3.052 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 03/08/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MIT-DMSE
|
|
|
- Jade Floyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE I LECTURE 9: QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS INTRA- AND INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Outline : LAST LECTURE : INTRODUCTION TO INTRA- and INTERMOLECULAR FORCES... BRIDGING TE GAP BETWEEN LENGT SCALES... 3 INTRA- AND INTERMOLECULAR POTENTIALS Review of Geneal Equations and LJ Potential... 4 Foms fo Diffeent Inteactions... 5 istoy and Pespectives... 6 Example : Chage -Dipole Inteaction... 7 Moe Complex Potentials and Additivity... 8 Binding Stengths and Equilibium Bond Lengths... 9 Objectives: To establish a quantitative famewok fo inta- and intemolecula foces Readings: Couse Reade documents 18-0, G. Malescio, "Intemolecula potentials- past, pesent, and futue" Natue Mateials, Multimedia : epain Biosenso Podcast; Monitoing of hepain and its low-molecula-weight analogs by silicon field effect, Nebojsa M. Milovic, Jonathan R. Beh, Michel Godin, Chih-Sheng Johnson ou, Kistofo R. Paye, Aathi Chandasekaan, Pete R. Russo, Ram Sasisekhaan, and Scott R. Manalis PNAS 006, 103, 36,
2 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE LAST LECTURE : INTRODUCTION TO INTRA- AND INTERMOLECULAR FORCES (within individual molecules) (between individual molecules) no eal physical diffeence -Definitions : Inteaction (moe geneal), foce (push o pull), bond (the attaction between atoms in a molecule o cystalline stuctue) all inta- and intemolecula foces ae electostatic in oigin key to life on eath (e.g. wate, cell membanes, potein folding, etc.), also mateials science (what holds matte togethe?). -stength measued elative to the themal enegy (oom tempeatue) : k B T= J : "ule" -Classifications; pimay o chemical, seconday o physical, and "special" -Biological systems and bottom-up self-assembly is based on the balance and inteplay of inta- and intemolecula foces. -Noncovalent inteactions allow fo dynamic systems, i.e. beaking evesible efoming bonds doesn't equie much enegy)/individually weak, foces ae cumulative stable in paallel. -Specific types of inta- and intemolecula foces; ionic, pola (e.g. -bonds), polaization, London dispesion, hydophobic (CR document 17) -Two examples (biological and synthetic) : noncovalent inteactions in folded poteins (human seum albumin) and selfassembling peptide amphiphiles (i.e. how chemical stuctue was designed ) Image emoved due to copyight estictions. Self assembly of peptide amphiphile molecule into a cylindical micelle. See Figue 1c in atgeink, et al. Science, 001 hieachical levels of potein stuctue-"native" and "denatued" atgeink, et al. Science, 001 See Review of Definitions fo Inte- and Inta-molecula foces
3 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE BRIDGING TE GAP BETWEEN LENGT SCALES -A typical inte- atomic, ionic, o intamolecula potential (e.g. LJ potential) 0.0 foce, f() (nn) Inteatomic o Intemolecula Sepaation Distance, (nm) A typical intesuface o intepaticle foce vs. sepaation distance cuve epulsive egime attactive egime 0 Tip-Sample Sepaation Distance, D (nm) k c Foce, F (nn) w() o U() f() (one atom, ion, o molecule) -1st step is to assume a mathematical fom of the potential W(D) F(D) (net inteaction between lage bodies, i.e. assemblies of atoms, ions, o molecules) D 3
4 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE REVIEW OF GENERAL EQUATIONS AND LENNARD JONES (LJ) POTENTIAL Inteatomic Potential o Bond Enegy (J o kbt) : -A B m n (1) -du() Inteatomic (Bond) Foce (nn): F() = = k()d () d -d U() df() Inteatomic (Bond) Stiffness (nn/nm) : k() = = (3) d d (nm)= inteatomic sepaation distance U() o w()= U attactive()+u epulsive()= + = - F()d A,B,m,n = constants detemined by the type of inteaction k -3 B = Boltzmann's constant = J/K T = absolute tempeatue (K) U ( m = 6, n = 1) = + =4E LJ LJ 7 -A B 6 1-6A 1B 13 F ( m=6, n=1) = + (5) B 1 6 σ σ - (4) E B = "binding enegy" o "bond dissociation enegy"; o depth of potential well s= distance at which U( s ) exhibits and inflection point, F( s )= minimum= FRUPTURE e = equilibium bond length = distance at which U( e )= minimum, F( e )= 0 =σ = distance at which U( )= 0, F( )= o o o w () (kbt) inteaction foce (nn) inteaction distance (nm) net o inteaction enegy (kj) A= Jm 6 B= Jm 1 epulsive E B e attactive -0.8 (nm)... Asymmetic o anhamonic potential, plotted in in...units of k B T s 4
5 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE FORMS OF INTERATOMIC / INTERMOLECULAR POTENTIALS Type of inteaction Schematic Inteaction Enegy, w() covalent, metallic -, chage-chage Cu Complicated, shot ange Cu + Q 1 Q QQ 1-1 w()= (Coulomb Enegy) u θ Q 4πε chage-dipole fixed dipole Qucosθ - u Q w()= - 4πε feely otating dipole Qu -4 w()= - φ ( ) dipole-dipole 6 4πε o kbt u 1 θ 1 θ u u u [ cosθ1cosθ sinθ1sin θ cos φ] w()= - fixed dipole 4πε o u u 1 u -6 w()= - feely otating dipoles 3( 4πε ) o kbt (Keesom Enegy) chage-induced dipole Q Q -4 w()= - ( ) 4πε dipole-induced dipole u θ u u ( 1+3cos θ) -6 w()= - ( ) 4πε fixed dipole feely otating dipole u -6 w()= - (Debye Enegy) induced dipole-induced dipole ( 4πε ) 3hν -6 O w()= - (London Dispesion) hydogen bond 4( 4πε o ) Complicated, shot ange, w() ~ - O O O 1-3 w() = inteaction fee enegy (J), Q = electic chage (C), u = electic dipole moment (C m), = electic polaizability (C m J -1 ), = distance between inteacting atoms o molecules (m), k B = Boltzmann's constant = J K -1, T = absolute tempeatue (K), h = Planck's constant = J s, ν = electonic absoption (ionization) fequency (s -1 ), ε o =dielectic pemittivity of fee space = C J -1 m -1. The foce is obtained by diffeentiating the enegy, w(), with espect to the distance,. (*Adapted fom Isaelachvili, Intemolecula and Suface Foces 199) 5
6 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE INTERMOLECULAR POTENTIALS: ISTORY AND PERSPECTIVE A eally inteesting aticle : "Intemolecula Potentials- past, pesent, futue" Gianpieto Malescio Natue Mateials 003,, Isaac Newton (1704) : Attaction between atoms -Roge Joseph Boscovich (1745) - 1st foce-distance cuve (qualitative) -Guiseppe Belli (1814) : fom expeimental data concluded ~1/ n -Maxwell, Van de Waals, Debye, London : - quantum mechanics/ coespondence with classical electostatics, inteactions between the electons and nuclei foming the molecules calculation equies solving the Schödinge equation fo a system of inteacting paticles. The enegy associated with the electonic motion is the potential enegy fo the motion of the nuclei, and can be egaded as the intemolecula (effective) inteaction potential. 6
7 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE SAMPLE POTENTIAL : CARGE - FIXED DIPOLE INTERACTION Qucosθ - w()= - (1) 4πε = chage-dipole sepaation distance (nm) u= electic dipole moment = ql (Cm) q= chage of dipole (C) l = sepaation distance between dipole chages(m) Q= chage of the ion (C) θ = dipole angle elative to hoizontal Chage Q=ze dipole moment = ql l/ +q θ 5 x W() (J) 0 +e +q -q θ (nm) 0.4 kt at 300 K -q l/ x Figue by MIT OCW. (*Fom Isaelachvili, Intemolecula and Suface Foces 199) 7
8 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE MORE COMPLEX POTENTIALS : ADDITIVITY w() VDW = w() oient + w() induced + w() dispesion (1) -u -6-6 Keesom Enegy : Feely otating dipole-feely otating dipole inteaction : w() oient = = C oient () 3kT(4πε o ) -u -6-6 Debye Enegy : Feely otating dipole- nonpola (induced dipole) inteaction : w() induced = = C induced (3) (4πε o ) -3hν -6-6 Dispesion Enegy : Induced dipole-induced dipole : w() dispesion = = C dispesion (4) 4(4πε o ) Biomolecula Adhesion : -contolled by bonds between molecula ligands and cell suface eceptos which exhibit the lock-n-key pinciple (e.g. biotin-steptavidin) complex, multiatomic, elatively weak fomed by an assembly of multiple, weak noncovalent inteactions (e.g. -bonding, coulombic, van de Waals, hydophilic / hydophobic, electostatic) complementay, steically-contained geometic consideations specificity Two images emoved due to copyight estictions. Coutesy of Bill Ross. Used with pemission. See Gubmülle, et al, Science 1996 (* and 8
9 3.05 Nanomechanics of Mateials and Biomateials Thusday 03/08/07 Pof. C. Otiz, MIT-DMSE BINDING STRENGT AND EQUILIBRIUM BOND LENGTS Inteaction Stength, kj/mol Stength, k B T dispesion hydophobic dipole-induced dipole TERMAL.5 1 ENERGY dipole-dipole 5 ion-ion bond lipid in bilaye 5 10 (hydophobic) cabohydate-lselection 6 5 biotin-avidin single covalent, C-C double covalent, C=C tiple covalent, C C Inteaction Inteaction Distance (nm) dispesion 0.35 hydophobic bonding 0.3 ion-ion 0.5 covalent Mateial metals ceamics and glasses semiconductos diamond wate inet gases solid salt cystals alkanes, hydocabons, flouocabons, amphiphiles in wate polymes/poteins Inteaction metallic covalent / ionic covalent / ionic covalent covalent, -bonding dispesion ionic hydophobic potentially alldepending on chemical stuctue 9
Spring 2009 EE 710: Nanoscience and Engineering
 Sping 009 EE 70: Nanoscience and Engineeing Pat 5: Chemical Inteactions at the Nanoscale Images and figues supplied fom Honyak, Dutta, Tibbals, and Rao, Intoduction to Nanoscience, CRC Pess, Boca Raton,
Sping 009 EE 70: Nanoscience and Engineeing Pat 5: Chemical Inteactions at the Nanoscale Images and figues supplied fom Honyak, Dutta, Tibbals, and Rao, Intoduction to Nanoscience, CRC Pess, Boca Raton,
Interatomic Forces. Overview
 Inteatomic Foces Oveview an de Walls (shot ange ~1/ 6, weak ~0.010.1 e) Ionic (long ange, ~1/, stong ~510 e) Metallic (no simple dependence, ~0.1e) Covalent (no simple dependence, diectional,~3 e) Hydogen
Inteatomic Foces Oveview an de Walls (shot ange ~1/ 6, weak ~0.010.1 e) Ionic (long ange, ~1/, stong ~510 e) Metallic (no simple dependence, ~0.1e) Covalent (no simple dependence, diectional,~3 e) Hydogen
Introduction to Dielectric Properties and Magnetism
 Intoduction to Dielectic opeties and Magnetism At the end of the last lectue we looked at some of the electical popeties of matte and intoduces the notions of electic field and electical conductivity.
Intoduction to Dielectic opeties and Magnetism At the end of the last lectue we looked at some of the electical popeties of matte and intoduces the notions of electic field and electical conductivity.
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 lectomagnetism Physics 15b Lectue #20 Dielectics lectic Dipoles Pucell 10.1 10.6 What We Did Last Time Plane wave solutions of Maxwell s equations = 0 sin(k ωt) B = B 0 sin(k ωt) ω = kc, 0 = B, 0 ˆk =
lectomagnetism Physics 15b Lectue #20 Dielectics lectic Dipoles Pucell 10.1 10.6 What We Did Last Time Plane wave solutions of Maxwell s equations = 0 sin(k ωt) B = B 0 sin(k ωt) ω = kc, 0 = B, 0 ˆk =
Ab Initio Calculations of Intermolecular Interactions. calculating dispersion energies is hard; (BSSE)
 V()/k B / K Ab Initio Calculations of Intemolecula Inteactions 100 80 0 40 20 0 Calculated Ne 2 Potentials basis=aug-cc-vqz HF MP2 QCISD(T) B3LYP V() / k B /K 100 80 0 40 20 0 Ne 2 Potentials - Calc &
V()/k B / K Ab Initio Calculations of Intemolecula Inteactions 100 80 0 40 20 0 Calculated Ne 2 Potentials basis=aug-cc-vqz HF MP2 QCISD(T) B3LYP V() / k B /K 100 80 0 40 20 0 Ne 2 Potentials - Calc &
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 11. The future of electronics? A pentacene molecule deposited on SiO 2. Image removed for copyright reasons.
 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lectue 11 BONDING IN MOLECULES The futue of electonics? A pentacene molecule deposited on SiO 2 as a thin film Image emoved fo copyight easons. 3.012 Fundamentals of Mateials
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lectue 11 BONDING IN MOLECULES The futue of electonics? A pentacene molecule deposited on SiO 2 as a thin film Image emoved fo copyight easons. 3.012 Fundamentals of Mateials
Charges, Coulomb s Law, and Electric Fields
 Q&E -1 Chages, Coulomb s Law, and Electic ields Some expeimental facts: Expeimental fact 1: Electic chage comes in two types, which we call (+) and (). An atom consists of a heavy (+) chaged nucleus suounded
Q&E -1 Chages, Coulomb s Law, and Electic ields Some expeimental facts: Expeimental fact 1: Electic chage comes in two types, which we call (+) and (). An atom consists of a heavy (+) chaged nucleus suounded
Physics 11 Chapter 20: Electric Fields and Forces
 Physics Chapte 0: Electic Fields and Foces Yesteday is not ous to ecove, but tomoow is ous to win o lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the futue. When I am depessed
Physics Chapte 0: Electic Fields and Foces Yesteday is not ous to ecove, but tomoow is ous to win o lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the futue. When I am depessed
17.1 Electric Potential Energy. Equipotential Lines. PE = energy associated with an arrangement of objects that exert forces on each other
 Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
Electic Potential Enegy, PE Units: Joules Electic Potential, Units: olts 17.1 Electic Potential Enegy Electic foce is a consevative foce and so we can assign an electic potential enegy (PE) to the system
Lecture 3.7 ELECTRICITY. Electric charge Coulomb s law Electric field
 Lectue 3.7 ELECTRICITY Electic chage Coulomb s law Electic field ELECTRICITY Inteaction between electically chages objects Many impotant uses Light Heat Rail tavel Computes Cental nevous system Human body
Lectue 3.7 ELECTRICITY Electic chage Coulomb s law Electic field ELECTRICITY Inteaction between electically chages objects Many impotant uses Light Heat Rail tavel Computes Cental nevous system Human body
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
% ionic character = {1 exp 0.25 X 2
 Pactice Poblems Set I MIME6 P1. Calculate the faction of bonding of MgO that is ionic (use the figue below). : % ionic chaacte = {1 exp.5 X A X } 1 Electonegativities of Mg and O ae 1. and 3.5 espectively.
Pactice Poblems Set I MIME6 P1. Calculate the faction of bonding of MgO that is ionic (use the figue below). : % ionic chaacte = {1 exp.5 X A X } 1 Electonegativities of Mg and O ae 1. and 3.5 espectively.
Aaa Hal ARC 103 Haq Mou Hill 114 Mug Seh PHY LH Sen Zzz SEC 111
 The Fist Midtem!!! The fist common hou midtem exam will be held on Thusday Octobe 5, 9:50 to 11:10 PM (at night) on the Busch campus. You should go to the oom coesponding to the fist 3 lettes of you last
The Fist Midtem!!! The fist common hou midtem exam will be held on Thusday Octobe 5, 9:50 to 11:10 PM (at night) on the Busch campus. You should go to the oom coesponding to the fist 3 lettes of you last
? this lecture. ? next lecture. What we have learned so far. a Q E F = q E a. F = q v B a. a Q in motion B. db/dt E. de/dt B.
 PHY 249 Lectue Notes Chapte 32: Page 1 of 12 What we have leaned so fa a a F q a a in motion F q v a a d/ Ae thee othe "static" chages that can make -field? this lectue d/? next lectue da dl Cuve Cuve
PHY 249 Lectue Notes Chapte 32: Page 1 of 12 What we have leaned so fa a a F q a a in motion F q v a a d/ Ae thee othe "static" chages that can make -field? this lectue d/? next lectue da dl Cuve Cuve
PES 3950/PHYS 6950: Homework Assignment 6
 PES 3950/PHYS 6950: Homewok Assignment 6 Handed out: Monday Apil 7 Due in: Wednesday May 6, at the stat of class at 3:05 pm shap Show all woking and easoning to eceive full points. Question 1 [5 points]
PES 3950/PHYS 6950: Homewok Assignment 6 Handed out: Monday Apil 7 Due in: Wednesday May 6, at the stat of class at 3:05 pm shap Show all woking and easoning to eceive full points. Question 1 [5 points]
Class 2. Lesson 1 Stationary Point Charges and Their Forces. Basic Rules of Electrostatics. Basic Rules of Electrostatics
 Lesson 1 Stationay Point Chages and Thei Foces Class Today we will: lean the basic chaacteistics o the electostatic oce eview the popeties o conductos and insulatos lean what is meant by electostatic induction
Lesson 1 Stationay Point Chages and Thei Foces Class Today we will: lean the basic chaacteistics o the electostatic oce eview the popeties o conductos and insulatos lean what is meant by electostatic induction
F = net force on the system (newton) F,F and F. = different forces working. E = Electric field strength (volt / meter)
 All the Impotant Fomulae that a student should know fom. XII Physics Unit : CHAPTER - ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD CHAPTER ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE S. Fomula No.. Quantization of chage Q =
All the Impotant Fomulae that a student should know fom. XII Physics Unit : CHAPTER - ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD CHAPTER ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE S. Fomula No.. Quantization of chage Q =
Review for Midterm-1
 Review fo Midtem-1 Midtem-1! Wednesday Sept. 24th at 6pm Section 1 (the 4:10pm class) exam in BCC N130 (Business College) Section 2 (the 6:00pm class) exam in NR 158 (Natual Resouces) Allowed one sheet
Review fo Midtem-1 Midtem-1! Wednesday Sept. 24th at 6pm Section 1 (the 4:10pm class) exam in BCC N130 (Business College) Section 2 (the 6:00pm class) exam in NR 158 (Natual Resouces) Allowed one sheet
Physics 202, Lecture 2
 Physics 202, Lectue 2 Todays Topics Electic Foce and Electic Fields Electic Chages and Electic Foces Coulomb's Law Physical Field The Electic Field Electic Field Lines Motion of Chaged Paticle in Electic
Physics 202, Lectue 2 Todays Topics Electic Foce and Electic Fields Electic Chages and Electic Foces Coulomb's Law Physical Field The Electic Field Electic Field Lines Motion of Chaged Paticle in Electic
Electrostatics. 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative object: excess of electrons
 Electostatics IB 12 1) electic chage: 2 types of electic chage: positive and negative 2) chaging by fiction: tansfe of electons fom one object to anothe 3) positive object: lack of electons negative object:
Electostatics IB 12 1) electic chage: 2 types of electic chage: positive and negative 2) chaging by fiction: tansfe of electons fom one object to anothe 3) positive object: lack of electons negative object:
Chapter Sixteen: Electric Charge and Electric Fields
 Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Chapter 22: Electric Fields. 22-1: What is physics? General physics II (22102) Dr. Iyad SAADEDDIN. 22-2: The Electric Field (E)
 Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Electric field generated by an electric dipole
 Electic field geneated by an electic dipole ( x) 2 (22-7) We will detemine the electic field E geneated by the electic dipole shown in the figue using the pinciple of supeposition. The positive chage geneates
Electic field geneated by an electic dipole ( x) 2 (22-7) We will detemine the electic field E geneated by the electic dipole shown in the figue using the pinciple of supeposition. The positive chage geneates
Primer Materials Spring
 Pime Mateials ping 07.06.07 Example 8. Calculate the bond stiffness of high puity diamond fom its dielectic constant at low fequencies, ε =5.5. Density of diamond is.55 gm/cm. c 8 m h 6.6 4 Js el.6 9 C
Pime Mateials ping 07.06.07 Example 8. Calculate the bond stiffness of high puity diamond fom its dielectic constant at low fequencies, ε =5.5. Density of diamond is.55 gm/cm. c 8 m h 6.6 4 Js el.6 9 C
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
 CHAPTER II THEORETICAL BACKGROUND 2.1. INTRODUCTION The electical chaacteistic of evey mateial is dependent on its dielectic popeties. Measuements of these dielectic popeties can povide valuable infomation
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL BACKGROUND 2.1. INTRODUCTION The electical chaacteistic of evey mateial is dependent on its dielectic popeties. Measuements of these dielectic popeties can povide valuable infomation
PHYSICS 272 Electric & Magnetic Interactions
 PHYS 7: Matte and Inteactions II -- Electic And Magnetic Inteactions http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic_pogams/couses/phys7/ PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Lectue 3 Chaged Objects; Polaization
PHYS 7: Matte and Inteactions II -- Electic And Magnetic Inteactions http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic_pogams/couses/phys7/ PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Lectue 3 Chaged Objects; Polaization
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
13.10 Worked Examples
 13.10 Woked Examples Example 13.11 Wok Done in a Constant Gavitation Field The wok done in a unifom gavitation field is a faily staightfowad calculation when the body moves in the diection of the field.
13.10 Woked Examples Example 13.11 Wok Done in a Constant Gavitation Field The wok done in a unifom gavitation field is a faily staightfowad calculation when the body moves in the diection of the field.
Electric Field. y s +q. Point charge: Uniformly charged sphere: Dipole: for r>>s :! ! E = 1. q 1 r 2 ˆr. E sphere. at <0,r,0> at <0,0,r>
 Electic Field Point chage: E " ˆ Unifomly chaged sphee: E sphee E sphee " Q ˆ fo >R (outside) fo >s : E " s 3,, at z y s + x Dipole moment: p s E E s "#,, 3 s "#,, 3 at
Electic Field Point chage: E " ˆ Unifomly chaged sphee: E sphee E sphee " Q ˆ fo >R (outside) fo >s : E " s 3,, at z y s + x Dipole moment: p s E E s "#,, 3 s "#,, 3 at
Chapter 3 Crystal Binding
 Chapte 3 Cystal Binding The intenal enegy of a cystal Ionic cystals The Bon theoy of ionic cystals Van De Waals cystals Dipoles Inet cases Induced dipoles The lattice enegy of an inet-gas solid The Debye
Chapte 3 Cystal Binding The intenal enegy of a cystal Ionic cystals The Bon theoy of ionic cystals Van De Waals cystals Dipoles Inet cases Induced dipoles The lattice enegy of an inet-gas solid The Debye
EELE 3331 Electromagnetic I Chapter 4. Electrostatic fields. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
EE-145L Properties of Materials Laboratory
 Univesity of Califonia at Santa Cuz Jack Baskin School of Engineeing EE-145L Popeties of Mateials Laboatoy Sping 2003 Holge Schmidt Developed by Ali Shakouti, based on the notes by Pof. Emily Allen, San
Univesity of Califonia at Santa Cuz Jack Baskin School of Engineeing EE-145L Popeties of Mateials Laboatoy Sping 2003 Holge Schmidt Developed by Ali Shakouti, based on the notes by Pof. Emily Allen, San
Physics 221 Lecture 41 Nonlinear Absorption and Refraction
 Physics 221 Lectue 41 Nonlinea Absoption and Refaction Refeences Meye-Aendt, pp. 97-98. Boyd, Nonlinea Optics, 1.4 Yaiv, Optical Waves in Cystals, p. 22 (Table of cystal symmeties) 1. Intoductoy Remaks.
Physics 221 Lectue 41 Nonlinea Absoption and Refaction Refeences Meye-Aendt, pp. 97-98. Boyd, Nonlinea Optics, 1.4 Yaiv, Optical Waves in Cystals, p. 22 (Table of cystal symmeties) 1. Intoductoy Remaks.
! E da = 4πkQ enc, has E under the integral sign, so it is not ordinarily an
 Physics 142 Electostatics 2 Page 1 Electostatics 2 Electicity is just oganized lightning. Geoge Calin A tick that sometimes woks: calculating E fom Gauss s law Gauss s law,! E da = 4πkQ enc, has E unde
Physics 142 Electostatics 2 Page 1 Electostatics 2 Electicity is just oganized lightning. Geoge Calin A tick that sometimes woks: calculating E fom Gauss s law Gauss s law,! E da = 4πkQ enc, has E unde
The Millikan Experiment: Determining the Elementary Charge
 LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
LAB EXERCISE 7.5.1 7.5 The Elementay Chage (p. 374) Can you think of a method that could be used to suggest that an elementay chage exists? Figue 1 Robet Millikan (1868 1953) m + q V b The Millikan Expeiment:
Force and Work: Reminder
 Electic Potential Foce and Wok: Reminde Displacement d a: initial point b: final point Reminde fom Mechanics: Foce F if thee is a foce acting on an object (e.g. electic foce), this foce may do some wok
Electic Potential Foce and Wok: Reminde Displacement d a: initial point b: final point Reminde fom Mechanics: Foce F if thee is a foce acting on an object (e.g. electic foce), this foce may do some wok
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #36
 Electomagnetism PHYSICS 151 Notes fo Online Lectue #36 Thee ae fou fundamental foces in natue: 1) gavity ) weak nuclea 3) electomagnetic 4) stong nuclea The latte two opeate within the nucleus of an atom
Electomagnetism PHYSICS 151 Notes fo Online Lectue #36 Thee ae fou fundamental foces in natue: 1) gavity ) weak nuclea 3) electomagnetic 4) stong nuclea The latte two opeate within the nucleus of an atom
1.1 THE ELECTRIC CHARGE
 1.1 THE ELECTRIC CHARGE - In a dy day, one obseves "light spaks" when a wool pull is taken out o when the finges touch a metallic object. Aound the yea 1600, one classified these effects as electic phenomena.
1.1 THE ELECTRIC CHARGE - In a dy day, one obseves "light spaks" when a wool pull is taken out o when the finges touch a metallic object. Aound the yea 1600, one classified these effects as electic phenomena.
The geometric construction of Ewald sphere and Bragg condition:
 The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
Key Questions. ECE 340 Lecture 4 : Bonding Forces and Energy Bands 1/28/14. Class Outline: v Crystal Diffraction Crystal Bonding
 ECE 340 Lectue 4 : onding Foces and Enegy ands v Cystal Diffaction Class Outline: Things you should know when you leave Key Questions Why is the oh model useful? What is the Schödinge equation? What is
ECE 340 Lectue 4 : onding Foces and Enegy ands v Cystal Diffaction Class Outline: Things you should know when you leave Key Questions Why is the oh model useful? What is the Schödinge equation? What is
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 5/6. Comic strip removed for copyright reasons.
 3.12 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lectue 5/6 THE HYDROGEN ATOM Comic stip emoved fo copyight easons. Last Time Metal sufaces and STM Diac notation Opeatos, commutatos, some postulates Homewok fo Mon Oct 3
3.12 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lectue 5/6 THE HYDROGEN ATOM Comic stip emoved fo copyight easons. Last Time Metal sufaces and STM Diac notation Opeatos, commutatos, some postulates Homewok fo Mon Oct 3
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
Chapter 20 Electrostatics and Coulomb s Law 20.1 Introduction electrostatics Separation of Electric Charge by Rubbing
 I wish to give an account of some investigations which have led to the conclusion that the caies of negative electicity ae bodies, which I have called copuscles, having a mass vey much smalle than that
I wish to give an account of some investigations which have led to the conclusion that the caies of negative electicity ae bodies, which I have called copuscles, having a mass vey much smalle than that
V7: Diffusional association of proteins and Brownian dynamics simulations
 V7: Diffusional association of poteins and Bownian dynamics simulations Bownian motion The paticle movement was discoveed by Robet Bown in 1827 and was intepeted coectly fist by W. Ramsay in 1876. Exact
V7: Diffusional association of poteins and Bownian dynamics simulations Bownian motion The paticle movement was discoveed by Robet Bown in 1827 and was intepeted coectly fist by W. Ramsay in 1876. Exact
PHYS 1441 Section 002. Lecture #3
 PHYS 1441 Section 00 Chapte 1 Lectue #3 Wednesday, Sept. 6, 017 Coulomb s Law The Electic Field & Field Lines Electic Fields and Conductos Motion of a Chaged Paticle in an Electic Field Electic Dipoles
PHYS 1441 Section 00 Chapte 1 Lectue #3 Wednesday, Sept. 6, 017 Coulomb s Law The Electic Field & Field Lines Electic Fields and Conductos Motion of a Chaged Paticle in an Electic Field Electic Dipoles
15 B1 1. Figure 1. At what speed would the car have to travel for resonant oscillations to occur? Comment on your answer.
 Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) F:EasteHolidaysAssignmentAns.doc Easte Holidays Assignment Answe Fom 6B Subject: Physics. (a) State the conditions fo a body to undego simple hamonic motion. ( mak) (a)
Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) F:EasteHolidaysAssignmentAns.doc Easte Holidays Assignment Answe Fom 6B Subject: Physics. (a) State the conditions fo a body to undego simple hamonic motion. ( mak) (a)
7.2. Coulomb s Law. The Electric Force
 Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
MOLECULES BONDS. ENERGY LEVELS electronic vibrational rotational. P461 - Molecules 1
 BONDS MOLECULES Ionic: closed shell (+) o open shell (-) Covalent: both open shells neutal ( shae e) Othe (skip): van de Waals (He- He) Hydogen bonds (in DNA, poteins, etc) ENERGY LEVELS electonic vibational
BONDS MOLECULES Ionic: closed shell (+) o open shell (-) Covalent: both open shells neutal ( shae e) Othe (skip): van de Waals (He- He) Hydogen bonds (in DNA, poteins, etc) ENERGY LEVELS electonic vibational
20-9 ELECTRIC FIELD LINES 20-9 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL. Answers to the Conceptual Questions. Chapter 20 Electricity 241
 Chapte 0 Electicity 41 0-9 ELECTRIC IELD LINES Goals Illustate the concept of electic field lines. Content The electic field can be symbolized by lines of foce thoughout space. The electic field is stonge
Chapte 0 Electicity 41 0-9 ELECTRIC IELD LINES Goals Illustate the concept of electic field lines. Content The electic field can be symbolized by lines of foce thoughout space. The electic field is stonge
AP Physics Electric Potential Energy
 AP Physics lectic Potential negy Review of some vital peviously coveed mateial. The impotance of the ealie concepts will be made clea as we poceed. Wok takes place when a foce acts ove a distance. W F
AP Physics lectic Potential negy Review of some vital peviously coveed mateial. The impotance of the ealie concepts will be made clea as we poceed. Wok takes place when a foce acts ove a distance. W F
(r) = 1. Example: Electric Potential Energy. Summary. Potential due to a Group of Point Charges 9/10/12 1 R V(r) + + V(r) kq. Chapter 23.
 Eample: Electic Potential Enegy What is the change in electical potential enegy of a eleased electon in the atmosphee when the electostatic foce fom the nea Eath s electic field (diected downwad) causes
Eample: Electic Potential Enegy What is the change in electical potential enegy of a eleased electon in the atmosphee when the electostatic foce fom the nea Eath s electic field (diected downwad) causes
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
EM-2. 1 Coulomb s law, electric field, potential field, superposition q. Electric field of a point charge (1)
 EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Mobility of atoms and diffusion. Einstein relation.
 Mobility of atoms and diffusion. Einstein elation. In M simulation we can descibe the mobility of atoms though the mean squae displacement that can be calculated as N 1 MS ( t ( i ( t i ( 0 N The MS contains
Mobility of atoms and diffusion. Einstein elation. In M simulation we can descibe the mobility of atoms though the mean squae displacement that can be calculated as N 1 MS ( t ( i ( t i ( 0 N The MS contains
PHYSICS 272 Electric & Magnetic Interactions. Prof. Andrew Hirsch Room: 178, Phone: 42218
 PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Pof. Andew Hisch Hisch@pudue.edu Room: 78, Phone: 48 Couse Content This couse deals with electic and magnetic inteactions, which ae cental to the stuctue of matte,
PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Pof. Andew Hisch Hisch@pudue.edu Room: 78, Phone: 48 Couse Content This couse deals with electic and magnetic inteactions, which ae cental to the stuctue of matte,
Field emission of Electrons from Negatively Charged Cylindrical Particles with Nonlinear Screening in a Dusty Plasma
 Reseach & Reviews: Jounal of Pue and Applied Physics Field emission of Electons fom Negatively Chaged Cylindical Paticles with Nonlinea Sceening in a Dusty Plasma Gyan Pakash* Amity School of Engineeing
Reseach & Reviews: Jounal of Pue and Applied Physics Field emission of Electons fom Negatively Chaged Cylindical Paticles with Nonlinea Sceening in a Dusty Plasma Gyan Pakash* Amity School of Engineeing
Roger Pynn. Basic Introduction to Small Angle Scattering
 by Roge Pynn Basic Intoduction to Small Angle Scatteing We Measue Neutons Scatteed fom a Sample Φ = numbe of incident neutons pe cm pe second σ = total numbe of neutons scatteed pe second / Φ dσ numbe
by Roge Pynn Basic Intoduction to Small Angle Scatteing We Measue Neutons Scatteed fom a Sample Φ = numbe of incident neutons pe cm pe second σ = total numbe of neutons scatteed pe second / Φ dσ numbe
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
 CHAPTER 0 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE 7 0. ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic
CHAPTER 0 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE 7 0. ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY Conside a chaged paticle of chage in a egion of an electic field E. This filed exets an electic
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Introduction to Nuclear Forces
 Intoduction to Nuclea Foces One of the main poblems of nuclea physics is to find out the natue of nuclea foces. Nuclea foces diffe fom all othe known types of foces. They cannot be of electical oigin since
Intoduction to Nuclea Foces One of the main poblems of nuclea physics is to find out the natue of nuclea foces. Nuclea foces diffe fom all othe known types of foces. They cannot be of electical oigin since
PHYSICS 272 Electric & Magnetic Interactions. Prof. Andrew Hirsch Room: 178, Phone: 42218
 PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Pof. Andew Hisch Hisch@pudue.edu Room: 78, Phone: 48 Couse Content This couse deals with electic and magnetic inteactions, which ae cental to the stuctue of matte,
PHYSICS 7 Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Pof. Andew Hisch Hisch@pudue.edu Room: 78, Phone: 48 Couse Content This couse deals with electic and magnetic inteactions, which ae cental to the stuctue of matte,
Electric Field, Potential Energy, & Voltage
 Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Universal Dielectric Response of Atmospheric Ice using COMSOL
 Univesal Dielectic Response of Atmospheic Ice using COMSOL Umai N. Mughal and Muhammad S. Vik Atmospheic Icing Reseach Team, Navik Univesity College, Navik, Noway Email : unm@hin.no My Today s Talk Will
Univesal Dielectic Response of Atmospheic Ice using COMSOL Umai N. Mughal and Muhammad S. Vik Atmospheic Icing Reseach Team, Navik Univesity College, Navik, Noway Email : unm@hin.no My Today s Talk Will
, and the curve BC is symmetrical. Find also the horizontal force in x-direction on one side of the body. h C
 Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Dynamics (Stömningsläa), 2013-05-31, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the textbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Dynamics (Stömningsläa), 2013-05-31, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the textbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
A new force Magnetic force. Today. Force Fields: A disturbance of space. The correspondence of a loop of current and magnet.
 Today A new foce Magnetic foce Announcements HW#6 and HW#7 ae both due Wednesday Mach 18th. Thanks to my being WAY behind schedule, you 2nd exam will be a take-home exam! Stay tuned fo details Even if
Today A new foce Magnetic foce Announcements HW#6 and HW#7 ae both due Wednesday Mach 18th. Thanks to my being WAY behind schedule, you 2nd exam will be a take-home exam! Stay tuned fo details Even if
ELECTROSTATICS::BHSEC MCQ 1. A. B. C. D.
 ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
Chapter Three: Crystal Binding
 Fouth Edition SI Vesion Chapte Thee: Cystal Binding 2010. Cengage Leaning, Engineeing. All Rights Reseved. 1 Classification of cystalline solid: (a) ionic, (b) van de Waals, (c) covalent, and (d) metallic
Fouth Edition SI Vesion Chapte Thee: Cystal Binding 2010. Cengage Leaning, Engineeing. All Rights Reseved. 1 Classification of cystalline solid: (a) ionic, (b) van de Waals, (c) covalent, and (d) metallic
Electrostatics. 1. Show does the force between two point charges change if the dielectric constant of the medium in which they are kept increase?
 Electostatics 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of the medium in which they ae kept incease? 2. A chaged od P attacts od R whee as P epels anothe chaged od
Electostatics 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of the medium in which they ae kept incease? 2. A chaged od P attacts od R whee as P epels anothe chaged od
Modeling Fermi Level Effects in Atomistic Simulations
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Poc. Vol. 717 Mateials Reseach Society Modeling Femi Level Effects in Atomistic Simulations Zudian Qin and Scott T. Dunham Depatment of Electical Engineeing, Univesity of Washington,
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Poc. Vol. 717 Mateials Reseach Society Modeling Femi Level Effects in Atomistic Simulations Zudian Qin and Scott T. Dunham Depatment of Electical Engineeing, Univesity of Washington,
3.23 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials
 MIT OpenCouseWae http://ocw.mit.edu 3.23 Electical, Optical, and Magnetic Popeties of Mateials Fall 27 Fo infomation about citing these mateials o ou Tems of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/tems. 3.23 Fall
MIT OpenCouseWae http://ocw.mit.edu 3.23 Electical, Optical, and Magnetic Popeties of Mateials Fall 27 Fo infomation about citing these mateials o ou Tems of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/tems. 3.23 Fall
Diffusion and Transport. 10. Friction and the Langevin Equation. Langevin Equation. f d. f ext. f () t f () t. Then Newton s second law is ma f f f t.
 Diffusion and Tanspot 10. Fiction and the Langevin Equation Now let s elate the phenomena of ownian motion and diffusion to the concept of fiction, i.e., the esistance to movement that the paticle in the
Diffusion and Tanspot 10. Fiction and the Langevin Equation Now let s elate the phenomena of ownian motion and diffusion to the concept of fiction, i.e., the esistance to movement that the paticle in the
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8. Lab 5. Magnetism
 Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Galilean Transformation vs E&M y. Historical Perspective. Chapter 2 Lecture 2 PHYS Special Relativity. Sep. 1, y K K O.
 PHYS-2402 Chapte 2 Lectue 2 Special Relativity 1. Basic Ideas Sep. 1, 2016 Galilean Tansfomation vs E&M y K O z z y K In 1873, Maxwell fomulated Equations of Electomagnetism. v Maxwell s equations descibe
PHYS-2402 Chapte 2 Lectue 2 Special Relativity 1. Basic Ideas Sep. 1, 2016 Galilean Tansfomation vs E&M y K O z z y K In 1873, Maxwell fomulated Equations of Electomagnetism. v Maxwell s equations descibe
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 10-: MOTION IN A GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Questions Fom Reading Activity? Gavity Waves? Essential Idea: Simila appoaches can be taken in analyzing electical
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 10-: MOTION IN A GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Questions Fom Reading Activity? Gavity Waves? Essential Idea: Simila appoaches can be taken in analyzing electical
From Atoms to Materials: Predictive Theory and Simulations. Materials are everywhere
 Fom Atoms to Mateials: Pedictive Theoy and Simulations Intoduction Ale Stachan stachan@pudue.edu School of Mateials Engineeing & Bick Nanotechnology Cente Pudue Univesity West Lafayette, Indiana USA Mateials
Fom Atoms to Mateials: Pedictive Theoy and Simulations Intoduction Ale Stachan stachan@pudue.edu School of Mateials Engineeing & Bick Nanotechnology Cente Pudue Univesity West Lafayette, Indiana USA Mateials
PHYSICS W term 2
 PHYSICS 153 08W tem Electicity, Magnetism, Electomagnetic Waves, Optics Pof. W. McCutcheon Henn. 81 604-8-634 mccutche@phas.ubc.ca Office hous: Monday 10:30-11:30 Fiday 10:30-11:30 o by appointment Text:
PHYSICS 153 08W tem Electicity, Magnetism, Electomagnetic Waves, Optics Pof. W. McCutcheon Henn. 81 604-8-634 mccutche@phas.ubc.ca Office hous: Monday 10:30-11:30 Fiday 10:30-11:30 o by appointment Text:
Electrostatic Potential
 Chapte 23 Electostatic Potential PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Copyight 2008 Peason Education Inc., publishing as Peason
Chapte 23 Electostatic Potential PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Copyight 2008 Peason Education Inc., publishing as Peason
Electricity Revision ELECTRICITY REVISION KEY CONCEPTS TERMINOLOGY & DEFINITION. Physical Sciences X-Sheets
 Electicity Revision KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on the following: Stating and apply Coulomb s Law. Defining electical field stength and applying the deived equations. Dawing electical field
Electicity Revision KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on the following: Stating and apply Coulomb s Law. Defining electical field stength and applying the deived equations. Dawing electical field
you of a spring. The potential energy for a spring is given by the parabola U( x)
 Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Waves and Polarization in General
 Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Phys102 Second Major-182 Zero Version Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1
 Monday, Mach 5, 019 Page: 1 Q1. Figue 1 shows thee pais of identical conducting sphees that ae to be touched togethe and then sepaated. The initial chages on them befoe the touch ae indicated. Rank the
Monday, Mach 5, 019 Page: 1 Q1. Figue 1 shows thee pais of identical conducting sphees that ae to be touched togethe and then sepaated. The initial chages on them befoe the touch ae indicated. Rank the
From last times. MTE1 results. Quiz 1. GAUSS LAW for any closed surface. What is the Electric Flux? How to calculate Electric Flux?
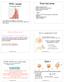 om last times MTE1 esults Mean 75% = 90/120 Electic chages and foce Electic ield and was to calculate it Motion of chages in E-field Gauss Law Toda: Moe on Gauss law and conductos in electostatic equilibium
om last times MTE1 esults Mean 75% = 90/120 Electic chages and foce Electic ield and was to calculate it Motion of chages in E-field Gauss Law Toda: Moe on Gauss law and conductos in electostatic equilibium
Introduction to classical molecular dynamics (cont d) Mechanics of Ductile Materials
 Fom nano to maco: Intoduction to atomistic modeling techniques IAP 2007 Intoduction to classical molecula dynamics (cont d) xxx Mechanics of Ductile Mateials Lectue 3 Makus J. Buehle Outline 1. Intoduction
Fom nano to maco: Intoduction to atomistic modeling techniques IAP 2007 Intoduction to classical molecula dynamics (cont d) xxx Mechanics of Ductile Mateials Lectue 3 Makus J. Buehle Outline 1. Intoduction
Substances that are liquids or solids under ordinary conditions may also exist as gases. These are often referred to as vapors.
 Chapte 0. Gases Chaacteistics of Gases All substances have thee phases: solid, liquid, and gas. Substances that ae liquids o solids unde odinay conditions may also exist as gases. These ae often efeed
Chapte 0. Gases Chaacteistics of Gases All substances have thee phases: solid, liquid, and gas. Substances that ae liquids o solids unde odinay conditions may also exist as gases. These ae often efeed
Chapter 2 Classical propagation
 Chapte Classical popagation Model: Light: electomagnetic wave Atom and molecule: classical dipole oscillato n. / / t c nz i z t z k i e e c i n k e t z Two popagation paametes: n. Popagation of light in
Chapte Classical popagation Model: Light: electomagnetic wave Atom and molecule: classical dipole oscillato n. / / t c nz i z t z k i e e c i n k e t z Two popagation paametes: n. Popagation of light in
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
 Pepaed by: M. S. KumaSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - - ELECTROSTATICS MARKS WEIGHTAGE 8 maks QUICK REVISION (Impotant Concepts & Fomulas) Chage Quantization: Chage is always in the fom of an integal multiple
Pepaed by: M. S. KumaSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - - ELECTROSTATICS MARKS WEIGHTAGE 8 maks QUICK REVISION (Impotant Concepts & Fomulas) Chage Quantization: Chage is always in the fom of an integal multiple
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
16.1 Permanent magnets
 Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Electric Forces: Coulomb s Law
 Electic Foces: Coulomb s Law All the matte aound you contains chaged paticles, and it is the electic foces between these chaged paticles that detemine the stength of the mateials and the popeties of the
Electic Foces: Coulomb s Law All the matte aound you contains chaged paticles, and it is the electic foces between these chaged paticles that detemine the stength of the mateials and the popeties of the
Chapter 5 Page 5.1 CHAPTER 5. r Force times distance has units of energy. Therefore, fxr=u, or f / is dimensionless.
 Chapte 5 Page 5.1 CHAPTER 5 Poblem 5.1: 1 (a) u () 4 0.90.93 3.0 (b) Foce times distance has units of enegy. Theefoe, fx=u, o f/ is dimensionless. d f = d u 1 d f 4ε 1 = f = 4 ε1 d 13 f = 4 ε 1 f ε = 4
Chapte 5 Page 5.1 CHAPTER 5 Poblem 5.1: 1 (a) u () 4 0.90.93 3.0 (b) Foce times distance has units of enegy. Theefoe, fx=u, o f/ is dimensionless. d f = d u 1 d f 4ε 1 = f = 4 ε1 d 13 f = 4 ε 1 f ε = 4
PHYSICS 272H Electric & Magnetic Interactions
 PHYSICS 7H Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Physics couse home page: http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic-pogams/couses/all_couses.php Blackboad Lean: https://mycouses.pudue.edu/webapps/login/ Couse Content
PHYSICS 7H Electic & Magnetic Inteactions Physics couse home page: http://www.physics.pudue.edu/academic-pogams/couses/all_couses.php Blackboad Lean: https://mycouses.pudue.edu/webapps/login/ Couse Content
Effect of ph on phase separation of globular protein
 Koean J. Chem. Eng., 6(3), 7-77 (009) SHORT COMMUNICATION Effect of ph on phase sepaation of globula potein Sang Gon Kim*, Young Chan Bae*,, and Jae-Jun Kim** *Division of Chemical Engineeing and Molecula
Koean J. Chem. Eng., 6(3), 7-77 (009) SHORT COMMUNICATION Effect of ph on phase sepaation of globula potein Sang Gon Kim*, Young Chan Bae*,, and Jae-Jun Kim** *Division of Chemical Engineeing and Molecula
Electric Charge and Field
 lectic Chage and ield Chapte 6 (Giancoli) All sections ecept 6.0 (Gauss s law) Compaison between the lectic and the Gavitational foces Both have long ange, The electic chage of an object plas the same
lectic Chage and ield Chapte 6 (Giancoli) All sections ecept 6.0 (Gauss s law) Compaison between the lectic and the Gavitational foces Both have long ange, The electic chage of an object plas the same
5.111 Lecture Summary #6 Monday, September 15, 2014
 5.111 Lectue Summay #6 Monday, Septembe 15, 014 Readings fo today: Section 1.9 Atomic Obitals. Section 1.10 Electon Spin, Section 1.11 The Electonic Stuctue of Hydogen. (Same sections in 4 th ed.) Read
5.111 Lectue Summay #6 Monday, Septembe 15, 014 Readings fo today: Section 1.9 Atomic Obitals. Section 1.10 Electon Spin, Section 1.11 The Electonic Stuctue of Hydogen. (Same sections in 4 th ed.) Read
Key Concepts for this section
 Key Concepts fo this section 1: Loentz foce law, Field, Maxwell s equation : Ion Tanspot, Nenst-Planck equation 3: (Quasi)electostatics, potential function, 4: Laplace s equation, Uniqueness 5: Debye laye,
Key Concepts fo this section 1: Loentz foce law, Field, Maxwell s equation : Ion Tanspot, Nenst-Planck equation 3: (Quasi)electostatics, potential function, 4: Laplace s equation, Uniqueness 5: Debye laye,
anubhavclasses.wordpress.com CBSE Solved Test Papers PHYSICS Class XII Chapter : Electrostatics
 CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
The mass of a water molecule is the mass of two hydrogens and one oxygen: 1u + 1u + 16u = 18u, where. = = 0.05 C/kg m. 65 kg 0.
 EECTRIC CHARGE, FORCE, AND FIED 0 EXERCISES Section 0.1 Electic Chage 1. INTERPRET We ll estimate the chage you body would cay if the electon chage slightly diffeed fom the poton chage. DEVEOP Since the
EECTRIC CHARGE, FORCE, AND FIED 0 EXERCISES Section 0.1 Electic Chage 1. INTERPRET We ll estimate the chage you body would cay if the electon chage slightly diffeed fom the poton chage. DEVEOP Since the
