A Class of Möbius Iterated Function Systems
|
|
|
- Rhoda Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 A Class of Möbius Iterated Function Systems arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 30 Jan 018 Gökçe ÇAKMAK, Ali DENİZ, Şahin KOÇAK Abstract We give a procedure to produce Möbius iterated function systems (MIFS) on the unit disc in the complex plane. Keywords: Iterated function system, Möbius iterated function system, Möbius transformation, attractors. MSC010:8A80,30D05 1 Introduction Iterated function systems (IFS) devised by Hutchinson ([1]) are primary tools to generate (and understand) a large class of fractals. It is however not an easy matter to analyze systems going beyond the similarity transformations on Euclidean spaces. A particularly interesting class of IFS are Möbius iterated function systems (MIFS), but there are rather few examples of this class in the literature (see []). In this note, we give a simple procedure to produce contractive Möbius functions on the unit disc in the complex plane which could serve for further investigations from various fractal Anadolu University, Science Faculty, Department of Mathematics, 6470, Eskişehir, Turkey, s: gokcecakmak@anadolu.edu.tr, adeniz@anadolu.edu.tr, skocak@anadolu.edu.tr Corresponding Author.
2 points of view such as attractor properties, dimension considerations, tube formulas etc. Using Proposition below one can produce easily all Möbius transformations which map the unit disc of the complex plane contractively into itself and use them to construct MIFS s at will. For the convenience of the reader, we first give the following lemma: Lemma 1 Let ϕ(z) az + b (ad bc 1) be a Möbius transformation on C { } cz + d and S C be a circle with center M and radius R. Then, ϕ(s) is a circle with center M (am + b)(cm + d) R ac (cm + d)(cm + d) R cc and radius R R cm + d R c. (The circle S is mapped onto a line iff cz + d vanishes at a point on S; this can also be expressed as cm + d R c.) Proof. The circle S can be expressed as z M R ; if we denote ϕ(z) az + b dw b by w and insert z into the equation of the circle we cz + d a cw obtain dw b a cw M R, i.e. (dw b M(a cw))(dw b M(a cw)) R (a cw)(a cw) or ( d + cdm + cdm + cm R c ) w (bd + adm + bcm + ac M R ac)w (bd + bcm + adm + ac M R ac)w R a b abm abm am. This equation shows that ϕ(s) is a circle with center M bd + bcm + adm + ac M R ac d + cdm + cdm + cm R c.
3 3 With a straightforward calculation one can see that the radius of ϕ(s) is R R cm + d R c. (As the expression for R shows, S is mapped onto a line iff cm + d R c.) Contractive Möbius Transformations on the Unit Disc We now give the following proposition which characterizes when a Möbius transformation ϕ(z) az + b maps the unit disc D {z C : z 1} contractively into itself. ( Contractively means that there exists 0 < s < 1 such that cz + d ϕ(z) ϕ(w) s z w for z, w D.) Proposition 1 Let ϕ(z) az + b cz + d C { }. (ad bc 1) be a Möbius transformation on 1. ϕ maps the unit disc D into itself (ϕ(d) D) if and only if the following two conditions hold: i. c < d ii. ac bd + 1 d c. ϕ maps D contractively into itself if and only if the following two conditions hold: i. d c > 1 ii. ac bd + 1 d c
4 4 Proof. For the first part, we remark that ϕ maps the unit disc into itself if and only if M + R 1, where M is the center of ϕ(s) (S {z C : z 1}) and R is the radius of ϕ(s); and additionally, ϕ(0) is mapped into the inside of ϕ(s), i.e. ϕ(0) M < R. By the lemma above (with M 0 and R 1) we have M bd ac d c and R 1. (For the circle S to be mapped into a circle it must be c d.) d c Inserting the formulas for M and R into the above inequalities we get; 1. i. ϕ(0) M b d bd ac bdd bcc bdd + acd c ad bc d c d d c d d c c d d c < 1 R, which gives c < d. d c ii. M + R bd ac d c + 1 bd ac + 1 d c d c ac bd + 1 d c since c < d. 1, which gives Conversely, if these two conditions are satisfied then 1. i. ϕ(0) M < R holds, since ϕ(0) M c d d c < 1 d c R by c < d. ii. M + R 1 holds, since M + R bd ac + 1 bd ac + 1 d c d c by c < d and thus M + R 1 by the second condition. We now consider the second part of the proposition. Let us first assume that the two given conditions are satisfied. Then by the first part of the proposition, the disc D is mapped into itself. So we just need to show that ϕ is a contraction. Since ϕ 1 (z) it will be enough to show that cz + d > 1 + α for all z D for (cz + d)
5 5 some α > 0, because we could then write ϕ(z) ϕ(w) < [z,w] ϕ (ζ)dζ [z,w] ϕ (ζ) dζ max ζ [z,w] ϕ (ζ) z w 1 z w ([z,w] is the segment connecting z and w.) (1 + α) and thus ϕ would be a contraction on D. Indeed, cz + d d cz d c > 1 and since D is compact and cz + d is continuous, we can write cz + d > 1 + α for some α > 0. Conversely, let us assume that ϕ maps D contractively into itself. By the first part of the proposition, the second condition holds and we must show the first condition d c > 1. Since ϕ is a contraction we can write ϕ(z) ϕ(w) s z w for some 0 < s < 1. This gives ϕ (z) s < 1. Since ϕ 1 (z) we get cz + d cz +d 1 > 1. Inserting z c d into this inequality, we get s c d c c d c d + d > 1, d c + d d > 1, thus d c > 1 because d > c by the first part of the d proposition. (It is obvious that d cannot vanish because d > c and in the case of c 0 we get d > 1 by cz + d > 1 and thus d c > 1.) Proposition Let r R with 0 < r < 1 and let m be a complex number satisfying m 1 r. Choose c C with c < 1 r and d C with d c + 1/r. Let r a mc + rd and b md + rc. Then, ϕ(z) az + b maps D contractively into itself. (Furthermore, the center cz + d of the image of unit circle is m and its radius is r.) Proof. By Proposition 1 (part ), it will be enough to show that d c > 1 and ac bd + 1 d c.
6 6 For the first condition, note that c < 1 r r 1 ( ) 1 r 1 1 ( d c 1), which gives c + c + 1 ( c + 1) < d and therefore d c > 1. For the second condition, inserting the expression for a and b we get ac bd (mc + r d)c (md + r c)d mc c + r c d md d r c d m( c d ) and thus ac bd +1 m c d +1 m ( d c )+1 m m + r +1 r r 1 r d c. (To find the center of the image of the unit circle and its radius, insert a mc + r d and b md + r c into the formulas for M and R of Lemma 1 with M 0 and R 1: M b d a c d c (md + r c) d (mc + r d) c md d mc c m and d c d c R 1 d c r.) Remark 1 Any Möbius transformation ϕ(z) az + b (ad bc 1) mapping cz + d the unit disc D contractively into itself can be obtained in the way prescribed in Proposition. Proof. Since ϕ(d) D, r and m are given as natural parameters; r being the radius of ϕ(d) and m its center. They satisfy 0 < r < 1 (r > 0 since ϕ is not constant and r < 1 since ϕ is contractive) and m + r 1. By Proposition 1, d c > 1 1 so that r can be expressed as r d c 1 by Lemma 1 and we get d c d c + 1/r. Inserting this into d c > 1 we get c < 1 r. On the other r
7 7 hand, m b d a c d c by Lemma 1, hence m (b d 1 a c) d c (b d a c)r. Now, b d a c m and ad bc 1 yield a mc + rd and b md + rc. r 3 Examples Using Proposition one can produce an infinitude of examples of Möbius iterated function systems. We give below several MIFS s by choosing r, m, c and d arbitrarily (only subject to the conditions of Proposition ) and then determining a and b according to Proposition. We depict the corresponding attractors also (we used the software Cinderella [3] to generate them). We remind that, for an IFS consisting of the contractions ϕ 1, ϕ,..., ϕ N on D (or on any complete metric space X), the Hausdorff limit A of the sequence ϕ k (Y ) ϕ ϕ... ϕ(y ), where Y X is any compact subset and ϕ(y ) ϕ 1 (Y ) ϕ (Y )... ϕ N (Y ), is called the attractor of the IFS {ϕ 1, ϕ,..., ϕ N }. For generalities on iterated function systems see [4]. Example 1 We determine ϕ 1 by choosing r 1 0.7, m i, c 1 0.i, d i; and ϕ by choosing r 0.6, m 0.3i, c 0.i, d Computing a 1, b 1 and a, b according to the Proposition, one obtains ϕ 1 (z) a 1z + b 1 c 1 z + d 1 ( i)z + ( i) (0.i)z + ( i) and ϕ (z) a z + b c z + d ( )z + (0.5119i) ( 0.i)z + ( ). We show in Fig. 1 (a) the images of the unit disc with respect to ϕ 1 and ϕ, and in Fig. 1 (b) the emerging attractor inside the unit disc.
8 8 (a) (b) Figure 1: The image of the unit circle with respect to ϕ 1 is shown with center m 1 and with respect to ϕ with center m in (a). The emerging attractor is shown in (b). Example We determine ϕ 1 by choosing r 1 0.6, m i, c i, d i; ϕ by choosing r 0.4, m i, c 0.7i, d i and ϕ 3 by choosing r 3 0.5, m i, c i, d i. Computing a 1, b 1, a, b and a 3, b 3 according to the Proposition, one obtains the transformations ϕ 1 (z) a 1z + b 1 c 1 z + d 1 ϕ (z) a z + b c z + d ( i)z + ( i), (0. 0.i)z + ( i) ( i)z + ( i) (0.7i)z + ( i) and ϕ 3 (z) a 3z + b 3 c 3 z + d 3 ( i)z + ( i). ( i)z + ( i) The emerging attractor inside the unit disc is shown in Fig..
9 9 (a) (b) Figure : The image of the unit circle with respect to ϕ 1 is shown with center m 1, with respect to ϕ with center m and with respect to ϕ 3 with center m 3 in (a). The emerging attractor is shown in (b). Example 3 We determine ϕ 1 by choosing r 1 0.6, m i, c i, d i; ϕ by choosing r 0.5, m i, c i, d i and ϕ 3 by choosing r 3 0.5, m i, c i, d i. Computing a 1, b 1, a, b and a 3, b 3 according to the Proposition, one obtains the transformations ϕ 1 (z) a 1z + b 1 c 1 z + d 1 ϕ (z) a z + b c z + d ( i)z + ( i) ( i)z + ( i), ( i)z + ( i) ( i)z + ( i) and ϕ 3 (z) a 3z + b 3 c 3 z + d 3 ( i)z + ( i) ( i)z + ( i).
10 10 (a) (b) Figure 3: The image of the unit circle with respect to ϕ 1 is shown with center m 1, with respect to ϕ with center m and with respect to ϕ 3 with center m 3 in (a). The emerging attractor is shown in (b). The emerging attractor inside the unit disc is shown in Fig. 3. References [1] Hutchinson, John E., Fractals and Self-Similarity, Indiana Univ. Math. J., Vol 30, Number 5, (1981), [] Vince A., Möbius Iterated Function Systems, Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, Vol 365, Number 1, (013), [3] Richter-Gebert, J., Kortenkamp, U., The interactive geometry software Cinderella., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, (1999). [4] Barnsley M. F., Fractals Everywhere Boston: Academic Press, (1993).
THE CONLEY ATTRACTORS OF AN ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEM
 Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 88 (2013), 267 279 doi:10.1017/s0004972713000348 THE CONLEY ATTRACTORS OF AN ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEM MICHAEL F. BARNSLEY and ANDREW VINCE (Received 15 August 2012; accepted 21 February
Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 88 (2013), 267 279 doi:10.1017/s0004972713000348 THE CONLEY ATTRACTORS OF AN ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEM MICHAEL F. BARNSLEY and ANDREW VINCE (Received 15 August 2012; accepted 21 February
Iterated function systems on functions of bounded variation
 Iterated function systems on functions of bounded variation D. La Torre, F. Mendivil and E.R. Vrscay December 18, 2015 Abstract We show that under certain hypotheses, an Iterated Function System on Mappings
Iterated function systems on functions of bounded variation D. La Torre, F. Mendivil and E.R. Vrscay December 18, 2015 Abstract We show that under certain hypotheses, an Iterated Function System on Mappings
ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS WITH CONTINUOUS PLACE DEPENDENT PROBABILITIES
 UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA, FASCICULUS XL 2002 ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS WITH CONTINUOUS PLACE DEPENDENT PROBABILITIES by Joanna Jaroszewska Abstract. We study the asymptotic behaviour
UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA, FASCICULUS XL 2002 ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS WITH CONTINUOUS PLACE DEPENDENT PROBABILITIES by Joanna Jaroszewska Abstract. We study the asymptotic behaviour
ON THE DIAMETER OF THE ATTRACTOR OF AN IFS Serge Dubuc Raouf Hamzaoui Abstract We investigate methods for the evaluation of the diameter of the attrac
 ON THE DIAMETER OF THE ATTRACTOR OF AN IFS Serge Dubuc Raouf Hamzaoui Abstract We investigate methods for the evaluation of the diameter of the attractor of an IFS. We propose an upper bound for the diameter
ON THE DIAMETER OF THE ATTRACTOR OF AN IFS Serge Dubuc Raouf Hamzaoui Abstract We investigate methods for the evaluation of the diameter of the attractor of an IFS. We propose an upper bound for the diameter
THE SHIFT SPACE FOR AN INFINITE ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEM
 THE SHIFT SPACE FOR AN INFINITE ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEM ALEXANDRU MIHAIL and RADU MICULESCU The aim of the paper is to define the shift space for an infinite iterated function systems (IIFS) and to describe
THE SHIFT SPACE FOR AN INFINITE ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEM ALEXANDRU MIHAIL and RADU MICULESCU The aim of the paper is to define the shift space for an infinite iterated function systems (IIFS) and to describe
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
Approximation of the attractor of a countable iterated function system 1
 General Mathematics Vol. 17, No. 3 (2009), 221 231 Approximation of the attractor of a countable iterated function system 1 Nicolae-Adrian Secelean Abstract In this paper we will describe a construction
General Mathematics Vol. 17, No. 3 (2009), 221 231 Approximation of the attractor of a countable iterated function system 1 Nicolae-Adrian Secelean Abstract In this paper we will describe a construction
Part II. Geometry and Groups. Year
 Part II Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2014 Paper 4, Section I 3F 49 Define the limit set Λ(G) of a Kleinian group G. Assuming that G has no finite orbit in H 3 S 2, and that Λ(G),
Part II Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2014 Paper 4, Section I 3F 49 Define the limit set Λ(G) of a Kleinian group G. Assuming that G has no finite orbit in H 3 S 2, and that Λ(G),
Möbius transformations and its applications
 Möbius transformation and its applications Every Möbius transformation is the composition of translations, dilations and the inversion. Proof. Let w = S(z) = az + b, ad bc 0 be a Möbius cz + d transformation.
Möbius transformation and its applications Every Möbius transformation is the composition of translations, dilations and the inversion. Proof. Let w = S(z) = az + b, ad bc 0 be a Möbius cz + d transformation.
Apollonian Circumcircles of IFS Fractals
 Apollonian Circumcircles of IFS Fractals József Vass arxiv:1301.1378v [cs.cg] 16 Apr 015 Faculty of Mathematics University of Waterloo jvass@uwaterloo.ca Abstract Euclidean triangles and IFS fractals seem
Apollonian Circumcircles of IFS Fractals József Vass arxiv:1301.1378v [cs.cg] 16 Apr 015 Faculty of Mathematics University of Waterloo jvass@uwaterloo.ca Abstract Euclidean triangles and IFS fractals seem
Fractals and Dimension
 Chapter 7 Fractals and Dimension Dimension We say that a smooth curve has dimension 1, a plane has dimension 2 and so on, but it is not so obvious at first what dimension we should ascribe to the Sierpinski
Chapter 7 Fractals and Dimension Dimension We say that a smooth curve has dimension 1, a plane has dimension 2 and so on, but it is not so obvious at first what dimension we should ascribe to the Sierpinski
NOTES ON BARNSLEY FERN
 NOTES ON BARNSLEY FERN ERIC MARTIN 1. Affine transformations An affine transformation on the plane is a mapping T that preserves collinearity and ratios of distances: given two points A and B, if C is
NOTES ON BARNSLEY FERN ERIC MARTIN 1. Affine transformations An affine transformation on the plane is a mapping T that preserves collinearity and ratios of distances: given two points A and B, if C is
RECURRENT ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS
 RECURRENT ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS ALEXANDRU MIHAIL The theory of fractal sets is an old one, but it also is a modern domain of research. One of the main source of the development of the theory of fractal
RECURRENT ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS ALEXANDRU MIHAIL The theory of fractal sets is an old one, but it also is a modern domain of research. One of the main source of the development of the theory of fractal
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping. 1 Conformality. 1.1 Preservation of angle. 1.2 Length and area. MATH-GA Complex Variables
 Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
One-parameter families of functions in the Pick class
 arxiv:0704.1716v1 [math.ds] 13 Apr 2007 One-parameter families of functions in the Pick class Waldemar Pa luba Institute of Mathematics Warsaw University Banacha 2 02-097 Warsaw, Poland e-mail: paluba@mimuw.edu.pl
arxiv:0704.1716v1 [math.ds] 13 Apr 2007 One-parameter families of functions in the Pick class Waldemar Pa luba Institute of Mathematics Warsaw University Banacha 2 02-097 Warsaw, Poland e-mail: paluba@mimuw.edu.pl
ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 5, 24 ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove some versions of the Schwarz
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 5, 24 ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove some versions of the Schwarz
Conformal Mapping, Möbius Transformations. Slides-13
 , Möbius Transformations Slides-13 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z).
, Möbius Transformations Slides-13 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z).
DERIVATIVE-FREE CHARACTERIZATIONS OF Q K SPACES
 ERIVATIVE-FREE CHARACTERIZATIONS OF Q K SPACES HASI WULAN AN KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. We give two characterizations of the Möbius invariant Q K spaces, one in terms of a double integral and the other in terms
ERIVATIVE-FREE CHARACTERIZATIONS OF Q K SPACES HASI WULAN AN KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. We give two characterizations of the Möbius invariant Q K spaces, one in terms of a double integral and the other in terms
arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014 arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014](/thumbs/94/121818359.jpg) ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS AND THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC arxiv:1307.4006v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014 MARIJAN MARKOVIĆ Abstract. Motivated by some recent results of Kalaj and Vuorinen (Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2012),
ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS AND THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC arxiv:1307.4006v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014 MARIJAN MARKOVIĆ Abstract. Motivated by some recent results of Kalaj and Vuorinen (Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2012),
Möbius Transformation
 Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
On some non-conformal fractals
 On some non-conformal fractals arxiv:1004.3510v1 [math.ds] 20 Apr 2010 Micha l Rams Institute of Mathematics, Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Śniadeckich 8, 00-950 Warszawa, Poland e-mail: rams@impan.gov.pl
On some non-conformal fractals arxiv:1004.3510v1 [math.ds] 20 Apr 2010 Micha l Rams Institute of Mathematics, Polish Academy of Sciences ul. Śniadeckich 8, 00-950 Warszawa, Poland e-mail: rams@impan.gov.pl
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis. A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India. and. V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India
 NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 36 Complex Analysis Module: 7:
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 36 Complex Analysis Module: 7:
THE CONTRACTION MAPPING THEOREM, II
 THE CONTRACTION MAPPING THEOREM, II KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction In part I, we met the contraction mapping theorem and an application of it to solving nonlinear differential equations. Here we will discuss
THE CONTRACTION MAPPING THEOREM, II KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction In part I, we met the contraction mapping theorem and an application of it to solving nonlinear differential equations. Here we will discuss
COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS
 Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
ON A CLASS OF IDEALS OF THE TOEPLITZ ALGEBRA ON THE BERGMAN SPACE
 ON A CLASS OF IDEALS OF THE TOEPLITZ ALGEBRA ON THE BERGMAN SPACE TRIEU LE Abstract Let T denote the full Toeplitz algebra on the Bergman space of the unit ball B n For each subset G of L, let CI(G) denote
ON A CLASS OF IDEALS OF THE TOEPLITZ ALGEBRA ON THE BERGMAN SPACE TRIEU LE Abstract Let T denote the full Toeplitz algebra on the Bergman space of the unit ball B n For each subset G of L, let CI(G) denote
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM. 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces
 8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
LINEAR FRACTIONAL COMPOSITION OPERATORS ON H 2
 J Integral Equations and Operator Theory (988, 5 60 LINEAR FRACTIONAL COMPOSITION OPERATORS ON H 2 CARL C COWEN Abstract If ϕ is an analytic function mapping the unit disk D into itself, the composition
J Integral Equations and Operator Theory (988, 5 60 LINEAR FRACTIONAL COMPOSITION OPERATORS ON H 2 CARL C COWEN Abstract If ϕ is an analytic function mapping the unit disk D into itself, the composition
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
Generation of Fractals via Self-Similar Group of Kannan Iterated Function System
 Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 9, No. 6, 3245-3250 (2015) 3245 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/090652 Generation of Fractals via Self-Similar
Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 9, No. 6, 3245-3250 (2015) 3245 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/090652 Generation of Fractals via Self-Similar
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Nonarchimedean Cantor set and string
 J fixed point theory appl Online First c 2008 Birkhäuser Verlag Basel/Switzerland DOI 101007/s11784-008-0062-9 Journal of Fixed Point Theory and Applications Nonarchimedean Cantor set and string Michel
J fixed point theory appl Online First c 2008 Birkhäuser Verlag Basel/Switzerland DOI 101007/s11784-008-0062-9 Journal of Fixed Point Theory and Applications Nonarchimedean Cantor set and string Michel
Key words and phrases. Hausdorff measure, self-similar set, Sierpinski triangle The research of Móra was supported by OTKA Foundation #TS49835
 Key words and phrases. Hausdorff measure, self-similar set, Sierpinski triangle The research of Móra was supported by OTKA Foundation #TS49835 Department of Stochastics, Institute of Mathematics, Budapest
Key words and phrases. Hausdorff measure, self-similar set, Sierpinski triangle The research of Móra was supported by OTKA Foundation #TS49835 Department of Stochastics, Institute of Mathematics, Budapest
A crash course the geometry of hyperbolic surfaces
 Lecture 7 A crash course the geometry of hyperbolic surfaces 7.1 The hyperbolic plane Hyperbolic geometry originally developed in the early 19 th century to prove that the parallel postulate in Euclidean
Lecture 7 A crash course the geometry of hyperbolic surfaces 7.1 The hyperbolic plane Hyperbolic geometry originally developed in the early 19 th century to prove that the parallel postulate in Euclidean
Fractals: A Mathematical Framework
 Fractals: A Mathematical Framework John E Hutchinson Department of Mathematics School of Mathematical Sciences Australian National University (e-mail: JohnHutchinson@anueduau) Abstract We survey some of
Fractals: A Mathematical Framework John E Hutchinson Department of Mathematics School of Mathematical Sciences Australian National University (e-mail: JohnHutchinson@anueduau) Abstract We survey some of
Computability of Koch Curve and Koch Island
 Koch 6J@~$H Koch Eg$N7W;;2DG=@- {9@Lw y wd@ics.nara-wu.ac.jp 2OM85*;R z kawamura@e.ics.nara-wu.ac.jp y F NI=w;RBgXM}XIt>pJs2JX2J z F NI=w;RBgX?M4VJ82=8&5f2J 5MW Koch 6J@~$O Euclid J?LL>e$NE57?E*$J
Koch 6J@~$H Koch Eg$N7W;;2DG=@- {9@Lw y wd@ics.nara-wu.ac.jp 2OM85*;R z kawamura@e.ics.nara-wu.ac.jp y F NI=w;RBgXM}XIt>pJs2JX2J z F NI=w;RBgX?M4VJ82=8&5f2J 5MW Koch 6J@~$O Euclid J?LL>e$NE57?E*$J
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 7 Mar 2019](/thumbs/94/119023314.jpg) ON POLYNOMIAL EXTENSION PROPERTY IN N-DISC arxiv:1903.02766v1 [math.cv] 7 Mar 2019 KRZYSZTOF MACIASZEK Abstract. In this note we show that an one-dimensional algebraic subset V of arbitrarily dimensional
ON POLYNOMIAL EXTENSION PROPERTY IN N-DISC arxiv:1903.02766v1 [math.cv] 7 Mar 2019 KRZYSZTOF MACIASZEK Abstract. In this note we show that an one-dimensional algebraic subset V of arbitrarily dimensional
Invertible Composition Operators: The product of a composition operator with the adjoint of a composition operator.
 Invertible Composition Operators: The product of a composition operator with the adjoint of a composition operator. John H. Clifford, Trieu Le and Alan Wiggins Abstract. In this paper, we study the product
Invertible Composition Operators: The product of a composition operator with the adjoint of a composition operator. John H. Clifford, Trieu Le and Alan Wiggins Abstract. In this paper, we study the product
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE
 MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
The Chaos Game on a General Iterated Function System
 arxiv:1005.0322v1 [math.mg] 3 May 2010 The Chaos Game on a General Iterated Function System Michael F. Barnsley Department of Mathematics Australian National University Canberra, ACT, Australia michael.barnsley@maths.anu.edu.au
arxiv:1005.0322v1 [math.mg] 3 May 2010 The Chaos Game on a General Iterated Function System Michael F. Barnsley Department of Mathematics Australian National University Canberra, ACT, Australia michael.barnsley@maths.anu.edu.au
Plane hyperbolic geometry
 2 Plane hyperbolic geometry In this chapter we will see that the unit disc D has a natural geometry, known as plane hyperbolic geometry or plane Lobachevski geometry. It is the local model for the hyperbolic
2 Plane hyperbolic geometry In this chapter we will see that the unit disc D has a natural geometry, known as plane hyperbolic geometry or plane Lobachevski geometry. It is the local model for the hyperbolic
USING THE RANDOM ITERATION ALGORITHM TO CREATE FRACTALS
 USING THE RANDOM ITERATION ALGORITHM TO CREATE FRACTALS UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND DIRECTED READING PROGRAM FALL 205 BY ADAM ANDERSON THE SIERPINSKI GASKET 2 Stage 0: A 0 = 2 22 A 0 = Stage : A = 2 = 4 A
USING THE RANDOM ITERATION ALGORITHM TO CREATE FRACTALS UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND DIRECTED READING PROGRAM FALL 205 BY ADAM ANDERSON THE SIERPINSKI GASKET 2 Stage 0: A 0 = 2 22 A 0 = Stage : A = 2 = 4 A
A Fixed point Theorem for Holomorphic Maps S. Dineen, J.F. Feinstein, A.G. O Farrell and R.M. Timoney
 A Fixed point Theorem for Holomorphic Maps S. Dineen, J.F. Feinstein, A.G. O Farrell and R.M. Timoney Abstract. We consider the action on the maximal ideal space M of the algebra H of bounded analytic
A Fixed point Theorem for Holomorphic Maps S. Dineen, J.F. Feinstein, A.G. O Farrell and R.M. Timoney Abstract. We consider the action on the maximal ideal space M of the algebra H of bounded analytic
ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS. C φ 2 e = lim sup w 1
 ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS PEKKA NIEMINEN AND EERO SAKSMAN Abstract. We give a negative answer to a conjecture of J. E. Shapiro concerning compactness of the dierence of
ON COMPACTNESS OF THE DIFFERENCE OF COMPOSITION OPERATORS PEKKA NIEMINEN AND EERO SAKSMAN Abstract. We give a negative answer to a conjecture of J. E. Shapiro concerning compactness of the dierence of
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
UNIFORMLY PERFECT ANALYTIC AND CONFORMAL ATTRACTOR SETS. 1. Introduction and results
 UNIFORMLY PERFECT ANALYTIC AND CONFORMAL ATTRACTOR SETS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Conditions are given which imply that analytic iterated function systems (IFS s) in the complex plane C have uniformly
UNIFORMLY PERFECT ANALYTIC AND CONFORMAL ATTRACTOR SETS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Conditions are given which imply that analytic iterated function systems (IFS s) in the complex plane C have uniformly
INVARIANT MEASURES FOR CERTAIN LINEAR FRACTIONAL TRANSFORMATIONS MOD 1
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 27, Number 2, Pages 3439 3444 S 0002-99399905008-X Article electronically published on July 20, 999 INVARIANT MEASURES FOR CERTAIN LINEAR FRACTIONAL
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 27, Number 2, Pages 3439 3444 S 0002-99399905008-X Article electronically published on July 20, 999 INVARIANT MEASURES FOR CERTAIN LINEAR FRACTIONAL
Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 2012 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file)
 Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 212 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file) February 9, 212 16. Prove: If u is a complex-valued harmonic function, then the real and the imaginary parts
Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 212 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file) February 9, 212 16. Prove: If u is a complex-valued harmonic function, then the real and the imaginary parts
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007](/thumbs/95/125521566.jpg) A NOTE ON THE HAYMAN-WU THEOREM EDWARD CRANE arxiv:0707.1772v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 Abstract. The Hayman-Wu theorem states that the preimage of a line or circle L under a conformal mapping from the unit
A NOTE ON THE HAYMAN-WU THEOREM EDWARD CRANE arxiv:0707.1772v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 Abstract. The Hayman-Wu theorem states that the preimage of a line or circle L under a conformal mapping from the unit
On Non-degeneracy of Solutions to SU(3) Toda System
 On Non-degeneracy of Solutions to SU3 Toda System Juncheng Wei Chunyi Zhao Feng Zhou March 31 010 Abstract We prove that the solution to the SU3 Toda system u + e u e v = 0 in R v e u + e v = 0 in R e
On Non-degeneracy of Solutions to SU3 Toda System Juncheng Wei Chunyi Zhao Feng Zhou March 31 010 Abstract We prove that the solution to the SU3 Toda system u + e u e v = 0 in R v e u + e v = 0 in R e
5.3 The Upper Half Plane
 Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15)
 Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains
 Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains September 29, 2005 1 Introduction Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic 1 Suppose that we are given a random sequence of holomorphic
Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains September 29, 2005 1 Introduction Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic 1 Suppose that we are given a random sequence of holomorphic
Hilbert s Metric and Gromov Hyperbolicity
 Hilbert s Metric and Gromov Hyperbolicity Andrew Altman May 13, 2014 1 1 HILBERT METRIC 2 1 Hilbert Metric The Hilbert metric is a distance function defined on a convex bounded subset of the n-dimensional
Hilbert s Metric and Gromov Hyperbolicity Andrew Altman May 13, 2014 1 1 HILBERT METRIC 2 1 Hilbert Metric The Hilbert metric is a distance function defined on a convex bounded subset of the n-dimensional
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019](/thumbs/94/121818370.jpg) 1 SCHWARZ LEMMA FOR HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN RIEMANN SURFACES arxiv:1903.05163v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove a Schwarz type lemma for harmonic mappings between the unit and a
1 SCHWARZ LEMMA FOR HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN RIEMANN SURFACES arxiv:1903.05163v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove a Schwarz type lemma for harmonic mappings between the unit and a
On a Topological Problem of Strange Attractors. Ibrahim Kirat and Ayhan Yurdaer
 On a Topological Problem of Strange Attractors Ibrahim Kirat and Ayhan Yurdaer Department of Mathematics, Istanbul Technical University, 34469,Maslak-Istanbul, Turkey E-mail: ibkst@yahoo.com and yurdaerayhan@itu.edu.tr
On a Topological Problem of Strange Attractors Ibrahim Kirat and Ayhan Yurdaer Department of Mathematics, Istanbul Technical University, 34469,Maslak-Istanbul, Turkey E-mail: ibkst@yahoo.com and yurdaerayhan@itu.edu.tr
Junior Seminar: Hyperbolic Geometry Lecture Notes
 Junior Seminar: Hyperbolic Geometry Lecture Notes Tim Campion January 20, 2010 1 Motivation Our first construction is very similar in spirit to an analogous one in Euclidean space. The group of isometries
Junior Seminar: Hyperbolic Geometry Lecture Notes Tim Campion January 20, 2010 1 Motivation Our first construction is very similar in spirit to an analogous one in Euclidean space. The group of isometries
Composition Operators with Multivalent Symbol
 Composition Operators with Multivalent Symbol Rebecca G. Wahl University of South Dakota, Vermillion, South Dakota 57069 March 10, 007 Abstract If ϕ is an analytic map of the unit disk D into itself, the
Composition Operators with Multivalent Symbol Rebecca G. Wahl University of South Dakota, Vermillion, South Dakota 57069 March 10, 007 Abstract If ϕ is an analytic map of the unit disk D into itself, the
Schwarz lemma and automorphisms of the disk
 Chapter 2 Schwarz lemma and automorphisms of the disk 2.1 Schwarz lemma We denote the disk of radius 1 about 0 by the notation D, that is, D = {z C : z < 1}. Given θ R the rotation of angle θ about 0,
Chapter 2 Schwarz lemma and automorphisms of the disk 2.1 Schwarz lemma We denote the disk of radius 1 about 0 by the notation D, that is, D = {z C : z < 1}. Given θ R the rotation of angle θ about 0,
ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS WITH A GIVEN CONTINUOUS STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION
 Fractals, Vol., No. 3 (1) 1 6 c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.114/S18348X1517X Fractals Downloaded from www.worldscientific.com by UPPSALA UNIVERSITY ANGSTROM on 9/17/1. For personal use only.
Fractals, Vol., No. 3 (1) 1 6 c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.114/S18348X1517X Fractals Downloaded from www.worldscientific.com by UPPSALA UNIVERSITY ANGSTROM on 9/17/1. For personal use only.
MCMULLEN S ROOT-FINDING ALGORITHM FOR CUBIC POLYNOMIALS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 130, Number 9, Pages 2583 2592 S 0002-9939(02)06659-5 Article electronically published on April 22, 2002 MCMULLEN S ROOT-FINDING ALGORITHM FOR CUBIC
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 130, Number 9, Pages 2583 2592 S 0002-9939(02)06659-5 Article electronically published on April 22, 2002 MCMULLEN S ROOT-FINDING ALGORITHM FOR CUBIC
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
HABILITATION THESIS. New results in the theory of Countable Iterated Function Systems
 HABILITATION THESIS New results in the theory of Countable Iterated Function Systems - abstract - Nicolae-Adrian Secelean Specialization: Mathematics Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu 2014 Abstract The
HABILITATION THESIS New results in the theory of Countable Iterated Function Systems - abstract - Nicolae-Adrian Secelean Specialization: Mathematics Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu 2014 Abstract The
A NOTE ON RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATION IN CONVEX DOMAINS
 Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society (2008) 51, 297 304 c DOI:10.1017/S0013091506001131 Printed in the United Kingdom A NOTE ON RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATION IN CONVEX DOMAINS FILIPPO BRACCI
Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society (2008) 51, 297 304 c DOI:10.1017/S0013091506001131 Printed in the United Kingdom A NOTE ON RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATION IN CONVEX DOMAINS FILIPPO BRACCI
arxiv: v2 [math.ca] 4 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v2 [math.ca] 4 Jun 2017 arxiv: v2 [math.ca] 4 Jun 2017](/thumbs/76/73528053.jpg) EXCURSIONS ON CANTOR-LIKE SETS ROBERT DIMARTINO AND WILFREDO O. URBINA arxiv:4.70v [math.ca] 4 Jun 07 ABSTRACT. The ternary Cantor set C, constructed by George Cantor in 883, is probably the best known
EXCURSIONS ON CANTOR-LIKE SETS ROBERT DIMARTINO AND WILFREDO O. URBINA arxiv:4.70v [math.ca] 4 Jun 07 ABSTRACT. The ternary Cantor set C, constructed by George Cantor in 883, is probably the best known
Spectrum of Fractal Interpolation Functions
 Spectrum of Fractal Interpolation Functions ikolaos Vasiloglou, Member, IEEE and Petros Maragos, Fellow, IEEE June 8, Abstract In this paper we compute the Fourier spectrum of the Fractal Interpolation
Spectrum of Fractal Interpolation Functions ikolaos Vasiloglou, Member, IEEE and Petros Maragos, Fellow, IEEE June 8, Abstract In this paper we compute the Fourier spectrum of the Fractal Interpolation
Fractals. Krzysztof Gdawiec.
 Fractals Krzysztof Gdawiec kgdawiec@ux2.math.us.edu.pl 1 Introduction In the 1970 s Benoit Mandelbrot introduced to the world new field of mathematics. He named this field fractal geometry (fractus from
Fractals Krzysztof Gdawiec kgdawiec@ux2.math.us.edu.pl 1 Introduction In the 1970 s Benoit Mandelbrot introduced to the world new field of mathematics. He named this field fractal geometry (fractus from
6 6 DISCRETE GROUPS. 6.1 Discontinuous Group Actions
 6 6 DISCRETE GROUPS 6.1 Discontinuous Group Actions Let G be a subgroup of Möb(D). This group acts discontinuously on D if, for every compact subset K of D, the set {T G : T (K) K } is finite. Proposition
6 6 DISCRETE GROUPS 6.1 Discontinuous Group Actions Let G be a subgroup of Möb(D). This group acts discontinuously on D if, for every compact subset K of D, the set {T G : T (K) K } is finite. Proposition
VOLUME OF A TETRAHEDRON IN THE TAXICAB SPACE
 VOLUME 21, NUMBER 1, 2009 21 VOLUME OF A TETRAHEDRON IN THE TAXICAB SPACE H. Barış Çolakoğlu and Rüstem Kaya Abstract. In this paper, we give the taxicab version of the Heron- Tartaglia formula to calculate
VOLUME 21, NUMBER 1, 2009 21 VOLUME OF A TETRAHEDRON IN THE TAXICAB SPACE H. Barış Çolakoğlu and Rüstem Kaya Abstract. In this paper, we give the taxicab version of the Heron- Tartaglia formula to calculate
arxiv: v2 [math.gm] 23 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v2 [math.gm] 23 Feb 2017 arxiv: v2 [math.gm] 23 Feb 2017](/thumbs/93/112807012.jpg) arxiv:1603.08548v2 [math.gm] 23 Feb 2017 Tricomplex dynamical systems generated by polynomials of even degree Pierre-Olivier Parisé 1, Thomas Ransford 2, and Dominic Rochon 1 1 Département de mathématiques
arxiv:1603.08548v2 [math.gm] 23 Feb 2017 Tricomplex dynamical systems generated by polynomials of even degree Pierre-Olivier Parisé 1, Thomas Ransford 2, and Dominic Rochon 1 1 Département de mathématiques
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
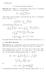 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
CONNECTEDNESS OF ATTRACTORS OF A CERTAIN FAMILY OF IFSS
 CONNECTEDNESS OF ATTRACTORS OF A CERTAIN FAMILY OF IFSS FILIP STROBIN AND JAROSLAW SWACZYNA Abstract. Let X be a Banach space and f,g : X X be contractions. We investigate the set arxiv:1812.06427v1 [math.ds]
CONNECTEDNESS OF ATTRACTORS OF A CERTAIN FAMILY OF IFSS FILIP STROBIN AND JAROSLAW SWACZYNA Abstract. Let X be a Banach space and f,g : X X be contractions. We investigate the set arxiv:1812.06427v1 [math.ds]
Fractals. R. J. Renka 11/14/2016. Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas. R. J. Renka Fractals
 Fractals R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 11/14/2016 Introduction In graphics, fractals are used to produce natural scenes with irregular shapes, such
Fractals R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 11/14/2016 Introduction In graphics, fractals are used to produce natural scenes with irregular shapes, such
The Hausdorff measure of a Sierpinski-like fractal
 Hokkaido Mathematical Journal Vol. 6 (2007) p. 9 19 The Hausdorff measure of a Sierpinski-like fractal Ming-Hua Wang (Received May 12, 2005; Revised October 18, 2005) Abstract. Let S be a Sierpinski-like
Hokkaido Mathematical Journal Vol. 6 (2007) p. 9 19 The Hausdorff measure of a Sierpinski-like fractal Ming-Hua Wang (Received May 12, 2005; Revised October 18, 2005) Abstract. Let S be a Sierpinski-like
A note on the σ-algebra of cylinder sets and all that
 A note on the σ-algebra of cylinder sets and all that José Luis Silva CCM, Univ. da Madeira, P-9000 Funchal Madeira BiBoS, Univ. of Bielefeld, Germany (luis@dragoeiro.uma.pt) September 1999 Abstract In
A note on the σ-algebra of cylinder sets and all that José Luis Silva CCM, Univ. da Madeira, P-9000 Funchal Madeira BiBoS, Univ. of Bielefeld, Germany (luis@dragoeiro.uma.pt) September 1999 Abstract In
A HARDY LITTLEWOOD THEOREM FOR BERGMAN SPACES
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 43, 2018, 807 821 A HARY LITTLEWOO THEOREM FOR BERGMAN SPACES Guanlong Bao, Hasi Wulan and Kehe Zhu Shantou University, epartment of Mathematics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 43, 2018, 807 821 A HARY LITTLEWOO THEOREM FOR BERGMAN SPACES Guanlong Bao, Hasi Wulan and Kehe Zhu Shantou University, epartment of Mathematics
Construction of Smooth Fractal Surfaces Using Hermite Fractal Interpolation Functions. P. Bouboulis, L. Dalla and M. Kostaki-Kosta
 BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 54 27 (79 95) Construction of Smooth Fractal Surfaces Using Hermite Fractal Interpolation Functions P. Bouboulis L. Dalla and M. Kostaki-Kosta Received
BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 54 27 (79 95) Construction of Smooth Fractal Surfaces Using Hermite Fractal Interpolation Functions P. Bouboulis L. Dalla and M. Kostaki-Kosta Received
RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATIONS AND DEGENERATE SUBDOMAINS OF THE UNIT DISK
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9939(XX)0000-0 RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATIONS AND DEGENERATE SUBDOMAINS OF THE UNIT DISK LINDA KEEN AND NIKOLA
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9939(XX)0000-0 RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATIONS AND DEGENERATE SUBDOMAINS OF THE UNIT DISK LINDA KEEN AND NIKOLA
THE HUTCHINSON BARNSLEY THEORY FOR INFINITE ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS
 Bull. Austral. Math. Soc. Vol. 72 2005) [441 454] 39b12, 47a35, 47h09, 54h25 THE HUTCHINSON BARNSLEY THEORY FOR INFINITE ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS Gertruda Gwóźdź- Lukawska and Jacek Jachymski We show
Bull. Austral. Math. Soc. Vol. 72 2005) [441 454] 39b12, 47a35, 47h09, 54h25 THE HUTCHINSON BARNSLEY THEORY FOR INFINITE ITERATED FUNCTION SYSTEMS Gertruda Gwóźdź- Lukawska and Jacek Jachymski We show
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS
 A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
The tangents and the chords of the Poincaré circle
 The tangents and the chords of the Poincaré circle Nilgün Sönmez Abstract. After defining the tangent and chord concepts, we determine the chord length and tangent lines of Poincaré circle and the relationship
The tangents and the chords of the Poincaré circle Nilgün Sönmez Abstract. After defining the tangent and chord concepts, we determine the chord length and tangent lines of Poincaré circle and the relationship
Geometric Limits of Julia Sets of Maps z^n + exp(2πiθ) as n
 Butler University Digital Commons @ Butler University Scholarship and Professional Work - LAS College of Liberal Arts & Sciences 2015 Geometric Limits of Julia Sets of Maps z^n + exp(2πiθ) as n Scott R.
Butler University Digital Commons @ Butler University Scholarship and Professional Work - LAS College of Liberal Arts & Sciences 2015 Geometric Limits of Julia Sets of Maps z^n + exp(2πiθ) as n Scott R.
The Mandelbrot Set. Andrew Brown. April 14, 2008
 The Mandelbrot Set Andrew Brown April 14, 2008 The Mandelbrot Set and other Fractals are Cool But What are They? To understand Fractals, we must first understand some things about iterated polynomials
The Mandelbrot Set Andrew Brown April 14, 2008 The Mandelbrot Set and other Fractals are Cool But What are They? To understand Fractals, we must first understand some things about iterated polynomials
Virasoro and Kac-Moody Algebra
 Virasoro and Kac-Moody Algebra Di Xu UCSC Di Xu (UCSC) Virasoro and Kac-Moody Algebra 2015/06/11 1 / 24 Outline Mathematical Description Conformal Symmetry in dimension d > 3 Conformal Symmetry in dimension
Virasoro and Kac-Moody Algebra Di Xu UCSC Di Xu (UCSC) Virasoro and Kac-Moody Algebra 2015/06/11 1 / 24 Outline Mathematical Description Conformal Symmetry in dimension d > 3 Conformal Symmetry in dimension
arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 29 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 29 Sep 2015 arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 29 Sep 2015](/thumbs/92/110647466.jpg) ON BODIES WITH DIRECTLY CONGRUENT PROJECTIONS AND SECTIONS arxiv:1412.2727v2 [math.mg] 29 Sep 2015 M. ANGELES ALFONSECA, MICHELLE CORDIER, AND DMITRY RYABOGIN Abstract. Let K and L be two convex bodies
ON BODIES WITH DIRECTLY CONGRUENT PROJECTIONS AND SECTIONS arxiv:1412.2727v2 [math.mg] 29 Sep 2015 M. ANGELES ALFONSECA, MICHELLE CORDIER, AND DMITRY RYABOGIN Abstract. Let K and L be two convex bodies
65 Fluid Flows (6/1/2018)
 65 Fluid Flows 6//08 Consider a two dimensional fluid flow which we describe by its velocity field, V x, y = p x, y, q x, y = p + iq R. We are only going to consider flows which are incompressible, i.e.
65 Fluid Flows 6//08 Consider a two dimensional fluid flow which we describe by its velocity field, V x, y = p x, y, q x, y = p + iq R. We are only going to consider flows which are incompressible, i.e.
arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 31 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 31 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 31 Jul 2018](/thumbs/83/88779811.jpg) arxiv:1807.11801v1 [math.ds] 31 Jul 2018 On the interior of projections of planar self-similar sets YUKI TAKAHASHI Abstract. We consider projections of planar self-similar sets, and show that one can create
arxiv:1807.11801v1 [math.ds] 31 Jul 2018 On the interior of projections of planar self-similar sets YUKI TAKAHASHI Abstract. We consider projections of planar self-similar sets, and show that one can create
A note on fixed point sets in CAT(0) spaces
 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 320 (2006) 983 987 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Note A note on fied point sets in CAT(0) spaces P. Chaoha,1, A. Phon-on Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn
J. Math. Anal. Appl. 320 (2006) 983 987 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Note A note on fied point sets in CAT(0) spaces P. Chaoha,1, A. Phon-on Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn
Compression on the digital unit sphere
 16th Conference on Applied Mathematics, Univ. of Central Oklahoma, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conf. 07, 001, pp. 1 4. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu
16th Conference on Applied Mathematics, Univ. of Central Oklahoma, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conf. 07, 001, pp. 1 4. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu
z, w = z 1 w 1 + z 2 w 2 z, w 2 z 2 w 2. d([z], [w]) = 2 φ : P(C 2 ) \ [1 : 0] C ; [z 1 : z 2 ] z 1 z 2 ψ : P(C 2 ) \ [0 : 1] C ; [z 1 : z 2 ] z 2 z 1
![z, w = z 1 w 1 + z 2 w 2 z, w 2 z 2 w 2. d([z], [w]) = 2 φ : P(C 2 ) \ [1 : 0] C ; [z 1 : z 2 ] z 1 z 2 ψ : P(C 2 ) \ [0 : 1] C ; [z 1 : z 2 ] z 2 z 1 z, w = z 1 w 1 + z 2 w 2 z, w 2 z 2 w 2. d([z], [w]) = 2 φ : P(C 2 ) \ [1 : 0] C ; [z 1 : z 2 ] z 1 z 2 ψ : P(C 2 ) \ [0 : 1] C ; [z 1 : z 2 ] z 2 z 1](/thumbs/95/123523548.jpg) 3 3 THE RIEMANN SPHERE 31 Models for the Riemann Sphere One dimensional projective complex space P(C ) is the set of all one-dimensional subspaces of C If z = (z 1, z ) C \ 0 then we will denote by [z]
3 3 THE RIEMANN SPHERE 31 Models for the Riemann Sphere One dimensional projective complex space P(C ) is the set of all one-dimensional subspaces of C If z = (z 1, z ) C \ 0 then we will denote by [z]
A NOTE ON CORRELATION AND LOCAL DIMENSIONS
 A NOTE ON CORRELATION AND LOCAL DIMENSIONS JIAOJIAO YANG, ANTTI KÄENMÄKI, AND MIN WU Abstract Under very mild assumptions, we give formulas for the correlation and local dimensions of measures on the limit
A NOTE ON CORRELATION AND LOCAL DIMENSIONS JIAOJIAO YANG, ANTTI KÄENMÄKI, AND MIN WU Abstract Under very mild assumptions, we give formulas for the correlation and local dimensions of measures on the limit
THE AUTOMORPHISM GROUP ON THE RIEMANN SPHERE
 THE AUTOMORPHISM GROUP ON THE RIEMANN SPHERE YONG JAE KIM Abstract. In order to study the geometries of a hyperbolic plane, it is necessary to understand the set of transformations that map from the space
THE AUTOMORPHISM GROUP ON THE RIEMANN SPHERE YONG JAE KIM Abstract. In order to study the geometries of a hyperbolic plane, it is necessary to understand the set of transformations that map from the space
Caristi-type Fixed Point Theorem of Set-Valued Maps in Metric Spaces
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 267-275 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.717 Caristi-type Fixed Point Theorem of Set-Valued Maps in Metric
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 267-275 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.717 Caristi-type Fixed Point Theorem of Set-Valued Maps in Metric
Geometry and topology of continuous best and near best approximations
 Journal of Approximation Theory 105: 252 262, Geometry and topology of continuous best and near best approximations Paul C. Kainen Dept. of Mathematics Georgetown University Washington, D.C. 20057 Věra
Journal of Approximation Theory 105: 252 262, Geometry and topology of continuous best and near best approximations Paul C. Kainen Dept. of Mathematics Georgetown University Washington, D.C. 20057 Věra
SCREEN TRANSVERSAL LIGHTLIKE SUBMANIFOLDS OF INDEFINITE KENMOTSU MANIFOLDS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.7 (19) (2011), 103 113 SCREEN TRANSVERSAL LIGHTLIKE SUBMANIFOLDS OF INDEFINITE KENMOTSU MANIFOLDS RAM SHANKAR GUPTA AND A. SHARFUDDIN Abstract. In this paper, we introduce
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.7 (19) (2011), 103 113 SCREEN TRANSVERSAL LIGHTLIKE SUBMANIFOLDS OF INDEFINITE KENMOTSU MANIFOLDS RAM SHANKAR GUPTA AND A. SHARFUDDIN Abstract. In this paper, we introduce
Constructions with ruler and compass.
 Constructions with ruler and compass. Semyon Alesker. 1 Introduction. Let us assume that we have a ruler and a compass. Let us also assume that we have a segment of length one. Using these tools we can
Constructions with ruler and compass. Semyon Alesker. 1 Introduction. Let us assume that we have a ruler and a compass. Let us also assume that we have a segment of length one. Using these tools we can
V -variable fractals and superfractals
 V -variable fractals and superfractals Michael Barnsley, John E Hutchinson and Örjan Stenflo Department of Mathematics, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT. 0200, Australia Department of Mathematics,
V -variable fractals and superfractals Michael Barnsley, John E Hutchinson and Örjan Stenflo Department of Mathematics, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT. 0200, Australia Department of Mathematics,
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
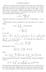 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
(7) Suppose α, β, γ are nonzero complex numbers such that α = β = γ.
 January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
Convergence theorems for a finite family. of nonspreading and nonexpansive. multivalued mappings and equilibrium. problems with application
 Theoretical Mathematics & Applications, vol.3, no.3, 2013, 49-61 ISSN: 1792-9687 (print), 1792-9709 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2013 Convergence theorems for a finite family of nonspreading and nonexpansive
Theoretical Mathematics & Applications, vol.3, no.3, 2013, 49-61 ISSN: 1792-9687 (print), 1792-9709 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2013 Convergence theorems for a finite family of nonspreading and nonexpansive
