Hindcasting to measure ice sheet model sensitivity to initial states: Supplement. A. Aschwanden, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, C. Khroulev
|
|
|
- Erick Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hindcasting to measure ice sheet model sensitivity to initial states: Supplement A. Aschwanden, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, C. Khroulev
2 1 Climate Forcing The hydrostatic atmospheric regional climate model HIRHAM5 (Christensen et al., 2006) provides monthly mean climatic mass balance and 2-m air temperature. HIRHAM is based on HIRLAM7 dynamics (Eerola, 2006) and ECHAM5 physics (Roeckner et al., 2003). HIRHAM5 is forced at the lateral boundaries using the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ERA-Interim reanalysis product (Dee et al., 2011) for the period The regional climate model dynamically downscales the temperature and precipitation fields and computes the climatic mass balance at a resolution of 0.05 ( 5.55 km) with 31 vertical levels and a time-step of 120 s in the dynamical scheme. HIRHAM5 has been validated both with ice core data and automatic weather station data and is shown to perform well over Greenland (Dethloff et al., 2002; Kiilsholm et al., 2004; Lucas-Picher et al., 2012; Rae et al., 2012). At present, formal error estimates are not available due to the lack of sufficient observations. 2
3 2 Ice Sheet Model Simulations are performed with the open-source Parallel Ice Sheet Model (PISM, 1, which is thermomechanically-coupled, polythermal, and includes a hybrid stress balance model (Bueler and Brown, 2009; Aschwanden et al., 2012). PISM has been used in a number of studies of the ice sheets on Greenland and Antarctica (e.g., Martin et al., 2011; Solgaard et al., 2011; Solgaard and Langen, 2012; Golledge et al., 2012). At the ocean boundary, ice is calved-off at the initial calving position, which is held fixed throughout the simulations. Basal topography and ice thickness are from Griggs et al. (2012). At the basal boundary, geothermal flux varies in space (Shapiro and Ritzwoller, 2004), and a nearly-plastic power law (Schoof and Hindmarsh, 2010) relates bed-parallel shear stress, τ b, and the sliding velocity, u b : u b τ b = τ c u b (1 q) u q, (2.1) 0 where τ c is the yield stress, q is the pseudo-plasticity exponent, and u 0 = 100 m a 1 is a threshold speed. The basal material (till) is partially water saturated. Saturation, yield stress and modeled liquid water pressure within the till are related by the pore water pressure, p w, given as a fraction of the overburden pressure: p w = α wρgh in τ c = (tan φ)(ρgh p w ). (2.2) Here, H is the ice thickness, ρgh is the overburden pressure, and φ is the till friction angle. The relative amount of stored water in the till, w, comes from time-integrating the basal melt rate. Excess water drains when the thickness of stored water reaches 2 m. The coefficient α is the allowed pore water pressure fraction. The yield stress τ c is also a function of the till friction angle φ, prescribed as a continuous function of the bed elevation, with φ = 5 for bed elevations lower than 300 m below sea level, φ = 20 for bed locations higher than 700 m above sea level, and changing linearly in between. The enhancement factor, E, is a simple tuning parameter for ice dynamics. This factor is commonly used in ice sheet models to change the ice flow properties to account for the effect of the anisotropic nature of ice as well as impurities. The enhancement factor appears in the definition of the effective viscosity of glacier ice, η, 2η = (E A) 1 ( τ 2 e + ɛ 2) 1 n 2n, (2.3) where τ e is the effective stress, A is the rate factor (softness), and n = 3 is the exponent of the power law. The small constant ɛ (units of stress) regularizes the flow law at low effective stress, avoiding the problem of infinite viscosity at zero deviatoric stress. 1 All simulations used development revision c52bdfd 3
4 The three tuning parameters that are used to obtain a close fit to the observed surface speed are the enhancement factor E, the pseudo-plasticity exponent q, and the allowed pore water pressure fraction α. We use (E, q, α) = (3, 0.25, 0.95). The three initialization procedures start from the same model state, obtained by running the model at a 20 km horizontal grid resolution with constant surface forcing for 50 ka while keeping the geometry fixed. Horizontal and vertical model resolutions are 2 km and 10 m, respectively. The computational domain extends horizontally over 1500 km 2800 km, and vertically over 4000 m and 2000 m in the ice and in the bedrock, respectively. For computational efficiency grid refinements are made during the initialization procedure. The runs are started on a 20 km grid, then refined from 20 km to 10 km at at a, to 5 km at a, to 2.5 km at -850 a, and finally to 2 km at -350 a. However, all the runs continue on their respective resolutions such that all initializations are available on all the listed grid resolutions. The run lengths are sufficiently long to remove unphysical transient noise resulting from the grid-refinement. Basal topography is remapped onto the respective grids using a first-order conservative algorithm. The correlation coefficient is consistent for all grid resolutions (Table 4.3). PISM uses an adaptive time-stepping scheme, and typical time-steps are about 2 days for a horizontal grid resolution of 2 km. 4
5 3 Flux-correction The flux-correction method explained below is applied during the last 2,000 years of the flux-corrected paleo-climate initialization. To obtain an ice sheet geometry in closer agreement with measurements we modify the climatic mass balance M. Let H tar be this target ice thickness, and let H be the current model thickness. Recall that the mass continuity equation is H t = M S q, (3.1) where M and S are the surface and basal mass balance, respectively, and q is the flux divergence. Replacing M with the modified surface mass balance yields the modified continuity equation H t = M S q, (3.2) with M = M + M = M + β (H tar H), (3.3) where β > 0 is set to 0.05 a 1. To reduce the shock arising from a switch in climate at the transition between initialization and hindcast, we apply the climate forcing during the hindcast as anomalies. Let χ and χ init be the climate of the hindcast and the average of the last 10 years of the initialization, respectively. Then, the hindcast climate for the simulation based on flux-corrected initial state χ is χ = χ init + (χ χ 0 ), (3.4) where χ 0 is the climate at the beginning of the hindcast (1 Jan 1989). Figure 3.1 shows the climatic mass balance of the last 10 years of the initialization for all three initialization methods. Largest differences occur in coastal areas and on small glaciers and ice caps. 5
6 Figure 3.1: Mean climatic mass balance of the last 10 years of the initialization. (a) constant-climate. (b). paleo-climate. (c) flux-corrected. 6
7 4 Supplementary Figures and Tables 7
8 a) b) c) Figure 4.1: Simulated mass fluxes as a function of grid resolution from 1990 to a) constant-climate hindcast. b) paleo-climate hindcast. c) flux-corrected hindcast. Climatic mass balance (solid line) and ice discharge (dashed line). For comparison the ice discharge estimate for 1996 (van den Broeke et al., 2009) is shown (black dotted line). Time-series are smoothed with a 13- month running-average filter. 8
9 Figure 4.2: Absolute difference in ice thickness (model-observation). a) constant-climate initialization. b) paleo-climate initialization. c) flux-corrected paleo-climate initialization; ice thickness was used in the initialization, hence only shown for comparison. Blue and red colors indicate the model under- and overestimates ice thickness, respectively. Figure 4.3: Absolute difference in surface speeds (model-observation). a, constantclimate initialization. b, paleo-climate initialization. c, flux-corrected paleoclimate initialization. Blue and red colors indicate the model under- and over-estimates surface speed, respectively. 9
10 Table 4.1: Root mean square error (RMSE, units m a 1 ) of simulated surface speeds of the inital state (1989) and at the end of the hindcast (2011) compared to observed surface speeds of , 2006, and simulation observation constant-climate paleo-climate flux-corrected Table 4.2: Mass loss trend b as a function of horizontal grid resolution g. Mean b and standard deviation b σ of the mass loss rates are also listed. g [km] b [Gt a 1 ] constant-climate paleo-climate flux-corrected b b σ Table 4.3: Correlation coefficient, r, of the correlation between simulated and observed mass loss time series as a function of horizontal grid resolution, g. g [km] r [-] constant-climate paleo-climate flux-corrected
11 Bibliography Aschwanden, A., Bueler, E., Khroulev, C., and Blatter, H.: An enthalpy formulation for glaciers and ice sheets, J. Glaciol., 58, , doi: /2012jog11j088, Bueler, E. and Brown, J.: The shallow shelf approximation as a sliding law in a thermomechanically coupled ice sheet model, J. Geophys. Res., 114, 1 21, doi: /2008JF001179, Christensen, O. B., Drews, M., Dethloff, K., Ketelsen, K., Hebestadt, I., and Rinke, A.: The HIRHAM Regional Climate Model. Version 5. Tech. Report 06-17, Tech. rep., DMI, Copenhagen, Dee, D. P., Uppala, S. M., Simmons, A. J., Berrisford, P., Poli, P., Kobayashi, S., Andrae, U., Balmaseda, M. A., Balsamo, G., Bauer, P., Bechtold, P., Beljaars, A. C. M., van de Berg, L., Bidlot, J., Bormann, N., Delsol, C., Dragani, R., Fuentes, M., Geer, A. J., Haimberger, L., Healy, S. B., Hersbach, H., Hólm, E. V., Isaksen, L., Kållberg, P., Köhler, M., Matricardi, M., McNally, A. P., Monge-Sanz, B. M., Morcrette, J.-J., Park, B.-K., Peubey, C., de Rosnay, P., Tavolato, C., Thépaut, J.-N., and Vitart, F.: The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system, Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, , doi: /qj.828, Dethloff, K., Schwager, M., Christensen, J. H., Kiilsholm, S., Rinke, A., Dorn, W., Jung-Rothenhäusler, F., Fischer, H., Kipfstuhl, S., and Miller, H.: Recent Greenland accumulation estimated from Regional Climate model simulations and ice core analysis, J. Climate, 15, , Eerola, K.: About the performance of the Hirlam version 7.0. Tech. Rep. 51, Article 14, Tech. Rep. 51, DMI, Copenhagen, Golledge, N. R., Fogwill, C. J., Mackintosh, A. N., and Buckley, K. M.: Dynamics of the last glacial maximum Antarctic ice-sheet and its response to ocean forcing, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, pp. 1 5, doi: /pnas , Griggs, J. A., Bamber, J. L.,, Hurkmans, R. T. W. L., Dowdesewell, J. A., Gogineni, S. P., Howat, I., Mouginot, J., Paden, J., Palmer, S., Rignot, E., and Steinhage, D.: A new bed elevation dataset for Greenland, The Cryosphere Discussions, 6, , doi: /tcd , URL /2012/, Kiilsholm, S., Christensen, J. H., Dethloff, K., and Rinke, A.: Net accumulation of the Greenland ice sheet: High resolution modeling of climate changes, Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, doi: /2002gl015742,
12 Lucas-Picher, P., Wulff-Nielsen, M., Christensen, J. H., Aðalgeirsdóttir, G., Mottram, R., and Simonsen, S. B.: Very high resolution regional climate model simulations over Greenland: Identifying added value, J. Geophys. Res., 117, doi: /2011JD016267, Martin, M. A., Winkelmann, R., Haseloff, M., Albrecht, T., Bueler, E., Khroulev, C., and Levermann, A.: The Potsdam Parallel Ice Sheet Model (PISM-PIK) Part 2: Dynamic equilibrium simulation of the Antarctic ice sheet, The Cryosphere, 5, , doi: /tc , Rae, J. G. L., Aðalgeirsdóttir, G., Edwards, T. L., Fettweis, X., Gregory, J. M., Hewitt, H. T., Lowe, J. a., Lucas-Picher, b., Mottram, R. H., Payne, a. J., Ridley, J. K., Shannon, S. R., van de Berg, W. J., van de Wal, R. S. W., and van den Broeke, M. R.: Greenland ice sheet surface mass balance: evaluating simulations and making projections with regional climate models, The Cryosphere, 6, , doi: / tc , URL Roeckner, E., Bäuml, G., Bonaventura, L., Brokopf, R., Esch, M., Giorgetta, M., Hagemann, S., Kirchner, I., Kornblueh, L., Manzini, E., Rhodin, A., Schlese, U., Schulzweida, U., and Tompkins, A.: The atmospheric general circulation model ECHAM5. Part I: model description, Tech Rep. 349, Tech. Rep. 349, Max-Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Schoof, C. and Hindmarsh, R. C. A.: Thin-Film Flows with Wall Slip: An Asymptotic Analysis of Higher Order Glacier Flow Models, Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math., 63, , doi: /qjmam/hbp025, Shapiro, N. M. and Ritzwoller, M. H.: Inferring surface heat flux distributions guided by a global seismic model: particular application to Antarctica, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 223, , Solgaard, A. M. and Langen, P. L.: Multistability of the Greenland Ice Sheet and the effects of an adaptive mass balance formulation, Clim. Dyn., Solgaard, A. M., Reeh, N., Japsen, P., and Nielsen, T.: Snapshots of the Greenland ice sheet configuration in the Pliocene to early Pleistocene, J. Glaciol., 57, , doi: / , van den Broeke, M. R., Bamber, J. L., Ettema, J., Rignot, E., Schrama, E., van de Berg, W. J., van Meijgaard, E., Velicogna, I., and Wouters, B.: Partitioning recent Greenland mass loss, Science, 326, , doi: /science ,
Comparison results: time series Margherita Grossi
 Comparison results: time series Margherita Grossi GOME Evolution Climate Product v2.01 vs. ECMWF ERAInterim GOME Evolution Climate Product v2.01 vs. SSM/I HOAPS4 In order to assess the quality and stability
Comparison results: time series Margherita Grossi GOME Evolution Climate Product v2.01 vs. ECMWF ERAInterim GOME Evolution Climate Product v2.01 vs. SSM/I HOAPS4 In order to assess the quality and stability
Danish Meteorological Institute
 Ministry for Climate and Energy Background information on the RiskChange simulations by BCCR and DMI Cathrine Fox Maule, Stephanie Mayer, Stefan Sobolowski, Ole B. Christensen www.dmi.dk/dmi/dkc14-05 Copenhagen
Ministry for Climate and Energy Background information on the RiskChange simulations by BCCR and DMI Cathrine Fox Maule, Stephanie Mayer, Stefan Sobolowski, Ole B. Christensen www.dmi.dk/dmi/dkc14-05 Copenhagen
EVALUATION OF TWO AMV POLAR WINDS RETRIEVAL ALGORITHMS USING FIVE YEARS OF REPROCESSED DATA
 EVALUATION OF TWO AMV POLAR WINDS RETRIEVAL ALGORITHMS USING FIVE YEARS OF REPROCESSED DATA Roger Huckle, Marie Doutriaux-Boucher, Rob Roebeling, and Jörg Schulz EUMETSAT, Eumetsat-Allee 1, Darmstadt,
EVALUATION OF TWO AMV POLAR WINDS RETRIEVAL ALGORITHMS USING FIVE YEARS OF REPROCESSED DATA Roger Huckle, Marie Doutriaux-Boucher, Rob Roebeling, and Jörg Schulz EUMETSAT, Eumetsat-Allee 1, Darmstadt,
LONG TERM VARIATIONS OF SIGNIFICANT WAVE HEIGHT AROUND INDONESIA SEAS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 9, September 2018, pp. 933 941, Article ID: IJCIET_09_09_089 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=9
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 9, September 2018, pp. 933 941, Article ID: IJCIET_09_09_089 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=9&itype=9
Atmospheric origins of variability in the South Atlantic meridional overturning circulation
 Atmospheric origins of variability in the South Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Timothy Smith Patrick Heimbach July 3, 2018 INSTITUTE FOR COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING & SCIENCES The South Atlantic
Atmospheric origins of variability in the South Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Timothy Smith Patrick Heimbach July 3, 2018 INSTITUTE FOR COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING & SCIENCES The South Atlantic
Modeled and observed fast flow in the Greenland ice sheet
 Modeled and observed fast flow in the Greenland ice sheet Ed Bueler 1 Constantine Khroulev 1 Andy Aschwanden 2 Ian Joughin 3 1 Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Alaska Fairbanks 2 Arctic
Modeled and observed fast flow in the Greenland ice sheet Ed Bueler 1 Constantine Khroulev 1 Andy Aschwanden 2 Ian Joughin 3 1 Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Alaska Fairbanks 2 Arctic
EVALUATION OF THE WRF METEOROLOGICAL MODEL RESULTS FOR HIGH OZONE EPISODE IN SW POLAND THE ROLE OF MODEL INITIAL CONDITIONS Wrocław, Poland
 EVALUATION OF THE WRF METEOROLOGICAL MODEL RESULTS FOR HIGH OZONE EPISODE IN SW POLAND THE ROLE OF MODEL INITIAL CONDITIONS Kinga Wałaszek 1, Maciej Kryza 1, Małgorzata Werner 1 1 Department of Climatology
EVALUATION OF THE WRF METEOROLOGICAL MODEL RESULTS FOR HIGH OZONE EPISODE IN SW POLAND THE ROLE OF MODEL INITIAL CONDITIONS Kinga Wałaszek 1, Maciej Kryza 1, Małgorzata Werner 1 1 Department of Climatology
Long term stability of the wind speed in reanalysis data
 Long term stability of the wind speed in reanalysis data In the following, we show for different regions of Germany and France, that the wind speed information in commonly used reanalysis data sets are
Long term stability of the wind speed in reanalysis data In the following, we show for different regions of Germany and France, that the wind speed information in commonly used reanalysis data sets are
SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Project Title: Small-scale severe weather events: Downscaling using Harmonie Computer Project Account: spnlster
SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Project Title: Small-scale severe weather events: Downscaling using Harmonie Computer Project Account: spnlster
ARCTIC WEATHER AND ABRUPT SEA ICE LOSS
 ARCTIC WEATHER AND ABRUPT SEA ICE LOSS Uriel Gutierrez 1, Steven Cavallo 2, and Nick Szapiro 2 1 National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates Program Norman, Oklahoma 2 University of
ARCTIC WEATHER AND ABRUPT SEA ICE LOSS Uriel Gutierrez 1, Steven Cavallo 2, and Nick Szapiro 2 1 National Weather Center Research Experiences for Undergraduates Program Norman, Oklahoma 2 University of
TRACK ANALYSIS OF CYCLONES RELATED TO TORNADOES OVER WESTERN GREECE
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 TRACK ANALYSIS OF CYCLONES RELATED TO TORNADOES OVER WESTERN GREECE MATSANGOURAS
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 TRACK ANALYSIS OF CYCLONES RELATED TO TORNADOES OVER WESTERN GREECE MATSANGOURAS
Trends of ozone and meteorological parameters at high alpine sites
 5 th Symposium Conference Volume for Research in Protected Areas pages 325-329 10 to 12 June 2013, Mittersill Trends of ozone and meteorological parameters at high alpine sites August Kaiser & Helfried
5 th Symposium Conference Volume for Research in Protected Areas pages 325-329 10 to 12 June 2013, Mittersill Trends of ozone and meteorological parameters at high alpine sites August Kaiser & Helfried
Comparison of the WRF and HIRHAM models over Svalbard
 Comparison of the WRF and HIRHAM models over Svalbard SVALI Deliverable D3.1 4 Report MARIA NORMAN 1, BJÖRN CLAREMAR 1 RUTH MOTTRAM 2, ANNA RUTGERSSON 1 1 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH SCIENCES, UPPSALA UNIVERSITY
Comparison of the WRF and HIRHAM models over Svalbard SVALI Deliverable D3.1 4 Report MARIA NORMAN 1, BJÖRN CLAREMAR 1 RUTH MOTTRAM 2, ANNA RUTGERSSON 1 1 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH SCIENCES, UPPSALA UNIVERSITY
Effect of ocean waves on ocean circulation
 Effect of ocean waves on ocean circulation Peter A.E.M. Janssen ECMWF Shinfield Park Reading, U.K. p.janssen@ecmwf.int ABSTRACT Ocean waves play an important role in processes that govern the fluxes accross
Effect of ocean waves on ocean circulation Peter A.E.M. Janssen ECMWF Shinfield Park Reading, U.K. p.janssen@ecmwf.int ABSTRACT Ocean waves play an important role in processes that govern the fluxes accross
PISM, a Parallel Ice Sheet Model: Current status of our Antarctic ice sheet simulation
 PISM, a Parallel Ice Sheet Model: Current status of our Antarctic ice sheet simulation Craig Lingle, 1 Ed Bueler, 2 Jed Brown, 1 and David Covey, 1 1 Geophysical Institute, Univ. of Alaska, Fairbanks 2
PISM, a Parallel Ice Sheet Model: Current status of our Antarctic ice sheet simulation Craig Lingle, 1 Ed Bueler, 2 Jed Brown, 1 and David Covey, 1 1 Geophysical Institute, Univ. of Alaska, Fairbanks 2
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5955/984/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partitioning Recent Greenland Mass Loss Michiel van den Broeke,* Jonathan Bamber, Janneke Ettema, Eric Rignot, Ernst
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5955/984/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partitioning Recent Greenland Mass Loss Michiel van den Broeke,* Jonathan Bamber, Janneke Ettema, Eric Rignot, Ernst
THE INFLUENCE OF THE METEOROLOGICAL FORCING DATA ON THE RECONSTRUCTIONS OF HISTORICAL STORMS IN THE BLACK SEA
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE METEOROLOGICAL FORCING DATA ON THE RECONSTRUCTIONS OF HISTORICAL STORMS IN THE BLACK SEA Vasko Galabov, Anna Kortcheva National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology- Bulgarian Academy
THE INFLUENCE OF THE METEOROLOGICAL FORCING DATA ON THE RECONSTRUCTIONS OF HISTORICAL STORMS IN THE BLACK SEA Vasko Galabov, Anna Kortcheva National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology- Bulgarian Academy
Title. Citation 低温科学 = Low Temperature Science, 75: Issue Date DOI. Doc URL. Type. File Information. prospects
 Title Surface mass balance of the Greenland ice sheet in t prospects Mottram, Ruth; Boberg, Fredrik; Langen, Peter; Yang, Author(s) Madsen, Marianne Sloth Citation 低温科学 = Low Temperature Science, 75: 105-115
Title Surface mass balance of the Greenland ice sheet in t prospects Mottram, Ruth; Boberg, Fredrik; Langen, Peter; Yang, Author(s) Madsen, Marianne Sloth Citation 低温科学 = Low Temperature Science, 75: 105-115
1 / 5. Climate Simulation CRCM5- LE ClimEx runs at Ouranos 2 May 2018 (v3)
 1 / 5 Terms of use of CRCM5- LE runs at Ouranos for the ClimEx project For reference to CRCM5- LE ClimEx outputs used in reports, publications and presentations. This document contains the following sections:
1 / 5 Terms of use of CRCM5- LE runs at Ouranos for the ClimEx project For reference to CRCM5- LE ClimEx outputs used in reports, publications and presentations. This document contains the following sections:
The prominence of a tropical convective signal in the wintertime Arctic temperature
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. (2013) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.455 The prominence of a tropical convective signal in the wintertime
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. (2013) Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.455 The prominence of a tropical convective signal in the wintertime
P81 STEPCLIM: SEVERE THUNDERSTORM EVALUATION AND PREDICTABILITY IN CLIMATE MODELS
 P81 STEPCLIM: SEVERE THUNDERSTORM EVALUATION AND PREDICTABILITY IN CLIMATE MODELS Georg Pistotnik 1, Pieter Groenemeijer, Thilo Kühne, and Kathrin Riemann-Campe European Severe Storms Laboratory, Wessling,
P81 STEPCLIM: SEVERE THUNDERSTORM EVALUATION AND PREDICTABILITY IN CLIMATE MODELS Georg Pistotnik 1, Pieter Groenemeijer, Thilo Kühne, and Kathrin Riemann-Campe European Severe Storms Laboratory, Wessling,
Multi-Modal Flow in a Thermocoupled Model of the Antarctic Ice Sheet, with Verification
 Multi-Modal Flow in a Thermocoupled Model of the Antarctic Ice Sheet, with Verification Craig Lingle 1 Jed Brown 2 Ed Bueler 2 1 Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, USA 2 Department of
Multi-Modal Flow in a Thermocoupled Model of the Antarctic Ice Sheet, with Verification Craig Lingle 1 Jed Brown 2 Ed Bueler 2 1 Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, USA 2 Department of
Would Bangkok Be More Vulnerable To The Anticipated Changing Climate?
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 Would Bangkok Be More Vulnerable To The Anticipated Changing Climate? Thannob Aribarg Minh Tue
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 Would Bangkok Be More Vulnerable To The Anticipated Changing Climate? Thannob Aribarg Minh Tue
Very high resolution regional climate model simulations over Greenland: Identifying added value
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016267, 2012 Very high resolution regional climate model simulations over Greenland: Identifying added value Philippe Lucas-Picher, 1,2 Maria
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd016267, 2012 Very high resolution regional climate model simulations over Greenland: Identifying added value Philippe Lucas-Picher, 1,2 Maria
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/12/e1701169/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Abrupt shift in the observed runoff from the southwestern Greenland ice sheet Andreas P. Ahlstrøm, Dorthe Petersen,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/12/e1701169/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Abrupt shift in the observed runoff from the southwestern Greenland ice sheet Andreas P. Ahlstrøm, Dorthe Petersen,
Decay of the Greenland Ice Sheet due to surface-meltwater-induced acceleration of basal sliding
 Decay of the Greenland Ice Sheet due to surface-meltwater-induced acceleration of basal sliding arxiv:0905.07v [physics.geo-ph] May 009 Ralf Greve Shin Sugiyama Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido
Decay of the Greenland Ice Sheet due to surface-meltwater-induced acceleration of basal sliding arxiv:0905.07v [physics.geo-ph] May 009 Ralf Greve Shin Sugiyama Institute of Low Temperature Science, Hokkaido
Lowest Astronomical Tide in the North Sea derived from a vertically referenced shallow water model, and an assessment of its suggested sense of safety
 Lowest Astronomical Tide in the North Sea derived from a vertically referenced shallow water model, and an assessment of its suggested sense of safety Cornelis Slobbe, The Netherlands, Delft University
Lowest Astronomical Tide in the North Sea derived from a vertically referenced shallow water model, and an assessment of its suggested sense of safety Cornelis Slobbe, The Netherlands, Delft University
ECMWF reanalyses: Diagnosis and application
 ECMWF reanalyses: Diagnosis and application Dick Dee ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom D.Dee@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction Reanalysis uses a modern data assimilation system to reprocess
ECMWF reanalyses: Diagnosis and application Dick Dee ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom D.Dee@ecmwf.int 1 Introduction Reanalysis uses a modern data assimilation system to reprocess
Long-term temperature and precipitation records from the Falkland Islands
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 35: 122 1231 (2015) Published online 27 May 201 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/joc.09 Long-term temperature and precipitation
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 35: 122 1231 (2015) Published online 27 May 201 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/joc.09 Long-term temperature and precipitation
Title. Author(s)Greve, Ralf. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information.
 Title Increased future sea level rise due to rapid decay o Author(s)Greve, Ralf CitationProceedings of the First International Symposium on Issue Date 008--04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/5/4868 Type
Title Increased future sea level rise due to rapid decay o Author(s)Greve, Ralf CitationProceedings of the First International Symposium on Issue Date 008--04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/5/4868 Type
ANALYSIS OF PROJECTED CLIMATE CHANGE FOR HUNGARY USING ENSEMBLES SIMULATIONS
 - 387 - ANALYSIS OF PROJECTED CLIMATE CHANGE FOR HUNGARY USING ENSEMBLES SIMULATIONS PONGRÁCZ, R. BARTHOLY, J. MIKLÓS, E. Eötvös Loránd University, Department of Meteorology 1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter
- 387 - ANALYSIS OF PROJECTED CLIMATE CHANGE FOR HUNGARY USING ENSEMBLES SIMULATIONS PONGRÁCZ, R. BARTHOLY, J. MIKLÓS, E. Eötvös Loránd University, Department of Meteorology 1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter
Danish Meteorological Institute Scientific Report 15-05
 usurf PIC usurf RCP8.5 coupled Relative change 2100 2100 10 260 510 760 1010 1260 1510 1760 2010 2260 2510 m 10 260 510 760 1010 1260 1510 1760 2010 2260 2510 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0
usurf PIC usurf RCP8.5 coupled Relative change 2100 2100 10 260 510 760 1010 1260 1510 1760 2010 2260 2510 m 10 260 510 760 1010 1260 1510 1760 2010 2260 2510 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0
Irish Storminess: What Does the Future Hold? Expert Statement: Royal Irish Academy Climate Change and Environmental Sciences Committee
 Irish Storminess: What Does the Future Hold? Expert Statement: Royal Irish Academy Climate Change and Environmental Sciences Committee May 2017 Irish Storminess: What Does the Future Hold? Ray McGrath
Irish Storminess: What Does the Future Hold? Expert Statement: Royal Irish Academy Climate Change and Environmental Sciences Committee May 2017 Irish Storminess: What Does the Future Hold? Ray McGrath
Visualization of 2D uncertainty in decadal climate predictions
 Workshop on Visualisation in Environmental Sciences (EnvirVis) (2015) A. Middel and K. Rink and G. H. Weber (Editors) Short Papers Visualization of 2D uncertainty in decadal climate predictions Michael
Workshop on Visualisation in Environmental Sciences (EnvirVis) (2015) A. Middel and K. Rink and G. H. Weber (Editors) Short Papers Visualization of 2D uncertainty in decadal climate predictions Michael
Role of tropical Indian Ocean air sea interactions in modulating Indian summer monsoon in a coupled model
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 16: 170 176 (2015) Published online 24 January 2015 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.561 Role of tropical Indian Ocean air
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 16: 170 176 (2015) Published online 24 January 2015 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.561 Role of tropical Indian Ocean air
RETRACTED ARTICLE. Hydrologic evaluation on the ERA-Interim output using observed river discharge data
 DOI 10.1007/s13201-014-0183-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hydrologic evaluation on the ERA-Interim output using observed river discharge data L. A. Djiotang Tchotchou A. Tompkins F. Mkankam Kamga Received: 13 September
DOI 10.1007/s13201-014-0183-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hydrologic evaluation on the ERA-Interim output using observed river discharge data L. A. Djiotang Tchotchou A. Tompkins F. Mkankam Kamga Received: 13 September
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia IUTAM 17 (2015 ) 40 46
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia IUTAM 17 (2015 ) 40 46 IUTAM Symposium on the Dynamics of Extreme Events Influenced by Climate Change (2013) The future wave climate of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia IUTAM 17 (2015 ) 40 46 IUTAM Symposium on the Dynamics of Extreme Events Influenced by Climate Change (2013) The future wave climate of
Geographic variation of surface energy partitioning in the climatic mean predicted from the maximum power limit. Abstract
 Geographic variation of surface energy partitioning in the climatic mean predicted from the maximum power limit Chirag Dhara, Maik Renner, and Axel Kleidon Max-Planck-Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena,
Geographic variation of surface energy partitioning in the climatic mean predicted from the maximum power limit Chirag Dhara, Maik Renner, and Axel Kleidon Max-Planck-Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena,
verification, validation, and basal strength in models for the present state of ice sheets
 verification, validation, and basal strength in models for the present state of ice sheets Ed Bueler 1 Constantine Khroulev 2 Andy Aschwanden 3 1 Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Alaska
verification, validation, and basal strength in models for the present state of ice sheets Ed Bueler 1 Constantine Khroulev 2 Andy Aschwanden 3 1 Dept of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Alaska
Ice in the climate system. Summary so far. Today. The Cryosphere. 1. Climate history of the Earth. 2. Paleo observations (1)
 Ice in the climate system 1. Climate history of the Earth 2. Paleo observations (1) 3. Paleo observations (2) 4. Ice ages 5. Climate sensitivity 6. Ice in the climate system Summary so far Radiation (Milankovitch
Ice in the climate system 1. Climate history of the Earth 2. Paleo observations (1) 3. Paleo observations (2) 4. Ice ages 5. Climate sensitivity 6. Ice in the climate system Summary so far Radiation (Milankovitch
Variability of weather regimes in the North Atlantic-European area: past and future
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 15: 314 320 (2014) Published online 10 May 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.505 Variability of weather regimes in the
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 15: 314 320 (2014) Published online 10 May 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.505 Variability of weather regimes in the
Glaciology (as opposed to Glacial Geology) Why important? What are glaciers? How do they work?
 Glaciology (as opposed to Glacial Geology) Why important? What are glaciers? How do they work? Glaciers are important because of their role in creating glacial landscapes (erosional and depositional features).
Glaciology (as opposed to Glacial Geology) Why important? What are glaciers? How do they work? Glaciers are important because of their role in creating glacial landscapes (erosional and depositional features).
The impact of climate change on glaciers and glacial runoff in the Nordic countries
 The impact of climate change on glaciers and glacial runoff in the Nordic countries Tómas Jóhannesson, Guðfinna Aðalgeirsdóttir, Andreas Ahlstrøm, Liss M. Andreassen, Stein Beldring, Helgi Björnsson, Philippe
The impact of climate change on glaciers and glacial runoff in the Nordic countries Tómas Jóhannesson, Guðfinna Aðalgeirsdóttir, Andreas Ahlstrøm, Liss M. Andreassen, Stein Beldring, Helgi Björnsson, Philippe
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs
 Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs Future sea-level rise from Greenland s main outlet glaciers in a warming climate Journal Item How
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs Future sea-level rise from Greenland s main outlet glaciers in a warming climate Journal Item How
Acceleration of the contribution of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets to sea level rise
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046583, 2011 Acceleration of the contribution of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets to sea level rise E. Rignot, 1,2 I. Velicogna, 1,2 M. R.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046583, 2011 Acceleration of the contribution of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets to sea level rise E. Rignot, 1,2 I. Velicogna, 1,2 M. R.
Modelling of surface to basal hydrology across the Russell Glacier Catchment
 Modelling of surface to basal hydrology across the Russell Glacier Catchment Sam GAP Modelling Workshop, Toronto November 2010 Collaborators Alun Hubbard Centre for Glaciology Institute of Geography and
Modelling of surface to basal hydrology across the Russell Glacier Catchment Sam GAP Modelling Workshop, Toronto November 2010 Collaborators Alun Hubbard Centre for Glaciology Institute of Geography and
Wind Related Faults on the GB Transmission Network
 Murray, Kirsty and Bell, Keith (2014) Wind related faults on the GB transmission network. In: 2014 International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems, PMAPS 2014, 2014-07-07-2014-07-10.,
Murray, Kirsty and Bell, Keith (2014) Wind related faults on the GB transmission network. In: 2014 International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems, PMAPS 2014, 2014-07-07-2014-07-10.,
Monsoon effect simulation on typhoon rainfall potential - Typhoon Morakot (2009)
 Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., Vol. 28, No. 1, 11-21, February 2017 doi: 10.3319/TAO.2016.08.17.01(CCA) Monsoon effect simulation on typhoon rainfall potential - Typhoon Morakot (2009) Yi-Ling Chang 1, Hsi-Chyi
Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., Vol. 28, No. 1, 11-21, February 2017 doi: 10.3319/TAO.2016.08.17.01(CCA) Monsoon effect simulation on typhoon rainfall potential - Typhoon Morakot (2009) Yi-Ling Chang 1, Hsi-Chyi
Improving Snow and Ice Albedo in Climate and NWP Models
 Improving Snow and Ice Albedo in Climate and NWP Models Ruth Mottram Arctic and Climate Research Danish Meteorological Institute With Contributions from: Simon Gascoin, Peter Lang Langen, Pia Englyst Nielsen,
Improving Snow and Ice Albedo in Climate and NWP Models Ruth Mottram Arctic and Climate Research Danish Meteorological Institute With Contributions from: Simon Gascoin, Peter Lang Langen, Pia Englyst Nielsen,
Sensitivity and tuning of parameterisation of precipitation in HIRHAM5
 Technical Report 12-13 Sensitivity and tuning of parameterisation of precipitation in HIRHAM5 Søren Højmark Rasmussen Copenhagen 2012 page 1 of 15 Colophon Serial title: Technical Report 12-13 Title: Sensitivity
Technical Report 12-13 Sensitivity and tuning of parameterisation of precipitation in HIRHAM5 Søren Højmark Rasmussen Copenhagen 2012 page 1 of 15 Colophon Serial title: Technical Report 12-13 Title: Sensitivity
Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves. Bryan Riel December 4, 2008
 Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves Bryan Riel December 4, 2008 Ice Sheet Mass Balance/WAIS Dynamics -Mass Balance = (Ice/Snow Accumulation) (Surface melting, ice outflux,
Effect of Ocean Warming on West Antarctic Ice Streams and Ice Shelves Bryan Riel December 4, 2008 Ice Sheet Mass Balance/WAIS Dynamics -Mass Balance = (Ice/Snow Accumulation) (Surface melting, ice outflux,
Evaluation of short-term climate change prediction in multi-model CMIP5 decadal hindcasts
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051644, 2012 Evaluation of short-term climate change prediction in multi-model CMIP5 decadal hindcasts Hye-Mi Kim, 1 Peter J. Webster, 1 and Judith
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051644, 2012 Evaluation of short-term climate change prediction in multi-model CMIP5 decadal hindcasts Hye-Mi Kim, 1 Peter J. Webster, 1 and Judith
Introduction to Global Warming
 Introduction to Global Warming Cryosphere (including sea level) and its modelling Ralf GREVE Institute of Low Temperature Science Hokkaido University Sapporo, 2010.09.14 http://wwwice.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/~greve/
Introduction to Global Warming Cryosphere (including sea level) and its modelling Ralf GREVE Institute of Low Temperature Science Hokkaido University Sapporo, 2010.09.14 http://wwwice.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/~greve/
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1449 Multistability and critical thresholds of the Greenland ice sheet Alexander Robinson 1,2,3, Reinhard Calov 1 & Andrey Ganopolski 1 February 7, 2012 1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1449 Multistability and critical thresholds of the Greenland ice sheet Alexander Robinson 1,2,3, Reinhard Calov 1 & Andrey Ganopolski 1 February 7, 2012 1
Manuscript prepared for The Cryosphere with version 2014/09/ Copernicus papers of the L A TEX class copernicus.cls. Date: 5 August 2016
 Manuscript prepared for The Cryosphere with version 14/9/16 7.15 Copernicus papers of the L A TEX class copernicus.cls. Date: 5 August 16 Balance between driving stress and basal drag results in linearity
Manuscript prepared for The Cryosphere with version 14/9/16 7.15 Copernicus papers of the L A TEX class copernicus.cls. Date: 5 August 16 Balance between driving stress and basal drag results in linearity
Glacier Hydrology II: Theory and Modeling
 Glacier Hydrology II: Theory and Modeling McCarthy Summer School 2018 Matt Hoffman Gwenn Flowers, Simon Fraser Operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's NNSA Observations
Glacier Hydrology II: Theory and Modeling McCarthy Summer School 2018 Matt Hoffman Gwenn Flowers, Simon Fraser Operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's NNSA Observations
Decomposition of the Brier score for weighted forecast-verification pairs
 Copyright c 2010 Royal Meteorological Society QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 136: 1364 1370 (2010) Published online in iley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)
Copyright c 2010 Royal Meteorological Society QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 136: 1364 1370 (2010) Published online in iley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com)
The Effect of a Basal-friction Parameterization on. Grounding-line Dynamics in Ice-sheet Models.
 The Effect of a Basal-friction Parameterization on Grounding-line Dynamics in Ice-sheet Models. by Gunter Leguy Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Ph.D of Applied &
The Effect of a Basal-friction Parameterization on Grounding-line Dynamics in Ice-sheet Models. by Gunter Leguy Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Ph.D of Applied &
Ice Sheets and Climate Change. William H. Lipscomb Los Alamos National Laboratory
 Ice Sheets and Climate Change William H. Lipscomb Los Alamos National Laboratory What is an expert? An expert is somebody who is more than 50 miles from home, has no responsibility for implementing the
Ice Sheets and Climate Change William H. Lipscomb Los Alamos National Laboratory What is an expert? An expert is somebody who is more than 50 miles from home, has no responsibility for implementing the
Does dynamical downscaling introduce novel information in climate model simulations of precipitation change over a complex topography region?
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln NASA Publications National Aeronautics and Space Administration 2011 Does dynamical downscaling introduce novel information
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln NASA Publications National Aeronautics and Space Administration 2011 Does dynamical downscaling introduce novel information
Assessment of ERA-Interim driven simulation over Italy with COSMO-CLM
 Research Papers Issue RP0183 December 2013 ISC - Impacts on Soil and Coasts Division Assessment of ERA-Interim driven simulation over Italy with COSMO-CLM By Edoardo Bucchignani Meteo Systems and Instrumentation,
Research Papers Issue RP0183 December 2013 ISC - Impacts on Soil and Coasts Division Assessment of ERA-Interim driven simulation over Italy with COSMO-CLM By Edoardo Bucchignani Meteo Systems and Instrumentation,
Impacts of Arctic sea-ice and continental snow-cover changes. on atmospheric winter teleconnections
 1 2 Impacts of Arctic sea-ice and continental snow-cover changes 3 on atmospheric winter teleconnections 4 5 Dörthe Handorf, Ralf Jaiser, Klaus Dethloff, Annette Rinke, Judah Cohen 6 7 8 9 Dörthe Handorf,
1 2 Impacts of Arctic sea-ice and continental snow-cover changes 3 on atmospheric winter teleconnections 4 5 Dörthe Handorf, Ralf Jaiser, Klaus Dethloff, Annette Rinke, Judah Cohen 6 7 8 9 Dörthe Handorf,
Buoyant flexure and basal crevassing in dynamic mass loss at Helheim Glacier
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2204 Buoyant flexure and basal crevassing in dynamic mass loss at Helheim Glacier Timothy D. James*, Tavi Murray, Nick Selmes, Kilian Scharrer and Martin O Leary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2204 Buoyant flexure and basal crevassing in dynamic mass loss at Helheim Glacier Timothy D. James*, Tavi Murray, Nick Selmes, Kilian Scharrer and Martin O Leary
Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model E. Scoccimarro
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE di GEOFISICA e VULCANOLOGIA Tropical Cyclones - Ocean feedbacks: Effects on the Ocean Heat Transport as simulated by a High Resolution Coupled General Circulation Model E. Scoccimarro
Mechanisms controlling the SST air-sea heat flux feedback and its dependence on spatial scale
 Mechanisms controlling the SST air-sea heat flux feedback and its dependence on spatial scale The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Mechanisms controlling the SST air-sea heat flux feedback and its dependence on spatial scale The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Glacier Thermodynamics: Ice Temperature and Heat Transfer Processes
 Glacier Thermodynamics: Ice Temperature and Heat Transfer Processes ESS431: Principles of Glaciology ESS505: The Cryosphere Wednesday, 10/24 Ben Hills Today s Objectives: Why do we care about ice temperature?
Glacier Thermodynamics: Ice Temperature and Heat Transfer Processes ESS431: Principles of Glaciology ESS505: The Cryosphere Wednesday, 10/24 Ben Hills Today s Objectives: Why do we care about ice temperature?
Danish Meteorological Institute Scientific Report 15-05
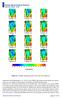 Danish Meteorological Institute Figure 6.2: Monthly temperature fields used to drive the spinup run. temperature data [Bindschadler et al., 2013] to drive PISM. This spinup run through the past glacial
Danish Meteorological Institute Figure 6.2: Monthly temperature fields used to drive the spinup run. temperature data [Bindschadler et al., 2013] to drive PISM. This spinup run through the past glacial
Ice-stream stability on a reverse bed slope
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1600 Supplementary Information: Ice stream stability on a reverse bed Ice-stream stability on a reverse bed slope slope Stewart S.R. Jamieson 1, Andreas Vieli
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1600 Supplementary Information: Ice stream stability on a reverse bed Ice-stream stability on a reverse bed slope slope Stewart S.R. Jamieson 1, Andreas Vieli
Experiences of using ECV datasets in ECMWF reanalyses including CCI applications. David Tan and colleagues ECMWF, Reading, UK
 Experiences of using ECV datasets in ECMWF reanalyses including CCI applications David Tan and colleagues ECMWF, Reading, UK Slide 1 Main points Experience shows benefit of integrated & iterative approach
Experiences of using ECV datasets in ECMWF reanalyses including CCI applications David Tan and colleagues ECMWF, Reading, UK Slide 1 Main points Experience shows benefit of integrated & iterative approach
Impacts of Arctic sea-ice and continental snow-cover changes. on atmospheric winter teleconnections
 Impacts of Arctic sea-ice and continental snow-cover changes on atmospheric winter teleconnections Dörthe Handorf, Ralf Jaiser, Klaus Dethloff, Annette Rinke, Judah Cohen Dörthe Handorf, Ralf Jaiser, Klaus
Impacts of Arctic sea-ice and continental snow-cover changes on atmospheric winter teleconnections Dörthe Handorf, Ralf Jaiser, Klaus Dethloff, Annette Rinke, Judah Cohen Dörthe Handorf, Ralf Jaiser, Klaus
Ice flux divergence anomalies on 79north Glacier, Greenland
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047338, 2011 Ice flux divergence anomalies on 79north Glacier, Greenland H. Seroussi, 1,2 M. Morlighem, 1,2 E. Rignot, 1,3 E. Larour, 1 D. Aubry,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047338, 2011 Ice flux divergence anomalies on 79north Glacier, Greenland H. Seroussi, 1,2 M. Morlighem, 1,2 E. Rignot, 1,3 E. Larour, 1 D. Aubry,
Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East Antarctica
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L16503, doi:10.1029/2008gl034728, 2008 Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L16503, doi:10.1029/2008gl034728, 2008 Subglacial topography inferred from ice surface terrain analysis reveals a large un-surveyed basin below sea level in East
Distinct linkage between winter Tibetan Plateau snow depth and early summer Philippine Sea anomalous anticyclone
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 7: 223 229 (26) Published online 8 February 26 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI:.2/asl.646 Distinct linkage between winter Tibetan Plateau
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 7: 223 229 (26) Published online 8 February 26 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI:.2/asl.646 Distinct linkage between winter Tibetan Plateau
Accumulation over the Greenland Ice Sheet as Represented in Reanalysis Data
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 28, NO. 5, 2011, 1 9 Accumulation over the Greenland Ice Sheet as Represented in Reanalysis Data CHEN Linling 1,2,3 ( ), Ola M. JOHANNESSEN 2,3, WANG Huijun 1 ( ),
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 28, NO. 5, 2011, 1 9 Accumulation over the Greenland Ice Sheet as Represented in Reanalysis Data CHEN Linling 1,2,3 ( ), Ola M. JOHANNESSEN 2,3, WANG Huijun 1 ( ),
Sea level projections with semiempirical and earth system models
 Sea level projections with semiempirical and earth system models John C. Moore College of Global Change and Earth System Science, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China and Arctic Centre, University
Sea level projections with semiempirical and earth system models John C. Moore College of Global Change and Earth System Science, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China and Arctic Centre, University
Ice Sheet Modeling and Sea Level Rise. William Lipscomb, NCAR CESM Sea Level Session 10 January 2018
 Ice Sheet Modeling and Sea Level Rise William Lipscomb, NCAR CESM Sea Level Session 10 January 2018 Ice sheets in IPCC AR4 The IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) projected 0.18 to 0.59 m of sea level
Ice Sheet Modeling and Sea Level Rise William Lipscomb, NCAR CESM Sea Level Session 10 January 2018 Ice sheets in IPCC AR4 The IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) projected 0.18 to 0.59 m of sea level
ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community
 ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community (and a few myth-busters) Paul Poli European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Shinfield Park, RG2 9AX, Reading, UK paul.poli
ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community (and a few myth-busters) Paul Poli European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Shinfield Park, RG2 9AX, Reading, UK paul.poli
Large-scale changes in Greenland outlet glacier dynamics triggered at the terminus
 PUBLISHED ONLINE: JANUARY 2 DOI:./NGEO Large-scale changes in Greenland outlet glacier dynamics triggered at the terminus Faezeh M. Nick 1 *, Andreas Vieli 1, Ian M. Howat 2 and Ian Joughin The recent
PUBLISHED ONLINE: JANUARY 2 DOI:./NGEO Large-scale changes in Greenland outlet glacier dynamics triggered at the terminus Faezeh M. Nick 1 *, Andreas Vieli 1, Ian M. Howat 2 and Ian Joughin The recent
Meltwater produced by wind-albedo interaction stored in an East Antarctic ice shelf Supplementary Information
 Meltwater produced by wind-albedo interaction stored in an East Antarctic ice shelf Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upper and (b) lower surface of an englacial lake surveyed by
Meltwater produced by wind-albedo interaction stored in an East Antarctic ice shelf Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upper and (b) lower surface of an englacial lake surveyed by
Comparison of hybrid schemes for the combination of shallow approximations in numerical simulations of the Antarctic Ice Sheet
 doi:10.5194/tc-11-247-2017 Author(s) 2017. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Comparison of hybrid schemes for the combination of shallow approximations in numerical simulations of the Antarctic Ice Sheet Jorge
doi:10.5194/tc-11-247-2017 Author(s) 2017. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Comparison of hybrid schemes for the combination of shallow approximations in numerical simulations of the Antarctic Ice Sheet Jorge
Supplement of Influence of temperature fluctuations on equilibrium ice sheet volume
 Supplement of The Cryosphere, 12, 39 47, 2018 https://doi.org/10.194/tc-12-39-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Supplement of
Supplement of The Cryosphere, 12, 39 47, 2018 https://doi.org/10.194/tc-12-39-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Supplement of
Weakening of nonlinear ENSO under global warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.19/, Weakening of nonlinear ENSO under global warming Tsubasa Kohyama 1, Dennis L. Hartmann 1, and David S. Battisti 1 Key points: Model experiments show
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.19/, Weakening of nonlinear ENSO under global warming Tsubasa Kohyama 1, Dennis L. Hartmann 1, and David S. Battisti 1 Key points: Model experiments show
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
Numerical simulations of cyclic behaviour in the Parallel Ice Sheet Model (PISM)
 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 58, No. 208, 2012 doi: 10.3189/2012JoG11J217 347 Numerical simulations of cyclic behaviour in the Parallel Ice Sheet Model (PISM) Ward J.J. VAN PELT, Johannes OERLEMANS Institute
Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 58, No. 208, 2012 doi: 10.3189/2012JoG11J217 347 Numerical simulations of cyclic behaviour in the Parallel Ice Sheet Model (PISM) Ward J.J. VAN PELT, Johannes OERLEMANS Institute
Total water vapour over polar regions from satellite microwave radiometer (AMSU-B) data and from a regional climate model (HIRHAM)
 Total water vapour over polar regions from satellite microwave radiometer (AMSU-B) data and from a regional climate model (HIRHAM) C. Melsheimer 1, A. Rinke 2, G. Heygster 1, K. Dethloff 2 1 Institut für
Total water vapour over polar regions from satellite microwave radiometer (AMSU-B) data and from a regional climate model (HIRHAM) C. Melsheimer 1, A. Rinke 2, G. Heygster 1, K. Dethloff 2 1 Institut für
The ECMWF coupled assimilation system for climate reanalysis
 The ECMWF coupled assimilation system for climate reanalysis Patrick Laloyaux Earth System Assimilation Section patrick.laloyaux@ecmwf.int Acknowledgement: Eric de Boisseson, Per Dahlgren, Dinand Schepers,
The ECMWF coupled assimilation system for climate reanalysis Patrick Laloyaux Earth System Assimilation Section patrick.laloyaux@ecmwf.int Acknowledgement: Eric de Boisseson, Per Dahlgren, Dinand Schepers,
Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets under 1.5 C global warming
 Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets under 1.5 C global warming Frank Pattyn, Catherine Ritz, Edward Hanna, Xylar Asay-Davis, Rob DeConto, Gaël Durand, Lionel Favier, Xavier Fettweis, Heiko Goelzer, Nicholas
Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets under 1.5 C global warming Frank Pattyn, Catherine Ritz, Edward Hanna, Xylar Asay-Davis, Rob DeConto, Gaël Durand, Lionel Favier, Xavier Fettweis, Heiko Goelzer, Nicholas
Product Validation Report (PVR) H111
 SAF/HSAF/CDOP3/PVR/ Page: 1/21 EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on Support to Operational Hydrology and Water Management http://hsaf.meteoam.it/ SAF/HSAF/CDOP3/PVR/ Page: 2/21 Revision History Revision
SAF/HSAF/CDOP3/PVR/ Page: 1/21 EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on Support to Operational Hydrology and Water Management http://hsaf.meteoam.it/ SAF/HSAF/CDOP3/PVR/ Page: 2/21 Revision History Revision
Ice Sheets and Glaciers
 Ice Sheets and Glaciers Technical University of Denmark Kees van der Veen Department of Geography University of Kansas Why are glaciers and ice sheets important? Large volume of fresh water stored in ice
Ice Sheets and Glaciers Technical University of Denmark Kees van der Veen Department of Geography University of Kansas Why are glaciers and ice sheets important? Large volume of fresh water stored in ice
RUSSIAN ARCTIC COASTAL DYNAMICS HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL FORCING: HALF-CENTURY HYSTORY AND CURRENT STATE. Abstract
 RUSSIAN ARCTIC COASTAL DYNAMICS HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL FORCING: HALF-CENTURY HYSTORY AND CURRENT STATE Natalia Shabanova1, Stanislav Ogorodov 1, Fedor Romanenko Abstract The Arctic coasts are dynamically
RUSSIAN ARCTIC COASTAL DYNAMICS HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL FORCING: HALF-CENTURY HYSTORY AND CURRENT STATE Natalia Shabanova1, Stanislav Ogorodov 1, Fedor Romanenko Abstract The Arctic coasts are dynamically
Figure ES1 demonstrates that along the sledging
 UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
1. Methods: Description of the climate model LOVECLIM
 SWINGEDOUW ET AL.: SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATIONS X - 1 1. Methods: Description of the climate model LOVECLIM LOVECLIM consists of five components representing the atmosphere (ECBilt), the ocean and sea ice
SWINGEDOUW ET AL.: SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATIONS X - 1 1. Methods: Description of the climate model LOVECLIM LOVECLIM consists of five components representing the atmosphere (ECBilt), the ocean and sea ice
The role of the Himalaya and the Tibetan Plateau for the Indian Monsoon
 June, 7 th June, 14 th 2009 The role of the Himalaya and the Tibetan Plateau for the Indian Monsoon Prof. Dr. Klaus Dethloff (AWI Potsdam) Stefan Polanski (AWI Potsdam 2008-2010) Dr. Annette Rinke (AWI
June, 7 th June, 14 th 2009 The role of the Himalaya and the Tibetan Plateau for the Indian Monsoon Prof. Dr. Klaus Dethloff (AWI Potsdam) Stefan Polanski (AWI Potsdam 2008-2010) Dr. Annette Rinke (AWI
DEVELOPMENT OF A DOWNSCALING MODEL FOR ESTIMATION OF AN 'ARTIFICIAL ICE CORE' DERIVED FROM LARGE SCALE PARAMETERS OF A 1000 YEAR GCM RUN
 PRACE GEOGRAFICZNE, zeszyt 107 Instytut Geografii UJ Krak6w 2000 Traute Criiger, Hans von Storch DEVELOPMENT OF A DOWNSCALING MODEL FOR ESTIMATION OF AN 'ARTIFICIAL ICE CORE' DERIVED FROM LARGE SCALE PARAMETERS
PRACE GEOGRAFICZNE, zeszyt 107 Instytut Geografii UJ Krak6w 2000 Traute Criiger, Hans von Storch DEVELOPMENT OF A DOWNSCALING MODEL FOR ESTIMATION OF AN 'ARTIFICIAL ICE CORE' DERIVED FROM LARGE SCALE PARAMETERS
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
Ice-sheet model sensitivities to environmental forcing and their use in projecting future sea level (the SeaRISE project)
 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 59, No. 214, 2013 doi:10.3189/2013jog12j125 195 Ice-sheet model sensitivities to environmental forcing and their use in projecting future sea level (the SeaRISE project) Robert
Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 59, No. 214, 2013 doi:10.3189/2013jog12j125 195 Ice-sheet model sensitivities to environmental forcing and their use in projecting future sea level (the SeaRISE project) Robert
The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data
 The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data Jianping Guo 1*, Yucong Miao 1, Yong Zhang 2, Huan Liu 1, Zhanqing Li 3, 4 *, Wanchun Zhang 1, Jing
The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data Jianping Guo 1*, Yucong Miao 1, Yong Zhang 2, Huan Liu 1, Zhanqing Li 3, 4 *, Wanchun Zhang 1, Jing
Near-surface observations for coupled atmosphere-ocean reanalysis
 Near-surface observations for coupled atmosphere-ocean reanalysis Patrick Laloyaux Acknowledgement: Clément Albergel, Magdalena Balmaseda, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Dick Dee, Paul Poli, Patricia de Rosnay, Adrian
Near-surface observations for coupled atmosphere-ocean reanalysis Patrick Laloyaux Acknowledgement: Clément Albergel, Magdalena Balmaseda, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Dick Dee, Paul Poli, Patricia de Rosnay, Adrian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1840 RECENT MULTIDECADAL STRENGTHENING OF THE WALKER CIRCULATION ACROSS THE TROPICAL PACIFIC (1) Supplementary_Figures.pdf Adobe document 1.5MB SI Guide Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1840 RECENT MULTIDECADAL STRENGTHENING OF THE WALKER CIRCULATION ACROSS THE TROPICAL PACIFIC (1) Supplementary_Figures.pdf Adobe document 1.5MB SI Guide Supplementary
Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction
 1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
