APPLICATION OF ENERGY ABSORBING CONNECTERS TO STEEL CONTINUOUS GIRDER BRIDGES
|
|
|
- Brendan Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 th World Conference on Earthqake Engineering Vancover, B.C., Canada Agst 1-6, 24 Paer No APPLICATION OF ENERGY ABSORBING CONNECTERS TO STEEL CONTINUOUS GIRDER BRIDGES Hiroshi ZUI 1 and Yoshio NAMITA 2 SUMMARY The efficienc of a seismic energ dissiation device is stdied. Steel bellows are connected between girders and abtments in order to redce the damage of steel bridges. The effectiveness of the bellows is verified b the dnamic resonse analses for three-san steel continos girders on rbber bearings. The iers are single colmn te made of reinforced concrete designed nder L1 or L2 earthqake condition of Jaanese code. Their heights are varied in three was. The seismic erformances are examined nder varios combinations of designed iers. Frthermore, estimation formlas concerning the maximm dislacement of serstrctre and iers are develoed b considering the energ balance between seismic int energ and dissiated hsteretic energ, and their validities are evalated b comaring with nonlinear dnamic resonse analses. The estimation formlas rodce good reslts in site of their simlicit, and therefore the are efficient for selection of sitable bellows. INTRODUCTION Passive base isolation sch as rbber bearings can redce damage of bridges de to the increase of the fndamental vibration eriod and the additional daming rovided to dissiate the seismic energ. However, it becomes ossible to case collision between girders or between girders and abtments de to large longitdinal dislacements of the serstrctre sbjected strong earthqakes. This collision reslts in increased failre of ser- and sbstrctres. The varios kinds of mitigation devices sch as rbber te and metal te have been investigated and these stdies show that onding forces can be considerabl redced [1-3]. Most of the roosed devices are effective onl after collision and for comression. Athors have roosed a design method in which steel bellows as energ absorbing devices are connected between girders in a row or between girders and abtments [4]. The are connected to the web of girders. The bellows are effective even before collision and, moreover, both in comression and tension. The 1 Professor, Setsnan Universit, Osaka, Jaan, zi@civ.setsnan.ac.j 2 The same as above
2 characteristics of bellows were investigated b loading tests and finite element method, and the design formlas as to the initial rigidit, the ield strength and the ield dislacement of bellows were develoed. The effectiveness of steel bellows for siml sorted steel girders on metallic bearings and for steel continos girders on rbber bearings was also stdied in the case of their lacement between abtments at both ends [4]. Frthermore, a ractical method was develoed in order to decide the characteristics of bellows b sing the resonse sectrm analsis based on the eqivalent linear method. This method is effective bt reeated dnamic analses are necessar and the dislacements of serstrctre and iers tend to be overestimated. In this aer, the efficienc of steel bellows for steel continos girders on rbber bearings is investigated and a more ractical and simle method for the selection of characteristics of bellows is roosed b considering energ balance between seismic int energ and dissiated hsteretic energ. Comter rograms were develoed sing MATLAB for resonse sectrm analses and non-linear time-histor analses. Dnamic analses are carried ot also b these rograms. ANALYTICAL MODELING OF A STEEL CONTINUOUS GIRDER BRIDGE Analtical model of bridge 4.m 4.m 4.m A model of three-san continos girder is shown in Fig.1. The serstrctre consists of five steel late girders, and the total dead load is 15MN. The characteristics of the ier sed for the analsis are shown in Table 1. The iers are A1 A2 single colmn te made of reinforced concrete. Their P1 heights are varied in three was. P2 Fig. 1 A Continos girder The ier section characteristics were decided for two strength level, small (L1 level) and medim (L2 level). In on rbber bearings the design of ier, effective weight of the serstrctre was assmed to be dead load reaction force (5.MN) to all iers regardless of their heights. The longitdinal strengths and the dislacements are shown in Table 1 at the oint of ield initiation of steel bars and at an ltimate state. The strengths are exressed b the seismic intensities. The intensities of the iers designed b L1 earthqake are abot.4 and the intensit of the ier designed b L2 earthqake is abot.6. Table 2 shows the case of analsis in terms of the combination of ier te. Lead rbber bearings (LRB) are sed for the rose of seismic base isolation. The dimensions of LRB are decided so that the fndamental eriod coincides with the target eriod, and the maximm shearing strain in rbber does not exceed 25%. Table 2 shows combination cases of iers and the maximm dislacements obtained b the static design based on the dctilit design method. In the first colmn of Table 2, S means small strength ier and C means medim strength ier. The nmbers next to S or C show ier heights of P1 and P2. For examle, S618 means the ier combination where P1 and P2 are designed b L1 earthqake and their heights are 6m and 18m, resectivel. Since LRB have non-linear hsteretic Table 1 Characteristics of concrete iers Strength of Piers Small (Level 1) Medim (Level 2) Height of Pier (m) Weight of Piers (kn) Steel Rods Area (cm 2 ) Yield initiation Ultimate state Horizontal strength (Seismic intensit) Strength (kn) Dis. (cm) Strength (kn) Dis. (cm)
3 Table 2 Combination cases of iers and Dislacements obtained b Static Design Name of case Serstrctre Pier P1 (cm) Pier P2 (cm) (cm) Pier LRB Pier LRB S S S S S S C C C C C C P P P P Fig. 2 Force vs. dis. relationshi of hsteretic bi-linear srings Fig. 3 Hsteretic modified Takeda model srings characteristics, the load dislacement crves of LRB are exressed b hsteretic bi-linear srings. The rigidit of nloading is eqal to the initial rigidit. The hsteretic model of bi-linear te is shown in Fig.2. We examine here the behaviors in longitdinal direction, and the serstrctre is treated as rigid bodies. The dislacements of abtment are disregarded since it is rigid enogh. The nmber of degrees of freedom is three in total (serstrctre and two middle iers). The force-dislacement law of iers is reresented b the modified Takeda model which can treat the degradation effects nder cclic loading. Fig.3 shows hsteretic load-dislacement crve of the modified Takeda model. Mechanical characteristics of steel bellows The steel bellow connected between a girder end and an abtment is shown in Fig.4. Two steel lates are bent in semicirclar shaes and are connected to the web of a girder and to the anchored late. Fig. 5 shows loading and nloading aths obtained b the laborator tests and FEM analses [4]. The width of the secimen is 25cm, the radis is 15cm and the thickness is 1.9cm. Strictl seaking, the inclinations of the loading ass after ielding of the comression side are less stee than the tension side, and as nloading-reloading advances to oosite direction, this tendenc becomes more consicos. However, the loading and nloading aths are aroximated b the hsteretic Steel bellows Girder Shoe Abtment Fig. 4 Steel bellows connected to abtment and its cross section
4 bi-linear srings shown in Fig.2 for simlicit. The design formlas were shown in [4] concerning the strctral characteristics sch as ield strength, ield dislacement and maximm strength of bellows. Resonse sectrm and seismic wave The resonse analses are carried ot in the next chater b taking into accont onl the behaviors in longitdinal direction for the whole strctre. Fig. 6(a) shows the sed resonse sectra that are given in Jaanese seismic code for soil te 2 [5]. Time-histor analses are also carried ot in the next chater b taking into accont the non-linear behaviors. As an int data of seismic wave we se acceleration time histories that are obtained from the actal Fig. 5 Loading and nloading aths of secimen earthqakes and so modified as to satisf the sectrm for L2 earthqake (Te II). The seismic wave sed is shown in Fig. 6(b). (b) A time histor of acceleration (a) Resonse sectrm (L2,TeII) Fig. 6 Resonse sectra and a time histor of acceleration APPLICATION OF STEEL BELLOWS TO A STEEL CONTINUOUS GIRDER BRIDGE Calclation reslts of dnamic analses in case withot bellows The cases with sal restrainers (withot bellows) in which the energ absorbing is not exected are calclated first for comarison. In these cases, both of stiffness and daming of the restrainers are ignored becase the are not effective before the dislacement of serstrctre exceeds a certain vale. Fig.7 shows the maximm dislacements of serstrctre and iers obtained b two dnamic resonse analses, the resonse sectrm analses based on the eqivalent linear method and the non-linear time-histor analses. The rocedre of the resonse sectrm analses is as follows. First, the effective dislacements of ier and LRB are assmed, and then eqivalent linear stiffness and the daming ratios of non-linear sring elements are calclated. The resonse vales are calclated from the resonse sectrm analses. Calclations are reeated ntil the differences between the obtained dislacements and the assmed dislacements become within 5% [4]. In Fig.7, s means reslts of the resonse sectrm analses and nl means reslts of the non-linear time-histor analses. The differences between calclated vales b resonse sectrm analses and non-linear time-histor analses are small. The resonse sectrm analses based on the eqivalent linear method can be a ractical and effective means as a design method in case withot bellows. The dislacements of small strength iers are considerabl large in comarison with those of medim strength iers. Some of the dislacements of small strength iers exceed the ltimate dislacement. Fig.8 shows the time-histor resonse of the dislacements of
5 .6 _max(m) t_s 1_s 2_s t_nl 1_nl 2_nl iers and the load dislacement crve of iers in case of S618 in which the difference of ier heights is largest. It can be confirmed that large energ absorbing is demonstrated from the load dislacement histor crve of the iers. To clarif the amonts of the energ absorbing of the iers and LRB qantitativel, the amonts of energ absortion of each set of iers and rbber bearings are calclated. Fig.9 shows the accmlated time-histor resonses in terms of energ absortion of iers and of the bearing, resectivel, for S618 and C618. In case of S618, the amonts of energ absortion of iers are larger than those of LRB, and in case of C618, the amonts of energ absortion of iers are less than those of LRB. The iers with small strength ma case severe damages. The maximm dislacements of serstrctre shown as t in Fig.7 are almost eqal regardless of ier strength. These vales exceed 5cm and collision ma be cased in the exansion joints in these cases. S66 S1212 S1818 S612 S618 S1218 C 66 C1212 C 1818 C612 C 618 C 1218 Fig.7 Calclation reslts of dnamic analses (the maximm dislacements withot bellows) Fig. 8 Reslts of S618 b nonlinear time histor analses (withot bellows) Fig. 9 Energ absorbing of bearings and iers (S618 and C618 withot bellows) Calclation reslts obtained b dnamic analses give large vales comared with the static design shown in Table 2. Effect of steel bellows as energ absorbing connecters In case withot bellows, the maximm dislacements of serstrctre exceed 5cm. In this section, the effects of steel bellows are examined. The bellows are connected between a girder end and an abtment as
6 shown in Fig.1. Yield strengths of S66 S66 steel bellows are so decided as to S1212 S S S1818 make the dislacements of BELS66 BELS66 middle iers less than ield 8 BELS BELS1212 BELS1818 BELS1818 dislacement, and to sress the C66 C66 dislacement of serstrctre 6 C C1212 C1818 C1818 within ca. 1cm-15cm which can BELC BELC66 be absorbed b exansion joint BELC1212 BELC1212 BEL1818 BELC1818 comarativel easil. The ield 2 2 strength of bellows is determined to be abot 2%-4% of the serstrctre weight that t(m ) t(m ) corresonds to times the (a) R es.sec. (b) N on linear Time Hist. seismic force cased b L1 earthqake. The comarison of Fig. 1 Comarison of maximm dislacements the maximm resonse with and withot bellows ( P / W =. 4 ) dislacement of cases with and withot bellows is shown in Fig.1 b sing same height iers model. The same ield strength of bellows, P / W =. 4 is sed for all cases where P is the total ield strength of both side bellows and W is the total weight of serstrctre. In Fig.1, (a) shows the reslts of the resonse sectrm analses and (b) shows the reslts of the non-linear time histor resonse analses. The ordinate of Fig.1 shows normalized ier dislacements sing ield dislacement of each ier. The abscissa of Fig.1 shows dislacements of serstrctre. The reslts with bellows are shown as BEL and their marks are ainted ot with black color. The reslts of the resonse sectrm analses give relativel larger vales than those of the non-linear time histor resonse analses of case with bellows. We observe that the dislacements of serstrctre and iers can be redced to large extent b sing steel bellows. We mst oint ot here that if the same ield strength of bellows are sed, the maximm dislacement of serstrctre becomes almost same regardless of ier strength or height on the reslts of the non-linear time histor analses. Since the resonse sectrm analses give relativel larger dislacements in case with bellows, a more recise design method is needed in order to decide the sitable characteristics of steel bellows. A design method of steel bellows as energ absorbing connecters We note here that the behavior of serstrctre with bellows is similar in case of same ield strength of bellows. Fig.11 shows energ absorbing of hsteretic members in case of small strength and high iers, BELS1818, and in case of medim strength and low iers, BELC66. The energ absorbing amont of bellows is dominant for both cases even thogh the energ absorbing of iers in BELS1818 is considerabl larger than in BELC66. This fact sggests that a continos girder with bellows can be modeled in one nonlinear hsteretic sring and one mass. Man methods have been roosed to estimate the maximm inelastic dislacement of single-degree-of-freedom sstems [6-7]. In most methods, the maximm dislacement is estimated from the maximm dislacement of linear elastic sstems. / Fig. 11 Energ absorbing of bellows, bearings and iers (S1818 and C66 with bellows) /
7 Matsda et al. show that a estimation method based on non-linear energ absortion resonse sectra gives more recise vales than a estimation method based on linear energ absortion resonse sectra [8]. Single-degree-of-freedom model sed is shown in Fig.12. The calclated the nonlinear histor absortion energ b sing bi-linear model of the erfect elasto-lasticit. So as not to deend on the size of mass, the absortion energ is converted into the eqivalent velocit. T T E = f ( ) & dt = f ( ) d, Ve = 2E / m (1) We calclated the eqivalent velocit sing the seismic wave shown in Fig.6(b). Since second stiffness of lastic region in bellows hsteretic crves affects the amont of absortion energ, the ratio of second stiffness to first stiffness is assmed to be.5 and is taken into accont. Fig.13 shows the non-linear sectra in which the eqivalent velocit is lotted for the elastic eriod. As shown in Fig.14, hsteretic absorbing energ in a ccle of the bi-linear sring is exressed as follows. Whs = 4(1 γ ) P ( max ) (2) When we assme that onl members of steel bellows absorb int seismic energ, total seismic energ is exressed: E = n W hs (3) where n means hsteretic nmber when assming that the bi-linear sring reeats hsteretic crve b the maximm dislacement. The maximm dislacement of the serstrctre with bellows is estimated from the following rocedre. 1) B assming the ratio, P / W, ield strength of bellows to total weight of serstrctre, the eqivalent velocit, V e, is read ot from the elastic eriod sing Fig.13. 2) The total seismic energ, E, is conted backward from V e. 3) Select the coefficient n. 4) Estimate the maximm dislacement from the balance between E and the absorbing hsteretic energ n Whs. E max = + (4) 4n(1 γ ) P B this method the maximm dislacement can be resmed withot reeating the calclation. Fig.15 shows the comarison of estimated maximm dislacement and calclated maximm dislacement from non-linear dnamic analsis. m ax(m ) Ve(m/s) m = W / g Hsteretic bisring li Fig.12 Single-degree-offreedom model P /W =.2 P /W =.25 P /W =.3 P /W =.35 P /W = Elastic Period T (s) Fig.13 Non-linear sectra of h t ti Absorbing energ γ = k / k 2 1 W W hs hs P Fig. 14 Hsteretic absorbing energ of bi-linear srings n=2.5 n=3. n=3.5 n=4. calclated P/W Fig. 15 Estimated maximm dislacement from energ balance P k 1 k 2 max = 4(1 γ ) P ( max )
8 The model sed in the non-linear dnamic analsis is S1218 in Table 2. LRB When n = 3 is adoted, the sring f b estimated maximm dislacement gives the vale of the safe side with a m = W / g excetion of the case P / W =. 4. f inert = αkhw Pier f The maximm dislacements of iers sring are estimated from the balance of forces acting on the ier as shown in Fig.16 Forces acting to a ier Fig.16. f = fb + f iner (5) where f b is the sring force of the LRB, f is the sring force of the ier and f iner is the inertia force of the ier. Assming iers are within elastic range: f = k, f iner = α khw (6) where k is ier stiffness within elastic range and k H is seismic coefficient obtained from the resonse sectra (Fig.6(a)) according to the elastic eriod of the ier, 2π W /( gk ) where W is the effective weight of the ier. In Eq. (6), α is the modified coefficient smaller than 1 for the rose of adjsting the inflence that neither the dislacement nor the acceleration becomes maximm at the same time. The sring force of the bearing, f b is obtained as follows: fb = Pb + kb2( T b ) (7) where P b and b is the ield strength and the ield dislacement of the LRB, resectivel. k b2 is the second stiffness of the LRB after ielding, and T is the dislacement of the serstrctre. Sbstitting Eqs. (6) and (7) into Eq. (5): = P + k ) + k W /( k + k (8) { } ) b b2 ( T b H b2 Evalation of the estimation method The exact estimation of the maximm dislacements of the serstrctre and the iers is imortant in erformance-based seismic design. Non-linear time histor analses are carried ot in order to evalate the roosed estimation method throgh the comarison with exact reslts. The maximm dislacements T _max(m) L R B S 61 8 t_es 1_es 2_es t_cal 1_cal 2_cal P/W _m ax LRB S1218 t_es 1_es 2_es t_c al 2_cal 2_es P/W (a) S618 (b) S1218 Fig. 17 Maximm dislacements estimated b the roosed method and obtained b non-linear analses
9 estimated b the roosed method and the maximm dislacements obtained b non-linear analses are shown in Fig.17. The reslts of model S618 are shown in (a) and the reslts of model S1218 are shown in (b) in Fig.17. In Fig.17, t means the maximm dislacements of the serstrctre, and 1 and 2 means the maximm dislacements of Pier 1 and Pier 2, resectivel. Also, _es exresses the estimated vales and _cal shows the calclated vales b non-linear time histor analses. The coefficients n in Eq.(4) and α in Eq.(6) are assmed to be 3 and.6, resectivel, for all cases. Thogh the roosed method tends to overestimate the maximm dislacements, it gives a relativel good estimation of the maximm dislacements for both serstrctre and iers. Steel bellows decrease the maximm dislacement of serstrctre within 15cm and the enable iers to be within the range of elasticit even for the ier designed for L1 earthqake. It can be seen that the maximm dislacements become small as the ield strength of the bellows is enlarged to some extent bt frther enlarging cannot be effective. Practicall, the recommended vales of the ratio of P / W are from.2 to.3 according to the extent of the maximm dislacement which the serstrctre demands in these models. CONCLUSION The effect of the steel bellows as girder connecters of energ absorbing te have been stdied b means of the non-linear time histor analses for continos girders on rbber bearings. Also, a ractical method is roosed to estimate the maximm dislacement of the serstrctre and iers sing energ balance when the steel bellows are attached between girders and abtments. The main conclsions of these stdies are: Steel bellows redce considerabl the dislacements of serstrctre and seismic forces to iers. Calclation vales obtained from the develoed estimation method agree fairl well with those of the non-linear time histor analses. Desired characteristics of steel bellows are satisfied b means of adjsting the ield strength of the bellows. REFERENCES 1 JANKOWSKI R, Wilde K, FUJINO Y Redction of onding effects in elevated bridges dring earthqakes Earthqake Engineering and Strctral Dnamics, 2: 29, OBATA M. et al. Mechanical behaviors of a shock absorbing bridge restrainer late JSCE Jornal of Strctral Mechanics and Earthqake Engineering, No.612, 1999: (in Jaanese) 3 KOSHITOUGE M. et al. Energ absortion erformance of the clindrical rbber shock absorber JSCE Jornal of Strctral Mechanics and Earthqake Engineering, No.675, 21: (in Jaanese) 4 ZUI H. et al. Alication of energ absorbing connecters to steel girder bridges IABSE Smosim, "Towards a better bilt environment - innovation, sstainabilit, information technolog", Melborne, Setember Jaan Road Association Secifications of Highwa Bridges JRA, Miranda E, Riz-Garcia J Evalation of aroximate methods to estimate maximm inelastic dislacement demands Earthqake Engineering and Strctral Dnamics, 22: 31, Riddell R., Garcia J. E., Graces E. Inelastic deformation resonse of SDOF sstems sbjected to earthqakes Earthqake Engineering and Strctral Dnamics, 22: 31, Matsda T. et al. A consideration on the dislacement based design of seismicall isolated highwa bridges JSCE Jornal of Strctral Engineering, 23: Vol.46A, (in Jaanese)
Chapter 2 Introduction to the Stiffness (Displacement) Method. The Stiffness (Displacement) Method
 CIVL 7/87 Chater - The Stiffness Method / Chater Introdction to the Stiffness (Dislacement) Method Learning Objectives To define the stiffness matrix To derive the stiffness matrix for a sring element
CIVL 7/87 Chater - The Stiffness Method / Chater Introdction to the Stiffness (Dislacement) Method Learning Objectives To define the stiffness matrix To derive the stiffness matrix for a sring element
Estimation of Lateral Displacements for Offshore Monopiles in Clays based on CPT Results
 Estimation of Lateral Dislacements for Offshore Monoiles in Clas based on CPT Reslts *Garam Kim 1), Jinoh Kim 2), Incheol Kim 3), Dongho Kim 4), Bngkwon Bn 5), Yanghoon Roh 6), Ohchang Kwon 7) and Jnhwan
Estimation of Lateral Dislacements for Offshore Monoiles in Clas based on CPT Reslts *Garam Kim 1), Jinoh Kim 2), Incheol Kim 3), Dongho Kim 4), Bngkwon Bn 5), Yanghoon Roh 6), Ohchang Kwon 7) and Jnhwan
Module 4. Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Structures by the Direct Stiffness Method. Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
 Modle Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Strctres by the Direct Stiffness Method Version CE IIT, Kharagr Lesson The Direct Stiffness Method: Trss Analysis (Contined) Version CE IIT, Kharagr Instrctional
Modle Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Strctres by the Direct Stiffness Method Version CE IIT, Kharagr Lesson The Direct Stiffness Method: Trss Analysis (Contined) Version CE IIT, Kharagr Instrctional
FEA Solution Procedure
 EA Soltion rocedre (demonstrated with a -D bar element problem) MAE - inite Element Analysis Many slides from this set are originally from B.S. Altan, Michigan Technological U. EA rocedre for Static Analysis.
EA Soltion rocedre (demonstrated with a -D bar element problem) MAE - inite Element Analysis Many slides from this set are originally from B.S. Altan, Michigan Technological U. EA rocedre for Static Analysis.
BENDING INDUCED VERTICAL OSCILLATIONS DURING SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC BRIDGE PIERS
 BENDING INDUCED VERTICAL OSCILLATIONS DURING SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC BRIDGE PIERS Giulio RANZO 1, Marco PETRANGELI And Paolo E PINTO 3 SUMMARY The aer resents a numerical investigation on the behaviour
BENDING INDUCED VERTICAL OSCILLATIONS DURING SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC BRIDGE PIERS Giulio RANZO 1, Marco PETRANGELI And Paolo E PINTO 3 SUMMARY The aer resents a numerical investigation on the behaviour
3.1 Experimental Design
 3 Relay Feedback Åström and Hägglnd [1] sggest the relay feedback test to generate sstained oscillation as an alternative to the conventional continos cycling techniqe. It is very effective in determining
3 Relay Feedback Åström and Hägglnd [1] sggest the relay feedback test to generate sstained oscillation as an alternative to the conventional continos cycling techniqe. It is very effective in determining
Design of Isolated Bridges from the Viewpoint of Collapse under Extreme Earthquakes
 Design of Isolated Bridges from the Viewoint of Collase under Extreme Earthquakes D.W. Chang, Y.T. Lin, C.H. Peng, C.Y. Liou CECI Engineering Consultants, Inc., Taiwan T.Y. Lee National Central University,
Design of Isolated Bridges from the Viewoint of Collase under Extreme Earthquakes D.W. Chang, Y.T. Lin, C.H. Peng, C.Y. Liou CECI Engineering Consultants, Inc., Taiwan T.Y. Lee National Central University,
Lecture Notes: Finite Element Analysis, J.E. Akin, Rice University
 9. TRUSS ANALYSIS... 1 9.1 PLANAR TRUSS... 1 9. SPACE TRUSS... 11 9.3 SUMMARY... 1 9.4 EXERCISES... 15 9. Trss analysis 9.1 Planar trss: The differential eqation for the eqilibrim of an elastic bar (above)
9. TRUSS ANALYSIS... 1 9.1 PLANAR TRUSS... 1 9. SPACE TRUSS... 11 9.3 SUMMARY... 1 9.4 EXERCISES... 15 9. Trss analysis 9.1 Planar trss: The differential eqation for the eqilibrim of an elastic bar (above)
Lab Manual for Engrd 202, Virtual Torsion Experiment. Aluminum module
 Lab Manal for Engrd 202, Virtal Torsion Experiment Alminm modle Introdction In this modle, o will perform data redction and analsis for circlar cross section alminm samples. B plotting the torqe vs. twist
Lab Manal for Engrd 202, Virtal Torsion Experiment Alminm modle Introdction In this modle, o will perform data redction and analsis for circlar cross section alminm samples. B plotting the torqe vs. twist
FEA Solution Procedure
 EA Soltion Procedre (demonstrated with a -D bar element problem) EA Procedre for Static Analysis. Prepare the E model a. discretize (mesh) the strctre b. prescribe loads c. prescribe spports. Perform calclations
EA Soltion Procedre (demonstrated with a -D bar element problem) EA Procedre for Static Analysis. Prepare the E model a. discretize (mesh) the strctre b. prescribe loads c. prescribe spports. Perform calclations
FEA Solution Procedure
 EA Soltion Procedre (demonstrated with a -D bar element problem) MAE 5 - inite Element Analysis Several slides from this set are adapted from B.S. Altan, Michigan Technological University EA Procedre for
EA Soltion Procedre (demonstrated with a -D bar element problem) MAE 5 - inite Element Analysis Several slides from this set are adapted from B.S. Altan, Michigan Technological University EA Procedre for
UNCERTAINTY FOCUSED STRENGTH ANALYSIS MODEL
 8th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING - 19-1 April 01, Tallinn, Estonia UNCERTAINTY FOCUSED STRENGTH ANALYSIS MODEL Põdra, P. & Laaneots, R. Abstract: Strength analysis is a
8th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING - 19-1 April 01, Tallinn, Estonia UNCERTAINTY FOCUSED STRENGTH ANALYSIS MODEL Põdra, P. & Laaneots, R. Abstract: Strength analysis is a
DISPLACEMENT ANALYSIS OF SUBMARINE SLOPES USING ENHANCED NEWMARK METHOD
 DISPLACEMENT ANALYSIS OF SUBMARINE SLOPES USING ENHANCED NEWMARK METHOD N. ZANGENEH and R. POPESCU Faclt of Engineering & Applied Science, Memorial Universit, St. John s, Newfondland, Canada A1B 3X5 Abstract
DISPLACEMENT ANALYSIS OF SUBMARINE SLOPES USING ENHANCED NEWMARK METHOD N. ZANGENEH and R. POPESCU Faclt of Engineering & Applied Science, Memorial Universit, St. John s, Newfondland, Canada A1B 3X5 Abstract
Title. Author(s)ALAMIRI, M. ASSAD; GOTO, YOSHIAKI. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information
 Title ULTIATE STATE O THIN-WALLED HOLLOW CIRCULAR STEEL DIRECTIONAL HORIZONTAL SEISIC ORCES AND TRI-DIRECT Athor(s)ALAIRI. ASSAD; GOTO OSHIAKI Isse Date 013-09-1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/115/54373
Title ULTIATE STATE O THIN-WALLED HOLLOW CIRCULAR STEEL DIRECTIONAL HORIZONTAL SEISIC ORCES AND TRI-DIRECT Athor(s)ALAIRI. ASSAD; GOTO OSHIAKI Isse Date 013-09-1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/115/54373
Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Linear Boundary Value Problems
 International Jornal of Crrent Engineering and Technolog E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/categor/ijcet Research Article Homotop
International Jornal of Crrent Engineering and Technolog E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/categor/ijcet Research Article Homotop
Chapter 1: Differential Form of Basic Equations
 MEG 74 Energ and Variational Methods in Mechanics I Brendan J. O Toole, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Howard R. Hghes College of Engineering Universit of Nevada Las Vegas TBE B- (7)
MEG 74 Energ and Variational Methods in Mechanics I Brendan J. O Toole, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Howard R. Hghes College of Engineering Universit of Nevada Las Vegas TBE B- (7)
SOIL NON-LINEAR BEHAVIOR AND HYSTERETIC DAMPING IN THE SPRING-DASHPOT ANALOG
 SOIL NON-LINEAR BEHAVIOR AND HYSTERETIC DAMPING IN THE SPRING-DASHPOT ANALOG Nikolaos OROLOGOPOULOS 1 and Dimitrios LOUKIDIS 2 ABSTRACT This paper presents reslts from nmerical simlations of footing vibration
SOIL NON-LINEAR BEHAVIOR AND HYSTERETIC DAMPING IN THE SPRING-DASHPOT ANALOG Nikolaos OROLOGOPOULOS 1 and Dimitrios LOUKIDIS 2 ABSTRACT This paper presents reslts from nmerical simlations of footing vibration
Simplified Identification Scheme for Structures on a Flexible Base
 Simplified Identification Scheme for Strctres on a Flexible Base L.M. Star California State University, Long Beach G. Mylonais University of Patras, Greece J.P. Stewart University of California, Los Angeles
Simplified Identification Scheme for Strctres on a Flexible Base L.M. Star California State University, Long Beach G. Mylonais University of Patras, Greece J.P. Stewart University of California, Los Angeles
A Parametrical Analysis for the Rotational Ductility of Reinforced Concrete Beams
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net 242 The Open Civil Engineering Jornal, 2013, 7, 242-253 Open Access A Parametrical Analsis for the Rotational Dctilit of Reinforced Concrete Beams
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net 242 The Open Civil Engineering Jornal, 2013, 7, 242-253 Open Access A Parametrical Analsis for the Rotational Dctilit of Reinforced Concrete Beams
A Numerical Method for Critical Buckling Load for a Beam Supported on Elastic Foundation
 A Numerical Method for Critical Buckling Load for a Beam Suorted on Elastic Foundation Guo-ing Xia Institute of Bridge Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning Province, P. R. China
A Numerical Method for Critical Buckling Load for a Beam Suorted on Elastic Foundation Guo-ing Xia Institute of Bridge Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning Province, P. R. China
Sareban: Evaluation of Three Common Algorithms for Structure Active Control
 Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 7, No. 3, 2017, 1638-1646 1638 Evalation of Three Common Algorithms for Strctre Active Control Mohammad Sareban Department of Civil Engineering Shahrood
Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 7, No. 3, 2017, 1638-1646 1638 Evalation of Three Common Algorithms for Strctre Active Control Mohammad Sareban Department of Civil Engineering Shahrood
COMPARISON OF FREQUENCY DEPENDENT EQUIVALENT LINEAR ANALYSIS METHODS
 October 2-7, 28, Beijing, China COMPARISON OF FREQUENCY DEPENDENT EQUIVALENT LINEAR ANALYSIS METHODS Dong-Yeo Kwak Chang-Gyun Jeong 2 Duhee Park 3 and Sisam Park 4 Graduate student, Det. of Civil Engineering,
October 2-7, 28, Beijing, China COMPARISON OF FREQUENCY DEPENDENT EQUIVALENT LINEAR ANALYSIS METHODS Dong-Yeo Kwak Chang-Gyun Jeong 2 Duhee Park 3 and Sisam Park 4 Graduate student, Det. of Civil Engineering,
Evaluation of the Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics Interfacial Behavior by using Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Method
 17th World Conference on Nondestrctive Testing, 5-8 Oct 008, Shanghai, China Evalation of the Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics Interfacial Behavior by sing Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Method Jnjie CHANG
17th World Conference on Nondestrctive Testing, 5-8 Oct 008, Shanghai, China Evalation of the Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics Interfacial Behavior by sing Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Method Jnjie CHANG
CONSIDERATION OF COLLAPSE AND RESIDUAL DEFORMATION IN RELIABILITY-BASED PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF BUILDINGS
 13 th World Conference on Earthqake Engineering Vancover, B.C., Canada Agst 1-6, 24 Paper No. 716 CONSIDERATION OF COLLAPSE AND RESIDUAL DEFORMATION IN RELIABILITY-BASED PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF BUILDINGS
13 th World Conference on Earthqake Engineering Vancover, B.C., Canada Agst 1-6, 24 Paper No. 716 CONSIDERATION OF COLLAPSE AND RESIDUAL DEFORMATION IN RELIABILITY-BASED PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF BUILDINGS
1 Differential Equations for Solid Mechanics
 1 Differential Eqations for Solid Mechanics Simple problems involving homogeneos stress states have been considered so far, wherein the stress is the same throghot the component nder std. An eception to
1 Differential Eqations for Solid Mechanics Simple problems involving homogeneos stress states have been considered so far, wherein the stress is the same throghot the component nder std. An eception to
Elements. Using ABSTRACT. 1. Introduction. Anish Bangalore, India. tioned devices. often consist packed. This offering both.
 Jornal of Alied Mathematics and Physics,, 201, 1, 20-25 Pblished Online November 201 (htt://www.scir.org/jornal/jam) htt://dx.doi.org/10.426/jam..201.16005 A Monolithic, FEM-Based Aroach for the Coled
Jornal of Alied Mathematics and Physics,, 201, 1, 20-25 Pblished Online November 201 (htt://www.scir.org/jornal/jam) htt://dx.doi.org/10.426/jam..201.16005 A Monolithic, FEM-Based Aroach for the Coled
IMPROVED ANALYSIS OF BOLTED SHEAR CONNECTION UNDER ECCENTRIC LOADS
 Jornal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 373-38 (17) 373 DOI: 1.6119/JMST-17-3-1 IMPROVED ANALYSIS OF BOLTED SHEAR ONNETION UNDER EENTRI LOADS Dng-Mya Le 1, heng-yen Liao, hien-hien
Jornal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 373-38 (17) 373 DOI: 1.6119/JMST-17-3-1 IMPROVED ANALYSIS OF BOLTED SHEAR ONNETION UNDER EENTRI LOADS Dng-Mya Le 1, heng-yen Liao, hien-hien
Effects of Soil Spatial Variability on Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundations
 Geotechnical Safety and Risk V T. Schweckendiek et al. (Eds.) 2015 The athors and IOS Press. This article is pblished online with Open Access by IOS Press and distribted nder the terms of the Creative
Geotechnical Safety and Risk V T. Schweckendiek et al. (Eds.) 2015 The athors and IOS Press. This article is pblished online with Open Access by IOS Press and distribted nder the terms of the Creative
BIFURCATIONS OF TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR A GENERALIZED CAMASSA-HOLM EQUATION
 Jornal of Alied Analsis and Comtation Volme 8, Nmber 6, December 8, 85 86 Website:htt://jaac.ijornal.cn DOI:.98/8.85 BIFURCATIONS OF TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR A GENERALIZED CAMASSA-HOLM EQUATION Minzhi
Jornal of Alied Analsis and Comtation Volme 8, Nmber 6, December 8, 85 86 Website:htt://jaac.ijornal.cn DOI:.98/8.85 BIFURCATIONS OF TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR A GENERALIZED CAMASSA-HOLM EQUATION Minzhi
ELASTO-PLASTIC BUCKLING BEHAVIOR OF H-SHAPED BEAM WITH LARGE DEPTH-THICKNESS RATIO UNDER CYCLIC LOADING
 SDSS Rio STABILITY AND DUCTILITY OF STEEL STRUCTURES E. Batista, P. Vellasco, L. de Lima (Eds.) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Setember 8 -, ELASTO-PLASTIC BUCKLING BEHAVIOR OF H-SHAPED BEA WITH LARGE DEPTH-THICKNESS
SDSS Rio STABILITY AND DUCTILITY OF STEEL STRUCTURES E. Batista, P. Vellasco, L. de Lima (Eds.) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Setember 8 -, ELASTO-PLASTIC BUCKLING BEHAVIOR OF H-SHAPED BEA WITH LARGE DEPTH-THICKNESS
Period #5: Strain. A. Context. Structural mechanics deals with the forces placed upon mechanical systems and the resulting deformations of the system.
 Period #5: Strain A. Contet Strctral mechanics deals with the forces placed pon mechanical sstems and the reslting deformations of the sstem. Solid mechanics on the smaller scale relates stresses in the
Period #5: Strain A. Contet Strctral mechanics deals with the forces placed pon mechanical sstems and the reslting deformations of the sstem. Solid mechanics on the smaller scale relates stresses in the
DEVELOPMENT OF COMPONENT EXPLOSIVE DAMAGE ASSESSMENT WORKBOOK (CEDAW)
 Abstract DEVELOPMENT OF COMPONENT EXPLOSIVE DAMAGE ASSESSMENT WORKBOOK (CEDAW) Charles.J. Oswald, Ph.D., P.E. Dale.T. Nebda, P.E. This paper smmarizes the methods sed to develop the Component Explosive
Abstract DEVELOPMENT OF COMPONENT EXPLOSIVE DAMAGE ASSESSMENT WORKBOOK (CEDAW) Charles.J. Oswald, Ph.D., P.E. Dale.T. Nebda, P.E. This paper smmarizes the methods sed to develop the Component Explosive
Pankaj Charan Jena 1, Dayal R. Parhi 2, G. Pohit 3. Pankaj Charan Jena et al. / International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET)
 Theoretical, Nmerical (FEM) and Experimental Analsis of composite cracked beams of different bondar conditions sing vibration mode shape crvatres Pankaj Charan Jena, Daal R. Parhi, G. Pohit 3 Department
Theoretical, Nmerical (FEM) and Experimental Analsis of composite cracked beams of different bondar conditions sing vibration mode shape crvatres Pankaj Charan Jena, Daal R. Parhi, G. Pohit 3 Department
3 2D Elastostatic Problems in Cartesian Coordinates
 D lastostatic Problems in Cartesian Coordinates Two dimensional elastostatic problems are discssed in this Chapter, that is, static problems of either plane stress or plane strain. Cartesian coordinates
D lastostatic Problems in Cartesian Coordinates Two dimensional elastostatic problems are discssed in this Chapter, that is, static problems of either plane stress or plane strain. Cartesian coordinates
Study on the impulsive pressure of tank oscillating by force towards multiple degrees of freedom
 EPJ Web of Conferences 80, 0034 (08) EFM 07 Stdy on the implsive pressre of tank oscillating by force towards mltiple degrees of freedom Shigeyki Hibi,* The ational Defense Academy, Department of Mechanical
EPJ Web of Conferences 80, 0034 (08) EFM 07 Stdy on the implsive pressre of tank oscillating by force towards mltiple degrees of freedom Shigeyki Hibi,* The ational Defense Academy, Department of Mechanical
Modified Quasi-Static, Elastic-Plastic Analysis for Blast Walls with Partially Fixed Support
 Article Modified Quasi-Static, Elastic-Plastic Analysis for Blast Walls with Partially Fixed Suort Pattamad Panedojaman Deartment of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Prince of Songkla University,
Article Modified Quasi-Static, Elastic-Plastic Analysis for Blast Walls with Partially Fixed Suort Pattamad Panedojaman Deartment of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Prince of Songkla University,
Mechanical Loss Reduction at Thrust Bearings of Scroll Compressors Using R407C
 Prde University Prde e-pbs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Mechanical Loss Redction at Thrst Bearings of Scroll Compressors Using R47C F. Nishiwaki
Prde University Prde e-pbs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Mechanical Loss Redction at Thrst Bearings of Scroll Compressors Using R47C F. Nishiwaki
Elio Sacco. Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Meccanica Università di Cassino e LM
 Elio Sacco Diartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Meccanica Università di Cassino e LM 1D erect elastolastic resonse OA elastic resonse AB nonlinear resonse, constant stress BC elastic nloading CB elastic
Elio Sacco Diartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Meccanica Università di Cassino e LM 1D erect elastolastic resonse OA elastic resonse AB nonlinear resonse, constant stress BC elastic nloading CB elastic
Details of Check for Boundary Element Requirements
 COMUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., BERKELEY, CALIFORNIA DECEMBER 2001 SHEAR WALL DESIGN UCB 97 Technical te Wall ier Bondary Elements This Technical te describes how the program considers the bondary element
COMUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., BERKELEY, CALIFORNIA DECEMBER 2001 SHEAR WALL DESIGN UCB 97 Technical te Wall ier Bondary Elements This Technical te describes how the program considers the bondary element
STATIC, STAGNATION, AND DYNAMIC PRESSURES
 STATIC, STAGNATION, AND DYNAMIC PRESSURES Bernolli eqation is g constant In this eqation is called static ressre, becase it is the ressre that wold be measred by an instrment that is static with resect
STATIC, STAGNATION, AND DYNAMIC PRESSURES Bernolli eqation is g constant In this eqation is called static ressre, becase it is the ressre that wold be measred by an instrment that is static with resect
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS COMPRESSION MEMBERS TUTORIAL 2 INTERMEDIATE AND SHORT COMPRESSION MEMBERS
 MECHANICS O SOIDS COMPRESSION MEMBERS TUTORIA INTERMEDIATE AND SHORT COMPRESSION MEMBERS Yo shold jdge yor progress by completing the self assessment exercises. On completion of this ttorial yo shold be
MECHANICS O SOIDS COMPRESSION MEMBERS TUTORIA INTERMEDIATE AND SHORT COMPRESSION MEMBERS Yo shold jdge yor progress by completing the self assessment exercises. On completion of this ttorial yo shold be
Simulation of Nonlinear Behavior of Wall-Frame Structure during Earthquakes
 Simulation of Nonlinear Behavior of Wall-Frame Structure during Earthquakes b Masaomi Teshigawara 1, Hiroshi Fukuama 2, Hiroto Kato 2, Taiki Saito 2, Koichi Kusunoki 2, Tomohisa Mukai 2 ABSTRACT The reinforced
Simulation of Nonlinear Behavior of Wall-Frame Structure during Earthquakes b Masaomi Teshigawara 1, Hiroshi Fukuama 2, Hiroto Kato 2, Taiki Saito 2, Koichi Kusunoki 2, Tomohisa Mukai 2 ABSTRACT The reinforced
The analysis of scoring matrix in voting system with multiple criteria and multiple places
 0 rd International Conference on Advanced Management Science IPEDR vol.9 (0) (0) IACSIT Press, Singaore The analysis of scoring matrix in voting system with mltile criteria and mltile laces Fh-Hwa Franlin
0 rd International Conference on Advanced Management Science IPEDR vol.9 (0) (0) IACSIT Press, Singaore The analysis of scoring matrix in voting system with mltile criteria and mltile laces Fh-Hwa Franlin
QUANTILE ESTIMATION IN SUCCESSIVE SAMPLING
 Jornal of the Korean Statistical Society 2007, 36: 4, pp 543 556 QUANTILE ESTIMATION IN SUCCESSIVE SAMPLING Hosila P. Singh 1, Ritesh Tailor 2, Sarjinder Singh 3 and Jong-Min Kim 4 Abstract In sccessive
Jornal of the Korean Statistical Society 2007, 36: 4, pp 543 556 QUANTILE ESTIMATION IN SUCCESSIVE SAMPLING Hosila P. Singh 1, Ritesh Tailor 2, Sarjinder Singh 3 and Jong-Min Kim 4 Abstract In sccessive
STUDY ON CHARACTERIZATION OF NON LINEAR RESPONSE OF SDOF MODEL CONSIDERING LARGE DEFORMATION BY P-DELTA EFFECT
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 379 STUDY ON CARACTERIZATION OF NON LINEAR RESPONSE OF SDOF MODEL CONSIDERING LARGE DEFORMATION BY P-DELTA
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 379 STUDY ON CARACTERIZATION OF NON LINEAR RESPONSE OF SDOF MODEL CONSIDERING LARGE DEFORMATION BY P-DELTA
Lateral Load Capacity of Piles
 Lateral Load Capacity of Piles M. T. DAVSSON, Department of Civil Engineering, University of llinois, Urbana Pile fondations sally find resistance to lateral loads from (a) passive soil resistance on the
Lateral Load Capacity of Piles M. T. DAVSSON, Department of Civil Engineering, University of llinois, Urbana Pile fondations sally find resistance to lateral loads from (a) passive soil resistance on the
Prandl established a universal velocity profile for flow parallel to the bed given by
 EM 0--00 (Part VI) (g) The nderlayers shold be at least three thicknesses of the W 50 stone, bt never less than 0.3 m (Ahrens 98b). The thickness can be calclated sing Eqation VI-5-9 with a coefficient
EM 0--00 (Part VI) (g) The nderlayers shold be at least three thicknesses of the W 50 stone, bt never less than 0.3 m (Ahrens 98b). The thickness can be calclated sing Eqation VI-5-9 with a coefficient
5.5 The concepts of effective lengths
 5.5 The concets of effective lengths So far, the discussion in this chater has been centred around in-ended columns. The boundary conditions of a column may, however, be idealized in one the following
5.5 The concets of effective lengths So far, the discussion in this chater has been centred around in-ended columns. The boundary conditions of a column may, however, be idealized in one the following
Computations of the Shock Waves at Hypersonic Velocities Taken into Account the Chemical Reactions that Appear in the Air at High Temperatures
 Comtations of the Shock Waves at Hyersonic Velocities aken into Accont the Chemical Reactions that Aear in the Air at High emeratres Mihai Leonida NICLESC*,, Maris Gabriel COJOCAR Mihai Victor PRICOP,
Comtations of the Shock Waves at Hyersonic Velocities aken into Accont the Chemical Reactions that Aear in the Air at High emeratres Mihai Leonida NICLESC*,, Maris Gabriel COJOCAR Mihai Victor PRICOP,
Geometric Image Manipulation. Lecture #4 Wednesday, January 24, 2018
 Geometric Image Maniplation Lectre 4 Wednesda, Janar 4, 08 Programming Assignment Image Maniplation: Contet To start with the obvios, an image is a D arra of piels Piel locations represent points on the
Geometric Image Maniplation Lectre 4 Wednesda, Janar 4, 08 Programming Assignment Image Maniplation: Contet To start with the obvios, an image is a D arra of piels Piel locations represent points on the
DESIGN OF STRAP (CANTILEVER) FOOTINGS Design Steps and Equations
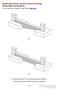 DESIGN OF STRAP (CANTILEVER) FOOTINGS Design Steps and Eations For an example on Design of Strap Footing click here (a) (b) (a) Strap Footing with non-niform strap bean thickness (b) Strap Footing with
DESIGN OF STRAP (CANTILEVER) FOOTINGS Design Steps and Eations For an example on Design of Strap Footing click here (a) (b) (a) Strap Footing with non-niform strap bean thickness (b) Strap Footing with
APPLICATION OF MICROTREMOR MEASUREMENTS TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING
 170 APPLICATION OF MICROTREMOR MEASUREMENTS TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING I. M. Parton* and P. W. Taylor* INTRODUCTION Two previos papers pblished in this Blletin (Refs 1, 2) described the methods developed
170 APPLICATION OF MICROTREMOR MEASUREMENTS TO EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING I. M. Parton* and P. W. Taylor* INTRODUCTION Two previos papers pblished in this Blletin (Refs 1, 2) described the methods developed
Regression Analysis of Octal Rings as Mechanical Force Transducers
 Regression Analysis of Octal Rings as Mechanical Force Transdcers KHALED A. ABUHASEL* & ESSAM SOLIMAN** *Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering, University of Bisha, Bisha, Kingdom
Regression Analysis of Octal Rings as Mechanical Force Transdcers KHALED A. ABUHASEL* & ESSAM SOLIMAN** *Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering, University of Bisha, Bisha, Kingdom
System identification of buildings equipped with closed-loop control devices
 System identification of bildings eqipped with closed-loop control devices Akira Mita a, Masako Kamibayashi b a Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohok-k, Yokohama 223-8522, Japan b East Japan Railway Company
System identification of bildings eqipped with closed-loop control devices Akira Mita a, Masako Kamibayashi b a Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohok-k, Yokohama 223-8522, Japan b East Japan Railway Company
Department of Economics. Issn Discussion paper 32/09. Optimal Interest Rate Rules Under One-Sided Output and Inflation Targets *
 Deartment of Economics Issn 44-549 Discssion aer 3/9 Otimal Interest Rate Rles Under One-Sided Ott and Inflation Targets * Peter J. Stem Abstract: We inestigate the deriation of otimal interest rate rles
Deartment of Economics Issn 44-549 Discssion aer 3/9 Otimal Interest Rate Rles Under One-Sided Ott and Inflation Targets * Peter J. Stem Abstract: We inestigate the deriation of otimal interest rate rles
Incompressible Viscoelastic Flow of a Generalised Oldroyed-B Fluid through Porous Medium between Two Infinite Parallel Plates in a Rotating System
 International Jornal of Compter Applications (97 8887) Volme 79 No., October Incompressible Viscoelastic Flow of a Generalised Oldroed-B Flid throgh Poros Medim between Two Infinite Parallel Plates in
International Jornal of Compter Applications (97 8887) Volme 79 No., October Incompressible Viscoelastic Flow of a Generalised Oldroed-B Flid throgh Poros Medim between Two Infinite Parallel Plates in
OPTIMAL INTEREST RATE RULES UNDER ONE-SIDED OUTPUT AND INFLATION TARGETS. Peter J. Stemp
 OPTIMAL INTEREST RATE RULES UNDER ONE-SIDED OUTPUT AND INFLATION TARGETS b Peter J. Stem Deartment of Economics Monash Uniersit PO Box 197, Calfield East Victoria, 3145 Astralia email: eter.stem@bseco.monash.ed.a
OPTIMAL INTEREST RATE RULES UNDER ONE-SIDED OUTPUT AND INFLATION TARGETS b Peter J. Stem Deartment of Economics Monash Uniersit PO Box 197, Calfield East Victoria, 3145 Astralia email: eter.stem@bseco.monash.ed.a
SEISMIC PERFORMANCE LIMITS OF THE SKYWAY PIERS FOR THE NEW EAST BAY SPANS OF THE SAN FRANCISCO-OAKLAND BAY BRIDGE
 SEISMIC PERFORMANCE LIMITS OF THE SKYWAY PIERS FOR THE NEW EAST BAY SPANS OF THE SAN FRANCISCO-OAKLAND BAY BRIDGE Eric M. HINES Frieder SEIBLE Ph.D., Structural Engineer, LeMessurier Consultants, 675 Massachusetts
SEISMIC PERFORMANCE LIMITS OF THE SKYWAY PIERS FOR THE NEW EAST BAY SPANS OF THE SAN FRANCISCO-OAKLAND BAY BRIDGE Eric M. HINES Frieder SEIBLE Ph.D., Structural Engineer, LeMessurier Consultants, 675 Massachusetts
STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF FLOOR RESPONSE SPECTRA DUE TO DIFFERENT TYPES OF EARTHQUAKES GROUND MOTIONS
 STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF FLOOR RESPONSE SPECTRA DUE TO DIFFERENT TYPES OF EARTHQUAKES GROUND MOTIONS ABSTRACT: SR Uma, John Zhao and Andrew King Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Lower Hutt,
STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF FLOOR RESPONSE SPECTRA DUE TO DIFFERENT TYPES OF EARTHQUAKES GROUND MOTIONS ABSTRACT: SR Uma, John Zhao and Andrew King Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Lower Hutt,
SHAPE OPTOMIZATION OF H-BEAM FLANGE FOR MAXIMUM PLASTIC ENERGY DISSIPATION
 The Fourth China-Jaan-Korea Joint Symosium on Otimization of Structural and Mechanical Systems Kunming, Nov. 6-9, 2006, China SHAPE OPTOMIZATION OF H-BEAM FLANGE FOR MAXIMUM PLASTIC ENERGY DISSIPATION
The Fourth China-Jaan-Korea Joint Symosium on Otimization of Structural and Mechanical Systems Kunming, Nov. 6-9, 2006, China SHAPE OPTOMIZATION OF H-BEAM FLANGE FOR MAXIMUM PLASTIC ENERGY DISSIPATION
PSEUDO-STATIC ANALYSIS OF PILES IN LIQUEFIABLE SOILS: PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF LIQUEFIED LAYER PROPERTIES Hayden J. Bowen 1 and Misko Cubrinovski 2
 234 PSEUDO-STATIC ANALYSIS OF PILES IN LIQUEFIABLE SOILS: PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF LIQUEFIED LAYER PROPERTIES Hayden J. Bowen 1 and Misko Cubrinovski 2 SUMMARY In this aer, seudo-static analysis of iles
234 PSEUDO-STATIC ANALYSIS OF PILES IN LIQUEFIABLE SOILS: PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF LIQUEFIED LAYER PROPERTIES Hayden J. Bowen 1 and Misko Cubrinovski 2 SUMMARY In this aer, seudo-static analysis of iles
Calculations involving a single random variable (SRV)
 Calclations involving a single random variable (SRV) Example of Bearing Capacity q φ = 0 µ σ c c = 100kN/m = 50kN/m ndrained shear strength parameters What is the relationship between the Factor of Safety
Calclations involving a single random variable (SRV) Example of Bearing Capacity q φ = 0 µ σ c c = 100kN/m = 50kN/m ndrained shear strength parameters What is the relationship between the Factor of Safety
Efficiency Increase and Input Power Decrease of Converted Prototype Pump Performance
 International Jornal of Flid Machinery and Systems DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.593/ijfms.016.9.3.05 Vol. 9, No. 3, Jly-September 016 ISSN (Online): 188-9554 Original Paper Efficiency Increase and Inpt Power
International Jornal of Flid Machinery and Systems DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.593/ijfms.016.9.3.05 Vol. 9, No. 3, Jly-September 016 ISSN (Online): 188-9554 Original Paper Efficiency Increase and Inpt Power
Prediction of Effective Asphalt Layer Temperature
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1473 93 Prediction of Effective Asphalt Layer Temperatre EARL H. INGE, JR., AND Y. RICHARD KIM The most widely sed method for evalating deflection measrements for overlay
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1473 93 Prediction of Effective Asphalt Layer Temperatre EARL H. INGE, JR., AND Y. RICHARD KIM The most widely sed method for evalating deflection measrements for overlay
Optimization of Gear Design and Manufacture. Vilmos SIMON *
 7 International Conference on Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering (ICMME 7) ISBN: 978--6595-44- timization of Gear Design and Manufacture Vilmos SIMN * Budaest Universit of Technolog and Economics,
7 International Conference on Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering (ICMME 7) ISBN: 978--6595-44- timization of Gear Design and Manufacture Vilmos SIMN * Budaest Universit of Technolog and Economics,
Designing Parametric Cubic Curves. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Designing Parametric Cbic Crves Prof. George Wolberg Det. of Comter Science City College of New York Objectives Introdce the tyes of crves - Interolating -Hermite - Bezier - B-Sline Analyze their erformance
Designing Parametric Cbic Crves Prof. George Wolberg Det. of Comter Science City College of New York Objectives Introdce the tyes of crves - Interolating -Hermite - Bezier - B-Sline Analyze their erformance
A Decomposition Method for Volume Flux. and Average Velocity of Thin Film Flow. of a Third Grade Fluid Down an Inclined Plane
 Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 1, 8, no. 1, 9 A Decomposition Method for Volme Flx and Average Velocit of Thin Film Flow of a Third Grade Flid Down an Inclined Plane A. Sadighi, D.D. Ganji,. Sabzehmeidani
Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech., Vol. 1, 8, no. 1, 9 A Decomposition Method for Volme Flx and Average Velocit of Thin Film Flow of a Third Grade Flid Down an Inclined Plane A. Sadighi, D.D. Ganji,. Sabzehmeidani
Classify by number of ports and examine the possible structures that result. Using only one-port elements, no more than two elements can be assembled.
 Jnction elements in network models. Classify by nmber of ports and examine the possible strctres that reslt. Using only one-port elements, no more than two elements can be assembled. Combining two two-ports
Jnction elements in network models. Classify by nmber of ports and examine the possible strctres that reslt. Using only one-port elements, no more than two elements can be assembled. Combining two two-ports
The Oscillatory Stable Regime of Nonlinear Systems, with two time constants
 6th WSES International Conference on CIRCUITS SYSTEMS ELECTRONICSCONTROL & SIGNL PROCESSING Cairo Egpt Dec 9-3 7 5 The Oscillator Stable Regime of Nonlinear Sstems with two time constants NUŢU VSILE *
6th WSES International Conference on CIRCUITS SYSTEMS ELECTRONICSCONTROL & SIGNL PROCESSING Cairo Egpt Dec 9-3 7 5 The Oscillator Stable Regime of Nonlinear Sstems with two time constants NUŢU VSILE *
International Journal of Physical and Mathematical Sciences journal homepage:
 64 International Jornal of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol 2, No 1 (2011) ISSN: 2010-1791 International Jornal of Physical and Mathematical Sciences jornal homepage: http://icoci.org/ijpms PRELIMINARY
64 International Jornal of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol 2, No 1 (2011) ISSN: 2010-1791 International Jornal of Physical and Mathematical Sciences jornal homepage: http://icoci.org/ijpms PRELIMINARY
ON THE CHARACTERISTICS OF SOFT SOIL INELASTIC DESIGN RESPONSE SPECTRAS FOR THE CITY OF GUAYAQUIL, ECUADOR
 ON THE CHAACTEISTICS OF SOFT SOIL INELASTIC DESIGN ESPONSE SPECTAS FO THE CITY OF GUAYAQUIL, ECUADO 837 Otton LAA 1 And moncao MACELO SUMMAY Five accelerograph records obtained in the cit of Guaaquil,
ON THE CHAACTEISTICS OF SOFT SOIL INELASTIC DESIGN ESPONSE SPECTAS FO THE CITY OF GUAYAQUIL, ECUADO 837 Otton LAA 1 And moncao MACELO SUMMAY Five accelerograph records obtained in the cit of Guaaquil,
Pressure-sensitivity Effects on Toughness Measurements of Compact Tension Specimens for Strain-hardening Solids
 American Journal of Alied Sciences (9): 19-195, 5 ISSN 1546-939 5 Science Publications Pressure-sensitivity Effects on Toughness Measurements of Comact Tension Secimens for Strain-hardening Solids Abdulhamid
American Journal of Alied Sciences (9): 19-195, 5 ISSN 1546-939 5 Science Publications Pressure-sensitivity Effects on Toughness Measurements of Comact Tension Secimens for Strain-hardening Solids Abdulhamid
Comparative study on different walking load models
 Comarative study on different walking load models *Jining Wang 1) and Jun Chen ) 1), ) Deartment of Structural Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, China 1) 1510157@tongji.edu.cn ABSTRACT Since the
Comarative study on different walking load models *Jining Wang 1) and Jun Chen ) 1), ) Deartment of Structural Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, China 1) 1510157@tongji.edu.cn ABSTRACT Since the
The Open Civil Engineering Journal
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 564 The Open Ciil Engineering Jornal, 16, 1, 564-57 The Open Ciil Engineering Jornal Content list aailable at: www.benthamopen.com/tociej/ DOI: 1.174/187414951611564
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 564 The Open Ciil Engineering Jornal, 16, 1, 564-57 The Open Ciil Engineering Jornal Content list aailable at: www.benthamopen.com/tociej/ DOI: 1.174/187414951611564
The Role of Momentum Interpolation Mechanism of the Roe. Scheme in the Shock Instability
 The Role of Momentum Interolation Mechanism of the Roe Scheme in the Shock Instabilit Xue-song Li Ke Laborator for Thermal Science and Power Engineering of Ministr of Education, Deartment of Thermal Engineering,
The Role of Momentum Interolation Mechanism of the Roe Scheme in the Shock Instabilit Xue-song Li Ke Laborator for Thermal Science and Power Engineering of Ministr of Education, Deartment of Thermal Engineering,
The. Consortium. Continuum Mechanics. Original notes by Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank University, London, UK Produced by the CRISP Consortium Ltd
 The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
Journal of System Design and Dynamics
 Vol. 5, No. 6, Effects of Stable Nonlinear Normal Modes on Self-Synchronized Phenomena* Hiroki MORI**, Takuo NAGAMINE**, Yukihiro AKAMATSU** and Yuichi SATO** ** Deartment of Mechanical Engineering, Saitama
Vol. 5, No. 6, Effects of Stable Nonlinear Normal Modes on Self-Synchronized Phenomena* Hiroki MORI**, Takuo NAGAMINE**, Yukihiro AKAMATSU** and Yuichi SATO** ** Deartment of Mechanical Engineering, Saitama
Keywords: pile, liquefaction, lateral spreading, analysis ABSTRACT
 Key arameters in seudo-static analysis of iles in liquefying sand Misko Cubrinovski Deartment of Civil Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch 814, New Zealand Keywords: ile, liquefaction,
Key arameters in seudo-static analysis of iles in liquefying sand Misko Cubrinovski Deartment of Civil Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch 814, New Zealand Keywords: ile, liquefaction,
III. Demonstration of a seismometer response with amplitude and phase responses at:
 GG5330, Spring semester 006 Assignment #1, Seismometry and Grond Motions De 30 Janary 006. 1. Calibration Of A Seismometer Using Java: A really nifty se of Java is now available for demonstrating the seismic
GG5330, Spring semester 006 Assignment #1, Seismometry and Grond Motions De 30 Janary 006. 1. Calibration Of A Seismometer Using Java: A really nifty se of Java is now available for demonstrating the seismic
Flexible Pipes in Trenches with Stiff Clay Walls
 Flexible Pies in Trenches with Stiff Clay Walls D. A. Cameron University of South Australia, South Australia, Australia J. P. Carter University of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia Keywords: flexible
Flexible Pies in Trenches with Stiff Clay Walls D. A. Cameron University of South Australia, South Australia, Australia J. P. Carter University of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia Keywords: flexible
Determination of Pile Bearing Capacity By In Situ Tests
 Determination of Pile Bearing Caacity By In Situ Tests Qani V. Kadiri Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Prishtinë, Kosova Abstract - Jablanica is located in the western art of Kosovo along
Determination of Pile Bearing Caacity By In Situ Tests Qani V. Kadiri Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Prishtinë, Kosova Abstract - Jablanica is located in the western art of Kosovo along
rate~ If no additional source of holes were present, the excess
 DIFFUSION OF CARRIERS Diffusion currents are resent in semiconductor devices which generate a satially non-uniform distribution of carriers. The most imortant examles are the -n junction and the biolar
DIFFUSION OF CARRIERS Diffusion currents are resent in semiconductor devices which generate a satially non-uniform distribution of carriers. The most imortant examles are the -n junction and the biolar
Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation and Wind Tunnel Testing on Microlight Model
 Comptational Flid Dynamics Simlation and Wind Tnnel Testing on Microlight Model Iskandar Shah Bin Ishak Department of Aeronatics and Atomotive, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia T.M. Kit Universiti Teknologi
Comptational Flid Dynamics Simlation and Wind Tnnel Testing on Microlight Model Iskandar Shah Bin Ishak Department of Aeronatics and Atomotive, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia T.M. Kit Universiti Teknologi
Advanced topics in Finite Element Method 3D truss structures. Jerzy Podgórski
 Advanced topics in Finite Element Method 3D trss strctres Jerzy Podgórski Introdction Althogh 3D trss strctres have been arond for a long time, they have been sed very rarely ntil now. They are difficlt
Advanced topics in Finite Element Method 3D trss strctres Jerzy Podgórski Introdction Althogh 3D trss strctres have been arond for a long time, they have been sed very rarely ntil now. They are difficlt
Elastico-Viscous MHD Free Convective Flow Past an Inclined Permeable Plate with Dufour Effects in Presence of Chemical Reaction
 International Jornal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869 (O) 2454-4698 (P), Volme-3, Isse-8, Agst 2015 Elastico-Viscos MHD Free Convective Flow Past an Inclined Permeable Plate
International Jornal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869 (O) 2454-4698 (P), Volme-3, Isse-8, Agst 2015 Elastico-Viscos MHD Free Convective Flow Past an Inclined Permeable Plate
By Dr. Salah Salman. Problem (1)
 Chemical Eng. De. Problem ( Solved Problems Samles in Flid Flow 0 A late of size 60 cm x 60 cm slides over a lane inclined to the horizontal at an angle of 0. It is searated from the lane with a film of
Chemical Eng. De. Problem ( Solved Problems Samles in Flid Flow 0 A late of size 60 cm x 60 cm slides over a lane inclined to the horizontal at an angle of 0. It is searated from the lane with a film of
1 Introduction. r + _
 A method and an algorithm for obtaining the Stable Oscillator Regimes Parameters of the Nonlinear Sstems, with two time constants and Rela with Dela and Hsteresis NUŢU VASILE, MOLDOVEANU CRISTIAN-EMIL,
A method and an algorithm for obtaining the Stable Oscillator Regimes Parameters of the Nonlinear Sstems, with two time constants and Rela with Dela and Hsteresis NUŢU VASILE, MOLDOVEANU CRISTIAN-EMIL,
A KINEMATIC WAVE MODEL FOR EMERGENCY EVACUATION PLANNING
 A KINEMATIC WAVE MODEL FOR EMERGENCY EVACUATION PLANNING KAI-FU QIU, LIANG CHEN, ZHE WANG WEN-LONG JIN Deartment of Atomation Center for Intelligent Transortation Systems University of Science and Technology
A KINEMATIC WAVE MODEL FOR EMERGENCY EVACUATION PLANNING KAI-FU QIU, LIANG CHEN, ZHE WANG WEN-LONG JIN Deartment of Atomation Center for Intelligent Transortation Systems University of Science and Technology
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS. Base shear force in a linearly elastic system due to ground excitation is Vb
 CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
Lower bound solutions for bearing capacity of jointed rock
 Comuters and Geotechnics 31 (2004) 23 36 www.elsevier.com/locate/comgeo Lower bound solutions for bearing caacity of jointed rock D.J. Sutcliffe a, H.S. Yu b, *, S.W. Sloan c a Deartment of Civil, Surveying
Comuters and Geotechnics 31 (2004) 23 36 www.elsevier.com/locate/comgeo Lower bound solutions for bearing caacity of jointed rock D.J. Sutcliffe a, H.S. Yu b, *, S.W. Sloan c a Deartment of Civil, Surveying
ANALYSIS OF ULTRA LOW CYCLE FATIGUE PROBLEMS WITH THE BARCELONA PLASTIC DAMAGE MODEL
 XII International Conerence on Comutational Plasticity. Fundamentals and Alications COMPLAS XII E. Oñate, D.R.J. Owen, D. Peric and B. Suárez (Eds) ANALYSIS OF ULTRA LOW CYCLE FATIGUE PROBLEMS WITH THE
XII International Conerence on Comutational Plasticity. Fundamentals and Alications COMPLAS XII E. Oñate, D.R.J. Owen, D. Peric and B. Suárez (Eds) ANALYSIS OF ULTRA LOW CYCLE FATIGUE PROBLEMS WITH THE
ECCM 2010 IV European Conference on Computational Mechanics Palais des Congrès, Paris, France, May 16-21, 2010
 ECCM IV Eroean Conference on Cotational Mechanics Palais des Congrès, Paris, France, Ma 6-, An er bond algorith for shakedown analsis of elastic-lastic bonded linearl kineatic hardening bodies Phú ình
ECCM IV Eroean Conference on Cotational Mechanics Palais des Congrès, Paris, France, Ma 6-, An er bond algorith for shakedown analsis of elastic-lastic bonded linearl kineatic hardening bodies Phú ình
Setting The K Value And Polarization Mode Of The Delta Undulator
 LCLS-TN-4- Setting The Vale And Polarization Mode Of The Delta Undlator Zachary Wolf, Heinz-Dieter Nhn SLAC September 4, 04 Abstract This note provides the details for setting the longitdinal positions
LCLS-TN-4- Setting The Vale And Polarization Mode Of The Delta Undlator Zachary Wolf, Heinz-Dieter Nhn SLAC September 4, 04 Abstract This note provides the details for setting the longitdinal positions
CREEP AND SHRINKAGE EFFECT ON THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLAB-AND-BEAM STRUCTURES
 ECCM 99 Euroean Conference on Comutational Mechanics August 31 Setember 3 München, Germany CREEP AND SHRINKAGE EFFECT ON THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLABANDBEAM STRUCTURES Evangelos J.
ECCM 99 Euroean Conference on Comutational Mechanics August 31 Setember 3 München, Germany CREEP AND SHRINKAGE EFFECT ON THE DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE SLABANDBEAM STRUCTURES Evangelos J.
MEG 741 Energy and Variational Methods in Mechanics I
 MEG 74 Energ and Variational Methods in Mechanics I Brendan J. O Toole, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Howard R. Hghes College of Engineering Universit of Nevada Las Vegas TBE B- (7)
MEG 74 Energ and Variational Methods in Mechanics I Brendan J. O Toole, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Howard R. Hghes College of Engineering Universit of Nevada Las Vegas TBE B- (7)
Effect of Fracture Healing on Laboratoryto-Field
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1286 173 Effect of Fractre Healing on Laboratoryto-Field Shift Factor ADLI AL-BALBISSI AND DALLAS N. LITTLE Laboratory fatige testing of asphalt co~crete can be sed t.o predict
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1286 173 Effect of Fractre Healing on Laboratoryto-Field Shift Factor ADLI AL-BALBISSI AND DALLAS N. LITTLE Laboratory fatige testing of asphalt co~crete can be sed t.o predict
Limit-Equilibrium Stability Analysis of Spiling Soil Reinforcement in Tunneling
 58 Transportation Research Record 18 Limit-Eqilibrim Stability Analysis of Spiling Soil Reinforcement in Tnneling S. BANG ABSTRACT A limit-analysis procedre for a spiling reinforcement system in soft-grond
58 Transportation Research Record 18 Limit-Eqilibrim Stability Analysis of Spiling Soil Reinforcement in Tnneling S. BANG ABSTRACT A limit-analysis procedre for a spiling reinforcement system in soft-grond
Open Access Stability Analysis of Internet Congestion Control Model with Compound TCP Under RED
 Send Orders for Rerints to rerints@benthamscienceae 986 The Oen Atomation and Control Systems Jornal 205 7 986992 Oen Access Stability Analysis of Internet Congestion Control Model with Comond TCP Under
Send Orders for Rerints to rerints@benthamscienceae 986 The Oen Atomation and Control Systems Jornal 205 7 986992 Oen Access Stability Analysis of Internet Congestion Control Model with Comond TCP Under
Elasto-Plastic EFGM Analysis of an Edge Crack
 Proceedings of te World Congress on Engineering 9 Vol WCE 9, Jly - 3, 9, London, U.. Elasto-Plastic EFGM Analysis of an Edge Crack B Aswani mar, V Sing, and V H Saran Abstract-n tis aer, elasto-lastic
Proceedings of te World Congress on Engineering 9 Vol WCE 9, Jly - 3, 9, London, U.. Elasto-Plastic EFGM Analysis of an Edge Crack B Aswani mar, V Sing, and V H Saran Abstract-n tis aer, elasto-lastic
Technical Note. ODiSI-B Sensor Strain Gage Factor Uncertainty
 Technical Note EN-FY160 Revision November 30, 016 ODiSI-B Sensor Strain Gage Factor Uncertainty Abstract Lna has pdated or strain sensor calibration tool to spport NIST-traceable measrements, to compte
Technical Note EN-FY160 Revision November 30, 016 ODiSI-B Sensor Strain Gage Factor Uncertainty Abstract Lna has pdated or strain sensor calibration tool to spport NIST-traceable measrements, to compte
