Name: Ahmad Alowais Class: ME476C Individual Analysis Team 20: Wonder Factory A Instructor: Dr. David Trevas
|
|
|
- Thomas Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Ahmad Alowais Class: ME476C Individual Analysis Team 20: Wonder Factory A Instructor: Dr. David Trevas
2 Introduction: Packaging engineering involves itself with the designing and creating of cartons, boxes, bottles and other packaging materials. It uses the chemical, physical and industrial factors for the formulation of these products. These inventions include helmets, pads, bubble wraps, peanuts packing cartons, and airbags Ever since helmets were put on, hundreds of years, by the Roman fighters in the Bible, we use them for various purposes. One, in sports events, where the current American footballers use them for head protection as they indulge in sports activities. This equipment can be used by the firefighters in all sector of life, as they attempt to put away fire hazards. The common pads worn by the footballers, hockey players, and basket players are some form of defensive materials that aid them from injuries. Though this type of engineering is not measured as a formal branch of the mechanical, chemical and physical based sciences, it borrows ideas from these subjects. It continues to be an area that continues to be relevant in what happens in today s world. It has major applications in the above-mentioned areas. Examples are helmets, head covers, infant car seats for protecting children, and sports pads. Automobiles use the present technologies to offer the safety of passengers. Problem design: Problem design problem starts by developing the model for this specific helmet. The survey data collected from the experiment is then used to come up with an economic helmet in terms of regarding costs. A literature survey is conducted to address the customer s needs and demands based on our design costs. Then we proposed helmet product that targets consumers, footballers, hockey players and race. Next, the designer provides the cover s specification. Most of these covers are designed based on the scientific facts and verification. Therefore the resulting product must absorb impact s energy in such a way that, it has a predetermined weighed of 300 grams. The shell should avoid falling at an angle of 60 degrees to the ground. This particular attribute affects the thickness size of the shell of the merchandise. The final product should be lightweight and offer ventilation. Motorbike Helmet Parts It is made up of four components namely the outer shell, impact absorbing liner, the comfort padding and the retention system. The outer shell is the first part visible to one s eyes. It is made of fiber-reinforced material called polycarbornate.it is a tough material that compresses whenever it hits the ground. Inside the shell, there is the liner that absorbs shock. Both the two layers, compresses if they are hit hard by any moving material or falls down. Unless hit hard, they crack and break. The comfort padding is the soft foam layer that sits next to one s head and provides comfort. Lastly the retention
3 system is the strap that keeps the helmet on one s head. The band is connected to each side of the shell. When you put the case on, you fasten it securely[1]. Motorbike Helmet Analysis While the color, the design and the part of the involved factors to consider before assembling one, a designer cannot do away with the comfort and protection elements. There are many materials that can be used for making of these cover elements. For example, cotton, linen, wool, silk, and hemp. Cotton is cheap and readily available.the major disadvantages include; it holds sweat and gives the wrong look or appearance whenever used. Materials used for staffing the cover come in variety; these are horse air, linen scraps, and tows. Hard-shell elements are more robust than the foam ones but heavier. A hybrid type combines both, and has a thinner hard outer shell but again slightly lighter than the hard-shell type to prevent deformation whenever an accident occurs. The foam elements are warmer because of the high isolation.hardshell helmets offer protection against impacts from above. They are most used in mountaineering and long distance routes. Foam provide impact from all direction, therefore they are suitable for sports. Cotton material is used because of its good tensile and elongation strength. The material contains high number of twists that increases the strength of each yarn. It has the highest value of water permeability, when it absorbs water they become bulkie.since the inner padding layer of the helmet matters, this fabric can be used. Foams are light and cheap. They can be cleaned with soap and water. They material used to make these devices are shock absorbent and fully ventilated. They provider great impact resistance than any other soft helmets. Besides these, they give they give the front and the back of head protection without obstructed vision through an open face design [2]. Papers are the cheapest materials available, and have minimal weight but poor ventilation. They are less water resistant as compared to other materials. They cannot be used in ice climbing, warm weather sport climbing and belaying.
4 Methodology and Analysis The following analysis was done based on the material used for making these covers. The sample materials included papers, foams and cotton. The results were recorded as follows Material Light Weight (out of 10) Durability (out of 10) Breathing (out of 10) Cheap (out of 10) Effectiveness Risk Priority Number calculation Cotton Foams Papers Table (1) The Risk Priority Number is given by multiplying the five factors of the material used Risk Priority Number= Light Weight X Durability X Breathing X Cheap X Effectiveness Therefore the best is the use of foams. Impulse Force and Momentum The impulse force refers to the force acting on an object for an interval of time leading to a change of momentum. The impulse hence is critical in the analysis of the collision impact of force. In other words, impulse forces depict the short interval forces that lead to rapid changes in motion [3]. On the other hand, momentum refers to the impetus that a moving object gains. Momentum, therefore, depicts the quantity of motion occurring in a body or a mass in motion. In other terms, momentum illustrates the strength and difficulty experienced in stopping an object. Impulse force and momentum, therefore, relates in such a way that when a force acts on an object for a short time interval, the force is referred to as an impulsive force because it shall result in a shift in momentum[3]. Momentum is hence dependent on the on the impulse force. The equation of the impulse on an object is given by: Force (F) = Mass accleration Force = Mass (M) Velocity(V) Time (t)
5 Ft = m v On the other hand, the equation of momentum is given by the product of mass and velocity. However, momentum is a vector quantity provided by the formula below [4]. p = mv The figure below illustrates the impact of impulse. Figure (1) From the video, two eggs were thrown using the same force. One of the eggs lands on a wall and the others lands on a piece of sheet. As a result, the egg that falls on the wall crushes while the one that lands on the sheet of cloth does not crush. Regarding the analysis of the impulse force and momentum, both of the eggs have same initial momentum because both of them have similar mass. Moreover, the eggs are also thrown at the same velocity in the same direction. However, the egg that lands on the wall crushed because it had a sudden change in its momentum. The impulsive force on the egged acted for a very short period. As result of this, there was a sudden change in momentum which caused the egg to crush because of the high impulse. On the other hand, the egg that landed on the hanging piece of sheet did not change because of the delayed change in momentum. The impulsive force on the egg acted for an extended period. As a result of this, the shift in momentum took place for a prolonged period making the egg not to crush because of the less impulse. If assumptions are made such that the velocity of an object is 10 m/s, the momentum of the object is lower than when the object is moving at a speed of 20 m/s. However, the impulse would be high in the object moving at 20 m/s. For an equal rate of change in momentum, an object moving at 20 m/s shall need more time. If an object moves at 100m/s, it has a higher momentum, and it shall have a strong impulse. The racer helmets are designed in such a way that they are hard on the outer part to distribute the force of impact over a large area [4]. They
6 are spongy on the inside to enable the soft part to absorb some of the force and increase the impulse time while minimizing the impulse force. Conclusion A helmet can be subjected to a load or a force. We analyze the strain energy, deformation, strain energy and the equivalent stress. In the dynamic analysis, the total helmet deformation is estimated and compared with the standard experimental data. The impact energy is influenced by how far the cover drops (drop height) together with the mass. The injuries to the body parts especially the head take various forms. Some experimental measurements deduce that whenever foam is used, there is a high resistance to impact force. a prolonged change in momentum results to reduced impulse force while a sudden change in momentum produces a large impulse force.
7 Work Cited [1] A.Gilchrist, N.J Mills, Fast fracture of rubber-toughened thermoplastic used for shells of motor Cycles, [2]Sample Module, Eggxpress-Egg Drop Project, California, [3]Giancoli, Douglas C. Physics: principles with applications. Pearson Education, [4]Lawson, Ronald A., and Lillian C. McDermott. Student understanding of the work- impulse-momentum theorems. American Journal of Physics 55.9 energy and (2007):
Egg Crash! Designing a Collision Safety Device
 TEACHER LESSON Key question(s) How do people survive major collisions? How does physics explain the effectiveness of seat belts and airbags? Crash Course Definitions impulse: product of force and time
TEACHER LESSON Key question(s) How do people survive major collisions? How does physics explain the effectiveness of seat belts and airbags? Crash Course Definitions impulse: product of force and time
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ENERGY & MOMENTUM L Momentum & Impulse (P.222-227) Momentum & Impulse The driver of this race car walked away from the crash without a scratch. Luck had little to do with this
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ENERGY & MOMENTUM L Momentum & Impulse (P.222-227) Momentum & Impulse The driver of this race car walked away from the crash without a scratch. Luck had little to do with this
New football helmets could limit brain injuries Their three layers are better than having just one
 New football helmets could limit brain injuries Their three layers are better than having just one BY KATHIANN KOWALSKI FEBRUARY 22, 2016 Two football players collide on the field. Both are wearing helmets.
New football helmets could limit brain injuries Their three layers are better than having just one BY KATHIANN KOWALSKI FEBRUARY 22, 2016 Two football players collide on the field. Both are wearing helmets.
Design and Finite Element Analysis of Helmeted Head Form in Impact
 , pp.15-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijast.2016.93.02 Design and Finite Element Analysis of Helmeted Head Form in Impact Suddapalli Praneeth Babu* 1 and Dr. Chandana Srinivas 2 1 Mechanical Engineering,
, pp.15-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijast.2016.93.02 Design and Finite Element Analysis of Helmeted Head Form in Impact Suddapalli Praneeth Babu* 1 and Dr. Chandana Srinivas 2 1 Mechanical Engineering,
Q1. (a) The diagram shows an athlete at the start of a race. The race is along a straight track.
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows an athlete at the start of a race. The race is along a straight track. In the first 2 seconds, the athlete accelerates constantly and reaches a speed of 9 m/s. (i) Use the equation
Q1. (a) The diagram shows an athlete at the start of a race. The race is along a straight track. In the first 2 seconds, the athlete accelerates constantly and reaches a speed of 9 m/s. (i) Use the equation
Momentum. Physics Momentum and Impulse Practice
 Physics Momentum and Impulse Practice Momentum Momentum is the resistance of an object to giving up kinetic energy. Momentum is times. It is abbreviated with a p. The equation is p = m*v Solve the following
Physics Momentum and Impulse Practice Momentum Momentum is the resistance of an object to giving up kinetic energy. Momentum is times. It is abbreviated with a p. The equation is p = m*v Solve the following
Q1. (a) The diagram shows a car being driven at 14 rn/s. The driver has forgotten to clear a thick layer of snow from the roof.
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows a car being driven at 14 rn/s. The driver has forgotten to clear a thick layer of snow from the roof. Which of the following has the smallest momentum? Draw a circle around your
Q1. (a) The diagram shows a car being driven at 14 rn/s. The driver has forgotten to clear a thick layer of snow from the roof. Which of the following has the smallest momentum? Draw a circle around your
Topics include Newton s laws, pressure, work, average velocity, kinetic energy, momentum and conservation of momentum, work-energy theorem
 Chapter 3: Safety Overall: Topics include Newton s laws, pressure, work, average velocity, kinetic energy, momentum and conservation of momentum, work-energy theorem Sections 1-2: These two sections introduce
Chapter 3: Safety Overall: Topics include Newton s laws, pressure, work, average velocity, kinetic energy, momentum and conservation of momentum, work-energy theorem Sections 1-2: These two sections introduce
Vocabulary. The mass of an object multiplied by its speed or velocity. The product of force x time that causes a change in momentum.
 Vocabulary Term Definition The mass of an object multiplied by its speed or. Kg m s The units for momentum. Impulse The product of force x time that causes a change in momentum. N s The units for impulse.
Vocabulary Term Definition The mass of an object multiplied by its speed or. Kg m s The units for momentum. Impulse The product of force x time that causes a change in momentum. N s The units for impulse.
Physics February 2, Hand-In 10.6 Energy Problems
 Physics February 2, 2018 Hand-In 10.6 Energy Problems Momentum and Impulse Momentum and Impulse Momentum A team is said to have Momentum if they are on a roll, or hard to stop. In Physics, momentum is
Physics February 2, 2018 Hand-In 10.6 Energy Problems Momentum and Impulse Momentum and Impulse Momentum A team is said to have Momentum if they are on a roll, or hard to stop. In Physics, momentum is
7.1 Momentum. Can you have inertia sitting in your seat? Do you have momentum (relative to the room) sitting in your seat? What is momentum?
 Impulse & Momentum 7.1 Momentum Can you have inertia sitting in your seat? Do you have momentum (relative to the room) sitting in your seat? What is momentum? 2 7.1 Momentum Which is harder to stop a truck
Impulse & Momentum 7.1 Momentum Can you have inertia sitting in your seat? Do you have momentum (relative to the room) sitting in your seat? What is momentum? 2 7.1 Momentum Which is harder to stop a truck
A. Incorrect! Remember that momentum depends on both mass and velocity. B. Incorrect! Remember that momentum depends on both mass and velocity.
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 08: Momentum and Collisions No. 1 of 10 1. A car and motor bike are travelling down the road? Which of these is a correct statement? (A) The car will have a higher momentum.
AP Physics - Problem Drill 08: Momentum and Collisions No. 1 of 10 1. A car and motor bike are travelling down the road? Which of these is a correct statement? (A) The car will have a higher momentum.
Momentum and Impulse
 Momentum and Impulse Momentum All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables:
Momentum and Impulse Momentum All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables:
Q Scheme Marks AOs. 1a States or uses I = F t M1 1.2 TBC. Notes
 Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a States or uses I = F t M1 1.2 TBC I = 5 0.4 = 2 N s Answer must include units. 1b 1c Starts with F = m a and v = u + at Substitutes to get Ft = m(v u) Cue ball begins at rest
Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a States or uses I = F t M1 1.2 TBC I = 5 0.4 = 2 N s Answer must include units. 1b 1c Starts with F = m a and v = u + at Substitutes to get Ft = m(v u) Cue ball begins at rest
Cart A Cart B Cart C Cart D Mass (kg) 4.0kg 1.0kg 3.5kg 12kg Velocity (m/s)
 Position (m) -40-20 20 40 Physics 03_14 Momentum Remediation 1. A 65 kg person runs to catch the bus at 1.31 m/s. What is their momentum? Name 4. A 10.2 kg ball has a momentum of 4340 kg m/s. What is the
Position (m) -40-20 20 40 Physics 03_14 Momentum Remediation 1. A 65 kg person runs to catch the bus at 1.31 m/s. What is their momentum? Name 4. A 10.2 kg ball has a momentum of 4340 kg m/s. What is the
EGG CRASH! DESIGNING A COLLISION SAFETY DEVICE
 T E AC H E R L E S S O N EGG CRASH! DESIGNING A COLLISION SAFETY DEVICE DEFINITIONS momentum: the inertia of moving objects; product of the mass and the velocity of an object (p = mv) impulse: product
T E AC H E R L E S S O N EGG CRASH! DESIGNING A COLLISION SAFETY DEVICE DEFINITIONS momentum: the inertia of moving objects; product of the mass and the velocity of an object (p = mv) impulse: product
Materials Needed: Procedure:
 How a force causes movement? What is Newton s first law of motion? Newton s first law of motion The ingenious English mathematician and physicist Sir Isaac Newton (164-177) was the first to fully understand
How a force causes movement? What is Newton s first law of motion? Newton s first law of motion The ingenious English mathematician and physicist Sir Isaac Newton (164-177) was the first to fully understand
Science 20. Unit B: Changes in Motion. Assignment Booklet B2
 Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion Assignment Booklet B2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 36 Your Mark Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion
Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion Assignment Booklet B2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 36 Your Mark Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion
Momentum and Impulse
 Momentum and Impulse Momentum in Sports - Momentum is a commonly used term in sports. - A team that has a lot of momentum is really on the move and is going to be hard to stop. - Momentum is a physics
Momentum and Impulse Momentum in Sports - Momentum is a commonly used term in sports. - A team that has a lot of momentum is really on the move and is going to be hard to stop. - Momentum is a physics
Momentum and Impulse Ch. 8 in your text book
 Momentum and Ch. 8 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Calculate the impulse of an object given a change in mass or velocity 2) Calculate the force felt by and object given an impulse
Momentum and Ch. 8 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Calculate the impulse of an object given a change in mass or velocity 2) Calculate the force felt by and object given an impulse
Chapter 7: Momentum and Impulse
 Chapter 7: Momentum and Impulse Momentum in Sports Momentum is a commonly used term in sports. A team that has a lot of momentum is really on the move and is going to be hard to stop. Momentum is a physics
Chapter 7: Momentum and Impulse Momentum in Sports Momentum is a commonly used term in sports. A team that has a lot of momentum is really on the move and is going to be hard to stop. Momentum is a physics
P11 Dynamics 3 Momentum and Impulse Bundle.notebook November 05, 2013
 Momentum 1 Momentum Momentum is a physics term that refers to the quantity of motion that an object has. Sometimes it is defined as "inertia in motion" or "mass in motion." The amount of momentum which
Momentum 1 Momentum Momentum is a physics term that refers to the quantity of motion that an object has. Sometimes it is defined as "inertia in motion" or "mass in motion." The amount of momentum which
Per 9 10 Momentum_Presentation.notebook. January 20, Momentum.
 Momentum www.njctl.org 1 Momentum Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse Momentum of a System of Objects Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions and Explosions Elastic Collisions
Momentum www.njctl.org 1 Momentum Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse Momentum of a System of Objects Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions and Explosions Elastic Collisions
14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions
 14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions Required Accessories o (2) Table stops (wooden bars) o (4) C-Clamps o (2) Recording Timers (#15210 or #15215) o (5) Bricks or Books (or other identical
14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions Required Accessories o (2) Table stops (wooden bars) o (4) C-Clamps o (2) Recording Timers (#15210 or #15215) o (5) Bricks or Books (or other identical
Name: Period: Date: 2. How is the ball s acceleration related to the force Julia applies to the ball?
 Name: Period: Date: IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM CONTENTS Impulse and Momentum... 1 Background... 1 The Concepts of Impulse and Momentum... 2 Relationship to Newton s Second Law... 4 Journaling Assignment... 5
Name: Period: Date: IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM CONTENTS Impulse and Momentum... 1 Background... 1 The Concepts of Impulse and Momentum... 2 Relationship to Newton s Second Law... 4 Journaling Assignment... 5
Momentum C HAPTER. Chapter Outline.
 www.ck12.org C HAPTER 7 Momentum Chapter Outline 7.1 M OMENTUM AND I MPULSE 7.2 C ONSERVATION OF M OMENTUM IN O NE D IMENSION 7.3 R EFERENCES This chapter is about momentum and impulse. There are an amazing
www.ck12.org C HAPTER 7 Momentum Chapter Outline 7.1 M OMENTUM AND I MPULSE 7.2 C ONSERVATION OF M OMENTUM IN O NE D IMENSION 7.3 R EFERENCES This chapter is about momentum and impulse. There are an amazing
LESSON 2.6. Impulse, Impulsive force and Safety features In Vehicles
 idang sains dan matematik LESSON 2.6. Impulse, Impulsive force and Safety features In Vehicles Definition and S.I. unit for Impulse Impulse is defined as the change in momentum Impulse = m ( v - u ) m
idang sains dan matematik LESSON 2.6. Impulse, Impulsive force and Safety features In Vehicles Definition and S.I. unit for Impulse Impulse is defined as the change in momentum Impulse = m ( v - u ) m
Per 3 4 Momentum_Presentation.notebook. January 23, Momentum.
 Momentum www.njctl.org 1 Momentum Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse Momentum of a System of Objects Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions and Explosions Elastic Collisions
Momentum www.njctl.org 1 Momentum Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse Momentum of a System of Objects Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions and Explosions Elastic Collisions
PHYSICS LICENCE. 6 Marks
 PHYSICS LICENCE 1. A SPEED CAMERA TAKES TWO PHOTOGRAPHS AT HALF-SECOND INTERVALS OF A MOTOR CYCLIST DRVING ALONG THE MOTORWAY. DESCRIBE HOW THESE COULD BE USED TO CALCULATE THE SPEED OF THE MOTOR CYCLIST.
PHYSICS LICENCE 1. A SPEED CAMERA TAKES TWO PHOTOGRAPHS AT HALF-SECOND INTERVALS OF A MOTOR CYCLIST DRVING ALONG THE MOTORWAY. DESCRIBE HOW THESE COULD BE USED TO CALCULATE THE SPEED OF THE MOTOR CYCLIST.
Which car (A or B) experiences the greatest change in momentum? Explain.
 MOM B - Impulse and Change of Momentum Original Assignment Start with #3. Using the F t = m v Equation to Analyze Impulses and Momentum Changes: 3. Two cars of equal mass are traveling down Lake Avenue
MOM B - Impulse and Change of Momentum Original Assignment Start with #3. Using the F t = m v Equation to Analyze Impulses and Momentum Changes: 3. Two cars of equal mass are traveling down Lake Avenue
It would be appropriate to pull out your phone or planner and write these dates down.
 Upcoming dates 11/11 (A) + 11/12 (B): Virtual Collision Lab 11/13 (A) + 11/14 (B): Momentum and Impulse Quiz and Collision Lab 11/17 (A) + 11/18 (B): Momentum and Impulse Vocabulary Quiz and Test Review
Upcoming dates 11/11 (A) + 11/12 (B): Virtual Collision Lab 11/13 (A) + 11/14 (B): Momentum and Impulse Quiz and Collision Lab 11/17 (A) + 11/18 (B): Momentum and Impulse Vocabulary Quiz and Test Review
Chapter 2: FORCE and MOTION
 Chapter 2: FORCE and MOTION Linear Motion Linear motion is the movement of an object along a straight line. Distance The distance traveled by an object is the total length that is traveled by that object.
Chapter 2: FORCE and MOTION Linear Motion Linear motion is the movement of an object along a straight line. Distance The distance traveled by an object is the total length that is traveled by that object.
(a) (i) The toy has a mass of 0.15 kg and moves forward with a velocity of 0.08 m/s. How is the momentum of the toy calculated?
 MOMENTUM Q1. The diagram shows an air-driven toy. When the electric motor is switched on the fan rotates. The fan pushes air backwards making the toy move forwards. The toy has a mass of 0.15 kg and moves
MOMENTUM Q1. The diagram shows an air-driven toy. When the electric motor is switched on the fan rotates. The fan pushes air backwards making the toy move forwards. The toy has a mass of 0.15 kg and moves
Egg Drop Project. By: Mara Yella Drafting P2 B Days
 Egg rop Project y: Mara Yella rafting P ays esign rief lient: HSMSE rafting Teachers: Ms. arlisle, Mr. hoi Target onsumer: HSMSE rafting Teachers: Ms. arlisle, Mr. hoi Problem Statement: Egg must survive
Egg rop Project y: Mara Yella rafting P ays esign rief lient: HSMSE rafting Teachers: Ms. arlisle, Mr. hoi Target onsumer: HSMSE rafting Teachers: Ms. arlisle, Mr. hoi Problem Statement: Egg must survive
Bellringer Day In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules?
 Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
The design of a formula student front impact attenuator
 The design of a formula student front impact attenuator J.M.J. Schormans MT 10.06 Supervisors: dr. ir. Varvara Kouznetsova Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Computational
The design of a formula student front impact attenuator J.M.J. Schormans MT 10.06 Supervisors: dr. ir. Varvara Kouznetsova Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Computational
Solution Figure 2(a) shows the situation. Since there is no net force acting on the system, momentum is conserved. Thus,
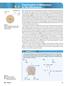 large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere.
 Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere. Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object
Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere. Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object
Science In Action 7 Structures and Forces Section Quiz
 Section 2 External and Internal Forces Act on Structures 2.1 Measuring Forces 1. A force is a push or a pull that tends to cause an object to change its height or length B. movement or shape C. colour
Section 2 External and Internal Forces Act on Structures 2.1 Measuring Forces 1. A force is a push or a pull that tends to cause an object to change its height or length B. movement or shape C. colour
An entire branch of Earth science, called, is devoted to the study of earthquakes.
 Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Improving Safety Features during a Head on Collision inside a Car Cabin
 Improving Safety Features during a Head on Collision inside a Car Cabin Harinarayan Vishwakarma Abstract The core theme of this research is directed towards the idea of providing more safety features inside
Improving Safety Features during a Head on Collision inside a Car Cabin Harinarayan Vishwakarma Abstract The core theme of this research is directed towards the idea of providing more safety features inside
CHAPTER 6 TEST. Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number.
 CHAPTER 6 TEST Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number. 1. What is inertia? A. the amount of matter in an object B. the force of gravity
CHAPTER 6 TEST Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number. 1. What is inertia? A. the amount of matter in an object B. the force of gravity
Drexel-SDP GK-12 LESSON
 Lesson: Collisions Drexel-SDP GK-1 LESSON Subject Area(s) Data Analysis & Probability, Measurement, Number & Operations, Physical Science, Science and Technology Associated Unit Vital Mechanics Lesson
Lesson: Collisions Drexel-SDP GK-1 LESSON Subject Area(s) Data Analysis & Probability, Measurement, Number & Operations, Physical Science, Science and Technology Associated Unit Vital Mechanics Lesson
Impulse. Observations
 Impulse Observations What is the physics behind breaking an egg? If we look at the situation in terms of force, an egg dropping seems to have the same force (of gravity) as an egg sitting on a counter,
Impulse Observations What is the physics behind breaking an egg? If we look at the situation in terms of force, an egg dropping seems to have the same force (of gravity) as an egg sitting on a counter,
An Introduction to Momentum (Doodle Science)
 Momentum An Introduction to Momentum (Doodle Science) Intro to Momentum part one Momentum Momentum is a way of describing the inertia of an object in motion. Momentum = Mass x Velocity P = m v When direction
Momentum An Introduction to Momentum (Doodle Science) Intro to Momentum part one Momentum Momentum is a way of describing the inertia of an object in motion. Momentum = Mass x Velocity P = m v When direction
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Calculate the acceleration of the car during the 11 seconds
 1. The manufacturer of a family car gave the following information. Mass of car 950 kg. The car will accelerate from 0 to 33 m/s in 11 seconds. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the car during the 11 seconds......
1. The manufacturer of a family car gave the following information. Mass of car 950 kg. The car will accelerate from 0 to 33 m/s in 11 seconds. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the car during the 11 seconds......
Graphene-Rubber Composites
 Rev:2016-11-12 Ver.1.0.0 Graphene-Rubber Composites Product Features Rubber material is one of the most important and widely deployed materials. It is utilized in high- tech products, military defense
Rev:2016-11-12 Ver.1.0.0 Graphene-Rubber Composites Product Features Rubber material is one of the most important and widely deployed materials. It is utilized in high- tech products, military defense
Optimization of a car seat under impact load
 Structures Under Shock and Impact X 9 Optimization of a car seat under impact load F. J. Szabó Department of Machine Elements, University of Miskolc, Hungary Abstract The behaviour of the metal structure
Structures Under Shock and Impact X 9 Optimization of a car seat under impact load F. J. Szabó Department of Machine Elements, University of Miskolc, Hungary Abstract The behaviour of the metal structure
Objectives 326 CHAPTER 7 MOMENTUM
 Objectives Define linear momentum. Explain the relationship between force and rate of change of momentum. Define impulse. Explain the relationship between impulse and change in momentum. Explain Newton
Objectives Define linear momentum. Explain the relationship between force and rate of change of momentum. Define impulse. Explain the relationship between impulse and change in momentum. Explain Newton
Basic Chemistry Laboratory Manual CHEM 101L Prof. Haber Prof. McPike Morrisville State College FALL 2017
 Basic Chemistry Laboratory Manual CHEM 101L Prof. Haber Prof. McPike Morrisville State College FALL 2017 1 P a g e Introduction The purpose of the chemistry laboratory is to further develop your understanding
Basic Chemistry Laboratory Manual CHEM 101L Prof. Haber Prof. McPike Morrisville State College FALL 2017 1 P a g e Introduction The purpose of the chemistry laboratory is to further develop your understanding
Checklist: Deposing the Driver in an Auto Accident
 Checklist: Deposing the Driver in an Auto Accident 1. PERSONAL BACKGROUND All names ever used Present and past residences for 10 years If the deponent has rented a residence, get the name and address of
Checklist: Deposing the Driver in an Auto Accident 1. PERSONAL BACKGROUND All names ever used Present and past residences for 10 years If the deponent has rented a residence, get the name and address of
11.6. Living and Working in Space. Breathing in Space
 11.6 Living and Working in Space LEARNING TIP Set a purpose for your reading of this section. First, read the headings and look at the illustrations in the section. Then make a list of questions that you
11.6 Living and Working in Space LEARNING TIP Set a purpose for your reading of this section. First, read the headings and look at the illustrations in the section. Then make a list of questions that you
Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
Basics. Student booklet
 Basics Student booklet Basics - INDEX - 2006-04-06-16:32 Basics This module deals with many basic facts about how an electric current is created and about how an atom is constructed. It also deals with
Basics Student booklet Basics - INDEX - 2006-04-06-16:32 Basics This module deals with many basic facts about how an electric current is created and about how an atom is constructed. It also deals with
Chapter 7 Linear Momentum
 Chapter 7 Linear Momentum Units of Chapter 7 Momentum and Its Relation to Force Conservation of Momentum Collisions and Impulse Conservation of Energy and Momentum in Collisions Elastic Collisions in One
Chapter 7 Linear Momentum Units of Chapter 7 Momentum and Its Relation to Force Conservation of Momentum Collisions and Impulse Conservation of Energy and Momentum in Collisions Elastic Collisions in One
Chapter 7 Lecture. Pearson Physics. Linear Momentum and Collisions. Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 7 Lecture Pearson Physics Linear Momentum and Collisions Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Collisions Momentum How can the effect of catching
Chapter 7 Lecture Pearson Physics Linear Momentum and Collisions Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Collisions Momentum How can the effect of catching
Test Report No.: GZHL HM Date: Aug 08, 2016 Page 1 of 10
 Test Report No.: GZHL1607032559HM Date: Aug 08, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Test Report No.: GZHL1607032559HM Date: Aug 08, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Newton s First Law of Motion - Inertia Aristotle (384-322 BC) on Motion (4 th century BC) Natural Motion It was thought to be either straight up or straight down a rock would fall, smoke would rise. Circular
Newton s First Law of Motion - Inertia Aristotle (384-322 BC) on Motion (4 th century BC) Natural Motion It was thought to be either straight up or straight down a rock would fall, smoke would rise. Circular
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Test Report No.: GZHL HM-01 Date: Aug 16, 2016 Page 1 of 10
 Test Report No.: GZHL1608034628HM-01 Date: Aug 16, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Test Report No.: GZHL1608034628HM-01 Date: Aug 16, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Momentum and Collisions. Phy 114
 Momentum and Collisions Phy 114 Momentum Momentum: p = mv Units are kg(m/s): no derived units A vector quantity: same direction as velocity v=2m/s p= 3 kg (2m/s) From Newton s 2nd ΣF = ΣF = ma v m t ΣF(
Momentum and Collisions Phy 114 Momentum Momentum: p = mv Units are kg(m/s): no derived units A vector quantity: same direction as velocity v=2m/s p= 3 kg (2m/s) From Newton s 2nd ΣF = ΣF = ma v m t ΣF(
3. A piece of candy is accelerated at 3.0 m/s 2 in the direction shown by a, over a frictionless horizontal surface. The acceleration is caused by 3
 3. A piece of candy is accelerated at 3.0 m/s 2 in the direction shown by a, over a frictionless horizontal surface. The acceleration is caused by 3 forces, 2 of which are shown. F 1 has a magnitude of
3. A piece of candy is accelerated at 3.0 m/s 2 in the direction shown by a, over a frictionless horizontal surface. The acceleration is caused by 3 forces, 2 of which are shown. F 1 has a magnitude of
EOSMS Guidelines Date: 01/16/2014 Page 1 of 5
 EOSMS Guidelines Date: 01/16/2014 Page 1 of 5 Introduction The Department of Environmental Health, Safety has developed generic standard operating procedures relevant to safety and health considerations
EOSMS Guidelines Date: 01/16/2014 Page 1 of 5 Introduction The Department of Environmental Health, Safety has developed generic standard operating procedures relevant to safety and health considerations
Thanks. You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction and save time prepping.
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Physics 10 Lecture 6A. "And in knowing that you know nothing, that makes you the smartest of all. --Socrates
 Physics 10 Lecture 6A "And in knowing that you know nothing, that makes you the smartest of all. --Socrates Momentum Which is harder to stop a small ball moving at 1 m/s or a car moving at 1 m/s? Obviously
Physics 10 Lecture 6A "And in knowing that you know nothing, that makes you the smartest of all. --Socrates Momentum Which is harder to stop a small ball moving at 1 m/s or a car moving at 1 m/s? Obviously
Science 24 Study Guide Final Exam June 2013
 Science 24 Study Guide Final Exam June 2013 Those students writing the exam in two parts, Unit A & B will be written on Thursday, June 20th from 8:45am - 12:00pm in Room #165 (Sports Medicine Room). Units
Science 24 Study Guide Final Exam June 2013 Those students writing the exam in two parts, Unit A & B will be written on Thursday, June 20th from 8:45am - 12:00pm in Room #165 (Sports Medicine Room). Units
Momentum and Impulse
 analyse impulse, and momentum transfer, in collisions between objects moving along a straight line; Momentum The momentum (p) of a body is the product of its mass and velocity. P = mv. The unit is kilogram
analyse impulse, and momentum transfer, in collisions between objects moving along a straight line; Momentum The momentum (p) of a body is the product of its mass and velocity. P = mv. The unit is kilogram
FIS Specifications for Flex Poles (Edition May 2008) Original Text: German
 FIS Specifications for Flex Poles (Edition May 2008) Original Text: German 1 Field of Application and Basic Information The following FIS specifications for flex poles are intended to ensure that flex
FIS Specifications for Flex Poles (Edition May 2008) Original Text: German 1 Field of Application and Basic Information The following FIS specifications for flex poles are intended to ensure that flex
Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum and Collisions Objectives: You Should Be Able To: Define and give examples of impulse and momentum along with appropriate units. Write and apply a relationship between impulse and momentum in
Momentum and Collisions Objectives: You Should Be Able To: Define and give examples of impulse and momentum along with appropriate units. Write and apply a relationship between impulse and momentum in
Summary. Chapter summary. Teaching Tip CHAPTER 6
 Chapter summary Teaching Tip Ask students to prepare a concept map for the chapter. The concept map should include most of the vocabulary terms, along with other integral terms and concepts. CHAPTER 6
Chapter summary Teaching Tip Ask students to prepare a concept map for the chapter. The concept map should include most of the vocabulary terms, along with other integral terms and concepts. CHAPTER 6
INTRODUCTION TO PIEZO TRANSDUCERS
 PIEZO SYSTEMS, INC. 65 Tower Office Park Woburn, MA 01801 USA Tel: 781 933 4850 Fax: 781 933 4743 email: sales@piezo.com Find Search for a product or category HOME PRODUCTS CUSTOM OEM CATALOG TECHNICAL
PIEZO SYSTEMS, INC. 65 Tower Office Park Woburn, MA 01801 USA Tel: 781 933 4850 Fax: 781 933 4743 email: sales@piezo.com Find Search for a product or category HOME PRODUCTS CUSTOM OEM CATALOG TECHNICAL
HT600 Dat e Code: 2 - HT MW Purchase Date: PLEASE RETAIN THIS INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE. All Rights Reserved
 We strive to ensure that our products are of the highest quality and free of manufacturing defects or missing parts. However, if you have any problems with your new product, D O NOT RETURN IT TO THE STORE,
We strive to ensure that our products are of the highest quality and free of manufacturing defects or missing parts. However, if you have any problems with your new product, D O NOT RETURN IT TO THE STORE,
I. What are Earthquakes?
 I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
Momentum and Collisions. Resource Class/momentum/momtoc.html
 Momentum and Collisions Resource http://www.physicsclassroom.com/ Class/momentum/momtoc.html Define Inertia The property of any body to resist changes in its state of motion. The measure of Inertia is:
Momentum and Collisions Resource http://www.physicsclassroom.com/ Class/momentum/momtoc.html Define Inertia The property of any body to resist changes in its state of motion. The measure of Inertia is:
Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object s momentum changes?
 Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere. Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object
Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere. Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object
Chapter5 SUMMARY. Key Equations
 Chapter5 SUMMARY Key Expectations define and describe the concepts and units related to momentum (momentum, impulse, elastic collisions, inelastic collisions) (5.1, 5.2, 5.3) analyze, with the aid of vector
Chapter5 SUMMARY Key Expectations define and describe the concepts and units related to momentum (momentum, impulse, elastic collisions, inelastic collisions) (5.1, 5.2, 5.3) analyze, with the aid of vector
Momentum & Impulse. To increase an objects momentum, either increase its or its. Momentum is a, so DIRECTION is a necessity.
 Momentum: p mv Momentum & Impulse To increase an objects momentum, either increase its or its. Momentum is a, so DIRECTION is a necessity. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Momentum: p mv Momentum & Impulse To increase an objects momentum, either increase its or its. Momentum is a, so DIRECTION is a necessity. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION
 CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Q 1. What is a force? Ans: Force is a push or pull which tries to bring the change in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Unit of force: force
CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Q 1. What is a force? Ans: Force is a push or pull which tries to bring the change in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Unit of force: force
Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator is allowed.
 SECONDARY SCHOOLS FINAL EXAMINATIONS 2002 Educational Assessment Unit - Education Division FORM 5 PHYSICS TIME: 1 hr 45 min NAME: CLASS: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator
SECONDARY SCHOOLS FINAL EXAMINATIONS 2002 Educational Assessment Unit - Education Division FORM 5 PHYSICS TIME: 1 hr 45 min NAME: CLASS: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator
Physics! Review Problems Unit A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s.
 Name Physics! Review Problems Unit 8 1. A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s. a) What is the initial momentum of the body? b) What is the final momentum
Name Physics! Review Problems Unit 8 1. A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s. a) What is the initial momentum of the body? b) What is the final momentum
FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION
 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q. 1 Which of the following has more inertia : (a) A rubber ball and a stone of the same size? (b) A bicycle and a train? (c) A five rupees
9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q. 1 Which of the following has more inertia : (a) A rubber ball and a stone of the same size? (b) A bicycle and a train? (c) A five rupees
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 6
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 6 1. Which has the greater momentum, an 18-wheeler parked at the curb or a Volkswagen rolling down a hill? a. 18-wheeler b. Volkswagen c. The
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 6 1. Which has the greater momentum, an 18-wheeler parked at the curb or a Volkswagen rolling down a hill? a. 18-wheeler b. Volkswagen c. The
Change in Time = Final speed -Beginning speed Acceleration
 Name: 1. Solving acceleratiol'1 problems Solve the following problems using the equation for acceleration. Remember the units for acceleration are meters per ond per ond or ml. The first problem is done
Name: 1. Solving acceleratiol'1 problems Solve the following problems using the equation for acceleration. Remember the units for acceleration are meters per ond per ond or ml. The first problem is done
m/s m/s m/s m/s
 P and J review Name 10-FEB-03 1. The diagram shows two carts on a horizontal, frictionless surface being pushed apart when a compressed spring attached to one of the carts is released. Cart A has a mass
P and J review Name 10-FEB-03 1. The diagram shows two carts on a horizontal, frictionless surface being pushed apart when a compressed spring attached to one of the carts is released. Cart A has a mass
1/9/2017. Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion, revisited
 Discuss the forces involved (relative size, direction, name of, etc.) in each of the following scenarios: Coasting to a stop at a stop sign Crashing into wall during a car race Accelerating to the speed
Discuss the forces involved (relative size, direction, name of, etc.) in each of the following scenarios: Coasting to a stop at a stop sign Crashing into wall during a car race Accelerating to the speed
AP Physics 1 Momentum
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 AP Physics 1 Momentum 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse-Momentum Equation The Momentum of a
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 AP Physics 1 Momentum 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse-Momentum Equation The Momentum of a
Instructions. 2. This examination consists of two parts. Part A: 10 multiple-choice questions and Part B: 15 constructed-response questions.
 PHY-500.A09! Question Booklet Instructions 1. Write the required information on the title page of the Student Booklet. 2. This examination consists of two parts. Part A: 10 multiple-choice questions and
PHY-500.A09! Question Booklet Instructions 1. Write the required information on the title page of the Student Booklet. 2. This examination consists of two parts. Part A: 10 multiple-choice questions and
Risk Assessment and Management System (RAMS)
 Risk Assessment and Management System (RAMS) The purpose of the RAMS is; To identify possible hazards To identify measures that will prevent, minimise or isolate those hazards In the event of harm, identify
Risk Assessment and Management System (RAMS) The purpose of the RAMS is; To identify possible hazards To identify measures that will prevent, minimise or isolate those hazards In the event of harm, identify
Momentum Mass in Motion
 Momentum Mass in Motion What do you think that means? Based on this description, what two things do you think affect momentum? 1 Momentum Inertia in motion Why are supertanker engines shut off 25 km from
Momentum Mass in Motion What do you think that means? Based on this description, what two things do you think affect momentum? 1 Momentum Inertia in motion Why are supertanker engines shut off 25 km from
Finite Element Modeling of an Aluminum Tricycle Frame
 Finite Element Modeling of an Aluminum Tricycle Frame A. Rodríguez, B. Chiné*, and J. A. Ramírez Costa Rica Institute of Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Cartago, Costa Rica *Corresponding
Finite Element Modeling of an Aluminum Tricycle Frame A. Rodríguez, B. Chiné*, and J. A. Ramírez Costa Rica Institute of Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Cartago, Costa Rica *Corresponding
Ordinary Level Physics Long Questions: ACCELERATION, FORCE, MOMENTUM, ENERGY
 Ordinary Level Physics Long Questions: ACCELERATION, FORCE, MOMENTUM, ENERGY Equations of motion (vuast) 2004 Question 6 [Ordinary Level] (i) Define velocity. (ii) Define acceleration. (iii)describe an
Ordinary Level Physics Long Questions: ACCELERATION, FORCE, MOMENTUM, ENERGY Equations of motion (vuast) 2004 Question 6 [Ordinary Level] (i) Define velocity. (ii) Define acceleration. (iii)describe an
HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum
 HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum LESSON OBJECTIVES Students will be able to... understand that forces can act over time (impulse) resulting in changes in momentum identify characteristics of motion with
HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum LESSON OBJECTIVES Students will be able to... understand that forces can act over time (impulse) resulting in changes in momentum identify characteristics of motion with
Grade 3: Rocks and Minerals
 Grade 3: Rocks and Minerals Lesson 2: Cracking the Crust Lesson Objective: Students Magic School Bus breaks through the soil of the crust and moves through the three layers of rock in the Earth s crust.
Grade 3: Rocks and Minerals Lesson 2: Cracking the Crust Lesson Objective: Students Magic School Bus breaks through the soil of the crust and moves through the three layers of rock in the Earth s crust.
Newton s Second Law of Motion
 Newton s Second Law of Motion Topic Newton s second law of motion describes how acceleration is related to force and mass. Introduction Newton s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an
Newton s Second Law of Motion Topic Newton s second law of motion describes how acceleration is related to force and mass. Introduction Newton s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an
Unit 2: Newton s Laws Note 1 : Forces
 Unit 2: Newton s Laws Note 1 : Forces Force: The units of force are: There are four fundamental forces that make up all of the forces in the universe: 1) 2) 3) 4) Force of Gravity Force of Gravity: The
Unit 2: Newton s Laws Note 1 : Forces Force: The units of force are: There are four fundamental forces that make up all of the forces in the universe: 1) 2) 3) 4) Force of Gravity Force of Gravity: The
1817. Research of sound absorption characteristics for the periodically porous structure and its application in automobile
 1817. Research of sound absorption characteristics for the periodically porous structure and its application in automobile Xian-lin Ren School of Mechatronics Engineering, University of Electronic Science
1817. Research of sound absorption characteristics for the periodically porous structure and its application in automobile Xian-lin Ren School of Mechatronics Engineering, University of Electronic Science
MECHANICS: LINEAR MECHANICS QUESTIONS
 MECHANICS: LINEAR MECHANICS QUESTIONS QUESTION ONE (2017;1) Two astronauts, Sylvia and Sam, are on a mission to another planet. During their journey they are doing a spacewalk outside their spaceship.
MECHANICS: LINEAR MECHANICS QUESTIONS QUESTION ONE (2017;1) Two astronauts, Sylvia and Sam, are on a mission to another planet. During their journey they are doing a spacewalk outside their spaceship.
Study Guide For Midterm - 25 weeks Physics Exam. d. the force exerted by a towing cable on the car. c. the upward force the road exerts on the car.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Study Guide For Midterm - 25 weeks Physics Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Study Guide For Midterm - 25 weeks Physics Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015 EXAM 2: April 2, 2015 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015 EXAM 2: April 2, 2015 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
