Chapter The Ionic Bond. Why are ionic compounds stable? Spontaneous Processes. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts.
|
|
|
- Lorin Foster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lewis Dot ymbols hapter 9 hemical Bonding I: Basic oncepts Introduced by G.. Lewis Element symbol plus 1 dot for each valence e Elements tend to form octets, noble gas configurations Useful for representative (sp block) elements only 9.2 The Ionic Bond Typical ionic reactions with Lewis structures Electrostatic force that holds ions together in an ionic compound Very strong force ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points Lewis dot symbols are used to represent formation of ionic compounds 2 + a + a + 2 Li + 2 Li Why are ionic compounds stable? onsider formation of a a(s) + 1/2 2 (g) d a(s) written on mole basis (6.02 x atoms) Ionization: a(g) d a + (g) requires energy I 1 (a) = 496 kj/mol e attachment: (g) d (g) releases energy EA() = 328 kj/mol ( = 328 kj/mol) E released is not enough to make up for E required! What is missing? pontaneous Processes Exothermic processes are more favorable than endothermic processes There s more to it than that! hap. 18 spontaneous, favorable reactions proceed to products 2 2 (g) + 2 (g) d 2 2 (l) = product reactants = 286 kj/mol (vigorous!)
2 9.3 Lattice energy Energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid, ionic compound into gaseous ions Lattice energy makes formation of an ionic compound favorable overcomes unfavorable ionization energy Physical basis of lattice energy is electrostatic attraction between cations and anions Bornaber ycle a + (g) + (g) I 1 = 495 kj e + e EA = 328 kj sub = 108 kj a(g) + (g) a(s) + 1/2 2 (g) 1/2 diss = 79 kj f = 574 kj latt = 928 kj provides driving force! Lattice energy (a) = U = D latt = 928 kj/mol a (s) U = = f + sub + I 1 + 1/2 diss EA Lattice Energy ummary E required to separate 1 mole of a solid, ionic compound into gaseous ions Physical basis of lattice energy is electrostatic attraction between cations and anions ighly charged ions d larger lattice energy (U) U (kj/mol): Li 1017 < Mg 3890 Attraction cation charge X anion charge igh U d high mp, bp mp: Li 845, Mg ovalent Bond Bond in which (2) electrons are shared by (2) atoms Bonds w/ more than 2 centers are possible ovalent ompounds compounds that contain only covalent bonds nly valence electrons are involved in bonding 2 l l l or l l Lone pairs Bonding pairs Usual representation Lone pairs pairs of valence electrons not involved in covalent bond formation Lewis structure representation of covalent bonding w/ lone pairs shown as pairs of dots and bonding pairs (usually) shown as lines ctet Rule an atom (other than ) tends to form bonds until it is surrounded by 8 valence e s full s and p orbitals doesn t work for transition elements l l Each l achieves octet, 6 from lone pairs and 2 from sharing in bond achieves octet, 2 from lone pair and 6 from shared pairs Each achieves "duet" from a shared pair
3 Multiple bonds (bond orders) ingle bond = 2 atoms held together w/ 1 e pair Double bond = 2 atoms held together w/ 2 e pairs Ethene (ethylene) d(=) = 133 pm Ethane d() = 107 pm d () = 154 pm arbon dioxide d(=) = 120 pm Triple bond = 2 atoms held together w/ 3 e pairs Ethyne (acetylene) d( ) = 120 pm arbon monoxide d( ) = 119 pm Bond Length Distance between the nuclei of 2 covalently bonded atoms in a molecule Bond is shorter (and stronger) as bond order increases triple < double < single ~120 pm < 130 pm < 150 pm for bonds Table 9.2 = bond lengths ovalent vs. Ionic ompounds has very small radius d short bonds I has very large radius d long bonds I 2 bond length = 272 pm ovalent compounds contain only covalent bonds Weak attractions between molecules usually leads to low mp and bp Do not conduct electricity if dissolved in water (rarely soluble) or molten Ionic compounds contain ionic bonds trong electrostatic attraction leads to high mp and bp onduct electricity when dissolved in water or molten Ions are mobile charge carriers ontinuum of bond polarity Electron Density Distribution in + a l Ionic bond (early) complete e transfer Low e density igh e density l Polar covalent bond unequal sharing of e pair e s are polarized toward l ow do we describe and predict this tendency to polarize? l l onpolar covalent bond equal sharing of e pair Representation of bond dipole Electrons are more strongly pulled by than Tendency to attract electron in a bond = electronegativity
4 9.5 Electronegativity (χ) Ability of an atom to attract e s in a chemical bond toward itself Electronegativity determines extent of e transfer in a chemical bond Pauling s relative electronegativity values are scaled to (maximum) χ() = 4.0 an be derived from I 1 and EA of an atom MI igure 9.5 Don t memorize values learn the trend! MAX + a l ontinuum of bond polarity l l l Ionic bond?dc = 2.0 (early) complete e transfer Polar covalent bond 0 < Dc < 2.0 unequal sharing of e pair e s are polarized toward l onpolar covalent bond?dc = 0 equal sharing of e pair Ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent? KBr χ(k) = 0.8, χ(br) = 2.8, ionic bond χ() = 2.5, χ() = 3.5, polar covalent bond Bl 3 χ(b) = 2.0, χ(l) = 3.0, polar covalent bonds 2 χ() = 3.5, nonpolar covalent bond Remember xidation umber Rules? (ec. 4.4) 3 x # of oxygen is usually 2 Why? χ() = 3.5, exceeded only by (Except 2 2, x # = 1; 2, x # = +2) 4 x # of hydrogen is usually +1 Why? χ() = 2.1, less than most nonmetals Except metal hydrides, e.g. Mg 2, x # () = 1 Why? χ(metals) < luorine has x # 1 in all compounds. Why? χ() = 4.0, largest χ 9.6 Writing Lewis tructures 1. Write skeletal structure Typically: lowest χ atom occupies central position and occupy terminal positions 2. Total valence electrons in molecule anion: add 1 e for every charge cation: subtract 1 e for every + charge
5 Lewis tructures (contd.) Examples 3. atisfy the octet rule for each atom. onnect terminal atoms to central atom w/ single bonds. Use lone pairs to fill octets of terminal atoms. Use all e counted in step Use lone pairs to form double or triple bond to central (or any) atom that does not have octet. 4 Pl P ormal harge Difference between the # valence e in an isolated atom and # e assigned to that atom in a Lewis structure. e s in a bond are divided equally between atoms to obtain formal charges differs from oxidation state, where e s in a bond are assigned to the more electronegative atom eutral molecules, Σ formal charges = 0 Ions, Σ formal charges = charge on ion ormal charges do not represent real, localized charges bookkeeping device ormal charge on atom = # valence e s of free atom # nonbonding e 1/2 (# bonds) [: : ] Examples: x# & ormal harge see next rule ormal charges indicate most plausible Lewis structures or a neutral molecule, structure with no formal charges is preferred. mall formal charges (0,+1, 1) are more favorable than larger formal charges. tructures w/ negative formal charges on most electronegative atoms are favorable. Avoid adjacent formal charges with same sign.
6 3 Lewis structures of nitrite anion Actual structure: each bond is 124 pm single bond, 143 pm Major contributor Major contributor Minor contributor Examples: x# & ormal harge see next rule = double bond, 120 pm (Back to examples) 9.8 Resonance Examples of Resonance Resonance structure 1 of 2 or more Lewis structures for a molecule (ion) that can t be represented w/ a single structure Resonance use of 2 or more Lewis structures to describe a molecule (ion) Each resonance structure contributes to the actual structure no single structure is a complete description positions of atoms must be the same in each actual structure is an average Benzene ( 6 6 ): distances 140 pm single bond, 154 pm = double bond, 133 pm ulfate ( 4 2 ): distances 149 pm 9.9 Exceptions to ctet Rule Incomplete ctet often groups 13, also 2 in gas phase react with electron donors ddelectron Molecules Molecule w/ odd number of electrons cannot satisfy octet rule and 2 form weak bonds B B B 2 Major resonance form w/ zero formal charges 1 of 3 minor resonance forms w/ nonzero formal charges ormation of dative (coordinate covalent) bond with electronpair donor 2
7 Expanded ctet Atoms of secondperiod elements are limited to eight valence e s around atom Atoms of third period and beyond can form compounds w/ > 8 e s around atom used this idea in 4 2 above ontroversial explanations: atoms w/ n = 3 can use d orbitals (not just s and p) atoms w/ n = 3 are large enough to fit more than 4 e pairs around them in multicentered bonds 4 e count : 1 6 = 6 : 4 7 = 28 total e 34 Extra e pair is placed on Expanded ctet Examples Pl 5 Xe 2 I 5 e Bond Dissociation Energy Bond energy = enthalpy change required to break a particular bond in one mole of gaseous molecules 2 (g) d 2 (g) = kj Table 9.4 (pg 356) gives averages exact value depends on molecule ingle bond < double bond < triple bond 347, = 620, o 812 kj/mol Use bond energies to estimate rxn Bonds to lighter elements often stronger Bond Energy (kj /mol) Bond Energy (kj/mol) l l 243 l 432 Br Br 192 Br 366 I I 151 I 298 D = BE(reactants) BE(products)
8 D = BE(reactants) BE(products) Why reactants products rather than products reactants? Bond dissociation energy = enthalpy change required to break a bond d negative sign built into tabulated values (g) + 4(g) d 4 (g) must be exothermic! = ΣBE(reactants) ΣBE(products) = 0 (4 mol)(414 kj/mol) = 1656 kj rxn from Bond Energies Write structures for substances in equation Determine bonds broken and formed Gives approximate answer less accurate than using f doesn t take phases, intermolecular forces into account or the reaction: (g) (g) d 4 2 (g) (g) predict the enthalpy of reaction from average bond energies (Table 9.4) = d 8 = + 12 rxn = 12 mol (414 kj/mol) + 2 mol (347 kj/mol) + 7 mol (498.7 kj/mol) 8 mol (799 kj/mol) 12 mol (460 kj/mol) D rxn = kj Alternative by using enthalpies of formation: rxn = 4 f ( 2 ) + 6 f ( 2 ) 2 f ( 2 6 ) = 4(393.5 kj) + 6(241.8 kj) 2(84.7 kj) D rxn = kj
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Chapter 8 Preview Ionic Bonding vs. covalent bonding. Electronegativity and dipole moment. Bond polarity. Lewis structure: ow to draw a Lewis
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Chapter 8 Preview Ionic Bonding vs. covalent bonding. Electronegativity and dipole moment. Bond polarity. Lewis structure: ow to draw a Lewis
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 hapter 8 Basic oncepts of hemical Bonding An Important Principle in hemistry The microscopic structure defines the properties of matter at our mesoscopic level. Ex. Graphite and Diamond (both are pure
hapter 8 Basic oncepts of hemical Bonding An Important Principle in hemistry The microscopic structure defines the properties of matter at our mesoscopic level. Ex. Graphite and Diamond (both are pure
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Topics Lewis Dot Symbols Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity and Polarity Drawing Lewis Structures Lewis Structures and Formal Charge Resonance
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Topics Lewis Dot Symbols Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity and Polarity Drawing Lewis Structures Lewis Structures and Formal Charge Resonance
Chapter Nine. Chapter Nine. Chemical Bonds: A Preview. Chemical Bonds. Electrostatic Attractions and Repulsions. Energy of Interaction
 1 Chemical Bonds: A Preview 2 Chemical Bonds Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid ionic compounds. Chemical bonds are electrostatic forces; they
1 Chemical Bonds: A Preview 2 Chemical Bonds Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid ionic compounds. Chemical bonds are electrostatic forces; they
Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding Learning Outcomes: Write Lewis symbols for atoms and ions. Define lattice energy and be able to arrange compounds in order of increasing lattice energy based on
Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding Learning Outcomes: Write Lewis symbols for atoms and ions. Define lattice energy and be able to arrange compounds in order of increasing lattice energy based on
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model. HIV-Protease. Lecture Presentation
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model HIV-Protease HIV-protease is a protein synthesized by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This particular protein is crucial to the
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model HIV-Protease HIV-protease is a protein synthesized by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This particular protein is crucial to the
Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonding I: The Covalent Bond. Chemical Bonding. Bonding Generalities
 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding I: The Covalent Bond I. Types of bonds a) Ionic b) Covalent II. Lewis Dot Structures a) ctet Rule b) Multiple Bonds c) Resonance d) Polyatomic Ions e) ormal Charge on
Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding I: The Covalent Bond I. Types of bonds a) Ionic b) Covalent II. Lewis Dot Structures a) ctet Rule b) Multiple Bonds c) Resonance d) Polyatomic Ions e) ormal Charge on
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration
Chemistry: The Central Science
 Chemistry: The Central Science Fourteenth Edition Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of
Chemistry: The Central Science Fourteenth Edition Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of
Chapter Nine. Chemical Bonding I
 Chapter Nine Chemical Bonding I 1 The Ionic Bond and Lattice Energies 2 Lewis Dot Symbols Consists of atomic symbol surrounded by 1 dot for each valence electron in the atom Only used for main group elements
Chapter Nine Chemical Bonding I 1 The Ionic Bond and Lattice Energies 2 Lewis Dot Symbols Consists of atomic symbol surrounded by 1 dot for each valence electron in the atom Only used for main group elements
Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds. Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds
 Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds Ionic bonding involves the complete TRANSFER of electrons from one atom to another. Usually observed when a metal bonds to a nonmetal. - - - - - - + + + + + + + + + +
Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds Ionic bonding involves the complete TRANSFER of electrons from one atom to another. Usually observed when a metal bonds to a nonmetal. - - - - - - + + + + + + + + + +
CHEMICAL BONDS. Electrical forces. Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces between electrically charged particles
 CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: Electrical forces. Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces between electrically charged particles Lewis Theory of Bonding: Electrons play a fundamental role
CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: Electrical forces. Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces between electrically charged particles Lewis Theory of Bonding: Electrons play a fundamental role
Chemical Bonding -- Lewis Theory (Chapter 9)
 Chemical Bonding -- Lewis Theory (Chapter 9) Ionic Bonding 1. Ionic Bond Electrostatic attraction of positive (cation) and negative (anion) ions Neutral Atoms e - transfer (IE and EA) cation + anion Ionic
Chemical Bonding -- Lewis Theory (Chapter 9) Ionic Bonding 1. Ionic Bond Electrostatic attraction of positive (cation) and negative (anion) ions Neutral Atoms e - transfer (IE and EA) cation + anion Ionic
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky
 Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds An attractive force that holds two atoms together in a more complex unit Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrons are transferred from one
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds An attractive force that holds two atoms together in a more complex unit Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrons are transferred from one
Chapter 8. Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Two Classes of Compounds Usually solids with high melting points Many are soluble in polar solvents such as water. Most are insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as hexane. Molten
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Two Classes of Compounds Usually solids with high melting points Many are soluble in polar solvents such as water. Most are insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as hexane. Molten
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Lewis Symbols and the Octet Rule When atoms or ions are strongly attracted to one another, we say that there is a chemical bond between them. In chemical
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Lewis Symbols and the Octet Rule When atoms or ions are strongly attracted to one another, we say that there is a chemical bond between them. In chemical
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 8: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 8: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding The properties of substances are determined in large part by the chemical bonds that hold their atoms together 8.1: Chemical
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 8: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding The properties of substances are determined in large part by the chemical bonds that hold their atoms together 8.1: Chemical
The energy associated with electrostatic interactions is governed by Coulomb s law:
 Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other
Bonding in Chemistry. Chemical Bonds All chemical reactions involve breaking of some bonds and formation of new ones where new products are formed.
 CHEMICAL BONDS Atoms or ions are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds. The type and number of electrons in the outer electronic shells of atoms or ions are instrumental in how atoms
CHEMICAL BONDS Atoms or ions are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds. The type and number of electrons in the outer electronic shells of atoms or ions are instrumental in how atoms
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding. The Molecular Nature of Matter. Jespersen Brady Hyslop SIXTH EDITION
 CEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXT EDITIN Jespersen Brady yslop Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chemical Bonds Attractive forces that hold atoms
CEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXT EDITIN Jespersen Brady yslop Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chemical Bonds Attractive forces that hold atoms
13 Bonding: General Concepts. Types of chemical bonds. Covalent bonding Ex. H 2. Repulsions of nuclei and e s. Zero interaction at long distance
 13 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) epulsions of nuclei and e s r 0 458 0.074 r (nm) - bond length Two e s shared by two s: covalent bonding Zero interaction
13 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) epulsions of nuclei and e s r 0 458 0.074 r (nm) - bond length Two e s shared by two s: covalent bonding Zero interaction
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 9 Bonding. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 9 Bonding Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and right)
Chapter 9 Bonding Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and right)
H-H bond length Two e s shared by two Hs: covalent bonding. Coulomb attraction: Stronger attraction for e Fractional charge A dipole
 8 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) Repulsions of nucleus and e s r 0 458 0.074 r (nm) Zero interaction at long distance - bond length Two e s shared by
8 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) Repulsions of nucleus and e s r 0 458 0.074 r (nm) Zero interaction at long distance - bond length Two e s shared by
Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond
 Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond Three basic types of bonds: Ionic - Electrostatic attraction between ions (NaCl) Metallic - Metal atoms bonded to each other Covalent - Sharing of electrons Ionic
Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond Three basic types of bonds: Ionic - Electrostatic attraction between ions (NaCl) Metallic - Metal atoms bonded to each other Covalent - Sharing of electrons Ionic
Lewis Dot Symbols. The Octet Rule ATOMS TEND TO GAIN, LOSE, or SHARE ELECTRONS to ATTAIN A FILLED OUTER SHELL of 8 ELECTRONS.
 Chapter 9, Part 1 Models of Chemical Bonding Recall Chapter 2: Chemical bonds hold atoms together in a compound. transfer of electrons, forming cations and anions, results in ionic bonding sharing of electron
Chapter 9, Part 1 Models of Chemical Bonding Recall Chapter 2: Chemical bonds hold atoms together in a compound. transfer of electrons, forming cations and anions, results in ionic bonding sharing of electron
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 of Chemical John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions. Covalent
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 of Chemical John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions. Covalent
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 9 P a g e 1 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Homework: Read Chapter 9: Work out sample/practice exercises. Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 9 P a g e 1 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Homework: Read Chapter 9: Work out sample/practice exercises. Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
Name: Hr: 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 8.1-8.2 8.3-8.5 8.5-8.7 8.8 Name: Hr: 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule State the type of bond (ionic, covalent, or metallic) formed between any
8.1-8.2 8.3-8.5 8.5-8.7 8.8 Name: Hr: 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule State the type of bond (ionic, covalent, or metallic) formed between any
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6-1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Valence electrons are attracted to other atoms, and that determines the kind of chemical bonding that occurs between
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6-1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Valence electrons are attracted to other atoms, and that determines the kind of chemical bonding that occurs between
Chapter 6. Table of Contents. Section 1 Covalent Bonds. Section 2 Drawing and Naming Molecules. Section 3 Molecular Shapes. Covalent Compounds
 Covalent Compounds Table of Contents Section 1 Covalent Bonds Section 2 Drawing and Naming Molecules Section 3 Molecular Shapes Section 1 Covalent Bonds Bellringer Make a list of the elements that form
Covalent Compounds Table of Contents Section 1 Covalent Bonds Section 2 Drawing and Naming Molecules Section 3 Molecular Shapes Section 1 Covalent Bonds Bellringer Make a list of the elements that form
Chemistry Review Unit 4 Chemical Bonding
 Chemistry Review The Nature of Chemical Bonding, Directional Nature of Covalent Bonds, Intermolecular Forces Bonding 1. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms are bonded together. Breaking a chemical
Chemistry Review The Nature of Chemical Bonding, Directional Nature of Covalent Bonds, Intermolecular Forces Bonding 1. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms are bonded together. Breaking a chemical
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical. Bonding. Ionic vs Covalent Simulation 3/13/2013. Why do TiCl 4 & TiCl 3 have different colors?
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice
Chpt 8 Chemical Bonding Forces holding atoms together = Chemical Bonds
 Chpt 8 Chemical Bonding Forces holding atoms together = Chemical Bonds Kinds of chemical bonds: 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic Useful guideline: Octet rule Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share e - to achieve
Chpt 8 Chemical Bonding Forces holding atoms together = Chemical Bonds Kinds of chemical bonds: 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic Useful guideline: Octet rule Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share e - to achieve
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical. Bonding
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Bonds Three
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Bonds Three
Chapter 8 Basic concepts of bonding
 Chapter 8 Basic concepts of bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule When atoms or ions are strongly attracted to one another, we say that there is a chemical bond between them. Types
Chapter 8 Basic concepts of bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule When atoms or ions are strongly attracted to one another, we say that there is a chemical bond between them. Types
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical. Bonding
 Chapter 8 Concepts of 8.1 Bonds Three basic types of bonds: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms. Electrons are free
Chapter 8 Concepts of 8.1 Bonds Three basic types of bonds: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms. Electrons are free
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts to: This is the first of two chapters on bonding. Upon completion of Chapter 9, the student should be able 1. Identify the valence electrons for all representative
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts to: This is the first of two chapters on bonding. Upon completion of Chapter 9, the student should be able 1. Identify the valence electrons for all representative
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory. Lewis Theory: An Overview
 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
CHEMICAL BONDS. Determining Percentage Composition, Empirical, and Molecular Formulas for Compounds:
 CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: The strong electrostatic forces of attraction holding atoms together in a unit are called chemical bonds (EU 2.C). Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces
CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: The strong electrostatic forces of attraction holding atoms together in a unit are called chemical bonds (EU 2.C). Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces
Single Covalent Bonds. Guidelines for Writing Lewis Structures. Guidelines for Writing Lewis Structures. Guidelines for Writing Lewis Structures
 ovalent Bonding hapter 8: ovalent Bonding Attraction Stable bond Repulsion umber of bonds = umber shared e - pairs. 2008 Brooks/ole 1 2008 Brooks/ole 2 ovalent Bonding Single ovalent Bonds Lewis structures:
ovalent Bonding hapter 8: ovalent Bonding Attraction Stable bond Repulsion umber of bonds = umber shared e - pairs. 2008 Brooks/ole 1 2008 Brooks/ole 2 ovalent Bonding Single ovalent Bonds Lewis structures:
Big Idea #5: The laws of thermodynamics describe the essential role of energy and explain and predict the direction of changes in matter.
 KUDs for Unit 6: Chemical Bonding Textbook Reading: Chapters 8 & 9 Big Idea #2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ion, or molecules
KUDs for Unit 6: Chemical Bonding Textbook Reading: Chapters 8 & 9 Big Idea #2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ion, or molecules
Models Of Chemical Bonding. Chapter Nine. AP Chemistry
 Models Of Chemical Bonding Chapter Nine AP Chemistry Q. Why do atoms bond? A. To lower the potential energy between positive and negative particles. Atoms like humans seek to become more stable. Metals
Models Of Chemical Bonding Chapter Nine AP Chemistry Q. Why do atoms bond? A. To lower the potential energy between positive and negative particles. Atoms like humans seek to become more stable. Metals
CHEM 110: CHAPTER 8 Basic Concepts of Chem Bonding. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
 1 CHEM 110: CHAPTER 8 Basic Concepts of Chem Bonding Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram Lewis Dot Diagrams (developed by chemist Gilbert Lewis) are used to indicate the number of valence
1 CHEM 110: CHAPTER 8 Basic Concepts of Chem Bonding Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram Lewis Dot Diagrams (developed by chemist Gilbert Lewis) are used to indicate the number of valence
What is a Bond? Chapter 8. Ionic Bonding. Coulomb's Law. What about covalent compounds?
 Chapter 8 What is a Bond? A force that holds atoms together. Why? We will look at it in terms of energy. Bond energy- the energy required to break a bond. Why are compounds formed? Because it gives the
Chapter 8 What is a Bond? A force that holds atoms together. Why? We will look at it in terms of energy. Bond energy- the energy required to break a bond. Why are compounds formed? Because it gives the
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical. Bonding
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice
Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together.
 Basics of Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together. Basics of Bonding A chemical bond occurs when atoms or
Basics of Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together. Basics of Bonding A chemical bond occurs when atoms or
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 9 MODELS OF CHEMICAL BONDING
 Chapter 9 MODELS OF CHEMICAL BONDING 1 H H A + B H H A B A comparison of metals and nonmetals 2 9.1 Atomic Properties & Chemical Bonds Chemical bond: A force that holds atoms together in a molecule or
Chapter 9 MODELS OF CHEMICAL BONDING 1 H H A + B H H A B A comparison of metals and nonmetals 2 9.1 Atomic Properties & Chemical Bonds Chemical bond: A force that holds atoms together in a molecule or
Chemical Bonding. The Octet Rule
 Chemical Bonding There are basically two types of chemical bonds: 1. Covalent bonds electrons are shared by more than one nucleus 2. Ionic bonds electrostatic attraction between ions creates chemical bond
Chemical Bonding There are basically two types of chemical bonds: 1. Covalent bonds electrons are shared by more than one nucleus 2. Ionic bonds electrostatic attraction between ions creates chemical bond
Carbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms
 hapter 1: hemical bonding and structure in organic compounds arbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms omposition: Mainly nonmetals; especially,, O, N, S, P and the halogens
hapter 1: hemical bonding and structure in organic compounds arbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms omposition: Mainly nonmetals; especially,, O, N, S, P and the halogens
Unit 7: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonds. Lewis Symbols. The Octet Rule. Transition Metal Ions. Ionic Bonding 11/17/15
 Unit 7: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Topics Covered Chemical bonds Ionic bonds Covalent bonds Bond polarity and electronegativity Lewis structures Exceptions to the octet rule Strength of covalent
Unit 7: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Topics Covered Chemical bonds Ionic bonds Covalent bonds Bond polarity and electronegativity Lewis structures Exceptions to the octet rule Strength of covalent
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 of Chemical John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chemical Bonds Chemical bonds are the forces that hold the atoms together in substances. Three
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 of Chemical John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chemical Bonds Chemical bonds are the forces that hold the atoms together in substances. Three
Chemistry 101 Chapter 9 CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical bonds are strong attractive force that exist between the atoms of a substance. Chemical bonds are commonly classified into 3 types: Ionic Bonding Ionic bonds form between metals
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical bonds are strong attractive force that exist between the atoms of a substance. Chemical bonds are commonly classified into 3 types: Ionic Bonding Ionic bonds form between metals
Covalent Bonding. Chapter 8. Diatomic elements. Covalent bonding. Molecular compounds. 1 and 7
 hapter 8 ovalent bonding ovalent Bonding A metal and a nonmetal transfer An ionic bond Two metals just mix and don t react An alloy What do two nonmetals do? Neither one will give away an electron So they
hapter 8 ovalent bonding ovalent Bonding A metal and a nonmetal transfer An ionic bond Two metals just mix and don t react An alloy What do two nonmetals do? Neither one will give away an electron So they
CHAPTER EIGHT BONDING: GENERAL CONCEPTS. For Review
 APTER EIGT BDIG: GEERAL EPTS or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the energy
APTER EIGT BDIG: GEERAL EPTS or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the energy
Ch 2 Polar Covalent Bonds
 h 2 Polar ovalent Bonds Two primary bond types: ovalent (shared e -1 s) and Ionic (transferred e -1 s) Ionic bonds can have covalent character, such as with Na:l. An e -1 pair on l -1 can fill the 3s orbital
h 2 Polar ovalent Bonds Two primary bond types: ovalent (shared e -1 s) and Ionic (transferred e -1 s) Ionic bonds can have covalent character, such as with Na:l. An e -1 pair on l -1 can fill the 3s orbital
Chemical Bonding Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapters 10 and 11
 Chemical Bonding Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapters 10 and 11 Aims: To look at bonding and possible shapes of molecules We will mainly do this through Lewis structures To look at ionic and covalent
Chemical Bonding Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapters 10 and 11 Aims: To look at bonding and possible shapes of molecules We will mainly do this through Lewis structures To look at ionic and covalent
Covalent Bonds. Chapter 8 Chemical Bonds (+VSEPR from Chapter 9) Li Be B C N O F Ne delocalized electron sea. 3. Introduction. Types of Chemical Bonds
 hapter 8: hemical Bonds (+ VSEPR) hapter bjectives: hapter 8 hemical Bonds (+VSEPR from hapter 9) Understand the principal types of chemical bonds. Understand the properties of ionic and molecular compounds.
hapter 8: hemical Bonds (+ VSEPR) hapter bjectives: hapter 8 hemical Bonds (+VSEPR from hapter 9) Understand the principal types of chemical bonds. Understand the properties of ionic and molecular compounds.
18. Ionic solids are held together by strong electrostatic forces that are omnidirectional.
 APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. In 2 and, the bonding is covalent in nature, with the bonding electrons pair shared between the atoms. In 2, the two atoms are identical, so the sharing is equal;
APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. In 2 and, the bonding is covalent in nature, with the bonding electrons pair shared between the atoms. In 2, the two atoms are identical, so the sharing is equal;
Announcements. Chem 7 Final Exam Wednesday, Oct 10 1:30-3:30AM Chapter or 75 multiple choice questions
 Exam III (Chapter 7-0) Wednesday, ctober 3, 202 Time 600PM - 730PM SEC A 24A and 25A SKIPPING THIS STUFF Announcements Chem 7 Final Exam Wednesday, ct 0 30-330AM Chapter -2 70 or 75 multiple choice questions
Exam III (Chapter 7-0) Wednesday, ctober 3, 202 Time 600PM - 730PM SEC A 24A and 25A SKIPPING THIS STUFF Announcements Chem 7 Final Exam Wednesday, ct 0 30-330AM Chapter -2 70 or 75 multiple choice questions
Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that particpate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration # of valence
Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that particpate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration # of valence
Chapter 6. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding 6.1 Objectives Define chemical bond. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. Describe ionic and covalent bonding. Explain why most chemical
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding 6.1 Objectives Define chemical bond. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. Describe ionic and covalent bonding. Explain why most chemical
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Section Chapter 8: Covalent Bonding CHAPTER 8 Table Of Contents Section 8.2 Section 8.3 Section 8.4 Section 8.5 Naming Molecules Molecular Structures Molecular Shapes Electronegativity
GENERAL BONDING REVIEW
 GENERAL BONDING REVIEW Chapter 8 November 2, 2016 Questions to Consider 1. What is meant by the term chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? 3. How do atoms bond with each
GENERAL BONDING REVIEW Chapter 8 November 2, 2016 Questions to Consider 1. What is meant by the term chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? 3. How do atoms bond with each
Chapter 8: Bonding. Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols
 Chapter 8: Bonding Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols The Lewis electron dot symbol is named after Gilbert Lewis. In the Lewis dot symbol, the element symbol represents the nucleus and the inner electrons.
Chapter 8: Bonding Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols The Lewis electron dot symbol is named after Gilbert Lewis. In the Lewis dot symbol, the element symbol represents the nucleus and the inner electrons.
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.9 - BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ATOMIC PROPERTIES AND CHEMICAL BONDS Before we examine the types of chemical bonding, we should ask why atoms bond at all. Generally, the reason is that ionic bonding the
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ATOMIC PROPERTIES AND CHEMICAL BONDS Before we examine the types of chemical bonding, we should ask why atoms bond at all. Generally, the reason is that ionic bonding the
Chapter 8 & 9 Concepts of Chemical. Bonding
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 & 9 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006,
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 8 & 9 Concepts of John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006,
Page III-7-1 / Chapter Seven Lecture Notes MAR. Ionic - complete transfer of. Covalent - electrons shared MAR. CH 221 Flashback:
 Page III-7-1 / hapter even Lecture otes hemical onding onding and Molecular tructure hapter 7 ocaine hemistry 222 Professor Michael Russell http://mhchem.org/222 Get the 222 ompanion and omposition Lab
Page III-7-1 / hapter even Lecture otes hemical onding onding and Molecular tructure hapter 7 ocaine hemistry 222 Professor Michael Russell http://mhchem.org/222 Get the 222 ompanion and omposition Lab
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
VOCABULARY Define. 1. chemical bond. 2. covalent bond. 3. ionic bonding. 4. polar-covalent bond
 Name Date lass Modern hemistry APTER 6 OMEWORK 6-1 (pp. 161 163) VOABULARY Define. 1. chemical bond 2. covalent bond 3. ionic bonding 4. polar-covalent bond SKILL BUILDER Use the electronegativity values
Name Date lass Modern hemistry APTER 6 OMEWORK 6-1 (pp. 161 163) VOABULARY Define. 1. chemical bond 2. covalent bond 3. ionic bonding 4. polar-covalent bond SKILL BUILDER Use the electronegativity values
Dr. Lori Stepan Van Der Sluys 2 Chapter 8 Part 3
 ovalent Bonding Describe covalent bonding and how it differs from ionic bonding Know how to tell if a substance is covalently bonded Know how to draw Lewis structures Know the two types of multiple bonds
ovalent Bonding Describe covalent bonding and how it differs from ionic bonding Know how to tell if a substance is covalently bonded Know how to draw Lewis structures Know the two types of multiple bonds
CHAPTER 10 CHEMICAL BONDING I: BASIC CONCEPTS
 APTER 10 EMIAL BDIG I: BAI EPT PRATIE EXAMPLE 1A 1B 2A 2B (E) Mg is in group 2(2A), and thus has 2 valence electrons and 2 dots in its Lewis symbol. Ge is in group 14(4A), and thus has 4 valence electrons
APTER 10 EMIAL BDIG I: BAI EPT PRATIE EXAMPLE 1A 1B 2A 2B (E) Mg is in group 2(2A), and thus has 2 valence electrons and 2 dots in its Lewis symbol. Ge is in group 14(4A), and thus has 4 valence electrons
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules
 Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL BONDING NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB SMK SULTAN ISMAIL, JB
 CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL BONDING NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB SMK SULTAN ISMAIL, JB LEARNING OUTCOMES (ionic bonding) 1. Describe ionic (electrovalent) bonding such as NaCl and MgCl 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES (metallic
CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL BONDING NUR FATHIN SUHANA BT AYOB SMK SULTAN ISMAIL, JB LEARNING OUTCOMES (ionic bonding) 1. Describe ionic (electrovalent) bonding such as NaCl and MgCl 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES (metallic
Chapter 9 Bonding 2 Polar Covalent Bond, Electronegativity, Formal Charge, Resonance. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 9 Bonding 2 Polar Covalent Bond, Electronegativity, Formal Charge, Resonance Dr. Sapna Gupta Writing Lewis Structures 1. Draw the skeleton structure of the molecule or ion by placing the lowest
Chapter 9 Bonding 2 Polar Covalent Bond, Electronegativity, Formal Charge, Resonance Dr. Sapna Gupta Writing Lewis Structures 1. Draw the skeleton structure of the molecule or ion by placing the lowest
Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond
 Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Apply the octet rule to atoms that form covalent bonds. Describe the formation of single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Contrast sigma and pi bonds. Relate the strength
Section 8.1 The Covalent Bond Apply the octet rule to atoms that form covalent bonds. Describe the formation of single, double, and triple covalent bonds. Contrast sigma and pi bonds. Relate the strength
17/11/2010. Lewis structures
 Reading assignment: 8.5-8.8 As you read ask yourself: How can I use Lewis structures to account for bonding in covalent molecules? What are the differences between single, double and triple bonds in terms
Reading assignment: 8.5-8.8 As you read ask yourself: How can I use Lewis structures to account for bonding in covalent molecules? What are the differences between single, double and triple bonds in terms
Chapter 9 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 Chem 1045 Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Last Update: 06-April-2009 Chapter 9 Ionic and Covalent Bonding These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do
Chem 1045 Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Last Update: 06-April-2009 Chapter 9 Ionic and Covalent Bonding These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 8. Ions and the Noble Gas. Chapter Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts 1 8.1 Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds Ionic compounds form when metals and nonmetals react The attraction between positive and negative
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts 1 8.1 Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds Ionic compounds form when metals and nonmetals react The attraction between positive and negative
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Questions to Consider What is meant by the term chemical bond? Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? How do atoms bond with each other to form
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Questions to Consider What is meant by the term chemical bond? Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? How do atoms bond with each other to form
CHAPTER 8 BONDING: GENERAL CONCEPTS. Questions
 APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. a. This diagram represents a polar covalent bond as in. In a polar covalent bond, there is an electron rich region (indicated by the red color) and an electron poor
APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. a. This diagram represents a polar covalent bond as in. In a polar covalent bond, there is an electron rich region (indicated by the red color) and an electron poor
Chapter 1: Structure Determines Properties 1.1: Atoms, Electrons, and Orbitals
 hapter 1: Structure Determines Properties 1.1: Atoms, Electrons, and rbitals Molecules are made up of atoms Atoms- protons- (+)-charge, mass = 1.676 X 10-7 kg neutrons- no charge, mass = 1.6750 X 10-7
hapter 1: Structure Determines Properties 1.1: Atoms, Electrons, and rbitals Molecules are made up of atoms Atoms- protons- (+)-charge, mass = 1.676 X 10-7 kg neutrons- no charge, mass = 1.6750 X 10-7
BONDING. Covalent bonding Two non- metal atoms can form a stable octet structure by sharing electrons.
 BODIG In the process of bonding electrons move to a lower energy level to form a more stable structure. This can be done by transferring electron(s) to another atom or by pairing with an electron from
BODIG In the process of bonding electrons move to a lower energy level to form a more stable structure. This can be done by transferring electron(s) to another atom or by pairing with an electron from
Covalent Bonding 10/29/2013
 Bond Energies or Bond Dissociation Energies Tables 8.4 and 8.5 on page 72 gives a list of the energy required to dissociate or break bonds. This value is used to determine whether covalent bonds will form
Bond Energies or Bond Dissociation Energies Tables 8.4 and 8.5 on page 72 gives a list of the energy required to dissociate or break bonds. This value is used to determine whether covalent bonds will form
Downloaded from
 Points to Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical
Points to Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical
K + 09/04/2018. Structure of Organic Molecules. Ionic bond. The compound potassium fluoride consists of potassium (K+) ions and fluoride (F-) ions
 Structure of rganic Molecules Ref. books: 1. A text book of rganic Chemistry - B.S. Bahl and Arun Bahl 2. rganic Chemistry - R.T. Morrison and R. N. Boyd Atom: The smallest part of an element that can
Structure of rganic Molecules Ref. books: 1. A text book of rganic Chemistry - B.S. Bahl and Arun Bahl 2. rganic Chemistry - R.T. Morrison and R. N. Boyd Atom: The smallest part of an element that can
Chapter 8. forces of attraction which hold atoms or ions together. 3 fundamental types of bonding. Ionic - metals & nonmetals
 Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds forces of attraction which hold atoms or ions together 3 fundamental types of bonding Ionic - metals & nonmetals Covalent - nonmetals (semimetals)
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds forces of attraction which hold atoms or ions together 3 fundamental types of bonding Ionic - metals & nonmetals Covalent - nonmetals (semimetals)
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6 th Ed. Introductory Chemistry, 6 th Ed. Basic Chemistry, 6 th Ed.
 Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6 th Ed. Introductory Chemistry, 6 th Ed. Basic Chemistry, 6 th Ed. by Steven S. Zumdahl & Donald J. DeCoste University of Illinois Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Structure
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6 th Ed. Introductory Chemistry, 6 th Ed. Basic Chemistry, 6 th Ed. by Steven S. Zumdahl & Donald J. DeCoste University of Illinois Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Structure
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.2 Electronegativity 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.4 Ions: Electron Configurations and Sizes 8.5 Energy
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.2 Electronegativity 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.4 Ions: Electron Configurations and Sizes 8.5 Energy
Chapter 12 Structures and Characteristics of Bonds Objectives
 Objectives 1. To learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed - what holds compounds together? 2. To learn about the polar covalent bond are all covalent bonds equal? 3. To understand
Objectives 1. To learn about ionic and covalent bonds and explain how they are formed - what holds compounds together? 2. To learn about the polar covalent bond are all covalent bonds equal? 3. To understand
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
Chapter 13: Phenomena
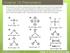 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
NOTES: UNIT 6: Bonding
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo NOTES: UNIT 6: Bonding www.mrpalermo.com Name: Key Ideas Compounds can be differentiated by their chemical and physical properties. (3.1dd) Two major categories of
Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo NOTES: UNIT 6: Bonding www.mrpalermo.com Name: Key Ideas Compounds can be differentiated by their chemical and physical properties. (3.1dd) Two major categories of
