PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR A WELL IN A RADIAL COMPOSITE RESERVOIR WITH A NON-NEWTONIAN/ NEWTONIAN INTERFACE
|
|
|
- Opal McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR A WELL IN A RADIAL COMPOSITE RESERVOIR WITH A NON-NEWTONIAN/ NEWTONIAN INTERFACE Freddy-Humberto Escobar 1*, Javier-Andrés Martínez 1* and Matilde Montealegre-Madero 1* 1 Universidad Surcolombiana, Av. Pastrana Cra. 1, Neiva, Huila, Colombia fescobar@usco.edu.co jandres@usco.edu.co matildemm@hotmail.com ABSTRACT (Received, Aug. 2, 20; Accepted, Dec. 9, 20) In many activities of the oil industry, engineers have to deal with completion and stimulation treatment fluids such as polymer solutions and some heavy crude oils which obey a non-newtonian power-law behavior. When it is required to conduct a treatment with a non-newtonian fluid in an oil-bearing formation, this comes in contact with conventional oil which possesses a Newtonian nature. This implies the definition of two media with entirely different mobilities. If a pressure test is run in such a system, the interpretation of data from such a test through the use of conventional straight-line method may be erroneous and may not provide a way for verification of the results obtained. In this work, the signature of the pressure derivative curve is investigated to understand and ease the interpretation of the well test data in reservoirs with non-newtonian power-law fluids. Specifically, the Tiab s Direct Synthesis (TDS) technique is implemented using some characteristics features found on the pressure and pressure derivative curves. Hence, new equations are introduced to estimate permeability, non-newtonian bank radius and skin factor. Permeability can be verified. The proposed methodology was successfully verified by its application to an example reported in the literature and a synthetic case. Keywords: radial flow, viscosity, reservoir characterization, pressure tests, mobility, permeability, mathematical model, pressure curve, Newtonian fluid, pressure analysis. * To whom correspondence may be addressed 33
2 RESUMEN En algunas actividades de la industria petrolera, los ingenieros tienen que tratar con fluidos de estimulación y completamiento tales como polímeros y algunos crudos pesados que obedecen un comportamiento no Newtoniano. Cuando se requiere un tratamiento con un fluido no Newtoniano en una formación productora de crudo, éste entra en contacto con el crudo convencional que posee naturaleza Newtoniana. Esto implica la definición de dos medios con movilidades completamente diferentes. Si allí se corre una prueba de presión, su interpretación mediante el método convencional de la línea recta podría conducir a resultados erróneos y tampoco permitiría la verificación de los resultados obtenidos. En este trabajo se estudió la huella de la derivada de presión para entender y facilitar la interpretación de pruebas de presión en yacimientos con fluidos no-newtonianos que obedecen la ley de potencia. Específicamente, se implementó la Síntesis Directa de Tiab (TDS) usando algunas características específicas halladas en la curva de la presión y la derivada de presión, de modo que se introdujeron nuevas ecuaciones para estimar permeabilidad, radio de la zona no Newtoniana y el factor de daño. La permeabilidad se puede verificar. La metodología propuesta se verificó satisfactoriamente mediante su aplicación a un problema reportado en la literatura y otro sintético. Palabras clave: flujo radial, viscosidad, caracterización de yacimientos, pruebas de presión, movilidad, permeabilidad, modelo matemático, curvas de presión, fluido newtoniano, análisis de presión. 34 CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20
3 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR A WELL IN A RADIAL COMPOSITE RESERVOIR 1. INTRODUCTION The oil literature contains several papers on the behavior of non-newtonian fluids in porous media. Odeh and Yang (1979) derived a partial differential equation for fluid flow of power-law through porous media. They used a power-law function relating the viscosity to the shear rate. The power-law viscosity function was coupled with the variable viscosity diffusivity equation and a shear-rate relationship proposed by Savins (1969) to give a new partial differential equation and an approximate analytical solution. Ikoku (1979) has been the most outstanding researcher in the field of non- Newtonian power-law fluids modeling, as shown by Ikoku (1979), Ikoku and Ramey (1979a, 1979b, 1979c) and Lund and Ikoku (1981). Vongvuthipornchai and Raghavan (1987) used the pressure-derivative method for well test analysis of non-newtonian fluids, however, the very first application to non-newtonian behavior by the TDS technique was reported by Katime-Meindl and Tiab (2001). Interpretation of pressure tests for non-newtonian fluids is performed differently to conventional Newtonian fluids. During radial flow regime, Non-Newtonian fluids exhibit a pressure derivative curve which is not horizontal but rather inclined. As shown by Katime- Meindl and Tiab (2001), the smaller the value of n (flow behavior index) the more inclined the infinite-acting pressure derivative line. (See Figure 1). This paper analyzes constant-rate injection tests and the extension of the TDS technique for a composite non-newtonian/newtonian system. For this purpose, a numerical simulator was built to generate the pressure and pressure derivative curves, and some characteristics points and lines were found on derivative curves to further develop analytical expressions which allow characterizing the reservoirs with fluids exhibiting non-newtonian power-law behaviors. 2. MATHEMATICAL MODEL A partial differential equation for radial flow of non- Newtonian fluids that follow a power-law relationship through porous media was proposed by Ikoku and Ramey (1979b). Coupling the non-newtonian Darcy's law with the continuity equation, they derived a rigorous partial differential equation: (1) This equation is nonlinear. For analytical solutions, a linearized approximation was also derived by Ikoku and Ramey (1979b): Where: (2) 1.E+02 (t D /C D )*P'D 1.E+01 1.E+00 1.E-01 1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 C e 2s C D e 2s 1x 3 1x 25 1x x 40 1.E+00 1.E+01 t D /C D 1.E+02 n = 0.2 0,2 n = 0.4 0,4 n = 0.6 0,6 n = 0.8 0,8 n = 1 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 Figure 1 Pressure derivative for a viscoplastic non-newtonian fluid in an infinite reservoir After Katime-Meindl and Tiab (2001) and, (3) (4) Ikoku and Ramey (1979b) solved Equation 1 using the predictor/corrector Douglas-Jones method for numerical solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations. They compared the results with the solution of the linear equation, (Equation 2). The errors introduced by the approximate linear equation were small and decrease with the increase in the value of the flow behavior index, n, and the increase of time. CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec
4 FREDDY-HUMBERTO ESCOBAR, JAVIER-ANDRÉS MARTÍNEZ AND MATILDE MONTEALEGRE-MADERO The system considered assumes radial flow of a non-newtonian fluid and a slightly compressible Newtonian fluid through porous media. It is assumed that the reservoir is homogeneous, isotropic and of a constant thickness. The shape of the reservoir is cylindrical with finite outer radius. The non-newtonian fluid is injected through a well in the center of the field. The fluid is considered to be non-newtonian pseudoplastic which obeys the power law. The Newtonian fluid possesses a constant viscosity, as usually considered in well test analysis. It is also assumed piston-like of the Newtonian fluid by the non-newtonian fluid. Figure 2 sketches the composite reservoir under consideration. transition period. Figure 3 illustrates such situation for different values of n. t D *P D ' 1 n 1 0, , , , , E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 1.E+07 1.E+08 1.E+09 1.E+ 2 t DNN Figure 3 Behavior Newtonian dimensionless pressure derivative for r a = 200 ft r w 1 r a = r a (t) NON-NEWTONIAN REGION r e The curves shown in Figure 3 were generated using the same input information given in the second example of Table 1. Notice than for n = 1, two different plateaus are observed since two different mobilities are dealt with. The smaller the n, the longer the time required to get the horizontal radial-flow line during the Newtonian zone. NEWTONIAN REGION ( = CONSTANT) 3. FUNDAMENTAL EQUATIONS The dimensionless pressure, P D, dimensionless time, t D, and dimensionless radius, r D, for each region are expressed as: Figure 2 Composite non-newtonian/newtonian radial reservoir Martínez, Escobar and Montealegre (20) solved numerically Equation 2 using the finite-difference approximation with the initial and boundary conditions normally used in well test analysis. Their results agree quite well with those reported by Ikoku and Ramey (1979b). Since the pressure diffuses through a porous medium saturated with a non-newtonian fluid, the pressure derivative has certain degree of inclination as the flow behavior index reduces its value. Once, the pressure diffusion reaches to the Newtonian zone, the pressure derivative forms a plateau, as expected, after an obvious (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) 36 CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20
5 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR A WELL IN A RADIAL COMPOSITE RESERVOIR 4. CHARACTERISTIC POINTS AND LINES The formulation of the equations follows the philosophy of the TDS Technique, introduced by Tiab (1995). It means, several specific regions on the pressure and pressure derivative behavior are dealt with: 2). The governing pressure equation during nonnewtonian radial flow can be express by: (16) 3). The skin factor, s1, can be obtained by dividing Equation 16 with Equation 12. 1). According to Katime-Meindl and Tiab (2001), the dimensionless equation for radial-flow regime derived in the non-newtonian region without considering storage effects is: () The value of this derivative is: (11) (17) 4). The radius of the injected non-newtonian fluid bank is calculated using the following correlation (not valid for n = 1), obtained from reading the time at which the pressure derivative has its maximum value: (12) Combination of Equations and 12 leads to obtain: (18) Lund and Ikoku (1981) found that the radius of the non-newtonian fluid bank can be found using the radius investigation equation proposed by Ikoku and Ramey (1979): (13) Substituting Equation 4 into Equation 13 and solving for k1 yields: (19) Where t is the end time of the straight line found on a non-newtonian Cartesian graph of P vs.t1-n/3-n. 5). For the Newtonian region the permeability and skin factor were presented by Tiab (1995) as: (20) (14) (21) Where is the slope of the pressure derivative curve on the non-newtonian region and is defined as: 6). Intercept of the non-newtonian/newtonian radial flow lines. The infinite-acting dimensionless pressure derivative is given by: (15) (22) CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec
6 FREDDY-HUMBERTO ESCOBAR, JAVIER-ANDRÉS MARTÍNEZ AND MATILDE MONTEALEGRE-MADERO Combination of Equations 22 and 12 will result in: Table 1 Reservoir and fluid data for the examples Rearranging, (23) (24) Replacing the dimensionless quantities and solving for k 1 : (25) Where t in_nn is the time of intersection of the non- Newtonian and Newtonian radial lines. TDS has been always applied to either drawdown or buildup tests, Tiab (1993); therefore, application of this work to fall-off tests seems to have no problem as long as superposition do not affect the behavior of the pressure derivative. For variable injection rate time superposition should be applied; but, this is out of scope of this paper. 5. EXAMPLES Example 1 An constant-rate injection test for a well in a closed reservoir was generated by Lund and Ikoku (1981) with the data given in Table 1 and reported in Figure 4. It is required to estimate the permeability and the skin factor in each area and the radius of injected non-newtonian fluid bank. t* P' and P, (psi) PARAMETER EXAMPLE 1 EXAMPLE 2 P R, Psi r e, ft r w, ft 0,33 0,25 h, ft 16,4 20, % 0,2 0,15 k, md q, Bbl/D B, rb/stb 1,0 1,1 c t, 1/Psi 6,89x -6 6,5x -6 r a, ft 131,2 400 H, cp*s n-1 20 N, cp 3 5 n 0,6 0,5 0 ( P) r1 P = 1 541,69. psi r (t* P) r1 1 = 5,45. psi psi r t, (hr) ( P) P r2 2 = 901,5. 5 psi psi Figure 4 Pressure and Pressure derivative for example 1 First, is evaluated with Equation 15 and the non- Newtonian effective fluid permeability is estimated with Equation 14. r (t* P) r2 2 = 39 39,02. psi psi t r1 tr1 = 0,3 0.3hr t rin_nn _ NN = 00, hr hr t t M = 11,3. 3 hr hr t r2 = t 0 r 2 0hr hr 0,0001 0,001 0,01 0, r Solution. The log-log plot of pressure and pressure derivative against injection time is given in Figure 4. From that plot the following information was read: t r1 = 0,3 hr P r1 = 541,54 psi (t* P ) r1 = 5,45 psi t r2 = 120 hr P r2 = 991,5 psi (t* P ) r2 = 39,02 psi t M = 1,3 hr t irn_nn = 0,0008 hr 38 CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20
7 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR A WELL IN A RADIAL COMPOSITE RESERVOIR Equation 4 is used to find the effective viscosity, then, the skin factor in the non-newtonian region is found with Equation 17, Example 2 Another injection test was simulated using the information from Table 1. Pressure and pressure derivative data are reported in Figure 5. It is required to estimate permeability and the skin factor in each area and the radius of non-newtonian fluid bank. Solution. The following information was read from Figure 5: tr1 = 0,5 hr Pr1 = 172,52 psi (t* P )r1 = 36,31 psi tr2 = 120 hr Pr2 = 380,898 psi (t* P )r2 = 27,87 psi Parameter G is estimated with Equation 3. This value is used in Equation 18 to find the non-newtonian fluid bank, tirn_nn = 0,17 hr tm = 3,6 hr As for the former example, is evaluated with Equation 15 and the non-newtonian effective fluid permeability is estimated with Equation P r 2= 380, psi psi ( P) t* P' and P, (psi) r2 Equations 20 and 21 are used to estimate permeability and skin factor of the Newtonian zone: 172,52 psi P r1= psi ( P) r1 0 0 P r1= 36, psi psi (t* P) t* P r 2 = 27, psi psi t*(t* P) r1 r2 =00,5 hr ttrr11.5 hr trin_nn 0,17 hr trin _= NN 0.17 hr 120 hr hr ttr2r 2 = 120 ttmm = 3,6 3.6 hr hr 0,01 0, t, (hr) Figure 5 Pressure and Pressure derivative for example 2 Equation 25 is used to re-estimate non-newtonian effective fluid permeability: Lund and Ikoku (1981) obtained k1 = 0,64 md and ra = 116,5 ft using conventional analysis. CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20 Effective viscosity is calculated with Equation 4, then, the skin factor in the non-newtonian region is found with Equation 17, 39
8 FREDDY-HUMBERTO ESCOBAR, JAVIER-ANDRÉS MARTÍNEZ AND MATILDE MONTEALEGRE-MADERO 6. ANALISIS OF RESULTS The first example (Example 1 in Section 5) was also analyzed by Lund and Ikoku (1981), and we obtained results in close agreement with the values used by Lund and Ikoku (1981) to generate the synthetic test. On the other hand, the synthetic problem, second example (Example 2 in Section 5) also indicated that the formulated methodology in this work provides results which match well the input data and therefore is recommended to be applied. 7. CONCLUSION Equation 3 is used to find G. This value is used in Equation 18 to find the non-newtonian fluid bank, New expressions, providing very good results for the synthetic examples considered, were introduced to estimate permeability, skin factor and non-newtonian fluid bank radius by means of TDS technique for a composite radial non-newtonian/newtonian reservoir. The applications did not take into account wellbore storage effects, and did not consider variable-rate injection tests. The methodology can be applied to falloff test. Permeability and skin factor of the Newtonian zone is, respectively, estimated with Equations 20 and 21, ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors gratefully thanks Universidad Surcolombiana for providing support to the completion of this work. REFERENCES Equation 25 is used to verify the non-newtonian effective fluid permeability, Ikoku, C. U. (1979). Practical Application of Non-Newtonian Transient Flow Analysis. Paper SPE 8351 presented at the SPE 64th Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Las Vegas, NV, Sept Ikoku, C. U., & Ramey, H. J. Jr., (1979a). Transient Flow of Non-Newtonian Power-law fluids Through in Porous Media. US DOE Publication, (SAN),/ Ikoku, C. U., & Ramey, H. J. Jr. (1979b). Transient Flow of Non-Newtonian Power-law fluids Through in Porous Media, Soc. Pet. Eng. J., June. 40 CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20
9 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR A WELL IN A RADIAL COMPOSITE RESERVOIR Ikoku, C. U., & Ramey, H. J. Jr. (1979c). Wellbore Storage and Skin Effects During the Transient Flow of Non- Newtonian Power-law fluids Through in Porous Media. Soc. Pet. Eng. J., Katime-Meindl, I., & Tiab, D. (2001). Analysis of Pressure Transient Test of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Infinite Reservoir and in the Presence of a Single Linear Boundary by the Direct Synthesis Technique. Paper SPE prepared for presentation at the 2001 SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition held in New Orleans, Louisiana, 30 Sept. 3 Oct. Lund, O., & Ikoku, C. U. (1981). Pressure Transient Behavior of Non-Newtonian/Newtonian Fluid Composite Reservoirs. Soc. of Petrol. Eng. of AIME, , April. Martínez, J. A., Escobar, F. H., & Montealegre-M., M. (20). Numerical Solution for a Radial Composite Reservoir Model with a No-Newtonian/Newtonian Interface. Sent to revista Dyna to request publication. Odeh, A. S., & Yang, H. T. (1979). Flow of non-newtonian Power-Law Fluids Through in Porous Media, Soc. Pet. Eng. J., , June. Savins, J. G. (1969). Non-Newtonian flow Through in Porous Media. Ind. Eng. Chem. 61 (): Tiab, D. (1993). Analysis of Pressure and Pressure Derivative without Type-Curve Matching: 1- Skin and Wellbore Storage. J. of Petrol. Science and Eng., 12: Tiab, D. (1993). Analysis of Pressure and Pressure Derivative without Type-Curve Matching: 1- Skin and Wellbore Storage. Paper SPE 25423, Production Operations Symposium held in Oklahoma City, OK Tiab, D. (1995). Analysis of Pressure Derivative without Type-Curve Matching: Vertically Fractured Wells in Closed Systems. J. of Petrol., Science and Eng., 11 (4): Vongvuthipornchai, S., & Raghavan, R. (1987). Well Test Analysis of Data Dominated by Storage and Skin: Non- Newtonian Power-Law Fluids. SPE Formation Evaluation, December, CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec
10 FREDDY-HUMBERTO ESCOBAR, JAVIER-ANDRÉS MARTÍNEZ AND MATILDE MONTEALEGRE-MADERO NOMENCLATURE B Oil formation factor, rb/stb c t System total compressibility, 1/psi h Formation thickness, ft H Consistency (Power-law parameter), cp*s n-1 k Permeability, md n Flow behavior index (power-law parameter) p Pressure, psi P R Reservoir Pressure, psi q Flow/injection rate, STB/D r Radius, ft s Skin Factor t Time, hr t* p Pressure derivative, psi GREEK Slope Pressure derivative non-newtonian Region Δ Change, drop (X) Gamma Function f Porosity, Fraction m Viscosity, cp m eff Effective viscosity for power-law fluids, cp*(s/ft) n-1 l Mobility, md/cp l eff Effective mobility for power-law fluids, md/ cp*(s/ft) n-1 SUFFICES 1 Non-Newtonian region 2 Newtonian region a Location of the non-newtonian fluid front app Apparent D Dimensionless e External eff Effective N Newtonian NN Non-Newtonian w Wellbore 42 CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro - Vol. 4 Num. 2 Dec. 20
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia
 CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar, Freddy-Humberto; Martínez, Javier-Andrés; Montealegre-M., Matilde PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar, Freddy-Humberto; Martínez, Javier-Andrés; Montealegre-M., Matilde PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE
APPLICATION OF TDS TECHNIQUE TO MULTIPHASE FLOW
 Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro APPLICATION OF TDS TECHNIQUE TO MULTIPHASE FLOW Freddy-Humberto Escobar 1 * and Matilde Montealegre-M. 2 * 1,2 Universidad Surcolombiana, Programa de Ingeniería de Petróleos,
Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro APPLICATION OF TDS TECHNIQUE TO MULTIPHASE FLOW Freddy-Humberto Escobar 1 * and Matilde Montealegre-M. 2 * 1,2 Universidad Surcolombiana, Programa de Ingeniería de Petróleos,
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia
 CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar, Freddy-Humberto; Montealegre-M., Matilde A complementary conventional analysis for channelized reservoirs
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar, Freddy-Humberto; Montealegre-M., Matilde A complementary conventional analysis for channelized reservoirs
CONVENTIONAL PRESSURE ANALYSIS FOR NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS
 Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro CONVENTIONAL PRESSURE ANALYSIS FOR NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS WITH TRANSITION PERIOD BEFORE AND AFTER THE RADIAL FLOW REGIME Freddy-Humberto Escobar 1*, Javier-Andrés Martinez
Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro CONVENTIONAL PRESSURE ANALYSIS FOR NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS WITH TRANSITION PERIOD BEFORE AND AFTER THE RADIAL FLOW REGIME Freddy-Humberto Escobar 1*, Javier-Andrés Martinez
PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR ASYMMETRY FINITE-CONDUCTIVITY FRACTURED VERTICAL WELLS
 Revista Fuentes: El Reventón Energético Vol. 15 Nº 2 de 2017 - Jul/Dic - pp 71/78 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR ASYMMETRY FINITE-CONDUCTIVITY FRACTURED VERTICAL WELLS Freddy Humberto Escobar
Revista Fuentes: El Reventón Energético Vol. 15 Nº 2 de 2017 - Jul/Dic - pp 71/78 PRESSURE AND PRESSURE DERIVATIVE ANALYSIS FOR ASYMMETRY FINITE-CONDUCTIVITY FRACTURED VERTICAL WELLS Freddy Humberto Escobar
Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions
 SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
Average reservoir pressure is used for characterizing a reservoir, computing oil in place, performing reservoir
 Application of the TDS Technique for Determining the Average Reservoir Pressure for Vertical Wells in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs Miguel-D. Molina 1, Freddy-Humberto Escobar *2, Matilde Montealegre
Application of the TDS Technique for Determining the Average Reservoir Pressure for Vertical Wells in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs Miguel-D. Molina 1, Freddy-Humberto Escobar *2, Matilde Montealegre
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia
 CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar, Freddy-Humberto; Montealegre-M., Matilde Effect of well stimulation on the skin factor in elongated
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar, Freddy-Humberto; Montealegre-M., Matilde Effect of well stimulation on the skin factor in elongated
Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well
 UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
SPE Uncertainty in rock and fluid properties.
 SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion.
 Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks
 SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions
 . Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
. Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VARIATION OF FLUID IN BOUNDED CIRCULAR RESERVOIRS UNDER THE CONSTANT PRESSURE OUTER BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Chapter Seven. For ideal gases, the ideal gas law provides a precise relationship between density and pressure:
 Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
SPE Copyright 2003, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc.
 SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
Non-Darcy Skin Effect with a New Boundary Condition
 International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
Rate Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Pressure Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Factors that affect pressure distribution of horizontal wells in a layered reservoir with simultaneous gas cap and bottom water drive
 Vol. 6(1), pp. 1-9, January, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JPGE 2013.0180 Article Number: 3C2A1DC50083 ISSN 2I41-2677 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jpge
Vol. 6(1), pp. 1-9, January, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JPGE 2013.0180 Article Number: 3C2A1DC50083 ISSN 2I41-2677 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jpge
Presentation of MSc s Thesis
 Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Oil and Gas Well Performance
 Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS
 THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals COPYRIGHT. Introduction
 Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
The technological development of the oil industry around the globe has resulted in an increase in
 HORIZONTAL PERMEABILITY DETERMINATION FROM THE ELLIPTICAL FLOW REGIME OF HORIZONTAL WELLS Freddy-Huberto Escobar* 1, Oscar-Fernando Muñoz* 1 and Jairo-Antonio Sepúlveda* 1 1 Universidad Surcolobiana, Prograa
HORIZONTAL PERMEABILITY DETERMINATION FROM THE ELLIPTICAL FLOW REGIME OF HORIZONTAL WELLS Freddy-Huberto Escobar* 1, Oscar-Fernando Muñoz* 1 and Jairo-Antonio Sepúlveda* 1 1 Universidad Surcolobiana, Prograa
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
XYZ COMPANY LTD. Prepared For: JOHN DOE. XYZ et al Knopcik 100/ W5/06 PAS-TRG. Dinosaur Park Formation
 All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
Dimensionless Wellbore Storage Coefficient: Skin Factor: Notes:
 This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
SPE MS. Copyright 2014, Society of Petroleum Engineers
 SPE-168966-MS Modeling Analysis of Transient Pressure and Flow Behavior at Horizontal Wells with Multi-Stage Hydraulic Fractures in Shale Gas Reservoirs Cong Wang, Colorado School of Mines and Yu-Shu Wu,
SPE-168966-MS Modeling Analysis of Transient Pressure and Flow Behavior at Horizontal Wells with Multi-Stage Hydraulic Fractures in Shale Gas Reservoirs Cong Wang, Colorado School of Mines and Yu-Shu Wu,
Declining productivity in geothermal wells as a function of the damage effect
 GEOFÍSICA INTERNACIONAL (2012) 51-4: 339-348 Declining productivity in geothermal wells as a function of the damage effect Alfonso Aragón Aguilar *, Georgina Izquierdo Montalvo, Víctor Arellano Gómez,
GEOFÍSICA INTERNACIONAL (2012) 51-4: 339-348 Declining productivity in geothermal wells as a function of the damage effect Alfonso Aragón Aguilar *, Georgina Izquierdo Montalvo, Víctor Arellano Gómez,
ENEL. ENEL - Gruppo Minerario Larderello, Italy. At present our model considers a non-penetrating wellbore as it will
 PROGRESS REPORT ON A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A PARALLELEPIPED RESERVOIR WITH NO PENETRATING WELLBORE AND MIXED BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ENEL A. Barelli and G. Manetti Centro Ricerca Geotermica, Pisa, Italy R.
PROGRESS REPORT ON A MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF A PARALLELEPIPED RESERVOIR WITH NO PENETRATING WELLBORE AND MIXED BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ENEL A. Barelli and G. Manetti Centro Ricerca Geotermica, Pisa, Italy R.
Inflow Performance 1
 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
An approximate analytical solution for non-darcy flow toward a well in fractured media
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 3, 1023, 10.1029/2001WR000713, 2002 An approximate analytical solution for non-arcy flow toward a well in fractured media Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences ivision, Lawrence
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 3, 1023, 10.1029/2001WR000713, 2002 An approximate analytical solution for non-arcy flow toward a well in fractured media Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences ivision, Lawrence
Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot
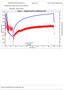 BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL. A Thesis ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL
 TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT
 THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT L. S. Mannon Atlantic Richfield Co. 1860 Lincoln Suite 501 Denver, Colorado 80295 and P. G. Atkinson Union Oil Co. P. 0. Box 6854 2099
THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT L. S. Mannon Atlantic Richfield Co. 1860 Lincoln Suite 501 Denver, Colorado 80295 and P. G. Atkinson Union Oil Co. P. 0. Box 6854 2099
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi
 A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
READ THIS PAGE COMPLETELY BEFORE STARTING
 READ THIS PAGE COMPLETELY BEFORE STARTING Exam Submission: Step 1: You are to enter your results for Problems 1-10 in e-campus (Dr. SEIDEL will provide instructions). Step 2: You are to submit a scanned
READ THIS PAGE COMPLETELY BEFORE STARTING Exam Submission: Step 1: You are to enter your results for Problems 1-10 in e-campus (Dr. SEIDEL will provide instructions). Step 2: You are to submit a scanned
Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media
 Fluid Structure Interaction VII 109 Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media A. J. Mahmood Department of Chemical Industries, Al-Anbar Technical Institute, Iraq Abstract One of the mathematical
Fluid Structure Interaction VII 109 Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media A. J. Mahmood Department of Chemical Industries, Al-Anbar Technical Institute, Iraq Abstract One of the mathematical
Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
Coalbed Methane Properties
 Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
J. A. Acuna, I. Ershaghi and Y. C. Yortsos
 PROCEEDINGS, Seventeenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 1992 SGY-7l-141 FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE TRANSIENTS IN THE GEYSERS GEOTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Seventeenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 29-31, 1992 SGY-7l-141 FRACTAL ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE TRANSIENTS IN THE GEYSERS GEOTHERMAL
Introduction to Well Stimulation
 Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY
 GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
SPE Copyright 1997, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Inc.
 SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
SPE Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow
 SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured Reservoirs
 Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate. Peter Yue Liang A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate by Peter Yue Liang A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate by Peter Yue Liang A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia
 CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Contreras, Oscar-M.; Corzo, Reinel; Saavedra, Néstor-F.; Calderón, Zuly-H. Methodology to calculate the fracture
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Contreras, Oscar-M.; Corzo, Reinel; Saavedra, Néstor-F.; Calderón, Zuly-H. Methodology to calculate the fracture
Algebra I Aim: How do we determine the equation of a function from its graph? HW: "Vacations" Worksheet
 Algebra I HW: "Vacations" Worksheet DO NOW 1) Name three points on the line graphed below Nombre tres puntos en la línea graficada por debajo 2) Write the equation (function rule) for the line Escribir
Algebra I HW: "Vacations" Worksheet DO NOW 1) Name three points on the line graphed below Nombre tres puntos en la línea graficada por debajo 2) Write the equation (function rule) for the line Escribir
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESERVOIR PRODUCTIVITY AND PORE PRESSURE DROP
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESERVOIR PRODUCTIVITY AND PORE PRESSURE DROP Musaed N. J. Al-Awad Petroleum Eng. Dept, College of Eng., King Saud University, ABSTRACT The significance of permeability sensitivity
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESERVOIR PRODUCTIVITY AND PORE PRESSURE DROP Musaed N. J. Al-Awad Petroleum Eng. Dept, College of Eng., King Saud University, ABSTRACT The significance of permeability sensitivity
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering. Texas A&M University. Lecture 07: Wellbore Phenomena
 Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Before beginning, I would like to acknowledge the amazing contributions of Ken Nolte. I suspect that the origins of most of our discussion during
 1 Before beginning, I would like to acknowledge the amazing contributions of Ken Nolte. I suspect that the origins of most of our discussion during this workshop can be traced to Dr. Nolte. He was a true
1 Before beginning, I would like to acknowledge the amazing contributions of Ken Nolte. I suspect that the origins of most of our discussion during this workshop can be traced to Dr. Nolte. He was a true
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Effect of Pressure-Dependent Natural-Fracture Permeability on Shale-Gas Well Production
 Effect of Pressure-Dependent Natural-Fracture Permeability on Shale-Gas Well Production Erdal Ozkan Colorado School of Mines Based on SPE159801, by, Cho, Y., Apaydin, O. G., and Ozkan, E. 1 Motivations
Effect of Pressure-Dependent Natural-Fracture Permeability on Shale-Gas Well Production Erdal Ozkan Colorado School of Mines Based on SPE159801, by, Cho, Y., Apaydin, O. G., and Ozkan, E. 1 Motivations
Imperial College London
 Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
National Exams May 2016
 National Exams May 2016 98-Pet-A3, Fundamental Reservoir Engineering 3 hours duration NOTES: I. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with tile answer
National Exams May 2016 98-Pet-A3, Fundamental Reservoir Engineering 3 hours duration NOTES: I. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with tile answer
AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST. A Thesis ZIWENJUE YE
 AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST A Thesis by ZIWENJUE YE Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST A Thesis by ZIWENJUE YE Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildup Test Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildup Test Analysis
Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction
 (Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
WATER INFLUX. Hassan S. Naji, Professor,
 WATER INFLUX Many reservoirs are bound on a portion or all of their peripheries by water-bearing rocks called aquifers. The aquifer may be so large compared to the reservoir size as to appear infinite,
WATER INFLUX Many reservoirs are bound on a portion or all of their peripheries by water-bearing rocks called aquifers. The aquifer may be so large compared to the reservoir size as to appear infinite,
Performance Productivity Curves in Geothermal Systems: A Case of Los Humeros, México
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005 Antalya, Turkey, 24-29 April 2005 Performance Productivity Curves in Geothermal Systems: A Case of Los Humeros, México Aragón A. A., Moya S. L. (2) and Izquierdo
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005 Antalya, Turkey, 24-29 April 2005 Performance Productivity Curves in Geothermal Systems: A Case of Los Humeros, México Aragón A. A., Moya S. L. (2) and Izquierdo
COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS. A Thesis VARTIT TIVAYANONDA
 COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS A Thesis by VARTIT TIVAYANONDA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS A Thesis by VARTIT TIVAYANONDA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Predicting the Dead Oil Viscosity of Reservoir Fluids: a case study of the Niger Delta
 Predicting the Dead Oil Viscosity of Reservoir Fluids: a case study of the Niger Delta Abstract Kamilu Folorunsho Oyedeko 1* and Ubong William Ulaeto 1 1.Chemical & Polymer Engineering, Lagos State University,
Predicting the Dead Oil Viscosity of Reservoir Fluids: a case study of the Niger Delta Abstract Kamilu Folorunsho Oyedeko 1* and Ubong William Ulaeto 1 1.Chemical & Polymer Engineering, Lagos State University,
American University of Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, Ras Al Khaimah
 Article Open Access DETERMINATION OF INFLOW PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP FOR A VERTICAL WELL IN NATU- RALLY FRACTURED OIL RESERVOIRS: NUMERICAL SIMULATION STUDY Reda Abdel Azim, Melissa Ramirez, and Mohammad
Article Open Access DETERMINATION OF INFLOW PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP FOR A VERTICAL WELL IN NATU- RALLY FRACTURED OIL RESERVOIRS: NUMERICAL SIMULATION STUDY Reda Abdel Azim, Melissa Ramirez, and Mohammad
Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE
 Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE 143613 Outline P-T diagram of Gas reservoirs Diffusion equation linearization using gas
Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE 143613 Outline P-T diagram of Gas reservoirs Diffusion equation linearization using gas
Two Questions and Three Equations on Distance of Investigation
 Two Questions and Three Equations on Distance of Investigation Hamed Tabatabaie and Louis Mattar, IHS Markit, August 2017 The distance of investigation concept is often used to answer two different types
Two Questions and Three Equations on Distance of Investigation Hamed Tabatabaie and Louis Mattar, IHS Markit, August 2017 The distance of investigation concept is often used to answer two different types
Simulation of Pressure Transient Behavior for Asymmetrically Finite-Conductivity Fractured Wells in Coal Reservoirs
 Transp Porous Med (2013) 97:353 372 DOI 10.1007/s11242-013-0128-z Simulation of Pressure Transient Behavior for Asymmetrically Finite-Conductivity Fractured Wells in Coal Reservoirs Lei Wang Xiaodong Wang
Transp Porous Med (2013) 97:353 372 DOI 10.1007/s11242-013-0128-z Simulation of Pressure Transient Behavior for Asymmetrically Finite-Conductivity Fractured Wells in Coal Reservoirs Lei Wang Xiaodong Wang
MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT
 MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT Osamah A. Al-Omair and Richard L. Christiansen Petroleum Engineering Department, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT A
MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT Osamah A. Al-Omair and Richard L. Christiansen Petroleum Engineering Department, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT A
Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA)
 PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies.
 The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies. M. salarieh, A. Doroudi, G.A. Sobhi and G.R. Bashiri Research Inistitute of petroleum Industry. Key words: Capillary pressure curve,
The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies. M. salarieh, A. Doroudi, G.A. Sobhi and G.R. Bashiri Research Inistitute of petroleum Industry. Key words: Capillary pressure curve,
IN SITU, 20(2), (1996)
 -. IN SITU, 20(2), 115-135 (1996) GELANT PLACEMENT IN ANISOTROPIC FLOW SYSTEMS Mei Ye and Randall S Seright New Mexico Petroleuin Recovery Research Center New Mexico Institute of Mmuig and Technology Socorro.
-. IN SITU, 20(2), 115-135 (1996) GELANT PLACEMENT IN ANISOTROPIC FLOW SYSTEMS Mei Ye and Randall S Seright New Mexico Petroleuin Recovery Research Center New Mexico Institute of Mmuig and Technology Socorro.
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics
 Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
Novel Approaches for the Simulation of Unconventional Reservoirs Bicheng Yan*, John E. Killough*, Yuhe Wang*, Yang Cao*; Texas A&M University
 SPE 168786 / URTeC 1581172 Novel Approaches for the Simulation of Unconventional Reservoirs Bicheng Yan*, John E. Killough*, Yuhe Wang*, Yang Cao*; Texas A&M University Copyright 2013, Unconventional Resources
SPE 168786 / URTeC 1581172 Novel Approaches for the Simulation of Unconventional Reservoirs Bicheng Yan*, John E. Killough*, Yuhe Wang*, Yang Cao*; Texas A&M University Copyright 2013, Unconventional Resources
National yams May Pet-B2, Nahiral Gas Engineering. 3 hours duration NOTES:
 ational yams May 2015 98-Pet-B2, ahiral Gas Engineering 3 hours duration OTES: 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with the answer paper, a clear
ational yams May 2015 98-Pet-B2, ahiral Gas Engineering 3 hours duration OTES: 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with the answer paper, a clear
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Sring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildu Test Analysis Lee
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Sring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildu Test Analysis Lee
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
results are usually interpreted on the basis of forward type curvematching or high gas content liquids.
 CAPACITIVE PERTURBATIONS IN WELL INTERFERENCE TESTING by Gunnar Bodvarsson, School of Oceanography, Oregon State University. Corvall is, Oregon 97331. Introduction Conventional well interference testing
CAPACITIVE PERTURBATIONS IN WELL INTERFERENCE TESTING by Gunnar Bodvarsson, School of Oceanography, Oregon State University. Corvall is, Oregon 97331. Introduction Conventional well interference testing
SLOWNESS SURFACE CALCULATION FOR DIFFERENT MEDIA USING THE SYMBOLIC MATHEMATICS LANGUAGE MAPLE
 EARTH SCIENCES RESEARCH JOURNAL Earth Sci. Res. J. Vol. 8, No. 1 (Dec. 004) : 63-67 SLOWNESS SURFACE CALCULATION FOR DIFFERENT MEDIA USING THE SYMBOLIC MATHEMATICS LANGUAGE MAPLE Miguel Duarte 1, Carlos
EARTH SCIENCES RESEARCH JOURNAL Earth Sci. Res. J. Vol. 8, No. 1 (Dec. 004) : 63-67 SLOWNESS SURFACE CALCULATION FOR DIFFERENT MEDIA USING THE SYMBOLIC MATHEMATICS LANGUAGE MAPLE Miguel Duarte 1, Carlos
Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University
 SPE 5960 Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University Copyright 0, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was
SPE 5960 Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University Copyright 0, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was
Assuming that the well s productivity index is constant, the oil flow rate can be calculated as follows:
 SPE 404 New Inflow Performance Relationship for Solution-Gas Drive Oil Reservoirs Mohamed Elias, SPE, H. Ahmed El-Banbi, SPE, K.A. Fattah, and El-Sayed Ahmed Mohamed El-Tayeb, SPE, Cairo University Copyright
SPE 404 New Inflow Performance Relationship for Solution-Gas Drive Oil Reservoirs Mohamed Elias, SPE, H. Ahmed El-Banbi, SPE, K.A. Fattah, and El-Sayed Ahmed Mohamed El-Tayeb, SPE, Cairo University Copyright
2. Standing's Method for Present IPR
 Koya University College of Engineering School of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department Petroleum Production Engineering II Predicting Present and Future IPRs (Standing Method).
Koya University College of Engineering School of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department Petroleum Production Engineering II Predicting Present and Future IPRs (Standing Method).
Analytical Coupled Axial and Radial Productivity Model for Steady-State Flow in Horizontal Wells. Thormod Johansen*, Lesley James, Jie Cao
 Int. J. Petroleum Engineering, Vol. x, No. x, 1 19 1 Analytical Coupled Axial and Radial Productivity Model for Steady-State Flow in Horizontal Wells Thormod Johansen*, Lesley James, Jie Cao Engineering
Int. J. Petroleum Engineering, Vol. x, No. x, 1 19 1 Analytical Coupled Axial and Radial Productivity Model for Steady-State Flow in Horizontal Wells Thormod Johansen*, Lesley James, Jie Cao Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING. December 14-15,1977
 SGPTR258 PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING December 1415,1977 *Conducted under Subcontract No. 16735 with Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Universityof California, sponsored by the
SGPTR258 PROCEEDINGS THIRD WORKSHOP GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ENGINEERING December 1415,1977 *Conducted under Subcontract No. 16735 with Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Universityof California, sponsored by the
Generalised Separable Solution of Double Phase Flow through Homogeneous Porous Medium in Vertical Downward Direction Due to Difference in Viscosity
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 932-9466 Vol. 8, Issue (June 203), pp. 305-37 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Generalised Separable Solution
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 932-9466 Vol. 8, Issue (June 203), pp. 305-37 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Generalised Separable Solution
Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization
 P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
SCA : A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP
 SCA2003-53: A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
SCA2003-53: A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Lecture:
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Lecture:
Waterflooding Performance of Communicating Stratified Reservoirs With Log-Normal Permeability Distribution
 Waterflooding Performance of Communicating Stratified Reservoirs With Log-Normal Permeability Distribution Noaman El-Khatib, SPE, King Saud U. Summary An analytical solution is developed for waterflooding
Waterflooding Performance of Communicating Stratified Reservoirs With Log-Normal Permeability Distribution Noaman El-Khatib, SPE, King Saud U. Summary An analytical solution is developed for waterflooding
Referências Bibliográficas
 68 Referências Bibliográficas Thompson, R.L., Souza Mendes, P.R., Naccache, M.F., A new constitutive equation and its performance in contraction flows, Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 86,
68 Referências Bibliográficas Thompson, R.L., Souza Mendes, P.R., Naccache, M.F., A new constitutive equation and its performance in contraction flows, Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 86,
Well Test Interpretation
 Well Test Interpretation Schlumberger 2002 All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transcribed in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
Well Test Interpretation Schlumberger 2002 All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transcribed in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CAPILLARY PRESSURE AND RESISTIVITY INDEX
 SCA2005-4 /2 ELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CAPILLAY PESSUE AND ESISTIVITY INDEX Kewen Li *, Stanford University and Yangtz University and Wade Williams, Core Lab, Inc. * Corresponding author This paper was prepared
SCA2005-4 /2 ELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CAPILLAY PESSUE AND ESISTIVITY INDEX Kewen Li *, Stanford University and Yangtz University and Wade Williams, Core Lab, Inc. * Corresponding author This paper was prepared
Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques
 1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia
 CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar Remolina, Juan-Carlos-M.; Coronado Parra, Carlos-Alberto Development of a super accelerated successive
CT&F Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro ISSN: 0122-5383 ctyf@ecopetrol.com.co ECOPETROL S.A. Colombia Escobar Remolina, Juan-Carlos-M.; Coronado Parra, Carlos-Alberto Development of a super accelerated successive
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering
 Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 70 (2010) 327 333 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/petrol Research
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 70 (2010) 327 333 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/petrol Research
PORE PRESSURE EVOLUTION AND CORE DAMAGE: A COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS APPROACH
 SCA211-41 1/6 PORE PRESSURE EVOLUTION AND CORE DAMAGE: A COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS APPROACH I. Zubizarreta, M. Byrne, M.A. Jimenez, E. Roas, Y. Sorrentino and M.A. Velazco. Senergy. Aberdeen, United
SCA211-41 1/6 PORE PRESSURE EVOLUTION AND CORE DAMAGE: A COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS APPROACH I. Zubizarreta, M. Byrne, M.A. Jimenez, E. Roas, Y. Sorrentino and M.A. Velazco. Senergy. Aberdeen, United
