Volume 22 Number April 2012 Pages
|
|
|
- Felicity Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume 22 Number April 2012 Pages ISSN PAPER Z. Liu et al. A novel solvothermal approach to synthesize SAPO molecular sieves using organic amines as the solvent and template (2012)22:14;1-I
2 Journal of Materials Chemistry Dynamic Article Links C < Cite this: J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, A novel solvothermal approach to synthesize SAPO molecular sieves using organic amines as the solvent and template Dong Fan, abc Peng Tian, ab Shutao Xu, ab Qinghua Xia, d Xiong Su, abc Lin Zhang, ab Ying Zhang, ab Yanli He ab and Zhongmin Liu* ab Received 18th October 2011, Accepted 25th November 2011 DOI: /c2jm15281a PAPER A novel solvothermal synthesis route designated as aminothermal synthesis, in which organic amines are used as both the dispersing medium and the template, is developed for the synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves. Three synthetic systems based on triethylamine (TEA), diethylamine (DEA) and TEA-DEA binary mixture were studied. SAPO-34 with good crystallinity and high yield (ca. 90%) was successfully synthesized from TEA and TEA-DEA systems. By adjusting the crystallization temperature, SAPO-18 was for the first time obtained using TEA template. In the case of DEA, a smallpore molecular sieve DNL-6 with RHO topology was synthesized. In an attempt to make the synthetic process environmentally benign and reduce the waste emission, organic liquid was collected after the synthesis of SAPO-34 and reused in next crystallization. It was found that the crystalline product and yield were almost the same as those synthesized with fresh amines. Moreover, CO 2 and CH 4 were chosen as the probe molecules to investigate the adsorption properties of products. SAPO molecular sieves synthesized by aminothermal method exhibited good adsorption capacities and high CO 2 /CH 4 ratios. Introduction Silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves (SAPOs), invented by Union Carbide Corporation in 1980s, are important crystalline materials with uniform pores. 1,2 They have exhibited many attractive properties as adsorbents, ion-exchangers, catalysts and catalyst supports. 3,4 Hitherto, hydrothermal method is a predominant strategy to synthesize SAPO molecular sieves. 5 In addition, solvothermal, 6 12 ionothermal and dry-gel conversion methods have also been explored for the preparation of SAPO molecular sieves. Novel synthetic methods are always attractive in the field of molecular sieves, which may have the possibility to create new materials or known phases with specific properties. 20 Solvothermal method was firstly introduced into the zeolite synthesis by Bibby and Dale, in which organic solvents instead of water were used as mass and heat transfer medium. 6 One of the advantages with solvothermal method is to prepare large a National Engineering Laboratory for Methanol to Olefins, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. O. Box 110, Dalian, P. R. China. liuzm@dicp.ac.cn b Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, P. R. China c Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, , P. R. China d Ministry- of- Education Key Laboratory for the Synthesis and Application of Organic Functional Molecules, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hubei University, Wuhan, , P. R. China crystals. Kuperman et al. obtained a series of giant zeolite crystals with diameters ranging from 0.4 to 5 mm in HF-alkylamine and HF-pyridine systems. 8 Xu and co-workers extended this method to the synthesis of aluminophosphate (AlPO) molecular sieves. 20 By employing alcohols as solvents, they synthesized many novel aluminophosphate materials with anionic frameworks, among which JDF-20 possessing 20-ring extra-large pores is the most attractive one. 9,10 Up to now, several SAPO molecular sieves have been synthesized through solvothermal route, such as SAPO-5, 11, 21, 31, 35 etc. 7,11,12 It is noteworthy that most solvothermal preparation of molecular sieves is not truly anhydrous, and the presence of small amount of water is essential to the crystallization process. 21,22 Liu et al. studied the effect of water amount on the solvothermal synthesis and found that the crystallization rate could be greatly accelerated with the increasing amount of water in the system. 22 SAPO-34 as one of the most important members of silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves has attracted great attention, because it behaves good property for CO 2 separation from CH 4 and exhibits excellent catalytic performance in methanol-to-olefin (MTO) reaction. 26,27 A commercial MTO process has been established based on SAPO-34 catalyst in SAPO-34 was normally synthesized with a hydrothermal method. Many organic amines have been reported as structure directing agents or templates, including tetraethylammonium hydroxide (TEAOH), 1,2 dipropylamine, 2 isopropylamine, 29 piperidine, 30 morpholine, 31 triethylamine (TEA), 32 and 6568 J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012
3 diethylamine (DEA), 33 etc. Other synthetic approaches for SAPO-34 involve microwave-assisted synthesis, 34 ionothermal synthesis 13,35 and dry-gel conversion method. 18 However, there is no open report on the solvothermal synthesis of SAPO-34. The main drawbacks associated with the conventional synthesis of SAPO-34 lie in the incomplete conversion of reagents and the generation of large amount of mother liquids, which would waste chemicals and cause environmental pollution, especially for the industrial production of SAPO-34. Dry-gel conversion may help to avoid such problems, but pitifully has difficulties in scaling up. Recycling unused reagents has been applied in the synthesis of aluminosilicate zeolites to increase the product yield and reduce the waste disposal. However, efficient utilization of unreacted chemicals from the synthesis of SAPO/AlPO molecular sieves has attracted less attention up to now. 36 In this paper, we report the use of organic amines as the solvent and template in the synthesis of SAPO-34 molecular sieve, in which the synthesis route was named as aminothermal synthesis. Two organic amines TEA and DEA, usually used as templates for hydrothermal synthesis of SAPO-34, were chosen to explore the aminothermal synthesis. Fortunately, some encouraging results have been achieved. Experimental General procedure of aminothermal synthesis Organic amines used in the synthesis were TEA (99.5 wt%), DEA (99.5 wt%) and their mixtures. Pseudoboehmite (70.5 wt%), phosphoric acid (85 wt%), and silica sol (27.5 wt%) were used as inorganic precursors. A typical synthesis procedure was as follows. Organic amine, pseudoboehmite, silica sol and water were added in sequence into a glass beaker. In some experiments, no additional water was added since water amount from reagents could satisfy the gel compositions. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 min, and then transferred into a stainless steel autoclave. After further addition of phosphoric acid, the autoclave was sealed quickly, placed in an oven and rotated at 60 rpm for 20 min to get a homogeneous mixture. Subsequently, the autoclave was heated in 60 min to the desired temperature under rotation and kept for a certain time. After the crystallization, organic liquid was collected from the autoclave with a burette or by decantation. The solid product was washed with distilled water and dried in air. The solid yield of samples was calculated by the following formula: Yield (%) ¼ (M sample 85%) 100/(M Al2 O 3 +M P2 O 5 + M SiO2 ) gel, where M sample, 85% and (M Al2 O 3 +M P2 O 5 +M SiO2 ) gel stand for the weight of solid sample, an estimated value of framework compounds included in the sample, and the dry mass of three inorganic oxides in the starting mixture, respectively. Characterization The powder XRD pattern was recorded on a PANalytical X Pert PRO X-ray diffractometer with Cu-Ka radiation (l ¼ A), operating at 40 kv and 40 ma. The chemical composition of the solid samples was determined with a Philips Magix-601 X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometer. The crystal morphology was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, KYKY- AMRAY-1000B). All NMR experiments were performed on a Varian Infinity plus 400WB spectrometer with BBO MAS probe operating at a magnetic field strength of 9.4 T. The resonance frequencies were 104.2, 161.9, 79.4, and MHz for 27 Al, 31 P, 29 Si, and 13 C, respectively. Chemical shifts were referenced to 1.0 M Al(NO 3 ) 3 for 27 Al, 85% H 3 PO 4 for 31 P, and 2, 2- dimethyl-2-ilapentane-5-sulfonate sodium salt (DSS) for 29 Si and 13 C. The spinning rates of the samples at the magic angle were 4, 10, 6 and 8 khz for 29 Si, 27 Al 31 P and 13 C, respectively. Textural properties of the calcined samples were determined by N 2 adsorption at 77 K on a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 system. The total surface area was calculated based on the BET equation. The micropore volume and micropore surface area were evaluated using the t-plot method. The collected organic amine solution was analyzed by a Varian GC3800 gas chromatograph equipped with a FID detector and a SE-30 capillary column. Adsorption experiments Adsorption isotherms of CH 4 and CO 2 of the samples were measured with a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 apparatus at 25 C and pressure up to 1 bar. The temperature was controlled by using a Dewar bottle with a circulating jacket connected to a thermostatic bath utilizing water as the coolant. Before analysis, all samples were degassed under vacuum at 350 C for 6 h. The free space of the tube was determined with helium gas. Ultrahigh purity grade CH 4 and CO 2 were used for all the adsorption experiments. Results and discussion Aminothermal synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves based on TEA system The synthesis conditions for the SAPO molecular sieves using TEA as the solvent and template are summarized in Table 1. At 160 C, pure phase of SAPO-34 (samples 2 and 3) could be obtained after 2 days of crystallization by the novel synthetic route. The product yields for samples 2 and 3 were calculated to be 89.5 and 88.1%, respectively. These values were higher than those obtained from the conventional hydrothermal synthesis performed at 200 C (75.4%, sample 10). The present yields became more prominent when compared with the hydrothermal yield of SAPO-34 synthesized at 160 C (46.8%, sample 11). This suggests that aminothermal environment could accelerate the crystallization rate of SAPO-34. Prolonged synthetic time from 2 to 4 days led to a slight increase of crystal yield (sample 4), indicating that the crystallization had approached completion after 2 days. It is important to note that the existence of certain amount of water in the aminothermal system was necessary for a successful synthesis. If the water amount was too low (V amine/water $ 8), only amorphous solid was produced (sample 1), in agreement with the previous finding that water amount in the solvothermal system had significant effect on the crystallization rate. 22 The elemental compositions of the obtained samples were determined by XRF and shown in Table 1. The solid compositions of samples 2 4 were similar to one another and close to their initial mixtures. It seems that small changes in water amount and crystallization time had little effect on the product composition. This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012 J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22,
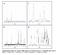
4 Table 1 Sample Aminothermal synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves based on TEA system and DEA system Gel composition a R:Al 2 O 3 :P 2 O 5 : SiO 2 :H 2 O V amine/water T/ C t (day) Product b Yield Product composition 1 c R ¼ TEA 7.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.3 : amorphous 2 R ¼ TEA 7.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.3 : SAPO % Al P Si R ¼ TEA 7.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.3 : SAPO % Al P Si R ¼ TEA 7.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.3 : SAPO % Al P Si R ¼ TEA 7.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : SAPO % Al P Si R ¼ TEA 7.0 : 1.2 : 0.9 : 0.5 : SAPO % Al P Si R ¼ DEA 9.0 : 1.2 : 0.9 : 0.5 : amorphous 8 R ¼ DEA 9.0 : 1.2 : 0.9 : 0.5 : DNL % Al P Si R ¼ DEA 9.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : DNL-6(16%) SAPO-34(84%) 44.1% Al P Si R ¼ TEA 3.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.3 : SAPO % 11 R ¼ TEA 3.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.3 : SAPO % 12 R ¼ DEA 2.0 : 1.0 : 0.8 : 0.6 : SAPO % Al P Si d R ¼ TEA 3.0 : 1.0 : 1.0 : 0.5 : 15.7 : 20EG SAPO % Al P Si a For samples 1, 2, 5 and 9, all water in the initial mixture came from reagents and no extra water was added. b The value in the brackets was calculated based on the relative intensity of the first peak of each phase in the XRD pattern. c Fumed silica was used as Si source in order to reduce the water amount in the system. d Experiment using ethylene glycol (EG) as the solvent. When the synthesis temperature was increased to 200 C, SAPO-18 (samples 5 and 6) instead of SAPO-34 was crystallized. SAPO-18 was previously synthesized utilizing expensive N,Ndiisopropylethylamine 37,38 or TEAOH 39 as the template via a hydrothermal route. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of SAPO-18 synthesis using TEA template. However, the result was not very unexpected, considering the structure similarity between SAPO-18 (AEI) and SAPO-34 (CHA). Both of them consist of layers of double six-rings, which are connected along z-axis via O-bridges to form three-dimensional structures. The lateral shift between the layers is zero for the CHA structure, while a rotation of 180 about z gives the AEI structure. Additionally, solvothermal synthesis with ethylene glycol as the solvent and TEA as the template was also investigated as a comparison. SAPO-5 was obtained as the final product (sample 13). This implies that solvent property could exert a great influence on the synthesis, and the strong basic environment arising from TEA solvent was important for the formation of SAPO-18. Fig. 1 displays the XRD patterns of the as-synthesized samples. For SAPO-34 (samples 2 4), both the crystallinity and relative intensity of each peak were comparable to those of sample 10 by hydrothermal method. The XRD patterns of SAPO-18 were similar to those reported in the previous literatures. 37,38,40 The SEM images (Fig. 2) reveal that SAPO-34 had a typical rhombohedral morphology. SAPO-18 was consisted of square-shaped plate-like crystals, in consistence with previous report. 39 The textual properties of samples are presented in Table 2. All samples possessed large surface areas and high pore volumes. These values were close to those of samples synthesized with hydrothermal method, implying that the aminothermal route was an effective methodology to synthesize SAPO molecular sieves with good crystallinity. Solid-state 29 Si, 31 P and 27 Al MAS NMR spectra were determined to investigate the local atomic environments in the assynthesized SAPO-34 (sample 4) and SAPO-18 (sample 6). The results are shown in Fig. 3. For SAPO-34, both 29 Si and 31 P MAS NMR spectra gave one single resonance peak, in accordance with Si (4Al) and P (4Al) environments. Two peaks centred at 39.3 and 12 ppm were observed for the as-synthesized SAPO-34 in the 27 Al MAS NMR spectrum. The strong peak at high field should arise from tetrahedrally coordinated aluminium atoms. The weak peak was ascribed to penta-coordinated Al formed by an additional interaction of one water or template molecule to the framework aluminium. 41 The assignment was confirmed by the 27 Al spectrum of the calcined SAPO-34, in which only one signal with a chemical shift of 33.8 ppm appeared. The 29 Si MAS NMR spectrum of SAPO-18 was complex and showed the coexistence of several Si environments. Since the silicon contents in SAPO-18 and SAPO-34 were low and very close, it could be inferred that the framework of SAPO-18 was facilitating the formation of Si islands. Chen et al. investigated the Si environments in SAPO-18 prepared by hydrothermal method to observe a similar phenomenon. 38 The 31 P spectrum of SAPO-18 consisted of a single peak centered at 29 ppm and the other small one at Fig. 1 XRD patterns of as-synthesized samples 2(a), 3(b), 4(c), 5(d), 6(e), 8(f) and 10(g) J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012
5 Fig. 2 SEM images of as-synthesized samples 2(a), 3(b), 4(c), 5(d), 6(e) and 8(f). Table 2 Textual properties of the samples Surface area (m 2 g 1 ) Pore volume (cm 3 g 1 ) Sample S total a S micro b S ext c V total V micro d a BET surface area. b t-plot micropore surface area. c t-plot external surface area. d t-plot micropore volume ppm. According to the literature, 42 the framework structure of AlPO-18 contains three phosphorus and three aluminium crystallographic positions. Therefore, these two signals should be ascribed to P (4Al) with different local geometries. Correspondingly, several peaks were observed in the 27 Al spectrum. The strong splitting signals were due to tetrahedral Al atoms at different crystallographic sites, and the small peak at ca. 9 ppm arose from penta-coordinated Al. Generally, the chemical environments of Si, P and Al in samples 4 and 6 were similar to those of the samples prepared by hydrothermal method. Fig Si MAS NMR (A), 31 P MAS NMR (B) and 27 Al MAS NMR (C) spectra of as-synthesized samples 4 (SAPO-34) and 6 (SAPO-18). Aminothermal synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves based on DEA system Diethylamine (DEA) is a kind of versatile structure-directing agent frequently employed in the synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves. Aminothermal synthesis of SAPO-molecular sieves based on DEA system was carried out. Detailed synthesis conditions and product compositions are listed in Table 1. XRD patterns and SEM images of the as-synthesized sample are shown in Fig. 1 and 2, respectively. It can be seen that DNL-6 with a good crystallinity was formed from a starting composition of 9.0DEA : 1.0Al 2 O 3 : 0.9P 2 O 5 : 0.5SiO 2 : 16.6H 2 O at 160 C for 4 days (sample 8). DNL-6 was a novel SAPO molecular sieve with RHO framework type. Our laboratory recently reported its first synthesis under hydrothermal conditions by using DEA as the template in the presence of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012 J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22,
6 (CTAB). 43,44 Along with increasing the synthetic temperature to 200 C, the product became a mixture of SAPO-34 and DNL-6 (sample 9). It should be mentioned that the solid yields of samples 8 and 9 were obviously lower than those synthesized with TEA solvent, but close to that obtained by the hydrothermal route with DEA template (sample 12). Possibly, the high Si incorporation into the framework of molecular sieves induced by DEA possibly resulted in the low yield. 33 SEM image reveals that DNL-6 has a rhombic dodecahedral morphology with crystal size distribution of 2 5 mm. The micropore surface area and volume of DNL-6 were respectively determined to be 586 m 2 g 1 and 0.27 cm 3 g 1 (see Table 2). The values were comparable to those of SAPO-34 and SAPO-18, in consistence with the similar framework densities of three molecular sieves. Aminothermal synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves based on TEA-DEA system The mixture of TEA and DEA was explored as the solvent and template to synthesize SAPO molecular sieves. A series of experiments with different TEA/DEA ratios were investigated and the results are shown in Table 3. Interestingly, SAPO-34 with a solid yield of 90% could be obtained from the systems with higher TEA/DEA ratios at 200 C for 2 days (samples 14, 15 and 18), different from the induction behaviour of any single amine under the same synthesis conditions. With the gradual increase of DEA concentration in TEA-DEA mixture, the product phase would change from SAPO-34 to DNL-6 containing a small amount of SAPO-34 impurity, accompanied with an obvious decrease of the solid yield. Elemental analyses by XRF (see Table 3) revealed that the product synthesized with the highest DEA concentration possessed the largest silicon content (sample 17), which was identical to that of sample 8 crystallized in individual DEA solvent. Thus, the low yield of sample 17 might be ascribed to the high Si incorporation induced by DEA template. The XRD patterns of as-synthesized samples are presented in Fig. 4. All samples exhibited good crystallinity. However, a clear distinction in the relative peak intensity was observed when comparing the XRD patterns of SAPO-34 synthesized from binary amines system with those from TEA system. According to the literature, the former had a pure CHA structure, but the latter was a CHA/AEI intergrowth with CHA as a dominant phase. 45 This suggests that the mixture of TEA and DEA have a strong structure-directing ability to the formation of pure CHA framework. Textual properties shown in Table 2 indicated that Fig. 4 17(d). XRD patterns of as-synthesized samples 14(a), 15(b), 16(c) and samples possessed large micropore surface area and micropore volume, further confirming the excellent crystallinity of the products. 13 C MAS NMR was employed to investigate the incorporation of DEA and TEA into the products (see Fig. 5). The assignments of all peaks were labelled in the spectra. The strong peak centred at ca. 11 ppm was ascribed to CH 3 group of two amines. The CH 2 group in DEA and TEA gave signals at and ppm, respectively. It can be seen that the signals from both TEA and DEA appeared in the spectra of all four samples, suggesting co-templated role of two amines. Deconvoluted results revealed that the molar ratio of TEA/DEA in the products was lower than that in the starting gels, possibly indicating that DEA was more easily incorporated into the as-synthesized sample than TEA. Synthesis of SAPO-34 using recycled amines Also, synthesis of SAPO-34 using recycled amines was investigated based on samples 3 (TEA system) and 18 (TEA-DEA binary system). Organic amines could be collected easily by a burette or by decantation after the synthesis, since there was a clear interface between organic solution and viscous gel-like product. It should be mentioned that experiment without extra water addition was not suitable for recycling synthesis due to the Table 3 Sample Aminothermal synthesis of SAPO molecular sieves based on TEA-DEA system Gel composition a TEA : DEA : Al 2 O 3 :P 2 O 5 : SiO 2 :H 2 O T/ C t (day) Product b Yield Product composition : 0.5 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : SAPO % Al P Si : 1.5 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : SAPO % Al P Si : 3.5 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : SAPO % Al P Si : 7.0 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : DNL-6(94.3%) + SAPO-34(5.7%) 60.3% Al P Si : 1.5 : 1.0 : 0.9 : 0.5 : SAPO % a For samples 14 17, all water in the initial mixture came from reagents and no extra water was added. b The value in the brackets was calculated based on the relative intensity of the first peak of each phase in the XRD pattern J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012
7 CO 2 and CH 4 on SAPO-34, SAPO-18 and DNL-6 synthesized by aminothermal method were collected and shown in Fig. 6. To evaluate the effect of the present synthesis method on the sorption properties of the samples, SAPO-34 synthesized by hydrothermal method (sample 10) was used as a reference material. Compared with the reference sample 10, sample 15 (SAPO- 34) exhibited a large CO 2 adsorption capacity and high CO 2 / CH 4 ratio, which is attractive for the separation of CO 2 /CH 4 mixture. The highest CO 2 /CH 4 adsorption ratio was observed for SAPO-18 (sample 6), though its adsorption capacities for both gases were relatively low. DNL-6 (sample 8) displayed the largest uptakes for CO 2 and CH 4. The CO 2 /CH 4 ratio on DNL- 6 was 9.2, quite close to 9.1 on the reference sample. These preliminary results indicate good adsorption/separation properties of SAPO molecular sieves synthesized by aminothermal method. Conclusions Fig C MAS NMR spectra of as-synthesized samples 14(a), 15(b), 16(c) and 17(d). Standard samples: SAPO-34-TEA and SAPO-34-DEA were synthesized hydrothermally with TEA and DEA templates, respectively. existence of small amount of water in the collected organic liquids. The detailed information of recycled liquids and the synthesis conditions are listed in Table 4. It can be seen that only small quantities of organic amines and water were added to attain the same solvent environment as the first batch. Pure SAPO-34 with good crystallinity and high yield was obtained in both experiments, almost identical to the product synthesized with fresh amines. This proves that recycled amines could be readily reused to synthesize SAPO-34 with high quality. CO 2 and CH 4 adsorption Molecular sieves with small pore size are promising adsorbents for CO 2 separation from methane. Adsorption isotherms of The present work demonstrates that the aminothermal method is an effective route to synthesize SAPO molecular sieves. SAPO-34 with 90% yield was obtained using TEA or TEA-DEA mixture as the solvent and template. Pure SAPO-18 could be synthesized by changing the crystallization temperature of the TEA system, which is the first synthesis report of SAPO-18 with TEA as the template. Employing DEA as the solvent and template, a novel SAPO molecular sieve DNL-6 was formed. Characterization results revealed that DEA could induce a high Si incorporation into the framework of molecular sieves to cause a low solid yield. In addition, DEA showed a stronger ability than TEA to incorporate into the as-synthesized sample when TEA-DEA binary mixture was used for aminothermal synthesis. Environmental benign approaches could be realized through recycling organic liquids collected after the synthesis. Finally, SAPO molecular sieves were evaluated as adsorbents for the CO 2 /CH 4 separation. As compared with the reference sample, SAPO-34 synthesized by the present route exhibited better adsorption capacity and high CO 2 /CH 4 ratio. The present work will further Table 4 Repeated synthesis of SAPO-34 with collected liquids Sample 3 a Sample 18 b Collected liquid mass 35.0 g 39.8 g Liquid component TEA 33.0 g TEA34.4 g H 2 O 2.0 g DEA 2.95 g H 2 O 2.4 g Added liquids TEA 2.4 g TEA 0.94 g H 2 O 3.64 g DEA 2.53 g H 2 O 1.39 g Product SAPO-34 SAPO-34 Crystalline yield 90% 89.7% a Initial gel composition for sample 3 : 7.03 g pseudoboehmite, g phosphoric acid, 3.20 g silica sol, 5.64 g water and g TEA. Initial gel composition for sample 18 : 7.03 g pseudoboehmite, g phosphoric acid, 5.36 g silica sol, 3.79 g water, g TEA and 5.48 g DEA. Fig. 6 CO 2 and CH 4 adsorption isotherms of samples 15(a), 6(b), 8(c) and 10(d). This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012 J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22,
8 arouse our interests to explore the aminothermal synthesis of other SAPO molecular sieves with a wide range of organic amines. References 1 B. M. Lok, C. A. Messina, R. L. Patton, R. T. Gajek, T. R. Cannan and E. M. Flanigen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, C. A. M. B. M. Lok, R. L. Patton, R. T. Gajek, T. R. Cannan and E. M. Flanigen, US pat , M. E. Davis, Nature, 2002, 417, A. Corma, Chem. Rev., 1997, 97, E. Fayad, N. Bats, C. Kirschhock, B. Rebours, A. A. Quoineaud and J. Martens, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 49, D. M. Bibby and M. P. Dale, Nature, 1985, 317, Q. S. HuoandR. R. Xu,J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1990, A. Kuperman, S. Nadimi, S. Oliver, G. A. Ozin, J. M. Garces and M. M. Olken, Nature, 1993, 365, R. H. Jones, J. M. Thomas, J. S. Chen, R. R. Xu, Q. S. Huo, S. G. Li, Z. G. Ma and A. M. Chippindale, J. Solid State Chem., 1993, 102, Q. H. Huo, R. R. Xu, S. G. Li, Z. G. Ma, J. M. Thomas, R. H. Jones and A. M. Chippindale, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1992, A. K. Sinha and S. Seelan, Appl. Catal., A, 2004, 270, N. Venkatathri, Catal. Commun., 2006, 7, E. R. Cooper, C. D. Andrews, P. S. Wheatley, P. B. Webb, P. Wormald and R. E. Morris, Nature, 2004, 430, Y. Wei, Z. Tian, H. Gies, R. Xu, H. Ma, R. Pei, W. Zhang, Y. Xu, L. Wang, K. Li, B. Wang, G. Wen and L. Lin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, E. R. Parnham, E. A. Drylie, P. S. Wheatley, A. M. Z. Slawin and R. E. Morris, Angew. Chem., 2006, 118, Y.-P. Xu, Z.-J. Tian, S.-J. Wang, Y. Hu, L. Wang, B.-C. Wang, Y.-C. Ma, L. Hou, J.-Y. Yu and L.-W. Lin, Angew. Chem., 2006, 118, W. Xu, J. Dong, J. Li, J. Li and F. Wu, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1990, B. Chen and Y. Huang, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2009, 123, P. Rao and M. Matsukata, Chem. Commun., 1996, R. E. Morris and S. J. Weigel, Chem. Soc. Rev., 1997, 26, S. Oliver, A. Kuperman and G. A. Ozin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1998, 37, Z. Q. Liu, W. G. Xu, G. D. Yang and R. R. Xu, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 1998, 22, S. G. Li, J. L. Falconer and R. D. Noble, J. Membr. Sci., 2004, 241, M. A. Carreon, S. Li, J. L. Falconer and R. D. Noble, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, S. R. Venna and M. A. Carreon, Langmuir, 2011, 27, J. Liang, Appl. Catal., 1990, 64, S. Wilson and P. Barger, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 1999, 29, N. Rajic, D. Stojakovic, S. Hocevar and V. Kaucic, Zeolites, 1993, 13, E. Dumitriu, A. Azzouz, V. Hulea, D. Lutic and H. Kessler, Microporous Mater., 1997, 10, A. M. Prakash and S. Unnikrishnan, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1994, 90, L. Xu, A. Du, Y. Wei, Y. Wang, Z. Yu, Y. He, X. Zhang and Z. Liu, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2008, 115, G. Liu, P. Tian, J. Li, D. Zhang, F. Zhou and Z. Liu, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2008, 111, S. H. Jhung, J. S. Chang, J. S. Hwang and S. E. Park, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2003, 64, R. Pei, Z. Tian, Y. Wei, K. Li, Y. Xu, L. Wang and H. Ma, Mater. Lett., 2010, 64, E. P. Ng, L. Delmotte and S. Mintova, Green Chem., 2008, 10, J. S. Chen, J. M. Thomas, P. A. Wright and R. P. Townsend, Catal. Lett., 1994, 28, J. S. Chen, P. A. Wright, J. M. Thomas, S. Natarajan, L. Marchese, S. M. Bradley, G. Sankar, C. R. A. Catlow, P. L. Gaiboyes, R. P. Townsend and C. M. Lok, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, R. Wendelbo, D. Akporiaye, A. Andersen, I. M. Dahl and H. B. Mostad, Appl. Catal., A, 1996, 142, L197 L H. van Heyden, S. Mintova and T. Bein, J. Mater. Chem., 2006, 16, J. Tan, Z. M. Liu, X. H. Bao, X. C. Liu, X. W. Han, C. Q. He and R. S. Zhai, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2002, 53, H. Y. He and J. Klinowski, J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97, X. Su, P. Tian, J. Li, Y. Zhang, S. Meng, Y. He, D. Fan and Z. Liu, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2011, 144, P. Tian, X. O. Su, Y. X. Wang, Q. H. Xia, Y. Zhang, D. Fan, S. H. Meng and Z. M. Liu, Chem. Mater., 2011, 23, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, This journal is ª The Royal Society of Chemistry 2012
Acetylene hydrochlorination over 13X zeolite. catalyst at high temperature
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Acetylene hydrochlorination over 13X zeolite catalyst at high temperature Zhijia Song, ab
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Acetylene hydrochlorination over 13X zeolite catalyst at high temperature Zhijia Song, ab
Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Effect of Synthesis Parameters on Phase Purity, Crystallinity and Particle Size of SAPO-34
 Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Research Note Vol. 30, No. 4, 2011 Effect of Synthesis Parameters on Phase Purity, Crystallinity and Particle Size of SAPO-34 Emrani, Peyman; Fatemi, Shohreh* + ; Ashraf Talesh,
Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Research Note Vol. 30, No. 4, 2011 Effect of Synthesis Parameters on Phase Purity, Crystallinity and Particle Size of SAPO-34 Emrani, Peyman; Fatemi, Shohreh* + ; Ashraf Talesh,
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of SAPO-34 synthesized using diethylamine as a template
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 111 (2008) 143 149 www.elsevier.com/locate/micromeso Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of SAPO-34 synthesized
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 111 (2008) 143 149 www.elsevier.com/locate/micromeso Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of SAPO-34 synthesized
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Characterization and optimization of SAPO-34 catalysts synthesized by mixed templates in MTO reaction
 Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 4 (Autumn 2015), IAChE Characterization and optimization of SAPO-34 catalysts synthesized by mixed templates in MTO reaction Sh. Masoumi, J. Towfighi*
Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 4 (Autumn 2015), IAChE Characterization and optimization of SAPO-34 catalysts synthesized by mixed templates in MTO reaction Sh. Masoumi, J. Towfighi*
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries
 Supporting Information for Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries Zhu-Yin Sui, Pei-Ying Zhang,, Meng-Ying Xu,
Supporting Information for Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries Zhu-Yin Sui, Pei-Ying Zhang,, Meng-Ying Xu,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation
 S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Stable aluminum metal-organic frameworks (Al-MOFs) for balanced CO 2 and water selectivity Haiwei Li, Xiao Feng, * Dou Ma, Mengxi Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Yi Liu, Jinwei Zhang,
Supplementary Information Stable aluminum metal-organic frameworks (Al-MOFs) for balanced CO 2 and water selectivity Haiwei Li, Xiao Feng, * Dou Ma, Mengxi Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Yi Liu, Jinwei Zhang,
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid
 Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION CATALYSTS BY HIGH-THROUGHPUT TECHNIQUE
 Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 93, No. 1, 11 17 (2008) and Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/s11144-008-5155-3 RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION
Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 93, No. 1, 11 17 (2008) and Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/s11144-008-5155-3 RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION
Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity
 1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
Supporting information. Mechanical Properties of Microcrystalline Metal-Organic Frameworks. (MOFs) Measured by Bimodal Amplitude Modulated-Frequency
 Supporting information Mechanical Properties of Microcrystalline Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Measured by Bimodal Amplitude Modulated-Frequency Modulated Atomic Force Microscopy Yao Sun, Zhigang Hu,
Supporting information Mechanical Properties of Microcrystalline Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Measured by Bimodal Amplitude Modulated-Frequency Modulated Atomic Force Microscopy Yao Sun, Zhigang Hu,
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
Supplementary Information. Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses
 Supplementary Information Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses of Extra-Large Pore Germanosilicate Zeolites Risheng Bai, Qiming Sun, Ning Wang, Yongcun Zou, Guanqi Guo, Sara Iborra, Avelino
Supplementary Information Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses of Extra-Large Pore Germanosilicate Zeolites Risheng Bai, Qiming Sun, Ning Wang, Yongcun Zou, Guanqi Guo, Sara Iborra, Avelino
Supporting Information. for. A Sustainable Protocol for the Spontaneous Synthesis of Zinc-Glutamate. Wet Conditions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for A Sustainable Protocol for the Spontaneous Synthesis of Zinc-Glutamate
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for A Sustainable Protocol for the Spontaneous Synthesis of Zinc-Glutamate
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Characterization of partially reduced graphene oxide as room
 Supporting Information Characterization of partially reduced graphene oxide as room temperature sensor for H 2 Le-Sheng Zhang a, Wei D. Wang b, Xian-Qing Liang c, Wang-Sheng Chu d, Wei-Guo Song a *, Wei
Supporting Information Characterization of partially reduced graphene oxide as room temperature sensor for H 2 Le-Sheng Zhang a, Wei D. Wang b, Xian-Qing Liang c, Wang-Sheng Chu d, Wei-Guo Song a *, Wei
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Multi-scale promoting effects
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Multi-scale promoting effects
Investigation of the Crystallization Process of SAPO-35 and Si Distribution in the Crystals
 pus.acs.org/jpcc Investigation of the Crystallization Process of SAPO-35 and Si Distriution in the Crystals Peng Tian, Bing Li,, Shutao Xu, Xiong Su,, Dehua Wang,, Lin Zhang, Dong Fan,, Yue Qi, and Zhongmin
pus.acs.org/jpcc Investigation of the Crystallization Process of SAPO-35 and Si Distriution in the Crystals Peng Tian, Bing Li,, Shutao Xu, Xiong Su,, Dehua Wang,, Lin Zhang, Dong Fan,, Yue Qi, and Zhongmin
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Supporting Information. Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-101(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid
 Supporting Information Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-11(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid Kunyue Leng a, Yinyong Sun a *, Xiaolin Li a, Shun Sun a, Wei Xu b a
Supporting Information Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-11(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid Kunyue Leng a, Yinyong Sun a *, Xiaolin Li a, Shun Sun a, Wei Xu b a
Research Progress in Ionothermal Synthesis of Molecular Sieves
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF CATALYSIS Volume 33, Issue 1, 2012 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Chin. J. Catal., 2012, 33: 39 50. ARTICLE Research Progress in Ionothermal
CHINESE JOURNAL OF CATALYSIS Volume 33, Issue 1, 2012 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Chin. J. Catal., 2012, 33: 39 50. ARTICLE Research Progress in Ionothermal
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Angewandte. Microwave-Enhanced Ionothermal Synthesis of Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves**
 Angewandte Chemie Microporous Materials DOI: 10.1002/anie.200600054 Microwave-Enhanced Ionothermal Synthesis of Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves** Yun-Peng Xu,* Zhi-Jian Tian, Shao-Jun Wang, Yue Hu, Lei
Angewandte Chemie Microporous Materials DOI: 10.1002/anie.200600054 Microwave-Enhanced Ionothermal Synthesis of Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves** Yun-Peng Xu,* Zhi-Jian Tian, Shao-Jun Wang, Yue Hu, Lei
NJC Accepted Manuscript
 NJC Accepted Manuscript This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted Manuscripts are published
NJC Accepted Manuscript This is an Accepted Manuscript, which has been through the Royal Society of Chemistry peer review process and has been accepted for publication. Accepted Manuscripts are published
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Synthesis of uniform hollow silica spheres with ordered mesoporous shells in a CO 2 induced nanoemulsion. Supporting Information
 Synthesis of uniform hollow silica spheres with ordered mesoporous shells in a CO 2 induced nanoemulsion Yueju Zhao, Jianling Zhang, Wei Li, Chaoxing Zhang, Buxing Han* Beijing National Laboratory for
Synthesis of uniform hollow silica spheres with ordered mesoporous shells in a CO 2 induced nanoemulsion Yueju Zhao, Jianling Zhang, Wei Li, Chaoxing Zhang, Buxing Han* Beijing National Laboratory for
Adsorptive separation of methanol-acetone on isostructural series of. metal-organic frameworks M-BTC (M = Ti, Fe, Cu, Co, Ru, Mo): A
 Supporting information Adsorptive separation of methanol-acetone on isostructural series of metal-organic frameworks M-BTC (M = Ti, Fe, Cu, Co, Ru, Mo): A computational study of adsorption mechanisms and
Supporting information Adsorptive separation of methanol-acetone on isostructural series of metal-organic frameworks M-BTC (M = Ti, Fe, Cu, Co, Ru, Mo): A computational study of adsorption mechanisms and
Supplementary Material for. Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive Nitrogen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C. composites for photodegradation of organic dye
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C composites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C composites
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic
 Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Supporting Information. for. Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under. Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via
 Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supplementary Information. for. Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High. Pressures
 S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information 2-Methylimidazole-Assisted Synthesis of Two-Dimensional MOF-5 Catalyst
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information 2-Methylimidazole-Assisted Synthesis of Two-Dimensional MOF-5 Catalyst
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
Metal-free and Solvent-free Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines with Mesoporous Carbon from Macrocyclic Compounds
 1 Supporting Information Metal-free and Solvent-free Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines with Mesoporous Carbon from Macrocyclic Compounds Bo Chen, 1, Lianyue Wang, 1 Wen Dai, 1 Sensen Shang, 1, Ying
1 Supporting Information Metal-free and Solvent-free Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines with Mesoporous Carbon from Macrocyclic Compounds Bo Chen, 1, Lianyue Wang, 1 Wen Dai, 1 Sensen Shang, 1, Ying
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Control of Wall Thickness and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability of Nanoporous MCM-41 Silica
 Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2007, 54, 35-40 35 Control of Wall Thickness and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability of Nanoporous MCM-41 Silica Chi-Feng Cheng* ( ), Shu-Hsien Chou ( ),
Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2007, 54, 35-40 35 Control of Wall Thickness and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability of Nanoporous MCM-41 Silica Chi-Feng Cheng* ( ), Shu-Hsien Chou ( ),
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information The directing effect of linking unit on building microporous architecture in tetraphenyladmantane-based poly(schiffbase) networks Guiyang Li, Biao Zhang, Jun Yan and
Electronic Supplementary Information The directing effect of linking unit on building microporous architecture in tetraphenyladmantane-based poly(schiffbase) networks Guiyang Li, Biao Zhang, Jun Yan and
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment
 Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Supplementary Information. ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni(0) Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane
 Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Hollow ceramic fiber supported ZIF-8 membrane with enhanced. gas separation performance prepared by hot dip-coating seeding
 Supporting information Hollow ceramic fiber supported ZIF-8 membrane with enhanced gas separation performance prepared by hot dip-coating seeding Kai Tao, Lujie Cao, Yichao Lin, Chunlong Kong * and liang
Supporting information Hollow ceramic fiber supported ZIF-8 membrane with enhanced gas separation performance prepared by hot dip-coating seeding Kai Tao, Lujie Cao, Yichao Lin, Chunlong Kong * and liang
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction activity of nitrogen-doped carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry A Electronic Supporting Information (ESI)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry A Electronic Supporting Information (ESI)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials
 Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2009, 25(4),
 CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2009, 25(4), 407 411 Synthesis, Characterization and Phase Transformation of 3D Open-framework Zinc Phosphate [Zn 6 (H 2 O)P 5 O 20 ][C 5 N 2 H 14 ][C 6 H 16 N 2 ] 0.5 3H
CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2009, 25(4), 407 411 Synthesis, Characterization and Phase Transformation of 3D Open-framework Zinc Phosphate [Zn 6 (H 2 O)P 5 O 20 ][C 5 N 2 H 14 ][C 6 H 16 N 2 ] 0.5 3H
General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported. Bicomponent Metal Monoxides as Alternative High- Performance Li-Ion Anodes to Binary Spinel Oxides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Division of Fuel Cells, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information Tuned Depositing Ag clusters on ZrO 2 Nanocrystals from Silver Mirror
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information Tuned Depositing Ag clusters on ZrO 2 Nanocrystals from Silver Mirror
Cooperative Template-Directed Assembly of Mesoporous Metal-Organic Frameworks
 Supporting Information Cooperative Template-Directed Assembly of Mesoporous Metal-Organic Frameworks Lin-Bing Sun, Jian-Rong Li, Jinhee Park, and Hong-Cai Zhou* Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University,
Supporting Information Cooperative Template-Directed Assembly of Mesoporous Metal-Organic Frameworks Lin-Bing Sun, Jian-Rong Li, Jinhee Park, and Hong-Cai Zhou* Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University,
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Supporting Information. Phenolic/resin assisted MOFs derived hierarchical Co/N-doping carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core
 A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Zirconium Oxide Based Metal-Organic Frameworks Weibin Liang and Deanna M. D Alessandro* School of Chemistry, The University of
Supplementary Information for Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Zirconium Oxide Based Metal-Organic Frameworks Weibin Liang and Deanna M. D Alessandro* School of Chemistry, The University of
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Information for Exceptional Ammonia Uptake by a Covalent Organic Framework Christian J. Doonan, David J. Tranchemontagne,T. Grant Glover, Joseph R. Hunt, Omar M.
Supplementary information Supplementary Information for Exceptional Ammonia Uptake by a Covalent Organic Framework Christian J. Doonan, David J. Tranchemontagne,T. Grant Glover, Joseph R. Hunt, Omar M.
High Salt Removal Capacity of Metal-Organic Gel Derived. Porous Carbon for Capacitive Deionization
 Supporting Information High Salt Removal Capacity of Metal-Organic Gel Derived Porous Carbon for Capacitive Deionization Zhuo Wang, Tingting Yan, Guorong Chen, Liyi Shi and Dengsong Zhang* Research Center
Supporting Information High Salt Removal Capacity of Metal-Organic Gel Derived Porous Carbon for Capacitive Deionization Zhuo Wang, Tingting Yan, Guorong Chen, Liyi Shi and Dengsong Zhang* Research Center
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Supporting information. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and adsorption of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and adsorption
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and adsorption
Supporting Information. Microwindows on the Shell
 Supporting Information Organic-inorganic Hybrid Hollow Nanospheres with Microwindows on the Shell Jian Liu,, Qihua Yang,*, Lei Zhang, Hengquan Yang, Jinsuo Gao,, and Can Li*, State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Supporting Information Organic-inorganic Hybrid Hollow Nanospheres with Microwindows on the Shell Jian Liu,, Qihua Yang,*, Lei Zhang, Hengquan Yang, Jinsuo Gao,, and Can Li*, State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Synthesis of homochiral zeolitic imidazolate frameworks via solvent-assisted linker exchange for enantioselective sensing and separation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Synthesis of homochiral zeolitic imidazolate frameworks via solvent-assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Synthesis of homochiral zeolitic imidazolate frameworks via solvent-assisted
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Novel Nanoporous Ferrocenyl Framework for Clean Energy Application Qingquan
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Novel Nanoporous Ferrocenyl Framework for Clean Energy Application Qingquan
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Lei Liu, ab Yijie Xia, b Jie Zhang* b a) China Center for Modernization
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Lei Liu, ab Yijie Xia, b Jie Zhang* b a) China Center for Modernization
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Supporting information A Porous Zr-cluster-based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Cr 2 O 7
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information A Porous Zr-cluster-based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information A Porous Zr-cluster-based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Supporting Information. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Research on Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis for Ion Exchange of Molecular Sieves
 Scientific Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2018, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp 1-5 June 30, 2018 Research on Bipolar Membrane for Ion Exchange of Molecular Sieves Chen Beiyan 1 ;
Scientific Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2018, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp 1-5 June 30, 2018 Research on Bipolar Membrane for Ion Exchange of Molecular Sieves Chen Beiyan 1 ;
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Controllable Adsorption of CO2 on Smart Adsorbents: An Interplay between Amines and Photoresponsive Molecules Lei Cheng, Yao Jiang, Shi-Chao Qi, Wei Liu, Shu-Feng Shan, Peng Tan,
Supporting Information Controllable Adsorption of CO2 on Smart Adsorbents: An Interplay between Amines and Photoresponsive Molecules Lei Cheng, Yao Jiang, Shi-Chao Qi, Wei Liu, Shu-Feng Shan, Peng Tan,
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Highly efficient and recyclable triple-shelled Ag@Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 @TiO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Highly efficient and recyclable triple-shelled Ag@Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 @TiO
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
