x, t > (7.1) Here k is a constant
Initial Boundary Value Problems for Scalar and Vector Burgers Equations
 Initial Boundary Value Problems for Scalar and Vector Burgers Equations By K. T. Joseph and P. L. Sachdev In this article we stu Burgers equation and vector Burgers equation with initial and boundary conditions.
Initial Boundary Value Problems for Scalar and Vector Burgers Equations By K. T. Joseph and P. L. Sachdev In this article we stu Burgers equation and vector Burgers equation with initial and boundary conditions.
THE WAVE EQUATION. F = T (x, t) j + T (x + x, t) j = T (sin(θ(x, t)) + sin(θ(x + x, t)))
 THE WAVE EQUATION The aim is to derive a mathematical model that describes small vibrations of a tightly stretched flexible string for the one-dimensional case, or of a tightly stretched membrane for the
THE WAVE EQUATION The aim is to derive a mathematical model that describes small vibrations of a tightly stretched flexible string for the one-dimensional case, or of a tightly stretched membrane for the
On Vibrations Of An Axially Moving Beam Under Material Damping
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-684,p-ISSN: 232-334X, Volume 3, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 26), PP 56-6 www.iosrjournals.org On Vibrations Of An Axially Moving
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-684,p-ISSN: 232-334X, Volume 3, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 26), PP 56-6 www.iosrjournals.org On Vibrations Of An Axially Moving
Mathématiques appliquées (MATH0504-1) B. Dewals, Ch. Geuzaine
 Lecture 2 The wave equation Mathématiques appliquées (MATH0504-1) B. Dewals, Ch. Geuzaine V1.0 28/09/2018 1 Learning objectives of this lecture Understand the fundamental properties of the wave equation
Lecture 2 The wave equation Mathématiques appliquées (MATH0504-1) B. Dewals, Ch. Geuzaine V1.0 28/09/2018 1 Learning objectives of this lecture Understand the fundamental properties of the wave equation
A COUNTEREXAMPLE TO AN ENDPOINT BILINEAR STRICHARTZ INEQUALITY TERENCE TAO. t L x (R R2 ) f L 2 x (R2 )
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2006(2006), No. 5, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) A COUNTEREXAMPLE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2006(2006), No. 5, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) A COUNTEREXAMPLE
UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS TO MATRIX EQUATIONS ON TIME SCALES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2013 (2013), No. 50, pp. 1 13. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu UNIQUENESS OF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2013 (2013), No. 50, pp. 1 13. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu UNIQUENESS OF
JUNXIA MENG. 2. Preliminaries. 1/k. x = max x(t), t [0,T ] x (t), x k = x(t) dt) k
![JUNXIA MENG. 2. Preliminaries. 1/k. x = max x(t), t [0,T ] x (t), x k = x(t) dt) k JUNXIA MENG. 2. Preliminaries. 1/k. x = max x(t), t [0,T ] x (t), x k = x(t) dt) k](/thumbs/75/72088237.jpg) Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 29(29), No. 39, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu POSIIVE PERIODIC SOLUIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 29(29), No. 39, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu POSIIVE PERIODIC SOLUIONS
THE EDDY CURRENT PROBLEM WITH TEMPERATURE DEPENDENT PERMEABILITY
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 003003, No. 91, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp THE EDDY CURRENT PROBLEM
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 003003, No. 91, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp THE EDDY CURRENT PROBLEM
Lecture 4: Numerical solution of ordinary differential equations
 Lecture 4: Numerical solution of ordinary differential equations Department of Mathematics, ETH Zürich General explicit one-step method: Consistency; Stability; Convergence. High-order methods: Taylor
Lecture 4: Numerical solution of ordinary differential equations Department of Mathematics, ETH Zürich General explicit one-step method: Consistency; Stability; Convergence. High-order methods: Taylor
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations
 Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations arise in a number of physical problems, such as fluid flow, heat transfer, solid mechanics and biological processes. These
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations arise in a number of physical problems, such as fluid flow, heat transfer, solid mechanics and biological processes. These
Higher Order Averaging : periodic solutions, linear systems and an application
 Higher Order Averaging : periodic solutions, linear systems and an application Hartono and A.H.P. van der Burgh Faculty of Information Technology and Systems, Department of Applied Mathematical Analysis,
Higher Order Averaging : periodic solutions, linear systems and an application Hartono and A.H.P. van der Burgh Faculty of Information Technology and Systems, Department of Applied Mathematical Analysis,
TRIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR A CLASS OF TWO-POINT BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 24(24), No. 6, pp. 8. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) TRIPLE POSITIVE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 24(24), No. 6, pp. 8. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) TRIPLE POSITIVE
Some asymptotic properties of solutions for Burgers equation in L p (R)
 ARMA manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Some asymptotic properties of solutions for Burgers equation in L p (R) PAULO R. ZINGANO Abstract We discuss time asymptotic properties of solutions
ARMA manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Some asymptotic properties of solutions for Burgers equation in L p (R) PAULO R. ZINGANO Abstract We discuss time asymptotic properties of solutions
GENERIC SOLVABILITY FOR THE 3-D NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS WITH NONREGULAR FORCE
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2(2), No. 78, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. UR: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) GENERIC SOVABIITY
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2(2), No. 78, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. UR: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) GENERIC SOVABIITY
EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE EQUATIONS WITH UNBOUNDED POTENTIAL. 1. Introduction In this article, we consider the Kirchhoff type problem
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 207 (207), No. 84, pp. 2. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE EQUATIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 207 (207), No. 84, pp. 2. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE EQUATIONS
DYNAMICS IN 3-SPECIES PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH TIME DELAYS. Wei Feng
 DISCRETE AND CONTINUOUS Website: www.aimsciences.org DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS SUPPLEMENT 7 pp. 36 37 DYNAMICS IN 3-SPECIES PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH TIME DELAYS Wei Feng Mathematics and Statistics Department
DISCRETE AND CONTINUOUS Website: www.aimsciences.org DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS SUPPLEMENT 7 pp. 36 37 DYNAMICS IN 3-SPECIES PREDATOR-PREY MODELS WITH TIME DELAYS Wei Feng Mathematics and Statistics Department
APPLIED PARTIM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems
 APPLIED PARTIM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fourth Edition Richard Haberman Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University PEARSON Prentice Hall PEARSON
APPLIED PARTIM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fourth Edition Richard Haberman Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University PEARSON Prentice Hall PEARSON
HARDY INEQUALITIES WITH BOUNDARY TERMS. x 2 dx u 2 dx. (1.2) u 2 = u 2 dx.
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 003(003), No. 3, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 107-6691. UL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) HADY INEQUALITIES
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 003(003), No. 3, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 107-6691. UL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) HADY INEQUALITIES
Exact Solutions for the Nonlinear (2+1)-Dimensional Davey-Stewartson Equation Using the Generalized ( G. )-Expansion Method
 Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 6, No. ; 04 ISSN 96-9795 E-ISSN 96-9809 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Exact Solutions for the Nonlinear +-Dimensional Davey-Stewartson Equation
Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 6, No. ; 04 ISSN 96-9795 E-ISSN 96-9809 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Exact Solutions for the Nonlinear +-Dimensional Davey-Stewartson Equation
SOLVABILITY OF A QUADRATIC INTEGRAL EQUATION OF FREDHOLM TYPE IN HÖLDER SPACES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 214 (214), No. 31, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SOLVABILITY OF A QUADRATIC
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 214 (214), No. 31, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SOLVABILITY OF A QUADRATIC
Quasireversibility Methods for Non-Well-Posed Problems
 Kennesaw State University DigitalCommons@Kennesaw State University Faculty Publications 11-29-1994 Quasireversibility Methods for Non-Well-Posed Problems Gordon W. Clark Kennesaw State University Seth
Kennesaw State University DigitalCommons@Kennesaw State University Faculty Publications 11-29-1994 Quasireversibility Methods for Non-Well-Posed Problems Gordon W. Clark Kennesaw State University Seth
EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR CROSS CRITICAL EXPONENTIAL N-LAPLACIAN SYSTEMS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2014 (2014), o. 28, pp. 1 10. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTECE OF SOLUTIOS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2014 (2014), o. 28, pp. 1 10. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTECE OF SOLUTIOS
Bilinear spatial control of the velocity term in a Kirchhoff plate equation
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1(1), No. 7, pp. 1 15. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Bilinear spatial control
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1(1), No. 7, pp. 1 15. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Bilinear spatial control
MIXED BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS FOR QUANTUM HYDRODYNAMIC MODELS WITH SEMICONDUCTORS IN THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No. 123, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) MIXED
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No. 123, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) MIXED
Positive solutions and nonlinear multipoint conjugate eigenvalue problems
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 997(997), No. 3, pp.. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp (login: ftp) 47.26.3. or 29.2.3.3 Positive solutions
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 997(997), No. 3, pp.. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp (login: ftp) 47.26.3. or 29.2.3.3 Positive solutions
Exponential decay for the solution of semilinear viscoelastic wave equations with localized damping
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 22(22), No. 44, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Exponential decay
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 22(22), No. 44, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Exponential decay
EXISTENCE OF WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A NONUNIFORMLY ELLIPTIC NONLINEAR SYSTEM IN R N. 1. Introduction We study the nonuniformly elliptic, nonlinear system
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20082008), No. 119, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu login: ftp) EXISTENCE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20082008), No. 119, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu login: ftp) EXISTENCE
Boundary. DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and. Value Problems APPLIED PARTIAL. Fifth Edition. Richard Haberman PEARSON
 APPLIED PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fifth Edition Richard Haberman Southern Methodist University PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
APPLIED PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fifth Edition Richard Haberman Southern Methodist University PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
NONLINEAR DECAY AND SCATTERING OF SOLUTIONS TO A BRETHERTON EQUATION IN SEVERAL SPACE DIMENSIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 5(5), No. 4, pp. 7. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) NONLINEAR DECAY
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 5(5), No. 4, pp. 7. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) NONLINEAR DECAY
2:2:1 Resonance in the Quasiperiodic Mathieu Equation
 Nonlinear Dynamics 31: 367 374, 003. 003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. ::1 Resonance in the Quasiperiodic Mathieu Equation RICHARD RAND Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,
Nonlinear Dynamics 31: 367 374, 003. 003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. ::1 Resonance in the Quasiperiodic Mathieu Equation RICHARD RAND Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,
MEAN VALUE THEOREMS FOR SOME LINEAR INTEGRAL OPERATORS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2929, No. 117, pp. 1 15. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MEAN VALUE THEOREMS FOR
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2929, No. 117, pp. 1 15. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MEAN VALUE THEOREMS FOR
Chapter 13. Eddy Diffusivity
 Chapter 13 Eddy Diffusivity Glenn introduced the mean field approximation of turbulence in two-layer quasigesotrophic turbulence. In that approximation one must solve the zonally averaged equations for
Chapter 13 Eddy Diffusivity Glenn introduced the mean field approximation of turbulence in two-layer quasigesotrophic turbulence. In that approximation one must solve the zonally averaged equations for
A HYPERBOLIC PROBLEM WITH NONLINEAR SECOND-ORDER BOUNDARY DAMPING. G. G. Doronin, N. A. Lar kin, & A. J. Souza
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1998(1998), No. 28, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp 147.26.13.11 or 129.12.3.113 (login: ftp) A
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1998(1998), No. 28, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp 147.26.13.11 or 129.12.3.113 (login: ftp) A
CONSTRUCTION OF GREEN S FUNCTIONS FOR THE BLACK-SCHOLES EQUATION. 1. Introduction The well-known function, in financial mathematics [3, 4, 6],
![CONSTRUCTION OF GREEN S FUNCTIONS FOR THE BLACK-SCHOLES EQUATION. 1. Introduction The well-known function, in financial mathematics [3, 4, 6], CONSTRUCTION OF GREEN S FUNCTIONS FOR THE BLACK-SCHOLES EQUATION. 1. Introduction The well-known function, in financial mathematics [3, 4, 6],](/thumbs/87/97256768.jpg) Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 007007, No. 53, pp. 4. ISSN: 07-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu login: ftp CONSTRUCTION OF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 007007, No. 53, pp. 4. ISSN: 07-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu login: ftp CONSTRUCTION OF
An Application of Perturbation Methods in Evolutionary Ecology
 Dynamics at the Horsetooth Volume 2A, 2010. Focused Issue: Asymptotics and Perturbations An Application of Perturbation Methods in Evolutionary Ecology Department of Mathematics Colorado State University
Dynamics at the Horsetooth Volume 2A, 2010. Focused Issue: Asymptotics and Perturbations An Application of Perturbation Methods in Evolutionary Ecology Department of Mathematics Colorado State University
Application of the perturbation iteration method to boundary layer type problems
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1859-4 RESEARCH Open Access Application of the perturbation iteration method to boundary layer type problems Mehmet Pakdemirli * *Correspondence: mpak@cbu.edu.tr Applied Mathematics
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1859-4 RESEARCH Open Access Application of the perturbation iteration method to boundary layer type problems Mehmet Pakdemirli * *Correspondence: mpak@cbu.edu.tr Applied Mathematics
ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION OF DIFFUSION EQUATIONS INVOLVING A NEW FRACTIONAL DERIVATIVE WITHOUT SINGULAR KERNEL
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 217 (217), No. 289, pp. 1 6. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION OF DIFFUSION EQUATIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 217 (217), No. 289, pp. 1 6. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION OF DIFFUSION EQUATIONS
ULAM-HYERS-RASSIAS STABILITY OF SEMILINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH IMPULSES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 213 (213), No. 172, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ULAM-HYERS-RASSIAS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 213 (213), No. 172, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ULAM-HYERS-RASSIAS
SINC PACK, and Separation of Variables
 SINC PACK, and Separation of Variables Frank Stenger Abstract This talk consists of a proof of part of Stenger s SINC-PACK computer package (an approx. 400-page tutorial + about 250 Matlab programs) that
SINC PACK, and Separation of Variables Frank Stenger Abstract This talk consists of a proof of part of Stenger s SINC-PACK computer package (an approx. 400-page tutorial + about 250 Matlab programs) that
The Riccati equation with variable coefficients expansion algorithm to find more exact solutions of nonlinear differential equations
 MM Research Preprints, 275 284 MMRC, AMSS, Academia Sinica, Beijing No. 22, December 2003 275 The Riccati equation with variable coefficients expansion algorithm to find more exact solutions of nonlinear
MM Research Preprints, 275 284 MMRC, AMSS, Academia Sinica, Beijing No. 22, December 2003 275 The Riccati equation with variable coefficients expansion algorithm to find more exact solutions of nonlinear
Global well-posedness for KdV in Sobolev spaces of negative index
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. (), No. 6, pp. 7. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Global well-posedness for
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. (), No. 6, pp. 7. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) Global well-posedness for
NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian UNDER NONHOMOGENEOUS NEUMANN BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 210, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 210, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian
New explicit solitary wave solutions for (2 + 1)-dimensional Boussinesq equation and (3 + 1)-dimensional KP equation
 Physics Letters A 07 (00) 107 11 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla New explicit solitary wave solutions for ( + 1)-dimensional Boussinesq equation and ( + 1)-dimensional KP equation Yong Chen, Zhenya Yan, Honging
Physics Letters A 07 (00) 107 11 www.elsevier.com/locate/pla New explicit solitary wave solutions for ( + 1)-dimensional Boussinesq equation and ( + 1)-dimensional KP equation Yong Chen, Zhenya Yan, Honging
GREEN S FUNCTIONAL FOR SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION WITH NONLOCAL CONDITIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1 (1), No. 11, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GREEN S FUNCTIONAL FOR
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1 (1), No. 11, pp. 1 1. ISSN: 17-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu GREEN S FUNCTIONAL FOR
Answers to Problem Set Number MIT (Fall 2005).
 Answers to Problem Set Number 5. 18.305 MIT Fall 2005). D. Margetis and R. Rosales MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139). November 23, 2005. Course TA: Nikos Savva, MIT, Dept. of Mathematics, Cambridge,
Answers to Problem Set Number 5. 18.305 MIT Fall 2005). D. Margetis and R. Rosales MIT, Math. Dept., Cambridge, MA 02139). November 23, 2005. Course TA: Nikos Savva, MIT, Dept. of Mathematics, Cambridge,
A LOWER BOUND FOR THE GRADIENT OF -HARMONIC FUNCTIONS Edi Rosset. 1. Introduction. u xi u xj u xi x j
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1996(1996) No. 0, pp. 1 7. ISSN 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu (147.6.103.110) telnet (login: ejde), ftp, and gopher access: ejde.math.swt.edu
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1996(1996) No. 0, pp. 1 7. ISSN 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu (147.6.103.110) telnet (login: ejde), ftp, and gopher access: ejde.math.swt.edu
PERIODIC SOLUTIONS FOR NON-AUTONOMOUS SECOND-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEMS WITH (q, p)-laplacian
 Electronic Journal of Differential Euations, Vol. 24 (24), No. 64, pp. 3. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu PERIODIC SOLUIONS FOR NON-AUONOMOUS
Electronic Journal of Differential Euations, Vol. 24 (24), No. 64, pp. 3. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu PERIODIC SOLUIONS FOR NON-AUONOMOUS
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER NONLINEAR HYPERBOLIC SYSTEM
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 211 (211), No. 78, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 211 (211), No. 78, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS
NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL INEQUALITY. 1. Introduction. In this paper the following nonlinear differential inequality
 M athematical Inequalities & Applications [2407] First Galley Proofs NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL INEQUALITY N. S. HOANG AND A. G. RAMM Abstract. A nonlinear differential inequality is formulated in the paper.
M athematical Inequalities & Applications [2407] First Galley Proofs NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL INEQUALITY N. S. HOANG AND A. G. RAMM Abstract. A nonlinear differential inequality is formulated in the paper.
Waves in a Shock Tube
 Waves in a Shock Tube Ivan Christov c February 5, 005 Abstract. This paper discusses linear-wave solutions and simple-wave solutions to the Navier Stokes equations for an inviscid and compressible fluid
Waves in a Shock Tube Ivan Christov c February 5, 005 Abstract. This paper discusses linear-wave solutions and simple-wave solutions to the Navier Stokes equations for an inviscid and compressible fluid
On Asymptotic Variational Wave Equations
 On Asymptotic Variational Wave Equations Alberto Bressan 1, Ping Zhang 2, and Yuxi Zheng 1 1 Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, PA 1682. E-mail: bressan@math.psu.edu; yzheng@math.psu.edu
On Asymptotic Variational Wave Equations Alberto Bressan 1, Ping Zhang 2, and Yuxi Zheng 1 1 Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, PA 1682. E-mail: bressan@math.psu.edu; yzheng@math.psu.edu
ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS WITH MEASURE DATA IN ORLICZ SPACES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2008(2008), No. 76, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) ELLIPTIC
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2008(2008), No. 76, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) ELLIPTIC
THE CAUCHY PROBLEM AND STEADY STATE SOLUTIONS FOR A NONLOCAL CAHN-HILLIARD EQUATION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 24(24), No. 113, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) THE CAUCHY
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 24(24), No. 113, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) THE CAUCHY
Piecewise Smooth Solutions to the Burgers-Hilbert Equation
 Piecewise Smooth Solutions to the Burgers-Hilbert Equation Alberto Bressan and Tianyou Zhang Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, University Park, Pa 68, USA e-mails: bressan@mathpsuedu, zhang
Piecewise Smooth Solutions to the Burgers-Hilbert Equation Alberto Bressan and Tianyou Zhang Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, University Park, Pa 68, USA e-mails: bressan@mathpsuedu, zhang
APPROXIMATE CONTROLLABILITY OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS BY DISTRIBUTED CONTROLLERS
 2004 Conference on Diff. Eqns. and Appl. in Math. Biology, Nanaimo, BC, Canada. Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 12, 2005, pp. 159 169. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu
2004 Conference on Diff. Eqns. and Appl. in Math. Biology, Nanaimo, BC, Canada. Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 12, 2005, pp. 159 169. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu
BLOW-UP OF SOLUTIONS FOR VISCOELASTIC EQUATIONS OF KIRCHHOFF TYPE WITH ARBITRARY POSITIVE INITIAL ENERGY
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 6 6, No. 33, pp. 8. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu BLOW-UP OF SOLUTIONS FOR VISCOELASTIC EQUATIONS OF KIRCHHOFF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 6 6, No. 33, pp. 8. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu BLOW-UP OF SOLUTIONS FOR VISCOELASTIC EQUATIONS OF KIRCHHOFF
Math 699 Reading Course, Spring 2007 Rouben Rostamian Homogenization of Differential Equations May 11, 2007 by Alen Agheksanterian
 . Introduction Math 699 Reading Course, Spring 007 Rouben Rostamian Homogenization of ifferential Equations May, 007 by Alen Agheksanterian In this brief note, we will use several results from functional
. Introduction Math 699 Reading Course, Spring 007 Rouben Rostamian Homogenization of ifferential Equations May, 007 by Alen Agheksanterian In this brief note, we will use several results from functional
EXISTENCE OF CONJUGACIES AND STABLE MANIFOLDS VIA SUSPENSIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), No. 172, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF CONJUGACIES AND STABLE MANIFOLDS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), No. 172, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF CONJUGACIES AND STABLE MANIFOLDS
EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS TO ASYMPTOTICALLY PERIODIC SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 017 (017), No. 15, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS TO ASYMPTOTICALLY PERIODIC
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 017 (017), No. 15, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS TO ASYMPTOTICALLY PERIODIC
AN EXTENSION OF THE LAX-MILGRAM THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATION TO FRACTIONAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 215 (215), No. 95, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu AN EXTENSION OF THE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 215 (215), No. 95, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu AN EXTENSION OF THE
POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF A NONLINEAR THREE-POINT BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM. Ruyun Ma
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1998(1998), No. 34, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) POSITIVE SOLUTIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 1998(1998), No. 34, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ftp) POSITIVE SOLUTIONS
MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS FOR CRITICAL ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS WITH FRACTIONAL LAPLACIAN
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 016 (016), No. 97, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 016 (016), No. 97, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS
GLOBAL WELL-POSEDNESS FOR NONLINEAR NONLOCAL CAUCHY PROBLEMS ARISING IN ELASTICITY
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), No. 55, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu GLOBAL WELL-POSEDNESS FO NONLINEA NONLOCAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), No. 55, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. UL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu GLOBAL WELL-POSEDNESS FO NONLINEA NONLOCAL
LIFE SPAN OF BLOW-UP SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER-ORDER SEMILINEAR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 21(21), No. 17, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu LIFE SPAN OF BLOW-UP
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 21(21), No. 17, pp. 1 9. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu LIFE SPAN OF BLOW-UP
Chapter 3 Second Order Linear Equations
 Partial Differential Equations (Math 3303) A Ë@ Õæ Aë áöß @. X. @ 2015-2014 ú GA JË@ É Ë@ Chapter 3 Second Order Linear Equations Second-order partial differential equations for an known function u(x,
Partial Differential Equations (Math 3303) A Ë@ Õæ Aë áöß @. X. @ 2015-2014 ú GA JË@ É Ë@ Chapter 3 Second Order Linear Equations Second-order partial differential equations for an known function u(x,
Nonlinear Wave Propagation in 1D Random Media
 Nonlinear Wave Propagation in 1D Random Media J. B. Thoo, Yuba College UCI Computational and Applied Math Seminar Winter 22 Typeset by FoilTEX Background O Doherty and Anstey (Geophysical Prospecting,
Nonlinear Wave Propagation in 1D Random Media J. B. Thoo, Yuba College UCI Computational and Applied Math Seminar Winter 22 Typeset by FoilTEX Background O Doherty and Anstey (Geophysical Prospecting,
SYMMETRY AND REGULARITY OF AN OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM RELATED TO A NONLINEAR BVP
 lectronic ournal of Differential quations, Vol. 2013 2013, No. 108, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SYMMTRY AND RGULARITY
lectronic ournal of Differential quations, Vol. 2013 2013, No. 108, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu SYMMTRY AND RGULARITY
LORENTZ ESTIMATES FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY REGULAR FULLY NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 27 27), No. 2, pp. 3. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu LORENTZ ESTIMATES FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY REGULAR FULLY NONLINEAR
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 27 27), No. 2, pp. 3. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu LORENTZ ESTIMATES FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY REGULAR FULLY NONLINEAR
