Finite Fields. SOLUTIONS Network Coding - Prof. Frank H.P. Fitzek
|
|
|
- Karin Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
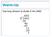
1 Finite Fields In practice most finite field applications e.g. cryptography and error correcting codes utilizes a specific type of finite fields, namely the binary extension fields. The following exercises will introduce you to calculations in binary extension fields. Exercise 1: The Binary Field... Thebinaryfield 2 consistsoftwoelements{0,1}andisofparticularinterestsincethebinaryoperations are easily implemented and represented in software and hardware. In the case of the binary fields, arithmetic operations are performed modulo-2. For addition and multiplication this corresponds to the bitwise exclusive or (XOR) and the bitwise and (AND) operations. (a) Fill in the missing values in the below table. XOR AND Table 1: The finite field 2 consists of elements 0 and 1 which satisfy the addition(xor) and multiplication(and) tables. XOR AND Exercise 2: The Butterfly Network... (a) The butterfly network shown in the below figure is a famous example of Network Coding. Show how the two bits b 1 and b 2 may be delivered at the two receivers R 1 and R 2 simultaneously using the operations from the binary field (hint: the XOR operation is enough). Each edge may carry 1 bit per time unit. S b 1 b R 1 R 2 Page 1
2 S b 1 b b 1 3 b 2 b 1 b 1 +b 2 b 2 4 b 1 +b 2 b 1 +b 2 R 1 R 2 Exercise 3: Binary Field Calculations... In practice calculations are typically performed w-bits at a time, where w corresponds to the word size of the hardware used. Typical values of w are {16,32,64} bits. The below table shows an example of XOR and AND between two 8-bit words XOR = (a) Fill in the missing values in the tables AN D = XOR = AN D = Table 2: Addition and multiplication in 2 with 8-bit words XOR = AN D = Exercise 4: The Binary Extension Field... In a previous exercise we found a solution for the butterfly network using the binary field. However, when implementing Network Coding it can in certain cases be necessary to increase the field size in order to find a solution (i.e. the number of elements contained in the field). In the binary field 2 the field size was 2, i.e. there are two elements 0,1. Binary extension fields have the form 2 m, where m 1. A binary extension field contains 2 m elements, all field elements may be represented as binary polynomials of degree at most m 1: 2 m = {f m 1 x m f 2 x 2 +f 1 x+f 0 : f i {0,1}} (1) Page 2
3 As an example consider the field given by 2 3 in the below table, in this case the field will consist of 2 3 = 8 polynomial elements of degree < m. In the binary extension field all polynomial elements can be represented as m bit binary numbers. It is important to notice the correspondence between the binary and polynomial representation. The bits from left to right are the coefficients of the powers of x in increasing order. (a) Fill in the missing values in the below table. GF2 3 Polynomial Binary Decimal x x x x x 2 +x x 2 +x GF2 m Polynomial Binary Decimal x 7 +x 6 +x 4 +x x 4 +x 2 +x GF2 m Polynomial Binary Decimal x 7 +x 6 +x 4 +x x 7 +x 6 x x 7 +x x 4 +x 2 +x x 4 +x x 3 +x (b) In the table what is the required value for m in order to represent the field elements. The value of m must be 8. Exercise 5: Polynomial Addition and Subtraction... Polynomials essentially allow the same arithmetic operations as integers, however when polynomials are used the operations are performed modulo-p(x), where p(x) is an irreducible polynomial instead of a prime integer (e.g. 2 as in the case of the binary field). As with a prime number an irreducible polynomial is one which cannot be factored into products of two polynomials. Ordinary polynomial addition is performed component-wise e.g. for two polynomials with a maximum degree of k: Page 3
4 f(x) = h(x)+g(x) (2) k f(x) = (h i +g i )x i (3) i=0 In p m we calculate f(x)+g(x) as f(x)+g(x) mod p(x). This uses the usual component-wise addition as given in Equation (??), the only difference is that the coefficient sum is modulo p i.e. h i +g i mod p. As the degree of the resulting polynomial f(x) cannot exceed the degree of the chosen prime polynomial, no further computations are needed. Example Lets consider a w = 8 bit architecture with the two polynomials a(x) = x 7 + x 6 + x 2 and b(x) = x 7 +x 5 +x 3 +x 2 with the binary representation of and respectively. In the following we use to denote the XOR operation. Addition or subtraction: = The result may be confirmed by adding the two polynomials directly: f(x) = (x 7 +x 6 +x 2 )+(x 7 +x 5 +x 3 +x 2 ) (4) = (1 1)x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 3 +(1 1)x 2 (5) = x 6 +x 5 +x 3 (6) Where x 6 +x 5 +x 3 has the expected binary representation (a) In 2 8 calculate (x 5 +x)+(x 3 +x 2 ) (x 5 +x)+(x 3 +x 2 ) = x 5 +x 3 +x 2 +x (b) In 2 8 calculate (x 7 +x 3 )+(x 7 +x+1) (x 7 +x 3 )+(x 7 +x+1) = x 3 +x+1 (c) In 2 8 calculate (x 3 +x 2 +x+1)+(x+1) (x 3 +x 2 +x+1)+(x+1) = x 3 +x 2 (d) In 2 8 calculate (x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +1)+(x 4 +x 2 +1) (x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +1)+(x 4 +x 2 +1) = x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 3 In the binary and binary extension field subtraction and addition are identical (based on the XOR). Subtraction of two field elements can be defined in terms of addition, if a,b then a b = a+( b), where b is the unique field element in such that b+( b) = 0 ( b is called the negative of b). (e) In 2 8 calculate (x 5 +x) (x 3 +x 2 ) Page 4
5 (x 5 +x) (x 3 +x 2 ) = x 5 +x 3 +x 2 +x (f) In 2 8 calculate (x 7 +x 3 ) (x 7 +x+1) (x 7 +x 3 ) (x 7 +x+1) = x 3 +x+1 (g) In 2 8 calculate (x 3 +x 2 +x+1) (x+1) (x 3 +x 2 +x+1) (x+1) = x 3 +x 2 (h) In 2 8 calculate (x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +1) (x 4 +x 2 +1) (x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +1) (x 4 +x 2 +1) = x 7 +x 6 +x 5 +x 3 Exercise 6: Polynomial Multiplication... For ordinary polynomial multiplication, the coefficients of f(x) = h(x)g(x) are determined by convolution, the resulting polynomial f(x) is of degree = deg(h)+deg(g): f i = i h j g i j (7) j=0 The product h(x)g(x) in p m can be found by first multiplying h(x) and g(x) using ordinary polynomial multiplication. Then ensuring that the resulting polynomial f(x) has degree < m by reducing it modulo p(x). The modulo operation can be implemented as polynomial long division and then taking the remainder. As for polynomial addition we must also ensure that all resulting coefficients are elements in p by reducing them modulo p. In the following use the irreducible prime polynomial p(x) = x 5 +x 2 +1 Example f(x) = (x 3 +x+1) (x 2 +1) (8) = x 5 +(1 1)x 3 +x 2 +x+1 (9) = x 5 +x 2 +x+1 (10) Since degree of f(x) equal m, we perform the modulo operation using the irreducible polynomial p(x) f(x) = x 5 +x 2 +x+1 mod p(x) (11) f(x) = x (12) The result of the modulo operation can be calculated as the remaineder of polynomial long division with the irreducible polynomial: x 5 +x 2 +1 x 5 +x 2 +x +1 x 5 +x qoutient x remainder Page 5
6 (a) In 2 5 calculate (x 4 +x) (x 3 +x 2 ) f(x) = (x 4 +x) (x 3 +x 2 ) = x 7 +x 6 +x 4 +x 3 Degree of f(x) > 5 so we must perform modulo i.e. long divsion with p(x): x 2 +x qoutient x 5 +x 2 +1 x 7 +x 6 +x 4 +x 3 x 7 +x 4 +x 2 x 6 +x 3 +x 2 x 6 +x 3 +x x 2 +x remainder Finally we therefore get: f(x) = (x 4 +x) (x 3 +x 2 ) mod p(x) = x 7 +x 6 +x 4 +x 3 mod p(x) = x 2 +x In Matlab this may be calculated as: gf(18, 5)*gf(12, 5) The first parameter represents the field element i.g. 18 is the decimal value of x 4 +x and 12 is the decimal value of x 3 +x 2. The second parameter represents the prime polynomial in Matlab decimal 5 represents the polynomial x 5 + x For this calulation Matlab returns decimal value 6 which represents the polynomial x 2 +x, as we have shown above. (b) In 2 5 calculate (x 3 ) (x 2 +x 1 +1) (x 3 ) (x 2 +x 1 +1) = x 4 +x 3 +x 2 +1 Exercise 7: Polynomial Division... Division can be implemented in terms of multiplication with the inverse element. Division can be defined in terms of multiplication: if a,b then a/b = a (b 1 ), where b 1 is the unique field element in such that b b 1 = 1 (b 1 is called the inverse of b). The inverse of a polynomial may be found using the Extended Euclidean algorithm. (a) In 2 5 calculate (x 4 +x)/(x 3 +x 2 ) given (x 3 +x 2 ) 1 = (x 2 +x+1) (x 4 +x)/(x 3 +x 2 ) = (x 4 +x) (x 3 +x 2 ) 1 = (x 4 +x) (x 2 +x+1) = x 4 +1 (b) In 2 5 verify (x 3 +x 2 ) 1 = (x 2 +x+1) Is true if (x 3 +x 2 ) (x 2 +x+1) = 1 (x 3 +x 2 ) (x 2 +x+1) = x 5 +(1 1)x 4 +(1 1)x 3 +x 2 (13) = x 5 +x 2 (14) Since degree of the resulting polynomial equal m, we perform the modulo operation using the choosen irreducible polynomial p(x) = x 5 +x 2 +1 = x 5 +x 2 mod p(x) (15) = 1 (16) Page 6
A field F is a set of numbers that includes the two numbers 0 and 1 and satisfies the properties:
 Byte multiplication 1 Field arithmetic A field F is a set of numbers that includes the two numbers 0 and 1 and satisfies the properties: F is an abelian group under addition, meaning - F is closed under
Byte multiplication 1 Field arithmetic A field F is a set of numbers that includes the two numbers 0 and 1 and satisfies the properties: F is an abelian group under addition, meaning - F is closed under
Chapter 4 Mathematics of Cryptography
 Chapter 4 Mathematics of Cryptography Part II: Algebraic Structures Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Chapter 4 Objectives To review the concept
Chapter 4 Mathematics of Cryptography Part II: Algebraic Structures Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Chapter 4 Objectives To review the concept
Finite Fields. Mike Reiter
 1 Finite Fields Mike Reiter reiter@cs.unc.edu Based on Chapter 4 of: W. Stallings. Cryptography and Network Security, Principles and Practices. 3 rd Edition, 2003. Groups 2 A group G, is a set G of elements
1 Finite Fields Mike Reiter reiter@cs.unc.edu Based on Chapter 4 of: W. Stallings. Cryptography and Network Security, Principles and Practices. 3 rd Edition, 2003. Groups 2 A group G, is a set G of elements
Chapter 4 Finite Fields
 Chapter 4 Finite Fields Introduction will now introduce finite fields of increasing importance in cryptography AES, Elliptic Curve, IDEA, Public Key concern operations on numbers what constitutes a number
Chapter 4 Finite Fields Introduction will now introduce finite fields of increasing importance in cryptography AES, Elliptic Curve, IDEA, Public Key concern operations on numbers what constitutes a number
Fields in Cryptography. Çetin Kaya Koç Winter / 30
 Fields in Cryptography http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Winter 2017 1 / 30 Field Axioms Fields in Cryptography A field F consists of a set S and two operations which we will call addition and multiplication,
Fields in Cryptography http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Winter 2017 1 / 30 Field Axioms Fields in Cryptography A field F consists of a set S and two operations which we will call addition and multiplication,
Mathematical Foundations of Cryptography
 Mathematical Foundations of Cryptography Cryptography is based on mathematics In this chapter we study finite fields, the basis of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and elliptical curve cryptography
Mathematical Foundations of Cryptography Cryptography is based on mathematics In this chapter we study finite fields, the basis of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and elliptical curve cryptography
MATH Dr. Halimah Alshehri Dr. Halimah Alshehri
 MATH 1101 haalshehri@ksu.edu.sa 1 Introduction To Number Systems First Section: Binary System Second Section: Octal Number System Third Section: Hexadecimal System 2 Binary System 3 Binary System The binary
MATH 1101 haalshehri@ksu.edu.sa 1 Introduction To Number Systems First Section: Binary System Second Section: Octal Number System Third Section: Hexadecimal System 2 Binary System 3 Binary System The binary
Math 261 Exercise sheet 5
 Math 261 Exercise sheet 5 http://staff.aub.edu.lb/~nm116/teaching/2018/math261/index.html Version: October 24, 2018 Answers are due for Wednesday 24 October, 11AM. The use of calculators is allowed. Exercise
Math 261 Exercise sheet 5 http://staff.aub.edu.lb/~nm116/teaching/2018/math261/index.html Version: October 24, 2018 Answers are due for Wednesday 24 October, 11AM. The use of calculators is allowed. Exercise
Polynomials. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Polynomials In this Chapter we shall see that everything we did with integers in the last Chapter we can also do with polynomials. Fix a field F (e.g. F = Q, R, C or Z/(p) for a prime p). Notation
Chapter 4 Polynomials In this Chapter we shall see that everything we did with integers in the last Chapter we can also do with polynomials. Fix a field F (e.g. F = Q, R, C or Z/(p) for a prime p). Notation
GF(2 m ) arithmetic: summary
 GF(2 m ) arithmetic: summary EE 387, Notes 18, Handout #32 Addition/subtraction: bitwise XOR (m gates/ops) Multiplication: bit serial (shift and add) bit parallel (combinational) subfield representation
GF(2 m ) arithmetic: summary EE 387, Notes 18, Handout #32 Addition/subtraction: bitwise XOR (m gates/ops) Multiplication: bit serial (shift and add) bit parallel (combinational) subfield representation
Homework 8 Solutions to Selected Problems
 Homework 8 Solutions to Selected Problems June 7, 01 1 Chapter 17, Problem Let f(x D[x] and suppose f(x is reducible in D[x]. That is, there exist polynomials g(x and h(x in D[x] such that g(x and h(x
Homework 8 Solutions to Selected Problems June 7, 01 1 Chapter 17, Problem Let f(x D[x] and suppose f(x is reducible in D[x]. That is, there exist polynomials g(x and h(x in D[x] such that g(x and h(x
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC. 13/05/2010 cryptography - math background pp. 1 / 162
 COMPUTER ARITHMETIC 13/05/2010 cryptography - math background pp. 1 / 162 RECALL OF COMPUTER ARITHMETIC computers implement some types of arithmetic for instance, addition, subtratction, multiplication
COMPUTER ARITHMETIC 13/05/2010 cryptography - math background pp. 1 / 162 RECALL OF COMPUTER ARITHMETIC computers implement some types of arithmetic for instance, addition, subtratction, multiplication
Math /Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined
 Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Homework #2 solutions Due: June 15, 2012
 All of the following exercises are based on the material in the handout on integers found on the class website. 1. Find d = gcd(475, 385) and express it as a linear combination of 475 and 385. That is
All of the following exercises are based on the material in the handout on integers found on the class website. 1. Find d = gcd(475, 385) and express it as a linear combination of 475 and 385. That is
LECTURE NOTES IN CRYPTOGRAPHY
 1 LECTURE NOTES IN CRYPTOGRAPHY Thomas Johansson 2005/2006 c Thomas Johansson 2006 2 Chapter 1 Abstract algebra and Number theory Before we start the treatment of cryptography we need to review some basic
1 LECTURE NOTES IN CRYPTOGRAPHY Thomas Johansson 2005/2006 c Thomas Johansson 2006 2 Chapter 1 Abstract algebra and Number theory Before we start the treatment of cryptography we need to review some basic
MTH310 EXAM 2 REVIEW
 MTH310 EXAM 2 REVIEW SA LI 4.1 Polynomial Arithmetic and the Division Algorithm A. Polynomial Arithmetic *Polynomial Rings If R is a ring, then there exists a ring T containing an element x that is not
MTH310 EXAM 2 REVIEW SA LI 4.1 Polynomial Arithmetic and the Division Algorithm A. Polynomial Arithmetic *Polynomial Rings If R is a ring, then there exists a ring T containing an element x that is not
Galois Fields and Hardware Design
 Galois Fields and Hardware Design Construction of Galois Fields, Basic Properties, Uniqueness, Containment, Closure, Polynomial Functions over Galois Fields Priyank Kalla Associate Professor Electrical
Galois Fields and Hardware Design Construction of Galois Fields, Basic Properties, Uniqueness, Containment, Closure, Polynomial Functions over Galois Fields Priyank Kalla Associate Professor Electrical
1. Algebra 1.5. Polynomial Rings
 1. ALGEBRA 19 1. Algebra 1.5. Polynomial Rings Lemma 1.5.1 Let R and S be rings with identity element. If R > 1 and S > 1, then R S contains zero divisors. Proof. The two elements (1, 0) and (0, 1) are
1. ALGEBRA 19 1. Algebra 1.5. Polynomial Rings Lemma 1.5.1 Let R and S be rings with identity element. If R > 1 and S > 1, then R S contains zero divisors. Proof. The two elements (1, 0) and (0, 1) are
How does the computer generate observations from various distributions specified after input analysis?
 1 How does the computer generate observations from various distributions specified after input analysis? There are two main components to the generation of observations from probability distributions.
1 How does the computer generate observations from various distributions specified after input analysis? There are two main components to the generation of observations from probability distributions.
Elliptic Curves I. The first three sections introduce and explain the properties of elliptic curves.
 Elliptic Curves I 1.0 Introduction The first three sections introduce and explain the properties of elliptic curves. A background understanding of abstract algebra is required, much of which can be found
Elliptic Curves I 1.0 Introduction The first three sections introduce and explain the properties of elliptic curves. A background understanding of abstract algebra is required, much of which can be found
Number Theory. CSS322: Security and Cryptography. Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University CSS322. Number Theory.
 CSS322: Security and Cryptography Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 29 December 2011 CSS322Y11S2L06, Steve/Courses/2011/S2/CSS322/Lectures/number.tex,
CSS322: Security and Cryptography Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 29 December 2011 CSS322Y11S2L06, Steve/Courses/2011/S2/CSS322/Lectures/number.tex,
Generator Matrix. Theorem 6: If the generator polynomial g(x) of C has degree n-k then C is an [n,k]-cyclic code. If g(x) = a 0. a 1 a n k 1.
![Generator Matrix. Theorem 6: If the generator polynomial g(x) of C has degree n-k then C is an [n,k]-cyclic code. If g(x) = a 0. a 1 a n k 1. Generator Matrix. Theorem 6: If the generator polynomial g(x) of C has degree n-k then C is an [n,k]-cyclic code. If g(x) = a 0. a 1 a n k 1.](/thumbs/72/66951550.jpg) Cyclic Codes II Generator Matrix We would now like to consider how the ideas we have previously discussed for linear codes are interpreted in this polynomial version of cyclic codes. Theorem 6: If the
Cyclic Codes II Generator Matrix We would now like to consider how the ideas we have previously discussed for linear codes are interpreted in this polynomial version of cyclic codes. Theorem 6: If the
ELG 5372 Error Control Coding. Lecture 12: Ideals in Rings and Algebraic Description of Cyclic Codes
 ELG 5372 Error Control Coding Lecture 12: Ideals in Rings and Algebraic Description of Cyclic Codes Quotient Ring Example + Quotient Ring Example Quotient Ring Recall the quotient ring R={,,, }, where
ELG 5372 Error Control Coding Lecture 12: Ideals in Rings and Algebraic Description of Cyclic Codes Quotient Ring Example + Quotient Ring Example Quotient Ring Recall the quotient ring R={,,, }, where
Rings. EE 387, Notes 7, Handout #10
 Rings EE 387, Notes 7, Handout #10 Definition: A ring is a set R with binary operations, + and, that satisfy the following axioms: 1. (R, +) is a commutative group (five axioms) 2. Associative law for
Rings EE 387, Notes 7, Handout #10 Definition: A ring is a set R with binary operations, + and, that satisfy the following axioms: 1. (R, +) is a commutative group (five axioms) 2. Associative law for
ADDITONAL MATHEMATICS
 ADDITONAL MATHEMATICS 2002 2011 CLASSIFIED REMAINDER THEOREM Compiled & Edited By Dr. Eltayeb Abdul Rhman www.drtayeb.tk First Edition 2011 7 5 (i) Show that 2x 1 is a factor of 2x 3 5x 2 + 10x 4. [2]
ADDITONAL MATHEMATICS 2002 2011 CLASSIFIED REMAINDER THEOREM Compiled & Edited By Dr. Eltayeb Abdul Rhman www.drtayeb.tk First Edition 2011 7 5 (i) Show that 2x 1 is a factor of 2x 3 5x 2 + 10x 4. [2]
CSCE 564, Fall 2001 Notes 6 Page 1 13 Random Numbers The great metaphysical truth in the generation of random numbers is this: If you want a function
 CSCE 564, Fall 2001 Notes 6 Page 1 13 Random Numbers The great metaphysical truth in the generation of random numbers is this: If you want a function that is reasonably random in behavior, then take any
CSCE 564, Fall 2001 Notes 6 Page 1 13 Random Numbers The great metaphysical truth in the generation of random numbers is this: If you want a function that is reasonably random in behavior, then take any
Chapter 4. Remember: F will always stand for a field.
 Chapter 4 Remember: F will always stand for a field. 4.1 10. Take f(x) = x F [x]. Could there be a polynomial g(x) F [x] such that f(x)g(x) = 1 F? Could f(x) be a unit? 19. Compare with Problem #21(c).
Chapter 4 Remember: F will always stand for a field. 4.1 10. Take f(x) = x F [x]. Could there be a polynomial g(x) F [x] such that f(x)g(x) = 1 F? Could f(x) be a unit? 19. Compare with Problem #21(c).
17 Galois Fields Introduction Primitive Elements Roots of Polynomials... 8
 Contents 17 Galois Fields 2 17.1 Introduction............................... 2 17.2 Irreducible Polynomials, Construction of GF(q m )... 3 17.3 Primitive Elements... 6 17.4 Roots of Polynomials..........................
Contents 17 Galois Fields 2 17.1 Introduction............................... 2 17.2 Irreducible Polynomials, Construction of GF(q m )... 3 17.3 Primitive Elements... 6 17.4 Roots of Polynomials..........................
Ch 7 Summary - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 Ch 7 Summary - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 1. An open-top box is to be made by cutting congruent squares of side length x from the corners of a 8.5- by 11-inch sheet of cardboard and bending up the sides. a)
Ch 7 Summary - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 1. An open-top box is to be made by cutting congruent squares of side length x from the corners of a 8.5- by 11-inch sheet of cardboard and bending up the sides. a)
EE 229B ERROR CONTROL CODING Spring 2005
 EE 9B ERROR CONTROL CODING Spring 005 Solutions for Homework 1. (Weights of codewords in a cyclic code) Let g(x) be the generator polynomial of a binary cyclic code of length n. (a) Show that if g(x) has
EE 9B ERROR CONTROL CODING Spring 005 Solutions for Homework 1. (Weights of codewords in a cyclic code) Let g(x) be the generator polynomial of a binary cyclic code of length n. (a) Show that if g(x) has
Lecture 6: Finite Fields (PART 3) PART 3: Polynomial Arithmetic. Theoretical Underpinnings of Modern Cryptography
 Lecture 6: Finite Fields (PART 3) PART 3: Polynomial Arithmetic Theoretical Underpinnings of Modern Cryptography Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak (kak@purdue.edu) January 26, 2017
Lecture 6: Finite Fields (PART 3) PART 3: Polynomial Arithmetic Theoretical Underpinnings of Modern Cryptography Lecture Notes on Computer and Network Security by Avi Kak (kak@purdue.edu) January 26, 2017
Lecture 7: Polynomial rings
 Lecture 7: Polynomial rings Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur You have seen polynomials many a times till now. The purpose of this lecture is to give a formal treatment to constructing polynomials and the rules
Lecture 7: Polynomial rings Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur You have seen polynomials many a times till now. The purpose of this lecture is to give a formal treatment to constructing polynomials and the rules
Solutions to Assignment 1
 Solutions to Assignment 1 Question 1. [Exercises 1.1, # 6] Use the division algorithm to prove that every odd integer is either of the form 4k + 1 or of the form 4k + 3 for some integer k. For each positive
Solutions to Assignment 1 Question 1. [Exercises 1.1, # 6] Use the division algorithm to prove that every odd integer is either of the form 4k + 1 or of the form 4k + 3 for some integer k. For each positive
3.4. ZEROS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 3.4. ZEROS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What You Should Learn Use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to determine the number of zeros of polynomial functions. Find rational zeros of polynomial functions. Find
3.4. ZEROS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What You Should Learn Use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to determine the number of zeros of polynomial functions. Find rational zeros of polynomial functions. Find
Section VI.33. Finite Fields
 VI.33 Finite Fields 1 Section VI.33. Finite Fields Note. In this section, finite fields are completely classified. For every prime p and n N, there is exactly one (up to isomorphism) field of order p n,
VI.33 Finite Fields 1 Section VI.33. Finite Fields Note. In this section, finite fields are completely classified. For every prime p and n N, there is exactly one (up to isomorphism) field of order p n,
3 The fundamentals: Algorithms, the integers, and matrices
 3 The fundamentals: Algorithms, the integers, and matrices 3.4 The integers and division This section introduces the basics of number theory number theory is the part of mathematics involving integers
3 The fundamentals: Algorithms, the integers, and matrices 3.4 The integers and division This section introduces the basics of number theory number theory is the part of mathematics involving integers
Today. Polynomials. Secret Sharing.
 Today. Polynomials. Secret Sharing. A secret! I have a secret! A number from 0 to 10. What is it? Any one of you knows nothing! Any two of you can figure it out! Example Applications: Nuclear launch: need
Today. Polynomials. Secret Sharing. A secret! I have a secret! A number from 0 to 10. What is it? Any one of you knows nothing! Any two of you can figure it out! Example Applications: Nuclear launch: need
2a 2 4ac), provided there is an element r in our
 MTH 310002 Test II Review Spring 2012 Absractions versus examples The purpose of abstraction is to reduce ideas to their essentials, uncluttered by the details of a specific situation Our lectures built
MTH 310002 Test II Review Spring 2012 Absractions versus examples The purpose of abstraction is to reduce ideas to their essentials, uncluttered by the details of a specific situation Our lectures built
Introduction to finite fields
 Chapter 7 Introduction to finite fields This chapter provides an introduction to several kinds of abstract algebraic structures, particularly groups, fields, and polynomials. Our primary interest is in
Chapter 7 Introduction to finite fields This chapter provides an introduction to several kinds of abstract algebraic structures, particularly groups, fields, and polynomials. Our primary interest is in
6A The language of polynomials. A Polynomial function follows the rule. Degree of a polynomial is the highest power of x with a non-zero coefficient.
 Unit Mathematical Methods Chapter 6: Polynomials Objectives To add, subtract and multiply polynomials. To divide polynomials. To use the remainder theorem, factor theorem and rational-root theorem to identify
Unit Mathematical Methods Chapter 6: Polynomials Objectives To add, subtract and multiply polynomials. To divide polynomials. To use the remainder theorem, factor theorem and rational-root theorem to identify
, a 1. , a 2. ,..., a n
 CHAPTER Points to Remember :. Let x be a variable, n be a positive integer and a 0, a, a,..., a n be constants. Then n f ( x) a x a x... a x a, is called a polynomial in variable x. n n n 0 POLNOMIALS.
CHAPTER Points to Remember :. Let x be a variable, n be a positive integer and a 0, a, a,..., a n be constants. Then n f ( x) a x a x... a x a, is called a polynomial in variable x. n n n 0 POLNOMIALS.
Warm-Up. Use long division to divide 5 into
 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
Cyclic codes. Vahid Meghdadi Reference: Error Correction Coding by Todd K. Moon. February 2008
 Cyclic codes Vahid Meghdadi Reference: Error Correction Coding by Todd K. Moon February 2008 1 Definitions Definition 1. A ring < R, +,. > is a set R with two binary operation + (addition) and. (multiplication)
Cyclic codes Vahid Meghdadi Reference: Error Correction Coding by Todd K. Moon February 2008 1 Definitions Definition 1. A ring < R, +,. > is a set R with two binary operation + (addition) and. (multiplication)
Finite Fields and Error-Correcting Codes
 Lecture Notes in Mathematics Finite Fields and Error-Correcting Codes Karl-Gustav Andersson (Lund University) (version 1.013-16 September 2015) Translated from Swedish by Sigmundur Gudmundsson Contents
Lecture Notes in Mathematics Finite Fields and Error-Correcting Codes Karl-Gustav Andersson (Lund University) (version 1.013-16 September 2015) Translated from Swedish by Sigmundur Gudmundsson Contents
Homework 9 Solutions to Selected Problems
 Homework 9 Solutions to Selected Problems June 11, 2012 1 Chapter 17, Problem 12 Since x 2 + x + 4 has degree 2 and Z 11 is a eld, we may use Theorem 17.1 and show that f(x) is irreducible because it has
Homework 9 Solutions to Selected Problems June 11, 2012 1 Chapter 17, Problem 12 Since x 2 + x + 4 has degree 2 and Z 11 is a eld, we may use Theorem 17.1 and show that f(x) is irreducible because it has
Introduction to Modern Cryptography. (1) Finite Groups, Rings and Fields. (2) AES - Advanced Encryption Standard
 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 3 (1) Finite Groups, Rings and Fields (2) AES - Advanced Encryption Standard +,0, and -a are only notations! Review - Groups Def (group): A set G with a binary
Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 3 (1) Finite Groups, Rings and Fields (2) AES - Advanced Encryption Standard +,0, and -a are only notations! Review - Groups Def (group): A set G with a binary
Algebra Review 2. 1 Fields. A field is an extension of the concept of a group.
 Algebra Review 2 1 Fields A field is an extension of the concept of a group. Definition 1. A field (F, +,, 0 F, 1 F ) is a set F together with two binary operations (+, ) on F such that the following conditions
Algebra Review 2 1 Fields A field is an extension of the concept of a group. Definition 1. A field (F, +,, 0 F, 1 F ) is a set F together with two binary operations (+, ) on F such that the following conditions
Lecture Notes. Advanced Discrete Structures COT S
 Lecture Notes Advanced Discrete Structures COT 4115.001 S15 2015-01-13 Recap Divisibility Prime Number Theorem Euclid s Lemma Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic Euclidean Algorithm Basic Notions - Section
Lecture Notes Advanced Discrete Structures COT 4115.001 S15 2015-01-13 Recap Divisibility Prime Number Theorem Euclid s Lemma Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic Euclidean Algorithm Basic Notions - Section
Finite Fields. Saravanan Vijayakumaran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay
 1 / 25 Finite Fields Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay September 25, 2014 2 / 25 Fields Definition A set F together
1 / 25 Finite Fields Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay September 25, 2014 2 / 25 Fields Definition A set F together
+ 1 3 x2 2x x3 + 3x 2 + 0x x x2 2x + 3 4
 Math 4030-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Polynomials at the Foundations: Rational Coefficients The rational numbers are our first field, meaning that all the laws of arithmetic hold, every number
Math 4030-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Polynomials at the Foundations: Rational Coefficients The rational numbers are our first field, meaning that all the laws of arithmetic hold, every number
Information Theory. Lecture 7
 Information Theory Lecture 7 Finite fields continued: R3 and R7 the field GF(p m ),... Cyclic Codes Intro. to cyclic codes: R8.1 3 Mikael Skoglund, Information Theory 1/17 The Field GF(p m ) π(x) irreducible
Information Theory Lecture 7 Finite fields continued: R3 and R7 the field GF(p m ),... Cyclic Codes Intro. to cyclic codes: R8.1 3 Mikael Skoglund, Information Theory 1/17 The Field GF(p m ) π(x) irreducible
2-4 Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 Write a polynomial function of least degree with real coefficients in standard form that has the given zeros. 33. 2, 4, 3, 5 Using the Linear Factorization Theorem and the zeros 2, 4, 3, and 5, write f
Write a polynomial function of least degree with real coefficients in standard form that has the given zeros. 33. 2, 4, 3, 5 Using the Linear Factorization Theorem and the zeros 2, 4, 3, and 5, write f
Frequency Domain Finite Field Arithmetic for Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 Frequency Domain Finite Field Arithmetic for Elliptic Curve Cryptography Selçuk Baktır, Berk Sunar {selcuk,sunar}@wpi.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Worcester Polytechnic Institute
Frequency Domain Finite Field Arithmetic for Elliptic Curve Cryptography Selçuk Baktır, Berk Sunar {selcuk,sunar}@wpi.edu Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Worcester Polytechnic Institute
Dividing Polynomials: Remainder and Factor Theorems
 Dividing Polynomials: Remainder and Factor Theorems When we divide one polynomial by another, we obtain a quotient and a remainder. If the remainder is zero, then the divisor is a factor of the dividend.
Dividing Polynomials: Remainder and Factor Theorems When we divide one polynomial by another, we obtain a quotient and a remainder. If the remainder is zero, then the divisor is a factor of the dividend.
Integer-Valued Polynomials
 Integer-Valued Polynomials LA Math Circle High School II Dillon Zhi October 11, 2015 1 Introduction Some polynomials take integer values p(x) for all integers x. The obvious examples are the ones where
Integer-Valued Polynomials LA Math Circle High School II Dillon Zhi October 11, 2015 1 Introduction Some polynomials take integer values p(x) for all integers x. The obvious examples are the ones where
Rings. Chapter 1. Definition 1.2. A commutative ring R is a ring in which multiplication is commutative. That is, ab = ba for all a, b R.
 Chapter 1 Rings We have spent the term studying groups. A group is a set with a binary operation that satisfies certain properties. But many algebraic structures such as R, Z, and Z n come with two binary
Chapter 1 Rings We have spent the term studying groups. A group is a set with a binary operation that satisfies certain properties. But many algebraic structures such as R, Z, and Z n come with two binary
4 Number Theory and Cryptography
 4 Number Theory and Cryptography 4.1 Divisibility and Modular Arithmetic This section introduces the basics of number theory number theory is the part of mathematics involving integers and their properties.
4 Number Theory and Cryptography 4.1 Divisibility and Modular Arithmetic This section introduces the basics of number theory number theory is the part of mathematics involving integers and their properties.
Coding Theory and Applications. Solved Exercises and Problems of Cyclic Codes. Enes Pasalic University of Primorska Koper, 2013
 Coding Theory and Applications Solved Exercises and Problems of Cyclic Codes Enes Pasalic University of Primorska Koper, 2013 Contents 1 Preface 3 2 Problems 4 2 1 Preface This is a collection of solved
Coding Theory and Applications Solved Exercises and Problems of Cyclic Codes Enes Pasalic University of Primorska Koper, 2013 Contents 1 Preface 3 2 Problems 4 2 1 Preface This is a collection of solved
Basic Concepts in Number Theory and Finite Fields
 Basic Concepts in Number Theory and Finite Fields Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 4-1 Overview
Basic Concepts in Number Theory and Finite Fields Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 4-1 Overview
Continuing discussion of CRC s, especially looking at two-bit errors
 Continuing discussion of CRC s, especially looking at two-bit errors The definition of primitive binary polynomials Brute force checking for primitivity A theorem giving a better test for primitivity Fast
Continuing discussion of CRC s, especially looking at two-bit errors The definition of primitive binary polynomials Brute force checking for primitivity A theorem giving a better test for primitivity Fast
We say that a polynomial is in the standard form if it is written in the order of decreasing exponents of x. Operations on polynomials:
 R.4 Polynomials in one variable A monomial: an algebraic expression of the form ax n, where a is a real number, x is a variable and n is a nonnegative integer. : x,, 7 A binomial is the sum (or difference)
R.4 Polynomials in one variable A monomial: an algebraic expression of the form ax n, where a is a real number, x is a variable and n is a nonnegative integer. : x,, 7 A binomial is the sum (or difference)
PETERSON'S TABLE OF IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER GF(2)
 PETERSON'S TABLE OF IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER GF(2) This table was taken from Error-Correcting Codes by W. Wesley Peterson, MIT Press (1970), pages 251-155. This table is to be used only by students
PETERSON'S TABLE OF IRREDUCIBLE POLYNOMIALS OVER GF(2) This table was taken from Error-Correcting Codes by W. Wesley Peterson, MIT Press (1970), pages 251-155. This table is to be used only by students
Math 109 HW 9 Solutions
 Math 109 HW 9 Solutions Problems IV 18. Solve the linear diophantine equation 6m + 10n + 15p = 1 Solution: Let y = 10n + 15p. Since (10, 15) is 5, we must have that y = 5x for some integer x, and (as we
Math 109 HW 9 Solutions Problems IV 18. Solve the linear diophantine equation 6m + 10n + 15p = 1 Solution: Let y = 10n + 15p. Since (10, 15) is 5, we must have that y = 5x for some integer x, and (as we
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Discussion 6A Solution
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Discussion 6A Solution 1. Polynomial intersections Find (and prove) an upper-bound on the number of times two distinct degree
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Discussion 6A Solution 1. Polynomial intersections Find (and prove) an upper-bound on the number of times two distinct degree
Simplifying Rational Expressions and Functions
 Department of Mathematics Grossmont College October 15, 2012 Recall: The Number Types Definition The set of whole numbers, ={0, 1, 2, 3, 4,...} is the set of natural numbers unioned with zero, written
Department of Mathematics Grossmont College October 15, 2012 Recall: The Number Types Definition The set of whole numbers, ={0, 1, 2, 3, 4,...} is the set of natural numbers unioned with zero, written
The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts.
 Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models
 Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models Learning Objectives: 1. Identify Polynomial Functions and Their Degree 2. Graph Polynomial Functions Using Transformations 3. Identify the Real Zeros of a Polynomial
Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models Learning Objectives: 1. Identify Polynomial Functions and Their Degree 2. Graph Polynomial Functions Using Transformations 3. Identify the Real Zeros of a Polynomial
COMP239: Mathematics for Computer Science II. Prof. Chadi Assi EV7.635
 COMP239: Mathematics for Computer Science II Prof. Chadi Assi assi@ciise.concordia.ca EV7.635 The Euclidean Algorithm The Euclidean Algorithm Finding the GCD of two numbers using prime factorization is
COMP239: Mathematics for Computer Science II Prof. Chadi Assi assi@ciise.concordia.ca EV7.635 The Euclidean Algorithm The Euclidean Algorithm Finding the GCD of two numbers using prime factorization is
Groups, Rings, and Finite Fields. Andreas Klappenecker. September 12, 2002
 Background on Groups, Rings, and Finite Fields Andreas Klappenecker September 12, 2002 A thorough understanding of the Agrawal, Kayal, and Saxena primality test requires some tools from algebra and elementary
Background on Groups, Rings, and Finite Fields Andreas Klappenecker September 12, 2002 A thorough understanding of the Agrawal, Kayal, and Saxena primality test requires some tools from algebra and elementary
Complex Numbers: Definition: A complex number is a number of the form: z = a + bi where a, b are real numbers and i is a symbol with the property: i
 Complex Numbers: Definition: A complex number is a number of the form: z = a + bi where a, b are real numbers and i is a symbol with the property: i 2 = 1 Sometimes we like to think of i = 1 We can treat
Complex Numbers: Definition: A complex number is a number of the form: z = a + bi where a, b are real numbers and i is a symbol with the property: i 2 = 1 Sometimes we like to think of i = 1 We can treat
Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is 10. Make an organized list.
 9.5 Study Guide For use with pages 582 589 GOAL Factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. EXAMPLE 1 Factor when b and c are positive Factor x 2 1 10x 1 24. Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is
9.5 Study Guide For use with pages 582 589 GOAL Factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. EXAMPLE 1 Factor when b and c are positive Factor x 2 1 10x 1 24. Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is
MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions
 MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions Name: Student Number: Answer all questions. Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown. Remarks by me in italics and would not be required in a test - J.P. Question
MS 2001: Test 1 B Solutions Name: Student Number: Answer all questions. Marks may be lost if necessary work is not clearly shown. Remarks by me in italics and would not be required in a test - J.P. Question
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Cyclic Codes March 22, 2007 1. A cyclic code, C, is an ideal genarated by its minimal degree polynomial, g(x). C = < g(x) >, = {m(x)g(x) : m(x) is
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Cyclic Codes March 22, 2007 1. A cyclic code, C, is an ideal genarated by its minimal degree polynomial, g(x). C = < g(x) >, = {m(x)g(x) : m(x) is
Computer Architecture 10. Residue Number Systems
 Computer Architecture 10 Residue Number Systems Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 A Puzzle What number has the reminders 2, 3 and 2 when divided by the numbers 7, 5 and 3? x mod 7 = 2 x mod 5 =
Computer Architecture 10 Residue Number Systems Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 A Puzzle What number has the reminders 2, 3 and 2 when divided by the numbers 7, 5 and 3? x mod 7 = 2 x mod 5 =
Algebra. Modular arithmetic can be handled mathematically by introducing a congruence relation on the integers described in the above example.
 Coding Theory Massoud Malek Algebra Congruence Relation The definition of a congruence depends on the type of algebraic structure under consideration Particular definitions of congruence can be made for
Coding Theory Massoud Malek Algebra Congruence Relation The definition of a congruence depends on the type of algebraic structure under consideration Particular definitions of congruence can be made for
Secondary Math 3 Honors - Polynomial and Polynomial Functions Test Review
 Name: Class: Date: Secondary Math 3 Honors - Polynomial and Polynomial Functions Test Review 1 Write 3x 2 ( 2x 2 5x 3 ) in standard form State whether the function is even, odd, or neither Show your work
Name: Class: Date: Secondary Math 3 Honors - Polynomial and Polynomial Functions Test Review 1 Write 3x 2 ( 2x 2 5x 3 ) in standard form State whether the function is even, odd, or neither Show your work
Error Detection & Correction
 Error Detection & Correction Error detection & correction noisy channels techniques in networking error detection error detection capability retransmition error correction reconstruction checksums redundancy
Error Detection & Correction Error detection & correction noisy channels techniques in networking error detection error detection capability retransmition error correction reconstruction checksums redundancy
Mathematics for Business and Economics - I. Chapter 5. Functions (Lecture 9)
 Mathematics for Business and Economics - I Chapter 5. Functions (Lecture 9) Functions The idea of a function is this: a correspondence between two sets D and R such that to each element of the first set,
Mathematics for Business and Economics - I Chapter 5. Functions (Lecture 9) Functions The idea of a function is this: a correspondence between two sets D and R such that to each element of the first set,
6.5 Dividing Polynomials
 Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Section 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition
 Section 8.6 Lecture Notes Page 1 of 10 Section 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Partial fraction decomposition involves decomposing a rational function, or reversing the process of combining two or more
Section 8.6 Lecture Notes Page 1 of 10 Section 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Partial fraction decomposition involves decomposing a rational function, or reversing the process of combining two or more
Lecture 2: Number Representations (2)
 Lecture 2: Number Representations (2) ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 1/29/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Number systems (cont'd) Floating point number system representations Residue number
Lecture 2: Number Representations (2) ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 1/29/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Number systems (cont'd) Floating point number system representations Residue number
CHAPTER 2 POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) 4-bit LFSR
 Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) These are n-bit counters exhibiting pseudo-random behavior. Built from simple shift-registers with a small number of xor gates. Used for: random number generation
CHAPTER 14. Ideals and Factor Rings
 CHAPTER 14 Ideals and Factor Rings Ideals Definition (Ideal). A subring A of a ring R is called a (two-sided) ideal of R if for every r 2 R and every a 2 A, ra 2 A and ar 2 A. Note. (1) A absorbs elements
CHAPTER 14 Ideals and Factor Rings Ideals Definition (Ideal). A subring A of a ring R is called a (two-sided) ideal of R if for every r 2 R and every a 2 A, ra 2 A and ar 2 A. Note. (1) A absorbs elements
Montgomery Multiplier and Squarer in GF(2 m )
 Montgomery Multiplier and Squarer in GF( m ) Huapeng Wu The Centre for Applied Cryptographic Research Department of Combinatorics and Optimization University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Canada h3wu@cacrmathuwaterlooca
Montgomery Multiplier and Squarer in GF( m ) Huapeng Wu The Centre for Applied Cryptographic Research Department of Combinatorics and Optimization University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Canada h3wu@cacrmathuwaterlooca
REDUNDANT TRINOMIALS FOR FINITE FIELDS OF CHARACTERISTIC 2
 REDUNDANT TRINOMIALS FOR FINITE FIELDS OF CHARACTERISTIC 2 CHRISTOPHE DOCHE Abstract. In this paper we introduce so-called redundant trinomials to represent elements of nite elds of characteristic 2. The
REDUNDANT TRINOMIALS FOR FINITE FIELDS OF CHARACTERISTIC 2 CHRISTOPHE DOCHE Abstract. In this paper we introduce so-called redundant trinomials to represent elements of nite elds of characteristic 2. The
Chapter 2 (Part 3): The Fundamentals: Algorithms, the Integers & Matrices. Integers & Algorithms (2.5)
 CSE 54 Discrete Mathematics & Chapter 2 (Part 3): The Fundamentals: Algorithms, the Integers & Matrices Integers & Algorithms (Section 2.5) by Kenneth H. Rosen, Discrete Mathematics & its Applications,
CSE 54 Discrete Mathematics & Chapter 2 (Part 3): The Fundamentals: Algorithms, the Integers & Matrices Integers & Algorithms (Section 2.5) by Kenneth H. Rosen, Discrete Mathematics & its Applications,
ECEN 604: Channel Coding for Communications
 ECEN 604: Channel Coding for Communications Lecture: Introduction to Cyclic Codes Henry D. Pfister Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University ECEN 604: Channel Coding for Communications
ECEN 604: Channel Coding for Communications Lecture: Introduction to Cyclic Codes Henry D. Pfister Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University ECEN 604: Channel Coding for Communications
PROBLEMS ON CONGRUENCES AND DIVISIBILITY
 PROBLEMS ON CONGRUENCES AND DIVISIBILITY 1. Do there exist 1,000,000 consecutive integers each of which contains a repeated prime factor? 2. A positive integer n is powerful if for every prime p dividing
PROBLEMS ON CONGRUENCES AND DIVISIBILITY 1. Do there exist 1,000,000 consecutive integers each of which contains a repeated prime factor? 2. A positive integer n is powerful if for every prime p dividing
CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
Modular Multiplication in GF (p k ) using Lagrange Representation
 Modular Multiplication in GF (p k ) using Lagrange Representation Jean-Claude Bajard, Laurent Imbert, and Christophe Nègre Laboratoire d Informatique, de Robotique et de Microélectronique de Montpellier
Modular Multiplication in GF (p k ) using Lagrange Representation Jean-Claude Bajard, Laurent Imbert, and Christophe Nègre Laboratoire d Informatique, de Robotique et de Microélectronique de Montpellier
Know the Well-ordering principle: Any set of positive integers which has at least one element contains a smallest element.
 The first exam will be on Monday, June 8, 202. The syllabus will be sections. and.2 in Lax, and the number theory handout found on the class web site, plus the handout on the method of successive squaring
The first exam will be on Monday, June 8, 202. The syllabus will be sections. and.2 in Lax, and the number theory handout found on the class web site, plus the handout on the method of successive squaring
Conversions between Decimal and Binary
 Conversions between Decimal and Binary Binary to Decimal Technique - use the definition of a number in a positional number system with base 2 - evaluate the definition formula ( the formula ) using decimal
Conversions between Decimal and Binary Binary to Decimal Technique - use the definition of a number in a positional number system with base 2 - evaluate the definition formula ( the formula ) using decimal
Novel Implementation of Finite Field Multipliers over GF(2m) for Emerging Cryptographic Applications
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Browse all Theses and Dissertations Theses and Dissertations 2017 Novel Implementation of Finite Field Multipliers over GF(2m) for Emerging Cryptographic Applications
Wright State University CORE Scholar Browse all Theses and Dissertations Theses and Dissertations 2017 Novel Implementation of Finite Field Multipliers over GF(2m) for Emerging Cryptographic Applications
Math 0320 Final Exam Review
 Math 0320 Final Exam Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Factor out the GCF using the Distributive Property. 1) 6x 3 + 9x 1) Objective:
Math 0320 Final Exam Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Factor out the GCF using the Distributive Property. 1) 6x 3 + 9x 1) Objective:
Chapter 4: Radicals and Complex Numbers
 Chapter : Radicals and Complex Numbers Section.1: A Review of the Properties of Exponents #1-: Simplify the expression. 1) x x ) z z ) a a ) b b ) 6) 7) x x x 8) y y y 9) x x y 10) y 8 b 11) b 7 y 1) y
Chapter : Radicals and Complex Numbers Section.1: A Review of the Properties of Exponents #1-: Simplify the expression. 1) x x ) z z ) a a ) b b ) 6) 7) x x x 8) y y y 9) x x y 10) y 8 b 11) b 7 y 1) y
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY. Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice a prime.
 PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
Introduction to Cryptology. Lecture 19
 Introduction to Cryptology Lecture 19 Announcements HW6 due today HW7 due Thursday 4/20 Remember to sign up for Extra Credit Agenda Last time More details on AES/DES (K/L 6.2) Practical Constructions of
Introduction to Cryptology Lecture 19 Announcements HW6 due today HW7 due Thursday 4/20 Remember to sign up for Extra Credit Agenda Last time More details on AES/DES (K/L 6.2) Practical Constructions of
Functions and Equations
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Euclid eworkshop # Functions and Equations c 006 CANADIAN
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Euclid eworkshop # Functions and Equations c 006 CANADIAN
Section 6.6 Evaluating Polynomial Functions
 Name: Period: Section 6.6 Evaluating Polynomial Functions Objective(s): Use synthetic substitution to evaluate polynomials. Essential Question: Homework: Assignment 6.6. #1 5 in the homework packet. Notes:
Name: Period: Section 6.6 Evaluating Polynomial Functions Objective(s): Use synthetic substitution to evaluate polynomials. Essential Question: Homework: Assignment 6.6. #1 5 in the homework packet. Notes:
