SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Anna Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: /nPHYS1463 Observation of Van Hove singularities in twisted graphene layers Guohong Li 1, A. Luican 1, J.M. B. Lopes dos Santos 2, A. H. Castro Neto 3, Alfonso Reina 4, Jing Kong 5 and E.Y. Andrei 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ CFP and Departamento de Física, Faculdade de Ciências Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal 3 Department of Physics, Boston University, 590 Commonwealth Avenue, Boston, MA Department of Materials Science and Engineering, MIT, Cambridge, MA Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, MIT, Cambridge, MA Experimental details Experiments were carried out in a home-built low-temperature (4K/2K) high-magneticfield (13T/15T) scanning tunnelling microscope developed in our group. The controller was a commercial SPM 1000 unit from RHK Technologies. The tunnelling tips were obtained from mechanically cut Pt-Ir wire (from nanoscience Instruments). The magnetic field was applied perpendicular to the sample surface with a superconducting magnet working in persistent mode. The di/dv measurements were carried out with a lock-in technique using a 340 Hz a.c. modulation of the bias voltage. All data shown in main text were taken at 4.4K. Large area coarse nanopositioners of STM were used to search for the moiré pattern. HOPG samples (grade 2 from SPI supplies) were cleaved in air shortly before experiments. CVD graphene layers were grown on Ni according to ref.[13]. The CVD graphene sample was transfered to Au grid and then cleaned in H 2 at 250 C. nature physics 1
2 supplementary information doi: /nphys Tight binding model for twisted graphene bilayers The simplest tight-binding model of single-layer graphene considers hopping amplitudes between nearest neighbor atoms, t 3e V. To model the bilayer, one adds the hopping amplitude between A1 and B2 atoms 6, ~ t / 1 0. The conduction and valence bands still touch at the Dirac t points, but the dispersion becomes quadratic, due to the hybridization of the linear bands of each layer, which are degenerate. In the twisted bilayer, we maintained hopping amplitudes from atoms of one layer to the closest atoms (of either sublattice) in the other layer. The corresponding positions can be worked out from the geometry, and the hopping amplitudes were calculated using a parameterization of Slater-Koster integral for graphite S1. One arrives at a position dependent hopping t αβ (r) (α = A2, B2, β = A1, B1) with the periodicity of the Moiré superlattice. When there is a rotation, the Dirac points of the two layers no longer coincide: there is a shift in the Dirac wave vector of the rotated layer to K θ =K+ΔK. In the continuum description of a single layer, momentum is measured relative to the Dirac value K; if we use the same origin of momentum for the two layers, such that a uniform hopping couples states of the same momentum in both layers (Fig.S1), the zero energy states do not occur at k=0, but rather at k=-δk/2 in layer 1 and k=δk/2 in layer 2 (ref.11). FIG.S1. Geometry of the Brillouin zone of the Moiré superlattice. G1 and G2 are the basis vectors of the reciprocal lattice of the Moiré super lattice. The position dependent hopping can be analyzed by its Fourier amplitude t αβ (G), which couple states of momentum k and k+g. These Fourier amplitudes were calculated in reference (11); for 2 nature physics
3 doi: /nphys1463 supplementary information small angles, three values of G, (G=0, G= -G 1, and G=-G 1 -G 2 where G 1 and G 2 are reciprocal superlattice vectors) are found to give the dominant amplitudes; they have the same modulus, which, for small angles is practically constant, t θ 0.4 t. The VHS in Fig. 4a can be understood as follows. The low energy states of, say, layer 2 occur near k = ΔK/2. They are coupled by the inter-layer hopping to states of layer 1 at three momentum values, represented by the symbol in Fig.S1: k =ΔK/2, ΔK/2-G 1, ΔK/2-G 1 -G 2 ; these three momentum values are at the same distance, ΔK=K 2sin(θ i /2) from the Dirac point of layer 1; the corresponding energies are ±v F ΔK. We can therefore perform a simple calculation of the lowest lying bands, in the manner of a quasi-free electron approximation, by including plane waves k, k+g 1 and k+g 1 +G 2 in layer 1 and k, k G 1 and k G 1 G 2 in layer 2 (twelve states overall, including positive and negative energies). The momentum shift between the two Dirac cones turns out to be the essential difference between this problem and that of the unrotated bilayer. In the latter, the degeneracy points of both layers occur at the same momentum and the inter-layer hopping couples two doublets of zero energy states. In the present case, we have one doublet of zero energy states coupling to three pairs of states at finite energies, ±v F ΔK. As a result, the linear dispersion near zero energy is retained. However, near the center of the superlattice Brillouin zone the cones intersect. The resulting energy degeneracy is lifted by the couplings between the layers t αβ (G). A saddle point is unavoidable as the energy has a maximum along the line joining K and K θ and a minimum along the intersection of the two cones. The Density of States has been calculated numerically by integration over the superlattice Brillouin Zone. To model the trilayer, we added a third layer with the same orientation as one of the previous ones, to which it couples with a zero G coupling t AB = t. nature physics 3
4 supplementary information doi: /nphys Scanning tunneling spectroscopy of Moiré pattern in magnetic fields Contrary to the naïve expectation that a small twist between layers would decouple them to reveal the electronic structure of an isolated graphene layer; we find that it drastically changes the density of states (DOS). In zero field the DOS develops sharp Van Hove singularities (VHS). In finite field the Landau level sequence of the twisted graphene at small rotation angles no longer follows the square root dependence in field and level index expected of the of massless Dirac fermions in single layer graphene. In the case of the decoupled layer the Landau levels consist of a single sequence with square root dependence on field and level index 16 in stark contrast to the twisted layer spectra where the Landau level sequence is seen as a small modulation on top of the VHS peaks. At large angles, the square-root sequence is seen in between the VHS but with a reduced Fermi velocity. (to be reported elsewhere). In a recent report 17, the observation of a Moiré pattern and a sequence of Landau levels on epitaxial graphene on SiC(000-1), was attributed to a twist-induced decoupling of the graphene layers. However, in view of the results presented here and in reference 16, this interpretation is incorrect. Although the period of the Moiré pattern in some regions of reference 17 was comparable to that observed here, no VHS were seen. More surprisingly the Landau levels have been shown 17 independent of the period of the moiré pattern. In fact, the Landau levels should depend on the twist angles for the moiré patterns shown in reference17 and the dependence becomes weak only for very large angle rotation (to be reported elsewhere). 4 nature physics
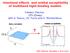
5 doi: /nphys1463 supplementary information 4. Large angle moiré pattern in CVD graphene Fig. S2 shows a moiré pattern in CVD graphene sample with a rotation angle of ~ 3.48, corresponding to i=9. Scanning tunneling spectrum also displays two VHS but with a larger separation of ~430mV. In contrast to the small angle data, there is no detectable difference in tunneling spectrum at peak or valley of moiré pattern, Fig.S3 (next page), indicating absence of charge density wave at large twisting angle. 20pA AC: 2mV 340Hz 0.6 ~430mV di/dv (a.u.) G-spec sample bias (mv) FIG.S2. Moire pattern in CVD graphene sample. (left) Topography of a moiré pattern with lattice constant of 3.9±0.2 nm. Tunneling current 20pA, sample bias voltage 200mV. (right) tunneling spectrum showing two VHS separated by ~430mV. nature physics 5
6 supplementary information doi: /nphys di/dv (a.u.) V1 P1 0.1 P2 V sample bias voltage (mv) di/dv (a.u.) P2 V2 0.1 P1 V sample bias voltage (mv) FIG.S3. Scanning tunneling spectra (left two panels) taken at different positions in Moire pattern (right) are identical within experimental noise, showing the absence of localization near VHS at large twisting angle. References S1. E. V. Castro et al arxiv: nature physics
Observation of Van Hove singularities in twisted graphene layers
 Observation of Van Hove singularities in twisted graphene layers Guohong Li 1, A. Luican 1, J.M. B. Lopes dos Santos 2,A. H. Castro Neto 3, A.Reina 4, J. Kong 5 and E.Y. Andrei 1 1 Department of Physics
Observation of Van Hove singularities in twisted graphene layers Guohong Li 1, A. Luican 1, J.M. B. Lopes dos Santos 2,A. H. Castro Neto 3, A.Reina 4, J. Kong 5 and E.Y. Andrei 1 1 Department of Physics
The twisted bilayer: an experimental and theoretical review. Graphene, 2009 Benasque. J.M.B. Lopes dos Santos
 Moiré in Graphite and FLG Continuum theory Results Experimental and theoretical conrmation Magnetic Field The twisted bilayer: an experimental and theoretical review J.M.B. Lopes dos Santos CFP e Departamento
Moiré in Graphite and FLG Continuum theory Results Experimental and theoretical conrmation Magnetic Field The twisted bilayer: an experimental and theoretical review J.M.B. Lopes dos Santos CFP e Departamento
Supplementary Figure S1. STM image of monolayer graphene grown on Rh (111). The lattice
 Supplementary Figure S1. STM image of monolayer graphene grown on Rh (111). The lattice mismatch between graphene (0.246 nm) and Rh (111) (0.269 nm) leads to hexagonal moiré superstructures with the expected
Supplementary Figure S1. STM image of monolayer graphene grown on Rh (111). The lattice mismatch between graphene (0.246 nm) and Rh (111) (0.269 nm) leads to hexagonal moiré superstructures with the expected
Electronic states on the surface of graphite
 Electronic states on the surface of graphite Guohong Li, Adina Luican, Eva Y. Andrei * Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers Univsersity, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA Elsevier use only: Received date
Electronic states on the surface of graphite Guohong Li, Adina Luican, Eva Y. Andrei * Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers Univsersity, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA Elsevier use only: Received date
Landau Quantization in Graphene Monolayer, Bernal Bilayer, and Bernal
 Landau Quantization in Graphene Monolayer, Bernal Bilayer, and Bernal Trilayer on Graphite Surface Long-Jing Yin, Si-Yu Li, Jia-Bin Qiao, Jia-Cai Nie, Lin He * Electronic properties of surface areas decoupled
Landau Quantization in Graphene Monolayer, Bernal Bilayer, and Bernal Trilayer on Graphite Surface Long-Jing Yin, Si-Yu Li, Jia-Bin Qiao, Jia-Cai Nie, Lin He * Electronic properties of surface areas decoupled
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nPHYS1736 Supplementary Information Real Space Mapping of Magnetically Quantized Graphene States David L. Miller, 1 Kevin D. Kubista, 1 Gregory M. Rutter, 2 Ming
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/nPHYS1736 Supplementary Information Real Space Mapping of Magnetically Quantized Graphene States David L. Miller, 1 Kevin D. Kubista, 1 Gregory M. Rutter, 2 Ming
Electronic bands of twisted graphene layers
 Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics https://www.condmatjclub.org JCCM November 2018 03 Electronic bands of twisted graphene layers 1. Origin of Mott Insulating Behavior and Superconductivity in Twisted
Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics https://www.condmatjclub.org JCCM November 2018 03 Electronic bands of twisted graphene layers 1. Origin of Mott Insulating Behavior and Superconductivity in Twisted
Scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy of graphene layers on graphite
 Scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy of graphene layers on graphite Adina Luican, Guohong Li and Eva Y. Andrei Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey
Scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy of graphene layers on graphite Adina Luican, Guohong Li and Eva Y. Andrei Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphene bilayer with a twist and a Magnetic Field. Workshop on Quantum Correlations and Coherence in Quantum Matter
 Ultra-thin graphite: methods Graphene signature: Dirac Fermions Moiré patterns in the bilayer (H=0) Hexagonal Superlattice and Magnetic Field Results Conclusion Graphene bilayer with a twist and a Magnetic
Ultra-thin graphite: methods Graphene signature: Dirac Fermions Moiré patterns in the bilayer (H=0) Hexagonal Superlattice and Magnetic Field Results Conclusion Graphene bilayer with a twist and a Magnetic
Supplementary Figure 1. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) of bilayer graphene and tblg. (a) AB
 Supplementary Figure 1. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) of bilayer graphene and tblg. (a) AB stacked bilayer graphene (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) are twisted bilayer graphene with twist angle
Supplementary Figure 1. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) of bilayer graphene and tblg. (a) AB stacked bilayer graphene (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) are twisted bilayer graphene with twist angle
BIASED TWISTED BILAYER GRAPHENE: MAGNETISM AND GAP
 BIASED TWISTED BILAYER GRAPHENE: MAGNETISM AND GAP A.V. Rozhkov, A.O. Sboychakov, A.L. Rakhmanov, F. Nori ITAE RAS, Moscow, Russia RIKEN, Wako-shi, Japan Presentation outline: General properties of twisted
BIASED TWISTED BILAYER GRAPHENE: MAGNETISM AND GAP A.V. Rozhkov, A.O. Sboychakov, A.L. Rakhmanov, F. Nori ITAE RAS, Moscow, Russia RIKEN, Wako-shi, Japan Presentation outline: General properties of twisted
STM spectra of graphene
 STM spectra of graphene K. Sengupta Theoretical Physics Division, IACS, Kolkata. Collaborators G. Baskaran, I.M.Sc Chennai, K. Saha, IACS Kolkata I. Paul, Grenoble France H. Manoharan, Stanford USA Refs:
STM spectra of graphene K. Sengupta Theoretical Physics Division, IACS, Kolkata. Collaborators G. Baskaran, I.M.Sc Chennai, K. Saha, IACS Kolkata I. Paul, Grenoble France H. Manoharan, Stanford USA Refs:
Spatially resolving density-dependent screening around a single charged atom in graphene
 Supplementary Information for Spatially resolving density-dependent screening around a single charged atom in graphene Dillon Wong, Fabiano Corsetti, Yang Wang, Victor W. Brar, Hsin-Zon Tsai, Qiong Wu,
Supplementary Information for Spatially resolving density-dependent screening around a single charged atom in graphene Dillon Wong, Fabiano Corsetti, Yang Wang, Victor W. Brar, Hsin-Zon Tsai, Qiong Wu,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10941 1. Motivation and summary of results. In this work we combine a central tenet of condensed matter physics how electronic band structure emerges from a periodic potential in a crystal
doi:10.1038/nature10941 1. Motivation and summary of results. In this work we combine a central tenet of condensed matter physics how electronic band structure emerges from a periodic potential in a crystal
Probing Dirac Fermions in Graphene by Scanning Tunneling Probes
 Probing Dirac Fermions in Graphene by Scanning Tunneling Probes Adina Luican-Mayer and Eva Y. Andrei Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA Abstract Graphene
Probing Dirac Fermions in Graphene by Scanning Tunneling Probes Adina Luican-Mayer and Eva Y. Andrei Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA Abstract Graphene
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1STM images of four GNBs and their corresponding STS spectra. a-d, STM images of four GNBs are shown in the left side. The experimental STS data with respective
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1STM images of four GNBs and their corresponding STS spectra. a-d, STM images of four GNBs are shown in the left side. The experimental STS data with respective
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS4186 Stripes Developed at the Strong Limit of Nematicity in FeSe film Wei Li 1,2,3*, Yan Zhang 2,3,4,5, Peng Deng 1, Zhilin Xu 1, S.-K.
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS4186 Stripes Developed at the Strong Limit of Nematicity in FeSe film Wei Li 1,2,3*, Yan Zhang 2,3,4,5, Peng Deng 1, Zhilin Xu 1, S.-K.
Supplementary Figure 1 Magneto-transmission spectra of graphene/h-bn sample 2 and Landau level transition energies of three other samples.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Magneto-transmission spectra of graphene/h-bn sample 2 and Landau level transition energies of three other samples. (a,b) Magneto-transmission ratio spectra T(B)/T(B 0 ) of graphene/h-bn
Supplementary Figure 1 Magneto-transmission spectra of graphene/h-bn sample 2 and Landau level transition energies of three other samples. (a,b) Magneto-transmission ratio spectra T(B)/T(B 0 ) of graphene/h-bn
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/7/e1700704/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Giant Rashba splitting in 2D organic-inorganic halide perovskites measured by transient spectroscopies Yaxin Zhai,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/7/e1700704/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Giant Rashba splitting in 2D organic-inorganic halide perovskites measured by transient spectroscopies Yaxin Zhai,
Evolution of Landau Levels into Edge States in Graphene
 Evolution of Landau Levels into Edge States in Graphene Guohong Li 1, Adina Luican-Mayer 1, Dmitry Abanin 2, Leonid Levitov 3, Eva Y. Andrei 1* 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University,
Evolution of Landau Levels into Edge States in Graphene Guohong Li 1, Adina Luican-Mayer 1, Dmitry Abanin 2, Leonid Levitov 3, Eva Y. Andrei 1* 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS4080 Topological states in engineered atomic lattices Robert Drost, Teemu Ojanen, Ari Harju, and Peter Liljeroth Department of Applied
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS4080 Topological states in engineered atomic lattices Robert Drost, Teemu Ojanen, Ari Harju, and Peter Liljeroth Department of Applied
Tuning Structures and Electronic Spectra of Graphene Layers by Tilt
 Tuning Structures and Electronic Spectra of Graphene Layers by Tilt Grain Boundaries Long-Jing Yin 1,, Jia-Bin Qiao 1,, Wen-Xiao Wang 1, Zhao-Dong Chu 1, Kai Fen Zhang 2, Rui-Fen Dou 1, *, Chun Lei Gao
Tuning Structures and Electronic Spectra of Graphene Layers by Tilt Grain Boundaries Long-Jing Yin 1,, Jia-Bin Qiao 1,, Wen-Xiao Wang 1, Zhao-Dong Chu 1, Kai Fen Zhang 2, Rui-Fen Dou 1, *, Chun Lei Gao
Evolution of Landau Levels into Edge States at an Atomically Sharp Edge in
 Evolution of Landau Levels into Edge States at an Atomically Sharp Edge in Graphene. Guohong Li 1, Adina Luican 1, Dmitry Abanin 2, Leonid Levitov 3, Eva Y. Andrei 1* 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Evolution of Landau Levels into Edge States at an Atomically Sharp Edge in Graphene. Guohong Li 1, Adina Luican 1, Dmitry Abanin 2, Leonid Levitov 3, Eva Y. Andrei 1* 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Nov 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Nov 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Nov 2007](/thumbs/93/112291523.jpg) Transport properties of graphene nanoribbon arxiv:7.6v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 6 Nov 7 heterostructures L. Rosales a,, P. Orellana b, Z. Barticevic a, M.Pacheco a a Departamento de Física, Universidad Técnica
Transport properties of graphene nanoribbon arxiv:7.6v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 6 Nov 7 heterostructures L. Rosales a,, P. Orellana b, Z. Barticevic a, M.Pacheco a a Departamento de Física, Universidad Técnica
STM spectroscopy (STS)
 STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum
 Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.138 Graphene Nanoribbons with Smooth Edges as Quantum Wires Xinran Wang, Yijian Ouyang, Liying Jiao, Hailiang Wang, Liming Xie, Justin Wu, Jing Guo, and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.138 Graphene Nanoribbons with Smooth Edges as Quantum Wires Xinran Wang, Yijian Ouyang, Liying Jiao, Hailiang Wang, Liming Xie, Justin Wu, Jing Guo, and
structure of graphene and carbon nanotubes which forms the basis for many of their proposed applications in electronics.
 Chapter Basics of graphene and carbon nanotubes This chapter reviews the theoretical understanding of the geometrical and electronic structure of graphene and carbon nanotubes which forms the basis for
Chapter Basics of graphene and carbon nanotubes This chapter reviews the theoretical understanding of the geometrical and electronic structure of graphene and carbon nanotubes which forms the basis for
Carbon nanotubes and Graphene
 16 October, 2008 Solid State Physics Seminar Main points 1 History and discovery of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes 2 Tight-binding approximation Dynamics of electrons near the Dirac-points 3 Properties
16 October, 2008 Solid State Physics Seminar Main points 1 History and discovery of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes 2 Tight-binding approximation Dynamics of electrons near the Dirac-points 3 Properties
Graphene and Planar Dirac Equation
 Graphene and Planar Dirac Equation Marina de la Torre Mayado 2016 Marina de la Torre Mayado Graphene and Planar Dirac Equation June 2016 1 / 48 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Dirac Model Tight-binding model
Graphene and Planar Dirac Equation Marina de la Torre Mayado 2016 Marina de la Torre Mayado Graphene and Planar Dirac Equation June 2016 1 / 48 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Dirac Model Tight-binding model
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Studies of Topological Insulators Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy
 EPJ Web of Conferences 23, 00020 ( 2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20122300020 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Studies of Topological Insulators Grown
EPJ Web of Conferences 23, 00020 ( 2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20122300020 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Studies of Topological Insulators Grown
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Mar 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Mar 2012](/thumbs/86/94300520.jpg) arxiv:1202.2612v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Mar 2012 Ab-initio analysis of superstructures revealed by STM on bilayer graphene E. Cisternas 1 and J. D. Correa 2 1 Departamento de Ciencias Físicas, Universidad
arxiv:1202.2612v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 13 Mar 2012 Ab-initio analysis of superstructures revealed by STM on bilayer graphene E. Cisternas 1 and J. D. Correa 2 1 Departamento de Ciencias Físicas, Universidad
Valley Zeeman effect in elementary optical excitations of monolayerwse 2
 Valley Zeeman effect in elementary optical excitations of monolayerwse 2 Ajit Srivastava 1, Meinrad Sidler 1, Adrien V. Allain 2, Dominik S. Lembke 2, Andras Kis 2, and A. Imamoğlu 1 1 Institute of Quantum
Valley Zeeman effect in elementary optical excitations of monolayerwse 2 Ajit Srivastava 1, Meinrad Sidler 1, Adrien V. Allain 2, Dominik S. Lembke 2, Andras Kis 2, and A. Imamoğlu 1 1 Institute of Quantum
Scanning probe microscopy of graphene with a CO terminated tip
 Scanning probe microscopy of graphene with a CO terminated tip Andrea Donarini T. Hofmann, A. J. Weymouth, F. Gießibl 7.5.2014 - Theory Group Seminar The sample Single monolayer of graphene Epitaxial growth
Scanning probe microscopy of graphene with a CO terminated tip Andrea Donarini T. Hofmann, A. J. Weymouth, F. Gießibl 7.5.2014 - Theory Group Seminar The sample Single monolayer of graphene Epitaxial growth
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature12186 S1. WANNIER DIAGRAM B 1 1 a φ/φ O 1/2 1/3 1/4 1/5 1 E φ/φ O n/n O 1 FIG. S1: Left is a cartoon image of an electron subjected to both a magnetic field, and a square periodic lattice.
doi:1.138/nature12186 S1. WANNIER DIAGRAM B 1 1 a φ/φ O 1/2 1/3 1/4 1/5 1 E φ/φ O n/n O 1 FIG. S1: Left is a cartoon image of an electron subjected to both a magnetic field, and a square periodic lattice.
The tunnelling spectra of quasi-free-standing graphene monolayer
 The tunnelling spectra of quasi-free-standing graphene monolayer Si-Yu Li, Ke-Ke Bai, Wei-Jie Zuo, Yi-Wen Liu, Zhong-Qiu Fu, Wen-Xiao Wang, Yu Zhang, Long-Jing Yin, Jia-Bin Qiao, Lin He* Department of
The tunnelling spectra of quasi-free-standing graphene monolayer Si-Yu Li, Ke-Ke Bai, Wei-Jie Zuo, Yi-Wen Liu, Zhong-Qiu Fu, Wen-Xiao Wang, Yu Zhang, Long-Jing Yin, Jia-Bin Qiao, Lin He* Department of
Direct imaging of topological edge states at a bilayer graphene domain wall
 Direct imaging of topological edge states at a bilayer graphene domain wall Long-Jing Yin 1, Hua Jiang 2, Jia-Bin Qiao 1, Lin He 1, * 1 Center for Advanced Quantum Studies, Department of Physics, Beijing
Direct imaging of topological edge states at a bilayer graphene domain wall Long-Jing Yin 1, Hua Jiang 2, Jia-Bin Qiao 1, Lin He 1, * 1 Center for Advanced Quantum Studies, Department of Physics, Beijing
STM and graphene. W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23
 STM and graphene W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23 Why graphene is important: It is a new form of material (two dimensional, single
STM and graphene W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23 Why graphene is important: It is a new form of material (two dimensional, single
Supersymmetry and Quantum Hall effect in graphene
 Supersymmetry and Quantum Hall effect in graphene Ervand Kandelaki Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Festköperphysik Institut für Theoretische Physik IV Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg March 14, 007 1 Introduction
Supersymmetry and Quantum Hall effect in graphene Ervand Kandelaki Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Festköperphysik Institut für Theoretische Physik IV Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg March 14, 007 1 Introduction
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS3968 Topological mosaic in Moiré superlattices of van der Waals heterobilayers Qingjun Tong 1, Hongyi Yu 1, Qizhong Zhu 1, Yong Wang
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS3968 Topological mosaic in Moiré superlattices of van der Waals heterobilayers Qingjun Tong 1, Hongyi Yu 1, Qizhong Zhu 1, Yong Wang
Magnetic control of valley pseudospin in monolayer WSe 2
 Magnetic control of valley pseudospin in monolayer WSe 2 Grant Aivazian, Zhirui Gong, Aaron M. Jones, Rui-Lin Chu, Jiaqiang Yan, David G. Mandrus, Chuanwei Zhang, David Cobden, Wang Yao, and Xiaodong Xu
Magnetic control of valley pseudospin in monolayer WSe 2 Grant Aivazian, Zhirui Gong, Aaron M. Jones, Rui-Lin Chu, Jiaqiang Yan, David G. Mandrus, Chuanwei Zhang, David Cobden, Wang Yao, and Xiaodong Xu
lattice that you cannot do with graphene! or... Antonio H. Castro Neto
 Theoretical Aspects What you can do with cold atomsof on agraphene honeycomb lattice that you cannot do with graphene! or... Antonio H. Castro Neto 2 Outline 1. Graphene for beginners 2. Fermion-Fermion
Theoretical Aspects What you can do with cold atomsof on agraphene honeycomb lattice that you cannot do with graphene! or... Antonio H. Castro Neto 2 Outline 1. Graphene for beginners 2. Fermion-Fermion
Magneto-spectroscopy of multilayer epitaxial graphene, of graphite and of graphene
 Magneto-spectroscopy of multilayer epitaxial graphene, of graphite and of graphene Marek Potemski Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique Grenoble, France
Magneto-spectroscopy of multilayer epitaxial graphene, of graphite and of graphene Marek Potemski Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique Grenoble, France
Observation of Dirac node formation and mass acquisition in a topological crystalline insulator
 Observation of Dirac node formation and mass acquisition in a topological crystalline insulator Yoshinori Okada 1, 2, Maksym Serbyn* 3, Hsin Lin* 4, Daniel Walkup 1, Wenwen Zhou 1, Chetan Dhital 1, Madhab
Observation of Dirac node formation and mass acquisition in a topological crystalline insulator Yoshinori Okada 1, 2, Maksym Serbyn* 3, Hsin Lin* 4, Daniel Walkup 1, Wenwen Zhou 1, Chetan Dhital 1, Madhab
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes
 Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Carbon nanotubes: Models, correlations and the local density of states
 Carbon nanotubes: Models, correlations and the local density of states Alexander Struck in collaboration with Sebastián A. Reyes Sebastian Eggert 15. 03. 2010 Outline Carbon structures Modelling of a carbon
Carbon nanotubes: Models, correlations and the local density of states Alexander Struck in collaboration with Sebastián A. Reyes Sebastian Eggert 15. 03. 2010 Outline Carbon structures Modelling of a carbon
Quantum Electrodynamics in Graphene
 Quantum Electrodynamics in Graphene Judy G. Cherian Kutztown University of PA Physics REU 2006 Univ. Of Washington Advisor- Dr. David Cobden Dr. Sam Fain Andrew Jones Graphene, a single layer of graphite,
Quantum Electrodynamics in Graphene Judy G. Cherian Kutztown University of PA Physics REU 2006 Univ. Of Washington Advisor- Dr. David Cobden Dr. Sam Fain Andrew Jones Graphene, a single layer of graphite,
Beautiful Graphene, Photonic Crystals, Schrödinger and Dirac Billiards and Their Spectral Properties
 Beautiful Graphene, Photonic Crystals, Schrödinger and Dirac Billiards and Their Spectral Properties Cocoyoc 2012 Something about graphene and microwave billiards Dirac spectrum in a photonic crystal Experimental
Beautiful Graphene, Photonic Crystals, Schrödinger and Dirac Billiards and Their Spectral Properties Cocoyoc 2012 Something about graphene and microwave billiards Dirac spectrum in a photonic crystal Experimental
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013](/thumbs/83/88173709.jpg) Berry phase and the unconventional quantum Hall effect in graphene Jiamin Xue Microelectronic Research Center, The University arxiv:1309.6714v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013 of Texas at Austin, Austin,
Berry phase and the unconventional quantum Hall effect in graphene Jiamin Xue Microelectronic Research Center, The University arxiv:1309.6714v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013 of Texas at Austin, Austin,
Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene
 Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene quantum dots 3 4 5 Juwon Lee, Dillon Wong, Jairo Velasco Jr., Joaquin F. Rodriguez-Nieva, Salman Kahn, Hsin- Zon Tsai, Takashi Taniguchi, Kenji
Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene quantum dots 3 4 5 Juwon Lee, Dillon Wong, Jairo Velasco Jr., Joaquin F. Rodriguez-Nieva, Salman Kahn, Hsin- Zon Tsai, Takashi Taniguchi, Kenji
3-month progress Report
 3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
Tunable Moiré Bands and Strong Correlations in Small-Twist-Angle Bilayer Graphene
 Tunable Moiré Bands and Strong Correlations in Small-Twist-Angle Bilayer Graphene Authors: Kyounghwan Kim 1, Ashley DaSilva 2, Shengqiang Huang 3, Babak Fallahazad 1, Stefano Larentis 1, Takashi Taniguchi
Tunable Moiré Bands and Strong Correlations in Small-Twist-Angle Bilayer Graphene Authors: Kyounghwan Kim 1, Ashley DaSilva 2, Shengqiang Huang 3, Babak Fallahazad 1, Stefano Larentis 1, Takashi Taniguchi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A Dirac point insulator with topologically non-trivial surface states D. Hsieh, D. Qian, L. Wray, Y. Xia, Y.S. Hor, R.J. Cava, and M.Z. Hasan Topics: 1. Confirming the bulk nature of electronic bands by
A Dirac point insulator with topologically non-trivial surface states D. Hsieh, D. Qian, L. Wray, Y. Xia, Y.S. Hor, R.J. Cava, and M.Z. Hasan Topics: 1. Confirming the bulk nature of electronic bands by
Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob
 Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob Rafael Roldán and Andres Castellanos-Gomez Modern electronics rely on devices whose functionality can be adjusted by the end-user with an external knob. A new
Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob Rafael Roldán and Andres Castellanos-Gomez Modern electronics rely on devices whose functionality can be adjusted by the end-user with an external knob. A new
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Zero-bias conductance peak in detached flakes of superconducting 2H-TaS2 probed by STS
 Zero-bias conductance peak in detached flakes of superconducting 2H-TaS2 probed by STS J. A. Galvis, L. C., I. Guillamon, S. Vieira, E. Navarro-Moratalla, E. Coronado, H. Suderow, F. Guinea Laboratorio
Zero-bias conductance peak in detached flakes of superconducting 2H-TaS2 probed by STS J. A. Galvis, L. C., I. Guillamon, S. Vieira, E. Navarro-Moratalla, E. Coronado, H. Suderow, F. Guinea Laboratorio
Nanoscience quantum transport
 Nanoscience quantum transport Janine Splettstößer Applied Quantum Physics, MC2, Chalmers University of Technology Chalmers, November 2 10 Plan/Outline 4 Lectures (1) Introduction to quantum transport (2)
Nanoscience quantum transport Janine Splettstößer Applied Quantum Physics, MC2, Chalmers University of Technology Chalmers, November 2 10 Plan/Outline 4 Lectures (1) Introduction to quantum transport (2)
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Jul 2012 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 26 Jul 2012](/thumbs/71/66089852.jpg) Graphene on metallic surfaces: problems and perspectives E. N. Voloshina 1, and Yu. S. Dedkov 2 1 Physikalische und Theoretische Chemie, Freie Universität Berlin, 14195 Berlin, Germany and 2 SPECS Surface
Graphene on metallic surfaces: problems and perspectives E. N. Voloshina 1, and Yu. S. Dedkov 2 1 Physikalische und Theoretische Chemie, Freie Universität Berlin, 14195 Berlin, Germany and 2 SPECS Surface
Band Structure of Isolated and Bundled Nanotubes
 Chapter 5 Band Structure of Isolated and Bundled Nanotubes The electronic structure of carbon nanotubes is characterized by a series of bands (sub- or minibands) arising from the confinement around the
Chapter 5 Band Structure of Isolated and Bundled Nanotubes The electronic structure of carbon nanotubes is characterized by a series of bands (sub- or minibands) arising from the confinement around the
Supplementary Figure 1: MoS2 crystals on WSe2-EG and EG and WSe2 crystals on MoSe2-EG and EG.
 Supplementary Figure 1: MoS2 crystals on WSe2-EG and EG and WSe2 crystals on MoSe2-EG and EG. (a) The MoS2 crystals cover both of EG and WSe2/EG after the CVD growth (Scar bar: 400 nm) (b) shows TEM profiles
Supplementary Figure 1: MoS2 crystals on WSe2-EG and EG and WSe2 crystals on MoSe2-EG and EG. (a) The MoS2 crystals cover both of EG and WSe2/EG after the CVD growth (Scar bar: 400 nm) (b) shows TEM profiles
Supplementary Figure 1 Typical angles of the corners of the 2D compact MoSe2 islands.
 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1 Typical angles of the corners of the 2D compact MoSe2 islands. 3 The scale bar at the bottom represents 500 nm. 60, 90, 120 and 150, originated from the inter- 4 junctioning
1 2 Supplementary Figure 1 Typical angles of the corners of the 2D compact MoSe2 islands. 3 The scale bar at the bottom represents 500 nm. 60, 90, 120 and 150, originated from the inter- 4 junctioning
Edge conduction in monolayer WTe 2
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 1.138/NPHYS491 Edge conduction in monolayer WTe 2 Contents SI-1. Characterizations of monolayer WTe2 devices SI-2. Magnetoresistance and temperature
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 1.138/NPHYS491 Edge conduction in monolayer WTe 2 Contents SI-1. Characterizations of monolayer WTe2 devices SI-2. Magnetoresistance and temperature
Physical Properties of Mono-layer of
 Chapter 3 Physical Properties of Mono-layer of Silicene The fascinating physical properties[ 6] associated with graphene have motivated many researchers to search for new graphene-like two-dimensional
Chapter 3 Physical Properties of Mono-layer of Silicene The fascinating physical properties[ 6] associated with graphene have motivated many researchers to search for new graphene-like two-dimensional
Electronic, optical, and phononic properties of graphene, boron nitride, and related materials. Cheol Hwan Park
 Electronic, optical, and phononic properties of graphene, boron nitride, and related materials by Cheol Hwan Park A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of
Electronic, optical, and phononic properties of graphene, boron nitride, and related materials by Cheol Hwan Park A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of
Electronic Properties of Ultimate Nanowires. F. J. Himpsel, S. C. Erwin, I. Barke,
 Electronic Properties of Ultimate Nanowires F. J. Himpsel, S. C. Erwin, I. Barke, Nanostructures with Atomic Precision Single-Atom Wire, Single Wave Function Ultimate Limits of Electronics, Data Storage
Electronic Properties of Ultimate Nanowires F. J. Himpsel, S. C. Erwin, I. Barke, Nanostructures with Atomic Precision Single-Atom Wire, Single Wave Function Ultimate Limits of Electronics, Data Storage
Multilayer graphene under vertical electric field
 Multilayer graphene under vertical electric field S. Bala kumar and Jing Guo a) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 3608, USA Abstract We study
Multilayer graphene under vertical electric field S. Bala kumar and Jing Guo a) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 3608, USA Abstract We study
2) Atom manipulation. Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment:
 2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
2) Atom manipulation D. Eigler & E. Schweizer, Nature 344, 524 (1990) Xe / Ni(110) Model: Experiment: G.Meyer, et al. Applied Physics A 68, 125 (1999) First the tip is approached close to the adsorbate
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator
 Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO 3 (001) film
 Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO 3 (001) film Z. F. Wang 1,2,3+, Huimin Zhang 2,4+, Defa Liu 5, Chong Liu 2, Chenjia Tang 2, Canli Song 2, Yong Zhong 2, Junping Peng
Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO 3 (001) film Z. F. Wang 1,2,3+, Huimin Zhang 2,4+, Defa Liu 5, Chong Liu 2, Chenjia Tang 2, Canli Song 2, Yong Zhong 2, Junping Peng
Breakdown of continuum mechanics for nanometre-wavelength rippling of graphene
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS2389 Breakdown of continuum mechanics for nanometre-wavelength rippling of graphene 1. Growth conditions and surface morphology of graphene on Cu(111) surface
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS2389 Breakdown of continuum mechanics for nanometre-wavelength rippling of graphene 1. Growth conditions and surface morphology of graphene on Cu(111) surface
S.1: Fabrication & characterization of twisted bilayer graphene 6.8
 Supplementary Materials: Tunable optical excitations in twisted bilayer graphene form strongly bound excitons Hiral Patel1, Robin W. Havener2,3, Lola Brown2,3, Yufeng Liang4, Li Yang4, Jiwoong Park2,3,and
Supplementary Materials: Tunable optical excitations in twisted bilayer graphene form strongly bound excitons Hiral Patel1, Robin W. Havener2,3, Lola Brown2,3, Yufeng Liang4, Li Yang4, Jiwoong Park2,3,and
Magneto-Optical Properties of Quantum Nanostructures
 Magneto-optics of nanostructures Magneto-Optical Properties of Quantum Nanostructures Milan Orlita Institute of Physics, Charles University Institute of Physics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic
Magneto-optics of nanostructures Magneto-Optical Properties of Quantum Nanostructures Milan Orlita Institute of Physics, Charles University Institute of Physics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic
The many forms of carbon
 The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
Tight binding and emergence of "Dirac" equation in graphene.
 Tight binding and emergence of "Dirac" equation in graphene. A. A. Kozhevnikov 1 1 Laboratory of Theoretical Physics, S. L. Sobolev Institute for Mathematics, and Novosibirsk State University April 22,
Tight binding and emergence of "Dirac" equation in graphene. A. A. Kozhevnikov 1 1 Laboratory of Theoretical Physics, S. L. Sobolev Institute for Mathematics, and Novosibirsk State University April 22,
FEATURE ARTICLE. Structure and Electronic Properties of Carbon Nanotubes. Teri Wang Odom, Jin-Lin Huang, Philip Kim, and Charles M.
 2794 J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2794-2809 FEATURE ARTICLE Structure and Electronic Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Teri Wang Odom, Jin-Lin Huang, Philip Kim, and Charles M. Lieber* Department of Chemistry
2794 J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2794-2809 FEATURE ARTICLE Structure and Electronic Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Teri Wang Odom, Jin-Lin Huang, Philip Kim, and Charles M. Lieber* Department of Chemistry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Method: Epitaxial graphene was prepared by heating an Ir(111) crystal to 550 K for 100 s under 2 x 10-5 Pa partial pressure of ethylene, followed by a flash anneal to 1420 K 1.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Method: Epitaxial graphene was prepared by heating an Ir(111) crystal to 550 K for 100 s under 2 x 10-5 Pa partial pressure of ethylene, followed by a flash anneal to 1420 K 1.
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy/Spectroscopy
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy/Spectroscopy 0 Scanning Tunneling Microscope 1 Scanning Tunneling Microscope 2 Scanning Tunneling Microscope 3 Typical STM talk or paper... The differential conductance di/dv
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy/Spectroscopy 0 Scanning Tunneling Microscope 1 Scanning Tunneling Microscope 2 Scanning Tunneling Microscope 3 Typical STM talk or paper... The differential conductance di/dv
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 25 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 25 Mar 2010 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 25 Mar 2010](/thumbs/75/72791534.jpg) Electronic structure of turbostratic graphene S. Shallcross 1, S. Sharma 2, E. Kandelaki 1,3, and O. A. Pankratov 1 1 Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Festkörperphysik, arxiv:0910.5811v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci]
Electronic structure of turbostratic graphene S. Shallcross 1, S. Sharma 2, E. Kandelaki 1,3, and O. A. Pankratov 1 1 Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Festkörperphysik, arxiv:0910.5811v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci]
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06219 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Abrupt Onset of Second Energy Gap at Superconducting Transition of Underdoped Bi2212 Wei-Sheng Lee 1, I. M. Vishik 1, K. Tanaka 1,2, D. H. Lu 1, T. Sasagawa
doi: 10.1038/nature06219 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Abrupt Onset of Second Energy Gap at Superconducting Transition of Underdoped Bi2212 Wei-Sheng Lee 1, I. M. Vishik 1, K. Tanaka 1,2, D. H. Lu 1, T. Sasagawa
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Self-assembled nanopatch with peptide-organic multilayers and mechanical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Self-assembled nanopatch with peptide-organic multilayers and mechanical
Supplementary information for Probing atomic structure and Majorana wavefunctions in mono-atomic Fe chains on superconducting Pb surface
 Supplementary information for Probing atomic structure and Majorana wavefunctions in mono-atomic Fe chains on superconducting Pb surface Rémy Pawlak 1, Marcin Kisiel 1, Jelena Klinovaja 1, Tobias Meier
Supplementary information for Probing atomic structure and Majorana wavefunctions in mono-atomic Fe chains on superconducting Pb surface Rémy Pawlak 1, Marcin Kisiel 1, Jelena Klinovaja 1, Tobias Meier
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Direct observation of the transition from indirect to direct bandgap in atomically thin epitaxial MoSe 2 Yi Zhang, Tay-Rong Chang, Bo Zhou, Yong-Tao Cui, Hao Yan, Zhongkai Liu, Felix Schmitt, James Lee,
Direct observation of the transition from indirect to direct bandgap in atomically thin epitaxial MoSe 2 Yi Zhang, Tay-Rong Chang, Bo Zhou, Yong-Tao Cui, Hao Yan, Zhongkai Liu, Felix Schmitt, James Lee,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Point-contact spectra of a Pt-Ir tip/lto film junction. The main panel shows differential conductance at 2, 12, 13, 16 K (0 T), and 10 K (2 T) to demonstrate
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Point-contact spectra of a Pt-Ir tip/lto film junction. The main panel shows differential conductance at 2, 12, 13, 16 K (0 T), and 10 K (2 T) to demonstrate
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems Anjan K. Gupta Physics Department, I. I. T Kanpur ICTS-GJ, IITK, Feb 2010 Acknowledgements
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy & Spectroscopy: A tool for probing electronic inhomogeneities in correlated systems Anjan K. Gupta Physics Department, I. I. T Kanpur ICTS-GJ, IITK, Feb 2010 Acknowledgements
Microscopical and Microanalytical Methods (NANO3)
 Microscopical and Microanalytical Methods (NANO3) 06.11.15 10:15-12:00 Introduction - SPM methods 13.11.15 10:15-12:00 STM 20.11.15 10:15-12:00 STS Erik Zupanič erik.zupanic@ijs.si stm.ijs.si 27.11.15
Microscopical and Microanalytical Methods (NANO3) 06.11.15 10:15-12:00 Introduction - SPM methods 13.11.15 10:15-12:00 STM 20.11.15 10:15-12:00 STS Erik Zupanič erik.zupanic@ijs.si stm.ijs.si 27.11.15
Chapter 5 Nanomanipulation. Chapter 5 Nanomanipulation. 5.1: With a nanotube. Cutting a nanotube. Moving a nanotube
 Objective: learn about nano-manipulation techniques with a STM or an AFM. 5.1: With a nanotube Moving a nanotube Cutting a nanotube Images at large distance At small distance : push the NT Voltage pulse
Objective: learn about nano-manipulation techniques with a STM or an AFM. 5.1: With a nanotube Moving a nanotube Cutting a nanotube Images at large distance At small distance : push the NT Voltage pulse
Direct Observation of Nodes and Twofold Symmetry in FeSe Superconductor
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6036/1410/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Direct Observation of Nodes and Twofold Symmetry in FeSe Superconductor Can-Li Song, Yi-Lin Wang, Peng Cheng, Ye-Ping
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6036/1410/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Direct Observation of Nodes and Twofold Symmetry in FeSe Superconductor Can-Li Song, Yi-Lin Wang, Peng Cheng, Ye-Ping
Twisted Bilayer Graphene Superlattices
 Twisted Bilayer Graphene Superlattices Yanan Wang 1, Zhihua Su 1, Wei Wu 1,2, Shu Nie 3, Nan Xie 4, Huiqi Gong 4, Yang Guo 4, Joon Hwan Lee 5, Sirui Xing 1,2, Xiaoxiang Lu 1, Haiyan Wang 5, Xinghua Lu
Twisted Bilayer Graphene Superlattices Yanan Wang 1, Zhihua Su 1, Wei Wu 1,2, Shu Nie 3, Nan Xie 4, Huiqi Gong 4, Yang Guo 4, Joon Hwan Lee 5, Sirui Xing 1,2, Xiaoxiang Lu 1, Haiyan Wang 5, Xinghua Lu
Graphene and Quantum Hall (2+1)D Physics
 The 4 th QMMRC-IPCMS Winter School 8 Feb 2011, ECC, Seoul, Korea Outline 2 Graphene and Quantum Hall (2+1)D Physics Lecture 1. Electronic structures of graphene and bilayer graphene Lecture 2. Electrons
The 4 th QMMRC-IPCMS Winter School 8 Feb 2011, ECC, Seoul, Korea Outline 2 Graphene and Quantum Hall (2+1)D Physics Lecture 1. Electronic structures of graphene and bilayer graphene Lecture 2. Electrons
Observation of an Electric-Field Induced Band Gap in Bilayer Graphene by Infrared Spectroscopy. Cleveland, OH 44106, USA
 Observation of an Electric-Field Induced Band Gap in Bilayer Graphene by Infrared Spectroscopy Kin Fai Mak 1, Chun Hung Lui 1, Jie Shan 2, and Tony F. Heinz 1* 1 Departments of Physics and Electrical Engineering,
Observation of an Electric-Field Induced Band Gap in Bilayer Graphene by Infrared Spectroscopy Kin Fai Mak 1, Chun Hung Lui 1, Jie Shan 2, and Tony F. Heinz 1* 1 Departments of Physics and Electrical Engineering,
Electrons in a periodic potential
 Chapter 3 Electrons in a periodic potential 3.1 Bloch s theorem. We consider in this chapter electrons under the influence of a static, periodic potential V (x), i.e. such that it fulfills V (x) = V (x
Chapter 3 Electrons in a periodic potential 3.1 Bloch s theorem. We consider in this chapter electrons under the influence of a static, periodic potential V (x), i.e. such that it fulfills V (x) = V (x
Program Operacyjny Kapitał Ludzki SCANNING PROBE TECHNIQUES - INTRODUCTION
 Program Operacyjny Kapitał Ludzki SCANNING PROBE TECHNIQUES - INTRODUCTION Peter Liljeroth Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University School of Science peter.liljeroth@aalto.fi Projekt współfinansowany
Program Operacyjny Kapitał Ludzki SCANNING PROBE TECHNIQUES - INTRODUCTION Peter Liljeroth Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University School of Science peter.liljeroth@aalto.fi Projekt współfinansowany
Supplementary Information for Solution-Synthesized Chevron Graphene Nanoribbons Exfoliated onto H:Si(100)
 Supplementary Information for Solution-Synthesized Chevron Graphene Nanoribbons Exfoliated onto H:Si(100) Adrian Radocea,, Tao Sun,, Timothy H. Vo, Alexander Sinitskii,,# Narayana R. Aluru,, and Joseph
Supplementary Information for Solution-Synthesized Chevron Graphene Nanoribbons Exfoliated onto H:Si(100) Adrian Radocea,, Tao Sun,, Timothy H. Vo, Alexander Sinitskii,,# Narayana R. Aluru,, and Joseph
Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models
 Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models Frédéric Piéchon LPS (Orsay) with A. Raoux, J-N. Fuchs and G. Montambaux Orbital suceptibility Berry curvature ky? kx GDR Modmat,
Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models Frédéric Piéchon LPS (Orsay) with A. Raoux, J-N. Fuchs and G. Montambaux Orbital suceptibility Berry curvature ky? kx GDR Modmat,
Two-phonon Raman scattering in graphene for laser excitation beyond the π-plasmon energy
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Two-phonon Raman scattering in graphene for laser excitation beyond the π-plasmon energy To cite this article: Valentin N Popov 2016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Two-phonon Raman scattering in graphene for laser excitation beyond the π-plasmon energy To cite this article: Valentin N Popov 2016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Nanoscale characteristics by Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy
 Related Topics Tunneling effect, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), (STS), Local Density of States (LDOS), Band structure, Band Gap, k-space, Brioullin Zone, Metal, Semi-Metal, Semiconductor Principle
Related Topics Tunneling effect, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), (STS), Local Density of States (LDOS), Band structure, Band Gap, k-space, Brioullin Zone, Metal, Semi-Metal, Semiconductor Principle
How Cooper Pairs Vanish Approaching the Mott Insulator in Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8+δ
 doi: 1.138/nature7243 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION How Cooper Pairs Vanish Approaching the Mott Insulator in Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8+δ Y. Kohsaka et al. Supplementary Information I Instruments and Samples The
doi: 1.138/nature7243 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION How Cooper Pairs Vanish Approaching the Mott Insulator in Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8+δ Y. Kohsaka et al. Supplementary Information I Instruments and Samples The
Impurities and graphene hybrid structures: insights from first-principles theory
 Impurities and graphene hybrid structures: insights from first-principles theory Tim Wehling Institute for Theoretical Physics and Bremen Center for Computational Materials Science University of Bremen
Impurities and graphene hybrid structures: insights from first-principles theory Tim Wehling Institute for Theoretical Physics and Bremen Center for Computational Materials Science University of Bremen
