Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis with Cobalt Catalysts Supported on Mesoporous Silica for Efficient Production of Diesel Fuel Fraction
|
|
|
- Julius Tyler Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 804 Energy & Fuels 2003, 17, Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis with Cobalt Catalysts Supported on Mesoporous Silica for Efficient Production of Diesel Fuel Fraction Yasuo Ohtsuka,* Takashi Arai, Satoshi Takasaki, and Naoto Tsubouchi Research Center for Sustainable Materials Engineering, Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University, Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai , Japan Received October 15, 2002 Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis with Co catalysts supported on mesoporous silica (SBA-15) with narrow pore size distribution has been carried out with a fixed bed stainless steel reactor at 503 K and 2.0 MPa. When 20 mass % Co is supported on SBA-15 with an average pore diameter of 8.6 nm by using an ethanol solution of Co acetate, nitrate, or an equimolar mixture of these compounds, denoted as Co(20A), Co(20N), or Co(10A+10N), respectively, the Co(20A) is almost inactive in FT synthesis, whereas the Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) drastically enhance CO conversion, which reaches 85-90%. Such differences arise partly from the formation of less or more reducible Co species. The latter two catalysts show selectivity to C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons of C-mol % and provide high space-time yields of this fraction as the main component of diesel fuel, g-c/kg-catalyst h. The yield with the Co(20N) catalyst depends on the amount and has a maximal value of 350 g-c/kg-catalyst h. The N 2 adsorption, X-ray diffraction, and temperature-programmed reduction measurements reveal that pore structures and dispersion states of Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) catalysts are not changed significantly, even after FT synthesis and subsequent air calcination at 773 K. Introduction Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis has recently attracted renewed interest, because a high quality diesel oil fraction without any sulfur and aromatic compounds can be produced from syngas derived from natural gas. 1-5 Cobalt-based catalysts loaded on different supports, such as SiO 2,Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2, have been widely used in this reaction to form long-chain aliphatic hydrocarbons. 2,6,7 It has been reported that the specific rate of CO conversion increases linearly with increasing dispersion of metallic Co, irrespective of the kind of support, under conditions that favor chain growth reactions, and that selectivity to C 5 + hydrocarbons relates with the diffusion of reaction intermediates within the pores of the catalyst support. 6,8,9 These observations suggest that physical structures of the support, for example surface area for catalyst dispersion and pore properties for product diffusion, are one of the * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. ohtsukay@tagen.tohoku.ac.jp. (1) Xu, L.; Bao, S.; O Brien, R. J.; Raje, A.; Davis, B. H. CHEMTECH 1998, (2) Schulz, H. Appl. Catal. A: General 1999, 186, (3) Davis, B. H. Fuel Process. Technol. 2001, 71, (4) Iglesia, E. Prepr. Pap.sAm. Chem. Soc., Div. Fuel. Chem. 2002, 47 (1), (5) Dry, M. E. Catal. Today 2002, 71, (6) Iglesia, E. Appl. Catal. A: General 1997, 161, (7) Van der Laan, G. P.; Beenackers, A. A. C. M. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1999, 41, (8) Iglesia, E.; Soled, S. L.; Fiato, R. A. J. Catal. 1992, 137, (9) Iglesia, E.; Reynes, S. C.; Madon, R. J.; Soled, S. L. Adv. Catal. 1993, 39, 239. key factors for efficient production of long-chain aliphatic hydrocarbons, such as C 10 -C 20 paraffins, as the main component of diesel oil. As is well-known, mesoporous silica materials recently developed, such as MCM-41, 10 FSM-16, 11 and SBA-15, 12 have unique physical structures: narrow pore size distribution, large pore diameters in the range of 2-30 nm, high surface areas reaching 1000 m 2 /g, and large pore volumes of 1-2 cm 3 /g, compared with those of conventional SiO 2 supports. Thus, the present authors have been working on the utilization of such mesoporous materials as catalyst supports in FT synthesis and have shown that, when 20 mass % Co is incorporated into SBA-15 with different pore diameters of 3-15 nm, 13 the Co/SBA-15 catalyst with an average diameter of about 8.5 nm exhibits the highest activity at 523 K and 2.0 MPa, although CH 4 selectivity is large due probably to the high temperature. 14 The present work thus (10) Kresge, C. T.; Leonowicz, M. E.; Roth, W. J.; Vartuli, J. C.; Beck, J. S. Nature 1992, 359, (11) Inagaki, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Kuroda, K. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1993, (12) Zhao, E.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.; Chmelka, B.; Stucky, G. Science 1998, 279, (13) Wang, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohtsuka, Y. Catal. Today 2001, 68, 3-9. (14) Wang, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Ohtsuka, Y. Proceedings of the 7th China-Japan Symposium on Coal and C 1 Chemistry (Hainan Island, China), 2001; pp (15) Mal, N. K.; Ohtsuka, Y. Proceedings of the Fourth Tokyo Conference of Advanced Catalytic Science and Technology (Tokyo, Japan), 2002; p 336. (16) Ohtsuka, Y.; Arai, T.; Takasaki, S.; Tsubouchi, N. Prepr. Pap.s Am. Chem. Soc., Div. Fuel Chem. 2002, 47 (2), /ef020235r CCC: $ American Chemical Society Published on Web 05/08/2003
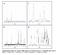
2 Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis for Diesel Fuel Production Energy & Fuels, Vol. 17, No. 4, focuses on FT synthesis at a low temperature of 503 K to increase C 5 + selectivity. The objectives are to examine the effects of Co precursor and catalyst amount on the performances of Co/SBA-15 catalysts, in particular, space-time yield (denoted as STY) of C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons, and to make clear the structural stability after reaction from a practical point of view. Experimental Section Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica. SBA-15 was synthesized in a manner similar to that reported earlier. 12 The procedure has been described in detail elsewhere 13 and thus is simply explained below. An acidic aqueous mixture of a triblock copolymer (Aldrich), poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) (EO 20PO 70EO 20), trimethylbenzene, and tetraethyl orthosilicate was first heated at 308 K for 24 h, followed by postsynthesis treatment at 370 K. Then, assynthesized SBA-15 was separated by filtration, followed by repeated washing with distilled water, and subsequently dried at room temperature under vacuum; it was finally calcined in air at 773 K for 6 h. The calcined SBA-15 was characterized by the N 2 adsorption measurements and used as a support for the Co catalyst. Catalyst Addition and Characterization. Co catalysts were loaded on the SBA-15 with an average pore diameter of 8.6 nm by the impregnation method 13 using an ethanol solution of Co(CH 3COO) 2, Co(NO 3) 2, or the equimolar mixture; these were denoted as Co(A), Co(N), or Co(A+N), respectively. After removal of ethanol, the resulting samples were again calcined at 773 K under flowing air. Loading of Co metal is expressed in x and y mass % of Co(xA+yN); for example, Co(10A+10N) denotes 10 mass % Co from Co(CH 3COO) 2 and 10 mass % Co from Co(NO 3) 2, and Co(20N) means 20 mass % Co from Co- (NO 3) 2 alone. All of the Co/SBA-15 catalysts after air calcination were subjected to X-ray diffraction (XRD) and N 2 adsorption measurements. The average crystalline size of Co 3O 4 identified by XRD was calculated by the Debye-Scherrer method. Pore size distribution and specific surface area were determined by the BJH and BET methods, respectively. The average pore diameter of each catalyst was estimated by using total volume and surface area of mesopores on the assumption that they are cylindrical. 12 To examine chemical forms and reducibility of Co species in some catalysts, the temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) measurements were made by heating at 10 K/min up to 1273 K in an atmospheric stream of H 2 diluted with Ar, and the changes in H 2 concentration were on-line monitored with a gas chromatograph. FT Runs and Product Analysis. FT runs were carried out with a high-pressure gas-phase reaction system including a cylindrical stainless reactor (8-mm i.d., 330 mm long). 13 About g of the catalyst charged into the reactor was first pretreated with atmospheric H 2 for 12 h at 673 K and then cooled to 373 K. After replacement of the H 2 with a pressurized mixture of H 2 and CO with a molar ratio of 2:1, the reactor was finally heated at 3 K/min up to the reaction temperature, a small amount of Ar as an internal standard being included in the mixed gas. After a predetermined soaking time, the reactor was quenched to room temperature. Catalyst amount (W), W/F (F, feed rate), reaction temperature, and pressure were 0.50 g, 4.0 ghmol -1, 503 K, and 2.0 MPa, respectively, unless otherwise stated. The temperature was controlled and measured with a thermocouple inserted into the catalyst bed. With product analysis, C 1-C 5 hydrocarbons in the effluent after recovery of liquid products were on-line analyzed with a high-speed micro GC. Liquid products were recovered with three kinds of traps held in the range of room temperature to 77 K, and C 6-C 28 hydrocarbons in them were determined with Figure 1. Pore size distribution for SBA-15 support and Co/ SBA-15 catalysts. Table 1. Characterization Results of Co/SBA-15 Catalysts catalyst name Co(A) (mass%) Co(N) (mass%) D av a (nm) a capillary GC-MS. Waxy materials remaining in the catalyst recovered after reaction were detected by the conventional elemental analyzer. The catalyst was also analyzed by XRD and N 2 adsorption measurements, as mentioned above. Results V p b (cm 3 /g) S BET c (m 2 /g) D(Co 3O 4) d (nm) Co(10N) Co(20N) Co(10A+10N) Co(20A) n.d. e a Average pore diameter. b Pore volume. c BET surface area. d Average crystalline size of Co 3O 4. e No species detectable. Properties and Structures of Co/SBA-15 Catalysts. Figure 1 shows typical profiles for the pore size distribution of SBA-15 support and three kinds of Co/ SBA-15 catalysts. As expected, all of the samples used exhibited the narrow size distribution. The support alone provided an asymmetric, sharp peak at 9.3 nm. Although the peak position was almost unchanged by Co impregnation, the height lowered, irrespective of kind of precursor salt, because Co oxide was held inside the mesopores. Table 1 summarizes pore properties and surface areas of all the catalysts used. The SBA-15 support had an average pore diameter (D av ) of 8.6 nm, which was slightly reduced to nm at total Co loading of 20 mass %. Pore volume and BET surface area of the support were 1.9 cm 3 /g and 880 m 2 /g, respectively. The addition of mass % Co decreased the volume and area to cm 3 /g and m 2 /g, respectively, and the extent of the decrease was higher at larger Co loading, showing the presence of larger amounts of Co particles within the mesopores. When four kinds of Co/SBA-15 catalysts were subjected to XRD measurements, no diffraction lines of Co
3 806 Energy & Fuels, Vol. 17, No. 4, 2003 Ohtsuka et al. Figure 3. Time changes in yields of CH 4 and C 2-C 4 hydrocarbons at 503 K with Co(10A+10N)/SBA-15 catalyst. Figure 2. CO conversion against time on stream in FT synthesis at 503 K and 2.0 MPa. species were detectable with Co(20A), whereas weak XRD peaks of Co 3 O 4 appeared with Co(10N), Co- (10A+10N), and Co(20N), and the peak intensities were larger with Co(20N). These observations show that Co species from the Co(20A) are less crystallized. As summarized in Table 1, the average crystalline sizes of Co 3 O 4 estimated were 12, 9.1, and 20 nm for the Co- (10N), Co(10A+10N), and Co(20N), respectively. Since these values were slightly larger than the corresponding D av, part of the Co 3 O 4 particles formed from these three catalysts may be present outside the mesopores. Performances of Co/SBA-15 Catalysts in FT Synthesis. Figure 2 shows CO conversion at 503 K against time on stream. The conversion was only 2% on the Co(20A), which was thus almost inactive. On the other hand, the Co(10A+10N) and Co(20N) were quite active, and CO conversions after apparent induction periods increased steeply with increasing time and reached 84-89% at a steady state after 6 h. The period may be regarded mainly as the time required for replacing the dead volume up to micro GC with unreacted syngas. As is seen in Figure 2, the activity of the Co(N) catalyst depended strongly on Co loading, and CO conversion after 6 h reaction decreased to 20 % at smaller loading of 10 mass %. The shorter induction period was observed with the Co(10N), due possibly to the lower conversion. It should be noted that the conversion on the Co(10A+10N), 84%, is much higher than the sum (22%) of those observed with the Co(20A) and Co(10N); in other words, the synergistic effect exists with the activity of the Co(10A+10N) catalyst. Time changes in yields of CH 4 and C 2 -C 4 hydrocarbons with Co(10A+10N) are provided in Figure 3, where the values are calculated by dividing the molar amount of CH 4 or C 2 -C 4 fraction by that of CO converted and seem unreliable at the beginning of reaction; that is, within 1 h, due to very low CO conversion. The yields were larger in the lower conversion region but decreased with time to reach stable values (4-8 mol %) after 3 h. Almost the same profiles were observed for the Co(20N). Table 2. Hydrocarbon Products in FT Synthesis with Co/SBA-15 Catalysts selectivity (C-mol %) catalyst name C 5-C 9 C 10-C 20 C 21+ c R a STY of C 10-C b 20 (g-c/kg-catalyst h) Co(10N) Co(20N) Co(10A+10N) a Chain growth probability. b Space time yield. c C 21-C 28 plus waxy materials. The results for liquid hydrocarbons produced over the Co(10N), Co(20N), and Co(10A+10N) catalysts are summarized in Table 2, where product selectivity for C 5 -C 9,C 10 -C 20, and C 21 + (C 21 -C 28 plus waxy materials remaining in recovered catalyst) fractions is expressed in C-mol % as the mean value for 6 h reaction. A small amount of CO 2 was formed for the Co(20N) alone. Selectivity to C 5 -C 9 was larger with the Co(10N), whereas selectivity to C 10 -C 20 was almost independent of the kind of catalyst and ranged C-mol %, and the C 21 + fraction was larger with the Co(20N) and Co- (10A+10N) catalysts, which roughly followed the Schultz-Flory distribution and lead to higher chain growth probabilities (R) of , though the linearity was not so good. Table 2 also shows space-time yield (denoted as STY) of C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons as the main components of diesel fuel, the value being estimated by using CO conversion after 6 h and selectivity to this fraction provided in Table 2. The STY was 58 g-c/kgcatalyst h with the Co(10N), whereas it was as high as g-c/kg-catalyst h with the Co(10A+10N) and Co(20N). The effect of W/F on catalytic performance of the Co- (20N) at 503 K is provided in Figure 4, where the W alone is varied while keeping the F constant. CO conversion after 6 h increased monotonically with increasing W/F, that is, contact time between catalyst and syngas. With product distribution, selectivity to long-chain hydrocarbons, such as C 10 -C 20 or C 21 + fraction, was higher at larger W/F. Consequently, the STY of the former fraction showed a maximal value of 350 g-c/kg-catalyst h atw/f of 2.4 g h/mol. Under these conditions, the productivity of C 5 -C 20 hydrocarbons reached 710 g-c/kg-catalyst h.
4 Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis for Diesel Fuel Production Energy & Fuels, Vol. 17, No. 4, Figure 4. Effect of W/F on FT performance of Co(20N)/SBA- 15 catalyst at 503 K. Figure 5. TPR profiles for three kinds of Co/SBA-15 catalysts. Reducibility of Co/SBA-15 Catalysts. As is seen in Figure 2, the Co(20A) was almost inactive, but contrarily the Co(10A+10N) and Co(20N) were quite active. To make clear this difference, TPR measurements of the fresh catalysts after air calcination were made. The profiles are shown in Figure 5. The Co(20A) had a broad peak at K. The peak may be identified to H 2 consumption by reduction of Co 2 SiO 4 to metallic Co. 17 On the other hand, the Co(20N) showed the main and shoulder peaks at 600 and 710 K, respectively, followed by two weak ones after 800 K. The former two peaks can be attributed to the reduction of Co 3 O 4 to CoO and subsequently to metallic Co, 18 which means that Co 3 O 4 is the predominant species in the fresh Co(20N) catalyst. The presence of this species agreed with the XRD results (Table 1). The Co- (10A+10N) provided the intermediate profile between the above twosin other words, the coexistence of Co 3 O 4 and Co 2 SiO 4. The former species was also detectable by (17) Rosynek, M. P.; Polansky, C. A. Appl. Catal. 1991, 73, (18) Ming, H.; Baker, B. G. Appl. Catal. A: General 1995, 123, Figure 6. Comparison of pore size distribution for Co- (10A+10N)/SBA-15 catalyst before and after FT synthesis. XRD (Table 1), but any diffraction lines of Co 2 SiO 4 were not observed in the Co(10A+10N) and Co(20A) as a result probably of the amorphous state. Because all of the fresh catalysts after air calcination are pretreated with H 2 at 673 K for 12 h before FT runs, as described in the Experimental Section, the results obtained in Figure 5 show that Co 3 O 4 in the Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) can be reduced to metallic Co, whereas Co 2 SiO 4 as the major species in the Co(20A) is not reduced and still remained even after H 2 pretreatment. It is likely that such differences in chemical forms of Co species and their consequent reducibility to metallic Co can account for the distinct activity observed with the Co(20A) and Co(20N) catalysts. Although the proportion of the readily reducible Co 3 O 4 was smaller in the Co(10A+10N) than in the Co(20N), their performances were almost the same (Figure 2 and Table 2). The reason is not clear at present and should be clarified in future work. It has been reported that Co acetate supported on commercial SiO 2 support is catalytically activated in FT synthesis in the presence of Co nitrate. 19 Structural Stability of Co/SBA-15 Catalysts with High Performances. Figure 6 shows the pore distribution of the used Co(10A+10N) catalyst after reaction and subsequent solvent washing. The peak height was reduced to be one-third of that before reaction, which means a considerable decrease in pore volume. Almost the same distribution was observed with the used Co- (20N). One may expect that such a reduction is caused by the retention of significant amounts of waxy materials inside the mesopores. To make this point clear, the used Co(10A+10N) and Co(20N) were subjected to the XRD measurements. Since both catalysts showed almost the same XRD patterns, the results for Co(10A+10N) alone are provided in Figure 7, where the profile for the sample before reaction, that is, the fresh Co(10A+10N) after air calcination, is also shown for a reference. The (19) Sun, S.; Tsubaki, N.; Fujimoto, K. Appl. Catal. A: General 2000, 202,
5 808 Energy & Fuels, Vol. 17, No. 4, 2003 Ohtsuka et al. Figure 7. Changes in XRD profiles for Co(10A+10N)/SBA- 15 catalyst before and after FT synthesis. profile after reaction confirmed the presence of very sharp XRD peaks attributable to long-chain saturated hydrocarbons (paraffin wax). With Co species, the weak XRD signals of Co 3 O 4 observed for the fresh catalyst disappeared after the reaction, but no diffraction lines due to metallic Co appeared. Although the reason for the difference in the XRD intensities of Co 3 O 4 and metallic Co is not clear, the same phenomenon was also observed with the Co(20N) catalyst. The absence of any XRD signals of metallic Co with the Co(10A+10N) and Co(20N) indicates that the Co is finely dispersed even after FT synthesis. When the used Co(10A+10N) was calcined again at 773 K, the XRD signals of the wax disappeared completely, and Co 3 O 4 appeared again (Figure 7), as is to be expected. The average crystalline size of the Co species was estimated to be 12 nm, which was nearly equal to that (9 nm) for the fresh catalyst (Table 1). In addition, the recalcination restored the pore distribution to almost the same state as that of the fresh catalyst, as is seen in Figure 6. Such changes in both XRD profiles and pore size distribution before and after reaction followed by air calcination were observed, quite similarly with the Co(20N) catalyst. Thus, these observations show that pore structures and dispersion states of the Co(10A+10N) and Co(20N) with high performances are almost unchanged before and after FT synthesis, even when these catalysts are exposed to hot gas including H 2 O and CO 2 evolved from the wax upon recalcination at 773 K. Such a structural stability may originate from thick walls of the mesopores in SBA-15, compared with those for other mesoporous silica materials, 12 and it suggests that catalytic performances of the Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) are also stable, though should be confirmed in the future study. Discussion Although many publications have reported on synthesis, characterization, and catalytic applications of mesoporous silica materials with narrow pore size distribution, only quite limited information on FT synthesis with them as catalyst supports, except for the presentauthors work, hasrecentlybeenprovided When 15 mass % Co supported on hexagonal mesoporous silica (HMS), 21 synthesized by a method different from that for MCM-41, with the pore size and volume of 3 nm and 0.4 cm 3 /g, respectively, was used in FT synthesis at 503 K and 2.0 MPa, high CO conversion of 88% was observed and long-chain waxy hydrocarbons were mainly formed. Compared with this result, the present Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) showed almost the same conversions of 84-89% (Figure 2), whereas these catalysts provided lower selectivity to the wax fraction, in other words, higher selectivity to C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons (Table 2), despite reaction conditions quite similar to those above. As shown in Table 1, the Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) catalysts had larger pore diameters ( nm) and consequently larger pore volumes ( cm 3 /g) than the Co/HMS catalyst. Such pore properties may provide longer residence times of long-chain hydrocarbons inside the mesopores, which may lead to secondary cracking reactions of the wax to increase the diesel oil fraction. It is of interest to compare FT performances of Co catalysts supported on mesoporous silica materials and conventional SiO 2 supports. Higher CO conversion at 510 K and 2.1 MPa was reported for Co catalysts on a uniform mesoporous silica (SCMM) with average pore diameter (D av ) of 3.6 nm than on commercial SiO 2 gel with D av of >10 nm. 20 The low conversion of 30% was also observed with a Co catalyst supported on conventional SiO 2 under the present conditions. When 20 mass % Co(N) was supported on SiO 2 gel with D av of 8.7 nm, nearly equal to that in this work, though the pore volume of 1.2 cm 3 /g and the surface area of 270 m 2 /g with the gel were smaller, CO conversion in a slurry phase FT run at 503 K and 1.0 MPa under W/F of 5.0 g h/mol was 30%, 19 which was much lower than that (89%) on the present Co(20N) catalyst. Since it appears that the effects of total pressure of more than 1 MPa and reaction phase on CO conversion with Co catalyst are not significant, 19,23,24 higher CO conversion observed in this work may be ascribed not only to uniform mesopores of SBA-15 support but also to the larger pore volume and higher surface area. The latter two factors should play the crucial roles in high dispersion of high loading of Co species. 13 In fact, the average crystalline size of metallic Co on the SiO 2 gel was estimated to be >16 nm, 19 whereas the Co on the present SBA-15 support was too fine to be detected by XRD (Figure 7). It has also been reported that, as the pore volume of commercial SiO 2 support for loading 20 mass % Co(N) increases from 0.7 to 2.3 cm 3 /g, Co 3 O 4 species formed after calcination can be more readily reduced with H 2 at a lower temperature, and the degree of the reduction becomes higher. 25 Larger reducibility and higher disper- (20) Iwasaki, T.; Reinikainen, M.; Onodera, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Ebina, T.; Nagase, T.; Torii, K.; Kataja, K.; Chatterjee, A. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 130, (21) Yin, D.; Li, W.; Xiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, B.; Peng, S. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 47, (22) Khodakov, A. Y.; Griboval-Constant, A.; Bechara, R.; Zholobenko, V. L. J. Catal. 2002, 260, (23) Sharma, B. K.; Sharma, M. P.; Roy, S. K.; Kumar, S.; Tendulkar, S. B.; Tambe, S. S.; Kukarni, B. D. Fuel 1998, 77, (24) Fan, L.; Han, Y. Z.; Yokota, K.; Fujimoto, K. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 1996, 39,
6 Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis for Diesel Fuel Production Energy & Fuels, Vol. 17, No. 4, sion of the Co(20N)/SBA-15 catalyst may account for the higher CO conversion obtained in the present study. It has been accepted in FT synthesis that, since severe restrictions on mass transport decrease CO concentration within catalyst pores and consequently lower chain growth probability, a catalyst with moderate transport restrictions can provide optimum selectivity to C 5 + hydrocarbons. 6,26 When 20 mass % Co(N) was supported on SiO 2 gel with a different D av of 2-15 nm, C 5 + selectivity and chain grown probability tended to show maximum values at D av of 10 nm. 25 These results suggest that the SBA-15 support with D av of 8.6 nm used in the present study may be suitable for metallic Co to promote chain growth reactions, which may lead to high STY of C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons on the Co(20N) and Co- (10A+10N) (Table 2 and Figure 4). The STY observed was g-c/kg-catalyst h, which was much higher than those (70-90 g-c/kg-catalyst h) 19,25 estimated for 20 mass % Co catalysts supported on conventional SiO 2 supports with almost the same D av as in the present work, when compared under similar reaction conditions. If significant amounts of waxy materials formed with the Co(20N) and Co(10A+10N) are secondarily cracked to C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons within catalyst pores, the STY could be increased further. The formation of weak acid sites by incorporating Al 3+ cations into the SBA-15 (25) Saib, A. M.; Claeys, M.; van Steen, E. Catal. Today 2002, 71, (26) Iglesia, E.; Soled, S. L.; Baumgartner, J. E.; Reynes, S. C. J. Catal. 1995, 153, support may be effective for this purpose. 21 To examine this point will be the subject of future work. Conclusions Gas-phase FT synthesis at 503 K and 2.0 MPa has been performed with 20 mass % Co catalysts supported on mesoporous silica (SBA-15) with an average pore diameter of 8.6 nm by the impregnation method using different precursor compounds. The conclusions are summarized as follows: (1) Co acetate is almost inactive, whereas the catalyst from the nitrate or an equimolar mixture of both compounds works quite effectively and provides high CO conversions of 85-90%, the former ineffectiveness being ascribed to the formation of less reducible Co species. (2) Active Co/SBA-15 catalysts achieve high spacetime yields of g-c/kg-catalyst h for C 10 -C 20 hydrocarbons as the main fraction of diesel oil, and the change in the catalyst amount leads to the optimum yield of 350 g-c/kg-catalyst h. (3) Pore structures and dispersion states of the used catalysts after FT synthesis do not change significantly, even when exposed to hot gas including H 2 O evolved during subsequent air calcination at 773 K. Acknowledgment. The present work was supported by Research for the Future Program of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under the Project Synthesis of Ecological High Quality Transportation Fuels (JSPS-RFTF98P01001). EF020235R
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas
 , July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas Ditlhobolo Seanokeng, Achtar Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract This study aimed at investigating
, July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas Ditlhobolo Seanokeng, Achtar Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract This study aimed at investigating
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction
 Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysis
 Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysis F. Morales Cano, O.L.J. Gijzeman, F.M.F. de Groot and B.M. Weckhuysen Department of Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis, Debye Institute, Utrecht
Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysis F. Morales Cano, O.L.J. Gijzeman, F.M.F. de Groot and B.M. Weckhuysen Department of Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis, Debye Institute, Utrecht
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NITROGEN-CONTAINING MICROPOROUS CARBON WITH A THREE-DIMENSIONAL NANO-ARRAY STRUCTURE
 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NITROGEN-CONTAINING MICROPOROUS CARBON WITH A THREE-DIMENSIONAL NANO-ARRAY STRUCTURE Peng-Xiang Hou 1, Takashi Kyotani 1, Koich Matsuoka 1, Akira Tomita 1, Norihiko Setoyama
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NITROGEN-CONTAINING MICROPOROUS CARBON WITH A THREE-DIMENSIONAL NANO-ARRAY STRUCTURE Peng-Xiang Hou 1, Takashi Kyotani 1, Koich Matsuoka 1, Akira Tomita 1, Norihiko Setoyama
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts
 Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Homogeneous Liquid phase Low temperature High selectivity High diffusivity Easy heat transfer Difficult catalyst separation Expensive recycling Well-defined active
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Homogeneous Liquid phase Low temperature High selectivity High diffusivity Easy heat transfer Difficult catalyst separation Expensive recycling Well-defined active
Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Supporting Information. Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic Compound Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Metal-free and Solvent-free Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines with Mesoporous Carbon from Macrocyclic Compounds
 1 Supporting Information Metal-free and Solvent-free Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines with Mesoporous Carbon from Macrocyclic Compounds Bo Chen, 1, Lianyue Wang, 1 Wen Dai, 1 Sensen Shang, 1, Ying
1 Supporting Information Metal-free and Solvent-free Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines with Mesoporous Carbon from Macrocyclic Compounds Bo Chen, 1, Lianyue Wang, 1 Wen Dai, 1 Sensen Shang, 1, Ying
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method
 Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Elucidation of the Influence of Ni-Co Catalytic Properties on Dry Methane Reforming Performance
 925 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 43, 2015 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-34-1; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
925 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 43, 2015 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-34-1; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Purification Influence of Synthesis Gas Derived from Methanol Cracking on the Performance of Cobalt Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 14(2005)193 198 Purification Influence of Synthesis Gas Derived from Methanol Cracking on the Performance of Cobalt Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Wei Zhou 1,2,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 14(2005)193 198 Purification Influence of Synthesis Gas Derived from Methanol Cracking on the Performance of Cobalt Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Wei Zhou 1,2,
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp , 2016
 KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
SBA-15-functionalized sulfonic acid confined acidic ionic liquid: a powerful and water-tolerant catalyst for solvent-free esterifications
 SBA-15-functionalized sulfonic acid confined acidic ionic liquid: a powerful and water-tolerant catalyst for solvent-free esterifications Babak Karimi* a, Majid Vafaeezadeh a a Department of Chemistry,
SBA-15-functionalized sulfonic acid confined acidic ionic liquid: a powerful and water-tolerant catalyst for solvent-free esterifications Babak Karimi* a, Majid Vafaeezadeh a a Department of Chemistry,
Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron double oxide catalyst
 Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with. High Oxidation-Resistant Property as Efficient and Durable
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with High
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with High
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Characterization of Re-Pd/SiO 2 catalysts for hydrogenation of stearic acid
 Supporting Information: Characterization of Re-Pd/SiO 2 catalysts for hydrogenation of stearic acid Yasuyuki Takeda, [a] Masazumi Tamura, [a] Yoshinao Nakagawa, [a] Kazu Okumura, [b] and Keiichi Tomishige*
Supporting Information: Characterization of Re-Pd/SiO 2 catalysts for hydrogenation of stearic acid Yasuyuki Takeda, [a] Masazumi Tamura, [a] Yoshinao Nakagawa, [a] Kazu Okumura, [b] and Keiichi Tomishige*
Time-resolved XANES studies on used silica supported cobalt catalysts
 Article Time-resolved XANES studies on used silica supported cobalt catalysts Siwaruk Chotiwan 1, Sutasinee Kityakarn 1, *, Yingyot Poo-arporn 2, and Pinsuda Viravathana 1 1 Department of Chemistry, Faculty
Article Time-resolved XANES studies on used silica supported cobalt catalysts Siwaruk Chotiwan 1, Sutasinee Kityakarn 1, *, Yingyot Poo-arporn 2, and Pinsuda Viravathana 1 1 Department of Chemistry, Faculty
CHAPTER 6. SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST
 135 CHAPTER 6 SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST 6.1 INTRODUCTION -Pinene is a terpenoid family of organic compound which is inexpensive, readily available and renewable
135 CHAPTER 6 SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST 6.1 INTRODUCTION -Pinene is a terpenoid family of organic compound which is inexpensive, readily available and renewable
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Hangzhou , PR China
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Influence of Ni based catalysts on CH 4 -CO 2 reforming reaction Hangjie Li 1, Dongming Shen 2, Xikun Gai 3,
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Influence of Ni based catalysts on CH 4 -CO 2 reforming reaction Hangjie Li 1, Dongming Shen 2, Xikun Gai 3,
Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department. Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials
 Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Hydrogenation of CO Over a Cobalt/Cerium Oxide Catalyst for Production of Lower Olefins
 Hydrogenation of CO Over a Cobalt/Cerium Oxide Catalyst for Production of Lower Olefins Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Hydrogenation of
Hydrogenation of CO Over a Cobalt/Cerium Oxide Catalyst for Production of Lower Olefins Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Hydrogenation of
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Effect of Ni Loading and Reaction Conditions on Partial Oxidation of Methane to Syngas
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 12(2003)205 209 Effect of Ni Loading and Reaction Conditions on Partial Oxidation of Methane to Syngas Haitao Wang, Zhenhua Li, Shuxun Tian School of Chemical Engineering
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 12(2003)205 209 Effect of Ni Loading and Reaction Conditions on Partial Oxidation of Methane to Syngas Haitao Wang, Zhenhua Li, Shuxun Tian School of Chemical Engineering
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Xiufang Chen, Jinshui Zhang, Xianzhi Fu, Markus Antonietti, and Xinchen Wang*
 -Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol Using Hydrogen Peroxide and Visible Light Xiufang Chen, Jinshui Zhang, Xianzhi Fu, Markus Antonietti, and Xinchen Wang* Supporting Information: Synthesis of :
-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol Using Hydrogen Peroxide and Visible Light Xiufang Chen, Jinshui Zhang, Xianzhi Fu, Markus Antonietti, and Xinchen Wang* Supporting Information: Synthesis of :
Developing Carbon Tolerance Catalyst for Dry Methane Reforming
 745 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
745 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Development of New Types of Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Reaction with Nano-Structured Catalysts ナノ触媒を用いた新型フィッシャー トロプシュ合成反応の開発
 Development of New Types of Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Reaction with Nano-Structured Catalysts ナノ触媒を用いた新型フィッシャー トロプシュ合成反応の開発 Jie LI 李杰 Supervisor: Prof. Noritatsu TSUBAKI Tsubaki Laboratory Graduate of
Development of New Types of Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Reaction with Nano-Structured Catalysts ナノ触媒を用いた新型フィッシャー トロプシュ合成反応の開発 Jie LI 李杰 Supervisor: Prof. Noritatsu TSUBAKI Tsubaki Laboratory Graduate of
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Effect of Transition Metal Mixing on Reactivities of Magnesium Oxide for Chemical Heat Pump
 Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, Vol. 40, No. 13, pp. 1281 1286, 2007 Research Paper Effect of Transition Metal Mixing on Reactivities of Magnesium Oxide for Chemical Heat Pump Junichi RYU, Rui
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, Vol. 40, No. 13, pp. 1281 1286, 2007 Research Paper Effect of Transition Metal Mixing on Reactivities of Magnesium Oxide for Chemical Heat Pump Junichi RYU, Rui
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Chemical Reactions and Kinetics of the Carbon Monoxide Coupling in the Presence of Hydrogen
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 11(2002)145 150 Chemical Reactions and Kinetics of the Carbon Monoxide Coupling in the Presence of Hydrogen Fandong Meng 1,2, Genhui Xu 1, Zhenhua Li 1, Pa Du 1 1. State
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 11(2002)145 150 Chemical Reactions and Kinetics of the Carbon Monoxide Coupling in the Presence of Hydrogen Fandong Meng 1,2, Genhui Xu 1, Zhenhua Li 1, Pa Du 1 1. State
Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of Benzene and Toluene with Hydrogen Peroxide in a Bubble Reactor
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Investigations on the effect of reaction parameters over Fe/Cu/K catalyst for the production of selective range of liquid hydrocarbon
 J. Chem. Sci. (2018) 130:64 Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-018-1471-y REGULAR ARTICLE Investigations on the effect of reaction parameters over Fe/Cu/K catalyst for the production
J. Chem. Sci. (2018) 130:64 Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-018-1471-y REGULAR ARTICLE Investigations on the effect of reaction parameters over Fe/Cu/K catalyst for the production
Methylation of benzene with methanol over zeolite catalysts in a low pressure flow reactor
 Catalysis Today 63 (2000) 471 478 Methylation of benzene with methanol over zeolite catalysts in a low pressure flow reactor Moses O. Adebajo, Russell F. Howe, Mervyn A. Long School of Chemistry, University
Catalysis Today 63 (2000) 471 478 Methylation of benzene with methanol over zeolite catalysts in a low pressure flow reactor Moses O. Adebajo, Russell F. Howe, Mervyn A. Long School of Chemistry, University
Synthesis and Alkylation of Phenol over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Group
 Zeolitic Materials, Vol. 3, No. 1, December 2002, 20-28 Synthesis and Alkylation of Phenol over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Group Xingdong Yuan, Hyung Ik Lee, Jin
Zeolitic Materials, Vol. 3, No. 1, December 2002, 20-28 Synthesis and Alkylation of Phenol over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Group Xingdong Yuan, Hyung Ik Lee, Jin
Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Glycerol as a Source for Fuels and Chemicals by Low-Temperature Catalytic Processing Ricardo R. Soares, Dante A. Simonetti, and James A. Dumesic*
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Glycerol as a Source for Fuels and Chemicals by Low-Temperature Catalytic Processing Ricardo R. Soares, Dante A. Simonetti, and James A. Dumesic*
Highly Efficient and Robust Au/MgCuCr 2 O 4 Catalyst for Gas-Phase Oxidation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde
 Highly Efficient and Robust Au/MgCuCr O 4 Catalyst for Gas-Phase Oxidation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde Peng Liu,*, and Emiel J. M. Hensen*, Department of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry, Eindhoven University
Highly Efficient and Robust Au/MgCuCr O 4 Catalyst for Gas-Phase Oxidation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde Peng Liu,*, and Emiel J. M. Hensen*, Department of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry, Eindhoven University
Catalytic performance and characterization of cobalt-nickel nano catalysts for CO hydrogenation
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 31(1), 37-44 (2014) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-013-0186-5 INVITED REVIEW PAPER pissn: 0256-1115 eissn: 1975-7220 Catalytic performance and characterization of cobalt-nickel nano catalysts
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 31(1), 37-44 (2014) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-013-0186-5 INVITED REVIEW PAPER pissn: 0256-1115 eissn: 1975-7220 Catalytic performance and characterization of cobalt-nickel nano catalysts
Supporting Information. SBA-15 Supported Fe, Ni, Fe-Ni Bimetallic Catalysts for Wet Oxidation of Bisphenol-A
 Wet Oxidation of Bisphenol A by Metal Supported SBA-15 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, Vol. 35, No. 12 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.12.xxx Supporting Information SBA-15 Supported Fe, Ni, Fe-Ni
Wet Oxidation of Bisphenol A by Metal Supported SBA-15 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, Vol. 35, No. 12 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.12.xxx Supporting Information SBA-15 Supported Fe, Ni, Fe-Ni
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Amino Acids to Amino Alcohols with Complete Retention of Configuration
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Catalytic Hydrogenation of Amino Acids to Amino Alcohols with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Catalytic Hydrogenation of Amino Acids to Amino Alcohols with
Babak Karimi* and Majid Vafaeezadeh
 Electronic upplementary Material (EI) for RC Advances This journal is The Royal ociety of Chemistry 2013 BA-15 functionalized sulfonic acid confined hydrophobic and acidic ionic liquid: a highly efficient
Electronic upplementary Material (EI) for RC Advances This journal is The Royal ociety of Chemistry 2013 BA-15 functionalized sulfonic acid confined hydrophobic and acidic ionic liquid: a highly efficient
A New Redox Strategy for Low-Temperature Formation of Strong Basicity on Mesoporous Silica
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information A New Redox Strategy for Low-Temperature Formation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information A New Redox Strategy for Low-Temperature Formation
RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION CATALYSTS BY HIGH-THROUGHPUT TECHNIQUE
 Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 93, No. 1, 11 17 (2008) and Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/s11144-008-5155-3 RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION
Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 93, No. 1, 11 17 (2008) and Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/s11144-008-5155-3 RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION
Propylene: key building block for the production of important petrochemicals
 Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Fe/Al 2 O 3 Catalyst with Low Fe Loading: Effect of Reaction Temperature
 , July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Fe/Al 2 O 3 Catalyst with Low Fe Loading: Effect of Reaction Temperature Guida Muala, R. A. Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract The aim of this study
, July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Fe/Al 2 O 3 Catalyst with Low Fe Loading: Effect of Reaction Temperature Guida Muala, R. A. Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract The aim of this study
Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ce 1-x M x O 2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) Solid Solution with Controlled Morphologies
 Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ce 1-x M x O 2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) Solid Solution with Controlled Morphologies Wei-Ta Chen, Kuei-Bo Chen, Ming-Fang Wang, Sheng-Feng Weng, Chi-Shen Lee* and M C. Lin Experimental
Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ce 1-x M x O 2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) Solid Solution with Controlled Morphologies Wei-Ta Chen, Kuei-Bo Chen, Ming-Fang Wang, Sheng-Feng Weng, Chi-Shen Lee* and M C. Lin Experimental
Hydrocarbons from a Renewable Resource with Zeolite Catalyst
 OSAKA GAS FOUNDATION OF INTERNATIONAL CULTURAL EXCHANGE RESEARCH CENTER FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF INDONESIA RESEARCH GRANT PROGRAM FINAL REPORT A Sustainable Production of C 3 Hydrocarbons
OSAKA GAS FOUNDATION OF INTERNATIONAL CULTURAL EXCHANGE RESEARCH CENTER FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF INDONESIA RESEARCH GRANT PROGRAM FINAL REPORT A Sustainable Production of C 3 Hydrocarbons
Co-Ni/Al 2 O 3 catalysts for CO 2 methanation at atmospheric pressure
 Co-Ni/Al 2 O 3 catalysts for CO 2 methanation at atmospheric pressure K. Nifantiev, O. Byeda, B. Mischanchuk, E. Ischenko a Taras Shevchenko National university of Kyiv, Kyiv, Ukraine knifantiev@gmail.com
Co-Ni/Al 2 O 3 catalysts for CO 2 methanation at atmospheric pressure K. Nifantiev, O. Byeda, B. Mischanchuk, E. Ischenko a Taras Shevchenko National university of Kyiv, Kyiv, Ukraine knifantiev@gmail.com
Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether
 Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper Nanostructures for Hydrogen Generation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper
Surface Oxidation Mechanism of Ni(0) Particle Supported on Silica
 Surface Oxidation Mechanism of Ni(0) Particle Supported on Silica Shohei Yamashita, Yusaku Yamamoto, Misaki Katayama, and Yasuhiro Inada Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Life Sciences,
Surface Oxidation Mechanism of Ni(0) Particle Supported on Silica Shohei Yamashita, Yusaku Yamamoto, Misaki Katayama, and Yasuhiro Inada Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Life Sciences,
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Co/SBA-15 CATALYSTS FOR FISCHER-TROPSCH SYNTHESIS ANAS BIN MOHD NAIM
 i SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Co/SBA-15 CATALYSTS FOR FISCHER-TROPSCH SYNTHESIS ANAS BIN MOHD NAIM A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Bachelor of
i SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Co/SBA-15 CATALYSTS FOR FISCHER-TROPSCH SYNTHESIS ANAS BIN MOHD NAIM A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Bachelor of
Effect of metal oxide additives on the properties of
 Effect of metal oxide additives on the properties of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-20 September 2007 Effect of metal oxide additives on the properties of Cu/ZnO/Al 2
Effect of metal oxide additives on the properties of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-20 September 2007 Effect of metal oxide additives on the properties of Cu/ZnO/Al 2
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Gasoline and Diesel Production via Fischer- Tropsch Synthesis over Cobalt based Catalyst
 Gasoline and Diesel Production via Fischer- Tropsch Synthesis over Cobalt based Catalyst N. Choosri, N. Swadchaipong, T. Utistham, and U. W. Hartley Abstract Performance of a cobalt doped sol-gel derived
Gasoline and Diesel Production via Fischer- Tropsch Synthesis over Cobalt based Catalyst N. Choosri, N. Swadchaipong, T. Utistham, and U. W. Hartley Abstract Performance of a cobalt doped sol-gel derived
Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 To cite this article: Norhasyimi Rahmat et al 2016 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 To cite this article: Norhasyimi Rahmat et al 2016 IOP
Controlled Preparation of Co 3 O 2 Nanocomposites for Fischer Tropsch Synthesis
 Catal Lett (2014) 144:516 523 DOI 10.1007/s10562-013-1187-z Controlled Preparation of Co 3 @porous-sio 2 Nanocomposites for Fischer Tropsch Synthesis Rongyong Xie Chunling Wang Lin Xia Hui Wang Tiejun
Catal Lett (2014) 144:516 523 DOI 10.1007/s10562-013-1187-z Controlled Preparation of Co 3 @porous-sio 2 Nanocomposites for Fischer Tropsch Synthesis Rongyong Xie Chunling Wang Lin Xia Hui Wang Tiejun
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2522 Catalyst design for natural-gas upgrading through oxybromination chemistry Vladimir Paunović, Guido Zichittella, Maximilian Moser, Amol P. Amrute, and Javier Pérez-Ramírez* Further
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2522 Catalyst design for natural-gas upgrading through oxybromination chemistry Vladimir Paunović, Guido Zichittella, Maximilian Moser, Amol P. Amrute, and Javier Pérez-Ramírez* Further
Mechanistic Study of Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with C2H5OH and CH3OCH3 over Ag/Al2O3 by in Situ DRIFTS
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF CATALYSIS Volume 27, Issue 11, November 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Chin J Catal, 2006, 27(11): 993 998. RESEARCH PAPER Mechanistic
CHINESE JOURNAL OF CATALYSIS Volume 27, Issue 11, November 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Chin J Catal, 2006, 27(11): 993 998. RESEARCH PAPER Mechanistic
Adsorption Processes. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
HYDROGEN PRODUCTION THROUGH GLYCEROL STEAM REFORMING REACTION USING TRANSITION METALS ON ALUMINA CATALYSTS
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 HYDROGEN PRODUCTION THROUGH GLYCEROL STEAM REFORMING REACTION USING TRANSITION
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 HYDROGEN PRODUCTION THROUGH GLYCEROL STEAM REFORMING REACTION USING TRANSITION
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Robust MOF-derived Cu/SiO 2 Catalyst with Low Copper Loading via Sol-gel Method for the Dimethyl Oxalate Hydrogenation Reaction Run-Ping Ye,,, # Ling Lin, # Chong-Chong
Supporting Information Synthesis of Robust MOF-derived Cu/SiO 2 Catalyst with Low Copper Loading via Sol-gel Method for the Dimethyl Oxalate Hydrogenation Reaction Run-Ping Ye,,, # Ling Lin, # Chong-Chong
NANOSILICEOUS MATRIX FOR DRUG INCAPSULATION
 NANOSILICEOUS MATRIX FOR DRUG INCAPSULATION L. G. HANU 1, A. M. HANU 1, E. POPOVICI 1, G. BURTICĂ 2, D. TIMPU 3 1 Faculty of Chemistry, Univ. Al. I. Cuza, Iaºi 2 University Politehnica, Timiºoara 3 P.
NANOSILICEOUS MATRIX FOR DRUG INCAPSULATION L. G. HANU 1, A. M. HANU 1, E. POPOVICI 1, G. BURTICĂ 2, D. TIMPU 3 1 Faculty of Chemistry, Univ. Al. I. Cuza, Iaºi 2 University Politehnica, Timiºoara 3 P.
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Alternating Chiral Selectivity of Aldol Reactions under the Confined Space
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Alternating Chiral Selectivity of Aldol Reactions under the Confined Space
EFFECT OF MORPHOLOGY OF NANOSTRUCTURED CERIA-BASED CATALYSTS OVER CO, SOOT AND NO OXIDATIONS
 EFFECT OF MORPHOLOGY OF NANOSTRUCTURED CERIA-BASED CATALYSTS OVER CO, SOOT AND NO OXIDATIONS Melodj Dosa, Marco Piumetti, Samir Bensaid, Tahrizi Andana, Debora Fino, Nunzio Russo* melodj.dosa@polito.it
EFFECT OF MORPHOLOGY OF NANOSTRUCTURED CERIA-BASED CATALYSTS OVER CO, SOOT AND NO OXIDATIONS Melodj Dosa, Marco Piumetti, Samir Bensaid, Tahrizi Andana, Debora Fino, Nunzio Russo* melodj.dosa@polito.it
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. especially in last 50 years. Industries, especially power industry, are the large anthropogenic
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The concentration of CO 2 in atmosphere has increased considerably in last 100 years, especially in last 50 years. Industries, especially power industry, are the large anthropogenic
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction The concentration of CO 2 in atmosphere has increased considerably in last 100 years, especially in last 50 years. Industries, especially power industry, are the large anthropogenic
A method for the Regeneration of used Fe-ZSM5 Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET1021175 1045
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET1021175 1045
Catalytic activity of liquid phase prepared Cu-Zn-Al catalyst for CO hydrogenation in a fixed bed reactor
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 51A, December 2012, pp. 1663-1668 Catalytic activity of liquid phase prepared Cu-Zn-Al catalyst for CO hydrogenation in a fixed bed reactor Chunhui Luan a, b, Anrong Zhang
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 51A, December 2012, pp. 1663-1668 Catalytic activity of liquid phase prepared Cu-Zn-Al catalyst for CO hydrogenation in a fixed bed reactor Chunhui Luan a, b, Anrong Zhang
Determination of Metal Dispersion of Pt/CeO2 Catalyst by CO-pulse Method
 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 48, (3), 173 177 (2005) 173 [Research Note] Determination of Metal Dispersion of Pt/CeO2 Catalyst by CO-pulse Method Shin ichi KOMAI 1), Yoshiteru YAZAWA 1), Atsushi
Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 48, (3), 173 177 (2005) 173 [Research Note] Determination of Metal Dispersion of Pt/CeO2 Catalyst by CO-pulse Method Shin ichi KOMAI 1), Yoshiteru YAZAWA 1), Atsushi
Quantification of silanol sites for the most. common mesoporous ordered silicas and. organosilicas: total versus accessible silanols.
 Quantification of silanol sites for the most common mesoporous ordered silicas and organosilicas: total versus accessible silanols. Matthias Ide a, Mohamad El-Roz b, Els De Canck a, Aurélie Vicente b,
Quantification of silanol sites for the most common mesoporous ordered silicas and organosilicas: total versus accessible silanols. Matthias Ide a, Mohamad El-Roz b, Els De Canck a, Aurélie Vicente b,
The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 261-268 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS D. A. BAISEITOV, SH. E. GABDRASHOVA, A. K. AKYLBAI,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 261-268 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS D. A. BAISEITOV, SH. E. GABDRASHOVA, A. K. AKYLBAI,
Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: HYD Lecture 08. Composite Membranes
 Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells HYD7007 01 Lecture 08. Composite Membranes Dept. of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Spring, 2011 Prof. David
Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells HYD7007 01 Lecture 08. Composite Membranes Dept. of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Spring, 2011 Prof. David
Methane production from CO2 over Ni-Hydrotalcite derived catalysts
 Methane production from CO2 over Ni-Hydrotalcite derived catalysts Keerthivarman Veerappanchatram Kaliappan vkkeerthivarman@gmail.com Instituto Superior Tecnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal. October
Methane production from CO2 over Ni-Hydrotalcite derived catalysts Keerthivarman Veerappanchatram Kaliappan vkkeerthivarman@gmail.com Instituto Superior Tecnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal. October
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core
 A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoporous Carbon Materials; The Effect of Surfactant Concentrations and Salts
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(1), 196-200 Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoporous Carbon Materials; The Effect of Surfactant Concentrations and Salts
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(1), 196-200 Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoporous Carbon Materials; The Effect of Surfactant Concentrations and Salts
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012254 TITLE: Fabrication of Metal Nanostructures in Mesoporous Silicas DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012254 TITLE: Fabrication of Metal Nanostructures in Mesoporous Silicas DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid
 Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation
 S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
NEW ROUTES FOR IMPROVING HYDROTHERMAL STABILITY OF ORDERED MESOPOROUS MATERIALS AND SYNTHESIS OF MESOPOROUS ZEOLITES
 NEW ROUTES FOR IMPROVING HYDROTHERMAL STABILITY OF ORDERED MESOPOROUS MATERIALS AND SYNTHESIS OF MESOPOROUS ZEOLITES FENG-SHOU XIAO College of Chemistry. Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China In comparison
NEW ROUTES FOR IMPROVING HYDROTHERMAL STABILITY OF ORDERED MESOPOROUS MATERIALS AND SYNTHESIS OF MESOPOROUS ZEOLITES FENG-SHOU XIAO College of Chemistry. Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China In comparison
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Zn-MCM-48 Supporting Hydrated Dibromodioxomolybdenum(Ⅵ) for Facile Conversion of Methane to Methyl Oxygenated Products Fengbo Li, Guoqing Yuan*
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Zn-MCM-48 Supporting Hydrated Dibromodioxomolybdenum(Ⅵ) for Facile Conversion of Methane to Methyl Oxygenated Products Fengbo Li, Guoqing Yuan*
Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity
 1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
Figure S1 XRD patterns of (a) Ti-MSE-A, (b) Ti-MSE-A-cal, (c) TS-1, (d) Ti-MWW, and (e) Ti-BEA.
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug Delivery
 Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
