Some Contributions to the Understanding of the Accelerating System During Natural Rubber Vulcanization
|
|
|
- Corey Rice
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ROHSTOFFE UND ANWENDUNGEN RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS NR vulcanization Accelerating system Squalene Sulfenamide CBS ZnO A method based on the modeling approach has been developed for the study of Natural Rubber vulcanization using two different accelerating systems. Squalene has been chosen as the model compound. The main reaction paths followed by sulfenamide (N-cyclohexylamine-2- benzothiazole, CBS) during the first stages of the process have been studied. In all cases, the active role of ZnO and the olefinic chain has been established. Some Contributions to the Understanding of the Accelerating System During Natural Rubber Vulcanization I. Behavior of Sulfenamide S. Borro s and N. AgulloÂ, Barcelona (Spain) BeitraÈge zum VerstaÈndnis des Beschleunigersystems waèhrend der Vulkanisation von NR I. Verhalten von Sulfenamid NR-Vulkanisation Beschleunigersystem Squalen Sulfenamid CBS ZnO Eine Methode auf der Grundlage der Modellvulkanisation wurde entwikkelt, um die NR-Vulkanisation mit zwei verschiedenen Beschleunigersystemen zu untersuchen. Squalen wurde als Modellkomponente ausgesucht. Die wichtigsten Reaktionswege des Sulfenamids CBS waè hrend des Angangsstadiums wurden verfolgt. In allen FaÈ llen wurde die aktive Rolle von ZnO und der aktiven Kette bestaè tigt. The complexity of sulfur accelerated vulcanization has given rise to many contradictory publications for the mechanism of the vulcanization process [1 ± 5]. There are two major problems scientists have to deal with when studying rubber vulcanization: the nature of rubber samples and the simultaneity of reactions. Despite these difficulties, there seems to be a general agreement with the proposed course for sulfur-accelerated vulcanization made by Morrison and Porter in 1984 [6] (Figure 1). Nevertheless, the exact reaction mechanisms that occur in each step of the scheme are not very clear yet. In order to simplify the study, a modeling approach has been traditionally used. The most well-known modeling approach for vulcanization is without any doubt the Model Compound Vulcanization (MCV), which consists of vulcanizing a low-molecular weight model for rubber, namely an olefin [7 ± 8]. Throughout the Figure 1. Proposed general course of sulfur-accelerated vulcanization KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 53. Jahrgang, Nr. 3/
2 literature, several model compounds can be found for the study of the vulcanization process of different types of rubbers [9 ± 11]. The choice of a model compound has been mainly done taking only into account the reactive site believed to play a principal role during the vulcanization, i. e. the allylic position. However, it is important not to forget that the process is really taking place between much larger molecules that contain more than one simple double bond. In an attempt to close the gap between model and real rubbers, in this paper a relatively novel model compound is presented for MCV studies, squalene. The usefulness of squalene for the study of NR vulcanization chemistry has been proved. This compound has been used in some studies focused on the adhesion between rubber and metal, and on the reversion problem NR presents. Recently it has been used as well for the identification of intermediates formed during sulfur-accelerated vulcanization of NR [12]. Usually, the vulcanization can be studied using two different approaches: * Characterization of the reaction attending to the fate of the ingredients of the vulcanizing systems and the formation of new intermediate compounds. * Investigation of network structures formed, i. e. number of crosslinks, number of sulfur atoms per crosslinks, accelerator moieties bound to the main chain and main chain modifications. The analytical strategy followed differs from one approach to the other, and so do the techniques applied. In this paper, due to the characteristics of the chosen model compound both aspects of the process have been taken into account. According to the before-mentioned proposed course for the rubber vulcanization, it is believed that during the first stages of the vulcanization the hydrocarbon backbone does not play a significant role, while ZnO is usually presented as being responsible for breaking down the initial organic accelerator [13]. In this paper it will be proved that the presence of the polymer is crucial for the vulcanization reactions to start. It will be shown as well, that the role of ZnO is highly dependent on the type of accelerator present in the initial vulcanizing system. Experimental Analytical strategy In order to be able to understand the importance of the role of every component in the accelerating system, the following analytical strategy has been used. All the mixtures have been characterized by several analytical techniques to cover both aspects of the process, the fading of the accelerator and the formation of crosslinks (Figure 2). First of all, a model mixture (reference mixture) which contains all the ingredients that are normally found in a vulcanizing system (accelerator/s, metal oxide and long chain fatty acid) has been characterized in order to establish the general course of the reaction. Afterwards, several experiments have been carried out on different mixtures containing determined components. This method allowed studying how the absence of each component affects the course of the reaction that has permitted to establish the exact role of each ingredient during the vulcanization. Model mixtures studied The vulcanization is carried out in a closed vessel at 140 8C. The model mixture is continuously stirred to assure its Figure 2. Analytical strategy Table 1. Composition of the mixture studied Mixture A Ingredients Amount (phr) Squalene 100 CBS 1,2 Sulfur 2 ZnO 5 Stearic acid 2 homogeneity. A nitrogen atmosphere is required in order to avoid oxidation of the double bonds of squalene. During the reaction, samples are taken from the mixture at previously established times. They are quickly cold quenched to stop the reaction. Since the work is done on a model mixture with squalene, liquid samples are handled, and complicated and long extraction stages are not required. The following vulcanizing system has been studied containing one single accelerator (N-cyclohexylamine-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide, CBS) (Table 1). High performance liquid chromatography HPLC experiments were conducted with a Hewlett Packard HP1050 chromatograph. An Ultrabase C-18 (5 lm, 150 4:6 mm) column was used with 132 KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 53. Jahrgang, Nr. 3/2000
3 an UV detector set at 254 nm, and the mobile phase flow was 1 ml/min. The experiments were carried out using a gradient elution with acetonitrile, water, and ammonium acetate buffer (5 mmol/l). Data processing was carried out using the Gyncosoft Chromatographie Datensystem version 4.12 software. 0,1 g of the cold quenched sample was dissolved in acetonitrile for 5 min in an ultrasonic bath at room temperature. Before injection, samples were filtered with a 0,45 lm Nylon filter in order to remove insoluble particles that would damage the column. The injection volume was 20 ll. The disappearance of the CBS occurs at the onset of the crosslink formation (Figure 3). This suggests that the reason for the cure delay period has to do with more rapid reaction of the intermediate compounds with the initial vulcanizing agents rather than with the reaction of intermediate compounds with the unsaturated hydrocarbon to yield crosslinks. The chemistry of sulfenamides, 2-mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) has a catalytic effect on the CBS decomposition [14]. This catalytic effect was detected when the reference mixture A (see Table 1) was heated in the presence of a small amount of MBT (Figure 4). The addition of MBT to the formulation provokes a considerable shortening of the scorch time. It seems logical to think then that CBS dissociation requires a certain amount of free MBT to start. Therefore, the formation of MBT during the first stages of the vulcanization reaction is very important for the onset of the process. However, there is still a lot of controversy on how this first amount of free MBT is formed. The different hypotheses postulated concerning this first step of the vulcanization have been studied focusing on the induction period for CBS dissociation. Some authors support the hypothesis of the dissociation of sulfenamide accelerators via thermal decomposition [15]. Such a reaction, however, exhibited an induction period of about 135 min (Figure 5), which is obviously too long to consider thermal decomposition as the unique reaction path for the dissociation of CBS. Concerning this first step of the vulcanization process, other authors emphasize the role of ZnO in this dissociation. If that is true, then taking out ZnO from the reference mixture A, should not result in changed CBS concentrations. The absence of ZnO in the reacting mixture resulted in a more delayed onset of the CBS dissociation (35 min) compared to the one observed with the reference mixture A (25 min) (Figure 6). The GPC results Gel permeation chromatography GPC experiments were carried out in a Hewlett Packard HP1090, using a Waters HR 0,5 Styragel (7,8 300 mm) column with a UV detector set at 275 nm. The mobile phase used was tetrahydrofuran (THF, HPLC quality) at a flow of 1 ml/ min. A Hewlett Packard HP 3D Chemstation was the software used for data adquisition. Samples taken from the reacting mixture were dissolved in THF at a concentration of 0,1 wt.-%, and the injected volume was 100 ll. Results and discussion Figure 3. Mixture A vulcanization at 140 8C: (~) CBS concentration vs. reaction time; (*) Crosslinked squalene vs. reaction time Figure 4. Comparison between the CBS concentration decrease in mixture A (~) and in the mixture with added free MBT, 0,2 phr (~) during vulcanization at 140 8C KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 53. Jahrgang, Nr. 3/
4 Figure 5. CBS concentration when heated at 140 8C in an inert solvent (CBS, 1,2 phr; sulfur, 2 phr; stearic acid, 2 phr) Figure 6. CBS concentration during vulcanization at 140 8C (~) mixture A (~) as A but without ZnO showed that, in this case, the crosslink formation occurred as well with the same delay. That fact confirms that CBS concentration decrease occurs when the crosslink formation starts. According to these results, this second hypotheses proposed turned out to be incomplete as well to explain the global course of the vulcanization process. There is a 5±10 min delay in the onset of the dissociation, but it did occur despite the fact that there was no ZnO in the mixture, and it was accompanied by crosslink formation. So there should exist still another parameter that is taking part in the reaction. A second modification was done on the reference mixture A, this time taking out the model molecule and carrying out the reaction in an inert solvent (octane). It has been observed that under those conditions the induction period for CBS dissociation is 85 min (Figure 7). The induction periods obtained for the 3 mixtures obtained are 1. Reference mixture A 25 min 2. Reference mixture A without ZnO 35 min 3. Reference mixture A without olefin 85 min the larger difference between the last and the former two seems to point out that the presence of the hydrocarbon model molecule could be influencing somehow the dissociation of the CBS. A third modification has been done on mixture A, this time taking out both the model molecule and ZnO. It has been observed that despite prolonging the reaction time for up to 120 min, no dissociation occurs at all. The following can be concluded from all these variations of the induction periods for CBS dissociation: both postulated reaction paths to obtain a small amount of the MBT required for the onset of CBS dissociation might be probable depending on the type of elastomer vulcanized. However, there is a third parameter that turned out to be the most favored one. It has been proved that in order to obtain the mentioned free MBT, an interaction between the accelerator and the model compound must occur (Figure 8). However, the product formed according to the above scheme is known to be non-reactive since it is a mono-sulfidic rubber-bound compound. The group of McGill proposed a first sulfuration of the accelerator-giving rise to compounds of type BtSS x NR 2 [16]. These sulfurated products were already mentioned in the earlier works of Campbell and Wise [17]. Considering this, the initial rubberbound compounds formed from CBS would be polysulfidic. These are known to be crosslink precursors with neighboring chains releasing MBT. The consumption of sulfur by the direct sulfuration of the accelerator is negligible and no significant decrease was observed. Only a very small amount of R 2 NS x SBt is required. Once the MBT is generated, its catalytic effect on CBS dissociation is much faster than the direct sulfuration of the accelerator, turning out to be the major reaction path within this period, until there is no more CBS left in the reacting mixture (Figure 9). However, throughout the work done in this paper, no CBP (sulfurated accelera- 134 KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 53. Jahrgang, Nr. 3/2000
5 Conclusions Figure 7. CBS concentration during vulcanization at 140 8C (CBS, 1,2 phr; sulfur, 2 phr; ZnO, 5 phr; stearic acid, 2 phr) Squalene has been proved to be a suitable model compound to study the vulcanization process. In this paper, the MCV approach has given more insight in the first stages of the natural rubber vulcanization using a sulfenamide type accelerator. Small amounts of MBT are required for the formation of the active sulfurating agents. It has been proved that this compound is formed from the direct interaction between the accelerator and the double bonds of the hydrocarbon. The role of the ZnO usually described as a catalyst for the breaking down of the accelerator has been proved not to be the most favored. Similarly, the thermal decomposition of the sulfenamide is neglected to be the cause of the active sulfurating agents formation. tor) was detected in any stage of the reaction. Some authors claim that such compounds are formed very rapidly in the earlier stages of the vulcanization and that they react readily, but this could not explain the fact that no decomposition at all was detected when CBS was heated in the presence of sulfur presented previously. On the other hand (Figure 10), some evidence was found to support the direct interaction between accelerator and the olefin proposed in Figure 8. The mass spectrometry detection [12] allowed the identification of certain compounds whose presence during the reaction could be explained by such an interaction. References [1] P.W. Allen, D. Banard, B. Saville, Chem. Ind. Britain 6 (1970) 382. [2] M.M. Coleman, J.R. Shelton, J.L. Koenig, Ind. Eng.Chem., Prod. Res. Develop. 13 (1974) 154. [3] A.Y. Coran, Chem. Techn. 13 (1983) 106. [4] C.J. Hahn, M. Runk, M. Schollmeyer, U. Theimer, E. Walter, Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 51 (1998) 206 [5] M.R. Krejsa, J.L. Koenig, Elastomer Technology Handbook, Chap. 11, CRC Press, New York, (1993). Figure 8. Interaction between the accelerator and the hydrocarbon Figure 9. Interaction between the accelerator and the hydrocarbon previous to the sulfuration of the former (CBP stands for polysulfide cyclohexylamine-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide) KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 53. Jahrgang, Nr. 3/
6 Figure 10. Schematic approach to the direct interaction between the CBS and the hydrocarbon [6] M.J. Morrison, M. Porter, Rubber Chem. Technol. 57 (1984) 63. [7] H.E. Westlake, Chemical Reviews 39 (1946) 219. [8] P.J. Nieuwenhuizen, et al., Rubber Chem. Technol. 79 (1997) 120. [9] F.K. Lautenschlaeger, K. Edwards, Rubber Chem. Technol. 53 (1980) 27. [10] J.H.M. van der Berg, et al., Rubber Chem. Technol. 57 (1984) 265. [11] P. Versloot, et al., Rubber Chem. Technol. 70 (1997) 106. [12] S. Borro s, Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst., in press, (1999). [13] J.A. McCleverty, Studies Inorg. Chem. 5 (1984) 311. [14] J.L. Craine, M. Raban, Rubber Chem. Technol. 62 (1989) 67. [15] G. KyselaÁ Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 49 (1996) 678. [16] R.H. Campbell, R.W. Wise, Rubber Chem. Technol. 37 (1964) 635. [17] M.H.S. Gradwell, W.J. McGill, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 61 (1996) The authors Prof. Dr. S. Borro s is Head of the Material Science Laboratory at the Institut Quimic de Sarria of the Universitat Ramon Llull, Bacelona, Spain. Ms. Dr. N. Agullo is a former PhD student in the research group of S. Borro s; she is now working in a pharmaceutical company. Correspondong author Dr. S. Borro s, Institut Quimic de SarriaÁ, Materials Science Laboratory, Via Augusta 390, E Barcelona 136 KGK Kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 53. Jahrgang, Nr. 3/2000
Time-Of-Flight SIMS as a useful Technique for the Study of the Influence of Carbon Black in Natural Rubber Vulcanization
 PRUÈ FEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING TOF-SIMS Vulcanization Mechanisms Carbon Black Accelerators The use of TOFSIMS technique to analyze the carbon black surface during the squalene vulcanization
PRUÈ FEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING TOF-SIMS Vulcanization Mechanisms Carbon Black Accelerators The use of TOFSIMS technique to analyze the carbon black surface during the squalene vulcanization
SULFUR VULCANIZATION OF NATURAL RUBBER FOR BENZOTHIAZOLE ACCELERATED FORMULATIONS: FROM REACTION MECHANISMS TO A RATIONAL KINETIC MODEL
 Y 592 03-R-19 8/18/03 3:21 PM Page 592 SULFUR VULCANIZATION OF NATURAL RUBBER FOR BENZOTHIAZOLE ACCELERATED FORMULATIONS: FROM REACTION MECHANISMS TO A RATIONAL KINETIC MODEL PRASENJEET GHOSH, + SANTHOJI
Y 592 03-R-19 8/18/03 3:21 PM Page 592 SULFUR VULCANIZATION OF NATURAL RUBBER FOR BENZOTHIAZOLE ACCELERATED FORMULATIONS: FROM REACTION MECHANISMS TO A RATIONAL KINETIC MODEL PRASENJEET GHOSH, + SANTHOJI
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC)
 Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
PHASE SELECTIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON BLACK IN BINARY RUBBER BLENDS
 HASE SEECTIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON BACK IN BINARY RUBBER BENDS S. Ilisch, H.H. e, H.-J. Radusch Martin uther University Halle-Wittenberg, Center of Engineering Sciences, D-699 Halle (Saale), Germany
HASE SEECTIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON BACK IN BINARY RUBBER BENDS S. Ilisch, H.H. e, H.-J. Radusch Martin uther University Halle-Wittenberg, Center of Engineering Sciences, D-699 Halle (Saale), Germany
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) or Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
 Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) or Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a non-interaction based separation mechanism in which compounds are retained for different
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) or Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a non-interaction based separation mechanism in which compounds are retained for different
INTRODUCTION S. CERVENY, 1 A. J. MARZOCCA 1,2. Pabellón 1, Buenos Aires 1428, Argentina. Received 5 July 1998; accepted 4 December 1998
 Analysis of Variation of Molecular Parameters of Natural Rubber during Vulcanization in Conformational Tube Model. II. Influence of Sulfur/Accelerator Ratio S. CERVENY, 1 A. J. MARZOCCA 1,2 1 Universidad
Analysis of Variation of Molecular Parameters of Natural Rubber during Vulcanization in Conformational Tube Model. II. Influence of Sulfur/Accelerator Ratio S. CERVENY, 1 A. J. MARZOCCA 1,2 1 Universidad
School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS.
 School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 100 Internal Examiners: Professor A Kindness Dr T Msagati
School of Chemistry UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL, WESTVILLE CAMPUS JUNE 2009 EXAMINATION CHEM340: INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS DURATION: 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS: 100 Internal Examiners: Professor A Kindness Dr T Msagati
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
Purification of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole by solvent extraction
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(2), 282-287 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Purification of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole by solvent extraction Prakorn Ramakul, Milan Hronec* and Ura Pancharoen Department of Chemical Engineering,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(2), 282-287 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Purification of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole by solvent extraction Prakorn Ramakul, Milan Hronec* and Ura Pancharoen Department of Chemical Engineering,
Analytical Properties of Silica ± a Key for Understanding Silica Reinforcement 1
 ROHSTOFFE UND ANWENDUNGEN RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS Rolling resistance Highly dispersible silica Filler network Silanol group density surface activity For a long time simultaneous improvements of
ROHSTOFFE UND ANWENDUNGEN RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS Rolling resistance Highly dispersible silica Filler network Silanol group density surface activity For a long time simultaneous improvements of
Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212. What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for?
 Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212 What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for? How does solvent extraction work? Write the partitioning coefficient for the following reaction:
Chromatography- Separation of mixtures CHEM 212 What is solvent extraction and what is it commonly used for? How does solvent extraction work? Write the partitioning coefficient for the following reaction:
Packed Column for Ultra-Fast Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography, TSKgel Super-ODS. Table of Contents
 No. 089 SEPARATION REPORT Packed Column for Ultra-Fast Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography, TSKgel Super-ODS Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Column Specification 1 3. Features of Packing Materials
No. 089 SEPARATION REPORT Packed Column for Ultra-Fast Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography, TSKgel Super-ODS Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Column Specification 1 3. Features of Packing Materials
ExA1. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons. Olefins. Experiment: Next Week. Structure Addition Reactions Mechanisms
 ExA1 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Olefins Structure Addition Reactions Mechanisms Experiment: part A - Setup part B - Reaction part C - Isolation part D - Analysis Next Week 1 Alkenes & Alkynes Hydrocarbons
ExA1 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Olefins Structure Addition Reactions Mechanisms Experiment: part A - Setup part B - Reaction part C - Isolation part D - Analysis Next Week 1 Alkenes & Alkynes Hydrocarbons
Liquid storage: Holds the solvent which is going to act as the mobile phase. Pump: Pushes the solvent through to the column at high pressure.
 High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a much more sensitive and useful technique than paper and thin layer chromatography. The instrument used for HPLC is called a high performance liquid chromatograph.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a much more sensitive and useful technique than paper and thin layer chromatography. The instrument used for HPLC is called a high performance liquid chromatograph.
Dilution(*) Chromatography
 WA20264 Poster # 184, HPLC 2002, Montreal, 4-5 June 2002 At-Column Column-Dilution for Preparative Dilution(*) Chromatography Cecilia Mazza, Jie Cavanaugh, Ziling Lu,Tom Sirard,Tom Wheat and Uwe Neue Waters
WA20264 Poster # 184, HPLC 2002, Montreal, 4-5 June 2002 At-Column Column-Dilution for Preparative Dilution(*) Chromatography Cecilia Mazza, Jie Cavanaugh, Ziling Lu,Tom Sirard,Tom Wheat and Uwe Neue Waters
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV*
 Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
HPLC Background Chem 250 F 2008 Page 1 of 24
 HPLC Background Chem 250 F 2008 Page 1 of 24 Outline: General and descriptive aspects of chromatographic retention and separation: phenomenological k, efficiency, selectivity. Quantitative description
HPLC Background Chem 250 F 2008 Page 1 of 24 Outline: General and descriptive aspects of chromatographic retention and separation: phenomenological k, efficiency, selectivity. Quantitative description
Thin Layer Chromatography
 Thin Layer Chromatography Thin-layer chromatography involves the same principles as column chromatography, it also is a form of solid-liquid adsorption chromatography. In this case, however, the solid
Thin Layer Chromatography Thin-layer chromatography involves the same principles as column chromatography, it also is a form of solid-liquid adsorption chromatography. In this case, however, the solid
Factors Affecting Reaction Rate
 Factors Affecting Reaction Rate Outcomes: Formulate an operational definition of reaction rate. State the collision theory. Perform a lab to identify factors that affect reaction rate. Describe, qualitatively,
Factors Affecting Reaction Rate Outcomes: Formulate an operational definition of reaction rate. State the collision theory. Perform a lab to identify factors that affect reaction rate. Describe, qualitatively,
Polymer analysis by GPC-SEC. Technical Note. Introduction
 Polymer analysis by GPC-SEC Technical Note Introduction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also referred to as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a mode of liquid chromatography in which the components
Polymer analysis by GPC-SEC Technical Note Introduction Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also referred to as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a mode of liquid chromatography in which the components
Xanthate Accelerators for Low Temperature Curing of Natural Rubber
 Xanthate Accelerators for Low Temperature Curing of Natural Rubber SHINY PALATY, RANI JOSEPH Department of Polymer Science and Rubber Technology, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin 682022,
Xanthate Accelerators for Low Temperature Curing of Natural Rubber SHINY PALATY, RANI JOSEPH Department of Polymer Science and Rubber Technology, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin 682022,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2633 Mechanically controlled radical polymerization initiated by ultrasound Hemakesh Mohapatra, Maya Kleiman, Aaron P. Esser-Kahn Contents 1. Materials and methods 2 2. Procedure for
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2633 Mechanically controlled radical polymerization initiated by ultrasound Hemakesh Mohapatra, Maya Kleiman, Aaron P. Esser-Kahn Contents 1. Materials and methods 2 2. Procedure for
Application Note. Author. Abstract. Pharmaceutical QA/QC. Siji Joseph Agilent Technologies, Inc. Bangalore, India
 Effective use of pharmacopeia guidelines to reduce cost of chromatographic analysis Optimized, cost-effective HPLC analysis of atorvastatin by varying column dimensions within the USP allowed limts
Effective use of pharmacopeia guidelines to reduce cost of chromatographic analysis Optimized, cost-effective HPLC analysis of atorvastatin by varying column dimensions within the USP allowed limts
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 High Performance Liquid Chromatography () Instrumentation Normal Phase Chromatography Normal Phase - a polar stationary phase with a less polar mobile phase.
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 High Performance Liquid Chromatography () Instrumentation Normal Phase Chromatography Normal Phase - a polar stationary phase with a less polar mobile phase.
Theory & Practice Of Vulcanization
 Theory & Practice Of Vulcanization DANIEL L. HERTZ, JR. SEALS EASTERN INC. RED BANK, NJ 07701 This paper concerns the theory and practice of vulcanization - the process of adding crosslinks to long-chain
Theory & Practice Of Vulcanization DANIEL L. HERTZ, JR. SEALS EASTERN INC. RED BANK, NJ 07701 This paper concerns the theory and practice of vulcanization - the process of adding crosslinks to long-chain
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework
 Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations
 Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations Homework Due Monday April 24 Problems 23-1, 23-2, 23-7, 23-15, 23-27, 23-29, 23-32 Analytical Separations: Universal approach to analyzing complex mixtures
Chapter 23 Introduction to Analytical Separations Homework Due Monday April 24 Problems 23-1, 23-2, 23-7, 23-15, 23-27, 23-29, 23-32 Analytical Separations: Universal approach to analyzing complex mixtures
Combined metallocene catalysts: an efficient technique to manipulate long-chain branching frequency of polyethylene
 Macromol. Rapid Commun. 20, 541 545 (1999) 541 Combined metallocene catalysts: an efficient technique to manipulate long-chain branching frequency of polyethylene Daryoosh Beigzadeh, João B. P. Soares*,
Macromol. Rapid Commun. 20, 541 545 (1999) 541 Combined metallocene catalysts: an efficient technique to manipulate long-chain branching frequency of polyethylene Daryoosh Beigzadeh, João B. P. Soares*,
Differentiation of polymer branching and composition using the Mark Houwink plot
 Differentiation of polymer branching and composition using the Mark Houwink plot MOLECULAR SIZE MOLECULAR STRUCTURE MOLECULAR WEIGHT Introduction The manipulation of polymer properties through changes
Differentiation of polymer branching and composition using the Mark Houwink plot MOLECULAR SIZE MOLECULAR STRUCTURE MOLECULAR WEIGHT Introduction The manipulation of polymer properties through changes
Size Exclusion Chromatography: Method Development
 Size Exclusion Chromatography: Method Development To develop a successful Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) method it is desired to find a column/solvent combination under which the follow conditions
Size Exclusion Chromatography: Method Development To develop a successful Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) method it is desired to find a column/solvent combination under which the follow conditions
CHAPTER Identification of side products in the synthesis of MMBC. As shown in the previous chapter, MMBC can be produced with high
 113 CHAPTER 6 IDENTIFICATION OF SIDE PRODUCTS IN THE PRODUCTION OF METHYL 4- (METHOXYMETHYL) BENZENE CARBOXYLATE (MMBC) FROM METHYL 5- (METHOXYMETHYL)-FURAN-2-CARBOXYLATE (MMFC) AND ETHYLENE 6.1 Identification
113 CHAPTER 6 IDENTIFICATION OF SIDE PRODUCTS IN THE PRODUCTION OF METHYL 4- (METHOXYMETHYL) BENZENE CARBOXYLATE (MMBC) FROM METHYL 5- (METHOXYMETHYL)-FURAN-2-CARBOXYLATE (MMFC) AND ETHYLENE 6.1 Identification
Microwave Dielectric Properties of Rubber Compounds Undergoing Vulcanisation
 PRUÈ FEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING Dielectric parameters microwave method vulcanisation elastomers monitoring The application of microwave measurements to the characterisation of rubber compounds
PRUÈ FEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING Dielectric parameters microwave method vulcanisation elastomers monitoring The application of microwave measurements to the characterisation of rubber compounds
Sulfur Curing of Natural Rubber in Presence of Zinc Di-n-Butylthiophosphate
 KONSTRUKTION UND SIMULATION CONSTRUCTION AND SIMULATION Thiophosphate Thiazole Accelerator combinations Natural rubber Sulfur curing Ageing, Network structure The influence of combinations of zinc din-butylthiophosphate
KONSTRUKTION UND SIMULATION CONSTRUCTION AND SIMULATION Thiophosphate Thiazole Accelerator combinations Natural rubber Sulfur curing Ageing, Network structure The influence of combinations of zinc din-butylthiophosphate
Mechanical Properties of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Cured by Ionizing Radiation in the Presence of Sulfur and Polyfunctional Agent
 MY9800964 Mechanical Properties of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Cured by Ionizing Radiation in the Presence of Sulfur and Polyfunctional Agent A.A. Basfar, M.M. Abdel-Aziz*, and F.A. Al-Harithy Institute of
MY9800964 Mechanical Properties of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Cured by Ionizing Radiation in the Presence of Sulfur and Polyfunctional Agent A.A. Basfar, M.M. Abdel-Aziz*, and F.A. Al-Harithy Institute of
Chapter 4. Results and Discussion. 4.1 Monomer Syntheses
 Chapter 4 Results and Discussion 4.1 Monomer Syntheses The syntheses of a family of novel, carbazole based methacrylate, dimethacrylate, and acrylate monomers, and subsequent purifications, were successful.
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion 4.1 Monomer Syntheses The syntheses of a family of novel, carbazole based methacrylate, dimethacrylate, and acrylate monomers, and subsequent purifications, were successful.
Liquid Crystal. Liquid Crystal. Liquid Crystal Polymers. Liquid Crystal. Orientation of molecules in the mesophase
 Liquid Crystal - Liquid crystals (LCs) are a state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal. (Fourth state of matter) Liquid Crystal Orientation
Liquid Crystal - Liquid crystals (LCs) are a state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal. (Fourth state of matter) Liquid Crystal Orientation
Leather Dyes Properties and Analysis
 Leather Dyes Properties and Analysis Campbell Page 1,*, Jens Fennen 1,Daniel Gagliardino 2 1 TFL Leather Technology Ltd, Postfach 264, CH-419 Basel, SWITZERLAD 2 TFL Argentina S.A., Cao de la Costa Brava
Leather Dyes Properties and Analysis Campbell Page 1,*, Jens Fennen 1,Daniel Gagliardino 2 1 TFL Leather Technology Ltd, Postfach 264, CH-419 Basel, SWITZERLAD 2 TFL Argentina S.A., Cao de la Costa Brava
Blending, Curing and Reinforcement of NR/BR/EPDM Compounds for Tire Sidewall Applications
 Blending, Curing and Reinforcement of NR/BR/EPDM Compounds for Tire Sidewall Applications Studies on EPDM Grafting by N-ChlorothioN Chlorothio-N-Butyl- Benzenesulfonamide DPI #356 H. Zhang, R.N. Datta,
Blending, Curing and Reinforcement of NR/BR/EPDM Compounds for Tire Sidewall Applications Studies on EPDM Grafting by N-ChlorothioN Chlorothio-N-Butyl- Benzenesulfonamide DPI #356 H. Zhang, R.N. Datta,
LC and LC/MS Column Selection Flow Chart
 LC and LC/MS Column Selection Flow Chart To use the column selection diagram below, simply follow the path for your analyte and mobile phase. At the far right, follow your final column selection to the
LC and LC/MS Column Selection Flow Chart To use the column selection diagram below, simply follow the path for your analyte and mobile phase. At the far right, follow your final column selection to the
NEVIRAPINE ORAL SUSPENSION Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (February 2009)
 February 2009. NEVIRAPINE ORAL SUSPENSION Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (February 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
February 2009. NEVIRAPINE ORAL SUSPENSION Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (February 2009) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
LUMEFANTRINUM LUMEFANTRINE
 July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
What type of samples are common? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses. Number of samples? Aims. Sources of error. Sample preparation
 What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
Agilent s New Weak Anion Exchange (WAX) Solid Phase Extraction Cartridges: SampliQ WAX
 Agilent s New Weak Anion Exchange (WAX) Solid Phase Extraction Cartridges: SampliQ WAX Technical Note Agilent s SampliQ WAX provides Applications for strongly acidic, acidic and neutral compounds Excellent
Agilent s New Weak Anion Exchange (WAX) Solid Phase Extraction Cartridges: SampliQ WAX Technical Note Agilent s SampliQ WAX provides Applications for strongly acidic, acidic and neutral compounds Excellent
Application of NMR in the Tire Industry
 PRÜFEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING Molecular mobility DMTA NMR-relaxation WLF-equation Mastercurve A series of unfilled elastomers, consisting of different polymers and crosslink densities is investigated
PRÜFEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING Molecular mobility DMTA NMR-relaxation WLF-equation Mastercurve A series of unfilled elastomers, consisting of different polymers and crosslink densities is investigated
IDENTIFICATION OF STEROIDS IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS BY TLC AND HPLC 1 02/12/2005 ACM 007 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC)
 Document A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC) 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate
Document A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC) 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate
Present State and Main Trends of Research on Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Organic Compounds
 1 Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on July 10, 2018 at 19:07:56 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Present State and Main Trends
1 Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on July 10, 2018 at 19:07:56 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Present State and Main Trends
DETERMINATION OF DRUG RELEASE DURING DISSOLUTION OF NICORANDIL IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY USING REVERSE PHASE HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 9 DETERMINATION OF DRUG RELEASE DURING DISSOLUTION OF NICORANDIL IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY USING REVERSE PHASE HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY CHAPTER 9 Determination of drug release during
CHAPTER 9 DETERMINATION OF DRUG RELEASE DURING DISSOLUTION OF NICORANDIL IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY USING REVERSE PHASE HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY CHAPTER 9 Determination of drug release during
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
 High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
8. Methods in Developing Mobile Phase Condition for C18 Column
 I. HPLC Columns Technical Information 8. Methods in Developing Mobile Phase Condition for C18 Column Introduction In reversed phase HPLC, octadecyl group bonded silica columns (C18, ODS) are the most widely
I. HPLC Columns Technical Information 8. Methods in Developing Mobile Phase Condition for C18 Column Introduction In reversed phase HPLC, octadecyl group bonded silica columns (C18, ODS) are the most widely
Appendix 1. GPC Characterization of Cyclic Polymers
 175 Appendix 1 GPC Characterization of Cyclic Polymers 176 Cyclic metathesis catalysts described in Chapters 2 and 3 also exhibit functional group tolerance, and can be used to readily polymerize functionalized
175 Appendix 1 GPC Characterization of Cyclic Polymers 176 Cyclic metathesis catalysts described in Chapters 2 and 3 also exhibit functional group tolerance, and can be used to readily polymerize functionalized
Accurate Mass Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing Waters: Identification of Polyethylene Glycol Surfactants by LC/Q-TOF-MS
 Accurate Mass Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing Waters: Identification of Polyethylene Glycol Surfactants by LC/Q-TOF-MS Application Note Authors E. Michael Thurman and Imma Ferrer Center for Environmental
Accurate Mass Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing Waters: Identification of Polyethylene Glycol Surfactants by LC/Q-TOF-MS Application Note Authors E. Michael Thurman and Imma Ferrer Center for Environmental
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Accelerated Cure of Phenol-Formaldehyde Resins: Studies With Model Compounds
 Accelerated Cure of Phenol-Formaldehyde Resins: Studies With Model Compounds Anthony H. Conner, Linda F. Lorenz, Kolby C. Hirth USDA Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory, One Gifford Pinchot Drive,
Accelerated Cure of Phenol-Formaldehyde Resins: Studies With Model Compounds Anthony H. Conner, Linda F. Lorenz, Kolby C. Hirth USDA Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory, One Gifford Pinchot Drive,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Rapid and sensitive detection of acrylic acid using a novel fluorescence
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Rapid and sensitive detection of acrylic acid using a novel fluorescence
Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution.
 Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution. Difficulty with M n and M w, etc. osome polymers are hard to describe from just M n, M w, etc. o Examples: Bimodal, multimodal, nonuniform, broad, etc. MWDs. oin early
Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution. Difficulty with M n and M w, etc. osome polymers are hard to describe from just M n, M w, etc. o Examples: Bimodal, multimodal, nonuniform, broad, etc. MWDs. oin early
HPLC Praktikum Skript
 HPLC Praktikum Skript Assistants: Gianluca Bartolomeo HCI D330, 3 46 68, bartolomeo@org.chem.ethz.ch Sahar Ghiasikhou HCI E330, 2 29 29, ghiasikhou@org.chem.ethz.ch 1. Introduction In chromatographic techniques,
HPLC Praktikum Skript Assistants: Gianluca Bartolomeo HCI D330, 3 46 68, bartolomeo@org.chem.ethz.ch Sahar Ghiasikhou HCI E330, 2 29 29, ghiasikhou@org.chem.ethz.ch 1. Introduction In chromatographic techniques,
Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate
 1 Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate ME Zeynali Petrochemical Synthesis Group, Petrochemical Faculty, Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute (IPPI), P.O.
1 Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate ME Zeynali Petrochemical Synthesis Group, Petrochemical Faculty, Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute (IPPI), P.O.
LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY
 INTRODUCTION WHAT IS IN YOUR PAIN RELIEVER (Revised: 12-8-92) Headache, sore muscles, arthritis pain... How do you spell relief? Pain serves the useful function of alerting you when some component of a
INTRODUCTION WHAT IS IN YOUR PAIN RELIEVER (Revised: 12-8-92) Headache, sore muscles, arthritis pain... How do you spell relief? Pain serves the useful function of alerting you when some component of a
IR-LC Deposition and Detection System. Polymer Deformulation and Additive Analysis by a Single GPC-IR Run
 DiscovIR-GPC DiscovIR-L IR-LC Deposition and Detection System Application Note 42 Polymer Deformulation and Additive Analysis by a Single GPC-IR Run ABSTRACT This application note describes the use of
DiscovIR-GPC DiscovIR-L IR-LC Deposition and Detection System Application Note 42 Polymer Deformulation and Additive Analysis by a Single GPC-IR Run ABSTRACT This application note describes the use of
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD)
 The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
VALIDATION OF A UPLC METHOD FOR A BENZOCAINE, BUTAMBEN, AND TETRACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE TOPICAL SOLUTION
 VALIDATION OF A UPLC METHOD FOR A BENZOCAINE, BUTAMBEN, AND TETRACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE TOPICAL SOLUTION Andrew J. Aubin and Tanya L. Jenkins Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA INTRODUCTION Benzocaine (4-Aminobenzoic
VALIDATION OF A UPLC METHOD FOR A BENZOCAINE, BUTAMBEN, AND TETRACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE TOPICAL SOLUTION Andrew J. Aubin and Tanya L. Jenkins Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA INTRODUCTION Benzocaine (4-Aminobenzoic
Polymer Reaction Engineering
 Polymer Reaction Engineering Polymerization Techniques Bulk Solution Suspension Emulsion Interfacial Polymerization Solid-State Gas-Phase Plasma Polymerization in Supercritical Fluids Bulk Polymerization
Polymer Reaction Engineering Polymerization Techniques Bulk Solution Suspension Emulsion Interfacial Polymerization Solid-State Gas-Phase Plasma Polymerization in Supercritical Fluids Bulk Polymerization
Anatoly K. Pogodaev 1, Sergey G. Tikhomirov 2, Olga V. Karmanova 2, Elena A. Balashova 2, Semen L. Podvalny 3, Anastasiya Yu.
 Journal of Chemical Semen L. Technology Podvalny, and Anastasiya Metallurgy, Yu. Fatneva 53, 5, 2018, 807-815 MODELING ELASTOMER PROPERTIES IN PRESENCE OF A COMPOSITE VULCANIZATION ACTIVATOR Anatoly K.
Journal of Chemical Semen L. Technology Podvalny, and Anastasiya Metallurgy, Yu. Fatneva 53, 5, 2018, 807-815 MODELING ELASTOMER PROPERTIES IN PRESENCE OF A COMPOSITE VULCANIZATION ACTIVATOR Anatoly K.
Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics
 Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics Thus far we have calculated rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, etc. based on observations of macroscopic properties, but what is happening at the molecular
Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics Thus far we have calculated rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, etc. based on observations of macroscopic properties, but what is happening at the molecular
Background on Solubility
 CHEM254 01 Open Notebook Science Solubility Challenge 1 For the first laboratory exercise of this semester we are going to participate in the Open Notebook Science (ONS) solubility challenge http://onschallenge.wikispaces.com/.
CHEM254 01 Open Notebook Science Solubility Challenge 1 For the first laboratory exercise of this semester we are going to participate in the Open Notebook Science (ONS) solubility challenge http://onschallenge.wikispaces.com/.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Polymerization-induced Self-Assembly of Homopolymer and Diblock copolymer: A Facile Approach for preparing Polymer Nano-objects with Higher Order Morphologies Jianbo Tan *a,b, Chundong
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Polymerization-induced Self-Assembly of Homopolymer and Diblock copolymer: A Facile Approach for preparing Polymer Nano-objects with Higher Order Morphologies Jianbo Tan *a,b, Chundong
HPLC Preparative Scaleup of Calcium Channel Blocker Pharmaceuticals Application
 HPLC Preparative Scaleup of Calcium Channel Blocker Pharmaceuticals Application Pharmaceuticals Author Cliff Woodward and Ronald Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2850 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 19808
HPLC Preparative Scaleup of Calcium Channel Blocker Pharmaceuticals Application Pharmaceuticals Author Cliff Woodward and Ronald Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2850 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 19808
Supporting information
 Supporting information Temperature and ph-dual Responsive AIE-Active Core Crosslinked Polyethylene Poly(methacrylic acid) Multimiktoarm Star Copolymers ` Zhen Zhang,*,, and Nikos Hadjichristidis*, School
Supporting information Temperature and ph-dual Responsive AIE-Active Core Crosslinked Polyethylene Poly(methacrylic acid) Multimiktoarm Star Copolymers ` Zhen Zhang,*,, and Nikos Hadjichristidis*, School
Reactivity of the Sulfur Chains of the Tetrasulfane Silane Si 69 and the Disulfane Silane TESPD 1
 ROHSTOFFE UND ANWENDUNGEN RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS Silane Silica Reaction mechanism cure Vulcanisation In this paper the different reactivities of the di- and polysulfane chains of the silanes TESPD
ROHSTOFFE UND ANWENDUNGEN RAW MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS Silane Silica Reaction mechanism cure Vulcanisation In this paper the different reactivities of the di- and polysulfane chains of the silanes TESPD
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB31604.35-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 31604.35-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB31604.35-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 31604.35-2016
Analytical Chemistry
 Analytical Chemistry Chromatographic Separations KAM021 2016 Dr. A. Jesorka, 6112, aldo@chalmers.se Introduction to Chromatographic Separations Theory of Separations -Chromatography Terms Summary: Chromatography
Analytical Chemistry Chromatographic Separations KAM021 2016 Dr. A. Jesorka, 6112, aldo@chalmers.se Introduction to Chromatographic Separations Theory of Separations -Chromatography Terms Summary: Chromatography
Liquid Chromatography
 Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
What is Chromatography?
 What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a physico-chemical process that belongs to fractionation methods same as distillation, crystallization or fractionated extraction. It is believed that the separation
What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a physico-chemical process that belongs to fractionation methods same as distillation, crystallization or fractionated extraction. It is believed that the separation
C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you)
 Name: C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
Name: C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
Amphiphilic diselenide-containing supramolecular polymers
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Amphiphilic diselenide-containing supramolecular polymers Xinxin Tan, Liulin Yang, Zehuan
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Amphiphilic diselenide-containing supramolecular polymers Xinxin Tan, Liulin Yang, Zehuan
Identification and Characterization of an Isolated Impurity Fraction: Analysis of an Unknown Degradant Found in Quetiapine Fumarate
 Identification and Characterization of an Isolated Impurity Fraction: Analysis of an Unknown Degradant Found in Quetiapine Fumarate Michael D. Jones, Xiang Jin Song, Robert S. Plumb, Peter J. Lee, and
Identification and Characterization of an Isolated Impurity Fraction: Analysis of an Unknown Degradant Found in Quetiapine Fumarate Michael D. Jones, Xiang Jin Song, Robert S. Plumb, Peter J. Lee, and
Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography. Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification
 Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep
Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep
Chapter 5. Ionic Polymerization. Anionic.
 Chapter 5. Ionic Polymerization. Anionic. Anionic Polymerization Dr. Houston S. Brown Lecturer of Chemistry UH-Downtown brownhs@uhd.edu What you should know: What is anionic polymerization? What is MWD,
Chapter 5. Ionic Polymerization. Anionic. Anionic Polymerization Dr. Houston S. Brown Lecturer of Chemistry UH-Downtown brownhs@uhd.edu What you should know: What is anionic polymerization? What is MWD,
FIVE MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES
 FIVE MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES 63 Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of five membered aromatic heterocycles X = O, S or NH a-substitution b-substitution The Substitution is regioselective
FIVE MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES 63 Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of five membered aromatic heterocycles X = O, S or NH a-substitution b-substitution The Substitution is regioselective
F G C G H H C B B A A DD E E
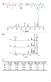 a D E F G H D E I F G H F F I DD E E G H H b c [1] 0 (M) [2a] 0 (M) [1] (M) [2a] (M) [3a] (M) K (M -1 ) a) 0.160 0.139 0.049 0.028 0.111 81 b) 0.147 0.180 0.025 0.058 0.122 84 c) 0.157 0.270 0.013 0.126
a D E F G H D E I F G H F F I DD E E G H H b c [1] 0 (M) [2a] 0 (M) [1] (M) [2a] (M) [3a] (M) K (M -1 ) a) 0.160 0.139 0.049 0.028 0.111 81 b) 0.147 0.180 0.025 0.058 0.122 84 c) 0.157 0.270 0.013 0.126
Zinc salts of ethyl, isopropyl and butyl xanthates were prepared in the laboratory. The
 Iranian Polymer Journal 13 (), 4, 891 Synergism of Xanthate/Dithiocarbamate Accelerator in Carbon Black Filled NR Compounds Shiny Palaty 1 and Rani Joseph,* (1) Department of Chemistry, Bharata Mata College,
Iranian Polymer Journal 13 (), 4, 891 Synergism of Xanthate/Dithiocarbamate Accelerator in Carbon Black Filled NR Compounds Shiny Palaty 1 and Rani Joseph,* (1) Department of Chemistry, Bharata Mata College,
Determination of Gallic acid from their Methanolic Extract of Punica granatum By HPLC Method
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.5, pp 2598-2602, July-Sept 2013 Determination of Gallic acid from their Methanolic Extract of Punica granatum By
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.5, pp 2598-2602, July-Sept 2013 Determination of Gallic acid from their Methanolic Extract of Punica granatum By
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST
 GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
INFLUENCE OF SUPERCRITICAL CO 2 IN THE REACTIVITY OF A REACTIVE DYE WITH A MODEL ALCOHOL IN A TUBULAR REACTOR
 IFLUECE OF SUPERCRITICAL CO 2 I THE REACTIVITY OF A REACTIVE DYE WITH A MODEL ALCOHOL I A TUBULAR REACTOR M.V. Fernandez Cid* a, M. van der Kraan a, W.J.T. Veugelers b, G.F. Woerlee b, G.J. Witkamp a a
IFLUECE OF SUPERCRITICAL CO 2 I THE REACTIVITY OF A REACTIVE DYE WITH A MODEL ALCOHOL I A TUBULAR REACTOR M.V. Fernandez Cid* a, M. van der Kraan a, W.J.T. Veugelers b, G.F. Woerlee b, G.J. Witkamp a a
Evaluation of Physical and Electrical Properties of Chloroprene Rubber and Natural Rubber Blends
 PRÜFEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING Chloroprene rubber Natural rubber Two-stage vulcanization Dielectric Rubber blend In the present study co-vulcanization of the blend containing CR and NR has been
PRÜFEN UND MESSEN TESTING AND MEASURING Chloroprene rubber Natural rubber Two-stage vulcanization Dielectric Rubber blend In the present study co-vulcanization of the blend containing CR and NR has been
This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products:
 A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
Chemistry 283g Experiment 4
 Chemistry 283g xperiment 4 XPRIMNT 4: lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution: A Friedel-Craft Acylation Reaction Relevant sections in the text: Fox & Whitesell, 3 rd d. Chapter 11, especially pg. 524-526,
Chemistry 283g xperiment 4 XPRIMNT 4: lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution: A Friedel-Craft Acylation Reaction Relevant sections in the text: Fox & Whitesell, 3 rd d. Chapter 11, especially pg. 524-526,
The Effects of Organotin Catalysts on Hydrolytic Condensation of
 Original Research Paper J. Jpn. Sco. Colour Mater. (SHIKIZAI), 76(10),373-379 (2003) Polymethylsiloxane Oligomer and Moisture Cure of the Coatings Akira IWASAWA*, Ryuichi Ape, Hiroharu SASAKI*, Toshiya
Original Research Paper J. Jpn. Sco. Colour Mater. (SHIKIZAI), 76(10),373-379 (2003) Polymethylsiloxane Oligomer and Moisture Cure of the Coatings Akira IWASAWA*, Ryuichi Ape, Hiroharu SASAKI*, Toshiya
ANALYTICAL METHOD DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE ALDEHYDES IN AMBIENT AIR Page 1 of 11 Air sampling and analysis
 DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE ALDEHYDES IN AMBIENT AIR Page 1 of 11 Replaces: Dated: Author: Date: AM-No.: New New Nils Arne Jentoft 18.06.2014 0 CHANGES This procedure is new. 1 SCOPE This document describes
DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE ALDEHYDES IN AMBIENT AIR Page 1 of 11 Replaces: Dated: Author: Date: AM-No.: New New Nils Arne Jentoft 18.06.2014 0 CHANGES This procedure is new. 1 SCOPE This document describes
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 37 Most analytes separated by HPLC are thermally stable and non-volatile (liquids) (unlike in GC) so not ionized easily by EI or CI techniques. MS must be at
Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH Analysis Topic 5
 Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH 5730-6730 Analysis Topic 5 Chromatography! Group of separation techniques based on partitioning (mobile phase/stationary phase). Two immiscible
Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH 5730-6730 Analysis Topic 5 Chromatography! Group of separation techniques based on partitioning (mobile phase/stationary phase). Two immiscible
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine?
 Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Nonlinear Viscoelastic Behaviour of Rubber Composites
 Nonlinear Viscoelastic Behaviour of Rubber Composites Sabu Thomas Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam India 1 Polymer Nanocomposites Spheres (0D) TiO 2, SiO 2
Nonlinear Viscoelastic Behaviour of Rubber Composites Sabu Thomas Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam India 1 Polymer Nanocomposites Spheres (0D) TiO 2, SiO 2
Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia.
 Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia. (a) Complete the word equation for the reaction that takes place in the first reaction vessel. ammonia +... nitrogen
Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia. (a) Complete the word equation for the reaction that takes place in the first reaction vessel. ammonia +... nitrogen
Waters GPC User Guide and Tutorial for Using the GPC in the Reynolds Research Group 2 nd Edition: April 2012
 Waters GPC User Guide and Tutorial for Using the GPC in the Reynolds Research Group 2 nd Edition: April 2012 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Chemistry & Biochemistry School of Materials Science
Waters GPC User Guide and Tutorial for Using the GPC in the Reynolds Research Group 2 nd Edition: April 2012 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Chemistry & Biochemistry School of Materials Science
A RP-HPLC METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF PARA- PHENYLENEDIAMINE IN PURE FORM AND IN MARKETED PRODUCTS
 A RP-HPLC METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF PARA- PHENYLENEDIAMINE IN PURE FORM AND IN MARKETED PRODUCTS CH.MOUNIKA*, M.KINNERA Research Article SIR.C.R.REDDY COLLEGE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES, ELURU.
A RP-HPLC METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF PARA- PHENYLENEDIAMINE IN PURE FORM AND IN MARKETED PRODUCTS CH.MOUNIKA*, M.KINNERA Research Article SIR.C.R.REDDY COLLEGE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES, ELURU.
MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER
 Thesis - MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL MODIFICATIONS OF POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) CHAPTER 8 BY TOHEI MORITANI MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER A functional monomer containing sodium sulfonate group,
Thesis - MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL MODIFICATIONS OF POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) CHAPTER 8 BY TOHEI MORITANI MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER A functional monomer containing sodium sulfonate group,
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS
 penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS penta-hilic Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS penta-hilic Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
