Schwarz lemma and automorphisms of the disk
|
|
|
- Laurel Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Schwarz lemma and automorphisms of the disk 2.1 Schwarz lemma We denote the disk of radius 1 about 0 by the notation D, that is, D = {z C : z < 1}. Given θ R the rotation of angle θ about 0, i.e. z e iθ z, preservesd. Due to the rotational symmetry of D most objects studied in complex analysis find special forms on D that have basic algebraic forms. We study some examples of these in this section, and will see more on this later on. A main application of the maximum principle (Theorem 1.6) is the lemma of Schwarz. It has a simple proof, but has far reaching applications. Lemma 2.1 (Schwarz lemma). Let f : D D be holomorphic with f(0) = 0. Then, (i) for all z D we have f(z) z ; (ii) f (0) 1; (iii) if either f(z) =z for some non-zero z D, or f (0) =1, then f is a rotation about 0. Proof. Since f is holomorphic on D, we have a series expansion for f centered at 0, f(z) =a 0 + a 1 z + a 2 z , that is convergent on D. Sincef(0) = 0, a 0 = 0, and we obtain f(z) =a 1 z + a 2 z 2 + = z(a 1 + a 2 z + a 3 z ). In particular, the series in the above parenthesis is convergent on D. In particular, the function g(z) =f(z)/z = a 1 + a 2 z + a 3 z is defined and holomorphic on D. Note that g(0) = a 1 = f (0). 11
2 On each circle z = r<1, as f(z) < 1, we have g(z) < 1 r. Then by the maximum principle, we must have the above inequality on z <r. Taking limit as r 1 from the left, we conclude that on D, g(z) 1. This implies part (i) and (ii) of the lemma. To prove part (iii) of the lemma, note that if any of the two equality holds, then g attains its maximum in the interior of D. Then, by the maximum principle, g must be a constant on D, sayg(z) a. Then, either of the relations f (0) = 1 and f(z) =z for some z 0, implies that a = 1. This finishes the proof of part (iii). As an application of the Schwarz lemma we classify the one-to-one and onto holomorphic mappings of D. 2.2 Automorphisms of the disk Definition 2.2. Let U and V be open subsets of C. A holomorphic map f : U V that is one-to-one and onto is called a biholomorphism from U to V. A biholomorphism from U to U is called an automorphism of U. The set of all automorphisms of U is denoted by Aut(U). Obviously, Aut(U) contains the identity map and hence is not empty. The composition of any two maps in Aut(U) is again an element of Aut(U). Indeed, Aut(U) forms a group with this operation. Proposition 2.3. For every non-empty and open set U in C, Aut(U) forms a group with the operation being the composition of the maps. Proof. The composition of any pair of one-to-one and onto holomorphic maps from U to U is a one-to-one and onto holomorphic map from U to itself. Thus the operation is well defined on Aut(U). The identity map z z is the identity element of the group. The associativity (f g) h = f (g h) holds because the relation is valid for general maps. The inverse of every f Aut(U) is given by the inverse mapping f 1. Note that the inverse of any one-to-one map is defined and is a holomorphic map. We have already seen that every rotation z e iθ z, for a fixed θ R, is an automorphism of the disk. For a D define ϕ a (z) = a z 1 az. 12
3 Lemma 2.4. For every a D, ϕ a is an automorphism of D. Proof. First note that ϕ a is defined and holomorphic at every z C, except at z =1/a where the denominator becomes 0. However, since a < 1, we have 1/a =1/ a > 1, and therefore, 1/a / D. Hence, ϕ a is holomorphic on D. To see that ϕ a maps D into D, fix an arbitrary z C with z = 1. Observe that ϕ a (z) = a z 1 az = a z 1 az 1 z = a z z a =1, since zz = z 2 = 1. By the maximum principle (Theorem 1.6), ϕ a (z) < 1 on D. We observe that ϕ a (a) =0, and ϕ a (0) = a. Then, ϕ a ϕ a (0) = 0, and ϕ a ϕ a (a) =a. By the Schwarz lemma, this implies that ϕ a ϕ a must be the identity map of D. It follows that ϕ a is both one-to-one and onto from D to D. It turns out that the composition of rotations and the maps of the form ϕ a are all the possible automorphisms of D. Theorem 2.5. Amapf is an automorphism of D iff there are θ R and a D such that f(z) =e iθ a z 1 az. Proof. Let f be an element of Aut(D). Since f is onto, there is a D with f(a) = 0. The map g = f ϕ a is an automorphism of D with g(0) = 0. By the Schwarz lemma, we must have g (0) 1. Applying the Schwarz lemma to g 1 we also obtain (g 1 ) (0) 1. By the two inequalities, we have g (0) = 1. Thus, by the same lemma, g(z) =e iθ z, for some θ R. That is, f ϕ a (z) =e iθ z, for z D. f(z) =e iθ ϕ a (z). Since ϕ a ϕ a is the identity map, we conclude that On the other hand, for any θ R and any a D, f belongs to Aut(D). because, f is the composition of the automorphism ϕ a (Lemma 2.4) and a rotation. That is 13
4 ϕ a Figure 2.1: The images of the circles and rays under the map ϕ a where a =0.5+i Automorphisms of the half-plane Define the upper half plane H as H = {z C :Imz>0}. There are biholomorphic maps between D and H given by explicit formulae and F : H D, G : D H, F(z) = i z, F(i) =0 (2.1) i + z G(w) =i 1 w, G(0) = i. 1+w G Figure 2.2: Similar line colors are mapped to one another by F. Lemma 2.6. The map F : H D is a biholomorphic map with inverse G : D H. 14
5 The proof of the above lemma is elementary and is left to the reader as an exercise. The explicit biholomorphic map F allows us to identify Aut(H) in terms of Aut(D). That is, define Γ : Aut(D) Aut(H) as Γ(ϕ) =F 1 ϕ F. It is clear that if ϕ Aut(D) then Γ(ϕ) =F 1 ϕ F Aut(H). The map Γ is one-to-one and onto with inverse given by Γ 1 (ψ) =F ψ F 1. Indeed, Γ is more than just a bijection, it also preserves the operations on the groups Aut(D) and Aut(H). To see this, assume that ϕ 1 and ϕ 2 belong to Aut(D). Γ(ϕ 1 ϕ 2 )=F 1 (ϕ 1 ϕ 2 ) F = F 1 ϕ 1 F F 1 ϕ 2 F = Γ(ϕ 1 ) Γ(ϕ 2 ). The isomorphism Γ : Aut(D) Aut(H) show that indeed the two groups are the same. However, we still would like to have explicit formulas for members of Aut(H). Using the explicit formulas for F and G, as well as the explicit formulas for elements of Aut(D) in Theorem 2.5, a long series of calculations shows that an element of Aut(H) is of the form z az + b cz + d, where a, b, c, and d are real, and ad bc = 1. We shall present an alternative proof of this, but before doing that we introduce some notations that simplify the presentation. Define {( ) } a b SL 2 (R) = : a, b, c, d R and ad bc =1. c d The set SL 2 (R) forms a group with the operation of matrix-multiplication. This is called the special linear group. To each matrix M = ( ab cd) in SL2 (R) we associate the map f M (z) = az + b cz + d. It is a straightforward calculation to see that for every M and M in SL 2 (R) wehave f M f M = f M M. (2.2) That is, the correspondence M f M respects the group operations. Theorem 2.7. For every M SL 2 (R) the map f M is an automorphism of H. Conversely, every automorphism of H is of the form f M for some M in SL 2 (R). Proof. We break the proof into several steps. 15
6 Step 1. Let M SL 2 (R). The map f M is holomorphic on H. Moreover, for every z H we have Im f M (z) =Im az + b + b)(cz + d) (ad bc)imz =Im(az = cz + d (cz + d)(cz + d) cz + d 2 = Im z cz + d 2 > 0. Thus, f M maps H into H. As SL 2 (R) forms a group, there is a matrix M 1 in SL 2 (R) such that M M 1 = M 1 M is the identity matrix. It follows that f M f M 1 is the identity map of H. In particular, f M is both one-to-one and onto. This proves the first part of the theorem. Step 2. Let h Aut(H) withh(i) =i. DefineI = F h F 1,whereF is the map in Equation (2.1). Then, I Aut(D) and I(0) = 0. Also, I 1 is a holomorphic map from D to D that sends 0 to 0. By the Schwarz lemma, I (0) 1, and (I 1 ) (0) 1. Thus, by the Schwarz lemma, I must be a rotation about 0, that is, there is θ R such that F h F 1 (z) =e iθ z. (2.3) Step 3. Let ( ) cos(θ/2) sin(θ/2) Q =. sin(θ/2) cos(θ/2) The matrix Q belongs to SL 2 (R), and one can verify that f Q (i) =i and f Q (i) =eiθ. Then the map F f Q F 1 is an automorphism of D that maps 0 to 0 and has derivative e iθ at 0. By the Schwarz lemma, F f Q F 1 is the rotation z e iθ z. That is, F f Q F 1 = F h F 1. Since F is one-to-one we conclude that h = f Q,wherehis the map in Step 1. Step 4. We claim that for every z 0 H there is N SL 2 (R) such that f N (i) =z 0. First we choose a re-scaling about 0 that maps i to a point whose imaginary part is equal to Im z 0. This map is given by the matrix ( ) Im z0 0 O = 0 1/, Im z 0 that is, Im f O (i) =Imz 0. Then we use the translation z +(z 0 f O (i)) to map f O (i) to z 0. The latter map is obtained from the matrix ( ) 1 z0 f M (i) P =. 0 1 The map f P f O = f P O maps i to z 0.SetN = P O. 16
7 Step 5. Let g be an automorphism of H. Thereisz 0 in H with g(z 0 )=i. By Step 4, there is N SL 2 (R) such that f N (i) =z 0. The composition h = g f N belongs to Aut(H) and sends i to i. Thus, by Steps 2 and 3, h = f Q. Now, using Equation (2.2), we have g = h (f N ) 1 = f Q f N 1 = f Q N 1. This shows that g has the desired form. 2.4 Exercises Exercise 2.1. For a C and r>0letb(a, r) ={z C : z a <r}, that is, the open disk of radius r about a. Let a and b be arbitrary points in C, and let r and s be positive real numbers. Prove that for every holomorphic map f : B(a, r) B(b, s) withf(a) =b we have f (a) s/r. Exercise 2.2. Let f : D D be a holomorphic map. (i) Prove that for every a D we have f (a) 1 f(a) a 2, (ii) Prove that for every a and b in D we have f(a) f(b) 1 f(a)f(b) a b 1 ab. The above inequalities are known as the Schwarz-Pick lemma. Exercise 2.3. Let h : H H be a holomorphic map. Prove that for every a H we have h (a) Im h(a) Im a. Exercise 2.4.* Let n 2 be a positive integer. Prove that there is an increasing C map f :[0, 1] [0, 1] that satisfies f(0) = 0, f(1) = 1, and for all x [0, 1/(3n)] we have f (x) =n. Then define F : D D as Show that F (z) =f( z ) z z. (i) F : D D is C and satisfies the maximum principle. 17
8 (ii) F is holomorphic on the disk z < 1/(3n), and F (0) = n. [hint: for the first part, use a suitable modification of the smooth function f in Chapter 1. In part (i), write F in terms of the polar coordinates r and θ.] Exercise 2.5. Prove that for every z and w in D there is f Aut(D) withf(z) =w. [For an open set U C, we say that Aut(U) acts transitively on U, if for every z and w in U there is f Aut(U) such that f(z) =w. By the above statements, Aut(D) act transitively on D. Exercise 2.6. Prove Lemma
Geometric Complex Analysis. Davoud Cheraghi Imperial College London
 Geometric Complex Analysis Davoud Cheraghi Imperial College London May 9, 2017 Introduction The subject of complex variables appears in many areas of mathematics as it has been truly the ancestor of many
Geometric Complex Analysis Davoud Cheraghi Imperial College London May 9, 2017 Introduction The subject of complex variables appears in many areas of mathematics as it has been truly the ancestor of many
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
5.3 The Upper Half Plane
 Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Conformal Mappings. Chapter Schwarz Lemma
 Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
Riemann sphere and rational maps
 Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping. 1 Conformality. 1.1 Preservation of angle. 1.2 Length and area. MATH-GA Complex Variables
 Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
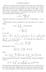 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
Review of complex analysis in one variable
 CHAPTER 130 Review of complex analysis in one variable This gives a brief review of some of the basic results in complex analysis. In particular, it outlines the background in single variable complex analysis
CHAPTER 130 Review of complex analysis in one variable This gives a brief review of some of the basic results in complex analysis. In particular, it outlines the background in single variable complex analysis
MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY
 MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. About 2 2. Complex Numbers 2 3. Fundamental inequalities 2 4. Continuously differentiable functions
MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. About 2 2. Complex Numbers 2 3. Fundamental inequalities 2 4. Continuously differentiable functions
III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations
 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations 1 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations Note. To graph y = f(x) where x,y R, we can simply plot points (x,y) in R 2 (that
III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations 1 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations Note. To graph y = f(x) where x,y R, we can simply plot points (x,y) in R 2 (that
Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation
 Chapter 7 Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation 7. Linear distortion Assume that f(x + iy) =u(x + iy)+iv(x + iy) be a (real) linear map from C C that is orientation preserving. Let z = x + iy and
Chapter 7 Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation 7. Linear distortion Assume that f(x + iy) =u(x + iy)+iv(x + iy) be a (real) linear map from C C that is orientation preserving. Let z = x + iy and
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE. Department of Mathematics. MA4247 Complex Analysis II. Lecture Notes Part IV
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part IV Chapter 2. Further properties of analytic/holomorphic functions (continued) 2.4. The Open mapping
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part IV Chapter 2. Further properties of analytic/holomorphic functions (continued) 2.4. The Open mapping
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Math 814 HW 3. October 16, p. 54: 9, 14, 18, 24, 25, 26
 Math 814 HW 3 October 16, 2007 p. 54: 9, 14, 18, 24, 25, 26 p.54, Exercise 9. If T z = az+b, find necessary and sufficient conditions for T to cz+d preserve the unit circle. T preserves the unit circle
Math 814 HW 3 October 16, 2007 p. 54: 9, 14, 18, 24, 25, 26 p.54, Exercise 9. If T z = az+b, find necessary and sufficient conditions for T to cz+d preserve the unit circle. T preserves the unit circle
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL
 PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM. 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces
 8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
Solutions to Exercises 6.1
 34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM
 RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
X G X by the rule x x g
 18. Maps between Riemann surfaces: II Note that there is one further way we can reverse all of this. Suppose that X instead of Y is a Riemann surface. Can we put a Riemann surface structure on Y such that
18. Maps between Riemann surfaces: II Note that there is one further way we can reverse all of this. Suppose that X instead of Y is a Riemann surface. Can we put a Riemann surface structure on Y such that
Solutions to practice problems for the final
 Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
7.2 Conformal mappings
 7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008
 Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Properties of Entire Functions
 Properties of Entire Functions Generalizing Results to Entire Functions Our main goal is still to show that every entire function can be represented as an everywhere convergent power series in z. So far
Properties of Entire Functions Generalizing Results to Entire Functions Our main goal is still to show that every entire function can be represented as an everywhere convergent power series in z. So far
Part II. Riemann Surfaces. Year
 Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
MATH5685 Assignment 3
 MATH5685 Assignment 3 Due: Wednesday 3 October 1. The open unit disk is denoted D. Q1. Suppose that a n for all n. Show that (1 + a n) converges if and only if a n converges. [Hint: prove that ( N (1 +
MATH5685 Assignment 3 Due: Wednesday 3 October 1. The open unit disk is denoted D. Q1. Suppose that a n for all n. Show that (1 + a n) converges if and only if a n converges. [Hint: prove that ( N (1 +
612 CLASS LECTURE: HYPERBOLIC GEOMETRY
 612 CLASS LECTURE: HYPERBOLIC GEOMETRY JOSHUA P. BOWMAN 1. Conformal metrics As a vector space, C has a canonical norm, the same as the standard R 2 norm. Denote this dz one should think of dz as the identity
612 CLASS LECTURE: HYPERBOLIC GEOMETRY JOSHUA P. BOWMAN 1. Conformal metrics As a vector space, C has a canonical norm, the same as the standard R 2 norm. Denote this dz one should think of dz as the identity
Exercises for Part 1
 MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
CHAPTER 9. Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak@gmail.com Module-3:
CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak@gmail.com Module-3:
Möbius Transformation
 Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
Math 425, Homework #1 Solutions
 Math 425, Homework #1 Solutions (1) (1.9) (a) Use complex algebra to show that for any four integers a, b, c, and d there are integers u and v so that (a 2 + b 2 )(c 2 + d 2 ) = u 2 + v 2 Proof. If we
Math 425, Homework #1 Solutions (1) (1.9) (a) Use complex algebra to show that for any four integers a, b, c, and d there are integers u and v so that (a 2 + b 2 )(c 2 + d 2 ) = u 2 + v 2 Proof. If we
ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ
![ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ](/thumbs/92/109116539.jpg) Lecture 6 Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem MATH-GA 45.00 Complex Variables Cauchy s Integral Formula. Index of a point with respect to a closed curve Let z C, and a piecewise differentiable closed curve
Lecture 6 Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem MATH-GA 45.00 Complex Variables Cauchy s Integral Formula. Index of a point with respect to a closed curve Let z C, and a piecewise differentiable closed curve
Hyperbolic Transformations
 C H A P T E R 17 Hyperbolic Transformations Though the text of your article on Crystal Symmetry and Its Generalizations is much too learned for a simple, selfmade pattern man like me, some of the text-illustrations
C H A P T E R 17 Hyperbolic Transformations Though the text of your article on Crystal Symmetry and Its Generalizations is much too learned for a simple, selfmade pattern man like me, some of the text-illustrations
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2003 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
(7) Suppose α, β, γ are nonzero complex numbers such that α = β = γ.
 January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS
 A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
Riemann surfaces. 3.1 Definitions
 3 Riemann surfaces In this chapter we define and give the first properties of Riemann surfaces. These are the holomorphic counterpart of the (real) differential manifolds. We will see how the Fuchsian
3 Riemann surfaces In this chapter we define and give the first properties of Riemann surfaces. These are the holomorphic counterpart of the (real) differential manifolds. We will see how the Fuchsian
1 Holomorphic functions
 Robert Oeckl CA NOTES 1 15/09/2009 1 1 Holomorphic functions 11 The complex derivative The basic objects of complex analysis are the holomorphic functions These are functions that posses a complex derivative
Robert Oeckl CA NOTES 1 15/09/2009 1 1 Holomorphic functions 11 The complex derivative The basic objects of complex analysis are the holomorphic functions These are functions that posses a complex derivative
MATH 185: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. and g b (z) = eπz/2 1
 MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 4
 274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 4 Dylan Thurston Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Fall 2012 4 Hyperbolic geometry Last time there was an exercise asking for braids giving the torsion elements in PSL 2 (Z). A 3-torsion
274 Curves on Surfaces, Lecture 4 Dylan Thurston Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Fall 2012 4 Hyperbolic geometry Last time there was an exercise asking for braids giving the torsion elements in PSL 2 (Z). A 3-torsion
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
MORE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOREM
 MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
1 Complex numbers and the complex plane
 L1: Complex numbers and complex-valued functions. Contents: The field of complex numbers. Real and imaginary part. Conjugation and modulus or absolute valued. Inequalities: The triangular and the Cauchy.
L1: Complex numbers and complex-valued functions. Contents: The field of complex numbers. Real and imaginary part. Conjugation and modulus or absolute valued. Inequalities: The triangular and the Cauchy.
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett/
 (February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
(February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
DYNAMICS ON THE CIRCLE I
 DYNAMICS ON THE CIRCLE I SIDDHARTHA GADGIL Dynamics is the study of the motion of a body, or more generally evolution of a system with time, for instance, the motion of two revolving bodies attracted to
DYNAMICS ON THE CIRCLE I SIDDHARTHA GADGIL Dynamics is the study of the motion of a body, or more generally evolution of a system with time, for instance, the motion of two revolving bodies attracted to
18.04 Practice problems exam 1, Spring 2018 Solutions
 8.4 Practice problems exam, Spring 8 Solutions Problem. omplex arithmetic (a) Find the real and imaginary part of z + z. (b) Solve z 4 i =. (c) Find all possible values of i. (d) Express cos(4x) in terms
8.4 Practice problems exam, Spring 8 Solutions Problem. omplex arithmetic (a) Find the real and imaginary part of z + z. (b) Solve z 4 i =. (c) Find all possible values of i. (d) Express cos(4x) in terms
1 Hermitian symmetric spaces: examples and basic properties
 Contents 1 Hermitian symmetric spaces: examples and basic properties 1 1.1 Almost complex manifolds............................................ 1 1.2 Hermitian manifolds................................................
Contents 1 Hermitian symmetric spaces: examples and basic properties 1 1.1 Almost complex manifolds............................................ 1 1.2 Hermitian manifolds................................................
Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF 11am, Fulton Hall 425 Homework 5 Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible.
 Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF am, Fulton Hall 425 Homework 5 Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book: 2.6.8, 2.6., 2.6.3, 2.6.4, 2.6.5 The
Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF am, Fulton Hall 425 Homework 5 Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book: 2.6.8, 2.6., 2.6.3, 2.6.4, 2.6.5 The
NOTES ON FINITE FIELDS
 NOTES ON FINITE FIELDS AARON LANDESMAN CONTENTS 1. Introduction to finite fields 2 2. Definition and constructions of fields 3 2.1. The definition of a field 3 2.2. Constructing field extensions by adjoining
NOTES ON FINITE FIELDS AARON LANDESMAN CONTENTS 1. Introduction to finite fields 2 2. Definition and constructions of fields 3 2.1. The definition of a field 3 2.2. Constructing field extensions by adjoining
1.1 Definition. A monoid is a set M together with a map. 1.3 Definition. A monoid is commutative if x y = y x for all x, y M.
 1 Monoids and groups 1.1 Definition. A monoid is a set M together with a map M M M, (x, y) x y such that (i) (x y) z = x (y z) x, y, z M (associativity); (ii) e M such that x e = e x = x for all x M (e
1 Monoids and groups 1.1 Definition. A monoid is a set M together with a map M M M, (x, y) x y such that (i) (x y) z = x (y z) x, y, z M (associativity); (ii) e M such that x e = e x = x for all x M (e
ISOMETRIES OF THE HYPERBOLIC PLANE
 ISOMETRIES OF THE HYPERBOLIC PLANE ALBERT CHANG Abstract. In this paper, I will explore basic properties of the group P SL(, R). These include the relationship between isometries of H, Möbius transformations,
ISOMETRIES OF THE HYPERBOLIC PLANE ALBERT CHANG Abstract. In this paper, I will explore basic properties of the group P SL(, R). These include the relationship between isometries of H, Möbius transformations,
Exercises for Part 1
 MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x+iy, x,y R:
MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x+iy, x,y R:
Declaration. Heidelberg, June 13, 2016
 Jørgensen Lemma Fabian Cejka Eingereicht bei Prof. Dr. Anna Wienhard an der Universität Heidelberg Betreuer: Prof. Dr. Anna Wienhard, Dr. Gye-Seon Lee B A C H E L O R A R B E I T im Juni 2016 Declaration
Jørgensen Lemma Fabian Cejka Eingereicht bei Prof. Dr. Anna Wienhard an der Universität Heidelberg Betreuer: Prof. Dr. Anna Wienhard, Dr. Gye-Seon Lee B A C H E L O R A R B E I T im Juni 2016 Declaration
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Scott Taylor 1. EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS. Definition 1.1. Let A be a set. An equivalence relation on A is a relation such that:
 Equivalence MA Relations 274 and Partitions Scott Taylor 1. EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS Definition 1.1. Let A be a set. An equivalence relation on A is a relation such that: (1) is reflexive. That is, (2) is
Equivalence MA Relations 274 and Partitions Scott Taylor 1. EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS Definition 1.1. Let A be a set. An equivalence relation on A is a relation such that: (1) is reflexive. That is, (2) is
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall Anton R. Schep
 Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Introduction to Proofs
 Real Analysis Preview May 2014 Properties of R n Recall Oftentimes in multivariable calculus, we looked at properties of vectors in R n. If we were given vectors x =< x 1, x 2,, x n > and y =< y1, y 2,,
Real Analysis Preview May 2014 Properties of R n Recall Oftentimes in multivariable calculus, we looked at properties of vectors in R n. If we were given vectors x =< x 1, x 2,, x n > and y =< y1, y 2,,
Definition We say that a topological manifold X is C p if there is an atlas such that the transition functions are C p.
 13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
4.5 The Open and Inverse Mapping Theorem
 4.5 The Open and Inverse Mapping Theorem Theorem 4.5.1. [Open Mapping Theorem] Let f be analytic in an open set U such that f is not constant in any open disc. Then f(u) = {f() : U} is open. Lemma 4.5.1.
4.5 The Open and Inverse Mapping Theorem Theorem 4.5.1. [Open Mapping Theorem] Let f be analytic in an open set U such that f is not constant in any open disc. Then f(u) = {f() : U} is open. Lemma 4.5.1.
Complex Analysis Important Concepts
 Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
AN INTRODUCTION TO ARITHMETIC AND RIEMANN SURFACE. We describe points on the unit circle with coordinate satisfying
 AN INTRODUCTION TO ARITHMETIC AND RIEMANN SURFACE 1. RATIONAL POINTS ON CIRCLE We start by asking us: How many integers x, y, z) can satisfy x 2 + y 2 = z 2? Can we describe all of them? First we can divide
AN INTRODUCTION TO ARITHMETIC AND RIEMANN SURFACE 1. RATIONAL POINTS ON CIRCLE We start by asking us: How many integers x, y, z) can satisfy x 2 + y 2 = z 2? Can we describe all of them? First we can divide
Old and new order of linear invariant family of harmonic mappings and the bound for Jacobian
 doi: 10.478/v1006-011-004-3 A N N A L E S U N I V E R S I T A T I S M A R I A E C U R I E - S K Ł O D O W S K A L U B L I N P O L O N I A VOL. LXV, NO., 011 SECTIO A 191 0 MAGDALENA SOBCZAK-KNEĆ, VIKTOR
doi: 10.478/v1006-011-004-3 A N N A L E S U N I V E R S I T A T I S M A R I A E C U R I E - S K Ł O D O W S K A L U B L I N P O L O N I A VOL. LXV, NO., 011 SECTIO A 191 0 MAGDALENA SOBCZAK-KNEĆ, VIKTOR
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
MA441: Algebraic Structures I. Lecture 18
 MA441: Algebraic Structures I Lecture 18 5 November 2003 1 Review from Lecture 17: Theorem 6.5: Aut(Z/nZ) U(n) For every positive integer n, Aut(Z/nZ) is isomorphic to U(n). The proof used the map T :
MA441: Algebraic Structures I Lecture 18 5 November 2003 1 Review from Lecture 17: Theorem 6.5: Aut(Z/nZ) U(n) For every positive integer n, Aut(Z/nZ) is isomorphic to U(n). The proof used the map T :
Algebraic Topology Homework 4 Solutions
 Algebraic Topology Homework 4 Solutions Here are a few solutions to some of the trickier problems... Recall: Let X be a topological space, A X a subspace of X. Suppose f, g : X X are maps restricting to
Algebraic Topology Homework 4 Solutions Here are a few solutions to some of the trickier problems... Recall: Let X be a topological space, A X a subspace of X. Suppose f, g : X X are maps restricting to
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
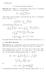 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 5
 DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 5 CLAY SHONKWILER 1 Check the calculations above that the Gaussian curvature of the upper half-plane and Poincaré disk models of the hyperbolic plane is 1. Proof. The calculations
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 5 CLAY SHONKWILER 1 Check the calculations above that the Gaussian curvature of the upper half-plane and Poincaré disk models of the hyperbolic plane is 1. Proof. The calculations
AUTOMORPHIC FORMS NOTES, PART I
 AUTOMORPHIC FORMS NOTES, PART I DANIEL LITT The goal of these notes are to take the classical theory of modular/automorphic forms on the upper half plane and reinterpret them, first in terms L 2 (Γ \ SL(2,
AUTOMORPHIC FORMS NOTES, PART I DANIEL LITT The goal of these notes are to take the classical theory of modular/automorphic forms on the upper half plane and reinterpret them, first in terms L 2 (Γ \ SL(2,
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
CHAPTER 9. Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-4:
CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-4:
Revision Problems for Examination 1 in Algebra 1
 Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination 1 in Algebra 1 Arithmetics 1 Determine a greatest common divisor to the integers a) 5431 and 1345, b)
Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination 1 in Algebra 1 Arithmetics 1 Determine a greatest common divisor to the integers a) 5431 and 1345, b)
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem
 MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
Fuchsian groups. 2.1 Definitions and discreteness
 2 Fuchsian groups In the previous chapter we introduced and studied the elements of Mob(H), which are the real Moebius transformations. In this chapter we focus the attention of special subgroups of this
2 Fuchsian groups In the previous chapter we introduced and studied the elements of Mob(H), which are the real Moebius transformations. In this chapter we focus the attention of special subgroups of this
Differential Topology Solution Set #2
 Differential Topology Solution Set #2 Select Solutions 1. Show that X compact implies that any smooth map f : X Y is proper. Recall that a space is called compact if, for every cover {U } by open sets
Differential Topology Solution Set #2 Select Solutions 1. Show that X compact implies that any smooth map f : X Y is proper. Recall that a space is called compact if, for every cover {U } by open sets
Complex Analysis Homework 1: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Fall 007 Homework 1: Solutions 1.1.. a) + i)4 + i) 8 ) + 1 + )i 5 + 14i b) 8 + 6i) 64 6) + 48 + 48)i 8 + 96i c) 1 + ) 1 + i 1 + 1 i) 1 + i)1 i) 1 + i ) 5 ) i 5 4 9 ) + 4 4 15 i ) 15 4
Complex Analysis Fall 007 Homework 1: Solutions 1.1.. a) + i)4 + i) 8 ) + 1 + )i 5 + 14i b) 8 + 6i) 64 6) + 48 + 48)i 8 + 96i c) 1 + ) 1 + i 1 + 1 i) 1 + i)1 i) 1 + i ) 5 ) i 5 4 9 ) + 4 4 15 i ) 15 4
MATH 434 Fall 2016 Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31
 Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31 Problem 1. Let z = 2 i and z = 3 + 4i. Write the product zz and the quotient z z in the form a + ib, with a, b R. Problem 2. Let z C be a complex number, and let
Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31 Problem 1. Let z = 2 i and z = 3 + 4i. Write the product zz and the quotient z z in the form a + ib, with a, b R. Problem 2. Let z C be a complex number, and let
SPRING 2006 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS
 SPRING 006 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS 1A. Let G be the subgroup of the free abelian group Z 4 consisting of all integer vectors (x, y, z, w) such that x + 3y + 5z + 7w = 0. (a) Determine a linearly
SPRING 006 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS 1A. Let G be the subgroup of the free abelian group Z 4 consisting of all integer vectors (x, y, z, w) such that x + 3y + 5z + 7w = 0. (a) Determine a linearly
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4
 MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
Notes for MATH 434 Geometry and Transformations. Francis Bonahon Fall 2015
 Notes for MATH 434 Geometry and Transformations Francis Bonahon Fall 2015 Version: October 21, 2016 Department of Mathematics University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-2532, U.S.A. E-mail
Notes for MATH 434 Geometry and Transformations Francis Bonahon Fall 2015 Version: October 21, 2016 Department of Mathematics University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-2532, U.S.A. E-mail
6.2 Mean value theorem and maximum principles
 Hence g = u x iu y is analytic. Since is simply connected, R g(z) dz =forany closed path =) g has an integral function, G = g in. Call G = U + iv. For analytic functions d G = d G. Hence dz dx g = d dz
Hence g = u x iu y is analytic. Since is simply connected, R g(z) dz =forany closed path =) g has an integral function, G = g in. Call G = U + iv. For analytic functions d G = d G. Hence dz dx g = d dz
E. Falbel and P.-V. Koseleff
 Mathematical Research Letters 9, 379 391 (2002) A CIRCLE OF MODULAR GROUPS IN PU(2,1) E. Falbel and P.-V. Koseleff Abstract. We prove that there exists a circle of discrete and faithful embeddings of the
Mathematical Research Letters 9, 379 391 (2002) A CIRCLE OF MODULAR GROUPS IN PU(2,1) E. Falbel and P.-V. Koseleff Abstract. We prove that there exists a circle of discrete and faithful embeddings of the
Chapter 1 Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Conventions and Notations Throughout the book we use the following notations for standard sets of numbers: N the set {1, 2,...} of natural numbers Z the set of integers Q the
Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Conventions and Notations Throughout the book we use the following notations for standard sets of numbers: N the set {1, 2,...} of natural numbers Z the set of integers Q the
Problem 1A. Find the volume of the solid given by x 2 + z 2 1, y 2 + z 2 1. (Hint: 1. Solution: The volume is 1. Problem 2A.
 Problem 1A Find the volume of the solid given by x 2 + z 2 1, y 2 + z 2 1 (Hint: 1 1 (something)dz) Solution: The volume is 1 1 4xydz where x = y = 1 z 2 This integral has value 16/3 Problem 2A Let f(x)
Problem 1A Find the volume of the solid given by x 2 + z 2 1, y 2 + z 2 1 (Hint: 1 1 (something)dz) Solution: The volume is 1 1 4xydz where x = y = 1 z 2 This integral has value 16/3 Problem 2A Let f(x)
Chapter 2 Linear Transformations
 Chapter 2 Linear Transformations Linear Transformations Loosely speaking, a linear transformation is a function from one vector space to another that preserves the vector space operations. Let us be more
Chapter 2 Linear Transformations Linear Transformations Loosely speaking, a linear transformation is a function from one vector space to another that preserves the vector space operations. Let us be more
Chapter 1. Sets and Numbers
 Chapter 1. Sets and Numbers 1. Sets A set is considered to be a collection of objects (elements). If A is a set and x is an element of the set A, we say x is a member of A or x belongs to A, and we write
Chapter 1. Sets and Numbers 1. Sets A set is considered to be a collection of objects (elements). If A is a set and x is an element of the set A, we say x is a member of A or x belongs to A, and we write
5. Connectedness. Corollary 5.4. Connectedness is a topological property.
 5. Connectedness We begin our introduction to topology with the study of connectedness traditionally the only topic studied in both analytic and algebraic topology. C. T. C. Wall, 197 The property at the
5. Connectedness We begin our introduction to topology with the study of connectedness traditionally the only topic studied in both analytic and algebraic topology. C. T. C. Wall, 197 The property at the
Lecture 1 The complex plane. z ± w z + w.
 Lecture 1 The complex plane Exercise 1.1. Show that the modulus obeys the triangle inequality z ± w z + w. This allows us to make the complex plane into a metric space, and thus to introduce topological
Lecture 1 The complex plane Exercise 1.1. Show that the modulus obeys the triangle inequality z ± w z + w. This allows us to make the complex plane into a metric space, and thus to introduce topological
MATH 223A NOTES 2011 LIE ALGEBRAS 35
 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS 35 9. Abstract root systems We now attempt to reconstruct the Lie algebra based only on the information given by the set of roots Φ which is embedded in Euclidean space E.
MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS 35 9. Abstract root systems We now attempt to reconstruct the Lie algebra based only on the information given by the set of roots Φ which is embedded in Euclidean space E.
Riemann Surfaces and Algebraic Curves
 Riemann Surfaces and Algebraic Curves JWR Tuesday December 11, 2001, 9:03 AM We describe the relation between algebraic curves and Riemann surfaces. An elementary reference for this material is [1]. 1
Riemann Surfaces and Algebraic Curves JWR Tuesday December 11, 2001, 9:03 AM We describe the relation between algebraic curves and Riemann surfaces. An elementary reference for this material is [1]. 1
Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15)
 Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
