The rheological and tribological properties of calcium sulfonate complex greases
|
|
|
- Gervase Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Friction 3(1): (215) ISS DOI 1.17/s C /TH RESEARCH ARTICLE The rheological and tribological properties of calcium sulfonate complex greases Zeyun WAG 1,2, Yanqiu XIA 3,*, Zhilu LIU 2 1 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, ingxia University, Yinchuan, 7521, China 2 State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, 73, China 3 School of Energy Power and Mechanical Engineering, orth China Electric Power University, Beijing, 2194, China Received: 2 February 214 / Revised: 28 May 214 / Accepted: 22 August 214 The author(s) 214. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract: In this study, we synthesized two types of calcium sulfonate complex greases (barium soap and calcium soap) and investigated their physical, rheological, and tribological properties in detail. The test results showed that the evolution of their linear viscoelasticity functions with frequency were quite similar to those of traditional lubricating greases. Moreover, these two calcium sulfonate complex greases had good frictionreducing and antiwear properties at room temperature and at 15 C. In addition, by adding an organic molybdenum compound (MoDTC) to the base greases, we obtained a very low friction coefficient (.65) for one of the greases (calcium soap) at 4 and 5 (maximum Hertzian pressures of 3.47 GPa and 3.74 GPa, respectively) at 15 C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis showed that the tribofilm was composed of some complex oxide species and CaCO 3 that had formed on the worn surface. Keywords: calcium sulfonate complex greases; tribological properties; rheology; viscoelasticity 1 Introduction Lubricating greases generally consist of a thickener dispersed in a mineral or synthetic oil. The thickener forms an entanglement network, which traps the oil and confers the appropriate rheological and tribological properties to the grease. Fatty acid soaps made of lithium, calcium, sodium, aluminum, and barium are most commonly used as thickeners [1, 2]. In recent years, a multipurpose grease known as calcium sulfonate complex grease, has attracted much attention due to its good performances at high and low temperatures and its resistance to clipping and rubbing friction. Calcium sulfonate complex grease contains calcium tetraborate and calcium 12-hydroxystearate together with ultrabasic calcium sulfonate (T16D). Its structural formula is shown in Fig. 1. The fabrication process for calcium sulfonate complex grease can be divided into two stages. In the first stage, ewtonian ultrabasic calcium sulfonate is changed to non-ewtonian ultrabasic calcium sulfonate. In the second stage, boric acid, 12-hydroxystearic acid, and calcium soap are added to the non-ewtonian ultrabasic calcium sulfonate, yielding the calcium sulfonate complex grease. Recent studies of calcium sulfonate complex grease have for the most part focused on manufacturing techniques and the mechanism of its extreme pressure and antiwear properties. There have been few studies reporting on the rheological and tribological properties of calcium sulfonate complex grease at higher temperatures. In this paper, we used barium and calcium soaps to fabricate ultrabasic calcium sulfonate and studied the physical, rheological, and tribological properties of each. We also investigated the sensitivity * Corresponding author: Yanqiu XIA. xiayanqiu@yahoo.com Fig. 1 The structural formula of ultrabasic calcium sulfonate.
2 Friction 3(1): (215) 29 of a MoDTC friction modifier in the two calcium sulfonate complex greases at room temperature and at a high temperature (15 C). 2 Experimental 2.1 Materials T16D, 12-hydroxystearate, and synthetic PAO (polyalpha-olefin) 4 were commercially obtained from the Lanzhou Refinery Company (Lanzhou, China). Calcium hydroxide was purchased from the Shanghai Chemical Regent Company. Barium hydroxide was obtained from the Laiyang Chemical Engineering Company. Acetic acid and boric acid were purchased from the Tianjin Chemical Regent Company. All chemical reagents were of analytical grade and were used without further purification. 2.2 Grease manufacture We prepared the greases using the base oil synthetic 1 PAO 4, which has a kinematic viscosity of 4 mm2 s at 1 C. The calcium sulfonate complex greases were prepared following patent C First, a certain amount of T16D was added to a prescribed amount of base oil, and the mixture was then stirred and heated. We then added to the above mixture a certain amount of acetic acid, as a promoter, in batches. When the ewtonian ultrabasic calcium sulfonate was completely changed to non-ewtonian ultrabasic calcium sulfonate, a prescribed amount of 12-hydroxystearic acid was added to it. When the 12-hydroxystearic acid was completely dissolved, calcium hydroxide and boric acid aqueous solutions were added to the above mixed solution to allow the saponification process to proceed at C for 4 h. Then, the mixed solution was heated to C to evaporate the water present at the end of the saponification process. Subsequently, the solution was heated to 21 C to thicken it. Finally, the solution was cooled to room temperature and then was ground on a three-roller mill three times to obtain calcium sulfonate complex grease (calcium soap) (abbreviated as calcium soap base grease ). The barium soap calcium sulfonate complex grease (barium soap) (abbreviated as barium soap base grease ) was obtained following the same procedures described above, with the only difference being that barium hydroxide was used instead of calcium hydroxide. To investigate the sensitivity of a MoDTC friction modifier, 3. wt% concentration MoDTC was added to the calcium sulfonate complex greases. 2.3 Characterization tests The dropping points of the prepared greases were measured by the BF-22 dropping point of lubricating grease over wide temperature range tester according to the China national standards GB/T 3498, which are similar to the American society for testing and materials (ASTM) D2265 standard. The penetrations were measured using a SYP41 lubricating grease cone penetrometer according to the China national standards GB/T 269, which are similar to the ASTM D217 standard. The copper strip tests of the prepared greases were conducted according to the China national standard GB/T Steel mesh sub-oil tests were measured using a SYP418 steel mesh sub-oil tester according to the China petrochemical industry standard SH/T 324. Thermogravimentric analyses (TGA) were carried out on a ZRY-2P thermal analyzer at a heating rate of 1 C min 1 in flowing air. The rheological properties of the prepared base greases were measured using a controlled-stress rheometry rheoscope (ThermoHaake, Germany). Smallamplitude oscillatory shear (SAOS) tests were carried out inside the linear viscoelastic region, using plate plate geometry (3 mm, 1 mm gap) in a frequency range of rad/s at room temperature. Stress sweep tests, at a frequency of 1 Hz, were performed earlier on each sample to determine their linear viscoelasticity regions. An Optimol SRV oscillating friction and wear tester (Optimol Instruments Prüftechnik GmbH, Munich, Germany) was used to evaluate the tribological properties of the lubricated greases, and the lubricated greases containing MoDTC, at room temperature and at 15 C. Upper ball (diameter of 1 mm, AISI 521 steel, hardness 71 HV) slides reciprocated at an amplitude of 1 mm against a stationary disk (AISI 521 steel, hardness 8 HV). All tests were conducted in the reciprocating mode under a normal load of 2 8 (corresponding to a maximum Hertzian
3 3 Friction 3(1): (215) pressure in the range of GPa) at a frequency of 25 Hz for a testing duration of 3 min. The friction coefficient was recorded automatically by a computer connected to the SRV tester. Prior to the friction and wear tests, about 1 g of grease was introduced to the ball-disk contact area. The wear volumes loss of the lower disk was measured using a MicroXAM-3D surface mapping microscope profilometer. The result reported here represents the average of duplicate tests. The morphologies of the worn surfaces lubricated with the base greases and the greases containing MoDTC were observed using a JEM-56LV scanning electron microscope (SEM). The binding energies of some typical elements in the worn surfaces were analyzed using a PHI-572 multi-functional X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS, America). Mg-Kα radiation was used as the excitation source and the binding energy of carbon (C1s: ev) was used as the reference. 3 Results and discussion 3.1 Physical properties of the prepared base greases The physical properties of the prepared base greases are shown in Table 1. We can clearly see that the dropping point of the calcium soap base grease was higher than that of the barium soap base grease. For the barium soap base grease, the steel mesh sub-oil result was %, which was lower than that of the calcium soap base grease. This means that the colloidal stability of the barium soap base grease is better than that of the calcium soap base grease. Figure 2 shows weight loss with temperature, using air flux, for the prepared base greases. As shown in the figure, the two lubricated base greases both decomposed at about 3 C. Table 1 The physical properties of the prepared base greases. Barium soap base grease Calcium soap base grease Penetration (1/4 mm) Dropping point ( ) Copper corrosion 1a 1a (1, 24 h) Steel mesh sub-oil (1, 24 h) (%) 1.3 Fig. 2 TGA thermograms for the prepared base greases under air atmosphere. 3.2 Rheological properties Figure 3(a) shows the stress sweep curves, with the change of the modulus as a function of stress at a frequency of 1 Hz. We can see that at low stress levels, the dominant modulus is the storage modulus (G') and before 1 Pa, the relationship between the storage modulus and the loss modulus (G'') is linear. This region is known as the linear viscoelastic region and 1 Pa is the critical stress. Beyond the critical stress, G' starts to decrease while G'' increases until a certain crossover point is reached where G' is equal to G'', and hence tanδ = 1 (tanδ = G''/G'). From then on, the loss modulus is greater than the storage modulus, indicating that the prepared base greases start to flow [3]. Figure 4(a) shows the evolution of the SAOS functions with frequency for the prepared base greases at room temperature. As we can see, their linear viscoelasticity responses are qualitatively similar to other lubricating greases [2, 4]. Across the frequency range studied, the storage modulus (G') is always higher than the loss modulus (G''), which is characteristic of polymeric systems with physical entanglements [2]. This shows that the prepared base greases are highly structured systems. In this region, G' slightly evolves with frequency, while G'' maintains a minimum value. Also, from Fig. 3(a), we can see that the values of G' and G'' for the calcium soap base grease are higher than those of the barium soap base grease, which indicates that the microstructural network of the calcium soap base grease is stronger than that of the barium soap base grease.
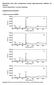
4 Friction 3(1): (215) 31 Fig. 3 Stress sweeps for the prepared base greases at room temperature. Fig. 4 Evolution of the SAOS functions with frequency for the prepared base grease at room temperature. The values of the loss tangent (tanδ = G''/G') versus frequency are plotted in Fig. 4(b). We can see that all greases show a minimum in tanδ at intermediate frequencies, which is a phenomenon related to the appearance of the plateau region. A characteristic viscoelastic parameter of this region is the plateau modulus, G. This parameter may be considered to be a measure of the aggregation number among dispersed units of sand, and is consequently related to the strength of the soap network. We used a short- cut method to estimate G from the loss tangent [5]. Using this method, we determined that the G value of calcium soap base grease is about 66,88 Pa, which was higher than the G value of barium soap base grease (29,249 Pa). The higher G value of the calcium soap base grease indicates that the calcium soap has more developed fibers than the barium soap. G G [ ] tan minimum 3.3 Tribological properties Tribological results Figure 5 shows the variations in the friction coefficient and wear volume under loads lubricated with the prepared base greases, with and without MoDTC, at room temperature. We can see that the friction coefficients and wear volumes of the barium and calcium soap base greases are quite similar under different loads at room temperature. However, after adding MoDTC to these two base greases, the friction coefficients significantly decrease at loads of 6 and 8 (maximum Hertzian pressure of 3.97 GPa and 4.37 GPa, respectively), and the wear volumes slightly decrease over the range of the loads studied. Figure 6 shows the friction coefficient and wear volume versus load with lubrication of the prepared base greases, with and without MoDTC, at 15 C.
5 32 Friction 3(1): (215) Lower friction coefficients and larger wear volumes are observed at 15 C than at room temperature. At 15 C, when MoDTC was added to the base greases, the load-carrying capacity increased from 5 to 6 and the maximum Hertzian pressure increased from 3.74 GPa to 3.97 GPa, respectively. Meanwhile, the friction coefficients decreased. From the figure, we can see that the friction coefficients and wear volumes of the two prepared base greases are quite similar at room temperature and at 15 C. However, after adding MoDTC to the base greases, the friction coefficients of the calcium soap base grease are lower than those of the barium soap base grease. We may deduce that the calcium soap base grease is more sensitive to MoDTC than the barium soap base grease. The difference in sensitivity to the MoDTC may be attributed to the different structure of the thickener. In the calcium soap base grease, the MoDTC easily makes contact and reacts with the metal surface to form a surface protective film that reduces friction and wear SEM analysis of the worn surface Figure 7 shows SEM images of the worn surfaces lubricated with the different greases at 6 (3.97 GPa), 25 Hz, and at room temperature. All the SEM images were obtained at the same magnification. As shown in the figure, the worn surfaces lubricated by the base greases were quite rough and showed obvious signs of severe adhesion (Figs. 7(b) and 7(f)). In contrast, only slight grooves are found on the worn surfaces lubricated by the base greases containing 3. wt% MoDTC (Figs. 7(d) and 7(h)). Figure 8 shows SEM images of the worn surfaces lubricated with the different greases at 4 (3.47 GPa), 25 Hz and at 15 C. All the SEM images were obtained Fig. 5 Variations in the friction coefficient and wear volume with the loads under the lubrication of the prepared base greases and the base greases containing MoDTC at room temperature. Fig. 6 Friction coefficient and wear volume versus the loads under the lubrication of the prepared base greases and the base greases containing MoDTC at 15.
6 Friction 3(1): (215) 33 Fig. 7 SEM images of the worn surfaces lubricated with different lubrication at 6, 25 Hz and room temperature: (a, b) barium soap base grease; (c, d) barium soap base grease containing 3. wt% MoDTC; (e, f) calcium soap base grease; (g, h) calcium soap base grease containing 3. wt% MoDTC. Fig. 8 SEM images of the worn surfaces lubricated with different lubrication at 4, 25 Hz and 15 : (a, b) barium soap base grease; (c, d) barium soap base grease containing 3. wt% MoDTC; (e, f) calcium soap base grease; (g, h) calcium soap base grease containing 3. wt% MoDTC. at the same magnification. As clearly shown, the worn surfaces lubricated by the base greases were quite rough (Figs. 8(b) and 8(f)). However, the worn surfaces lubricated with the base greases containing MoDTC showed only slight grooves and smooth surfaces (Figs. 8(d) and 8(h)), thereby demonstrating the antiwear properties of greases containing MoDTC XPS analysis of the worn surface In recent years, much attention has been given to the mechanism of extreme pressure and the antiwear properties of calcium sulfonate complex grease. In this paper, using barium soap base grease, we performed XPS analysis to investigate the mechanism of extreme pressure and the antiwear properties of calcium sulfonate complex grease. Figure 9 shows XPS spectra of typical elements on worn surfaces lubricated with barium soap base grease, with and without MoDTC, at room temperature and at 15 C. As shown in the figure, these XPS spectra are almost identical, which indicates that similar chemical reactions occurred. The binding energy of Ba3d at 78. ev corresponds to BaO [6]. The peak of Fe2p at about ev is assigned to Fe2O3 [7]. The B1s peak at ev is
7 34 Friction 3(1): (215) Fig. 9 The XPS spectra of typical elements on the worn surfaces lubricated with the barium soap base grease and the base grease containing MoDTC at room temperature and 15. assigned to B 2 O 3 [8, 9]. The wide peak of O1s, which appears in the range of ev, verifies the existence of a complex oxide species on the worn surfaces. The Ca2p peak at ev corresponds to the CaCO 3 [6] absorbed on the worn surfaces. Based on these data, we conclude that the barium soap base grease can reduce friction and wear due to the generation of a surface protective film composed of BaO, Fe 2 O 3, B 2 O 3, and CaCO 3. After adding MoDTC to the base grease, the Mo3d peaks at ev and 232. ev correspond to MoS 2 and MoO 3 [8], respectively. The S2p peak at ev verifies the existence of MoS 2 on the worn surface. From the above analysis, we can conclude that a tribochemical reaction occurs during the sliding process and a tribofilm consisting of MoS 2 and MoO 3 is formed. Therefore, the presence of MoDTC in the base grease can effectively reduce friction and wear. 4 Conclusions In this study, we used barium and calcium soaps to form non-ewtonian ultrabasic calcium sulfonate complexes to obtain two kinds of calcium sulfonate complex grease. The physical properties of the greases show that the dropping point and the colloid stability values for the calcium soap base grease are respectively higher and poorer than those of the barium soap base grease. The evolution of the linear viscoelasticity functions with frequency is similar to that of other lubricating greases. The SAOS modulus values of the calcium soap base grease are slightly higher than those of the barium soap base grease. The tribological properties of the two prepared base greases are quite similar at room temperature and at 15 C. However, the calcium soap base grease is more sensitive to the MoDTC than the barium base grease. XPS analysis
8 Friction 3(1): (215) 35 results show that the good extreme pressure, antiwear, and friction-reducing properties of barium soap base grease may be attributed to a tribofilm, consisting of BaO, Fe 2 O 3, B 2 O 3, and CaCO 3, that forms during the sliding process. Also, the good friction-reducing and antiwear properties of the barium soap base grease containing MoDTC may be attributed to a tribofilm consisting of MoS 2 and MoO 3. Acknowledgements This work is supported by the open project of State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1211) and atural Science foundation of ingxia University (ZR1216). Open Access: This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited. References [1] Mas R, Magnin A. Rheology of colloidal suspensions: Case of lubricating greases. J Rheol 38: (1994) [2] Delgado M A, Valencia C, Sánchez M C, Franco J M, Gallegos C. Influence of soap concentration and oil viscosity on the rheology and microstructure of lubricating greases. Ind Eng Chem Res 45: (26) [3] Yeong S K, Luckham P F, Tadros T F. Steady flow and viscoelastic properties of lubricating grease containing various thickener concentrations. J Colloid Interf Sci 274: (24) [4] Madiedo J M, Franco J M, Valencia C, Gallegos C J. Modeling of the nonlinear rheological behavior of lubricating grease at low shear rates. J Tribol 122: (2) [5] García Morales J A, Franco J M, Valencia C, Sánchez M C, Gallegos C. Influence of processing variables on the rheological properties of lubricating grease manufactured in a stirred tank. J Ind Eng Chem 1: (24) [6] [7] Sun Y B, Hu LT, Xue Q J. Tribological properties and action mechanism of, -dialkyl dithiocarbamate-derived S-hydroxyethyl borate esters as additives in rapeseed oil. Wear 266: (29) [8] Wang Z Y, Xia Y Q, Liu Z L. Study the sensitivity of solid lubricating additives to attapulgite clay base grease. Tribol Lett 42: (211) [9] Jia Z F, Xia Y Q, Li J L, Pang X J, Shao X. Friction and wear behavior of diamond-like carbon coating on plasma nitrided mild steel under boundary lubrication. Tribol Int 43: (29) Yanqiu XIA. He received his Ph.D. degree in mechanical design and theory from ortheast University in China, in He continued his postdoctoral study at the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and ational Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) at Tsukuba, Japan, in 22 and 27 respectively. In 25, he was offered a titled professorship, Hundreds Talent Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Currently he has moved to School of Energy Power and Mechanical Engineering, orth China Electric Power University at Beijing. His research areas cover the lubricants, grease, additives, lubrication for power equipment, equipment fault diagnosis etc. Zeyun WAG. She received her Ph.D. degree in physical chemistry in 212 from the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. ow she is a lecturer at ingxia University. Her research interests include lubricating grease and additives.
Tribological Properties of Oil Soluble Polyacrylates with Hydroxyl Group
 Tribological Properties of Oil Soluble Polyacrylates with Hydroxyl Group *Kenji YAMAMTO 1, Kenta NAKAMURA 2, Masayoshi MURAKI 3 1: Surface Specialties Department, ADEKA Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. 2: Research
Tribological Properties of Oil Soluble Polyacrylates with Hydroxyl Group *Kenji YAMAMTO 1, Kenta NAKAMURA 2, Masayoshi MURAKI 3 1: Surface Specialties Department, ADEKA Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. 2: Research
EFFECT OF RECYCLED PLASTIC WASTE ON RHEOLOGICAL MODIFICATION OF CALCIUM GREASES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article EFFECT OF RECYCLED PLASTIC WASTE ON RHEOLOGICAL MODIFICATION OF CALCIUM GREASES E. A. Ismail 1,. R A. El-Adly 1, Modather
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article EFFECT OF RECYCLED PLASTIC WASTE ON RHEOLOGICAL MODIFICATION OF CALCIUM GREASES E. A. Ismail 1,. R A. El-Adly 1, Modather
Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of SDS stabilized. Antiwear Lubricant Additives
 Supporting Information Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of SDS stabilized Magnesium-Doped-Zinc Oxide (Zn 0.88 Mg 0. O) Nanoparticles as Efficient Antiwear Lubricant Additives Kalyani,
Supporting Information Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Evaluation of SDS stabilized Magnesium-Doped-Zinc Oxide (Zn 0.88 Mg 0. O) Nanoparticles as Efficient Antiwear Lubricant Additives Kalyani,
Key words: Tribology, Geometrical product specification, Boundary lubrication, Surface texturing
 Effect of surface roughness on friction behavior of steel under boundary lubrication Kazuma Yamaguchi 1, Chiaki Sasaki 1, Ryo Tsuboi 1, Mark Atherton 2, Tadeusz Stolarski 1, Shinya Sasaki 1, 1 Department
Effect of surface roughness on friction behavior of steel under boundary lubrication Kazuma Yamaguchi 1, Chiaki Sasaki 1, Ryo Tsuboi 1, Mark Atherton 2, Tadeusz Stolarski 1, Shinya Sasaki 1, 1 Department
Experimental Analysis of Tribological Properties of Lubricating Oil Using Nanoparticle Additives
 ISSN 2395-1621 Experimental Analysis of Tribological Properties of Lubricating Oil Using Nanoparticle Additives #1 S.N.Mandlik, #2 Prof. S.R.Nimbalkar 1 mandliksantosh8@gmail.com 2 nimbalkarsr@pravaraengg.org.in
ISSN 2395-1621 Experimental Analysis of Tribological Properties of Lubricating Oil Using Nanoparticle Additives #1 S.N.Mandlik, #2 Prof. S.R.Nimbalkar 1 mandliksantosh8@gmail.com 2 nimbalkarsr@pravaraengg.org.in
Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoplatelets with Excellent Tribological Properties under High Contact Pressure as Water-based Lubricant Additives
 Supplementary Information Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoplatelets with Excellent Tribological Properties under High Contact Pressure as Water-based Lubricant Additives Hongdong Wang, Yuhong Liu, Zhe Chen,
Supplementary Information Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoplatelets with Excellent Tribological Properties under High Contact Pressure as Water-based Lubricant Additives Hongdong Wang, Yuhong Liu, Zhe Chen,
Research Article Synthesis, Characterization, and Tribological Behavior of Oleic Acid Capped Graphene Oxide
 Nanomaterials, Article ID 654145, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/654145 Research Article Synthesis, Characterization, and Tribological Behavior of Oleic Acid Capped Graphene Oxide Tiedan Chen,
Nanomaterials, Article ID 654145, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/654145 Research Article Synthesis, Characterization, and Tribological Behavior of Oleic Acid Capped Graphene Oxide Tiedan Chen,
Supporting Information. Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive Photocatalyst for the Suzuki Coupling Reaction**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-Functionalized Boron Nitride. Nanotube Based Epoxy Nanocomposites with Simultaneous High
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-Functionalized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-Functionalized
Supporting information
 Supporting information A Facile and Large-area Fabrication Method of Superhydrophobic Self-cleaning Flourinated Polysiloxane/TiO 2 Nanocomposite Coatings with Long-term Durability Xiaofeng Ding, Shuxue
Supporting information A Facile and Large-area Fabrication Method of Superhydrophobic Self-cleaning Flourinated Polysiloxane/TiO 2 Nanocomposite Coatings with Long-term Durability Xiaofeng Ding, Shuxue
Colloidal Particles with Complex Microstructures via Phase Separation in Swelled Polymer Microspheres
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Colloidal Particles with Complex Microstructures via Phase Separation in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Colloidal Particles with Complex Microstructures via Phase Separation in
Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials with multiple cavities
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Electronic Supplementary Infomaton Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Electronic Supplementary Infomaton Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials
Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron double oxide catalyst
 Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Influence of electric potentials on friction of sliding contacts lubricated by an ionic liquid
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Influence of electric potentials on friction of sliding contacts lubricated by
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Influence of electric potentials on friction of sliding contacts lubricated by
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Facet-Selective Deposition of FeO x on α-moo 3 Nanobelts for Lithium Storage Yao Yao, 1 Nuo Xu, 2 Doudou Guan, 1 Jiantao Li, 1 Zechao Zhuang, 1 Liang Zhou,*,1 Changwei Shi 1, Xue
Supporting Information Facet-Selective Deposition of FeO x on α-moo 3 Nanobelts for Lithium Storage Yao Yao, 1 Nuo Xu, 2 Doudou Guan, 1 Jiantao Li, 1 Zechao Zhuang, 1 Liang Zhou,*,1 Changwei Shi 1, Xue
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011
 Supplementary Information for Selective adsorption toward toxic metal ions results in selective response: electrochemical studies on polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite Experimental Section
Supplementary Information for Selective adsorption toward toxic metal ions results in selective response: electrochemical studies on polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite Experimental Section
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach
 Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Trapping Lithium into Hollow Silica Microspheres. with a Carbon Nanotube Core for Dendrite-Free
 Supporting Information Trapping Lithium into Hollow Silica Microspheres with a Carbon Nanotube Core for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Anodes Tong-Tong Zuo,, Ya-Xia Yin,, Shu-Hua Wang, Peng-Fei Wang,, Xinan
Supporting Information Trapping Lithium into Hollow Silica Microspheres with a Carbon Nanotube Core for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Anodes Tong-Tong Zuo,, Ya-Xia Yin,, Shu-Hua Wang, Peng-Fei Wang,, Xinan
Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene. quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
applied as UV protective films
 Nanocomposite gels via in-situ photoinitiation and disassembly of TiO 2 -Clay composites with polymers applied as UV protective films Chuanan Liao, Qing Wu, Teng Su, Da Zhang, Qingsheng Wu and Qigang Wang*
Nanocomposite gels via in-situ photoinitiation and disassembly of TiO 2 -Clay composites with polymers applied as UV protective films Chuanan Liao, Qing Wu, Teng Su, Da Zhang, Qingsheng Wu and Qigang Wang*
CHAPTER TWO: EXPERIMENTAL AND INSTRUMENTATION TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER TWO: EXPERIMENTAL AND INSTRUMENTATION TECHNIQUES 25 2.1 INSTRUMENTATION The prepared samples were characterized using various techniques. Among which are Dynamic Light Scattering, Zeta Potential
CHAPTER TWO: EXPERIMENTAL AND INSTRUMENTATION TECHNIQUES 25 2.1 INSTRUMENTATION The prepared samples were characterized using various techniques. Among which are Dynamic Light Scattering, Zeta Potential
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Hydrothermal synthesis of - alloy nanooctahedra and their enhanced electrocatalytic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Hydrothermal synthesis of - alloy nanooctahedra and their enhanced electrocatalytic
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil
 Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Hybrid Engineering Materials with high water-collecting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information Hybrid Engineering Materials with high water-collecting efficiency inspired
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information Hybrid Engineering Materials with high water-collecting efficiency inspired
High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by
 Supporting Information for: High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by Engineering Graphene Assemblies Min Zhou,, Xianglong Li, *, Bin Wang, Yunbo Zhang, Jing Ning, Zhichang Xiao, Xinghao Zhang,
Supporting Information for: High-Performance Silicon Battery Anodes Enabled by Engineering Graphene Assemblies Min Zhou,, Xianglong Li, *, Bin Wang, Yunbo Zhang, Jing Ning, Zhichang Xiao, Xinghao Zhang,
1. Experimental section
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information for Trans-Cis configuration regulated Supramolecular Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information for Trans-Cis configuration regulated Supramolecular Polymer
Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag Nanoclusters
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag
Determination and Assessment of the Rheological Properties of Pastes for Screen Printing Ceramics
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 17, 2009 Determination and Assessment of the Rheological Properties of Pastes for Screen Printing Ceramics John W. Phair 1 and Andreas F-J. Kaiser
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 17, 2009 Determination and Assessment of the Rheological Properties of Pastes for Screen Printing Ceramics John W. Phair 1 and Andreas F-J. Kaiser
Redox-Responsive Gel-Sol/Sol-Gel Transition in Poly(acrylic. acid) Aqueous Solution Containing Fe(III) Ions Switched by
 Supporting Information Journal of the American Chemical Society Redox-Responsive Gel-Sol/Sol-Gel Transition in Poly(acrylic acid) Aqueous Solution Containing Fe(III) Ions Switched by Light Fei Peng, Guangzhao
Supporting Information Journal of the American Chemical Society Redox-Responsive Gel-Sol/Sol-Gel Transition in Poly(acrylic acid) Aqueous Solution Containing Fe(III) Ions Switched by Light Fei Peng, Guangzhao
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supporting Information for:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
R&D on New Friction Modifier for Lubricant for Fuel economy improvement
 2000E1.1.5 R&D on New Friction Modifier for Lubricant for Fuel economy improvement (Group on New Friction Modifier for Fuel economy improvement) Yasunori Sogawa, Narihiko Yoshimura, Hiroyuki Iwasaki 1.
2000E1.1.5 R&D on New Friction Modifier for Lubricant for Fuel economy improvement (Group on New Friction Modifier for Fuel economy improvement) Yasunori Sogawa, Narihiko Yoshimura, Hiroyuki Iwasaki 1.
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Rheology of cellulose solutions. Puu Cellulose Chemistry Michael Hummel
 Rheology of cellulose solutions Puu-23.6080 - Cellulose Chemistry Michael Hummel Contents Steady shear tests Viscous flow behavior and viscosity Newton s law Shear thinning (and critical concentration)
Rheology of cellulose solutions Puu-23.6080 - Cellulose Chemistry Michael Hummel Contents Steady shear tests Viscous flow behavior and viscosity Newton s law Shear thinning (and critical concentration)
Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage
 Electronic Supplementary Information Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage Bin Luo, a Yan Fang, a Bin Wang, a Jisheng Zhou, b Huaihe Song, b and Linjie
Electronic Supplementary Information Two Dimensional Graphene/SnS 2 Hybrids with Superior Rate Capability for Lithium ion Storage Bin Luo, a Yan Fang, a Bin Wang, a Jisheng Zhou, b Huaihe Song, b and Linjie
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
N-doped Carbon-Coated Cobalt Nanorod Arrays Supported on a Titanium. Mesh as Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information N-doped Carbon-Coated Cobalt Nanorod
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information N-doped Carbon-Coated Cobalt Nanorod
USE OF RHEOLOGY AS A DEVELOPING AND TROUBLESHOOTING TOOL FOR PSA APPLICATIONS.
 USE OF RHEOLOGY AS A DEVELOPING AND TROUBLESHOOTING TOOL FOR PSA APPLICATIONS. Michael DeFrancisis, Applications Engineer, Henkel, Bridgewater, NJ Yayun Liu, Senior Development Scientist, Henkel, Bridgewater,
USE OF RHEOLOGY AS A DEVELOPING AND TROUBLESHOOTING TOOL FOR PSA APPLICATIONS. Michael DeFrancisis, Applications Engineer, Henkel, Bridgewater, NJ Yayun Liu, Senior Development Scientist, Henkel, Bridgewater,
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor
 Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supplementary material to On the rheology of pendular gels and morphological developments in paste- like ternary systems based on capillary attraction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supplementary material to On the rheology of pendular gels and morphological developments in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supplementary material to On the rheology of pendular gels and morphological developments in
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Self-assembled Graphene Hydrogel via a One-Step Hydrothermal Process Yuxi Xu, Kaixuan Sheng, Chun Li, and Gaoquan Shi * Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Supporting Information for Self-assembled Graphene Hydrogel via a One-Step Hydrothermal Process Yuxi Xu, Kaixuan Sheng, Chun Li, and Gaoquan Shi * Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Two-dimensional dendritic Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties
 Supporting Information for Two-dimensional dendritic Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties Yingpu Bi, *a Hongyan Hu, a Zhengbo Jiao, a Hongchao Yu, a Gongxuan Lu, a and Jinhua Ye
Supporting Information for Two-dimensional dendritic Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructures and their photocatalytic properties Yingpu Bi, *a Hongyan Hu, a Zhengbo Jiao, a Hongchao Yu, a Gongxuan Lu, a and Jinhua Ye
FORMULATION, RHEOLOGY AND THERMAL AGING OF POLYMER GREASES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5752 FORMULATION, RHEOLOGY AND
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5752 FORMULATION, RHEOLOGY AND
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Characterization of partially reduced graphene oxide as room
 Supporting Information Characterization of partially reduced graphene oxide as room temperature sensor for H 2 Le-Sheng Zhang a, Wei D. Wang b, Xian-Qing Liang c, Wang-Sheng Chu d, Wei-Guo Song a *, Wei
Supporting Information Characterization of partially reduced graphene oxide as room temperature sensor for H 2 Le-Sheng Zhang a, Wei D. Wang b, Xian-Qing Liang c, Wang-Sheng Chu d, Wei-Guo Song a *, Wei
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information MoS 2 nanosheet/mo 2 C-embedded N-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information MoS 2 nanosheet/mo 2 C-embedded N-doped
Supplementary Information. Synthesis of soft colloids with well controlled softness
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Synthesis of soft colloids with well controlled softness Fuhua Luo, Zhifeng
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Synthesis of soft colloids with well controlled softness Fuhua Luo, Zhifeng
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bamboo-Like Carbon Nanotube/Fe 3 C Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Highly Efficient Catalysis for Oxygen Reduction Wenxiu Yang a,b, Xiangjian Liu a,b, Xiaoyu Yue a,b, Jianbo Jia,
Supporting Information Bamboo-Like Carbon Nanotube/Fe 3 C Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Highly Efficient Catalysis for Oxygen Reduction Wenxiu Yang a,b, Xiangjian Liu a,b, Xiaoyu Yue a,b, Jianbo Jia,
Pt-Ni alloyed nanocrystals with controlled archtectures for enhanced. methanol oxidation
 Supplementary Information Pt-Ni alloyed nanocrystals with controlled archtectures for enhanced methanol oxidation Xiao-Jing Liu, Chun-Hua Cui, Ming Gong, Hui-Hui Li, Yun Xue, Feng-Jia Fan and Shu-Hong
Supplementary Information Pt-Ni alloyed nanocrystals with controlled archtectures for enhanced methanol oxidation Xiao-Jing Liu, Chun-Hua Cui, Ming Gong, Hui-Hui Li, Yun Xue, Feng-Jia Fan and Shu-Hong
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
RSC Advances PAPER. Tribological characteristic and mechanism analysis of borate ester as a lubricant additive in different base oils. 1.
 PAPER Cite this: RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 7944 Received 16th November 2016 Accepted 4th January 2017 DOI: 10.1039/c6ra26896j www.rsc.org/advances 1. Introduction Lubricants play an indispensable role in enhancing
PAPER Cite this: RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 7944 Received 16th November 2016 Accepted 4th January 2017 DOI: 10.1039/c6ra26896j www.rsc.org/advances 1. Introduction Lubricants play an indispensable role in enhancing
Electronic Supplementary Information. Facile Synthesis of Germanium-Graphene Nanocomposites. and Their Application as Anode Material for Lithium Ion
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngCommunity This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis of Germanium-Graphene Nanocomposites and
Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngCommunity This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis of Germanium-Graphene Nanocomposites and
Nanotribology Application in the Coining Industry (II) Optimization of Lubricant Film Formation on Blanks
 Nanotribology Application in the Coining Industry (II) Optimization of Lubricant Film Formation on Blanks Extended Abstract As discussed in the Nanotribology surface thermodynamic model, the reaction rate
Nanotribology Application in the Coining Industry (II) Optimization of Lubricant Film Formation on Blanks Extended Abstract As discussed in the Nanotribology surface thermodynamic model, the reaction rate
A Smart Core-sheath Nanofiber that Captures and Releases Red
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A Smart Core-sheath Nanofiber that Captures and Releases Red Blood Cells
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A Smart Core-sheath Nanofiber that Captures and Releases Red Blood Cells
Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang
 Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang Supplementary information 1. XPS survey spectra of BHSNs 5 4 O1s
Bifunctional hairy silica nanoparticles towards high-performance additives for lubricant Tianyi Sui, Baoyu Song*, Yu-ho Wen, Feng Zhang Supplementary information 1. XPS survey spectra of BHSNs 5 4 O1s
In Situ Observation of Lubricant Film of Semi-Solid Lubricants at EHL Contact Using Micro-FTIR
 Tribology Online, 11, 2 (2016) 376-381. ISSN 1881-2198 DOI 10.2474/trol.11.376 Article In Situ Observation of Lubricant Film of Semi-Solid Lubricants at EHL Contact Using Micro-FTIR Koji Takiwatari 1)*,
Tribology Online, 11, 2 (2016) 376-381. ISSN 1881-2198 DOI 10.2474/trol.11.376 Article In Situ Observation of Lubricant Film of Semi-Solid Lubricants at EHL Contact Using Micro-FTIR Koji Takiwatari 1)*,
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Molybdenum compound MoP as an efficient. electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Molybdenum compound MoP as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Molybdenum compound MoP as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution
Supporting Information. High Wettable and Metallic NiFe-Phosphate/Phosphide Catalyst Synthesized by
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information High Wettable and Metallic NiFe-Phosphate/Phosphide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information High Wettable and Metallic NiFe-Phosphate/Phosphide
Material Analysis Technology R&D Efforts
 TECHNICAL REPORT Material Analysis Technology R&D Efforts H. KUWABARA Material analysis technology has become a core technology indispensable not only for R&D and product development but also for securing
TECHNICAL REPORT Material Analysis Technology R&D Efforts H. KUWABARA Material analysis technology has become a core technology indispensable not only for R&D and product development but also for securing
Supporting Information. Modulating the photocatalytic redox preferences between
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Modulating the photocatalytic redox preferences between anatase TiO 2 {001}
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Modulating the photocatalytic redox preferences between anatase TiO 2 {001}
A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal
 Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Simultaneous Reduction-Etching Route to Pt/ZnSnO 3 Hollow Polyhedral Architectures for Methanol Electrooxidation in Alkaline Media with Superior Performance Han Jiang, Baoyou Geng
Supporting Information Simultaneous Reduction-Etching Route to Pt/ZnSnO 3 Hollow Polyhedral Architectures for Methanol Electrooxidation in Alkaline Media with Superior Performance Han Jiang, Baoyou Geng
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Efficient vapor-assisted aging synthesis of functional and high
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Efficient vapor-assisted aging synthesis of functional and high
A Robust and Highly Active Copper-Based Electrocatalyst. for Hydrogen Production at Low Overpotential in Neutral
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information A Robust and Highly Active Copper-Based Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Production
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information A Robust and Highly Active Copper-Based Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Production
JOURNAL OF THE CHINESE CERAMIC SOCIETY
 2012 9 Ag 3 PO 4 /TiO 2 JOURNAL OF THE CHINESE CERAMIC SOCIETY 1247 Vol. 40 No. 9 September 2012 Ag/DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ 1 2 2 1 1 (1. 136000 2. 212013) Ag/DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ (Ag/Dy123) 10% ( )Ag/Dy123 0.20
2012 9 Ag 3 PO 4 /TiO 2 JOURNAL OF THE CHINESE CERAMIC SOCIETY 1247 Vol. 40 No. 9 September 2012 Ag/DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ 1 2 2 1 1 (1. 136000 2. 212013) Ag/DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ (Ag/Dy123) 10% ( )Ag/Dy123 0.20
Experimental Investigation of Tribological Properties Using Nanoparticles as Modifiers in Lubricating Oil
 Experimental Investigation of Tribological Properties Using Nanoparticles as Modifiers in Lubricating Oil Mr. A.B. Najan 1, Dr. R.R. Navthar 2, Mr. M.J. Gitay 3 1,2 PG Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Investigation of Tribological Properties Using Nanoparticles as Modifiers in Lubricating Oil Mr. A.B. Najan 1, Dr. R.R. Navthar 2, Mr. M.J. Gitay 3 1,2 PG Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Thermal and mechanical properties of several phthalonitrile resin system
 Thermal and mechanical properties of several phthalonitrile resin system Heng Zhou, Feng Liu, Yuehai Li, Tong Zhao* Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190, China Abstract:An
Thermal and mechanical properties of several phthalonitrile resin system Heng Zhou, Feng Liu, Yuehai Li, Tong Zhao* Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190, China Abstract:An
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Remarkable performance of Ir 1 /FeO x single-atom catalyst in water gas shift reaction Jian Lin, Aiqin Wang, Botao Qiao, Xiaoyan Liu, Xiaofeng Yang, Xiaodong Wang, Jinxia Liang,
Supporting Information Remarkable performance of Ir 1 /FeO x single-atom catalyst in water gas shift reaction Jian Lin, Aiqin Wang, Botao Qiao, Xiaoyan Liu, Xiaofeng Yang, Xiaodong Wang, Jinxia Liang,
An inorganic-organic hybrid supramolecular nanotube as high-performance anode for lithium ion batteries
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 An inorganic-organic hybrid supramolecular nanotube as high-performance anode for lithium
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 An inorganic-organic hybrid supramolecular nanotube as high-performance anode for lithium
Mechanically Strong and Highly Conductive Graphene Aerogels and Its Use as. Electrodes for Electrochemical Power Sources
 Supporting Information for Mechanically Strong and Highly Conductive Graphene Aerogels and Its Use as Electrodes for Electrochemical Power Sources Xuetong Zhang, Zhuyin Sui, Bin Xu, Shufang Yue, Yunjun
Supporting Information for Mechanically Strong and Highly Conductive Graphene Aerogels and Its Use as Electrodes for Electrochemical Power Sources Xuetong Zhang, Zhuyin Sui, Bin Xu, Shufang Yue, Yunjun
GCr M cm.
 29 4 Vol. 29 No. 4 2009 7 Tribology July, 2009 1, 1, 2 (1., 200240; 2., 730000) : (CNTs), CNTs, (AFM ) ( SEM ), X (XPS), UMT - 2MT : 3 - (MPTS),., 0. 85 0. 10,, : ; ; ; : TH117. 1 : A : 1004-0595 (2009)
29 4 Vol. 29 No. 4 2009 7 Tribology July, 2009 1, 1, 2 (1., 200240; 2., 730000) : (CNTs), CNTs, (AFM ) ( SEM ), X (XPS), UMT - 2MT : 3 - (MPTS),., 0. 85 0. 10,, : ; ; ; : TH117. 1 : A : 1004-0595 (2009)
The Rheology Handbook
 Thomas G. Mezger The Rheology Handbook For users of rotational and oscillatory rheometers 2nd revised edition 10 Contents Contents 1 Introduction 16 1.1 Rheology, rheometry and viscoelasticity 16 1.2 Deformation
Thomas G. Mezger The Rheology Handbook For users of rotational and oscillatory rheometers 2nd revised edition 10 Contents Contents 1 Introduction 16 1.1 Rheology, rheometry and viscoelasticity 16 1.2 Deformation
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
CONSISTENCY OF RHEOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS FOR PSA CHARACTERIZATION
 CONSISTENCY OF RHEOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS FOR PSA CHARACTERIZATION Dr. Laura Yao, Senior Research Chemist, Scapa North America, Windsor, CT Robert Braiewa, Research Chemist, Scapa North America, Windsor,
CONSISTENCY OF RHEOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS FOR PSA CHARACTERIZATION Dr. Laura Yao, Senior Research Chemist, Scapa North America, Windsor, CT Robert Braiewa, Research Chemist, Scapa North America, Windsor,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Coating Fe 3 O 4 Magnetic Nanoparticles with Humic Acid for High Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals in Water Jing-fu Liu, Zong-shan Zhao, and Gui-bin Jiang* State Key Laboratory of
Supporting Information Coating Fe 3 O 4 Magnetic Nanoparticles with Humic Acid for High Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals in Water Jing-fu Liu, Zong-shan Zhao, and Gui-bin Jiang* State Key Laboratory of
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Synthesis of condensed polynuclear aromatic resin from furfural extract oil of reduced-pressure route II
 Synthesis of condensed polynuclear aromatic resin from furfural extract oil of reduced-pressure route II Wu Mingbo, Jiang Wei, Wang Yuwei, Li Shibin and Zheng Jingtang Abstract: with high aromatic content
Synthesis of condensed polynuclear aromatic resin from furfural extract oil of reduced-pressure route II Wu Mingbo, Jiang Wei, Wang Yuwei, Li Shibin and Zheng Jingtang Abstract: with high aromatic content
Hydrogen desorption properties of Ca-N-H system
 Hydrogen desorption properties of Ca-N-H system Satoshi Hino, *Takayuki Ichikawa, Haiyan Leng and Hironobu Fujii Graduate School of Advanced Sciences of Matter, Hiroshima University, 1-3-1Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshima
Hydrogen desorption properties of Ca-N-H system Satoshi Hino, *Takayuki Ichikawa, Haiyan Leng and Hironobu Fujii Graduate School of Advanced Sciences of Matter, Hiroshima University, 1-3-1Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshima
A ph-sensitive Graphene Oxide Composite Hydrogel
 Electronic Supplementary Information for A ph-sensitive Graphene Oxide Composite Hydrogel Hua Bai, a,b Chun li, a Xiaolin Wang, b Gaoquan Shi* a a Department of Chemistry and the Key Laboratory of Bio-organic
Electronic Supplementary Information for A ph-sensitive Graphene Oxide Composite Hydrogel Hua Bai, a,b Chun li, a Xiaolin Wang, b Gaoquan Shi* a a Department of Chemistry and the Key Laboratory of Bio-organic
and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment
 Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
DEVELOP WEAR-RESISTANT POLYMERIC COMPOSITES BY USING NANOPARTICLES
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS DEVELOP WEAR-RESISTANT POLYMERIC COMPOSITES BY USING NANOPARTICLES 1 Abstract L. Chang 1 *, K. Friedrich 2 1 School of Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS DEVELOP WEAR-RESISTANT POLYMERIC COMPOSITES BY USING NANOPARTICLES 1 Abstract L. Chang 1 *, K. Friedrich 2 1 School of Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic
Electronic supplementary information. Amorphous carbon supported MoS 2 nanosheets as effective catalyst for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information Amorphous carbon supported MoS 2 nanosheets as effective
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information Amorphous carbon supported MoS 2 nanosheets as effective
Programmable and Bidirectional Bending of Soft Actuators. Based on Janus Structure with Sticky Tough PAA-clay Hydrogel
 Supporting Information Programmable and Bidirectional Bending of Soft Actuators Based on Janus Structure with Sticky Tough PAA-clay Hydrogel Lei Zhao, Jiahe Huang, Yuancheng Zhang, Tao Wang,*, Weixiang
Supporting Information Programmable and Bidirectional Bending of Soft Actuators Based on Janus Structure with Sticky Tough PAA-clay Hydrogel Lei Zhao, Jiahe Huang, Yuancheng Zhang, Tao Wang,*, Weixiang
Electrodeposited nickel hydroxide on nickel foam with ultrahigh. capacitance
 Electrodeposited nickel hydroxide on nickel foam with ultrahigh capacitance Guang-Wu Yang, Cai-Ling Xu* and Hu-Lin Li* College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Lanzhou University, 73 (PR China) 1.
Electrodeposited nickel hydroxide on nickel foam with ultrahigh capacitance Guang-Wu Yang, Cai-Ling Xu* and Hu-Lin Li* College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Lanzhou University, 73 (PR China) 1.
Supporting Information. hollow nanofibers: enhanced photocatalytic activity based on. highly efficient charge separation and transfer
 Supporting Information Assembling n-bi 2 MoO 6 nanosheets on electrospun p-cual 2 O 4 hollow nanofibers: enhanced photocatalytic activity based on highly efficient charge separation and transfer Jian Zhang,
Supporting Information Assembling n-bi 2 MoO 6 nanosheets on electrospun p-cual 2 O 4 hollow nanofibers: enhanced photocatalytic activity based on highly efficient charge separation and transfer Jian Zhang,
SBS/Carbon Black Compounds Give Asphalts With Improved High-Temperature Storage Stability
 SBS/Carbon Black Compounds Give Asphalts With Improved High-Temperature Storage Stability SBS/Carbon Black Compounds Give Asphalts With Improved High-Temperature Storage Stability Shifeng Wang*, Yong Zhang
SBS/Carbon Black Compounds Give Asphalts With Improved High-Temperature Storage Stability SBS/Carbon Black Compounds Give Asphalts With Improved High-Temperature Storage Stability Shifeng Wang*, Yong Zhang
Guideline for Rheological Measurements
 Guideline for Rheological Measurements Typical Measurements, Diagrams and Analyses in Rheology www.anton-paar.com General Information: = Measurement = Diagram = Analysis Important Rheological Variables:
Guideline for Rheological Measurements Typical Measurements, Diagrams and Analyses in Rheology www.anton-paar.com General Information: = Measurement = Diagram = Analysis Important Rheological Variables:
College of Mechanical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou , China; 2
 Proceedings Light-Assisted Room-Temperature NO2 Sensors Based on Black Sheet-Like NiO Xin Geng 1,2,3, Driss Lahem 4, Chao Zhang 1, *, Marie-Georges Olivier 3 and Marc Debliquy 3 1 College of Mechanical
Proceedings Light-Assisted Room-Temperature NO2 Sensors Based on Black Sheet-Like NiO Xin Geng 1,2,3, Driss Lahem 4, Chao Zhang 1, *, Marie-Georges Olivier 3 and Marc Debliquy 3 1 College of Mechanical
COST EFFECTIVE DETERMINATION OF LUBRICANT PROPERTIES THAT INFLUENCE FILM FORMATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY. A 2015/2016 SAIF Project Report
 1 COST EFFECTIVE DETERMINATION OF LUBRICANT PROPERTIES THAT INFLUENCE FILM FORMATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY A 2015/2016 SAIF Project Report Thomas J. Zolper University of Wisconsin-Platteville Abstract
1 COST EFFECTIVE DETERMINATION OF LUBRICANT PROPERTIES THAT INFLUENCE FILM FORMATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY A 2015/2016 SAIF Project Report Thomas J. Zolper University of Wisconsin-Platteville Abstract
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Graphene oxide hydrogel at solid/liquid interface
 Electronic Supplementary Information Graphene oxide hydrogel at solid/liquid interface Jiao-Jing Shao, Si-Da Wu, Shao-Bo Zhang, Wei Lv, Fang-Yuan Su and Quan-Hong Yang * Key Laboratory for Green Chemical
Electronic Supplementary Information Graphene oxide hydrogel at solid/liquid interface Jiao-Jing Shao, Si-Da Wu, Shao-Bo Zhang, Wei Lv, Fang-Yuan Su and Quan-Hong Yang * Key Laboratory for Green Chemical
Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction
 Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2014 1 Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction Shiyu Hu, Yuanyue Zhang, Tianmin Shao* State Key Lab of Tribology, Tsinghua University shaotm@tsinghua.edu.cn
Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2014 1 Study of electrostatic potential induced by friction Shiyu Hu, Yuanyue Zhang, Tianmin Shao* State Key Lab of Tribology, Tsinghua University shaotm@tsinghua.edu.cn
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/321/5894/1331/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation Andrew A. Herzing, Christopher J.
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/321/5894/1331/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation Andrew A. Herzing, Christopher J.
