Observation of white-light amplified spontaneous emission from carbon nanodots under laser excitation
|
|
|
- Jade Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Observation of white-light amplified spontaneous emission from carbon nanodots under laser excitation Wen Fei Zhang, Li Bin Tang, Siu Fung Yu,* and Shu Ping Lau Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong Abstract: A conventional laser irradiation method is applied to fabricate carbon nanodots (C-dots). By uniformly dispersing the C-dots into N- Methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solution, white-light amplified spontaneous emission can be observed from the mixture under laser excitation at 266 nm. Peak wavelength and linewidth of the emission spectra are found to be around 450 and 120 nm respectively. It is verified that the presence of NMP enhances the emission efficiency of C-dots over the broad emission spectrum. This is because the excitation energy, which is not absorbed by the C-dots, is captured by the NMP and is subsequently transferred to the C- dots. Optical gain per peak power of the mixture at ~450 nm is found to be ~64 cm 1 MW 1, which is about 39% higher than that without the use of NMP Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Laser materials; ( ) Nanophotonics and photonic crystals. References and links 1. A. K. Geim and K. S. Novoselov, The rise of graphene, Nat. Mater. 6(3), (2007). 2. J. E. Riggs, Z. X. Guo, D. L. Carroll, and Y. P. Sun, Strong luminescence of solubilized carbon nanotubes, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122(24), (2000). 3. L. Cao, X. Wang, M. J. Meziani, F. S. Lu, H. F. Wang, P. G. Luo, Y. Lin, B. A. Harruff, L. M. Veca, D. Murray, S. Y. Xie, and Y. P. Sun, Carbon dots for multiphoton bioimaging, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(37), (2007). 4. H. Peng and J. Travas-Sejdic, Simple aqueous solution route to luminescent carbogenic dots from carbohydrates, Chem. Mater. 21(23), (2009). 5. C. H. Lui, K. F. Mak, J. Shan, and T. F. Heinz, Ultrafast photoluminescence from graphene, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(12), (2010). 6. X. M. Wu, H. Q. Cao, B. J. Li, and G. Yin, The synthesis and fluorescence quenching properties of well soluble hybrid graphene material covalently functionalized with indolizine, Nanotechnology 22(7), (2011). 7. X. M. Sun, D. C. Luo, J. F. Liu, and D. G. Evans, Monodisperse chemically modified graphene obtained by density gradient ultracentrifugal rate separation, ACS Nano 4(6), (2010). 8. G. X. Chen, M. H. Hong, T. C. Chong, H. I. Elim, G. H. Ma, and W. Ji, Preparation of carbon nanoparticles with strong optical limiting properties by laser ablation in water, J. Appl. Phys. 95(3), (2004). 9. G. X. Chen, M. H. Hong, T. S. Ong, M. Lam, W. Z. Chen, H. I. Elim, W. Ji, and T. C. Chong, Carbon nanoparticles based nonlinear optical liquid, Carbon 42(12-13), (2004). 10. X. Y. Li, H. Q. Wang, Y. Shimizu, A. Pyatenko, K. Kawaguchi, and N. Koshizaki, Preparation of carbon quantum dots with tunable photoluminescence by rapid laser passivation in ordinary organic solvents, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 47(3), (2010). 11. S. L. Hu, K. Y. Niu, J. Sun, J. Yang, N. Q. Zhao, and X. W. Du, One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation, J. Mater. Chem. 19(4), (2009). 12. Y. P. Sun, B. Zhou, Y. Lin, W. Wang, K. A. Fernando, P. Pathak, M. J. Meziani, B. A. Harruff, X. Wang, H. Wang, P. G. Luo, H. Yang, M. E. Kose, B. Chen, L. M. Veca, and S. Y. Xie, Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(24), (2006). 13. H. T. Li, X. D. He, Z. H. Kang, H. Huang, Y. Liu, J. Liu, S. Lian, C. H. Tsang, X. Yang, and S. T. Lee, Watersoluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49(26), (2010). 14. J. Valenta, I. Pelant, and J. Linnros, Waveguiding effects in the measurement of optical gain in a layer of Si nanocrystal, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81(8), (2002). (C) 2012 OSA 1 April 2012 / Vol. 2, No. 4 / OPTICAL MATERIALS EXPRESS 490
2 1. Introduction Carbon nanostructures have attracted intensive research interests due to its superior properties of chemical stability, low toxicity and potential applications in photonics [1]. Since the first observation of photoluminescence (PL) from carbon nanotubes in 2000 [2], optical properties of carbon nanostructures are widely studied [3 9]. Different fabrication methods have been proposed to fabricate carbon nanostructures. For example, laser ablation method is commonly used to break graphite into carbon nanodots (C-dots) [10,11] with average diameter down to about 5 nm [12]. On the other hand, if the as-prepared C-dots have passivated with diamineterminated oligomeric poly-(ethylene glycol), PL emission ranging from blue to red can be observed under different excitation energy. Chemical solution method, which has the capability to support multi-color emission and up-conversion luminescence, is also a simple approach to obtain carbon nanostructures [6,7]. C-dots fabricated by electrochemical method have demonstrated size-dependent PL and up-conversion radiations [13]. Nevertheless, mainly spontaneous emission was recorded from the previous PL measurement of carbon nanostructures. In this paper, we report our observation of room-temperature white-light amplified spontaneous from C-dots, which can be fabricated by laser irradiation method, under high-power laser excitation. Furthermore, optical gain per peak power of the C-dots dispersed inside N-Methylpyrrolidone (NMP) is found to be ~64 cm 1 MW 1 at the peak wavelength. This indicates that C-dots, which demonstrate population inversion under laser excitation at room temperature, can be a potential optical gain medium to realize widebandwidth light-emitting nanostructured devices. Fig. 1. (a) TEM images of C-dots, and (b) Photos of C-dots dispersed inside NMP. 2. Experimental methods and results C-dots can be synthesized by a conventional laser irradiation method [11]. Graphite powder, which can be purchased from Fluka Analytical with size < 0.1 mm, is used in the experiment. A 25 mg of the graphite powder is baked inside a furnace at 100 C for 1 hour in order to remove the moisture and to increase the solubility. Then, the graphite powder is poured into a glass macro-cell containing 1.5 ml of NMP. NMP, which is a transparent organic solvent and is highly compatible with multicyclocene particles, is chosen to disperse the graphite over the volume of the macro-cell. A Q-switched Nd:YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) laser, which has a wavelength of 1064 nm and at pulsed operation (~6 ns, 10 Hz), is used to irradiate the black suspension (i.e., mixture of graphite powder and NMP). A laser beam, which has a diameter of 10 mm and a peak power density of ~100 MW/cm 2, is irradiated onto the glass macro-cell. After 30 minutes of laser irradiation, a homogenous dark-brown transparent suspension can be observed from the macro-cell. The suspension is separated and removed from the macro-cell and then further diluted by NMP until the corresponding emission intensity is maximized under 266 nm laser excitation. It is noted that the high density of C-dots will result in fluorescence quenching and there is an optimized density of C-dots in NMP to obtain (C) 2012 OSA 1 April 2012 / Vol. 2, No. 4 / OPTICAL MATERIALS EXPRESS 491
3 maximum emission efficiency. This optimized density of C-dots in NMP is used throughout the experiment. Figure 1(a) shows the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of the C-dots. A small portion of C-dot and NMP mixture is dropped onto a commercially available TEM grid. The measurement is performed after the NMP is completely evaporated from the TEM grid. From the TEM image, it is estimated that the size of C-dot is roughly varied between ~1.5 and ~3.5 nm. In order to measure the PL characteristics of the C-dot, the mixture is poured into a UV quartz micro-cell. Figure 1(b) shows a photo of the micro-cell filled with the mixture of C-dot and NMP. The mixture shows a uniform light-brown color, indicating that the C-dots should be uniformly distributed over the volume. Figure 1(b) also shows the photos of C-dots dispersed inside NMP under laser excitation by a quadruplet Q-switched Nd:YAG laser (at 266 nm) at pulsed operation (~6 ns, 10 Hz). A laser beam with a diameter of 1 cm is incident onto one side (with an internal width of 10 mm) of the micro-cell. It is observed that the mixture generates a very bright white-light emission. Fig. 2. (a) Plot of PL intensity as a function of excitation light intensity, and (b) FWHM of the emission spectra of the C-dots and NMP mixture under 266 nm laser excitation at room temperature. Figure 2 shows a plot of light emission intensity as a function of light excitation intensity, or so-called light-light curve and emission spectra of the mixture measured under 266 nm laser excitation at room temperature. During the analysis, emission of the mixture is collected from the shorter side of the micro-cell with an internal width of 2 mm (i.e., perpendicular to the direction of the laser beam) through an objective lens and is coupled to an Oriel MS257 monochromator (spectral resolution of ~0.5 nm) attached with a photo-multiplier tube. From the above plot, it is noted that there is a kink occurs at an input intensity of ~0.21 MW/cm 2. Furthermore, peak wavelength and full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the emission spectra are found to be ~450 and ~120 nm respectively. The light emission may be due to the n π* transition from the C = O bond of the carboxylic groups which are attached on the C- dots by C-C bonding. As the emission spectra cover a wide range of wavelength over the visible spectrum, it is not surprised that white-light emission can be observed from the mixture. In fact, it can be shown that the corresponding (x, y) coordinates on the CIE (commission on illumination) chromaticity diagram were found to be around (0.363, 0.356). Narrowing of the FWHM of the emission spectra from ~120 to ~115 nm was also recorded for the input intensities larger than the value of the kink (i.e., for the input peak power density larger than ~0.21 MW/cm 2 ). Hence, the kink observed from the light-light curve represents the pumping threshold of the mixture. In addition, the kink represents the change of radiative process from spontaneous emission to amplified spontaneous emission. (C) 2012 OSA 1 April 2012 / Vol. 2, No. 4 / OPTICAL MATERIALS EXPRESS 492
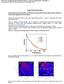
4 Fig. 3. Plot of output intensity versus pumping length L of the C-dots and NMP mixture for different pump intensities. The inset photo shows the experimental setup for the measurement. Net optical gain of the C-dots dispersed inside the NMP can be measured by the variable stripe length (VSL) method. If L is the length of the pumping stripe and I tot is the total intensity detected from the side of the micro-cell with an internal width of 2 mm, the corresponding net optical gain, G, can be obtained from the classical VSL equation as follows [14]: I sp( λ) Itot ( L, λ) = exp ( G( λ) L) 1 G( λ) (1) where I sp is the spontaneous emission intensity and λ is the wavelength of the net optical gain to be selected. Therefore, if the output intensity of the mixture at a particular λ is measured with different values of L, the corresponding G for some pump intensities can be deduced. In order to perform the calculation, the optical setup has been slightly modified. This can be done by using a cylindrical lens to focus a variable pumping stripe of maximum length and width equal to 10 and ~2.5 mm respectively onto the side of the micro-cell with an internal width of 10 mm, see the inset photo of Fig. 3. The pumping stripe is used in order to maintain the uniformity of the pumping intensity over the stripe region. Figure 3 also plots the roomtemperature output intensity of the mixture at λ = ~450 nm versus L for different pump intensities. It is observed that kinks occur at around 2.0, 0.85 and 0.75 mm for pump power equal to 0.10, 0.17 and 0.27 MW respectively. The kinks represent the onset of the noncoherent optical feedback (i.e., light scattered by the C-dots). In fact, it can be shown that the light is weakly diffused inside the mixture due to the weak scattering strength of the C-dots. Therefore, the data recorded before the occurrence of the kink should be used to fit Eq. (1) for the estimation of G. It can be shown that the deduced value of G is 7.3, 11.3 and 16 cm 1 for input power equal to 0.10, 0.17 and 0.27 MW respectively. The optical gain per peak power of the mixture is estimated to be ~64 cm 1 MW 1. It is noted that NMP can emit visible radiation under ultraviolet excitation. Therefore, it is not sure whether the observed amplified spontaneous emission is from either C-dots or NMP. Hence, the emission characteristics of the NMP solution are also analyzed. Figure 4(a) plots the emission spectra of the NMP solution at different excitation intensities. It is noted that a dominant emission peak with peak wavelength at ~295 nm is detected after the excitation of 266 nm light. Light-blue emission from the NMP can be observed from the naked eyes. (C) 2012 OSA 1 April 2012 / Vol. 2, No. 4 / OPTICAL MATERIALS EXPRESS 493
5 However, emission peak at ~295 nm is not recorded from the emission spectra of the C-dots dispersed inside NMP, see Fig. 2(b). In addition, the emission intensity of NMP does not contribute much to the emission peak intensity of the mixture. This is because the emission intensity of NMP solution at around 450 nm is closed to the tail of its emission spectrum. The inset figure of Fig. 4(a) shows the light-light curve of the NMP solution. The light-light curve is a straight line which indicated that the emission obtained from the NMP solution is mainly spontaneous emission. These observations have verified that the NMP do not directly contribute to the white-light amplified spontaneous emission observed from the mixture and the ~295 nm emission from the NMP solution may be re-absorbed by the C-dots. In fact, UV/vis absorption spectrum of C-dots has indicated that the C-dots have a strong absorption at around 300 nm, see Fig. 4(b). Hence, it is suspected that the emission intensity of C-dots dispersed inside the NMP is enhanced by the presence of NMP. Fig. 4. (a) Plot of emission spectra of the NMP versus different pump intensities at room temperature. The inset shows the light-light curve and photo of the NMP under 266 nm laser excitation, and (b) Absorption spectrum of the C-dots. Thin film of C-dots can be formed by evaporating the mixture on a quartz substrate so that the emission characteristics of the C-dots can be studied. Figure 5 plots the light-light curve and emission spectra of the C-dots thin film under laser excitation at room temperature. It is noted that the light-light curve has a kink at pump intensity equal to ~0.21 MW/cm 2. The image of the C-dots thin film under laser excitation is also shown in the inset of Fig. 5(b). Bright white-light emission can be clearly observed from the substrate. Furthermore, FWHM of the emission peaks, which have peak wavelength located at around 440 nm, reduces from ~200 to ~175 nm for the input intensity increase above the threshold. Hence, the C-dots thin film exhibits amplified spontaneous emission and the corresponding threshold value is close to that of the mixture. However, the emission intensity (FWHM of emission peaks) of C-dots thin film is lower (wider) than that of the mixture. These observations have confirmed that the presence of NMP enhances the optical-conversion efficiency of C-dots under laser excitation. This is because although a large portion of pump light has been scattered away and without being absorbed by the C-dots, the presence of NMP absorbs the remained pumping light and transfers the energy to the C-dots for the second time. As a result, the presence of NMP improves the emission intensity of C-dots and without affecting the emission characteristics. The optical gain per peak power of the C-dots can be estimated to be ~46 cm 1 MW 1. This implies that the presence of NMP can improve the optical gain per unit power of the C-dots by more than 39%. (C) 2012 OSA 1 April 2012 / Vol. 2, No. 4 / OPTICAL MATERIALS EXPRESS 494
6 3. Conclusions Fig. 5. (a) Plot of light light curve and FWHM of the emission spectra of the C-dots deposited on a quartz substrate, and (b) The corresponding emission spectra. The inset shows the photo of C-dots on quartz substrate under laser excitation. In summary, C-dots with diameter varies from ~1.5 to ~3.5 nm are fabricated by a conventional laser irradiation method. White-light amplified spontaneous emission is observed at room temperature for the C-dots under laser excitation at 266 nm. This is because the C-dots exhibit 1) a kink from their light-light curve and 2) narrowing of FWHM of the emission peaks for pump intensity increase beyond the kink position. For the C-dots uniformly dispersed inside NMP, it is found that the emission performance of the mixture can be improved the optical gain per peak power increases by 39% to about ~64 cm 1 MW 1 at the peak wavelength. The enhancement of emission efficiency of the C-dots with the presence of NMP is due to 1) the ~295 nm emission from NMP after the excitation at 266 nm, and 2) the optical absorption of C-dots at ~295 nm. Hence, the remained excitation light energy, which is not absorbed by the C-dots, is transferred indirectly to the C-dots via NMP. As a result, the optical gain per unit power of the C-dots can be improved by the NMP. The absorption and emission mechanism of NMP, however, do not affect the emission characteristics of the C-dots. Therefore, the results have indicated that the mixture may have potential applications as wide-bandwidth light-emitting nanostructured devices. Acknowledgments This work was supported by the HK PolyU grants (Grant no. 1-ZV6X and G-YJ73). (C) 2012 OSA 1 April 2012 / Vol. 2, No. 4 / OPTICAL MATERIALS EXPRESS 495
Supplementary documents
 Supplementary documents Low Threshold Amplified Spontaneous mission from Tin Oxide Quantum Dots: A Instantiation of Dipole Transition Silence Semiconductors Shu Sheng Pan,, Siu Fung Yu, Wen Fei Zhang,
Supplementary documents Low Threshold Amplified Spontaneous mission from Tin Oxide Quantum Dots: A Instantiation of Dipole Transition Silence Semiconductors Shu Sheng Pan,, Siu Fung Yu, Wen Fei Zhang,
Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Selective Detection of Tartrazine in Food Samples
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Supporting Information Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Selective Detection of Tartrazine in Food Samples Hua Xu, Xiupei Yang, *, Gu
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Supporting Information Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Selective Detection of Tartrazine in Food Samples Hua Xu, Xiupei Yang, *, Gu
Optical Science of Nano-graphene (graphene oxide and graphene quantum dot) Introduction of optical properties of nano-carbon materials
 Optical Science of Nano-graphene (graphene oxide and graphene quantum dot) J Kazunari Matsuda Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University Introduction of optical properties of nano-carbon materials
Optical Science of Nano-graphene (graphene oxide and graphene quantum dot) J Kazunari Matsuda Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University Introduction of optical properties of nano-carbon materials
Waveguiding-assisted random lasing in epitaxial ZnO thin film
 Waveguiding-assisted random lasing in epitaxial ZnO thin film P.-H. Dupont a), C. Couteau a)*, D. J. Rogers b), F. Hosseini Téhérani b), and G. Lérondel a) a) Laboratoire de Nanotechnologie et d Instrumentation
Waveguiding-assisted random lasing in epitaxial ZnO thin film P.-H. Dupont a), C. Couteau a)*, D. J. Rogers b), F. Hosseini Téhérani b), and G. Lérondel a) a) Laboratoire de Nanotechnologie et d Instrumentation
Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene. quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Modify morphology of colloidal Ag 2 Se nanostructures by laser irradiation
 Supporting information for Modify morphology of colloidal Ag 2 Se nanostructures by laser irradiation Ling-Ling Zhao a, Zhi-Ming Gao a, Hui Liu a, Jing Yang a, Shi-Zhang Qiao a,b, Xi-Wen Du a a School
Supporting information for Modify morphology of colloidal Ag 2 Se nanostructures by laser irradiation Ling-Ling Zhao a, Zhi-Ming Gao a, Hui Liu a, Jing Yang a, Shi-Zhang Qiao a,b, Xi-Wen Du a a School
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) variable light emission created via direct ultrasonic exfoliation of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Hydrogen Bonded Dimer Stacking Induced Emission of Amino-Benzoic Acid Compounds
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Hydrogen Bonded Dimer Stacking Induced Emission of Amino-Benzoic Acid Compounds Tianlei Zhou, Feng Li, Yan Fan, Weifeng Song, Xiaoyue Mu, Hongyu Zhang* and Yue
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Hydrogen Bonded Dimer Stacking Induced Emission of Amino-Benzoic Acid Compounds Tianlei Zhou, Feng Li, Yan Fan, Weifeng Song, Xiaoyue Mu, Hongyu Zhang* and Yue
HYPER-RAYLEIGH SCATTERING AND SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDIES OF PLATINUM NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol19issue1/ijrras_19_1_06.pdf HYPER-RAYLEIGH SCATTERING AND SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDIES OF PLATINUM NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS M. Eslamifar Physics Department, BehbahanKhatamAl-Anbia
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol19issue1/ijrras_19_1_06.pdf HYPER-RAYLEIGH SCATTERING AND SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDIES OF PLATINUM NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS M. Eslamifar Physics Department, BehbahanKhatamAl-Anbia
Supporting Information. 1T-Phase MoS 2 Nanosheets on TiO 2 Nanorod Arrays: 3D Photoanode with Extraordinary Catalytic Performance
 Supporting Information 1T-Phase MoS 2 Nanosheets on Nanorod Arrays: 3D Photoanode with Extraordinary Catalytic Performance Yuxi Pi, Zhen Li, Danyun Xu, Jiapeng Liu, Yang Li, Fengbao Zhang, Guoliang Zhang,
Supporting Information 1T-Phase MoS 2 Nanosheets on Nanorod Arrays: 3D Photoanode with Extraordinary Catalytic Performance Yuxi Pi, Zhen Li, Danyun Xu, Jiapeng Liu, Yang Li, Fengbao Zhang, Guoliang Zhang,
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Engineering the Intermediate Band States in Amorphous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Engineering the Intermediate Band States in Amorphous
CHAPTER 3. OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES
 42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
GRAPHENE EFFECT ON EFFICIENCY OF TiO 2 -BASED DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELLS (DSSC)
 Communications in Physics, Vol. 26, No. 1 (2016), pp. 43-49 DOI:10.15625/0868-3166/26/1/7961 GRAPHENE EFFECT ON EFFICIENCY OF TiO 2 -BASED DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELLS (DSSC) NGUYEN THAI HA, PHAM DUY LONG,
Communications in Physics, Vol. 26, No. 1 (2016), pp. 43-49 DOI:10.15625/0868-3166/26/1/7961 GRAPHENE EFFECT ON EFFICIENCY OF TiO 2 -BASED DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELLS (DSSC) NGUYEN THAI HA, PHAM DUY LONG,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Bright, Stable, and Tunable Solid-State Luminescence
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Bright, Stable, and Tunable Solid-State Luminescence
Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. University of Central Florida, 4000 Central Florida Blvd. Orlando, Florida, 32816,
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly
Electrically Driven White Light Emission from Intrinsic Metal. Organic Framework
 Supporting Information Electrically Driven White Light Emission from Intrinsic Metal Organic Framework Golam Haider 1,2,3, Muhammad Usman 4, Tzu-Pei Chen 3, Packiyaraj Perumal 3, Kuang-Lieh Lu 4 * and
Supporting Information Electrically Driven White Light Emission from Intrinsic Metal Organic Framework Golam Haider 1,2,3, Muhammad Usman 4, Tzu-Pei Chen 3, Packiyaraj Perumal 3, Kuang-Lieh Lu 4 * and
performance electrocatalytic or electrochemical devices. Nanocrystals grown on graphene could have
 Nanocrystal Growth on Graphene with Various Degrees of Oxidation Hailiang Wang, Joshua Tucker Robinson, Georgi Diankov, and Hongjie Dai * Department of Chemistry and Laboratory for Advanced Materials,
Nanocrystal Growth on Graphene with Various Degrees of Oxidation Hailiang Wang, Joshua Tucker Robinson, Georgi Diankov, and Hongjie Dai * Department of Chemistry and Laboratory for Advanced Materials,
Visible Light Assisted Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation and Organic Dye Degradation by CdS Metal Oxide hybrids in presence of Graphene Oxide
 Visible Light Assisted Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation and Organic Dye Degradation by CdS Metal Oxide hybrids in presence of Graphene Oxide Ziyauddin Khan, Tridip Ranjan Chetia, Anil Kumar Vardhaman,
Visible Light Assisted Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation and Organic Dye Degradation by CdS Metal Oxide hybrids in presence of Graphene Oxide Ziyauddin Khan, Tridip Ranjan Chetia, Anil Kumar Vardhaman,
A project report on SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERISATION OF COPPER NANOPARTICLE-GRAPHENE COMPOSITE. Submitted by Arun Kumar Yelshetty Roll no 410 CY 5066
 A project report on SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERISATION OF COPPER NANOPARTICLE-GRAPHENE COMPOSITE Submitted by Arun Kumar Yelshetty Roll no 410 CY 5066 Under the guidance of Prof. (Ms). Sasmita Mohapatra Department
A project report on SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERISATION OF COPPER NANOPARTICLE-GRAPHENE COMPOSITE Submitted by Arun Kumar Yelshetty Roll no 410 CY 5066 Under the guidance of Prof. (Ms). Sasmita Mohapatra Department
Supporting Information Available:
 Supporting Information Available: Photoresponsive and Gas Sensing Field-Effect Transistors based on Multilayer WS 2 Nanoflakes Nengjie Huo 1, Shengxue Yang 1, Zhongming Wei 2, Shu-Shen Li 1, Jian-Bai Xia
Supporting Information Available: Photoresponsive and Gas Sensing Field-Effect Transistors based on Multilayer WS 2 Nanoflakes Nengjie Huo 1, Shengxue Yang 1, Zhongming Wei 2, Shu-Shen Li 1, Jian-Bai Xia
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization
 Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization Abstract The preparation of stable, uniform silver nanoparticles by reduction of silver ions by ethanol is reported in the present paper.
Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization Abstract The preparation of stable, uniform silver nanoparticles by reduction of silver ions by ethanol is reported in the present paper.
maximal photofluorescence decay time of 6 hours (purchased from Shenzhen HuiDuoSheng
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental section Preparation of m-tio 2 /LPP photoanodes. TiO 2 colloid was synthesized according
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental section Preparation of m-tio 2 /LPP photoanodes. TiO 2 colloid was synthesized according
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices
 Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information 1. Synthesis of perovskite materials CH 3 NH 3 I
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information 1. Synthesis of perovskite materials CH 3 NH 3 I
Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots Keith Linehan and Hugh
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots Keith Linehan and Hugh
Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices
 Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices Xiaoyong Hu, Cuicui Lu, Yulan Fu, Yu Zhu, Yingbo Zhang, Hong Yang, Qihuang Gong Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China Contents Motivation
Nanocomposite photonic crystal devices Xiaoyong Hu, Cuicui Lu, Yulan Fu, Yu Zhu, Yingbo Zhang, Hong Yang, Qihuang Gong Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing, P. R. China Contents Motivation
Strong light matter coupling in two-dimensional atomic crystals
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2014.304 Strong light matter coupling in two-dimensional atomic crystals Xiaoze Liu 1, 2, Tal Galfsky 1, 2, Zheng Sun 1, 2, Fengnian Xia 3, Erh-chen Lin 4,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2014.304 Strong light matter coupling in two-dimensional atomic crystals Xiaoze Liu 1, 2, Tal Galfsky 1, 2, Zheng Sun 1, 2, Fengnian Xia 3, Erh-chen Lin 4,
Seminars in Nanosystems - I
 Seminars in Nanosystems - I Winter Semester 2011/2012 Dr. Emanuela Margapoti Emanuela.Margapoti@wsi.tum.de Dr. Gregor Koblmüller Gregor.Koblmueller@wsi.tum.de Seminar Room at ZNN 1 floor Topics of the
Seminars in Nanosystems - I Winter Semester 2011/2012 Dr. Emanuela Margapoti Emanuela.Margapoti@wsi.tum.de Dr. Gregor Koblmüller Gregor.Koblmueller@wsi.tum.de Seminar Room at ZNN 1 floor Topics of the
as-deposited and low temperature annealed Si-rich SiO 2 films
 Excitation wavelength-independent sensitized Er 3+ concentration in as-deposited and low temperature annealed Si-rich SiO 2 films Oleksandr Savchyn, 1,a) Ravi M. Todi, 2 Kevin R. Coffey, 2,3 Luis K. Ono
Excitation wavelength-independent sensitized Er 3+ concentration in as-deposited and low temperature annealed Si-rich SiO 2 films Oleksandr Savchyn, 1,a) Ravi M. Todi, 2 Kevin R. Coffey, 2,3 Luis K. Ono
Down-conversion monochrome light-emitting diodeswith the color determined
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for Down-conversion monochrome
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for Down-conversion monochrome
PREPARATION OF LUMINESCENT SILICON NANOPARTICLES BY PHOTOTHERMAL AEROSOL SYNTHESIS FOLLOWED BY ACID ETCHING
 Phase Transitions Vol. 77, Nos. 1 2, January February 2004, pp. 131 137 PREPARATION OF LUMINESCENT SILICON NANOPARTICLES BY PHOTOTHERMAL AEROSOL SYNTHESIS FOLLOWED BY ACID ETCHING X. LI, Y. HE, S.S. TALUKDAR
Phase Transitions Vol. 77, Nos. 1 2, January February 2004, pp. 131 137 PREPARATION OF LUMINESCENT SILICON NANOPARTICLES BY PHOTOTHERMAL AEROSOL SYNTHESIS FOLLOWED BY ACID ETCHING X. LI, Y. HE, S.S. TALUKDAR
X-ray excitable luminescent polymer dots doped with iridium(iii)
 Electronic Supporting Information for X-ray excitable luminescent polymer dots doped with iridium(iii) complex Yasuko Osakada,* a,b Guillem Pratx, c Lindsey Hanson, a Paige Elana Solomon, a Lei Xing* c
Electronic Supporting Information for X-ray excitable luminescent polymer dots doped with iridium(iii) complex Yasuko Osakada,* a,b Guillem Pratx, c Lindsey Hanson, a Paige Elana Solomon, a Lei Xing* c
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers
 Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline
 Supplementary Information Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline Tapan Barman, Amreen A. Hussain, Bikash Sharma, Arup R. Pal* Plasma Nanotech Lab, Physical Sciences Division,
Supplementary Information Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline Tapan Barman, Amreen A. Hussain, Bikash Sharma, Arup R. Pal* Plasma Nanotech Lab, Physical Sciences Division,
The CdS and CdMnS nanocrystals have been characterized using UV-visible spectroscopy, TEM, FTIR, Particle Size Measurement and Photoluminiscence.
 Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Efficient Inorganic Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes with Polyethylene Glycol Passivated Ultrathin CsPbBr 3 Films
 Supporting information Efficient Inorganic Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes with Polyethylene Glycol Passivated Ultrathin CsPbBr 3 Films Li Song,, Xiaoyang Guo, *, Yongsheng Hu, Ying Lv, Jie Lin, Zheqin
Supporting information Efficient Inorganic Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes with Polyethylene Glycol Passivated Ultrathin CsPbBr 3 Films Li Song,, Xiaoyang Guo, *, Yongsheng Hu, Ying Lv, Jie Lin, Zheqin
A microring multimode laser using hollow polymer optical fibre
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 923 927 A microring multimode laser using hollow polymer optical fibre M KAILASNATH, V P N NAMPOORI and P RADHAKRISHNAN
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 923 927 A microring multimode laser using hollow polymer optical fibre M KAILASNATH, V P N NAMPOORI and P RADHAKRISHNAN
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: Vol.7, No.3, pp ,
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.3, pp 1162-1166, 2014-2015 ICONN 2015 [4 th -6 th Feb 2015] International Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology-2015
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.3, pp 1162-1166, 2014-2015 ICONN 2015 [4 th -6 th Feb 2015] International Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology-2015
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Supramolecular interactions via hydrogen bonding contributing to
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Supramolecular interactions via hydrogen bonding contributing to
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Low-Temperature Solid-Phase Method to Synthesize Highly Fluorescent Carbon Nitride Dots with Tunable Emission Juan Zhou, Yong Yang, and Chun-yang Zhang* Single-Molecule Detection
Supporting Information A Low-Temperature Solid-Phase Method to Synthesize Highly Fluorescent Carbon Nitride Dots with Tunable Emission Juan Zhou, Yong Yang, and Chun-yang Zhang* Single-Molecule Detection
Plasmon-enhanced yellow light emission in hybrid nanostructures formed by fluorescent molecules and polymer
 Nano Energy (]]]]) ], ]]] ]]] Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nanoenergy Plasmon-enhanced yellow light emission in hybrid nanostructures formed by fluorescent
Nano Energy (]]]]) ], ]]] ]]] Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nanoenergy Plasmon-enhanced yellow light emission in hybrid nanostructures formed by fluorescent
Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State
 Supporting information Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State -Controlled Luminescence Mechanism Hui Ding, Shang-Bo Yu, Ji-Shi Wei and Huan-Ming Xiong* Department of Chemistry, Fudan
Supporting information Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State -Controlled Luminescence Mechanism Hui Ding, Shang-Bo Yu, Ji-Shi Wei and Huan-Ming Xiong* Department of Chemistry, Fudan
Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil
 Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Design of Pyrrolic-N-rich Carbon Dots with. Absorption in the First Near Infrared Window for. Photothermal Therapy
 Supporting Information Design of Pyrrolic-N-rich Carbon Dots with Absorption in the First Near Infrared Window for Photothermal Therapy Fitri A. Permatasari, Hiromitsu Fukazawa, Takashi Ogi,*, Ferry Iskandar,,
Supporting Information Design of Pyrrolic-N-rich Carbon Dots with Absorption in the First Near Infrared Window for Photothermal Therapy Fitri A. Permatasari, Hiromitsu Fukazawa, Takashi Ogi,*, Ferry Iskandar,,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) 3,4-Donor- and 2,5-acceptor-functionalized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) 3,4-Donor- and 2,5-acceptor-functionalized
Fluorescence Enhancement on Silver Nanoplate at the. Single- and Sub-Nanoparticle Level
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supporting 2015 Information Fluorescence Enhancement on Silver Nanoplate at the Single- and Sub-Nanoparticle
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supporting 2015 Information Fluorescence Enhancement on Silver Nanoplate at the Single- and Sub-Nanoparticle
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy
 Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures. based on a nano-obelisk
 Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK AND SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK
 161 CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK AND SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK 7.1 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK Nonlinear optical materials are required in a wide range of important applications, such as optical
161 CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK AND SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE WORK 7.1 SUMMARY OF THE PRESENT WORK Nonlinear optical materials are required in a wide range of important applications, such as optical
Electrically switchable organo inorganic hybrid for a white-light laser source
 Supporting Information Electrically switchable organo inorganic hybrid for a white-light laser source Jui-Chieh Huang 1,, Yu-Cheng Hsiao 2,, Yu-Ting Lin 2, Chia-Rong Lee 3 & Wei Lee 2,* 1 Institute of
Supporting Information Electrically switchable organo inorganic hybrid for a white-light laser source Jui-Chieh Huang 1,, Yu-Cheng Hsiao 2,, Yu-Ting Lin 2, Chia-Rong Lee 3 & Wei Lee 2,* 1 Institute of
Mechanisms of Visible Photoluminescence from Size-Controlled Silicon Nanoparticles
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 737 23 Materials Research Society F1.5.1 Mechanisms of Visible Photoluminescence from Size-Controlled Silicon Nanoparticles Toshiharu Makino *, Nobuyasu Suzuki, Yuka Yamada,
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 737 23 Materials Research Society F1.5.1 Mechanisms of Visible Photoluminescence from Size-Controlled Silicon Nanoparticles Toshiharu Makino *, Nobuyasu Suzuki, Yuka Yamada,
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C. composites for photodegradation of organic dye
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C composites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as precursors towards TiO x /C composites
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Inverted Planar Solar Cell with 13% Efficiency and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Inverted Planar Solar Cell with 13% Efficiency and
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like. to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating
 Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal
 Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supporting information A Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Janus Inverse-Opal Actuator via Gradient Infiltration Dajie Zhang #, Jie Liu //#, Bo Chen *, Yong Zhao, Jingxia Wang * //, Tomiki Ikeda, Lei Jiang //. CAS
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Sample characterization The presence of Si-QDs is established by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), by which the average QD diameter of d QD 2.2 ± 0.5 nm has been determined
Supplementary Materials Sample characterization The presence of Si-QDs is established by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), by which the average QD diameter of d QD 2.2 ± 0.5 nm has been determined
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Graphene is a single, two-dimensional nanosheet of aromatic sp 2 hybridized carbons that
 Chemical Identity and Applications of Graphene-Titanium Dioxide Graphene is a single, two-dimensional nanosheet of aromatic sp 2 hybridized carbons that enhances the performance of photocatalysts. 1 The
Chemical Identity and Applications of Graphene-Titanium Dioxide Graphene is a single, two-dimensional nanosheet of aromatic sp 2 hybridized carbons that enhances the performance of photocatalysts. 1 The
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Preparation of Few-Layer Bismuth Selenide by Liquid-Phase-Exfoliation and Its Optical Absorption Properties Liping Sun 1, Zhiqin Lin 1, Jian Peng 1, Jian Weng 1,3 *, Yizhong Huang
Supplementary information Preparation of Few-Layer Bismuth Selenide by Liquid-Phase-Exfoliation and Its Optical Absorption Properties Liping Sun 1, Zhiqin Lin 1, Jian Peng 1, Jian Weng 1,3 *, Yizhong Huang
In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to synthesis sulfide-graphene nanocomposites
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to
Photonic Crystal Nanocavities for Efficient Light Confinement and Emission
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 42, No., February 2003, pp. 768 773 Photonic Crystal Nanocavities for Efficient Light Confinement and Emission Axel Scherer, T. Yoshie, M. Lončar, J. Vučković
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 42, No., February 2003, pp. 768 773 Photonic Crystal Nanocavities for Efficient Light Confinement and Emission Axel Scherer, T. Yoshie, M. Lončar, J. Vučković
TECHNICAL INFORMATION. Quantum Dot
 Quantum Dot Quantum Dot is the nano meter sized semiconductor crystal with specific optical properties originates from the phenomenon which can be explained by the quantum chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Quantum Dot Quantum Dot is the nano meter sized semiconductor crystal with specific optical properties originates from the phenomenon which can be explained by the quantum chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information From the Aggregation-Induced Emission of Au(I)-Thiolate Complexes to Ultra- Bright Au(0)@Au(I)-Thiolate Core-Shell Nanoclusters Zhentao Luo, a Xun Yuan, a Yue Yu, a Qingbo Zhang,
Supporting Information From the Aggregation-Induced Emission of Au(I)-Thiolate Complexes to Ultra- Bright Au(0)@Au(I)-Thiolate Core-Shell Nanoclusters Zhentao Luo, a Xun Yuan, a Yue Yu, a Qingbo Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Observation of tunable electrical bandgap in large-area twisted bilayer graphene synthesized by chemical vapor deposition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Observation of tunable electrical bandgap in large-area twisted bilayer graphene synthesized by chemical vapor deposition Jing-Bo Liu 1 *, Ping-Jian Li 1 *, Yuan-Fu Chen 1, Ze-Gao
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Observation of tunable electrical bandgap in large-area twisted bilayer graphene synthesized by chemical vapor deposition Jing-Bo Liu 1 *, Ping-Jian Li 1 *, Yuan-Fu Chen 1, Ze-Gao
Debjit Roy, Saptarshi Mandal, Chayan K. De, Kaushalendra Kumar and Prasun K. Mandal*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Nearly Suppressed Photoluminescence Blinking of Small Sized, Blue-Green-Orange-Red
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Nearly Suppressed Photoluminescence Blinking of Small Sized, Blue-Green-Orange-Red
Effect of Addition Au Nanoparticles on Emission Spectra of Laser Dye
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 973-462 Volume 2, Number 24 (27) pp. 4833-484 Effect of Addition Au Nanoparticles on Emission Spectra of Laser Dye Sara Ali Razzak, Lazem Hassan
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 973-462 Volume 2, Number 24 (27) pp. 4833-484 Effect of Addition Au Nanoparticles on Emission Spectra of Laser Dye Sara Ali Razzak, Lazem Hassan
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Decorating Graphene Sheets with Gold Nanoparticles Ryan Muszynski, Brian Seeger and, Prashant V. Kamat* Radiation Laboratory, Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical
Supporting Information Decorating Graphene Sheets with Gold Nanoparticles Ryan Muszynski, Brian Seeger and, Prashant V. Kamat* Radiation Laboratory, Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 5. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 5 Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation High Intensities Narrow Bandwidths Coherent Outputs Applications CD/DVD Readers Fiber Optics Spectroscopy
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 5 Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation High Intensities Narrow Bandwidths Coherent Outputs Applications CD/DVD Readers Fiber Optics Spectroscopy
Supporting Information for. Near infrared-to-blue photon upconversion by exploiting direct. S-T absorption of a molecular sensitizer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for Near infrared-to-blue photon upconversion by
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for Near infrared-to-blue photon upconversion by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.97 Supplementary Information Far-field Imaging of Non-fluorescent Species with Sub-diffraction Resolution Pu Wang et al. 1. Theory of saturated transient absorption microscopy
DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2013.97 Supplementary Information Far-field Imaging of Non-fluorescent Species with Sub-diffraction Resolution Pu Wang et al. 1. Theory of saturated transient absorption microscopy
Final Report for AOARD grant FA Measurement of the third-order nonlinear susceptibility of graphene and its derivatives
 Final Report for AOARD grant FA2386-12-1-4095 Measurement of the third-order nonlinear susceptibility of graphene and its derivatives Principal investigator: A/Prof. Tang Dingyuan Division of Microelectronics
Final Report for AOARD grant FA2386-12-1-4095 Measurement of the third-order nonlinear susceptibility of graphene and its derivatives Principal investigator: A/Prof. Tang Dingyuan Division of Microelectronics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Facile Synthesis of High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons Liying Jiao, Xinran Wang, Georgi Diankov, Hailiang Wang & Hongjie Dai* Supplementary Information 1. Photograph of graphene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Facile Synthesis of High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons Liying Jiao, Xinran Wang, Georgi Diankov, Hailiang Wang & Hongjie Dai* Supplementary Information 1. Photograph of graphene
Light Interaction with Small Structures
 Light Interaction with Small Structures Molecules Light scattering due to harmonically driven dipole oscillator Nanoparticles Insulators Rayleigh Scattering (blue sky) Semiconductors...Resonance absorption
Light Interaction with Small Structures Molecules Light scattering due to harmonically driven dipole oscillator Nanoparticles Insulators Rayleigh Scattering (blue sky) Semiconductors...Resonance absorption
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Adding refractory 5d transition metal W into PtCo
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Adding refractory 5d transition metal W into PtCo
ESH Benign Processes for he Integration of Quantum Dots (QDs)
 ESH Benign Processes for he Integration of Quantum Dots (QDs) PIs: Karen K. Gleason, Department of Chemical Engineering, MIT Graduate Students: Chia-Hua Lee: PhD Candidate, Department of Material Science
ESH Benign Processes for he Integration of Quantum Dots (QDs) PIs: Karen K. Gleason, Department of Chemical Engineering, MIT Graduate Students: Chia-Hua Lee: PhD Candidate, Department of Material Science
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Bicolour electroluminescence of 2 (carbazol 9 yl)anthraquinone
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Bicolour electroluminescence of 2 (carbazol 9 yl)anthraquinone
A tunable corner-pumped Nd:YAG/YAG composite slab CW laser
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 21, No. 1 (212) 1428 A tunable corner-pumped Nd:YAG/YAG composite slab CW laser Liu Huan( 刘欢 ) and Gong Ma-Li( 巩马理 ) State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Center for Photonics and Electronics,
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 21, No. 1 (212) 1428 A tunable corner-pumped Nd:YAG/YAG composite slab CW laser Liu Huan( 刘欢 ) and Gong Ma-Li( 巩马理 ) State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Center for Photonics and Electronics,
Department of Chemistry of The College of Staten Island and The Graduate Center, The City University of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 /Carbon quantum dots hybrid nanoflowers for highly active and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 /Carbon quantum dots hybrid nanoflowers for highly active and
Dmitriy Churin. Designing high power single frequency fiber lasers
 Dmitriy Churin Tutorial for: Designing high power single frequency fiber lasers Single frequency lasers with narrow linewidth have long coherence length and this is an essential property for many applications
Dmitriy Churin Tutorial for: Designing high power single frequency fiber lasers Single frequency lasers with narrow linewidth have long coherence length and this is an essential property for many applications
Graphene Based Saturable Absorber Modelockers at 2µm
 ISLA Workshop Munich Integrated disruptive components for 2µm fibre Lasers ISLA Graphene Based Saturable Absorber Modelockers at 2µm Prof. Werner Blau - Trinity College Dublin Friday, 26th of June 2015
ISLA Workshop Munich Integrated disruptive components for 2µm fibre Lasers ISLA Graphene Based Saturable Absorber Modelockers at 2µm Prof. Werner Blau - Trinity College Dublin Friday, 26th of June 2015
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Supplementary Information In situ ion exchange synthesis of the novel Ag/AgBr/BiOBr hybrid with highly efficient decontamination of pollutants Hefeng Cheng, Baibiao Huang*, Peng Wang, Zeyan Wang, Zaizhu
Laser Basics. What happens when light (or photon) interact with a matter? Assume photon energy is compatible with energy transition levels.
 What happens when light (or photon) interact with a matter? Assume photon energy is compatible with energy transition levels. Electron energy levels in an hydrogen atom n=5 n=4 - + n=3 n=2 13.6 = [ev]
What happens when light (or photon) interact with a matter? Assume photon energy is compatible with energy transition levels. Electron energy levels in an hydrogen atom n=5 n=4 - + n=3 n=2 13.6 = [ev]
Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric
 Modern Applied Science January, 2009 Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric Fan Zhang & Junling Yang School of Material Science and Chemical Engineer Tianjin Polytechnic
Modern Applied Science January, 2009 Application of Nano-ZnO on Antistatic Finishing to the Polyester Fabric Fan Zhang & Junling Yang School of Material Science and Chemical Engineer Tianjin Polytechnic
A novel AgIO 4 semiconductor with ultrahigh activity in photodegradation of organic dyes: insights into the photosensitization mechanism
 Supporting Information for: A novel AgIO 4 semiconductor with ultrahigh activity in photodegradation of organic dyes: insights into the photosensitization mechanism Jianting Tang*, Datang Li*, Zhaoxia
Supporting Information for: A novel AgIO 4 semiconductor with ultrahigh activity in photodegradation of organic dyes: insights into the photosensitization mechanism Jianting Tang*, Datang Li*, Zhaoxia
Flexible Organic Photovoltaics Employ laser produced metal nanoparticles into the absorption layer 1. An Introduction
 Flexible Organic Photovoltaics Employ laser produced metal nanoparticles into the absorption layer 1. An Introduction Among the renewable energy sources that are called to satisfy the continuously increased
Flexible Organic Photovoltaics Employ laser produced metal nanoparticles into the absorption layer 1. An Introduction Among the renewable energy sources that are called to satisfy the continuously increased
Supporting Information. Black Brookite Titania with High Solar Absorption and. Excellent Photocatalytic Perfomance
 Supporting Information Black Brookite Titania with High Solar Absorption and Excellent Photocatalytic Perfomance Guilian Zhu, a Tianquan Lin, a HaoYin, a Xujie Lü, a Wei Zhao, a Zhanqiang Liu, a and Fuqiang
Supporting Information Black Brookite Titania with High Solar Absorption and Excellent Photocatalytic Perfomance Guilian Zhu, a Tianquan Lin, a HaoYin, a Xujie Lü, a Wei Zhao, a Zhanqiang Liu, a and Fuqiang
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information All inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information All inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector
Model Answer (Paper code: AR-7112) M. Sc. (Physics) IV Semester Paper I: Laser Physics and Spectroscopy
 Model Answer (Paper code: AR-7112) M. Sc. (Physics) IV Semester Paper I: Laser Physics and Spectroscopy Section I Q1. Answer (i) (b) (ii) (d) (iii) (c) (iv) (c) (v) (a) (vi) (b) (vii) (b) (viii) (a) (ix)
Model Answer (Paper code: AR-7112) M. Sc. (Physics) IV Semester Paper I: Laser Physics and Spectroscopy Section I Q1. Answer (i) (b) (ii) (d) (iii) (c) (iv) (c) (v) (a) (vi) (b) (vii) (b) (viii) (a) (ix)
Supplementary Information. Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye. Nanostructures
 Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
CHAPTER 3. FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES. 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES
 CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
GREEN SYNTHESIS OF STARCH-CAPPED
 GREEN SYNTHESIS OF STARCH-CAPPED CdSe QUANTUM DOTS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION Tanutkun Palakawong Na Aayudhaya 1, *, Panida Viwattana 2, Kheamrutai Thamaphat 2,#, Khemika Lomthaisong 1 1 Program of Forensic Science,
GREEN SYNTHESIS OF STARCH-CAPPED CdSe QUANTUM DOTS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION Tanutkun Palakawong Na Aayudhaya 1, *, Panida Viwattana 2, Kheamrutai Thamaphat 2,#, Khemika Lomthaisong 1 1 Program of Forensic Science,
All-optically controllable nanoparticle random laser in a well-aligned laser-dye-doped liquid crystal
 Vol. 24, No. 25 12 Dec 2016 OPTICS EXPRESS 28739 All-optically controllable nanoparticle random laser in a well-aligned laser-dye-doped liquid crystal CHI-HUANG CHANG, 1,2 CHIE-TONG KUO, 3 HAN-YING SUN,
Vol. 24, No. 25 12 Dec 2016 OPTICS EXPRESS 28739 All-optically controllable nanoparticle random laser in a well-aligned laser-dye-doped liquid crystal CHI-HUANG CHANG, 1,2 CHIE-TONG KUO, 3 HAN-YING SUN,
Progress Report to AOARD
 Progress Report to AOARD C. C. (Chih-Chung) Yang The Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering National Taiwan University No. 1, Roosevelt Road, Section 4, Taipei, Taiwan (phone) 886-2-23657624
Progress Report to AOARD C. C. (Chih-Chung) Yang The Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering National Taiwan University No. 1, Roosevelt Road, Section 4, Taipei, Taiwan (phone) 886-2-23657624
General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported. Bicomponent Metal Monoxides as Alternative High- Performance Li-Ion Anodes to Binary Spinel Oxides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Shuo Li, Qidong Zhao, Dejun Wang and Tengfeng Xie *
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Work Function Engineering Derived All-solid-state Z-scheme Semiconductor-Metal-Semiconductor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Work Function Engineering Derived All-solid-state Z-scheme Semiconductor-Metal-Semiconductor
