Mechanistic Studies in Copper Catalysis
|
|
|
- Mercy Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 chanistic Studies in Copper Catalysis Jen Alleva May 1st 2013
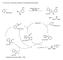
2 Timeline of Achievements in Copper Chemistry General istorical verview first cross-couplings 1869 Ullmann Goldberg Glaser 1903 Glaser, C. Ann. D. Chemie U. Pharm, 1869, 2,
3 Timeline of Achievements in Copper Chemistry General istorical verview first cross-couplings 1869 Ullmann Goldberg Glaser 1903 Ullman, F. Ber. 1903, 36, Goldberg, I. Ber. 1906, 39,
4 Timeline of Achievements in Copper Chemistry General istorical verview first cross-couplings Ullmann Goldberg Glaser 1903 eich Gilman synthesis of first copper organometallic reagents Gilman,.; Jones,. G.; Woods, L. A. J. rg. Chem, 1952, 17,
5 Timeline of Achievements in Copper Chemistry General istorical verview first cross-couplings "Click" Chemistry Ullmann Goldberg uisgen Glaser 1903 eich Gilman 1961 Sharpless synthesis of first copper organometallic reagents uisgen,. Proc. Chem Soc., 1961,
6 Timeline of Achievements in Copper Chemistry General istorical verview first cross-couplings "Click" Chemistry Ullmann Goldberg uisgen Glaser 1903 eich Gilman 1961 Sharpless synthesis of first copper organometallic reagents Chan-Evans-Lam Cu C couplings uisgen,. Proc. Chem Soc., 1961,
7 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions
8 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions B u =,, S = halide nucleophile = halide oxidative coupling standard cross-coupling oxidative coupling u Chan-Evans-Lam Ullmann-Goldberg "Aromatic Glaser-ay"
9 Electronic Properties of Copper E 1/2 = 0.16V E 1/2 = 2.4V Cu I Cu II Cu III d 10 isoelectronic with i(0) d 9 d 8, metal cation isoelectronic with Pd(II) * Vs. SCE in C, Bratsch, S. G. J. Phys. Chem. ef. Data 1989, 18, 1 21
10 Electronic Properties of Copper E 1/2 = 0.16V E 1/2 = 2.4V Cu I Cu II Cu III d 10 isoelectronic with i(0) d 9 d 8, metal cation isoelectronic with Pd(II) forms shorter bonds than Pd harder Lewis acidity than Pd higher affinity for, ligands smaller coordination shell can not accomodate large ancillary ligands Beletskaya, I. P; Cheprakov, A. V. rganometallics 2012, 31, * Vs. SCE in C, Bratsch, S. G. J. Phys. Chem. ef. Data 1989, 18, 1 21
11 Electronic Properties of Copper E 1/2 = 0.16V E 1/2 = 2.4V Cu I Cu II Cu III d 10 isoelectronic with i(0) d 9 d 8, metal cation isoelectronic with Pd(II) forms shorter bonds than Pd harder Lewis acidity than Pd higher affinity for, ligands smaller coordination shell can not accomodate large ancillary ligands highly electrophilic and unstable potent oxidizer requires highly stabilizing ligands Br Cu III Beletskaya, I. P; Cheprakov, A. V. rganometallics 2012, 31, * Vs. SCE in C, Bratsch, S. G. J. Phys. Chem. ef. Data 1989, 18, 1 21
12 Electronic Properties of Copper E 1/2 = 0.16V E 1/2 = 2.4V Cu I Cu II Cu III d 10 isoelectronic with i(0) d 9 d 8, metal cation isoelectronic with Pd(II) forms shorter bonds than Pd harder Lewis acidity than Pd higher affinity for, ligands smaller coordination shell can not accomodate large ancillary ligands highly electrophilic and unstable potent oxidizer requires highly stabilizing ligands unstable towards the reverse reductive elimination can not take part in ligand exchange requires the nucleophile to be in the coordination sphere prior to oxidative addition Beletskaya, I. P; Cheprakov, A. V. rganometallics 2012, 31, * Vs. SCE in C, Bratsch, S. G. J. Phys. Chem. ef. Data 1989, 18, 1 21
13 Cross-Coupling Classifications regular cross-coupling: transition metal mediated nucleophilic substitution B M L B organic electrophile nucleophile base
14 Cross-Coupling Classifications regular cross-coupling: transition metal mediated nucleophilic substitution B M L B organic electrophile nucleophile base 1 Pd II B Pd 0 Pd 0 /Pd II 2 1 Pd II B
15 Cross-Coupling Classifications regular cross-coupling: transition metal mediated nucleophilic substitution B M L B organic electrophile nucleophile base 1 Pd II B 2 Cu I Pd 0 /Pd II Cu I /Cu III Pd Pd II 3 Cu I 2 3 Cu III B nucleophile plays the role of ancillary ligand in Cu I /Cu III
16 Cross-Coupling Classifications oxidative cross-coupling: transition metal mediated coupling of two nucleophiles 1 M organic nucleophile 2 3 M L M 2e nucleophile M
17 Cross-Coupling Classifications oxidative cross-coupling: transition metal mediated coupling of two nucleophiles 1 M organic nucleophile 2 3 M L M 2e nucleophile M 1 M Pd II 1 M 2 3 Pd II Pd II /Pd IV 2 1 Pd II Pd IV 3
18 Cross-Coupling Classifications oxidative cross-coupling: transition metal mediated coupling of two nucleophiles 1 M organic nucleophile 2 3 M L M 2e nucleophile M 1 M Pd II 1 M Cu II Pd II Pd II /Pd IV 2 1 Pd II 3 2 Cu II Cu I /Cu II /Cu III 2 3 Cu II Cu I Cu II Pd IV Cu III 1
19 Cross-Coupling Classifications inverse or Umpolung cross-coupling: transition metal mediated electrophilic substitution 1 LG 2 3 M L LG organic nucleophile electrophile nucleofugal leaving group
20 Cross-Coupling Classifications inverse or Umpolung cross-coupling: transition metal mediated electrophilic substitution 1 LG 2 3 M L LG organic nucleophile electrophile nucleofugal leaving group 2 LG LG Pd II 1 Pd 0 Pd 0 /Pd II 2 1 Pd II
21 Cross-Coupling Classifications inverse or Umpolung cross-coupling: transition metal mediated electrophilic substitution 1 LG 2 3 M L LG organic nucleophile electrophile nucleofugal leaving group 2 LG LG Pd II Cu I LG 2 3 Pd 0 /Pd II Cu I /Cu III Pd Pd II 3 Cu I 2 3 Cu III
22 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions B u =,, S = halide nucleophile = halide oxidative coupling standard cross-coupling oxidative coupling u Chan-Evans-Lam Ullmann-Goldberg "Aromatic Glaser-ay"
23 chanistic Studies in Copper Catalysis Shannon Stahl avi ibas Ted Cohen
24 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions B u =,, S = halide nucleophile = halide oxidative coupling standard cross-coupling oxidative coupling u Chan-Evans-Lam Ullmann-Goldberg "Aromatic Glaser-ay"
25 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling oxidative cross-coupling B 2 equiv. Cu(Ac) 2 4Å mol sieves, 2 EtAc heteroatom boronic acid diaryl ether nucleophile Chan D. M. T.; Monaco, K. L.; Wang,.-P.; Winters, M. P. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, Evans, D. A.; Katz, J. L.; West, T.. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, Lam, P. Y. S.; Clark, C. G.; Saubern, S.; Adams, J.; Winters, M. P.; Chan, D. T., Combs, A. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 2941.
26 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling oxidative cross-coupling B 2 equiv. Cu(Ac) 2 4Å mol sieves, 2 EtAc heteroatom boronic acid diaryl ether nucleophile 2 Cu II Cu II Cu I /Cu II /Cu III 2 Cu II can be made catalytic with an added oxidant 2 Cu I 3 1 Cu II CEL is stoichiometric in Cu II Cu III 1
27 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling select catalytic methods B 20 mol% [Cu() TMEDA] 2 Cl 2 C 2 Cl 2, 2, r.t. 72% Collman, J. P.; Zhong, M. rg. Lett. 2000, 2,
28 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling select catalytic methods B 20 mol% [Cu() TMEDA] 2 Cl 2 C 2 Cl 2, 2, r.t. 72% 2 Si() equiv Cu(Ac) 2 TBAF, DMF, 2, r.t. 61% Lam, P. S.; Deudon, S.; auptman, E.; Clark, C. G. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, Collman, J. P.; Zhong, M. rg. Lett. 2000, 2,
29 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling select catalytic methods B 20 mol% [Cu() TMEDA] 2 Cl 2 C 2 Cl 2, 2, r.t. 72% 2 Si() equiv Cu(Ac) 2 TBAF, DMF, 2, r.t. 61% 2 B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 10 mol% myristic acid 2,6-lutidine, Ph, r.t. 91% Antilla, J. C.; Buchwald, S. L. rg Lett, 2001, 3, Lam, P. S.; Deudon, S.; auptman, E.; Clark, C. G. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, Collman, J. P.; Zhong, M. rg. Lett. 2000, 2,
30 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling determining reaction stoichiometry B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
31 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling determining reaction stoichiometry B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% Cu and 2 stoichiometry determined from anaerobic single-turnover experiment Cu II /product ratio is 2:1 King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
32 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling determining reaction stoichiometry B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% Cu and 2 stoichiometry determined from anaerobic single-turnover experiment result consistent with Cu oxidase mechanism Cu II /product ratio is 2:1 Cu I / 2 ratio is 4:1 King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
33 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling initial rates experiment reveals turnover-limiting step B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% Initial rates experiment: suggest transmetalation as turnover-limiting King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
34 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling initial rates experiment reveals turnover-limiting step B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% Initial rates experiment: suggest transmetalation as turnover-limiting 1 st order dependence on Cu(Ac) 2 saturation dependence on boronic ester King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
35 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling initial rates experiment reveals turnover-limiting step B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% Initial rates experiment: suggest transmetalation as turnover-limiting 1 st order dependence on Cu(Ac) 2 Cu I oxidation is relatively fast compared to transmetalation saturation dependence on boronic ester 0 order dependence on 2 King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
36 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d xy d z 2 d yz d xz ground state
37 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d xy d xy d z 2 d z 2 d yz d xz d yz d xz ground state coupling excited state
38 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d xy d xy d xy d z 2 d z 2 d z 2 d yz d xz d yz d xz d yz d xz ground state coupling excited state d z 2 does not couple orbitals have incorrect symmetry
39 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d xy d xy d xy d z 2 d z 2 d z 2 d yz d xz d yz d xz d yz d xz ground state coupling excited state d z 2 does not couple orbitals have incorrect symmetry g obs = g e xλ ΔE
40 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d xy d xy d xy d z 2 d z 2 d z 2 d yz d xz d yz d xz d yz d xz ground state coupling excited state d z 2 does not couple orbitals have incorrect symmetry g obs = g e xλ ΔE g obs : empirical value from spectrum g e : energy of free electron ( )
41 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d xy d xy d xy d z 2 d z 2 d z 2 d yz d xz d yz d xz d yz d xz ground state coupling excited state d z 2 does not couple orbitals have incorrect symmetry g obs = g e xλ ΔE g obs : empirical value from spectrum g e : energy of free electron ( ) x: modification factor of the free electron based on orbital mixing
42 Electron Paramagnetic esonance Spectroscopy Cu II : d 9, square planar d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d x 2 y 2 d xy d xy d xy d z 2 d z 2 d z 2 d yz d xz d yz d xz d yz d xz ground state coupling excited state d z 2 does not couple orbitals have incorrect symmetry g obs = g e xλ ΔE g obs : empirical value from spectrum g e : energy of free electron ( ) x: modification factor of the free electron based on orbital mixing λ: spin orbit coupling constant ΔE: energy between two orbitals
43 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling initial rates experiment reveals turnover-limiting step B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% EP spectroscopy shows catalyst resting state as Cu II no strong field aryl ligand evident consistent with transmetalation being as turnover-limiting reaction progress correlated with EP spectra King, A. E.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl. S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
44 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling equilibrium prior to transmetalation B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
45 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling equilibrium prior to transmetalation B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% deviation from standard conditions effect on efficiency added acetate inhibition added acetic acid inhibition Cu(Cl 4 ) 2 instead of Cu(Ac) 2 no reactivity King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
46 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling equilibrium prior to transmetalation B 5 mol% Cu(Ac) 2 1 atm 2, 27 C, 6h B() 2 () 88% 12% deviation from standard conditions effect on efficiency added acetate inhibition added acetic acid inhibition Cu(Cl 4 ) 2 instead of Cu(Ac) 2 no reactivity Cu(Cl 4 ) equiv aac rate acceleration Cu(Cl 4 ) equiv a rate acceleration King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
47 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling EP spectroscopy King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
48 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling EP spectroscopy EP signals appears after addition of boronic ester King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
49 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling EP spectroscopy EP signals appears after addition of boronic ester exhibits a saturation depedence on concentration of ester King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
50 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling EP spectroscopy acetic acid additive sodium acetate additive both display an inhibitory effect on EP signal suggesting that paddlewheel structure is stabilized King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
51 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling EP spectroscopy EP signal obtained immediately after mixing Cu(Ac) 2 and boronic ester displays two species King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
52 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling EP spectroscopy EP signal obtained immediately after mixing Cu(Ac) 2 and boronic ester displays two species relative concentrations of the two species are altered by the addition of additives King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
53 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of transmetalation B 1/2[Cu(Ac) 2 ] 2 Cu II (Ac) B Ac Cu II B inhibitory effect of added acetate King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
54 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of transmetalation B 1/2[Cu(Ac) 2 ] 2 Cu II (Ac) B Ac Cu II B Cu II B Cu II B Ac inhibitory effect of added acetic acid King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
55 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of transmetalation B 1/2[Cu(Ac) 2 ] 2 Cu II (Ac) B Ac Cu II B Cu II B Cu II B irreversible transmetalation Cu II Ac inhibitory effect of added acetic acid B aryl Cu(II) King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
56 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of oxidative coupling Cu(II) nucleophile coordination lowerscu II /Cu III redox potential Cu(II) Copper xidase mechanism King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
57 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of oxidative coupling Cu(II) B irreversible and turnover-limiting transmetalation nucleophile coordination lowerscu II /Cu III redox potential Cu(II) Cu(II) Copper xidase mechanism King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
58 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of oxidative coupling Cu(II) B irreversible and turnover-limiting transmetalation nucleophile coordination lowerscu II /Cu III redox potential Cu(II) Cu(II) Copper xidase mechanism Cu(II) Cu(III) Cu(I) xidation to Cu(III) stoichiometry determined from single turnover experiment King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
59 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of oxidative coupling Cu(II) B irreversible and turnover-limiting transmetalation nucleophile coordination lowerscu II /Cu III redox potential Cu(II) Cu(II) Copper xidase mechanism Cu(I) Cu(II) reductive elimination Cu(III) Cu(I) xidation to Cu(III) stoichiometry determined from single turnover experiment King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
60 Chan-Evans-Lam Coupling mechanism of oxidative coupling Cu(II) B irreversible and turnover-limiting transmetalation nucleophile coordination lowerscu II /Cu III redox potential Cu(II) Cu(II) 2 Copper xidase stoichiometry determined from single turnover experiment 2 Cu(I) mechanism Cu(II) reductive elimination Cu(III) Cu(I) xidation to Cu(III) stoichiometry determined from single turnover experiment King, A. E.; yland, B. L.; Brunold, T. C.; Stahl, S. S. rganometallics, 2012, 31, 7948.
61 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions B u =,, S = halide nucleophile = halide oxidative coupling standard cross-coupling oxidative coupling u Chan-Evans-Lam Ullmann-Goldberg "Aromatic Glaser-ay"
62 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle Classic Ullmann-Goldberg reaction 2 equiv. Cu I L 2 equiv. = Br, Cl, I symmetric biaryl bond
63 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle Classic Ullmann-Goldberg reaction 2 equiv. Cu I L 2 equiv. = Br, Cl, I symmetric biaryl bond Ullmann-type coupling u Cu I L u = Br, Cl, I C heteroatom bond
64 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle nucleophile coordination/ deprotonation Cu I Cu I proposed mechanism
65 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle nucleophile coordination/ deprotonation 1 2 Cu I reversible oxidative addition 1 2 proposed mechanism Cu I 1 CuIII 2
66 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle nucleophile coordination/ deprotonation 1 2 Cu I reversible oxidative addition 1 2 proposed mechanism Cu I 1 CuIII 2 reductive elimination 1 2
67 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle 1 2 CuIII putative aryl Cu III Cu III has been widely proposed as an intermediate oxidative addition product has never been observed oxidative addition to Cu has no precedent
68 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction cross-coupling reaction mediated by Cu I /Cu III redox cycle 1 2 CuIII putative aryl Cu III utilization of constraining macrocyclic ligands UV-Vis spectroscopy (M, CV, -ray) kinetics
69 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction kinetics reveal reversible oxidative addition 2 CuTf, aq Br acetone 2 Cohen, T.; Cristea, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98,
70 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction kinetics reveal reversible oxidative addition 2 CuTf, aq Br acetone 2 formation of 2, 2'-dinitro-biphenyl: formation of nitrobenzene: 2 CuTf 2 CuTf Br Br 2 nd order dependence 1 st order 1 st order 1 st order Cohen, T.; Cristea, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98,
71 Ullmann-Goldberg eaction kinetics reveal reversible oxidative addition 2 CuTf, aq Br acetone 2 2 k 1 2 Cu Tf Cu III Br Br k Cu III Br k 2 2 Br 2 Cohen, T.; Cristea, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98,
72 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction direction observation of Cu I /Cu III redox steps ibas and Stahl's strategy: x Cu Cu III Cu I macrocyclic ligand shown to undergo C insertion with Cu highly constrained and stabilized aryl Cu III species Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
73 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction direction observation of Cu I /Cu III redox steps ibas and Stahl's strategy: x Cu Cu III Cu I macrocyclic ligand shown to undergo C insertion with Cu highly constrained and stabilized aryl Cu III species allows for characterization by 1 M, CV and UV-Vis allows for study of reductive elmination Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
74 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction direction observation of Cu I /Cu III redox steps ibas and Stahl's strategy: Cu I Cu III x Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
75 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction direction observation of Cu I /Cu III redox steps ibas and Stahl's strategy: Cu I Cu III x allows for study of oxidative addition allows for study of mechanism of C bond formation Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
76 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction characterization of aryl-cu III complex CuCl 2 or CuBr 2 Cu III x CuCl or CuBr Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
77 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction characterization of aryl-cu III complex CuCl 2 or CuBr 2 Cu III x CuCl or CuBr Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
78 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction characterization of aryl-cu III complex CuCl 2 or CuBr 2 Cu III x CuCl or CuBr electronic spectra (LMCT): agrees with ligand field strengths of the halides 369 and 521 nm 399 and 550 nm 422 and 635 nm Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
79 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction characterization of aryl-cu III complex CuCl 2 or CuBr 2 Cu III x CuCl or CuBr cyclic voltammetry: values for Cu III /Cu II redox couple 330mV 310mV 300mV Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
80 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction reductive elimination CuCl 2 Cu III x Tf ( equiv) C, 298K <1hr Cl quantitative Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
81 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction reductive elimination CuCl 2 Cu III x Tf ( equiv) C, 298K <1hr Cl quantitative Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
82 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction reductive elimination CuCl 2 Cu III x Tf ( equiv) C, 298K <1hr Cl quantitative E 1/2 (mv) k obs (S 1 ) (298K) complex x Cl (6)x10-2 Cu III Br Cl (5)x (5)x10-3 rate of reductive elimination controlled by C halogen bond strength C reductive elimination rates do not correlate with E 1/2 values Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
83 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction reductive elimination -pyr Cu III Br Br Br 3.3 mol% Cu(C) 4 PF 6 CD 3 C, 298K -pyr Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
84 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction relationship of this study to the Ullmann reaction Br 3.3 mol% Cu(C) 4 PF 6 CD 3 C, 298K -pyr 2 Cu I Cu I /Cu III Cu I 2 3 Cu III Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
85 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction relationship of this study to the Ullmann reaction Br 3.3 mol% Cu(C) 4 PF 6 CD 3 C, 298K -pyr 2 Cu I macrocyclic ligand lowers barrier to oxidative addition macrocyclic ligand stabilizes Cu III Cu I /Cu III *effectively inverts the relative rates of both redox steps Cu I 2 3 Cu III Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
86 Ullmann-type Coupling eaction relationship of this study to the Ullmann reaction Br 3.3 mol% Cu(C) 4 PF 6 CD 3 C, 298K -pyr 2 Cu I macrocyclic ligand lowers barrier to oxidative addition macrocyclic ligand stabilizes Cu III Cu I /Cu III *effectively inverts the relative rates of both redox steps Cu I 2 3 Cu III 1 mechanism of Ullmann-Goldberg can vary *use of less coordinating nucleophiles or higher coordinate ligands can affect key redox steps Casitas, A.; King, A. E.; Parella, T.; Costas, M.; Stahl, S. S.; ibas,. Chem Sci. 2010, 1,
87 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions B u =,, S = halide nucleophile = halide oxidative coupling standard cross-coupling oxidative coupling u Chan-Evans-Lam Ullmann-Goldberg "Aromatic Glaser-ay"
88 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling xidative coupling of a Cu-bound nucleophile and a C bond Cu 2 2 Z 2 Z amada, T; Ye,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130,
89 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling xidative coupling of a Cu-bound nucleophile and a C bond Cu 2 2 Z 2 Z Cu II Cu III Cu I amada, T; Ye,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, Brasche, G.; Buchwald, S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
90 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling xidative coupling of a Cu-bound nucleophile and a C bond Cu 2 2 Z 2 Z Ar Cu 2 Ar =, Li Cu = Cl, Br 2 amada, T; Ye,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, Brasche, G.; Buchwald, S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
91 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling xidative coupling of a Cu-bound nucleophile and a C bond Cu 2 2 Z 2 Z Ar Cu 2 Ar =, Li Cu = Cl, Br 2 amada, T; Ye,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, Brasche, G.; Buchwald, S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
92 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 2 equiv. Cu 2 Ac Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
93 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 2 equiv. Cu 2 Ac Cu(Ac) 2 Cu(Tf) 2 Cu(Cl 4 ) 2 CuF 2 CuCl 2 CuBr 2 Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
94 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 2 equiv. Cu 2 Cl Cl Ac Cl Cu(Ac) 2 70% 7% Cu(Tf) 2 Cu(Cl 4 ) 2 CuF 2 CuCl 2 CuBr 2 Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
95 Glaser-ay Type Couplings preliminary investigations Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 LiBr 25 mol% CuBr 2 Br Ac, 60 C Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
96 Glaser-ay Type Couplings preliminary investigations Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 LiBr 25 mol% CuBr 2 Br Ac, 60 C LiCl 25 mol% CuCl 2 Cl 6 equiv. Ac, 100 C Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
97 Glaser-ay Type Couplings preliminary investigations Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 LiBr 25 mol% CuBr 2 Br Ac, 60 C Δ CuBr 2 2 CuBr Br 2 regioselectivity follows that of electrophilic aromatic bromination Barnes, J. C.; ume, D.. Inorg. Chem. 1963, 2, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
98 Glaser-ay Type Couplings preliminary investigations Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 20 mol% a equiv Br Br Δ CuBr 2 2 CuBr Br 2 regioselectivity follows that of electrophilic aromatic bromination Zhang, G.; Liu,.; u, Q.; Ma, L.; Liang,. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 346, Barnes, J. C.; ume, D.. Inorg. Chem. 1963, 2, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
99 Glaser-ay Type Couplings preliminary investigations Li = Cl, Br Cu 2 25 mol% CuBr 2 Br Ac, 2, LiBr Br 75% Δ CuBr 2 2 CuBr Br 2 regioselectivity follows that of electrophilic aromatic bromination Zhang, G.; Liu,.; u, Q.; Ma, L.; Liang,. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 346, Barnes, J. C.; ume, D.. Inorg. Chem. 1963, 2, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
100 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling xidative coupling of a Cu-bound nucleophile and a C bond Cu 2 2 Z 2 Z Ar Cu 2 Ar =, Li Cu = Cl, Br 2 amada, T; Ye,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, Brasche, G.; Buchwald, S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
101 Glaser-ay Type Couplings oxidative cross-coupling xidative coupling of a Cu-bound nucleophile and a C bond Cu 2 2 Z 2 Z Ar Cu 2 Ar =, Li Cu = Cl, Br 2 amada, T; Ye,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, Brasche, G.; Buchwald, S. L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Stahl, S. S. Chem Commun, 2009,
102 Glaser-ay Type Couplings evidence for an aryl-cu III King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
103 Glaser-ay Type Couplings evidence for an aryl-cu III CuBr 2 Br C Cu III Br Cu I King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
104 Glaser-ay Type Couplings evidence for an aryl-cu III CuBr 2 Br C Cu III Br Cu I Cu III Br C King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
105 Glaser-ay Type Couplings evidence for an aryl-cu III CuBr 2 Br C Cu III Br Cu I Cu III Br C Br Cu III C pyr King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
106 Glaser-ay Type Couplings kinetics of methoxylation reaction using the method of intial rates Cu III Br C kinetics determined by 2 consumption King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
107 Glaser-ay Type Couplings kinetics of methoxylation reaction using the method of intial rates Cu III Br C arene ligand (mm) Cu II (mm) p 2 (torr) 1 st order dependence 1 st order dependence 0 order dependence King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
108 Glaser-ay Type Couplings kinetics of methoxylation reaction using the method of intial rates Cu III Br C arene ligand (mm) Cu II (mm) p 2 (torr) 1 st order dependence 1 st order dependence 0 order dependence catalytic steps involving 2 are comparatively fast Cu reoxidation is not rate-determining King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
109 Glaser-ay Type Couplings kinetics of methoxylation reaction using the method of intial rates Cu III Br C 1 M complicated due to paramagnetic line broadening indicates that Cu II is formed during reaction King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
110 Glaser-ay Type Couplings kinetics of methoxylation reaction using the method of intial rates Cu III Br C Cu III Cu II King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
111 Glaser-ay Type Couplings kinetics of methoxylation reaction using the method of intial rates Cu III Br C Cu III Cu II King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
112 Glaser-ay Type Couplings proposed mechanism of Aromatic Glaser-ay coupling Cu II Cu II King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
113 Glaser-ay Type Couplings proposed mechanism of Aromatic Glaser-ay coupling Cu II Cu I Br Cu II Cu III King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
114 Glaser-ay Type Couplings proposed mechanism of Aromatic Glaser-ay coupling Cu II Cu I Br Cu II Cu III 2 2 Cu I King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
115 Glaser-ay Type Couplings proposed mechanism of Aromatic Glaser-ay coupling Cu II Cu I Br accounts for apparent build-up of Cu II during reaction Cu II Cu III 2 2 Cu I King, A. E.; uffman, L. M.; Casitas, A.; Costas, M.; ibas,.; Stahl, S. S. J. Am Chem. Soc, 2010,
116 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions B u =,, S = halide nucleophile = halide oxidative coupling standard cross-coupling oxidative coupling u Chan-Evans-Lam Ullmann-Goldberg "Aromatic Glaser-ay"
117 Copper in Cross-Coupling eactions
Additions to Metal-Alkene and -Alkyne Complexes
 Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Arylhalide-Tolerated Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acids with N-Chloroamides Catalyzed by CuCl at Room Temperature
 Current Literature July 19, 08 Jitendra Mishra Arylhalide-Tolerated Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acids with -Chloroamides Catalyzed by CuCl at Room Temperature Aiwen Lei et.al. College of the
Current Literature July 19, 08 Jitendra Mishra Arylhalide-Tolerated Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acids with -Chloroamides Catalyzed by CuCl at Room Temperature Aiwen Lei et.al. College of the
CH 3 TMG, DMF N H 3 CO 2 S. (PPh 3 ) 2 Pd 0
 1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
Copper-Catalyzed Reaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium Reagent
 Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
Direct Oxidative Heck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans
 Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group.
 Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
Reductive Elimination from High-Valent Palladium. Kazunori Nagao MacMillan Group Meeting
 Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles
 Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Organocopper Chemistry
 rganocopper Chemistry ave a great historical importance, but still remain highly useful reactions. If not the first organometallic reactions developed they are among the first. Most often used in conjugate
rganocopper Chemistry ave a great historical importance, but still remain highly useful reactions. If not the first organometallic reactions developed they are among the first. Most often used in conjugate
Metalloporphyrin. ~as efficient Lewis acid catalysts with a unique reaction-field~ and. ~Synthetic study toward complex metalloporphyrins~
 Metalloporphyrin ~as efficient Lewis acid catalysts with a unique reaction-field~ and ~Synthetic study toward complex metalloporphyrins~ Literature Seminar Kenta Saito (D1) 1 Topics Chapter 1 ~as efficient
Metalloporphyrin ~as efficient Lewis acid catalysts with a unique reaction-field~ and ~Synthetic study toward complex metalloporphyrins~ Literature Seminar Kenta Saito (D1) 1 Topics Chapter 1 ~as efficient
Direct, Catalytic Hydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated Olefins with N-Alkyl Arylamines
 Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Zr-Catalyzed Carbometallation
 -Catalyzed Carbometallation C C C C ML n C C ML n ML n C C C C ML n ML n C C ML n Wipf Group esearch Topic Seminar Juan Arredondo November 13, 2004 Juan Arredondo @ Wipf Group 1 11/14/2004 Carbometallation
-Catalyzed Carbometallation C C C C ML n C C ML n ML n C C C C ML n ML n C C ML n Wipf Group esearch Topic Seminar Juan Arredondo November 13, 2004 Juan Arredondo @ Wipf Group 1 11/14/2004 Carbometallation
Electrophilic Carbenes
 Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing Oxazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129,
 Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon
 Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Spiro Monophosphite and Monophosphoramidite Ligand Kit
 Spiro Monophosphite and Monophosphoramidite Ligand Kit metals inorganics organometallics catalysts ligands custom synthesis cgm facilities nanomaterials 15-5162 15-5150 15-5156 15-5163 15-5151 15-5157
Spiro Monophosphite and Monophosphoramidite Ligand Kit metals inorganics organometallics catalysts ligands custom synthesis cgm facilities nanomaterials 15-5162 15-5150 15-5156 15-5163 15-5151 15-5157
Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo
 Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo 2014.1.6 1 Content Introduction Progress of Catellani Reaction o-alkylation and Applications o-arylation and Applications Conclusion and Outlook
Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo 2014.1.6 1 Content Introduction Progress of Catellani Reaction o-alkylation and Applications o-arylation and Applications Conclusion and Outlook
VI. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion
 V. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion A. Carbonylation - C insertion very facile, metal acyls easily cleaved, all substrates which undergo oxidative addition can in principle be carbonylated.
V. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion A. Carbonylation - C insertion very facile, metal acyls easily cleaved, all substrates which undergo oxidative addition can in principle be carbonylated.
Modern C(sp 2 )-F bond forming reactions:
 Modern C(sp 2 )-F bond forming reactions: From C-A to C-F (A = H, X, M) Yan Xu Jun. 17, 2015 Reference T. Ritter, Modern Carbon Fluorine Bond Forming Reactions for Aryl Fluoride Synthesis Chem. Rev. 2015,
Modern C(sp 2 )-F bond forming reactions: From C-A to C-F (A = H, X, M) Yan Xu Jun. 17, 2015 Reference T. Ritter, Modern Carbon Fluorine Bond Forming Reactions for Aryl Fluoride Synthesis Chem. Rev. 2015,
Iron Catalysed Coupling Reactions
 LONG LITERATURE REPORT Iron Catalysed Coupling Reactions Mingyu Liu 2017. 8. 31 1 Fe [Ar]3d 6 4s 2 The fourth most common element in the Earth s crust Relatively less understanding and manipulation of
LONG LITERATURE REPORT Iron Catalysed Coupling Reactions Mingyu Liu 2017. 8. 31 1 Fe [Ar]3d 6 4s 2 The fourth most common element in the Earth s crust Relatively less understanding and manipulation of
Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid
 Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid Shiqing Xu, Akimichi Oda, Thomas Bobinski, Haijun Li, Yohei Matsueda, and Ei-ichi Negishi Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid Shiqing Xu, Akimichi Oda, Thomas Bobinski, Haijun Li, Yohei Matsueda, and Ei-ichi Negishi Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
Short Literature Presentation 10/4/2010 Erika A. Crane
 Copper-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of trans-1- Alkyl-2-substituted Cyclopropanes via Tandem Conjugate Additions-Intramolecular Enolate Trapping artog, T. D.; Rudolph, A.; Macia B.; Minnaard, A.
Copper-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of trans-1- Alkyl-2-substituted Cyclopropanes via Tandem Conjugate Additions-Intramolecular Enolate Trapping artog, T. D.; Rudolph, A.; Macia B.; Minnaard, A.
Microwave-promoted synthesis in water
 Microwave-promoted synthesis in water icholas E. Leadbeater nicholas.leadbeater@uconn.edu Outline of what we do Synthesis / Methodology / ew techniques Pure organic synthesis eg. Baylis-Hillman eaction
Microwave-promoted synthesis in water icholas E. Leadbeater nicholas.leadbeater@uconn.edu Outline of what we do Synthesis / Methodology / ew techniques Pure organic synthesis eg. Baylis-Hillman eaction
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Chem 530A Chemistry 530A Advanced Organic Chemistry Lecture notes part 8 Carbanions Organolithium and Grignard reagents Organocopper reagents 1. Direct metalation 2. From radical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Chem 530A Chemistry 530A Advanced Organic Chemistry Lecture notes part 8 Carbanions Organolithium and Grignard reagents Organocopper reagents 1. Direct metalation 2. From radical
Transition-metal catalyzed C C bond cleavage
 Transition-metal catalyzed C C bond cleavage 2011.09.17 Chaoren Shen Wanbin Group Literature Seminar 1.Decarboxylation(Cu Ag Pd Rh) 2. Decarbonylation(i Pd) 3. Deacylation(Pd Rh) Jon A. Tunge( University
Transition-metal catalyzed C C bond cleavage 2011.09.17 Chaoren Shen Wanbin Group Literature Seminar 1.Decarboxylation(Cu Ag Pd Rh) 2. Decarbonylation(i Pd) 3. Deacylation(Pd Rh) Jon A. Tunge( University
Negishi Coupling of Secondary Alkylzinc Halides with Aryl Bromides and Chlorides
 Negishi Coupling of Secondary Alkylzinc alides with Aryl Bromides and Chlorides X X = Br, Cl 2 1 ZnBr 1, 2 = Alkyl Cat. Pd(OAc) 2 Ligand TF/Toluene rt or 60 o C 1 2 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, ASAP Article
Negishi Coupling of Secondary Alkylzinc alides with Aryl Bromides and Chlorides X X = Br, Cl 2 1 ZnBr 1, 2 = Alkyl Cat. Pd(OAc) 2 Ligand TF/Toluene rt or 60 o C 1 2 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, ASAP Article
Oxidative Addition and Reductive Elimination
 xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. Itispossiblethatinthenextseveraldecadeswemayhavetoshifttowardothercarbonsources for these
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. Itispossiblethatinthenextseveraldecadeswemayhavetoshifttowardothercarbonsources for these
Suggested solutions for Chapter 40
 s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
Nucleophilic Fluorination. Souvik Rakshit Burke group Literature Seminar July 13, 2013
 Nucleophilic Fluorination Souvik Rakshit Burke group Literature Seminar July 13, 2013 Relevance 20% of pharmaceuticals contain fluorine 5-fluorouracil Antineoplastic agent, 1957 Lipitor (Atorvastatin)
Nucleophilic Fluorination Souvik Rakshit Burke group Literature Seminar July 13, 2013 Relevance 20% of pharmaceuticals contain fluorine 5-fluorouracil Antineoplastic agent, 1957 Lipitor (Atorvastatin)
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Cross-Electrophile-Coupling Between Aryl and Alkyl Halides
 ickel-catalyzed Reductive Cross-Electrophile-Coupling Between Aryl and Alkyl Halides Eunjae Shim Zakarian Group Literature Talk / Dec 13 th, 2018 University of California, Santa Barbara Table of Contents
ickel-catalyzed Reductive Cross-Electrophile-Coupling Between Aryl and Alkyl Halides Eunjae Shim Zakarian Group Literature Talk / Dec 13 th, 2018 University of California, Santa Barbara Table of Contents
Chapter 12. Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds Oxidation-Reduction & Organometallic Compounds. Structure
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chem 634. Introduction to Transition Metal Catalysis. Reading: Heg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, , 11.3 Grossman Ch 6
 Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex. CHM 5.33 Fall 2005
 Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex CHM 5.33 Fall 2005 Introduction The experiment is based on research performed in the laboratory of Professor Cummins during the early 90 s.
Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex CHM 5.33 Fall 2005 Introduction The experiment is based on research performed in the laboratory of Professor Cummins during the early 90 s.
transmetallate displace ox. add. M + (insert) (β-elim.)
 Chapter IV. Transition Metal σ-alkyl Complexes I. General For much of the rest of this course it will be necessary to understand how σ-alkyl metal complexes are formed and how they react. This is summarized
Chapter IV. Transition Metal σ-alkyl Complexes I. General For much of the rest of this course it will be necessary to understand how σ-alkyl metal complexes are formed and how they react. This is summarized
Lewis Base Activation of Lewis Acids: Development of a Lewis Base Catalyzed Selenolactonization
 Lewis Base Activation of Lewis Acids: Development of a Lewis Base Catalyzed Selenolactonization Denmark, S.E. and Collins, W.R. rg. Lett. 2007, 9, 3801-3804. C 2 H + Se Lewis Base CH 2 Cl 2 Se Presented
Lewis Base Activation of Lewis Acids: Development of a Lewis Base Catalyzed Selenolactonization Denmark, S.E. and Collins, W.R. rg. Lett. 2007, 9, 3801-3804. C 2 H + Se Lewis Base CH 2 Cl 2 Se Presented
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis via Azolium Dienolates: An Efficient Strategy for Enantioselective Remote Functionalizations
 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 10.1002. 1 N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis via Azolium Dienolates: An Efficient Strategy for Enantioselective Remote Functionalizations Reporter: En Li Supervisor: Prof. Yong
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 10.1002. 1 N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis via Azolium Dienolates: An Efficient Strategy for Enantioselective Remote Functionalizations Reporter: En Li Supervisor: Prof. Yong
Literature Report IX. Cho, S. H. et al. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, Cho, S. H. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56,
 Literature Report IX ynthesis of β-aminoboronates by Copper(I)- Catalyzed Addition of Diborylalkanes to Imines Reporter Checker Date : hubo Hu : Xiaoyong Zhai : 2017-9-1818 Cho,. H. et al. rg. Lett. 2016,
Literature Report IX ynthesis of β-aminoboronates by Copper(I)- Catalyzed Addition of Diborylalkanes to Imines Reporter Checker Date : hubo Hu : Xiaoyong Zhai : 2017-9-1818 Cho,. H. et al. rg. Lett. 2016,
"-Amino Acids: Function and Synthesis
 "-Amino Acids: Function and Synthesis # Conformations of "-Peptides # Biological Significance # Asymmetric Synthesis Sean Brown MacMillan Group eting ovember 14, 2001 Lead eferences: Cheng,. P.; Gellman,
"-Amino Acids: Function and Synthesis # Conformations of "-Peptides # Biological Significance # Asymmetric Synthesis Sean Brown MacMillan Group eting ovember 14, 2001 Lead eferences: Cheng,. P.; Gellman,
Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium
 Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Metallaphotoredox Catalysis (Including my work in Shū Kobayashi group from Oct to Aug. 2015)
 tallaphotoredox (ncluding my work in Shū Kobayashi group from ct. 2013 to Aug. 2015) otoredox Transition tal Tatsuhiro Tsukamoto Literature Talk: Jan. 6 th, 2016 the Dong group 1 Contents 1. Visible Light
tallaphotoredox (ncluding my work in Shū Kobayashi group from ct. 2013 to Aug. 2015) otoredox Transition tal Tatsuhiro Tsukamoto Literature Talk: Jan. 6 th, 2016 the Dong group 1 Contents 1. Visible Light
Direct Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich Reactions of Ketimines: An Approach to Optically Active Quaternary α-amino Acid Derivatives
 Direct rganocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich eactions of Ketimines: An Approach to ptically Active Quaternary α-amino Acid Derivatives Wei Zhang, Steen Saaby, and Karl Anker Jorgensen The Danish ational
Direct rganocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich eactions of Ketimines: An Approach to ptically Active Quaternary α-amino Acid Derivatives Wei Zhang, Steen Saaby, and Karl Anker Jorgensen The Danish ational
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
 Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
Regioselective Reductive Cross-Coupling Reaction
 Lit. Seminar. 2010. 6.16 Shinsuke Mouri (D3) Regioselective Reductive Cross-Coupling Reaction Glenn C. Micalizio obtained a Ph.D. at the University of Michigan in 2001 under the supervision of Professor
Lit. Seminar. 2010. 6.16 Shinsuke Mouri (D3) Regioselective Reductive Cross-Coupling Reaction Glenn C. Micalizio obtained a Ph.D. at the University of Michigan in 2001 under the supervision of Professor
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N6 Kashiwa Campus, November 27, 2009 Group VIB: Cr, Mo, W -Oxidation states from -2 to +6 -While +2 and +3 for Cr are quite
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N6 Kashiwa Campus, November 27, 2009 Group VIB: Cr, Mo, W -Oxidation states from -2 to +6 -While +2 and +3 for Cr are quite
Self-stable Electrophilic Reagents for Trifluoromethylthiolation. Reporter: Linrui Zhang Supervisor: Prof. Yong Huang Date:
 Self-stable Electrophilic Reagents for Trifluoromethylthiolation Reporter: Linrui Zhang Supervisor: Prof. Yong Huang Date: 2017-12-25 Content Introduction Trifluoromethanesulfenates: Preparation and reactivity
Self-stable Electrophilic Reagents for Trifluoromethylthiolation Reporter: Linrui Zhang Supervisor: Prof. Yong Huang Date: 2017-12-25 Content Introduction Trifluoromethanesulfenates: Preparation and reactivity
Rhodium Carbenoids and C-H Insertion
 hodium Carbenoids and C- Insertion Literature Talk Uttam K. Tambar March 1, 2004 8pm, oyes 147 h h h h h h irreversible reversible carbenoid 2 h2l4 1 h2l4 or h2l4 2 utline I. What is a Carbene? II. What
hodium Carbenoids and C- Insertion Literature Talk Uttam K. Tambar March 1, 2004 8pm, oyes 147 h h h h h h irreversible reversible carbenoid 2 h2l4 1 h2l4 or h2l4 2 utline I. What is a Carbene? II. What
CHEM 153 PRACTICE TEST #1 ANSWER KEY
 CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
R 2 R 4 Ln catalyst. This manuscript describes the methods for the synthesis and application of group 4 metallocene bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene
 VII Abstracts 2011 p1 2.12.15 rganometallic Complexes of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides P. Dissanayake, D. J. Averill, and M. J. Allen This manuscript is an update to the existing Science of Synthesis
VII Abstracts 2011 p1 2.12.15 rganometallic Complexes of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides P. Dissanayake, D. J. Averill, and M. J. Allen This manuscript is an update to the existing Science of Synthesis
Ready; Catalysis Conjugate Addition
 eady; Catalysis Conjugate Addition Topics covered 1. 1,4 addition involving copper a. stoichiometric reactions b. catalytic reactions c. allylic substitution. Conjugate addition without copper a. Ni-based
eady; Catalysis Conjugate Addition Topics covered 1. 1,4 addition involving copper a. stoichiometric reactions b. catalytic reactions c. allylic substitution. Conjugate addition without copper a. Ni-based
Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis. Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat)
 Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat) Introduction Novel cross coupling was reported! Highly selective sp 3 C-H functionalization!
Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat) Introduction Novel cross coupling was reported! Highly selective sp 3 C-H functionalization!
Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
Palladium-Catalyzed Oxygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C-H Bonds
 Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C- Bonds Pd(Ac) 2 5 mol% PhI(Ac) 2 1.1 eq. Pd 2 Ac Desai, L. P.; ull, K. L.; Sanford *, M. S. University of Michigan J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, ASAP
Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C- Bonds Pd(Ac) 2 5 mol% PhI(Ac) 2 1.1 eq. Pd 2 Ac Desai, L. P.; ull, K. L.; Sanford *, M. S. University of Michigan J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, ASAP
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
CHEM 330. Final Exam December 5, 2014 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. The use of molecular models is allowed
 CEM 330 Final Exam December 5, 2014 Your name: ASWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam The use of molecular models is allowed This exam consists of 12 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 30 2. / 30 3. / 30
CEM 330 Final Exam December 5, 2014 Your name: ASWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam The use of molecular models is allowed This exam consists of 12 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 30 2. / 30 3. / 30
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
Unraveling the Mechanism of Water Oxidation by Ruthenium-Oxo Complexes
 Unraveling the Mechanism of Water xidation by thenium-xo Complexes Casseday Richers Literature Seminar ovember 20, 2007 The oxidation of water to dioxygen and protons represents one half the watersplitting
Unraveling the Mechanism of Water xidation by thenium-xo Complexes Casseday Richers Literature Seminar ovember 20, 2007 The oxidation of water to dioxygen and protons represents one half the watersplitting
OC 2 (FS 2013) Lecture 3 Prof. Bode. Redox Neutral Reactions and Rearrangements
 C 2 (F 203) Lecture 3 Prof. Bode edox eutral eactions and earrangements Types of edox eutral rganic eactions. eactions with no external reducing or oxidizing agent In this case, one part of the starting
C 2 (F 203) Lecture 3 Prof. Bode edox eutral eactions and earrangements Types of edox eutral rganic eactions. eactions with no external reducing or oxidizing agent In this case, one part of the starting
Reaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. Reactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b.
 eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 19. Chem 4631
 Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 19 Chem 4631 Organic Electrochemistry is a multidisciplinary science overlapping the fields of organic chemistry, biochemistry, physical chemistry and electrochemistry.
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 19 Chem 4631 Organic Electrochemistry is a multidisciplinary science overlapping the fields of organic chemistry, biochemistry, physical chemistry and electrochemistry.
Introduction. A1.1 (a) Shell number and number of subshells 1. A1.1 (b) Orbitals 2. A1.1 (c ) Orbital shapes (s, p & d) 2
 Preface Table of Contents Introduction i A1.1 (a) Shell number and number of subshells 1 A1.1 (b) Orbitals 2 A1.1 (c ) Orbital shapes (s, p & d) 2 A1.1 (d) Relative energies of s,p,d,f sub-shells 4 A 1.1
Preface Table of Contents Introduction i A1.1 (a) Shell number and number of subshells 1 A1.1 (b) Orbitals 2 A1.1 (c ) Orbital shapes (s, p & d) 2 A1.1 (d) Relative energies of s,p,d,f sub-shells 4 A 1.1
The Mechanism of Pd-Catalyzed Amination Controversy.. And Conclusion?
 The chanism of d-catalyzed Amination Controversy.. And Conclusion? R H R1 R 2 d(dba) 2 BIA, h R R1 R 2 Steve Tymonko SED Group eting 5/9/06 d-catalyzed Amination- Tin Initial Report- Kosugi, 1983 n-bu
The chanism of d-catalyzed Amination Controversy.. And Conclusion? R H R1 R 2 d(dba) 2 BIA, h R R1 R 2 Steve Tymonko SED Group eting 5/9/06 d-catalyzed Amination- Tin Initial Report- Kosugi, 1983 n-bu
Chapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM Catalysis
 hapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM atalysis + + ligand exchange A oxidative addition > n + A B n+2 reductive elimination < B n n+2 oxidative coupling + M' + M' transmetallation migratory insertion > (carbo-,
hapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM atalysis + + ligand exchange A oxidative addition > n + A B n+2 reductive elimination < B n n+2 oxidative coupling + M' + M' transmetallation migratory insertion > (carbo-,
CuI CuI eage lic R tal ome rgan gbr ommon
 Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
Nucleophilic attack on ligand
 Nucleophilic attack on ligand Nucleophile "substitutes" metal hapticity usually decreases xidation state mostly unchanged Competition: nucleophilic attack on metal usually leads to ligand substitution
Nucleophilic attack on ligand Nucleophile "substitutes" metal hapticity usually decreases xidation state mostly unchanged Competition: nucleophilic attack on metal usually leads to ligand substitution
Organocopper Reagents
 rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
Elementary Organometallic Reactions
 Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Coupling Reactions Using Excited State Organonickel Complex _LS_Daiki_Kamakura
 Coupling eactions Using Excited State rganonickel Complex 171118_LS_Daiki_Kamakura i Catalysis in Coupling eactions 9 10 11 Co 28 i Cu h Pd Ag Ir Pt Au Features of i d electrons: 8 relatively inexpensive
Coupling eactions Using Excited State rganonickel Complex 171118_LS_Daiki_Kamakura i Catalysis in Coupling eactions 9 10 11 Co 28 i Cu h Pd Ag Ir Pt Au Features of i d electrons: 8 relatively inexpensive
Mn Reagent & Organomanganese: Neglected Powerful Tool. Reporter: Li Zhuo Advisor: Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang
 Mn Reagent & Organomanganese: Neglected Powerful Tool Reporter: Li Zhuo Advisor: Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 1 Content Introduction Oxidation by Mn(VII) & Mn(IV) Epoxidation & Cyclopropanation Radical
Mn Reagent & Organomanganese: Neglected Powerful Tool Reporter: Li Zhuo Advisor: Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 1 Content Introduction Oxidation by Mn(VII) & Mn(IV) Epoxidation & Cyclopropanation Radical
Theophylline (TH), the structure of which is presented below, is a bronchial-dilator used for the treatment of asthma.
 1 EXAM SCIETIIC CULTURE CEMISTRY PRBLEM 1: Theophylline (T), the structure of which is presented below, is a bronchial-dilator used for the treatment of asthma. 3 C 7 1 3 9 1.1 Structural study and acid-base
1 EXAM SCIETIIC CULTURE CEMISTRY PRBLEM 1: Theophylline (T), the structure of which is presented below, is a bronchial-dilator used for the treatment of asthma. 3 C 7 1 3 9 1.1 Structural study and acid-base
Bond length (pm) Bond strength (KJ/mol)
 hapter 10: Alkyl alides = F, l,, I Alkyl halide Aryl halide Vinyl halide 10.1 Naming alkyl halides- ead 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides Table 10.1 alomethane 3 -F 3 -l 3-3 -I Bond length (pm) 139 178 193
hapter 10: Alkyl alides = F, l,, I Alkyl halide Aryl halide Vinyl halide 10.1 Naming alkyl halides- ead 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides Table 10.1 alomethane 3 -F 3 -l 3-3 -I Bond length (pm) 139 178 193
Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines
 Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines Asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis - Chiral (bisooxazoline) copper (II) complexes - Monodentate Lewis acids: the formyl -bond Amine catalysed reactions Asymmetric
Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines Asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis - Chiral (bisooxazoline) copper (II) complexes - Monodentate Lewis acids: the formyl -bond Amine catalysed reactions Asymmetric
Copper-Catalyzed Diastereoselective Arylation of Tryptophan Derivatives: Total Synthesis of (+)-
 Literature Report Copper-Catalyzed Diastereoselective Arylation of Tryptophan Derivatives: Total Synthesis of (+)- aseseazines A and B Reporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Zhang-Pei Chen Date: 2013-05-28 Reisman,
Literature Report Copper-Catalyzed Diastereoselective Arylation of Tryptophan Derivatives: Total Synthesis of (+)- aseseazines A and B Reporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Zhang-Pei Chen Date: 2013-05-28 Reisman,
Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation
 M.C. White, Chem 253 Cross-Coupling -120- Week of ctober 11, 2004 Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation catalytic cycle: ' (h 3 ) n d II The first report: h Sonogashira T 1975 (50) 4467. h
M.C. White, Chem 253 Cross-Coupling -120- Week of ctober 11, 2004 Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation catalytic cycle: ' (h 3 ) n d II The first report: h Sonogashira T 1975 (50) 4467. h
Use of Cp 2 TiCl in Synthesis
 Use of 2 TiCl in Synthesis eagent Control of adical eactions Jeff Kallemeyn May 21, 2002 eactions of 2 TiCl 1. Pinacol Coupling H H H 2. Epoxide pening H H E H Chemoselectivity Activated aldehydes (aromatic,
Use of 2 TiCl in Synthesis eagent Control of adical eactions Jeff Kallemeyn May 21, 2002 eactions of 2 TiCl 1. Pinacol Coupling H H H 2. Epoxide pening H H E H Chemoselectivity Activated aldehydes (aromatic,
Mechanistic Insides into Nickamine-Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions
 Mechanistic Insides into Nickamine-Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions Abstract Within the last decades the transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl halides has significantly
Mechanistic Insides into Nickamine-Catalyzed Alkyl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling Reactions Abstract Within the last decades the transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl halides has significantly
Chiral Diol Promoted Boronates Addi3on Reac3ons. Lu Yan Morken Group Boston College
 Chiral Diol Promoted Boronates Addi3on Reac3ons Lu Yan Morken Group Boston College Main Idea R R B or R R B Ar * exchange B * * or B Ar R 1 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 Products not nucleophilic enough nucleophilic
Chiral Diol Promoted Boronates Addi3on Reac3ons Lu Yan Morken Group Boston College Main Idea R R B or R R B Ar * exchange B * * or B Ar R 1 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 Products not nucleophilic enough nucleophilic
Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Why this Chapter? Continuation of coverage of aromatic compounds in preceding chapter focus shift to understanding reactions Examine relationship
Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Why this Chapter? Continuation of coverage of aromatic compounds in preceding chapter focus shift to understanding reactions Examine relationship
Department CMIC Lecture 5c FR5c Free-Radicals: Chemistry and Biology
 Department CMIC Lecture 5c F5c Free-adicals: Chemistry and Biology Prof. Dipartimento CMIC Giulio atta http://iscamap.chem.polimi.it/citterio/education/free-radical-chemistry/ Content 1. Introduction Current
Department CMIC Lecture 5c F5c Free-adicals: Chemistry and Biology Prof. Dipartimento CMIC Giulio atta http://iscamap.chem.polimi.it/citterio/education/free-radical-chemistry/ Content 1. Introduction Current
Iron Catalyzed Cross Coupling: Mechanism and Application. Matthew Burk Denmark Group Meeting
 Iron Catalyzed Cross Coupling: Mechanism and Application Matthew Burk Denmark Group Meeting 3-10-2009 Long Induction Period: Early History Of Iron Catalyzed Cross Coupling 1941: Effect of metal impurities
Iron Catalyzed Cross Coupling: Mechanism and Application Matthew Burk Denmark Group Meeting 3-10-2009 Long Induction Period: Early History Of Iron Catalyzed Cross Coupling 1941: Effect of metal impurities
The version of SI posted May 6, 2004 contained errors. The correct version was posted October 21, 2004.
 The version of SI posted May 6, 2004 contained errors. The correct version was posted October 21, 2004. Sterically Bulky Thioureas as Air and Moisture Stable Ligands for Pd-Catalyzed Heck Reactions of
The version of SI posted May 6, 2004 contained errors. The correct version was posted October 21, 2004. Sterically Bulky Thioureas as Air and Moisture Stable Ligands for Pd-Catalyzed Heck Reactions of
Cu- Catalyzed Synthesis of Diaryl Thioethers and S- Cycles by reaction of Aryl Iodides with Carbon Disul;ide in the Presence of DBU.
 Cu- Catalyzed ynthesis of Diaryl Thioethers and - Cycles by reaction of Aryl odides with Carbon Disul;ide in the Presence of DBU. Peng Zhao, Hang Yin, Hongxin, Gao, Chanjuan Xi.; J. rg. Chem. ArCcle AAP
Cu- Catalyzed ynthesis of Diaryl Thioethers and - Cycles by reaction of Aryl odides with Carbon Disul;ide in the Presence of DBU. Peng Zhao, Hang Yin, Hongxin, Gao, Chanjuan Xi.; J. rg. Chem. ArCcle AAP
Chromium Arene Complexes
 Go through Reviews Chem. Reviews Chem. Soc. Reviews Book by Prof. A. J. Elias Chromium Arene Complexes Complexation of Cr(CO) 3 with ARENES Chromium arene complexes Metal complexation is appealing in organic
Go through Reviews Chem. Reviews Chem. Soc. Reviews Book by Prof. A. J. Elias Chromium Arene Complexes Complexation of Cr(CO) 3 with ARENES Chromium arene complexes Metal complexation is appealing in organic
Chem 253 Problem Set 7 Due: Friday, December 3, 2004
 Chem 253 roblem Set 7 ue: Friday, ecember 3, 2004 Name TF. Starting with the provided starting material, provide a concise synthesis of. You may use any other reagents for your synthesis. It can be assumed
Chem 253 roblem Set 7 ue: Friday, ecember 3, 2004 Name TF. Starting with the provided starting material, provide a concise synthesis of. You may use any other reagents for your synthesis. It can be assumed
Catalytic Chan Lam coupling using a tube-in-tube reactor to deliver molecular oxygen as an oxidant
 Catalytic Chan Lam coupling using a tube-in-tube reactor to deliver molecular oxygen as an oxidant Carl J. Mallia 1, Paul M. Burton 2, Alexander M. R. Smith 2, Gary C. Walter 2 and Ian R. Baxendale *1
Catalytic Chan Lam coupling using a tube-in-tube reactor to deliver molecular oxygen as an oxidant Carl J. Mallia 1, Paul M. Burton 2, Alexander M. R. Smith 2, Gary C. Walter 2 and Ian R. Baxendale *1
Metal Catalyzed Outer Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated Olefins and Alkynes
 Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
Functionalization of C O Bonds. Stefan McCarver. MacMillan Lab Group Meeting
 Functionalization of C Bonds Stefan McCarver MacMillan Lab Group eting November 23 rd, 2016 Functionalization of C Bonds "X" X homolytic cleavage catalyst M oxidative addition Why is C Bond Manipulation
Functionalization of C Bonds Stefan McCarver MacMillan Lab Group eting November 23 rd, 2016 Functionalization of C Bonds "X" X homolytic cleavage catalyst M oxidative addition Why is C Bond Manipulation
Atovaquone: An Antipneumocystic Agent
 Atovaquone: An Antipneumocystic Agent Atovaquone is a pharmaceutical compound marketed in the United States under different combinations to prevent and treat pneumocystosis and malaria. In a report from
Atovaquone: An Antipneumocystic Agent Atovaquone is a pharmaceutical compound marketed in the United States under different combinations to prevent and treat pneumocystosis and malaria. In a report from
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Aza-Wacker-Type Cyclization. Group Meeting Tuesday, April 19, 2011 William Kuester
 Aza-Wacker-Type Cyclization Group Meeting Tuesday, April 19, 2011 William Kuester N-heterocylization Reductive Amination Hydroamination Oxidative Cyclization Chemler, S.R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 3009-3019.
Aza-Wacker-Type Cyclization Group Meeting Tuesday, April 19, 2011 William Kuester N-heterocylization Reductive Amination Hydroamination Oxidative Cyclization Chemler, S.R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 3009-3019.
Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed or -mediated cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids: New methodologies for the synthesis of butenolides*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 76, No. 3, pp. 651 656, 2004. 2004 IUPAC Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed or -mediated cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids: New methodologies for the synthesis of butenolides*
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 76, No. 3, pp. 651 656, 2004. 2004 IUPAC Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed or -mediated cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids: New methodologies for the synthesis of butenolides*
C H Activated Trifluoromethylation
 Literature report C H Activated Trifluoromethylation Reporter:Yan Fang Superior:Prof. Yong Huang Jun. 17 th 2013 Contents Background Trifluoromethylation of sp-hybridized C-H Bonds Trifluoromethylation
Literature report C H Activated Trifluoromethylation Reporter:Yan Fang Superior:Prof. Yong Huang Jun. 17 th 2013 Contents Background Trifluoromethylation of sp-hybridized C-H Bonds Trifluoromethylation
Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates. Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02
![Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates. Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02 Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates. Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02](/thumbs/93/114018431.jpg) Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02 Xiao, W.-J. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8360.
Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02 Xiao, W.-J. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8360.
Basics of Catalysis and Kinetics
 Basics of Catalysis and Kinetics Nobel laureates in catalysis: Haber (1918) Ziegler and Natta (1963) Wilkinson, Fischer (1973) Knowles, Noyori, Sharpless (2001) Grubbs, Schrock, Chauvin (2006) Ertl (2007)
Basics of Catalysis and Kinetics Nobel laureates in catalysis: Haber (1918) Ziegler and Natta (1963) Wilkinson, Fischer (1973) Knowles, Noyori, Sharpless (2001) Grubbs, Schrock, Chauvin (2006) Ertl (2007)
Carbonyl Ylide Cycloadditions
 Carbonyl Ylide Cycloadditions cond. icholas Anderson Denmark Group eting 07/13/10 Carbonyl Ylides Uncharged 1,3-Dipole Conjugated π-system ighly reactive on-isolable Generate in-situ Carbonyl Ylide Stability
Carbonyl Ylide Cycloadditions cond. icholas Anderson Denmark Group eting 07/13/10 Carbonyl Ylides Uncharged 1,3-Dipole Conjugated π-system ighly reactive on-isolable Generate in-situ Carbonyl Ylide Stability
