Liquid Chromatography
|
|
|
- Rosanna Cameron
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Liquid Chromatoraphy An LC instrument consists of the solvent system, pump, injector, column and detector (Fi 28-4 or R5 Fi 5.7). Solvent system Solvent reservoirs are equipped with a means of removin dissolved ases (to avoid bubble formation) (i.e. vacuum pumpin system, sparin by inert ases,e.. He), and particulates (i.e. filter). Several reservoirs are available for mixed solvent isocratic elution, stepwise and radient elution. Expensive hih-purity solvents are often required. umpin system An HLC pumpin system has the followin strinent requirements: 1. eneration of pressures of up to 6000 psi 2. pulse-free output 3. flow rates rane from 0.1 to 10 ml/min 4. ood flow control to provide flow reproducibility of 0.5% or better 5. corrosion-resistant components There are 3 main types of HLC pumps: 1. reciprocatin pump 90% usae. The solvent is drawn into a small chamber (when the solvent chec valve is open) and pumped out of it (when the column chec valve is open) by the bac and forth motion of a motor-driven piston (Fi 28-6 or R5 Fi 6.9). The pump has the advantaes of (a) small solvent chamber volume ( µl), (b) hih output pressure (up to 10,000 psi), (c) ready for use in radient elution, (d) constant flow rate which is independent of column bac pressure and solvent viscosity, but disadvantae of a pulsed flow which must be smoothed out usin a pulse damper. 2. Displacement (or syrine) pump The solvent is pumped out of a lare chamber by a pluner (R5 Fi 6.10). The pump produces a pulse-free flow which is also independent of column bac pressure and solvent viscosity. But it has a limited solvent capacity (~250 ml) and requires refillin of solvent chamber for continual use. 3. neumatic (or constant pressure) pump: use a compressed as tan. Sample injection system It is convenient to use a sample loop injector (of size µl) so that the sample can be introduced without depressurin the system. In addition, injection reproducibility is hih (better than 2%) (Fi 28-7 and Fi 27-4). Analytical column Because of pressure limitations, the most LC columns are straiht, have lenth of cm and inside diameters of 4-10 mm, and are paced with particles of size 5-10 µm in diameter. Microbore columns (i.d mm) are sometimes used. Smaller column diameter will result in reater sensitivity because sample dilution within a column decreases as column i.d. decreases (R5 Fi. 6.55). Guard column A short uard column is usually placed before the expensive analytical column to protect it from damae due to (1) particulate matter, (2) irreversible bindin of contaminant to the stationary phase (3) bleedin. But loss in resolution may result (R1* Fi 19.11). Chem 316/. Li/HLC/.1
2 Extra-column band broadenin This occurs in tubins connectin between the column and other parts, such as injection system, the detector reion, etc. The smaller is the radius of the connectin tube, the less is the extra-column band broadenin. 2 πr u Hex = 24DM This effect is neliible in GC because D M is lare. Column heater Better chromatorams may be obtained by increasin column temperature (R1* Fi 19.2). Column pacin ellicular particles: A thin porous layer (e.. silica) is deposited on the surfacd of non-porous beads (e.. lass of larer diameter of µm) (R5 Fi 6.32). These are usually used in uard columns, with a loss in resolution (see R1* Fi ). orous particles: small-sized porous particles (e.. silica of diameter of 3-10 µm) are used in analytical columns. Detector Unlie GC, LC has no universal detectors such as FID and TCD. In addition to the requirements for an ideal GC detector (except temperature rane), LC detectors should have minimal internal volume to reduce extra-column band broadenin. LC detectors are classified as bul property detectors (e.. refractive index) and more selective solute property detectors (e.. UV absorbance, fluorescence). UV absorbance detector The detector volume must be small (1-10 µl) to reduce extra-column band broadenin. This detector withstands a pressure only up to 600 psi and thus requires a pressure reduction device. These detectors are usually double-beam devices in which one beam passes throuh the eluent cell and the other throuh a filter. Matched photoelectric cells are used to compare the 2 beam intensities. The chromatoram consists of a plot of the lo of the ratio of the 2 transduced sinals as a function of time. The intense line of a H lamp (254 nm) isolated by filters is commonly used as the UV source. Deuterium or tunsten filament sources with interference filters are also used (Fi 28-9 & R5 Fi 6.17). A spectrophotometer with ratin optics in the scannin monochromator is a more sophisicated source. The most powerful UV spectrophotometric detectors are diode-array instruments which permit collection of an entire spectrum in about 1 s as each chromatoraphic pea is eluted (Fi and R1* Fi 19.16). Fluorescence detector The excitation sources rane from the H lamp with filters to Xe lamp with ratin monochromator, and to tunable lasers (Fi 15-4). The fluorescence method typically has a hiher sensitivity (by more than an order of manitude) than the absorbance method. Often the samples are treated (or derivatized) with fluoroenic reaents (e.. dansyl chloride) to form fluorescent derivatives. This can be either pre-column or post-column derivatization. Refractive index detector If the solute and solvent in the 2 halves of the flow chamber differ in refractive index, the liht beam incident on the chamber will be bent (fi or R5 Fi 6-26). This results in the beam displacement, Chem 316/. Li/HLC/.2
3 and variation in the output sinal of the detector. As compared to FID and TCD in GC, the RI detector responds to nearly all solutes. But it is less sensitive and is hihly temperature-dependent. Electrochemical detector ossible oxidation or reduction of many oranic functional roups can be exploited for detection by amperometric, polaroraphic or coulometric methods (Fi 28-12). In the thin-layer flow cell for amperometric detection, the worin electrode is part of a channel wall (Fi 28-13). The reference and counter electrodes are located downstream. Detectors with dual worin electrodes are also available. Mass spectrometric detector A major problem in interfacin LC with MS is the enormous mismatch between the relatively lare solvent volume from the former and the vacuum requirement of the latter. For microbore columns with µl/min flow, the method of split flow can be used. In the thermospray method (for flow up to 2 ml/min), the liquid is vaporized as it passes throuh a heated SS capillary tube to form an aerosol jet of solvent and analyte molecules, which are ionized throuh a chare-exchane mechanism with a salt (e.. NH 4 OAc) present in the mobile phase. However, the method is applicable only to polar analytes and mobile phase and can only provide MW data (no framentation). In the electrospray method, the liquid is pumped throuh an SS capillary needle maintained at a hih potential (few V) with respect to a cylindrical electrode surroundin the needle (R6 Fi 25-30, Fi 25-31). A chared spray is resulted and desolvation, solvent evaporation, chare attachment to the analyte molecules occur. Comparison of various HLC detectors is iven in Table 28-1 or R5 Table 6.2. Stationary phase Amon various LC modes (LSC, TLC, IEC, SEC), partition chromatoraphy has become the most widely used one. Liquid-liquid chromatoraphy: the liquid stationary phase, which is physiosorbed on the column pacin, may bleed away. Bonded-phase chromatoraphy: the liquid stationary phase which is chemically bonded to the silicabased column pacin is the predominant form. The bonded phase are siloxanes formed by reaction of the silanol (Si-OH, 8µ/m 2 ) with an oranochlorosilane (Fi in 28D-1). Surface coverae by silanization is limited to 4 µmol/m 2 (i.e. 50%) or less. The unreacted silanol roups are capped by reactin with less sterically hindered chlorotrimethylsilane to avoid tailin problems, especially for basic solutes. 2 types of stationary phases: normal-phase: hihly polar (e.. triethylenelycol), and a non-polar M (e.. n-hexane) is used to elute polar solutes. Reversed-phase (75% usae): non-polar (e.. C18), and a polar M (e.. water, MeOH or MeCN) is used to elute less polar solutes. In reversed-phase chromatoraphy, the most polar component is eluted first because it is more soluble in the polar M and least soluble in the non-polar S (Fi and Fi a & b). Increasin M polarity increases the elution times of all components (e.. water > 50% MeOH/50% water > 80% MeOH/20% water). The ph of water should not be reater than 7.5 to avoid base hydrolysis of siloxane S. Chem 316/. Li/HLC/.3
4 Reverse reasonin applies to normal-phase chromatoraphy (Fi and R1* Fi ). Loner chain lenth in the reversed-phase S will provide reater solute retention and larer sample capacity (Fi 28-15). Mobile phase Unlie GC, separations are hihly affected by the composition (or polarity) of the M. A rule of thumb is to select a S with polarity that is rouhly matched with that of the solutes; a M of considerably different polarity is then used for elution. Gradient Elution Isocratic elution is first carried out to determine the appropriate radient elution for optimizin separations (R6 Fi & 25.11). R6: DC Harris Quantitative Chemical Analysis 5 th ed, 1999 olarity index, This parameter is based on solubility measurement for the substance in 3 solvents (Table 28-2): Dioxane (low dipole proton acceptor) Nitromethane (hih dipole proton acceptor), Ethyl alcohol (hih dipole proton donor) = lo( K ) + lo( K ) + lo( K ) e d n For a binary solvent mixture, AB = φ A A + φ B B φ is volume fraction Chane in M composition will affect 2-unit difference in results in 10-fold increase in (E and Fi a & b). 2 ( 2 1 )/ 2 2 ( 1 2 )/ 2 Re versed phase = 10 Normal phase = In many cases, adjustin is all that is needed to produce a satisfactory separation. If not, adjustment of α is necessary (Fi c-e). More details are available in R3. Moreover, a systematic way to achieve this has been demonstrated usin an optimization procedure usin 4 solvents. Derivative formation 1. To reduce polarity of the analyte so that partition, rather than adsorption or ion-exchane columns are used. 2. To increase the detector response and thus sensitivity of all or some analytes (Fi 28-18) Other partition chromatoraphy techniques: chiral chrom (chirality in S), ion-pair chrom (counter ions in M) Other LC modes: Adsorption chrom or LSC, IEC or IC, SEC and TLC. Different modes of LC used accordin to the MW and polarity of the solutes (Fi 28-1 or equiv) Exercise 28-1 a-c, 28-2 to 4, 28-6 a-j, 28-8, 28-10, to 13, a-b, to 19. Chem 316/. Li/HLC/.4
5 Chem 316/. Li/HLC/.5
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
HPLC. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Harris Chapter 25
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Harris Chapter 25 12/1/2005 Chem 253 - Chapter 25 1 HPLC Separation of nonvolatile or thermally unstable compounds. If the analyte/sample can be found to be
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Harris Chapter 25 12/1/2005 Chem 253 - Chapter 25 1 HPLC Separation of nonvolatile or thermally unstable compounds. If the analyte/sample can be found to be
Ch.28 HPLC. Basic types of Liquid Chromatography Partition (LLC) Adsorption (LSC) Ion Exchange (IC) Size Exclusion (SEC or Gel Chromatography)
 Ch.28 HPLC 28.1 Basic types of Liquid Chromatography Partition (LLC) Adsorption (LSC) Ion Exchange (IC) Size Exclusion (SEC or Gel Chromatography) High Performance (Pressure) LC Glass column st.steel (high
Ch.28 HPLC 28.1 Basic types of Liquid Chromatography Partition (LLC) Adsorption (LSC) Ion Exchange (IC) Size Exclusion (SEC or Gel Chromatography) High Performance (Pressure) LC Glass column st.steel (high
LC III: HPLC. Originally referred to as High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography. Now more commonly called High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 LC III: HPLC What is HPLC? Originally referred to as High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Now more commonly called High Performance Liquid Chromatography In general: The instrument controlled version of
LC III: HPLC What is HPLC? Originally referred to as High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Now more commonly called High Performance Liquid Chromatography In general: The instrument controlled version of
Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS
 Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS 1. List two advantages of temperature programming in GC. a) Allows separation of solutes with widely varying retention factors in a reasonable
Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS 1. List two advantages of temperature programming in GC. a) Allows separation of solutes with widely varying retention factors in a reasonable
GC Instruments. GC Instruments - Columns
 GC Instruments 1 Fairly simple instrumentation Maintaining constant average pressure is important! Pressure controls flow rate T influences retention (k ) Flow rate monitoring Changing flow rate changes
GC Instruments 1 Fairly simple instrumentation Maintaining constant average pressure is important! Pressure controls flow rate T influences retention (k ) Flow rate monitoring Changing flow rate changes
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 STANDARDBASE techniques: High Performance Liquid Chromatography Drenthe College, The Netherlands 1. Introduction HPLC. High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
STANDARDBASE techniques: High Performance Liquid Chromatography Drenthe College, The Netherlands 1. Introduction HPLC. High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Biochemistry. Biochemical Techniques HPLC
 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 13 1. Objectives 1.1. To understand the basic concept and principle of 1.2. To understand the components and techniques of 1.3. To know
Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 13 1. Objectives 1.1. To understand the basic concept and principle of 1.2. To understand the components and techniques of 1.3. To know
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
 High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography
 Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas): gas (He, N 2, H 2 ) - do not interact with analytes - only transport the analyte through the column Analyte: volatile liquid
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas): gas (He, N 2, H 2 ) - do not interact with analytes - only transport the analyte through the column Analyte: volatile liquid
 HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 31. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 31 High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Solvent Delivery
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 31 High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Solvent Delivery
Fall 2012 Due In Class Friday, Oct. 19. Complete the following on separate paper. Show your work and clearly identify your answers.
 CHEM 322 Name Fall 2012 Due In Class Friday, Oct. 19 Complete the following on separate paper. Show your work and clearly identify your answers. General Separations 1. Describe the relative contributions
CHEM 322 Name Fall 2012 Due In Class Friday, Oct. 19 Complete the following on separate paper. Show your work and clearly identify your answers. General Separations 1. Describe the relative contributions
Basic principles of HPLC
 Introduction to the theory of HPLC HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) depends on interaction of sample analytes with the stationary phase (packing) and the mobile phase to effect a separation.
Introduction to the theory of HPLC HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) depends on interaction of sample analytes with the stationary phase (packing) and the mobile phase to effect a separation.
Gas Chromatography. Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC
 Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC What is Gas Chromatography? It is also known as Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC) GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Separation of gaseous
Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC What is Gas Chromatography? It is also known as Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC) GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Separation of gaseous
Chapter content. Reference
 Chapter 7 HPLC Instrumental Analysis Rezaul Karim Environmental Science and Technology Jessore University of Science and Technology Chapter content Liquid Chromatography (LC); Scope; Principles Instrumentation;
Chapter 7 HPLC Instrumental Analysis Rezaul Karim Environmental Science and Technology Jessore University of Science and Technology Chapter content Liquid Chromatography (LC); Scope; Principles Instrumentation;
Gas Chromatography. Vaporization of sample Gas-solid Physical absorption Gas-liquid Liquid immobilized on inert solid
 Gas Chromatography Vaporization of sample Gas-solid Physical absorption Gas-liquid Liquid immobilized on inert solid Principles Instrumentation Applications 18-1 Retention Volumes Volumes rather than times
Gas Chromatography Vaporization of sample Gas-solid Physical absorption Gas-liquid Liquid immobilized on inert solid Principles Instrumentation Applications 18-1 Retention Volumes Volumes rather than times
Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC
 Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC Murphy, B. (2017). Introduction to Chromatography: Lecture 1. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC Murphy, B. (2017). Introduction to Chromatography: Lecture 1. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
Luminescence transitions. Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212. What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for?
 Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212 What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for? How does solvent extraction work? Write the partitioning coefficient for the following reaction:
Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212 What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for? How does solvent extraction work? Write the partitioning coefficient for the following reaction:
HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY INSTRUMENTATION. Mrs. G. Aruna Mpharm (PhD) Dept. of PA & QA KTPC
 HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY INSTRUMENTATION Mrs. G. Aruna Mpharm (PhD) Dept. of PA & QA KTPC 1 HPLC INSTRUMENTATION CONSIST OF Solvent Reservoir( hplc solvent reservoir systems) Pumps Pre Guard
HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY INSTRUMENTATION Mrs. G. Aruna Mpharm (PhD) Dept. of PA & QA KTPC 1 HPLC INSTRUMENTATION CONSIST OF Solvent Reservoir( hplc solvent reservoir systems) Pumps Pre Guard
Instrumental Analysis II Course Code: CH3109. Chromatographic &Thermal Methods of Analysis Part 1: General Introduction. Prof. Tarek A.
 Instrumental Analysis II Course Code: CH3109 Chromatographic &Thermal Methods of Analysis Part 1: General Introduction Prof. Tarek A. Fayed What is chemical analysis? Qualitative analysis (1) Chemical
Instrumental Analysis II Course Code: CH3109 Chromatographic &Thermal Methods of Analysis Part 1: General Introduction Prof. Tarek A. Fayed What is chemical analysis? Qualitative analysis (1) Chemical
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis
 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Gas Chromatography (GC)
 Gas Chromatography (GC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11541 Saudi Arabia Office: AA53
Gas Chromatography (GC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11541 Saudi Arabia Office: AA53
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography. Principles Instrumentation Detectors Columns and Stationary Phases Applications
 Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Principles Instrumentation Detectors Columns and Stationary Phases Applications GC-MS Schematic Interface less critical for capillary columns Several types of Mass Specs
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Principles Instrumentation Detectors Columns and Stationary Phases Applications GC-MS Schematic Interface less critical for capillary columns Several types of Mass Specs
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY. Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC
 PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
HPLC Praktikum Skript
 HPLC Praktikum Skript Assistants: Gianluca Bartolomeo HCI D330, 3 46 68, bartolomeo@org.chem.ethz.ch Sahar Ghiasikhou HCI E330, 2 29 29, ghiasikhou@org.chem.ethz.ch 1. Introduction In chromatographic techniques,
HPLC Praktikum Skript Assistants: Gianluca Bartolomeo HCI D330, 3 46 68, bartolomeo@org.chem.ethz.ch Sahar Ghiasikhou HCI E330, 2 29 29, ghiasikhou@org.chem.ethz.ch 1. Introduction In chromatographic techniques,
GPC/SEC Practical Tips and Tricks. Thomas Dent Applications Scientist Agilent Technologies. October, 2011 Gulf Coast Conference
 GPC/SEC Practical Tips and Tricks Thomas Dent Applications Scientist Agilent Technologies October, 2011 Gulf Coast Conference 1 Section 1: Introduction Goals Brief introduction to GPC/SEC Highlight considerations
GPC/SEC Practical Tips and Tricks Thomas Dent Applications Scientist Agilent Technologies October, 2011 Gulf Coast Conference 1 Section 1: Introduction Goals Brief introduction to GPC/SEC Highlight considerations
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC)
 Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Liquid Chromatography
 Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
for Acclaim Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column
 for Acclaim Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Page 1 of 17 Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column 5µm, 4.6 x 250mm, P/N 066844 5µm, 4.6 x 150mm, P/N
for Acclaim Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Page 1 of 17 Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column 5µm, 4.6 x 250mm, P/N 066844 5µm, 4.6 x 150mm, P/N
Instrumental Chemical Analysis
 L2 Page1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Chromatography (General aspects of chromatography) Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2 nd semester,
L2 Page1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Chromatography (General aspects of chromatography) Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2 nd semester,
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 Two types in general use: -packed (stationary phase) -open tubular or capillary determine selectivity and efficiency of the sample. Column Materials Column
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 Two types in general use: -packed (stationary phase) -open tubular or capillary determine selectivity and efficiency of the sample. Column Materials Column
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 High Performance Liquid Chromatography () Instrumentation Normal Phase Chromatography Normal Phase - a polar stationary phase with a less polar mobile phase.
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 High Performance Liquid Chromatography () Instrumentation Normal Phase Chromatography Normal Phase - a polar stationary phase with a less polar mobile phase.
GC Instruments. GC Instruments - Sample Introduction
 GC Instruments 1 Fairly simple instrumentation Maintaining constant average pressure is important! Pressure controls flow rate T influences retention (k ) Flow rate monitoring Changing flow rate changes
GC Instruments 1 Fairly simple instrumentation Maintaining constant average pressure is important! Pressure controls flow rate T influences retention (k ) Flow rate monitoring Changing flow rate changes
Chemistry 311: Instrumental Analysis Topic 4: Basic Chromatography. Chemistry 311: Instrumental Analysis Topic 4: Basic Chromatography
 Introductory Theory, Basic Components, Qualitative and Quantitative applications. HPLC, GC, Ion Chromatography. Rouessac Ch. 1-7 Winter 2011 Page 1 Chromatography: The separation of analytes based on differences
Introductory Theory, Basic Components, Qualitative and Quantitative applications. HPLC, GC, Ion Chromatography. Rouessac Ch. 1-7 Winter 2011 Page 1 Chromatography: The separation of analytes based on differences
Figure 1. Structures for Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B1.
 CH 461 & CH 461H F 18 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
CH 461 & CH 461H F 18 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
Lab.2. Thin layer chromatography
 Key words: Separation techniques, compounds and their physicochemical properties (molecular volume/size, polarity, molecular interactions), mobile phase, stationary phase, liquid chromatography, thin layer
Key words: Separation techniques, compounds and their physicochemical properties (molecular volume/size, polarity, molecular interactions), mobile phase, stationary phase, liquid chromatography, thin layer
Chromatographic Analysis
 Chromatographic Analysis Distribution of Analytes between Phases An analyte is in equilibrium between the two phases [S 1 ] [S 2 ] (in phase 1) (in phase 2) AS [S2 ] K 2 A S [S1 ] 1 AS, A 1 S Activity
Chromatographic Analysis Distribution of Analytes between Phases An analyte is in equilibrium between the two phases [S 1 ] [S 2 ] (in phase 1) (in phase 2) AS [S2 ] K 2 A S [S1 ] 1 AS, A 1 S Activity
Maximizing Performance Through GPC Column Selection
 Maximizing Performance Through GPC Column Selection What Are Polymers? Polymers are long chain molecules produced by linking small repeat units (monomers) together There are many ways to link different
Maximizing Performance Through GPC Column Selection What Are Polymers? Polymers are long chain molecules produced by linking small repeat units (monomers) together There are many ways to link different
LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY (LC/MS) Presented by: Dr. T. Nageswara Rao M.Pharm PhD KTPC
 LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY (LC/MS) Presented by: Dr. T. Nageswara Rao M.Pharm PhD KTPC INTRODUCTION Principle: LC/MS is a technique that combines physical separation capabilities of liquid
LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY (LC/MS) Presented by: Dr. T. Nageswara Rao M.Pharm PhD KTPC INTRODUCTION Principle: LC/MS is a technique that combines physical separation capabilities of liquid
Experiment 1: Thin Layer Chromatography
 Experiment 1: Thin Layer Chromatography Part A: understanding R f values Part B: R f values & solvent polarity Part C: R f values & compound functionality Part D: identification of commercial food dye
Experiment 1: Thin Layer Chromatography Part A: understanding R f values Part B: R f values & solvent polarity Part C: R f values & compound functionality Part D: identification of commercial food dye
CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit V Gas Chromatography. M. Subramanian
 CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit V Gas Chromatography M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603
CH 2252 Instrumental Methods of Analysis Unit V Gas Chromatography M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603
2501 High Performance Liquid Chromatography
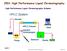 2501 High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme Chp25:: 1 High Performance Liquid Chromatography Components of HPLC High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme
2501 High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme Chp25:: 1 High Performance Liquid Chromatography Components of HPLC High Performance Liquid Chromatography Scheme
Nexera UC Unified Chromatography
 Nexera UC Unified Chromatography The latest addition to the chromatography toolbox Dr. Gesa J. Schad Shimadzu Europa GmbH A brief history of SFC ϒ Late 1800 s: it was found that heavy, non-volatile organic
Nexera UC Unified Chromatography The latest addition to the chromatography toolbox Dr. Gesa J. Schad Shimadzu Europa GmbH A brief history of SFC ϒ Late 1800 s: it was found that heavy, non-volatile organic
Introduction to Capillary GC
 ?? Kβ? Page 1 Typical GC System Gas supply Injector Detector Data handling GAS Column Oven Page 2 CARRIER GAS Carries the solutes down the column Selection and velocity influences efficiency and retention
?? Kβ? Page 1 Typical GC System Gas supply Injector Detector Data handling GAS Column Oven Page 2 CARRIER GAS Carries the solutes down the column Selection and velocity influences efficiency and retention
in The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) Draft for comment
 July 2012 RESTRICTED PROPOSAL FOR REVISION OF HIGH-PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY in The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) Draft for comment Should you have any comments on the attached revision,
July 2012 RESTRICTED PROPOSAL FOR REVISION OF HIGH-PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY in The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) Draft for comment Should you have any comments on the attached revision,
Selecting an LC/MS Interface Becky Wittrig, Ph.D.
 Selecting an LC/MS Interface Becky Wittrig, Ph.D. RESTEK CORPORATION LC/MS Interfaces I. Background of LC/MS I. Historical Perspective II. Reasons for use II. Interfaces I. Transport devices II. Particle
Selecting an LC/MS Interface Becky Wittrig, Ph.D. RESTEK CORPORATION LC/MS Interfaces I. Background of LC/MS I. Historical Perspective II. Reasons for use II. Interfaces I. Transport devices II. Particle
Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution.
 Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution. Difficulty with M n and M w, etc. osome polymers are hard to describe from just M n, M w, etc. o Examples: Bimodal, multimodal, nonuniform, broad, etc. MWDs. oin early
Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution. Difficulty with M n and M w, etc. osome polymers are hard to describe from just M n, M w, etc. o Examples: Bimodal, multimodal, nonuniform, broad, etc. MWDs. oin early
Chromatography and other Separation Methods
 Chromatography and other Separation Methods Probably the most powerful class of modern analytical methods for analyzing mixture of components---and even for detecting a single component in a complex mixture!
Chromatography and other Separation Methods Probably the most powerful class of modern analytical methods for analyzing mixture of components---and even for detecting a single component in a complex mixture!
Gel Permeation Chromatography - GPC
 Isolation and Separation Methods J. Poustka, VŠCHT Praha, ÚAPV 2014, http://web.vscht.cz/poustkaj Gel Permeation Chromatography - GPC Separation and clean-up method Group separation of compounds with similar
Isolation and Separation Methods J. Poustka, VŠCHT Praha, ÚAPV 2014, http://web.vscht.cz/poustkaj Gel Permeation Chromatography - GPC Separation and clean-up method Group separation of compounds with similar
Understanding Gas Chromatography
 Understanding Gas Chromatography What is Really Going on Inside the Box? Simon Jones GC Applications Engineer Page 1 Group/Presentation Title Month ##, 200X ?? K? Page 2 Typical GC System Gas supply Injector
Understanding Gas Chromatography What is Really Going on Inside the Box? Simon Jones GC Applications Engineer Page 1 Group/Presentation Title Month ##, 200X ?? K? Page 2 Typical GC System Gas supply Injector
Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 23: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
 Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 23: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Chapter 23. Gas Chromatography What did they eat in the year 1,000? GC of Cholesterol and other lipids extracted from
Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 23: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Chapter 23. Gas Chromatography What did they eat in the year 1,000? GC of Cholesterol and other lipids extracted from
Lecture 15: Introduction to mass spectrometry-i
 Lecture 15: Introduction to mass spectrometry-i Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass/charge ratio of charged particles in vacuum. Mass spectrometry can determine masse/charge
Lecture 15: Introduction to mass spectrometry-i Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass/charge ratio of charged particles in vacuum. Mass spectrometry can determine masse/charge
CHEM 429 / 529 Chemical Separation Techniques
 CHEM 429 / 529 Chemical Separation Techniques Robert E. Synovec, Professor Department of Chemistry University of Washington Lecture 1 Course Introduction Goal Chromatography and Related Techniques Obtain
CHEM 429 / 529 Chemical Separation Techniques Robert E. Synovec, Professor Department of Chemistry University of Washington Lecture 1 Course Introduction Goal Chromatography and Related Techniques Obtain
Partitioning. Separation is based on the analyte s relative solubility between two liquid phases or a liquid and solid.
 Chromatography Various techniques for the separation of complex mixtures that rely on the differential affinities of substances for a gas or liquid mobile medium and for a stationary adsorbing medium through
Chromatography Various techniques for the separation of complex mixtures that rely on the differential affinities of substances for a gas or liquid mobile medium and for a stationary adsorbing medium through
DATES: LAB: Liquid Chromatography Separation of Grape Kool-Aid
 NAME: AP CHEMISTRY DATES: LAB: Liquid Chromatography Separation of Grape Kool-Aid PURPOSE There are a number of analytical techniques used to separate components of a mixture, or solution. They include
NAME: AP CHEMISTRY DATES: LAB: Liquid Chromatography Separation of Grape Kool-Aid PURPOSE There are a number of analytical techniques used to separate components of a mixture, or solution. They include
HPLC Background Chem 250 F 2008 Page 1 of 24
 HPLC Background Chem 250 F 2008 Page 1 of 24 Outline: General and descriptive aspects of chromatographic retention and separation: phenomenological k, efficiency, selectivity. Quantitative description
HPLC Background Chem 250 F 2008 Page 1 of 24 Outline: General and descriptive aspects of chromatographic retention and separation: phenomenological k, efficiency, selectivity. Quantitative description
CHEM 3590 Final examination 2017 Instructor : Dr. Hélène Perreault Monday December 11, 1:30-4:30 pm, Frank Kennedy Gold Gym seats
 CHEM 3590 Final examination 2017 Instructor : Dr. Hélène Perreault Monday December 11, 1:30-4:30 pm, Frank Kennedy Gold Gym seats 310-343 Questions 1-15 have multiple choices (50 pts). Please answer on
CHEM 3590 Final examination 2017 Instructor : Dr. Hélène Perreault Monday December 11, 1:30-4:30 pm, Frank Kennedy Gold Gym seats 310-343 Questions 1-15 have multiple choices (50 pts). Please answer on
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD)
 The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations
 Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations Homework Due Monday April 24 Problems 23-1, 23-2, 23-7, 23-15, 23-27, 23-29, 23-32 Analytical Separations: Universal approach to analyzing complex mixtures
Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations Homework Due Monday April 24 Problems 23-1, 23-2, 23-7, 23-15, 23-27, 23-29, 23-32 Analytical Separations: Universal approach to analyzing complex mixtures
Figure 1. Structures for Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B1.
 CH 461 & CH 461H F 15 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
CH 461 & CH 461H F 15 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
Determination of Caffeine by HPLC
 Determination of Caffeine by HPLC Introduction It was a long history before real high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) had evolved. The very first indication of a chromatographic separation was
Determination of Caffeine by HPLC Introduction It was a long history before real high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) had evolved. The very first indication of a chromatographic separation was
Introduction to Capillary GC. Page 1. Agilent Restricted February 2, 2011
 ?? Kβ? Page 1 Typical GC System Gas supply Injector Detector Data handling GAS Column Oven Page 2 CARRIER GAS Carries the solutes down the column Selection and velocity influences efficiency and retention
?? Kβ? Page 1 Typical GC System Gas supply Injector Detector Data handling GAS Column Oven Page 2 CARRIER GAS Carries the solutes down the column Selection and velocity influences efficiency and retention
Pure Chromatography Consumables Pure flexibility. Pure specialization. Pure convenience.
 Pure Chromatography Consumables Pure flexibility. Pure specialization. Pure convenience. Pure Consumables More focus on your application The Pure consumable portfolio offers an unrivaled range of products
Pure Chromatography Consumables Pure flexibility. Pure specialization. Pure convenience. Pure Consumables More focus on your application The Pure consumable portfolio offers an unrivaled range of products
LECTURE 2. Advanced Separation Science Techniques Present and Future Separation Tools
 LECTURE 2 Advanced Separation Science Techniques Present and Future Separation Tools Jack Henion, Ph.D. Emeritus Professor, Analytical Toxicology Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14850 Lecture 2, Page 1 Contents
LECTURE 2 Advanced Separation Science Techniques Present and Future Separation Tools Jack Henion, Ph.D. Emeritus Professor, Analytical Toxicology Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14850 Lecture 2, Page 1 Contents
M > ACN > > THF
 Method Development in HPLC Dr. Amitha Hewavitharana School of Pharmacy University of Queensland Method Development in HPLC References: D A Skoog Principles of instrumental analysis, 3 rd Edition Chapters
Method Development in HPLC Dr. Amitha Hewavitharana School of Pharmacy University of Queensland Method Development in HPLC References: D A Skoog Principles of instrumental analysis, 3 rd Edition Chapters
Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets
 Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets Liquid chromatography was developed by Tswett in early 1900 s and was shown to be a powerful separation
Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets Liquid chromatography was developed by Tswett in early 1900 s and was shown to be a powerful separation
What type of samples are common? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses. Number of samples? Aims. Sources of error. Sample preparation
 What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
LEARNING OBJECTIVES CHEM 212: SEPARATION SCIENCE CHROMATOGRAPHY UNIT. Thomas Wenzel, Bates College. In-class Problem Set Extraction.
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES CHEM 212: SEPARATION SCIENCE CHROMATOGRAPHY UNIT Thomas Wenzel, Bates College In-class Problem Set Extraction Problem #1 1. Devise a scheme to be able to isolate organic acids, bases
LEARNING OBJECTIVES CHEM 212: SEPARATION SCIENCE CHROMATOGRAPHY UNIT Thomas Wenzel, Bates College In-class Problem Set Extraction Problem #1 1. Devise a scheme to be able to isolate organic acids, bases
HPLC. GRATE Chromatography Lab Course. Dr. Johannes Ranke. September 2003
 HPLC GRATE Chromatography Lab Course Dr. Johannes Ranke Organisation The groups Start at 9:00 am End at 18:00 pm at the latest Friday, 19th we will finish at 2:00 pm Thursday, 11th: Lecture at 08:15 am
HPLC GRATE Chromatography Lab Course Dr. Johannes Ranke Organisation The groups Start at 9:00 am End at 18:00 pm at the latest Friday, 19th we will finish at 2:00 pm Thursday, 11th: Lecture at 08:15 am
Transferring HPLC methods from the HP 1090 Series to the Agilent 1100 Series HPLC system
 Transferring HPLC methods from the HP 1090 Series to the Agilent 1100 Series HPLC system Technical Note Introduction The HP 1090 Series HPLC system, introduced in 1983, is regarded to be an outstanding
Transferring HPLC methods from the HP 1090 Series to the Agilent 1100 Series HPLC system Technical Note Introduction The HP 1090 Series HPLC system, introduced in 1983, is regarded to be an outstanding
Gel Permeation Chromatography Basics and Beyond eseminar March 13, Jean Lane Technical and Applications Support LSCA, Columns and Supplies
 Gel Permeation Chromatography Basics and Beyond eseminar March 13, 2013 Jean Lane Technical and Applications Support LSCA, Columns and Supplies 1 Content Overview of GPC/SEC What is it? Why do we use it?
Gel Permeation Chromatography Basics and Beyond eseminar March 13, 2013 Jean Lane Technical and Applications Support LSCA, Columns and Supplies 1 Content Overview of GPC/SEC What is it? Why do we use it?
LC Technical Information
 LC Technical Information Method Transfer to Accucore.6 μm Columns Containing solid core particles, which are engineered to a diameter of.6μm and a very narrow particle size distribution; Accucore HPLC
LC Technical Information Method Transfer to Accucore.6 μm Columns Containing solid core particles, which are engineered to a diameter of.6μm and a very narrow particle size distribution; Accucore HPLC
Mass Spectrometry in MCAL
 Mass Spectrometry in MCAL Two systems: GC-MS, LC-MS GC seperates small, volatile, non-polar material MS is detection devise (Agilent 320-MS TQ Mass Spectrometer) Full scan monitoring SIM single ion monitoring
Mass Spectrometry in MCAL Two systems: GC-MS, LC-MS GC seperates small, volatile, non-polar material MS is detection devise (Agilent 320-MS TQ Mass Spectrometer) Full scan monitoring SIM single ion monitoring
Gas Chromatography. Introduction
 Gas Chromatography Introduction 1.) Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas) is a gas - Usually N 2, He, Ar and maybe H 2 - Mobile phase in liquid chromatography is a liquid Requires analyte to be
Gas Chromatography Introduction 1.) Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas) is a gas - Usually N 2, He, Ar and maybe H 2 - Mobile phase in liquid chromatography is a liquid Requires analyte to be
CHAPTER CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS OF SEPARATIONS
 Islamic University in Madinah Department of Chemistry CHAPTER - ----- CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS OF SEPARATIONS Prepared By Dr. Khalid Ahmad Shadid Chemistry Department Islamic University in Madinah TRADITIONAL
Islamic University in Madinah Department of Chemistry CHAPTER - ----- CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS OF SEPARATIONS Prepared By Dr. Khalid Ahmad Shadid Chemistry Department Islamic University in Madinah TRADITIONAL
SEPARATIONS ESSENTIALS IN MODERN HPLC. 2University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania
 ESSENTIALS IN MODERN HPLC SEPARATIONS Serban C. Moldoveanu1, Victor David2 'R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co., Winston-Salem, NC, USA 2University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG
ESSENTIALS IN MODERN HPLC SEPARATIONS Serban C. Moldoveanu1, Victor David2 'R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co., Winston-Salem, NC, USA 2University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG
CHROMATOGRAPHY. The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments.
 CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
Dionex IonPac AS28-Fast-4µm column
 CHROMATOGRAPHY Thermo Scientific Dionex IonPac AS-Fast-4µm Columns Product Specifications The Thermo Scientific Dionex IonPac AS-Fast-4µm column is a high-capacity, hydroxide-selective anionexchange column
CHROMATOGRAPHY Thermo Scientific Dionex IonPac AS-Fast-4µm Columns Product Specifications The Thermo Scientific Dionex IonPac AS-Fast-4µm column is a high-capacity, hydroxide-selective anionexchange column
Sem /2007. Fisika Polimer Ariadne L. Juwono
 Chapter 8. Measurement of molecular weight and size 8.. End-group analysis 8.. Colligative property measurement 8.3. Osmometry 8.4. Gel-permeation chromatography 8.5. Ultracentrifugation 8.6. Light-scattering
Chapter 8. Measurement of molecular weight and size 8.. End-group analysis 8.. Colligative property measurement 8.3. Osmometry 8.4. Gel-permeation chromatography 8.5. Ultracentrifugation 8.6. Light-scattering
Atomization. In Flame Emission
 FLAME SPECTROSCOPY The concentration of an element in a solution is determined by measuring the absorption, emission or fluorescence of electromagnetic by its monatomic particles in gaseous state in the
FLAME SPECTROSCOPY The concentration of an element in a solution is determined by measuring the absorption, emission or fluorescence of electromagnetic by its monatomic particles in gaseous state in the
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. Mobile phase is a gas! Stationary phase could be anything but a gas
 GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Mobile phase is a gas! Stationary phase could be anything but a gas Gas Chromatography (GC) GC is currently one of the most popular methods for separating and analyzing compounds. This
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Mobile phase is a gas! Stationary phase could be anything but a gas Gas Chromatography (GC) GC is currently one of the most popular methods for separating and analyzing compounds. This
Method Development in Solid Phase Extraction using Non-Polar ISOLUTE SPE Columns for the Extraction of Aqueous Samples
 Technical Note 101 Method Development in Solid Phase Extraction using Non-Polar ISOLUTE SPE Columns for the Extraction of Aqueous Samples This technical note includes by specific information on the extraction
Technical Note 101 Method Development in Solid Phase Extraction using Non-Polar ISOLUTE SPE Columns for the Extraction of Aqueous Samples This technical note includes by specific information on the extraction
Refractive Index Detection Using an Ultraviolet Detector with a Capillary Flow Cell in Preparative SFC
 Refractive Index Detection Using an Ultraviolet Detector with a Capillary Flow Cell in Preparative SFC Yukio Hirata*, Yukinori Kawaguchi, and Yasuhiro Funada School of Materials Science, Toyohashi University
Refractive Index Detection Using an Ultraviolet Detector with a Capillary Flow Cell in Preparative SFC Yukio Hirata*, Yukinori Kawaguchi, and Yasuhiro Funada School of Materials Science, Toyohashi University
Packed Column for Ultra-Fast Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography, TSKgel Super-ODS. Table of Contents
 No. 089 SEPARATION REPORT Packed Column for Ultra-Fast Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography, TSKgel Super-ODS Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Column Specification 1 3. Features of Packing Materials
No. 089 SEPARATION REPORT Packed Column for Ultra-Fast Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography, TSKgel Super-ODS Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Column Specification 1 3. Features of Packing Materials
Chapter 33. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Chapter 33 High-Performance Liquid Chromatography 1 High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is the most versatile and widely used type of elution chromatography. The technique is used by scientists
Chapter 33 High-Performance Liquid Chromatography 1 High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is the most versatile and widely used type of elution chromatography. The technique is used by scientists
Chapter 11 Column Liquid Chromatography
 Chapter 11 Column Liquid Chromatography Types of Liquid Chromatography Partition chromatography Adsorption or liquid-solid chromatography Ion Exchange chromatography Size exclusion or gel chromatography
Chapter 11 Column Liquid Chromatography Types of Liquid Chromatography Partition chromatography Adsorption or liquid-solid chromatography Ion Exchange chromatography Size exclusion or gel chromatography
An Advanced Base Deactivated Capillary Column for analysis of Volatile amines Ammonia and Alcohols.
 An Advanced Base Deactivated Capillary Column for analysis of Volatile amines Ammonia and Alcohols. Jaap de Zeeuw, Ron Stricek and Gary Stidsen Restek Corp Bellefonte, USA To analyze basic compounds at
An Advanced Base Deactivated Capillary Column for analysis of Volatile amines Ammonia and Alcohols. Jaap de Zeeuw, Ron Stricek and Gary Stidsen Restek Corp Bellefonte, USA To analyze basic compounds at
2014 학년도 1 학기 분석화학실험. 담당교수 : 이원용 ( 연구실 : 과 443-C, 전화 : , 전자우편 : 분광분석 / / 분리분석 / 전기분석화학
 2014 학년도 1 학기 분석화학실험 담당교수 : 이원용 ( 연구실 : 과 443-C, 전화 : 2123-2649, 전자우편 : wylee@yonsei.ac.kr) 분광분석 / / 분리분석 / 전기분석화학 Instrumental Analysis General concept Spectrophotometric experiment I A Lamp Monochromator
2014 학년도 1 학기 분석화학실험 담당교수 : 이원용 ( 연구실 : 과 443-C, 전화 : 2123-2649, 전자우편 : wylee@yonsei.ac.kr) 분광분석 / / 분리분석 / 전기분석화학 Instrumental Analysis General concept Spectrophotometric experiment I A Lamp Monochromator
Chromatographic Methods
 10.537 Nanomaterial Characterization I Chromatographic Methods Prof. David Ryan Department of Chemistry UMass Lowell 1 Definitions Analytical Chemistry qualitative and quantitative measurement of chemical
10.537 Nanomaterial Characterization I Chromatographic Methods Prof. David Ryan Department of Chemistry UMass Lowell 1 Definitions Analytical Chemistry qualitative and quantitative measurement of chemical
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Polymer analysis by GPC-SEC. Technical Note. Introduction
 Polymer analysis by GPC-SEC Technical Note Introduction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also referred to as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a mode of liquid chromatography in which the components
Polymer analysis by GPC-SEC Technical Note Introduction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also referred to as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a mode of liquid chromatography in which the components
Optimizing GPC Separations
 Optimizing GPC Separations Criteria for Solvent Selection True sample solubility (Polarity and Time dependant) Compatibility with columns Avoid non-size exclusion effects (eg adsorption by reverse phase
Optimizing GPC Separations Criteria for Solvent Selection True sample solubility (Polarity and Time dependant) Compatibility with columns Avoid non-size exclusion effects (eg adsorption by reverse phase
Reversed Phase Solvents
 Part 1. General Chromatographic Theory Part 2. verview of HPLC Media Part 3. The Role of the Mobile Phase in Selectivity Part 4. Column Care and Use Reversed Phase Solvents 2 Solvents for RP Chromatography
Part 1. General Chromatographic Theory Part 2. verview of HPLC Media Part 3. The Role of the Mobile Phase in Selectivity Part 4. Column Care and Use Reversed Phase Solvents 2 Solvents for RP Chromatography
