Structure-constrained relative acoustic impedance using stratigraphic coordinates a
|
|
|
- Marjory Ball
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure-constrained relative acoustic impedance using stratigraphic coordinates a a Published in Geophysics, 80, no. 3, A63-A67 (2015) Parvaneh Karimi ABSTRACT Acoustic impedance inversion involves conversion of seismic traces to a reflection coefficient time series, and then into acoustic impedance. The usual assumption for the transformation of post-stack seismic data into impedance, is that seismic traces can be modeled using the simple convolutional model. According to the convolutional model, a seismic trace is a normal-incidence record, which is an assumption that is strictly true only if the earth structure is composed of horizontal layers. In the presence of dipping layers, such an assumption is violated, which introduces bias in the result of impedance inversion. I propose to implement impedance inversion in the stratigraphic coordinate system, where the vertical direction is normal to reflectors and seismic traces represent normalincidence seismograms. Tests on field data produce more accurate and detailed impedance results from inversion in the stratigraphic coordinate system, compared to impedance results using the conventional Cartesian coordinate system. INTRODUCTION Acoustic impedance inversion involves conversion of seismic traces to a reflection coefficient time series, and then into acoustic impedance (Lavergne and Willim, 1977; Lindseth, 1979). These impedance traces can enhance accuracy of interpretation and correlation with properties measured in well logs. Duboz et al. (1998) and Latimer and Riel (2000), among others, point out the advantages of impedance data over conventional seismic: acoustic impedance is a rock property and a product of velocity and density, both of which can be measured at well locations. Seismic reflection, in contrast, is an interface property and a relative measurement of changes in acoustic impedance between layers. Therefore having the data in layers, rather than at interfaces, improves visualization, including both layering and vertical resolution. In addition, the elimination of wavelet side-lobes and false stratigraphic-like effects makes sequence-stratigraphic analysis easier. Acoustic impedance has been shown to be correlated with lithology (Pendrel and van Riel, 1997), porosity (Brown, 1996; Burge and Neff, 1998), and other fundamental rock properties.
2 2 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance Although seismic-derived acoustic impedance is a powerful tool in many aspects mentioned above, it is trace-based, which can cause errors in the presence of dipping layers. According to the convolutional model, seismic traces are considered normalincidence 1D seismograms, which is strictly true only in the case of horizontal layers. When the subsurface exhibits dipping layers, the convolutional model will no longer hold true, because the seismic waveform will be sampled vertically instead of normally to the reflector (Guo and Marfurt, 2010), introducing a possible bias in the acousticimpedance result. In this paper, I propose to approach this problem and improve the accuracy of impedance estimates by employing the stratigraphic coordinate system (Karimi and Fomel, 2011, 2014) for impedance inversion. In stratigraphic coordinates, the vertical direction stays normal to reflectors (Mallet, 2014), conforming to the assumption of the convolutional model. In the following sections, I start by briefly reviewing the algorithm used to generate stratigraphic coordinates. Then, I explain the proposed methodology for impedance inversion. I use a field-data example to test the proposed approach and to verify that, in the presence of dipping layers, seismic-derived impedance becomes biased and can be improved significantly by the use of stratigraphic coordinates. METHOD Inversion of post-stack seismic data into acoustic impedance is a classic trace-based process (Russell and Hampson, 1991). The usual assumption behind post-stack inversion methods is that a seismic trace in a stacked section satisfies the convolutional equation, which can be written as s t = r t w t, (1) where s t is the seismic trace, r t is the earth s normal incidence reflectivity, and w t is the seismic wavelet. According to equation 1, by deconvolving the seismic wavelet, one can acquire the earth s normal incidence reflectivity, which, in turn, is related to acoustic impedance through the recursive equation (Lindseth, 1979) [ ] 1 + rt Z t+1 = Z t. (2) 1 r t In practice, when the subsurface shows dipping layers, the convolutional model no longer holds true. Neither will the equation that relates earth s normal-incidence reflectivity to acoustic impedance (equation 2), because seismic traces in this case cannot be considered as simple 1D normal-incidence seismograms. In order to improve the accuracy of seismic-derived acoustic impedance, I propose to employ the stratigraphic coordinate system (Karimi and Fomel, 2011, 2014), in which the convolutional model assumption is more accurate.
3 3 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance Stratigraphic coordinates In order to define the first step for transformation to stratigraphic coordinates, I follow the predictive-painting algorithm (Fomel, 2010), which is based on the method of plane-wave destruction for measuring local slopes of seismic events (Claerbout, 1992; Fomel, 2002). By writing plane-wave destruction in the linear operator notation as: r = D s, (3) where, s is a seismic section ( s = [s 1 s 2... s N ] T ), r is the destruction residual, and D, the non-stationary plane-wave destruction operator, is I P 1,2 I 0 0 D = 0 P 2,3 I 0, (4) 0 0 P N 1,N I where I is the identity operator and P i,j is the prediction of trace j from trace i determined by being shifted along the local slopes of seismic events. Local slopes are estimated by minimizing the destruction residual using a regularized least-squares optimization. The prediction of trace s k from a distant reference trace s r is P r,k s r, where P r,k = P k 1,k P r+1,r+2 P r,r+1. (5) This is a simple recursion, and P r,k is called the predictive painting operator (Fomel, 2010). Predictive painting spreads the time values along a reference trace in order to output the relative geologic age attribute (Z 0 (x, y, z)). These painted horizons outputted by predictive painting are used as the first axis of the stratigraphic coordinate system. In the next step, following Karimi and Fomel (2011, 2014), I find the two other axes, X 0 (x, y, z) and Y 0 (x, y, z), orthogonal to the first axis, Z 0 (x, y, z), by numerically solving the following gradient equations: and Z 0 X 0 = 0 (6) Z 0 Y 0 = 0. (7) Equations 6 and 7 simply state that the X 0 and Y 0 axes should be perpendicular to Z 0. The boundary condition for the first gradient equation (equation 6) is and the boundary condition for equation 7 is X 0 (x, y, 0) = x (8) Y 0 (x, y, 0) = y. (9) These two boundary conditions mean that the stratigraphic coordinate system and the regular coordinate system (x, y, z) meet at the surface (z = 0). Note that the
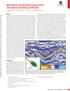
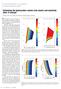
4 4 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance stratigraphic coordinates are designed for depth images (Mallet, 2004, 2014). When applied to time-domain images, a scaling factor with dimensions of velocity-squared is added to equations 6 and 7, because the definition of the gradient operator becomes = ( x, y, ) z. (10) z t EXAMPLE I use a 3D field data volume from Heidrun Field in the Halten Terrace area, offshore Mid-Norway (Moscardelli et al., 2013) to test the proposed approach (Figure 1a). I begin by estimating local slopes of seismic events through the data volume using plane-wave destruction. After that, I apply the predictive painting algorithm to obtain the first axis of the stratigraphic coordinates. The two other axes are found by solving gradient equations 6 and 7. Figure 1b shows the image in the Cartesian coordinate system, overlain by its stratigraphic coordinates grid. Figure 1c shows the image in the stratigraphic coordinate system, where major reflectors appear nearly flat, and Figure 1d displays the image reconstruction by returning from stratigraphic coordinates to Cartesian coordinates. I use model-based inversion (Russell and Hampson, 1991; Cooke and Schneider, 1983) to extract acoustic impedance information from the seismic image. Because of the band-limited nature of seismic data, low-frequency variations are extracted from the well data, and then added back to the seismic data in order to obtain a proper broad-band result. Model-based inversion starts with a low-frequency model of P-impedance and perturbs this model until the derived synthetic section from the application of equations 1 and 2 best fits the actual seismic data. In the model-based inversion, extraction of the seismic wavelet is necessary. Figure 2 shows the extracted wavelet from the seismic image in the Cartesian coordinates, Figure 2a is the time response, and Figure 2b is the frequency response of the seismic wavelet. Figure 3 shows the extracted wavelet from the seismic image in the stratigraphic coordinate system. Figure 4a is a zoomed-in part of the image, and Figure 4b is the impedance results obtained from inversion in the Cartesian coordinates. Figure 4c shows the impedance inversion result acquired in the stratigraphic coordinate system and transferred back to Cartesian coordinate system to provide a better comparison. Comparing the impedance acquired from inversion in the conventional Cartesian coordinates (Figures 4b) with the result obtained from inversion in the stratigraphic coordinates (Figures 4c) shows that result from inversion in stratigraphic coordinates (Figures 4c) appears to be more consistent with the geological structure and also more detailed. Interfaces are noticeably better defined and laterally more continuous. This improved accuracy result because, in the stratigraphic coordinates, layers get flattened and the vertical direction corresponds to the normal direction to reflectors, and therefore allows for a more accurate analysis of the earth s normal incidence reflectivity and its impedance.
5 Karimi 5 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance a b c d Figure 1: (a) 3D field data from Heidrun. (b) Three axes of stratigraphic coordinates of Figure 1a plotted as grid in their Cartesian coordinates. (c) Heidrun image after flattening by transferring the image to stratigraphic coordinates. (d) Heidrun image reconstruction by returning from stratigraphic coordinates to Cartesian coordinates. a b Figure 2: Extracted wavelet from the seismic data in Figure 1a in the Cartesian coordinates, (a) is the time response and (b) is the frequency response.
6 Karimi 6 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance a b Figure 3: Extracted wavelet from the seismic data in Figure 1c in the stratigraphic coordinates, (a) is the time response and (b) is the frequency response. a b c Figure 4: (a) A zoomed-in part of the Figure 1a and the impedance result obtained from inversion in the Cartesian coordinates (b), and in the stratigraphic coordinates (the result is transferred back to Cartesian coordinates to provide a better comparison) (c).
7 7 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS Post-stack impedance inversion involves the assumption that seismic traces can be modeled using the convolutional and vertical-incidence reflection-coefficient equations. In the presence of dipping layers, these assumptions are false, and therefore seismic-derived acoustic impedance can be biased. To solve this problem, I have employed the stratigraphic coordinate system, which offers a local reference frame extracted from the seismic image and naturally designed to sample the unbiased normal incidence seismic traces, and hence yield more accurate impedance estimates. Performance of the stratigraphic coordinate system is based on the predictivepainting algorithm, which produces the best results when seismic traces can be predicted from neighboring traces. Note that the predictive painting approach may require further improvements to deal with areas where either structural or stratigraphic discontinuities are present. Future research should concentrate on using a small number of control points especially near discontinuities interactively in the predictive painting algorithm to make sure that the events across structural or stratigraphic discontinuities are accurately captured. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I thank ConocoPhillips, the Norwegian Petroleum Directorate, the Quantitative Clastics Laboratory (QCL) Industrial Associates Program, and personally Lorena Moscardelli for facilitating access to data used in this study. I would like to thank Sergey Fomel and Mehdi Far for helpful discussions. I also thank reviewers for their constructive suggestions, which helped improve this paper. REFERENCES Brown, A. R., 1996, Interpretation of three-dimensional seismic data: 4 th ed, AAPG Memoir 42, 424. Burge, D. W., and D. B. Neff, 1998, Well-based seismic lithology inversion for porosity and pay-thickness mapping: The Leading Edge, 17, no. 2, Claerbout, J. F., 1992, Earth sounding analysis: Processing versus inversion: Blackwell Science. Cooke, D. A., and W. A. Schneider, 1983, Generalized linear inversion of reflection seismic data: Geophysics, 48, Duboz, P., Y. Lafet, and D. Mougnot, 1998, Moving to a layered impedance cube: advantages of 3D stratigraphic inversion: First Break, 16, no. 9, Fomel, S., 2002, Applications of plane-wave destruction filters: Geophysics, 67, no. 6, , 2010, Predictive painting of 3-D seismic volumes: Geophysics, 75, no. 4, A25 A30.
8 8 Structure-constrained acoustic impedance Guo, H., and K. J. Marfurt, 2010, Spectral decomposition along the travel path of signal wavelets: Expanded Abstracts 80 th SEG International Convention, Karimi, P., and S. Fomel, 2011, Stratigraphic coordinate system: 81 st Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts., 2014, Stratigraphic coordinates, a coordinate system tailored to seismic interpretation: Geophys. Prosp., in press. Latimer, R. B., and R. D. P. V. Riel, 2000, An interpreter s guide to understanding and working with seismic-derived acoustic impedance data: The Leading Edge, 19, Lavergne, M., and C. Willim, 1977, Inversion of seismograms and pseudo velocity logs: Geophysical Prospecting, 25, no. 2, Lindseth, R. O., 1979, Synthetic sonic logs a process for stratigraphic interpretation: Geophysics, 44, no. 1, Mallet, J. L., 2004, Space-time mathematical framework for sedimentary geology: Mathematical Geology, 36, A25 A30., 2014, Elements of mathematical sedimentary geology: the geochron model: EAGE Publications bv. Moscardelli, L., S. K. Ramnarine, L. Wood, and D. Dunlap, 2013, Seismic geomorphological analysis and hydrocarbon potential of the lower Cretaceous Cromer Knoll Group, Heidrun Field, Norway: AAPG Bulletin, 97, no. 8, Pendrel, J. V., and P. van Riel, 1997, Methodology for seismic inversion, a western Canadian reef example: Canadian Society of Exploration Geophysicists Recorder, 22, no. 5. Russell, B., and D. Hampson, 1991, A comparison of post-stack seismic inversion methods: Annual Meeting Abstracts, Society of Exploration Geophysicists,
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait
 Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Earth models for early exploration stages
 ANNUAL MEETING MASTER OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING Earth models for early exploration stages Ângela Pereira PhD student angela.pereira@tecnico.ulisboa.pt 3/May/2016 Instituto Superior Técnico 1 Outline Motivation
ANNUAL MEETING MASTER OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING Earth models for early exploration stages Ângela Pereira PhD student angela.pereira@tecnico.ulisboa.pt 3/May/2016 Instituto Superior Técnico 1 Outline Motivation
Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Seismic Inversion Techniques
 P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON
 FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 10 14 July 2017 Jakarta The course is aimed at teaching the physical concepts involved in the application of seismic
FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 10 14 July 2017 Jakarta The course is aimed at teaching the physical concepts involved in the application of seismic
Seismic Inversion on 3D Data of Bassein Field, India
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 526-532 Seismic Inversion on 3D Data of Bassein Field, India K.Sridhar, A.A.K.Sundaram, V.B.G.Tilak & Shyam Mohan Institute
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 526-532 Seismic Inversion on 3D Data of Bassein Field, India K.Sridhar, A.A.K.Sundaram, V.B.G.Tilak & Shyam Mohan Institute
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION LOCALIZED PHASE ESTIMATION
 Local similarity with the envelope as a seismic phase detector Sergey Fomel, The University of Texas at Austin, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Alberta SUMMARY We propose a new seismic attribute,
Local similarity with the envelope as a seismic phase detector Sergey Fomel, The University of Texas at Austin, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Alberta SUMMARY We propose a new seismic attribute,
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd., VRC(Panvel), WOB, ONGC, Mumbai. 1
 P-259 Summary Data for identification of Porosity Behaviour in Oligocene Lime Stone of D18 Area Of Western Offshore, India V.K. Baid*, P.H. Rao, P.S. Basak, Ravi Kant, V. Vairavan 1, K.M. Sundaram 1, ONGC
P-259 Summary Data for identification of Porosity Behaviour in Oligocene Lime Stone of D18 Area Of Western Offshore, India V.K. Baid*, P.H. Rao, P.S. Basak, Ravi Kant, V. Vairavan 1, K.M. Sundaram 1, ONGC
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection
 A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
technical article Satinder Chopra 1*, Kurt J. Marfurt 2 and Ha T. Mai 2
 first break volume 27, October 2009 technical article Using automatically generated 3D rose diagrams for correlation of seismic fracture lineaments with similar lineaments from attributes and well log
first break volume 27, October 2009 technical article Using automatically generated 3D rose diagrams for correlation of seismic fracture lineaments with similar lineaments from attributes and well log
Improving Resolution with Spectral Balancing- A Case study
 P-299 Improving Resolution with Spectral Balancing- A Case study M Fatima, Lavendra Kumar, RK Bhattacharjee, PH Rao, DP Sinha Western Offshore Basin, ONGC, Panvel, Mumbai Summary: The resolution limit
P-299 Improving Resolution with Spectral Balancing- A Case study M Fatima, Lavendra Kumar, RK Bhattacharjee, PH Rao, DP Sinha Western Offshore Basin, ONGC, Panvel, Mumbai Summary: The resolution limit
We apply a rock physics analysis to well log data from the North-East Gulf of Mexico
 Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
Instantaneous Spectral Analysis Applied to Reservoir Imaging and Producibility Characterization
 Instantaneous Spectral Analysis Applied to Reservoir Imaging and Producibility Characterization Feng Shen 1* and Gary C. Robinson 1, Tao jiang 2 1 EP Tech, Centennial, CO, 80112, 2 PetroChina Oil Company,
Instantaneous Spectral Analysis Applied to Reservoir Imaging and Producibility Characterization Feng Shen 1* and Gary C. Robinson 1, Tao jiang 2 1 EP Tech, Centennial, CO, 80112, 2 PetroChina Oil Company,
SUMMARY ANGLE DECOMPOSITION INTRODUCTION. A conventional cross-correlation imaging condition for wave-equation migration is (Claerbout, 1985)
 Comparison of angle decomposition methods for wave-equation migration Natalya Patrikeeva and Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Angle domain common image gathers offer
Comparison of angle decomposition methods for wave-equation migration Natalya Patrikeeva and Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Angle domain common image gathers offer
Bertrand Six, Olivier Colnard, Jean-Philippe Coulon and Yasmine Aziez CGGVeritas Frédéric Cailly, Total
 4-D Seismic Inversion: A Case Study Offshore Congo Bertrand Six, Olivier Colnard, Jean-Philippe Coulon and Yasmine Aziez CGGVeritas Frédéric Cailly, Total Summary The first 4D seismic survey in Congo was
4-D Seismic Inversion: A Case Study Offshore Congo Bertrand Six, Olivier Colnard, Jean-Philippe Coulon and Yasmine Aziez CGGVeritas Frédéric Cailly, Total Summary The first 4D seismic survey in Congo was
Regularizing seismic inverse problems by model reparameterization using plane-wave construction
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 71, NO. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2006 ; P. A43 A47, 6 FIGS. 10.1190/1.2335609 Regularizing seismic inverse problems by model reparameterization using plane-wave construction Sergey Fomel 1
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 71, NO. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2006 ; P. A43 A47, 6 FIGS. 10.1190/1.2335609 Regularizing seismic inverse problems by model reparameterization using plane-wave construction Sergey Fomel 1
Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data
 Inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Patricia E. Gavotti, Don C. Lawton, Gary F. Margrave and J. Helen Isaac ABSTRACT The Hussar
Inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Patricia E. Gavotti, Don C. Lawton, Gary F. Margrave and J. Helen Isaac ABSTRACT The Hussar
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation. for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea. R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.
 Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology
 Academic article Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology Sanhasuk Koson, Piyaphong Chenrai* and Montri Choowong Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University,
Academic article Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology Sanhasuk Koson, Piyaphong Chenrai* and Montri Choowong Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University,
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion
 23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
Multiple horizons mapping: A better approach for maximizing the value of seismic data
 Multiple horizons mapping: A better approach for maximizing the value of seismic data Das Ujjal Kumar *, SG(S) ONGC Ltd., New Delhi, Deputed in Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Govt. of India Email:
Multiple horizons mapping: A better approach for maximizing the value of seismic data Das Ujjal Kumar *, SG(S) ONGC Ltd., New Delhi, Deputed in Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Govt. of India Email:
Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin
 P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
Tim Carr - West Virginia University
 Tim Carr - West Virginia University Understanding Seismic Data Resolution (Vertical and Horizontal) Common Depth Points (CDPs) Two way time (TWT) Time versus depth Interpretation of Reflectors 2 Able to
Tim Carr - West Virginia University Understanding Seismic Data Resolution (Vertical and Horizontal) Common Depth Points (CDPs) Two way time (TWT) Time versus depth Interpretation of Reflectors 2 Able to
Quantitative Seismic Interpretation An Earth Modeling Perspective
 Quantitative Seismic Interpretation An Earth Modeling Perspective Damien Thenin*, RPS, Calgary, AB, Canada TheninD@rpsgroup.com Ron Larson, RPS, Calgary, AB, Canada LarsonR@rpsgroup.com Summary Earth models
Quantitative Seismic Interpretation An Earth Modeling Perspective Damien Thenin*, RPS, Calgary, AB, Canada TheninD@rpsgroup.com Ron Larson, RPS, Calgary, AB, Canada LarsonR@rpsgroup.com Summary Earth models
Bandlimited impedance inversion: using well logs to fill low frequency information in a non-homogenous model
 Bandlimited impedance inversion: using well logs to fill low frequency information in a non-homogenous model Heather J.E. Lloyd and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT An acoustic bandlimited impedance inversion
Bandlimited impedance inversion: using well logs to fill low frequency information in a non-homogenous model Heather J.E. Lloyd and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT An acoustic bandlimited impedance inversion
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Constrained inversion of P-S seismic data
 PS Inversion Constrained inversion of P-S seismic data Robert J. Ferguson, and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT A method to estimate S-wave interval velocity, using P-S seismic data is presented. The method
PS Inversion Constrained inversion of P-S seismic data Robert J. Ferguson, and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT A method to estimate S-wave interval velocity, using P-S seismic data is presented. The method
Comparison between least-squares reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion
 Comparison between least-squares reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion Lei Yang, Daniel O. Trad and Wenyong Pan Summary The inverse problem in exploration geophysics usually consists of two
Comparison between least-squares reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion Lei Yang, Daniel O. Trad and Wenyong Pan Summary The inverse problem in exploration geophysics usually consists of two
Reservoir connectivity uncertainty from stochastic seismic inversion Rémi Moyen* and Philippe M. Doyen (CGGVeritas)
 Rémi Moyen* and Philippe M. Doyen (CGGVeritas) Summary Static reservoir connectivity analysis is sometimes based on 3D facies or geobody models defined by combining well data and inverted seismic impedances.
Rémi Moyen* and Philippe M. Doyen (CGGVeritas) Summary Static reservoir connectivity analysis is sometimes based on 3D facies or geobody models defined by combining well data and inverted seismic impedances.
Delineating a sandstone reservoir at Pikes Peak, Saskatchewan using 3C seismic data and well logs
 Delineating a sandston reservoir at Pikes Peak Delineating a sandstone reservoir at Pikes Peak, Saskatchewan using 3C seismic data and well logs Natalia L. Soubotcheva and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT To
Delineating a sandston reservoir at Pikes Peak Delineating a sandstone reservoir at Pikes Peak, Saskatchewan using 3C seismic data and well logs Natalia L. Soubotcheva and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT To
Porosity prediction using cokriging with multiple secondary datasets
 Cokriging with Multiple Attributes Porosity prediction using cokriging with multiple secondary datasets Hong Xu, Jian Sun, Brian Russell, Kris Innanen ABSTRACT The prediction of porosity is essential for
Cokriging with Multiple Attributes Porosity prediction using cokriging with multiple secondary datasets Hong Xu, Jian Sun, Brian Russell, Kris Innanen ABSTRACT The prediction of porosity is essential for
~:;~~:~~io:.n.j:-!~~~:~:r:~~~~~ces:i::~cheme, the processed section reveals encouraging lateral and vertical improvements.
 Geo!. Soc. MaLay"ia, BuLLetin 36, December J9g4i pp. Il-18 Post migration processing of seismic data DASHUKI MOHD. Exploration Research Department Petroleum Research Institute PETRONAS..... d' a clear
Geo!. Soc. MaLay"ia, BuLLetin 36, December J9g4i pp. Il-18 Post migration processing of seismic data DASHUKI MOHD. Exploration Research Department Petroleum Research Institute PETRONAS..... d' a clear
Seismic attributes for fault/fracture characterization
 Satinder Chopra* and Kurt J. Marfurt + *Arcis Corporation, Calgary; + University of Houston, Houston Summary Seismic attributes have proliferated in the last three decades at a rapid rate and have helped
Satinder Chopra* and Kurt J. Marfurt + *Arcis Corporation, Calgary; + University of Houston, Houston Summary Seismic attributes have proliferated in the last three decades at a rapid rate and have helped
Acoustic impedance inversion analysis: Croatia offshore and onshore case studies
 Acoustic impedance inversion analysis: Croatia offshore and onshore case studies Domagoj Vukadin, mag. ing. geol. Stipica Brnada, mag. geol. SPE Conference Hungarian Section Visegrád, November, 19. 2015
Acoustic impedance inversion analysis: Croatia offshore and onshore case studies Domagoj Vukadin, mag. ing. geol. Stipica Brnada, mag. geol. SPE Conference Hungarian Section Visegrád, November, 19. 2015
Pre-stack (AVO) and post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data
 Pre-stack (AVO) and post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data A.Nassir Saeed, Gary F. Margrave and Laurence R. Lines ABSTRACT Post-stack and pre-stack (AVO) inversion were performed
Pre-stack (AVO) and post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data A.Nassir Saeed, Gary F. Margrave and Laurence R. Lines ABSTRACT Post-stack and pre-stack (AVO) inversion were performed
Comparison of spectral decomposition methods
 Comparison of spectral decomposition methods John P. Castagna, University of Houston, and Shengjie Sun, Fusion Geophysical discuss a number of different methods for spectral decomposition before suggesting
Comparison of spectral decomposition methods John P. Castagna, University of Houston, and Shengjie Sun, Fusion Geophysical discuss a number of different methods for spectral decomposition before suggesting
Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion and Amplitude Versus Angle Modeling Reduces the Risk in Hydrocarbon Prospect Evaluation
 Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
Interpretive advantages of 90 -phase wavelets: Part 1 Modeling
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 70, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 2005); P. C7 C15, 11 FIGS. 10.1190/1.1925740 Interpretive advantages of 90 -phase wavelets: Part 1 Modeling Hongliu Zeng 1 and Milo M. Backus 1 ABSTRACT We discuss,
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 70, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 2005); P. C7 C15, 11 FIGS. 10.1190/1.1925740 Interpretive advantages of 90 -phase wavelets: Part 1 Modeling Hongliu Zeng 1 and Milo M. Backus 1 ABSTRACT We discuss,
P S-wave polarity reversal in angle domain common-image gathers
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? P S-wave polarity reversal in angle domain common-image gathers Daniel Rosales and James Rickett 1 ABSTRACT The change in the reflection
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? P S-wave polarity reversal in angle domain common-image gathers Daniel Rosales and James Rickett 1 ABSTRACT The change in the reflection
Deterministic and stochastic inversion techniques used to predict porosity: A case study from F3-Block
 Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Dissertations, Master's Theses and Master's Reports 2015 Deterministic and stochastic inversion techniques used to predict porosity: A
Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Dissertations, Master's Theses and Master's Reports 2015 Deterministic and stochastic inversion techniques used to predict porosity: A
Implicit 3-D depth migration by wavefield extrapolation with helical boundary conditions
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 1998, pages 1 13 Implicit 3-D depth migration by wavefield extrapolation with helical boundary conditions James Rickett, Jon Claerbout, and Sergey Fomel
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 1998, pages 1 13 Implicit 3-D depth migration by wavefield extrapolation with helical boundary conditions James Rickett, Jon Claerbout, and Sergey Fomel
The reason why acoustic and shear impedances inverted
 SPECIAL The Rocky SECTION: Mountain The Rocky region Mountain region Comparison of shear impedances inverted from stacked PS and SS data: Example from Rulison Field, Colorado ELDAR GULIYEV, Occidental
SPECIAL The Rocky SECTION: Mountain The Rocky region Mountain region Comparison of shear impedances inverted from stacked PS and SS data: Example from Rulison Field, Colorado ELDAR GULIYEV, Occidental
Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains
 Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
P137 Our Experiences of 3D Synthetic Seismic Modeling with Tip-wave Superposition Method and Effective Coefficients
 P137 Our Experiences of 3D Synthetic Seismic Modeling with Tip-wave Superposition Method and Effective Coefficients M. Ayzenberg (StatoilHydro), A. Aizenberg (Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics),
P137 Our Experiences of 3D Synthetic Seismic Modeling with Tip-wave Superposition Method and Effective Coefficients M. Ayzenberg (StatoilHydro), A. Aizenberg (Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics),
Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO*
 Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO* *This paper has been submitted to the EAGE for presentation at the June 2001 EAGE meeting. SUMMARY
Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO* *This paper has been submitted to the EAGE for presentation at the June 2001 EAGE meeting. SUMMARY
A seismic reservoir characterization and porosity estimation workflow to support geological model update: pre-salt reservoir case study, Brazil
 A seismic reservoir characterization and porosity estimation workflow to support geological model update: pre-salt reservoir case study, Brazil Laryssa Oliveira 1*, Francis Pimentel 2, Manuel Peiro 1,
A seismic reservoir characterization and porosity estimation workflow to support geological model update: pre-salt reservoir case study, Brazil Laryssa Oliveira 1*, Francis Pimentel 2, Manuel Peiro 1,
J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU)
 U008 Seismic Imaging Below "Dirty" Salt J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU) SUMMARY Base and sub salt seismic imaging is still an unresolved issue. To solve
U008 Seismic Imaging Below "Dirty" Salt J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU) SUMMARY Base and sub salt seismic imaging is still an unresolved issue. To solve
Characterization and occurrence of opal-reflectors
 Characterization and occurrence of opal-reflectors T. Pedersen*, T. Throndsen**, F.T. Lysell***, Å.H. Drottning**** and T. Rautakorpi** EAGE Madrid 16. June 2005 *Institute for Energy Technology, Norway
Characterization and occurrence of opal-reflectors T. Pedersen*, T. Throndsen**, F.T. Lysell***, Å.H. Drottning**** and T. Rautakorpi** EAGE Madrid 16. June 2005 *Institute for Energy Technology, Norway
Porosity. Downloaded 09/22/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Geostatistical Reservoir Characterization of Deepwater Channel, Offshore Malaysia Trisakti Kurniawan* and Jahan Zeb, Petronas Carigali Sdn Bhd, Jimmy Ting and Lee Chung Shen, CGG Summary A quantitative
Geostatistical Reservoir Characterization of Deepwater Channel, Offshore Malaysia Trisakti Kurniawan* and Jahan Zeb, Petronas Carigali Sdn Bhd, Jimmy Ting and Lee Chung Shen, CGG Summary A quantitative
THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS
 THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS Cuesta, Julián* 1, Pérez, Richard 1 ; Hernández, Freddy 1 ; Carrasquel, Williams 1 ; Cabrera,
THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS Cuesta, Julián* 1, Pérez, Richard 1 ; Hernández, Freddy 1 ; Carrasquel, Williams 1 ; Cabrera,
Fifteenth International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society. Copyright 2017, SBGf - Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica
 Geostatistical Reservoir Characterization in Barracuda Field, Campos Basin: A case study Frank Pereira (CGG)*, Ted Holden (CGG), Mohammed Ibrahim (CGG) and Eduardo Porto (CGG). Copyright 2017, SBGf - Sociedade
Geostatistical Reservoir Characterization in Barracuda Field, Campos Basin: A case study Frank Pereira (CGG)*, Ted Holden (CGG), Mohammed Ibrahim (CGG) and Eduardo Porto (CGG). Copyright 2017, SBGf - Sociedade
New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay. Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round
 New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round Multiclient data interpretation provides key deliverables
New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round Multiclient data interpretation provides key deliverables
INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION
 INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 31 July 4 August 2017 Jakarta COURSE OUTLINE The course is aimed at imparting working knowledge
INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 31 July 4 August 2017 Jakarta COURSE OUTLINE The course is aimed at imparting working knowledge
3D geologic modelling of channellized reservoirs: applications in seismic attribute facies classification
 first break volume 23, December 2005 technology feature 3D geologic modelling of channellized reservoirs: applications in seismic attribute facies classification Renjun Wen, * president and CEO, Geomodeling
first break volume 23, December 2005 technology feature 3D geologic modelling of channellized reservoirs: applications in seismic attribute facies classification Renjun Wen, * president and CEO, Geomodeling
Time-lapse seismic modelling for Pikes Peak field
 Time-lapse seismic modelling for Pikes Peak field Ying Zou*, Laurence R. Bentley and Laurence R. Lines University of Calgary, 2500 University Dr, NW, Calgary, AB, T2N 1N4 zou@geo.ucalgary.ca ABSTRACT Predicting
Time-lapse seismic modelling for Pikes Peak field Ying Zou*, Laurence R. Bentley and Laurence R. Lines University of Calgary, 2500 University Dr, NW, Calgary, AB, T2N 1N4 zou@geo.ucalgary.ca ABSTRACT Predicting
THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS
 Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt Dan Hampson GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir
Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt Dan Hampson GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir
Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer
 Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer Saul E. Guevara and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite difference 2D elastic modeling is used to study characteristics of the
Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer Saul E. Guevara and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite difference 2D elastic modeling is used to study characteristics of the
An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration
 An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration Philip Kearey Department of Earth Sciences University of Bristol Michael Brooks Ty Newydd, City Near Cowbridge Vale of Glamorgan Ian Hill Department of Geology
An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration Philip Kearey Department of Earth Sciences University of Bristol Michael Brooks Ty Newydd, City Near Cowbridge Vale of Glamorgan Ian Hill Department of Geology
Interpretation of baseline surface seismic data at the Violet Grove CO 2 injection site, Alberta
 Violet Grove seismic interpretation Interpretation of baseline surface seismic data at the Violet Grove CO 2 injection site, Alberta Fuju Chen and Don Lawton ABSTRACT Time-lapse seismic technology has
Violet Grove seismic interpretation Interpretation of baseline surface seismic data at the Violet Grove CO 2 injection site, Alberta Fuju Chen and Don Lawton ABSTRACT Time-lapse seismic technology has
Kurt Marfurt Arnaud Huck THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS
 The Society of Exploration Geophysicists and GeoNeurale announce Kurt Marfurt Arnaud Huck THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization
The Society of Exploration Geophysicists and GeoNeurale announce Kurt Marfurt Arnaud Huck THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization
Delineating Karst features using Advanced Interpretation
 P-152 Asheesh Singh, Sibam Chakraborty*, Shafique Ahmad Summary We use Amplitude, Instantaneous Phase, Trace Envelope and Dip of Maximum Similarity Attributes as a tool to delineate Karst induced features
P-152 Asheesh Singh, Sibam Chakraborty*, Shafique Ahmad Summary We use Amplitude, Instantaneous Phase, Trace Envelope and Dip of Maximum Similarity Attributes as a tool to delineate Karst induced features
Robust one-step (deconvolution + integration) seismic inversion in the frequency domain Ivan Priezzhev* and Aaron Scollard, Schlumberger
 Robust one-step (deconvolution + integration) seismic inversion in the frequency domain Ivan Priezzhev and Aaron Scollard, Schlumberger Summary Seismic inversion requires two main operations relative to
Robust one-step (deconvolution + integration) seismic inversion in the frequency domain Ivan Priezzhev and Aaron Scollard, Schlumberger Summary Seismic inversion requires two main operations relative to
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach
 Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Seismic lab exercises
 Seismic lab exercises SEISMIC LAB 1st Exercise This type of analysis involves taking either seismic or geologic cross-sections and building a chronostratigraphic chart. Chronostratigraphic charts, also
Seismic lab exercises SEISMIC LAB 1st Exercise This type of analysis involves taking either seismic or geologic cross-sections and building a chronostratigraphic chart. Chronostratigraphic charts, also
THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS
 Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt Dan Hampson GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir
Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt Dan Hampson GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
 An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
Short Note. Plane wave prediction in 3-D. Sergey Fomel 1 INTRODUCTION
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report SERGEY, November 9, 2000, pages 291?? Short Note Plane wave prediction in 3-D Sergey Fomel 1 INTRODUCTION The theory of plane-wave prediction in three dimensions is
Stanford Exploration Project, Report SERGEY, November 9, 2000, pages 291?? Short Note Plane wave prediction in 3-D Sergey Fomel 1 INTRODUCTION The theory of plane-wave prediction in three dimensions is
Seismic Inversion and EMERGE Studies for Porosity distribution analysis in DCS area, Bombay Offshore Basin
 P-118 Seismic Inversion and EMERGE Studies for Porosity distribution analysis in DCS area, Summary Phukan, R.K*; Mishra, J; Lohani, N.C Oil Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, KDMIPE, Dehradun 248195, India Estimation
P-118 Seismic Inversion and EMERGE Studies for Porosity distribution analysis in DCS area, Summary Phukan, R.K*; Mishra, J; Lohani, N.C Oil Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, KDMIPE, Dehradun 248195, India Estimation
PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Eighth Annual Convention & Exhibition, May 2014
 IPA14-G-227 PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Eighth Annual Convention & Exhibition, May 2014 A COMPARISON OF DEPTH CONVERSION METHODS IN BUNTAL GAS FIELD, BLOCK B, NATUNA SEA, INDONESIA
IPA14-G-227 PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Eighth Annual Convention & Exhibition, May 2014 A COMPARISON OF DEPTH CONVERSION METHODS IN BUNTAL GAS FIELD, BLOCK B, NATUNA SEA, INDONESIA
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing
 From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
We LHR5 03 Seismic Diffraction Response from Boreholes
 We LHR5 3 Seismic Diffraction Response from Boreholes T.J. Moser* (Moser Geophysical Services), B. Arntsen (Norwegian University of Science and Technology), S. Johansen (Norwegian University of Science
We LHR5 3 Seismic Diffraction Response from Boreholes T.J. Moser* (Moser Geophysical Services), B. Arntsen (Norwegian University of Science and Technology), S. Johansen (Norwegian University of Science
Building more robust low-frequency models for seismic impedance inversion
 first break volume 34, May 2016 technical article Building more robust low-frequency models for seismic impedance inversion Amit Kumar Ray 1 and Satinder Chopra 1* Abstract Seismic impedance inversion
first break volume 34, May 2016 technical article Building more robust low-frequency models for seismic impedance inversion Amit Kumar Ray 1 and Satinder Chopra 1* Abstract Seismic impedance inversion
THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS
 Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization 29-31 May
Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization 29-31 May
Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs
 Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Worldwide interest
Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Worldwide interest
An overview of AVO and inversion
 P-486 An overview of AVO and inversion Brian Russell, Hampson-Russell, CGGVeritas Company Summary The Amplitude Variations with Offset (AVO) technique has grown to include a multitude of sub-techniques,
P-486 An overview of AVO and inversion Brian Russell, Hampson-Russell, CGGVeritas Company Summary The Amplitude Variations with Offset (AVO) technique has grown to include a multitude of sub-techniques,
Sensitivity Analysis of Pre stack Seismic Inversion on Facies Classification using Statistical Rock Physics
 Sensitivity Analysis of Pre stack Seismic Inversion on Facies Classification using Statistical Rock Physics Peipei Li 1 and Tapan Mukerji 1,2 1 Department of Energy Resources Engineering 2 Department of
Sensitivity Analysis of Pre stack Seismic Inversion on Facies Classification using Statistical Rock Physics Peipei Li 1 and Tapan Mukerji 1,2 1 Department of Energy Resources Engineering 2 Department of
Th P7 02 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling
 Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
Recent advances in application of AVO to carbonate reservoirs: case histories
 Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
IJMGE Int. J. Min. & Geo-Eng. Vol.49, No.1, June 2015, pp
 IJMGE Int. J. Min. & Geo-Eng. Vol.49, No.1, June 2015, pp.131-142 Joint Bayesian Stochastic Inversion of Well Logs and Seismic Data for Volumetric Uncertainty Analysis Moslem Moradi 1, Omid Asghari 1,
IJMGE Int. J. Min. & Geo-Eng. Vol.49, No.1, June 2015, pp.131-142 Joint Bayesian Stochastic Inversion of Well Logs and Seismic Data for Volumetric Uncertainty Analysis Moslem Moradi 1, Omid Asghari 1,
Quantitative interpretation using inverse rock-physics modeling on AVO data
 Quantitative interpretation using inverse rock-physics modeling on AVO data Erling Hugo Jensen 1, Tor Arne Johansen 2, 3, 4, Per Avseth 5, 6, and Kenneth Bredesen 2, 7 Downloaded 08/16/16 to 129.177.32.62.
Quantitative interpretation using inverse rock-physics modeling on AVO data Erling Hugo Jensen 1, Tor Arne Johansen 2, 3, 4, Per Avseth 5, 6, and Kenneth Bredesen 2, 7 Downloaded 08/16/16 to 129.177.32.62.
IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. 2 Issue 9, September 2015.
 Prediction of petrophysical parameters applying multi attribute analysis and probabilistic neural network techniques of seismic data for Komombo Basin, Upper Egypt. Othman, A. A. A. 1, Ewida, H. F. 2,
Prediction of petrophysical parameters applying multi attribute analysis and probabilistic neural network techniques of seismic data for Komombo Basin, Upper Egypt. Othman, A. A. A. 1, Ewida, H. F. 2,
The relationship between elastic-wave velocities and density in sedimentary rocks: A proposal
 260 The relationship between elastic-wave velocities and density in sedimentary rocks: A proposal Susan L.M. Miller and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT When information about density (0) is unavailable, it
260 The relationship between elastic-wave velocities and density in sedimentary rocks: A proposal Susan L.M. Miller and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT When information about density (0) is unavailable, it
Derived Rock Attributes Analysis for Enhanced Reservoir Fluid and Lithology Discrimination
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 95-105 www.iosrjournals.org Derived Rock Attributes Analysis
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. - Apr. 2017), PP 95-105 www.iosrjournals.org Derived Rock Attributes Analysis
Churning seismic attributes with principal component analysis
 Satinder Chopra + * and Kurt J. Marfurt + Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary; The University of Oklahoma, Norman Summary Seismic attributes are an invaluable aid in the interpretation of seismic data. Different
Satinder Chopra + * and Kurt J. Marfurt + Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary; The University of Oklahoma, Norman Summary Seismic attributes are an invaluable aid in the interpretation of seismic data. Different
Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma
 Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary The Woodford Shale is one of the more important resource
Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary The Woodford Shale is one of the more important resource
KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. Publication
 KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. Publication Yu, G., Ma, Y., Zhu, X., Guo, T., Rebec, T. & Azbel, K. 2006 Reservoir characterization with high frequency bandwidth seismic data and coherence processing
KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. Publication Yu, G., Ma, Y., Zhu, X., Guo, T., Rebec, T. & Azbel, K. 2006 Reservoir characterization with high frequency bandwidth seismic data and coherence processing
Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study
 Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study Suresh Thampi, Aqeel Ahmed, Yahya Al-Ansari, Ali Shehab, Ahmed Fateh, Anindya Ghosh, Ghada Almoulani. The
Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study Suresh Thampi, Aqeel Ahmed, Yahya Al-Ansari, Ali Shehab, Ahmed Fateh, Anindya Ghosh, Ghada Almoulani. The
RC 1.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1307
 from seismic AVO Xin-Gong Li,University of Houston and IntSeis Inc, De-Hua Han, and Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Donn McGuire, Anadarko Petroleum Corp Summary A new inversion method is tested to directly
from seismic AVO Xin-Gong Li,University of Houston and IntSeis Inc, De-Hua Han, and Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Donn McGuire, Anadarko Petroleum Corp Summary A new inversion method is tested to directly
P125 AVO for Pre-Resonant and Resonant Frequency Ranges of a Periodical Thin-Layered Stack
 P125 AVO for Pre-Resonant and Resonant Frequency Ranges of a Periodical Thin-Layered Stack N. Marmalyevskyy* (Ukrainian State Geological Prospecting Institute), Y. Roganov (Ukrainian State Geological Prospecting
P125 AVO for Pre-Resonant and Resonant Frequency Ranges of a Periodical Thin-Layered Stack N. Marmalyevskyy* (Ukrainian State Geological Prospecting Institute), Y. Roganov (Ukrainian State Geological Prospecting
Framework for AVO gradient and intercept interpretation
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 63, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1998); P. 948 956, 10 FIGS., 2 TABLES. Framework for AVO gradient and intercept interpretation John P. Castagna, Herbert W. Swan, and Douglas J. Foster ABSTRACT Amplitude
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 63, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1998); P. 948 956, 10 FIGS., 2 TABLES. Framework for AVO gradient and intercept interpretation John P. Castagna, Herbert W. Swan, and Douglas J. Foster ABSTRACT Amplitude
11301 Reservoir Analogues Characterization by Means of GPR
 11301 Reservoir Analogues Characterization by Means of GPR E. Forte* (University of Trieste) & M. Pipan (University of Trieste) SUMMARY The study of hydrocarbon reservoir analogues is increasing important
11301 Reservoir Analogues Characterization by Means of GPR E. Forte* (University of Trieste) & M. Pipan (University of Trieste) SUMMARY The study of hydrocarbon reservoir analogues is increasing important
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 248 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 First-order lateral interval velocity estimates without picking
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 248 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 First-order lateral interval velocity estimates without picking
Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study
 The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
SPE MS. Abstract
 Seismically Derived Porosity Prediction for Field Development- An Onshore Abu Dhabi Jurassic Carbonate Reservoir Case Study Shraddha Chatterjee, CGG; Matthew Burreson, Al Hosn Gas; Bertrand Six, CGG; Jean-Marc
Seismically Derived Porosity Prediction for Field Development- An Onshore Abu Dhabi Jurassic Carbonate Reservoir Case Study Shraddha Chatterjee, CGG; Matthew Burreson, Al Hosn Gas; Bertrand Six, CGG; Jean-Marc
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site
 Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
Potential field migration for rapid interpretation of gravity gradiometry data
 Potential field migration for rapid interpretation of gravity gradiometry data M. S. Zhdanov 1,2, X. Liu 1 and G. Wilson 2 1 The University of Utah, 2 TechnoImaging Summary We introduce potential field
Potential field migration for rapid interpretation of gravity gradiometry data M. S. Zhdanov 1,2, X. Liu 1 and G. Wilson 2 1 The University of Utah, 2 TechnoImaging Summary We introduce potential field
A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography
 A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography Ian Jones* GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom ijones@gxt.com Emma Evans and Darren Judd GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom and
A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography Ian Jones* GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom ijones@gxt.com Emma Evans and Darren Judd GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom and
Geological Classification of Seismic-Inversion Data in the Doba Basin of Chad*
 Geological Classification of Seismic-Inversion Data in the Doba Basin of Chad* Carl Reine 1, Chris Szelewski 2, and Chaminda Sandanayake 3 Search and Discovery Article #41899 (2016)** Posted September
Geological Classification of Seismic-Inversion Data in the Doba Basin of Chad* Carl Reine 1, Chris Szelewski 2, and Chaminda Sandanayake 3 Search and Discovery Article #41899 (2016)** Posted September
Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform a
 Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform a a Published in Journal of Seismic Exploration, 23, no. 4, 303-312, (2014) Yangkang Chen, Tingting Liu, Xiaohong Chen,
Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform a a Published in Journal of Seismic Exploration, 23, no. 4, 303-312, (2014) Yangkang Chen, Tingting Liu, Xiaohong Chen,
Adaptive multiple subtraction using regularized nonstationary regression
 GEOPHSICS, VOL. 74, NO. 1 JANUAR-FEBRUAR 29 ; P. V25 V33, 17 FIGS. 1.119/1.343447 Adaptive multiple subtraction using regularized nonstationary regression Sergey Fomel 1 ABSTRACT Stationary regression
GEOPHSICS, VOL. 74, NO. 1 JANUAR-FEBRUAR 29 ; P. V25 V33, 17 FIGS. 1.119/1.343447 Adaptive multiple subtraction using regularized nonstationary regression Sergey Fomel 1 ABSTRACT Stationary regression
