Estimating effective damping introduced by a Pendulum Tuned Mass Damper using the Extended Kalman Filter
|
|
|
- Roy Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 Poto, Potugl, 3 Jun - July 4 A. Cunh, E. Ctno, P. Ribio, G. Müll (ds. ISSN: 3-9; ISBN: Estimting ffctiv dmping intoducd by Pndulum und Mss Dmp using th Extndd Klmn Filt Aon J. Roffl, Sim Nsimhn Stff II Stuctus, Engining Mchnics & Infstuctu, Simpson, Gumptz & Hg Inc., 4 Syon Stt, Wlthm, Msschustts, 453, Unitd Stts Associt Pofsso, Dptmnt of Civil & Envionmntl Engining, Univsity of Wtloo, Univsity Avnu Wst, Wtloo, Ontio, NL 3G, Cnd mil: joffl@sgh.com, snsim@uwtloo.c ABSRAC: Pndulum tund mss dmps (PMDs common uxiliy dmping dvics usd to ttnut xcssiv motion in tll stuctus. h concpt of ffctiv o quivlnt dmping is commonly fncd whn quntifying tund mss dmp (MD pfomnc. Effctiv dmping fs to dtmining th dmping in singl-dg-of-fdom (SDOF oscillto opting t th sm ntul fquncy tht would poduc n qul mn squd displcmnt spons s th combind min nd uxiliy systm. Dspit its simplicity, ffctiv dmping intoducd by MD hs xpincd ltivly littl us in dscibing th pfomnc of in-svic MDs, sinc its thoticl computtion is bsd on th displcmnt spons of th stuctu, which is sldom msud. Instd, ccltion spons msumnts tn fom which displcmnts nd to b infd. h poposd mthod pplis th xtndd Klmn filt fo combind stt nd pmt stimtion fo th pupos of stimting th ffctiv dmping intoducd by PMD. h ccltion spons msumnts fittd to th spons of SDOF systm, wh th unnown modl dmping is ppndd to th stt vcto nd stimtd. h ssumption of nown b stuctu ntul fquncy is subsquntly lxd nd th ntul fquncy of th stuctu without th PMD is stimtd longsid th ffctiv dmping. h lgoithm is fist dmonsttd using numicl xmpl nd compd to th thoticl clcultion. h mthodology is lso shown using full-scl ccltion spons msumnts collctd fom stuctu quippd with PMD. h sults of th study dmonstt th ppoch is n ccut nd libl mns of quntifying th pfomnc of in-svic PMDs without dict msu of th displcmnt spons of th ttnutd stuctu nd pioi nowldg of th undlying stuctu s ntul fquncy. KEY WORDS: Effctiv dmping, Equivlnt dmping, und mss dmps, Extndd Klmn filt INRODUCION und mss dmps (MDs dvics, usd in stuctus suscptibl to vibtions, which intoduc supplmntl dmping to ttnut th sponss. MDs consist of smll intil mss with stiffnss nd dmping lmnts. h stiffnss lmnt is gnlly sping usd to djust th fquncy chctistics of th dvic to closly mtch th min stuctu fquncy fo th mod of vibtion to b contolld; ltntivly, suspndd mss is usd wh fquncy djustmnt is pfomd by chnging th suspnsion lngth, nown s pndulum tund mss dmp (PMD. MDs dsignd to minimiz th oot mn squ (RMS displcmnt o ccltion spons of th stuctu, o to mximiz th ffctiv o quivlnt dmping intoducd. h ltt tm fs to th lvl of modl dmping in singl-dg-of-fdom (SDOF oscillto opting t th sm fquncy s th contolld mod of vibtion (gnlly th mod with th lgst contibution to th ovll spons tht would poduc th sm RMS displcmnt spons s th ttnutd systm. hoticl qutions lting th vious min nd uxiliy systm pmts (fquncy tio, mss tio, min mss dmping tio, nd uxiliy mss dmping tio to th ffctiv dmping [7,, 6] commonly usd in pdicting th pfomnc of MD duing th dsign phs; howv, th msu hs xpincd ltivly littl us in dscibing th pfomnc of in-svic MDs. his is bcus th computtion is bsd on th msud RMS displcmnt spons of th min stuctu, which is gnlly impcticl to msu dictly. his is pticully tu fo flxibl tll stuctus, which most suscptibl to wind-inducd vibtions nd commonly mploy MDs. h ccltion sponss usully msud, fom which th displcmnts nd to b infd. h noisy ntu of ccltion spons msumnts pclud dict intgtion fo th displcmnt spons, nd initil nd finl t-st ssumptions to coct cclomt bis gnlly not ppopit fo wind-xcitd stuctus. h issu is of pticul significnc whn it must b dmonsttd tht pscibd lvl of ffctiv dmping hs bn chivd. h cunt wo poposs using concpt nown s stt stimtion to dtmin th ffctiv dmping intoducd by th PMD. PMDs considd xclusivly hft, but th concpts cn b dily pplid to convntionl MDs. Stt stimtion is pfomd by modling pocss in od to povid n stimt of n intnl (gnlly unobsvd stt givn th msumnt of th ctul systm. A mthmticl modl of nown physicl systm is dvlopd lting th nown inputs, msud outputs, nd unnown intnl stts to b dtmind. Clssiclly, this hs bn ccomplishd using th Klmn filt [9, 8]. Estimting th ffctiv dmping is combind stt nd pmt stimtion poblm, which is inhntly nonlin, nd quis th ltd xtndd Klmn filt (EKF. h pp is ognizd s follows. Fist, bif thoticl bcgound of PMDs nd ffctiv dmping is intoducd. 543
2 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 Scond, th concpt of combind stt nd pmt stimtion using th EKF is psntd. hid, th ffctiv dmping fo simpl numicl modl with nown ntul fquncy is stimtd nd compd with th thoticl clcultion. Finlly, th ffctiv dmping of full-scl stuctu is stimtd using ccltion spons msumnts; in this instnc, th quimnt of nown fquncy fo th contolld mod of vibtion fo th b stuctu is lxd. h findings dmonstt tht th poposd mthodology is ccut nd libl fo stimting th ffctiv dmping intoducd by PMD on n in-svic stuctu. Figu. Schmtic gomty of PMD ttnutd systm xpssd in modl coodints. HEOREICAL COMPUAION OF EFFECIVE DAMPING h concpt of ffctiv o quivlnt dmping intoducd by MD ws fist poposd by Vicy [7] nd McNm []. h mthod ss to mtch th mn squ displcmnt spons of th MD-ttnutd systm with SDOF oscillto opting t th sm fquncy of th contolld mod. h dmping in th SDOF systm is th ffctiv dmping of th ttnutd stuctu. Equtions lting th pmts of th min nd uxiliy systms of th MD-quippd stuctu to th ffctiv dmping hv bn dvlopd fo min mss xcitd [] nd bs xcitd stuctus [8] with convntionl tnsltionl MDs nd PMDs. PMDs considd hin, but th concpts cn b sily pplid to convntionl MDs. h qutions of motion fo PMD ttnutd stuctu (Figu xpssd in modl coodints s follows: M &&y(t + C &y(t + K y j (t + m && θ L = F (t m L θ(t && + c h θ(t & + ( m gl + h θ(t ( +m L&&y(t = wh M, C, K, nd F ( t th modl mss, dmping, stiffnss, nd foc nd yt ( is th modl coodint. θ ( t is th ottion of th uxiliy mss, m, with uxiliy dmping, c, nd stiffnss,. L is th lngth of th pndulum nd h is th lngth to th ttchmnt of th uxiliy sping nd dmping. h function i t Ft ( = ω is slctd in od to comput th complx fquncy spons functions, y H iω nd H ( i θ ω, wh ω is th focing fquncy. h sponss thn F ( t yt ( = Hy ( iω K ( F ( t θ( t = Hθ ( iω KL Computing th fist nd scond divtiv of th sponss in Equtions ( nd substituting into Equtions ( givs ω M / + m + iωc + K ω m H L y K = ω ml H / K L ω ml + iωch + h θ (3 ω = K M is th cicul ntul fquncy. wh n Eqution (3 is solvd simultnously fo th complx fquncy spons functions, plcing som of th tms with thi non-dimnsionl countpts. h non-dimnsionl focing fquncy is φ ω ω = (4 n h non-dimnsionl uxiliy to min mss tio is m μ = (5 M ζ nd ζ th min nd uxiliy dmping tios. h complx fquncy spons functions 544
3 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 wh H y H θ φ ( + iφ f iω = ζ + f φ 4 iφ 3 A φ B+ iφc + f φ ( iω = φ 4 iφ 3 A φ B+ iφc + f f ζ f + 4 f ζζ ( f ζ +ζ A f ζ A= ζ + + μ B = + + μ C = f D = ζ + + μ Fo th cs of whit nois with constnt spctl dnsity, S, th mn squ sponss [8] ω ns E y( t = H y i d K φ φ (8 ω ns E θ ( t = H ( i d θ φ φ KL Fo SDOF oscillto opting t th sm fquncy s th ttnutd systm with modl dmping, ζ, th mn squ spons is [6] n Kζ (6 (7 ω S E y( t = (9 Equting th Equtions (8 nd (9 fo th min stuctu modl sponss, th thoticl vlu fo th ffctiv dmping fo th combind min nd uxiliy systm is ζ = ( C BD C f D f BD C + A( ζ + C wh A, B, C, nd D dfind in Eqution (7. ( 3 EXENDED KALMAN FILER FOR COMBINED SAE AND PARAMEER ESIMAION Stt stimtion quis nown mthmticl modl to psnt physicl systm, nd ss to stimt unnown intnl stts by lting thm to msud outputs. h Klmn filt ddsss th poblm of stimting th stt x bsd on nowldg of th lin disct-tim pocss givn by x ( = A x + G u + w wh A, G, nd C th systm, input, nd msumnt mtics, u is th nown input, nd w nd v th unnown pocss nd msumnt noiss with covinc Q nd R, spctivly. Whn th modl pmts unnown (s is th cs whn th ffctiv dmping pmt is to b stimtd, th convntionl ppoch is to ppnd th unnown pmts to th stt vcto with constnt tnsitions, nd pfom tditionl stt stimtion. Howv, th systm of qutions bcom nonlin (dspit th fct tht undlying systm is lin du to th psnc of stts (ppndd pmts in th systm nd msumnt mtics, poducing poduct of stts within th tnsition nd msumnt qutions. h EKF is pplid fo nonlin stt stimtion. h EKF is Klmn filt tht linizs bout th cunt mn nd covinc. Fo wind-xcitd stuctus, th input is gnlly unnown. Fo th cs of ccltion spons msumnts of windxcitd stuctus, th is lso dict fd-though of th unnown input in th msumnt qution. Fo th cs of unnown fd-though stochstic distubnc nois, d with covinc S, th tnsition of th stts is govnd by th following nonlin diffnc qution: ( x d + x (3 = f, w with noisy msumnt givn by ( x d z = h, + v (4 Fo th s of bvity, th d is fd lswh fo dtild divtion of th EKF fo th bov systm [4]; summy is povidd nxt. Fo ch tim stp, th filt qutions f (, h(, J = E S F F S F + R = + J z P = A J C P A J C + E S E + Q J F S E J is on-stp pdicto gin mtix, x is th pioi (whn ll msumnts up to vilbl stimt of th stt x, nd ˆ (5 with noisy msumnt z givn by z C x + v = ( 545
4 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 A E C F ( x, f = x ( xd, f = d ( x, h = x ( xd, h = d (6 th Jcobin mtics of ptil divtivs of f ( x,, f ( xd,, h( h,, nd h( xd, with spct to x nd d, vlutd t th cunt o pvious pioi stt stimt. P is th pioi stt stimt o covinc. Aft nw msumnt is tn, th msumnt updt qutions ( h( K = P C C P C + F S F + R ˆ ˆ = x + K z x, P = I K C P K is th Klmn gin, ˆ (7 x is th postioi (whn ll msumnts up to nd including vilbl stt stimt nd P is th cosponding stt stimt o covinc. An updtd stimt of th msumnt is givn by [7] zˆ = h ( ( ˆ h, + FS F FS F + R z x h lgoithm is initilizd s follows: P = E = E [ x ] [( x ( x ] (8 (9 Klmn filting quis nowldg of th unnown stochstic distubnc nois, pocss nois, nd msumnt nois covinc mtics S, Q, nd R. hs sttistics gnlly unnown fo mbint vibtion msumnts of wind-xcitd stuctus, nd thfo must b fist stimtd fom th msud dt. A nois covinc stimtion ppoch fist poposd by Bélng [3] nd dptd by Roffl [4] fo th cs of th dict fd-though of n unnown distubnc nois is usd in this nlysis. 4 ESIMAING EFFECIVE DAMPING USING HE EXENDED KALMAN FILER h ffctiv dmping of n in-svic PMD cn b computd using Eqution (9, povidd th displcmnt spons msumnts vilbl. Estimting th ffctiv dmping intoducd by th PMD using th EKF is poposd to ovcom th chllng of lc of vilbl displcmnt spons msumnts of th ttnutd systm. In th simplst cs, th ntul fquncy of th min stuctu (without th PMD nd min mss is nown, nd th only unnown pmt is th ffctiv dmping. 4. Effctiv Dmping Estimtion fo SDOF Oscillto with PMD h EKF lgoithm is fist pplid to synthtic ccltion spons dt gntd fo SDOF min systm quippd with PMD; th stimtd ffctiv dmping is compd with th thoticl vlu computd using Eqution (. Sinc th ffctiv dmping is stimtd in th modl domin, th msumnts fit to SDOF systm xpssd in modl coodints. h modl displcmnt nd ccltion slctd s th stts of th systm. x(t = x (t x (t x 3 (t = y(t &y(t ζ ( Following disctiztion, th nonlin tnsition qutions x[ + ] = x[ ] + x[ ] + w[ ] x[ + ] = x[ ] + x3[ ] x[ ] m m + d[ ] + w[ ] m x [ + ] = x [ ] + w [ ] wh = [ ] ( w [ ] [ ] 3[ ] w w w th dditiv pocss nois tms with covinc Q nd d [ ] is th unnown stochstic input with covinc S. h msumnt qution is z[ ] = x[ ] x3[ ] x[ ] + d[ ] + v[ ] ( m m m wh v [ ] is th dditiv msumnt nois with covinc R. h synthtic ccltion spons dt fom th PMD ttnutd stuctu is gntd using th mthmticl modl of th systm using whit nois xcittion with th following pmt vlus. h min nd uxiliy msss m = g nd m = g, spctivly. h min stuctu stiffnss is = N/m, sulting in ntul fquncy of f =.5 Hz ( ω n = 3.6 d/s. h dmping cofficint is slctd bsd on modl dmping tio of 546
5 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 ζ =.. h fquncy tio is f =.996, sulting in n optiml pndulum lngth of L=.995 bsd on th slction of optiml PMD pmts vilbl in th littu [8]. h initil stimt of th ppndd pmt is ˆ ζ =.. h initil stt stimt o covinc is, slctd s % of th initil stt stimt. On hundd liztions of filt tht ws sconds long w un. h vg finl stimt of th ffctiv dmping ws ˆ ζ.33 = with cofficint of vition (COV of c ˆv = 9.55%. his psnts.3% o whn compd to th thoticl vlu of th ffctiv dmping computd li. his dmonstts tht th EKF lgoithm is cn ccutly nd consistntly stimt th ffctiv dmping intoducd by th PMD. h thoticl ffctiv dmping fo th ttnutd systm is ζ =.38 bsd on Eqution (. h stimtion of th ffctiv dmping is plottd with tim nd compd to th thoticl vlu in Figu. h mthodology is now xtndd fo unixil multi-dg-of-fdom systms quippd with PMD. x[ + ] = x[ ] + x [ ] + w[ ] x [ ] x[ ] x [ ] x [ ] + = ωn, j +, 3 + φ jd + w[ ] M, j x [ + ] = x [ ] + w [ ] wh ω n, j, φ j, nd, j ( ωn j (3 M th ntul fquncy, mod shp vcto, nd modl mss fo th contolld mod, spctivly. h msumnt qutions z (, x [ ], x3[ ] x[ ] = φ ω ω j n j n j + φ φ d + v j j M, j (4 h pfomnc of th ffctiv dmping stimtion fo th PMD-quippd MDOF systm is dmonsttd nxt using msumnt dt fom full-scl stuctu. 5 EFFECIVE DAMPING ESIMAION FROM FULL- SCALE MEASUREMEN DAA h Apon ow t Pson Intntionl Aipot in oonto, Ontio, Cnd is considd s th tst bd fo dmonstting th lgoithm fo stimting ffctiv dmping intoducd by PMD (Figu 3. h tow iss 49 m bov th tminl oof blow. It is stl stuctu, with igid diphgm floos nd combintion of bcd nd momnt fms to sist ltl lods. h tow consists of six min columns nd sts on sis of lg tnsf gids t th oof lvl of th suppoting tminl. h fundmntl mod of vibtion is ppoximtly.67 Hz in th noth-south (y- diction. Figu. Effctiv dmping stimtion fo SDOF PMDttnutd systm. 4. Effctiv Dmping Estimtion fo MDOF Stuctu With PMD Fo MDOF systm, th ddd compliction is th gt numb of msumnts nd th incsd numb of mods in th stuctu without th PMD. h sttgy is to pfom modl tnsfomtion within th msumnt qution in od to lt th stts (modl displcmnts nd vlocitis fo th contolld mod of vibtion to th msumnts t th dgs of fdom (DOF using th mod shp vcto. hfo, th modl mss nd mod shp vcto fo th contolld mod, in ddition to th ntul fquncy, must b nown pioi. Fo th MDOF systm, th tnsition qutions s follows (using th sm slction of stts s pviously: Figu 3. Apon ow t oonto Pson Intntionl Aipot. Du to th stuctu s inhnt flxibility nd suscptibility to wind lods, it is quippd with pi of PMDs loctd within th tuss oof stuctu (Figu 4. h PMDs w instlld to duc us discomfot du to motion duing high wind vnts. Ech mss is 5, g, psnting mss tio of μ =.4%. 547
6 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 Figu 4. PMD instlld in oof stuctu of Apon ow. h PMDs suspndd by sis of cbls fom th stuctul stl bov; ch cbl is xctly vticl whn th PMD is t st, pvnting ocing mod nd nsuing th PMD bhvs s point mss. It is gnlly difficult to pdict th ctul fquncis of th b stuctu duing th dsign phs to th dg of ccucy ncssy to tun th PMD. hfo, it is quippd with n djustmnt mchnism to djust th pndulum lngth. h msud lngth ws.57 m. Ech mss is quippd with fou doubl-cting fluid viscous dmps (two in ch hoizontl diction with p dmping foc of 3. N nd mximum sto of 78 mm. h dmping foc is vlocity-squd popotionl; th quivlnt lin viscous dmping cofficint ws clcultd 3 to b c =.3 N m/s [3]. 5. Msumnt Pogm An xtnsiv msumnt pogm ws conductd, wh th stuctu ws instumntd with sismic cclomts long th hight of th stuctu. Svl significnt wind vnts w msud, duing which high-fidlity msumnts w obtind contin ngy in svl mods. h stuctu ws instumntd with PCB Pizotonics high snsitivity sismic cmic flxul ICP cclomts. hs snsos idl fo low-fquncy vibtions nd povid stong output signl with high signl to nois tios. h dt ws msud continuously t smpling t of Hz. n snsos w instlld hoizontlly on th thid nd fist uppmost floos s wll s th top chod of th oof tuss stuctu. h snsos w ngd such tht th ltl motion in ch diction s wll s th ottion bout th vticl xis could b msud. h mining snsos w instlld in ch hoizontl diction on on of th PMDs to gth ltl ccltion spons msumnts of th uxiliy mss. A totl of ppoximtly 3 hous nd minuts of dt w collctd duing significnt wind vnt. h EKF ffctiv dmping lgoithm is pplid sptly in ch spons diction. Sinc th fundmntl mod of vibtion is nown to b in th noth-south (y- diction, only th y-diction spons is considd futh. 5. Filt Initiliztion h ffctiv dmping stimtion hs so f lid on pioi nowldg of th fquncy nd modl mss fo th contolld mod of vibtion. Altntivly, th qutions of motion fo PMD-quippd stuctu cn b cst in such wy tht th modl chctistics of th b stuctu (ntul fquncy, dmping tio, nd mod shp vctos of th stuctu without th PMD cn b stimtd ith in dvnc of o simultnously with th ffctiv dmping. A dtild ttmnt of this ppoch hs bn dvlopd by Roffl [4], nd is usd in th psnt nlysis fo poviding th cunt stimt of th ntul fquncy nd mod shp vcto fo th ffctiv dmping stimtion filt. hfo, two simultnous EKFs un. h fist filt stimts th b stuctu ntul fquncy, dmping tio, nd mod shp. h scond filt uss th cunt stimt of th ntul fquncy nd mod shp vcto fo th b stuctu nd stimts th ffctiv dmping of th combind min nd uxiliy mss systm. A sonbl stimt of th modl mss fo th contolld mod usd thoughout th filt option, s wll s th initil ntul fquncy nd mod shp stimts, ws stblishd by dvloping finit lmnt modl of th stuctu using softw pcg SAP [5]. h initil stimt of th ntul fquncy of th contolld mod is.656 Hz; th initil dmping stimt fo th b stuctu ws slctd s.5%. h nois covinc mtics w stblishd using th stimtion ppoch mntiond li. h dt sts w split into non-ovlpping dt sts ch with totl lngth of minuts. Ech st ws smpld t 4 Hz in od to limit th ffct of th ppoximtion intoducd by th disctiztion ppoch. 5.3 Effctiv Dmping Idntifiction Rsults h fist mod ntul fquncy, vgd ov th liztions of th filt, is shown in Figu 5. h ws sonbly fst convgnc on th finl stimt of f n, =.676 Hz with high dg of confidnc ( c ˆv =.98%. h initil nd finl convgd stimt of th mod shp vcto fo th contolld mod is shown in Figu 6. h finl stimt of th b stuctul dmping tio is ˆ ζ =.8. Figu 5. Ntul fquncy stimt fo th contolld mod of vibtion. 548
7 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 pfom sttisticl nlysis using vious vnts ov piod of tim in od to btt stblish th pfomnc of th PMD. h poposd ppoch is vy mnbl to this, s th lgoithm cn sily b implmntd in l tim nd cn continuously povid n stimt on th ffctiv dmping of th systm. Figu 6. Initil nd finl stimt of th mod shp vcto fo th contolld mod of vibtion. h ffctiv dmping EKF is un simultnously with th filt stimting th b stuctul modl chctistics. At ch tim stp,, th cunt stimt of th cicul ntul fquncy, ω n, j, nd th mod shp vcto, φ j, usd to updt th nown modl pmts in th ffctiv dmping filt (Equtions 3 nd 4. h initil stimt of th ffctiv dmping is 7.5% ( ˆ ζ, =.75. h nois covinc mtics, S nd R, th sm usd fo th b stuctu modl idntifiction filt. h pfomnc of th ffctiv dmping stimtion, vgd ov th liztions of th filt, is shown in Figu 7. h finl convgd vlu is ˆ ζ =.36 with COV of c ˆv = 8.%. his psnts n incs in dmping intoducd by th PMD of Δ ζ =.88. h sults within th ng of th xpctd pfomnc of PMDs [5]. Figu 7. Estimtion of ffctiv dmping intoducd by th Apon ow PMDs. h vition in th finl convgd stimt of th ffctiv dmping coss th dt sts is du to th fct tht dmping in stuctus is blivd to b dpndnt on th lvl nd ntu of th xcittion. Although th concpt of viscous dmping is indpndnt of th mplitud of th xcittion [], it is usd in this cs to modl n inhntly mo complx phnomnon. his vlu is xpctd to vy dpnding on th tun piod of th spcific wind vnts. A mo comphnsiv ssssmnt of th pfomnc would 6 CONCLUSIONS h EKF lgoithm is n ccut nd libl mns of stimting th ffctiv dmping intoducd by th PMD. Whn th opting fquncy of th ffctiv dmping systm is nown, th o in th stimt ws only.3% whn compd to th thoticl vlu. h lgoithm ws xtndd to stimt ffctiv dmping whn th modl chctistics of th undlying stuctu w unnown. h lgoithm cn b implmntd onlin, nd povid l tim msu of th ffctiv dmping fo th pticul loding vnt. h pimy dvntg of th ppoch is ovcoming issus ltd th lc of libl mns of msuing o infing th displcmnt spons of th ttnutd stuctu. ACKNOWLEDGEMENS h uthos gtful to th Ntul Scinc nd Engining Rsch Council of Cnd (NSERC nd th Ontio Cnts of Excllnc (OCE fo poviding finncil suppot fo this wo. h uthos lso thn th Gt oonto Aipots Authoity (GAA nd Rown Willims Dvis nd Iwin, Inc. (RWDI who sv s industil ptns in this sch. Insights on th pcticl dsign spcts of MDs by Gg hompson, Scott Gmbl, D. Pt Iwin, nd vo Hstt of RWDI gtfully cnowldgd. his wo ws md possibl by th fcilitis of th Shd Hichicl Acdmic Rsch Computing Ntwo (SHARCNE nd Comput/Clcul Cnd [4]. REFERENCES [] J. Simpson nd E. Win, Eds., h Oxfod English dictiony, Clndon Pss, Oxfod, UK, scond dition, 989. [] Buu Intntionl ds Poids t Msus, h intntionl systm of units (SI, BIPM, Pis, Fnc, ighth dition, 6. [3] P. R. Bélng, Estimtion of nois covinc mtics fo lin tim-vying stochstic pocss, Automtic, (3:67-75, 974. [4] Comput/Clcul Cnd, Shd Hichicl Acdmic Rsch Computing Ntwo (SHARCNE,. [5] Computs nd Stuctus Inc., SAP, Vsion..8, 8. [6] S. H. Cndll nd W. D. M, Rndom Vibtions in Mchnicl Systms, Acdmic Pss, 963. [7] G. A. Einic nd L. B. Whit, Robust xtndd Klmn filting, IEEE nsctions on Signl Pocssing, 47(9: , 999. [8] R. R. Ggs nd B. J. Vicy, Optiml dsign of pndulum-typ tund mss dmps, h Stuctul Dsign of ll nd Spcil Buildings, 4(4: , 5. [9] R. E. Klmn, A nw ppoch to lin filting nd pdiction poblms, nsctions of th ASME Jounl of Bsic Engining, 8(Sis D:35-45, 96. [] A. Km nd K. Guly, Dmping in stuctus: its vlution nd ttmnt of unctinty, Jounl of Wind Engining nd Industil Aodynmics, 59(-3:3-57, 996. [] K. C. S. Kwo nd B. Smli, Pfomnc of tund mss dmps und wind lods, Engining Stuctus, 7(9: , 995. [] R. J. McNm, und mss dmps fo buildings, ASCE Jounl of Stuctul Division, 3(9: , 977. [3] G. Pcn, J. B. Mnd, nd S. S. Chn, Fundmntl considtions fo th dsign of non-lin viscous dmps, Ethqu Engining nd Stuctul Dynmics, 8(:45-45,
8 Pocdings of th 9th Intntionl Confnc on Stuctul Dynmics, EURODYN 4 [4] A. J. Roffl, Condition ssssmnt of in-svic pndulum tund mss dmps, Doctol dissttion, Univsity of Wtloo, Wtloo, Ontio,. [5] M. P. Scs nd J. C. Swllow, und mss dmps fo tow nd buildings, Pocdings of th Symposium of Stuctul Engining in Ntul Hzds Mitigtion, , 993. [6] H. n nd C. Y. M, Effct of tund mss dmps on wind inducd spons of tll buildings, Jounl of Win Engining nd Industil Aodynmics, 4(-3: , 983. [7] B. J. Vicy nd A. G. Dvnpot, An invstigtion of th bhvio in wind of th poposd Cntpoint ow in Sydny, Austli, Engining Scinc Rsch Rpot, Univsity of Wstn Ontio, Fculty of Engining Scinc, 97. [8] G. Wlch nd G. Bishop, An intoduction to th Klmn filt, IEEE nsctions on Rlibility,. 55
C-Curves. An alternative to the use of hyperbolic decline curves S E R A F I M. Prepared by: Serafim Ltd. P. +44 (0)
 An ltntiv to th us of hypolic dclin cuvs Ppd y: Sfim Ltd S E R A F I M info@sfimltd.com P. +44 (02890 4206 www.sfimltd.com Contnts Contnts... i Intoduction... Initil ssumptions... Solving fo cumultiv...
An ltntiv to th us of hypolic dclin cuvs Ppd y: Sfim Ltd S E R A F I M info@sfimltd.com P. +44 (02890 4206 www.sfimltd.com Contnts Contnts... i Intoduction... Initil ssumptions... Solving fo cumultiv...
Path (space curve) Osculating plane
 Fo th cuilin motion of pticl in spc th fomuls did fo pln cuilin motion still lid. But th my b n infinit numb of nomls fo tngnt dwn to spc cu. Whn th t nd t ' unit ctos mod to sm oigin by kping thi ointtions
Fo th cuilin motion of pticl in spc th fomuls did fo pln cuilin motion still lid. But th my b n infinit numb of nomls fo tngnt dwn to spc cu. Whn th t nd t ' unit ctos mod to sm oigin by kping thi ointtions
Theory of Spatial Problems
 Chpt 7 ho of Sptil Polms 7. Diffntil tions of iliim (-D) Z Y X Inol si nknon stss componnts:. 7- 7. Stt of Stss t Point t n sfc ith otd noml N th sfc componnts ltd to (dtmind ) th 6 stss componnts X N
Chpt 7 ho of Sptil Polms 7. Diffntil tions of iliim (-D) Z Y X Inol si nknon stss componnts:. 7- 7. Stt of Stss t Point t n sfc ith otd noml N th sfc componnts ltd to (dtmind ) th 6 stss componnts X N
Part II, Measures Other Than Conversion I. Apr/ Spring 1
 Pt II, Msus Oth hn onvsion I p/7 11 Sping 1 Pt II, Msus Oth hn onvsion II p/7 11 Sping . pplictions/exmpls of th RE lgoithm I Gs Phs Elmnty Rction dditionl Infomtion Only fd P = 8. tm = 5 K =. mol/dm 3
Pt II, Msus Oth hn onvsion I p/7 11 Sping 1 Pt II, Msus Oth hn onvsion II p/7 11 Sping . pplictions/exmpls of th RE lgoithm I Gs Phs Elmnty Rction dditionl Infomtion Only fd P = 8. tm = 5 K =. mol/dm 3
E. Computation of Permanent Magnetic Fields
 E. Computtion of Pmnnt Mgntic Filds Th following pssgs should giv n impssion, how pmnnt mgnts cn b clcultd in spct of thi fild distibution. This ovviw ctinl cnnot cov ll subjcts. It will ml intoduc th
E. Computtion of Pmnnt Mgntic Filds Th following pssgs should giv n impssion, how pmnnt mgnts cn b clcultd in spct of thi fild distibution. This ovviw ctinl cnnot cov ll subjcts. It will ml intoduc th
E F. and H v. or A r and F r are dual of each other.
 A Duality Thom: Consid th following quations as an xampl = A = F μ ε H A E A = jωa j ωμε A + β A = μ J μ A x y, z = J, y, z 4π E F ( A = jω F j ( F j β H F ωμε F + β F = ε M jβ ε F x, y, z = M, y, z 4π
A Duality Thom: Consid th following quations as an xampl = A = F μ ε H A E A = jωa j ωμε A + β A = μ J μ A x y, z = J, y, z 4π E F ( A = jω F j ( F j β H F ωμε F + β F = ε M jβ ε F x, y, z = M, y, z 4π
40th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit January 14 17, 2002/Reno, NV
 AIAA 2002 0788 Rsistnc Appoc fo Annul Fins wit Contct Conductnc nd End Cooling Susnt K. Mit nd M. Micl Yovnovic Dptmnt of Mcnicl Engining, Univsity of Wtloo, Wtloo, Cnd, N2 3G 40t AIAA Aospc Scincs Mting
AIAA 2002 0788 Rsistnc Appoc fo Annul Fins wit Contct Conductnc nd End Cooling Susnt K. Mit nd M. Micl Yovnovic Dptmnt of Mcnicl Engining, Univsity of Wtloo, Wtloo, Cnd, N2 3G 40t AIAA Aospc Scincs Mting
ELEC 351 Notes Set #18
 Assignmnt #8 Poblm 9. Poblm 9.7 Poblm 9. Poblm 9.3 Poblm 9.4 LC 35 Nots St #8 Antnns gin nd fficincy Antnns dipol ntnn Hlf wv dipol Fiis tnsmission qution Fiis tnsmission qution Do this ssignmnt by Novmb
Assignmnt #8 Poblm 9. Poblm 9.7 Poblm 9. Poblm 9.3 Poblm 9.4 LC 35 Nots St #8 Antnns gin nd fficincy Antnns dipol ntnn Hlf wv dipol Fiis tnsmission qution Fiis tnsmission qution Do this ssignmnt by Novmb
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 9, September ISSN
 Intntinl Junl f Scintific & Engining Rsch, Vlum, Issu 9, Sptmb- bstct: Jcbin intgl nd Stbility f th quilibium psitin f th cnt f mss f n xtnsibl cbl cnnctd stllits systm in th lliptic bit. Vijy Kum ssistnt
Intntinl Junl f Scintific & Engining Rsch, Vlum, Issu 9, Sptmb- bstct: Jcbin intgl nd Stbility f th quilibium psitin f th cnt f mss f n xtnsibl cbl cnnctd stllits systm in th lliptic bit. Vijy Kum ssistnt
[2009] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from Xu, Wei; Zhu, Jianguo; Tan, Longcheng; Guo, Youguang; Wang, Shuhong; Wang, Yi. 2009, 'Optimal Design of
![[2009] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from Xu, Wei; Zhu, Jianguo; Tan, Longcheng; Guo, Youguang; Wang, Shuhong; Wang, Yi. 2009, 'Optimal Design of [2009] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from Xu, Wei; Zhu, Jianguo; Tan, Longcheng; Guo, Youguang; Wang, Shuhong; Wang, Yi. 2009, 'Optimal Design of](/thumbs/73/68734881.jpg) [9] IEEE. Rpintd, with pmission, fom Xu, Wi; Zhu, Jinguo; Tn, Longchng; Guo, Yougung; Wng, Shuhong; Wng, Yi. 9, Dsign of Lin Induction Moto Applid in Tnspottion, Pocdings of Intntionl onfnc on Industil
[9] IEEE. Rpintd, with pmission, fom Xu, Wi; Zhu, Jinguo; Tn, Longchng; Guo, Yougung; Wng, Shuhong; Wng, Yi. 9, Dsign of Lin Induction Moto Applid in Tnspottion, Pocdings of Intntionl onfnc on Industil
THE CARTAN GEOMETRY OF THE PLANE POLAR COORDINATES: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS IN TERMS OF THE CARTAN SPIN CONNECTION
 Jounl of Foundtions of Physics nd Chmisty 3 HE CARAN GEOMERY OF HE PLANE POLAR COORDINAES: ROAIONAL DYNAMICS IN ERMS OF HE CARAN SPIN CONNECION M. W. Evns nd H. Eck Alph Institut fo Advncd Studis (www.wbchiv.og.uk,
Jounl of Foundtions of Physics nd Chmisty 3 HE CARAN GEOMERY OF HE PLANE POLAR COORDINAES: ROAIONAL DYNAMICS IN ERMS OF HE CARAN SPIN CONNECION M. W. Evns nd H. Eck Alph Institut fo Advncd Studis (www.wbchiv.og.uk,
Current Status of Orbit Determination methods in PMO
 unt ttus of Obit Dtintion thods in PMO Dong Wi, hngyin ZHO, Xin Wng Pu Mountin Obsvtoy, HINEE DEMY OF IENE bstct tit obit dtintion OD thods hv vovd ot ov th st 5 ys in Pu Mountin Obsvtoy. This tic ovids
unt ttus of Obit Dtintion thods in PMO Dong Wi, hngyin ZHO, Xin Wng Pu Mountin Obsvtoy, HINEE DEMY OF IENE bstct tit obit dtintion OD thods hv vovd ot ov th st 5 ys in Pu Mountin Obsvtoy. This tic ovids
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signls & Systms Pf. Mk Fwl Discussin #1 Cmplx Numbs nd Cmplx-Vlud Functins Rding Assignmnt: Appndix A f Kmn nd Hck Cmplx Numbs Cmplx numbs is s ts f plynmils. Dfinitin f imginy # j nd sm sulting
EECE 301 Signls & Systms Pf. Mk Fwl Discussin #1 Cmplx Numbs nd Cmplx-Vlud Functins Rding Assignmnt: Appndix A f Kmn nd Hck Cmplx Numbs Cmplx numbs is s ts f plynmils. Dfinitin f imginy # j nd sm sulting
8 - GRAVITATION Page 1
 8 GAVITATION Pag 1 Intoduction Ptolmy, in scond cntuy, gav gocntic thoy of plantay motion in which th Eath is considd stationay at th cnt of th univs and all th stas and th plants including th Sun volving
8 GAVITATION Pag 1 Intoduction Ptolmy, in scond cntuy, gav gocntic thoy of plantay motion in which th Eath is considd stationay at th cnt of th univs and all th stas and th plants including th Sun volving
Jie Zhang and Yunqing Zhang
 Pocdings of th 7th Wold Congss on Intllignt Contol nd Automtion Jun 5-7, 008, Chongqing, Chin Fctionl-Od μ Contol nd Optimiztion fo Vhicl Acti Sting Ji Zhng nd Yunqing Zhng Cnt fo Comput-Aidd Dsign Huzhong
Pocdings of th 7th Wold Congss on Intllignt Contol nd Automtion Jun 5-7, 008, Chongqing, Chin Fctionl-Od μ Contol nd Optimiztion fo Vhicl Acti Sting Ji Zhng nd Yunqing Zhng Cnt fo Comput-Aidd Dsign Huzhong
Elastic Analysis of Pavement Structure with Application of Vertical and Centripetal Surface Forces
 Elstic nlysis of Pvmnt Stct with ppliction of Vticl nd ntiptl Sfc Focs Min. W. SIR ilt Envionmnt Ptoi Soth fic Fjinmi K. & Mtsi K. ptmnt of ivil nd Envionmntl Engining Tokyo nki Univsity Sitm pn Tkmi Ino
Elstic nlysis of Pvmnt Stct with ppliction of Vticl nd ntiptl Sfc Focs Min. W. SIR ilt Envionmnt Ptoi Soth fic Fjinmi K. & Mtsi K. ptmnt of ivil nd Envionmntl Engining Tokyo nki Univsity Sitm pn Tkmi Ino
Instructions for Section 1
 Instructions for Sction 1 Choos th rspons tht is corrct for th qustion. A corrct nswr scors 1, n incorrct nswr scors 0. Mrks will not b dductd for incorrct nswrs. You should ttmpt vry qustion. No mrks
Instructions for Sction 1 Choos th rspons tht is corrct for th qustion. A corrct nswr scors 1, n incorrct nswr scors 0. Mrks will not b dductd for incorrct nswrs. You should ttmpt vry qustion. No mrks
Modeling Diameter Growth and Self-Thinning in Planted Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) Stands
 Th Opn Fost Scinc Jounl, 211, 4, 49-56 49 Opn Accss Modling imt Gowth nd Slf-Thinning in Plntd Sugi (Cyptomi jponic) Stnds Tohu Nkjim *,1, Mitsuo Mtsumoto 2 nd Noihiko Shiishi 3 1 Lbotoy of Globl Fost
Th Opn Fost Scinc Jounl, 211, 4, 49-56 49 Opn Accss Modling imt Gowth nd Slf-Thinning in Plntd Sugi (Cyptomi jponic) Stnds Tohu Nkjim *,1, Mitsuo Mtsumoto 2 nd Noihiko Shiishi 3 1 Lbotoy of Globl Fost
CIVL 8/ D Boundary Value Problems - Rectangular Elements 1/7
 CIVL / -D Boundr Vlu Prolms - Rctngulr Elmnts / RECANGULAR ELEMENS - In som pplictions, it m mor dsirl to us n lmntl rprsnttion of th domin tht hs four sids, ithr rctngulr or qudriltrl in shp. Considr
CIVL / -D Boundr Vlu Prolms - Rctngulr Elmnts / RECANGULAR ELEMENS - In som pplictions, it m mor dsirl to us n lmntl rprsnttion of th domin tht hs four sids, ithr rctngulr or qudriltrl in shp. Considr
GRAVITATION 4) R. max. 2 ..(1) ...(2)
 GAVITATION PVIOUS AMCT QUSTIONS NGINING. A body is pojctd vtically upwads fom th sufac of th ath with a vlocity qual to half th scap vlocity. If is th adius of th ath, maximum hight attaind by th body
GAVITATION PVIOUS AMCT QUSTIONS NGINING. A body is pojctd vtically upwads fom th sufac of th ath with a vlocity qual to half th scap vlocity. If is th adius of th ath, maximum hight attaind by th body
, between the vertical lines x a and x b. Given a demand curve, having price as a function of quantity, p f (x) at height k is the curve f ( x,
 Clculus for Businss nd Socil Scincs - Prof D Yun Finl Em Rviw vrsion 5/9/7 Chck wbsit for ny postd typos nd updts Pls rport ny typos This rviw sht contins summris of nw topics only (This rviw sht dos hv
Clculus for Businss nd Socil Scincs - Prof D Yun Finl Em Rviw vrsion 5/9/7 Chck wbsit for ny postd typos nd updts Pls rport ny typos This rviw sht contins summris of nw topics only (This rviw sht dos hv
A Simple Method for Determining the Manoeuvring Indices K and T from Zigzag Trial Data
 Rind 8-- Wbsi: wwwshimoionsnl Ro 67, Jun 97, Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy, Shi Hydomchnics Lbooy, Mklw, 68 CD Dlf, h Nhlnds A Siml Mhod fo Dminin h Mnouvin Indics K nd fom Ziz il D JMJ Jouné Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy
Rind 8-- Wbsi: wwwshimoionsnl Ro 67, Jun 97, Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy, Shi Hydomchnics Lbooy, Mklw, 68 CD Dlf, h Nhlnds A Siml Mhod fo Dminin h Mnouvin Indics K nd fom Ziz il D JMJ Jouné Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy
Modelling of Fission Chambers in Current Mode Analytical Approach
 Modlling of Fission Chmbs in Cunt Mod Anlyticl Appoch Sébstin Chbod,, Gbil Fioni, Alin Ltounu, Fédéic Mi DSM/DAPNIA/SPhN, CA-Scly, 99 Gif-Su-Yvtt, Fnc DSM, CA-Scly, 99 Gif-Su-Yvtt, Fnc Abstct A comphnsiv
Modlling of Fission Chmbs in Cunt Mod Anlyticl Appoch Sébstin Chbod,, Gbil Fioni, Alin Ltounu, Fédéic Mi DSM/DAPNIA/SPhN, CA-Scly, 99 Gif-Su-Yvtt, Fnc DSM, CA-Scly, 99 Gif-Su-Yvtt, Fnc Abstct A comphnsiv
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLMNTARY INFORMATION. Dtmin th gat inducd bgap cai concntation. Th fild inducd bgap cai concntation in bilay gaphn a indpndntly vaid by contolling th both th top bottom displacmnt lctical filds D t
SUPPLMNTARY INFORMATION. Dtmin th gat inducd bgap cai concntation. Th fild inducd bgap cai concntation in bilay gaphn a indpndntly vaid by contolling th both th top bottom displacmnt lctical filds D t
Important design issues and engineering applications of SDOF system Frequency response Functions
 Impotnt design issues nd engineeing pplictions of SDOF system Fequency esponse Functions The following desciptions show typicl questions elted to the design nd dynmic pefomnce of second-ode mechnicl system
Impotnt design issues nd engineeing pplictions of SDOF system Fequency esponse Functions The following desciptions show typicl questions elted to the design nd dynmic pefomnce of second-ode mechnicl system
Hydrogen atom. Energy levels and wave functions Orbital momentum, electron spin and nuclear spin Fine and hyperfine interaction Hydrogen orbitals
 Hydogn atom Engy lvls and wav functions Obital momntum, lcton spin and nucla spin Fin and hypfin intaction Hydogn obitals Hydogn atom A finmnt of th Rydbg constant: R ~ 109 737.3156841 cm -1 A hydogn mas
Hydogn atom Engy lvls and wav functions Obital momntum, lcton spin and nucla spin Fin and hypfin intaction Hydogn obitals Hydogn atom A finmnt of th Rydbg constant: R ~ 109 737.3156841 cm -1 A hydogn mas
CBSE , ˆj. cos CBSE_2015_SET-1. SECTION A 1. Given that a 2iˆ ˆj. We need to find. 3. Consider the vector equation of the plane.
 CBSE CBSE SET- SECTION. Gv tht d W d to fd 7 7 Hc, 7 7 7. Lt,. W ow tht.. Thus,. Cosd th vcto quto of th pl.. z. - + z = - + z = Thus th Cts quto of th pl s - + z = Lt d th dstc tw th pot,, - to th pl.
CBSE CBSE SET- SECTION. Gv tht d W d to fd 7 7 Hc, 7 7 7. Lt,. W ow tht.. Thus,. Cosd th vcto quto of th pl.. z. - + z = - + z = Thus th Cts quto of th pl s - + z = Lt d th dstc tw th pot,, - to th pl.
Section 35 SHM and Circular Motion
 Section 35 SHM nd Cicul Motion Phsics 204A Clss Notes Wht do objects do? nd Wh do the do it? Objects sometimes oscillte in simple hmonic motion. In the lst section we looed t mss ibting t the end of sping.
Section 35 SHM nd Cicul Motion Phsics 204A Clss Notes Wht do objects do? nd Wh do the do it? Objects sometimes oscillte in simple hmonic motion. In the lst section we looed t mss ibting t the end of sping.
Derivation of Annular Plate Sector Element for General Bending Analysis
 Jounl of Engining nd Dvlopmnt, Vol. 9, No., Jnuy 05, ISSN 8-78 Divtion of Annul Plt Scto Elmnt fo Gnl Bnding Anlysis Lctu D. Hyd Abdulm Mhdi Civil ngining dptmnt, Engining collg, Al_ Mustnsiiyh Univsity
Jounl of Engining nd Dvlopmnt, Vol. 9, No., Jnuy 05, ISSN 8-78 Divtion of Annul Plt Scto Elmnt fo Gnl Bnding Anlysis Lctu D. Hyd Abdulm Mhdi Civil ngining dptmnt, Engining collg, Al_ Mustnsiiyh Univsity
Chapter 16. 1) is a particular point on the graph of the function. 1. y, where x y 1
 Prctic qustions W now tht th prmtr p is dirctl rltd to th mplitud; thrfor, w cn find tht p. cos d [ sin ] sin sin Not: Evn though ou might not now how to find th prmtr in prt, it is lws dvisl to procd
Prctic qustions W now tht th prmtr p is dirctl rltd to th mplitud; thrfor, w cn find tht p. cos d [ sin ] sin sin Not: Evn though ou might not now how to find th prmtr in prt, it is lws dvisl to procd
Aakash. For Class XII Studying / Passed Students. Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics
 Aakash A UNIQUE PPRTUNITY T HELP YU FULFIL YUR DREAMS Fo Class XII Studying / Passd Studnts Physics, Chmisty & Mathmatics Rgistd ffic: Aakash Tow, 8, Pusa Road, Nw Dlhi-0005. Ph.: (0) 4763456 Fax: (0)
Aakash A UNIQUE PPRTUNITY T HELP YU FULFIL YUR DREAMS Fo Class XII Studying / Passd Studnts Physics, Chmisty & Mathmatics Rgistd ffic: Aakash Tow, 8, Pusa Road, Nw Dlhi-0005. Ph.: (0) 4763456 Fax: (0)
INTEGRALS. Chapter 7. d dx. 7.1 Overview Let d dx F (x) = f (x). Then, we write f ( x)
 Chptr 7 INTEGRALS 7. Ovrviw 7.. Lt d d F () f (). Thn, w writ f ( ) d F () + C. Ths intgrls r clld indfinit intgrls or gnrl intgrls, C is clld constnt of intgrtion. All ths intgrls diffr y constnt. 7..
Chptr 7 INTEGRALS 7. Ovrviw 7.. Lt d d F () f (). Thn, w writ f ( ) d F () + C. Ths intgrls r clld indfinit intgrls or gnrl intgrls, C is clld constnt of intgrtion. All ths intgrls diffr y constnt. 7..
Ch 1.2: Solutions of Some Differential Equations
 Ch 1.2: Solutions of Som Diffrntil Equtions Rcll th fr fll nd owl/mic diffrntil qutions: v 9.8.2v, p.5 p 45 Ths qutions hv th gnrl form y' = y - b W cn us mthods of clculus to solv diffrntil qutions of
Ch 1.2: Solutions of Som Diffrntil Equtions Rcll th fr fll nd owl/mic diffrntil qutions: v 9.8.2v, p.5 p 45 Ths qutions hv th gnrl form y' = y - b W cn us mthods of clculus to solv diffrntil qutions of
Elliptical motion, gravity, etc
 FW Physics 130 G:\130 lctur\ch 13 Elliticl motion.docx g 1 of 7 11/3/010; 6:40 PM; Lst rintd 11/3/010 6:40:00 PM Fig. 1 Elliticl motion, grvity, tc minor xis mjor xis F 1 =A F =B C - D, mjor nd minor xs
FW Physics 130 G:\130 lctur\ch 13 Elliticl motion.docx g 1 of 7 11/3/010; 6:40 PM; Lst rintd 11/3/010 6:40:00 PM Fig. 1 Elliticl motion, grvity, tc minor xis mjor xis F 1 =A F =B C - D, mjor nd minor xs
be two non-empty sets. Then S is called a semigroup if it satisfies the conditions
 UZZY SOT GMM EGU SEMIGOUPS V. Chinndi* & K. lmozhi** * ssocit Pofsso Dtmnt of Mthmtics nnmli Univsity nnmling Tmilnd ** Dtmnt of Mthmtics nnmli Univsity nnmling Tmilnd bstct: In this w hv discssd bot th
UZZY SOT GMM EGU SEMIGOUPS V. Chinndi* & K. lmozhi** * ssocit Pofsso Dtmnt of Mthmtics nnmli Univsity nnmling Tmilnd ** Dtmnt of Mthmtics nnmli Univsity nnmling Tmilnd bstct: In this w hv discssd bot th
sin sin 1 d r d Ae r 2
 Diffction k f c f Th Huygn-Fnl Pincil tt: Evy unobtuct oint of vfont, t givn intnt, v ouc of hicl cony vlt (ith th m funcy tht of th imy v. Th mlitu of th oticl fil t ny oint byon i th uoition of ll th
Diffction k f c f Th Huygn-Fnl Pincil tt: Evy unobtuct oint of vfont, t givn intnt, v ouc of hicl cony vlt (ith th m funcy tht of th imy v. Th mlitu of th oticl fil t ny oint byon i th uoition of ll th
217Plus TM Integrated Circuit Failure Rate Models
 T h I AC 27Plu s T M i n t g at d c i c u i t a n d i n d u c to Fa i lu at M o d l s David Nicholls, IAC (Quantion Solutions Incoatd) In a pvious issu o th IAC Jounal [nc ], w povidd a highlvl intoduction
T h I AC 27Plu s T M i n t g at d c i c u i t a n d i n d u c to Fa i lu at M o d l s David Nicholls, IAC (Quantion Solutions Incoatd) In a pvious issu o th IAC Jounal [nc ], w povidd a highlvl intoduction
Lecture contents. Bloch theorem k-vector Brillouin zone Almost free-electron model Bands Effective mass Holes. NNSE 508 EM Lecture #9
 Lctur contnts Bloch thorm -vctor Brillouin zon Almost fr-lctron modl Bnds ffctiv mss Hols Trnsltionl symmtry: Bloch thorm On-lctron Schrödingr qution ch stt cn ccommo up to lctrons: If Vr is priodic function:
Lctur contnts Bloch thorm -vctor Brillouin zon Almost fr-lctron modl Bnds ffctiv mss Hols Trnsltionl symmtry: Bloch thorm On-lctron Schrödingr qution ch stt cn ccommo up to lctrons: If Vr is priodic function:
IFYFM002 Further Maths Appendix C Formula Booklet
 Ittol Foudto Y (IFY) IFYFM00 Futh Mths Appd C Fomul Booklt Rltd Documts: IFY Futh Mthmtcs Syllbus 07/8 Cotts Mthmtcs Fomul L Equtos d Mtcs... Qudtc Equtos d Rmd Thom... Boml Epsos, Squcs d Ss... Idcs,
Ittol Foudto Y (IFY) IFYFM00 Futh Mths Appd C Fomul Booklt Rltd Documts: IFY Futh Mthmtcs Syllbus 07/8 Cotts Mthmtcs Fomul L Equtos d Mtcs... Qudtc Equtos d Rmd Thom... Boml Epsos, Squcs d Ss... Idcs,
The Angular Momenta Dipole Moments and Gyromagnetic Ratios of the Electron and the Proton
 Journl of Modrn hysics, 014, 5, 154-157 ublishd Onlin August 014 in SciRs. htt://www.scir.org/journl/jm htt://dx.doi.org/.436/jm.014.51415 Th Angulr Momnt Diol Momnts nd Gyromgntic Rtios of th Elctron
Journl of Modrn hysics, 014, 5, 154-157 ublishd Onlin August 014 in SciRs. htt://www.scir.org/journl/jm htt://dx.doi.org/.436/jm.014.51415 Th Angulr Momnt Diol Momnts nd Gyromgntic Rtios of th Elctron
PH427/PH527: Periodic systems Spring Overview of the PH427 website (syllabus, assignments etc.) 2. Coupled oscillations.
 Dy : Mondy 5 inuts. Ovrviw of th PH47 wsit (syllus, ssignnts tc.). Coupld oscilltions W gin with sss coupld y Hook's Lw springs nd find th possil longitudinl) otion of such syst. W ll xtnd this to finit
Dy : Mondy 5 inuts. Ovrviw of th PH47 wsit (syllus, ssignnts tc.). Coupld oscilltions W gin with sss coupld y Hook's Lw springs nd find th possil longitudinl) otion of such syst. W ll xtnd this to finit
What Makes Production System Design Hard?
 What Maks Poduction Systm Dsign Had? 1. Things not always wh you want thm whn you want thm wh tanspot and location logistics whn invntoy schduling and poduction planning 2. Rsoucs a lumpy minimum ffctiv
What Maks Poduction Systm Dsign Had? 1. Things not always wh you want thm whn you want thm wh tanspot and location logistics whn invntoy schduling and poduction planning 2. Rsoucs a lumpy minimum ffctiv
Shor s Algorithm. Motivation. Why build a classical computer? Why build a quantum computer? Quantum Algorithms. Overview. Shor s factoring algorithm
 Motivation Sho s Algoith It appas that th univs in which w liv is govnd by quantu chanics Quantu infoation thoy givs us a nw avnu to study & tst quantu chanics Why do w want to build a quantu coput? Pt
Motivation Sho s Algoith It appas that th univs in which w liv is govnd by quantu chanics Quantu infoation thoy givs us a nw avnu to study & tst quantu chanics Why do w want to build a quantu coput? Pt
Physics 240: Worksheet 15 Name
 Physics 40: Woksht 15 Nam Each of ths poblms inol physics in an acclatd fam of fnc Althouh you mind wants to ty to foc you to wok ths poblms insid th acclatd fnc fam (i.. th so-calld "won way" by som popl),
Physics 40: Woksht 15 Nam Each of ths poblms inol physics in an acclatd fam of fnc Althouh you mind wants to ty to foc you to wok ths poblms insid th acclatd fnc fam (i.. th so-calld "won way" by som popl),
PAVEMENT DESIGN AND EVALUATION
 THE REQUIRED MATHEMATICS AND ITS APPLICATIONS F. Vn Cuwlt Edito: Mc Stt Fdtion of th Blgin Cmnt Industy B-7 Bussls, Ru Volt 9. i ii INTRODUCTION Pvmnt Dsign nd Evlution: Th Rquid Mthmtics nd Its Applictions
THE REQUIRED MATHEMATICS AND ITS APPLICATIONS F. Vn Cuwlt Edito: Mc Stt Fdtion of th Blgin Cmnt Industy B-7 Bussls, Ru Volt 9. i ii INTRODUCTION Pvmnt Dsign nd Evlution: Th Rquid Mthmtics nd Its Applictions
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 7.6: Complex Eigenvalues
 BocDPm 9 h d Ch 7.6: Compl Egvlus Elm Dffl Equos d Boud Vlu Poblms 9 h do b Wllm E. Boc d Rchd C. DPm 9 b Joh Wl & Sos Ic. W cosd g homogous ssm of fs od l quos wh cos l coffcs d hus h ssm c b w s ' A
BocDPm 9 h d Ch 7.6: Compl Egvlus Elm Dffl Equos d Boud Vlu Poblms 9 h do b Wllm E. Boc d Rchd C. DPm 9 b Joh Wl & Sos Ic. W cosd g homogous ssm of fs od l quos wh cos l coffcs d hus h ssm c b w s ' A
Theoretical Study on the While Drilling Electromagnetic Signal Transmission of Horizontal Well
 7 nd ntrntionl Confrnc on Softwr, Multimdi nd Communiction Enginring (SMCE 7) SBN: 978--6595-458-5 Thorticl Study on th Whil Drilling Elctromgntic Signl Trnsmission of Horizontl Wll Y-huo FAN,,*, Zi-ping
7 nd ntrntionl Confrnc on Softwr, Multimdi nd Communiction Enginring (SMCE 7) SBN: 978--6595-458-5 Thorticl Study on th Whil Drilling Elctromgntic Signl Trnsmission of Horizontl Wll Y-huo FAN,,*, Zi-ping
Chapter 7 Electrodynamics
 Cpt 7 Elctonics 7. Elctootiv Foc 7.. O s Lw Cunt Dnsity: ( n ) q ( n l) Q q qnv Fo lcton: n( )v nd d qnv Fo ost sustncs, t cunt dnsity is popotionl to t foc p unit cg: F ( E + v B) q. : conductivity, pfct
Cpt 7 Elctonics 7. Elctootiv Foc 7.. O s Lw Cunt Dnsity: ( n ) q ( n l) Q q qnv Fo lcton: n( )v nd d qnv Fo ost sustncs, t cunt dnsity is popotionl to t foc p unit cg: F ( E + v B) q. : conductivity, pfct
Midterm Exam. CS/ECE 181B Intro to Computer Vision. February 13, :30-4:45pm
 Nam: Midtm am CS/C 8B Into to Comput Vision Fbua, 7 :-4:45pm las spa ouslvs to th dg possibl so that studnts a vnl distibutd thoughout th oom. his is a losd-boo tst. h a also a fw pags of quations, t.
Nam: Midtm am CS/C 8B Into to Comput Vision Fbua, 7 :-4:45pm las spa ouslvs to th dg possibl so that studnts a vnl distibutd thoughout th oom. his is a losd-boo tst. h a also a fw pags of quations, t.
Classical Theory of Fourier Series : Demystified and Generalised VIVEK V. RANE. The Institute of Science, 15, Madam Cama Road, Mumbai
 Clssil Thoy o Foi Sis : Dmystii Glis VIVEK V RANE Th Istitt o Si 5 Mm Cm Ro Mmbi-4 3 -mil ss : v_v_@yhoooi Abstt : Fo Rim itgbl tio o itvl o poit thi w i Foi Sis t th poit o th itvl big ot how wh th tio
Clssil Thoy o Foi Sis : Dmystii Glis VIVEK V RANE Th Istitt o Si 5 Mm Cm Ro Mmbi-4 3 -mil ss : v_v_@yhoooi Abstt : Fo Rim itgbl tio o itvl o poit thi w i Foi Sis t th poit o th itvl big ot how wh th tio
Integration Continued. Integration by Parts Solving Definite Integrals: Area Under a Curve Improper Integrals
 Intgrtion Continud Intgrtion y Prts Solving Dinit Intgrls: Ar Undr Curv Impropr Intgrls Intgrtion y Prts Prticulrly usul whn you r trying to tk th intgrl o som unction tht is th product o n lgric prssion
Intgrtion Continud Intgrtion y Prts Solving Dinit Intgrls: Ar Undr Curv Impropr Intgrls Intgrtion y Prts Prticulrly usul whn you r trying to tk th intgrl o som unction tht is th product o n lgric prssion
GAUSS PLANETARY EQUATIONS IN A NON-SINGULAR GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL
 GAUSS PLANETARY EQUATIONS IN A NON-SINGULAR GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL Ioannis Iaklis Haanas * and Michal Hany# * Dpatmnt of Physics and Astonomy, Yok Univsity 34 A Pti Scinc Building Noth Yok, Ontaio, M3J-P3,
GAUSS PLANETARY EQUATIONS IN A NON-SINGULAR GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL Ioannis Iaklis Haanas * and Michal Hany# * Dpatmnt of Physics and Astonomy, Yok Univsity 34 A Pti Scinc Building Noth Yok, Ontaio, M3J-P3,
Data Structures. Element Uniqueness Problem. Hash Tables. Example. Hash Tables. Dana Shapira. 19 x 1. ) h(x 4. ) h(x 2. ) h(x 3. h(x 1. x 4. x 2.
 Element Uniqueness Poblem Dt Stuctues Let x,..., xn < m Detemine whethe thee exist i j such tht x i =x j Sot Algoithm Bucket Sot Dn Shpi Hsh Tbles fo (i=;i
Element Uniqueness Poblem Dt Stuctues Let x,..., xn < m Detemine whethe thee exist i j such tht x i =x j Sot Algoithm Bucket Sot Dn Shpi Hsh Tbles fo (i=;i
Extinction Ratio and Power Penalty
 Application Not: HFAN-.. Rv.; 4/8 Extinction Ratio and ow nalty AVALABLE Backgound Extinction atio is an impotant paamt includd in th spcifications of most fib-optic tanscivs. h pupos of this application
Application Not: HFAN-.. Rv.; 4/8 Extinction Ratio and ow nalty AVALABLE Backgound Extinction atio is an impotant paamt includd in th spcifications of most fib-optic tanscivs. h pupos of this application
5.61 Fall 2007 Lecture #2 page 1. The DEMISE of CLASSICAL PHYSICS
 5.61 Fall 2007 Lctu #2 pag 1 Th DEMISE of CLASSICAL PHYSICS (a) Discovy of th Elcton In 1897 J.J. Thomson discovs th lcton and masus ( m ) (and inadvtntly invnts th cathod ay (TV) tub) Faaday (1860 s 1870
5.61 Fall 2007 Lctu #2 pag 1 Th DEMISE of CLASSICAL PHYSICS (a) Discovy of th Elcton In 1897 J.J. Thomson discovs th lcton and masus ( m ) (and inadvtntly invnts th cathod ay (TV) tub) Faaday (1860 s 1870
GRAVITATION. (d) If a spring balance having frequency f is taken on moon (having g = g / 6) it will have a frequency of (a) 6f (b) f / 6
 GVITTION 1. Two satllits and o ound a plant P in cicula obits havin adii 4 and spctivly. If th spd of th satllit is V, th spd of th satllit will b 1 V 6 V 4V V. Th scap vlocity on th sufac of th ath is
GVITTION 1. Two satllits and o ound a plant P in cicula obits havin adii 4 and spctivly. If th spd of th satllit is V, th spd of th satllit will b 1 V 6 V 4V V. Th scap vlocity on th sufac of th ath is
CBSE SAMPLE PAPER SOLUTIONS CLASS-XII MATHS SET-2 CBSE , ˆj. cos. SECTION A 1. Given that a 2iˆ ˆj. We need to find
 BSE SMLE ER SOLUTONS LSS-X MTHS SET- BSE SETON Gv tht d W d to fd 7 7 Hc, 7 7 7 Lt, W ow tht Thus, osd th vcto quto of th pl z - + z = - + z = Thus th ts quto of th pl s - + z = Lt d th dstc tw th pot,,
BSE SMLE ER SOLUTONS LSS-X MTHS SET- BSE SETON Gv tht d W d to fd 7 7 Hc, 7 7 7 Lt, W ow tht Thus, osd th vcto quto of th pl z - + z = - + z = Thus th ts quto of th pl s - + z = Lt d th dstc tw th pot,,
Lecture 35. Diffraction and Aperture Antennas
 ctu 35 Dictin nd ptu ntnns In this lctu u will ln: Dictin f lctmgntic ditin Gin nd ditin pttn f ptu ntnns C 303 Fll 005 Fhn Rn Cnll Univsit Dictin nd ptu ntnns ptu ntnn usull fs t (mtllic) sht with hl
ctu 35 Dictin nd ptu ntnns In this lctu u will ln: Dictin f lctmgntic ditin Gin nd ditin pttn f ptu ntnns C 303 Fll 005 Fhn Rn Cnll Univsit Dictin nd ptu ntnns ptu ntnn usull fs t (mtllic) sht with hl
Errata for Second Edition, First Printing
 Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1 G( x)] = θp( R) + ( θ R)[1 G( R)] pg 15, problm 6: dmnd of
Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1 G( x)] = θp( R) + ( θ R)[1 G( R)] pg 15, problm 6: dmnd of
CHAPTER 5 CIRCULAR MOTION
 CHAPTER 5 CIRCULAR MOTION and GRAVITATION 5.1 CENTRIPETAL FORCE It is known that if a paticl mos with constant spd in a cicula path of adius, it acquis a cntiptal acclation du to th chang in th diction
CHAPTER 5 CIRCULAR MOTION and GRAVITATION 5.1 CENTRIPETAL FORCE It is known that if a paticl mos with constant spd in a cicula path of adius, it acquis a cntiptal acclation du to th chang in th diction
STATISTICAL MECHANICS OF DIATOMIC GASES
 Pof. D. I. ass Phys54 7 -Ma-8 Diatomic_Gas (Ashly H. Cat chapt 5) SAISICAL MECHAICS OF DIAOMIC GASES - Fo monatomic gas whos molculs hav th dgs of fdom of tanslatoy motion th intnal u 3 ngy and th spcific
Pof. D. I. ass Phys54 7 -Ma-8 Diatomic_Gas (Ashly H. Cat chapt 5) SAISICAL MECHAICS OF DIAOMIC GASES - Fo monatomic gas whos molculs hav th dgs of fdom of tanslatoy motion th intnal u 3 ngy and th spcific
New Advanced Higher Mathematics: Formulae
 Advcd High Mthmtics Nw Advcd High Mthmtics: Fomul G (G): Fomul you must mmois i od to pss Advcd High mths s thy ot o th fomul sht. Am (A): Ths fomul giv o th fomul sht. ut it will still usful fo you to
Advcd High Mthmtics Nw Advcd High Mthmtics: Fomul G (G): Fomul you must mmois i od to pss Advcd High mths s thy ot o th fomul sht. Am (A): Ths fomul giv o th fomul sht. ut it will still usful fo you to
Design/Modeling for Periodic Nano Structures t for EMC/EMI. Outline
 /4/00 Dsign/Modling for Priodic Nno Structurs t for EMC/EMI Ji Chn Dprtmnt of ricl nd Computr Enginring Houston, TX, 7704 Outlin Introduction Composit Mtrils Dsign with Numricl Mixing-Lw FDTD dsign of
/4/00 Dsign/Modling for Priodic Nno Structurs t for EMC/EMI Ji Chn Dprtmnt of ricl nd Computr Enginring Houston, TX, 7704 Outlin Introduction Composit Mtrils Dsign with Numricl Mixing-Lw FDTD dsign of
Keywords: Soil-structure interaction, Across wind, Chimney, Annular raft
 Th Eighth Asi-Pifi Confn on Wind Engining, Dm 0, 03, Chnni, Indi EVALUATION OF TE EFFECT OF SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION ON TE RAFT OF TALL REINFORCED CONCRETE CINEYS UNDER ACROSS WIND LOAD Jish S.V, Jylkshmi
Th Eighth Asi-Pifi Confn on Wind Engining, Dm 0, 03, Chnni, Indi EVALUATION OF TE EFFECT OF SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION ON TE RAFT OF TALL REINFORCED CONCRETE CINEYS UNDER ACROSS WIND LOAD Jish S.V, Jylkshmi
I. The Connection between Spectroscopy and Quantum Mechanics
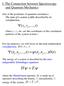 I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
Study on Generation Mechanism of Rogue Wave Phenomenon in Optical Fiber Based on Soliton's Eigenvalue
 Titl Autho(s) Study on Gntion Mchnism of Rogu Wv Phnomnon in Opticl Fib Bsd on Soliton's Eignvlu Wsk, R.W.M.G.K.B. Cittion Issu Dt Txt Vsion ETD URL https://doi.og/10.18910/61750 DOI 10.18910/61750 ights
Titl Autho(s) Study on Gntion Mchnism of Rogu Wv Phnomnon in Opticl Fib Bsd on Soliton's Eignvlu Wsk, R.W.M.G.K.B. Cittion Issu Dt Txt Vsion ETD URL https://doi.og/10.18910/61750 DOI 10.18910/61750 ights
Chapter 5. Control of a Unified Voltage Controller. 5.1 Introduction
 Chapt 5 Contol of a Unifid Voltag Contoll 5.1 Intoduction In Chapt 4, th Unifid Voltag Contoll, composd of two voltag-soucd convts, was mathmatically dscibd by dynamic quations. Th spac vcto tansfomation
Chapt 5 Contol of a Unifid Voltag Contoll 5.1 Intoduction In Chapt 4, th Unifid Voltag Contoll, composd of two voltag-soucd convts, was mathmatically dscibd by dynamic quations. Th spac vcto tansfomation
Radial geodesics in Schwarzschild spacetime
 Rdil geodesics in Schwzschild spcetime Spheiclly symmetic solutions to the Einstein eqution tke the fom ds dt d dθ sin θdϕ whee is constnt. We lso hve the connection components, which now tke the fom using
Rdil geodesics in Schwzschild spcetime Spheiclly symmetic solutions to the Einstein eqution tke the fom ds dt d dθ sin θdϕ whee is constnt. We lso hve the connection components, which now tke the fom using
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Problm A town hs st of houss nd st of rods A rod conncts nd only houss A rod conncting houss u nd v hs rpir cost w(u, v) Gol: Rpir nough (nd no mor) rods such tht:
Minimum Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Problm A town hs st of houss nd st of rods A rod conncts nd only houss A rod conncting houss u nd v hs rpir cost w(u, v) Gol: Rpir nough (nd no mor) rods such tht:
ریاضیات عالی پیشرفته
 ریاضیات عالی پیشرفته Numic Mthods o Enins مدرس دکتر پدرام پیوندی http://www.pdm-pyvndy.com ~ in Aic Equtions ~ Guss Eimintion Chpt 9 http://numicmthods.n.us.du Sovin Systms o Equtions A in qution in n
ریاضیات عالی پیشرفته Numic Mthods o Enins مدرس دکتر پدرام پیوندی http://www.pdm-pyvndy.com ~ in Aic Equtions ~ Guss Eimintion Chpt 9 http://numicmthods.n.us.du Sovin Systms o Equtions A in qution in n
Previously. Extensions to backstepping controller designs. Tracking using backstepping Suppose we consider the general system
 436-459 Advnced contol nd utomtion Extensions to bckstepping contolle designs Tcking Obseves (nonline dmping) Peviously Lst lectue we looked t designing nonline contolles using the bckstepping technique
436-459 Advnced contol nd utomtion Extensions to bckstepping contolle designs Tcking Obseves (nonline dmping) Peviously Lst lectue we looked t designing nonline contolles using the bckstepping technique
1 Using Integration to Find Arc Lengths and Surface Areas
 Novembe 9, 8 MAT86 Week Justin Ko Using Integtion to Find Ac Lengths nd Sufce Aes. Ac Length Fomul: If f () is continuous on [, b], then the c length of the cuve = f() on the intevl [, b] is given b s
Novembe 9, 8 MAT86 Week Justin Ko Using Integtion to Find Ac Lengths nd Sufce Aes. Ac Length Fomul: If f () is continuous on [, b], then the c length of the cuve = f() on the intevl [, b] is given b s
Chapter 2 Reciprocal Lattice. An important concept for analyzing periodic structures
 Chpt Rcpocl Lttc A mpott cocpt o lyzg podc stuctus Rsos o toducg cpocl lttc Thoy o cystl dcto o x-ys, utos, d lctos. Wh th dcto mxmum? Wht s th tsty? Abstct study o uctos wth th podcty o Bvs lttc Fou tsomto.
Chpt Rcpocl Lttc A mpott cocpt o lyzg podc stuctus Rsos o toducg cpocl lttc Thoy o cystl dcto o x-ys, utos, d lctos. Wh th dcto mxmum? Wht s th tsty? Abstct study o uctos wth th podcty o Bvs lttc Fou tsomto.
UNIT # 08 (PART - I)
 . r. d[h d[h.5 7.5 mol L S d[o d[so UNIT # 8 (PRT - I CHEMICL INETICS EXERCISE # 6. d[ x [ x [ x. r [X[C ' [X [[B r '[ [B [C. r [NO [Cl. d[so d[h.5 5 mol L S d[nh d[nh. 5. 6. r [ [B r [x [y r' [x [y r'
. r. d[h d[h.5 7.5 mol L S d[o d[so UNIT # 8 (PRT - I CHEMICL INETICS EXERCISE # 6. d[ x [ x [ x. r [X[C ' [X [[B r '[ [B [C. r [NO [Cl. d[so d[h.5 5 mol L S d[nh d[nh. 5. 6. r [ [B r [x [y r' [x [y r'
STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION COMPLETE EXAM DETAILS
 STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION COMPLETE EXAM DETAILS SSC MTS Pp-1 Exm Pttn Pp-1 i n onlin pp hving multipl choic qution in ction: Roning, Englih Lngug, Numicl Aptitud nd Gnl Awn Th nti pp i of totl 1 m nd
STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION COMPLETE EXAM DETAILS SSC MTS Pp-1 Exm Pttn Pp-1 i n onlin pp hving multipl choic qution in ction: Roning, Englih Lngug, Numicl Aptitud nd Gnl Awn Th nti pp i of totl 1 m nd
Errata for Second Edition, First Printing
 Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 71: Eqution (.3) should rd B( R) = θ R 1 x= [1 G( x)] pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1
Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 71: Eqution (.3) should rd B( R) = θ R 1 x= [1 G( x)] pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1
TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION
 TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION. Th indfinit intgrl In mny rspcts, th oprtion of intgrtion tht w r studying hr is th invrs oprtion of drivtion. Dfinition.. Th function F is n ntidrivtiv (or primitiv) of th function
TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION. Th indfinit intgrl In mny rspcts, th oprtion of intgrtion tht w r studying hr is th invrs oprtion of drivtion. Dfinition.. Th function F is n ntidrivtiv (or primitiv) of th function
COMP108 Algorithmic Foundations
 Grdy mthods Prudn Wong http://www.s.liv..uk/~pwong/thing/omp108/01617 Coin Chng Prolm Suppos w hv 3 typs of oins 10p 0p 50p Minimum numr of oins to mk 0.8, 1.0, 1.? Grdy mthod Lrning outoms Undrstnd wht
Grdy mthods Prudn Wong http://www.s.liv..uk/~pwong/thing/omp108/01617 Coin Chng Prolm Suppos w hv 3 typs of oins 10p 0p 50p Minimum numr of oins to mk 0.8, 1.0, 1.? Grdy mthod Lrning outoms Undrstnd wht
(a) Counter-Clockwise (b) Clockwise ()N (c) No rotation (d) Not enough information
 m m m00 kg dult, m0 kg bby. he seesw stts fom est. Which diection will it ottes? ( Counte-Clockwise (b Clockwise ( (c o ottion ti (d ot enough infomtion Effect of Constnt et oque.3 A constnt non-zeo toque
m m m00 kg dult, m0 kg bby. he seesw stts fom est. Which diection will it ottes? ( Counte-Clockwise (b Clockwise ( (c o ottion ti (d ot enough infomtion Effect of Constnt et oque.3 A constnt non-zeo toque
igid nd non-leky two-comptment building. Yu et l [8] developed non-line govening equtions by consideing the effect of bckgound lekge. Howeve, thee e n
![igid nd non-leky two-comptment building. Yu et l [8] developed non-line govening equtions by consideing the effect of bckgound lekge. Howeve, thee e n igid nd non-leky two-comptment building. Yu et l [8] developed non-line govening equtions by consideing the effect of bckgound lekge. Howeve, thee e n](/thumbs/87/96798187.jpg) The Seventh Intentionl Colloquium on Bluff Body Aeodynmics nd Applictions (BBAA7) Shnghi, Chin; Septembe -, Coupled vibtion between wind-induced intenl pessues nd lge spn oof fo two-comptment building
The Seventh Intentionl Colloquium on Bluff Body Aeodynmics nd Applictions (BBAA7) Shnghi, Chin; Septembe -, Coupled vibtion between wind-induced intenl pessues nd lge spn oof fo two-comptment building
EE243 Advanced Electromagnetic Theory Lec # 22 Scattering and Diffraction. Reading: Jackson Chapter 10.1, 10.3, lite on both 10.2 and 10.
 Appid M Fa 6, Nuuth Lctu # V //6 43 Advancd ctomagntic Thoy Lc # Scatting and Diffaction Scatting Fom Sma Obcts Scatting by Sma Dictic and Mtaic Sphs Coction of Scatts Sphica Wav xpansions Scaa Vcto Rading:
Appid M Fa 6, Nuuth Lctu # V //6 43 Advancd ctomagntic Thoy Lc # Scatting and Diffaction Scatting Fom Sma Obcts Scatting by Sma Dictic and Mtaic Sphs Coction of Scatts Sphica Wav xpansions Scaa Vcto Rading:
CDS 110b: Lecture 8-1 Robust Stability
 DS 0b: Lct 8- Robst Stabilit Richad M. Ma 3 Fba 006 Goals: Dscib mthods fo psnting nmodld dnamics Div conditions fo obst stabilit Rading: DFT, Sctions 4.-4.3 3 Fb 06 R. M. Ma, altch Gam lan: Robst fomanc
DS 0b: Lct 8- Robst Stabilit Richad M. Ma 3 Fba 006 Goals: Dscib mthods fo psnting nmodld dnamics Div conditions fo obst stabilit Rading: DFT, Sctions 4.-4.3 3 Fb 06 R. M. Ma, altch Gam lan: Robst fomanc
Fourier transforms (Chapter 15) Fourier integrals are generalizations of Fourier series. The series representation
 Pof. D. I. Nass Phys57 (T-3) Sptmb 8, 03 Foui_Tansf_phys57_T3 Foui tansfoms (Chapt 5) Foui intgals a gnalizations of Foui sis. Th sis psntation a0 nπx nπx f ( x) = + [ an cos + bn sin ] n = of a function
Pof. D. I. Nass Phys57 (T-3) Sptmb 8, 03 Foui_Tansf_phys57_T3 Foui tansfoms (Chapt 5) Foui intgals a gnalizations of Foui sis. Th sis psntation a0 nπx nπx f ( x) = + [ an cos + bn sin ] n = of a function
Last time: introduced our first computational model the DFA.
 Lctur 7 Homwork #7: 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3 (hnd in c nd d), Misc: Givn: M, NFA Prov: (q,xy) * (p,y) iff (q,x) * (p,) (follow proof don in clss tody) Lst tim: introducd our first computtionl modl th DFA. Tody
Lctur 7 Homwork #7: 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3 (hnd in c nd d), Misc: Givn: M, NFA Prov: (q,xy) * (p,y) iff (q,x) * (p,) (follow proof don in clss tody) Lst tim: introducd our first computtionl modl th DFA. Tody
Michael Rotkowitz 1,2
 Novembe 23, 2006 edited Line Contolles e Unifomly Optiml fo the Witsenhusen Counteexmple Michel Rotkowitz 1,2 IEEE Confeence on Decision nd Contol, 2006 Abstct In 1968, Witsenhusen intoduced his celebted
Novembe 23, 2006 edited Line Contolles e Unifomly Optiml fo the Witsenhusen Counteexmple Michel Rotkowitz 1,2 IEEE Confeence on Decision nd Contol, 2006 Abstct In 1968, Witsenhusen intoduced his celebted
Chapter 6 Frequency Response & System Concepts
 hpte 6 Fequency esponse & ystem oncepts Jesung Jng stedy stte (fequency) esponse Phso nottion Filte v v Foced esponse by inusoidl Excittion ( t) dv v v dv v cos t dt dt ince the focing fuction is sinusoid,
hpte 6 Fequency esponse & ystem oncepts Jesung Jng stedy stte (fequency) esponse Phso nottion Filte v v Foced esponse by inusoidl Excittion ( t) dv v v dv v cos t dt dt ince the focing fuction is sinusoid,
Class Summary. be functions and f( D) , we define the composition of f with g, denoted g f by
 Clss Summy.5 Eponentil Functions.6 Invese Functions nd Logithms A function f is ule tht ssigns to ech element D ectly one element, clled f( ), in. Fo emple : function not function Given functions f, g:
Clss Summy.5 Eponentil Functions.6 Invese Functions nd Logithms A function f is ule tht ssigns to ech element D ectly one element, clled f( ), in. Fo emple : function not function Given functions f, g:
Walk Like a Mathematician Learning Task:
 Gori Dprtmnt of Euction Wlk Lik Mthmticin Lrnin Tsk: Mtrics llow us to prform mny usful mthmticl tsks which orinrily rquir lr numbr of computtions. Som typs of problms which cn b on fficintly with mtrics
Gori Dprtmnt of Euction Wlk Lik Mthmticin Lrnin Tsk: Mtrics llow us to prform mny usful mthmticl tsks which orinrily rquir lr numbr of computtions. Som typs of problms which cn b on fficintly with mtrics
(, ) which is a positively sloping curve showing (Y,r) for which the money market is in equilibrium. The P = (1.4)
 ots lctu Th IS/LM modl fo an opn conomy is basd on a fixd pic lvl (vy sticky pics) and consists of a goods makt and a mony makt. Th goods makt is Y C+ I + G+ X εq (.) E SEK wh ε = is th al xchang at, E
ots lctu Th IS/LM modl fo an opn conomy is basd on a fixd pic lvl (vy sticky pics) and consists of a goods makt and a mony makt. Th goods makt is Y C+ I + G+ X εq (.) E SEK wh ε = is th al xchang at, E
Study Material with Classroom Practice solutions. To Electromagnetic Theory CONTENTS. 01 Static Fields Maxwell Equations & EM Waves 06 11
 Pg No. Stud Mtil with lssoom Pctic solutions To lctomgntic Tho ONTNTS hpt No. Nm of th hpt Pg No. Sttic Filds 5 Mwll qutions & M Wvs 6 Tnsmission ins Wvguids 5 6 5 lmnts of ntnns 7 hpt. ns: V cos cos î
Pg No. Stud Mtil with lssoom Pctic solutions To lctomgntic Tho ONTNTS hpt No. Nm of th hpt Pg No. Sttic Filds 5 Mwll qutions & M Wvs 6 Tnsmission ins Wvguids 5 6 5 lmnts of ntnns 7 hpt. ns: V cos cos î
10 m, so the distance from the Sun to the Moon during a solar eclipse is. The mass of the Sun, Earth, and Moon are = =
 Chpte 1 nivesl Gvittion 11 *P1. () The un-th distnce is 1.4 nd the th-moon 8 distnce is.84, so the distnce fom the un to the Moon duing sol eclipse is 11 8 11 1.4.84 = 1.4 The mss of the un, th, nd Moon
Chpte 1 nivesl Gvittion 11 *P1. () The un-th distnce is 1.4 nd the th-moon 8 distnce is.84, so the distnce fom the un to the Moon duing sol eclipse is 11 8 11 1.4.84 = 1.4 The mss of the un, th, nd Moon
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2008
 Mk Scheme (Results) Jnuy 00 GCE GCE Mthemtics (6679/0) Edecel Limited. Registeed in Englnd nd Wles No. 4496750 Registeed Office: One90 High Holbon, London WCV 7BH Jnuy 00 6679 Mechnics M Mk Scheme Question
Mk Scheme (Results) Jnuy 00 GCE GCE Mthemtics (6679/0) Edecel Limited. Registeed in Englnd nd Wles No. 4496750 Registeed Office: One90 High Holbon, London WCV 7BH Jnuy 00 6679 Mechnics M Mk Scheme Question
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HAYSTACK OBSERVATORY WESTFORD, MASSACHUSETTS
 VSRT MEMO #05 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HAYSTACK OBSERVATORY WESTFORD, MASSACHUSETTS 01886 Fbrury 3, 009 Tlphon: 781-981-507 Fx: 781-981-0590 To: VSRT Group From: Aln E.E. Rogrs Subjct: Simplifid
VSRT MEMO #05 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HAYSTACK OBSERVATORY WESTFORD, MASSACHUSETTS 01886 Fbrury 3, 009 Tlphon: 781-981-507 Fx: 781-981-0590 To: VSRT Group From: Aln E.E. Rogrs Subjct: Simplifid
Physics 111. Lecture 38 (Walker: ) Phase Change Latent Heat. May 6, The Three Basic Phases of Matter. Solid Liquid Gas
 Physics 111 Lctu 38 (Walk: 17.4-5) Phas Chang May 6, 2009 Lctu 38 1/26 Th Th Basic Phass of Matt Solid Liquid Gas Squnc of incasing molcul motion (and ngy) Lctu 38 2/26 If a liquid is put into a sald contain
Physics 111 Lctu 38 (Walk: 17.4-5) Phas Chang May 6, 2009 Lctu 38 1/26 Th Th Basic Phass of Matt Solid Liquid Gas Squnc of incasing molcul motion (and ngy) Lctu 38 2/26 If a liquid is put into a sald contain
Weighted Matching and Linear Programming
 Wightd Mtching nd Linr Progrmming Jonthn Turnr Mrch 19, 01 W v sn tht mximum siz mtchings cn b found in gnrl grphs using ugmnting pths. In principl, this sm pproch cn b pplid to mximum wight mtchings.
Wightd Mtching nd Linr Progrmming Jonthn Turnr Mrch 19, 01 W v sn tht mximum siz mtchings cn b found in gnrl grphs using ugmnting pths. In principl, this sm pproch cn b pplid to mximum wight mtchings.
Problem Session (3) for Chapter 4 Signal Modeling
 Pobm Sssio fo Cht Sig Modig Soutios to Pobms....5. d... Fid th Pdé oimtio of scod-od to sig tht is giv by [... ] T i.. d so o. I oth wods usig oimtio of th fom b b b H fid th cofficits b b b d. Soutio
Pobm Sssio fo Cht Sig Modig Soutios to Pobms....5. d... Fid th Pdé oimtio of scod-od to sig tht is giv by [... ] T i.. d so o. I oth wods usig oimtio of th fom b b b H fid th cofficits b b b d. Soutio
This immediately suggests an inverse-square law for a "piece" of current along the line.
 Electomgnetic Theoy (EMT) Pof Rui, UNC Asheville, doctophys on YouTube Chpte T Notes The iot-svt Lw T nvese-sque Lw fo Mgnetism Compe the mgnitude of the electic field t distnce wy fom n infinite line
Electomgnetic Theoy (EMT) Pof Rui, UNC Asheville, doctophys on YouTube Chpte T Notes The iot-svt Lw T nvese-sque Lw fo Mgnetism Compe the mgnitude of the electic field t distnce wy fom n infinite line
Multi-Section Coupled Line Couplers
 /0/009 MultiSction Coupld Lin Couplrs /8 Multi-Sction Coupld Lin Couplrs W cn dd multipl coupld lins in sris to incrs couplr ndwidth. Figur 7.5 (p. 6) An N-sction coupld lin l W typiclly dsign th couplr
/0/009 MultiSction Coupld Lin Couplrs /8 Multi-Sction Coupld Lin Couplrs W cn dd multipl coupld lins in sris to incrs couplr ndwidth. Figur 7.5 (p. 6) An N-sction coupld lin l W typiclly dsign th couplr
Solid state physics. Lecture 3: chemical bonding. Prof. Dr. U. Pietsch
 Solid stat physics Lctu 3: chmical bonding Pof. D. U. Pitsch Elcton chag dnsity distibution fom -ay diffaction data F kp ik dk h k l i Fi H p H; H hkl V a h k l Elctonic chag dnsity of silicon Valnc chag
Solid stat physics Lctu 3: chmical bonding Pof. D. U. Pitsch Elcton chag dnsity distibution fom -ay diffaction data F kp ik dk h k l i Fi H p H; H hkl V a h k l Elctonic chag dnsity of silicon Valnc chag
CDS 101/110: Lecture 7.1 Loop Analysis of Feedback Systems
 CDS 11/11: Lctu 7.1 Loop Analysis of Fdback Systms Novmb 7 216 Goals: Intoduc concpt of loop analysis Show how to comput closd loop stability fom opn loop poptis Dscib th Nyquist stability cition fo stability
CDS 11/11: Lctu 7.1 Loop Analysis of Fdback Systms Novmb 7 216 Goals: Intoduc concpt of loop analysis Show how to comput closd loop stability fom opn loop poptis Dscib th Nyquist stability cition fo stability
