Neutralization Reactions
|
|
|
- Roger Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neutralization Reactions According to industry representatives, % of discarded car batteries in Ontario are recycled. This process prevents the hazardous contents of car batteries from contaminating the environment. An automotive lead-acid battery consists of plates of lead and lead (IV) oxide immersed in a corrosive fluid containing concentrated sulfuric acid. Lead is to a number of organs and systems in the body, including the heart and the nervous system. Every part of a discarded battery is recycled into a useful product. The plastic cases of the batteries are cleaned, ground into pellets, and reused to manufacture new battery cases. Lead is recovered, purified, and used to manufacture new batteries. The sulfuric acid drained from the batteries is treated in two ways. Some is cleaned and reused in new batteries. The remainder is neutralized with sodium carbonate (also called soda ash), Na 2 CO 3 : Sodium sulfate collected from this process is a key ingredient in the manufacture of glass and detergents.
2 Types of Neutralization Reactions Neutralization reactions are a special case of double displacement reactions. During a neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with a base to produce a solution with a ph closer to than its reactants. NEUTRALIZATION WITH A COMPOUND The reaction of hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq), with sodium hydroxide, NaOH (aq), is a typical neutralization reaction. The chemical equation for this reaction is This type of neutralization reaction follows the general pattern: Not all neutralization reactions follow this general equation. For most neutralization reactions, however, the hydrogen ions from an acid react with the hydroxide ions from a base to produce water. The ionic compound, which is sometimes called a salt is made up of the remaining ions. NEUTRALIZATION WITH A COMPOUND Acids can also be neutralized by carbonate compounds. Calcium carbonate is the major component in limestone rock. It also makes up the shells of aquatic animals, such as clams, snails, and corals. Calcium carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid to produce carbonic acid, H 2 CO 3(aq). The chemical equation for this reaction is However, carbonic acid immediately decomposes into water and carbon dioxide: Therefore, the chemical equation for the net reaction of calcium carbonate with sulfuric acid is Carbonate compounds react similarly with other acids. In general, the reaction of acid with carbonate compound yields water, carbon dioxide, and an ionic compound:
3 Neutralization Reactions in Action Acids and bases are some of the most widely used industrial chemicals. Many useful household products also contain acids and bases. The neutralization of these compounds has important consumer and environmental applications. NEUTRALIZING ACIDS The digestive fluids in your stomach have a ph of about 1.5, acidic enough to slowly "eat" through a strip of zinc metal. The source of this acidity is hydrochloric acid produced by specialized cells in the stomach lining. Hydrochloric acid aids in the digestion of proteins and suppresses the growth of unwanted bacteria. Since your digestive fluids cannot distinguish between food and stomach tissue, they could easily digest the stomach itself. Fortunately, the stomach has defences against being digested: other cells in the stomach lining produce mucus that coats the inside of the stomach, keeping the acid away from the living cells. Another defence is the ability of the cells of the stomach lining to replace themselves very quickly: at a rate of about half a million per minute. Stomach acid can become a problem if it leaks upward out of the stomach, through a valve-like structure and into the esophagus. Irritation of the esophagus by stomach acid is called gastroesophageal reflux, acid reflux, or heartburn. This condition can be caused by a number of factors, including overeating and spicy foods. A short-term fix for heartburn is to consume an antacid medication that will neutralize the excess acid in the stomach. The active ingredient in an antacid must be effective at neutralizing excess stomach acid and yet it must not irritate tissue on its way to the stomach. Ideally, the neutralizing compound would produce only enough hydroxide ions to react with the acid. Weakly basic substances such as magnesium hydroxide and aluminum hydroxide are used in some antacid products. Because they are only slightly soluble, neither compound produces enough hydroxide ions to irritate the mouth or throat as the tablet is chewed and swallowed. The chemical equation for the neutralization of hydrochloric acid with aluminum hydroxide is Carbonate compounds are also safe yet effective ingredients in antacid products. Sodium hydrogen carbonate, NaHCO 3, and calcium carbonate, CaCO 3, are commonly used. The equations for the neutralization of hydrochloric acid with these compounds are
4 Frequent consumption of sodium hydrogen carbonate is not recommended because it adds to the sodium ions we already consume by salting our food. Excess sodium ions have been linked to hypertension and stroke. Too much calcium carbonate may increase the risk of kidney stones. Emissions of sulfur oxide and nitrogen oxide are largely responsible for the acidification of Ontario's lakes. These oxides are acidic, and cause acid precipitation. Despite considerable progress in curbing these emissions over the last 30 years, the problem persists. Aquatic ecosystems generally can only tolerate small reductions in the ph of their water. Organisms fail to reproduce and populations crash. As ph drops below, only the most acid-tolerant organisms survive. Lakes differ in their ability to resist changes in acidity. One factor that helps offset the effects of acid precipitation is the type of rock beneath the lake. Much of the surface rock of southern Ontario is (mostly calcium carbonate, CaCO 3 ). An important characteristic of limestone is that it reacts slowly with acids. Limestone in southern Ontario lakes acts as a natural antacid, helping to neutralize acidified lake water. Unfortunately, the surface geology of northern Ontario is mostly granite. Granite is a hard, impervious rock that is less reactive than limestone. As a result, the lakes in this region have little natural capacity to neutralize acid precipitation. Consequently, these northern lakes are the most prone to environmental damage from acid precipitation. One way to assist lakes threatened by acid precipitation is to neutralize the acidity by adding calcium oxide or lime. However, "liming" a lake only solves the acidity problem in the short term. The longterm solution is to eliminate the pollutants at their source. BAKING Substances that make bread dough rise are called leavening agents. Leavening agents produce bubbles of that are trapped within the dough. As the bubbles expand, they push the elastic dough upward. The carbon dioxide bubbles could be produced either by baker's yeast or by a neutralization reaction involving a carbonate compound. Baking soda and baking powder are both leavening agents. Baking soda is pure sodium hydrogen carbonate. The leavening action of baking soda is activated when it is mixed with an acidic ingredient like fruit juice, vinegar, or buttermilk. The chemical equation for the reaction of the citric acid, H 3 C 6 H 5 O 7(aq), in fruit juice with baking soda is Bubbles of carbon dioxide gas from this reaction cause the dough to rise. The warmth of the oven makes the bubbles expand. Because baking soda is unstable at high temperatures, it is generally used when a short baking time is required. That is why you will see baking soda listed as an ingredient in many cookie recipes. Baking powder, however, is a mixture of several ingredients. Two essential ingredients in most types of baking powder are baking soda and a dry acid such as tartaric acid, H 2 C 4 H 4 O 6. Baking powder is activated by moisture. As solid tartaric acid dissolves and produces hydrogen ions, sodium hydrogen carbonate neutralizes its acidity. The resulting products are carbon
5 dioxide (which makes the dough rise), water, and sodium tartrate. The chemical equation for this reaction is Baking powders can be fast acting and slow acting, depending on the acid they contain. The acids in fast-acting baking powders (usually tartaric acid) react immediately with baking soda to produce carbon dioxide. Slow-acting baking powders contain acids that only begin to react when heated in the oven. Slow-acting baking powders are used when longer baking times are required. The recipes for cakes usually specify baking powder as the leavening agent. Choice of Neutralizing Reactant Neutralization reactions are important parts of many chemical processes. Some, like the recycling of car batteries, are large industrial processes in which corrosive substances must be neutralized before they can be discharged into the environment. Other reactions involve consumer products such as antacids and hair dyes. In each case, the effectiveness of the process depends on the properties of the reactants used. Factors when selecting an appropriate neutralizing reactant: For example, solutions of sulfuric acid vs. ethanoic acid (HC 2 H 3 O 2(aq) ) Similarly, sodium hydroxide vs. calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) 2 ) A Versatile Neutralizing Agent Sodium hydrogen carbonate, NaHCO 3, or baking soda, is unusual because it can neutralize both acids and bases. It is therefore a very versatile neutralizing compound. It is also one of the safest, since it is not corrosive at all. In fact, it is safe enough to be used in food and consumer products such as toothpaste. Acids react with sodium hydrogen carbonate following the general pattern for carbonate reactions. For example, sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid as follows: Sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with bases to produce water and sodium carbonate. For example:
6 Worksheet 2.7: Neutralization Reactions 1. Complete and balance the following equations: (a) HNO 3(aq) + Ca(OH) 2(aq) (b) HNO 3(aq) + K 2 CO 3(s)(aq) (c) HC 2 H 3 O 2(aq) + AI(OH) 3(aq) (d) H 3 PO 4(aq) + NaHCO 3(aq) (e) H 3 PO 4(aq) + Ca(OH) 2(aq) (f) H 2 SO 4(aq) + Ca(HCO 3 ) 2(aq) (g) HCIO 3(aq) + CaCO 3(s) 2. Barium sulfate can be made using two different neutralization reactions, using the following substances: Ba(OH) 2, Ba(HCO 3 ) 2, H 2 SO 4 Write chemical equations for these two reactions. Each reaction should have only two reactants. 3. Carbonated drinks are made by bubbling pressurized carbon dioxide gas into them. (a) What acid forms as a result of this addition? (b) Sodium hydroxide is a common ingredient in drain openers. Write the chemical equation for the neutralization of dissolved sodium hydroxide in a drain opener with a solution of the acid in (a). (c) What do you think are the advantages of using pop instead of hydrochloric acid, HCI (aq), to neutralize a spill of drain cleaner? 4. Sometimes cooked fish has a distinctive fishy smell because of basic compounds called amines. Describe why a squirt of lemon juice can eliminate these odours. 5. In 2007, a train derailment spilled a large volume of concentrated sulfuric acid into the Blanche River near Englehart, Ontario. During the cleanup, calcium oxide (lime) was added to the river upstream from the site of the accident. How did this action help restore the river? 6. Industrial acid spill kits contain, among other things, an absorbent material to soak the spill and a neutralizing reactant. Often, the neutralizing agent is incorporated into the absorbent material. Why is this advantageous to the workers cleaning up a spill?
SNC2D CHEMISTRY 3/12/2013. CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Neutralization Reactions (P ) ph & Plants. ph & Plants
 SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Reactions (P.204-212) ph & Plants Growing plants for a living can be risky. Many factors can affect the success of a crop, from weather conditions to the nutrient content
SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Reactions (P.204-212) ph & Plants Growing plants for a living can be risky. Many factors can affect the success of a crop, from weather conditions to the nutrient content
Elements and Their Oxides
 Elements and Their Oxides An oxide is a. Oxides can form when an element reacts with oxygen, often in air. This reaction can be rapid with the release of a great deal of energy, as in the combustion of
Elements and Their Oxides An oxide is a. Oxides can form when an element reacts with oxygen, often in air. This reaction can be rapid with the release of a great deal of energy, as in the combustion of
Understand what acids and alkalis are, and where they are found.
 Lesson Aims- Understand what acids and alkalis are, and where they are found. Test a range of household products with litmus indicator to see whether they are acidic or alkaline. Found in citrus fruit
Lesson Aims- Understand what acids and alkalis are, and where they are found. Test a range of household products with litmus indicator to see whether they are acidic or alkaline. Found in citrus fruit
SNC2D CHEMISTRY 2/24/2013. CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Acids & Bases (P ) Activity: Introduction to (2DCHEM-ASG3) Introduction to Acids & Bases
 SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Acids & Bases (P.198-201) Activity: Introduction to (2DCHEM-ASG3) INSTRUCTIONS A. Read the activity 2DCHEM - ASG3 (Introduction to Acids & Bases). B. Follow the instructions
SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Acids & Bases (P.198-201) Activity: Introduction to (2DCHEM-ASG3) INSTRUCTIONS A. Read the activity 2DCHEM - ASG3 (Introduction to Acids & Bases). B. Follow the instructions
Downloaded from
 1 X Chemistry Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter Notes Top concepts: 1. Definition of acids, bases and salts: Acids Bases Salts Sour in taste Bitter in taste & soapy to touch Acid + Base Salt + Water
1 X Chemistry Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter Notes Top concepts: 1. Definition of acids, bases and salts: Acids Bases Salts Sour in taste Bitter in taste & soapy to touch Acid + Base Salt + Water
Acids, Bases & Salts
 Introduction Acids, Bases & Salts Elements combine to form numerous compounds. On the basis of their chemical properties, compounds can be classified into three categories: Acids Bases Salts Acids and
Introduction Acids, Bases & Salts Elements combine to form numerous compounds. On the basis of their chemical properties, compounds can be classified into three categories: Acids Bases Salts Acids and
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS. Double your pleasure, double your fun
 DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Double your pleasure, double your fun Industrial processes produce unwanted by-products. Dissolved toxic metal ions-copper, mercury, and cadmium-are common leftovers in the
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Double your pleasure, double your fun Industrial processes produce unwanted by-products. Dissolved toxic metal ions-copper, mercury, and cadmium-are common leftovers in the
How do Metal Carbonates and Metal Hydrogencarbonates React
 Acids, Bases, and Salts] This chapter is about: Reaction of acids and bases, how acids and bases cancel out each other s effects and many more interesting things that we use and see in our day-to-day life.
Acids, Bases, and Salts] This chapter is about: Reaction of acids and bases, how acids and bases cancel out each other s effects and many more interesting things that we use and see in our day-to-day life.
the universal solvent
 Chapter 7: Acids, Bases, and Solutions Solution a homogeneous mixture Solutions have the same properties throughout, containing solute particles (molecules or ions) that are too small to see Solvent the
Chapter 7: Acids, Bases, and Solutions Solution a homogeneous mixture Solutions have the same properties throughout, containing solute particles (molecules or ions) that are too small to see Solvent the
Unit 13 Acids and Bases E.Q. What are the differences between acids and bases?
 Unit 13 Acids and Bases E.Q. What are the differences between acids and bases? What are Properties of Acids? They taste sour (don t try this in lab). They can conduct electricity. Can be strong or weak
Unit 13 Acids and Bases E.Q. What are the differences between acids and bases? What are Properties of Acids? They taste sour (don t try this in lab). They can conduct electricity. Can be strong or weak
! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! *+&$(,)#$! *+&$(,)#$!
 Learning Checkpoint, p. 197 1. A solution with a ph of 11 is basic. 2. A solution with a ph of 5 is acidic. 3. The ph of pure water is 7 (neutral).! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! 4. No, litmus paper does not
Learning Checkpoint, p. 197 1. A solution with a ph of 11 is basic. 2. A solution with a ph of 5 is acidic. 3. The ph of pure water is 7 (neutral).! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! 4. No, litmus paper does not
Introducing Science Summary Sheet
 Introducing Science Summary Sheet Acids in the laboratory Dilute acids You will have used some dilute acids at school, such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid. Their bottles are labelled
Introducing Science Summary Sheet Acids in the laboratory Dilute acids You will have used some dilute acids at school, such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid. Their bottles are labelled
Topic 5 National Chemistry Summary Notes. Acids and Alkalis
 Topic 5 National Chemistry Summary Notes Acids and Alkalis Experiment Collect some samples of rain water LI 1 The ph Scale The ph scale is a continuous range of numbers from below 0 to above 14. Acids
Topic 5 National Chemistry Summary Notes Acids and Alkalis Experiment Collect some samples of rain water LI 1 The ph Scale The ph scale is a continuous range of numbers from below 0 to above 14. Acids
Have a ph value less than ph 7 Turn blue litmus indicator red Can neutralise an alkali Have a sour taste (WARNING: never taste any chemicals)
 Acids and Alkalis ACIDS (acidic solutions) Acids have the following properties: Have a ph value less than ph 7 Turn blue litmus indicator red Can neutralise an alkali Have a sour taste (WARNING: never
Acids and Alkalis ACIDS (acidic solutions) Acids have the following properties: Have a ph value less than ph 7 Turn blue litmus indicator red Can neutralise an alkali Have a sour taste (WARNING: never
Examples of Strong Acids: Strong Acid Formula Common Source Hydrochloric Acid HCl Stomach Acid
 ACIDS AND BASES: PH AND BUFFERS PURPOSE: To determine the ph of common acids and bases using a ph meter, ph paper, and red cabbage indicator. To test the effect of adding an acid or base to a buffer solution.
ACIDS AND BASES: PH AND BUFFERS PURPOSE: To determine the ph of common acids and bases using a ph meter, ph paper, and red cabbage indicator. To test the effect of adding an acid or base to a buffer solution.
Classifying Substances
 Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some compounds as acids or bases. You are very familiar with acids and bases because you see
Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some compounds as acids or bases. You are very familiar with acids and bases because you see
Acids, Bases and Salts
 Acids, Bases and Salts Synopsis Substances are classified into acids, bases and salts depending on their chemical behavior and properties. Acids are of sour taste and turn blue litmus to red. Bases are
Acids, Bases and Salts Synopsis Substances are classified into acids, bases and salts depending on their chemical behavior and properties. Acids are of sour taste and turn blue litmus to red. Bases are
Name Date Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write no
Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write no
10.2. Neutralization Reactions and Acid-base Titrations. HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) HOH(l) + KCl(aq) Neutralization Reactions SECTION.
 SECTION 10.2 Neutralization Reactions and Acid-base Titrations Key Terms neutralization reaction salt titration titrant burette end point equivalence point Acids and bases are found in air, soil, oceans,
SECTION 10.2 Neutralization Reactions and Acid-base Titrations Key Terms neutralization reaction salt titration titrant burette end point equivalence point Acids and bases are found in air, soil, oceans,
ACIDS & BASES. Acids & Bases 1
 ACIDS & BASES Acids and bases have real-life significance. The human body functions properly only when delicate acid-base balances are maintained and crops grow best in soil with the proper ph. In addition,
ACIDS & BASES Acids and bases have real-life significance. The human body functions properly only when delicate acid-base balances are maintained and crops grow best in soil with the proper ph. In addition,
Lab: Cabbages in Chemistry 3pts ec printing in COLOR / 2pts B&W
 Lab: Cabbages in Chemistry 3pts ec printing in COLOR / 2pts B&W Telltale Colors 1. In the mixing tray, place 5 drops of the chemical in 13 compartments 2. DIP test the ph paper & record the ph measurement
Lab: Cabbages in Chemistry 3pts ec printing in COLOR / 2pts B&W Telltale Colors 1. In the mixing tray, place 5 drops of the chemical in 13 compartments 2. DIP test the ph paper & record the ph measurement
Which other compounds react with acids to produce salts? Acids can also react with metals and carbonates to produce salts.
 Salts Textbook pages 234 243 Section 5.2 Summary Before You Read How many different uses for salts can you name? Write your answers on the lines below. What are salts? In chemistry, salts are a class of
Salts Textbook pages 234 243 Section 5.2 Summary Before You Read How many different uses for salts can you name? Write your answers on the lines below. What are salts? In chemistry, salts are a class of
Chapter 13 Acids and Bases: The Molecules Responsible for Sour and Bitter
 Nivaldo J. Tro http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/tro Chapter 13 Acids and Bases: The Molecules Responsible for Sour and Bitter Mark Erickson Hartwick College Acids Sourness in foods is caused by acids,
Nivaldo J. Tro http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/tro Chapter 13 Acids and Bases: The Molecules Responsible for Sour and Bitter Mark Erickson Hartwick College Acids Sourness in foods is caused by acids,
Everyday you encounter a variety of different acids and bases. Below is a list of som common acids and bases
 Acids and Bases Everyday you encounter a variety of different acids and bases. Below is a list of som common acids and bases Milk carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ) calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) s ) sodium hydroxide
Acids and Bases Everyday you encounter a variety of different acids and bases. Below is a list of som common acids and bases Milk carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ) calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) s ) sodium hydroxide
Describe in full the colour change at the end-point of this titration. ... (1)
 Q1. (a) A solution of barium hydroxide is often used for the titration of organic acids. A suitable indicator for the titration is thymol blue. Thymol blue is yellow in acid and blue in alkali. In a titration
Q1. (a) A solution of barium hydroxide is often used for the titration of organic acids. A suitable indicator for the titration is thymol blue. Thymol blue is yellow in acid and blue in alkali. In a titration
ACIDS & BASES PROPERTIES OF ACIDS ACIDS PROPERTIES OF ACIDS PROPERTIES OF ACIDS 11/1/2016
 SC STANDARD COVERED ACIDS & BASES Standard PS-3.7 Classify various solutions as acids or bases according to their physical properties, chemical properties (including neutralization and reaction with metals),
SC STANDARD COVERED ACIDS & BASES Standard PS-3.7 Classify various solutions as acids or bases according to their physical properties, chemical properties (including neutralization and reaction with metals),
Reactions with Acids. Chemistry 10 Mrs. Page
 Reactions with Acids Chemistry 10 Mrs. Page Learning Objectives Predict the products and balance chemical equations for the reactions with acids involving; reactive metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides,
Reactions with Acids Chemistry 10 Mrs. Page Learning Objectives Predict the products and balance chemical equations for the reactions with acids involving; reactive metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides,
The Determination of ph of some Common Acids & Bases
 The Determination of ph of some Common Acids & Bases Introduction: An acid is a substance that when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions, H +. Inorganic acids do not contain carbon but organic acids
The Determination of ph of some Common Acids & Bases Introduction: An acid is a substance that when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions, H +. Inorganic acids do not contain carbon but organic acids
4.2. Double Displacement Reactions. Characteristics of Double Displacement Reactions SECTION. Key Terms
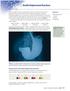 SECTION 4.2 Double Displacement Reactions X rays are highly useful for creating images of bones in the human body, but they generally do not show soft tissues clearly. To help doctors diagnose conditions
SECTION 4.2 Double Displacement Reactions X rays are highly useful for creating images of bones in the human body, but they generally do not show soft tissues clearly. To help doctors diagnose conditions
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=te4668aarck&feature=related The Five Major Class of Chemical Reaction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i HHvx1VC_8 Jan 2 8:07 PM 1 Nov 19 8:48 AM
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=te4668aarck&feature=related The Five Major Class of Chemical Reaction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i HHvx1VC_8 Jan 2 8:07 PM 1 Nov 19 8:48 AM
Name: Block: Date: Student Notes
 Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Acids and Bases Student Notes OBJECTIVES Students will: recognize some acids and bases as common and familiar household chemicals. realize that acids and bases are
Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Acids and Bases Student Notes OBJECTIVES Students will: recognize some acids and bases as common and familiar household chemicals. realize that acids and bases are
Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions
 1 Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions Part 1. Acid and Base Chemistry A. Introduction BIO 105 Summer 2013 Name One of the most important concepts in biology is acid/base chemistry. We are familiar
1 Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions Part 1. Acid and Base Chemistry A. Introduction BIO 105 Summer 2013 Name One of the most important concepts in biology is acid/base chemistry. We are familiar
Chapter 8. Table of Contents. Section 1 Acids, Bases, and ph. Section 2 Reactions of Acids with Bases. Section 3 Acids, Bases, and Salts in the Home
 Acids, Bases, and Salts Table of Contents Section 2 Reactions of Acids with Bases Section 3 Acids, Bases, and Salts in the Home What Are Acids? An acid is a compound that dissolves in water to increase
Acids, Bases, and Salts Table of Contents Section 2 Reactions of Acids with Bases Section 3 Acids, Bases, and Salts in the Home What Are Acids? An acid is a compound that dissolves in water to increase
Wherever chemical solutions are involved, ph matters. Some
 47 Acids, Bases, and the ph Scale R EA D I N G Wherever chemical solutions are involved, ph matters. Some important chemical reactions, such as those involved in corrosion of iron or digestion of food,
47 Acids, Bases, and the ph Scale R EA D I N G Wherever chemical solutions are involved, ph matters. Some important chemical reactions, such as those involved in corrosion of iron or digestion of food,
Page 1 of 14. Website: Mobile:
 Question 1: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red
Question 1: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red
Name: Date: Number: Acids
 Acids The sour taste of the lemon juice tells us that it is an acid. Acids are special kinds of chemicals. They are common in everyday life. Some are helpful, others are harmful. There are some that are
Acids The sour taste of the lemon juice tells us that it is an acid. Acids are special kinds of chemicals. They are common in everyday life. Some are helpful, others are harmful. There are some that are
Section Four Structured questions
 Section Four Structured questions 1 For each of the following experiments, state ONE observable change and write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. a) Magnesium strip is added to dilute hydrochloric
Section Four Structured questions 1 For each of the following experiments, state ONE observable change and write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. a) Magnesium strip is added to dilute hydrochloric
reacts with ammonium sulfate to form ammonia It reacts with a carbonate to form carbon dioxide. It reacts with an ammonium salt to form ammonia.
 1 Which statements are properties of an acid? 1 reacts with ammonium sulfate to form ammonia 2 turns red litmus blue 1 2 2 Which property is not characteristic of a base? It reacts with a carbonate to
1 Which statements are properties of an acid? 1 reacts with ammonium sulfate to form ammonia 2 turns red litmus blue 1 2 2 Which property is not characteristic of a base? It reacts with a carbonate to
2. What characteristic of water makes it the universal solvent? Nonpolar large molecules long-chain hydrocarbon molecules polar
 PS Chemistry Chapter 22 & 23 Review Test Date Chapter 22 Suggestions for Studying Section 1 Know that a solution is made up of a solute and solvent. Be able to provide an example of a solute and a solvent.
PS Chemistry Chapter 22 & 23 Review Test Date Chapter 22 Suggestions for Studying Section 1 Know that a solution is made up of a solute and solvent. Be able to provide an example of a solute and a solvent.
white precipitate white precipitate, dissolves in excess of NaOH brown precipitate Identity of Q Identity of R Identity of S...
 Q1.The table below shows observations of changes from some test-tube reactions of aqueous solutions of compounds Q, R and S with five different aqueous reagents. The initial colours of the solutions are
Q1.The table below shows observations of changes from some test-tube reactions of aqueous solutions of compounds Q, R and S with five different aqueous reagents. The initial colours of the solutions are
Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia.
 Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia. (a) Complete the word equation for the reaction that takes place in the first reaction vessel. ammonia +... nitrogen
Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia. (a) Complete the word equation for the reaction that takes place in the first reaction vessel. ammonia +... nitrogen
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases
 Chemistry 12 Ch 1 4 : Acids and Bases Page 1 Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Check MasteringChemistry Deadlines Acids and Bases: The sour taste of lemons and lime, the bite of sourdough bread, and the tang
Chemistry 12 Ch 1 4 : Acids and Bases Page 1 Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Check MasteringChemistry Deadlines Acids and Bases: The sour taste of lemons and lime, the bite of sourdough bread, and the tang
3/26/2011. explosion
 Chemistry Acids and Bases Year 10 Study of Chemicals and how they react Everything is made of chemicals They are made of elements. There are over 100 elements Acids are common Some are dangerous and can
Chemistry Acids and Bases Year 10 Study of Chemicals and how they react Everything is made of chemicals They are made of elements. There are over 100 elements Acids are common Some are dangerous and can
REACTIONS OF ACIDS. J:\Science\Chemistry\Stage 1 Notes\Acids & Bases\Reactionsofacids.doc
 REACTIONS OF ACIDS 1. Acids taste sour We do not attempt to taste strong acids as they are too dangerous. They do taste sour, but then they proceed to destroy cells on your tongue and mouth. If you vomit,
REACTIONS OF ACIDS 1. Acids taste sour We do not attempt to taste strong acids as they are too dangerous. They do taste sour, but then they proceed to destroy cells on your tongue and mouth. If you vomit,
Science 10. Unit 2: Chemistry. Book 5: Acid -Base Chemistry & the ph Scale. Block: Name:
 Science 10 Unit 2: Chemistry Book 5: Acid -Base Chemistry & the ph Scale Name: Block: 1 Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some
Science 10 Unit 2: Chemistry Book 5: Acid -Base Chemistry & the ph Scale Name: Block: 1 Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some
Railways (Group-D & ALP) Science Questions with solution
 Railways (Group-D & ALP) Science Questions with solution RRB Science MCQs Quiz 5 Directions: Study the following questions carefully and choose the right answer: 1. The process of dissolving an acid or
Railways (Group-D & ALP) Science Questions with solution RRB Science MCQs Quiz 5 Directions: Study the following questions carefully and choose the right answer: 1. The process of dissolving an acid or
Chapter 19 Acids and Bases
 Chapter 19 Acids and Bases p.1/11 19.1 Introducing Acids and Alkalis Acids and bases are common stuff in everyday life. Domestic Acids and Alkalis Common domestic acids Many foods and drinks contain acids.
Chapter 19 Acids and Bases p.1/11 19.1 Introducing Acids and Alkalis Acids and bases are common stuff in everyday life. Domestic Acids and Alkalis Common domestic acids Many foods and drinks contain acids.
Neutralisation. November 29, neutral
 Neutralisation November 29, 2015 neutral STARTER Decide if the statements are true or false. 1. Vinegar is an example of an alkali. FALSE 2. Tea contains tannic acid. TRUE 3. Coke is an alkali. FALSE 4.
Neutralisation November 29, 2015 neutral STARTER Decide if the statements are true or false. 1. Vinegar is an example of an alkali. FALSE 2. Tea contains tannic acid. TRUE 3. Coke is an alkali. FALSE 4.
Water, the SPECIAL Equilibrium
 THE ACID TEST Water, the SPECIAL Equilibrium I. Characteristics of Water A. Water are highly. B. They are in continuous. C. Always. D. Water is dense in the solid phase than in the phase. i.e. ice floats
THE ACID TEST Water, the SPECIAL Equilibrium I. Characteristics of Water A. Water are highly. B. They are in continuous. C. Always. D. Water is dense in the solid phase than in the phase. i.e. ice floats
Unit 5 Lesson 3 Measuring ph. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 What s Your Number? What is the ph scale? The ph of a solution is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. A solution that has a ph value of exactly 7 is neutral neither acidic nor basic. A solution
What s Your Number? What is the ph scale? The ph of a solution is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. A solution that has a ph value of exactly 7 is neutral neither acidic nor basic. A solution
Acids and Bases. Acids
 1 Acids and Bases Acids Although some acids can burn and are dangerous to handle, most acids in foods are safe to eat. What acids have in common, however, is that they contain at least one hydrogen atom
1 Acids and Bases Acids Although some acids can burn and are dangerous to handle, most acids in foods are safe to eat. What acids have in common, however, is that they contain at least one hydrogen atom
Chapter 14. Preview Then skip to section 2. Section 1 Ionic and Covalent Compounds. Section 2 Acids and Bases. Section 3 Solutions of Acids and Bases
 Chemical Compounds Preview Then skip to section 2 Section 1 Ionic and Covalent Compounds Section 2 Acids and Bases Section 3 Solutions of Acids and Bases Section 4 Organic Compounds Concept Mapping Section
Chemical Compounds Preview Then skip to section 2 Section 1 Ionic and Covalent Compounds Section 2 Acids and Bases Section 3 Solutions of Acids and Bases Section 4 Organic Compounds Concept Mapping Section
The grade 5 English science unit, Acids and Bases, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This area addresses ph among different characteristics of solutions. It will be interesting for students to classify a variety of solutions into acids and bases by using the characteristics of the solutions.
This area addresses ph among different characteristics of solutions. It will be interesting for students to classify a variety of solutions into acids and bases by using the characteristics of the solutions.
An acidic substance always contains (1) in its name. An (2) is a chemical that changes colour to tell you
 Test Part A Fill in the gaps An acidic substance always contains (1) in its name. An (2) is a chemical that changes colour to tell you whether a substance is an acid or a (3). Another name for (4)/(5)
Test Part A Fill in the gaps An acidic substance always contains (1) in its name. An (2) is a chemical that changes colour to tell you whether a substance is an acid or a (3). Another name for (4)/(5)
8.3 WORKING WITH SOLUTIONS 8.4 ACID BASE THEORIES 8.4 ACID BASE THEORIES PRACTICE. Applying Inquiry Skills PRACTICE. Making Connections PRACTICE
 8.3 WORKING WITH SOLUTIONS (Page 376) Applying Inquiry Skills 1. Name Use Erlenmeyer flask for temporarily containing reacting substances (specifically shaped to allow mixing of contents by swirling) and
8.3 WORKING WITH SOLUTIONS (Page 376) Applying Inquiry Skills 1. Name Use Erlenmeyer flask for temporarily containing reacting substances (specifically shaped to allow mixing of contents by swirling) and
sodium carbonate + hydrochloric acid sodium chloride water Name the salt produced if sodium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric acid.
 Q1. Sodium carbonate reacts with acids. Complete the word equation. sodium carbonate + hydrochloric acid sodium chloride +... + water Name the salt produced if sodium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric
Q1. Sodium carbonate reacts with acids. Complete the word equation. sodium carbonate + hydrochloric acid sodium chloride +... + water Name the salt produced if sodium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric
ADEng. Programme Chemistry for Engineers Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil.
 ADEng. Programme Chemistry for Engineers Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil. Department of Pure and Applied Sciences Portmore Community College Main Campus 1 LECTURE OBJECTIVES Define acid, bases, alkali,
ADEng. Programme Chemistry for Engineers Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil. Department of Pure and Applied Sciences Portmore Community College Main Campus 1 LECTURE OBJECTIVES Define acid, bases, alkali,
Aim: What is ph? Mr. M. Gonzalez. What is ph?
 Aim: Mr. M. Gonzalez Do now: What happens when you combine baking soda and vinegar? A Chemical Reaction!!! Answer The reaction between baking soda (NaHCO3) and vinegar (CH3COOH) is actually two reactions,
Aim: Mr. M. Gonzalez Do now: What happens when you combine baking soda and vinegar? A Chemical Reaction!!! Answer The reaction between baking soda (NaHCO3) and vinegar (CH3COOH) is actually two reactions,
Chemical Reactions. Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions have a standard format when written:
 0.3.notebook A chemical property is a behaviour that occurs when substances change to create a new substance. When a new substance is created, a chemical change has occurred. New colour Evidence of chemical
0.3.notebook A chemical property is a behaviour that occurs when substances change to create a new substance. When a new substance is created, a chemical change has occurred. New colour Evidence of chemical
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin
 Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Acids and Bases Properties of Acids An acid is any substance that releases hydrogen ions, H +, into water.
Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Acids and Bases Properties of Acids An acid is any substance that releases hydrogen ions, H +, into water.
Ch. 8 - Solutions, Acids & Bases. Solution = a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances
 Ch. 8 - Solutions, Acids & Bases Solution = a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances Solute substance whose particles are dissolved in a solution Solvent substance in which the solute dissolves in
Ch. 8 - Solutions, Acids & Bases Solution = a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances Solute substance whose particles are dissolved in a solution Solvent substance in which the solute dissolves in
Name Partner Lab Section M Tu W Th F Chemistry 130 Experiment 6: Titration and Analysis
 Name Partner Lab Section M Tu W Th F Chemistry 130 Experiment 6: Titration and Analysis Introduction A neutralization reaction is one in which an acid (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor) react
Name Partner Lab Section M Tu W Th F Chemistry 130 Experiment 6: Titration and Analysis Introduction A neutralization reaction is one in which an acid (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor) react
4.5: Acids and Bases. SCH3U: Solutions and Solubility. Properties of Pure and Aqueous Substances. Arrhenius Theory. Acid:
 4.5: Acids and Bases Properties of Pure and Aqueous Substances Arrhenius Theory Acid: Acids are sour tasting and corrosive. They react readily with active metals such as Zn, Ca, Mg and carbonate-based
4.5: Acids and Bases Properties of Pure and Aqueous Substances Arrhenius Theory Acid: Acids are sour tasting and corrosive. They react readily with active metals such as Zn, Ca, Mg and carbonate-based
Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases
 Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases The ph Scale Properties Acids Alkalis Physical. Substances that ionized in water to produce hydrogen ions.. Sour taste.. Turn blue litmus paper red. 4. Give a ph value
Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases The ph Scale Properties Acids Alkalis Physical. Substances that ionized in water to produce hydrogen ions.. Sour taste.. Turn blue litmus paper red. 4. Give a ph value
4. Aqueous Solutions. Solution homogeneous mixture of two components
 4. Aqueous Solutions Solution homogeneous mixture of two components Many chemical reactions occur in solution Solutions in water called aqueous Definitions Solute component(s) in smaller amount 2 types:
4. Aqueous Solutions Solution homogeneous mixture of two components Many chemical reactions occur in solution Solutions in water called aqueous Definitions Solute component(s) in smaller amount 2 types:
Page 2. Q1.A student investigated food dyes using paper chromatography. This is the method used.
 Q1.A student investigated food dyes using paper chromatography. This is the method used. 1. Put a spot of food colouring X on the start line. 2. Put spots of four separate dyes, A, B, C and D, on the start
Q1.A student investigated food dyes using paper chromatography. This is the method used. 1. Put a spot of food colouring X on the start line. 2. Put spots of four separate dyes, A, B, C and D, on the start
Empirical formula C 4 H 6 O
 AP Chem Test- Titration and Gravimetric Analysis p. 2 Name date 4. Empirical Formula A compound is analyzed and found to contain 68.54% carbon, 8.63% hydrogen, and 22.83% oxygen. The molecular weight of
AP Chem Test- Titration and Gravimetric Analysis p. 2 Name date 4. Empirical Formula A compound is analyzed and found to contain 68.54% carbon, 8.63% hydrogen, and 22.83% oxygen. The molecular weight of
What is a chemical property of matter?
 What is a chemical property of matter? A. Chemical properties of matter involve a chemical change. 1. Observations of matter that involve a chemical change cause new matter to be formed. a. Chemical changes
What is a chemical property of matter? A. Chemical properties of matter involve a chemical change. 1. Observations of matter that involve a chemical change cause new matter to be formed. a. Chemical changes
Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 3: Chemical Properties
 Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 3: Chemical Properties 1. How is a chemical property different from a physical property? Name Date Section 2. How is a chemical change different from a physical change? 3. Give two
Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 3: Chemical Properties 1. How is a chemical property different from a physical property? Name Date Section 2. How is a chemical change different from a physical change? 3. Give two
-log [H+][OH-] = - log [1 x ] Left hand side ( log H + ) + ( log OH - ) = ph + poh Right hand side = ( log 1) + ( log ) = 14 ph + poh = 14
![-log [H+][OH-] = - log [1 x ] Left hand side ( log H + ) + ( log OH - ) = ph + poh Right hand side = ( log 1) + ( log ) = 14 ph + poh = 14 -log [H+][OH-] = - log [1 x ] Left hand side ( log H + ) + ( log OH - ) = ph + poh Right hand side = ( log 1) + ( log ) = 14 ph + poh = 14](/thumbs/77/75028098.jpg) Autoionization of Water H 2 O H + + OH - K = [H + ][OH - ]/[H 2 O] = 1.802 x 10-16 Concentration of [H 2 O] is so HIGH autoionization is just a drop in the bucket, so [H 2 O] stays constant at 55.5 M,
Autoionization of Water H 2 O H + + OH - K = [H + ][OH - ]/[H 2 O] = 1.802 x 10-16 Concentration of [H 2 O] is so HIGH autoionization is just a drop in the bucket, so [H 2 O] stays constant at 55.5 M,
1. Base your answer to the following question on information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on information below and on your knowledge of A sample of nitric acid contains both ions and ions. This sample has a ph value of 1. Write a name of the positive
1. Base your answer to the following question on information below and on your knowledge of A sample of nitric acid contains both ions and ions. This sample has a ph value of 1. Write a name of the positive
Acids, Bases and ph. Biology Honors. Acidic, Basic or Neutral (indicate if strong or weak acid or base) Substance ph More H + More OH - Vitamin C
 Biology Honors Name Acids, Bases and ph Substance ph More H + More OH - Acidic, Basic or Neutral (indicate if strong or weak acid or base) Vitamin C Tap water Hydrochloric acid (HCl) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Biology Honors Name Acids, Bases and ph Substance ph More H + More OH - Acidic, Basic or Neutral (indicate if strong or weak acid or base) Vitamin C Tap water Hydrochloric acid (HCl) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Chapter 9 Acid-base reactions
 CHEM, 2nd edition Cengage Learning Chapter 9 Acid-base reactions Acids and bases are chemical compounds that occur regularly in 'everyday life'. These two types of substances have opposite properties.
CHEM, 2nd edition Cengage Learning Chapter 9 Acid-base reactions Acids and bases are chemical compounds that occur regularly in 'everyday life'. These two types of substances have opposite properties.
Basic Principles of Chemistry Lecture Notes #11 Types of Chemical Reactions
 Basic Principles of Chemistry Lecture Notes #11 Types of Chemical Reactions Types of Chemical Reactions Part 1 Precipitation Reactions In a precipitation reaction, a solid substance is formed in a solution
Basic Principles of Chemistry Lecture Notes #11 Types of Chemical Reactions Types of Chemical Reactions Part 1 Precipitation Reactions In a precipitation reaction, a solid substance is formed in a solution
Types of reactions: Acid-base reactions *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m39088 1 Types of reactions: Acid-base reactions * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m39088 1 Types of reactions: Acid-base reactions * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Acids and Bases. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Acids and Bases Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Acids and Bases Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
NaCl (aq) + HOH (l) + (aq) + Cl (l) Eg. HCl (aq) + NH 3(aq) In both cases the acid and base react and neutralize each other.
 Acid Base Reactions An acid base reaction is called a neutralization reaction. Eg. HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + HOH (l) In grade 10 you learned that acid base reactions produce salt and water, however,
Acid Base Reactions An acid base reaction is called a neutralization reaction. Eg. HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + HOH (l) In grade 10 you learned that acid base reactions produce salt and water, however,
UNIT 10 COMMON ACIDS AND ALKALIS
 ABLE EDUCATION CENTRE UNIT 10 COMMON ACIDS AND ALKALIS A Multiple-choice questions 1 Which of the following are the properties of alkalis? (1) They taste sour. (2) They are slippery. (3) They can turn
ABLE EDUCATION CENTRE UNIT 10 COMMON ACIDS AND ALKALIS A Multiple-choice questions 1 Which of the following are the properties of alkalis? (1) They taste sour. (2) They are slippery. (3) They can turn
Acids, Bases, and Salts
 Acids, Bases, and Salts 1 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates. H +1 Cl -1 Cl -1 H +1 2 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates in water.
Acids, Bases, and Salts 1 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates. H +1 Cl -1 Cl -1 H +1 2 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates in water.
(b) Calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid in mol/dm 3. Calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid reacting.
 Answer = mol/dm 3 Answer = mol/dm 3 Chemical Changes Part 4 Q1. An oven cleaner solution contained sodium hydroxide. A 25.0 cm 3 sample of the oven cleaner solution was placed in a flask. The sample was
Answer = mol/dm 3 Answer = mol/dm 3 Chemical Changes Part 4 Q1. An oven cleaner solution contained sodium hydroxide. A 25.0 cm 3 sample of the oven cleaner solution was placed in a flask. The sample was
CHEMICAL CONCEPTS USED IN THIS CHAPTER: Antacid medicines: what are they, and how do they work?
 CHAPTER 8 ACIDS AND BASES CHEMICAL CONCEPTS USED IN THIS CHAPTER: Acids and bases, strong and weak Electrolytes and their behavior Neutralization reactions ph and acidity CONTEMPORARY ISSUES IN THIS CHAPTER:
CHAPTER 8 ACIDS AND BASES CHEMICAL CONCEPTS USED IN THIS CHAPTER: Acids and bases, strong and weak Electrolytes and their behavior Neutralization reactions ph and acidity CONTEMPORARY ISSUES IN THIS CHAPTER:
Acids and Bases. Two important classification of compounds - Acids and Bases. Properties of BASES
 ACIDS AND BASES Acids and Bases Two important classification of compounds - Acids and Bases Properties of ACIDS Taste Sour/Tart Stings and burns the skin Reacts with bases Turns blue litmus paper red Reacts
ACIDS AND BASES Acids and Bases Two important classification of compounds - Acids and Bases Properties of ACIDS Taste Sour/Tart Stings and burns the skin Reacts with bases Turns blue litmus paper red Reacts
Chemistry and Reactions Year 9 Extension Science. 1 GZ Science Resources 2014
 Chemistry and Reactions Year 9 Extension Science 1 GZ Science Resources 2014 1a Reactants join together to form new products during chemical reactions The atoms present in the reactants rearrange themselves
Chemistry and Reactions Year 9 Extension Science 1 GZ Science Resources 2014 1a Reactants join together to form new products during chemical reactions The atoms present in the reactants rearrange themselves
Acids and Bases. Properties, Reactions, ph, and Titration
 Acids and Bases Properties, Reactions, ph, and Titration C-19 2017 Properties of acids 1. Taste Sour (don t try this except with foods). 2. Are electrolytes (conduct electricity). Some are strong, some
Acids and Bases Properties, Reactions, ph, and Titration C-19 2017 Properties of acids 1. Taste Sour (don t try this except with foods). 2. Are electrolytes (conduct electricity). Some are strong, some
Problem Solving. Percentage Yield
 Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Percentage Yield Although we can write perfectly balanced equations to represent perfect reactions, the reactions themselves are often not perfect. A reaction does not
Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Percentage Yield Although we can write perfectly balanced equations to represent perfect reactions, the reactions themselves are often not perfect. A reaction does not
Downloaded from
 CHAPTER 2--ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS Acids: Substances which turn blue litmus solution red are called acids. Acids are sour in taste Bases: Substances which change red litmus solution blue are called bases.
CHAPTER 2--ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS Acids: Substances which turn blue litmus solution red are called acids. Acids are sour in taste Bases: Substances which change red litmus solution blue are called bases.
Chemistry review. Energy levels: The six most abundant elements of life. Types of bonds. Atom:
 Atom: Chemistry review Energy levels: Energy Levels: move around the nucleus in regions. Different levels have different numbers of electrons. Outermost Energy Level: Atoms are most when they have a outermost
Atom: Chemistry review Energy levels: Energy Levels: move around the nucleus in regions. Different levels have different numbers of electrons. Outermost Energy Level: Atoms are most when they have a outermost
MONDAY (12/12) TUESDAY (12/13) WEDNESDAY (12/14) THURSDAY (12/15) FRIDAY (12/16) Making Acid Rain (a lab) Quiz
 Homework Activities Name: Date: Period: This week, we will be using our knowledge of acids and bases and studying how acids, specifically acid rain, affect our lives and our environment. We will also end
Homework Activities Name: Date: Period: This week, we will be using our knowledge of acids and bases and studying how acids, specifically acid rain, affect our lives and our environment. We will also end
5.1. Acids and Doses. Before You Read. Section. Summary. What are acids and bases? What is ph?
 Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Summary Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines
Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Summary Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines
Acids and Doses. Before You Read. Section 5.1. Summary. What are acids and bases? What is ph?
 Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines below.
Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines below.
CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY
 Advanced Chemistry Name Hour Advanced Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY Day Plans
Advanced Chemistry Name Hour Advanced Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY Day Plans
Chemical Reactions. Section 9.1 Reactions and Equations
 9 Chemical Reactions Section 9.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write
9 Chemical Reactions Section 9.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write
4. Alison decomposes a sample of matter into different substances. The original substance was not a/an:
 Name: Practice Problems 1. Monica makes the following observations on an object: I- Volume: 12.0 ml II- Length: 12.0 cm III- Mass: 1.25 g IV- Melting point: 450 o C Which observation is a characteristic
Name: Practice Problems 1. Monica makes the following observations on an object: I- Volume: 12.0 ml II- Length: 12.0 cm III- Mass: 1.25 g IV- Melting point: 450 o C Which observation is a characteristic
Sample Problem Set. Teacher Notes and Answers. Skills Worksheet PERCENTAGE YIELD. Name: Class: Date:
 Skills Worksheet Sample Problem Set Teacher Notes and Answers PERCENTAGE YIELD 1. a. 64.3% yield b. 58.0% yield c. 69.5% yield d. CH 3 CH OH is limiting; 79% yield. a. 69.5% yield b. 79.0% yield c. 48%
Skills Worksheet Sample Problem Set Teacher Notes and Answers PERCENTAGE YIELD 1. a. 64.3% yield b. 58.0% yield c. 69.5% yield d. CH 3 CH OH is limiting; 79% yield. a. 69.5% yield b. 79.0% yield c. 48%
A salt is a neutral ionic compound composed of cations and anions. It is the result of an acid-base neutralisation reaction.
 Acid-base reactions When an acid and a base react, they form a salt. If the base contains hydroxide (OH ) ions, then water will also be formed. The word salt is a general term which applies to the products
Acid-base reactions When an acid and a base react, they form a salt. If the base contains hydroxide (OH ) ions, then water will also be formed. The word salt is a general term which applies to the products
7E Acids and alkalis Multiple-choice main test
 For each question, circle the correct answer. Question 1 Vinegar is an acid. Like some other acids vinegar tastes... A) salty B) sour C) sugary D) sweet Question 2 Acids may be hazardous chemicals. Concentrated
For each question, circle the correct answer. Question 1 Vinegar is an acid. Like some other acids vinegar tastes... A) salty B) sour C) sugary D) sweet Question 2 Acids may be hazardous chemicals. Concentrated
Mixtures, Solubility, and Acid/Base Solutions
 Mixtures, Solubility, and Acid/Base Soluts Acid and Base Soluts What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
Mixtures, Solubility, and Acid/Base Soluts Acid and Base Soluts What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
Worked solutions to student book questions Chapter 4 Analysing acids and bases
 Q. Antacid tablets should normally be chewed before they are swallowed. Why? A. Antacid tablets are normally chewed to provide a larger surface area for faster reaction with stomach acids. Q. A laboratory
Q. Antacid tablets should normally be chewed before they are swallowed. Why? A. Antacid tablets are normally chewed to provide a larger surface area for faster reaction with stomach acids. Q. A laboratory
c. K 2 CO 3 d. (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Answer c
 Chem 130 Name Exam 2, Ch 4-6 July 7, 2016 100 Points Please follow the instructions for each section of the exam. Show your work on all mathematical problems. Provide answers with the correct units and
Chem 130 Name Exam 2, Ch 4-6 July 7, 2016 100 Points Please follow the instructions for each section of the exam. Show your work on all mathematical problems. Provide answers with the correct units and
SESSION 13: CHEMICAL REACTIONS. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade 11.
 SESSION 13: CHEMICAL REACTIONS Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Redox reactions Direct transfer of electrons Rules for assigning oxidation numbers
SESSION 13: CHEMICAL REACTIONS Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Redox reactions Direct transfer of electrons Rules for assigning oxidation numbers
