Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi The Fourier Transform
|
|
|
- Martin Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 4 The Fourier Transform Yung-Hsiang Huang Exercises 1. Suppose f L 1 (), and f 0. Show that f 0. emark 1. This proof is observed by Newmann (published in Monthly 1974 pp ). However, it can not be applied to d, d 2. For each t and ξ, f(ξ) = 0 implies that 0 = t f(x)e 2πixξ dx + =: F t (ξ) + ( G t (ξ)) t f(x)e 2πixξ dx = t f(x)e 2πi(x t)ξ dx + t f(x)e 2πi(x t)ξ dx Let A t (z) equals F t (z) = G t (z) if z, equals F t (z) if Im(z) > 0 and equals G t (z) if Im(z) < 0. By Lebesgue Dominated Convergence Theorem (LDCT), A t is continuous on C and analytic on the upper and lower half-plane, so by Morera s theorem (also see Problem 3 of Chapter 2), A t is entire and bounded by f. Liouville s Theorem implies A t c t for some constant c t. Such constant is 0, since c t = A t (is) = F t (is) 0 as s, by LDCT. So for each t, 0 = A t (0) = t f(x) dx. Lebesgue Differentiate Theorem implies that f = 0 a.e. emark 2. Chapter 4 of Peter Lax s book, Complex Proofs for eal Theorems, contains more interesting results proved by complex analysis, e.g. uniqueness for adon Transform. 2. If f F a with a > 0, then for any positive integer n one has f (n) F b whenever 0 b < a. Department of Math., National Taiwan University. d @ntu.edu.tw 1
2 3. Show, by contour integration, that if a > 0 and ξ then 1 a π a 2 + x 2 e 2πixξ dx = e 2πa ξ, and check that e 2πa ξ e 2πixξ dξ = 1 a π a 2 + x. 2 emark 3. The proof for d case needs more efforts, based on the subordinate principle (one also need the residue formula to prove e β = 2 π Book I. 0 cos(βx) 1+x 2 dx when β 0), see Exercise 6.8 in 4. Suppose Q is a polynomial of degree 2 with distinct roots, none lying on the real axis. Calculate e 2πixξ Q(x) dx, ξ in terms of the roots of Q. What happens when several roots coincide? [Hint: Consider separately the cases ξ < 0, ξ = 0, and ξ > 0. Use residues.] 5. More generally, let (x) = P (x)/q(x) be a rational function with (degree Q) (degree P ) + 2 and Q(x) 0 on the real axis. (a) Prove that if α 1,, α k are the roots of Q in the upper half-plane, then there exists polynomials P j (ξ) of degree less than the multiplicity of α j so that k (x)e 2πixξ dx = P j (ξ)e 2πiαjξ when ξ < 0 j=1 (b) In particular, if Q(z) has no zeros in the upper half-plane, then (x)e 2πixξ dx = 0 for ξ < 0. (c) Show that similar results hold in the case ξ > 0. (d) Show that (x)e 2πixξ dx = O(e a ξ ), ξ as ξ for some a > 0. Determine the best possible as in terms of the roots of. 2
3 6. By Poisson summation formula and Exercise 3, we have 1 a π a 2 + n = e 2πa n = e 2πa = cosh πa. 2 1 e 2πa n= n= 7. The Poisson summation formula applied to specific examples often provides interesting identities. (a) Let τ be fixed with Im(τ) > 0. Apply the Poisson summation formula to f(z) = (τ + z) k, where k is an integer 2, to obtain 1 (τ + n) = ( 2πi)k k (k 1)! n= m k 1 e 2πimτ. (b) Set k = 2 in the above formula to show that if Im(τ) > 0, then 1 (τ + n) = π 2 2 sin 2 (πτ). n= (c) Can one conclude that the above formula holds true whenever τ is any complex number that is not an integer? [Hint: For (a), use residues to prove that f(ξ) = 0, if ξ < 0, and m=1 f(ξ) = ( 2πi)k (k 1)! ξk 1 e 2πiξτ, when ξ > 0.] 8. Suppose f has compact support contained in [ M, M] and let f(z) = n=0 a nz n. Show that and as a result a n = (2πi)n n! M M f(ξ)ξ n dξ, lim sup(n! a n ) 1/n 2πM. n In the converse direction, let f be any power series f(z) = n=0 a nz n with lim sup n (n! a n ) 1/n 2πM. Then, f is holomorphic in the complex plane, and for every ɛ > 0 there exists A ɛ > 0 such that f(z) A ɛ e 2π(M+ɛ) z. 3
4 9. Here are further results similar to the Phragmén-Lindelöf theorem. (a) Let F be a holomorphic function in the right half-plane that extends continuously to the boundary. Suppose that F (iy) 1 for all y, and F (z) Ce c z γ for some c, C > 0 and γ < 1. Prove that F (z) 1 for all z in the right half-plane. (b) More generally, let S be a sector whose vertex is the origin, and forming an angle of π/β. Let F be a holomorphic function in S that is continuous on the closure of S, so that F (z) 1 on the boundary of S and F (z) Ce c z α for all z S for some c, C > 0 and 0 < α < β. Prove that F (z) 1 for all z S. 10. This exercise generalizes some of the properties of e πx2 related to the fact that it is its own Fourier transform. Suppose f(z) is an entire function that satisfies f(x + iy) ce ax2 +by 2 for some a, b, c > 0. Let f(ζ) = f(x)e 2πixζ dx. Then f is an entire function of ζ that satisfies f(ξ + iη) c e a ξ 2 +b η 2 for some a, b, c > One can give a neater formulation of the result in Exercise 10 by probing the following fact. 4
5 Suppose f(z) is an entire function of strict order 2, that is, f(z) = O(e c 1 z 2 ) for some c 1 > 0. Suppose also that for x real, f(x) = O(e c 2 x 2 ) for some c 2 > 0. Then f(x + iy) = O(e ax2 +by 2 ) for some a, b > The principle that a function and its Fourier transform cannot both be too small at infinity is illustrated by the following theorem of Hardy. Theorem 4. (Hardy) If f is a function on that satisfies f(x) = O(e πx2 ) and f(ξ) = O(e πξ2 ), then f is a constant multiple of e πx2. As a result, if f(x) = O(e πax2 ), and f(ξ) = O(e πbξ2 ), with AB > 1 and A, B > 0, then f is identically zero. (a) If f is even, show that f extends to an even entire function. g(z) = f(z 1/2 ), then g satisfies Moreover, if g(x) ce πx and g(z) e π sin2 (θ/2) ce π z when x and z = e iθ with 0 and θ. (b) Apply the Phragmën-Lindelöf principle to the function F (z) = g(z)e γz where γ = iπ e iπ/(2β) sin π/(2β) and the sector 0 θ π/β < π, and let β π to deduce that e πz g(z) is bounded in the closed upper half-plane. The same result holds in the lower half-plane, so by Liouville s theorem e πz g(z) is constant, as desired. (c) If f is odd, then f(0) = 0, and apply the above argument to f(z)/z to deduce that f = f = 0. function and an odd function. emark 5. Also check Problem 1. Finally, write an arbitrary f as an appropriate sum of an even 5
6 2 Problems 1. Suppose f(ξ) = O(e a ξ p ) as ξ, for some p > 1. Then f is holomorphic for all z and satisfies the growth condition f(z) Ae a z q where 1/p + 1/q = 1. Note that on the one hand, when p then q 1, and this limiting case can be interpreted as part of Theorem 3.3. On the other hand, when p 1 then q, and this limiting case in a sense brings us back to Theorem 2.1. [Hint: To prove the result, use the inequality ξ p + ξu u q, which is valid when ξ and u are non-negative. To establish this inequality, examine separately the cases ξ p ξu and ξ p < ξu; note also that the functions ξ = u q 1 and u = ξ p 1 are inverses of each other because (p 1)(q 1) = 1.] 2. The problem is to solve the differential equation d n 1 d n a n dt u(t) + a n n 1 dt u(t) + + a 0u(t) = f(t), n 1 where a 0, a 1,, a n are complex constants, and f is a given function. Here we suppose that f has bounded support and is smooth (say of class C 2 ). (a) Let f(z) = f(t)e 2πizt dt Observe that f is an entire function, and using integration by parts show that if y a for any fixed a 0. f(x + iy) A 1 + x 2 (b) Write P (z) = a n (2πiz) n + a n 1 (2πiz) n a 0. Find a real number c so that P (z) does not vanish on the line L = {z : z = x + ic, x }. (c) Set u(t) = L e 2πizt P (z) f(z) dz. 6
7 Check that and n ( d ) ju(t) a j = dt j=0 L e 2πizt f(z) dz e 2πizt f(z) dz = e 2πixt f(x) dx L Conclude by the Fourier inversion theorem that n ( d ju(t) a j = f(t). dt) j=0 Note that the solution u depends on the choice c. 3. In this problem, we investigate the behavior of certain bounded holomorphic functions in an infinite strip. The particular result described here is sometimes called the three-lines lemma. (a) Suppose F (z) is holomorphic and bounded in the strip 0 < Im(z) < 1 and continuous on its closure. If F (z) 1 on the boundary lines, then F (z) 1 throughout the strip. (b) For the more general F, let sup x F (x) = M 0 and sup x F (x + i) = M 1. Then sup F (x + iy) M 1 y 0 M y 1, if 0 y 1. x (c) As a consequence, prove that log sup x F (x + iy) is a convex function of y when 0 y 1. [Hint: For part (a), apply the maximum modulus principle to F ɛ (z) = F (z)e ɛz2. For part (b), consider M z 1 0 M z 1 F (z).] 4. There is a relation between the Paley-Wiener theorem and an earlier representation due to E. Borel. (a) A function f(z), holomorphic for all z, satisfies f(z) A ɛ e 2π(M+ɛ) z for all ɛ if and only if it is representable in the form f(z) = e 2πizw g(w) dw C 7
8 where g is holomorphic outside the circle of radius M centered at the origin, and g vanishes at infinity. Here C is any circle centered at the origin of radius larger than M. In fact, if f(z) = a n z n, then g(w) = w=0 A nw n 1 with a n = A n (2πi) n+1 /n!. (b) The connection with Theorem 3.3 is as follows. For these functions f (for which in addition f and f are of moderate decrease on the real axis), one can assert that the g above is holomorphic in the larger region, which consists of the slit plane C \ [ M, M]. Moreover, the relation between g and the Fourier transform f is g(z) = 1 M 2πi M f(ξ) ξ z dξ so that f represents the jump of g across the segment [ M, M]; that is, See Problem 5 in Chapter 3. f(x) = lim g(x + iɛ) g(x iɛ). ɛ 0,ɛ>0 8
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Solutions to practice problems for the final
 Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
POISSON SUMMATION AND PERIODIZATION
 POISSON SUMMATION AND PERIODIZATION PO-LAM YUNG We give some heuristics for the Poisson summation formula via periodization, and provide an alternative proof that is slightly more motivated.. Some heuristics
POISSON SUMMATION AND PERIODIZATION PO-LAM YUNG We give some heuristics for the Poisson summation formula via periodization, and provide an alternative proof that is slightly more motivated.. Some heuristics
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
Part IB. Complex Analysis. Year
 Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
MORE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOREM
 MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
2 Infinite products and existence of compactly supported φ
 415 Wavelets 1 Infinite products and existence of compactly supported φ Infinite products.1 Infinite products a n need to be defined via limits. But we do not simply say that a n = lim a n N whenever the
415 Wavelets 1 Infinite products and existence of compactly supported φ Infinite products.1 Infinite products a n need to be defined via limits. But we do not simply say that a n = lim a n N whenever the
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE
 MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
MATH 452. SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, (10 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic.
 MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I
 MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
Math 220A - Fall Final Exam Solutions
 Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
MORE NOTES FOR MATH 823, FALL 2007
 MORE NOTES FOR MATH 83, FALL 007 Prop 1.1 Prop 1. Lemma 1.3 1. The Siegel upper half space 1.1. The Siegel upper half space and its Bergman kernel. The Siegel upper half space is the domain { U n+1 z C
MORE NOTES FOR MATH 83, FALL 007 Prop 1.1 Prop 1. Lemma 1.3 1. The Siegel upper half space 1.1. The Siegel upper half space and its Bergman kernel. The Siegel upper half space is the domain { U n+1 z C
z b k P k p k (z), (z a) f (n 1) (a) 2 (n 1)! (z a)n 1 +f n (z)(z a) n, where f n (z) = 1 C
 . Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
. Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
Part IB. Complex Methods. Year
 Part IB Year 218 217 216 215 214 213 212 211 21 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 218 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal mapping from the right half z-plane, Re(z)
Part IB Year 218 217 216 215 214 213 212 211 21 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 218 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal mapping from the right half z-plane, Re(z)
Complex Analysis Problems
 Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Complex Variables...Review Problems (Residue Calculus Comments)...Fall Initial Draft
 Complex Variables........Review Problems Residue Calculus Comments)........Fall 22 Initial Draft ) Show that the singular point of fz) is a pole; determine its order m and its residue B: a) e 2z )/z 4,
Complex Variables........Review Problems Residue Calculus Comments)........Fall 22 Initial Draft ) Show that the singular point of fz) is a pole; determine its order m and its residue B: a) e 2z )/z 4,
UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLES WITH FOURIER ANALYSIS
 UNETAINTY PINIPLES WITH FOUIE ANALYSIS ALDE SHEAGEN Abstract. We describe the properties of the Fourier transform on in preparation for some relevant physical interpretations. These include the Heisenberg
UNETAINTY PINIPLES WITH FOUIE ANALYSIS ALDE SHEAGEN Abstract. We describe the properties of the Fourier transform on in preparation for some relevant physical interpretations. These include the Heisenberg
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
4 Uniform convergence
 4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
MATH SPRING UC BERKELEY
 MATH 85 - SPRING 205 - UC BERKELEY JASON MURPHY Abstract. These are notes for Math 85 taught in the Spring of 205 at UC Berkeley. c 205 Jason Murphy - All Rights Reserved Contents. Course outline 2 2.
MATH 85 - SPRING 205 - UC BERKELEY JASON MURPHY Abstract. These are notes for Math 85 taught in the Spring of 205 at UC Berkeley. c 205 Jason Murphy - All Rights Reserved Contents. Course outline 2 2.
Exercises for Part 1
 MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
Math Homework 2
 Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall Anton R. Schep
 Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
1 Discussion on multi-valued functions
 Week 3 notes, Math 7651 1 Discussion on multi-valued functions Log function : Note that if z is written in its polar representation: z = r e iθ, where r = z and θ = arg z, then log z log r + i θ + 2inπ
Week 3 notes, Math 7651 1 Discussion on multi-valued functions Log function : Note that if z is written in its polar representation: z = r e iθ, where r = z and θ = arg z, then log z log r + i θ + 2inπ
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
17 The functional equation
 18.785 Number theory I Fall 16 Lecture #17 11/8/16 17 The functional equation In the previous lecture we proved that the iemann zeta function ζ(s) has an Euler product and an analytic continuation to the
18.785 Number theory I Fall 16 Lecture #17 11/8/16 17 The functional equation In the previous lecture we proved that the iemann zeta function ζ(s) has an Euler product and an analytic continuation to the
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Problems for MATH-6300 Complex Analysis
 Problems for MATH-63 Complex Analysis Gregor Kovačič December, 7 This list will change as the semester goes on. Please make sure you always have the newest version of it.. Prove the following Theorem For
Problems for MATH-63 Complex Analysis Gregor Kovačič December, 7 This list will change as the semester goes on. Please make sure you always have the newest version of it.. Prove the following Theorem For
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
MATH COMPLEX ANALYSIS. Contents
 MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
THE FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPLEX ANALYSIS AND ITS IMMEDIATE APPLICATIONS
 THE FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPLEX ANALYSIS AND ITS IMMEDIATE APPLICATIONS SKULI GUDMUNDSSON Abstract. This paper is an exposition on the basic fundamental theorems of complex analysis. Given is a brief introduction
THE FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPLEX ANALYSIS AND ITS IMMEDIATE APPLICATIONS SKULI GUDMUNDSSON Abstract. This paper is an exposition on the basic fundamental theorems of complex analysis. Given is a brief introduction
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 11
 MAT389 Fall 216, Problem Set 11 Improper integrals 11.1 In each of the following cases, establish the convergence of the given integral and calculate its value. i) x 2 x 2 + 1) 2 ii) x x 2 + 1)x 2 + 2x
MAT389 Fall 216, Problem Set 11 Improper integrals 11.1 In each of the following cases, establish the convergence of the given integral and calculate its value. i) x 2 x 2 + 1) 2 ii) x x 2 + 1)x 2 + 2x
Complex Variables. Cathal Ormond
 Complex Variables Cathal Ormond Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Definition: Polar Form.............................. 3 1.2 Definition: Length................................ 3 1.3 Definitions.....................................
Complex Variables Cathal Ormond Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Definition: Polar Form.............................. 3 1.2 Definition: Length................................ 3 1.3 Definitions.....................................
Math 341: Probability Seventeenth Lecture (11/10/09)
 Math 341: Probability Seventeenth Lecture (11/10/09) Steven J Miller Williams College Steven.J.Miller@williams.edu http://www.williams.edu/go/math/sjmiller/ public html/341/ Bronfman Science Center Williams
Math 341: Probability Seventeenth Lecture (11/10/09) Steven J Miller Williams College Steven.J.Miller@williams.edu http://www.williams.edu/go/math/sjmiller/ public html/341/ Bronfman Science Center Williams
Math 421 Midterm 2 review questions
 Math 42 Midterm 2 review questions Paul Hacking November 7, 205 () Let U be an open set and f : U a continuous function. Let be a smooth curve contained in U, with endpoints α and β, oriented from α to
Math 42 Midterm 2 review questions Paul Hacking November 7, 205 () Let U be an open set and f : U a continuous function. Let be a smooth curve contained in U, with endpoints α and β, oriented from α to
III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem
 MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
LECTURE-15 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS
 LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
Ma 416: Complex Variables Solutions to Homework Assignment 6
 Ma 46: omplex Variables Solutions to Homework Assignment 6 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Thursday, October th, 2 Read R. P. Boas, nvitation to omplex Analysis, hapter 2, sections 9A.. Evaluate the definite integral
Ma 46: omplex Variables Solutions to Homework Assignment 6 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Thursday, October th, 2 Read R. P. Boas, nvitation to omplex Analysis, hapter 2, sections 9A.. Evaluate the definite integral
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
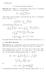 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Fourier Series. 1. Review of Linear Algebra
 Fourier Series In this section we give a short introduction to Fourier Analysis. If you are interested in Fourier analysis and would like to know more detail, I highly recommend the following book: Fourier
Fourier Series In this section we give a short introduction to Fourier Analysis. If you are interested in Fourier analysis and would like to know more detail, I highly recommend the following book: Fourier
Math 565: Introduction to Harmonic Analysis - Spring 2008 Homework # 2, Daewon Chung
 Math 565: Introduction to Harmonic Analysis - Spring 8 Homework #, Daewon Chung. Show that, and that Hχ [a, b] : lim H χ [a, b] a b. H χ [a, b] : sup > H χ [a, b] a b. [Solution] Let us pick < min a, b
Math 565: Introduction to Harmonic Analysis - Spring 8 Homework #, Daewon Chung. Show that, and that Hχ [a, b] : lim H χ [a, b] a b. H χ [a, b] : sup > H χ [a, b] a b. [Solution] Let us pick < min a, b
Complex Analysis Important Concepts
 Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Homework Summer 2014
 omplex Homework Summer 24 Based on Brown hurchill 7th Edition June 2, 24 ontents hw, omplex Arithmetic, onjugates, Polar Form 2 2 hw2 nth roots, Domains, Functions 2 3 hw3 Images, Transformations 3 4 hw4
omplex Homework Summer 24 Based on Brown hurchill 7th Edition June 2, 24 ontents hw, omplex Arithmetic, onjugates, Polar Form 2 2 hw2 nth roots, Domains, Functions 2 3 hw3 Images, Transformations 3 4 hw4
Real and Complex Analysis, 3rd Edition, W.Rudin Elementary Hilbert Space Theory
 Real and Complex Analysis, 3rd Edition, W.Rudin Chapter 4 Elementary Hilbert Space Theory Yung-Hsiang Huang. It s easy to see M (M ) and the latter is a closed subspace of H. Given F be a closed subspace
Real and Complex Analysis, 3rd Edition, W.Rudin Chapter 4 Elementary Hilbert Space Theory Yung-Hsiang Huang. It s easy to see M (M ) and the latter is a closed subspace of H. Given F be a closed subspace
MATH5685 Assignment 3
 MATH5685 Assignment 3 Due: Wednesday 3 October 1. The open unit disk is denoted D. Q1. Suppose that a n for all n. Show that (1 + a n) converges if and only if a n converges. [Hint: prove that ( N (1 +
MATH5685 Assignment 3 Due: Wednesday 3 October 1. The open unit disk is denoted D. Q1. Suppose that a n for all n. Show that (1 + a n) converges if and only if a n converges. [Hint: prove that ( N (1 +
Part IB Complex Analysis
 Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Real Analysis, 2nd Edition, G.B.Folland Elements of Functional Analysis
 Real Analysis, 2nd Edition, G.B.Folland Chapter 5 Elements of Functional Analysis Yung-Hsiang Huang 5.1 Normed Vector Spaces 1. Note for any x, y X and a, b K, x+y x + y and by ax b y x + b a x. 2. It
Real Analysis, 2nd Edition, G.B.Folland Chapter 5 Elements of Functional Analysis Yung-Hsiang Huang 5.1 Normed Vector Spaces 1. Note for any x, y X and a, b K, x+y x + y and by ax b y x + b a x. 2. It
We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by
![We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by](/thumbs/74/71304729.jpg) Chapter 9 The functional equation for the Riemann zeta function We will eventually deduce a functional equation, relating ζ(s to ζ( s. There are various methods to derive this functional equation, see
Chapter 9 The functional equation for the Riemann zeta function We will eventually deduce a functional equation, relating ζ(s to ζ( s. There are various methods to derive this functional equation, see
= F (b) F (a) F (x i ) F (x i+1 ). a x 0 x 1 x n b i
 Real Analysis Problem 1. If F : R R is a monotone function, show that F T V ([a,b]) = F (b) F (a) for any interval [a, b], and that F has bounded variation on R if and only if it is bounded. Here F T V
Real Analysis Problem 1. If F : R R is a monotone function, show that F T V ([a,b]) = F (b) F (a) for any interval [a, b], and that F has bounded variation on R if and only if it is bounded. Here F T V
Complex Variables & Integral Transforms
 Complex Variables & Integral Transforms Notes taken by J.Pearson, from a S4 course at the U.Manchester. Lecture delivered by Dr.W.Parnell July 9, 007 Contents 1 Complex Variables 3 1.1 General Relations
Complex Variables & Integral Transforms Notes taken by J.Pearson, from a S4 course at the U.Manchester. Lecture delivered by Dr.W.Parnell July 9, 007 Contents 1 Complex Variables 3 1.1 General Relations
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES. 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) ax 2 + bx + c = 0. x = b ± b 2 4ac 2a. i = 1.
 MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
Mid Term-1 : Solutions to practice problems
 Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Complex Analysis. Travis Dirle. December 4, 2016
 Complex Analysis 2 Complex Analysis Travis Dirle December 4, 2016 2 Contents 1 Complex Numbers and Functions 1 2 Power Series 3 3 Analytic Functions 7 4 Logarithms and Branches 13 5 Complex Integration
Complex Analysis 2 Complex Analysis Travis Dirle December 4, 2016 2 Contents 1 Complex Numbers and Functions 1 2 Power Series 3 3 Analytic Functions 7 4 Logarithms and Branches 13 5 Complex Integration
Math 213br HW 1 solutions
 Math 213br HW 1 solutions February 26, 2014 Problem 1 Let P (x) be a polynomial of degree d > 1 with P (x) > 0 for all x 0. For what values of α R does the integral I(α) = 0 x α P (x) dx converge? Give
Math 213br HW 1 solutions February 26, 2014 Problem 1 Let P (x) be a polynomial of degree d > 1 with P (x) > 0 for all x 0. For what values of α R does the integral I(α) = 0 x α P (x) dx converge? Give
Assignment 2 - Complex Analysis
 Assignment 2 - Complex Analysis MATH 440/508 M.P. Lamoureux Sketch of solutions. Γ z dz = Γ (x iy)(dx + idy) = (xdx + ydy) + i Γ Γ ( ydx + xdy) = (/2)(x 2 + y 2 ) endpoints + i [( / y) y ( / x)x]dxdy interiorγ
Assignment 2 - Complex Analysis MATH 440/508 M.P. Lamoureux Sketch of solutions. Γ z dz = Γ (x iy)(dx + idy) = (xdx + ydy) + i Γ Γ ( ydx + xdy) = (/2)(x 2 + y 2 ) endpoints + i [( / y) y ( / x)x]dxdy interiorγ
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Math 715 Homework 1 Solutions
 . [arrier, Krook and Pearson Section 2- Exercise ] Show that no purely real function can be analytic, unless it is a constant. onsider a function f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) where z = x + iy and where u
. [arrier, Krook and Pearson Section 2- Exercise ] Show that no purely real function can be analytic, unless it is a constant. onsider a function f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) where z = x + iy and where u
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 204 Cauchy and Runge Under the Same Roof. These notes can be used as an alternative to Section 5.5 of Chapter 2 in the textbook. They assume the theorem on winding numbers of the
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 204 Cauchy and Runge Under the Same Roof. These notes can be used as an alternative to Section 5.5 of Chapter 2 in the textbook. They assume the theorem on winding numbers of the
2 Write down the range of values of α (real) or β (complex) for which the following integrals converge. (i) e z2 dz where {γ : z = se iα, < s < }
 Mathematical Tripos Part II Michaelmas term 2007 Further Complex Methods, Examples sheet Dr S.T.C. Siklos Comments and corrections: e-mail to stcs@cam. Sheet with commentary available for supervisors.
Mathematical Tripos Part II Michaelmas term 2007 Further Complex Methods, Examples sheet Dr S.T.C. Siklos Comments and corrections: e-mail to stcs@cam. Sheet with commentary available for supervisors.
Bernstein s inequality and Nikolsky s inequality for R d
 Bernstein s inequality and Nikolsky s inequality for d Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of athematics University of Toronto February 6 25 Complex Borel measures and the Fourier transform Let
Bernstein s inequality and Nikolsky s inequality for d Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of athematics University of Toronto February 6 25 Complex Borel measures and the Fourier transform Let
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
On the Bilateral Laplace Transform of the positive even functions and proof of the Riemann Hypothesis. Seong Won Cha Ph.D.
 On the Bilateral Laplace Transform of the positive even functions and proof of the Riemann Hypothesis Seong Won Cha Ph.D. Seongwon.cha@gmail.com Remark This is not an official paper, rather a brief report.
On the Bilateral Laplace Transform of the positive even functions and proof of the Riemann Hypothesis Seong Won Cha Ph.D. Seongwon.cha@gmail.com Remark This is not an official paper, rather a brief report.
Here are brief notes about topics covered in class on complex numbers, focusing on what is not covered in the textbook.
 Phys374, Spring 2008, Prof. Ted Jacobson Department of Physics, University of Maryland Complex numbers version 5/21/08 Here are brief notes about topics covered in class on complex numbers, focusing on
Phys374, Spring 2008, Prof. Ted Jacobson Department of Physics, University of Maryland Complex numbers version 5/21/08 Here are brief notes about topics covered in class on complex numbers, focusing on
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
Topics in Harmonic Analysis Lecture 1: The Fourier transform
 Topics in Harmonic Analysis Lecture 1: The Fourier transform Po-Lam Yung The Chinese University of Hong Kong Outline Fourier series on T: L 2 theory Convolutions The Dirichlet and Fejer kernels Pointwise
Topics in Harmonic Analysis Lecture 1: The Fourier transform Po-Lam Yung The Chinese University of Hong Kong Outline Fourier series on T: L 2 theory Convolutions The Dirichlet and Fejer kernels Pointwise
1 Euler s idea: revisiting the infinitude of primes
 8.785: Analytic Number Theory, MIT, spring 27 (K.S. Kedlaya) The prime number theorem Most of my handouts will come with exercises attached; see the web site for the due dates. (For example, these are
8.785: Analytic Number Theory, MIT, spring 27 (K.S. Kedlaya) The prime number theorem Most of my handouts will come with exercises attached; see the web site for the due dates. (For example, these are
PRIME NUMBER THEOREM
 PRIME NUMBER THEOREM RYAN LIU Abstract. Prime numbers have always been seen as the building blocks of all integers, but their behavior and distribution are often puzzling. The prime number theorem gives
PRIME NUMBER THEOREM RYAN LIU Abstract. Prime numbers have always been seen as the building blocks of all integers, but their behavior and distribution are often puzzling. The prime number theorem gives
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008
 Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Complex Analysis Qual Sheet
 Complex Analysis Qual Sheet Robert Won Tricks and traps. traps. Basically all complex analysis qualifying exams are collections of tricks and - Jim Agler Useful facts. e z = 2. sin z = n=0 3. cos z = z
Complex Analysis Qual Sheet Robert Won Tricks and traps. traps. Basically all complex analysis qualifying exams are collections of tricks and - Jim Agler Useful facts. e z = 2. sin z = n=0 3. cos z = z
Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 auchy s integral formula 4. Introduction auchy s theorem is a big theorem which we will use almost daily from here on out. Right away it will reveal a number of interesting
Topic 4 Notes Jeremy Orloff 4 auchy s integral formula 4. Introduction auchy s theorem is a big theorem which we will use almost daily from here on out. Right away it will reveal a number of interesting
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
HARDY S THEOREM AND ROTATIONS
 HARDY S THEOREM AND ROTATIONS J.A. HOGAN AND J.D. LAKEY Abstract. We prove an extension of Hardy s classical characterization of real Gaussians of the form e παx2, α > 0 to the case of complex Gaussians
HARDY S THEOREM AND ROTATIONS J.A. HOGAN AND J.D. LAKEY Abstract. We prove an extension of Hardy s classical characterization of real Gaussians of the form e παx2, α > 0 to the case of complex Gaussians
MATH243 First Semester 2013/14. Exercises 1
 Complex Functions Dr Anna Pratoussevitch MATH43 First Semester 013/14 Exercises 1 Submit your solutions to questions marked with [HW] in the lecture on Monday 30/09/013 Questions or parts of questions
Complex Functions Dr Anna Pratoussevitch MATH43 First Semester 013/14 Exercises 1 Submit your solutions to questions marked with [HW] in the lecture on Monday 30/09/013 Questions or parts of questions
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions Please hand solutions in at the lecture on Monday 6th March..) Prove Gauss Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Hint:
MA30056: Complex Analysis Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions Please hand solutions in at the lecture on Monday 6th March..) Prove Gauss Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Hint:
Chapter 4: Open mapping theorem, removable singularities
 Chapter 4: Open mapping theorem, removable singularities Course 44, 2003 04 February 9, 2004 Theorem 4. (Laurent expansion) Let f : G C be analytic on an open G C be open that contains a nonempty annulus
Chapter 4: Open mapping theorem, removable singularities Course 44, 2003 04 February 9, 2004 Theorem 4. (Laurent expansion) Let f : G C be analytic on an open G C be open that contains a nonempty annulus
ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 2016: SOLUTIONS. = lim. F n
 ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 206: SOLUTIONS Problem. Let m be Lebesgue measure on R. For a subset E R and r (0, ), define E r = { x R: dist(x, E) < r}. Let E R be compact. Prove that m(e) = lim m(e /n).
ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 206: SOLUTIONS Problem. Let m be Lebesgue measure on R. For a subset E R and r (0, ), define E r = { x R: dist(x, E) < r}. Let E R be compact. Prove that m(e) = lim m(e /n).
MATH FINAL SOLUTION
 MATH 185-4 FINAL SOLUTION 1. (8 points) Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required. (1) (1 point) Let D be a domain and let u,v : D R be two harmonic functions,
MATH 185-4 FINAL SOLUTION 1. (8 points) Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required. (1) (1 point) Let D be a domain and let u,v : D R be two harmonic functions,
Partial Differential Equations, 2nd Edition, L.C.Evans Chapter 5 Sobolev Spaces
 Partial Differential Equations, nd Edition, L.C.Evans Chapter 5 Sobolev Spaces Shih-Hsin Chen, Yung-Hsiang Huang 7.8.3 Abstract In these exercises always denote an open set of with smooth boundary. As
Partial Differential Equations, nd Edition, L.C.Evans Chapter 5 Sobolev Spaces Shih-Hsin Chen, Yung-Hsiang Huang 7.8.3 Abstract In these exercises always denote an open set of with smooth boundary. As
Measure and Integration: Solutions of CW2
 Measure and Integration: s of CW2 Fall 206 [G. Holzegel] December 9, 206 Problem of Sheet 5 a) Left (f n ) and (g n ) be sequences of integrable functions with f n (x) f (x) and g n (x) g (x) for almost
Measure and Integration: s of CW2 Fall 206 [G. Holzegel] December 9, 206 Problem of Sheet 5 a) Left (f n ) and (g n ) be sequences of integrable functions with f n (x) f (x) and g n (x) g (x) for almost
We denote the space of distributions on Ω by D ( Ω) 2.
 Sep. 1 0, 008 Distributions Distributions are generalized functions. Some familiarity with the theory of distributions helps understanding of various function spaces which play important roles in the study
Sep. 1 0, 008 Distributions Distributions are generalized functions. Some familiarity with the theory of distributions helps understanding of various function spaces which play important roles in the study
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Lecture Notes Complex Analysis. Complex Variables and Applications 7th Edition Brown and Churchhill
 Lecture Notes omplex Analysis based on omplex Variables and Applications 7th Edition Brown and hurchhill Yvette Fajardo-Lim, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics De La Salle University - Manila 2 ontents THE
Lecture Notes omplex Analysis based on omplex Variables and Applications 7th Edition Brown and hurchhill Yvette Fajardo-Lim, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics De La Salle University - Manila 2 ontents THE
Linear independence of exponentials on the real line
 Linear independence of exponentials on the real line Alexandre Eremenko August 25, 2013 The following question was asked on Math Overflow. Let (λ n ) be a sequence of complex numbers tending to infinity.
Linear independence of exponentials on the real line Alexandre Eremenko August 25, 2013 The following question was asked on Math Overflow. Let (λ n ) be a sequence of complex numbers tending to infinity.
THE ZERO-DISTRIBUTION AND THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF A FOURIER INTEGRAL. Haseo Ki and Young One Kim
 THE ZERO-DISTRIBUTION AND THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF A FOURIER INTEGRAL Haseo Ki Young One Kim Abstract. The zero-distribution of the Fourier integral Q(u)eP (u)+izu du, where P is a polynomial with leading
THE ZERO-DISTRIBUTION AND THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF A FOURIER INTEGRAL Haseo Ki Young One Kim Abstract. The zero-distribution of the Fourier integral Q(u)eP (u)+izu du, where P is a polynomial with leading
SPRING 2006 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS
 SPRING 006 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS 1A. Let G be the subgroup of the free abelian group Z 4 consisting of all integer vectors (x, y, z, w) such that x + 3y + 5z + 7w = 0. (a) Determine a linearly
SPRING 006 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS 1A. Let G be the subgroup of the free abelian group Z 4 consisting of all integer vectors (x, y, z, w) such that x + 3y + 5z + 7w = 0. (a) Determine a linearly
POLYNOMIALS WITH COEFFICIENTS FROM A FINITE SET
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9947(XX)0000-0 POLYNOMIALS WITH COEFFICIENTS FROM A FINITE SET PETER BORWEIN, TAMÁS ERDÉLYI, FRIEDRICH LITTMANN
TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9947(XX)0000-0 POLYNOMIALS WITH COEFFICIENTS FROM A FINITE SET PETER BORWEIN, TAMÁS ERDÉLYI, FRIEDRICH LITTMANN
Fourier Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi The Fourier Transform on R
 Fourier Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 5 The Fourier Transform on Yung-Hsiang Huang 8.3.7 Abstract After Problem 6, we contain a proof for Widder s uniqueness theorem in the class of nonnegative
Fourier Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 5 The Fourier Transform on Yung-Hsiang Huang 8.3.7 Abstract After Problem 6, we contain a proof for Widder s uniqueness theorem in the class of nonnegative
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2003 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
Math 172 Problem Set 8 Solutions
 Math 72 Problem Set 8 Solutions Problem. (i We have (Fχ [ a,a] (ξ = χ [ a,a] e ixξ dx = a a e ixξ dx = iξ (e iax e iax = 2 sin aξ. ξ (ii We have (Fχ [, e ax (ξ = e ax e ixξ dx = e x(a+iξ dx = a + iξ where
Math 72 Problem Set 8 Solutions Problem. (i We have (Fχ [ a,a] (ξ = χ [ a,a] e ixξ dx = a a e ixξ dx = iξ (e iax e iax = 2 sin aξ. ξ (ii We have (Fχ [, e ax (ξ = e ax e ixξ dx = e x(a+iξ dx = a + iξ where
