2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 1
|
|
|
- Lauren Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 1 Rayleigh Scatter Lidar Observations of the Midlatitude Mesosphere's Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings Leda Sox 1, Vincent B. Wickwar 1, Chad Fish 2, Joshua P. Herron 2 1 Center for Atmospheric and Space Sciences, USU; 2 Space Dynamics Laboratory, USU Abstract-The original Rayleigh-scatter lidar that operated at the Atmospheric Lidar Observatory (ALO; 41.7 N, W) in the Center for Atmospheric and Space Sciences (CASS) on the campus of Utah State University (USU) collected a very dense set of temperature data for 11 years, from 1993 through The temperatures derived from these data extended over the mesosphere, from 45 to 90 km. This work will focus on the extensive Rayleigh lidar observations made during the seven major SSW events that occurred between 1993 and In order to determine the characteristics of the midlatitude mesospheric temperatures during SSWs, comparisons were made between the temperature profile on an individual night during a SSW event and the climatological (11-year average) temperature profile for that night. An overall disturbance pattern was observed in the mesospheric temperatures during these SSWs. It included coolings (sometimes very significant) in the upper mesosphere and warmings in the lower mesosphere. I. INTRODUCTION Sudden Stratospheric Warmings (SSWs) are major disturbances in the polar region of the winter hemisphere that cause major changes in stratospheric temperature and circulation. SSWs are characterized by a temperature increase of tens of degrees Kelvin, averaged over N or S latitude, and a weakening of the polar vortex that persists for the order of a week at the 10 hpa level (roughly 32 km) [Labitzke and Naujokat, 2000]. The polar vortices are cyclones centered on both of the Earth s poles that are present from the upper troposphere to the upper stratosphere. Strong eastward zonal winds define the polar vortices in the winter. Increased planetary wave (PW) activity in the winter hemisphere leads to increased PW breaking in the polar stratosphere and the deposition of the PW s westward momentum in the polar vortex. This weakens the polar vortex, and in the case of major SSWs, can reverse the zonal wind direction to westward. The reversal of the stratospheric jet allows more eastward propagating gravity waves (GWs) to travel up into the mesosphere where, in normal winter conditions, westward propagating GWs dominate [Liu and Roble, 2002]. The atypical wintertime GW filtering and the resulting dominating westward GWs induce an equatorward circulation in the mesosphere, similar to what it is in summer, which leads to the cooling of the upper mesosphere. While these mesospheric coolings have been observed in the polar regions for several decades [Labitzke, 1972], they have only recently been observed at midlatitudes [Yuan et al., 2012]. II. MAJOR SSWs FROM The types of SSW events described in Labitzke and Naujokat [2000] make up one of the most widely accepted SSW classification systems. This system defines four different types of SSWs as follows: Major. These events involve a stratospheric temperature increase averaged over the latitudes 60 and poleward at 10 hpa. They also must include a complete reversal of the zonal-mean zonal winds from eastward to westward at 60 at 10 hpa. This creates a complete change in the circulation, or a breakdown, of the polar vortex. Minor. These events are the same as major SSWs save for the zonal wind field reversal.
2 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 2 They often have smaller stratospheric temperature increases than major SSWs. Final. These warmings mark the transition from winter to summer stratospheric circulation in that in the summer, the stratospheric polar vortex switches from an eastward direction to a westward direction. These warmings can either include or not include the zonal wind reversal, however if they do, they are almost immediately followed by the usual seasonal transition from eastward to westward zonal winds. Canadian. These geographically localized events take place when the Aleutian anticyclone (rotates clockwise), which is located in the Northern Pacific, intensifies and moves poleward. These involve warmings over the Canadian Arctic Pole and sometimes, briefly, zonal wind reversals, but never a full breakdown of the polar vortex. In this initial study of the mesosphere s response to SSWs above Logan, UT, we will focus on periods when there were major SSW events during the ALO Rayleigh- Scatter Lidar s (RSL s) original operational Table 1. List of major SSWs and RSL data from SSW Event Peak Date Nights of RSL Data Jan-Feb Feb Dec Jan Dec Feb-Mar Mar Mar-Apr Mar Jan-Mar Feb Feb-Mar Feb Jan-Feb Jan run, from For the duration of this paper, the term sudden stratospheric warming will refer to the major events during this period. Table 1 gives a summary of the seven major SSW event periods that were captured by the RSL. The major SSW events were defined using the NASA s Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA) database s zonal mean temperatures averaged over N and the 60 N zonal-mean zonal winds, both at 10 hpa [NASA MERRA]. Examples of the MERRA zonal temperatures and winds can be seen in Figure 1 for the January-February 2003 SSW. The vertical blue lines denote the peak date of the January 2003 major warming. Figure 1. NASA MERRA temperature (top) and zonal wind (bottom) data for the winter. The vertical blue lines mark the onset of wind reversal, also known as the peak date, of the Jan 2003 major SSW [NASA MERRA]. III. ALO RSL CONFIGURATION The original Rayleigh-scatter lidar system lidar that ran at the midlatitude site (41.7 N, W), on the campus of Utah State University from was comprised of a Nd:YAG laser operating at 30 Hz and either 18 or 24 W at a wavelength of 532 nm. The receiving telescope had a diameter of 44 cm and thus a receiving aperture of 0.15 m 2. Overall the system had a Power-Aperture Product (PAP) of 2.7 Wm 2 or 3.6 Wm 2, depending on which laser was being used. The RSL measured relative densities that were then reduced using the Chanin- Hauchecorne method [Hauchecorne and Chanin, 1980], which uses hydrostatic equilibrium and the ideal gas law to give absolute temperatures. The initial temperature values for the downward integration came from the CSU climatology [She et al., 2000].
3 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 3 (a) (b) Figure 2. Winter (a) and summer (b) temperature climatologies from the 11-year ALO Rayleigh Lidar dataset The composite year temperature climatology was created by averaging over a window 31 nights wide and 11 years deep, centered on each night. [Herron, 2007]. IV. ALO RSL SSW OBSERVATIONS During a SSW event, the polar stratosphere switches from typical winter conditions to summer conditions for the order of a week. At approximately the same time, we will show that the midlatitude mesosphere undergoes a similar season-like transformation. The winter (January-March) and summer (June-August) ALO climatologies are seen in Figures 2a and 2b, respectively. In Figure 3 (a-g), the ALO RSL temperatures for each of the seven SSW event periods are shown with red vertical lines denoting the peak of the SSW event. For most of these event periods, the RSL temperatures have a range closer to the temperature range characteristic of the climatological summer (~ K) rather than that of the climatological winter (~ K). In fact, of all the SSW event temperatures, the temperature minimum is approximately 134 K, which is over 30 K cooler than the climatological temperature minimum of 165 K. The RSL temperatures during the SSW periods show the coldest temperatures between km and the warmest temperatures from km, which is similar to the summer climatological values. The coldest temperatures in the upper mesosphere occur before, during, and/or after the peak date of the SSW, depending on the particular event, in these time series plots. To gain a better understanding of the time evolution of the mesospheric coolings at mid-latitudes, temperature difference plots were created and can be seen in Figure 4 (a-g). The temperature differences were calculated by subtracting the climatological night s temperatures from the night-time average s. This way, coolings are represented by negative temperature difference values and warmings are represented by positive values. Temperature difference values of ± 5 K are taken to be the noise level in these plots. Night zero is the peak date of the corresponding SSW event, negative night values are prior to the peak of the event and positive night values are after the peak of the event. In Figure 4, a time evolution rise-and-fall pattern emerges from five of the six plots that includes a cooling, between km that precedes night zero, that then intensifies and moves up (rises) in altitude near night zero and dissipates and lowers (falls) in altitude after night zero. The magnitude of these coolings range from -6 to - 45 K. This puts them on par with the coolings
4 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 4 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Figure 3. ALO Rayleigh-scatter lidar mesospheric temperatures for the seven major stratospheric warming event periods from that are seen in the polar mesosphere and makes them much stronger than what was predicted for the midlatitude mesosphere [Liu and Roble, 2002]. Additionally, two of the seven events in Figure 4 show warmings below approximately 70 km of K magnitude. Again, these are much stronger than what has been predicted for the midlatitude mesosphere. V. CONCLUSIONS In this study, we have shown that the mesospheric coolings in the upper mesosphere, associated with sudden stratospheric warmings, extend down to midlatitudes for almost every major SSW event between 1993 and These coolings were shown to have significant magnitudes of up to -45 K, which is much higher than what had been predicted at midlatitudes. Mesospheric warmings of significant magnitude were also
5 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 5 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Figure 4. ALO Rayleigh-scatter lidar mesospheric temperature differences for the seven major stratospheric warming event periods from Temperature differences were calculated by subtracting the temperatures from the corresponding day of the year of the climatology from the all-night averaged temperatures for a given night in an SSW event period. observed in the lower mesosphere, at this midlatitude site, though less frequently than the coolings at higher altitudes. Finally, a riseand-fall pattern in the time evolution of the upper mesospheric coolings was illustrated using the differences between the climatological temperatures and the night-time averaged temperatures. VI. FUTURE WORK To further this work, additional event periods, which correspond to the other types of SSWs (minor, final) can be examined. Additionally, future zonal wind and temperature measurements from the nearby meteor wind radar, Dynasonde and ALO Na lidar and the SABER instrument aboard the TIMED satellite can be combined with the temperatures from the soon-to-be-completed
6 2014 Utah NASA Space Grant Consortium Symposium 6 Rayleigh-Mie-Raman Scatter (RMR) lidar at ALO, to provide a more comprehensive description of the midlatitude mesosphere during sudden stratospheric warmings. The new, large aperture RMR lidar, that is currently being built at the ALO in place of the original Rayleigh-scatter lidar, will provide a much more complete picture of the latitudinal extent of sudden stratospheric warmings and their associated mesospheric coolings and lower thermospheric warmings. With an altitudinal observing range of km, the new RMR lidar will capture temperatures from the midlatitude stratosphere, mesosphere and lower thermosphere. Thusly, with temperature measurements from the RMR lidar, this work can be extended to both the stratosphere and lower thermosphere in order to compare observations with the temperature anomalies that have already been predicted for these regions at midlatitudes. Labitzke, K., and B. Naujokat (2000), The lower arctic stratosphere in winter since 1952, SPARC Newsl., 15, Liu, H.-L., and R. G. Roble (2002), A study of a selfgenerated stratospheric sudden warming and its mesospheric-lower thermospheric impacts using the coupled TIME-GCM/CCM3, J. Geophys. Res., 107 (D23), 4695, doi: /2001jd NASA MERRA Database Website: She, C. Y., S. Chen, Z. Hu, J. Sherman, J. D. Vance, V. Vasoli, M. A. White, J. R. Yu, and D. A. Krueger (2000), Eight-year climatology of nocturnal temperature and sodium density in the mesopause region (80 to 105 km) over Fort Collins, CO (41 N, 105 W), Geophys Res. Lett., 27, Yuan, T., B. Thurairajah, C.-Y. She, A. Chandran, R. L. Collins, and D. A. Krueger (2012), Wind and temperature response of midlatitude mesopause region to the 2009 Sudden Stratospheric Warming, J. Geophys. Res., 117, D09114, doi: /2011jd VII. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Leda Sox would like to acknowledge, above all, financial support from USU and the UNSGC. In addition, she is grateful for support from the USU Physics Department s Blood Scholarship and Gene Adams Scholarship. The data were acquired with support from several grants from the Atmospheric Sciences Division of the National Science Foundation. REFERENCES Hauchecorne, A. and M. L. Chanin (1980), Density and temperature profiles obtained by lidar between 35 and 70 km, Geophys. Res. Lett. 7, Herron, J. P. (2007), Rayleigh-Scatter Lidar Observations at USU s Atmospheric Lidar Observatory (Logan, UT) Temperature Climatology Comparisons with MSIS, and Noctilucent Clouds, PhD Dissertation, Utah State University, Logan, UT, pp156. Labitzke, K. (1972), Temperature changes in the mesosphere and stratosphere connected with circulation changes in winter, J. Atmos. Sci., 29,
The Mid-Latitude Mesosphere s Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings as Determined from Rayleigh Lidar Temperatures
 Utah State University From the SelectedWorks of Leda Sox August 26, 2013 The Mid-Latitude Mesosphere s Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings as Determined from Rayleigh Lidar Temperatures Leda Sox,
Utah State University From the SelectedWorks of Leda Sox August 26, 2013 The Mid-Latitude Mesosphere s Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings as Determined from Rayleigh Lidar Temperatures Leda Sox,
EARLY RAYLEIGH-SCATTER LIDAR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENTS FROM THE LOWER THERMOSPHERE
 EARLY RAYLEIGH-SCATTER LIDAR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENTS FROM THE LOWER THERMOSPHERE Leda Sox and Vincent B. Wickwar Physics Department and Center for Atmospheric and Space Sciences, Utah State University,
EARLY RAYLEIGH-SCATTER LIDAR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENTS FROM THE LOWER THERMOSPHERE Leda Sox and Vincent B. Wickwar Physics Department and Center for Atmospheric and Space Sciences, Utah State University,
Multi-year Observations of Mid-latitude Middle Atmospheric Winds, Waves, and Temperature associated with SSW Events over Northern Utah
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Presentations Green Beam (Rayleigh-Scatter LIDAR) 8-27-2013 Multi-year Observations of Mid-latitude Middle Atmospheric Winds, Waves, and Temperature associated
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Presentations Green Beam (Rayleigh-Scatter LIDAR) 8-27-2013 Multi-year Observations of Mid-latitude Middle Atmospheric Winds, Waves, and Temperature associated
Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric sudden warming
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042351, 2010 Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl042351, 2010 Responses of mesosphere and lower thermosphere temperatures to gravity wave forcing during stratospheric
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM
 Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Elevated stratopause and mesospheric intrusion following a stratospheric sudden warming in WACCM Yvan J. Orsolini 1,V. Limpasuvan 2, J. Richter 3, O. K. Kvissel 4, F. Stordal 4,D. Marsh 3 1 Norwegian Institute
Wind and temperature response of midlatitude mesopause region to the 2009 Sudden Stratospheric Warming
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd017142, 2012 Wind and temperature response of midlatitude mesopause region to the 2009 Sudden Stratospheric Warming Tao Yuan, 1 B. Thurairajah,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd017142, 2012 Wind and temperature response of midlatitude mesopause region to the 2009 Sudden Stratospheric Warming Tao Yuan, 1 B. Thurairajah,
CHAPTER 5. Low latitude temperature change in the stratosphere and mesosphere. relation to Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW)
 CHAPTER 5 Low latitude temperature change in the stratosphere and mesosphere relation to Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) 5.1 Introduction To understand middle atmosphere dynamics, the basic thermal
CHAPTER 5 Low latitude temperature change in the stratosphere and mesosphere relation to Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) 5.1 Introduction To understand middle atmosphere dynamics, the basic thermal
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events
 Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
Modeling the Downward Influence of Stratospheric Final Warming events Lantao Sun Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Walter A. Robinson Division of Atmospheric
Non-vertical propagation of gravity waves generated over the monsoon region and its effect on polar mesospheric clouds
 Non-vertical propagation of gravity waves generated over the monsoon region and its effect on polar mesospheric clouds Brentha Thurairajah 1 David Siskind 2 Scott Bailey 1 Justin Carstens 1 1 Space@VT,
Non-vertical propagation of gravity waves generated over the monsoon region and its effect on polar mesospheric clouds Brentha Thurairajah 1 David Siskind 2 Scott Bailey 1 Justin Carstens 1 1 Space@VT,
Gravity wave variations during the 2009 stratospheric sudden
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.109/010gl045437, 010 Gravity wave variations during the 009 stratospheric sudden warming as revealed by ECMWF T799 and observations Chihoko Yamashita, 1,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.109/010gl045437, 010 Gravity wave variations during the 009 stratospheric sudden warming as revealed by ECMWF T799 and observations Chihoko Yamashita, 1,
Rayleigh-Scatter Lidar Measurements of the Mesosphere and Thermosphere and their Connections to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate Studies 2016 Rayleigh-Scatter Lidar Measurements of the Mesosphere and Thermosphere and their Connections to Sudden
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate Studies 2016 Rayleigh-Scatter Lidar Measurements of the Mesosphere and Thermosphere and their Connections to Sudden
Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere
 Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere N. Harnik, Tel Aviv University J. Perlwitz, CIRES U. Colorado/NOAA ESRL T. A. Shaw, Columbia University, NY, NY, USA The following
Stratospheric planetary wave reflection and its influence on the troposphere N. Harnik, Tel Aviv University J. Perlwitz, CIRES U. Colorado/NOAA ESRL T. A. Shaw, Columbia University, NY, NY, USA The following
Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models
 Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models Alexey Karpechko Finnish Meteorological Institute with contributions from A. Charlton-Perez, N. Tyrrell, M. Balmaseda, F.
Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models Alexey Karpechko Finnish Meteorological Institute with contributions from A. Charlton-Perez, N. Tyrrell, M. Balmaseda, F.
The Arctic polar troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere during IPY
 The Arctic polar troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere during IPY V. Lynn Harvey, R. Collins, D. Atkinson, B. Thurairajah, D. Wheeler km 70 60 stratopause 50 40 30 20 10 tropopause Outline Motivation:
The Arctic polar troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere during IPY V. Lynn Harvey, R. Collins, D. Atkinson, B. Thurairajah, D. Wheeler km 70 60 stratopause 50 40 30 20 10 tropopause Outline Motivation:
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere?
 What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
Vertical and interhemispheric links in the stratosphere-mesosphere as revealed by the day-to-day variability of Aura-MLS temperature data
 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Vertical and interhemispheric links in the stratosphere-mesosphere as revealed by the day-to-day
Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Vertical and interhemispheric links in the stratosphere-mesosphere as revealed by the day-to-day
Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling -
 Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling - Yvan J. Orsolini NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research and Birkeland
Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling - Yvan J. Orsolini NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research and Birkeland
Tidal Coupling in the Earth s Atmosphere. Maura Hagan NCAR High Altitude Observatory
 Tidal Coupling in the Earth s Atmosphere Maura Hagan NCAR High Altitude Observatory OUTLINE Motivation - Observations Tidal Nomenclature/Characteristics/Sources Results from the Global-Scale Wave Model
Tidal Coupling in the Earth s Atmosphere Maura Hagan NCAR High Altitude Observatory OUTLINE Motivation - Observations Tidal Nomenclature/Characteristics/Sources Results from the Global-Scale Wave Model
Structure of Atmosphere. (University of Washington ESS, 2015)
 Structure of Atmosphere (University of Washington ESS, 2015) Motivation and Current State of Knowledge Spatial and temporal variations in ionospheric parameters cannot be explained by solar forcing Solid
Structure of Atmosphere (University of Washington ESS, 2015) Motivation and Current State of Knowledge Spatial and temporal variations in ionospheric parameters cannot be explained by solar forcing Solid
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode
 The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
The stratospheric response to extratropical torques and its relationship with the annular mode Peter Watson 1, Lesley Gray 1,2 1. Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Oxford University 2. National
State of polar boreal winter stratosphere ( ) The middle and upper regions of the atmosphere are now recognized as important and
 CHAPTER 3 State of polar boreal winter stratosphere (1993-2009) 3.1 Introduction The middle and upper regions of the atmosphere are now recognized as important and sensitive indicators of the polar middle
CHAPTER 3 State of polar boreal winter stratosphere (1993-2009) 3.1 Introduction The middle and upper regions of the atmosphere are now recognized as important and sensitive indicators of the polar middle
On atmospheric lidar performance comparison: from power aperture product to power aperture mixing ratio scattering cross-section product
 Journal of Modern Optics Vol. 52, No. 18, 15 December 2005, 2723 2729 On atmospheric lidar performance comparison: from power aperture product to power aperture mixing ratio scattering cross-section product
Journal of Modern Optics Vol. 52, No. 18, 15 December 2005, 2723 2729 On atmospheric lidar performance comparison: from power aperture product to power aperture mixing ratio scattering cross-section product
Polar mesosphere and lower thermosphere dynamics: 2. Response to sudden stratospheric warmings
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd008127, 2007 Polar mesosphere and lower thermosphere dynamics: 2. Response to sudden stratospheric warmings Andrew J. Dowdy, 1 Robert A. Vincent,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd008127, 2007 Polar mesosphere and lower thermosphere dynamics: 2. Response to sudden stratospheric warmings Andrew J. Dowdy, 1 Robert A. Vincent,
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
Lecture #3: Gravity Waves in GCMs. Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005)
 Lecture #3: Gravity Waves in GCMs Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Role of GWs in the middle atmosphere 2. Background theory 3. Resolved GWs in GCMs 4. Parameterized
Lecture #3: Gravity Waves in GCMs Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Role of GWs in the middle atmosphere 2. Background theory 3. Resolved GWs in GCMs 4. Parameterized
A comparison of Rayleigh and sodium lidar temperature climatologies
 Ann. Geophys., 2, 27 3, 27 www.ann-geophys.net/2/27/27/ European Geosciences Union 27 Annales Geophysicae A comparison of Rayleigh and sodium lidar temperature climatologies P. S. Argall and R. J. Sica
Ann. Geophys., 2, 27 3, 27 www.ann-geophys.net/2/27/27/ European Geosciences Union 27 Annales Geophysicae A comparison of Rayleigh and sodium lidar temperature climatologies P. S. Argall and R. J. Sica
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
On the Control of the Residual Circulation and Stratospheric Temperatures in the Arctic by Planetary Wave Coupling
 JANUARY 2014 S H A W A N D P E R L W I T Z 195 On the Control of the Residual Circulation and Stratospheric Temperatures in the Arctic by Planetary Wave Coupling TIFFANY A. SHAW Department of Earth and
JANUARY 2014 S H A W A N D P E R L W I T Z 195 On the Control of the Residual Circulation and Stratospheric Temperatures in the Arctic by Planetary Wave Coupling TIFFANY A. SHAW Department of Earth and
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation
 The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
The Impact of the Extratropical Transition of Typhoon Dale (1996) on the Early 1996-97 Wintertime Stratospheric Circulation Andrea L. Lang 1, Jason M. Cordeira 2, Lance F. Bosart 1 and Daniel Keyser 1
Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere Coupling and Their Potential Use in Seasonal to Decadal Climate Predictions
 US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012273, 2009 On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009 K. Labitzke 1 and M. Kunze 1 Received 17 April 2009; revised 11 June 2009; accepted
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012273, 2009 On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009 K. Labitzke 1 and M. Kunze 1 Received 17 April 2009; revised 11 June 2009; accepted
Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1
 1 1 Gravity Waves and the High-Resolution Modeling (Using ECMWF-T799) Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1 1. NCAR/HAO 2. University of Colorado at Boulder AWMG/WAWG Workshop 2012-02-01 Motivations Gravity
1 1 Gravity Waves and the High-Resolution Modeling (Using ECMWF-T799) Chihoko Yamashita 1,2, Han-Li Liu 1 1. NCAR/HAO 2. University of Colorado at Boulder AWMG/WAWG Workshop 2012-02-01 Motivations Gravity
High-Latitude Short-Period Mesospheric Gravity Wave Dynamics and Winter Climatology
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Physics Student Research Physics Student Research 2013 High-Latitude Short-Period Mesospheric Gravity Wave Dynamics and Winter Climatology Michael Negale Utah State
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Physics Student Research Physics Student Research 2013 High-Latitude Short-Period Mesospheric Gravity Wave Dynamics and Winter Climatology Michael Negale Utah State
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure
 Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Observational responses of stratospheric sudden warming to blocking highs and its feedbacks on the troposphere
 Article SPECIAL ISSUE: Extreme Climate in China April 2013 Vol.58 No.12: 1374 1384 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5505-4 SPECIAL TOPICS: Observational responses of stratospheric sudden warming to blocking highs
Article SPECIAL ISSUE: Extreme Climate in China April 2013 Vol.58 No.12: 1374 1384 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5505-4 SPECIAL TOPICS: Observational responses of stratospheric sudden warming to blocking highs
An Earlier Lidar Observation of a Noctilucent Cloud above Logan, Utah (41.7º N, 111.8º W)
 An Earlier Lidar Observation of a Noctilucent Cloud above Logan, Utah (41.7º N, 111.8º W) Joshua P. Herron 1 and Vincent B. Wickwar 1, Patrick J. Espy 2, and John W. Meriwether 3 1 Center for Atmospheric
An Earlier Lidar Observation of a Noctilucent Cloud above Logan, Utah (41.7º N, 111.8º W) Joshua P. Herron 1 and Vincent B. Wickwar 1, Patrick J. Espy 2, and John W. Meriwether 3 1 Center for Atmospheric
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Mesopause structure from Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Mesosphere, Energetics, and Dynamics (TIMED)/Sounding of the Atmosphere
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007711, 2007 Mesopause structure from Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Mesosphere, Energetics, and Dynamics (TIMED)/Sounding
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007711, 2007 Mesopause structure from Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Mesosphere, Energetics, and Dynamics (TIMED)/Sounding
Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring
 Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring U. Langematz and M. Kunze Abstract Short- and long-term changes in the intensity and persistence of the Arctic and Antarctic stratospheric
Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring U. Langematz and M. Kunze Abstract Short- and long-term changes in the intensity and persistence of the Arctic and Antarctic stratospheric
Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM
 Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Jeff France, Laura Holt, Katelynn Greer Richard Collins Dan Marsh, Doug Kinnison Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Shape and Chemical Diagnostics of the Polar Vortices in WACCM V. Lynn Harvey, Cora Randall, Jeff France, Laura Holt, Katelynn Greer Richard Collins Dan Marsh, Doug Kinnison Laboratory for Atmospheric and
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Ionosphere Variability at Mid Latitudes during Sudden Stratosphere Warmings
 Ionosphere Variability at Mid Latitudes during Sudden Stratosphere Warmings Nick Pedatella 1 and Astrid Maute 2 1 COSMIC Program Office, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research 2 High Altitude
Ionosphere Variability at Mid Latitudes during Sudden Stratosphere Warmings Nick Pedatella 1 and Astrid Maute 2 1 COSMIC Program Office, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research 2 High Altitude
Veretenenko S., Ogurtsov M.
 First VarSITI General Symposium Albena, Bulgaria 6-10 June 2016 Veretenenko S., Ogurtsov M. Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute Saint-Petersburg, Russia Correlation coefficient between globally averaged
First VarSITI General Symposium Albena, Bulgaria 6-10 June 2016 Veretenenko S., Ogurtsov M. Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute Saint-Petersburg, Russia Correlation coefficient between globally averaged
SCIENCE CHINA Technological Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Technological Sciences RESEARCH PAPER May 2012 Vol.55 No.5: 1258 1263 doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-4802-0 Longitudinal distribution of O 2 nightglow brightness observed by TIEMD/SABER satellite
SCIENCE CHINA Technological Sciences RESEARCH PAPER May 2012 Vol.55 No.5: 1258 1263 doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-4802-0 Longitudinal distribution of O 2 nightglow brightness observed by TIEMD/SABER satellite
All Physics Faculty Publications
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Physics Faculty Publications Physics 2-8-2008 Climatology of mesopause region temperature, zonal wind, and meridional wind over Fort Collins,Colorado (41 N,
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Physics Faculty Publications Physics 2-8-2008 Climatology of mesopause region temperature, zonal wind, and meridional wind over Fort Collins,Colorado (41 N,
State of the art in mesosphere science John Meriwether Department of Physics and Astronomy Clemson University
 CEDAR Tutorial #3 Thursday June 28, 2007 State of the art in mesosphere science John Meriwether Department of Physics and Astronomy Clemson University 22+ years of progress since ignorasphere was coined
CEDAR Tutorial #3 Thursday June 28, 2007 State of the art in mesosphere science John Meriwether Department of Physics and Astronomy Clemson University 22+ years of progress since ignorasphere was coined
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
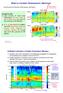 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations. Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland
 EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
The Earth s Atmosphere-II. GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology
 The Earth s Atmosphere-II GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Vertical Structure of Atmosphere Vertical profile of the atmosphere reveals that it can be divided into a series of layers. Each layer
The Earth s Atmosphere-II GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Vertical Structure of Atmosphere Vertical profile of the atmosphere reveals that it can be divided into a series of layers. Each layer
Uncertainties in atmospheric dynamics and infrasound monitoring
 Uncertainties in atmospheric dynamics and infrasound monitoring Elisabeth Blanc1, Alexis Le Pichon11, Doriane Tailpied11 Alain Hauchecorne2, Andrew Charlton Perez3, Pieter Smets4 1- CEA DAM DIF F-91297
Uncertainties in atmospheric dynamics and infrasound monitoring Elisabeth Blanc1, Alexis Le Pichon11, Doriane Tailpied11 Alain Hauchecorne2, Andrew Charlton Perez3, Pieter Smets4 1- CEA DAM DIF F-91297
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
Lunar Tide Effects on the Atmosphere during the 2013 Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) as Simulated by TIME- GCM
 Lunar Tide Effects on the Atmosphere during the 2013 Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) as Simulated by TIME- GCM Jonathan Barta Whitworth University, Spokane, WA Astrid Maute High Al8tude Observatory
Lunar Tide Effects on the Atmosphere during the 2013 Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) as Simulated by TIME- GCM Jonathan Barta Whitworth University, Spokane, WA Astrid Maute High Al8tude Observatory
Dynamical. regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event)
 Dynamical Coupling between high and low latitude regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event) Vinay Kumar 1,S. K. Dhaka 1,R. K. Choudhary 2,Shu-Peng Ho 3,M. Takahashi
Dynamical Coupling between high and low latitude regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event) Vinay Kumar 1,S. K. Dhaka 1,R. K. Choudhary 2,Shu-Peng Ho 3,M. Takahashi
Overview of the Major Northern Hemisphere Stratospheric Sudden Warming: Evolution and Its Association with Surface Weather
 NO.4 LIU Yi and ZHANG Yuli 561 Overview of the Major 2012 2013 Northern Hemisphere Stratospheric Sudden Warming: Evolution and Its Association with Surface Weather LIU Yi 1 ( ) and ZHANG Yuli 1,2 ( ) 1
NO.4 LIU Yi and ZHANG Yuli 561 Overview of the Major 2012 2013 Northern Hemisphere Stratospheric Sudden Warming: Evolution and Its Association with Surface Weather LIU Yi 1 ( ) and ZHANG Yuli 1,2 ( ) 1
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere
 ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ANGWIN Research Activities at Utah State University: Summary and Future Plans
 ANGWIN Research Activities at Utah State University: Summary and Future Plans Mike J. Taylor, P.-D. Pautet, Y. Zhao, M. Negale, V. Chambers, W.R. Pendleton Jr., and ANGWIN Colleagues 4 th International
ANGWIN Research Activities at Utah State University: Summary and Future Plans Mike J. Taylor, P.-D. Pautet, Y. Zhao, M. Negale, V. Chambers, W.R. Pendleton Jr., and ANGWIN Colleagues 4 th International
ATMOSPHERE M E T E O R O LO G Y
 1.05.01 ATMOSPHERE 1. 0 5 M E T E O R O LO G Y INTRODUCTION ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, commonly known as air, that surrounds the planet Earth and is retained
1.05.01 ATMOSPHERE 1. 0 5 M E T E O R O LO G Y INTRODUCTION ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, commonly known as air, that surrounds the planet Earth and is retained
F = ma. ATS 150 Global Climate Change Winds and Weather. Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1. Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook
 Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation
 Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation Peter Hitchcock1, Ted Shepherd2 University of Toronto Now at Cambridge 2Now at Reading 1 Gloria Manney JPL, NMT, Now at NWRA NAM
Stratospheric Predictability and the Arctic Polar-night Jet Oscillation Peter Hitchcock1, Ted Shepherd2 University of Toronto Now at Cambridge 2Now at Reading 1 Gloria Manney JPL, NMT, Now at NWRA NAM
Thermospheric Winds. Astrid Maute. High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA
 Thermospheric Winds Astrid Maute High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Research
Thermospheric Winds Astrid Maute High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR) Boulder CO, USA High Altitude Observatory (HAO) National Center for Atmospheric Research
Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial oscillation
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012542, 2010 Solar cycle signal in a general circulation and chemistry model with internally generated quasi biennial
L. Coy 1, S. D. Eckermann 1, K. W. Hoppel 2, and F. Sassi 1
 Mesospheric Precursors to the Major Stratospheric Sudden Warming of 9: Validation and Dynamical Attribution using a Ground-to-Edge-of-Space Data Assimilation System L. Coy, S. D. Eckermann, K. W. Hoppel,
Mesospheric Precursors to the Major Stratospheric Sudden Warming of 9: Validation and Dynamical Attribution using a Ground-to-Edge-of-Space Data Assimilation System L. Coy, S. D. Eckermann, K. W. Hoppel,
Observed long-term temperature change in a midlatitude mesopause region in response to external perturbations
 Earth Planets Space, 51, 809 814, 1999 Observed long-term temperature change in a midlatitude mesopause region in response to external perturbations David A. Krueger and C. Y. She Physics Department, Colorado
Earth Planets Space, 51, 809 814, 1999 Observed long-term temperature change in a midlatitude mesopause region in response to external perturbations David A. Krueger and C. Y. She Physics Department, Colorado
Lecture #1 Tidal Models. Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005)
 Lecture #1 Tidal Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Introduction 2. Brief description of tides 3. Observations of tides 4. Simulating tides using a general
Lecture #1 Tidal Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Introduction 2. Brief description of tides 3. Observations of tides 4. Simulating tides using a general
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Lecture 17. Temperature Lidar (6) Integration Technique
 Lecture 17. Temperature Lidar (6) Integration Technique Doppler effects in absorption/backscatter coefficient Integration technique for temperature Searchlight integration lidar Rayleigh integration temperature
Lecture 17. Temperature Lidar (6) Integration Technique Doppler effects in absorption/backscatter coefficient Integration technique for temperature Searchlight integration lidar Rayleigh integration temperature
Reversal of Arctic Oscillation pattern and its relation to extreme hot summer in Japan in 2010
 Reversal of Arctic Oscillation pattern and its relation to extreme hot summer in Japan in 2010 Climate and Ecosystems Dynamics Division Department of Environmental Science & Technology Mie University 507322
Reversal of Arctic Oscillation pattern and its relation to extreme hot summer in Japan in 2010 Climate and Ecosystems Dynamics Division Department of Environmental Science & Technology Mie University 507322
Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models. Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005)
 Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Observational motivation 2. Forced planetary waves in the stratosphere 3. Traveling planetary
Lecture #2 Planetary Wave Models Charles McLandress (Banff Summer School 7-13 May 2005) 1 Outline of Lecture 1. Observational motivation 2. Forced planetary waves in the stratosphere 3. Traveling planetary
Overturning instability in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere: analysis of instability conditions in lidar data
 Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University From the SelectedWorks of Alan Z Liu 2009 Overturning instability in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere: analysis of instability conditions in lidar data Lucas Hurd,
Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University From the SelectedWorks of Alan Z Liu 2009 Overturning instability in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere: analysis of instability conditions in lidar data Lucas Hurd,
Observational investigations of gravity wave momentum flux with spectroscopic imaging
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jd004778, 2005 Observational investigations of gravity wave momentum flux with spectroscopic imaging J. Tang, G. R. Swenson, A. Z. Liu, and F.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004jd004778, 2005 Observational investigations of gravity wave momentum flux with spectroscopic imaging J. Tang, G. R. Swenson, A. Z. Liu, and F.
Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere
 Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Nick Pedatella 1,2 1 High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research 2 COSMIC Program Office, University
Influence of Sudden Stratosphere Warmings on the Ionosphere and Thermosphere Nick Pedatella 1,2 1 High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research 2 COSMIC Program Office, University
Sodium fluorescence Doppler lidar to measure atmospheric temperature in the mesopause region
 Article Atmospheric Science February 2011 Vol.56 No.4-5: 417 423 doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4306-x SPECIAL TOPICS: Sodium fluorescence Doppler lidar to measure atmospheric temperature in the mesopause region
Article Atmospheric Science February 2011 Vol.56 No.4-5: 417 423 doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4306-x SPECIAL TOPICS: Sodium fluorescence Doppler lidar to measure atmospheric temperature in the mesopause region
Long-term lidar observations of gravity waves over northern Sweden
 Long-term lidar observations of gravity waves over northern Sweden Master thesis written at the Department of Meteorology, Stockholm University written by Benedikt Ehard, born Mai 5th 1990 in Roth, Germany
Long-term lidar observations of gravity waves over northern Sweden Master thesis written at the Department of Meteorology, Stockholm University written by Benedikt Ehard, born Mai 5th 1990 in Roth, Germany
Atmospheric forcing of the Beaufort Sea ice gyre: Surface-stratosphere coupling
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jc004849, 2009 Atmospheric forcing of the Beaufort Sea ice gyre: Surface-stratosphere coupling J. V. Lukovich, 1
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jc004849, 2009 Atmospheric forcing of the Beaufort Sea ice gyre: Surface-stratosphere coupling J. V. Lukovich, 1
Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
On the Interannual Variability of the Middle Stratosphere during the Northern Winters. By Karin Labitzke
 124 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 60, No. 1 On the Interannual Variability of the Middle Stratosphere during the Northern Winters By Karin Labitzke Institut fur Meteorologie, Freie
124 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 60, No. 1 On the Interannual Variability of the Middle Stratosphere during the Northern Winters By Karin Labitzke Institut fur Meteorologie, Freie
Seasonal variation of nocturnal temperatures between 1 and 105 km altitude at 54 N observed by lidar
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 7465 7482, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Seasonal variation of nocturnal temperatures
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 7465 7482, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Seasonal variation of nocturnal temperatures
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE. V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva
 HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming
 Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming Bryn Ronalds Adv: Elizabeth Barnes CVCWG Meeting: March 2, 27 The story: Midlatitude jets are fundamental to weather and climate It is generally agreed
Seasonality of the Jet Response to Arctic Warming Bryn Ronalds Adv: Elizabeth Barnes CVCWG Meeting: March 2, 27 The story: Midlatitude jets are fundamental to weather and climate It is generally agreed
Predictability of the Stratospheric Polar Vortex Breakdown
 International Symposium on the Whole Atmosphere (ISWA) Session 4: Sudden stratospheric warming and SSW-initiated global coupling 14 September 2016 @ Ito Hall, The University of Tokyo Predictability of
International Symposium on the Whole Atmosphere (ISWA) Session 4: Sudden stratospheric warming and SSW-initiated global coupling 14 September 2016 @ Ito Hall, The University of Tokyo Predictability of
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Statistical characteristics of gravity waves observed by an all-sky imager at Darwin, Australia
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jd004336, 2004 Statistical characteristics of gravity waves observed by an all-sky imager at Darwin, Australia S. Suzuki, K. Shiokawa, Y. Otsuka,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jd004336, 2004 Statistical characteristics of gravity waves observed by an all-sky imager at Darwin, Australia S. Suzuki, K. Shiokawa, Y. Otsuka,
Evidence Linking Arctic Amplification with Changing Weather Patterns in Mid-Latitudes
 Evidence Linking Arctic Amplification with Changing Weather Patterns in Mid-Latitudes Jennifer Francis Institute of Marine and Coastal Sciences Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Steve Vavrus
Evidence Linking Arctic Amplification with Changing Weather Patterns in Mid-Latitudes Jennifer Francis Institute of Marine and Coastal Sciences Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Steve Vavrus
Dynamical connection between tropospheric blockings and stratospheric polar vortex
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl043819, 2010 Dynamical connection between tropospheric blockings and stratospheric polar vortex J. M. Castanheira 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl043819, 2010 Dynamical connection between tropospheric blockings and stratospheric polar vortex J. M. Castanheira 1
Cooling of the wintertime Arctic stratosphere induced by
 1 2 3 Cooling of the wintertime Arctic stratosphere induced by the Western Pacific teleconnection pattern 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Kazuaki Nishii (nishii@eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp) Hisashi Nakamura (hisashi@eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp)
1 2 3 Cooling of the wintertime Arctic stratosphere induced by the Western Pacific teleconnection pattern 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Kazuaki Nishii (nishii@eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp) Hisashi Nakamura (hisashi@eps.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp)
Blocking precursors to stratospheric sudden warming events
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L14806, doi:10.1029/2009gl038776, 2009 Blocking precursors to stratospheric sudden warming events O. Martius, 1 L. M. Polvani, 2 and H. C. Davies 1 Received 27 April
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L14806, doi:10.1029/2009gl038776, 2009 Blocking precursors to stratospheric sudden warming events O. Martius, 1 L. M. Polvani, 2 and H. C. Davies 1 Received 27 April
particular regional weather extremes
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE2271 Amplified mid-latitude planetary waves favour particular regional weather extremes particular regional weather extremes James A Screen and Ian Simmonds
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NCLIMATE2271 Amplified mid-latitude planetary waves favour particular regional weather extremes particular regional weather extremes James A Screen and Ian Simmonds
The Morphology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking
 MAY 2008 T Y R L I S A N D H O S K I N S 1653 The Morphology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking E. TYRLIS AND B. J. HOSKINS Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom (Manuscript
MAY 2008 T Y R L I S A N D H O S K I N S 1653 The Morphology of Northern Hemisphere Blocking E. TYRLIS AND B. J. HOSKINS Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom (Manuscript
Effect of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings on Subseasonal Prediction Skill in the NASA S2S Forecast System
 Effect of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings on Subseasonal Prediction Skill in the NASA S2S Forecast System M. Joan Alexander 1, Lawrence Coy 2, Laura Holt 1, Zhao Li 3, Andrea Molod 3, and Steven Pawson 3
Effect of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings on Subseasonal Prediction Skill in the NASA S2S Forecast System M. Joan Alexander 1, Lawrence Coy 2, Laura Holt 1, Zhao Li 3, Andrea Molod 3, and Steven Pawson 3
Gravity Waves Over Antarctica
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Physics Capstone Project Physics Student Research 5-2018 Gravity Waves Over Antarctica Vanessa Chambers Utah State University Follow this and additional works at:
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Physics Capstone Project Physics Student Research 5-2018 Gravity Waves Over Antarctica Vanessa Chambers Utah State University Follow this and additional works at:
Lecture 18. Temperature Lidar (7) Rayleigh Doppler Technique
 Lecture 18. Temperature Lidar (7) Rayleigh Doppler Technique Review of integration technique Resonance fluorescence Doppler technique vs. Rayleigh Doppler technique Rayleigh Doppler lidar High-spectral-resolution
Lecture 18. Temperature Lidar (7) Rayleigh Doppler Technique Review of integration technique Resonance fluorescence Doppler technique vs. Rayleigh Doppler technique Rayleigh Doppler lidar High-spectral-resolution
Joule heating and nitric oxide in the thermosphere, 2
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015565, 2010 Joule heating and nitric oxide in the thermosphere, 2 Charles A. Barth 1 Received 14 April 2010; revised 24 June 2010; accepted
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015565, 2010 Joule heating and nitric oxide in the thermosphere, 2 Charles A. Barth 1 Received 14 April 2010; revised 24 June 2010; accepted
The Atmospheric Circulation
 The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
Zonal-mean global teleconnection from 15 to 110 km derived from SABER and WACCM
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016750, 2012 Zonal-mean global teleconnection from 15 to 110 km derived from SABER and WACCM Bo Tan, 1 Xinzhao Chu, 1 Han-Li Liu, 2 Chihoko
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016750, 2012 Zonal-mean global teleconnection from 15 to 110 km derived from SABER and WACCM Bo Tan, 1 Xinzhao Chu, 1 Han-Li Liu, 2 Chihoko
Analysing Major Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in the coupled middle atmosphere ocean model MAECHAM5/MPI-OM
 Analysing Major Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in the coupled middle atmosphere ocean model MAECHAM5/MPI-OM Master Thesis of Severin Bancalá Kiel, September 21 Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
Analysing Major Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in the coupled middle atmosphere ocean model MAECHAM5/MPI-OM Master Thesis of Severin Bancalá Kiel, September 21 Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
Winter Forecast. Allan Huffman RaleighWx
 Winter 2014-15 Forecast Allan Huffman RaleighWx Winter 2014-15 Combination of weak/moderate El Nino/+PDO/-QBO and well above average snow cover and snow cover increase this Fall in Siberia point to a winter
Winter 2014-15 Forecast Allan Huffman RaleighWx Winter 2014-15 Combination of weak/moderate El Nino/+PDO/-QBO and well above average snow cover and snow cover increase this Fall in Siberia point to a winter
Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in specified-dynamics WACCM
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 8346 8358, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50651, 2013 Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in specified-dynamics WACCM Olga
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 8346 8358, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50651, 2013 Nighttime secondary ozone layer during major stratospheric sudden warmings in specified-dynamics WACCM Olga
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
