A COUPLED RANS-VOF AND FINITE ELEMENT MODEL FOR WAVE INTERACTION WITH HIGHLY FLEXIBLE VEGETATION
|
|
|
- Joel Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A COUPLED RANS-VOF AND FINITE ELEMENT MODEL FOR WAVE INTERACTION WITH HIGHLY FLEXIBLE VEGETATION Haifei Chen 1, Qingping Zou * an Zhilong Liu 1 This paper presents a couple wae-egetation interaction moel suitable for ery flexible egetation with large eflections. The wae hyroynamics is moele by a Naier-Stokes flow soler along with a Volume of Flui surface capturing metho. The goerning equation for flexible egetation motion is sole by a Finite Element Metho using a semi-implicit time ifferencing scheme. The coupling between wae hyroynamics an egetation motion is achiee using an immerse bounary metho. The moel is aliate with experimental measurements for a single-stem egetation an a large-scale egetation patch in a wae flume. Keywors: wae interaction with egetation; flexible egetation; large eflection; IHFOAM; OpenFOAM; RANS- VOF; finite element metho; immerse bounary metho INTRODUCTION Vegetation plays an important role in protecting natural shoreline against storm surge an waes. Majority of preious stuies of wae-egetation interaction focus on fixe egetation. Li & Yan (2007) an Marsooli & Wu (2014) consiere rigi egetation in their Reynols Aerage Naier-Stokes (RANS) moels an neglecte the swaying motion of the egetation. Maza et al. (2013) use a twoimensional RANS moel couple with a submerge egetation moel, which soles only the isplacement at the top of each stem an assumes a linear ariation of eflection along the stem. Zhu an Chen (2015) couple a non-hyrostatic phase resoling wae moel, NHWAVE, with a Finite Element Metho (FEM) base egetation moel. The complete force balance equation for the egetation motion was sole. Their egetation moel is suitable for small eflections only. The objectie of this stuy is to eelop a new couple wae an egetation moel suitable for flexible egetation with large sway of motion. A Reynols Aerage Naier-Stokes soler with Volume of Flui surface capturing scheme (RANS-VOF) is extene to inclue the effect of flexible egetation on flow. The egetation is assume to behae like a slener ro, whose goerning equations are sole by Finite Element Metho (Garrett 1982; Chen et al. 2011). There is no constraint with regar to the magnitue of the egetation motion in this couple moel as with most preious wae-egetation moels. NUMERICAL MODEL FEM Moel for Flexible Vegetation Figure 1. Coorinate system of the ro moel for flexible egetation. r(s,t) is a position ector of the ro s centerline, s is the arc length, an q(s,t) is istribute force per unit length. 1 Ciil an Enironmental Engineering, Uniersity of Maine, 5711 Boarman Hall, Orono, ME 04473, USA. * qingping.zou@maine.eu 1
2 2 COASTAL ENGINEERING 2016 The flexible egetation is treate as a slener ro. The goerning equation for the egetation motion consiers the buoyancy, stiffness, an graity as restoring forces, rag an inertia as riing forces, an is gien by EIr r q m r (1) where r s,t is the position ector of the ro, the prime an ot enote the ifferentiation with respect to arc length s an time t, respectiely, EI is bening stiffness, m mass per unit length, 2 s, t T EI with T being the local effectie tension an r ro curature. The external e e istribute loa on the egetation, q w F s F, is the sum of self-weight, w, hyrostatic force, s an hyroynamic force, F, acting on a unit length of single-stem egetation. The hyroynamic force on a single-stem egetation is gien by the Morrison equation, 1 n n n n n n F U r U r U 1 2 C b b t C b C U r (2) D M A 2 4 where C, C, an C D M A are the rag, inertia, an ae mass coefficients, is the ensity of the egetation, b, t are the with an thickness of the rectangular cross-section of the egetation blae, U, U are flui elocity an acceleration, r, r are the ro elocity an acceleration, the superscript n inicates the normal component of the ariable perpenicular to the ro. FEM is use to iscretize the goerning equations. For static problems such as egetation reconfiguration uner current action, the Newton-Raphson metho is use to sole the equations. For ynamic problems where transient wae motion is inole, a semi-implicit time ifferencing scheme is use. Reaers shoul refer to Garret (1982) an Ran (2000) for more etails. RANS-VOF Wae Moel The Reynols Aerage Naier-Stokes Soler couple with a Volume of Flui surface capturing scheme has been use extensiely to sole free surface flow problems with large an complex eformations of free surface (Lin an Liu 1998; Lubin et al. 2006; Christensen 2006; L et al. 2009; Wang et al. 2009; Zou an Peng 2011). A Naier-Stokes soler built on the OpenFOAM platform is aopte to simulate the wae hyroynamics. The open-source package, IHFOAM, can actiely generate an absorb waes at the inlet an outlet bounaries (Higuera et al. 2013). The Volume of Flui (VOF) metho is use to capture the air-water interface. The goerning equations for the RANS-VOF soler are gien by U 0 (3) U UU U eff p * g X U eff F (4) t U U 1 r 0 (5) t * where is the flui ensity, p the pseuo-ynamic pressure, g the graitational acceleration, X the position ector, is the effectie ynamic iscosity, which takes into account of molecular eff t ynamic iscosity an the turbulent ey iscosity. Note that the egetation-inuce t hyroynamic forces, F, are ae as a source term in the momentum equation (4). Eq. (5) is the aection equation for the olume of flui function,, with an extra term to achiee a sharp interface (Weller 2002). Coupling Wae an Vegetation Moels Using an Immerse Bounary Metho The egetation motion, Eq. (1), is sole by Finite Element Metho consiering rag an inertia as riing forces, while the RANS-VOF wae moel consiers the rag an inertia as a source term in the momentum equation (4). The two moels are hence couple through the egetation-inuce hyroynamic forces. The common coupling approach use in the literature is base on the porous meia flow theory, which consiers the egetate region as a porous meia continuum an is thus concerne with only the olume-aerage flow fiel. Different from preious stuies using the porous meia approach, we use an immerse bounary metho suitable for a ery thin object to account for the two way coupling of wae an egetation (Perskin 2002). The force exerte by the egetation on the flow, -F, is incorporate as a source term F,
3 COASTAL ENGINEERING in the momentum equation (4), an is applie only whereer stans the egetation stem. The immerse bounary metho is a popular approach in simulating flui-structure interactions (Lin 2007; Zhang et al. 2009). Fig. 2 illustrates the flow chart of the proceure of soling the couple wae-egetation interaction moel. At each time step of the computation, the egetation motion is sole first with the known wae elocities. The egetation eflection an isplacement elocity are fe back to the wae moel to calculate new flow elocities. Both the flow elocity an egetation motion will then be fe to the egetation moel to obtain the new egetation eflection an elocity at the next time step. The turbulence transport equations may be sole at the en of each time step. Vegetation motion - FEM Next time step VOF aection PISO loop Momentum preictor Pressure correction Immerse bounary metho Turbulence Figure 2. Flow chart of soling the couple RANS-VOF flow moel an FEM egetation moel. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In this section, both the iniiual moel components an the couple wae-egetation moel is aliate against the aailable experimental measurements. The IHFOAM wae moel has been aliate extensiely by Higuera et al. (2013). The FEM moel for flexible egetation will be first aliate using measurements for single-stem egetation. The couple moel is then aliate by a large-scale flume experiment of wae interaction with a egetation patch. Wae Interaction with a Single-stem Flexible Vegetation Abelrhman (2007) photographe Z. marina blaes expose to three ifferent current spees U c = 0.06, 0.12 an 0.14 m/s. Fig. 3 shows a comparison of the preicte an obsere blae postures for this aquatic egetation. The blae with an thickness are b =0.8 cm an t =0.35 mm, blae length 40 cm, an ensity =700 kg/m 3. The rag coefficient use is ientical to that for flat plates, C D =1.95. The preicte two blae postures are obtaine using the higher (E = 2.4 GPa) an lower (E = 0.4 GPa) boun alues of the elastic moulus for the blae. It is apparent that a higher elastic moulus correspons to a more upright configuration. Gien the uncertainty in the blae geometry an mechanical properties in the real egetation, it can be state that reasonable agreement is achiee between the preicte postures an the obserations.
4 4 COASTAL ENGINEERING 2016 Figure 3. Comparison of moel preictions for blae posture (left column) with the obserations (right column) by Abelrhman (2007) for the seagrass Zostera marina expose to a current of spee U c (a) 0.06 m/s, (b) 0.12 m/s, an (c) 0.14 m/s. Maza et al. (2013) conucte a set of experiments to measure the extent of plant motion uner wae action. The egetation mimics were compose of four PVC strips, one pair 45 cm long an another pair 27.5 cm. The PVC strips were 1 mm thick an 1 cm wie, with a Young's moulus E=0.9 GPa an a ensity =700 kg/m 3. Since the two-pair, four-stem egetation mimics respon freely to the wae action, it s ifficult to etermine the extent to which the four stems bin together to resist the wae action. To simplify the moel simulation, an equialent single-stem egetation is use an moel tests are thus use to etermine the geometric an mechanical properties of the equialent egetation. Figure 4. Instantaneous configuration of single-stem egetation at eery one tenth of the wae perio uner a perioic wae T=4.0 s, H=0.2 m, =0.8 m. Re squares correspon to the measurements of the two extreme isplacements uner the wae motion by Maza et al. (2013). Fig. 4 shows the preicte instantaneous configurations for the flexible egetation oer one wae perio. The rag coefficient use is ientical to that for flat plates, C =1.95. The bening stiffness D
5 COASTAL ENGINEERING use is equialent to that when approximately 2 PVC strips were bining together to resist the wae motion. The obsere two maximum isplacements of egetation in the same an opposite irection as the wae irection are also shown as re squares in Fig. 4. The present moel preictions are in goo agreement with the measurements. Due to the asymmetry of wae kinematics, the egetation flexibility an nonlinear wae-egetation coupling, the egetation motion is asymmetric relatie to the ertical axis, i.e. the egetation has a larger sway uner wae crest (~0.25 m) than uner trough (~0.17 m). Wae Interaction with a Patch of Flexible Vegetation The experimental measurements by Stratigaki et al. (2011) are use to aliate the couple waeegetation moel. Fig. 5 shows the present moel setup simulating a regular wae, T= 3.5 s an H= 0.5 m, propagating through a egetation meaow. The water epth is 2.4 m at the waemaker bounary an transitions, through a 12 m long, 1:17 sany slope, to 1.7 m at the onshore bounary. A 10.7 m long artificial egetation meaow was place oer the flat portion of the sany bottom. The beginning of this egetation patch was locate at m from the wae pale. The remaining sany sloping beach beyon the egetation patch is ignore in the simulation. The waes propagating through the egetation fiel are absorbe by using proper outlet bounary conitions. The egetation mimics use in this experiment were the same as escribe aboe (Maza et al. 2013). The egetation ensity for this special case is N=180 stems/m z (m) m : x (m) Figure 5. Moel setup for couple wae-egetation interaction (Stratigaki et al. 2011). Fig. 6 shows the spatial eolution of wae height oer the egetation patch. The x-coorinate of the egetation patch has been shifte to compare with experimental measurements easily. It is eient that the present moel reprouces the tren of wae height ecay as well as the magnitue of wae height oscillation oer the egetation fiel. Howeer, the oscillation pattern is shifte probably ue to the unknown wae reflection patterns in the physical flume not present in the numerical flume. Figure 6. Preicte an measure (Stratigaki et al. 2011) spatial ariation of wae height along the egetation patch. Fig. 7 presents the ertical profiles of horizontal an ertical wae elocity components at a location 2.0 m into the egetation patch. It s seen that the ertical istribution of wae elocities are
6 6 COASTAL ENGINEERING 2016 obiously altere by the presence of the egetation, see Fig. 8 for illustration. Both the numerical preictions an the measurements show that the horizontal elocity increases aroun the upper en of the egetation fiel. This skimming flow results from the strong iscontinuity in the rag force between the area occupie by the meaow an the free flow aboe it. The strong iscontinuity woul cause a non-zero wae shear stress, leaing to a mean current flowing in the irection of the wae propagation. Figure 7. Moel-ata comparisons of ertical istribution of maximum, mean, an minimum (a) horizontal an (b) ertical wae elocities at a location 2.0 m into the egetation patch. Soli lines: moel preiction; squares: measurements by Stratigaki et al. (2011). Figure 8. Snapshot of instantaneous configuration of the egetation patch an color contour of wae horizontal elocity at t=53 s. CONCLUSIONS A couple RANS-VOF an finite element moel is eelope to simulate the wae-egetation interaction. The wae hyroynamics is simulate by a RANS-VOF moel. A Finite Element Metho is aopte for soling the egetation motion, which is applicable to flexible egetation with either small or large eflections. The flexible egetation moel was aliate with experiments for single-stem egetation. The moels of wae hyroynamics an egetation motion is couple through a iffuse immerse bounary metho. The couple moel was aliate with measurements for a large-scale flume experiment, where a regular wae propagating though a egetation meaow was inestigate. Both the obsere wae height ecay an oscillation magnitue an wae kinematics were reasonably preicte by the couple moel. REFERENCES Abelrhman, M.A Moeling coupling between eelgrass Zostera marina an water flow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 338, Chen, H., S. Xu, an H. Guo Nonlinear analysis of flexible an steel catenary risers with internal flow an seabe interaction effects. Journal of Marine Science an Application, 10(2),
7 COASTAL ENGINEERING Christensen, E.D Large ey simulation of spilling an plunging breakers. Coastal Engineering, 53 (5-6), Garrett, D.L Dynamic analysis of slener ros, Journal of Energy Resources Tech., 104(4), Higuera, P., J.L Lara, an I.J. Losaa Realistic wae generation an actie wae absorption for Naier-Stokes moels: application to OpenFOAM. Coast. Eng. 71, Li, C.W., an K. Yan Numerical inestigation of wae-current-egetation interaction. J. Hyraul. Eng., (2007)133:7(794), Lin, P.Z., an P.L.-F. Liu A numerical stuy of breaking waes in the surf zone. J. Flui Mech., 359, Lin, P.Z A fixe-gri moel for simulation of a moing boy in free surface flows. Computers & fluis, 36(3), Lubin, P., S. Vincent, S. Abaie, an J.P. Caltagirone Three-imensional large ey simulation of air entrainment uner plunging breaking waes, Coastal Engineering, 53, L, X., Q.P. Zou, D.E. Reee, an Y. Zhao A noel couple leel set an olume of flui metho for sharp interface capturing on 3D tetraheral gris, Journal of Computational Physics, 229(7), Marsooli, R., an W. Wu Numerical inestigation of wae attenuation by egetation using a 3D RANS moel. Aances in Water Resources, 74, Maza, M., J.L. Lara, an I.J. Losaa A couple moel of submerge egetation uner oscillatory flow using Naier-Stokes equations. Coast. Eng., 80, Peskin, C.S The immerse bounary metho. Acta numerica, 11, Ran, Z Couple ynamic analysis of floating structures in wae an current. Ph.D thesis, Texas A&M Uniersity, College Station, TX. Stratigaki, V., E. Manca, P. Prinos, I.J. Losaa, J.L. Lara, M. Sclao, C.L. Amos, I. Caceres, an A. Sanchez-Arcilla Large-scale experiments on wae propagation oer Posionia oceanica. Journal of Hyraulic Research, 49, Wang, Z.Y., Q.P. Zou, an D.E. Reee Simulation of spilling breaking waes using a two phase flow CFD moel, Computers & Fluis, 38 (10), Weller, H.G Deriation, moelling an solution of the conitionally aerage two-phase flow equations. Technical Report TR/HGW/02, OpenCFD Lt. Zhang, Y.L., Q.-P. Zou, D. Greaes, D. Reee, A. Hunt-Raby, D. Graham, P. James, an X. L A leel set immerse bounary metho for water entry an exit. Communications in Computational Physics, 8(2), Zhu, L., an Q. Chen Numerical Moeling of Surface Waes oer Submerge Flexible Vegetation. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, A Zou, Q.-P., an Z. Peng Eolution of wae shape oer a low-creste structure, Coastal Engineering, 58(6),
Fundamental Laws of Motion for Particles, Material Volumes, and Control Volumes
 Funamental Laws of Motion for Particles, Material Volumes, an Control Volumes Ain A. Sonin Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambrige, MA 02139, USA August 2001
Funamental Laws of Motion for Particles, Material Volumes, an Control Volumes Ain A. Sonin Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambrige, MA 02139, USA August 2001
Fundamental Laws of Motion for Particles, Material Volumes, and Control Volumes
 1 Funamental Laws of Motion for Particles, Material Volumes, an Control Volumes Ain A. Sonin Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambrige, MA 02139, USA March 2003
1 Funamental Laws of Motion for Particles, Material Volumes, an Control Volumes Ain A. Sonin Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambrige, MA 02139, USA March 2003
P1D.6 IMPACTS OF THE OCEAN SURFACE VELOCITY ON WIND STRESS COEFFICIENT AND WIND STRESS OVER GLOBAL OCEAN DURING
 P1D.6 IMPATS OF THE OEAN SURFAE VELOITY ON WIND STRESS OEFFIIENT AND WIND STRESS OVER GLOBAL OEAN DURING 1958-001 Zengan Deng 1* Lian Xie Ting Yu 1 an Kejian Wu 1 1. Physical Oceanography Laboratory, Ocean
P1D.6 IMPATS OF THE OEAN SURFAE VELOITY ON WIND STRESS OEFFIIENT AND WIND STRESS OVER GLOBAL OEAN DURING 1958-001 Zengan Deng 1* Lian Xie Ting Yu 1 an Kejian Wu 1 1. Physical Oceanography Laboratory, Ocean
05 The Continuum Limit and the Wave Equation
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Founations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of 1-1-2004 05 The Continuum Limit an the Wave Equation Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Founations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of 1-1-2004 05 The Continuum Limit an the Wave Equation Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
for which the garbage will fall within the can. If the range is large, the shot is easy; if the range is small, the target is hard to hit.
 EN40: Dynamics an Vibrations Homework : Soling equations of motion for particles Due Friay Feb 18 011 School of Engineering Brown Uniersity 1. Suppose that you wish to throw a piece of garbage into a garbage
EN40: Dynamics an Vibrations Homework : Soling equations of motion for particles Due Friay Feb 18 011 School of Engineering Brown Uniersity 1. Suppose that you wish to throw a piece of garbage into a garbage
Appendix to the paper on Significance of the microfluidic concepts for the improvement of macroscopic models of transport phenomena
 ppenix to the paper on ignificance of the microfluiic concepts for the improement of macroscopic moels of transport phenomena Michael Krol *1, * Tel. ++49171577557; Email: michael_krol48@yahoo.com 1: Chemical
ppenix to the paper on ignificance of the microfluiic concepts for the improement of macroscopic moels of transport phenomena Michael Krol *1, * Tel. ++49171577557; Email: michael_krol48@yahoo.com 1: Chemical
Water vapour transport through perforated foils
 Water apour transport through perforate foils Wim an er Spoel TU Delft, Faculty of Ciil Engineering an Geosciences, Section Builing Engineering, Steinweg, 68 CN Delft, The Netherlans E-mail: w.h.anerspoel@citg.tuelft.nl
Water apour transport through perforate foils Wim an er Spoel TU Delft, Faculty of Ciil Engineering an Geosciences, Section Builing Engineering, Steinweg, 68 CN Delft, The Netherlans E-mail: w.h.anerspoel@citg.tuelft.nl
3-D FEM Modeling of fiber/matrix interface debonding in UD composites including surface effects
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science an Engineering 3-D FEM Moeling of fiber/matrix interface eboning in UD composites incluing surface effects To cite this article: A Pupurs an J Varna 2012 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science an Engineering 3-D FEM Moeling of fiber/matrix interface eboning in UD composites incluing surface effects To cite this article: A Pupurs an J Varna 2012 IOP Conf.
Vibration Analysis of Railway Tracks Forced by Distributed Moving Loads
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 6, No. 4 / December 13, pp. 155-159 The Korean Society for Railway Vibration Analysis of Railway Tracks Force by Distribute Moving Loas Sinyeob Lee*, Dongkyu Kim*,
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 6, No. 4 / December 13, pp. 155-159 The Korean Society for Railway Vibration Analysis of Railway Tracks Force by Distribute Moving Loas Sinyeob Lee*, Dongkyu Kim*,
Strength Analysis of CFRP Composite Material Considering Multiple Fracture Modes
 5--XXXX Strength Analysis of CFRP Composite Material Consiering Multiple Fracture Moes Author, co-author (Do NOT enter this information. It will be pulle from participant tab in MyTechZone) Affiliation
5--XXXX Strength Analysis of CFRP Composite Material Consiering Multiple Fracture Moes Author, co-author (Do NOT enter this information. It will be pulle from participant tab in MyTechZone) Affiliation
Approaches for Predicting Collection Efficiency of Fibrous Filters
 Volume 5, Issue, Summer006 Approaches for Preicting Collection Efficiency of Fibrous Filters Q. Wang, B. Maze, H. Vahei Tafreshi, an B. Poureyhimi Nonwovens Cooperative esearch Center, North Carolina State
Volume 5, Issue, Summer006 Approaches for Preicting Collection Efficiency of Fibrous Filters Q. Wang, B. Maze, H. Vahei Tafreshi, an B. Poureyhimi Nonwovens Cooperative esearch Center, North Carolina State
This section outlines the methodology used to calculate the wave load and wave wind load values.
 COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., JUNE 2014 AUTOMATIC WAVE LOADS TECHNICAL NOTE CALCULATION O WAVE LOAD VALUES This section outlines the methoology use to calculate the wave loa an wave win loa values. Overview
COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., JUNE 2014 AUTOMATIC WAVE LOADS TECHNICAL NOTE CALCULATION O WAVE LOAD VALUES This section outlines the methoology use to calculate the wave loa an wave win loa values. Overview
Combining Time Series and Cross-sectional Data for Current Employment Statistics Estimates 1
 JSM015 - Surey Research Methos Section Combining Time Series an Cross-sectional Data for Current Employment Statistics Estimates 1 Julie Gershunskaya U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Massachusetts Ae NE,
JSM015 - Surey Research Methos Section Combining Time Series an Cross-sectional Data for Current Employment Statistics Estimates 1 Julie Gershunskaya U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Massachusetts Ae NE,
Non-Equilibrium Continuum Physics TA session #10 TA: Yohai Bar Sinai Dislocations
 Non-Equilibrium Continuum Physics TA session #0 TA: Yohai Bar Sinai 0.06.206 Dislocations References There are countless books about islocations. The ones that I recommen are Theory of islocations, Hirth
Non-Equilibrium Continuum Physics TA session #0 TA: Yohai Bar Sinai 0.06.206 Dislocations References There are countless books about islocations. The ones that I recommen are Theory of islocations, Hirth
Chapter 2 Governing Equations
 Chapter 2 Governing Equations In the present an the subsequent chapters, we shall, either irectly or inirectly, be concerne with the bounary-layer flow of an incompressible viscous flui without any involvement
Chapter 2 Governing Equations In the present an the subsequent chapters, we shall, either irectly or inirectly, be concerne with the bounary-layer flow of an incompressible viscous flui without any involvement
A 3D SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODEL FOR COMBINED WAVE-CURRENT FLOWS
 A 3D SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODEL FOR COMBINED WAVE-CURRENT FLOWS Peifeng Ma 1 an Ole Secher Masen Accurate preiction of current velocity an bottom shear stress, which both can be significantly influence by
A 3D SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODEL FOR COMBINED WAVE-CURRENT FLOWS Peifeng Ma 1 an Ole Secher Masen Accurate preiction of current velocity an bottom shear stress, which both can be significantly influence by
The effect of nonvertical shear on turbulence in a stably stratified medium
 The effect of nonvertical shear on turbulence in a stably stratifie meium Frank G. Jacobitz an Sutanu Sarkar Citation: Physics of Fluis (1994-present) 10, 1158 (1998); oi: 10.1063/1.869640 View online:
The effect of nonvertical shear on turbulence in a stably stratifie meium Frank G. Jacobitz an Sutanu Sarkar Citation: Physics of Fluis (1994-present) 10, 1158 (1998); oi: 10.1063/1.869640 View online:
Journal of Computational Physics
 Journal of Computational Physics 228 (2009) 5978 5988 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Computational Physics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jcp Elastic property of multiphase
Journal of Computational Physics 228 (2009) 5978 5988 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Computational Physics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jcp Elastic property of multiphase
A General Analytical Model for Lateral Velocity Distributions in Vegetated Channels
 Rier Flow - Dittrich, Koll, Aberle & Geisenhainer (es) - Bunesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-9393--7 A General Analtical Moel for Lateral Velocit Distributions in Vegetate Channels X. Tang School of
Rier Flow - Dittrich, Koll, Aberle & Geisenhainer (es) - Bunesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-9393--7 A General Analtical Moel for Lateral Velocit Distributions in Vegetate Channels X. Tang School of
Microscopic traffic simulation tools and their use for emission calculations
 Microscopic traffic simulation tools an their use for emission calculations Stephan Rosswog & Peter Wagner, MS, DLR, Köln-Porz an ZAIK, Uniersity of Cologne Nils Eissfelt, ZAIK, Uniersity of Cologne I.
Microscopic traffic simulation tools an their use for emission calculations Stephan Rosswog & Peter Wagner, MS, DLR, Köln-Porz an ZAIK, Uniersity of Cologne Nils Eissfelt, ZAIK, Uniersity of Cologne I.
Study on aero-acoustic structural interactions in fan-ducted system
 Stuy on aero-acoustic structural interactions in fan-ucte system Yan-kei CHIANG 1 ; Yat-sze CHOY ; Li CHENG 3 ; Shiu-keung TANG 4 1,, 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University,
Stuy on aero-acoustic structural interactions in fan-ucte system Yan-kei CHIANG 1 ; Yat-sze CHOY ; Li CHENG 3 ; Shiu-keung TANG 4 1,, 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University,
Math 1272 Solutions for Spring 2005 Final Exam. asked to find the limit of the sequence. This is equivalent to evaluating lim. lim.
 Math 7 Solutions for Spring 5 Final Exam ) We are gien an infinite sequence for which the general term is a n 3 + 5n n + n an are 3 + 5n aske to fin the limit of the sequence. This is equialent to ealuating
Math 7 Solutions for Spring 5 Final Exam ) We are gien an infinite sequence for which the general term is a n 3 + 5n n + n an are 3 + 5n aske to fin the limit of the sequence. This is equialent to ealuating
1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics 1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity. A soli conucting sphere is given a positive charge Q.
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics 1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity. A soli conucting sphere is given a positive charge Q.
Chapter 4. Electrostatics of Macroscopic Media
 Chapter 4. Electrostatics of Macroscopic Meia 4.1 Multipole Expansion Approximate potentials at large istances 3 x' x' (x') x x' x x Fig 4.1 We consier the potential in the far-fiel region (see Fig. 4.1
Chapter 4. Electrostatics of Macroscopic Meia 4.1 Multipole Expansion Approximate potentials at large istances 3 x' x' (x') x x' x x Fig 4.1 We consier the potential in the far-fiel region (see Fig. 4.1
TMA 4195 Matematisk modellering Exam Tuesday December 16, :00 13:00 Problems and solution with additional comments
 Problem F U L W D g m 3 2 s 2 0 0 0 0 2 kg 0 0 0 0 0 0 Table : Dimension matrix TMA 495 Matematisk moellering Exam Tuesay December 6, 2008 09:00 3:00 Problems an solution with aitional comments The necessary
Problem F U L W D g m 3 2 s 2 0 0 0 0 2 kg 0 0 0 0 0 0 Table : Dimension matrix TMA 495 Matematisk moellering Exam Tuesay December 6, 2008 09:00 3:00 Problems an solution with aitional comments The necessary
fv = ikφ n (11.1) + fu n = y v n iσ iku n + gh n. (11.3) n
 Chapter 11 Rossby waves Supplemental reaing: Pelosky 1 (1979), sections 3.1 3 11.1 Shallow water equations When consiering the general problem of linearize oscillations in a static, arbitrarily stratifie
Chapter 11 Rossby waves Supplemental reaing: Pelosky 1 (1979), sections 3.1 3 11.1 Shallow water equations When consiering the general problem of linearize oscillations in a static, arbitrarily stratifie
FINITE POINTSET METHOD (FPM): A MESHFREE APPROACH FOR INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOW SIMULATIONS APPLIED TO COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 FINITE POINTSET METHOD (FPM): A MESHFREE APPROACH FOR INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOW SIMULATIONS APPLIED TO COMPOSITE MATERIALS Alain Trameçon 1, Patrick e Luca 1, Christophe Binetruy 2 an Jörg Kuhnert 3 1 ESI-GROUP
FINITE POINTSET METHOD (FPM): A MESHFREE APPROACH FOR INCOMPRESSIBLE FLOW SIMULATIONS APPLIED TO COMPOSITE MATERIALS Alain Trameçon 1, Patrick e Luca 1, Christophe Binetruy 2 an Jörg Kuhnert 3 1 ESI-GROUP
Damage identification based on incomplete modal data and constrained nonlinear multivariable function
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Damage ientification base on incomplete moal ata an constraine nonlinear multivariable function To cite this article: S S Kourehli 215 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Damage ientification base on incomplete moal ata an constraine nonlinear multivariable function To cite this article: S S Kourehli 215 J. Phys.:
Two- and Three-Dimensional Validation of Icing Model
 APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 13, Singapore To- an Three-Dimensional Valiation of Icing Moel *Ryosuke Hayashi¹ an Makoto Yamamoto 1 Grauate School of Mechanical Engineering, Tokyo University of Science
APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 13, Singapore To- an Three-Dimensional Valiation of Icing Moel *Ryosuke Hayashi¹ an Makoto Yamamoto 1 Grauate School of Mechanical Engineering, Tokyo University of Science
v r 1 E β ; v r v r 2 , t t 2 , t t 1 , t 1 1 v 2 v (3) 2 ; v χ αβγδ r 3 dt 3 , t t 3 ) βγδ [ R 3 ] exp +i ω 3 [ ] τ 1 exp i k v [ ] χ αβγ , τ 1 dτ 3
![v r 1 E β ; v r v r 2 , t t 2 , t t 1 , t 1 1 v 2 v (3) 2 ; v χ αβγδ r 3 dt 3 , t t 3 ) βγδ [ R 3 ] exp +i ω 3 [ ] τ 1 exp i k v [ ] χ αβγ , τ 1 dτ 3 v r 1 E β ; v r v r 2 , t t 2 , t t 1 , t 1 1 v 2 v (3) 2 ; v χ αβγδ r 3 dt 3 , t t 3 ) βγδ [ R 3 ] exp +i ω 3 [ ] τ 1 exp i k v [ ] χ αβγ , τ 1 dτ 3](/thumbs/88/117806307.jpg) ON CLASSICAL ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS PAGE 58 VII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- CLASSICAL PICTURE: AN EXTENDED PHENOMENOLOGICAL MODEL OF POLARIZATION : As an introuction to the subject of nonlinear optical phenomena,
ON CLASSICAL ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS PAGE 58 VII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- CLASSICAL PICTURE: AN EXTENDED PHENOMENOLOGICAL MODEL OF POLARIZATION : As an introuction to the subject of nonlinear optical phenomena,
AIR BUBBLE ENTRAINMENT IN HYDRAULIC JUMPS: PHYSICAL MODELING AND SCALE EFFECTS
 AIR BUBBLE ENTRAINMENT IN HYDRAULIC JUMPS: PHYSICAL MODELING AND SCALE EFFECTS Hubert CHANSON Professor in Civil Engineering The University of Queenslan Brisbane QLD 4072 Australia Ph.: (6 7) 3365 463
AIR BUBBLE ENTRAINMENT IN HYDRAULIC JUMPS: PHYSICAL MODELING AND SCALE EFFECTS Hubert CHANSON Professor in Civil Engineering The University of Queenslan Brisbane QLD 4072 Australia Ph.: (6 7) 3365 463
Modelling of Multiphase Flow in Pressure Swirl Atomizer
 International Journal of Engineering an Technology olume 6 No.5, May, 216 Moelling of Multiphase Flow in Pressure wirl Atomizer.K. Ameorme chool of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Thermofluis an Combustion,
International Journal of Engineering an Technology olume 6 No.5, May, 216 Moelling of Multiphase Flow in Pressure wirl Atomizer.K. Ameorme chool of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Thermofluis an Combustion,
Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm
 Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm 1. Maxwell s Equations Quasi-statics o a An air core, N turn, cylinrical solenoi of length an raius a, carries a current I Io cos t. a. Using Ampere s Law, etermine
Homework 7 Due 18 November at 6:00 pm 1. Maxwell s Equations Quasi-statics o a An air core, N turn, cylinrical solenoi of length an raius a, carries a current I Io cos t. a. Using Ampere s Law, etermine
Fluid Mechanics EBS 189a. Winter quarter, 4 units, CRN Lecture TWRF 12:10-1:00, Chemistry 166; Office hours TH 2-3, WF 4-5; 221 Veihmeyer Hall.
 Flui Mechanics EBS 189a. Winter quarter, 4 units, CRN 52984. Lecture TWRF 12:10-1:00, Chemistry 166; Office hours TH 2-3, WF 4-5; 221 eihmeyer Hall. Course Description: xioms of flui mechanics, flui statics,
Flui Mechanics EBS 189a. Winter quarter, 4 units, CRN 52984. Lecture TWRF 12:10-1:00, Chemistry 166; Office hours TH 2-3, WF 4-5; 221 eihmeyer Hall. Course Description: xioms of flui mechanics, flui statics,
'HVLJQ &RQVLGHUDWLRQ LQ 0DWHULDO 6HOHFWLRQ 'HVLJQ 6HQVLWLYLW\,1752'8&7,21
 Large amping in a structural material may be either esirable or unesirable, epening on the engineering application at han. For example, amping is a esirable property to the esigner concerne with limiting
Large amping in a structural material may be either esirable or unesirable, epening on the engineering application at han. For example, amping is a esirable property to the esigner concerne with limiting
Newton Euler equations in general coordinates
 Newton Euler equations in general coorinates y ertol ongar an Frank Kirchner Robotics Innoation Center, DFKI GmbH, remen, Germany Abstract For the computation of rigi boy ynamics, the Newton Euler equations
Newton Euler equations in general coorinates y ertol ongar an Frank Kirchner Robotics Innoation Center, DFKI GmbH, remen, Germany Abstract For the computation of rigi boy ynamics, the Newton Euler equations
PHYS1169: Tutorial 8 Solutions
 PHY69: Tutorial 8 olutions Wae Motion ) Let us consier a point P on the wae with a phase φ, so y cosϕ cos( x ± ωt) At t0, this point has position x0, so ϕ x0 ± ωt0 Now, at some later time t, the position
PHY69: Tutorial 8 olutions Wae Motion ) Let us consier a point P on the wae with a phase φ, so y cosϕ cos( x ± ωt) At t0, this point has position x0, so ϕ x0 ± ωt0 Now, at some later time t, the position
Table of Common Derivatives By David Abraham
 Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
V = Flow velocity, ft/sec
 1 Drag Coefficient Preiction Chapter 1 The ieal force acting on a surface positione perpenicular to the airflow is equal to a ynamic pressure, enote by q, times the area of that surface. Dynamic pressure
1 Drag Coefficient Preiction Chapter 1 The ieal force acting on a surface positione perpenicular to the airflow is equal to a ynamic pressure, enote by q, times the area of that surface. Dynamic pressure
THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE
 Journal of Soun an Vibration (1996) 191(3), 397 414 THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE E. M. WEINSTEIN Galaxy Scientific Corporation, 2500 English Creek
Journal of Soun an Vibration (1996) 191(3), 397 414 THE VAN KAMPEN EXPANSION FOR LINKED DUFFING LINEAR OSCILLATORS EXCITED BY COLORED NOISE E. M. WEINSTEIN Galaxy Scientific Corporation, 2500 English Creek
Numerical modelling of foam Couette flows
 EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserte by the eitor) Numerical moelling of foam Couette flows I. Cheai, P. Saramito, C. Raufaste 2 a, P. Marmottant 2, an F. Graner 2 CNRS, INRIA an Laboratoire Jean Kuntzmann,
EPJ manuscript No. (will be inserte by the eitor) Numerical moelling of foam Couette flows I. Cheai, P. Saramito, C. Raufaste 2 a, P. Marmottant 2, an F. Graner 2 CNRS, INRIA an Laboratoire Jean Kuntzmann,
Thermal conductivity of graded composites: Numerical simulations and an effective medium approximation
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 34 (999)5497 5503 Thermal conuctivity of grae composites: Numerical simulations an an effective meium approximation P. M. HUI Department of Physics, The Chinese University
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 34 (999)5497 5503 Thermal conuctivity of grae composites: Numerical simulations an an effective meium approximation P. M. HUI Department of Physics, The Chinese University
Crack onset assessment near the sharp material inclusion tip by means of modified maximum tangential stress criterion
 Focuse on Mechanical Fatigue of Metals Crack onset assessment near the sharp material inclusion tip by means of moifie maximum tangential stress criterion Onřej Krepl, Jan Klusák CEITEC IPM, Institute
Focuse on Mechanical Fatigue of Metals Crack onset assessment near the sharp material inclusion tip by means of moifie maximum tangential stress criterion Onřej Krepl, Jan Klusák CEITEC IPM, Institute
Asymptotics of a Small Liquid Drop on a Cone and Plate Rheometer
 Asymptotics of a Small Liqui Drop on a Cone an Plate Rheometer Vincent Cregan, Stephen B.G. O Brien, an Sean McKee Abstract A cone an a plate rheometer is a laboratory apparatus use to measure the viscosity
Asymptotics of a Small Liqui Drop on a Cone an Plate Rheometer Vincent Cregan, Stephen B.G. O Brien, an Sean McKee Abstract A cone an a plate rheometer is a laboratory apparatus use to measure the viscosity
Non-Conservative Stability Analysis of Hauger Types of Columns with Different Boundary Conditions
 Proceeings of the Worl Congress on Engineering 08 Vol II WCE 08, July 4-6, 08, onon, U.K. on-conservative Stability nalysis of Hauger Types of Columns with Different Bounary Conitions S.. Fazelzaeh,. Tashakorian,
Proceeings of the Worl Congress on Engineering 08 Vol II WCE 08, July 4-6, 08, onon, U.K. on-conservative Stability nalysis of Hauger Types of Columns with Different Bounary Conitions S.. Fazelzaeh,. Tashakorian,
Work and Kinetic Energy
 Work Work an Kinetic Energy Work (W) the prouct of the force eerte on an object an the istance the object moes in the irection of the force (constant force only). W = " = cos" (N " m = J)! is the angle
Work Work an Kinetic Energy Work (W) the prouct of the force eerte on an object an the istance the object moes in the irection of the force (constant force only). W = " = cos" (N " m = J)! is the angle
(2012) , ISBN
 Cregan, V. an O'Brien, Stephen B.G. an McKee, Sean (2012) Asymptotics of a small liqui rop on a cone an plate rheometer. In: Progress in Inustrial Mathematics at ECMI 2010. Mathematics in Inustry: Progress
Cregan, V. an O'Brien, Stephen B.G. an McKee, Sean (2012) Asymptotics of a small liqui rop on a cone an plate rheometer. In: Progress in Inustrial Mathematics at ECMI 2010. Mathematics in Inustry: Progress
CONTROL AND PERFORMANCE OF A NINE PHASE SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE DRIVE
 CONTRO AN PERFORMANCE OF A NINE PHASE SYNCHRONOUS REUCTANCE RIVE Abstract C.E. Coates*,. Platt** an V.J. Gosbell ** * epartment of Electrical an Computer Engineering Uniersity of Newcastle ** epartment
CONTRO AN PERFORMANCE OF A NINE PHASE SYNCHRONOUS REUCTANCE RIVE Abstract C.E. Coates*,. Platt** an V.J. Gosbell ** * epartment of Electrical an Computer Engineering Uniersity of Newcastle ** epartment
EXPONENTIAL FOURIER INTEGRAL TRANSFORM METHOD FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF BOUNDARY LOAD ON SOIL
 Tome XVI [18] Fascicule 3 [August] 1. Charles Chinwuba IKE EXPONENTIAL FOURIER INTEGRAL TRANSFORM METHOD FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF BOUNDARY LOAD ON SOIL 1. Department of Civil Engineering, Enugu State University
Tome XVI [18] Fascicule 3 [August] 1. Charles Chinwuba IKE EXPONENTIAL FOURIER INTEGRAL TRANSFORM METHOD FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF BOUNDARY LOAD ON SOIL 1. Department of Civil Engineering, Enugu State University
On the Nature of Coherent Turbulent Structures in Channel Bends: Burst-Sweep Orientations in Three-Dimensional Flow Fields
 On the Nature of Coherent Turbulent Structures in Channel Bends: Burst-Sweep Orientations in Three-Dimensional Flow Fields M. Tilston 1, C. Rennie 2, R.W.C. Arnott 1 and G. Post 3 1 Department of Earth
On the Nature of Coherent Turbulent Structures in Channel Bends: Burst-Sweep Orientations in Three-Dimensional Flow Fields M. Tilston 1, C. Rennie 2, R.W.C. Arnott 1 and G. Post 3 1 Department of Earth
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 May 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 May 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 8 May 2014](/thumbs/87/97199974.jpg) Energetics of a flui uner the Boussinesq approximation arxiv:1405.1921v1 [physics.flu-yn] 8 May 2014 Kiyoshi Maruyama Department of Earth an Ocean Sciences, National Defense Acaemy, Yokosuka, Kanagawa
Energetics of a flui uner the Boussinesq approximation arxiv:1405.1921v1 [physics.flu-yn] 8 May 2014 Kiyoshi Maruyama Department of Earth an Ocean Sciences, National Defense Acaemy, Yokosuka, Kanagawa
Inferring dynamic architecture of cellular networks using time series of gene expression, protein and metabolite data. Supplementary Information
 Inferring ynamic architecture of cellular networks using time series of gene expression, protein an metabolite ata Euaro Sontag, Anatoly Kiyatkin an Boris N. Kholoenko *, Department of Mathematics, Rutgers
Inferring ynamic architecture of cellular networks using time series of gene expression, protein an metabolite ata Euaro Sontag, Anatoly Kiyatkin an Boris N. Kholoenko *, Department of Mathematics, Rutgers
EVALUATION OF LIQUEFACTION RESISTANCE AND LIQUEFACTION INDUCED SETTLEMENT FOR RECLAIMED SOIL
 386 EVALUATION OF LIQUEFACTION RESISTANCE AND LIQUEFACTION INDUCED SETTLEMENT FOR RECLAIMED SOIL Lien-Kwei CHIEN 1, Yan-Nam OH 2 An Chih-Hsin CHANG 3 SUMMARY In this stuy, the fille material in Yun-Lin
386 EVALUATION OF LIQUEFACTION RESISTANCE AND LIQUEFACTION INDUCED SETTLEMENT FOR RECLAIMED SOIL Lien-Kwei CHIEN 1, Yan-Nam OH 2 An Chih-Hsin CHANG 3 SUMMARY In this stuy, the fille material in Yun-Lin
TOWARDS THERMOELASTICITY OF FRACTAL MEDIA
 ownloae By: [University of Illinois] At: 21:04 17 August 2007 Journal of Thermal Stresses, 30: 889 896, 2007 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0149-5739 print/1521-074x online OI: 10.1080/01495730701495618
ownloae By: [University of Illinois] At: 21:04 17 August 2007 Journal of Thermal Stresses, 30: 889 896, 2007 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0149-5739 print/1521-074x online OI: 10.1080/01495730701495618
Numerical Investigation of Non-Stationary Parameters on Effective Phenomena of a Pitching Airfoil at Low Reynolds Number
 Journal of Applie Flui Mechanics, Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 643-651, 2016. Available online at www.jafmonline.net, ISSN 1735-3572, EISSN 1735-3645. Numerical Investigation of Non-Stationary Parameters on Effective
Journal of Applie Flui Mechanics, Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 643-651, 2016. Available online at www.jafmonline.net, ISSN 1735-3572, EISSN 1735-3645. Numerical Investigation of Non-Stationary Parameters on Effective
DAMAGE DETECTIONS IN NONLINEAR VIBRATING THERMALLY LOADED STRUCTURES 1
 11 th National Congress on Theoretical an Applie Mechanics, 2-5 Sept. 2009, Borovets, Bulgaria DAMAGE DETECTIONS IN NONLINEAR VIBRATING THERMALLY LOADED STRUCTURES 1 E. MANOACH Institute of Mechanics,
11 th National Congress on Theoretical an Applie Mechanics, 2-5 Sept. 2009, Borovets, Bulgaria DAMAGE DETECTIONS IN NONLINEAR VIBRATING THERMALLY LOADED STRUCTURES 1 E. MANOACH Institute of Mechanics,
CE2253- APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING (FOR IV SEMESTER)
 CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING (FOR IV SEMESTER) UNIT II- UNIFORM FLOW CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC
CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING (FOR IV SEMESTER) UNIT II- UNIFORM FLOW CE5-APPLIED HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING/UNIT-II/UNIFORM FLOW CE5- APPLIED HYDRAULIC
2.20 Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 3
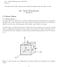 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.7 Stress Tensor 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 1.7.1 Stress Tensor τ ij
2.20 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.7 Stress Tensor 2.20 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 1.7.1 Stress Tensor τ ij
Reconstructions for some coupled-physics inverse problems
 Reconstructions for some couple-physics inerse problems Guillaume al Gunther Uhlmann March 9, 01 Abstract This letter announces an summarizes results obtaine in [8] an consiers seeral natural extensions.
Reconstructions for some couple-physics inerse problems Guillaume al Gunther Uhlmann March 9, 01 Abstract This letter announces an summarizes results obtaine in [8] an consiers seeral natural extensions.
Nonlinear Dielectric Response of Periodic Composite Materials
 onlinear Dielectric Response of Perioic Composite aterials A.G. KOLPAKOV 3, Bl.95, 9 th ovember str., ovosibirsk, 639 Russia the corresponing author e-mail: agk@neic.nsk.su, algk@ngs.ru A. K.TAGATSEV Ceramics
onlinear Dielectric Response of Perioic Composite aterials A.G. KOLPAKOV 3, Bl.95, 9 th ovember str., ovosibirsk, 639 Russia the corresponing author e-mail: agk@neic.nsk.su, algk@ngs.ru A. K.TAGATSEV Ceramics
Characterization of lead zirconate titanate piezoceramic using high frequency ultrasonic spectroscopy
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 85, NUMBER 1 15 JUNE 1999 Characterization of lea zirconate titanate piezoceramic using high frequency ultrasonic spectroscopy Haifeng Wang, Wenhua Jiang, a) an Wenwu
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 85, NUMBER 1 15 JUNE 1999 Characterization of lea zirconate titanate piezoceramic using high frequency ultrasonic spectroscopy Haifeng Wang, Wenhua Jiang, a) an Wenwu
Prediction of anode arc root position in a DC arc plasma torch
 Prediction of anode arc root position in a DC arc plasma torch He-Ping Li 1, E. Pfender 1, Xi Chen 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Uniersity of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA Department
Prediction of anode arc root position in a DC arc plasma torch He-Ping Li 1, E. Pfender 1, Xi Chen 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Uniersity of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA Department
Problem 1 (20 points)
 ME 309 Fall 01 Exam 1 Name: C Problem 1 0 points Short answer questions. Each question is worth 5 points. Don t spen too long writing lengthy answers to these questions. Don t use more space than is given.
ME 309 Fall 01 Exam 1 Name: C Problem 1 0 points Short answer questions. Each question is worth 5 points. Don t spen too long writing lengthy answers to these questions. Don t use more space than is given.
Finite element analysis of the dynamic behavior of concrete-filled double skin steel tubes (CFDST) under lateral impact with fixed-simply support
 Structures Uner Shock an Impact XIII 383 Finite element analysis of the ynamic behavior of concrete-fille ouble skin steel tubes (CFDST) uner lateral impact with fixe-simply support M. Liu & R. Wang Architecture
Structures Uner Shock an Impact XIII 383 Finite element analysis of the ynamic behavior of concrete-fille ouble skin steel tubes (CFDST) uner lateral impact with fixe-simply support M. Liu & R. Wang Architecture
A new identification method of the supply hole discharge coefficient of gas bearings
 Tribology an Design 95 A new ientification metho of the supply hole ischarge coefficient of gas bearings G. Belforte, F. Colombo, T. Raparelli, A. Trivella & V. Viktorov Department of Mechanics, Politecnico
Tribology an Design 95 A new ientification metho of the supply hole ischarge coefficient of gas bearings G. Belforte, F. Colombo, T. Raparelli, A. Trivella & V. Viktorov Department of Mechanics, Politecnico
Two Dimensional Numerical Simulator for Modeling NDC Region in SNDC Devices
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Two Dimensional Numerical Simulator for Moeling NDC Region in SNDC Devices To cite this article: Dheeraj Kumar Sinha et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Two Dimensional Numerical Simulator for Moeling NDC Region in SNDC Devices To cite this article: Dheeraj Kumar Sinha et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ADVANCES IN MATERIALS AND PROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES (AMPT2010), October 2010, Paris, (France)
 Provie by the author(s) an University College Dublin Library in accorance with publisher policies. Please cite the publishe version when available. Title Extrusion process by finite volume metho using
Provie by the author(s) an University College Dublin Library in accorance with publisher policies. Please cite the publishe version when available. Title Extrusion process by finite volume metho using
Physics Concept Review
 Physics oncept eiew Newton eelope 3 laws that goern motion of eerything Newton s Law Definition Example FIST LW (the law of inertia) an object at rest will remain at rest an an object in motion will remain
Physics oncept eiew Newton eelope 3 laws that goern motion of eerything Newton s Law Definition Example FIST LW (the law of inertia) an object at rest will remain at rest an an object in motion will remain
Crack-tip stress evaluation of multi-scale Griffith crack subjected to
 Crack-tip stress evaluation of multi-scale Griffith crack subjecte to tensile loaing by using periynamics Xiao-Wei Jiang, Hai Wang* School of Aeronautics an Astronautics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University,
Crack-tip stress evaluation of multi-scale Griffith crack subjecte to tensile loaing by using periynamics Xiao-Wei Jiang, Hai Wang* School of Aeronautics an Astronautics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University,
1.2 - Stress Tensor Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 3
 13.021 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.2 - Stress Tensor 13.021 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 Stress Tensor τ ij:. The
13.021 Marine Hyroynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 3 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserve. 1.2 - Stress Tensor 13.021 Marine Hyroynamics Lecture 3 Stress Tensor τ ij:. The
AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WING FLUTTER Revision A
 AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WIN FLUTTER Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com January 8, 000 Introuction Certain aircraft wings have experience violent oscillations uring high spee flight.
AN INTRODUCTION TO AIRCRAFT WIN FLUTTER Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com January 8, 000 Introuction Certain aircraft wings have experience violent oscillations uring high spee flight.
Situation awareness of power system based on static voltage security region
 The 6th International Conference on Renewable Power Generation (RPG) 19 20 October 2017 Situation awareness of power system base on static voltage security region Fei Xiao, Zi-Qing Jiang, Qian Ai, Ran
The 6th International Conference on Renewable Power Generation (RPG) 19 20 October 2017 Situation awareness of power system base on static voltage security region Fei Xiao, Zi-Qing Jiang, Qian Ai, Ran
Three-Dimensional Modeling of Green Sand and Squeeze Molding Simulation Yuuka Ito 1,a and Yasuhiro Maeda 2,b*
 Materials Science Forum Submitte: 2017-08-13 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vol. 925, pp 473-480 Revise: 2017-12-09 oi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.925.473 Accepte: 2018-01-12 2018 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerlan
Materials Science Forum Submitte: 2017-08-13 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vol. 925, pp 473-480 Revise: 2017-12-09 oi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.925.473 Accepte: 2018-01-12 2018 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerlan
The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 72.
![The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 72. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 72.](/thumbs/96/127505807.jpg) ADVANCED GCE UNIT 76/ MATHEMATICS (MEI Mechanics MONDAY MAY 7 Additional materials: Answer booklet (8 pages Graph paper MEI Examination Formulae and Tables (MF Morning Time: hour minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO
ADVANCED GCE UNIT 76/ MATHEMATICS (MEI Mechanics MONDAY MAY 7 Additional materials: Answer booklet (8 pages Graph paper MEI Examination Formulae and Tables (MF Morning Time: hour minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO
Placement and tuning of resonance dampers on footbridges
 Downloae from orbit.tu.k on: Jan 17, 19 Placement an tuning of resonance ampers on footbriges Krenk, Steen; Brønen, Aners; Kristensen, Aners Publishe in: Footbrige 5 Publication ate: 5 Document Version
Downloae from orbit.tu.k on: Jan 17, 19 Placement an tuning of resonance ampers on footbriges Krenk, Steen; Brønen, Aners; Kristensen, Aners Publishe in: Footbrige 5 Publication ate: 5 Document Version
Chapter 14: Vibration Generations Mechanisms: Self Excited Vibration
 hapter 14: ibration Generations echanisms: Self Ecite ibration Introuction: Self-ecite systems begin to vibrate of their own accor spontaneously, the amplitue increasing until some nonlinear effect limits
hapter 14: ibration Generations echanisms: Self Ecite ibration Introuction: Self-ecite systems begin to vibrate of their own accor spontaneously, the amplitue increasing until some nonlinear effect limits
APPROXIMATE SOLUTION FOR TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSFER IN STATIC TURBULENT HE II. B. Baudouy. CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/STCM Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France
 APPROXIMAE SOLUION FOR RANSIEN HEA RANSFER IN SAIC URBULEN HE II B. Bauouy CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/SCM 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Ceex, France ABSRAC Analytical solution in one imension of the heat iffusion equation
APPROXIMAE SOLUION FOR RANSIEN HEA RANSFER IN SAIC URBULEN HE II B. Bauouy CEA/Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/SCM 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Ceex, France ABSRAC Analytical solution in one imension of the heat iffusion equation
CHARACTERISTICS OF A DYNAMIC PRESSURE GENERATOR BASED ON LOUDSPEAKERS. Jože Kutin *, Ivan Bajsić
 Sensors an Actuators A: Physical 168 (211) 149-154 oi: 1.116/j.sna.211..7 211 Elsevier B.V. CHARACTERISTICS OF A DYNAMIC PRESSURE GENERATOR BASED ON LOUDSPEAKERS Jože Kutin *, Ivan Bajsić Laboratory of
Sensors an Actuators A: Physical 168 (211) 149-154 oi: 1.116/j.sna.211..7 211 Elsevier B.V. CHARACTERISTICS OF A DYNAMIC PRESSURE GENERATOR BASED ON LOUDSPEAKERS Jože Kutin *, Ivan Bajsić Laboratory of
REDUCING the cost of launching a space vehicle into space is
 AIAA JOURNAL Vol. 45, No., September Micromechanical Analysis of Composite Corrugate-Core Sanwich Panels for Integral Thermal Protection Systems Oscar A. Martinez, Bhavani V. Sankar, Raphael T. Haftka,
AIAA JOURNAL Vol. 45, No., September Micromechanical Analysis of Composite Corrugate-Core Sanwich Panels for Integral Thermal Protection Systems Oscar A. Martinez, Bhavani V. Sankar, Raphael T. Haftka,
DOUBLE PENDULUM VIBRATION MOTION IN FLUID FLOW
 ENGINEERING FOR RURA DEEOPMENT Jelgava,.-.5.5. DOUBE PENDUUM IBRATION MOTION IN FUID FOW Janis iba, Maris Eiuks, Martins Irbe Riga Technical University, atvia janis.viba@rtu.lv, maris.eiuks@rtu.lv, martins.irbe@rtu.lv
ENGINEERING FOR RURA DEEOPMENT Jelgava,.-.5.5. DOUBE PENDUUM IBRATION MOTION IN FUID FOW Janis iba, Maris Eiuks, Martins Irbe Riga Technical University, atvia janis.viba@rtu.lv, maris.eiuks@rtu.lv, martins.irbe@rtu.lv
MOTION OF FALLING OBJECTS WITH RESISTANCE
 DOING PHYSICS WIH MALAB MECHANICS MOION OF FALLING OBJECS WIH RESISANCE Ian Cooper School of Physics, Uniersity of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOAD DIRECORY FOR MALAB SCRIPS mec_fr_mg_b.m Computation
DOING PHYSICS WIH MALAB MECHANICS MOION OF FALLING OBJECS WIH RESISANCE Ian Cooper School of Physics, Uniersity of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOAD DIRECORY FOR MALAB SCRIPS mec_fr_mg_b.m Computation
Lecture 2 Lagrangian formulation of classical mechanics Mechanics
 Lecture Lagrangian formulation of classical mechanics 70.00 Mechanics Principle of stationary action MATH-GA To specify a motion uniquely in classical mechanics, it suffices to give, at some time t 0,
Lecture Lagrangian formulation of classical mechanics 70.00 Mechanics Principle of stationary action MATH-GA To specify a motion uniquely in classical mechanics, it suffices to give, at some time t 0,
Purpose of the experiment
 Impulse and Momentum PES 116 Adanced Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment Measure a cart s momentum change and compare to the impulse it receies. Compare aerage and peak forces in impulses. To put the
Impulse and Momentum PES 116 Adanced Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment Measure a cart s momentum change and compare to the impulse it receies. Compare aerage and peak forces in impulses. To put the
DISCRETE MODELING OF STRAIN ACCUMULATION IN GRANULAR SOILS UNDER CYCLIC LOADING
 11th Worl Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Flui Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
11th Worl Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Flui Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
Fluid Kinematics. by Dr. Nor Azlina binti Alias Faculty of Civil and Earth Resources Engineering
 Flui Kinematics by Nor A Alias For upate ersion, please click on http://ocw.ump.eu.my Flui Kinematics by Dr. Nor Azlina binti Alias Faculty of Ciil an Earth Resources Enineerin azlina@ump.eu.my Flui Kinematics
Flui Kinematics by Nor A Alias For upate ersion, please click on http://ocw.ump.eu.my Flui Kinematics by Dr. Nor Azlina binti Alias Faculty of Ciil an Earth Resources Enineerin azlina@ump.eu.my Flui Kinematics
OF CHS. associated. indicate. the need. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. a) Footbridge Rio. d) Maria Lenk. CHS K joints
 EUROSTEEL 2, August 3 September 2, 2, Buapest, Hungary A NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF CHS T JOINTS UNDER AXIAL LOADS Raphael S. a Silva a, Luciano R. O. e Lima b, Pero C. G. a S. Vellasco b, José G. S. a Silva
EUROSTEEL 2, August 3 September 2, 2, Buapest, Hungary A NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF CHS T JOINTS UNDER AXIAL LOADS Raphael S. a Silva a, Luciano R. O. e Lima b, Pero C. G. a S. Vellasco b, José G. S. a Silva
An inductance lookup table application for analysis of reluctance stepper motor model
 ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 60(), pp. 5- (0) DOI 0.478/ v07-0-000-y An inuctance lookup table application for analysis of reluctance stepper motor moel JAKUB BERNAT, JAKUB KOŁOTA, SŁAWOMIR
ARCHIVES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 60(), pp. 5- (0) DOI 0.478/ v07-0-000-y An inuctance lookup table application for analysis of reluctance stepper motor moel JAKUB BERNAT, JAKUB KOŁOTA, SŁAWOMIR
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 3 The Surface Layer
 ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 3 he Surface Layer References: Air-sea Interaction: Laws and Mechanisms, Csanady Structure of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Sorbjan HE PLANEARY BOUNDARY LAYER he atmospheric
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 3 he Surface Layer References: Air-sea Interaction: Laws and Mechanisms, Csanady Structure of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Sorbjan HE PLANEARY BOUNDARY LAYER he atmospheric
A. unchanged increased B. unchanged unchanged C. increased increased D. increased unchanged
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER B TEST REVIEW. A rocket is fired ertically. At its highest point, it explodes. Which one of the following describes what happens
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER B TEST REVIEW. A rocket is fired ertically. At its highest point, it explodes. Which one of the following describes what happens
Modelling dowel action of discrete reinforcing bars in cracked concrete structures
 Title Moelling owel action of iscrete reinforcing bars in cracke concrete structures Author(s) Kwan, AKH; Ng, PL; Lam, JYK Citation The 2n International Symposium on Computational Mechanics an the 12th
Title Moelling owel action of iscrete reinforcing bars in cracke concrete structures Author(s) Kwan, AKH; Ng, PL; Lam, JYK Citation The 2n International Symposium on Computational Mechanics an the 12th
Role of parameters in the stochastic dynamics of a stick-slip oscillator
 Proceeing Series of the Brazilian Society of Applie an Computational Mathematics, v. 6, n. 1, 218. Trabalho apresentao no XXXVII CNMAC, S.J. os Campos - SP, 217. Proceeing Series of the Brazilian Society
Proceeing Series of the Brazilian Society of Applie an Computational Mathematics, v. 6, n. 1, 218. Trabalho apresentao no XXXVII CNMAC, S.J. os Campos - SP, 217. Proceeing Series of the Brazilian Society
Generalization of the persistent random walk to dimensions greater than 1
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 1998 Generalization of the persistent ranom walk to imensions greater than 1 Marián Boguñá, Josep M. Porrà, an Jaume Masoliver Departament e Física Fonamental,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 1998 Generalization of the persistent ranom walk to imensions greater than 1 Marián Boguñá, Josep M. Porrà, an Jaume Masoliver Departament e Física Fonamental,
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE RECTLINEAR MOTION: UNIFORM ACCELERATION
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE RECTLINEAR MOTION: UNIFORM ACCELERATION Predict Obsere Explain Exercise 1 Take an A4 sheet of paper and a heay object (cricket ball, basketball, brick, book, etc). Predict what will
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE RECTLINEAR MOTION: UNIFORM ACCELERATION Predict Obsere Explain Exercise 1 Take an A4 sheet of paper and a heay object (cricket ball, basketball, brick, book, etc). Predict what will
ECE 422 Power System Operations & Planning 7 Transient Stability
 ECE 4 Power System Operations & Planning 7 Transient Stability Spring 5 Instructor: Kai Sun References Saaat s Chapter.5 ~. EPRI Tutorial s Chapter 7 Kunur s Chapter 3 Transient Stability The ability of
ECE 4 Power System Operations & Planning 7 Transient Stability Spring 5 Instructor: Kai Sun References Saaat s Chapter.5 ~. EPRI Tutorial s Chapter 7 Kunur s Chapter 3 Transient Stability The ability of
International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015)
 International Conference on Avances in Energy, Environment an Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015) Stuy on Damage Characteristic of Unergroun Cavern Blasting Excavation Base on Dynamic Damage Constitutive
International Conference on Avances in Energy, Environment an Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015) Stuy on Damage Characteristic of Unergroun Cavern Blasting Excavation Base on Dynamic Damage Constitutive
Non-Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Water Flow around a Carbon Nanotube
 Copyright c 27 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.22, no.1, pp.31-4, 27 Non-Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Water Flow aroun a Carbon Nanotube Wenzhong Tang 1 an Suresh G. Avani 1,2 Abstract: In
Copyright c 27 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.22, no.1, pp.31-4, 27 Non-Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Water Flow aroun a Carbon Nanotube Wenzhong Tang 1 an Suresh G. Avani 1,2 Abstract: In
UNDERSTAND MOTION IN ONE AND TWO DIMENSIONS
 SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 UNDERSTAND MOTION IN ONE AND TWO DIMENSIONS MECHANICS Skill 1.1 Calculating displacement, aerage elocity, instantaneous elocity, and acceleration in a gien frame of reference
SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 UNDERSTAND MOTION IN ONE AND TWO DIMENSIONS MECHANICS Skill 1.1 Calculating displacement, aerage elocity, instantaneous elocity, and acceleration in a gien frame of reference
Finite element analysis of electromagnetic bulging of sheet metals
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 2, Febraury-212 1 Finite element analysis of electromagnetic bulging of sheet metals Ali M. Abelhafeez, M. M. Nemat-Alla, M. G.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 2, Febraury-212 1 Finite element analysis of electromagnetic bulging of sheet metals Ali M. Abelhafeez, M. M. Nemat-Alla, M. G.
2008 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 FINITE DIFFERENCE TIME DOMAIN MODELING OF INFRASOUND PROPAGATION: APPLICATION TO SHADOW ZONE ARRIVALS AND REGIONAL PROPAGATION Catherine de Groot-Hedlin Uniersity of California at San Diego Sponsored by
FINITE DIFFERENCE TIME DOMAIN MODELING OF INFRASOUND PROPAGATION: APPLICATION TO SHADOW ZONE ARRIVALS AND REGIONAL PROPAGATION Catherine de Groot-Hedlin Uniersity of California at San Diego Sponsored by
To understand how scrubbers work, we must first define some terms.
 SRUBBERS FOR PARTIE OETION Backgroun To unerstan how scrubbers work, we must first efine some terms. Single roplet efficiency, η, is similar to single fiber efficiency. It is the fraction of particles
SRUBBERS FOR PARTIE OETION Backgroun To unerstan how scrubbers work, we must first efine some terms. Single roplet efficiency, η, is similar to single fiber efficiency. It is the fraction of particles
