220A Solutions. Assignment 2
|
|
|
- Dylan Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 220A Solutions Assignment A picture is worth 1000 words. Draw an arrow from the starting to the ending point to get the displacement as follows: y x cm 3.4 cm x The displacement is just 7.6 cm to the left, which we write x cm. The average velocity is this displacement divided by the elapsed time 3.1 s which gives cm/ 3.1 s cm/s. Once we gain experience, we feel comfortable using the definition of the average velocity, eq 2-2, as follows: _ x 2 - x 1 v t 2 - t cm- 3.4 cm 6.1 s- 3.0 s cm/s, and we understand that the minus sign means that the velocity is to the left We need to have a clear understanding of the meaning of the words "speed" and "average velocity". Speed is the total distance traveled divided by the elapsed time. The total distance is 8 times the track distance or mile 2 miles. The elapsed time is 12.5 min, so speed 2 miles/12.5 min miles/min. The problem requests the answer in m/s, so we multiply by 1 as follows: (0.160 miles/min) (1 min/60 s) (1.61 km/mile) (1000 m/km) 4.29 m/s. The conversion factor from km to mile is on the insider cover of your text. The average velocity is the displace divided by the elapsed time, but since the person ends up where she began the displacement is zero, so v _ 0.
2 2-11. The instantaneous velocity is the slope of the curve in Fig (a). At 10 s, we have a straight line whose slope we can get by computing the rise/run. Pick any two points on the straight line; for example, (0,0) and (15 s, 4 m). v rise/run (4 m - 0(/(15 s - 0) 0.27 m/s (b). At 30 s, the tangent to the curve is about 45 on the scale of Fig Draw the tangent and get the rise/run. I took the two points (15 s, 0) and (38 s, 25 m). This gives v rise/run (25 m - 0)/(38 s - 15 s) 1.1 m/s. Your tangent will be a little bit different than mine and you may use two different points. The author gives 1.2 m/s as the answer. (c). The velocity is constant in the interval including 5 s, so the average velocity is equal to the velocity. v _ 0.27 m/s. (d). Look at Fig. 2-3 and pick off the starting and ending values of x. x 2 16 t 30 s and x 1 8 t 25 s, so _ v (16 m - 8 m)/( 30 s - 25 s) 1.6 m/s. (e). x 2 10 t 50 s and x 1 20 t 40 s, so _ v (10 m - 20 m)/( 50s - 40 s) m/s The acceleration is a 1.6 m/s2. The definition of the average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the elapsed time. a v/ t. The change in velocity is final velocity minus the initial velocity; v 110 km/hr - 80 km/hr 30 km/hr. Thus, 1.6 m/s2 30 km/hr/ t. Multiply through by t and divided by 1.6 m/s 2 to get t 30 km/hr/1.6 m/s 2 (1000 m/km) (1 hr/3600 s) 5.2 s.
3 2-27. The velocity is defined to be the time derivative of the displacement and the acceleration is the time derivative of the velocity. First, we need to understand the units of the "8.5". Since 8.5t2 has units meters, the 8.5 has units m/s2. Since the displacement is given by x 6.0t + 8.5t 2, v d dt [ 6.0 m t + 8.5m/s2 t 2 ] 6.0m m/s 2 t a d dt [ 6.0m + 17 m/s2 t] 17 m/s Analyze what is known. The final and intial velocities are given and the elapsed time is given. Figure out what is asked for. In this case, it is the acceleration in the first question and the displacement in the second. Note: "how far" is the English version of the physics definition displacement, x - x0. Since the acceleration is constant, we may select from one of the following: v v0 + at, (1) x x0 + v0t at 2 (2) v2 v0 2 +2a(x - x0) (3) Equation 1 will work to get the acceleration, because everything else is given; thus, subtract 12 m/s from both sides, divide both sides by 6.0 s, 21 m/s 12 m/s + a 6.0 s, 9 m/s a 6.0 s, a (9 m/s)/6.0 s 1.5 m/s2. Now that the acceleration is known, we can use either eq 2 or 3. From eq 2 x - x0 12 m/s 6.0 s m/s 2 (6.0 s)2 72 m + 27 m 99 m.
4 From eq 3, Subtract (12 m/s)2 from both sides, Divide both sides by 3.0 m/s2, (21 m/s)2 (12 m/s) m/s2(x - x0). (21 m/s)2 -(12 m/s)2 3.0 m/s2(x - x0). (x - x0) [(21 m/s)2 -(12 m/s)2]/3.0 m/s2 99 m Analyze what is known. During the first second, the velocity is constant, so a 0. Let us get the units in order: v0 90 km/hr (1000 m/km) (1 hr/ 3600 s) 25 m/s. Equation 2 gives x x0 + v0t, so the displacement in the first second is x - x0 v0t 25 m/s 1 s 25 m. (a) After the first second a -4.0 m/s2 is known, the initial velocity is known, v0 25 m/s, and the final velocity is known, v 0. We cannot use eqs 1 or 2 because we don't know the elapsed time. Equation 3 is so, during the braking period, 02 (25 m/s)2 +2(-4.0 m/s2)(x - x0), (x - x0) (25 m/s)2/(-8.0 m/s2) 78.1 m, giving a total displacement of 25 m m 103 m. (b) Equation 3 is 02 (25 m/s)2 +2(-8.0 m/s2)(x - x0), so, during the braking period, (x - x0) (25 m/s)2/(-16.0 m/s2) 39 m, giving a total displacement of 25 m + 39 m 64 m.
5 2-55. Analyze what is known. The initial velocity of the package is known, v m/s. The acceleration is known a -9.8 m/s2. The original position is known y0 115 m, taking the origin at the ground, and the final position is known y 0. The time is requested so only eqs 1 and 2 can be of direct use. Equation 1 won't work, because we don't know the final velocity. Equation 2 is m m/s t (-9.80 m/s 2)t2 This is the quadratic formula with A m/s2, B 5.60 m/s, and C 115 m. Therefore, t - B ± B2-4AC 2A m ± (5.60 m)2-4(-4.9 m/s2)115 m 2(-4.9 m/s2) 5.60 m ± 2.28 x 103 m2/s2 9.8 m/s2 5.60m/9.8 m/s2 ± (47.8 m/s)/9.8 m/s s ± 4.88 s. Thus, t 5.44 s or t s. The answer must be positive so t 5.44 s. The speed just before striking the ground is not requested, but it is useful to compute it so the next problem is easy. From eq 1 v 5.60 m/s + (-9.80 m/s2) 5.44s m/s. Notice how this number (actually with round-off 47.8 m/s) appears in the above calculation Analyze what is known. The initial velocity of the package is known, v m/s. The acceleration is known a -9.8 m/s2. The original position is known y m, taking the origin at the ground, and the final position is known y 0. (a) The time is requested so only eqs 1 and 2 can be of direct use. Equation 1 won't work, because we don't know the final velocity. Equation 2 is 0 65 m + 10 m/s t (-9.80 m/s 2)t2
6 This is the quadratic formula with A m/s2, B 10 m/s, and C 65 m. Therefore, t - B ± B2-4AC 2A - 10 m ± (10 m)2-4(-4.9 m/s2)65 m 2(-4.9 m/s2) 10 m ± 1.37 x 103 m2/s2 9.8 m/s2 10 m/9.8 m/s2 ± (37.1 m/s)/9.8 m/s2 10 m/9.8 m/s2 ± (37.1 m/s)/9.8 m/s s ± 3.79 s. Thus, t 4.81 s or t s. The answer must be positive so t 4.81 s. (b) To get the final velocity, we can use either eq 1 or 3. Equation 1 gives v 10 m/s + (-9.8 m/s)(4.81 s) m/s alternatively, eq 3 gives, using y 0 and y0 65 m v2 (10 m/s)2 +2(- 9.8 m/s2)(0-65 m) 1.37 x 103, so v ± 37.1 m/s The physical answer is m/s since it is going down when it hits the ground.
If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph.
 Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Displacement, Velocity & Acceleration
 Displacement, Velocity & Acceleration Honors/AP Physics Mr. Velazquez Rm. 254 1 Velocity vs. Speed Speed and velocity can both be defined as a change in position or displacement over time. However, speed
Displacement, Velocity & Acceleration Honors/AP Physics Mr. Velazquez Rm. 254 1 Velocity vs. Speed Speed and velocity can both be defined as a change in position or displacement over time. However, speed
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Units of Chapter 2 Reference Frames and Displacement Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Solving
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Units of Chapter 2 Reference Frames and Displacement Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Solving
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
9/7/2017. Week 2 Recitation: Chapter 2: Problems 5, 19, 25, 29, 33, 39, 49, 58.
 9/7/7 Week Recitation: Chapter : Problems 5, 9, 5, 9, 33, 39, 49, 58. 5. The data in the following table describe the initial and final positions of a moving car. The elapsed time for each of the three
9/7/7 Week Recitation: Chapter : Problems 5, 9, 5, 9, 33, 39, 49, 58. 5. The data in the following table describe the initial and final positions of a moving car. The elapsed time for each of the three
12/06/2010. Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement. 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014)
 Name: Date: AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014) Instructions: 1. Read and study Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2. Answer the questions below. 3. Submit your answers online
Name: Date: AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (2014) Instructions: 1. Read and study Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension. 2. Answer the questions below. 3. Submit your answers online
Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics Units of Chapter 3 Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Chapter 3 Vectors in Physics Units of Chapter 3 Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors
Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value
 AP Calculus Unit 6 Basic Integration & Applications Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value b (1) v( t) dt p( b) p( a), where v(t) represents the velocity and
AP Calculus Unit 6 Basic Integration & Applications Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value b (1) v( t) dt p( b) p( a), where v(t) represents the velocity and
Graphical Analysis; and Vectors
 Graphical Analysis; and Vectors Graphs Drawing good pictures can be the secret to solving physics problems. It's amazing how much information you can get from a diagram. We also usually need equations
Graphical Analysis; and Vectors Graphs Drawing good pictures can be the secret to solving physics problems. It's amazing how much information you can get from a diagram. We also usually need equations
1.1 Graphing Motion. IB Physics 11 Kinematics
 IB Physics 11 Kinematics 1.1 Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. We will need to learn some definitions: A Scalar quantity is a measurement that has
IB Physics 11 Kinematics 1.1 Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. We will need to learn some definitions: A Scalar quantity is a measurement that has
Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration. Unit 1: Kinematics
 Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure
Velocity, Speed, and Acceleration Unit 1: Kinematics Speed vs Velocity Speed is a precise measurement of how fast you are going. It is your distance traveled over time. Speed is a scalar quantity. To measure
Four Types of Motion We ll Study
 Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE
 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 2 21 IDENTIFY: The average velocity is Let be upward EXECUTE: (a) EVALUATE: For the first 115 s of the flight, When the velocity isn t constant the average velocity depends
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 2 21 IDENTIFY: The average velocity is Let be upward EXECUTE: (a) EVALUATE: For the first 115 s of the flight, When the velocity isn t constant the average velocity depends
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s rotation
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s rotation
Chapter 2. Preview. Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically
 Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Preview Objectives One Dimensional Motion Displacement Average Velocity Velocity and Speed Interpreting Velocity Graphically Section 1 Displacement and Velocity Objectives
CHAPTER 2: Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
During the second part of the trip then we travelled at 50 km/hr for hour so x = v avg t =
 PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics
 Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics Kari Eloranta 2018 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio Pre Diploma Program Year October 11, 2017 1 / 17 3.1 Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change
Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics Kari Eloranta 2018 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio Pre Diploma Program Year October 11, 2017 1 / 17 3.1 Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST
 STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
Representing Motion Chapter 2
 Phenomena Representing Motion Chapter 2 Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving at this moment? o A.) 0m/s o B.) 783 mi/h o C.) 350m/s o D.) 30 km/s Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving? oa.) 0m/s ob.) 783 mi/h
Phenomena Representing Motion Chapter 2 Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving at this moment? o A.) 0m/s o B.) 783 mi/h o C.) 350m/s o D.) 30 km/s Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving? oa.) 0m/s ob.) 783 mi/h
Physics 11 Chapter 2: Kinematics in One Dimension
 Physics 11 Chapter 2: Kinematics in One Dimension Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford It is our attitude at the beginning of a difficult task which, more than
Physics 11 Chapter 2: Kinematics in One Dimension Whether you think you can or think you can t, you re usually right. Henry Ford It is our attitude at the beginning of a difficult task which, more than
Physics 101 Discussion Week 3 Explanation (2011)
 Physics 101 Discussion Week 3 Explanation (2011) D3-1. Velocity and Acceleration A. 1: average velocity. Q1. What is the definition of the average velocity v? Let r(t) be the total displacement vector
Physics 101 Discussion Week 3 Explanation (2011) D3-1. Velocity and Acceleration A. 1: average velocity. Q1. What is the definition of the average velocity v? Let r(t) be the total displacement vector
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Topic 2.1 Motion. Topic 2.1 Motion. Kari Eloranta Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio. August 18, Kari Eloranta 2017 Topic 2.
 Topic 2.1 Motion Kari Eloranta 2017 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio August 18, 2017 Velocity and Speed 2.1: Kinematic Quanties: Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change in position. The
Topic 2.1 Motion Kari Eloranta 2017 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio August 18, 2017 Velocity and Speed 2.1: Kinematic Quanties: Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change in position. The
Jan 31 8:19 PM. Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion
 Unit 3: Kinematics Uniform Rectilinear Motion (velocity is constant) Uniform Accelerated Rectilinear Motion The Motion of Projectiles Jan 31 8:19 PM Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion Position: point
Unit 3: Kinematics Uniform Rectilinear Motion (velocity is constant) Uniform Accelerated Rectilinear Motion The Motion of Projectiles Jan 31 8:19 PM Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion Position: point
Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion
 Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion Motion... Particle Models Vectors vs. Scalars Position, Displacement and Distance Velocity vs. Speed Instantaneous vs. Average Acceleration start time Particle motion
Chapter 3: Introduction to Motion Motion... Particle Models Vectors vs. Scalars Position, Displacement and Distance Velocity vs. Speed Instantaneous vs. Average Acceleration start time Particle motion
To conduct the experiment, each person in your group should be given a role:
 Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Solving Problems In Physics
 Solving Problems In Physics 1. Read the problem carefully. 2. Identify what is given. 3. Identify the unknown. 4. Find a useable equation and solve for the unknown quantity. 5. Substitute the given quantities.
Solving Problems In Physics 1. Read the problem carefully. 2. Identify what is given. 3. Identify the unknown. 4. Find a useable equation and solve for the unknown quantity. 5. Substitute the given quantities.
Calculus I Homework: The Tangent and Velocity Problems Page 1
 Calculus I Homework: The Tangent and Velocity Problems Page 1 Questions Example The point P (1, 1/2) lies on the curve y = x/(1 + x). a) If Q is the point (x, x/(1 + x)), use Mathematica to find the slope
Calculus I Homework: The Tangent and Velocity Problems Page 1 Questions Example The point P (1, 1/2) lies on the curve y = x/(1 + x). a) If Q is the point (x, x/(1 + x)), use Mathematica to find the slope
Chapter 2 Motion Along A Straight Line
 Chapter 2 Motion Along A Straight Line Kinematics: Description of Motion Motion in one dimension (1-D) Motion of point particles Treat larger objects as particles center of mass Chapter 2 Motion in 1-D
Chapter 2 Motion Along A Straight Line Kinematics: Description of Motion Motion in one dimension (1-D) Motion of point particles Treat larger objects as particles center of mass Chapter 2 Motion in 1-D
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down?
 5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
x is also called the abscissa y is also called the ordinate "If you can create a t-table, you can graph anything!"
 Senior Math Section 6-1 Notes Rectangular Coordinates and Lines Label the following 1. quadrant 1 2. quadrant 2 3. quadrant 3 4. quadrant 4 5. origin 6. x-axis 7. y-axis 8. Ordered Pair (x, y) at (2, 1)
Senior Math Section 6-1 Notes Rectangular Coordinates and Lines Label the following 1. quadrant 1 2. quadrant 2 3. quadrant 3 4. quadrant 4 5. origin 6. x-axis 7. y-axis 8. Ordered Pair (x, y) at (2, 1)
ONE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS
 ONE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS Chapter 2 Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
ONE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATICS Chapter 2 Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Physical Science Chapter 11. Motion
 Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
Physical Science Chapter 11 Motion Motion Definition An object is in motion when its distance from another object is changing. Relative Motion Relative motion is movement in relation to a REFERENCE POINT.
MITOCW MIT8_01F16_W01PS05_360p
 MITOCW MIT8_01F16_W01PS05_360p You're standing at a traffic intersection. And you start to accelerate when the light turns green. Suppose that your acceleration as a function of time is a constant for
MITOCW MIT8_01F16_W01PS05_360p You're standing at a traffic intersection. And you start to accelerate when the light turns green. Suppose that your acceleration as a function of time is a constant for
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
Particle Motion. Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x()
 Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS
 Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS 31. On the position-time graph below, sketch a plot representing the motion of an object which is.... Label each line with the corresponding letter (e.g., "a", "b",
Part D: Kinematic Graphing - ANSWERS 31. On the position-time graph below, sketch a plot representing the motion of an object which is.... Label each line with the corresponding letter (e.g., "a", "b",
Trigonometry I. Pythagorean theorem: WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Trigonometry I Pythagorean theorem: Trigonometry II 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 sin(x) and cos(x) are mathematical functions that describe oscillations. This will be important later, when we talk about
Trigonometry I Pythagorean theorem: Trigonometry II 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 sin(x) and cos(x) are mathematical functions that describe oscillations. This will be important later, when we talk about
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications of
Chapter One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications of
CHAPTER 4 -- KINEMATICS
 Solutions--Ch. 4 (Kinematics CHAPTER 4 -- KINEMATICS 4.1 a. The total distance traversed (versus the net displacement divided by the elapsed time. That scalar is: s = dist/time = (440 m/(49 sec = 8.98
Solutions--Ch. 4 (Kinematics CHAPTER 4 -- KINEMATICS 4.1 a. The total distance traversed (versus the net displacement divided by the elapsed time. That scalar is: s = dist/time = (440 m/(49 sec = 8.98
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-1 02-1 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Using graphs to solve problems Constant acceleration, free fall 02-1 2 1-2.6-8: Acceleration from graph of
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-1 02-1 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Using graphs to solve problems Constant acceleration, free fall 02-1 2 1-2.6-8: Acceleration from graph of
KINEMATICS. File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation. Monday, June 17, 13
 KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
STAAR Science Tutorial 21 TEK 6.8D: Graphing Motion
 Distance (meters) Name: _ Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 21 TEK 6.8D: Graphing Motion TEK 6.8D: Measure and graph changes in motion. Graphing Speed on a Distance Graph Speed is defined as the
Distance (meters) Name: _ Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 21 TEK 6.8D: Graphing Motion TEK 6.8D: Measure and graph changes in motion. Graphing Speed on a Distance Graph Speed is defined as the
acceleration versus time. LO Determine a particle s change in position by graphical integration on a graph of velocity versus time.
 Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Position, Velocity, Acceleration
 191 CHAPTER 7 Position, Velocity, Acceleration When we talk of acceleration we think of how quickly the velocity is changing. For example, when a stone is dropped its acceleration (due to gravity) is approximately
191 CHAPTER 7 Position, Velocity, Acceleration When we talk of acceleration we think of how quickly the velocity is changing. For example, when a stone is dropped its acceleration (due to gravity) is approximately
r y The angle theta defines a vector that points from the boat to the top of the cliff where rock breaks off. That angle is given as 30 0
 From a boat in the English Channel, you slowly approach the White Cliffs of Dover. You want to know how far you are from the base of the cliff. Then suddenly you see a rock break off from the top and hit
From a boat in the English Channel, you slowly approach the White Cliffs of Dover. You want to know how far you are from the base of the cliff. Then suddenly you see a rock break off from the top and hit
MATH CALCULUS I 4.1: Area and Distance
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 4.1: Area and Distance Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 8 The Area and Distance Problems
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 4.1: Area and Distance Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 8 The Area and Distance Problems
Physics 201 Homework 1
 Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
Physics 103 Laboratory Fall Lab #2: Position, Velocity and Acceleration
 Physics 103 Laboratory Fall 011 Lab #: Position, Velocity and Acceleration Introduction In this lab, we will study one-dimensional motion looking at position (x), velocity (v) and acceleration (a) which
Physics 103 Laboratory Fall 011 Lab #: Position, Velocity and Acceleration Introduction In this lab, we will study one-dimensional motion looking at position (x), velocity (v) and acceleration (a) which
Linear Motion: Velocity and Acceleration
 Linear Motion: Velocity and Acceleration Relative Motion Everything moves, even things at rest Relative regarded in relation to something else; depends on point of view, or frame of reference A book at
Linear Motion: Velocity and Acceleration Relative Motion Everything moves, even things at rest Relative regarded in relation to something else; depends on point of view, or frame of reference A book at
PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 y 3 5 Graph of f ' x 76. The graph of f ', the derivative f, is shown above for x 5. n what intervals is f increasing? (A) [, ] only (B) [, 3] (C) [3, 5] only (D) [0,.5] and [3, 5] (E) [, ], [, ], and
y 3 5 Graph of f ' x 76. The graph of f ', the derivative f, is shown above for x 5. n what intervals is f increasing? (A) [, ] only (B) [, 3] (C) [3, 5] only (D) [0,.5] and [3, 5] (E) [, ], [, ], and
Chapter 2 Describing Motion
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]
![Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]](/thumbs/77/76428187.jpg) Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION
 INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1-12.2) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to find the kinematic quantities (position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration)
INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1-12.2) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to find the kinematic quantities (position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration)
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
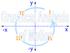 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
The key difference between speed and velocity is the. object s motion, while velocity designates an object s speed plus the direction of its motion.
 Article retrieved from Brittanica, Retrieved 6/27/2016 Velocity Velocity has a scientific meaning that is slightly different from that of speed. Speed is the rate of an object s motion, while velocity
Article retrieved from Brittanica, Retrieved 6/27/2016 Velocity Velocity has a scientific meaning that is slightly different from that of speed. Speed is the rate of an object s motion, while velocity
Motion along a straight line. Physics 11a. 4 Basic Quantities in Kinematics. Motion
 Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change
 1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
10.2 Introduction to Vectors
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 10.2 Introduction to Vectors In the previous calculus classes we have seen that the study of motion involved the introduction of a variety
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 10.2 Introduction to Vectors In the previous calculus classes we have seen that the study of motion involved the introduction of a variety
PHYSICS 1 REVIEW PACKET
 PHYSICS 1 REVIEW PACKET Powers of Ten Scientific Notation and Prefixes Exponents on the Calculator Conversions A Little Trig Accuracy and Precision of Measurement Significant Figures Motion in One Dimension
PHYSICS 1 REVIEW PACKET Powers of Ten Scientific Notation and Prefixes Exponents on the Calculator Conversions A Little Trig Accuracy and Precision of Measurement Significant Figures Motion in One Dimension
2. (a) Using the fact that time = distance/velocity while the velocity is constant, we find m 73.2 m 1.74 m/s m 73.2 m v m. 1.
 Chapter. The speed (assumed constant) is v = (9 km/h)( m/km) (36 s/h) = 5 m/s. Thus, in.5 s, the car travels a distance d = vt = (5 m/s)(.5 s) 3 m.. (a) Using the fact that time = distance/velocity while
Chapter. The speed (assumed constant) is v = (9 km/h)( m/km) (36 s/h) = 5 m/s. Thus, in.5 s, the car travels a distance d = vt = (5 m/s)(.5 s) 3 m.. (a) Using the fact that time = distance/velocity while
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Welcome back to Physics 215
 Welcome back to Physics 215 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 2-2.1: An object moves with constant acceleration, starting from
Welcome back to Physics 215 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 2-2.1: An object moves with constant acceleration, starting from
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics. Free Response Problems
 PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS
 Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS The motion of an American kestrel through the air can be described by the bird s displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. When it flies in a straight line without any change
Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS The motion of an American kestrel through the air can be described by the bird s displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. When it flies in a straight line without any change
Name: Total Points: Physics 201. Midterm 1
 Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
LESSON 2-4: Acceleration
 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PRE-IB PHYSICS LESSON 2-4: Acceleration 1. Objectives. By the end of this class you should be able to: a) SC.912.P.12.2: Analyze the motion of an object in terms of
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PRE-IB PHYSICS LESSON 2-4: Acceleration 1. Objectives. By the end of this class you should be able to: a) SC.912.P.12.2: Analyze the motion of an object in terms of
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Speed how fast an object is moving (also, the magnitude of the velocity) scalar
 Mechanics Recall Mechanics Kinematics Dynamics Kinematics The description of motion without reference to forces. Terminology Distance total length of a journey scalar Time instant when an event occurs
Mechanics Recall Mechanics Kinematics Dynamics Kinematics The description of motion without reference to forces. Terminology Distance total length of a journey scalar Time instant when an event occurs
Motion. Slope. Slope. Distance and Displacement
 Steepness or slope base (run), height (rise) slope = rise/run slope down (\) : - (rise/run) slope up (/) : + (rise/run) sudden change of slope curved hill - the slope is always changing procedure to find
Steepness or slope base (run), height (rise) slope = rise/run slope down (\) : - (rise/run) slope up (/) : + (rise/run) sudden change of slope curved hill - the slope is always changing procedure to find
Particle Motion. Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x()
 Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Chapter 2: Kinematics
 Section 1 Chapter 2: Kinematics To simplify the concept of motion, we will first consider motion that takes place in one direction. To measure motion, you must choose a frame of reference. Frame of reference
Section 1 Chapter 2: Kinematics To simplify the concept of motion, we will first consider motion that takes place in one direction. To measure motion, you must choose a frame of reference. Frame of reference
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 4. Physical Science Motion
 SCIENCE 1206 Unit 4 Physical Science Motion What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Called the Fundamental Science Famous Physicists Galileo Galilei Albert Einstein
SCIENCE 1206 Unit 4 Physical Science Motion What is Physics? Physics is the study of motion, matter, energy, and force. Called the Fundamental Science Famous Physicists Galileo Galilei Albert Einstein
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
Chapter 4 Linear Motion
 Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Some Motion Terms. Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector
 Motion Some Motion Terms Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector Scalar versus Vector Scalar - magnitude only (e.g. volume, mass, time) Vector - magnitude
Motion Some Motion Terms Distance & Displacement Velocity & Speed Acceleration Uniform motion Scalar.vs. vector Scalar versus Vector Scalar - magnitude only (e.g. volume, mass, time) Vector - magnitude
Goals for Today. Introduce relativity Understand speed, velocity, and acceleration Text lol activity
 Goals for Today Introduce relativity Understand speed, velocity, and acceleration Text lol activity Relativity 101 All motion is relative! This means when we describe motion, we are moving relative to
Goals for Today Introduce relativity Understand speed, velocity, and acceleration Text lol activity Relativity 101 All motion is relative! This means when we describe motion, we are moving relative to
New HW : complete handout work on lab (due Tuesday) review new notes on website (pdf)
 Physics HW due Today a. Read in book: pages 43 51 b. define/explain in notes: particle model, position vector, vector quantity, scalar quantity, displacement, distance c. p.60: 2 3 4 5 d. Write this list
Physics HW due Today a. Read in book: pages 43 51 b. define/explain in notes: particle model, position vector, vector quantity, scalar quantity, displacement, distance c. p.60: 2 3 4 5 d. Write this list
KINEMATICS WHERE ARE YOU? HOW FAST? VELOCITY OR SPEED WHEN YOU MOVE. Typical Cartesian Coordinate System. usually only the X and Y axis.
 KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16
 PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
PS113 Chapter 2. Kinematics in one dimension
 PS113 Chapter 2 Kinematics in one dimension 1 Displacement Displacement is defined as the vector drawn from an object s initial position toward its final position and has a magnitude that equals the shortest
PS113 Chapter 2 Kinematics in one dimension 1 Displacement Displacement is defined as the vector drawn from an object s initial position toward its final position and has a magnitude that equals the shortest
(f) none of the above
 Honors Physics TEST: Kinematics in 1D 10/30/12 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Answer the following multiple choice questions by picking the selection that best answers the question. Write your answers on a separate
Honors Physics TEST: Kinematics in 1D 10/30/12 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Answer the following multiple choice questions by picking the selection that best answers the question. Write your answers on a separate
Section 1.1 Distance, Position and Displacement
 Unit 1 Motion Section 1.1 Distance, Position and Displacement Kinematics is the study of MOTION. Motion is the CHANGE in an object's location as measured by a particular observer. Why is the OBSERVER important
Unit 1 Motion Section 1.1 Distance, Position and Displacement Kinematics is the study of MOTION. Motion is the CHANGE in an object's location as measured by a particular observer. Why is the OBSERVER important
Interactive Engagement via Thumbs Up. Today s class. Next class. Chapter 2: Motion in 1D Example 2.10 and 2.11 Any Question.
 PHYS 01 Interactive Engagement via Thumbs Up 1 Chap.1 Sumamry Today s class SI units Dimensional analysis Scientific notation Errors Vectors Next class Chapter : Motion in 1D Example.10 and.11 Any Question
PHYS 01 Interactive Engagement via Thumbs Up 1 Chap.1 Sumamry Today s class SI units Dimensional analysis Scientific notation Errors Vectors Next class Chapter : Motion in 1D Example.10 and.11 Any Question
Today s lecture. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Today s lecture Units, Estimations, Graphs, Trigonometry: Units - Standards of Length, Mass, and Time Dimensional Analysis Uncertainty and significant digits Order of magnitude estimations Coordinate Systems
Today s lecture Units, Estimations, Graphs, Trigonometry: Units - Standards of Length, Mass, and Time Dimensional Analysis Uncertainty and significant digits Order of magnitude estimations Coordinate Systems
AP Calculus BC Class Starter January 22, 2018
 January 22, 2018 1. Given the function, find the following. (a) Evaluate f(4). (b) The definition of the derivative can be written two ways, as indicated below. Find both forms and evaluate the derivative
January 22, 2018 1. Given the function, find the following. (a) Evaluate f(4). (b) The definition of the derivative can be written two ways, as indicated below. Find both forms and evaluate the derivative
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards
 Lesson 5 CALCULUS (8) Rate of change Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome : Functions and Algebra Assessment standard 1..7(e) Solve practical problems involving optimisation and
Lesson 5 CALCULUS (8) Rate of change Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome : Functions and Algebra Assessment standard 1..7(e) Solve practical problems involving optimisation and
Example problem: Free Fall
 Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10
 1 / 37 Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 12 th, 2018 Contact Already read the syllabus
1 / 37 Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 12 th, 2018 Contact Already read the syllabus
Thursday Jan 18. Today s Material: 1-d Motion/Kinematics Displacement Velocity Acceleration Graphing Motion
 Thursday Jan 18 Assign 1 Friday Long Pre-class for Tuesday Math Quiz Due Monday Lab next week Print lab and do pre-lab NO OPEN-TOED SHOES NO FOOD/GUM/DRINKS Help Room Tonight 6-9 - Walter 245 Office Hours:
Thursday Jan 18 Assign 1 Friday Long Pre-class for Tuesday Math Quiz Due Monday Lab next week Print lab and do pre-lab NO OPEN-TOED SHOES NO FOOD/GUM/DRINKS Help Room Tonight 6-9 - Walter 245 Office Hours:
1. (P2.1A) The picture below shows a ball rolling along a table at 1 second time intervals. What is the object s average velocity after 6 seconds?
 PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS 1-30
 . Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
. Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions
 Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions Section 5.1 - Differentiating Functions Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change of a function. We have proven that if f is a variable dependent
Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions Section 5.1 - Differentiating Functions Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change of a function. We have proven that if f is a variable dependent
a. Determine the sprinter's constant acceleration during the first 2 seconds.
 AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
