In situ permeability measurements inside compaction bands using X-ray CT and lattice Boltzmann calculations
|
|
|
- Evangeline Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Permeability measurements inside compaction bands In situ permeability measurements inside compaction bands using X-ray CT and lattice Boltzmann calculations N. Lenoir, J.E. Andrade, W.C. Sun, J.W. Rudnicki Northwestern University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 2145 Sheridan road Evanston, IL USA ABSTRACT: The paper presents some results of the characterization of microstuctural differences inside and outside compaction bands in natural sandstone. Specimens of Aztec sandstone were scanned at the synchrotron APS, at Argonne National Laboratory (USA). Porosity measurements obtained by image analysis show a sharp transition inside/outside the compaction band. Finally, preliminary permeability measurements were conducted via the lattice Boltzmann method and demonstrate the dramatic decrease in permeability caused by the reduced porosity inside the compaction band relative to the host rock. KEYWORDS: compaction band, sandstone, permeability, lattice Boltzmann, synchrotron
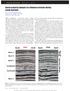
2 GeoX2010: Advances in Computed Tomography for Geomaterials 1. Introduction The study of deformation bands including compaction bands (CB) in granular porous rocks is an important topic for many applications ranging from oil and gas reservoirs to CO 2 sequestration to geologic repositories for nuclear waste. For instance, compaction bands have been found in sandstones typical of possible repository host rock for CO 2 sequestration. There is the question of how formation, presence or extension of compaction affects the injection of CO 2 into reservoirs. Due to the observed dramatic decrease in permeability relative to the host rock (see for a review, Holcomb et al., 2007), CB could play the important role of flow barriers and trap the CO 2 injected or, on the other hand, adversely affect injection. In the last decade, observations and permeability characterizations in geomaterials have been made at different scales. In particular, lattice Boltzmann (LB) calculations applied to 3D images obtained from X-ray CT have proven to be an efficient method in this area (e.g. Arns et al., 2004, White et al., 2006). However, the method has only been used for characterizing permeability in pristine sandstones without the presence of a CB (e.g. Fredrich et al., 2006). The only LB computation inside of CB was conducted on a simulated 3D image created from a 2D SEM image with a geostatistical model (Keehm et al., 2006). Thus, to our knowledge, this is the first instance of application of these methods to a sample obtained from a CB in the field.. The purpose of this work is to use direct experimental observations and LB calculations to characterize the difference in permeability inside and outside CB obtained from field cores of sandstone. Small specimens of Aztec sandstone cored from the inside and outside of a CB were scanned at a synchrotron in order to characterize the 3D change in microstructure. Porosity was then measured from the images, allowing us to obtain a clear profile of the void-space and observe the transition from the host rock into the CB. From the 3D images, some preliminary permeability measurements were performed using the LB method and show the dramatic effect of CB on the rock s flow properties. 2. Material and methods The material studied in this work is Aztec sandstone from the Valley of Fire State park (Nevada, USA) where Sternlof (2006) had conducted a field study of the geometry and physical characterization of the bands.. This rock is an eolian sandstone with a mean grain size of about 0.25 mm and a porosity ranging from 15 to 25% (Antonellini et al., 1994). Blocks were taken in the field and small cylindrical specimens were cored with a diamond core drill inside and outside of a CB. In order to prevent disturbance of the microstructure due to the coring process, the block was first impregnated with a low viscosity epoxy. The left part of Figure 1
3 Permeability measurements inside compaction bands shows, a small block of sandstone with the compaction band appearing in lighter color and on the right, the block used in this study, first impregnated with epoxy. The two white rectangles indicate the location of the cored specimens presented here. Specimen n 1 was cored inside the CB with the inside/outside CB transition included at its end. The specimen n 2 was cored just straight ahead of n 1 outside of the CB. Both were cored in a direction perpendicular to the CB. The specimen diameter is about 4.2 mm. The heights are about 20 and 11 mm for n 1 and n 2 respectively. Figure 1. (a) Piece of Aztec sandstone obtained from the field. The compaction band CB appears in lighter color here. (b) core impregnated of epoxy with the coring location of the 2 specimens presented here. For scanning the specimens, a synchrotron was chosen as it provides the possibility to get a monochromatic beam. This avoids the artefact of beam hardening that can occur with images obtained with laboratory X-ray scanners. Thus, the image segmentation is simplified and makes it possible to obtain a high quality binary image of the microstructure. The specimens were scanned on the DND-CAT 5-BM- C beamline at the Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory (USA). The specimens were mounted on a rotating stage by using wax in order to avoid any motion of the sample during the scanning process. The data were collected with a scintillator associated with a CCD camera. The energy used was 25 kev and 1200 radiographies were recorded over half rotation of the specimen, with an exposure time of 725 ms. The spatial resolution was a voxel size of 6x6x6 µm 3. The specimens were scanned in different overlapping sequential sections equally spaced (every 3 mm) in order to obtain a full image of the cylinders. The images are 16bit and the volume size for a section was 1299x1299x600 voxels which corresponds to a height of 3.6 mm. The images were then stacked and the final volumes were 800x800x3360 and 800x800x1860 voxels for specimen n 1 and n 2 respectively.
4 GeoX2010: Advances in Computed Tomography for Geomaterials 3. X-ray CT images and porosity measurements The CT images clearly show the microstructure of the sandstone and the difference in the microstructure inside and outside the CB. Figure 2 presents a horizontal slice obtained from specimen n 2 on the left and one from n 1 on the right. Aztec sandstone is mainly composed of round quartz grains (99%) appearing in light gray, and some hematite appearing in white. The porous network mainly filled of epoxy appears in dark grey and black. A packing phenomenon of the grains inside the CB is clearly observed by simple comparison of the images as previously noted by Sternlof (2006) in his field study of CB in Aztec sandstone. Figure 2. (a) Horizontal CT slice from specimen n 2. (b) Horizontal CT slice from specimen n 1. Porosity measurements were performed through image analysis by using the open source software ImageJ ( The 16bit images were first cropped to keep an inner core of 600 voxels width and then converted to binary form in order to measure the permeability. As the grains, especially the boundary grain/pore space, are well defined due to the high spatial resolution, the segmentation was done by a 'manual' threshold method. The choice of the threshold value was made as follows. A wide range of grey level values was used and the corresponding porosities were calculated. The obtained profile consists of a linear increase in porosity while within the porous area and a sudden change of slope once the grain boundaries are reached. The onset of this sudden increase was chosen as the threshold value. An example of the obtained 3D porous network after segmentation is shown in Figure 3 on a
5 Permeability measurements inside compaction bands small volume (200x200x200 voxels) obtained from outside the CB. The mean porosity obtained is about 21% outside and 14.5% inside the CB which is in accordance with the literature (Antonellini et al., 1994; Holcomb et al., 2007). Study of the transition from the CB to the outside material in more detail is possible in the images from specimen n 1. Figure 3 shows the evolution of the porosity along the continuous specimens n 1 and n 2. The transition is very sharp. The porosity decreases from 21% to 14.5% within a zone of approximately 2 mm. Note, however, that within this transition zone is a region of slightly lower porosity (12%). We will perform further studies to determine whether this lower porosity (than with the band itself) is a feature of this particular specimen is more prevalent. If the latter, it may give some insight into factors controlling the width of the band (since it seems to bear no simple relation to the grain size). Figure 3. Image segmentation and porosity profile inside/outside compaction band.
6 GeoX2010: Advances in Computed Tomography for Geomaterials 4. Permeability measurements with lattice Boltzmann method The lattice Boltzmann (LB) method is employed to estimate the permeability of selected sub-domains of the specimen inside and outside the CB. Known for its ability to handle complex geometry, LB method takes advantage of the kinetic theory to seek probability density functions that leads to velocity and pressure fields satisfying momentum and mass balance principles without solving the Navier-Stokes equation directly at the continuum level (Succi, 2001). In this study, the effective permeability is estimated via the procedures described as follows. First, a hydraulic gradient is applied along a basis direction. Then, LB simulations are performed until the pore-fluid velocity field reaches its steady state. Since LB flow is by nature compressible, the permeability corresponding to the basis direction is obtained via the Darcy's law augmented with the continuity equation. Some preliminary simulations were conducted on two small sub-domains (50x50x50 voxels), one inside and one outside the CB, with a measured porosity about 15% and 20% respectively. Figure 4 depicts the obtained simulated flows within the 3D porous network. The permeability along the vertical direction of the subdomain i.e. perpendicular to the CB, outside and inside are estimated as k in =1x10-12 m 2 and k out =6x10-19 m 2 respectively. Such a dramatic change on permeability reflects the geometrical difference of pore space inside and outside the band. Figure 4 suggests that due to the packing phenomenon inside the CB, pore-scale flow channels are likely to be either severely narrowed or completed blocked when a CB forms. Although the difference in porosity between the two sub-domains is about 25%, the results of the LB simulation show that the geometric changes of flow channels triggered by the formation of CB can significantly reduce the flow velocity and cause a low effective permeability. Note that the obtained ratio in permeabilities k in /k out is about 10-7 which is higher than the one reported in the literature ( ) (Sternlof et al., 2004). The smaller ratio obtained here occurs because the calculated permeability is an averaged property having a spatial fluctuation that is larger at smaller scales. LB simulations at a sufficiently large scale would suppress spatial fluctuation but have a high computational cost. The choice for the size of the samples used for permeability calculations is bounded by the minimum size necessary for continuum to make sense and a maximum size imposed by our computational capability. Work is ongoing to parallelize the code and to overcome that limitation of computational cost. Thus, LB simulations will be performed on a large range of volumes in order to determine the elementary volume that will give more representative results of the macroscopic permeability. Moreover, those preliminary results were
7 Permeability measurements inside compaction bands obtained in a single direction. The anisotropy in permeability will be investigated in a forthcoming publication. Figure 4. Fluid flow (represented by arrows) within the 3D porous network obtained with LB computation outside (on the left) and inside the CB (on the right). 5. Conclusions and perspectives We have used synchrotron measurements to obtain detailed three dimensional images of the microstructure outside and inside a CB formed in the field (Valley of Fire, Nevada). These images are consistent with previous observations of increased grain packing within the band. Porosity measurements made it possible to study the transition from outside of the compaction band to inside in more detail than has been done previously. The porosity decreases sharply, over about 2 mm. A new feature observed here is that within the transition zone, there is a region with porosity slightly lower than within the CB. Further investigation is needed to determine whether this feature is particular to this specimen or more typical of CBs formed in the field. Preliminary permeability measurements obtained using LB method on small volumes outside and inside the CB gave promising results. As anticipated, the reduced porosity in the band results in a dramatic decrease in permeability. Work is ongoing to reduce the computation time in order to perform computations in larger volumes and more samples, which will give more representative results. Moreover, it should be emphasized that this study concerns a single specimen and, though the results are promising, more analysis is necessary to get a faithful picture of the overall hydraulic properties in the context of compaction bands.
8 GeoX2010: Advances in Computed Tomography for Geomaterials Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank P. Eichhubl, University of Texas, for providing the sandstone blocks and D.T. Keane, APS-Argonne Laboratory, for his guidance and help on the scanning process. This work is funded by the U. S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under the project n DE-FG02-08ER Use of the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the U. S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH References Antonellini, M.A., Aydin, A., Pollard, A.A. and D'Onfro, P., Petrophysical study of faults in sandstone using petrophic image anlaysis and x-ray computerized tomography, vol.143, No.1-3, pp , Pure and Applied Geophysics, Arns, C.H., Knackstedt, M.A., Val Pinczewski, W. and Martys, N.S., Virtual permeametry on microtomographic images, vol.45, No.1-2, pp.41 46, Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, Fredrich, J.T., Di Giovanni, A.A. and Noble, D.R., Predicting macroscopic transport properties using microscopic image data, vol.111, B03201, Journal of Geophysical Research, Holcomb, D., Rudnicki, J.W., Issen, K.A. and Sternlof, K., Compaction localization in the Earth and the laboratory: state of the research and research directions, vol.2, No.1, pp.1 15, Acta Geotechnica, Keehm, Y., Sternlof, K. and Mukerji, T., Computational estimation of compaction band permeability in sandstone, vol.10, No.4, pp , Geosciences Journal, Sternlof, K.R., Chapin, J.R., Pollard, D.D. and Durlofsky, L.J., Permeability effects of deformation band arrays in sandstone, vol.88, No.9, pp , AAPG Bulletin, Sternlof, K.R., Structural geology, propagation mechanics and hydraulic effects of compaction bands in sandstone, PhD Thesis, Stanford University, Succi, S., The lattice Boltzmann equations, Oxford Science Publications, White, J.A., Borja, R.I. and Fredrich, J.T., Calculating the effective permeability of sandstone with multiscale lattice Boltzmann/finite element simulations, vol.1, No.4, pp , Acta Geotechnica, 2006.
Th P06 05 Permeability Estimation Using CFD Modeling in Tight Carboniferous Sandstone
 Th P06 05 Permeability Estimation Using CFD Modeling in Tight Carboniferous Sandstone P.I. Krakowska (AGH University of Science and Technology in Krakow), P.J. Madejski* (AGH University of Science and
Th P06 05 Permeability Estimation Using CFD Modeling in Tight Carboniferous Sandstone P.I. Krakowska (AGH University of Science and Technology in Krakow), P.J. Madejski* (AGH University of Science and
Formation and Extension of Localized Compaction in Porous Sandstone
 Formation and Extension of Localized Compaction in Porous Sandstone J. W. Rudnicki Dept. of Civil and Env. Eng. and Dept. of Mechanical Eng. Northwestern University June 26, 20012 Plenary Talk, ARMA, Chicago,
Formation and Extension of Localized Compaction in Porous Sandstone J. W. Rudnicki Dept. of Civil and Env. Eng. and Dept. of Mechanical Eng. Northwestern University June 26, 20012 Plenary Talk, ARMA, Chicago,
X-RAY MICRO-TOMOGRAPHY OF PORE-SCALE FLOW AND TRANSPORT. University of California Davis. Dorthe Wildenschild & Annette Mortensen
 X-RAY MICRO-TOMOGRAPHY OF PORE-SCALE FLOW AND TRANSPORT Jan W. Hopmans University of California Davis Volker Clausnitzer Dorthe Wildenschild & Annette Mortensen ISSUES: Measurements and modeling of water
X-RAY MICRO-TOMOGRAPHY OF PORE-SCALE FLOW AND TRANSPORT Jan W. Hopmans University of California Davis Volker Clausnitzer Dorthe Wildenschild & Annette Mortensen ISSUES: Measurements and modeling of water
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008
 MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON THE ROADMAP MOTIVATION
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON THE ROADMAP MOTIVATION
Calculating the effective permeability of sandstone with multiscale lattice Boltzmann/finite element simulations
 Acta Geotechnica (2006) 1:195 209 DOI 10.1007/s11440-006-0018-4 RESEARCH PAPER Calculating the effective permeability of sandstone with multiscale lattice Boltzmann/finite element simulations Joshua A.
Acta Geotechnica (2006) 1:195 209 DOI 10.1007/s11440-006-0018-4 RESEARCH PAPER Calculating the effective permeability of sandstone with multiscale lattice Boltzmann/finite element simulations Joshua A.
Exercise: concepts from chapter 6
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Chapter 6 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Chapter 6 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area
Pore Scale Analysis of Oil Shale Pyrolysis by X-ray CT and LB Simulation
 Pore Scale Analysis of Oil Shale Pyrolysis by X-ray CT and LB Simulation C.L. Lin 1, J.D. Miller 1, C.H. Hsieh 1, P. Tiwari 2 and M.D. Deo 2 1 Department of Metallurgical Engineering, University of Utah,
Pore Scale Analysis of Oil Shale Pyrolysis by X-ray CT and LB Simulation C.L. Lin 1, J.D. Miller 1, C.H. Hsieh 1, P. Tiwari 2 and M.D. Deo 2 1 Department of Metallurgical Engineering, University of Utah,
Pore Scale Analysis of Oil Shale/Sands Pyrolysis
 Pore Scale Analysis of Oil Shale/Sands Pyrolysis C.L. Lin, J.D. Miller, and C.H. Hsieh Department of Metallurgical Engineering College of Mines and Earth Sciences University of Utah Outlines Introduction
Pore Scale Analysis of Oil Shale/Sands Pyrolysis C.L. Lin, J.D. Miller, and C.H. Hsieh Department of Metallurgical Engineering College of Mines and Earth Sciences University of Utah Outlines Introduction
Formation and Extension of Compaction Bands in Porous Sandstone
 Formation and Extension of Compaction Bands in Porous Sandstone J. W. Rudnicki Dept. of Civil and Env. Eng. and Dept. of Mechanical Eng. Northwestern University September 8, 2011 Statoil, Bergen, Norway
Formation and Extension of Compaction Bands in Porous Sandstone J. W. Rudnicki Dept. of Civil and Env. Eng. and Dept. of Mechanical Eng. Northwestern University September 8, 2011 Statoil, Bergen, Norway
FOCUSSED ION BEAM ASSISTED THREE-DIMENSIONAL ROCK IMAGING AT SUBMICRON SCALE
 FOCUSSED ION BEAM ASSISTED THREE-DIMENSIONAL ROCK IMAGING AT SUBMICRON SCALE 1 Liviu Tomutsa and 2 Velimir Radmilovic 1 Earth Science Division and 2 National Center for Electron Microscopy, Lawrence Berkeley
FOCUSSED ION BEAM ASSISTED THREE-DIMENSIONAL ROCK IMAGING AT SUBMICRON SCALE 1 Liviu Tomutsa and 2 Velimir Radmilovic 1 Earth Science Division and 2 National Center for Electron Microscopy, Lawrence Berkeley
Effect of grain size distribution on the development of compaction localization in porous sandstone
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053739, 2012 Effect of grain size distribution on the development of compaction localization in porous sandstone Cecilia S. N. Cheung, 1 Patrick
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053739, 2012 Effect of grain size distribution on the development of compaction localization in porous sandstone Cecilia S. N. Cheung, 1 Patrick
Fault gouge porosity from 2D simulations of fractal particle size distribution
 Fault gouge porosity from 2D simulations of fractal particle size distribution Reza Sehhati (1), Sujana Ganta (2), and Jafar Hadizadeh (3) Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, University of
Fault gouge porosity from 2D simulations of fractal particle size distribution Reza Sehhati (1), Sujana Ganta (2), and Jafar Hadizadeh (3) Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, University of
Multiscale method for characterization of porous microstructures and their impact on macroscopic effective permeability
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng (2011) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)..3220 Multiscale method for characterization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng (2011) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)..3220 Multiscale method for characterization
PREDICTION OF INTRINSIC PERMEABILITIES WITH LATTICE BOLTZMANN METHOD
 PREDICTION OF INTRINSIC PERMEABILITIES WITH LATTICE BOLTZMANN METHOD Luís Orlando Emerich dos Santos emerich@lmpt.ufsc.br Carlos Enrique Pico Ortiz capico@lmpt.ufsc.br Henrique Cesar de Gaspari henrique@lmpt.ufsc.br
PREDICTION OF INTRINSIC PERMEABILITIES WITH LATTICE BOLTZMANN METHOD Luís Orlando Emerich dos Santos emerich@lmpt.ufsc.br Carlos Enrique Pico Ortiz capico@lmpt.ufsc.br Henrique Cesar de Gaspari henrique@lmpt.ufsc.br
Micro-Structural Rock Modeling: Methodology and Application in Formation Evaluation
 Micro-Structural Rock Modeling: Methodology and Application in Formation Evaluation Guodong Jin 1, Chun Lan 1, Wei Shao 1, and Songhua Chen 1, 2 1 Baker Hughes Incorporated, Houston, Texas, USA 2 Now at
Micro-Structural Rock Modeling: Methodology and Application in Formation Evaluation Guodong Jin 1, Chun Lan 1, Wei Shao 1, and Songhua Chen 1, 2 1 Baker Hughes Incorporated, Houston, Texas, USA 2 Now at
Permeability and fluid transport
 Permeability and fluid transport Thermal transport: Fluid transport: q = " k # $p with specific discharge (filter velocity) q [m s 1 ] pressure gradient p [N m 3 ] dynamic viscosity η [N s m 2 ] (intrinsic)
Permeability and fluid transport Thermal transport: Fluid transport: q = " k # $p with specific discharge (filter velocity) q [m s 1 ] pressure gradient p [N m 3 ] dynamic viscosity η [N s m 2 ] (intrinsic)
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002](/thumbs/74/69829551.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0212257v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 International Journal of Modern Physics B c World Scientific Publishing Company VISCOUS FINGERING IN MISCIBLE, IMMISCIBLE AND REACTIVE FLUIDS PATRICK
arxiv:cond-mat/0212257v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 International Journal of Modern Physics B c World Scientific Publishing Company VISCOUS FINGERING IN MISCIBLE, IMMISCIBLE AND REACTIVE FLUIDS PATRICK
MICRO-SCALE EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROSTATIC STRESS ON PORE- SPACE DEFORMATION AND FLUID OCCUPANCY
 SCA2016-026 1/12 MICRO-SCALE EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROSTATIC STRESS ON PORE- SPACE DEFORMATION AND FLUID OCCUPANCY M. Asadollahkhan Vali 1, A.H. Alizadeh 1, M. Piri 1, and J. Wallace
SCA2016-026 1/12 MICRO-SCALE EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROSTATIC STRESS ON PORE- SPACE DEFORMATION AND FLUID OCCUPANCY M. Asadollahkhan Vali 1, A.H. Alizadeh 1, M. Piri 1, and J. Wallace
HETEROGENOUS CARBONATES INTEGRATING PLUG AND WHOLE CORE DATA USING ROCK TYPES
 SCA2012-12 1/12 HETEROGENOUS CARBONATES INTEGRATING PLUG AND WHOLE CORE DATA USING ROCK TYPES Mark Skalinski, Rafael Salazar, Gerry LaTorraca, Zheng Yang, and John Urbach Chevron ETC This paper was prepared
SCA2012-12 1/12 HETEROGENOUS CARBONATES INTEGRATING PLUG AND WHOLE CORE DATA USING ROCK TYPES Mark Skalinski, Rafael Salazar, Gerry LaTorraca, Zheng Yang, and John Urbach Chevron ETC This paper was prepared
1 Modeling Immiscible Fluid Flow in Porous Media
 Excerpts from the Habilitation Thesis of Peter Bastian. For references as well as the full text, see http://cox.iwr.uni-heidelberg.de/people/peter/pdf/bastian_habilitationthesis.pdf. Used with permission.
Excerpts from the Habilitation Thesis of Peter Bastian. For references as well as the full text, see http://cox.iwr.uni-heidelberg.de/people/peter/pdf/bastian_habilitationthesis.pdf. Used with permission.
UNDERSTANDING IMBIBITION DATA IN COMPLEX CARBONATE ROCK TYPES
 SCA2014-059 1/6 UNDERSTANDING IMBIBITION DATA IN COMPLEX CARBONATE ROCK TYPES Moustafa Dernaika 1, Zubair Kalam 2, Svein Skjaeveland 3 1 Ingrain Inc.-Abu Dhabi, 2 ADCO, 3 University of Stavanger This paper
SCA2014-059 1/6 UNDERSTANDING IMBIBITION DATA IN COMPLEX CARBONATE ROCK TYPES Moustafa Dernaika 1, Zubair Kalam 2, Svein Skjaeveland 3 1 Ingrain Inc.-Abu Dhabi, 2 ADCO, 3 University of Stavanger This paper
Research Article. Experimental Analysis of Laser Drilling Impacts on Rock Properties
 International Journal of Petroleum & Geoscience Engineering (IJPGE) 1 (2): 106- ISSN 2289-4713 Academic Research Online Publisher Research Article Experimental Analysis of Laser Drilling Impacts on Rock
International Journal of Petroleum & Geoscience Engineering (IJPGE) 1 (2): 106- ISSN 2289-4713 Academic Research Online Publisher Research Article Experimental Analysis of Laser Drilling Impacts on Rock
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks
 Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Characterisation of hydraulic fractures in limestones using X-ray microtomography
 Characterisation of hydraulic fractures in limestones using X-ray microtomography François Renard *,** Dominique Bernard *** Jacques Desrues **** Erwan Plougonven *** Audrey Ougier-Simonin * * LGIT-CNRS-OSUG,
Characterisation of hydraulic fractures in limestones using X-ray microtomography François Renard *,** Dominique Bernard *** Jacques Desrues **** Erwan Plougonven *** Audrey Ougier-Simonin * * LGIT-CNRS-OSUG,
CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS USING RESISTIVITY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 01 SGP-TR-194 CHARACTERIZATION OF FRACTURES IN GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIRS
AS3D goniometer : a powerful tool for cored-based structural analysis. Core CT Scanning: 3D imaging for a deeper formation evaluation.
 AS3D goniometer : a powerful tool for cored-based structural analysis. Core CT Scanning: 3D imaging for a deeper formation evaluation. Presented by: Marco Azevedo & Mathilde Rousselle LPS, New Technology
AS3D goniometer : a powerful tool for cored-based structural analysis. Core CT Scanning: 3D imaging for a deeper formation evaluation. Presented by: Marco Azevedo & Mathilde Rousselle LPS, New Technology
Anisotropic permeabilities evolution of reservoir rocks under pressure:
 Extended reserves Clean refining Fuel-efficient vehicles Diversified fuels Controlled CO 2 Anisotropic permeabilities evolution : New experimental and numerical approaches (1) Dautriat J. 1-2*, Gland N.
Extended reserves Clean refining Fuel-efficient vehicles Diversified fuels Controlled CO 2 Anisotropic permeabilities evolution : New experimental and numerical approaches (1) Dautriat J. 1-2*, Gland N.
MAPPING FRACTURE APERTURES USING MICRO COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 MAPPING FRACTURE APERTURES USING MICRO COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Z. Karpyn, A. Alajmi, C. Parada, A. S. Grader, P.M. Halleck, and O. Karacan. The Pennsylvania State University ABSTRACT Multi-phase flow in fractures
MAPPING FRACTURE APERTURES USING MICRO COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Z. Karpyn, A. Alajmi, C. Parada, A. S. Grader, P.M. Halleck, and O. Karacan. The Pennsylvania State University ABSTRACT Multi-phase flow in fractures
Rock visualization using micro-ct scanner and X-ray transparent triaxial apparatus
 SCA2017-073 1/9 Rock visualization using micro-ct scanner and X-ray transparent triaxial apparatus M. Soldal 1, H. D. Wilkinson 1, I. Viken 1 and G. Sauvin 1. The Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
SCA2017-073 1/9 Rock visualization using micro-ct scanner and X-ray transparent triaxial apparatus M. Soldal 1, H. D. Wilkinson 1, I. Viken 1 and G. Sauvin 1. The Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
THE IMPACT OF HETEROGENEITY AND MULTI-SCALE MEASUREMENTS ON RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND STOOIP ESTIMATIONS
 SCA2011-49 1/6 THE IMPACT OF HETEROGENEITY AND MULTI-SCALE MEASUREMENTS ON RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND STOOIP ESTIMATIONS Moustafa Dernaika 1, Samy Serag 2 and M. Zubair Kalam 2 1 Ingrain Inc., Abu
SCA2011-49 1/6 THE IMPACT OF HETEROGENEITY AND MULTI-SCALE MEASUREMENTS ON RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND STOOIP ESTIMATIONS Moustafa Dernaika 1, Samy Serag 2 and M. Zubair Kalam 2 1 Ingrain Inc., Abu
Exercise solutions: concepts from chapter 6
 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area approaches a definite value at every point. Use the
1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area approaches a definite value at every point. Use the
COMPLEMENTARY METHODS FOR CHARACTERISING SLICK ROCK AEOLIAN SANDSTONE
 COMPLEMENTARY METHODS FOR CHARACTERISING SLICK ROCK AEOLIAN SANDSTONE S. Baraka-Lokmane, I. Main, S. Elphick, B. Ngwenya Department of Geology & Geophysics, University of Edinburgh, UK INTRODUCTION The
COMPLEMENTARY METHODS FOR CHARACTERISING SLICK ROCK AEOLIAN SANDSTONE S. Baraka-Lokmane, I. Main, S. Elphick, B. Ngwenya Department of Geology & Geophysics, University of Edinburgh, UK INTRODUCTION The
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks
 Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Numerical and Laboratory Study of Gas Flow through Unconventional Reservoir Rocks RPSEA Piceance Basin Tight Gas Research Review Xiaolong Yin, Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering, Colorado School
Stochastic geometry and porous media
 Stochastic geometry and transport in porous media Hans R. Künsch Seminar für Statistik, ETH Zürich February 15, 2007, Reisensburg Coauthors Thanks to the coauthors of this paper: P. Lehmann, A. Kaestner,
Stochastic geometry and transport in porous media Hans R. Künsch Seminar für Statistik, ETH Zürich February 15, 2007, Reisensburg Coauthors Thanks to the coauthors of this paper: P. Lehmann, A. Kaestner,
Search and Discovery Article # (2015) Posted April 20, 2015
 Considering the Vertical Variation in Rock Mechanical Properties of a Lithologic Zone Using Laboratory Derived Data Is it Time for Geomechanical Stratigraphy?* Douglas E. Wyatt 1, Jesse Hampton 1, Dandan
Considering the Vertical Variation in Rock Mechanical Properties of a Lithologic Zone Using Laboratory Derived Data Is it Time for Geomechanical Stratigraphy?* Douglas E. Wyatt 1, Jesse Hampton 1, Dandan
Compaction localization in the Earth and the laboratory: state of the research and research directions
 Acta Geotechnica (07) 2:1 15 DOI 10.1007/s114-007-0027-y REVIEW ARTICLE Compaction localization in the Earth and the laboratory: state of the research and research directions David Holcomb Æ John W. Rudnicki
Acta Geotechnica (07) 2:1 15 DOI 10.1007/s114-007-0027-y REVIEW ARTICLE Compaction localization in the Earth and the laboratory: state of the research and research directions David Holcomb Æ John W. Rudnicki
PORE-SCALE PHASE FIELD MODEL OF TWO-PHASE FLOW IN POROUS MEDIUM
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris PORE-SCALE PHASE FIELD MODEL OF TWO-PHASE FLOW IN POROUS MEDIUM Igor Bogdanov 1*, Sylvain Jardel 1, Anis Turki 1, Arjan Kamp 1 1 Open &
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris PORE-SCALE PHASE FIELD MODEL OF TWO-PHASE FLOW IN POROUS MEDIUM Igor Bogdanov 1*, Sylvain Jardel 1, Anis Turki 1, Arjan Kamp 1 1 Open &
MICRO-CT IMAGING AND MICROFLUIDICS FOR UNDERSTANDING FLOW IN COAL SEAM RESERVOIRS
 SCA2015-051 1/6 MICRO-CT IMAGING AND MICROFLUIDICS FOR UNDERSTANDING FLOW IN COAL SEAM RESERVOIRS Peyman Mostaghimi 1, Ryan T. Armstrong 1, Alireza Gerami 1, Majid Ebrahimi Warkaini 2, Hamed Lamei Ramandi
SCA2015-051 1/6 MICRO-CT IMAGING AND MICROFLUIDICS FOR UNDERSTANDING FLOW IN COAL SEAM RESERVOIRS Peyman Mostaghimi 1, Ryan T. Armstrong 1, Alireza Gerami 1, Majid Ebrahimi Warkaini 2, Hamed Lamei Ramandi
Multiscale Seismic Signature of a Small Fault Zone in a Carbonate Reservoir: Relationships Between V P Imaging, Fault Zone Architecture and Cohesion*
 Multiscale Seismic Signature of a Small Fault Zone in a Carbonate Reservoir: Relationships Between V P Imaging, Fault Zone Architecture and Cohesion* Pierre Jeanne 1,2, Yves Guglielmi 2, and Frédéric Cappa
Multiscale Seismic Signature of a Small Fault Zone in a Carbonate Reservoir: Relationships Between V P Imaging, Fault Zone Architecture and Cohesion* Pierre Jeanne 1,2, Yves Guglielmi 2, and Frédéric Cappa
Project Description: MODELING FLOW IN VUGGY MEDIA. Todd Arbogast, Mathematics
 Project Description: MODELING FLOW IN VUGGY MEDIA Todd Arbogast, Mathematics Steve Bryant, Petroleum & Geosystems Engineering Jim Jennings, Bureau of Economic Geology Charlie Kerans, Bureau of Economic
Project Description: MODELING FLOW IN VUGGY MEDIA Todd Arbogast, Mathematics Steve Bryant, Petroleum & Geosystems Engineering Jim Jennings, Bureau of Economic Geology Charlie Kerans, Bureau of Economic
Anisotropy of Shale Properties: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Physics Characterization
 Observation Scale Wavelength 10 0 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 12 10 16 10 18 10 20 Frequency (Hz) Anisotropy of Shale Properties: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Physics Characterization Elastic, Mechanical, Petrophysical
Observation Scale Wavelength 10 0 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 12 10 16 10 18 10 20 Frequency (Hz) Anisotropy of Shale Properties: A Multi-Scale and Multi-Physics Characterization Elastic, Mechanical, Petrophysical
Reservoir Rock Properties COPYRIGHT. Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
Tu P8 08 Modified Anisotropic Walton Model for Consolidated Siliciclastic Rocks: Case Study of Velocity Anisotropy Modelling in a Barents Sea Well
 Tu P8 08 Modified Anisotropic Walton Model for Consolidated Siliciclastic Rocks: Case Study of Velocity Anisotropy Modelling in a Barents Sea Well Y. Zhou (Rock Solid Images), F. Ruiz (Repsol), M. Ellis*
Tu P8 08 Modified Anisotropic Walton Model for Consolidated Siliciclastic Rocks: Case Study of Velocity Anisotropy Modelling in a Barents Sea Well Y. Zhou (Rock Solid Images), F. Ruiz (Repsol), M. Ellis*
A multiscale DEM-LBM analysis on permeability evolutions inside a dilatant shear band
 DOI 10.1007/s11440-013-0210-2 RESEARCH PAPER A multiscale DEM-LBM analysis on permeability evolutions inside a dilatant shear band WaiChing Sun Matthew R. Kuhn John W. Rudnicki Received: 26 October 2012
DOI 10.1007/s11440-013-0210-2 RESEARCH PAPER A multiscale DEM-LBM analysis on permeability evolutions inside a dilatant shear band WaiChing Sun Matthew R. Kuhn John W. Rudnicki Received: 26 October 2012
X-Ray Microtomography and NMR: complimentary tools for evaluation of pore structure within a core
 SCA2014-038 1/6 X-Ray Microtomography and NMR: complimentary tools for evaluation of pore structure within a core Aleksandr Denisenko, Ivan Yakimchuk Schlumberger This paper was prepared for presentation
SCA2014-038 1/6 X-Ray Microtomography and NMR: complimentary tools for evaluation of pore structure within a core Aleksandr Denisenko, Ivan Yakimchuk Schlumberger This paper was prepared for presentation
Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood
 Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood R. Sanaee *, G. F. Oluyemi, M. Hossain, and M. B. Oyeneyin Robert Gordon University *Corresponding
Fracture-Matrix Flow Partitioning and Cross Flow: Numerical Modeling of Laboratory Fractured Core Flood R. Sanaee *, G. F. Oluyemi, M. Hossain, and M. B. Oyeneyin Robert Gordon University *Corresponding
Experiment and Simulation on NMR and Electrical Measurements on Liège Chalk
 The Open-Access Journal for the Basic Principles of Diffusion Theory, Experiment and Application Experiment and Simulation on NMR and Electrical Measurements on Liège Chalk Liangmou Li, Igor Shikhov, Yong
The Open-Access Journal for the Basic Principles of Diffusion Theory, Experiment and Application Experiment and Simulation on NMR and Electrical Measurements on Liège Chalk Liangmou Li, Igor Shikhov, Yong
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES ABSTRACT
 ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
Determination of the Laminar, Structural and Disperse Shale Volumes Using a Joint Inversion of Conventional Logs*
 Determination of the Laminar, Structural and Disperse Shale Volumes Using a Joint Inversion of Conventional Logs* Ambrosio Aquino-López 1, Aleksandr Mousatov 1, Mikhail Markov 1, and Elena Kazatchenko
Determination of the Laminar, Structural and Disperse Shale Volumes Using a Joint Inversion of Conventional Logs* Ambrosio Aquino-López 1, Aleksandr Mousatov 1, Mikhail Markov 1, and Elena Kazatchenko
Producing Oil Sands Thin Sections for Reservoir Characterization
 Producing Oil Sands Thin Sections for Reservoir Characterization Julie D. Bell (1), Giacomo Mele (2), Bruno Di Matteo (2), Fabio Terribile (3) 1) petroregos.inc, Canada 2) National Council of Research,
Producing Oil Sands Thin Sections for Reservoir Characterization Julie D. Bell (1), Giacomo Mele (2), Bruno Di Matteo (2), Fabio Terribile (3) 1) petroregos.inc, Canada 2) National Council of Research,
DIRECT MEASUREMENT OF IN-SITU WATER SATURATION IN THE GEYSERS ROCK
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 27-29, 2003 SGP-TR-173 DIRECT MEASUREMENT OF IN-SITU WATER SATURATION IN THE GEYSERS
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 27-29, 2003 SGP-TR-173 DIRECT MEASUREMENT OF IN-SITU WATER SATURATION IN THE GEYSERS
IMPACT OF DEFORMATION BANDS ON FLUID FLOW AND OIL RECOVERY
 SCA010-1/6 IMPACT OF DEFORMATION BANDS ON FLUID FLOW AND OIL RECOVERY Ersland, G., Graue, A., Moe, R.W. Θ, Aspenes E., Skar, T., Berg, S. University of Bergen, Norway Θ Currently at ConocoPhillips, Norway
SCA010-1/6 IMPACT OF DEFORMATION BANDS ON FLUID FLOW AND OIL RECOVERY Ersland, G., Graue, A., Moe, R.W. Θ, Aspenes E., Skar, T., Berg, S. University of Bergen, Norway Θ Currently at ConocoPhillips, Norway
On the origin of Darcy s law 1
 Chapter 1 On the origin of Darcy s law 1 Cyprien Soulaine csoulain@stanford.edu When one thinks about porous media, the immediate concepts that come to mind are porosity, permeability and Darcy s law.
Chapter 1 On the origin of Darcy s law 1 Cyprien Soulaine csoulain@stanford.edu When one thinks about porous media, the immediate concepts that come to mind are porosity, permeability and Darcy s law.
A MICRO-CT STUDY OF CHANGES IN THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF DAQING AND YAN AN OIL SHALES AT HIGH TEMPERATURES
 Oil Shale, 2012, Vol. 29, No. 4, pp. 357 367 ISSN 0208-189X doi: 10.3176/oil.2012.4.06 2012 Estonian Academy Publishers A MICRO-CT STUDY OF CHANGES IN THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF DAQING AND YAN AN OIL SHALES
Oil Shale, 2012, Vol. 29, No. 4, pp. 357 367 ISSN 0208-189X doi: 10.3176/oil.2012.4.06 2012 Estonian Academy Publishers A MICRO-CT STUDY OF CHANGES IN THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF DAQING AND YAN AN OIL SHALES
Time & place: Fridays, 10:30-11:30am Natural Science Bldg 235, 1st meeting Friday Sept 8
 GEOS 692, Transport Processes and Physical Properties of Rocks (1 CR) Time & place: Fridays, 10:30-11:30am Natural Science Bldg 235, 1st meeting Friday Sept 8 Instructor: Hajo Eicken, Geophysical Institute,
GEOS 692, Transport Processes and Physical Properties of Rocks (1 CR) Time & place: Fridays, 10:30-11:30am Natural Science Bldg 235, 1st meeting Friday Sept 8 Instructor: Hajo Eicken, Geophysical Institute,
SCA : A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP
 SCA2003-53: A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
SCA2003-53: A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
MINERAL DISTRIBUTION IN RESERVOIR ROCKS AND ITS IMPACT ON ENHANCED OIL RECOVERY
 SCA2011-57 1/6 MINERAL DISTRIBUTION IN RESERVOIR ROCKS AND ITS IMPACT ON ENHANCED OIL RECOVERY James J. Howard and Gary L. Lovell ConocoPhillips This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
SCA2011-57 1/6 MINERAL DISTRIBUTION IN RESERVOIR ROCKS AND ITS IMPACT ON ENHANCED OIL RECOVERY James J. Howard and Gary L. Lovell ConocoPhillips This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
Ability of Darcy s Law for Extension in Two- Phase Flow for Sedimentary Medium in Capillary Non-equilibrium Situations
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Resources, Recycling and Waste Management Ability of Darcy s Law for Extension in Two- Phase Flow for Sedimentary Medium in Capillary Non-equilibrium
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Resources, Recycling and Waste Management Ability of Darcy s Law for Extension in Two- Phase Flow for Sedimentary Medium in Capillary Non-equilibrium
Characterization of Pore Structure Based on Nondestructive Testing Technology
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 05, Issue 10 (October. 2015), V2 PP 20-24 www.iosrjen.org Characterization of Pore Structure Based on Nondestructive
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 05, Issue 10 (October. 2015), V2 PP 20-24 www.iosrjen.org Characterization of Pore Structure Based on Nondestructive
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales
 P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
Permeability of Dual-Structured Porous Media
 56 The Open Transport Phenomena Journal, 2011, 3, 56-61 Permeability of Dual-Structured Porous Media Open Access Ehsan Khajeh * and Daan M. Maijer Department of Materials Engineering, The University of
56 The Open Transport Phenomena Journal, 2011, 3, 56-61 Permeability of Dual-Structured Porous Media Open Access Ehsan Khajeh * and Daan M. Maijer Department of Materials Engineering, The University of
Poromechanics Investigation at Pore-scale Using Digital Rock Physics Laboratory
 Poromechanics Investigation at Pore-scale Using Digital Rock Physics Laboratory Session: Multiphysics October 3, 2 Shawn Zhang,*, Nishank Saxena 2, Patrick arthelemy, Mike Marsh, Gary Mavko 2, Tapan Mukerji
Poromechanics Investigation at Pore-scale Using Digital Rock Physics Laboratory Session: Multiphysics October 3, 2 Shawn Zhang,*, Nishank Saxena 2, Patrick arthelemy, Mike Marsh, Gary Mavko 2, Tapan Mukerji
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6025/88/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Microtomography of Partially Molten Rocks: Three-Dimensional Melt Distribution in Mantle Peridotite Wenlu Zhu, * Glenn
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6025/88/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Microtomography of Partially Molten Rocks: Three-Dimensional Melt Distribution in Mantle Peridotite Wenlu Zhu, * Glenn
Introduction to Formation Evaluation Abiodun Matthew Amao
 Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
Hydraulic fracturing in unconventional shale gas reservoirs. Dr.-Ing. Johannes Will, Dynardo GmbH, Weimar, Germany
 Hydraulic fracturing in unconventional shale gas reservoirs Dr.-Ing. Johannes Will, Dynardo GmbH, Weimar, Germany Founded: 2001 (Will, Bucher, CADFEM International) More than 35 employees, offices at Weimar
Hydraulic fracturing in unconventional shale gas reservoirs Dr.-Ing. Johannes Will, Dynardo GmbH, Weimar, Germany Founded: 2001 (Will, Bucher, CADFEM International) More than 35 employees, offices at Weimar
Application of the TRT LB model to simulate pesticide transport in cultivated soils
 Application of the TRT LB model to simulate pesticide transport in cultivated soils V. POT, N. ELYEZNASNI EGC INRA AgroParisTech,Thiverval-Grignon, France I. GINZBURG HBAN Cemagref, Antony, France H. HAMMOU
Application of the TRT LB model to simulate pesticide transport in cultivated soils V. POT, N. ELYEZNASNI EGC INRA AgroParisTech,Thiverval-Grignon, France I. GINZBURG HBAN Cemagref, Antony, France H. HAMMOU
PORE CHARACTERISATION, RELATING MINI- PERMEABILITY AND CT-SCAN POROSITY OF CARBONATE CORES
 SCA5-72 /7 PORE CHARACTERISATION, RELATING MINI- PERMEABILITY AND CT-SCAN POROSITY OF CARBONATE CORES M.T. Tweheyo, A.S. Lackner 2, G.K. Andersen 2, J.K. Ringen 3 and O. Torsaeter 2 Stavanger University,
SCA5-72 /7 PORE CHARACTERISATION, RELATING MINI- PERMEABILITY AND CT-SCAN POROSITY OF CARBONATE CORES M.T. Tweheyo, A.S. Lackner 2, G.K. Andersen 2, J.K. Ringen 3 and O. Torsaeter 2 Stavanger University,
The Hangingstone steam-assisted gravity drainage
 SPECIAL Heavy SECTION: oil H e a v y o i l Elastic property changes in a bitumen reservoir during steam injection AYATO KATO, University of Houston, USA SHIGENOBU ONOZUKA, JOGMEC, Chiba, Japan TORU NAKAYAMA,
SPECIAL Heavy SECTION: oil H e a v y o i l Elastic property changes in a bitumen reservoir during steam injection AYATO KATO, University of Houston, USA SHIGENOBU ONOZUKA, JOGMEC, Chiba, Japan TORU NAKAYAMA,
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Petrophysical Rock Typing: Enhanced Permeability Prediction and Reservoir Descriptions*
 Petrophysical Rock Typing: Enhanced Permeability Prediction and Reservoir Descriptions* Wanida Sritongthae 1 Search and Discovery Article #51265 (2016)** Posted June 20, 2016 *Adapted from oral presentation
Petrophysical Rock Typing: Enhanced Permeability Prediction and Reservoir Descriptions* Wanida Sritongthae 1 Search and Discovery Article #51265 (2016)** Posted June 20, 2016 *Adapted from oral presentation
Downloaded 02/05/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Relationship among porosity, permeability, electrical and elastic properties Zair Hossain Alan J Cohen RSI, 2600 South Gessner Road, Houston, TX 77063, USA Summary Electrical resisivity is usually easier
Relationship among porosity, permeability, electrical and elastic properties Zair Hossain Alan J Cohen RSI, 2600 South Gessner Road, Houston, TX 77063, USA Summary Electrical resisivity is usually easier
Using maximal inscribed spheres for image-based compaction forecasting
 ARMA 16-47 Using maximal inscribed spheres for image-based compaction forecasting Louis, L., and Boitnott, G. New England Research, White River Junction, Vermont, USA Bhattad, P., and Knackstedt, M. FEI,
ARMA 16-47 Using maximal inscribed spheres for image-based compaction forecasting Louis, L., and Boitnott, G. New England Research, White River Junction, Vermont, USA Bhattad, P., and Knackstedt, M. FEI,
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
 CONSTITUTIVE MODELS AND CHALK Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION Computing power has advanced significantly in the years since soil mechanics and rock mechanics first became mature fields. Probably the single most
CONSTITUTIVE MODELS AND CHALK Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION Computing power has advanced significantly in the years since soil mechanics and rock mechanics first became mature fields. Probably the single most
Analysis of Micro-fractures in Coal for Coal Bed Methane Exploitation in Jharia Coal Field
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 904-909 Analysis of Micro-fractures in Coal for Coal Bed Methane Exploitation in Jharia Coal Field Dipak Mandal, D.C. Tewari
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 904-909 Analysis of Micro-fractures in Coal for Coal Bed Methane Exploitation in Jharia Coal Field Dipak Mandal, D.C. Tewari
Sub-Micron Digital Image Analysis (BIBSEM-DIA), Pore Geometries, and Electrical Resistivity in Carbonate Rocks*
 Sub-Micron Digital Image Analysis (BIBSEM-DIA), Pore Geometries, and Electrical Resistivity in Carbonate Rocks* Jan H. Norbisrath 1, Ben Laurich 2, Janos Urai 2, Guillaume Desbois 2, Gregor P. Eberli 1,
Sub-Micron Digital Image Analysis (BIBSEM-DIA), Pore Geometries, and Electrical Resistivity in Carbonate Rocks* Jan H. Norbisrath 1, Ben Laurich 2, Janos Urai 2, Guillaume Desbois 2, Gregor P. Eberli 1,
Computing permeability of fault zones in eolian sandstone from outcrop measurements
 Computing permeability of fault zones in eolian sandstone from outcrop measurements Hervé Jourde, Eric A. Flodin, Atilla Aydin, Louis J. Durlofsky, and Xian-Huan Wen ABSTRACT The large-scale equivalent
Computing permeability of fault zones in eolian sandstone from outcrop measurements Hervé Jourde, Eric A. Flodin, Atilla Aydin, Louis J. Durlofsky, and Xian-Huan Wen ABSTRACT The large-scale equivalent
Assessing the Effect of Realistic Reservoir Features on the Performance of Sedimentary Geothermal Systems
 GRC Transactions, Vol. 39, 205 Assessing the Effect of Realistic Reservoir Features on the Performance of Sedimentary Geothermal Systems Luis E. Zerpa, JaeKyoung Cho, and Chad Augustine 2 Colorado School
GRC Transactions, Vol. 39, 205 Assessing the Effect of Realistic Reservoir Features on the Performance of Sedimentary Geothermal Systems Luis E. Zerpa, JaeKyoung Cho, and Chad Augustine 2 Colorado School
Rock Physics Laboratory at the PIRC (rooms 1-121, B-185)
 Rock Physics Laboratory at the PIRC (rooms 1-121, B-185) Description: The Rock Physics Lab at The PIRC examines the properties of rocks throughout experimental, imagining and numerical techniques. It focuses
Rock Physics Laboratory at the PIRC (rooms 1-121, B-185) Description: The Rock Physics Lab at The PIRC examines the properties of rocks throughout experimental, imagining and numerical techniques. It focuses
Effect of CO 2 phase states and flow rate on salt precipitation in shale caprocks a microfluidic study
 Supporting Information Effect of CO 2 phase states and flow rate on salt precipitation in shale caprocks a microfluidic study Mohammad Nooraiepour a, *, Hossein Fazeli a, Rohaldin Miri a, Helge Hellevang
Supporting Information Effect of CO 2 phase states and flow rate on salt precipitation in shale caprocks a microfluidic study Mohammad Nooraiepour a, *, Hossein Fazeli a, Rohaldin Miri a, Helge Hellevang
Microscopic and X-ray fluorescence researches on sandstone from Shahejie Formation, China
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 04 (April. 2016), V2 PP 27-32 www.iosrjen.org Microscopic and X-ray fluorescence researches on sandstone from
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 04 (April. 2016), V2 PP 27-32 www.iosrjen.org Microscopic and X-ray fluorescence researches on sandstone from
EVALUATION OF CRITICAL FRACTURE SKIN POROSITY FOR CONTAMINANT MIGRATION IN FRACTURED FORMATIONS
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
Ingrain Laboratories INTEGRATED ROCK ANALYSIS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY
 Ingrain Laboratories INTEGRATED ROCK ANALYSIS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY 3 INGRAIN We Help Identify and Develop the Most Productive Reservoir by Characterizing Rocks at Pore Level and Upscaling to the
Ingrain Laboratories INTEGRATED ROCK ANALYSIS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY 3 INGRAIN We Help Identify and Develop the Most Productive Reservoir by Characterizing Rocks at Pore Level and Upscaling to the
RESEARCH PROPOSAL. Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q. Yi Shen
 RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
Simulating Fluid-Fluid Interfacial Area
 Simulating Fluid-Fluid Interfacial Area revealed by a pore-network model V. Joekar-Niasar S. M. Hassanizadeh Utrecht University, The Netherlands July 22, 2009 Outline 1 What s a Porous medium 2 Intro to
Simulating Fluid-Fluid Interfacial Area revealed by a pore-network model V. Joekar-Niasar S. M. Hassanizadeh Utrecht University, The Netherlands July 22, 2009 Outline 1 What s a Porous medium 2 Intro to
MULTISCALE MODELING OF GAS TRANSPORT AND STORAGE IN SHALE RESOURCES
 MULTISCALE MODELING OF GAS TRANSPORT AND STORAGE IN SHALE RESOURCES Ali Takbiri-Borujeni 12/02/2014 WHAT TO EXPECT An introduction to gas transport modeling techniques and their complexities at different
MULTISCALE MODELING OF GAS TRANSPORT AND STORAGE IN SHALE RESOURCES Ali Takbiri-Borujeni 12/02/2014 WHAT TO EXPECT An introduction to gas transport modeling techniques and their complexities at different
Geologic and Reservoir Characterization and Modeling
 Geologic and Reservoir Characterization and Modeling Scott M. Frailey and James Damico Illinois State Geological Survey Midwest Geologic Sequestration Science Conference November 8 th, 2011 Acknowledgements
Geologic and Reservoir Characterization and Modeling Scott M. Frailey and James Damico Illinois State Geological Survey Midwest Geologic Sequestration Science Conference November 8 th, 2011 Acknowledgements
Simulation of Soot Filtration on the Nano-, Micro- and Meso-scale
 Simulation of Soot Filtration on the Nano-, Micro- and Meso-scale L. Cheng 1, S. Rief 1, A. Wiegmann 1, J. Adler 2, L. Mammitzsch 2 and U. Petasch 2 1 Fraunhofer-Institut Techno- und Wirtschaftsmathematik,
Simulation of Soot Filtration on the Nano-, Micro- and Meso-scale L. Cheng 1, S. Rief 1, A. Wiegmann 1, J. Adler 2, L. Mammitzsch 2 and U. Petasch 2 1 Fraunhofer-Institut Techno- und Wirtschaftsmathematik,
Petroleum Geomechanics for Shale Gas
 Petroleum Geomechanics for Shale Gas Prof. Lyesse LALOUI Chair Professor «Gaz Naturel» Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL Acknowledgement: V. Favero, A. Ferrari, L. Chao Unconventional Gas
Petroleum Geomechanics for Shale Gas Prof. Lyesse LALOUI Chair Professor «Gaz Naturel» Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL Acknowledgement: V. Favero, A. Ferrari, L. Chao Unconventional Gas
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Statement of the Problem Engineering properties of geomaterials are very important for civil engineers because almost everything we build - tunnels, bridges, dams and others
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Statement of the Problem Engineering properties of geomaterials are very important for civil engineers because almost everything we build - tunnels, bridges, dams and others
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES
 MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AFOSR WORKSHOP ON PARTICULATE MECHANICS JANUARY 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AFOSR WORKSHOP ON PARTICULATE MECHANICS JANUARY 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON
Advances in the Investigation on Behavior of Carbonate Reservoir Rocks
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov. Dec. 2017), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Advances in the Investigation on
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 5, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov. Dec. 2017), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Advances in the Investigation on
Permeability Variations During Crack Damage Evolution in Rocks
 Permeability Variations During Crack Damage Evolution in Rocks Philip Meredith Mineral, Ice & Rock Physics Laboratory Department of Earth Sciences University College London Euroconference, Erice, September
Permeability Variations During Crack Damage Evolution in Rocks Philip Meredith Mineral, Ice & Rock Physics Laboratory Department of Earth Sciences University College London Euroconference, Erice, September
Constraining Uncertainty in Static Reservoir Modeling: A Case Study from Namorado Field, Brazil*
 Constraining Uncertainty in Static Reservoir Modeling: A Case Study from Namorado Field, Brazil* Juliana F. Bueno 1, Rodrigo D. Drummond 1, Alexandre C. Vidal 1, Emilson P. Leite 1, and Sérgio S. Sancevero
Constraining Uncertainty in Static Reservoir Modeling: A Case Study from Namorado Field, Brazil* Juliana F. Bueno 1, Rodrigo D. Drummond 1, Alexandre C. Vidal 1, Emilson P. Leite 1, and Sérgio S. Sancevero
Microscale Modeling of Carbonate Precipitation. ERC Team Members CBBG Faculty Narayanan Neithalath, ASU Edward Kavazanjian ASU
 Microscale Modeling of Carbonate Precipitation ERC Team Members CBBG Faculty Narayanan Neithalath, ASU Edward Kavazanjian ASU Graduate Students Pu Yang Other Research Staff Nasser Hamdan Project Goals
Microscale Modeling of Carbonate Precipitation ERC Team Members CBBG Faculty Narayanan Neithalath, ASU Edward Kavazanjian ASU Graduate Students Pu Yang Other Research Staff Nasser Hamdan Project Goals
The effect of CO 2 -fluid-rock interactions on the porosity and permeability of calcite-bearing sandstone
 The effect of CO 2 -fluid-rock interactions on the porosity and permeability of calcite-bearing sandstone Benoit Lamy-Chappuis, Bruce Yardley, Carlos Grattoni School of Earth and Environment, University
The effect of CO 2 -fluid-rock interactions on the porosity and permeability of calcite-bearing sandstone Benoit Lamy-Chappuis, Bruce Yardley, Carlos Grattoni School of Earth and Environment, University
Geometry modeling of open-cell foams for efficient fluid flow and heat transfer computations using modified Kelvin cells
 E. Werzner, M.A.A. Mendes, J. Storm, M. Laurinat, S. Ray, D. Trimis Chair of Gas and Heat Technology Institute of Thermal Engineering Gustav-Zeuner-Str. 7 09596 Freiberg Germany Geometry modeling of open-cell
E. Werzner, M.A.A. Mendes, J. Storm, M. Laurinat, S. Ray, D. Trimis Chair of Gas and Heat Technology Institute of Thermal Engineering Gustav-Zeuner-Str. 7 09596 Freiberg Germany Geometry modeling of open-cell
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
D.R. Rector, M.L. Stewart and A.P. Poloski Pacific Northwest National Laboratory P.O. Box 999, Richland, WA
 Modeling of Sediment Bed Behavior for Critical Velocity in Horizontal Piping 9263 D.R. Rector, M.L. Stewart and A.P. Poloski Pacific Northwest National Laboratory P.O. Box 999, Richland, WA ABSTRACT A
Modeling of Sediment Bed Behavior for Critical Velocity in Horizontal Piping 9263 D.R. Rector, M.L. Stewart and A.P. Poloski Pacific Northwest National Laboratory P.O. Box 999, Richland, WA ABSTRACT A
3D IMAGING AND FLOW CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PORE SPACE OF CARBONATE CORE SAMPLES
 SCA2006-23 1/13 3D IMAGING AND FLOW CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PORE SPACE OF CARBONATE CORE SAMPLES Mark Knackstedt 1,2, Christoph Arns 1, Abid Ghous 1,2, Arthur Sakellariou 1, Tim Senden 1, Adrian Sheppard
SCA2006-23 1/13 3D IMAGING AND FLOW CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PORE SPACE OF CARBONATE CORE SAMPLES Mark Knackstedt 1,2, Christoph Arns 1, Abid Ghous 1,2, Arthur Sakellariou 1, Tim Senden 1, Adrian Sheppard
Comparison of the Effects of k-ϵ, k-ω, and Zero Equation Models on Characterization of Turbulent Permeability of Porous Media
 Comparison of the Effects of k-ϵ, k-ω, and Zero Equation Models on Characterization of Turbulent Permeability of Porous Media Charlie Matsubara *, Tim Kuo, Helen Wu PIM Consulting, No. 16, Gonyequ 1 st
Comparison of the Effects of k-ϵ, k-ω, and Zero Equation Models on Characterization of Turbulent Permeability of Porous Media Charlie Matsubara *, Tim Kuo, Helen Wu PIM Consulting, No. 16, Gonyequ 1 st
