Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth
|
|
|
- Ruth Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(7), (2011) DOI: /s z INVITED REVIEW PAPER Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth Jun Zhou, Wentao Bi, and Kyung Ho Row Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha University, 253 Yonghyun-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon , Korea (Received 8 November 2010 accepted 15 January 2011) Abstract The recovery of lactic acid from fermentation broth plays an important part in production of lactic acid. In this case, the extraction of lactic acid from simulated fermentation broth was processed by tri-n-octylamine dissolved in oleyl alcohol. The extraction efficiency was investigated with several variables, and the optimal condition of extraction of lactic acid (10 mg ml 1 ) from aqueous solution was tri-n-octylamine/oleyl alcohol (30/70, v/v) and solvent phase/ fermentation (1/2, v/v) stirred for 60 min under room temperature. The optimal back extraction of lactic acid was obtained by hot water (~90 o C) with solvent phase/water (1/4, v/v). The back extracted racemic lactic acid was direct enantiomeric analyzed and separated by chiral ligand chromatography due to strict requirement of absolute configuration in pharmaceutical field and food science. The effect of various parameters on enantioselectivity was discussed and the (L)-phenylalaninamide HCl (6.0 mmol L 1 ) and CuSO 4 5H 2 O (3.0 mmol L 1 ) dissolved in methanol/water (5/95, v/v) at ph=6.0 was the suitable mobile phase for chiral ligand exchange separation of (D, L)-lactic acids. By the investigations, a convenient systemic method was established for extraction and separation of (D, L)-lactic acid. Key words: Lactic Acid, Fermentation, Extraction, Separation, Ligand Exchange INTRODUCTION Lactic acid is an important chemical that can be used in food, pharmaceutical, leather and textile industries [1]. It can be produced either by synthesis or by fermentation [2,3]. The conventional fermentation was considered to be prevailing method. To recover the lactic acid from fermentation broth, several kinds of methods have been employed, such as solvent extraction [1,4,5], reverse osmosis [6], adsorption [7,8], distillation [9], electrodialysis [10] and nanoflitration [11]. Solvent extraction has been proposed to be a convenient method for lactic acid recovery with low cost. Von Frieling et al. [4] reported that the recovery of lactic acid from fermentation broths can be obtained by a carrier/modifier/solvent combination. A secondary amine (Hoe F 2562), a tertiary amine (Hostarex A 327) as well as a phosphine oxide as carriers and butylacetate and kerosene as solvents were adopted in the experiments. Yankov et al. [5] carried out an extraction of lactic acid from aqueous solutions and simulated fermentation broth by the selected system (30% tri-n-octylamine, 20% decanol and 50% dodecane) with high efficiency. Recently, a high performance extractive fermentation process with high extractive efficiency was achieved by the use of tri-n-decylamine (TDA) as the extractant was developed [1]. The D or L lactic acid can be directly produced by the bacterial fermentation and extracted by solvent extraction. However, enantiomeric analysis and separation should be adopted due to the strict requirement of optical purity in pharmaceutical and food industries. Previous studies indicated that the analysis of enantiomeric purity of lactic acid can be obtained by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) [12] or chromatographic methods with chiral stationary phase [13]. Later, Galaverna et al. [14] developed a ligand exchange HPLC for To whom correspondence should be addressed. rowkho@inha.ac.kr 1608 chiral separation of (D, L)-lactic acid. This method provides a convenient approach for analysis and separation of (D, L)-lactic acid. We developed a method to extract lactic acid from lactic acid aqueous solution and simulated fermentation broth by a solvent composed of tri-n-octylamine (TOA) and oleyl alcohol (OAL). The influences on the extraction were studied. Subsequently, the lactic acid was enantiomeric analyzed and separated by chiral ligand exchange HPLC after the removal of interference in fermentation broth by solvent extraction. The extraction and enantiomeric separation were combined to establish a convenient system method for the procedure of recovery of (D, L)-lactic acid from fermentation broth. MATERIALS AND METHODS 1. Materials (D, L)-Lactic acid (90%) was purchased from Fluka (Milwaukee, USA) Tri-n-octylamine (TOA), (L)-phenylalanine, and (L)- phenylalaninol (L)-phenylalaninamide HCl were obtained from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), methanol and oleyl alcohol (OAL) were purchased from DAE JUNG Chemicals and Metals Co., LTD. (Ansan, Korea). Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic 12-water (Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O), Copper (II) Sulfate pent hydrate (CuSO 4 5H 2 O) and Sodium Acetate (CH 3 COONa) were from DUKSAN Pure Chemical CO., LTD. (Ansan, Korea), Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO 4 7H 2 O) was from SAMCHUN Pure Chemical CO., LTD. (Pyongtack, Korea). Distilled water was filtered using a vacuum pump (Division of Millipore, Waters, USA) and a filter (HA-0.45, Division of Millipore, Waters, USA). All solvents used in the experiment were HPLC or analytical grade. All the samples were filtered by a filter (MFS-25, 0.2 µm TF, WHATMAN, U.S.A.) before being injected into the HPLC system. 2. Extraction of Lactic Acid The aqueous solution, containing g L 1 (A 0 ) two enanti-
2 Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth 1609 omers of lactic acid, was used for the extraction studies. TOA was used as a carrier. The solvent phase was composed from TOA dissolved in OAL. The experiment was performed in a 100 ml flask. Aqueous phase (20 ml) containing lactic acid and solvent phase was stirred under different temperatures. After complete separation of the phases, the concentration of lactic acid (A 1 ) in aqueous phase was measured by HPLC. The extracted amount of lactic acid was obtained by A 1 subtracting from A 0 according to the mass balance. To simulate the real fermentation broth, salts (CH 3 COONa, Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O and MgSO 4 7H 2 O) were added in the lactic acid aqueous solution with different ph values adjusted by 1.0 mol L 1 NaOH aqueous solution. The back extraction was obtained by extracting lactic acid from the solvent phase containing lactic acid (A 1 ) with hot water (~90 o C). After 60 min stirring, the concentration of lactic acid in hot water (A 2 ) was determined by HPLC. 3. HPLC Analysis The HPLC system was comprised of an M930 solvent delivery pump (Young Lin Co. Korea), a UV detector (M 720 Absorbance Detector, Young-In Scientific Co., Korea) and an integrated data system (Autochrowin. Ver. 1.42, Young Lin Co., Korea). Injection valves with 20 µl sample loops were used. The HPLC analysis was performed with a commercial C 18 column (4.6 * 150 mm, 5 µm) purchased from RStech Co. (Daejeon, Korea). In the extraction of lactic acid process, the mobile phase was methanol/water (20/80, v/v), the flow-rate was set at 0.5 ml min 1, the UV wavelength was set at 210 nm, and the injection volume was 10 µl. While in the analysis of (D, L)-lactic acid, the (L)-phenylalaninamide and CuSO 4 5H 2 O (3 mmol L 1 ) were dissolved in methanol/water solution with different ph values. The flow rate was 0.5 ml min -1 and the UV wavelength was at 254 nm. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 1. Extraction and Back Extraction of Lactic Acid from Aqueous Solution and Simulated Fermentation Broth The principle of extraction was due to the interactions between lactic acid and tertiary amine through hydrogen bonding (Eq. (1)) or ion-pair formation (Eq. (2)) [5]. Table 1. The factors that influence the extraction of lactic acid from aqueous solution Variables Range Extraction of lactic acid from aqueous solution Time/min 30, 60, 90, 120 Temperature/ o C 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 ph 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 RCS 0 : 100, 10 : 90, 20 : 80, 30 : 70, 40 : 60, 50 : 50 RSF 1:4, 1:2, 1:1, 2:1 Concentration of lactic acid in aqueous solution/mg ml 1 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 Back extraction of lactic acid by hot water (~90 o C) RSW 1 : 4, 1 : 2, 1 : 1, 2 : 1, 4 : 1 A2 Back extraction efficiency (%) = A0 A1 100 Where, A 0 and A 1 represent the concentration (g L 1 ) of lactic acid in the fermentation solutions before extraction and after extraction, A 2 represents the concentration (g L 1 ) of lactic acid in hot water of back extraction, respectively Extraction of Lactic Acid from Aqueous Solution The extraction efficiency was first investigated by extraction of lactic acid from its aqueous solution. The effect of extraction time was investigated by mixing the solvent phase (RCS=10/90) with the lactic acid aqueous solution and stirring for a period of min under room temperature. Fig. 1 shows that with different RSF (1/4, 1/2, 1/1 and 2/1), there was no obvious increase of extraction efficiency after 60 min, so 60 min was selected in the following experiments. The effect of RCS on extraction efficiency with different RSF was then investigated under room temperature. The results are shown in Fig. 2. With increasing the RCS and RSF, the extraction efficiency of lactic acid increased. However, the extraction efficiencies (4) R 3 N+HA R 3 N HA (1) R 3 N+HA R 3 NH + A (2) Where, R 3 N represents the tertiary amine and HA, H + and A represent lactic acid and its ions, respectively. The factors that might influence the extraction were investigated, such as time, temperature, the ratio of tri-n-oxtylamine (carrier) to oleyl alcohol (solvent) on the base of volume (RCS), the ratio of solvent phase to fermentation on the base of volume (RSF), the concentration of lactic acid in aqueous solution and ph values (Table 1). The ratio of solvent phase (with lactic acid) to water (~90 o C) on the base of volume (RSW) was investigated for the back extraction. The extraction efficiency and back extraction efficiency of lactic acid were calculated by the following equations: Extraction efficiency (%) = A A0 (3) Fig. 1. Effect of extraction time on extraction efficiency with different RSF (Temperature=20 o C, RCS=10 : 90, concentration of lactic acid=10 mg ml 1 ). Korean J. Chem. Eng.(Vol. 28, No. 7)
3 1610 J. Zhou et al. Fig. 2. Effect of RCS on extraction efficiency with different RSF (Temperature=20 o C, time=60 min, concentration of lactic acid=10 mg ml 1 ). Fig. 4. Effect of concentration of lactic acid on extraction efficiency (RCS=30/70, RSF=1/2, temperature=20 o C, extraction time =60 min). Fig. 3. Effect of temperature on extraction efficiency (RCS=20/80, RSF=1/1, extraction time=60 min, concentration of lactic acid=10 mg ml 1 ). Fig. 5. Effect of ph on extraction efficiency (Na 2 HPO 4 =2 mg ml 1, CH 3 COONa=5 mg ml 1, MgSO 4 =0.6 mg ml 1, RCS=30/ 70, RSF=1/2, temperature=20 o C, extraction time=60 min, concentration of lactic acid=10 mg ml 1 ). did not increase significantly when RCS increased to 30/70. To minimize the use of TOA and solvent phase, RCS=30/70 and RSF=1/2 were preferred. To study the effect of temperature on extraction efficiency, solvent phase (RCS=20/80) and lactic acid aqueous solution were mixed (RSF=1/1) and stirred for 60 min at o C. The results are in Fig. 3, which shows that the highest extraction efficiency (86.3%) was obtained at 30 o C. Further increase of temperature caused the decrease of extraction efficiency. This result was caused by the equilibrium between diffusion and interactions of extraction. The diffusion of lactic acid increased with increasing the temperature, but the interactions between lactic acid and tertiary amine decreased. Although the highest extraction efficiency was obtained at 30 o C, the 20 o C with moderate extraction efficiency was adopted, considering the energy consumption. The effect of the concentration of lactic acid in aqueous solution on extraction efficiency was obtained by adding different concentration of lactic acid into aqueous solution and stirring with solvent phase (RCS=30/70, RSF=1/2) under room temperature for 60 min. The extraction efficiency decreased to 60% with the concentration of lactic acid increasing from 5 g L 1 to 100 g L 1 (Fig. 4) Extraction of Lactic Acid from Simulated Solution The previous studies have shown that glucose, peptone, yeast extract [15] and lactose [16] do not affect the lactic acid extraction. In this case, Na 2 HPO 4, sodium acetate and MgSO 4 were contained in the lactic acid aqueous solution according to the reference [17]. Because the extraction efficiency depended on the acidity of the aqueous solution, the ph values were adjusted from 2-6 (Fig. 5). It was seen that the extraction efficiency was poor at high ph value, which also could be explained by the equilibrium of the interactions between lactic acid and tertiary amine Back Extraction of Lactic Acid from Solvent Phase The back extraction of lactic acid with hot water (~90 o C), which July, 2011
4 Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth 1611 is plotted in Fig. 6, increased with the RSW increasing. Because of the increase of water amount and temperature, the equilibrium of interactions (Eqs. (1) and (2)) moved to the left, and the highest back extraction efficiency was obtained at the RSW=1/4. 2. Chiral Separation of (D, L)-Lactic Acid by Ligand Exchange Chromatography The extracted (D, L)-lactic acids were enantiomeric analyzed and separated by ligand exchange chromatography using chiral ligand and copper (II) sulfate as additives to the mobile phase in connection with an achiral reversed phase column (C 18 ). Due to the copper complex, the detection was performed by monitoring the UV absorption at 254 nm. The retention factor was calculated from the equation k=(t t 0 )/t 0, where t and t 0 are the retention times of analyte and unretained solutes, respectively. And the enantioseparation factor was calculated from the equation α=k L /k D, where k L and k D are the retention factors of (L)-enantiomer and (D)-enantiomer, respectively. To investigate the effects of different ligands on the chiral separa- Fig. 6. Effect of RSW on back extraction efficiency (RCS=30/70, temperature=~90 o C, extraction time=60 min). tion, (L)-phenylalanine, (L)-phenylalaninamide and (L)-phenylalaninol were used as ligand agents, respectively. (L)-phenylalaninamide was the only ligand agent which was found to be suitable for chiral separation of (D, L)-lactic acid. The effects of different concentration of (L)-phenylalaninamide in the mobile phase on the enantioselectivity were investigated in the range of mmol L 1 and the results are shown in Fig. 7. It indicated that the concentration of ligand agent in the mobile phase could affect the k and α. The value of k and α increased when the concentration of (L)-phenylalaninamide was varied from 2.0 to 6.0 mmol L 1 and tended to decrease above the latter value. Increasing the concentration of ligand in the mobile phase could result in the formation of more ligand complexes, and as a result, the retention and separation of the enatiomers would be increased. When the concentration of ligand reached a certain threshold (6 mmol L 1 ), the ligand would compete with ligand complexes to distribute on the stationary phase, so the k and α decreased. The ph of the mobile phase was another critical factor affection enatioselectivity. To investigate the effect of ph on the enantioseparation, the ph of the mobile phase was varied from 4.0 to 7.0. Fig. 8 shows that the selectivity and retention of the two enantiomers increased with the ph increasing to 6.0; further increase of the ph tended to decrease the k and α. Moreover, higher ph would cause the precipitation of exceeding Cu 2+. In this case, ph=6.0 was a suitable ph value. Different concentrations of methanol were used as the organic modifier in the mobile phase to investigate the effect of organic modifier on chiral separation. Fig. 8 shows that both the retention and separation of the two enantiomers decreased when the concentration of methanol in the mobile phase increased. This was attributed to the high concentration of organic solvent, which resulted in precipitation of the electrolyte in the mobile phase. Although the k and α increased when methanol was below 5%, the mobile phase was not suitable for the protection of C 18 column. By previous investigations, the optimal condition was fixed. The (L)-phenylalaninamide HCl (6.0 mmol L 1 ) and CuSO 4 5H 2 O (3.0 mmol L 1 ) dissolved in methanol/water (5/95, v/v) at ph=6.0 was Fig. 7. Effect of the concentration of ligand (L-Phenylalaninamide, Cu(SO 4 ) 2 5H 2 O (3 mmol L 1 ), ph=6.0, room temperature, C 18 column (150 * 4.6 mm), flow rate 0.5 ml min 1, UV detector at 254 nm). Fig. 8. Effect of ph value (L-Phenylalaninamide (6 mmol L 1 ), Cu (SO 4 ) 2 5H 2 O (3 mmol L 1 ), room temperature, C 18 column (150 * 4.6 mm), flow rate 0.5 ml min 1, UV detector at 254 nm). Korean J. Chem. Eng.(Vol. 28, No. 7)
5 1612 J. Zhou et al. The studies showed that the selected system (TOA and OAL) was effective for the extraction of lactic acid from aqueous solutions and simulated fermentation broth. All the variables that affected the extraction of lactic acid were investigated to get the suitable condition. After the extraction of lactic acid, the extracted two enantiomers of lactic acid were applied to investigate the enantiomeric analysis and separation by ligand exchange chromatography and a conventional method was established. The combination of extraction and enantiomeric separation was established as a convenient system for the procedure of recovery of (D, L)-lactic acid from fermentation broth. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology ( ). Fig. 9. Effect of concentration of methanol (L-Phenylalaninamide (6 mmol L 1 ), Cu(SO 4 ) 2 5H 2 O (3 mmol L 1 ), room temperature, C 18 column (150 * 4.6 mm), flow rate 0.5 ml min 1, UV detector at 254 nm). Fig. 10. Chromatogram of chiral separation of (D, L)-lactic acid (L-Phenylalaninamide (6 mmol L 1 ), Cu(SO 4 ) 2 5H 2 O (3 mmol L 1 ), room temperature, C 18 column (150 * 4.6 mm), flow rate 0.5 ml min 1, UV detector at 254 nm). the suitable mobile phase for chiral ligand exchange separation of (D, L)-lactic acids (Fig. 10). CONCLUSION REFERENCES 1. M. T. Gao, T. Shimamura, N. Ishida and H. Takahashi, Biochem. Eng. J., 44, 251 (2009). 2. K. O. Shin, J. R. Jeon and J. S. Lee, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 11, 240 (2006). 3. L. P. Huang, B. Jin, P. Lant, X. L. Qiao, J. W. Chen and W. Sun, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 9, 245 (2004). 4. P. Frieling and K. Schugerl, Process Biochem., 34, 685 (1999). 5. D. Yankov, J. Molinier, J. Albet, G. Malmary and G. Kyuchoukov, Biochem. Eng. J., 21, 63 (2004). 6. M. K. H. Liew, S. Tanaka and M. Morita, Desalination, 101, 269 (1995). 7. R. S. Juang, R. H. Huang and R. T. Wu, J. Membr. Sci., 136, 89 (1997). 8. A. V. Sosa, J. Ochoa and N. I. Perotti, Biosep., 9, 283 (2001). 9. J. Y. Kim, W. H. Hong and G. Wozny, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 5, 196 (2000). 10. M. T. Gao, M. Hirata, M. Koide, H. Takanashi and T. Hano, Process Biochem., 39, 1903 (2004). 11. E. G. Lee, S. H. Kang, H. H. Kim and Y. K. Chang, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 11, 313 (2006). 12. D. Parker, Chem. Rev., 91, 1441 (1991). 13. B. Koppenhoefer, H. Allmendinger, G. J. Hicholson and E. Bayer, J. Chromatogr., 260, 63 (1983). 14. G. Galaverna, F. Panto, A. Dossena, R. Marchelli and F. Bigi, Chirality, 7, 331 (1995). 15. B. Choudhury, A. Basha and T. Swaminathan, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 72,111 (1998). 16. M. San-Martin, C. Pazos and J. Coca, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 54, 1 (1992). 17. X. Sun, Q. Wang, W. Zhao, H. Ma and K. Sakata, Sep. Purif. Technol., 49, 43 (2006). July, 2011
Effect of operating parameters on precipitation for recovery of lactic acid from calcium lactate fermentation broth
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(10), 1969-1974 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-011-0082-9 RAPID COMMUNICATION Effect of operating parameters on precipitation for recovery of lactic acid from calcium lactate fermentation
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(10), 1969-1974 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-011-0082-9 RAPID COMMUNICATION Effect of operating parameters on precipitation for recovery of lactic acid from calcium lactate fermentation
Retention mechanism of some solutes using ionic liquids as mobile phase modifier in RP-high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(2), 357-363 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-010-0273-9 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Retention mechanism of some solutes using ionic liquids as mobile phase modifier in RP-high-performance liquid
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(2), 357-363 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-010-0273-9 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Retention mechanism of some solutes using ionic liquids as mobile phase modifier in RP-high-performance liquid
Determination of Retention Factors of Aromatic Compounds by Gradient-Elution Reverse-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 19(6), 978-985 (22) Determination of Retention Factors of Aromatic Compounds by Gradient-Elution Reverse-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography Ju Weon Lee and Kyung Ho Row
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 19(6), 978-985 (22) Determination of Retention Factors of Aromatic Compounds by Gradient-Elution Reverse-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography Ju Weon Lee and Kyung Ho Row
Sushil Kumar 1, T R Mavely 2 and B V Babu* Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS), PILANI (Rajasthan) India
 Reactive Extraction of Carboxylic s (Butyric-, Lactic-, Tartaric-, Itaconic- Succinic- and Citric s) using Tri-n-Butylphosphate (TBP) Dissolved in 1-Dodecanol and n-octane (1:1 v/v) Sushil Kumar 1, T R
Reactive Extraction of Carboxylic s (Butyric-, Lactic-, Tartaric-, Itaconic- Succinic- and Citric s) using Tri-n-Butylphosphate (TBP) Dissolved in 1-Dodecanol and n-octane (1:1 v/v) Sushil Kumar 1, T R
CHAPTER 19 PARACETAMOL + IBUPROFEN
 CHAPTER 19 PARACETAMOL + IBUPROFEN SUMMARY 246 A combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen is marketed in India. Literature survey indicated that one titrimetnc-1-** and one HPLC193 methods are reported
CHAPTER 19 PARACETAMOL + IBUPROFEN SUMMARY 246 A combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen is marketed in India. Literature survey indicated that one titrimetnc-1-** and one HPLC193 methods are reported
Draft Method proposal: determination of glucoheptonic acid (HGA) in fertilizers.
 Draft Method proposal: determination of glucoheptonic acid (HGA) in fertilizers. 1 Scope This document describes a chromatographic method which allows the identification as well as the determination of
Draft Method proposal: determination of glucoheptonic acid (HGA) in fertilizers. 1 Scope This document describes a chromatographic method which allows the identification as well as the determination of
1Determination of optical purity of N-acetyl-1-naphthylethylamine by chiral chromatography and NMR spectroscopy
 Printed in the Republic of Korea "/"-:5*$"- 4$*&/$& 5&$)/0-0(: Vol. 23, No. 1, 97-101, 2010 1Determination of optical purity of N-acetyl-1-naphthylethylamine by chiral chromatography and NMR spectroscopy
Printed in the Republic of Korea "/"-:5*$"- 4$*&/$& 5&$)/0-0(: Vol. 23, No. 1, 97-101, 2010 1Determination of optical purity of N-acetyl-1-naphthylethylamine by chiral chromatography and NMR spectroscopy
A rapid and highly selective colorimetric method for direct detection of tryptophan in proteins via DMSO acceleration
 A rapid and highly selective colorimetric method for direct detection of tryptophan in proteins via DMSO acceleration Yanyan Huang, Shaoxiang Xiong, Guoquan Liu, Rui Zhao Beijing National Laboratory for
A rapid and highly selective colorimetric method for direct detection of tryptophan in proteins via DMSO acceleration Yanyan Huang, Shaoxiang Xiong, Guoquan Liu, Rui Zhao Beijing National Laboratory for
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Organocatalytic Enantioselective Formal Synthesis of Bromopyrrole Alkaloids via Aza-Michael Addition Su-Jeong Lee, Seok-Ho Youn and Chang-Woo Cho* Department of Chemistry, Kyungpook
Supporting Information Organocatalytic Enantioselective Formal Synthesis of Bromopyrrole Alkaloids via Aza-Michael Addition Su-Jeong Lee, Seok-Ho Youn and Chang-Woo Cho* Department of Chemistry, Kyungpook
2017 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide
 217 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide O O Cl NH 3 NH 2 C 9 H 7 ClO (166.6) (17.) C 9 H 9 NO (147.2) Classification Reaction types and substance classes reaction of
217 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide O O Cl NH 3 NH 2 C 9 H 7 ClO (166.6) (17.) C 9 H 9 NO (147.2) Classification Reaction types and substance classes reaction of
A dual-model and on off fluorescent Al 3+ /Cu 2+ - chemosensor and the detection of F /Al 3+ with in situ prepared Al 3+ /Cu 2+ complex
 Supporting Information (SI) A dual-model and on off fluorescent Al 3+ /Cu 2+ - chemosensor and the detection of F /Al 3+ with in situ prepared Al 3+ /Cu 2+ complex Xiaoya Li, Mingming Yu, Faliu Yang, Xingjiang
Supporting Information (SI) A dual-model and on off fluorescent Al 3+ /Cu 2+ - chemosensor and the detection of F /Al 3+ with in situ prepared Al 3+ /Cu 2+ complex Xiaoya Li, Mingming Yu, Faliu Yang, Xingjiang
A New Model for Asymmetric Amplification in Amino Acid Catalysis - Supporting information
 A New Model for Asymmetric Amplification in Amino Acid Catalysis - Supporting information Martin Klussmann, Hiroshi Iwamura, Suju P. Mathew, David H. Wells, Urvish Pandya, Alan Armstrong and Donna G. Blackmond
A New Model for Asymmetric Amplification in Amino Acid Catalysis - Supporting information Martin Klussmann, Hiroshi Iwamura, Suju P. Mathew, David H. Wells, Urvish Pandya, Alan Armstrong and Donna G. Blackmond
Water. A New Protocol for the Preparation of Optically Active Norstatines.
 SUPPRTING INFRMATINS First ne-pot Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of α-hydroxy-β-amino Acids in Water. A New Protocol for the Preparation of ptically Active Norstatines. Francesco Fringuelli,* Ferdinando Pizzo,
SUPPRTING INFRMATINS First ne-pot Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of α-hydroxy-β-amino Acids in Water. A New Protocol for the Preparation of ptically Active Norstatines. Francesco Fringuelli,* Ferdinando Pizzo,
Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown.
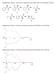 Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown. Supplementary Figure 2. CD spectra obtained using 1 and (R)-3 (blue) and (S)-3 (red) Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown. Supplementary Figure 2. CD spectra obtained using 1 and (R)-3 (blue) and (S)-3 (red) Supplementary Figure 3.
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.28-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE GB PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.28-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.28-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE GB PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.28-2016
Purification of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole by solvent extraction
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(2), 282-287 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Purification of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole by solvent extraction Prakorn Ramakul, Milan Hronec* and Ura Pancharoen Department of Chemical Engineering,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(2), 282-287 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Purification of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole by solvent extraction Prakorn Ramakul, Milan Hronec* and Ura Pancharoen Department of Chemical Engineering,
Determination of Caffeine by HPLC
 Determination of Caffeine by HPLC Introduction It was a long history before real high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) had evolved. The very first indication of a chromatographic separation was
Determination of Caffeine by HPLC Introduction It was a long history before real high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) had evolved. The very first indication of a chromatographic separation was
Synthesis of Secondary and Tertiary Amine- Containing MOFs: C-N Bond Cleavage during MOF Synthesis
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Synthesis of Secondary and Tertiary Amine- Containing MFs: C-N Bond
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Synthesis of Secondary and Tertiary Amine- Containing MFs: C-N Bond
LUMEFANTRINUM LUMEFANTRINE
 July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets
 Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets Dissolution Perform the test with 1 tablet of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets at 50 revolutions per minute according to the Paddle method, using 900 ml of water
Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets Dissolution Perform the test with 1 tablet of Ondansetron Hydrochloride Tablets at 50 revolutions per minute according to the Paddle method, using 900 ml of water
BRIEFING. (EXC: K. Moore.) RTS C Propylparaben C 10 H 12 O Benzoic acid, 4 hydroxy, propyl ester; Propyl p hydroxybenzoate [ ].
![BRIEFING. (EXC: K. Moore.) RTS C Propylparaben C 10 H 12 O Benzoic acid, 4 hydroxy, propyl ester; Propyl p hydroxybenzoate [ ]. BRIEFING. (EXC: K. Moore.) RTS C Propylparaben C 10 H 12 O Benzoic acid, 4 hydroxy, propyl ester; Propyl p hydroxybenzoate [ ].](/thumbs/76/73319525.jpg) BRIEFING Propylparaben. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Propylparaben monograph, as part of the process
BRIEFING Propylparaben. The European Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Propylparaben monograph, as part of the process
Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for phenolic. compounds from model oil
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for phenolic compounds from model oil Tongnian
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for phenolic compounds from model oil Tongnian
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV*
 Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
Fluorescent probe for Lewisite Simulant
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2016 Supporting information (New
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2016 Supporting information (New
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Efficient Temperature Sensing Platform Based on Fluorescent Block Copolymer Functionalized Graphene Oxide Hyunseung Yang, Kwanyeol Paek, and Bumjoon J. Kim * : These authors contributed
Supporting Information Efficient Temperature Sensing Platform Based on Fluorescent Block Copolymer Functionalized Graphene Oxide Hyunseung Yang, Kwanyeol Paek, and Bumjoon J. Kim * : These authors contributed
Synthesis of Dihydroquinoline Based Merocyanines as Naked Eye and Fluorogenic sensors for Hydrazine Hydrate in Aqueous Medium
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Synthesis of Dihydroquinoline Based Merocyanines as Naked Eye and Fluorogenic sensors for Hydrazine
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Synthesis of Dihydroquinoline Based Merocyanines as Naked Eye and Fluorogenic sensors for Hydrazine
Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light
 Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE AND ESTIMATION OF ENTHALPY AND ENTROPY FOR REACTIVE EXTRACTION OF LACTIC ACID
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: (3), 22, 39-36 ISSN 972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE AND ESTIMATION OF ENTHALPY AND ENTROPY FOR REACTIVE EXTRACTION OF LACTIC ACID HUSSEIN SALIH HUSSEIN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: (3), 22, 39-36 ISSN 972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE AND ESTIMATION OF ENTHALPY AND ENTROPY FOR REACTIVE EXTRACTION OF LACTIC ACID HUSSEIN SALIH HUSSEIN
Optimization of Batch Distillation Involving Hydrolysis System
 273 Optimization of Batch Distillation Involving Hydrolysis System Elmahboub A. Edreder 1, Iqbal M. Mujtaba 2, Mansour Emtir 3* 1 Libyan Petroleum Institute, P.O. Box 6431, Tripoli, Libya 2 School of Engineering
273 Optimization of Batch Distillation Involving Hydrolysis System Elmahboub A. Edreder 1, Iqbal M. Mujtaba 2, Mansour Emtir 3* 1 Libyan Petroleum Institute, P.O. Box 6431, Tripoli, Libya 2 School of Engineering
Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets
 Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets Liquid chromatography was developed by Tswett in early 1900 s and was shown to be a powerful separation
Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets Liquid chromatography was developed by Tswett in early 1900 s and was shown to be a powerful separation
Separation Characteristics of Lactic Acid in Reactive Extraction and Stripping
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 17(5), 528-533 (2000) Separation Characteristics of Lactic Acid in Reactive and Stripping Dong Hoon Han*, Yeon Ki Hong and Won Hi Hong Department of Chemical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 17(5), 528-533 (2000) Separation Characteristics of Lactic Acid in Reactive and Stripping Dong Hoon Han*, Yeon Ki Hong and Won Hi Hong Department of Chemical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Enantioselectivity switch in copper-catalyzed conjugate addition. reaction under influence of a chiral N-heterocyclic carbene-silver complex
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Enantioselectivity switch in copper-catalyzed conjugate addition
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Enantioselectivity switch in copper-catalyzed conjugate addition
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information S1 Reversible stereodivergent cycloaddition of racemic helicenes to [60]fullerene: a chiral resolution strategy Rosa M. Girón, Jiangkun Ouyang, Ludovic Favereau, Nicolas Vanthuyne,
Supporting Information S1 Reversible stereodivergent cycloaddition of racemic helicenes to [60]fullerene: a chiral resolution strategy Rosa M. Girón, Jiangkun Ouyang, Ludovic Favereau, Nicolas Vanthuyne,
Synthesis of Peptide-Grafted Comb Polypeptides via Polymerisation of NCA-Peptides
 Supporting Information to Synthesis of Peptide-Grafted Comb Polypeptides via Polymerisation of NCA-Peptides Hiroshi Enomoto, Benjamin Nottelet, Soultan Al Halifa, Christine Enjalbal, Mathieu Dupré, Julien
Supporting Information to Synthesis of Peptide-Grafted Comb Polypeptides via Polymerisation of NCA-Peptides Hiroshi Enomoto, Benjamin Nottelet, Soultan Al Halifa, Christine Enjalbal, Mathieu Dupré, Julien
Convenient Synthesis of Nucleoside 5 -Triphosphates for RNA Transcription. Supplemental Materials
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010 Convenient Synthesis of ucleoside 5 -Triphosphates for RA Transcription Julianne Caton-Williams,
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010 Convenient Synthesis of ucleoside 5 -Triphosphates for RA Transcription Julianne Caton-Williams,
Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediol
 Fluid Phase Equilibria 202 (2002) 359 366 Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediol Jung-Yeon Park a, Sang Jun Yoon a, Huen Lee a,, Ji-Ho Yoon b, Jae-Goo Shim
Fluid Phase Equilibria 202 (2002) 359 366 Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediol Jung-Yeon Park a, Sang Jun Yoon a, Huen Lee a,, Ji-Ho Yoon b, Jae-Goo Shim
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information C aryl -C alkyl bond formation from Cu(ClO 4 ) 2 -mediated oxidative cross coupling reaction between arenes and alkyllithium reagents through structurally well-defined Ar-Cu(III)
Supplementary Information C aryl -C alkyl bond formation from Cu(ClO 4 ) 2 -mediated oxidative cross coupling reaction between arenes and alkyllithium reagents through structurally well-defined Ar-Cu(III)
Cation Exchange HPLC Columns
 Cation Exchange HPLC Columns Hamilton offers seven polymeric packing materials for cation exchange separations. Type Recommended Application(s) PRP-X00 PRP-X00 PRP-X800 HC-0 HC-7 Ca + HC-7 H + HC-7 Pb
Cation Exchange HPLC Columns Hamilton offers seven polymeric packing materials for cation exchange separations. Type Recommended Application(s) PRP-X00 PRP-X00 PRP-X800 HC-0 HC-7 Ca + HC-7 H + HC-7 Pb
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic supplementary information Surface plasmon resonance enhanced upconversion luminescence in aqueous media for TNT selective detection Nina Tu and Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource
Electronic supplementary information Surface plasmon resonance enhanced upconversion luminescence in aqueous media for TNT selective detection Nina Tu and Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2008
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 Supporting Information for Electrochemically Protected
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 Supporting Information for Electrochemically Protected
Highly Efficient and Low Toxic Skin Penetrants Composed of Amino Acid Ionic Liquids
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 206 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Highly Efficient and Low Toxic Skin Penetrants
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 206 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Highly Efficient and Low Toxic Skin Penetrants
Analytical method related to authorised feed additive - 1i534
 Title DETERMINATION OF MESO-TARTARIC ACID, (D- + L-TARTARIC ACID), OXALIC ACID, MONO- AND DIHYDROXYMALONIC ACID IN mta-solutions Subtitle Liquid chromatography 1 SCOPE Determination of 50-60 mg of meso-tartaric
Title DETERMINATION OF MESO-TARTARIC ACID, (D- + L-TARTARIC ACID), OXALIC ACID, MONO- AND DIHYDROXYMALONIC ACID IN mta-solutions Subtitle Liquid chromatography 1 SCOPE Determination of 50-60 mg of meso-tartaric
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information of Appointed exploding microcapsules as drug carriers By Jing Zhang, Cao Li, Ya Wang, Ren-Xi Zhuo and Xian-Zheng Zhang * Materials Propargyl alcohol (PA-OH), dextran (M w ~20 k &
Supporting Information of Appointed exploding microcapsules as drug carriers By Jing Zhang, Cao Li, Ya Wang, Ren-Xi Zhuo and Xian-Zheng Zhang * Materials Propargyl alcohol (PA-OH), dextran (M w ~20 k &
Determination of trace anions in concentrated hydrofluoric acid
 APPLICATION NOTE 78 Determination of trace anions in concentrated hydrofluoric acid Authors Archava Siriraks Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA Keywords HF, ICS-5000 +, IonPac AS10, IonPac AC10, ion
APPLICATION NOTE 78 Determination of trace anions in concentrated hydrofluoric acid Authors Archava Siriraks Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA Keywords HF, ICS-5000 +, IonPac AS10, IonPac AC10, ion
Chemistry 20 Final Review Solutions Checklist Knowledge Key Terms Solutions
 Chemistry 20 Final Review Solutions Checklist Have you mastered the concepts, applications, and skills associated with the following items? Check them off when you are confident in your understanding.
Chemistry 20 Final Review Solutions Checklist Have you mastered the concepts, applications, and skills associated with the following items? Check them off when you are confident in your understanding.
Effect of Mobile Phase Additives on the Resolution of Four Bioactive Compounds by RP-HPLC
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2229-2240; doi:10.3390/ijms11052229 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Effect of Mobile Phase Additives
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2229-2240; doi:10.3390/ijms11052229 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Effect of Mobile Phase Additives
The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ag.1 Pd.9 /rgo: An Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid/Sodium Formate Yun Ping, Jun-Min Yan*, Zhi-Li Wang, Hong-Li Wang, Qing Jiang Key Laboratory of Automobile
Supporting Information Ag.1 Pd.9 /rgo: An Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid/Sodium Formate Yun Ping, Jun-Min Yan*, Zhi-Li Wang, Hong-Li Wang, Qing Jiang Key Laboratory of Automobile
Determination of Iodate by HPLC-UV after On-Line Electrochemical Reduction to Iodide
 Journal of Chromatographic Science 2015;53:280 284 doi:10.1093/chromsci/bmu053 Advance Access publication July 6, 2014 Article Determination of Iodate by HPLC-UV after On-Line Electrochemical Reduction
Journal of Chromatographic Science 2015;53:280 284 doi:10.1093/chromsci/bmu053 Advance Access publication July 6, 2014 Article Determination of Iodate by HPLC-UV after On-Line Electrochemical Reduction
PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: MELTING POINTS, BOILING POINTS, DENSITY
 CRYSTALLIZATION: PURIFICATION OF SOLIDS ANSWERS TO PROBLEMS: 1. (a) (b) (c) (d) A plot similar to line A in Figure 5.1 on page 559 will be obtained. The line will be slightly curved. All of the substance
CRYSTALLIZATION: PURIFICATION OF SOLIDS ANSWERS TO PROBLEMS: 1. (a) (b) (c) (d) A plot similar to line A in Figure 5.1 on page 559 will be obtained. The line will be slightly curved. All of the substance
Hongyuan Yan and Kyung Ho Row *
 Preparation and Characterization of Monolithic Columns Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, Vol. 27, No. 1 71 Preparation and Characterization of Monolithic Poly(methacrylic acid ethylene glycol dimethacrylate)
Preparation and Characterization of Monolithic Columns Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, Vol. 27, No. 1 71 Preparation and Characterization of Monolithic Poly(methacrylic acid ethylene glycol dimethacrylate)
ANALYTICAL METHOD PROCEDURES
 HPLC ASSAY AND RELATED SUBSTANCE Column Eurospher 100, C18, 25 x 0.40 cm 5µ Mobile Phase Buffer ph 2.0*: Acetonitrile (88:12 v/v) * Buffer ph 2 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ) - 0.68g Hepatane
HPLC ASSAY AND RELATED SUBSTANCE Column Eurospher 100, C18, 25 x 0.40 cm 5µ Mobile Phase Buffer ph 2.0*: Acetonitrile (88:12 v/v) * Buffer ph 2 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ) - 0.68g Hepatane
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Volume 6, Issue 2, January February 2011; Article-015
 Research Article DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A RP-HPLC METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF DAPOXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION USING AN EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN Pratik Mehta*, Ujjwal Sahoo,
Research Article DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A RP-HPLC METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF DAPOXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION USING AN EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN Pratik Mehta*, Ujjwal Sahoo,
Aziridine in Polymers: A Strategy to Functionalize Polymers by Ring- Opening Reaction of Aziridine
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Aziridine in Polymers: A Strategy to Functionalize
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Aziridine in Polymers: A Strategy to Functionalize
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions. Copyright McGraw-Hill
 Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions Solution - a homogeneous mixture Solute: the component that is dissolved Solvent: the component
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous Solutions Solution - a homogeneous mixture Solute: the component that is dissolved Solvent: the component
A NEW HPLC METHOD FOR THE QUANTIFICATION OF PANTOPRAZOLE IN PHARMACEUTICALS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 6(2), 2008, 579-586 A NEW HPLC METHOD FOR THE QUANTIFICATION OF PANTOPRAZOLE IN PHARMACEUTICALS K. BASAVAIAH, U. R. ANIL KUMAR and K. THARAPA Department of Chemistry, University of
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 6(2), 2008, 579-586 A NEW HPLC METHOD FOR THE QUANTIFICATION OF PANTOPRAZOLE IN PHARMACEUTICALS K. BASAVAIAH, U. R. ANIL KUMAR and K. THARAPA Department of Chemistry, University of
FLUDEOXYGLUCOSE ( 18 F) INJECTION: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (January 2009)
 January 2009 FLUDEOXYGLUCOSE ( 18 F) INJECTION: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (January 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
January 2009 FLUDEOXYGLUCOSE ( 18 F) INJECTION: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (January 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
In vivo monitoring of hydrogen sulfide using a cresyl violet-based ratiometric fluorescence probe
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: In vivo monitoring of hydrogen sulfide using a cresyl violet-based ratiometric fluorescence probe Qiongqiong Wan, Yanchao Song, Zhao Li, Xinghui Gao and Huimin
Electronic Supplementary Information for: In vivo monitoring of hydrogen sulfide using a cresyl violet-based ratiometric fluorescence probe Qiongqiong Wan, Yanchao Song, Zhao Li, Xinghui Gao and Huimin
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communication
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communication Syntheses and Characterization of Polymer-Supported Organotrifluoroborates: Applications in Radioiodination Reactions Li Yong; Min-Liang Yao; James
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communication Syntheses and Characterization of Polymer-Supported Organotrifluoroborates: Applications in Radioiodination Reactions Li Yong; Min-Liang Yao; James
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information German Edition: DOI: High Catalytic Activity of Heteropolynuclear Cyanide Complexes Containing Cobalt and Platinum Ions: Visible-Light Driven Water Oxidation** Yusuke Yamada,* Kohei
Supporting Information German Edition: DOI: High Catalytic Activity of Heteropolynuclear Cyanide Complexes Containing Cobalt and Platinum Ions: Visible-Light Driven Water Oxidation** Yusuke Yamada,* Kohei
John Abbott College Department of Chemistry Chemistry 202-NYB-05 Sample Final Exam
 John Abbott College Department of Chemistry Chemistry 202-NYB-05 Sample Final Exam Please Note: 1. Available space for answers has been removed from some questions to conserve space. 2. The questions begin
John Abbott College Department of Chemistry Chemistry 202-NYB-05 Sample Final Exam Please Note: 1. Available space for answers has been removed from some questions to conserve space. 2. The questions begin
Spectrophotometric Determination of Anionic Surfactants in River Water with Cationic Azo Dye by Solvent Extraction- Flow Injection Analysis
 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES JUNE 1987, VOL. 3 265 Spectrophotometric Determination of Anionic Surfactants in River Water with Cationic Azo Dye by Solvent Extraction- Flow Injection Analysis Shoji MOTOMIZU, Yoshito
ANALYTICAL SCIENCES JUNE 1987, VOL. 3 265 Spectrophotometric Determination of Anionic Surfactants in River Water with Cationic Azo Dye by Solvent Extraction- Flow Injection Analysis Shoji MOTOMIZU, Yoshito
Experiment : Reduction of Ethyl Acetoacetate
 Experiment 7-2007: eduction of Ethyl Acetoacetate EXPEIMENT 7: eduction of Carbonyl Compounds: Achiral and Chiral eduction elevant sections in the text: Fox & Whitesell, 3 rd Ed. Chapter 12, pg.572-584.
Experiment 7-2007: eduction of Ethyl Acetoacetate EXPEIMENT 7: eduction of Carbonyl Compounds: Achiral and Chiral eduction elevant sections in the text: Fox & Whitesell, 3 rd Ed. Chapter 12, pg.572-584.
An Efficient Total Synthesis and Absolute Configuration. Determination of Varitriol
 An Efficient Total Synthesis and Absolute Configuration Determination of Varitriol Ryan T. Clemens and Michael P. Jennings * Department of Chemistry, University of Alabama, 500 Campus Dr. Tuscaloosa, AL
An Efficient Total Synthesis and Absolute Configuration Determination of Varitriol Ryan T. Clemens and Michael P. Jennings * Department of Chemistry, University of Alabama, 500 Campus Dr. Tuscaloosa, AL
Cu-Creatinine- Metol system
 Quantification of Creatinine in Human Serum using Metol as a Chromogenic Probe Materials and methods 6.1. Reagents 6.1.1. N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate also denoted as Metol
Quantification of Creatinine in Human Serum using Metol as a Chromogenic Probe Materials and methods 6.1. Reagents 6.1.1. N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate also denoted as Metol
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Control the Structure of Zr-Tetracarboxylate Frameworks through Steric Tuning Jiandong Pang,,,,# Shuai Yuan,,# Junsheng Qin, Caiping Liu, Christina Lollar, Mingyan Wu,*, Daqiang
Supporting Information Control the Structure of Zr-Tetracarboxylate Frameworks through Steric Tuning Jiandong Pang,,,,# Shuai Yuan,,# Junsheng Qin, Caiping Liu, Christina Lollar, Mingyan Wu,*, Daqiang
Supplementary Material
 10.1071/CH18138_AC CSIRO 2018 Australian Journal of Chemistry Supplementary Material Efficient hydrolytic breakage of β 1,4 glycosidic bond catalyzed by a difunctional magnetic nano catalyst Ren-Qiang
10.1071/CH18138_AC CSIRO 2018 Australian Journal of Chemistry Supplementary Material Efficient hydrolytic breakage of β 1,4 glycosidic bond catalyzed by a difunctional magnetic nano catalyst Ren-Qiang
Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron double oxide catalyst
 Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Quantitative determination of ethephon in soluble concentration (SL) by Ion chromatography
 Quantitative determination of ethephon in soluble concentration (SL) by Ion chromatography Author : Li Guoping Yu Rong Shui Rong Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture, P.
Quantitative determination of ethephon in soluble concentration (SL) by Ion chromatography Author : Li Guoping Yu Rong Shui Rong Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture, P.
A Facile and High-Recovery Material for Rare Metals Based on a Water- Soluble Polyallylamine with Side-Chain Thiourea Groups
 Manuscript for Supporting Information A Facile and High-Recovery Material for Rare Metals Based on a Water- Soluble Polyallylamine with Side-Chain Thiourea Groups Daisuke Nagai*, Megumi Yoshida, Takuya
Manuscript for Supporting Information A Facile and High-Recovery Material for Rare Metals Based on a Water- Soluble Polyallylamine with Side-Chain Thiourea Groups Daisuke Nagai*, Megumi Yoshida, Takuya
Chiral Columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC
 Chiral Columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC SUMICHIRAL OA columns are high-performance chiral columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC. On SUMICHIRAL OA columns direct separation of various enantiomers
Chiral Columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC SUMICHIRAL OA columns are high-performance chiral columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC. On SUMICHIRAL OA columns direct separation of various enantiomers
Distribution of Glycolic Acid Between Water and Different Organic Solutions
 . NCI, Distribution of Glycolic Acid Between Water and Different Organic Solutions, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 16 (2) 81 85 (2002) 81 Distribution of Glycolic Acid Between Water and Different Organic Solutions.
. NCI, Distribution of Glycolic Acid Between Water and Different Organic Solutions, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 16 (2) 81 85 (2002) 81 Distribution of Glycolic Acid Between Water and Different Organic Solutions.
Egualen Sodium Granules
 Egualen Sodium Granules Dissolution Weigh accurately an amount of Egualen Sodium Granules, equivalent to about 5 mg of egualen sodium (C 15 H 17 NaO 3 S 1/3 H2O) according to the labeled amount,
Egualen Sodium Granules Dissolution Weigh accurately an amount of Egualen Sodium Granules, equivalent to about 5 mg of egualen sodium (C 15 H 17 NaO 3 S 1/3 H2O) according to the labeled amount,
Reactive Extraction of L (+) Tartaric Acid by Amberlite LA-2 in Different Solvents
 http://www.e-journals.net ISSN: 973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry 211, 8(S1), S59-S515 Reactive Extraction of L (+) Tartaric Acid by Amberlite LA-2 in Different Solvents İ. İNCİ, Y. S. AŞÇI and A. F.
http://www.e-journals.net ISSN: 973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry 211, 8(S1), S59-S515 Reactive Extraction of L (+) Tartaric Acid by Amberlite LA-2 in Different Solvents İ. İNCİ, Y. S. AŞÇI and A. F.
Synthesis and Application of a Light-sensitive Polymer Forming Aqueous Two-phase Systems
 J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 3, (2007) 424-428 Synthesis and Application of a Light-sensitive Polymer Forming Aqueous Two-phase Systems Kong FanQi, Cao Xuejun, Xia Jinan*, and Byung-Ki Hur** State
J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 3, (2007) 424-428 Synthesis and Application of a Light-sensitive Polymer Forming Aqueous Two-phase Systems Kong FanQi, Cao Xuejun, Xia Jinan*, and Byung-Ki Hur** State
ProPac WCX-10 Columns
 ProPac WCX-10 Columns Guidance for column use Tips to maximize column lifetime ProPac WCX-10 Column Tips and Tricks This guide provides essential information and invaluable guidelines for mobile phases,
ProPac WCX-10 Columns Guidance for column use Tips to maximize column lifetime ProPac WCX-10 Column Tips and Tricks This guide provides essential information and invaluable guidelines for mobile phases,
*Correspondence to:
 Supporting Information for Carbonate-promoted hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to multi-carbon carboxylates Aanindeeta Banerjee 1 and Matthew W. Kanan 1 * 1 Department of Chemistry, Stanford University,
Supporting Information for Carbonate-promoted hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to multi-carbon carboxylates Aanindeeta Banerjee 1 and Matthew W. Kanan 1 * 1 Department of Chemistry, Stanford University,
EFAVIRENZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia
 Document QAS/05.145/FIAL March 07 EFAVIREZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Fortieth W Expert ommittee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Document QAS/05.145/FIAL March 07 EFAVIREZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Fortieth W Expert ommittee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Please do not adjust margins. New Approach for the Reduction of Graphene Oxide with Triphenylphosphine Dihalide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2016 not adjust margins Supporting Information: New Approach for the Reduction of Graphene Oxide with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2016 not adjust margins Supporting Information: New Approach for the Reduction of Graphene Oxide with
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, Vol. 23, No 2, (2016)
 Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, Vol. 23, No 2, 175 180 (2016) Effect of Quaternary Ammonium Salts on the Extraction of 1,3-Propanediol with Phenylboronic Acid Michiaki MATSUMOTO*, Kikuko
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, Vol. 23, No 2, 175 180 (2016) Effect of Quaternary Ammonium Salts on the Extraction of 1,3-Propanediol with Phenylboronic Acid Michiaki MATSUMOTO*, Kikuko
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Controlled Radical Polymerization and Quantification of Solid State Electrical Conductivities of Macromolecules Bearing Pendant Stable Radical Groups Lizbeth Rostro, Aditya G. Baradwaj,
Supporting Information Controlled Radical Polymerization and Quantification of Solid State Electrical Conductivities of Macromolecules Bearing Pendant Stable Radical Groups Lizbeth Rostro, Aditya G. Baradwaj,
A supramolecular approach for fabrication of photo- responsive block-controllable supramolecular polymers
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information A supramolecular approach for fabrication of photo- responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information A supramolecular approach for fabrication of photo- responsive
Novel fluorescent cationic benzothiazole dye response to G-quadruplex aptamer as a novel K + sensor
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Novel fluorescent cationic benzothiazole dye response to G-quadruplex aptamer as a novel K + sensor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Novel fluorescent cationic benzothiazole dye response to G-quadruplex aptamer as a novel K + sensor
CYCLOSERINE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia. (November 2008) CYCLOSERINUM CYCLOSERINE
 December 2008 CYCLOSERINE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
December 2008 CYCLOSERINE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
A Novel Approach of Reduction of CO 2 into Methanol by Water Splitting with Aluminum over Copper Catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A Novel Approach of Reduction of CO 2 into Methanol by Water Splitting
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A Novel Approach of Reduction of CO 2 into Methanol by Water Splitting
School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS.
 School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 100 Internal Examiners: Professor A Kindness Dr T Msagati
School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 100 Internal Examiners: Professor A Kindness Dr T Msagati
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2007
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Supporting Information for Head-to-Tail Cyclized
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Supporting Information for Head-to-Tail Cyclized
Supplementary Methods. Materials:
 Supplementary Methods Materials: The following reagents were purchased and used as received: oxaloacetic acid ( 97%, Sigma- Aldrich O4126), DL-malic acid ( 99%, Sigma-Aldrich 240176), sodium malonate dibasic
Supplementary Methods Materials: The following reagents were purchased and used as received: oxaloacetic acid ( 97%, Sigma- Aldrich O4126), DL-malic acid ( 99%, Sigma-Aldrich 240176), sodium malonate dibasic
--> Buy True-PDF --> Auto-delivered in 0~10 minutes. GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.35-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF GB THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA National Food Safety Standard Determination
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.35-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF GB THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA National Food Safety Standard Determination
Molecular Weight Distribution of Living Chains in Polystyrene Pre-pared by Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization
 Molecular Weight Distribution of Living Chains in Polystyrene Pre-pared by Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Joongsuk Oh, a Jiae Kuk, a Taeheon Lee, b Jihwa Ye, b Huyn-jong Paik, b* Hyo Won Lee, c*
Molecular Weight Distribution of Living Chains in Polystyrene Pre-pared by Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Joongsuk Oh, a Jiae Kuk, a Taeheon Lee, b Jihwa Ye, b Huyn-jong Paik, b* Hyo Won Lee, c*
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB31604.11-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF GB THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 31604.11-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB31604.11-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF GB THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 31604.11-2016
Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Using Sulfonated β-cyclodextrin and Ag Colloids as Additives
 Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, Vol. 26, No. 10 1549 Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Using Sulfonated β-cyclodextrin
Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, Vol. 26, No. 10 1549 Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Using Sulfonated β-cyclodextrin
ASPARTAME. Not less than 98% and not more than 102% on the dried basis. White, odourless, crystalline powder, having a strong sweet taste
 ASPARTAME Prepared at the 25th JECFA (1981), published in FNP 19 (1981) and in FNP 52 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at the 57th JECFA (2001) An ADI of 0-40 mg/kg bw was established
ASPARTAME Prepared at the 25th JECFA (1981), published in FNP 19 (1981) and in FNP 52 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at the 57th JECFA (2001) An ADI of 0-40 mg/kg bw was established
IDENTIFICATION AND DETERMINATION OF HYDROQUINONE IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS 2 14/11/17 ACM 003 BY TLC AND HPLC
 A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The method describes the identification of hydroquinone in cosmetic products. 2. PRINCIPLE Hydroquinone is identified by thin layer chromatography
A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The method describes the identification of hydroquinone in cosmetic products. 2. PRINCIPLE Hydroquinone is identified by thin layer chromatography
637. Thiamethoxam. HPLC method
 637. Thiamethoxam HPLC method CIPAC Collaborative Trial according to CIPAC Information Sheet N o 293 Dr. Sven Adolph Syngenta Crop Protection Münchwilen AG CH-4333 Münchwilen Switzerland May 212 page 1
637. Thiamethoxam HPLC method CIPAC Collaborative Trial according to CIPAC Information Sheet N o 293 Dr. Sven Adolph Syngenta Crop Protection Münchwilen AG CH-4333 Münchwilen Switzerland May 212 page 1
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Rational Design of Highly Controlled Suzuki-Miyaura Catalyst-Transfer Polycondensation for Precision Synthesis of Polythiophenes and their Block Copolymers: Marriage of Palladacycle
Supporting Information A Rational Design of Highly Controlled Suzuki-Miyaura Catalyst-Transfer Polycondensation for Precision Synthesis of Polythiophenes and their Block Copolymers: Marriage of Palladacycle
Yujuan Zhou, Kecheng Jie and Feihe Huang*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A redox-responsive selenium-containing pillar[5]arene-based macrocyclic amphiphile: synthesis,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A redox-responsive selenium-containing pillar[5]arene-based macrocyclic amphiphile: synthesis,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis of a new class of ribose functionalized dinucleotide cap analogues for biophysical studies on interaction of cap-binding proteins with the 5 end of mrna. Karolina Piecyk,
Supporting Information Synthesis of a new class of ribose functionalized dinucleotide cap analogues for biophysical studies on interaction of cap-binding proteins with the 5 end of mrna. Karolina Piecyk,
Salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol from fermentation broth
 Salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol from fermentation broth Beata RUKOWICZ, Krzysztof ALEJSKI, Ireneusz MIESIĄC Keywords: 1,3-propanediol; fermentation broth; solvent extraction Abstract: 1,3-propanediol
Salting-out extraction of 1,3-propanediol from fermentation broth Beata RUKOWICZ, Krzysztof ALEJSKI, Ireneusz MIESIĄC Keywords: 1,3-propanediol; fermentation broth; solvent extraction Abstract: 1,3-propanediol
