SUZ-4 Zeolite Synthesis Derived from Rice Husk Ash
|
|
|
- Bertha Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) 109 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) : Contributed Paper SUZ-4 Zeolite Synthesis Derived from Rice Husk Ash Napapan Jaroonvechatam [a,c], Pakkarada Sansuksom [a], Patcharin Worathanakul [b] and Paisan Kongkachuichay*[a,c] [a] Center of Excellence on Petrochemical and Materials Technology, Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,Kasetsart University, Bangkok Thailand. [b] Department of Chemical Engineering, King Mongkut s University of Technology North Bangkok, 1518 Pibulsongkram Road, Wongsawang, Bangsue, Bangkok Thailand. [c] Center for Advanced Studies in Nanotechnology and Its Applications in Chemical, Food and Agricultural Industries, Kasetsart University, Bangkok 10900, Thailand. *Author for correspondence; fengpsk@ku.ac.th Received: 28 November 2011 Accepted: 18 April 2012 ABSTRACT Rice husk ash (RHA) as a raw material was used to synthesize SUZ-4 zeolite via a hydrothermal process in the presence of tetraethyl ammonium hydroxide as the template. The molar ratios of silica from RHA:silica sol were varied as the following: 0:100, 50:50, 70:30, 90:10 and 100:0. The synthesized zeolite was characterized using various techniques including X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and BET-N 2 adsorption method. The results show that the obtained SUZ-4 zeolite using pure silica sol has a needle-shape crystal having diameter in a range of 0.07 ± 0.02 μm and length in a range of 1.7 ± 0.2 μm, while the SUZ-4 crystal from using 50% RHA has a larger needle-shape than that of pure silica sol, having diameter of 0.2 ± 0.01 μm and length of 5.0 ± 1.5 μm. The crystallite size was shrunk to 0.13 ± 0.01 x 2.8 ± 0.2 μm when 90% and 100% RHA were used. With 50 % RHA, high purity of SUZ-4 was obtained having the same surface area as that of 100 % silica sol. The increase in RHA content did change the pore size distribution due to the competitive formation of Merlinoite zeolite (MER) during the crystallization process. Keywords: SUZ-4 zeolite, merlinoite (MER), rice husk ash (RHA), silica sol 1. INTRODUCTION Biomass is a renewable resource with great utilization due to environmental considerations and the increasing demands of energy worldwide. Rice husk ash (RHA), a by-product of rice mill industry, is one of the alternative sources with high silica content and can be used for production of valuable materials and chemicals. The silica in RHA is amorphous and transforms to crystalline silica when it is heated at high temperatures. Crystalline silica is recognized as a material that can cause damages to respiratory track and other tissues, and cancer according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) announced in Finding an appropriate utilization of the ash is necessary to protect the environment and to decrease the
2 110 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) amount of RHA waste requiring storage area. There have been many researches encouraging the utilization of SiO 2 from RHA for the synthesis of various types of zeolites and nanomaterials [1-8], the experimental results so far show its high potential for utilization, due to the differences in the nature of the RHA prepared and in the composition of the precursor gel. There are approximately 175 unique zeolite frameworks identified by the International Zeolites Association (IZA) [9] and over 40 naturally occurring zeolite frameworks are known. SUZ-4 is a new type of synthetic zeolite [10-14]. There are some researches demonstrated and claimed that SUZ-4 has an excellent catalytic properties, high thermal stability as well as high organic solvents resistance [15-22]. However, the preparation of SUZ-4 from RHA has not been reported yet. Zeolites are normally synthesized from aqueous basic aluminosilicate precursor gels under hydrothermal conditions [23-25]. Therefore, it is very interesting to synthesize and characterize this type of zeolite under these conditions for potential applications. In this work, RHA was used as a silica source instead of silica sol. Different molar ratios of RHA and silica sol were used in order to obtain desired SUZ-4 zeolite. The synthesized SUZ-4 zeolite was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, BET N 2 -adsorption and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). This obtained SUZ-4 zeolite is expected to be used as a catalyst for reduction of NOx and production of alcohols from greenhouse gases such as CO 2 and CH MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 RHA Preparation Dried rice husk (RH) was well washed with water and refluxed with 1 M HCl at 373 K for 3 h to remove impurities. After rinsing with water, it was dried and burned at 973 K for 1 h under oxygen flowing followed by Kongkachuichay and Lohsoontorn method [3]. The obtained white ash (RHA) was further used as natural silica source altogether with silica sol. Aluminum powder (99.7% Al, Hi Media), silica sol (LUDOX AS-40 colloidal silica, 40 wt. % SiO 2, Aldrich), tetraethylammonium hydroxide (TEAOH, 35% in water, Aldrich), potassium hydroxide (85% KOH pellet, Carlo Erba), and hydrochloric acid (37 wt.% HCl, Merck) were used as a source of alumina, silica, template, alkali and acid leaching, respectively. The TEAOH is an organic structure directing agent that can form 8-membered and 10-membered rings, which are the pore structures of a SUZ-4 zeolite. 2.2 SUZ-4 Synthesis The SUZ-4 was synthesized following our previous work [25]. The starting molar ratio of used chemicals was 7.9K 2 O:Al 2 O 3 :21.22SiO 2 :2.6TEA 2 O:498.6 H 2 O. The RHA and silica sol were used as silica sources with the RHA:silica sol molar ratio of 0:100, 50:50, 70:30, 90:10 and 100:0, respectively. As a representative, the molar ratio of 50:50 is described for an example of chemical preparation. Firstly, a solution containing potassium aluminate solution was prepared by dissolving 3.54 g of KOH in distilled water, adding 0.25 g of aluminum powder and stirring continuously until the aluminum was completely dissolved forming a clear solution. The second solution containing RHA: silica sol was prepared by adjusting the molar ratio of RHA and silica sol in the range of 0 to 100 percent. The TEAOH was then added into the silica solution.
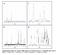
3 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) 111 Subsequently, both solutions were mixed inside a Teflon cup and kept stirring at 500 rpm (Model M6, CAT Ingenieurbuero M. Zipperer, Germany) for 3 h. The resulting white gel with ph was formed and then transferred to a stainless steel autoclave with 250 rpm stirring for crystallization at 423 K under autogenous pressure for 4 days. The powder product was filtered, washed with distilled water thoroughly, dried at 393 K for 2 h, and calcined at 823 K for 4 h. 2.3 Material Characterization The chemical analysis of RHA silica was performed by an X-ray fluorescence (HORIBA, MESA 500-W X-ray Fluorescence Element Analyzer). The crystal structure of synthesized SUZ-4 zeolites were carried out using an X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) (Phillips, PW 1830/40) with Cu-Ka radiation (λ = ). The crystal morphology and size of the obtained zeolite were observed by a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) (Jeol, JSM 5600 LV). BET specific surface area, pore size, and pore size distribution were determined using a BET-N 2 adsorption (Autosorb -1-C, Quantachrome). 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 3.1 Effect of RHA on SUZ-4 Formation By a mean of an XRF the prepared RHA silica was found to contain 99.7% wt. SiO 2 and traces of Al 2 O 3 and other metal oxides. Then it was used as a silica source for SUZ-4 zeolite synthesis under autogeneous pressure using a stainless steel autoclave at 423 K for 4 days crystallization time. The gel composition of 7.9K 2 O: Al 2 O 3 : 21.22SiO 2 : 2.6TEA 2 O: 498.6H 2 O was kept with different RHA: silica sol molar ratios (0:100, 50:50, 70:30, 90:10 and 100:0). The XRD patterns of the synthesized products having different RHA amount are presented in Figure 1. They were identified the corresponding phases by comparing to the reported standard patterns [26-28]. It is clearly shown that when the RHA was added into the silica sol the Merlinoite zeolite (MER) started to be formed. The amount of MER increased with increasing amount of RHA, based on the height of the corresponding peaks. Refer to the structure formulae of calcined MER (K 11 Al 11 Si 21 O 64 ) and SUZ-4 (K x Al 5 Si 37 O 72 ) Figure 1. XRD patterns of synthesized products prepared at different RHA: silica sol molar ratios ( SUZ-4 zeolite MER zeolite).
4 μ ν ο ; 112 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) [26-28], the Si/Al ratio of MER is 1.9 that is lower than that of SUZ-4 (Si/Al = 6.2). It implies that formation of MER requires less silica than SUZ-4. In this study, RHA was used in a solid form (average particle diameter 55 μm) while the silica sol was in a form of colloidal solution. Thus, the RHA required longer time to be dissolved completely to form silicate unit ([SiO] -4 ), the primary unit of 3-D structure of zeolite, compared to the higher active silica sol. Moreover, zeolite crystallization is a competitive reaction which depends on the conditions of the set up system and nature of each involving chemical species. Therefore, when RHA was used the availability of silicate unit was quite limited and favored the formation of MER instead of SUZ-4. This result is in well agreement with Gujar et al. [17] who reported that the SUZ-4 formation was occurred in narrow range conditions and was very sensitive to various factors. 3.2 Product Characterization The SEM micrographs of the products were taken as shown in Figure 2. The pictures confirm the formation of SUZ-4 as needle-shape crystals and MER as ovalshape crystals. The amount of MER presented in the pictures conforms to the XRD results, which is varied with the amount of RHA used. By using an image analyzing software (ImageJ) on the SEM micrographs (Figure 2), it is evident that the crystal of SUZ-4 was enlarged from approximately 0.07 ± ± 0.2 μm (Figure 2a) to 0.2 ± ± 1.5 μm (Figure 2b) and (Figure 2c). However, when RHA was used at 90 % and 100 % the SUZ-4 crystal was shrunk to 0.13 ± ± 0.2 μm (Figure 2d) and 0.09 ± ± 0.2 μm (Figure 2e), respectively. This decrease was influenced by the formation of the competing MER, which is also consistent with the XRD results. Nitrogen adsorption-desorption Figure 2. SEM micrographs of as-synthesized SUZ-4 from different molar ratios of RHA: silica sol (a) 0:100 (b) 50:50 (c) 70:30 (d) 90:10 (e) 100:0.
5 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) 113 isotherms of calcined samples were measured at 77 K while the degassing temperature was carried at 523 K. They all revealed the type A hysteresis that corresponds to cylindrical-shape pores. Figure 3 shows a typical isotherm obtained from the product prepared by using 50 % RHA. Additionally, Figure 4 illustrates the pore size distribution curves of SUZ-4 with different amount of RHA used. With 100 % silica sol, the pore size of the obtained SUZ-4 exhibits almost mono-distribution having the main peak that has a mean size at approximately 5.6 and a small shoulder at approximately 4.4. This is Figure 3. N 2 adsorption (open symbols) and desorption (solid symbols) isotherms of SUZ-4 (RHA: silica sol = 50:50). Figure 4. Pore size distribution of as-synthesized SUZ-4 zeolite from different mole percentages of RHA.
6 114 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) corresponded to the sizes of two types of channels comprising 10-membered ring and 8-membered ring, respectively [11]. When the RHA was used together with the silica sol, according to the evidences from XRD and SEM micrographs, the more RHA used the lesser amount SUZ-4 was formed and also the lower peak height at 4.4 and 5.6. The detected pores with the sizes larger than 5.6 should be the voids created among the crystals. These voids seem to be enhanced by the coexistence of SUZ-4 and MER phases. Accompanied with pore size distribution, the surface area and the micropore volume as well as total pore volume of the products were also analyzed and summarized in Table 1. The result clearly shows that the surface area and pore volume are directly related to the amount of SUZ-4 formed. With 50 % RHA, high purity of SUZ-4 was obtained having the same surface area (~ 247 m 2 /g) as that of 100 % silica sol. With 70 % RHA and above, the surface area and pore volume drastically decrease by 61% and 76%, respectively, as the result of coexistence of MER phase. Table 1. Surface areas, micropore volume and total pore volume of obtained zeolites. RHA:silica sol a t- plot micropore analysis method b MP micropore analysis method Specific surface area a (m 2 /g) Micropore volume a (cm 3 /g) Total pore volume b (cm 3 /g) 0: : : : : CONCLUSIONS SUZ-4 zeolite was successfully synthesized from RHA silica under autogenous pressure using a stainless steel autoclave at 423 K for 4 days crystallization time with TEAOH as a structure directing agent. As a result, the amount of Merlinoite zeolite (MER) phase increased with increasing amount of RHA used. The differences in crystal size, specific surface areas, pore volume, and pore size distribution have been reported. With 50% RHA, high purity of SUZ-4 was obtained having the same surface area (~247 m 2 /g) as that of 100 % silica sol. The SUZ-4 crystal size was shrunk when 90 % and 100 % RHA were used due to the influence from the formation of MER. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors gratefully acknowledge the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI) and the Thailand Research Fund (Grant No. MRG ).
7 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) 115 REFERENCES [1] Chareonpanich M., Namto T., Kongkachuichay P. and Limtrakul J., Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash, Fuel Process. Technol., 2004; 85: [2] Katsuki H. and Komarneni S., Synthesis of Na-A and/or Na-X zeolite/porous carbon composites from carbonized rice husk, J. Solid State Chem., 2009; 182: [3] Kongkachuichay P. and Lohsoontorn P., Phase diagram of zeolite synthesized from perlite and rice husk ash, ScienceAsia, 2006; 32: [4] Witoon T., Chareonpanich M. and Limtrakul J., Effect of acidity on the formation of silica chitosan hybrid materials and thermal conductive property, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2009; 51: [5] Ahmed A.E. and Adam F., The catalytic performances of silica supported aluminum, gallium and indium for the tert-butylation of aromatics, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2010; 54: [6] Loiha S., Prayoonpokarach S., Songsiriritthigun P. and Wittayakun J., Synthesis of zeolite beta with pretreated rice husk silica and its transformation to ZSM-12, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2009; 115: [7] Thuadaij N. and Nuntiya A., Preparation of nanosilica powder from rice husk ash by precipitation method, Chiang Mai J. Sci., 2008; 35: [8] Arayapranee W. and Rempel G.L., A comparative study of the Cure characteristics, processability, mechanical properties, heat aging, and morphology of rice husk ash and silica fillers in natural rubber compounds, Chiang Mai J. Sci., 2004; 31: [9] International Zeolite Association Database of Zeolite Structures, / (Accessed 10 May 2010). [10] Barri S.A., US. Pat. No. 5,118, 483 (1992). [11] Lawton S.L, Bennett J.M., Schlenker J.L. and Rubin M.K., Synthesis and proposed framework topology of zeolite SUZ-4, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm., 1993; 11: [12] Paik W.C., Shin C.H., Lee J.M., Ahn B.J. and Hong S.B., Host-guest Interactions in P1, SUZ-4, and ZSM- 57 zeolites containing N,N,N,N, N,N hexaethylpentanediammonium ion as a guest molecule, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001; 105: [13] Strohmaier K.G., Afeworki M. and Dorset D.L., The crystal structures of polymorphic SUZ-4, Z. Kristallogr., 2006; 221: [14] Worathanakul P. and Kongkachuichay P., New SUZ-4 zeolite membrane from sol-gel technique, Int. J. Chem. Biomol. Eng., 2008; 1: [15] Asensi M.A., Camblor M.A. and Martinez A., Zeolite SUZ-4: Reproducible synthesis, physicochemical characterization and catalytic evaluation for the skeletal isomerization of n-butenes, Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 1999; 28: [16] Choo H., Hong S.B. and Keven L., Comparative ESR and catalytic studies of ethylene dimerization on Pd(II)- exchanged clinoptilolite, mordenite,
8 116 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013; 40(1) ferrierite, and SUZ-4, J. Phys. Chem. B., 2001; 105: [17] Gujar A.C., Moye A.A., Coghill P.A., Teeters D.C., Roberts K.P. and Price G.L., Raman investigation of the SUZ-4 zeolite, Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2005; 78: [18] Jiang S., Hwang Y.K., Jhung S.H., Chang J.S. and Hwang J.S., Zeolite SUZ-4 as selective dehydration catalyst for methanol conversion to dimethyl ether, Chem. Lett., 2004; 33:, [19] Lee S.H., Shin C.H., Choi G.J., Park T.J., Nam I.S., Han B. and Hong S.B., Zeolite synthesis in the presence of flexible diquaternary alkylammonium ions (C 2 H 5 ) 3 N + (CH 2 ) n N + (C 2 H 5 ) 3 with n = 3-10 as structure-directing agents, Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2003; 60: [20] Lukyanov D.B., Zholobenko V.L., Dwyer J., Barri S.A. and Smith W.J., On the structural, acidic and catalytic properties of zeolite SUZ-4, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999; 103: [21] Subbiah A., Cho B.K., Blint R.J., Gujar A.C., Price G.L. and Yie J.E., NO x Reduction over metal-ion exchanged novel zeolite under lean conditions: activity and hydrothermal stability, Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2003; 42: [22] Zholobenko V.L., Lukyanov D.B. and Dwyer J., Ferrierite and SUZ-4 zeolites: characterization of acid sites, J. Phys. Chem., 1998; 102:, [23] Jiao G.F., Min P. and Chen B.H., Theoretical study of formation mechanism of aluminosilicate in the synthesis of zeolites, Struct. Chem., 2008; 19: [24] Tsai W.T., Hsien K.J. and Hsu H.C., Preparation and characterization of a novel zeolite using hydrothermal synthesis in a stirred reactor, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn., 2009; 49: [25] Worathanakul P., Trisuwan D., Phatruk A. and Kongkachuichay P., Effect of sol-gel synthesis parameters and Cu loading on the physicochemical properties of a new SUZ-4 zeolite, Colloid. Surface. A, 2011; 377: [26] Gujar A.C. and Price G.L., Synthesis of SUZ-4 in the K + /TEA + system, Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2002; 54: [27] Treacy M.M.J. and Higgins J.B., Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, 4 th rev. edn., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (2001). [28] Robson H., Verified Syntheses of Materials, 2 nd edn., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (2001). [29] Hasegawa Y., Nagasea T., Kiyozumia Y. and Mizukamia F., Preparation, characterization, and dehydration performance of MER-type zeolite membranes, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2010; 73:
Synthesis of Zeolite A Membrane from Rice Husk Ash
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.79-83, 2009 Chayakorn BHAVORNTHANAYOD and Pesak RUNGROJCHAIPON * Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.79-83, 2009 Chayakorn BHAVORNTHANAYOD and Pesak RUNGROJCHAIPON * Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.9 No.2 pp.6-65, 29 Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application Piyawan PRAWINGWONG, Chaiyan CHAIYA 2, Prasert REUBROYCHAROEN 3
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.9 No.2 pp.6-65, 29 Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application Piyawan PRAWINGWONG, Chaiyan CHAIYA 2, Prasert REUBROYCHAROEN 3
Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash
 Fuel Processing Technology 85 (2004) 1623 1634 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash Metta Chareonpanich a, *, Teerapong Namto a, Paisan Kongkachuichay
Fuel Processing Technology 85 (2004) 1623 1634 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash Metta Chareonpanich a, *, Teerapong Namto a, Paisan Kongkachuichay
Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash
 BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Effect of pore size and surface chemistry of porous silica on CO 2
 Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 34 (4), 3-7, Jul. - Aug. 12 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Effect of pore size and surface chemistry of porous silica on Thongthai Witoon 1,2* and Metta Chareonpanich
Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 34 (4), 3-7, Jul. - Aug. 12 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Effect of pore size and surface chemistry of porous silica on Thongthai Witoon 1,2* and Metta Chareonpanich
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 2006, 6, 318-323 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2006 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors Gas Sensing Properties of Ordered Mesoporous SnO 2 Thorsten Wagner 1,2,*, Claus-Dieter Kohl 1, Michael Fröba 2 and
Sensors 2006, 6, 318-323 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2006 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors Gas Sensing Properties of Ordered Mesoporous SnO 2 Thorsten Wagner 1,2,*, Claus-Dieter Kohl 1, Michael Fröba 2 and
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation
 Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
SNRU Jou r n al of Sc ien ce an d T ech n olo gy 8 ( 3 ) S ep tem ber D ec em be r ( ) SNRU Journal of Science and Technology
 SNRU Jou r n al of Sc ien ce an d T ech n olo gy 8 ( 3 ) S ep tem ber D ec em be r ( 2 01 6 ) 3 20 32 6 SNRU Journal of Science and Technology J ou rn al h om e pa ge : sn r u j st. s n r u. ac. t h Synthesis
SNRU Jou r n al of Sc ien ce an d T ech n olo gy 8 ( 3 ) S ep tem ber D ec em be r ( 2 01 6 ) 3 20 32 6 SNRU Journal of Science and Technology J ou rn al h om e pa ge : sn r u j st. s n r u. ac. t h Synthesis
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information. for. Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High. Pressures
 S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
S1 Supplementary Information for Zeolites ZSM-25 and PST-20: Selective Carbon Dioxide Adsorbents at High Pressures Jung Gi Min, K. Christian Kemp, and Suk Bong Hong* Center for Ordered Nanoporous Materials
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution
 Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Synthesis of Zeolite from Aluminium Etching By-Product: The Effect of Reaction Temperature on Crystallinity and Its CO 2 Adsorption Property
 American Journal of Environmental Sciences 4 (6): 666-674, 2008 ISSN 1553-345X 2008 Science Publications Synthesis of Zeolite from Aluminium Etching By-Product: The Effect of Reaction Temperature on Crystallinity
American Journal of Environmental Sciences 4 (6): 666-674, 2008 ISSN 1553-345X 2008 Science Publications Synthesis of Zeolite from Aluminium Etching By-Product: The Effect of Reaction Temperature on Crystallinity
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
Eco-Compatible Continuous Halogenation of Aromatics
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Eco-Compatible Continuous Halogenation of Aromatics P. Losch, a J. F. Kolb, a A. Astafan,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Eco-Compatible Continuous Halogenation of Aromatics P. Losch, a J. F. Kolb, a A. Astafan,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method
 Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Preparation of Silica Gel from Rice Husk Ash Using Microwave Heating
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.45-50, 2009. Preparation of Silica Gel from Rice Husk Ash Using Microwave Heating Supitcha RUNGRODNIMITCHAI *, Wachira PHOKHANUSAI and Natthapong
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.45-50, 2009. Preparation of Silica Gel from Rice Husk Ash Using Microwave Heating Supitcha RUNGRODNIMITCHAI *, Wachira PHOKHANUSAI and Natthapong
Catalytic activity of the beta zeolite with enhanced textural properties in the Friedel-Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds
 Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Porous Carbon Materials with Controllable Surface Area Synthsized from Metal-Organic Frameworks
 Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Porous Carbon Materials with Controllable Surface Area Synthsized from Metal-Organic Frameworks Seunghoon Lim, Kyungwon Suh, Yelin Kim, Minyoung Yoon, Hyeran Park,
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Porous Carbon Materials with Controllable Surface Area Synthsized from Metal-Organic Frameworks Seunghoon Lim, Kyungwon Suh, Yelin Kim, Minyoung Yoon, Hyeran Park,
ICTR 2004 CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA EM RESÍDUOS E DESENVOLVIMENTO SUSTENTÁVEL Costão do Santinho Florianópolis Santa Catarina
 ICTR 2004 CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA EM RESÍDUOS E DESENVOLVIMENTO SUSTENTÁVEL Costão do Santinho Florianópolis Santa Catarina A LOW COST ZSM-5 ZEOLITE OBTAINED FROM RICE HULL ASH A.
ICTR 2004 CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA EM RESÍDUOS E DESENVOLVIMENTO SUSTENTÁVEL Costão do Santinho Florianópolis Santa Catarina A LOW COST ZSM-5 ZEOLITE OBTAINED FROM RICE HULL ASH A.
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9
 Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION. Keywords: Ethylene oxide, Partial oxidation, Ethane epoxidation, Second metal.
 DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
Crystallization of ZSM-12 Zeolite with Different Si/Al Ratio
 Adsorption 11: 159 165, 2005 c 2005 Springer Science + Business Media, Inc. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Crystallization of ZSM-12 Zeolite with Different Si/Al Ratio ANTONIO S. ARAUJO, ANTONIO O.S.
Adsorption 11: 159 165, 2005 c 2005 Springer Science + Business Media, Inc. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Crystallization of ZSM-12 Zeolite with Different Si/Al Ratio ANTONIO S. ARAUJO, ANTONIO O.S.
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
Isotherm study on adsorption removal of Pb (II) by MCM-41 zeolite synthesized from biomass ash TAN Gang1,a, XUE Yongjie2,b and CAI Jun3,c
 214 International Conference on Computer Science and Electronic Technology (ICCSET 214) Isotherm study on adsorption removal of Pb (II) by MCM-41 zeolite synthesized from biomass ash TAN Gang1,a, XUE Yongjie2,b
214 International Conference on Computer Science and Electronic Technology (ICCSET 214) Isotherm study on adsorption removal of Pb (II) by MCM-41 zeolite synthesized from biomass ash TAN Gang1,a, XUE Yongjie2,b
STUDY ON SORPTION OF SOME TOXIC AND HEAVY IONS IN DILUTE SOLUTIONS BY CLINOPTILOLITE
 J. Sci. I. R. Iran Vol. 12, No. 3, Summer 2001 STUDY ON SORPTION OF SOME TOXIC AND HEAVY IONS IN DILUTE SOLUTIONS BY CLINOPTILOLITE F. Farzaneh *, Z. Shivapour, N. Khosravi Talebi and J. Sayyad Mashhoor
J. Sci. I. R. Iran Vol. 12, No. 3, Summer 2001 STUDY ON SORPTION OF SOME TOXIC AND HEAVY IONS IN DILUTE SOLUTIONS BY CLINOPTILOLITE F. Farzaneh *, Z. Shivapour, N. Khosravi Talebi and J. Sayyad Mashhoor
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
SYNTHESIS OF FAUJASITE WITH HIGH THERMAL STABILITY FROM FLY ASH
 26 SYNTHESIS OF FAUJASITE WITH HIGH THERMAL STABILITY FROM FLY ASH Sutarno and Yateman Arryanto Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta ABSTRACT
26 SYNTHESIS OF FAUJASITE WITH HIGH THERMAL STABILITY FROM FLY ASH Sutarno and Yateman Arryanto Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta ABSTRACT
Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure
 Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure Xiao-Feng Guo, Yong-Suk Kim, and Geon-Joong Kim Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha UniVersity,
Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure Xiao-Feng Guo, Yong-Suk Kim, and Geon-Joong Kim Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha UniVersity,
Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper Nanostructures for Hydrogen Generation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp , 2016
 KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
CHAPTER 4. SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL
 93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
Effect of Synthesis Parameters on Phase Purity, Crystallinity and Particle Size of SAPO-34
 Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Research Note Vol. 30, No. 4, 2011 Effect of Synthesis Parameters on Phase Purity, Crystallinity and Particle Size of SAPO-34 Emrani, Peyman; Fatemi, Shohreh* + ; Ashraf Talesh,
Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Research Note Vol. 30, No. 4, 2011 Effect of Synthesis Parameters on Phase Purity, Crystallinity and Particle Size of SAPO-34 Emrani, Peyman; Fatemi, Shohreh* + ; Ashraf Talesh,
OXIDATIVE DESULPHURIZATION OF MODEL FUEL BY METAL IMPREGNATED Ti-β CATALYSTS
 OXIDATIVE DESULPHURIZATION OF MODEL FUEL BY METAL IMPREGNATED CATALYSTS Sankhajit Pal 1, Biswajit Saha 2, Sonali Sengupta 3 1Department of Chemical Engineering, C.V. Raman College of Engineering, Bhubaneswar,
OXIDATIVE DESULPHURIZATION OF MODEL FUEL BY METAL IMPREGNATED CATALYSTS Sankhajit Pal 1, Biswajit Saha 2, Sonali Sengupta 3 1Department of Chemical Engineering, C.V. Raman College of Engineering, Bhubaneswar,
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment
 Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity
 1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
1 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Amine-impregnated silica monolith with a hierarchical pore structure: enhancement of CO 2 capture capacity for Chao Chen, Seung-Tae Yang, Wha-Seung Ahn* and
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative Technology to Produce Commercial Zeolite material of High Cation Exchange Capacity
 Proceedings of NAWTEC16 16th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference May 19-21, 2008, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA NAWTEC16-1919 Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative
Proceedings of NAWTEC16 16th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference May 19-21, 2008, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA NAWTEC16-1919 Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative
Supporting Information. SBA-15 Supported Fe, Ni, Fe-Ni Bimetallic Catalysts for Wet Oxidation of Bisphenol-A
 Wet Oxidation of Bisphenol A by Metal Supported SBA-15 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, Vol. 35, No. 12 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.12.xxx Supporting Information SBA-15 Supported Fe, Ni, Fe-Ni
Wet Oxidation of Bisphenol A by Metal Supported SBA-15 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, Vol. 35, No. 12 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.12.xxx Supporting Information SBA-15 Supported Fe, Ni, Fe-Ni
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins
 Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals
 Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
Adsorption of Free Fatty Acid from Crude Palm Oil on Magnesium Silicate Derived From Rice Husk
 Adsorption of Free Fatty Acid from Crude Palm Oil on Magnesium Silicate Derived From Rice Husk Weerawat Clowutimon, Prakob Kitchaiya, and Pornsawan Assawasaengrat* Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty
Adsorption of Free Fatty Acid from Crude Palm Oil on Magnesium Silicate Derived From Rice Husk Weerawat Clowutimon, Prakob Kitchaiya, and Pornsawan Assawasaengrat* Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Experimental section Synthesis of Ni-Co Prussian
PRODUCTION HYDROGEN AND NANOCARBON VIA METHANE DECOMPOSITION USING Ni-BASED CATALYSTS. EFFECT OF ACIDITY AND CATALYST DIAMETER
 MAKARA, TEKNOLOGI, VOL. 9, NO. 2, NOPEMBER 25: 48-52 PRODUCTION HYDROGEN AND NANOCARBON VIA METHANE DECOMPOSITION USING BASED CATALYSTS. EFFECT OF ACIDITY AND CATALYST DIAMETER Widodo W. Purwanto, M. Nasikin,
MAKARA, TEKNOLOGI, VOL. 9, NO. 2, NOPEMBER 25: 48-52 PRODUCTION HYDROGEN AND NANOCARBON VIA METHANE DECOMPOSITION USING BASED CATALYSTS. EFFECT OF ACIDITY AND CATALYST DIAMETER Widodo W. Purwanto, M. Nasikin,
Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene oxide) templated nickel oxide nanofibers for dye degradation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
A flexible MMOF exhibiting high selectivity for CO 2 over N 2, CH 4 and other small gases. Supporting Information
 A flexible MMOF exhibiting high selectivity for CO 2 over N 2, CH 4 and other small gases Jingming Zhang, a Haohan Wu, a Thomas J. Emge, a and Jing Li* a a Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology,
A flexible MMOF exhibiting high selectivity for CO 2 over N 2, CH 4 and other small gases Jingming Zhang, a Haohan Wu, a Thomas J. Emge, a and Jing Li* a a Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology,
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of Benzene and Toluene with Hydrogen Peroxide in a Bubble Reactor
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) KC-014 163 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008; 35(1) : 163-170 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Catalytic Activity of TS-1 on the Hydroxylation of
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 121 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 121 (2015 ) 961 966 9th International Symposium on Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (ISHVAC) and the 3rd International
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 121 (2015 ) 961 966 9th International Symposium on Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (ISHVAC) and the 3rd International
Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification.
 Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification. Synthesis of the Steep Rhombohedra MnCO 3 : In a typical synthesis,
Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification. Synthesis of the Steep Rhombohedra MnCO 3 : In a typical synthesis,
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Multi-stage synthesis of nanopore NaA zeolite membranes for separation of water/ethanol mixtures
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation Vol-1, Issue-6 (2017), 42-46 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation (IJREI) journal home page: http://www.ijrei.com
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation Vol-1, Issue-6 (2017), 42-46 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation (IJREI) journal home page: http://www.ijrei.com
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Molecular Sieves Principles of Synthesis and Identification
 Molecular Sieves Principles of Synthesis and Identification Second Edition R. SZOSTAK Clark Atlanta University Atlanta, GA USA V D BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hail London Weinheim
Molecular Sieves Principles of Synthesis and Identification Second Edition R. SZOSTAK Clark Atlanta University Atlanta, GA USA V D BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman & Hail London Weinheim
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Nafion/Analcime and Nafion/Faujasite Composite Membranes for High Temperature Operation of PEMFC
 Nafion/ and Nafion/ Composite Membranes for High Temperature Operation of PEMFC Paisan Kongkachuichay and Siraprapa Pimprom Abstract The Nafion/zeolite composite membranes were synthesized for polymer
Nafion/ and Nafion/ Composite Membranes for High Temperature Operation of PEMFC Paisan Kongkachuichay and Siraprapa Pimprom Abstract The Nafion/zeolite composite membranes were synthesized for polymer
EFFECTS OF ADDITIONAL GASES ON THE CATALYTIC DECOMPOSITION OF N20 OVER Cu-ZSM-5
 Jointly published by Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam and Akad~miai Kiad6, Budapest RKCL3296 Reaet.Kinet. Catal.Lett. Vol. 64, No. 2, 215-220 (1998) EFFECTS OF ADDITIONAL GASES ON THE CATALYTIC DECOMPOSITION
Jointly published by Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam and Akad~miai Kiad6, Budapest RKCL3296 Reaet.Kinet. Catal.Lett. Vol. 64, No. 2, 215-220 (1998) EFFECTS OF ADDITIONAL GASES ON THE CATALYTIC DECOMPOSITION
Supporting Information. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite
 Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts
 A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2016. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201604015 High Performance Graphene/Ni 2 P Hybrid Anodes for Lithium
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2016. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201604015 High Performance Graphene/Ni 2 P Hybrid Anodes for Lithium
The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS
 Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 30 Edited by Donald W. Murphy, Leonard V. Interrante Copyright 1995 by Inorganic Syntheses, Inc. Chapter Six MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS 43. ZEOLITE MOLECULAR SIEVES
Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 30 Edited by Donald W. Murphy, Leonard V. Interrante Copyright 1995 by Inorganic Syntheses, Inc. Chapter Six MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS 43. ZEOLITE MOLECULAR SIEVES
Supporting information
 Supporting information Manipulating the Concavity of Rhodium Nanocubes Enclosed with High-index Facets via Site-selective Etching Yumin Chen, Qing-Song Chen, Si-Yan Peng, Zhi-Qiao Wang, Gang Lu, and Guo-Cong
Supporting information Manipulating the Concavity of Rhodium Nanocubes Enclosed with High-index Facets via Site-selective Etching Yumin Chen, Qing-Song Chen, Si-Yan Peng, Zhi-Qiao Wang, Gang Lu, and Guo-Cong
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Nucleation of FAU and LTA Zeolites from Heterogeneous Aluminosilicate Precursors Matthew D. Oleksiak 1, Jennifer A. Soltis 2,4, Marlon T. Conato, 1,3 R. Lee Penn 2, Jeffrey D. Rimer 1* 1 University of
Nucleation of FAU and LTA Zeolites from Heterogeneous Aluminosilicate Precursors Matthew D. Oleksiak 1, Jennifer A. Soltis 2,4, Marlon T. Conato, 1,3 R. Lee Penn 2, Jeffrey D. Rimer 1* 1 University of
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres
 Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres Seong-Ick Kim, Takuji Yamamoto, Akira Endo, Takao Ohmori, and Masaru Nakaiwa
Influence of Nonionic Surfactant Concentration on Physical Characteristics of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Carbon Cryogel Microspheres Seong-Ick Kim, Takuji Yamamoto, Akira Endo, Takao Ohmori, and Masaru Nakaiwa
Wet-chemistry processing of powdery raw material for high-tech ceramics
 NANO EXPRESS Open Access Wet-chemistry processing of powdery raw material for high-tech ceramics Elena A Trusova, Kirill V Vokhmintcev * and Igor V Zagainov * Abstract The purpose of this study was to
NANO EXPRESS Open Access Wet-chemistry processing of powdery raw material for high-tech ceramics Elena A Trusova, Kirill V Vokhmintcev * and Igor V Zagainov * Abstract The purpose of this study was to
Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ce 1-x M x O 2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) Solid Solution with Controlled Morphologies
 Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ce 1-x M x O 2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) Solid Solution with Controlled Morphologies Wei-Ta Chen, Kuei-Bo Chen, Ming-Fang Wang, Sheng-Feng Weng, Chi-Shen Lee* and M C. Lin Experimental
Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ce 1-x M x O 2 (M = Ti, Zr, and Hf) Solid Solution with Controlled Morphologies Wei-Ta Chen, Kuei-Bo Chen, Ming-Fang Wang, Sheng-Feng Weng, Chi-Shen Lee* and M C. Lin Experimental
A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene to azoxybenzene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Synthesis of Zeolite Monolith with Hierarchical Micro/Macropores by Ice-Templating and Steam-Assisted Crystallization
 A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 259 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
