C-H Bond Activation Using Homogeneous Transition Metal Catalysts
|
|
|
- Adele Pope
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C- Bond Activation Using omogeneous Transition tal Catalysts Kevin Campos March 1, 1996 Reviews: R. Bergman, Acc. Chem. Res., 1995, 28, 154 R. Crabtree, Chem. Rev., 1985, 245 M. Brookhart, J. rganomet. Chem., 1983, 250, /29/96 4:25 PM
2 Some Interesting Early Examples Co 2 (C) 8, 238 C, C Ph S. oriie,bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1960, 23, 247 i(cp) 2, 135 C i Ph Cp J. Kilman, M. ubeck, JACS 1963, 85, /29/96 4:30 PM
3 Early Examples of xidative Addition P 2 P 2 P Ru 2 P Ru 2 P P2 2 P P2 d 8, 16 e - d 6, 18 e - P 2 P 2 2 P Ru 2 P Ru 2 P P2 2 P P2 J. Chatt, J. avidson, JCS 1965, 843 P 2 P Ru 2 P = P2 2 P P 2 P Ru Ru 2 P P P2 P 2 P 2 Intramolecular cyclometallated product determined to be a dimer by X-ray crystallography F. Cotton, JCS CC, 1974, /29/96 4:32 PM
4 Intramolecular C- Bond Activation PPh 3 Cl d 8, 16 e -, C 6 12 Cl PPh 2 d 6, 18 e - M. Bennet, JCS CC 1967, 581 Et 3 P Et 3 P Pt C 2 C 3 C 2 C 3 - C 4 Et 3 P Et 3 P d 8, 16 e - d 8, 16 e - Pt G.M. Whitesides, rganomet. 1982, 1, 13 Cl d 6, 18 e - t-bu P P t-bu t-bu t-bu Et t-bu P P t-bu Cl t-bu t-bu d 6, 16 e t-bu P P t-bu Cl t-bu t-bu d 8, 16 e - C. Crocker, JCS CC 1979, 498 (PPh 3 ) 3 (d 8, 16 e - ) TF, - 2 PPh 2 C 3 PPh 2 P h2 P PPh /29/96 5:07 PM PPh 3 d 8, 16 e - Cl Cl Ph 2 P PPh 2 3 C PPh 3 d 6, 18 e -. Milstein, ature, 1993, 364, 699
5 Intramolecular C- Bond Activation C- agostic interaction observed in X-ray structure of iridium-methylquinoline complex: (cod)(pph 3 ) 2 d 8, 16 e - C 3 2, 25 C C PPh 3 2 d 6, 18 e - R. Crabtree, Inorganic Chem 1985, 24, 1986 xidative addition was observed in X-ray structure when benzoquinoline was used: (cod)(pph 3 ) 2 2, 25 C 2 PPh 3 d 6, 18 e - R. Crabtree, JCS CC 1985, /29/96 5:15 PM
6 Potential ifficulties in Intermolecular C- Bond Activation Cp 2 W 2 d 2, 18 e - hυ, C 6 6 Cp 2 W Cp 2 W(Ph)() d 4, 16 e - d 2, 18 e - Cp 2 W 2 hυ 4 Si Cp W W Cp C 2 Si 3 Cp 2 W 2 hυ Alkanes Cp W W Cp xidative addition into a variety of aryl C- bonds was observed Stronger C- bonds were unreactive, causing oxidative additon into Cp- Green, JCS CC 1972, 1114 Green, JCS alton Trans. 1979, /29/96 5:18 PM
7 ehydrogenation of Alkanes Transfer dehydrogenation of alkanes: 2 S 2 (PPh 3 ) t-bu L L d 7, 19 e - d 7, 19 e t-bu C 3 R.. Crabtree, JACS 1979, 101, 7738 R.. Crabtree, JACS 1982, 104, 6994 Catalytic dehydrogenation of alkanes: hυ, 7 days! 2 (F 3 CC 2 )(PCy 3 ) mol% PCy 3 F 3 C PCy 3 hυ F 3 C PCy 3 PCy 3 d 6, 18 e - d 8, 16 e - Reaction may proceed via coordinatively unsaturated iridium complex 07 2/29/96 5:22 PM R.. Crabtree, JCS CC 1985, 1829 R.. Crabtree, JACS 1987,109, 8025
8 σ-bond tathesis Proposed for Some rganolanthanide Complexes C 2 -C 4 C 4 Lu * Lu C 3 * C 4 C 4 Lu * C 3 3 C 3 C Lu Lu 3 C C * * 3 ther straight-chain alkanes were also added, but quickly decomposed to yield the alkene and metal hydride 08 2/7/96 11:22 PM G.Parshall, P. Watson, Acc. Chem. Res. 1985, 18, 51
9 Intermolecular xidative Additions via Photochemically Induced Complex [( 5 C 5 ) Cl 2 ] 2 1) PPh 3 2) LiEt 3 B hυ, C 6 6 hυ, C 3 C Ph 2 P R. Bergman, JACS 1982, 104, P hυ 3 P d6, 18 e - d8, 16 e - 2 radiation to coordinatively unsaturated complex 09 2/8/96 8:13 AM Similar photolysis/oxidative addition has been reported for Cp * (C) 2 - W. Graham, JACS 1982, 104, 3723
10 chanistic Studies [( 5 C 5 ) Cl 2 ] 2 1) P 3 2) LiEt 3 B 3 P hυ, R- R R = Ph, c-ex, neopentyl Characterization of complexes by MR -18 ppm) and mass spectrometry Ruling out Free Radical chanisms:. R + Cp*(PR 3 ) 2. + R Cp*(PR 3 ) Cp*(PR 3 ) R. Cp*(PR 3 )()(R). o () exchange observed between iridium-hydride and C P hυ, C 6 12 C 6 11 R. Bergman, JACS 1983, 105, /29/96 6:47 PM
11 chanistic Studies: Lending Proof Against a Free Radical chanism Cp*(PR 3 ). Cp*(PR 3 ) 2 R + Cp*(PR 3 ) Cp*(PR 3 ) + R R +. Cp*(PR 3 ) Cp*(PR 3 )()(R) idium complex reacts three times as fast with Ar- than with Ar-C 3 3 P hυ C 3 3 C C 3 2 C C 3 3 C 5.5 : /29/96 6:48 PM R. Bergman, JACS 1982, 104, 352
12 chanistic Studies: Lending Proof Against a Free Radical chanism Ruling out Free Radical chanisms: Cp*(PR 3 ). R + Cp*(PR 3 ) 2 + R Cp*(PR 3 ) Cp*(PR 3 ). R + Cp*(PR 3 ) Cp*(PR 3 )()(R) o crossover observed between deuterated and non-deuterated hydrocarbons 3 P hυ Cyclohexane-d 12 (C 3 ) 4 C 3 P C 2 C(C 3 ) P C 6 11 R. Bergman, JACS 1983, 105, /8/96 8:34 AM
13 Relative Rates of Reaction with Various ydrocarbons 3 P hυ, R- R ydrocarbon Benzene Cyclopropane Cyclopentane eopentane Cyclohexane Cyclodecane Cyclooctane Ethylene Propane (1 :2 ) Pentane (1 :2 ) Rel. Rate () : 1 10 : 1 Rel. Rate () : 1 59 : 1 R. Bergman, JACS 1983, 105, /8/96 8:38 AM
14 Little Kinetic Selectivity, But igh Thermodynamic Selectivity 3 P hυ C 5 12, 6 C Cp * Cp * 110 C / C 5 12 R. Bergman, JACS 1983, 105, /8/96 8:40 AM
15 We Can Activate the C- Bond, But Can We Functionalize the Alkane? 3 P hυ, R- R CBr 3 Br R gcl 2 RBr Br 2 RgCl Br Cl R. Bergman, JACS 1983, 105, /29/96 5:23 PM
16 Can We Activate thane? xidative Additon Reversible at 140 C: 3 P C K eq = P + Applications Towards Activation of thane: 3 P 20 atm C 4 c-c 8 16, 145 C 3 P C 3 Thermodynamic sink R. Bergman, Science 1984, 223, /8/96 8:47 AM
17 Similar Chemistry bserved With odium 3 P hυ, R- CBr 3 Br 2 R Br R Br Br RBr The Advantages igher selectivities for 1 vs 2 C- bonds observed irect conversion to alkylhalides from haloalkyl complexes by treatment with Br 2 The isadvantages ydridoalkyl complexes only stable at temperatures below -20 C 17 2/8/96 8:55 AM R. Bergman, Pure & Appl. Chem. 1984, 56, 13
18 An Interesting () Exchange bserved in Alkyliridiumdeuterides 130 C C 6 6, + euterium exchange was observed between hydride position and α-position of cyclohexane As the reaction progressed, the rate of combined disappearance of cyclohexyl complexes decreased For reductive elimination, k obs (C 6 11 ) / k obs (C 6 11 ) = 0.7 (Inverse Isotope effect) Similar scrambling was observed in hydridomethyl iridium complex 18 2/8/96 9:12 AM R. Bergman, JACS 1986, 108, 1537
19 Inverse Isotope Effect? PPh 3 PPh 3 k 2 C 6 6 Reductive elimination/oxidative addition consistent with observed kinetic data except for inverse isotope effect Intermediate σ-complex postulated to explain both inverse isotope effect A deuterium exchange Inverse isotope effect observed for various alkyl/aryl hydride complexes 19 2/8/96 9:21 AM W.. Jones, JACS 1985, 107, 620 J. orton, JACS 1989, 111, eineky, JACS 1989, 111, 5502 R. Bergman, JACS 1986, 108, 1537
20 Attempts to Identify the Intermediate in α-c- Exchange 2 : 1 mixture of diastereomers at rhodium at -60 C -50 C 2 : 1 mixture of diastereomers retained! -30 C 1 : 1 mixture of diastereomers obtained after equilibration Proposed explanation for stereospecific exchange R. Bergman, JACS 1986, 108, /8/96 9:31 AM
21 Can We bserve β-c- Exchange? * C 3-80 C * C 3-30 C C 2 * -80 C * C 3-30 C C 2 * C 2 * Reactions run at 0.025M in toluene-d 8 Perdeuterated ethyl deuteride complex was doped with ethane in toluene-d 8 to show no ethyl hydride Perdeuterated ethyl deuteride complex and ethyl hydride complex mixed together showed no crossover products 21 2/8/96 9:43 AM R. Bergman, JACS 1986, 108, 7332
22 Transient tal-alkane σ-complex bserved Using IR Flash Kineitc Spectroscopy C C hυ, Kr K C Kr C 4 C C 3 I.R. C cm -1 σ-complex 1946 cm -1 C C cm -1 C C hυ, Kr K C Kr C(C 3 ) 4 C 1946 cm -1 σ-complex 1947 cm -1 C(C 3 ) 3 C C(C 3 ) cm -1 tal-alkane intermediate grows at a rate equal to the decay of the metal-krypton complex Intermediate decays at a rate equal to the decay of the metal-krypton complex and growth of the product k / k = 25 C for oxidative addition K eq () / K eq () = 0.1 Similar results observed for cyclohexane-d 0, d /29/96 5:44 PM R. Bergman, JACS 1994, 116,
23 C- Bond Activation of Alkenes C 2 C=C 2 C 2 C 2 2 C 66 : 34 C C Benzene C 2 2 C 66 : 34 represents a kinetic product ratio of coordinatively unsaturated iridium complex with ethylene η 2 -ethylene complex is thermodynamic product of the reaction η 2 -ethylene complex cannot be an intermediate to the formation of the C- inserted complex The reaction proceeds without reversion to ethylene and the reactive iridium intermediate The η 2 -ethylene complex and the C- inserted complex are formed through unique transition states Interconversion between the two complexes proceeds through a third unique transition state 23 2/8/96 9:51 AM R. Bergman, JACS 1985, 107, 4581
24 Similar Kinetic Results Were bserved with ther tal Systems Re PPh 3 d 6, 18e - hυ, 20 C PPh 3 10 : 1 Re 2 C=C 2 d 4, 16e - C 2 Equilibration at 30 C Re 2 C d 6, 16e - C 2 R. Bergman, JACS 1986, 108, P 2 P P 2 Fe P 2 hυ, 80 C 2 C=C 2 2 P 2 P P 2 Fe C 2 P 2 9 : 1 2 P 2 P P 2 Fe P 2 C 2 C 2 d 6, 18e - d 6, 18e - d 8, 18e - Equilibration at 30 C M. Baker, L. Field, JACS 1986, 108, /29/96 5:43 PM
25 Two istinct chanisms are Proposed C 2 C 2 C C C 2 C 2 C 2 2 C C 2 C R. Bergman, JACS 1985, 107, /8/96 10:21 AM
26 Isotope Studies to efine chanism 2 C=C 2 k / k = C=C 2 () C 2 ( 2 ) () k / k = 1.38 (Cyclohexane) k / k = 1.05 (Benzene) 2 C=C 2 k / k = C=C 2 C 2 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 2 C 2 C=C 2 C 2 vs C 2 k / k = 1.20 R. Bergman, JACS 1988, 110, /8/96 10:26 AM
27 Revised chanism Based on Isotope Studies C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 2 C R. Bergman, JACS 1988, 110, /8/96 10:29 AM
28 An Interesting Contrast to Bergman's Ethylene Activation Studies [1,2] shift observed in rhodium aryl hydride complex: -13 C k / k = 0.37 W. Jones, JACS 1984, 106, /8/96 10:32 AM
29 η 2 - Arene Postulated as the Intermediate in Aryl- xidative Addition Two examples of an η 2 -arene-metal complex C 7 13 t-bu -20 C t-bu t-bu t-bu -12 C C 6 6 Proposed mechanism for Ar- activation based on experimental results: C 6 5 W. Jones, JACS 1984, 106, /8/96 10:39 AM
30 Isotope Studies Lend Proof Toward an η 2 -Arene Intermediate hυ, 10 C C 6 6, C 6 6 C k /k = 1.05 C 6 5 hυ, -40 C + k /k = 1.4 () 51.2 C, C () k /k = /8/96 10:44 AM W. Jones, JACS 1986, 108, 4814
31 C- Activation Using Imidozirconocene Complexes Zr t-bu Ph- Zr t-bu Ph (t-bu) 3 Si (t-bu) 3 Si d 0, 16 e - d 0, 16 e - Zr Si(t-Bu) 3 C 6 6 R. Bergman, JACS, 1988, 110, 8729 (t-bu) 3 Si Zr Si(t-Bu) 3 (t-bu) 3 Si C 6 5 C 4, 3 atm, C 6 12 (t-bu) 3 Si (t-bu) 3 Si Zr Si(t-Bu) Zr 3 (t-bu) 3 Si C (t-bu) 3 Si C C 3 Si(t-Bu) 3 Extrusion of alkane correlates with C- bond strength k (C 3 ) / k ( 3 /C 3 = 7.3), k (C 3 ) / k ( 3 /C 3 ) = 1.32 thane binding not detected in this system Standard β-elimination mechanism? C. Cummins, P. Wolczanski, JACS 1988, 110, 8731 C. Cummins, P. Wolczanski, JACS 1991, 113, 2985 P. Wolczanski, JACS 1994, 116, /29/96 5:50 PM
32 Intermolecular ydroacylation: C- Bond Activation / C-C Bond Formation 3 P Cl 3 P P 3 d 8, 16 e - 3 P 3 P 3 P P Cl 3 3 P Cl d 6, 18 e - d 6, 18 e - 3 P 3 P Cl d 6, 18 e - Sakai, Tet. Lett. 1972, Milstein, JCS CC, 1982, 1357 C C, C 2 4 (1000 psi). Milstein, rganomet., 1988, /29/96 6:03 PM
33 C- Bond Activation Using omogeneous Transition tal Catalysts R (S-Binap)(B) Cl 4, 2 5 min. C 2 Cl 2 or Acetone R R e.e. Ph t-bu 3 Si C(C 3 ) 2 PhC() t-buc() EtC() t-bu vs Favored t-bu isfavored B. Bosnich, JACS, 1994, 116, /29/96 6:06 PM
34 irected Functionalization of Aromatic C- Bonds Using Catalytic Ruthenium R 2 R 1 C Ru PPh 3 Toluene reflux 2-5 mol % R 2 Ru R 1 Y R 2 R % yld Y Si(Et) 3 C 3 C 3 Si(Et) 3 C 3 Si(Et) 3 S Si(Et) 3 Si(Et) 3 Murai, ature, 1993, 366, /8/96 11:02 AM
35 Shinji Murai oes It Again Ru 3 (C) 12 Toluene, 20 atm C 160 C, 20 h (C) 3 Ru (C) 4 Ru Ru(C) 3 Y R 42-95% yld 99:1 regioselectivity Ph Ph t-bu t-bu Murai, JACS, 1996, 118, /8/96 11:57 AM
36 Trends in the (II) Catalyzed C- Insertion Y 2 Y Y C 3 C 3 C 3 R 1 R 1 R 1 2 (X) 4 R 1 Y Ratio 2 (Ac) 4 2 (Ac) 4 2 (Cap) 4 2 (Ac) 4 2 (Cap) 4 Ac : 1 1 : 8 1 : 30 1 : : > 2 ~ Ar- > 1 Alkyl > allyl ~ aryl C- α to heteroatoms are activated towards C- insertion C- α and β to electron withdrawing groups are deactivated towards C- insertion More hindered sites undergo slower rates of C- insertion The reaction proceeds with retention of configuration at the reacting site Five-member rings are preferentially formed More basic ligands on rhodium will increase the afformentioned selectivity 36 2/9/96 10:49 AM J. Adams, Tet. Letters, 1989, 30, 1749 G. Stork, Tet. Letters, 1988, 29, 2283 M. oyle, Tet. Letters, 1989, 30, 7001 J. Adams, JACS, 1994, 116, 3296
37 chanism of (II) Catalyzed C- Insertion C 3 C 3 C 3 R E 3 C C 3 C 3 R E + 2 C 3 II Ac C 3 II R E II Ac C 3 C 3 III C 3 I 3 C C 3 III C 3 C 3 C 3 R E E III Ac R C 3 C 3 III R - E III Ac C 3 C 3 III 37 2/9/96 5:27 PM Speculation by K. Campos based on J. Adams, Tetrahedron, 1991, 47, 1765
38 C- Insertion Reactions: Applications to Synthesis C 2 C 3 C 3 (II) cat. C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 2 2 (Ac) 4 C 3 1) LA 2) I C 3 3 C 1) Ts 2 2) C 3 Li C 3 3 C (+)-albene C 3 3 C 1) 2 C 3 2) PCl 2) i-pr-br, PPh 5 3 C 1) ibal C 3 (-)-β-santalene. Sonawa, J. rg. Chem. 1991, 56, /8/96 9:19 PM
39 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: Applications to Synthesis endrobatid Alkaloid (251F) 3 C C 3 octanoate (cat.) 2 C 2 C 3 2 C 3 C C 3 C 3 1) LiAl 4 2) a, BnBr 3) +, 2 4) TsCl, pyr. Bn Ts C 3 Et 2 C C 3 K 2 C 3, Toluene cat. Bu 4 I, 66% 3 C C 3 3 C 3 C C 2 Et Bn 1) BsCl 2) LiMS 53% C 2 Et C 3 Bn 1) LiAl 4 2) PhSSPh / PPh 3 3) a / 3 66% C 3 C 3. Taber, JACS, 1995, 5757 C /9/96 10:56 AM Some insight on the stereochemical outcome. Taber, JACS, 1996, 118, 547
40 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: Synthesis of ibenzylbutyrolactone Lignans 2 C 2 R C 2 Cl 2 R = Et Bn R 91% e.e. 89% e.e. 87% e.e. M. oyle, JACS 1991, 113, 8982 Ph 2 2 C C 2 Cl 2 63% yld. 93% e.e. (-) - enterolactone M. oyle, J. rg. Chem. 1995, 60, /9/96 5:00 PM
41 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: Synthesis of eoxyxylolactone 2 C 2 Bn Bn mol%, C 2 Cl % Bn Bn Bn Bn 93% 7% 94% e.e. 45% e.e. R R vs R Favored R isfavored Postulated Conformation Leading to bserved Product 41 2/9/96 5:29 PM M. oyle, A. yatkin, J. Tedrow, Tet. Letters, 1994, 35, 3853
42 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: More oyle Results A 2 C 2 C 2 Cl 2 A= C 2 C()C 3 55% (96% e.e.) 75% (97% e.e.) 99% (97% e.e.) 45% (95% e.e.) 25% (91% e.e.) 1% (65% e.e.) vs Favored isfavored Postulated Conformation Leading to bserved iastereomer 42 2/9/96 5:30 PM M. oyle, JACS 1994, 116, 4507
43 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: ouble Stereodifferentiation bserved A 2 C 2 C 2 Cl 2 A= C 2 C()C 3 99% (98% e.e.) 98% (98% e.e.) 99% (98% e.e.) <1% 2% (84% e.e.) <1% A 2 C 2 C 2 Cl 2 A= C 2 C()C 3 10% (68% e.e.) 15% (82% e.e.) 63% (93% e.e.) 90% (95% e.e.) 85% (91% e.e.) 37% (57% e.e.) 43 2/9/96 5:56 PM M. oyle, JACS 1994, 116, 4507
44 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: More oyle Results vs Very Favored Very isfavored The Matched Case vs isfavored Favored The Mismatched Case 44 2/9/96 5:46 PM M. oyle, JACS 1994, 116, 4507
45 Asymmetric C- Insertion Reactions: Insertion α to itrogen 2 2 (5S-MEPY) 4 C 2 Cl 2, 67% 97% e.e. M. oyle C 2 C 3 2 C 3 C 3 3 C C 3 R CuTf C 2 Cl 2 R C 2 C 3 A C 3 C 3 C 2 C 3 B C 3 C 3 Catalyst 2 (Ac) 4 2 (5(S)-MEPY) 4 CuTf, R = ipr CuTf, R = t-bu CuTf, R = Ph %A (trans : cis) 50% (3:1) 38% (5:95) 33% (1:1) 33% (9:1) 33% (13:1) %B (trans : cis) 50% (10:1) 62% (5:95) 67% (2:1) 67% (1:1) 67% (1:2) 45 2/9/96 4:54 PM G. Sulikowski, J. rg. Chem. 1995, 60, 2326
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst
 Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
Electrophilic Carbenes
 Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY )
 CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
Direct, Catalytic Hydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated Olefins with N-Alkyl Arylamines
 Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Sp 3 C-H Bond Activation Catalyzed by Transition Metal. Reporter: Wan Xiaobing Supervisor: Prof. Shi Zhangjie
 Sp 3 C- Bond Activation Catalyzed by Transition Metal Reporter: Wan Xiaobing Supervisor: Prof. Shi Zhangjie Academic: high bond energy Practical: abundant, cheap, clean 2 hv C n 2n+2 Cl 2 C n 2n+2-m Cl
Sp 3 C- Bond Activation Catalyzed by Transition Metal Reporter: Wan Xiaobing Supervisor: Prof. Shi Zhangjie Academic: high bond energy Practical: abundant, cheap, clean 2 hv C n 2n+2 Cl 2 C n 2n+2-m Cl
Strained Molecules in Organic Synthesis
 Strained Molecules in rganic Synthesis 0. Introduction ~ featuring on three-membered rings ~ Tatsuya itabaru (M) Lit. Seminar 08068 for cyclobutadienes : see Mr. Yamatsugu's Lit. Sem. 069 eat of Formation
Strained Molecules in rganic Synthesis 0. Introduction ~ featuring on three-membered rings ~ Tatsuya itabaru (M) Lit. Seminar 08068 for cyclobutadienes : see Mr. Yamatsugu's Lit. Sem. 069 eat of Formation
Functionalization of terminal olefins via H migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence Hydrogenation
 M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting Timothy Chang
 Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions
 Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Chem 253 Problem Set 7 Due: Friday, December 3, 2004
 Chem 253 roblem Set 7 ue: Friday, ecember 3, 2004 Name TF. Starting with the provided starting material, provide a concise synthesis of. You may use any other reagents for your synthesis. It can be assumed
Chem 253 roblem Set 7 ue: Friday, ecember 3, 2004 Name TF. Starting with the provided starting material, provide a concise synthesis of. You may use any other reagents for your synthesis. It can be assumed
VI. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion
 V. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion A. Carbonylation - C insertion very facile, metal acyls easily cleaved, all substrates which undergo oxidative addition can in principle be carbonylated.
V. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion A. Carbonylation - C insertion very facile, metal acyls easily cleaved, all substrates which undergo oxidative addition can in principle be carbonylated.
Rhodium Carbenoids and C-H Insertion
 hodium Carbenoids and C- Insertion Literature Talk Uttam K. Tambar March 1, 2004 8pm, oyes 147 h h h h h h irreversible reversible carbenoid 2 h2l4 1 h2l4 or h2l4 2 utline I. What is a Carbene? II. What
hodium Carbenoids and C- Insertion Literature Talk Uttam K. Tambar March 1, 2004 8pm, oyes 147 h h h h h h irreversible reversible carbenoid 2 h2l4 1 h2l4 or h2l4 2 utline I. What is a Carbene? II. What
Radical Reactions. Radical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X + Y. bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 95 O H R 2 C H
 adical eactions adical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X Y bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) C 3 104 108 C 3 C 2 98 110 95 2 C 102 (-) 93 (C-) 92 C 3 C 3 36 89 85 C 3 C 3 80 adical eactions
adical eactions adical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X Y bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) C 3 104 108 C 3 C 2 98 110 95 2 C 102 (-) 93 (C-) 92 C 3 C 3 36 89 85 C 3 C 3 80 adical eactions
Oxidative Addition and Reductive Elimination
 xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
Transition Metal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation
 literature seminar 2 H. Mitsunuma(M1) 2010/09/08 Transition tal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation 0. Introduction Currently, selective C-H and C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes has
literature seminar 2 H. Mitsunuma(M1) 2010/09/08 Transition tal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation 0. Introduction Currently, selective C-H and C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes has
Some Hartwig Chemistry Experimental Approaches and Detailed Mechanistic Analysis
 Some artwig Chemistry Experimental Approaches and Detailed chanistic Analysis b. 1964 1986 A.B. Princeton U, Maitland Jones 1990.D. UC Berkeley, obert Bergman and ichard Anderson 1990-92 Post-doc, MIT,
Some artwig Chemistry Experimental Approaches and Detailed chanistic Analysis b. 1964 1986 A.B. Princeton U, Maitland Jones 1990.D. UC Berkeley, obert Bergman and ichard Anderson 1990-92 Post-doc, MIT,
Reductive Elimination
 Reductive Elimination Reductive elimination, the reverse of oxidative addition, is most often seen in higher oxidation states because the formal oxidation state of the metal is reduced by two units in
Reductive Elimination Reductive elimination, the reverse of oxidative addition, is most often seen in higher oxidation states because the formal oxidation state of the metal is reduced by two units in
Total Synthesis of (+/-)-Goniomitine via a Formal Nitrile/Donor-Acceptor Cyclopropane [3 + 2] Cyclization
![Total Synthesis of (+/-)-Goniomitine via a Formal Nitrile/Donor-Acceptor Cyclopropane [3 + 2] Cyclization Total Synthesis of (+/-)-Goniomitine via a Formal Nitrile/Donor-Acceptor Cyclopropane [3 + 2] Cyclization](/thumbs/82/85235286.jpg) Total Synthesis of (+/-)-Goniomitine via a Formal itrile/donor-acceptor Cyclopropane [3 + 2] Cyclization (-)-Goniomitine Christian L. Morales and Brian Pagenkopf* rganic Letters, ASAP Current Literature
Total Synthesis of (+/-)-Goniomitine via a Formal itrile/donor-acceptor Cyclopropane [3 + 2] Cyclization (-)-Goniomitine Christian L. Morales and Brian Pagenkopf* rganic Letters, ASAP Current Literature
Direct Oxidative Heck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans
 Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
 Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
A Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)-Gonyautoxin 3
 A Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)-Gonyautoxin 3 Mulcahy, J. V.; Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12630-12631 Total Synthesis of (+)-Lithospermic Acid by Asymmetric Intramolecular Alkylation via
A Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)-Gonyautoxin 3 Mulcahy, J. V.; Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12630-12631 Total Synthesis of (+)-Lithospermic Acid by Asymmetric Intramolecular Alkylation via
Highlights of Schmidt Reaction in the Last Ten Years
 ighlights of Schmidt eaction in the Last Ten Years Dendrobates histrionicus Jack Liu ov. 18, 2003 Introduction Classical Schmidt reaction of aldehydes and carboxylic acids Classical Schmidt reaction of
ighlights of Schmidt eaction in the Last Ten Years Dendrobates histrionicus Jack Liu ov. 18, 2003 Introduction Classical Schmidt reaction of aldehydes and carboxylic acids Classical Schmidt reaction of
Repeated insertion. Multiple insertion leads to dimerization, oligomerization or polymerization. κ 1: mainly dimerization κ
 Repeated insertion ultiple insertion leads to dimerization, oligomerization or polymerization. k prop Et Key factor: k CT / k prop = κ κ 1: mainly dimerization κ 0.1-1.0: oligomerization (always mixtures)
Repeated insertion ultiple insertion leads to dimerization, oligomerization or polymerization. k prop Et Key factor: k CT / k prop = κ κ 1: mainly dimerization κ 0.1-1.0: oligomerization (always mixtures)
Problem session (3) Daiki Kuwana. Please fill in the blank and explain reaction mechanisms and stereoselectivities.
 Problem session (3) Daiki Kuwana Please fill in the blank and explain reaction mechanisms and stereoselectivities. 1. 1-1 1. (Ac) 2 (10 mol%), DPEphos (20 mol%) Et 3, toluene, 90 C 2. s 4 (14 mol%), M;
Problem session (3) Daiki Kuwana Please fill in the blank and explain reaction mechanisms and stereoselectivities. 1. 1-1 1. (Ac) 2 (10 mol%), DPEphos (20 mol%) Et 3, toluene, 90 C 2. s 4 (14 mol%), M;
Initials: 1. Chem 633: Advanced Organic Chemistry 2011 Final Exam
 Initials: 1 ame: Chem 633: Advanced rganic Chemistry 2011 Final Exam Please answer the following questions clearly and concisely. In general, use pictures and less than 10 words in your answers. Write
Initials: 1 ame: Chem 633: Advanced rganic Chemistry 2011 Final Exam Please answer the following questions clearly and concisely. In general, use pictures and less than 10 words in your answers. Write
Non-Linear Effects in Asymmetric Catalysis: A Useful Tool in Understanding Reaction Mechanisms. Group Meeting Aaron Bailey 12 May 2009
 Non-Linear Effects in Asymmetric Catalysis: A Useful Tool in Understanding Reaction chanisms Group eting Aaron Bailey 12 May 2009 What is a Non-Linear Effect? In asymmetric catalysis, the ee (er) of the
Non-Linear Effects in Asymmetric Catalysis: A Useful Tool in Understanding Reaction chanisms Group eting Aaron Bailey 12 May 2009 What is a Non-Linear Effect? In asymmetric catalysis, the ee (er) of the
Additions to Metal-Alkene and -Alkyne Complexes
 Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
CEM 852 Final Exam. May 5, 2011
 CEM 852 Final Exam May 5, 2011 This exam consists of 8 pages. Please make certain that your exam has all of the necessary pages. Total points possible for this exam are 150. In answering your questions,
CEM 852 Final Exam May 5, 2011 This exam consists of 8 pages. Please make certain that your exam has all of the necessary pages. Total points possible for this exam are 150. In answering your questions,
Rhodium Catalyzed Alkyl C-H Insertion Reactions
 Rhodium Catalyzed Alkyl C-H Insertion Reactions Rh Rh Jeff Kallemeyn 5/17/05 1. Cyclopropanation The Versatile and Reactive Rhodium Carbene R + Et Rh 2 (Ac) 4 R C 2 Et N 2 2. [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement
Rhodium Catalyzed Alkyl C-H Insertion Reactions Rh Rh Jeff Kallemeyn 5/17/05 1. Cyclopropanation The Versatile and Reactive Rhodium Carbene R + Et Rh 2 (Ac) 4 R C 2 Et N 2 2. [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement
CH 3 TMG, DMF N H 3 CO 2 S. (PPh 3 ) 2 Pd 0
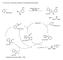 1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
Organocopper Reagents
 rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker Oxidation. Tyler W. Wilson SED Group Meeting
 The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing Oxazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129,
 Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Olefin Metathesis ROMP. L n Ru= ROMP n RCM. dilute
 lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
Insertion Reactions. 1) 1,1 insertion in which the metal and the X ligand end up bound to the same (1,1) atom
 Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Total Syntheses of Minfiensine
 Total Syntheses of Minfiensine Douany, A. B.; umphreys, P. G.; verman, L. E.*; Wrobelski, A. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, ASAP. D: 10.1021/ja800163v Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.*, Angew. Chem. nt.
Total Syntheses of Minfiensine Douany, A. B.; umphreys, P. G.; verman, L. E.*; Wrobelski, A. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, ASAP. D: 10.1021/ja800163v Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.*, Angew. Chem. nt.
Catalytic carbene insertion into C-H H bonds
 Catalytic carbene insertion into C- bonds Reporter: 谢奇强 December 30, 2015 Content 2 Introduction Reaction Mechanism Catalysts and reactions Summary and outlook Introduction 3 Selectivity: Thermally or
Catalytic carbene insertion into C- bonds Reporter: 谢奇强 December 30, 2015 Content 2 Introduction Reaction Mechanism Catalysts and reactions Summary and outlook Introduction 3 Selectivity: Thermally or
Asymmetric Radical Reactions. Zhen Liu 08/30/2018
 Asymmetric adical eactions Zhen Liu 08/30/2018 Contents Introduction eactions Using Chiral Auxiliary Chiral Lewis Acid-diated eactions Transition tal-catalyzed eactions eactions Using Chiral rganocatalysts
Asymmetric adical eactions Zhen Liu 08/30/2018 Contents Introduction eactions Using Chiral Auxiliary Chiral Lewis Acid-diated eactions Transition tal-catalyzed eactions eactions Using Chiral rganocatalysts
O CH 3. Mn CH 3 OC C. 16eelimination
 igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito
 1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014
 sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins, Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014 1) sp 3 C-H Alkylation via Directed C-H activation 2) Hydroaminoalkylation (still via C-H activation) 3) Hydrohydroxyalkylation (via radical chemistry)
sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins, Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014 1) sp 3 C-H Alkylation via Directed C-H activation 2) Hydroaminoalkylation (still via C-H activation) 3) Hydrohydroxyalkylation (via radical chemistry)
Spiro Monophosphite and Monophosphoramidite Ligand Kit
 Spiro Monophosphite and Monophosphoramidite Ligand Kit metals inorganics organometallics catalysts ligands custom synthesis cgm facilities nanomaterials 15-5162 15-5150 15-5156 15-5163 15-5151 15-5157
Spiro Monophosphite and Monophosphoramidite Ligand Kit metals inorganics organometallics catalysts ligands custom synthesis cgm facilities nanomaterials 15-5162 15-5150 15-5156 15-5163 15-5151 15-5157
Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation
 EPFL - ISIC - LSPN Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation History and selected examples The Research of Prof. Michael Krische (University of Texas at Austin) LSPN Group Seminar Mathias Mamboury Table of
EPFL - ISIC - LSPN Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation History and selected examples The Research of Prof. Michael Krische (University of Texas at Austin) LSPN Group Seminar Mathias Mamboury Table of
Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1. Oxidative Addition
 Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
EWG EWG EWG EDG EDG EDG
 Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
Asymmetric Nucleophilic Catalysis
 Asymmetric ucleophilic Catalysis Chiral catalyst X 2 Chiral catalyst X = alkyl, X 1 2 1 Vedejs, E.; Daugulis,. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4166-4173 Shaw, S. A.; Aleman,.; Vedejs, E. J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Asymmetric ucleophilic Catalysis Chiral catalyst X 2 Chiral catalyst X = alkyl, X 1 2 1 Vedejs, E.; Daugulis,. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4166-4173 Shaw, S. A.; Aleman,.; Vedejs, E. J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation with Chiral P,N Ligands
 Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation with Chiral P, Ligands 贾佳 utline Brief Introduction Hydrogenation of C=C Bonds Hydrogenation of C= Bonds Hydrogenation of C= Bonds Conclusion Brief Introduction First example
Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation with Chiral P, Ligands 贾佳 utline Brief Introduction Hydrogenation of C=C Bonds Hydrogenation of C= Bonds Hydrogenation of C= Bonds Conclusion Brief Introduction First example
Elementary Organometallic Reactions
 Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Chiral Bronsted Acids as Catalysts
 Chiral Bronsted Acids as Catalysts Short Literature Seminar 6/3/08 Dustin aup BIL Derived osphoric Acids - First reported in 1992 as a ligand by irrung and coworkers. 4 h 2 irrung Tet. Lett. 1992, 33,
Chiral Bronsted Acids as Catalysts Short Literature Seminar 6/3/08 Dustin aup BIL Derived osphoric Acids - First reported in 1992 as a ligand by irrung and coworkers. 4 h 2 irrung Tet. Lett. 1992, 33,
Copper-Catalyzed Diastereoselective Arylation of Tryptophan Derivatives: Total Synthesis of (+)-
 Literature Report Copper-Catalyzed Diastereoselective Arylation of Tryptophan Derivatives: Total Synthesis of (+)- aseseazines A and B Reporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Zhang-Pei Chen Date: 2013-05-28 Reisman,
Literature Report Copper-Catalyzed Diastereoselective Arylation of Tryptophan Derivatives: Total Synthesis of (+)- aseseazines A and B Reporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Zhang-Pei Chen Date: 2013-05-28 Reisman,
Chem 634. Introduction to Transition Metal Catalysis. Reading: Heg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, , 11.3 Grossman Ch 6
 Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Answers To Chapter 7 Problems.
 Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Organometallic Rections 1: Reactions at the Metal
 E Organometallic Rections 1: Reactions at the Metal Three major classes of reactions: 1 Ligand Substitution associative (cf. S N 2) dissociative (cf. S N 1) interchange (not dealt with in this course)
E Organometallic Rections 1: Reactions at the Metal Three major classes of reactions: 1 Ligand Substitution associative (cf. S N 2) dissociative (cf. S N 1) interchange (not dealt with in this course)
The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: favored. disfavored. favored. disfavored
 The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: Z-enolates: M 2 M 2 syn 2 C 2 favored 2 M 2 anti disfavored E-enolates: M 2 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 favored 2 M M disfavored In
The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: Z-enolates: M 2 M 2 syn 2 C 2 favored 2 M 2 anti disfavored E-enolates: M 2 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 favored 2 M M disfavored In
Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) H Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group
 Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Reductive Elimination from High-Valent Palladium. Kazunori Nagao MacMillan Group Meeting
 Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Hydrogenation Catalysis
 Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Hydrogenation Catalysis Synthesis of Organometallic Complex Hydrides Reaction of MCO with OH -, H -, or CH 2 CHR 2 M(CO) n + OH - = M(CO) n-1 (COOH) - = HM(CO) n-1 -
Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Hydrogenation Catalysis Synthesis of Organometallic Complex Hydrides Reaction of MCO with OH -, H -, or CH 2 CHR 2 M(CO) n + OH - = M(CO) n-1 (COOH) - = HM(CO) n-1 -
Ch.16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Ch.16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution: E + E + + Some electrophilic aromatic substitution: X N 2 S 3 R C R alogenation Nitration Sulfonation
Ch.16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution: E + E + + Some electrophilic aromatic substitution: X N 2 S 3 R C R alogenation Nitration Sulfonation
Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes
![Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes](/thumbs/77/74720708.jpg) Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes Selective Synthesis of Multisubstituted Cycloheptadienes 1 2 Cat. Ni 0 1 2 Komagawa, S.; Saito, S. Angew.
Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes Selective Synthesis of Multisubstituted Cycloheptadienes 1 2 Cat. Ni 0 1 2 Komagawa, S.; Saito, S. Angew.
Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Lessons from Organometallic Chemistry. Lecture 9
 ydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Lessons from Organometallic Chemistry Lecture 9 Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 1: Figure 10.1 2009 W.. Freeman Synthesis of Organometallic Complex ydrides Reaction of MCO
ydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Lessons from Organometallic Chemistry Lecture 9 Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 1: Figure 10.1 2009 W.. Freeman Synthesis of Organometallic Complex ydrides Reaction of MCO
CHEM 153 PRACTICE TEST #1 ANSWER KEY
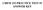 CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
Oxidative Addition oxidative addition reductive elimination
 Oxidative Addition We have seen how neutral ligands such as C 2 H 4 or CO can enter the coordination sphere of a metal by substitution. We now look at a general method for simultaneously introducing pairs
Oxidative Addition We have seen how neutral ligands such as C 2 H 4 or CO can enter the coordination sphere of a metal by substitution. We now look at a general method for simultaneously introducing pairs
Course 201N 1 st Semester Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. Bera
 andout-9 ourse 201N 1 st Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic hemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. Bera ontents 3. rganometallic hemistry xidative Addition, Reductive Elimination, Migratory Insertion, Elimination
andout-9 ourse 201N 1 st Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic hemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. Bera ontents 3. rganometallic hemistry xidative Addition, Reductive Elimination, Migratory Insertion, Elimination
A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
 A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Reporter: Supervisor: Zhe Niu Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 2016/2/3 Content Introduction Intermolecular Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Intramolecular Mizoroki-Heck
A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Reporter: Supervisor: Zhe Niu Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 2016/2/3 Content Introduction Intermolecular Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Intramolecular Mizoroki-Heck
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group.
 Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
Please inquire for pricing and availability of listed products to our local sales representatives.
 lease inquire for pricing and availability of listed products to our local sales representatives. 1 C- Bond Activation Reaction Recently, there have been a large number of reports on C- bond activation
lease inquire for pricing and availability of listed products to our local sales representatives. 1 C- Bond Activation Reaction Recently, there have been a large number of reports on C- bond activation
Reaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. Reactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b.
 eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
 PAGE 1 of 11 UNVESTY F MANTBA DEPATMENT F CEMSTY 2.339 STUCTUAL TANSFMATNS N GANC CEMSTY FNAL EXAMNATN - PAPE # 432 Dr. Phil ultin Friday December 17, 2004. NAME: STUDENT NUMBE: 1. (20 Marks) For each
PAGE 1 of 11 UNVESTY F MANTBA DEPATMENT F CEMSTY 2.339 STUCTUAL TANSFMATNS N GANC CEMSTY FNAL EXAMNATN - PAPE # 432 Dr. Phil ultin Friday December 17, 2004. NAME: STUDENT NUMBE: 1. (20 Marks) For each
Chapter 5 Three and Four-Membered Ring Systems
 Chapter 5 Three and Four-mbered ing ystems 5.1 Aziridines Aziridines are good alkylating agents because of their tendency to undergo ring-opening reaction with nucleophiles 例 mitomycin C antibiotic and
Chapter 5 Three and Four-mbered ing ystems 5.1 Aziridines Aziridines are good alkylating agents because of their tendency to undergo ring-opening reaction with nucleophiles 例 mitomycin C antibiotic and
Chiral Catalyst II. Palladium Catalysed Allylic Displacement ( -allyl complexes) 1. L n Pd(0) 2. Nuc
 Chiral Catalyst II ast lecture we looked at asymmetric catalysis for oxidation and reduction Many other organic transformations, this has led to much investigation Today we will look at some others...
Chiral Catalyst II ast lecture we looked at asymmetric catalysis for oxidation and reduction Many other organic transformations, this has led to much investigation Today we will look at some others...
Catalytic Asymmetric Pauson-Khand Reaction. Won-jin Chung 02/25/2003
 Catalytic Asymmetric Pauson-Khand eaction U. Khand; G.. Knox; P. L. Pauson; W. E. Watts J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1971, 36 Won-jin Chung 02/25/2003 The General Pattern of the Pauson-Khand eaction Co
Catalytic Asymmetric Pauson-Khand eaction U. Khand; G.. Knox; P. L. Pauson; W. E. Watts J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1971, 36 Won-jin Chung 02/25/2003 The General Pattern of the Pauson-Khand eaction Co
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
Studies on Heck and Suzuki Reactions Catalyzed by Palladium(0) and Wacker- Type Oxidative Cyclization Catalyzed by Palladium(II)
 Studies on eck and Suzuki Reactions Catalyzed by Palladium(0) and Wacker- Type xidative Cyclization Catalyzed by Palladium() Zuhui Zhang enmark Group Meeting 10/21/2008 1 Part ne: Palladium(0)-Catalyzed
Studies on eck and Suzuki Reactions Catalyzed by Palladium(0) and Wacker- Type xidative Cyclization Catalyzed by Palladium() Zuhui Zhang enmark Group Meeting 10/21/2008 1 Part ne: Palladium(0)-Catalyzed
Studies of Carbon-Sulfur Bond Cleavage by Homogeneous Transition Metal Complexes
 CE 9421727 William D. Jones Final Report for NF Grant CE-9421727 for the period January 15, 1997-January 14, 1998 (year 3 of 3) tudies of Carbon-ulfur Bond eavage by omogeneous Transition Metal mplexes
CE 9421727 William D. Jones Final Report for NF Grant CE-9421727 for the period January 15, 1997-January 14, 1998 (year 3 of 3) tudies of Carbon-ulfur Bond eavage by omogeneous Transition Metal mplexes
O + k 2. H(D) Ar. MeO H(D) rate-determining. step?
 ame: CEM 633: Advanced rganic Chem: ysical Problem Set 6 (Due Thurs, 12/8/16) Please do not look up references until after you turn in the problem set unless otherwise noted. For the following problems,
ame: CEM 633: Advanced rganic Chem: ysical Problem Set 6 (Due Thurs, 12/8/16) Please do not look up references until after you turn in the problem set unless otherwise noted. For the following problems,
Suggested solutions for Chapter 40
 s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
Chapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM Catalysis
 hapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM atalysis + + ligand exchange A oxidative addition > n + A B n+2 reductive elimination < B n n+2 oxidative coupling + M' + M' transmetallation migratory insertion > (carbo-,
hapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM atalysis + + ligand exchange A oxidative addition > n + A B n+2 reductive elimination < B n n+2 oxidative coupling + M' + M' transmetallation migratory insertion > (carbo-,
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon
 Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Nucleophilic attack on ligand
 Nucleophilic attack on ligand Nucleophile "substitutes" metal hapticity usually decreases xidation state mostly unchanged Competition: nucleophilic attack on metal usually leads to ligand substitution
Nucleophilic attack on ligand Nucleophile "substitutes" metal hapticity usually decreases xidation state mostly unchanged Competition: nucleophilic attack on metal usually leads to ligand substitution
Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines
 Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines Asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis - Chiral (bisooxazoline) copper (II) complexes - Monodentate Lewis acids: the formyl -bond Amine catalysed reactions Asymmetric
Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines Asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis - Chiral (bisooxazoline) copper (II) complexes - Monodentate Lewis acids: the formyl -bond Amine catalysed reactions Asymmetric
Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates. Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02
![Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates. Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02 Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates. Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02](/thumbs/93/114018431.jpg) Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02 Xiao, W.-J. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8360.
Catalytic Asymmetric [4+1] Annulation of Sulfur Ylides with Copper Allenylidene Intermediates Reporter: Jie Wang Checker: Shubo Hu Date: 2016/08/02 Xiao, W.-J. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8360.
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Carbonyl Ylide Cycloadditions
 Carbonyl Ylide Cycloadditions cond. icholas Anderson Denmark Group eting 07/13/10 Carbonyl Ylides Uncharged 1,3-Dipole Conjugated π-system ighly reactive on-isolable Generate in-situ Carbonyl Ylide Stability
Carbonyl Ylide Cycloadditions cond. icholas Anderson Denmark Group eting 07/13/10 Carbonyl Ylides Uncharged 1,3-Dipole Conjugated π-system ighly reactive on-isolable Generate in-situ Carbonyl Ylide Stability
Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysts: Design and Applications. Junqi Li CHEM Sep 2010
 Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysts: Design and Applications Junqi Li CHEM 535 27 Sep 2010 Enzyme Catalysis vs Small-Molecule Catalysis Bronsted acid Lewis acid Lewis acid Bronsted base Activation of both
Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysts: Design and Applications Junqi Li CHEM 535 27 Sep 2010 Enzyme Catalysis vs Small-Molecule Catalysis Bronsted acid Lewis acid Lewis acid Bronsted base Activation of both
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N6 Kashiwa Campus, November 27, 2009 Group VIB: Cr, Mo, W -Oxidation states from -2 to +6 -While +2 and +3 for Cr are quite
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N6 Kashiwa Campus, November 27, 2009 Group VIB: Cr, Mo, W -Oxidation states from -2 to +6 -While +2 and +3 for Cr are quite
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation
 Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation (a) Asymmetric allylic substitution 1 u - d u (b) Asymmetric eck reaction 2 3 Ar- d (0) Ar 2 3 (c) Asymmetric olefin metathesis alladium π-allyl
Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation (a) Asymmetric allylic substitution 1 u - d u (b) Asymmetric eck reaction 2 3 Ar- d (0) Ar 2 3 (c) Asymmetric olefin metathesis alladium π-allyl
Recapping where we are so far
 Recapping where we are so far Valence bond constructions, valence, valence electron counting, formal charges, etc Equivalent neutral classification and MLX plots Basic concepts for mechanism and kinetics
Recapping where we are so far Valence bond constructions, valence, valence electron counting, formal charges, etc Equivalent neutral classification and MLX plots Basic concepts for mechanism and kinetics
Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways
 Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways Xiao Cheng, Charles Goodhue, and Jin-Quan Yu Brandeis University
Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways Xiao Cheng, Charles Goodhue, and Jin-Quan Yu Brandeis University
Titanacyclopropanes as versatile intermediates for carbon carbon bond formation in reactions with unsaturated compounds*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 72, No. 9, pp. 1715 1719, 2000. 2000 IUPAC Titanacyclopropanes as versatile intermediates for carbon carbon bond formation in reactions with unsaturated compounds* O. G. Kulinkovich
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 72, No. 9, pp. 1715 1719, 2000. 2000 IUPAC Titanacyclopropanes as versatile intermediates for carbon carbon bond formation in reactions with unsaturated compounds* O. G. Kulinkovich
Solvias (R)-MeO-BIPHEP Ligand Kit
 metals inorganics organometallics catalysts ligands custom synthesis cgm facilities nanomaterials Catalog # 96-3655 Solvias ()- and (S)-Me BIE Ligand Kits for asymmetric hydrogenation and other catalytic
metals inorganics organometallics catalysts ligands custom synthesis cgm facilities nanomaterials Catalog # 96-3655 Solvias ()- and (S)-Me BIE Ligand Kits for asymmetric hydrogenation and other catalytic
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Catalytic alkylation of remote C H bonds enabled by proton-coupled electron transfer
 Catalytic alkylation of remote C bonds enabled by proton-coupled electron transfer Reporter: Ji Zhou Checker: Shubo u Date: 2016/11/14 Choi, G. J.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Miller, D. C.; Gu, C. J.; Knowles, R. R.
Catalytic alkylation of remote C bonds enabled by proton-coupled electron transfer Reporter: Ji Zhou Checker: Shubo u Date: 2016/11/14 Choi, G. J.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Miller, D. C.; Gu, C. J.; Knowles, R. R.
Metal Catalyzed Outer Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated Olefins and Alkynes
 Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
