arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 16 Apr 2016
|
|
|
- Clyde Joshua Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Th Cauchy problm for a combuson modl n porous mda J. C. da Moa M. M. Sanos. A. Sanos arxv: v [mah.ap] 6 Apr 6 Absrac W prov h xsnc of a global soluon o h Cauchy problm for a nonlnar racon-dffuson sysm coupld wh a sysm of ordnary dffrnal quaons. Th sysm modls h propagaon of a combuson fron n a porous mdum wh wo layrs, as drvd by J. C. da Moa and S. Schcr n Combuson frons n a porous mdum wh wo layrs, Journal of Dynamcs and Dffrnal Equaons, 8(3) (6). For h parcular cas, whn h ful concnraons n boh layrs ar knownfuncons, hcauchyproblmwas solvdbyj. C. damoaandm. M. Sanos nan applcaon of h monoon rav mhod o a combuson problm n porous mda, Nonlnar Analyss: al World Applcaon, (). For h full sysm, n whch h ful concnraons ar also unknown funcons, w consruc an rav schm ha conans a squnc whch convrgs o a soluon of h sysm, locally n m, undr h condons ha h nal daa ar Höldr connuous, boundd and nonngav funcons. W also show h xsnc of a global soluon, f h nal da ar addonally n h Lbsgu spac L p, for som p (, ). Our proof of h local xsnc rls on a carful analyss on h consrucon of h fundamnal soluon for parabolc quaons oband by h paramrx mhod. In parcular, w show h connuous dpndnc of h fundamnal soluon for parabolc quaons wh rspc o h coffcns of h quaons. To oban h global xsnc, w mploy h mhod of auxlary funcons as usd by O. A. Olnk and S. N. Kruzhkov n Quas-lnar scond-ordr parabolc quaons wh many ndpndn varabls, ussan Mahmacal Survys, 6(5) (96). Furhrmor, for a broad class of racon-dffuson sysms w show ha h non ngav quadran s a posvly nvaran rgon, and, as a consqunc, ha classcal soluons of smlar sysms, wh h racons funcons bng non dcrasng n on unknown and sm-lpschz connuous n h ohr, ar boundd by lowr and uppr soluons for any posv m f so hy ar a m zro. Inroducon W ar manly concrnd wh a spcfc sysm of h yp (u ) α (y )(u ) xx β (y )(u ) x = f (y,u,u ), x, > (.) for h unknowns u, y, wh =,, whr y sasfs an ordnary dfrnal quaon whch can b solvd dpndng on u, and α (y ),β (y ) ar gvn funcons of y, and f (y,u,u ) s a funcon (also gvn) of y, u and u. For fxd y, h quaons (.) ar a sysm of parabolc quaons for u,u coupld by h funcon f. For h full sysm, n h unknowns u,u,y,y, snc y can b xprssd dpndng on u, our sysm can b wrn n h unknowns u,u only, bu wh coffcns dpndng n a pcular way on u,u. In fac, h sysm w shall consdr can b wrn n h form for gvn funcons a, b, f, and F. (u ) a(x, f(u )d) (u ) xx b(x, f(u )d) (u ) x = F (x,u,u, f(u )d) (.) Dparamno d Mamáca, IME-UFG (Insuo d Mamáca Esaísca Unvrsdad Fdral d Goás). Cx. Posal 3, Campus II, Goâna, GO, Brazl. jsus@ufg.br, rasanos@ufg.br Dparamno d Mamáca, IMECC-UNICAMP (Insuo d Mamáca, Esaísca Compuação Cnífca Unvrsdad Esadual d Campnas). ua Sérgo Buarqu d Holanda, 65, Cdad Unvrsára Zfrno Vaz, Campnas, SP, Brazl. msanos@m.uncamp.br J.C. da Moa hanks FAPEG Fundação d Amparo à Psqusa do Esado d Goás, Brazl, for paral suppor of hs work, undr gran # 5/-Unvrsal..A. Sanos hanks CAPES Coordnação d Aprfçoamno d Pssoal d Nívl Supror, Brazl, for fnancal suppor hrough a scholarshp durng hs docora a IMECC-UNICAMP, Brazl, undr projc # /-48-AUXPE 747/.
2 Spcfcally, h funcons α, β and f n (.) ar gvn by whr f(u ) s h Arrhnus funcon λ c α (y ) =, β (y ) = and a b y a b y f (y,u,u ) = b A u d y f(u )( ) q u u (.3) a b y a b y f(u ) = E u, (.4) bng E s a posv consan, and λ,a,b,c,d,a, =,, and q ar posv consans. Th unknown y sasfs h ordnary dffrnal quaon Jon wh quaons (.) w add h nal daa and for gvn funcons u,,y,. Solvng (.5) for y w fnd Subsung (.8) n (.) w oban (.), wh a(x, (y ) = A y f(u ). (.5) u = = u, (.6) y = = y,, (.7) y = y, (x) A f(u)d. (.8) f(u )d) = α (y, (x) A f(u))d ), (.9) and b(x, F (x,u,u, f(u )d) = β (y, (x) A f(u)d ) (.) f(u )d) = f (y, (x) A f(u)d,u,u ). (.) Th sysm formd by h quaons (.) and (.5), wh h consuv funcons (.3) and (.4), modls h propagaon of a combuson fron n a porous mdum wh wo layrs [4]. Th unknowns u and y sands for h mpraur and h ful concnraon, rspcvly, n on layr, and u and y sands for h sam n h ohr layr, and h consans λ,a, c. ar paramrs rlad o h mdum. W rfr o [4] for a dald drvaon of hs modl. In hs papr w solv h Cauchy problm (.), (.3) (.7) (or, quvalnly, (.) jon wh h nal condons (.6), for gvn funcons y, and a,b,f n (.9)-(.), bng α,β,f and f gvn n (.3) and (.4)). Furhrmor, for a broad class of racon-dffuson sysms (s (.4) and (4.)) w show ha h non ngav quadran s a posvly nvaran rgon, and, as a consqunc, ha classcal soluons of smlar sysms, wh h racons funcons bng non dcrasng n on unknown and sm-lpschz connuous n h ohr (s (.5)), ar boundd by lowr and uppr soluons for any posv m f so hy ar a m zro. Sng som noaons, w say ha a funcon s of class C, n a s S d [, ) f has connuous drvavs up o scond ordr wh rspc o x and up o frs ordr wh rspc o for all (x,) S, and dno hs class by C, (S) (or smply by C, ), and of class C α,α n S, for som α (,], f s boundd and Höldr connuous n S wh xponn α wh rspc o x (Lpschz connuous f α = ) and wh xponn α wh rspc o, and dno hs class by Cα,α (S) (or smply by C α,α ),.. a funcon u(x,) s sad o b n C α, α (S), for som α (,], f hr s a consan C > such ha u(x,) C for all (x,) S and u(x, ) u(x, ) C( x x α α ) for all (x, ),(x, ) S. Th spac C α,α (S) s ndowd wh h norm u α, α u C α, α (S) := sup (x,) S u(x,) sup {(x,) (y,s),(x,),(y,s) S} u(x,) u(y,s) x y α s α. For h spac of lpschzan boundd W noc ha h funcon f(s) = E s, s, can b xndd by zro connuously from s > o s =. In fac, d lm k f s ds = for any k =,,,. Dsp h dsconnuy whn s (lm s f(s) = ), hs wll no caus problms n k our analyss bcaus ssnally w wll dal only wh non ngav funcons u, =,, cf. horms and.
3 3 funcons u, dfnd n a s S n d or d [, ), w us h norm u(x) u(y) u := sup S u sup {x y,x,y S} x y. Throughou h papr,j =, wh j. W dno by ϕ h uppr soluon ϕ() = (M β) α β for h Cauchy problm (.), (.6) wh gvn y, sasfyng y y,, whr M = max =, u,, α = max =, { Ab y, a } and β = max =, { d A b }, and, for < T, w dno by,ϕ T h scor (s) of vcor funcons u = (u,u ) : [,T) such ha u (x,) ϕ() (for =, and) for all (x,) [,T). 3 I s asy o chck ha h par of (vcor) funcons û := (,) and ũ := (ϕ,ϕ) s an ordrd par (ordrd n h sns ha û ũ ) of lowr and uppr soluons o h sysm (.) [3, Lmma ]. S Scon 3., p., for dals. Our man rsuls assurng h xsnc of a local and a global soluon o h Cauchy problm (.), (.3) (.7) (or, quvalnly, (.) (.6), (.9) (.)) ar h followng horms: Thorm. (Local soluon). L u, and y, b nonngav, lpschz connuous and boundd funcons n. Thn hr s a posv numbr T such ha h Cauchy problm (.) (.6), (.9) (.) has a soluon u = (u,u ) n h class C, ( (,T]) C, ( [,T]) sasfyng u (x,) ϕ() for all(x,) [,T]. Bsds, faddonallyu, L p () forsomp (, ) hnu L ((,T);L p ()), wh a possbl smallr T. Thorm. (Global soluon). Assum ha h hypohss of Thorm ar n forc, ncludng u, L p () for som p (, ), and, n addon, ha y, C () and (y, ) s boundd. Thn h Cauchy problm (.) (.6), (.9) (.) has a soluon u = (u,u ) n C, ( (, )) C, loc ( [, )) L loc ((, );L p ()) 4 sasfyng u (x,) ϕ(), for all (x,) [, ). Furhrmor, consdrng gnral parabolc opraors L = d a,kl (x,) xk x l k,l= d b,k (x,) xk, (.) whr x = (x,,x d ) d, < < T, d, and h opraor L s unformly parabolc,.. for somconsanλ >, d k,l= a,kl(x,)ξ k ξ l λ ξ forallξ = (ξ,,ξ d ) d andall(x,) Ω T := d (,T), usng h argumns on nvaran rgons gvn n [, 8], whch bascs s h proof of h maxmum prncpl for h ha quaon, w sa and prov Thorm 3 blow, and as a consqunc, Thorm 4. In hs horms w ak (vcor) funcons u = (u,u ) n h class C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) 5 sasfyng h condon lm nf u (x,) (.3) x, (cf. condon K n [8]). Thorm 3. L δ b a posv numbr and c (x,) a boundd funcon n Ω T. If f (x,,u,u ) s a funcon such ha, for som posv numbr ε, sasfs f whn ε < u < and u j > ε, for ach (x,) Ω T (whr j,,j =,) hn h quadran Q = {(u,u ); u,u } s a posvly nvaran rgon o h sysm L (u )c u = f (x,,u,u )δ (.4) for any classcal soluon u = (u,u ) sasfyng h condon (.3). Mor prcsly, undr h abov hypohss, f u = (u,u ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) sasfs (.3) and h nqualy ((L c )u )(x,) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) δ, for all (x,) Ω T, and u(x,) Q for all x d, hn, u(x,) Q for all (x,) d [,T). And as a corollary w oban If g s a boundd funcon dfnd n, g := sup x g(x). 3 If T < and h funcon u s dfnd and connuous n [,T], obvously w can xnd h nqualy u (x,) ϕ() o = T. 4 Hrh rm loc sands for locally n m,.. a funcon u C, loc ( [, )) L loc ((, );Lp ()) fu [,T] C, ( [,T]) L ((,T);L p ()), for any T >. 5 C( d [,T)) dnos h spac of connuous vcor funcons n d [,T). k=
4 4 Thorm 4. L δ b a posv numbr. Suppos ha for ach fxd (x,) Ω T, f (x,,u,u ) s a non dcrasng funcon wh rspc o u j (whr j,,j =,) and, for som posv numbr ε, sasfs h sm-lpschz condon f (x,,su,u ) f (x,,u,u ) c (x,)s, f (x,,u,su ) f (x,,u,u ) c (x,)s (.5) for all s ( ε,) and all ((x,),(u,u )) Ω T, whr c (x,) s som boundd funcon n Ω T, 6 and ls f (x,,u,su ) f (x,,u,u ) δ, f (x,,su,u ) f (x,,u,u ) δ (.6) for all s ( ε,) and all ((x,),(u,u )) Ω T, whr δ s som posv numbr lss han δ.. If û = (û,û ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) s a lowr soluon o h sysm L (u ) = f (x,,u,u ) (.7).. (L û )(x,) f (x,,û (x,),û (x,)), for all (x,) Ω T, and u = (u,u ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) s an uppr soluon o h sysm L (u ) = f (x,,u,u )δ (.8).. L (u )(x,) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) δ for all (x,) Ω T, and such ha u û sasfs h condon (.3), and u (x,) û (x,) for all x d, hn u (x,) û (x,) for all (x,) Ω T.. Analogously, f ũ = (ũ,ũ ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) s an uppr soluon o h sysm (.7),.. (L ũ )(x,) f (x,,ũ (x,),ũ (x,)), for all (x,) Ω T and u = (u,u ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) s a lowr soluon o h sysm L (u ) = f (x,,u,u ) δ (.9).. L (u )(x,) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) δ for all (x,) Ω T, and such ha ũ u sasfs h condon (.3), and ũ (x,) u (x,) for all x d, hn ũ (x,) u (x,) for all (x,) Ω T. Nx w gv h man das o prov horms and. From now on, w rfr o problm (.), (.3) (.7), or, quvalnly, (.) (.6), (.9) (.), smply as problm (.) (.7), or, (.) (.6). W prov Thorm by akng h lm of a subsqunc gvn by h rav schm )(u n ) xx β (y n )(u n ) x = f (y n ) = A y n f(u n (u n ) α (y n (y n (u n,yn ) ) = = (u,,y, ),,u n,u n ) (.) n =,,, sarng from an nal funcon (u,u ) n C, ( [,T]) for som suffcnly small m T >, whr f s h funcon ha concds wh h Arrhnus funcon f(s) = E s for s > and s qual o zro for s, and, f s h funcon f n (.3) xcp for h Arrhnus funcon f whch s rplacd by f. Mor prcsly, w show ha hr s a posv m T, dpndng on h nal daa u,,y, and on h paramrs n h quaons (.. on λ,a, c.), such ha h opraor A(u,u ) = (w,w ), whr (w,w ) solvs (w ) α (y )(w ) xx β (y )(w ) x = f (y,u,u ) (y ) = A y f(u ) (w,y ) = = (u,,y, ), (.) s wll dfnd n som ball Σ := {u = (u,u ) C, ( [,T]); u C,, =,}, >, ( [,T]).. hr xs posv numbr,t such ha A(u) Σ for all u Σ. S Lmma 6. In parcular, h squnc {u n } = {(u n,un )} gvn by A(un ) = A(u n ), sarng from any u Σ, s boundd n h norm,/. Thrfor, by Arzlà-Ascol s horm, hr xss a funcon u = (u,u ) Σ and a subsqunc of {u n }, whch w sll dno by {u n }, ha convrgs o u, unformly on boundd ss n [,T]. To show ha h lm u s a soluon of (.) and (.6), w us h ngral rprsnaon u n (x,) = Γ,n(x,,ξ,)u, (ξ)dξ Γ,n(x,,ξ,) f (y n,u n,u n )(ξ,)dξd, 6 Th condons (.5) ar usd n [6,.g. (.)/ 8.]. (.)
5 5 for h soluon u n of h parabolc quaon (u n ) α (y n )(u n ) xx β (y n )(u n ) x = f (y n,u n,u n ) (.3) occurrng n (.), whr Γ,n dnos h fundamnal soluon of h assocad homognous quaon L,n w =, for L,n := α (y n ) xx β (y n ) x. Now suppos ha h squnc of fundamnal soluons {Γ,n } convrgs, n som appropra sns, o h fundamnal soluon Γ of h also parabolc quaon L w =, for L := α (y ) xx β (y ) x, whn n nds o nfn, whr y = y, (x) A f(u))ds. Thn, havng ha h squnc {u n } s boundd n [,T], for som posv T, and ha convrgs unformly o u C,/ ( [,T]) n boundd ss n [,T], follows from (.) ha u sasfs h ngral quaon u (x,) = Γ (x,,ξ,)u, (ξ)dξ Γ (x,,ξ,) f (y,u,u )(ξ,)dξd, (.4) for (x, ) [, T]. Thus, by sandard argumns, follows ha u C, ( (,T]) C, ( [,T]) and s a soluon of (.) (.6). In Scon w show h connuous dpndnc of fundamnal soluons of parabolc quaons wh rspc o h coffcns of h quaons and, as a consqunc, h convrgnc of {Γ,n } o {Γ }, whn n. To conclud h las assron n Thorm w shall show n Scon 3., wh h hlp of h gnralzd Young s nqualy [6, p. 9] and h fac ha h fundamnal soluon Γ,n s a rgular krnl, unformly wh rspc o n (s Scon 3.), ha h squnc {u n } rmans n Lp for all (,T), wh u n (,) L p unformly boundd wh rspc o and n, f h nal daa u, L p and T s suffcnly small. Thn h assron follows by Banach-Alaoglu s horm. To show ha h oband soluon u = (u,u ) s n h scor,ϕ T, w obsrv ha u = (u,u ) s a soluon of h Cauchy problm { L (w ) (w ) α (y )(w ) xx β (y )(w ) x = f (y,w,w ), x, > (.5) w (x,) = u, (x), x n h unknown w, for y gvn by (.8), and show n Scon 3 ha h funcon f (x,,w,w ) f (y (x,),w,w ) sasfs all h hypohss of Thorm 4, or, mor prcsly, Corollary 4 n Scon 4. L us jus mnon hr ha h racon funcon f n (.5) s ncrasng wh rspc o w j (,j =,, j ). Indd, from (.3) w hav f / w j = q/(a b y ) for all w j. In Subscon 3. w show ha h sysm (.5) fulflls all h hypohss of Corollary 4. To prov Thorm, w l [,T ), < T, o b a maxmal nrval n whch hr xss a soluon u o h problm (.)-(.6) n h spac X T := C, ( (,T )) C, loc ( [,T )) L loc ((,T );L p ()) 7 nrcpdwhhscor,ϕ T,.. f T T and u s a soluon of (.)-(.6) n X T,ϕ T ha concds wh u n [,T ) hn T = T. (Th xsnc of T can b assurd n h sandard way by Zorn s lmma: w consdr h s of pars (u,x T,ϕ T ), such ha u s a soluon of (.)-(.6) n X T,ϕ T, < T, ordrd wh h rlaon (u,x T,ϕ T ) (u,x T,ϕ T ) f T T and u [,T] = u. Any subs C of hs s of pars ha s oally ordrd has h uppr bound (u,x T,ϕ T ), whr T s h suprmum of h s of T such ha (u,x T,ϕ T ) C (T = f hs s oft s unboundd) and u s dfnd by u [,T] = u whavr s (u,x T,ϕ T ) C. Thn, by Zorn s lmma h abov s of pars has a maxmum lmn,.. hr xss a par (u,x T,ϕ T ) such ha f (u,x T,ϕ T ) s any ohr par such ha (u,x T,ϕ T ) (u,x T,ϕ T ) hn (u,x T,ϕ T ) (u,x T,ϕ T ).. fus asoluonof (.)-(.6) n X T,ϕ T suchha T T and u [,T ) = u hn T = T and u = u.) Thn w shall show n Scon 5 ha f T < hn w hav a conradcon, by provng ha, n hs cas, h maxmal soluon u has a connuous xnson up o h m T, and ha hs xnson s lpschz connuous and s n L p, as a funcon of x, for = T, hus u can b xndd o a largr m, accordngly wh Thorm. Th da o xnd u up o h m T s, agan, o us h ngral rprsnaon (.4), for u = u, (x,) [,T ), wh Γ bng h fundamnal soluon of h quaon L w =, for L := α (y ) xx β (y ) x, whr y = y,(x) A f(u )ds, and wh f (y,u,u ) = f (y,u,u ). To accomplsh hs, w nd o prov ha h drvavs x u ar boundd n (,T ) (s Corollary 5) and w do ha by h mhod of auxlary funcons 8,.. followng [] (or [3, 4]; s [, p. 7]), w mak a subsuon u = h (v ) 7 Smlarly as n h samn of Thorm, hr h rm loc sands for locally n m,.. a funcon u C, loc ( [,T )) L loc ((,T );L p ()) f u [,T] C, ( [,T]) L ((,T);L p ()), for any T (,T ). 8 Ths rmnology was usd by. Fnn n h MahScN rvw #M6486 (6,59b). In hs rvw h also pons ou ha hs mhod was dvlopd by Pcard [s,.g., Couran and Hlbr, Mhodn dr mahmaschn Physk, Bd II, Sprngr, Brln, 937, pp ], Brnsn [Mah. Ann. 69, 8 36 (9); Doklady Akad. Nauk SSS (N.S.) 8, (938)] and ohrs.
6 6 for an appropra funcon h (n parcular, such ha h s posv and boundd) and sma xv (nsad of ryng o sma x u ) a a maxmum pon, by lookng for h quaon sasfd by v. Ths lads o som chncal smas whr w us h xplc forms for h funcons α(y ), β (y ) and f (y,u,u ) n (.3) (s Scon 5). Cranly, would b a vry nrsng nvsgaon o xnd our man rsuls rgardng h sysm (.) (horms and ) o mor gnral funcons α(y ), β (y ) and f (y,u,u ) (or funcons a, b and F n (.)). Th prcdng paragraphs gv h fundamnal and nuv das o prov horms and. In h nx scons w gv h rgorous and compl proofs of all horms sad abov. In Scon w prsn a brf summary of h consrucon of fundamnal soluons for parabolc quaons by h paramrx mhod and sa som mporan known smas. Also n hs scon w show h dpndnc of h fundamnal soluon on h coffcns of h quaons. In Scon 3 w prov horm and n Scon 4 w prov horms 3 and 4 and sa and prov wo corollars whch ar vrson of hs horms n h cas on has connuous dpndnc of h soluon of h sysm wh rspc o h racon funcons, and also mak hr rmarks gvng alrnav condons for h hypohss of horms 3 and 4. Fnally, n Scon 5 w prov horm. Th fundamnal soluon In hs scon, w prsn a summary on h consrucon by h paramrx mhod and man proprs of h fundamnal soluon for parabolc quaons, and show s connuous dpndnc wh rspc o h coffcns of h quaons.. Dfnon and som proprs Consdr h quaon and h opraor L gvn by Lu u u a(x,) x b(x,) u c(x,)u =, (.) x n h s Ω T := {(x,); x, T}, for som posv numbr T, wh h coffcns a,b,c n h class C α,α (Ω T ), for som α (,], wh L bng a unform parabolc opraor n Ω T,.., hr ar srcly posv consans λ,λ such ha for all (x,) n Ω T. λ a(x,) λ (.) Dfnon. A fundamnal soluon of h parabolc quaon (.) s a funcon Γ(x,,ξ,), dfnd for all (x,) and (ξ,) n Ω T wh >, such ha LΓ = n Ω T, as a funcon of (x,), for ach fxd (ξ,) Ω T, and lm Γ(x,,ξ,)ψ(ξ)dξ = ψ(x), for all x and [,T), for any connuous funcon ψ(x) such ha ψ(x) c hx, for all x, for som posv consans c and h wh h < /(4λ T). Fundamnal soluons for parabolc quaons was found by E. E. Lv [], usng h paramrx mhod. Our prsnaon n hs scon follows mosly [8] and []. Accordngly, h fundamnal soluon o h quaon (.) s gvn by Γ(x,,ξ,) = Z(x,,ξ,) Z(x,,y,σ)φ(y,σ,ξ,)dydσ, (.3) whr (x,), (ξ,) Ω T, >, h funcon Z(x,,ξ,), as a funcon (x,), s h fundamnal soluon of h ha quaon u u a(ξ,) x =,.. for ach fxd (ξ,) Ω T, and Z(x,,ξ,) = (4πa(ξ,)( )) φ(x,,ξ,) = (x ξ) 4a(ξ,)( ), (.4) ( ) m (LZ) m (x,,ξ,), (.5) m=
7 7 whr (LZ) = LZ = (a(ξ,) a(x,)) Z x b Z x cz and, for m, (LZ) m (x,,ξ,) = [LZ(x,,y,σ)](LZ) m (y,σ,ξ,)dydσ. (.6) Nx w gv som mporan smas, whch, n parcular, show ha h funcon Γ gvn by (.3) s wll dfnd,.. h srs n (.5) convrgs and (.3) ylds a smooh funcon Γ, for >. In h squl, (x,),(ξ,) Ω T, >, and, K and C dno any posv consans. For h funcon Z(x,,ξ,), w hav h sma DD r xz(x,,ξ,) s K( ) rs (x ξ), (.7) for all nonngav ngrs r,s, whr hroughou D r or r and Ds x or s x sand for h drvavs wh rspc o and x of ordr r and s, rspcvly. Bsds, snc Z(z,,ξ,)dz =, w hav ha D r Ds zz(z,,ξ,)dz =, (.8) for all r,s Z such ha rs >. Fnally, Z and s drvavs ar Höldr connuous n ξ,.. D r Ds z Z(z,,ξ,) Dr Ds z Z(z,ξ,,) K ξ ξ α ( ) rs z, (.9) whr C = C(λ ) and K = K(λ,λ, a α, α). For h funcon φ(x,,ξ,), w hav h smas φ(x,,ξ,) K ( ) 3 α φ(x,,ξ,) φ(y,,ξ,) K x y γ ( ) 3 (α γ) (x ξ), (.) whr C = C(λ ) and K = K(λ,λ, a α, α, b, c,t), and, for any γ (,α), ( (x ξ) (y ξ) ), (.) whr C and K ar as n (.). Fnally, for h funcon Γ(x,,ξ,) w hav h sma (s also Corollary n hs papr) D r Ds x Γ(x,,ξ,) K (x ξ) ( ) rs, (.) for all r,s Z such ha r s, and, agan, C and K ar as n (.). Bsds, h fundamnal soluon Γ s nonngav (s [] and [9]). Now consdr h Cauchy problm { Lu(x,) = f(x,), n (,T], T > u(x,) = u (x), n, (.3) whr L s dfnd n (.) and f and u ar gvn connuous funcons, n (,T] and, rspcvly, boundd by h xponnal growh f(x,), u (x) c hx (.4) for posv consans c and h such ha h < 4/(λ T), and for all x and [,T]. Th followng horm gvs a rprsnaon formula for s soluon usng h fundamnal soluon. Thorm 5. L Γ b h fundamnal soluon of h quaon Lu =, whr L s h parabolc opraor n (.3). If, bsds (.4), h funcon f s locally Höldr connuous n x, unformly wh rspc o, hn h funcon u(x,) = Γ(x,,ξ,)u (ξ)dξ Γ(x,,ξ,)f(ξ,)dξd (.5) s h unqu soluon of h Cauchy problm (.3) n C, ( (,T]) C( [,T]) boundd by an xponnal growh wh rspc o x, as n (.4).
8 8 For a proof, s.g. [8, p. 5] and [7, p.8]. mark. In h parcular cas whr c(x,), w hav Γ(x,,ξ,)dξ = and Dr Ds x Γ(x,,ξ,)dξ = for all r,s Z such ha < rs ; cf. (.8). Indd, h scond clam coms from h frs, by h Lbsgu s convrgnc domnad horm, and f c(x,) =, u(x,) = s h unqu soluon (n h C, class wh an xponnal growh for larg x) of h problm { Lu(x,) =, n (,T], (.6) u(x,) =, n, hus, by h Thorm 5, follows ha = Γ(x,,ξ,)dξd, so h() Γ(x,,ξ,)dξ =, snc f h( ) for som [,T] hn, assumng, whou loss of gnraly, ha h( ) >, by connuy of h(), hr would xs an nrval [a,b] [,T] such ha h() > for any [a,b], and hus w would g h conradcon b a = b a Γ(x,,ξ,)dξd Γ(x,,ξ,)dξd = b a Γ(x,,ξ,)dξd > b a.. Connuous dpndnc on h coffcns W bgn hs scon by sng a noaon for boundd ss of coffcns a,b,c of parabolc quaons (.). GvnposvnumbrsT,, λandα, wh < α andλ <, l B(,λ,α) b hsofvcor valudfunconsv = (a(x,),b(x,),c(x,)) nc α,α (Ω T )suchhaa λand a α, α, b α, α, c α, α <. = max{ a α, α, b α, α, c α, α }. Any v = (a,b,c) For a v B(,λ,α), w dfn h norm v α, α B(,λ,α) dfns a parabolc quaon of h form (.) (wh (.) sasfd wh λ = λ and λ = ) and, rcprocally, any (unformly) parabolc quaon of h form (.) (sasfyng (.)) ylds a v = (a,b,c) B(,λ,α), for any λ (,λ ) and > v α, α. To hghlgh h dpndnc of h opraor L gvn n (.) on h coffcns a,b,c v, w shall wr L = L [v],.. L [v] u Lu = u a(x,) u x b(x,) u x c(x,)u and for h fundamnal soluon of L [v] u = w shall wr Γ = Γ [v],.. Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) = Z [v] (x,,ξ,) Z [v] (x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,)dydσ, (.7) whr Z [v] = Z [(a,,)] Z and φ [v] φ ar gvn n (.4) and (.5). In h nx lmmas w sablsh som smas for h fundamnal soluon (.7) and s drvavs whch aks no accoun h dpndnc on s coffcns a,b,c v. W frs sablsh hs smas for h funcons Z [v] and φ [v] and hn, usng (.7) and h srs (.5) for φ [v], w xnd hm for Γ [v]. Ths smas ar h ky pon o oban h local soluon sad n Thorm. W shall wr C and K o dno posv consans ha mgh dpnd on h paramrs,λ,α,t, bu no on h coffcns v nhr on h soluons u or h daa f, u, unlss ohrws sad. Bsds, K dpnds connuously on T. Lmma. Gvn v,v B(,λ,α), w hav ha (D s x Z [v] D s x Z [v])(x,,ξ,) K a a for s =,,, whr C < /(4) and K = K(,λ). ( ) s (x ξ) ( ), Proof. SncZ [v] (x,,ξ,) = (x ξ) (4πa(ξ,)( )) 4a(ξ,)( ) andsdrvavsonxdpndsonhcoffcn a of L [v], bu no dpnds on h ohr coffcns b and c, compung h drvav of DxZ s [v] wh rspc o a, w fnd D a DxZ s (x ξ) K [v] (x,,ξ,) ( ) s ( ), for s =,,, and consans K and C as n samn of h lmma. Thn h dsrd nqualy follows by h Man Valu Thorm. Lmma. L A and α b srcly posv numbrs bng α, and l g dno h gamma funcon g(x) := x d. Thn m= mam /g( mα ) s a convrgn srs.
9 9 Proof. W bgn by rcallng h rlaon g(x)g(y) g(xy) = B(x,y) bwn h gamma funcon g and h ba funcon, B(x,y) = x ( ) y d (s [5, p.4]). Dnong h gnral rm of h gvn srs by b m, and usng h abov rlaon, w oban lm m b m b m B( = Alm mα,α ) m g( α ) = Alm m g( α ) mα ( ) α d =. Thrfor, h rsul follows. Lmma 3. L β [,] and γ (,α). If v,v B(,λ,α) hn and whr C < 4 (φ [v] φ [v] )(x,,ξ,) K v v α, α ( ) 3 α (x ξ) (.8) (φ [v] (x,,ξ,) φ [v] (x,,ξ,)) (φ [v] (y,,ξ,) φ [v] (y,,ξ,)) (.9) K v v β α, x y γ( β) ( α (x ξ) ( ) 3 (α γ( β)) and K = K(,λ,α,T). Proof. Th proof of (.8) follows from h followng nqualy: (y ξ) ), ((LZ [v] ) m (LZ [v] ) m )(x,,ξ,) mk m( )m π g( C v v α α, α )m (x ξ) g( mα ) ( ) 3 mα, (.) whr, for smplcy, w s L L [v], and g dnos h gamma funcon; s Lmma. W show hs nqualy by nducon on m. For m =, w hav ((L [v] Z [v] ) (L [v] Z [v] ) )(x,,ξ,) ((a(ξ,) a(x,)) xx Z [v] b(x,) x Z [v] c(x,)z [v] ) ((a(ξ,) a(x,)) xx Z [v] b(x,) x Z [v] c(x,)z [v] ) ((a(ξ,) a(x,)) ((a(ξ,) a(x,)))) xx Z [v] (a(ξ,) a(x,)) xx Z [v] xx Z [v] b(x,) b(x,) x Z [v] b(x,) x Z [v] x Z [v] c(x,) c(x,) Z [v] c(x,) Z [v] Z [v] I. Thn from Lmma, (.7), and h sma x ξ α (x ξ) = ( (x ξ) ) α( ) α/ (x ξ) 8 (C 8) (x ξ) K( ) α/ (x ξ), whr C s a nw consan whch w shall connu dnong by C, w oban I K v v α, α ( (x ξ) ( ) 3 (x ξ) α ( ) K v v α, α ( ) 3 α (x ξ), ( ) (x ξ) )
10 whr C < /(4) and K = K(,λ,α,T). Now, assumng ha (.) s ru for an m, w oban: ((L [v] Z [v] ) m (L [v] Z [v] ) m )(x,,ξ,) [L [v] Z [v] (x,y,,σ)](l [v] Z [v] ) m (y,ξ,σ,) [L [v] Z [v] (x,y,,σ)](l [v] Z [v] ) m (y,ξ,σ,)dydσ (L [v] Z [v] L [v] Z [v] )(x,y,,σ) (L [v] Z [v] ) m (y,ξ,σ,) dydσ L [v] Z [v] (x,,ξ,) (L [v] Z [v] ) m (y,ξ,σ,) (L [v] Z [v] ) m (y,ξ,σ,) dydσ K v v α, α ( σ) 3 α K ( σ) 3 α (x y) ( σ K m π C (x y) ( σ mk m π C =(m)k m( π ) m g( α v v )m α, α C g( mα ) whr w usd ha and (s [, p. 36]). So, ) m g( α )m (y ξ) g( mα ) (σ ) 3 mα σ dydσ )m ( σ) 3 α ( (x y) σ (y ξ) σ π ) dy = C ( σ) α (σ ) mα dσ = ((L [v] Z [v] ) m (L [v] Z [v] ) m )(x,,ξ,) (m)k m( π C ) m g( α ( )m g (m)α v v α, α g(α )m (y ξ) g( mα ) (σ ) 3 mα σ dydσ (x y) σ ( ( σ)(σ ) ( ) (m)α (σ ) 3 mα ) v v α, α ( ) 3 (m)α ) (x ξ) g( α )g(mα ) g ( (m)α (y ξ) σ dydσ, (x ξ). Ths provs h nqualy (.). Th nqualy (.), (.5) and Lmma mply ha (φ [v] φ [v] )(x,,ξ,) m= ((L [v] Z [v] ) m (L [v] Z [v] ) m )(x,,ξ,) m= mk m( π ) m g( α )m v v α,α C g( mα ) ( ) 3 mα K v v α, α (x ξ) ( ) 3 α, whrc < 4 and K = m= mkm ( π)m C by T. Ths nds h proof of (.8). To prov (.9), w wr g( α )m (m )α g( mα )T (x ξ) ar posv consans and was smad (φ [v] (x,,ξ,) φ [v] (x,,ξ,)) (φ [v] (y,,ξ,) φ [v] (y,,ξ,)) J = J β.j β and hn us (.8) o sma J β and (.) o sma J β, nocng ha w can sma J by (Φ [v] Φ [v] )(x,,ξ,) (Φ [v] Φ [v] )(y,,ξ,) andalsoby Φ [v] (x,,ξ,) Φ [v] (y,,ξ,) Φ [v] (x,,ξ,) Φ [v] (y,,ξ,).
11 Lmma 4. L v,v B(,λ,α), β (,), γ (,α), and Γ [v], Γ [v], h fundamnal soluons of h quaons L [v] u =, L [v] u =, as dfnd n (.7) and (.4)-(.6). Thn w hav h followng smas: and whr C < 4 (Dx s Γ [v] Dx s Γ [v])(x,,ξ,) K v v α, α ( ) s (x ξ), s =,; (.) ( xx Γ [v] xx Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) (.) K( v v α, α v v β α, )( α x ξ (α γ( β)) γ( β) ( ) ( ) 3 (x ξ) ) ; ( Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) (.3) K( v v α, α v v β α, )( α x ξ (α γ( β)) γ( β) ( ) and K = K(,λ,α,T). ( ) 3 Proof. For s = w hav ha (Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) (Z [v] Z [v] )(x,,ξ,) Z [v](x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) Z [v] (x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) dydσ Z [v] Z [v] Z [v] Z [v] φ [v] Z [v] φ [v] φ [v] dydσ. From smas (.7) and (.) and Lmmas and 3 follows ha (x ξ) ) ; (Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) Snc, w oban (x ξ) K a a ( ) K a a ( σ) K ( σ) (x y) σ (x y) σ (y ξ) π σ dy = ( K (σ ) 3 α (y ξ) σ dydσ (x y) K v v α, α (y ξ) σ (σ ) 3 α σ dydσ. ( σ)(σ ) C ) ( ) (x ξ), (.4) (Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) (.5) (( π C ) (σ ) α dσ ( π C ) ( σ) α dσ) K v v α, α ( ) (x ξ) K v v α, α ( ) whr K = K(,λ,α,T). For h cas s =, w hav (x ξ) ( x Γ [v] x Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) =( x Z [v] x Z [v] )(x,,ξ,) x Z [v] (x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) x Z [v] (x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,)dydσ =( x Z [v] x Z [v] ) J J J 3. ( x Z [v] x Z [v] )φ [v] dydσ x Z [v] (φ [v] φ [v] )dydσ
12 From Lmma, w hav J = ( x Z [v] x Z [v] )(x,,ξ,) K a a (x ξ). (.6) Usng Lmma, h sma (.) and h dny (.4), w hav J ( x Z [v] x Z [v] )(x,y,,σ) φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) dydσ (.7) K a a σ K a a (x y) ( σ) σ K a a (x ξ) ( ) α (x y) σ Fnally, usng Lmma 3, (.7) and (.4), w oban J 3 K v v α, α ( ) K v v α, α K (σ ) 3 α (y ξ) σ dydσ ( σ) (σ ) α dσ K a a (x ξ). x Z [v] (x,y,,σ) (φ [v] φ [v] )(y,σ,ξ,) dydσ (.8) K (x y) σ (x ξ) (x ξ), K v v α, α (σ ) 3 α whr K = K(,λ,α,T). From (.6), (.7) and (.8), w g ( x Γ [v] x Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) K v v α, α for a K as abov. gardng h scond drvav wh rspc o x, w hav From Lmma, (y ξ) σ dydσ ( σ) (σ ) α dσ (x ξ), ( xx Γ [v] xx Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) = ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )(x,,ξ,) xx Z [v] (x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) xx Z [v] (x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,)dydσ =( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] ) I I I 3. To sma I, w wr I = = xx Z [v] (φ [v] φ [v] )dydσ ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )φ [v] dydσ I = ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )(x,,ξ,) K a a (x ξ) ( ) 3. (.9) I I. ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )(x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,)dydσ ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )φ [v] dydσ ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )φ [v] dydσ
13 3 Applyng Lmma, (.) and (.4) w g Now, I = = = I K a a ( σ) 3 K a a (x ξ) ( ) K a a (x ξ) ( ) 3 α (x y) σ K (σ ) 3 α ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )(x,y,,σ)φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,)dydσ (y ξ) σ dydσ ( σ) (σ ) α dσ ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )(x,y,,σ)(φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) φ [v] (x,ξ,σ,) φ [v] (x,ξ,σ,))dydσ ( xx Z [v] xx Z [v] )(x,y,,σ)(φ [v] (y,σ,ξ,) φ [v] (x,ξ,σ,))dydσ (( xxz [v] xxz [v])(x,y,,σ) ( xxz [v] xxz [v])(x,x,,σ) ) φ [v](x,ξ,σ,)dydσ, snc ( xx Z [v] (x,x,,σ) xx Z [v] (x,x,,σ))dy = (s (.8)). Thn, applyng Lmma, (.9), (.) and (.), w oban Thus, I K a a ( σ) 3 (x y) σ (x y) K a a β ( σ ) ( σ) 3 K a a ( σ) 3 γ K a a β (x y) σ (x y) σ K x y γ (σ ) 3 (α γ) β ( σ) 3 α( β) (y ξ) ( σ (x ξ) σ )dydσ (x y) β (x ξ) x y α( β) ( σ ) ( σ )dydσ ( σ) 3 (σ ) 3 α (σ ) 3 (α γ) (x ξ) K( a a a a β ). ( ) 3 α To sma I 3, w wr I 3 = = (x ξ) σ (σ ) 3 α (y ξ) ( σ dydσ (x ξ) I I I K( a a a a β ) ( ) 3 α xx Z [v] (x,y,,σ)(φ [v] φ [v] )(y,σ,ξ,)dydσ (x ξ) σ )dydσ xx Z [v] (x,y,,σ)[(φ [v] φ [v] )(y,σ,ξ,) (φ [v] φ [v] )(x,ξ,σ,)]dydσ ( xx Z [v] (x,y,,σ) xx Z [v] (x,x,,σ))(φ [v] φ [v] )(x,ξ,σ,)dydσ I 3 I 3,. (.3)
14 4 whr w hav usd (.8). Applyng Lmma 3 and (.7), w g I 3 K ( σ) 3 K v v β α, α K v v β α, α K v v β α, α K ( σ) 3 γ( β) x y γ( β) (x y) K v v β α, α σ (σ ) 3 (α γ( β)) K v v β α, α ( ) (x y) σ ( σ) 3 γ( β) ( σ) 3 γ( β) ( σ) γ( β) (x ξ) K v v β α, ( α ( ) 3 α K v v β α, α ( ) 3 α (x ξ) (σ ) 3 (α γ( β)) (x ξ) (y ξ) ( σ σ )dydσ K v v β α, α (x ξ) (y ξ) ( (σ ) 3 (α γ( β)) σ σ )dydσ (x ξ) σ ( (σ ) 3 (α γ( β)) (σ ) 3 (α γ( β)) ( σ) γ( β) ( (x y) σ dy)dσ (x y) σ (y ξ) σ dy)dσ (x ξ) σ dσ (σ ) (α γ( β)) x ξ (α γ( β)) α( β) ( ) K v v β α, ( α x ξ (α γ( β)) γ( β) ( ) In ordr o sma I 3, w us Lmma 3 and (.9) as follows: I 3 K x y α ( σ) 3 K v v α, α K v v α, α ( ) 3 α (x y) v v α, α (x ξ) σ (σ ) 3 α σ dydσ ( σ) 3 α ( σ) α (σ ) 3 α (σ ) 3 α (x ξ) σ ( (x ξ) σ dσ dσ (x ξ) ) (x ξ) ). (x y) σ dy)dσ Thn, K v v α, α T α γ( β)β ( σ) γ( β) T γ( β) (σ ) 3 (α γ( β)) K v v α, α ( x ξ (α γ( β)) ( ) γ( β) (x ξ) σ dσ ( ) 3 α (x ξ) ). I 3 I 3 I 3 K( v v α, α v v β α, α )( x ξ (α γ( β)) ( ) γ( β) From h abov smas, (.9), (.3) and (.3), w oban ( ) 3 α (x ξ) ). (.3) ( xx Γ [v] xx Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,) K( v v α, α v v β α, ) α ( x ξ (α γ( β)) γ( β) ( ) ( ) 3 (x ξ) ). Fnally, h proof of (.3) follows from (.), (.) and h quaons L [v] Γ [v] = L [v] Γ [v] =.
15 5 Corollary. For v B(,λ,α) w hav h followng unform sma: whr K = K(,λ,α,T). Proof. Tak v = (,,) n (.). D s xγ [v] (x,,ξ,) W also hav h followng lmma. K ( ) s (x ξ), s =, (.3) Lmma 5. L v n,v B(,λ,α), n =,,. If v n (x,) convrgs o v(x,) ponws n [,T], as n gos o nfny, hn Γ [vn](x,,ξ,) convrgs o Γ [v] (x,,ξ,), for any (x,), (ξ,) [,T], wh >. Proof. Frs w show h ponws convrgnc of Z [vn] and φ [vn]. From (.4) s asy o s ha D r D s xz [vn] D r D s xz [v] (.33) ponws, whr r and s ar nonngav ngrs. To proof ha φ [vn] convrgs ponws o φ [v], w noc ha so, follows from (.33) ha ponws. Bsds, w hav L [vn](z [vn]) = (a n (ξ,) a n (x,)) xx Z [vn] b n (x,) x Z [vn] c n (x,)z [vn], L [vn](z [vn]) L [v] (Z [v] ), (.34) L [vn](z [vn](x,,ξ,)) K ( ) 3 α (x ξ), (.35) whr K and C ar posv consans whch do no dpnds on n. Now, rcallng (.6), on can show by nducon on m ha (L [vn]) m convrgs o (L [v] ) m, ponws, as m gos o nfny. Indd, followng h consrucon of h fundamnal soluon n [, p. 36], w hav (L [vn]) m (Z [vn](x,,ξ,)) K m( )m π g( α )m (x ξ) C g( mα ) ( ) 3 mα, (.36) whr g s h gamma funcon. So, (L [vn])(z [vn](x,y,,σ))(l [vn]) m (Z [vn](y,ξ,σ,)) (x y) K σ K m ( π g( α ( σ) 3 α C )m )m g( mα (y ξ) σ ) (σ ) 3 mα and hus, by h nducon hypohss, w oban(l [vn])(z [vn])(l [vn]) m (Z [vn]) (L [v] )(Z [v] )(L [v] ) m (Z [v] ), ponws. Thn, by h Lbsgu s Domnad Convrgnc Thorm, (L [vn]) m (Z [vn](x,,ξ,)) = (L[vn])(Z [vn](x,y,,σ))(l [vn]) m (Z [vn](y,ξ,σ,))dydσ convrgs o (L [v] ) m (Z [v] (x,,ξ,)). Th sma (.36) nsurs h unform convrgnc of m= ( )m (L [vn](z [vn]) m (x,,ξ,) wh rspc o (x,ξ) and > δ, for ach fxd δ >, and so, φ [vn] φ [v], ponws. To nd h proof of h Lmma, noc ha Z [vn](x,y,,σ)φ [vn](y,σ,ξ,) K (x y) (y ξ) ( σ) σ (σ ) 3 α σ and Z [vn]φ [vn] convrgs ponws o Z [v] φ [v], so, agan from h Lbsgu s Domnad Convrgnc Thorm follows ha Z[vn]φ [vn]dydσ Z[v] φ [v] dydσ. Thus, w conclud ha Γ [vn] Γ [v], ponws. Thorm 6. L T >, β (,), v = (a,b,), v = (a,b,) B(,λ,), f,f C, (Ω T ) and u,u b Lpschz connuous and boundd funcons n. If u and u ar h soluons of h problms hn L [v] u = f, n (,T], u(x,) = u, x, (.37) L [v] u = f, n (,T], u(x,) = u, x, (.38) u u, K[ v v, v v β u, u (.39) whr K = K(,λ,T, u ). T ( f, )( f f, v v, v v β )],,
16 6 Proof. From Thorm 5 w hav (u u)(x,) = Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)u (ξ) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)u (ξ)dξ Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,)dξd V(x,)W(x,). By Lma 4 and (.), w g V(x,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)u (ξ) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)u (ξ) dξ (.4) (Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,)u (ξ) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)(u (ξ) u (ξ)) dξ K v v, (x ξ) u K K( v v, u u ), (x ξ) u u dξ whr K = K(,λ,T, u ). In vw of mark, w can wr x V(x,) = x Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)u (ξ) x Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)u (ξ)dξ = ( x Γ [v] x Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,)(u (ξ) u (x))dξ x Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)[(u (ξ) u (ξ)) (u (x) u (x))]dξ, so, by Lmma 4 and sma (.) and usng ha w g x ξ (x ξ) = /( x ξ (x ξ) (C/) / x V(x,) ( K v v, u x ξ K u v v, K( v v, u u ), ) (C/)(x ξ) cons. / (C/) (x ξ), K u u x ξ (x ξ) ) dξ (.4) K u u ) (x ξ) dξ wh K = K(,λ,T, u ). In ordr o g h Höldr connuy wh rspc o, usng agan mark, w wr V(x,) V(x, ) = (Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,))u (ξ) (Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,))u (ξ)dξ = = = Γ [v] (x,s,ξ,)u (ξ) Γ [v] (x,s,ξ,)u (ξ)dsdξ ( Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,s,ξ,)u (ξ) Γ [v] (x,s,ξ,)(u u )(ξ)dξds ( Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,s,ξ,)(u (ξ) u (x))dξds Γ [v] (x,s,ξ,)[(u u )(ξ) (u u )(x)]dξds.
17 7 Thnc, from Lmma 4 and sma (.), w oban V(x,) V(x, ) (.4) Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,s,ξ,) u (ξ) u (x) dξds Γ [v] (x,s,ξ,) (u u )(ξ) (u u )(x) dξds K( v v, v v β, K u u x ξ s 3 ) u x ξ ( (x ξ) s dξds K( v v, v v β ) u, ( T K u u s (x ξ) s dξds K( v v, v v β u, u ) K( v v, v v β u, u ) x ξ γ( β) s γ( β) (x ξ) ) s 3 s dξds s (x ξ) s ) s s K( v v, v v β u, u )( ), whr K = K(,λ,T, u ). From smas (.4), (.4) and (.4), w hav wh a nw K. Smlarly, w can sma W: W(x,) = dξds (x ξ) s s dξds V, K(,λ,T, u )( v v, v v β u, u ), (.43) = Hnc, usng Lmma 4 and (.), w hav Bsds, W(x,) x W(x,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,)dξd (Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,)f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)(f f)(ξ,)dξd. ds (Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,)f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)(f f)(ξ,) dξd (.44) K( v v, f f f ) ( ) K(,λ,T)( f )T( v v, f f ). (x ξ) dξd ( x Γ [v] x Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,)f(ξ,) x Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)(f f)(ξ,) dξd (.45) K( v v, f f f ) ( ) K(,λ,T)( f )T ( v v, f f ) (x ξ) dξd
18 8 To prov h Höldr connuy wh rspc o, w wr W(x,) W(x, ) = [(Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)]f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,)dξd = = ǫ ǫ [(Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)]f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,)dξd (Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)]f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)f(ξ,))dξd [(Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,))f(ξ,) (Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,))f(ξ,)]dξd ((Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,,ξ,)]f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,)(f f)(ξ,))dξd [(Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,))f(ξ,) (Γ [v] (x,,ξ,) Γ [v] (x,,ξ,))f(ξ,)]dξd W W W 3 [ Γ [v] (x,ξ,s,)f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,ξ,s,)f(ξ,)]dsdξd, whr < ǫ < s arbrary. Usng Lmma 4 and (.8), w sma W gardng W, w apply (.8) o g W ǫ (x ξ) (K v v, f K f f ) dξd (.46) ( ) K(,λ,T)( f )T ( v v, f f )( ) ( K ( ) K( f f )ǫ. (x ξ) K ( ) Th rm W 3 can b smad usng mark as follows: W 3 = = ǫ ǫ (x ξ) ) ( f f )dξd (.47) [ Γ [v] (x,ξ,s,)f(ξ,) Γ [v] (x,ξ,s,)f(ξ,)]dsdξd [( Γ [v] Γ [v] )(x,ξ,s,)(f(ξ,) f(x,)) Γ [v] (x,ξ,s,)((f f)(ξ,) (f f)(x,))]dξdsd
19 9 Now, applyng Lmma 4 and (.8), and wrng K = K( v v, v v β ) f,,, follows ha W 3 ǫ K ( x ξ γ( β) (s ) γ( β) K (s ) 3 K( f, )[ v v, v v β, ǫ f f, ] (s ) 3 (x ξ) s f f, x ξ dξdsd ( x ξ γ( β) (s ) γ( β) x ξ (x ξ) ) (s ) 3 s dξdsd K( f, )[ v v, v v β, ǫ f f, ] ( (x ξ) (s ) s ) s dξdsd K( f, )[ v v, v v β, ǫ f f, ](T (x ξ) ) s s dξdsd K( f, )[ v v, v v β f f,, ] (x ξ) ) s x ξ (.48) ǫ K( f, )[ v v, v v β f f,, ]T( ), (s ) whr for h las nqualy w usd ha (.47) s ru for all ǫ (, ). From (.46), (.47) and (.48), w conclud ha dsd W(x,) W(x, ) K( f, )( v v, v v β f f,, )T ( ), (.49) whr K = K(,λ,T). I follows from (.44), (.45) and (.49) ha W, K(,λ,T)T ( f, )( v v, v v β, Fnally, from (.43) and (.5), w hav f f, ). (.5) u u, V, W, K( v v, v v β u, u T ( f, )( f f, v v, v v β )),, (.5) whr K = K(,λ,T, u ). In parcular w hav h followng sma for a soluon of (.37) Corollary. In h sam condons of Thorm 6, f u s a soluon of (.37) hn whr K = K(,λ,T, u ). u, K(,λ,T, u )( u T ( f, ) f, ), (.5) Proof. Th proof follows from Thorm 6 by akng v = v, f = f and u = u. 3 Local soluon In hsscon wprovthorm. Forsmplcy wshallwr f and f nsadof f and f, rspcvly. Consdr h opraor A gvn n (.). In h lmma blow w consruc an nvaran s for A. ( a b λ a b y,,t, u, ) b h consan gvn n λ a b y,,t, u, ), M > K u, and Σ = {(u,u ) Lmma 6. L = λc a y, ), K(, h Corollary, K = sup T K(, ( ; C ( [,T])), u, M }. Thn A(Σ) Σ, f T > s suffcnly small.
20 Proof. Gvn (u,u ) Σ w g y y (u ) xplcly solvng (y ) = A y f(u ),.. and, so, y y,, and ls, y, y, A f(u(x,s))ds, = y, ( sup (x,) Ω T ( A y (x,) = y, (x) A f(u(x,s))ds (3.) f(u(x,s))ds ) sup ( A f(u(x,s))ds A f(u(x,s))ds )) (x,),(x,) Ω T x x f(u(x,s))ds A f(u(x,s))ds y, ( sup ) x x (x,),(x,) Ω T ( A sup ( A f(u(x,s))ds A f(u(x,s))ds )) (x,),(x,) Ω T y, ( sup (A (x,),(x,) Ω T sup (x,),(x,) Ω T ( A y, ( sup (A (x,),(x,) Ω T f(u (x,s) f(u (x,s) ds) x x y, (TA u, f T A ) f(u (x,s))ds )) f u, ds) (3.) sup (A f )) (3.3) (x,),(x,) Ω T y, (TA M f T A ) y,, whr, for h las nqualy, w ook ( T > suffcnly ) small such ha T TA M f λ. Furhrmor, v v (u ) = a, c b y (u ) a, λ b y (u ) B(, a b y,,); s h dfnon of h s B(,λ,α) a h bgnnng of scon.. Indd, λ a b y (u ), = sup (x,) Ω T λ a b y (u ) sup (x,),(x,) Ω T λ a b y (u (x,)) λ b λ y (u (x,)) y (u (x,)) a a ( sup ) (x,),(x,) Ω T x x λ b λ y a, λ b λ y,, a a a x x λ a b y (u (x,)) whr w usd (3.). Analogously, w can vrfy ha a b y (u ), c c a bc y, a and, so, λ c a b y (u ), a b y (u ), λ c ( b y, ) = a a Addng o h fac ha < ( λ v (u ) B, a b y,, λ a b y, ). λ a b y (u ), w conclud ha From h abov, h hyposs of Thorm 5 ar sasfd. Thrfor, h problm { L[v(u )](w ) = f (y,u,u ), n (,T], w (x,) = u, (x), x, (3.4) has a unqu soluon wh an xponal growh n h spac C, ( (,T]) C( [,T]).
21 From Corollary, w hav provdd ha T s suffcnly small. 3. Proof of Thorm w, λ K(,,T, u, )[ u, a b y, T ( f (y,u,u ), ) F (y,u,u ), ] K [ u, T ( f (y,u,u ), ) F (y,u,u ), K [ u, T K(M,M, y, )] M, L T, A and Σ b as n Lmma 6, and for any fxd (u,u ) Σ, l (u n,u n ), n =,,, b h squnc dfnd by (u n,un ) = A(un,u n ). From Lmma 6 w hav ha hs squnc s boundd n C, (Ω T )(Ω T = (,T)). Thn, byarzlà-ascol shorm(s[5, p. 635]), hrxssa(u,u ) Σ and a subsqunc of (u n,u n ), whch w shall sll dno by (u n,u n ), such ha convrgs o (u,u ), unformly n compacs ss n [,T]. By Thorm 5 w can wr wh and u n (x,) = Γ [v(u n )] (x,,ξ,)u, (ξ)dξ ( v (u n ) = Γ[v(u n )] (x,,ξ,)f (y (u n ),un,un )(ξ,)dξd, (3.5) λ a y (u n ), ) c a y (u n ), ] (3.6) y (u n )(x,) = y, (x) A f(un (x,s))ds. (3.7) As u n convrgs o u, w hav ha y (u n ), v (u n ) and f (y (u n ),un,u n ) convrg o y (u ), v (u ) and f (y (u ),u,u ), rspcvly. Such convrgncs ar unform on compacs ss n [,T], bcaus u n so convrgs, f s boundd on, and f s boundd on [,M ] [,M ] [, y (, ]. Morovr, ) as u n, M, foralln N, whavha u, M and so, v (u n ),v λ (u ) B, a b y,,. From Lmma 5 w hav ha Γ [v(u n )] convrgs o Γ [v(u )] ponws. As Γ [v(u n )] (x,,ξ,)u, (ξ) K (x ξ) and Γ [v(u n )] (x,,ξ,)f (y (u n ),u n,u n )(ξ,) K( ) (x ξ), whr K and C ar consans ha do dpnd on n (s Corollary ), follows, by h Lbsgu s domnad convrgnc horm, ha u (x,) = Γ (x,,ξ,)u, (ξ)dξ Γ (x,,ξ,)f (y,u,u )(ξ,)dξd. (3.8) whr Γ s h fundamnal soluon o h quaon (w ) α (y )(w ) xx β (y )(w ) x =, whh y y (x,) = y, (x) A f(u(x,))d. Thn, by Thorm 5, u = (u,u ) s a soluon of h sysm (.) (.7), wh u C, ( (,T]) C, ( [,T]). To oban ha u s n h scor,ϕ T, by wha w dscussd n h Inroducon (s p. 5) w nd o show h connuous dpndnc of h soluon of h Cauchy problm (.5) wh rspc o racon funcons f (hr, dnod smply by f ).. (mor prcsly) ha h soluon u δ = (u δ,uδ ), δ >, of { (w ) α (y )(w ) xx β (y )(w ) x = f δ (y,w,w ), x, > w (x,) = u, (x), x, (3.9) whr f δ(y,w,w ) := f (y,w,w )±δ, y y (x,) = y, (x) A f(u(x,))d, convrgs ponws o u whn δ, and, ha all hypohss of Corollary 4 ar fulflld. L us frs obsrv ha û = (,) and ũ = (ϕ,ϕ), whr (s p. 3) ϕ() = (M β) α β (bng M = max =, u,, α = max =, { Ab y, a }and β = max =, { d A b }) araparoflowrand uppr soluons o h sysm L (w ) (w ) α (y )(w ) xx β (y )(w ) x = f (y,w,w ) f (x,,w,w )
22 occurrngn(.5) (.. h sysmn (3.9)whou dla). (S Lmman[3].) Indd, sobvousha û = (, ) s a lowr soluon (n fac, a soluon) o hs sysm, snc f (,) =. gardng ũ = (ϕ,ϕ), noc ha f = b A w d y f(w ) a b y b A w d y, whn w = w and w (rcall ha f s h funcon ha concds wh h a Arrhnus funcon E s for s > and vanshs for s ) and L (ϕ) = ϕ () = α(m β) α, so, L (ϕ)(x,) f (x,,ϕ,ϕ) α(m β) α A b ϕ()d y, a = (M β)(α A b y,. a ) α A b a (β d A b ) y, Nx, as w nocd n h Inroducon, w obsrv ha f s ncrasng wh rspc o w j (,j =,; j ) for (a b y ) f / w j = q >. On h ohr hand, (a b y ) f / w = b A y f(w )(b A w d )y f (w ) q b A y k (b A d )y q b A y, k (b A d ) y, q, whr k s som posv consan, so f / w s boundd by a consan,.. f s unformly lpschz connuous n h varabl w, and hus h sm-lpschz condon (.5) s sasfd wh c bng a consan, for an arbrary ε (n h noaon of Thorm (4)). Concrnng h condon (.6), w hav f w j=su j = sq, w j=u j so, s sasfd wh any ε < δ/q and δ = ε q. Now, w noc ha boh h lowr soluon û = (,) and h uppr soluon ũ = (ϕ,ϕ) sasfy rvally h condon (.3), snc hr componns ar non ngav funcons. As for u, usng h ngral rprsnaon (3.8), w also s asly ha sasfs (.3), snc h frs par Γ (x,,ξ,)u, (ξ)dξ s non ngav (Γ,u, ) and h modulus of h scond par Γ (x,,ξ,)f (y,u,u )(ξ,)dξd can b smad by a consan ms, bcaus u s boundd and Γ dξ = (s mark ). I rmans o show h connuous dpndnc,.. ha u δ convrgs ponws o u, bu up o hr, w can conclud, by Thorm 4, ha u δ,ϕ T. In parcular, u δ s boundd, unformly wh rspc o δ. To show h connuous dpndnc, usng h ngral rprsnaon (.5), wh Γ bng h fundamnal soluon o h quaon (w ) α (y )(w ) xx β (y )(w ) x =, and agan ha Γ (x,,ξ,)ξdξd = (s mark ), w hav (u u δ )(x,) = Γ (x,,ξ,)[f(y,u,u ) f(y,u δ,uδ )](ξ,)dξd ±δ hus, usng h lpschz connuy of f n boundd ss (rcall ha u s boundd and u δ s n h scor,ϕ T ; h lar bng a consqunc of Thorm 4) w oban sup x (u u δ )(x,) K sup x (u u δ )(x,) dδt, so,bygronwall slmma, sup x (u u δ )(x,) δt KT,forsomconsanK. Thsshows ha lm δ u δ = u ponws (n fac, unformly) n Ω T = (,T). Now rmans o show h L p assron (h las assron) n Thorm. Ths s ssnally a consqunc of h gnralzd Young s nqualy [6, p. 9] and h fac ha h fundamnal soluon Γ [v(u n )] s a rgular krnl, unformly wh rspc o n. Mor prcsly, w shall show n h nx paragraph ha hr xs posv numbrs T T and S such ha, f u n (.,) Lp S for all [,T] hn u n (.,) L p S for all [,T] as wll. Thn h assron follows by Banach-Alaoglu shorm. From (3.5), h gnralzd Young s nqualy [6, p. 9] and h Mnkowsk s ngualy for ngrals
23 3 [7, p. 94]), w hav (.,) L p Γ [v(u n )] (,,ξ,)u, (ξ)dξ L p Γ [v(u n )] (.,,ξ,)f (u n,un,y (u n ))(ξ,)dξd L p (sup Γ [v(u n )] (x,,ξ,) dx) u, L p u n ξ (sup Γ [v(u n )] (x,,ξ,) dx) f (u n,un,y (u n ))(,) L pd ξ K (sup ξ (sup ξ (x ξ) K ( ) dx) u, L p (x ξ) dx) f (u n,u n,y (u n ))(,) L pd =K u, L p K f (u n,un,y (u n ))(,) L pd (K K x dx) K u, L p K( S K( sup f ) n a compac s sup f )ST n a compac s ( u n (,) L p un (,) L p)d f S K u, L p and u n (,) Lp S for all [,T] S, f T /4K( sup f ). n a compac s Ths nds h proof of Thorm. 4 Proofs of horms 3 and 4 and ohr rsuls In hs scon w ar concrnd wh gnral parabolc opraors L gvn by (.). W prov horms 3 and 4 and sa and prov wo corollars whch ar vrson of hs horms n h cas on has connuous dpndnc of h soluon of h sysm wh rspc o h racon funcons, and also mak hr rmarks gvng alrnav condons for h hypohss of horms 3 and 4. W bgn by gvng h man da o prov Thorm 3, cf. [, Thorm 4.] ([8, Thorm 4.7]). Undr h hypohss of Thorm 3, xcp for h condon (.3) for now, suppos for an arbrary small posv numbr ε ( < ε < ε ) hr s a pon (x, ) d (,T) on whch u = (u,u ) blongs o h boundary of h slghly nlargd quadran Q ε := {u ε and u ε} and such ha u(x,) blongs o s nror for all (x,) d (, ). If u(x, ) blongs o h vrcal par V ε := {u = ε and u ε} of h boundary Q ε, akng h quaon (.4) a h h pon (x,) = (x, ) w oban u = ε and L (u), so f (x,, ε,u (x, )) δ = (L (u )c u )(x, ) c ε, whch conradcs h hypohss f (x,,u,u ), whn ε < u < and u > ε, snc w can ak ε (,ε ) suffcnly small such ha c ε < δ. Analogously, w oban a conradcon f u(x, ) blongs o h horzonal par H ε := {u ε and u = ε}. Thus, h crux pon of hs argumn s o show h xsnc of h pon (x, ) havng h abov proprs. Th da s ha f w assum ha u(x,) dos no blong o Q ε for all (x,) Ω T = (,T) hn, snc a =, u n.(q ε ), hr would xs hs frs pon (x, ) d (,T) (wh > ) on whch u blongs o h boundary of Q ε, from hnc w oban h conradcon wh h assumpon f whn ε < u < and u j > ε (bng j,,j =,). Howvr, a pror mgh occur ha u(x n, n ) Q ε for a squnc of pons (x n, n ) Ω T wh n ց and x n, vn hough u(x,) n.(q ε ) for all x d, and n hs cas, hs pon (x, ) would no xs. Ths suaon s avodd wh h condon (.3). Proof of Thorm 3. L us assum hr s a pon (x,) Ω T such ha u(x,) Q ε and w shall oban a conradcon. If hs s h cas hn, by h connuy of u, hr xss anohr pon on whch u blongs o V ε or H ε (dfnd abov). Consdr h cas ha u V ε (h cas u H ε s
24 4 smlar). Thn w dfn = nf{ (,T);u(x,) V ε for som x d }. W clam ha >. L (x n, n ) Ω T = (,T) b a squnc wh n ց and u (x n, n ) = ε. Now, from (.3) hr ar posvnumbrs and such u (x,) > ε/for(x,) Ω T wh x < and < <. Thn f =, w would hav x n for all n suffcnly larg, so, by passng o som subsqunc w can assum ha (x n ) convrgs o som x. By connuy agan, w arrv a u (x,) = ε. Ths conradcs h hypohss u (x,) for all x d. Thus, w conclud ha >. Morovr, u (x, ) = ε, and, as w show abov hs conradcs h hypohss f whn ε < u < and u > ε. Proof of Thorm 4. Thorm 4 s oband by comparson, va Thorm 3. Indd, n h cas ha u s an uppr soluon o (.8), dfnng w = u û, w hav (L c )w = L (u ) L (û ) c w f (x,,u,u ) f (x,,û,û ) c w δ = f (x,,w û,w û ) f (x,,û,û ) c w δ g (x,,w,w )δ δ, whr g (x,,w,w ) = f (x,,w û,w û ) f (x,,û,û ) c w δ. Now, omng h dpndnc on som argumns for smplcy, and consdrng h cas = (h cas = s smlar), subracng and addng h rm f (û,w û ), w hav g = [f (w û,w û ) f (û,w û )] c w [f (û,w û ) f (û,û )]δ for all w ( ε,) and w ε, by (.5), h monooncy of f wh rspc o u, and (.6). Thus w hav shown ha w sasfs all h hypohss of Thorm 3 wh w, c and δ δ n plac of u, c and δ, rspcvly, hn, w conclud ha w (x,), and, smlarly, w can show ha w (x,), for all (x,) Ω T. Ths nds h proof of h frs samn of Thorm 4. gardng h scond samn, ha s, h cas ha u s a lowr soluon, w obsrv ha rducs o h frs samn by subsung f by f δ and akng ũ n plac of h u n h frs samn and h u n h scond samn n plac of û. Corollary 3. (Corollary of Thorm 3.) Undr h hypohss and noaons of Thorm 3 bu wh δ =, suppos w hav a connuous dpndnc of h soluons of h sysm L (u )c u = f (x,,u,u ) (4.) (x,) Ω T = d (,T), < T, wh rspc o h racon funcons f. Thn h quadran Q = {(u,u ); u,u } s a posvly nvaran rgon o h sysm (4.). Mor prcsly, l u = (u,u ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) b a soluon o h sysm (4.) such ha u(x,) Q for all x d. If u s h ponws lm, whn δ, of u δ, whr u δ C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) sasfyng (.3) s a soluon of h Cauchy problm (assumng has such a soluon) { L (u δ )c u δ = f (x,,u δ,uδ )δ, (x,) Ω T u δ (x,) = u(x,), x d (4.) hn u(x,) Q for all (x,) d [,T). Proof. By Thorm 3 w hav u δ (x,) Q for all (x,) d [,T), for any δ >. Snc u(x,) = lm δ u δ (x,) for ach (x,) d [,T) and Q s a closd s n d, follows ha u(x,) Q for all (x,) d [,T) as wll. mark. As w can s by h proofs of Thorm 3 and Corollary 3, w can rplac n hs rsuls h condon on h racon funcons f whn ε < u < and u j > ε (,j =,, j ) by f > whn u = and u j, f w assum ha u(x,) n.(q) for all x d, or, f w assum a connuous dpndnc also on h nal daa,.. u(x,) Q (for all x d ) and u s h ponws lm, whn δ, of h soluon u δ = (u δ,u δ ) n h spac C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) and sasfyng (.3) of h Cauchy problm (assumng has such a soluon) { L (u δ )c u δ = f (x,,u δ,uδ )δ, (x,) Ω T u δ (x,) = u (x,)δ, x d (4.3). mark 3. In Thorm 3 and Corollary 3, and n mark as wll, w noc ha o oban u(x,) Q for all (x,) Ω T, suffcs o show ha u(x,) Q ε,s for all (x,) Ω T, for arbrarly small ε > and larg S >, whr Q ε,s = {(u,u ); ε u S}. Thn w oban h sam rsuls f w dspns h condon f or f >, whn ε < u < and u j > ε, (,j =,, j ), and assum ha f > whn u = and f s connuous a h pon u =, unformly wh rspc o (x,) Ω T and ε u j S, for any S > and som ε >. Indd, n hs cas, gvn S >, hr xss som ε > such ha f > whn ε < u < and ε < u j S.
25 5 Corollary 4. (Corollary of Thorm 4.) L h hypohss of Thorm 4 on h racons funcons f b n forc and suppos w hav a connuous dpndnc of h soluons of h sysm (.7) wh rspc o h racon funcons f ; mor prcsly, suppos u = (u,u ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) ( < T, Ω T = d (,T)) s a soluon of (.7) whch s h ponws lm, n Ω T, of (u δ ) and also of (u δ ), whn δ, whr u δ = (u δ,uδ ) (rspc. u δ = (u δ,u δ )), n h spac C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) and sasfyng (.3), s a soluon of h Cauchy problm (assumng such a soluon xss) { L (u ±δ ) = f (x,,u ±δ,u±δ )±δ, (x,) Ω T u ±δ (x,) = u(x,), x d, δ >. Thn f û = (û,û ) (rspc. ũ = (ũ,ũ )), n h spac C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) and sasfyng (.3), s alowr (rspc. uppr) soluon o h sysm (.7) (.. L (û )(x,) f (x,,û (x,),û (x,)) for all (x,) Ω T ; rspc. L (ũ )(x,) f (x,,ũ (x,),ũ (x,)) for all (x,) Ω T ) such ha û (x,) u (x,) (rspc. u (x,) ũ (x,)) for all x d, hn û (x,) u (x,) (rspc. u (x,) ũ (x,)) for all (x,) d [,T). Proof. L us consdr only h cas rgardng h lowr soluon û, snc h cas rgardng h uppr soluonũcanbprovnanalogously. ThproofconsssnapplyngThorm4wh f ˆδ (f ˆδ fwr h cas rgardngũ) n plac of f, whr ˆδ s som numbr bwm δ and δ,.g. (δ δ)/. Noc ha û and u δ ar, rspcvly, a lowrand an uppr soluon o h sysm L (u ) = f (x,,u,u )(δδ )/. Bsds, u δ û sasfs (.3), snc boh u δ and û do sasfy, and u δ (x,) = u (x,) û (x,) for all x d. Thn, by Thorm 4, w hav ha u δ (x,) û (x,) for all (x,) d [,T). Snc hs s ru for any δ and u(x,) = lm δ u δ (x,) for all (x,) Ω T, w oban h rsul. mark 4. In h samn (rspc. samn ) of Thorm 4 w can rplac h condons (.5) and (.6) by (4.4) f (x,,su (x,),u (x,)) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) c (x,)s, f (x,,u (x,),su (x,)) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) c (x,)s (4.5) and f (x,,u (x,),su (x,)) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) δ, f (x,,su (x,),u (x,)) f (x,,u (x,),u (x,)) δ (4.6) for all (x,) Ω T = d (,T), s ( ε,), and all u = (u,u ) C, (Ω T ) C( d [,T)) sasfyng (.3) and such ha u û (rspc. u ũ ). Cf. [6, 8.]. Indd, followng h proof of Thorm 3, p. 3, f hr was a pon (x,) Ω T such ha w(x,) := (u û)(x,) Q ε (rspc. w(x,) := (ũ u)(x,) Q ε ) for som arbrarly small ε, hn w would g h conradcon (L c )w and (s h proofofthorm 4) (L c )w f (x,,u,u ) f (x,,û,û ) c w δ > a som pon n (x, ) Ω T. Noc ha u ũ (rspc. u ũ ) for all (x,) Ω. 5 Global soluon In hs scon w prov Thorm. L us dno n hs scon by u = (u,u ) a maxmal soluon of (.) (.6), dfnd n a maxmal nrval [,T ), (s h Inroducon, p. 5), n h spac X T = C, ( (,T )) C, loc ( [,T )) L loc ((, );Lp ()), whch was also prsnd n h Inroducon, nrcpd wh h scor,ϕ T. Thn w shall show ha T =. Throughou hs scon w assum all h hypohss n Thorm, spcally u, L p (), for som p (, ). W suppos ha T < and w shall oban a conradcon. L us rcall ha h convoluon produc of funcons n conjuga Lbsgu spacs on n dcay o zro a nfny, mor prcsly, f f L p ( n ) and g L q ( n ), wh < p < and /p /q =, hn f g C ( n ), whr C ( n ) dno h spac of connuous funcons h on n such ha lm x h(x) =. Bsds, sup x n (f g)(x) f L p g L q. S [7, p. 4]. 9 Usng hs fac w can prov h followng lmma. Lmma 7. For any (,T ) and s =,, w hav ( s x u)(.,) C (). Furhrmor, hr xs h paral drvavs ( 3 x u)(x,) and ( x )u(x,), for any (x,) (,T ). 9 W would lk o hank Prof. Lucas C. F. Frrra for brngng our anon o hs fac and suggsng us o ak h nal daa u, n L p.
Consider a system of 2 simultaneous first order linear equations
 Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Soluon of sysms of frs ordr lnar quaons onsdr a sysm of smulanous frs ordr lnar quaons a b c d I has h alrna mar-vcor rprsnaon a b c d Or, n shorhand A, f A s alrady known from con W know ha h abov sysm
Summary: Solving a Homogeneous System of Two Linear First Order Equations in Two Unknowns
 Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
Summary: Solvng a Homognous Sysm of Two Lnar Frs Ordr Equaons n Two Unknowns Gvn: A Frs fnd h wo gnvalus, r, and hr rspcv corrspondng gnvcors, k, of h coffcn mar A Dpndng on h gnvalus and gnvcors, h gnral
The Variance-Covariance Matrix
 Th Varanc-Covaranc Marx Our bggs a so-ar has bn ng a lnar uncon o a s o daa by mnmzng h las squars drncs rom h o h daa wh mnsarch. Whn analyzng non-lnar daa you hav o us a program l Malab as many yps o
Th Varanc-Covaranc Marx Our bggs a so-ar has bn ng a lnar uncon o a s o daa by mnmzng h las squars drncs rom h o h daa wh mnsarch. Whn analyzng non-lnar daa you hav o us a program l Malab as many yps o
innovations shocks white noise
 Innovaons Tm-srs modls ar consrucd as lnar funcons of fundamnal forcasng rrors, also calld nnovaons or shocks Ths basc buldng blocks sasf var σ Srall uncorrlad Ths rrors ar calld wh nos In gnral, f ou
Innovaons Tm-srs modls ar consrucd as lnar funcons of fundamnal forcasng rrors, also calld nnovaons or shocks Ths basc buldng blocks sasf var σ Srall uncorrlad Ths rrors ar calld wh nos In gnral, f ou
SIMEON BALL AND AART BLOKHUIS
 A BOUND FOR THE MAXIMUM WEIGHT OF A LINEAR CODE SIMEON BALL AND AART BLOKHUIS Absrac. I s shown ha h paramrs of a lnar cod ovr F q of lngh n, dmnson k, mnmum wgh d and maxmum wgh m sasfy a cran congrunc
A BOUND FOR THE MAXIMUM WEIGHT OF A LINEAR CODE SIMEON BALL AND AART BLOKHUIS Absrac. I s shown ha h paramrs of a lnar cod ovr F q of lngh n, dmnson k, mnmum wgh d and maxmum wgh m sasfy a cran congrunc
9. Simple Rules for Monetary Policy
 9. Smpl Ruls for Monar Polc John B. Talor, Ma 0, 03 Woodford, AR 00 ovrvw papr Purpos s o consdr o wha xn hs prscrpon rsmbls h sor of polc ha conomc hor would rcommnd Bu frs, l s rvw how hs sor of polc
9. Smpl Ruls for Monar Polc John B. Talor, Ma 0, 03 Woodford, AR 00 ovrvw papr Purpos s o consdr o wha xn hs prscrpon rsmbls h sor of polc ha conomc hor would rcommnd Bu frs, l s rvw how hs sor of polc
Advanced Queueing Theory. M/G/1 Queueing Systems
 Advand Quung Thory Ths slds ar rad by Dr. Yh Huang of Gorg Mason Unvrsy. Sudns rgsrd n Dr. Huang's ourss a GMU an ma a sngl mahn-radabl opy and prn a sngl opy of ah sld for hr own rfrn, so long as ah sld
Advand Quung Thory Ths slds ar rad by Dr. Yh Huang of Gorg Mason Unvrsy. Sudns rgsrd n Dr. Huang's ourss a GMU an ma a sngl mahn-radabl opy and prn a sngl opy of ah sld for hr own rfrn, so long as ah sld
Frequency Response. Response of an LTI System to Eigenfunction
 Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
Frquncy Rsons Las m w Rvsd formal dfnons of lnary and m-nvaranc Found an gnfuncon for lnar m-nvaran sysms Found h frquncy rsons of a lnar sysm o gnfuncon nu Found h frquncy rsons for cascad, fdbac, dffrnc
t=0 t>0: + vr - i dvc Continuation
 hapr Ga Dlay and rcus onnuaon s rcu Equaon >: S S Ths dffrnal quaon, oghr wh h nal condon, fully spcfs bhaor of crcu afr swch closs Our n challng: larn how o sol such quaons TUE/EE 57 nwrk analys 4/5 NdM
hapr Ga Dlay and rcus onnuaon s rcu Equaon >: S S Ths dffrnal quaon, oghr wh h nal condon, fully spcfs bhaor of crcu afr swch closs Our n challng: larn how o sol such quaons TUE/EE 57 nwrk analys 4/5 NdM
CONTINUOUS TIME DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING
 Eon. 511b Sprng 1993 C. Sms I. Th Opmaon Problm CONTINUOUS TIME DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING W onsdr h problm of maxmng subj o and EU(C, ) d (1) j ^ d = (C, ) d + σ (C, ) dw () h(c, ), (3) whr () and (3) hold for
Eon. 511b Sprng 1993 C. Sms I. Th Opmaon Problm CONTINUOUS TIME DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING W onsdr h problm of maxmng subj o and EU(C, ) d (1) j ^ d = (C, ) d + σ (C, ) dw () h(c, ), (3) whr () and (3) hold for
EE243 Advanced Electromagnetic Theory Lec # 10: Poynting s Theorem, Time- Harmonic EM Fields
 Appl M Fall 6 Nuruhr Lcur # r 9/6/6 4 Avanc lcromagnc Thory Lc # : Poynng s Thorm Tm- armonc M Fls Poynng s Thorm Consrvaon o nrgy an momnum Poynng s Thorm or Lnar sprsv Ma Poynng s Thorm or Tm-armonc
Appl M Fall 6 Nuruhr Lcur # r 9/6/6 4 Avanc lcromagnc Thory Lc # : Poynng s Thorm Tm- armonc M Fls Poynng s Thorm Consrvaon o nrgy an momnum Poynng s Thorm or Lnar sprsv Ma Poynng s Thorm or Tm-armonc
State Observer Design
 Sa Obsrvr Dsgn A. Khak Sdgh Conrol Sysms Group Faculy of Elcrcal and Compur Engnrng K. N. Toos Unvrsy of Tchnology Fbruary 2009 1 Problm Formulaon A ky assumpon n gnvalu assgnmn and sablzng sysms usng
Sa Obsrvr Dsgn A. Khak Sdgh Conrol Sysms Group Faculy of Elcrcal and Compur Engnrng K. N. Toos Unvrsy of Tchnology Fbruary 2009 1 Problm Formulaon A ky assumpon n gnvalu assgnmn and sablzng sysms usng
Problem 1: Consider the following stationary data generation process for a random variable y t. e t ~ N(0,1) i.i.d.
 A/CN C m Sr Anal Profor Òcar Jordà Wnr conomc.c. Dav POBLM S SOLIONS Par I Analcal Quon Problm : Condr h followng aonar daa gnraon proc for a random varabl - N..d. wh < and N -. a Oban h populaon man varanc
A/CN C m Sr Anal Profor Òcar Jordà Wnr conomc.c. Dav POBLM S SOLIONS Par I Analcal Quon Problm : Condr h followng aonar daa gnraon proc for a random varabl - N..d. wh < and N -. a Oban h populaon man varanc
Supplementary Figure 1. Experiment and simulation with finite qudit. anharmonicity. (a), Experimental data taken after a 60 ns three-tone pulse.
 Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Supplmnar Fgur. Eprmn and smulaon wh fn qud anharmonc. a, Eprmnal daa akn afr a 6 ns hr-on puls. b, Smulaon usng h amlonan. Supplmnar Fgur. Phagoran dnamcs n h m doman. a, Eprmnal daa. Th hr-on puls s
Midterm exam 2, April 7, 2009 (solutions)
 Univrsiy of Pnnsylvania Dparmn of Mahmaics Mah 26 Honors Calculus II Spring Smsr 29 Prof Grassi, TA Ashr Aul Midrm xam 2, April 7, 29 (soluions) 1 Wri a basis for h spac of pairs (u, v) of smooh funcions
Univrsiy of Pnnsylvania Dparmn of Mahmaics Mah 26 Honors Calculus II Spring Smsr 29 Prof Grassi, TA Ashr Aul Midrm xam 2, April 7, 29 (soluions) 1 Wri a basis for h spac of pairs (u, v) of smooh funcions
Convergence of Quintic Spline Interpolation
 Inrnaonal Journal o ompur Applcaons 97 8887 Volum 7 No., Aprl onvrgnc o Qunc Spln Inrpolaon Y.P. Dub Dparmn O Mamacs, L.N..T. Jabalpur 8 Anl Sukla Dparmn O Mamacs Gan Ganga ollg O Tcnog, Jabalpur 8 ASTRAT
Inrnaonal Journal o ompur Applcaons 97 8887 Volum 7 No., Aprl onvrgnc o Qunc Spln Inrpolaon Y.P. Dub Dparmn O Mamacs, L.N..T. Jabalpur 8 Anl Sukla Dparmn O Mamacs Gan Ganga ollg O Tcnog, Jabalpur 8 ASTRAT
Wave Superposition Principle
 Physcs 36: Was Lcur 5 /7/8 Wa Suroson Prncl I s qu a common suaon for wo or mor was o arr a h sam on n sac or o xs oghr along h sam drcon. W wll consdr oday sral moran cass of h combnd ffcs of wo or mor
Physcs 36: Was Lcur 5 /7/8 Wa Suroson Prncl I s qu a common suaon for wo or mor was o arr a h sam on n sac or o xs oghr along h sam drcon. W wll consdr oday sral moran cass of h combnd ffcs of wo or mor
Chapter 9 Transient Response
 har 9 Transn sons har 9: Ouln N F n F Frs-Ordr Transns Frs-Ordr rcus Frs ordr crcus: rcus conan onl on nducor or on caacor gornd b frs-ordr dffrnal quaons. Zro-nu rsons: h crcu has no ald sourc afr a cran
har 9 Transn sons har 9: Ouln N F n F Frs-Ordr Transns Frs-Ordr rcus Frs ordr crcus: rcus conan onl on nducor or on caacor gornd b frs-ordr dffrnal quaons. Zro-nu rsons: h crcu has no ald sourc afr a cran
Chapter 13 Laplace Transform Analysis
 Chapr aplac Tranorm naly Chapr : Ouln aplac ranorm aplac Tranorm -doman phaor analy: x X σ m co ω φ x X X m φ x aplac ranorm: [ o ] d o d < aplac Tranorm Thr condon Unlaral on-dd aplac ranorm: aplac ranorm
Chapr aplac Tranorm naly Chapr : Ouln aplac ranorm aplac Tranorm -doman phaor analy: x X σ m co ω φ x X X m φ x aplac ranorm: [ o ] d o d < aplac Tranorm Thr condon Unlaral on-dd aplac ranorm: aplac ranorm
On the Derivatives of Bessel and Modified Bessel Functions with Respect to the Order and the Argument
 Inrnaional Rsarch Journal of Applid Basic Scincs 03 Aailabl onlin a wwwirjabscom ISSN 5-838X / Vol 4 (): 47-433 Scinc Eplorr Publicaions On h Driais of Bssl Modifid Bssl Funcions wih Rspc o h Ordr h Argumn
Inrnaional Rsarch Journal of Applid Basic Scincs 03 Aailabl onlin a wwwirjabscom ISSN 5-838X / Vol 4 (): 47-433 Scinc Eplorr Publicaions On h Driais of Bssl Modifid Bssl Funcions wih Rspc o h Ordr h Argumn
CIVL 8/ D Boundary Value Problems - Triangular Elements (T6) 1/8
 CIVL 8/7 -D Boundar Valu Problm - rangular Elmn () /8 SI-ODE RIAGULAR ELEMES () A quadracall nrpolad rangular lmn dfnd b nod, hr a h vrc and hr a h mddl a ach d. h mddl nod, dpndng on locaon, ma dfn a
CIVL 8/7 -D Boundar Valu Problm - rangular Elmn () /8 SI-ODE RIAGULAR ELEMES () A quadracall nrpolad rangular lmn dfnd b nod, hr a h vrc and hr a h mddl a ach d. h mddl nod, dpndng on locaon, ma dfn a
Institute of Actuaries of India
 Insiu of Acuaris of India ubjc CT3 Probabiliy and Mahmaical aisics Novmbr Examinaions INDICATIVE OLUTION Pag of IAI CT3 Novmbr ol. a sampl man = 35 sampl sandard dviaion = 36.6 b for = uppr bound = 35+*36.6
Insiu of Acuaris of India ubjc CT3 Probabiliy and Mahmaical aisics Novmbr Examinaions INDICATIVE OLUTION Pag of IAI CT3 Novmbr ol. a sampl man = 35 sampl sandard dviaion = 36.6 b for = uppr bound = 35+*36.6
A Note on Estimability in Linear Models
 Intrnatonal Journal of Statstcs and Applcatons 2014, 4(4): 212-216 DOI: 10.5923/j.statstcs.20140404.06 A Not on Estmablty n Lnar Modls S. O. Adymo 1,*, F. N. Nwob 2 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatcs and Statstcs,
Intrnatonal Journal of Statstcs and Applcatons 2014, 4(4): 212-216 DOI: 10.5923/j.statstcs.20140404.06 A Not on Estmablty n Lnar Modls S. O. Adymo 1,*, F. N. Nwob 2 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatcs and Statstcs,
Homework: Introduction to Motion
 Homwork: Inroducon o Moon Dsanc vs. Tm Graphs Nam Prod Drcons: Answr h foowng qusons n h spacs provdd. 1. Wha do you do o cra a horzona n on a dsancm graph? 2. How do you wak o cra a sragh n ha sops up?
Homwork: Inroducon o Moon Dsanc vs. Tm Graphs Nam Prod Drcons: Answr h foowng qusons n h spacs provdd. 1. Wha do you do o cra a horzona n on a dsancm graph? 2. How do you wak o cra a sragh n ha sops up?
OUTLINE FOR Chapter 2-2. Basic Laws
 0//8 OUTLINE FOR Chapr - AERODYNAMIC W-- Basc Laws Analss of an problm n fld mchancs ncssarl nclds samn of h basc laws gornng h fld moon. Th basc laws, whch applcabl o an fld, ar: Consraon of mass Conn
0//8 OUTLINE FOR Chapr - AERODYNAMIC W-- Basc Laws Analss of an problm n fld mchancs ncssarl nclds samn of h basc laws gornng h fld moon. Th basc laws, whch applcabl o an fld, ar: Consraon of mass Conn
Boosting and Ensemble Methods
 Boosng and Ensmbl Mhods PAC Larnng modl Som dsrbuon D ovr doman X Eampls: c* s h arg funcon Goal: Wh hgh probably -d fnd h n H such ha rrorh,c* < d and ar arbrarly small. Inro o ML 2 Wak Larnng
Boosng and Ensmbl Mhods PAC Larnng modl Som dsrbuon D ovr doman X Eampls: c* s h arg funcon Goal: Wh hgh probably -d fnd h n H such ha rrorh,c* < d and ar arbrarly small. Inro o ML 2 Wak Larnng
Safety and Reliability of Embedded Systems. (Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Stochastic Reliability Analysis
 (Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons of Falurs ovr Tm Rlably Modlng Exampls of Dsrbuon Funcons Th xponnal
(Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons of Falurs ovr Tm Rlably Modlng Exampls of Dsrbuon Funcons Th xponnal
Safety and Reliability of Embedded Systems. (Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit eingebetteter Systeme) Stochastic Reliability Analysis
 Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms (Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons
Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms (Schrh und Zuvrlässgk ngbr Sysm) Sochasc Rlably Analyss Safy and Rlably of Embddd Sysms Conn Dfnon of Rlably Hardwar- vs. Sofwar Rlably Tool Asssd Rlably Modlng Dscrpons
FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS
 FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS hp://www.cs.umass.du/c/orn/faultolransysms ar 4 Analyss Mhods Chapr HW Faul Tolranc ar.4.1 Duplx Sysms Boh procssors xcu h sam as If oupus ar n agrmn - rsul s assumd o b corrc If
FAULT TOLERANT SYSTEMS hp://www.cs.umass.du/c/orn/faultolransysms ar 4 Analyss Mhods Chapr HW Faul Tolranc ar.4.1 Duplx Sysms Boh procssors xcu h sam as If oupus ar n agrmn - rsul s assumd o b corrc If
Lecture 4 : Backpropagation Algorithm. Prof. Seul Jung ( Intelligent Systems and Emotional Engineering Laboratory) Chungnam National University
 Lcur 4 : Bacpropagaon Algorhm Pro. Sul Jung Inllgn Sm and moonal ngnrng Laboraor Chungnam Naonal Unvr Inroducon o Bacpropagaon algorhm 969 Mn and Papr aac. 980 Parr and Wrbo dcovrd bac propagaon algorhm.
Lcur 4 : Bacpropagaon Algorhm Pro. Sul Jung Inllgn Sm and moonal ngnrng Laboraor Chungnam Naonal Unvr Inroducon o Bacpropagaon algorhm 969 Mn and Papr aac. 980 Parr and Wrbo dcovrd bac propagaon algorhm.
Bethe-Salpeter Equation Green s Function and the Bethe-Salpeter Equation for Effective Interaction in the Ladder Approximation
 Bh-Salp Equaon n s Funcon and h Bh-Salp Equaon fo Effcv Inacon n h Ladd Appoxmaon Csa A. Z. Vasconcllos Insuo d Físca-UFRS - upo: Físca d Hadons Sngl-Pacl Popagao. Dagam xpanson of popagao. W consd as
Bh-Salp Equaon n s Funcon and h Bh-Salp Equaon fo Effcv Inacon n h Ladd Appoxmaon Csa A. Z. Vasconcllos Insuo d Físca-UFRS - upo: Físca d Hadons Sngl-Pacl Popagao. Dagam xpanson of popagao. W consd as
10.5 Linear Viscoelasticity and the Laplace Transform
 Scn.5.5 Lnar Vclacy and h Lalac ranfrm h Lalac ranfrm vry uful n cnrucng and analyng lnar vclac mdl..5. h Lalac ranfrm h frmula fr h Lalac ranfrm f h drvav f a funcn : L f f L f f f f f c..5. whr h ranfrm
Scn.5.5 Lnar Vclacy and h Lalac ranfrm h Lalac ranfrm vry uful n cnrucng and analyng lnar vclac mdl..5. h Lalac ranfrm h frmula fr h Lalac ranfrm f h drvav f a funcn : L f f L f f f f f c..5. whr h ranfrm
CSE 245: Computer Aided Circuit Simulation and Verification
 CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
Grand Canonical Ensemble
 Th nsmbl of systms mmrsd n a partcl-hat rsrvor at constant tmpratur T, prssur P, and chmcal potntal. Consdr an nsmbl of M dntcal systms (M =,, 3,...M).. Thy ar mutually sharng th total numbr of partcls
Th nsmbl of systms mmrsd n a partcl-hat rsrvor at constant tmpratur T, prssur P, and chmcal potntal. Consdr an nsmbl of M dntcal systms (M =,, 3,...M).. Thy ar mutually sharng th total numbr of partcls
"Science Stays True Here" Journal of Mathematics and Statistical Science, Volume 2016, Science Signpost Publishing
 "Scnc Says r Hr" Jornal of Mahmacs and Sascal Scnc Volm 6 343-356 Scnc Sgnpos Pblshng Mhod for a Solon o Som Class of Qas-Sac Problms n Lnar Vscolascy hory as Appld o Problms of Lnar orson of a Prsmac
"Scnc Says r Hr" Jornal of Mahmacs and Sascal Scnc Volm 6 343-356 Scnc Sgnpos Pblshng Mhod for a Solon o Som Class of Qas-Sac Problms n Lnar Vscolascy hory as Appld o Problms of Lnar orson of a Prsmac
ELEN E4830 Digital Image Processing
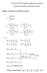 ELEN E48 Dgal Imag Procssng Mrm Eamnaon Sprng Soluon Problm Quanzaon and Human Encodng r k u P u P u r r 6 6 6 6 5 6 4 8 8 4 P r 6 6 P r 4 8 8 6 8 4 r 8 4 8 4 7 8 r 6 6 6 6 P r 8 4 8 P r 6 6 8 5 P r /
ELEN E48 Dgal Imag Procssng Mrm Eamnaon Sprng Soluon Problm Quanzaon and Human Encodng r k u P u P u r r 6 6 6 6 5 6 4 8 8 4 P r 6 6 P r 4 8 8 6 8 4 r 8 4 8 4 7 8 r 6 6 6 6 P r 8 4 8 P r 6 6 8 5 P r /
Analysis of decentralized potential field based multi-agent navigation via primal-dual Lyapunov theory
 Analyss of dcnralzd ponal fld basd mul-agn navgaon va prmal-dual Lyapunov hory Th MIT Faculy has mad hs arcl opnly avalabl. Plas shar how hs accss bnfs you. Your sory mars. Caon As Publshd Publshr Dmarogonas,
Analyss of dcnralzd ponal fld basd mul-agn navgaon va prmal-dual Lyapunov hory Th MIT Faculy has mad hs arcl opnly avalabl. Plas shar how hs accss bnfs you. Your sory mars. Caon As Publshd Publshr Dmarogonas,
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 0 Canoncal Transformaons (Chaper 9) Wha We Dd Las Tme Hamlon s Prncple n he Hamlonan formalsm Dervaon was smple δi δ Addonal end-pon consrans pq H( q, p, ) d 0 δ q ( ) δq ( ) δ
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecure 0 Canoncal Transformaons (Chaper 9) Wha We Dd Las Tme Hamlon s Prncple n he Hamlonan formalsm Dervaon was smple δi δ Addonal end-pon consrans pq H( q, p, ) d 0 δ q ( ) δq ( ) δ
Exercise 1. Sketch the graph of the following function. (x 2
 Writtn tst: Fbruary 9th, 06 Exrcis. Sktch th graph of th following function fx = x + x, spcifying: domain, possibl asymptots, monotonicity, continuity, local and global maxima or minima, and non-drivability
Writtn tst: Fbruary 9th, 06 Exrcis. Sktch th graph of th following function fx = x + x, spcifying: domain, possibl asymptots, monotonicity, continuity, local and global maxima or minima, and non-drivability
CH.3. COMPATIBILITY EQUATIONS. Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC
 CH.3. COMPATIBILITY EQUATIONS Connuum Mechancs Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Overvew Compably Condons Compably Equaons of a Poenal Vecor Feld Compably Condons for Infnesmal Srans Inegraon of he Infnesmal
CH.3. COMPATIBILITY EQUATIONS Connuum Mechancs Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Overvew Compably Condons Compably Equaons of a Poenal Vecor Feld Compably Condons for Infnesmal Srans Inegraon of he Infnesmal
Relative controllability of nonlinear systems with delays in control
 Relave conrollably o nonlnear sysems wh delays n conrol Jerzy Klamka Insue o Conrol Engneerng, Slesan Techncal Unversy, 44- Glwce, Poland. phone/ax : 48 32 37227, {jklamka}@a.polsl.glwce.pl Keywor: Conrollably.
Relave conrollably o nonlnear sysems wh delays n conrol Jerzy Klamka Insue o Conrol Engneerng, Slesan Techncal Unversy, 44- Glwce, Poland. phone/ax : 48 32 37227, {jklamka}@a.polsl.glwce.pl Keywor: Conrollably.
Comparative Study of Finite Element and Haar Wavelet Correlation Method for the Numerical Solution of Parabolic Type Partial Differential Equations
 ISS 746-7659, England, UK Journal of Informaon and Compung Scnc Vol., o. 3, 6, pp.88-7 Comparav Sudy of Fn Elmn and Haar Wavl Corrlaon Mhod for h umrcal Soluon of Parabolc Typ Paral Dffrnal Equaons S.
ISS 746-7659, England, UK Journal of Informaon and Compung Scnc Vol., o. 3, 6, pp.88-7 Comparav Sudy of Fn Elmn and Haar Wavl Corrlaon Mhod for h umrcal Soluon of Parabolc Typ Paral Dffrnal Equaons S.
Control Systems (Lecture note #6)
 6.5 Corol Sysms (Lcur o #6 Las Tm: Lar algbra rw Lar algbrac quaos soluos Paramrzao of all soluos Smlary rasformao: compao form Egalus ad gcors dagoal form bg pcur: o brach of h cours Vcor spacs marcs
6.5 Corol Sysms (Lcur o #6 Las Tm: Lar algbra rw Lar algbrac quaos soluos Paramrzao of all soluos Smlary rasformao: compao form Egalus ad gcors dagoal form bg pcur: o brach of h cours Vcor spacs marcs
Theoretical Seismology
 Thorcal Ssmology Lcur 9 Sgnal Procssng Fourr analyss Fourr sudd a h Écol Normal n Pars, augh by Lagrang, who Fourr dscrbd as h frs among Europan mn of scnc, Laplac, who Fourr rad lss hghly, and by Mong.
Thorcal Ssmology Lcur 9 Sgnal Procssng Fourr analyss Fourr sudd a h Écol Normal n Pars, augh by Lagrang, who Fourr dscrbd as h frs among Europan mn of scnc, Laplac, who Fourr rad lss hghly, and by Mong.
The Hyperelastic material is examined in this section.
 4. Hyprlastcty h Hyprlastc matral s xad n ths scton. 4..1 Consttutv Equatons h rat of chang of ntrnal nrgy W pr unt rfrnc volum s gvn by th strss powr, whch can b xprssd n a numbr of dffrnt ways (s 3.7.6):
4. Hyprlastcty h Hyprlastc matral s xad n ths scton. 4..1 Consttutv Equatons h rat of chang of ntrnal nrgy W pr unt rfrnc volum s gvn by th strss powr, whch can b xprssd n a numbr of dffrnt ways (s 3.7.6):
Lecture 1: Numerical Integration The Trapezoidal and Simpson s Rule
 Lcur : Numrical ngraion Th Trapzoidal and Simpson s Rul A problm Th probabiliy of a normally disribud (man µ and sandard dviaion σ ) vn occurring bwn h valus a and b is B A P( a x b) d () π whr a µ b -
Lcur : Numrical ngraion Th Trapzoidal and Simpson s Rul A problm Th probabiliy of a normally disribud (man µ and sandard dviaion σ ) vn occurring bwn h valus a and b is B A P( a x b) d () π whr a µ b -
Chapter 5 The Laplace Transform. x(t) input y(t) output Dynamic System
 EE 422G No: Chapr 5 Inrucor: Chung Chapr 5 Th Laplac Tranform 5- Inroducion () Sym analyi inpu oupu Dynamic Sym Linar Dynamic ym: A procor which proc h inpu ignal o produc h oupu dy ( n) ( n dy ( n) +
EE 422G No: Chapr 5 Inrucor: Chung Chapr 5 Th Laplac Tranform 5- Inroducion () Sym analyi inpu oupu Dynamic Sym Linar Dynamic ym: A procor which proc h inpu ignal o produc h oupu dy ( n) ( n dy ( n) +
Final Exam : Solutions
 Comp : Algorihm and Daa Srucur Final Exam : Soluion. Rcuriv Algorihm. (a) To bgin ind h mdian o {x, x,... x n }. Sinc vry numbr xcp on in h inrval [0, n] appar xacly onc in h li, w hav ha h mdian mu b
Comp : Algorihm and Daa Srucur Final Exam : Soluion. Rcuriv Algorihm. (a) To bgin ind h mdian o {x, x,... x n }. Sinc vry numbr xcp on in h inrval [0, n] appar xacly onc in h li, w hav ha h mdian mu b
V.Abramov - FURTHER ANALYSIS OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR LARGE CLIENT/SERVER COMPUTER NETWORKS
 R&RATA # Vol.) 8, March FURTHER AALYSIS OF COFIDECE ITERVALS FOR LARGE CLIET/SERVER COMPUTER ETWORKS Vyacheslav Abramov School of Mahemacal Scences, Monash Unversy, Buldng 8, Level 4, Clayon Campus, Wellngon
R&RATA # Vol.) 8, March FURTHER AALYSIS OF COFIDECE ITERVALS FOR LARGE CLIET/SERVER COMPUTER ETWORKS Vyacheslav Abramov School of Mahemacal Scences, Monash Unversy, Buldng 8, Level 4, Clayon Campus, Wellngon
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Random Process Part 1
 Random Procss Part A random procss t (, ζ is a signal or wavform in tim. t : tim ζ : outcom in th sampl spac Each tim w rapat th xprimnt, a nw wavform is gnratd. ( W will adopt t for short. Tim sampls
Random Procss Part A random procss t (, ζ is a signal or wavform in tim. t : tim ζ : outcom in th sampl spac Each tim w rapat th xprimnt, a nw wavform is gnratd. ( W will adopt t for short. Tim sampls
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Notes on the stability of dynamic systems and the use of Eigen Values.
 Noes on he sabl of dnamc ssems and he use of Egen Values. Source: Macro II course noes, Dr. Davd Bessler s Tme Seres course noes, zarads (999) Ineremporal Macroeconomcs chaper 4 & Techncal ppend, and Hamlon
Noes on he sabl of dnamc ssems and he use of Egen Values. Source: Macro II course noes, Dr. Davd Bessler s Tme Seres course noes, zarads (999) Ineremporal Macroeconomcs chaper 4 & Techncal ppend, and Hamlon
Lucas Test is based on Euler s theorem which states that if n is any integer and a is coprime to n, then a φ(n) 1modn.
 Modul 10 Addtonal Topcs 10.1 Lctur 1 Prambl: Dtrmnng whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or compost s known as prmalty tstng. Thr ar prmalty tsts whch mrly tll us whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or not, wthout gvng us th factors
Modul 10 Addtonal Topcs 10.1 Lctur 1 Prambl: Dtrmnng whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or compost s known as prmalty tstng. Thr ar prmalty tsts whch mrly tll us whthr a gvn ntgr s prm or not, wthout gvng us th factors
ON RIGHT(LEFT) DUO PO-SEMIGROUPS. S. K. Lee and K. Y. Park
 Kangwon-Kyungki Math. Jour. 11 (2003), No. 2, pp. 147 153 ON RIGHT(LEFT) DUO PO-SEMIGROUPS S. K. L and K. Y. Park Abstract. W invstigat som proprtis on right(rsp. lft) duo po-smigroups. 1. Introduction
Kangwon-Kyungki Math. Jour. 11 (2003), No. 2, pp. 147 153 ON RIGHT(LEFT) DUO PO-SEMIGROUPS S. K. L and K. Y. Park Abstract. W invstigat som proprtis on right(rsp. lft) duo po-smigroups. 1. Introduction
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SPECTRAL PEAK FREQUENCIES OF A CAUSAL AR(P) PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS OF ROOTS OF THE ASSOCIATED AR POLYNOMIAL.
 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SPECTRAL PEAK FREQUENCIES OF A CAUSAL AR(P) PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS OF ROOTS OF THE ASSOCIATED AR POLYNOMIAL A Wrng Proc Prsnd o T Faculy of Darmn of Mamacs San Jos Sa Unvrsy In Paral
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN SPECTRAL PEAK FREQUENCIES OF A CAUSAL AR(P) PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS OF ROOTS OF THE ASSOCIATED AR POLYNOMIAL A Wrng Proc Prsnd o T Faculy of Darmn of Mamacs San Jos Sa Unvrsy In Paral
EXERCISE - 01 CHECK YOUR GRASP
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION EXERCISE - CHECK YOUR GRASP 7. m hn D() m m, D () m m. hn givn D () m m D D D + m m m m m m + m m m m + ( m ) (m ) (m ) (m + ) m,, Hnc numbr of valus of mn will b. n ( ) + c sinc
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION EXERCISE - CHECK YOUR GRASP 7. m hn D() m m, D () m m. hn givn D () m m D D D + m m m m m m + m m m m + ( m ) (m ) (m ) (m + ) m,, Hnc numbr of valus of mn will b. n ( ) + c sinc
Implementation of the Extended Conjugate Gradient Method for the Two- Dimensional Energized Wave Equation
 Lonardo Elcronc Jornal of raccs and Tchnolos ISSN 58-078 Iss 9 Jl-Dcmbr 006 p. -4 Implmnaon of h Endd Cona Gradn Mhod for h Two- Dmnsonal Enrd Wav Eqaon Vcor Onoma WAZIRI * Snda Ass REJU Mahmacs/Compr
Lonardo Elcronc Jornal of raccs and Tchnolos ISSN 58-078 Iss 9 Jl-Dcmbr 006 p. -4 Implmnaon of h Endd Cona Gradn Mhod for h Two- Dmnsonal Enrd Wav Eqaon Vcor Onoma WAZIRI * Snda Ass REJU Mahmacs/Compr
Section 6.1. Question: 2. Let H be a subgroup of a group G. Then H operates on G by left multiplication. Describe the orbits for this operation.
 MAT 444 H Barclo Spring 004 Homwork 6 Solutions Sction 6 Lt H b a subgroup of a group G Thn H oprats on G by lft multiplication Dscrib th orbits for this opration Th orbits of G ar th right costs of H
MAT 444 H Barclo Spring 004 Homwork 6 Solutions Sction 6 Lt H b a subgroup of a group G Thn H oprats on G by lft multiplication Dscrib th orbits for this opration Th orbits of G ar th right costs of H
Dynamic Power Allocation in MIMO Fading Systems Without Channel Distribution Information
 PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 Dynamc Powr Allocaon n MIMO Fadng Sysms Whou Channl Dsrbuon Informaon Hao Yu and Mchal J. Nly Unvrsy of Souhrn Calforna Absrac Ths papr consdrs dynamc powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms
PROC. IEEE INFOCOM 06 Dynamc Powr Allocaon n MIMO Fadng Sysms Whou Channl Dsrbuon Informaon Hao Yu and Mchal J. Nly Unvrsy of Souhrn Calforna Absrac Ths papr consdrs dynamc powr allocaon n MIMO fadng sysms
Chapter 7. Now, for 2) 1. 1, if z = 1, Thus, Eq. (7.20) holds
 Chapr 7, n, 7 Ipuls rspons of h ovng avrag flr s: h[, ohrws sn / / Is frquny rspons s: sn / Now, for a BR ransfr funon,, For h ovng-avrag flr, sn / W shall show by nduon ha sn / sn / sn /,, Now, for sn
Chapr 7, n, 7 Ipuls rspons of h ovng avrag flr s: h[, ohrws sn / / Is frquny rspons s: sn / Now, for a BR ransfr funon,, For h ovng-avrag flr, sn / W shall show by nduon ha sn / sn / sn /,, Now, for sn
Existence and Uniqueness Results for Random Impulsive Integro-Differential Equation
 Global Journal of Pure and Appled Mahemacs. ISSN 973-768 Volume 4, Number 6 (8), pp. 89-87 Research Inda Publcaons hp://www.rpublcaon.com Exsence and Unqueness Resuls for Random Impulsve Inegro-Dfferenal
Global Journal of Pure and Appled Mahemacs. ISSN 973-768 Volume 4, Number 6 (8), pp. 89-87 Research Inda Publcaons hp://www.rpublcaon.com Exsence and Unqueness Resuls for Random Impulsve Inegro-Dfferenal
Conventional Hot-Wire Anemometer
 Convnonal Ho-Wr Anmomr cro Ho Wr Avanag much mallr prob z mm o µm br paal roluon array o h nor hghr rquncy rpon lowr co prormanc/co abrcaon roc I µm lghly op p layr 8µm havly boron op ch op layr abrcaon
Convnonal Ho-Wr Anmomr cro Ho Wr Avanag much mallr prob z mm o µm br paal roluon array o h nor hghr rquncy rpon lowr co prormanc/co abrcaon roc I µm lghly op p layr 8µm havly boron op ch op layr abrcaon
4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b
![4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b 4.1 The Uniform Distribution Def n: A c.r.v. X has a continuous uniform distribution on [a, b] when its pdf is = 1 a x b](/thumbs/71/65779443.jpg) 4. Th Uniform Disribuion Df n: A c.r.v. has a coninuous uniform disribuion on [a, b] whn is pdf is f x a x b b a Also, b + a b a µ E and V Ex4. Suppos, h lvl of unblivabiliy a any poin in a Transformrs
4. Th Uniform Disribuion Df n: A c.r.v. has a coninuous uniform disribuion on [a, b] whn is pdf is f x a x b b a Also, b + a b a µ E and V Ex4. Suppos, h lvl of unblivabiliy a any poin in a Transformrs
Chapter 10. The singular integral Introducing S(n) and J(n)
 Chaptr Th singular intgral Our aim in this chaptr is to rplac th functions S (n) and J (n) by mor convnint xprssions; ths will b calld th singular sris S(n) and th singular intgral J(n). This will b don
Chaptr Th singular intgral Our aim in this chaptr is to rplac th functions S (n) and J (n) by mor convnint xprssions; ths will b calld th singular sris S(n) and th singular intgral J(n). This will b don
(heat loss divided by total enthalpy flux) is of the order of 8-16 times
 16.51, Rok Prolson Prof. Manl Marnz-Sanhz r 8: Convv Ha ransfr: Ohr Effs Ovrall Ha oss and Prforman Effs of Ha oss (1) Ovrall Ha oss h loal ha loss r n ara s q = ρ ( ) ngrad ha loss s a S, and sng m =
16.51, Rok Prolson Prof. Manl Marnz-Sanhz r 8: Convv Ha ransfr: Ohr Effs Ovrall Ha oss and Prforman Effs of Ha oss (1) Ovrall Ha oss h loal ha loss r n ara s q = ρ ( ) ngrad ha loss s a S, and sng m =
NAME: ANSWER KEY DATE: PERIOD. DIRECTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the letter of the correct answer.
 R A T T L E R S S L U G S NAME: ANSWER KEY DATE: PERIOD PREAP PHYSICS REIEW TWO KINEMATICS / GRAPHING FORM A DIRECTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Chs h r f h rr answr. Us h fgur bw answr qusns 1 and 2. 0 10 20
R A T T L E R S S L U G S NAME: ANSWER KEY DATE: PERIOD PREAP PHYSICS REIEW TWO KINEMATICS / GRAPHING FORM A DIRECTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Chs h r f h rr answr. Us h fgur bw answr qusns 1 and 2. 0 10 20
UNIT #5 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
 Answr Ky Nam: Da: UNIT # EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Par I Qusions. Th prssion is quivaln o () () 6 6 6. Th ponnial funcion y 6 could rwrin as y () y y 6 () y y (). Th prssion a is quivaln o
Answr Ky Nam: Da: UNIT # EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Par I Qusions. Th prssion is quivaln o () () 6 6 6. Th ponnial funcion y 6 could rwrin as y () y y 6 () y y (). Th prssion a is quivaln o
On One Analytic Method of. Constructing Program Controls
 Appled Mahemacal Scences, Vol. 9, 05, no. 8, 409-407 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hkar.com hp://dx.do.org/0.988/ams.05.54349 On One Analyc Mehod of Consrucng Program Conrols A. N. Kvko, S. V. Chsyakov and Yu. E. Balyna
Appled Mahemacal Scences, Vol. 9, 05, no. 8, 409-407 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hkar.com hp://dx.do.org/0.988/ams.05.54349 On One Analyc Mehod of Consrucng Program Conrols A. N. Kvko, S. V. Chsyakov and Yu. E. Balyna
Guaranteed Cost Control for a Class of Uncertain Delay Systems with Actuator Failures Based on Switching Method
 49 Inrnaonal Journal of Conrol, Ru Wang Auomaon, and Jun and Zhao Sysms, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 49-5, Ocobr 7 Guarand Cos Conrol for a Class of Uncran Dlay Sysms wh Acuaor Falurs Basd on Swchng Mhod Ru Wang
49 Inrnaonal Journal of Conrol, Ru Wang Auomaon, and Jun and Zhao Sysms, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 49-5, Ocobr 7 Guarand Cos Conrol for a Class of Uncran Dlay Sysms wh Acuaor Falurs Basd on Swchng Mhod Ru Wang
Yutaka Suzuki Faculty of Economics, Hosei University. Abstract
 Equlbrum ncnvs and accumulaon of rlaonal sklls n a dynamc modl of hold up Yuaka uzuk Faculy of Economcs, Hos Unvrsy Absrac W consruc a dynamc modl of Holdup by applyng a framwork n capal accumulaon gams,
Equlbrum ncnvs and accumulaon of rlaonal sklls n a dynamc modl of hold up Yuaka uzuk Faculy of Economcs, Hos Unvrsy Absrac W consruc a dynamc modl of Holdup by applyng a framwork n capal accumulaon gams,
Heat/Di usion Equation. 2 = 0 k constant w(x; 0) = '(x) initial condition. ( w2 2 ) t (kww x ) x + k(w x ) 2 dx. (w x ) 2 dx 0.
 Hat/Di usion Equation @w @t k @ w @x k constant w(x; ) '(x) initial condition w(; t) w(l; t) boundary conditions Enrgy stimat: So w(w t kw xx ) ( w ) t (kww x ) x + k(w x ) or and thrfor E(t) R l Z l Z
Hat/Di usion Equation @w @t k @ w @x k constant w(x; ) '(x) initial condition w(; t) w(l; t) boundary conditions Enrgy stimat: So w(w t kw xx ) ( w ) t (kww x ) x + k(w x ) or and thrfor E(t) R l Z l Z
CPSC 211 Data Structures & Implementations (c) Texas A&M University [ 259] B-Trees
![CPSC 211 Data Structures & Implementations (c) Texas A&M University [ 259] B-Trees CPSC 211 Data Structures & Implementations (c) Texas A&M University [ 259] B-Trees](/thumbs/74/70718364.jpg) CPSC 211 Daa Srucurs & Implmnaions (c) Txas A&M Univrsiy [ 259] B-Trs Th AVL r and rd-black r allowd som variaion in h lnghs of h diffrn roo-o-laf pahs. An alrnaiv ida is o mak sur ha all roo-o-laf pahs
CPSC 211 Daa Srucurs & Implmnaions (c) Txas A&M Univrsiy [ 259] B-Trs Th AVL r and rd-black r allowd som variaion in h lnghs of h diffrn roo-o-laf pahs. An alrnaiv ida is o mak sur ha all roo-o-laf pahs
Solution in semi infinite diffusion couples (error function analysis)
 Soluon n sem nfne dffuson couples (error funcon analyss) Le us consder now he sem nfne dffuson couple of wo blocks wh concenraon of and I means ha, n a A- bnary sysem, s bondng beween wo blocks made of
Soluon n sem nfne dffuson couples (error funcon analyss) Le us consder now he sem nfne dffuson couple of wo blocks wh concenraon of and I means ha, n a A- bnary sysem, s bondng beween wo blocks made of
Deift/Zhou Steepest descent, Part I
 Lctur 9 Dift/Zhou Stpst dscnt, Part I W now focus on th cas of orthogonal polynomials for th wight w(x) = NV (x), V (x) = t x2 2 + x4 4. Sinc th wight dpnds on th paramtr N N w will writ π n,n, a n,n,
Lctur 9 Dift/Zhou Stpst dscnt, Part I W now focus on th cas of orthogonal polynomials for th wight w(x) = NV (x), V (x) = t x2 2 + x4 4. Sinc th wight dpnds on th paramtr N N w will writ π n,n, a n,n,
Introduction to Arithmetic Geometry Fall 2013 Lecture #20 11/14/2013
 18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
18.782 Introduction to Arithmtic Gomtry Fall 2013 Lctur #20 11/14/2013 20.1 Dgr thorm for morphisms of curvs Lt us rstat th thorm givn at th nd of th last lctur, which w will now prov. Thorm 20.1. Lt φ:
Engineering Circuit Analysis 8th Edition Chapter Nine Exercise Solutions
 Engnrng rcu naly 8h Eon hapr Nn Exrc Soluon. = KΩ, = µf, an uch ha h crcu rpon oramp. a For Sourc-fr paralll crcu: For oramp or b H 9V, V / hoo = H.7.8 ra / 5..7..9 9V 9..9..9 5.75,.5 5.75.5..9 . = nh,
Engnrng rcu naly 8h Eon hapr Nn Exrc Soluon. = KΩ, = µf, an uch ha h crcu rpon oramp. a For Sourc-fr paralll crcu: For oramp or b H 9V, V / hoo = H.7.8 ra / 5..7..9 9V 9..9..9 5.75,.5 5.75.5..9 . = nh,
S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sem. III. Applied Mathematics. Q.1 Attempt the following (any THREE) [15]
![S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sem. III. Applied Mathematics. Q.1 Attempt the following (any THREE) [15] S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sem. III. Applied Mathematics. Q.1 Attempt the following (any THREE) [15]](/thumbs/92/108666103.jpg) S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sm. III Applid Mahmaics Tim : ½ Hrs.] Prlim Qusion Papr Soluion [Marks : 75 Q. Amp h following (an THREE) 3 6 Q.(a) Rduc h mari o normal form and find is rank whr A 3 3 5 3 3 3 6 Ans.:
S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sm. III Applid Mahmaics Tim : ½ Hrs.] Prlim Qusion Papr Soluion [Marks : 75 Q. Amp h following (an THREE) 3 6 Q.(a) Rduc h mari o normal form and find is rank whr A 3 3 5 3 3 3 6 Ans.:
GENERATING CERTAIN QUINTIC IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS. Youngwoo Ahn and Kitae Kim
 Korean J. Mah. 19 (2011), No. 3, pp. 263 272 GENERATING CERTAIN QUINTIC IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS Youngwoo Ahn and Kae Km Absrac. In he paper [1], an explc correspondence beween ceran
Korean J. Mah. 19 (2011), No. 3, pp. 263 272 GENERATING CERTAIN QUINTIC IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER FINITE FIELDS Youngwoo Ahn and Kae Km Absrac. In he paper [1], an explc correspondence beween ceran
Basic Polyhedral theory
 Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Folding of Regular CW-Complexes
 Ald Mathmatcal Scncs, Vol. 6,, no. 83, 437-446 Foldng of Rgular CW-Comlxs E. M. El-Kholy and S N. Daoud,3. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty of Scnc Tanta Unvrsty,Tanta,Egyt. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty
Ald Mathmatcal Scncs, Vol. 6,, no. 83, 437-446 Foldng of Rgular CW-Comlxs E. M. El-Kholy and S N. Daoud,3. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty of Scnc Tanta Unvrsty,Tanta,Egyt. Dartmnt of Mathmatcs, Faculty
Chapter 7 Stead St y- ate Errors
 Char 7 Say-Sa rror Inroucon Conrol ym analy an gn cfcaon a. rann ron b. Sably c. Say-a rror fnon of ay-a rror : u c a whr u : nu, c: ouu Val only for abl ym chck ym ably fr! nu for ay-a a nu analy U o
Char 7 Say-Sa rror Inroucon Conrol ym analy an gn cfcaon a. rann ron b. Sably c. Say-a rror fnon of ay-a rror : u c a whr u : nu, c: ouu Val only for abl ym chck ym ably fr! nu for ay-a a nu analy U o
2/20/2013. EE 101 Midterm 2 Review
 //3 EE Mderm eew //3 Volage-mplfer Model The npu ressance s he equalen ressance see when lookng no he npu ermnals of he amplfer. o s he oupu ressance. I causes he oupu olage o decrease as he load ressance
//3 EE Mderm eew //3 Volage-mplfer Model The npu ressance s he equalen ressance see when lookng no he npu ermnals of he amplfer. o s he oupu ressance. I causes he oupu olage o decrease as he load ressance
Function Spaces. a x 3. (Letting x = 1 =)) a(0) + b + c (1) = 0. Row reducing the matrix. b 1. e 4 3. e 9. >: (x = 1 =)) a(0) + b + c (1) = 0
 unction Spacs Prrquisit: Sction 4.7, Coordinatization n this sction, w apply th tchniqus of Chaptr 4 to vctor spacs whos lmnts ar functions. Th vctor spacs P n and P ar familiar xampls of such spacs. Othr
unction Spacs Prrquisit: Sction 4.7, Coordinatization n this sction, w apply th tchniqus of Chaptr 4 to vctor spacs whos lmnts ar functions. Th vctor spacs P n and P ar familiar xampls of such spacs. Othr
CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 Collg Physcs Studnt s Manual Chaptr 33 CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS 33. THE FOUR BASIC FORCES 4. (a) Fnd th rato of th strngths of th wak and lctromagntc forcs undr ordnary crcumstancs. (b) What dos that
Collg Physcs Studnt s Manual Chaptr 33 CHAPTER 33: PARTICLE PHYSICS 33. THE FOUR BASIC FORCES 4. (a) Fnd th rato of th strngths of th wak and lctromagntc forcs undr ordnary crcumstancs. (b) What dos that
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 2.1: Linear Equations; Method of Integrating Factors
 Boc/DiPrima 9 h d, Ch.: Linar Equaions; Mhod of Ingraing Facors Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms, 9 h diion, b William E. Boc and Richard C. DiPrima, 009 b John Wil & Sons, Inc. A linar
Boc/DiPrima 9 h d, Ch.: Linar Equaions; Mhod of Ingraing Facors Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms, 9 h diion, b William E. Boc and Richard C. DiPrima, 009 b John Wil & Sons, Inc. A linar
Combinatorial Networks Week 1, March 11-12
 1 Nots on March 11 Combinatorial Ntwors W 1, March 11-1 11 Th Pigonhol Principl Th Pigonhol Principl If n objcts ar placd in hols, whr n >, thr xists a box with mor than on objcts 11 Thorm Givn a simpl
1 Nots on March 11 Combinatorial Ntwors W 1, March 11-1 11 Th Pigonhol Principl Th Pigonhol Principl If n objcts ar placd in hols, whr n >, thr xists a box with mor than on objcts 11 Thorm Givn a simpl
SCHUR S THEOREM REU SUMMER 2005
 SCHUR S THEOREM REU SUMMER 2005 1. Combinatorial aroach Prhas th first rsult in th subjct blongs to I. Schur and dats back to 1916. On of his motivation was to study th local vrsion of th famous quation
SCHUR S THEOREM REU SUMMER 2005 1. Combinatorial aroach Prhas th first rsult in th subjct blongs to I. Schur and dats back to 1916. On of his motivation was to study th local vrsion of th famous quation
2.1. Differential Equations and Solutions #3, 4, 17, 20, 24, 35
 MATH 5 PS # Summr 00.. Diffrnial Equaions and Soluions PS.# Show ha ()C #, 4, 7, 0, 4, 5 ( / ) is a gnral soluion of h diffrnial quaion. Us a compur or calculaor o skch h soluions for h givn valus of h
MATH 5 PS # Summr 00.. Diffrnial Equaions and Soluions PS.# Show ha ()C #, 4, 7, 0, 4, 5 ( / ) is a gnral soluion of h diffrnial quaion. Us a compur or calculaor o skch h soluions for h givn valus of h
Charging of capacitor through inductor and resistor
 cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
A universal saturation controller design for mobile robots
 A unvrsal sauraon conrollr sgn for mobl robos K.D. Do,,Z.P.Jang an J. Pan Dparmn of Elcrcal an Compur Engnrng, Polychnc Unvrsy, NY, USA. Emal: uc@mch.uwa.u.au, zjang@conrol.poly.u Dparmn of Mchancal Engnrng,
A unvrsal sauraon conrollr sgn for mobl robos K.D. Do,,Z.P.Jang an J. Pan Dparmn of Elcrcal an Compur Engnrng, Polychnc Unvrsy, NY, USA. Emal: uc@mch.uwa.u.au, zjang@conrol.poly.u Dparmn of Mchancal Engnrng,
ON THE WEAK LIMITS OF SMOOTH MAPS FOR THE DIRICHLET ENERGY BETWEEN MANIFOLDS
 ON THE WEA LIMITS OF SMOOTH MAPS FOR THE DIRICHLET ENERGY BETWEEN MANIFOLDS FENGBO HANG Absrac. We denfy all he weak sequenal lms of smooh maps n W (M N). In parcular, hs mples a necessary su cen opologcal
ON THE WEA LIMITS OF SMOOTH MAPS FOR THE DIRICHLET ENERGY BETWEEN MANIFOLDS FENGBO HANG Absrac. We denfy all he weak sequenal lms of smooh maps n W (M N). In parcular, hs mples a necessary su cen opologcal
10/7/14. Mixture Models. Comp 135 Introduction to Machine Learning and Data Mining. Maximum likelihood estimation. Mixture of Normals in 1D
 Comp 35 Introducton to Machn Larnng and Data Mnng Fall 204 rofssor: Ron Khardon Mxtur Modls Motvatd by soft k-mans w dvlopd a gnratv modl for clustrng. Assum thr ar k clustrs Clustrs ar not rqurd to hav
Comp 35 Introducton to Machn Larnng and Data Mnng Fall 204 rofssor: Ron Khardon Mxtur Modls Motvatd by soft k-mans w dvlopd a gnratv modl for clustrng. Assum thr ar k clustrs Clustrs ar not rqurd to hav
Spectral Synthesis in the Heisenberg Group
 Intrnational Journal of Mathmatical Analysis Vol. 13, 19, no. 1, 1-5 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ijma.19.81179 Spctral Synthsis in th Hisnbrg Group Yitzhak Wit Dpartmnt of Mathmatics,
Intrnational Journal of Mathmatical Analysis Vol. 13, 19, no. 1, 1-5 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ijma.19.81179 Spctral Synthsis in th Hisnbrg Group Yitzhak Wit Dpartmnt of Mathmatics,
Week 3: Connected Subgraphs
 Wk 3: Connctd Subgraphs Sptmbr 19, 2016 1 Connctd Graphs Path, Distanc: A path from a vrtx x to a vrtx y in a graph G is rfrrd to an xy-path. Lt X, Y V (G). An (X, Y )-path is an xy-path with x X and y
Wk 3: Connctd Subgraphs Sptmbr 19, 2016 1 Connctd Graphs Path, Distanc: A path from a vrtx x to a vrtx y in a graph G is rfrrd to an xy-path. Lt X, Y V (G). An (X, Y )-path is an xy-path with x X and y
9.5 Complex variables
 9.5 Cmpl varabls. Cnsdr th funtn u v f( ) whr ( ) ( ), f( ), fr ths funtn tw statmnts ar as fllws: Statmnt : f( ) satsf Cauh mann quatn at th rgn. Statmnt : f ( ) ds nt st Th rrt statmnt ar (A) nl (B)
9.5 Cmpl varabls. Cnsdr th funtn u v f( ) whr ( ) ( ), f( ), fr ths funtn tw statmnts ar as fllws: Statmnt : f( ) satsf Cauh mann quatn at th rgn. Statmnt : f ( ) ds nt st Th rrt statmnt ar (A) nl (B)
Partition Functions for independent and distinguishable particles
 0.0J /.77J / 5.60J hrodynacs of oolcular Syss Insrucors: Lnda G. Grffh, Kbrly Haad-Schffrl, Moung G. awnd, Robr W. Fld Lcur 5 5.60/0.0/.77 vs. q for dsngushabl vs ndsngushabl syss Drvaon of hrodynac Proprs
0.0J /.77J / 5.60J hrodynacs of oolcular Syss Insrucors: Lnda G. Grffh, Kbrly Haad-Schffrl, Moung G. awnd, Robr W. Fld Lcur 5 5.60/0.0/.77 vs. q for dsngushabl vs ndsngushabl syss Drvaon of hrodynac Proprs
Mathematical Statistics. Chapter VIII Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem
 Mahmacal ascs 8 Chapr VIII amplg Dsrbos ad h Cral Lm Thorm Fcos of radom arabls ar sall of rs sascal applcao Cosdr a s of obsrabl radom arabls L For ampl sppos h arabls ar a radom sampl of s from a poplao
Mahmacal ascs 8 Chapr VIII amplg Dsrbos ad h Cral Lm Thorm Fcos of radom arabls ar sall of rs sascal applcao Cosdr a s of obsrabl radom arabls L For ampl sppos h arabls ar a radom sampl of s from a poplao
Robust decentralized control with scalar output of multivariable structurally uncertain plants with state delay 1
 rprns of h 8h IFAC World Congrss lano Ial Augus 8 - Spmbr obus dcnralzd conrol wh scalar oupu of mulvarabl srucurall uncran plans wh sa dla Elzava arshva Absrac h problm of a robus conrol ssm dsgn for
rprns of h 8h IFAC World Congrss lano Ial Augus 8 - Spmbr obus dcnralzd conrol wh scalar oupu of mulvarabl srucurall uncran plans wh sa dla Elzava arshva Absrac h problm of a robus conrol ssm dsgn for
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
