Remediation of biochar on heavy metal polluted soils
|
|
|
- Prosper Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Remediation of biochar on heavy metal polluted soils To cite this article: Shuguang Wang et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci View the article online for updates and enhancements. This content was downloaded from IP address on 22/11/2018 at 01:09
2 Remediation of biochar on heavy metal polluted soils Shuguang Wang a, Yan Xu *, Namkha Norbu, Zhan Wang Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., LTD, Xi'an , China a @qq.com *Corresponding author @qq.com Abstract. Unreasonable mining and smelting of mineral resources, solid waste disposal, sewage irrigation, utilization of pesticides and fertilizers would result in a large number of heavy metal pollutants into the water and soil environment, causing serious damage to public health and ecological safety. In recent years, a majority of scholars tried to use biochar to absorb heavy metal pollutants, which has some advantages of extensive raw material sources, low-cost and high environmental stability. This paper reviewed the definition, properties of biochar, the mechanism of heavy metal sorption by biochar and some related problems and prospects, to provide some technical support for the application of biochar into heavy metal polluted soils. 1. Introduction In 2014, National soil pollution investigation gazette issued by the Ministry of Environmental Protection and the Ministry of Land and Resources said that the total polluted soil in China accounted for 16.1%. Among them, the inorganic polluting point accounted for 82.8% of the total standard points, and pollutants were mainly composed of heavy metals. Soil heavy metal pollution becomes increasingly serious, which not only makes the soil fertility degradation, reduces the crop yield and quality, also threatens human health via the food chain (Wang et al, 2017), thus it is quite urgent to develop an environmental-friendly heavy metal pollution repair technology (Suguihiro et al, 2013). It was proved that biochar can promote the fixation of heavy metal pollutants in the environment (Singh et al, 2010; Liu et al, 2014). Lots of studies had shown that different pyrolytic temperatures, raw materials could affect the ash content, carbon content, aromaticity and ph of biochar, etc, which further impact the repair effect of biochars on heavy metal pollutants (Uchimiya et al, 2010). So choosing efficient biochar restorers is critical to the treatment of heavy metal polluted soil. 2. Defination Of Biochar Biochar is a kind of insoluble, stable, highly aromatic and carbon-rich solid material produced by abandoned biomass under the condition of hypoxia and high temperature slow pyrolysis (usually<700 ) (Sohi et al, 2010; Li et al, 2011; Xu et al, 2012). The abandoned biomass usually consists of wood, agricultural waste, plant tissue and animal waste. As a new type of environmental functional material, biochar shows great potential in soil improvement, pollution repair and utilization of waste biomass resources, and has become a hot topic in environmental amendment and agricultural science. Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence. Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI. Published under licence by Ltd 1
3 3. The Properties Of Biochar According to the source of biomass materials, biochar can be divided into three categories: plant residue biochar, animal faecal biochar and sludge biochar. To be specific, it is composed of woody biochar, bamboo biochar, straw biochar, rice shell biochar, animal excrement biochar etc Ash and mineral elements Biochar is mainly composed of aromatic hydrocarbons and single carbon or carbon with graphite structures, with a carbon content of more than 60%, and other elements such as H, O, N, S etc. The chemical composition and pyrolysis temperature of raw materials make big difference on the properties of biochar. With the increasing temperature, the volatile components of biochar decrease, also the content of hydrogen and oxygen; while the content of carbon and ash are gradually increasing (Cao et al, 2010). In the pyrolysis process, large numbers of mineral elements such as K, Na, Ca, Mg and nutrient elements such as N, P riched in animal waste and sludge do not decrease with the temperature but increase, so the ash contents of animal waste and sludge biochar are obviously higher than that of plant residue biochar. Therefore, the cation exchange capacity and the amount of exchangeable ions in animal waste and sludge biochars are relatively higher, while the carbon content of them is obviously lower than that of plant residue biochar Aromaticity properties (H/C and O/C) The aromatization of biochar can be indicated by H/C and O/C (Chum et al, 2004; Chen et al, 2008). Pyrolysis temperature affects the aromaticity of biochar. The crystalline structure and pore structure of biochar change dramatically with the increasing pyrolysis temperature. During the process of dewatering and polymerization, the lignin and cellulose in plant residue biochar decompose into smaller molecules, H/C and O/C decrease. However, there are no lignocellulosic compounds in animal fecal and sludge biochar, the carbon content is significantly lower than that of plant residues. Therefore, the aromaticity of plant residue biochar is obviously higher than that of the two. The aromatic structure of biochar can be used as a π-electron donor or acceptor, forming pollutant-π bond with pollutants, further impacting the adsorption effect of biochar on pollutants (Chen et al, 2008) Surface structure and functional groups The pyrolysis temperature and raw materials also affect the surface structure and morphology of biochar. As the pyrolysis temperature rises, the fat alkyl and ester group are destroyed and the aromatic lignin nuclear are exposed to the surface, making surface area larger (Zhang, 2012). The carbon content of animal fecal and sludge biochar is lower, H/C and O/C are higher, and the degree of aromatization is lower than that of plant residue biochar, so their surface areas are smaller than that of plant biochar. In addition, the functional structure of biochar also changes obviously. The biochar produced under high pyrolysis temperature has a strong aromaticity and its adsorption of heavy metals mainly associates with the specific surface area and π-bond, however, biochar produced under low temperature includes more oxygenic functional groups, and its adsorption of heavy metals primarily is attributed to the complexation with functional groups ph of biochar Most biochar is alkaline and the alkalinity increases with the rise of pyrolysis temperature. The higher ph of biochar may be associated with a large number of alkaline salts, alkali metals (Na, K, Ca, and Mg) and CaCO3 (Xu et al, 2012; Cao et al, 2010). Different raw materials result in different ph of biochar, in which animal manure is obviously higher than that of plant residue. The alkaline biochar made from high pyrolysis temperature can improve the acidic soil, also promote the formation of metal hydroxide precipitation and adsorption of heavy metals (Ahmad et al. 2014). 2
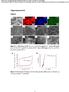
4 4. The Mechnisms Of Metal Sorption By Biochars At present, researchers mainly focus on the remediation of heavy metals such as As, Pb, Cd, Zn, Cr, Cu and Hg. Unlike organic pollutants, heavy metals are hard to be biodegraded, which increases the difficulty of reparation. While the new material, biochar, has wide sources, porous structure, larger surface area and abundant surface functional groups, which can effectively repair a certain amount of heavy metal pollutants (Jin, 2011). Now the adsorption mechanism of biochar on heavy metal pollutants has not been determined, and the main mechanisms are generally considered as follows: 4.1. Ion exchange and adsorption of cationic π function The exchange adsorption of biochar surface is one of important reasons for the reduction of heavy metal activities. The bigger the number of cation exchange, the stronger the retention of heavy metals (Lehmann, 2006; Reesa et al, 2014). The nature of ion exchange is electrostatic interaction between negative charge groups on the biochar surface and positive charges in the soil. This kind of reaction, with lower adsorption energy, belongs to nonspecific adsorption and has obvious reversibility. The cationicπfunction depends on the aromatization of biochar. The more theπ conjugate aromatic structure exists, the greater the negative charge inπorbital changes, thus the ability of losing electrons of function groups increases and the adsorption effect becomes more significant ( Li et al, 2017) Coprecipitation Biochar can effectively reduce the activities of heavy metals by adsorption and dissolution- precipitation of mineral constituent. The addition of biochar can increase the ph of soil (Reesa et al, 2014), and the reaction of heavy metal ions with -OH, PO 4 3-, CO 3 2- can form hydroxide, carbonate or phosphate precipitation, which effectively solids the heavy metal pollutants Complexation This complexation is siginificant for the fixation of heavy metal ions with strong affinity. A large number of studies have shown that the reactions of heavy metal ions with oxygenic functional groups like hydroxyl group (-OH), carboxyl group (-COOH) and amino-group (-NH2) on biochar surface make great contributions to the adsorption of heavy metal ions (Xu et al, 2012; Li et al, 2017) Electrostatic absorption The larger surface area and higher surface energy are helpful for biochars to strongly absorb the heavy metal pollutants and remove them from the soil. Figure 1. The removal mechanism of heavy metals by biochars (Li et al, 2017) According to table 1, the remediation mechanism of biochar is different for different heavy metal pollutants. For the same heavy metal ion, the adsorption mechanism is different when the biochar is different. The adsorption effect of biochar on heavy metal ions is influenced by many factors such as 3
5 raw materials of biochar, pyrolysis temperature, ph of soil, physical and chemical properties of heavy metal ions and the amount of biochar addition. Studies have shown that condition, although plant biochar has the largest surface area, the adsorption effect of animal faecal biochar on heavy metal ions is better than sludge biochar and plant biochar. This is because P riched in the animal waste biochar can react with certain heavy metal ions through precipitation or coprecipitation, and make the greatest contributions during the repair process. Studies also showed that the adsorption effect of animal excrement biochar on Pb2+ is the best among the three kinds of biochars. heavy metals Pb 2+ Hg 2+ Cu 2+ Cr(VI) Cd 2+ TABLE 1. The adsorption effect of different biochars on different heavy metals types of adsorption mechanism remark biochar sludge biochar dairy manure dairy manure, rice straw Walnut green husk peanut shell, Chinese medicine residue Beanpoles Brazilian pepper sugarcane, walnut wood chips crispus, Rice husk, Rice straws biochar oak biochar sugarcane leaves, tapioca stem, rice straw, silkworm excrement maize straw Complex reaction with hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) Precipitation and complexation adsorption, ion exchange and precipitate with PO4 3-, CO3 2- electrostatic adsorption, ion exchange react with aromatic structure and ion exchange with oxygen functional groups ion exchange, electrostatic adsorption, complexation, the increase of ph make Pb 2+ -carbonate bounded state transform into Pb 2+ -insoluble phosphate and silicate state precipitation, forming Hg(OH)2, HgCl2 complex reaction with hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) react with aromatic structure to form Hg-π complex reaction with hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH), ion exchange, electrostatic adsorption complex reaction with hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH),ion exchange literature sources Adsorption rate: 38.2%-42.3% Lu et al (2012) adsorption rate: 57.7%-61.8% condition: dairy manure>rice straw pyrolytic temperature: low pyrolytic temperature: high condition: sugarcane >walnut wood chips crispus is better when ph=5 Cao et al (2010) Liang et al(2013) Xie et al (2016) Liu et al (2016) Kong et al (2011) Dong et al (2014) Xu (2015) Zhao (2015) complexation with functional groups ph is 6-7 Ippolito et to form Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2, CuO ph is 8-9 al (2012) deoxidize Cr(VI) into Cr(VIII) Mohan et complex reaction with hydroxyl (-OH) al and carboxyl (-COOH) (2007) electrostatic adsorption precipitate with CO3 2-,OH - electrostatic adsorption,precipitation condition: silkworm excrement>rice straw >tapioca stem> sugarcane leaves Yang et al (2015) Zhang (2012) 4
6 As 5+ As 3+ pine needle, maize straw, dairy manure maize straw electrostatic adsorption non-electrostatic physical reversible adsorption and chemical irreversible adsorption with polar groups condition: dairy manure>pine needle >maize straw water solution As 3- biochar increase the solubility of As 3- soil Guan et al (2013) Huang et al(2014) Wang et al (2015) Ni 2+ Almond Putamina, reed straw complex reaction with hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) condition: almond putamina>reed straw Wu et al (2015) Zn 2+ Water hyacinth Hardwood ion exchange,electrostatic adsorption Wang et al (2017) Chen et al (2011) Pb 2+,C u 2+ Zn 2+,C d 2+ dairy manure rice husk oxygenic functional groups and precipitate with PO4 3-,CO3 2- Surface complex with phenolic hydroxy group dairy manure has the best adsorption effect on four heavy metals, and among them, Pb 2+ is most easily absorbed Xu (2015) In addition, David(2013), Xu (2015) studied the adsorption effect of different biochars on compound heavy metals (Pb 2+, Cu 2+ and Zn 2+, Cd 2+ ) pollution and showed that the competitive adsorption of heavy metal ions can affect the adsorption result of biochar on heavy metals when Pb 2+, Cu 2+, Zn 2+, Cd 2+ coexist in the soil. Compared to a single heavy metal adsorption, the adsorption effect of biochar on complex heavy metals is significantly reduced. Due to the limited adsorption sites on biochar surface, the degree of competitive adsorption increases with the increase of initial concentration (Park et al, 2016). Among the four kinds of heavy metals, Pb2+ is most easily absorbed. On one hand, Pb 2+ has the strongest combining capacity with PO 4 3-, CO 3 2+, on the other hand, the largest electronegativity constant and smallest hydrated ion radius make Pb2+ react with oxygenic functional group most easily. 5. Problems And Prospects It was proved that the adsorption effect of biochar on heavy metal pollution is quite remarkable and the mechanism mainly includes ion exchange, adsorption of cationic π function, complexation with oxygenic functional groups on biochar surface to form specific metal complexes, electrostatic adsorption, and precipitation etc. Among the three kinds of biochars, animal excrement biochar has great priority than sludge and plant residue biochar, which is attributes to the ash and mineral elements riched in animal waste biochar. For different heavy metals, the adsorption effect of biochar on Pb2+ is the best, which is related to its physical and chemical properties. Biochar has a promising future in remediation of heavy metal polluted soil, especially the animal faecal biochar, but there are still some problems in its theoretical system and research directions. (1) Using biochar to repair heavy metal polluted soil is currently in the laboratory research phase and directly using it into large areas of contaminated sites is much less. In addition, a kind of biochar cannot solve all kinds of heavy metal pollutions. The raw material, prepared pyrolysis temperature, properities and cost of biochar can make big difference on the repair effect of heavy metal pollutants; therefore, to ensure the successful application of biochar technology and wide use, we need to develop optimum specific biochar for concrete heavy metal polluted soil in practical applications. 5
7 (2) The influence of different soil types, competitive adsorption of heavy metal compound pollutions, optimal pyrolytic temperature for biochar preparation, and complex soil conditions on the adsorption effect of biochar to heavy metal pollution is still unknown. (3) The update cycle of biochar in soil is not clear, how its properities vary with time and how to influence the environment remains to be studied. In addition, biochar itself may have a small amount of heavy metals, which should be evaluated for its potential negative effects before application. Acknowledgments Scientific research project: Shaanxi provincial land engineering construction group DJNY Shaanxi provincial land engineering construction group DJNY Biography: Shuguang Wang (1967- ), male, senior economist, mainly engaged in land Reclamation and soil remediation work @qq.com Corresponding author:yan Xu (1989-), female, postgraduate, mainly engaged in petroleum geology and soil remediation work @qq.com References [1] Wang H, Xia W, Lu P, et al. Adsorption characteristics of biochar on heavy metals of Pb and Zn in Soil. Environmental Science, 2017, 9: 1-9 (in Chinese). [2] Suguihiro T M, Oliveira P R, Mangrich A S, et al. An electroanalytical approach for evaluation of biochar adsorption characteristics and its application for lead and cadmium determination [J].Bioresource Technology. 2013, 143: [3] Singh B P, Hatton B J, Singh B, et al. Influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen leaching from two contrasting soils. Journal of Environmental Quality [J].2010, 39: [4] Liu Y, Wu J, Yang G, et al. The growth of three kinds of grass in lead-zinc mining area and their bioaccumulation characteristics of heavy metals [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(5): [5] Uchimiya M, Lima I M, Klasson K T, et al. Contaminant immobilization and nutrient release by biochar soil amendment: roles of natural organic matter[j].chemosphere,2010,80: [6] Sohi S P, Krull E, Lopez-Capel E, Bol R. A review of biochar and its use and function in soil [J]. Adv Agron,2010, 105: [7] Li L, Liu Y, Lu Y C, et al. Review on environmental effects and application of biochar [J]. Environment Chemistry, 2011, 30(8): [8] Xu X Y. The Sorption and transformation of inorganic contaminants by biochars and the underlying mechanisms. Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2015 (in Chinese). [9] Cao X D, Harris W. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation[j]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(14): [10] Lu H, Zhang W, Yang Y. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar[j].water Research, 2012, 46(3): [11] Chum Y, Sheng G, Chiou C T, et al. Compositions and sorptive properties of crop residue-derived chars[j]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(17): [12] Chen B L, Zhou D D, Zhu L Z. Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures[j]. Environmental science & Technology, 2008, 42(14): [13] Zhang W M. Physical and chemical properties of biochar and its application in crop production. Shenyang : Shenyang Agricultural University, 2012 (in Chinese). [14] Singly B, Singly B P, Cowie A L. Characterisation and evaluation of biochars for their application as a soil amendment[j].soil Research,2010,48(7): [15] Xu C, Lin X, Wu Q, et al. Impacts of biochar on availability of heavy metals and nutrient content of contaminated soil under waterlogged conditions[j].journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012,26(6): [16] Ahmad M, Lee S S, Lim J E, et al. Speciation and phytoavailability of lead and antimony in a 6
8 small arms range soil amended with mussel shell, cow bone and biochar: EXAFS spectroscopy and chemical extractions[j]. Chemosphere, 2014, 95: [17] Jin H P, Girish K, Choppala N, et al. Biochar reduces the bioavailability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals[j].plant Soil, 2011, 348: [18] Lehmann J, Gaunt J, Rondon M. Biochar sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems-a review[j].miting Adapt Strat for Glob Change, 2006,11: [19] Reesa F, Simonnotb J, Morela L. Short-term effects of biochar on soil heavy metal mobility are controlled by intra-particle diffusion and soil ph increase[j]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 65(1): [20] Li H B, Xiao L, Evandro B, et al. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications[j]. Chemosphere. 2017, 178: [21] Ippolito J A, Strawn D G, Scheckel K G, et al. Macroscopic and molecular investigations of copper sorption by a steam-activated biochar[j].journal of Environmental Quality, 2012, 41(4): [22] Guan L Z, Zhou J J, Zhang J, et al. Effects of biochars produced from different sources on arsenic adsorption and desorption in soil[j]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(10): (in Chinese). [23] Huang D K, Li X Q, Dong Z Q, et al. Soil environmental influence of biochar and its application in soil heavy metal restoration[j]. Gui Zhou Agricultural Science, 2014, 42(11): (in Chinese). [24] Xie C R, Wang Z Y, Zhu J M, et al. Adsorption of lead and copper from aqueous solutions on biochar produced from walnut green husk[j]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(4): (in Chinese). [25] Liu M H, Wang Z Y, Chen L. Application of peanut shell and Chinese medication mixed biochar as soil amendment to lead contaminated soil[j].periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(1): (in Chinese). [26] Kong H, He J, Gao Y, et al. Cosorption of phenanthrene and mercury(ii) from aqueous solution by soybean stalk-based biochar[j].journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011,59(22): [27] Dong X, Wang C, Li H, et al. The sorption of heavy metals on thermally treated sediments with high organic matter content [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 160: [28] Zhao L Y. Different sources of biochar on mercury removal performance and fixing mechanism research. Jiangsu: Nanjing Normal University, 2015 (in Chinese). [29] Mohan D, Pittman C U, Jr B M, et al. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production[j].journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2007, 310(1): [30] Wu Q W, Meng L, Zhang Z H, et al. Adsorption behaviors of Ni2+onto reed straw biochar in the aquatic solutions[j].. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(9): (in Chinese). [31] Chen X C, Chen G C, Chen LG, et al. Sorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution[j]. Bioresour Technol, 2011, 102: [32] David H, Laurent E, Philippe S, et al. Beneficial effects of biochar application to contaminated soils on the bioavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn and the biomass production of rapeseed (Brassica napus L)[J]. Biomass and bio energy, 2013, 57: [33] Park J H, Ok Y S, Kim S H, et al. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions[j]. Chemosphere, 2016, 142:
Experimental study on biochar modified characteristics
 2nd Annual International Conference on Energy, Environmental & Sustainable Ecosystem Development (EESED 2016) Experimental study on biochar modified characteristics Yan-Ru Ma, Li-Ming Wang, Wen-Yang Sun,
2nd Annual International Conference on Energy, Environmental & Sustainable Ecosystem Development (EESED 2016) Experimental study on biochar modified characteristics Yan-Ru Ma, Li-Ming Wang, Wen-Yang Sun,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Environmental Sciences 31 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Environmental Sciences 31 (2016 ) 247 254 The Tenth International Conference on Waste Management and Technology (ICWMT) Experimental study
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Environmental Sciences 31 (2016 ) 247 254 The Tenth International Conference on Waste Management and Technology (ICWMT) Experimental study
Sorptive treatment of explosives and heavy metals in water using biochar
 2013 US Biochar Conference U. Mass, Amherst, MA, USA October 14, 2013 Sorptive treatment of explosives and heavy metals in water using biochar Seok-Young Oh 1*, Yong-Deuk Seo 1, Hyun-Su Yoon 1, Myong-Keun
2013 US Biochar Conference U. Mass, Amherst, MA, USA October 14, 2013 Sorptive treatment of explosives and heavy metals in water using biochar Seok-Young Oh 1*, Yong-Deuk Seo 1, Hyun-Su Yoon 1, Myong-Keun
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Distributing Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in A Tributary of Zhedong River in Laowangzhai Gold Deposit, Yunnan (China):
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Distributing Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in A Tributary of Zhedong River in Laowangzhai Gold Deposit, Yunnan (China):
Lecture 15: Adsorption; Soil Acidity
 Lecture 15: Adsorption; Soil Acidity Surface Complexation (Your textbook calls this adsorption ) Surface Complexation Both cations and anions can bind to sites on the external surfaces of soil minerals
Lecture 15: Adsorption; Soil Acidity Surface Complexation (Your textbook calls this adsorption ) Surface Complexation Both cations and anions can bind to sites on the external surfaces of soil minerals
Kaolinite Enhances the Stability of the Dissolvable and Undissolvable Fractions
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Kaolinite Enhances the Stability of the Dissolvable and Undissolvable Fractions of Biochar via Different Mechanisms 5 6 7 Fan Yang a, b, Zibo Xu a, Lu Yu a, Bin Gao c, a,
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Kaolinite Enhances the Stability of the Dissolvable and Undissolvable Fractions of Biochar via Different Mechanisms 5 6 7 Fan Yang a, b, Zibo Xu a, Lu Yu a, Bin Gao c, a,
Pyrolytic Temperature Dependent and Ash Catalyzed Formation of Sludge Char. Xiao-Qing Liu, Hong-Sheng Ding, Yuan-Ying Wang, Wu-Jun Liu, Hong Jiang*
 Pyrolytic Temperature Dependent and Ash Catalyzed Formation of Sludge Char with Ultra-High Adsorption to 1-Naphthol Xiao-Qing Liu, Hong-Sheng Ding, Yuan-Ying Wang, Wu-Jun Liu, Hong Jiang* CAS Key Laboratory
Pyrolytic Temperature Dependent and Ash Catalyzed Formation of Sludge Char with Ultra-High Adsorption to 1-Naphthol Xiao-Qing Liu, Hong-Sheng Ding, Yuan-Ying Wang, Wu-Jun Liu, Hong Jiang* CAS Key Laboratory
Prof. Dr. Biljana Škrbić, Jelena Živančev
 5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
Study on kinetics of adsorption of humic acid modified by ferric chloride on U(VI)
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study on kinetics of adsorption of humic acid modified by ferric chloride on U(VI) To cite this article: Y Y Zhang et al 2017 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study on kinetics of adsorption of humic acid modified by ferric chloride on U(VI) To cite this article: Y Y Zhang et al 2017 IOP
Properties of Compounds
 Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Acid Soil. Soil Acidity and ph
 Acid Soil Soil Acidity and ph ph ph = - log (H + ) H 2 O H + + OH - (H + ) x (OH - )= K w = 10-14 measures H + activity with an electrode (in the lab), solutions (in the field) reflects the acid intensity,
Acid Soil Soil Acidity and ph ph ph = - log (H + ) H 2 O H + + OH - (H + ) x (OH - )= K w = 10-14 measures H + activity with an electrode (in the lab), solutions (in the field) reflects the acid intensity,
Study on form distribution of soil iron in western Jilin and its correlation with soil properties
 35 2 2016 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 2 Jun. 2016 1004 5589 2016 02 0593 08 1 1 2 1 1 1. 130061 2. 130012 50 A > B > C > D > E > F > G A A CEC B ph C E A C D G B C D P595 S151. 9 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn.
35 2 2016 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 2 Jun. 2016 1004 5589 2016 02 0593 08 1 1 2 1 1 1. 130061 2. 130012 50 A > B > C > D > E > F > G A A CEC B ph C E A C D G B C D P595 S151. 9 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn.
 http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper presented at 16th International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment (ICHMET), SEP 23-27, 2012, Rome, ITALY. Citation for the
http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper presented at 16th International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment (ICHMET), SEP 23-27, 2012, Rome, ITALY. Citation for the
AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL FOR ADSORPTION PERFORMANCE OF SILVER-LOADED ACTIVATED CARBON
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2017, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 1645-1649 1645 AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL FOR ADSORPTION PERFORMANCE OF SILVER-LOADED ACTIVATED CARBON by a, Xue-Feng YAN b, Xue-Rong FAN a*, Qiang WANG
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2017, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 1645-1649 1645 AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL FOR ADSORPTION PERFORMANCE OF SILVER-LOADED ACTIVATED CARBON by a, Xue-Feng YAN b, Xue-Rong FAN a*, Qiang WANG
Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon
Reference pg and in Textbook
 Reference pg. 154-164 and 188-202 in Textbook Combustion Reactions During combustion (burning) of fossil fuels, collisions between the molecules of the fuel and oxygen result in the formation of new molecules.
Reference pg. 154-164 and 188-202 in Textbook Combustion Reactions During combustion (burning) of fossil fuels, collisions between the molecules of the fuel and oxygen result in the formation of new molecules.
ALPHA OMEGA ZEOLITES FOR THE OILFIELD BRIEF
 ALPHA-OMEGA ALPHA OMEGA ZEOLITES FOR THE OILFIELD BRIEF ALPHA OMEGA ECOLOGICAL SOLUTIONS Athens Office: 8, R. Garibaldi & Sofroniskou str. Tel. +30.210.9228225 Email: info@alpha-omega.com.gr SKYPE PHONE:
ALPHA-OMEGA ALPHA OMEGA ZEOLITES FOR THE OILFIELD BRIEF ALPHA OMEGA ECOLOGICAL SOLUTIONS Athens Office: 8, R. Garibaldi & Sofroniskou str. Tel. +30.210.9228225 Email: info@alpha-omega.com.gr SKYPE PHONE:
Scientific Base of the Technologies for Heavy Metals and Petrochemical Hydrocarbons Detoxification by Polyelectrolyte Enhanced Biopolymer
 Scientific Base of the Technologies for Heavy Metals and Petrochemical Hydrocarbons Detoxification by Polyelectrolyte Enhanced Biopolymer Polyelectrolyte Enhanced Biopolymer (PEB) is an organic substance
Scientific Base of the Technologies for Heavy Metals and Petrochemical Hydrocarbons Detoxification by Polyelectrolyte Enhanced Biopolymer Polyelectrolyte Enhanced Biopolymer (PEB) is an organic substance
Chemical Reactions REDOX
 Chemical Reactions REDOX There are two types of Chemical Changes: 1. Reactions in which ions are being rearranged with no change in their oxidation states. METATHESIS. Reactions in which electrons are
Chemical Reactions REDOX There are two types of Chemical Changes: 1. Reactions in which ions are being rearranged with no change in their oxidation states. METATHESIS. Reactions in which electrons are
Catalytically Facilitated Sequestration and Transformation of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Soils and Sediments. Walter J. Weber, Jr.
 Catalytically Facilitated Sequestration and Transformation of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Soils and Sediments Walter J. Weber, Jr. Energy and Environment Program Department of Chemical Engineering
Catalytically Facilitated Sequestration and Transformation of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Soils and Sediments Walter J. Weber, Jr. Energy and Environment Program Department of Chemical Engineering
The characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption in gray desert soil of Xinjiang, China
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS The characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption in gray desert soil of Xinjiang, China To cite this article: B Wang
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS The characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption in gray desert soil of Xinjiang, China To cite this article: B Wang
Current State of Extraction Don t Be Deceived! Sharon F. Webb, Ph.D. Director of Quality Program
 Current State of Extraction Don t Be Deceived! Sharon F. Webb, Ph.D. Director of Quality Program Overview Factors Purpose of Dissolution Quality Objectives of Program Effectiveness of Dissolution Technique
Current State of Extraction Don t Be Deceived! Sharon F. Webb, Ph.D. Director of Quality Program Overview Factors Purpose of Dissolution Quality Objectives of Program Effectiveness of Dissolution Technique
Effect of Ionic Strength on Adsorption of Corncob Xylitol Residue on. Cr(VI)
 3rd International Conference on Material, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (IC3ME 5) Effect of Ionic Strength on Adsorption of Corncob Xylitol Residue on Cr(VI) Jingwen Xue a,*, Fandeng Meng b,
3rd International Conference on Material, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (IC3ME 5) Effect of Ionic Strength on Adsorption of Corncob Xylitol Residue on Cr(VI) Jingwen Xue a,*, Fandeng Meng b,
REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS USING COMBINATION OF ADSORBENTS - A CASE STUDY USING INDUSTRIAL WASTE WATER
 REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS USING COMBINATION OF ADSORBENTS - A CASE STUDY USING INDUSTRIAL WASTE WATER PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1399 COLLEGE : DAYANANDA SAGAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH :
REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS USING COMBINATION OF ADSORBENTS - A CASE STUDY USING INDUSTRIAL WASTE WATER PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1399 COLLEGE : DAYANANDA SAGAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH :
elemental state. There are two different possibilities: DESCRIPTION 1. One cation (+ ion) replaces another. 2. One anion (- ion) replaces another.
 CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
1. Let s quickly review some of the phosphorus fixation reactions in soils. 2. At low ph (acidic conditons below 6.0), phosphorus fixation occurs
 1 1. Let s quickly review some of the phosphorus fixation reactions in soils. 2. At low ph (acidic conditons below 6.0), phosphorus fixation occurs between phosphates and iron or aluminum in the soil solution
1 1. Let s quickly review some of the phosphorus fixation reactions in soils. 2. At low ph (acidic conditons below 6.0), phosphorus fixation occurs between phosphates and iron or aluminum in the soil solution
Partitioning the contributions of biochar properties to enhanced biological nitrogen
 Supporting online material Partitioning the contributions of biochar properties to enhanced biological nitrogen fixation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) David T. Güereña 1, Johannes Lehmann 1*, Janice
Supporting online material Partitioning the contributions of biochar properties to enhanced biological nitrogen fixation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) David T. Güereña 1, Johannes Lehmann 1*, Janice
Evaluation of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in Maozhou River in Shenzhen City
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Evaluation of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in Maozhou River in Shenzhen City To cite this article: Daiwen Zhu et al 2018 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Evaluation of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in Maozhou River in Shenzhen City To cite this article: Daiwen Zhu et al 2018 IOP
12. Lead, Pb (atomic no. 82)
 12. Lead, Pb (atomic no. 82) - Sources of Pb contamination include mining, metal processing, lead battery manufacturing, chemical and paint manufacturing, and lead wastes. -USEPA drinking water action
12. Lead, Pb (atomic no. 82) - Sources of Pb contamination include mining, metal processing, lead battery manufacturing, chemical and paint manufacturing, and lead wastes. -USEPA drinking water action
Feedback between nutrient availability, NPP and N release
 Feedback between nutrient availability, NPP and N release 1 Redfield ratios A typical plant = 45% C, 1.5% N, 0.2%P or C:N = 30 : 1 and C:P = 225 : 1 or C:N:P = 225 : 7.5 : 1 N:P = 7.5 : 1 Mobility of nutrients
Feedback between nutrient availability, NPP and N release 1 Redfield ratios A typical plant = 45% C, 1.5% N, 0.2%P or C:N = 30 : 1 and C:P = 225 : 1 or C:N:P = 225 : 7.5 : 1 N:P = 7.5 : 1 Mobility of nutrients
Abstract. Introduction
 REMOVAL OF Pb +2 IONS FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS BY ACTIVATED CARBONS PRODUCED FROM PEANUT SHELLS Ayşe Eren Pütün, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey Esin Apaydın Varol, Dept.
REMOVAL OF Pb +2 IONS FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS BY ACTIVATED CARBONS PRODUCED FROM PEANUT SHELLS Ayşe Eren Pütün, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey Esin Apaydın Varol, Dept.
Synthesis of ternary chalcogenide colloidal nanocrystals in aqueous medium
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Synthesis of ternary chalcogenide colloidal nanocrystals in aqueous medium To cite this article: D S Mazing et al 28 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 38 25 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Synthesis of ternary chalcogenide colloidal nanocrystals in aqueous medium To cite this article: D S Mazing et al 28 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 38 25 View
Effects of Magnesium Impregnation on Stability and Sorption Performance of Biochar Derived from Sawdust and Corn Husks
 Effects of Magnesium Impregnation on Stability and Sorption Performance of Biochar Derived from Sawdust and Corn Husks Zhao Xu, a Ting Chen, a Zhuhong Ding, a, * Xin Hu, b and Guangze Nie a Biochar was
Effects of Magnesium Impregnation on Stability and Sorption Performance of Biochar Derived from Sawdust and Corn Husks Zhao Xu, a Ting Chen, a Zhuhong Ding, a, * Xin Hu, b and Guangze Nie a Biochar was
Lesson 3.1 Matter and the Environment. Water s abundance is a primary reason there is life on Earth.
 Lesson 3.1 Matter and the Environment Water s abundance is a primary reason there is life on Earth. Lesson 3.1 Matter and the Environment Atoms and Elements Atoms are the basic unit of matter. Nucleus:
Lesson 3.1 Matter and the Environment Water s abundance is a primary reason there is life on Earth. Lesson 3.1 Matter and the Environment Atoms and Elements Atoms are the basic unit of matter. Nucleus:
10.3 Types of Chemical Reactions
 10.3 Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical equations follow certain patterns Combination (synthesis ) The number of possible chemical is very large. However, there are a limited number of structural patterns
10.3 Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical equations follow certain patterns Combination (synthesis ) The number of possible chemical is very large. However, there are a limited number of structural patterns
Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Straw Activated Carbon by Zinc Chloride Xu Zhong, Zhao Dan
 2nd International Conference on Machinery, Materials Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (MMECEB 215) Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Straw Activated Carbon by Zinc Chloride
2nd International Conference on Machinery, Materials Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (MMECEB 215) Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Straw Activated Carbon by Zinc Chloride
THE BINDING OF ORGANIC CONTAMINANTS TO HUMIN
 THE BINDING OF ORGANIC CONTAMINANTS TO HUMIN S. Kohl and J.A. Rice *, Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry, South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, 57007-0896 ABSTRACT It has been recognized for
THE BINDING OF ORGANIC CONTAMINANTS TO HUMIN S. Kohl and J.A. Rice *, Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry, South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, 57007-0896 ABSTRACT It has been recognized for
Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with EDTA. functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network
 Supporting Information Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel Jianhong Ma a,b, Guiyin Zhou c, Lin Chu c, Yutang Liu a,b, *, Chengbin
Supporting Information Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel Jianhong Ma a,b, Guiyin Zhou c, Lin Chu c, Yutang Liu a,b, *, Chengbin
Environmental Chemistry Spring 2005 Chapter 5
 Environmental Chemistry Spring 2005 Chapter 5 Ji Yang, Ph.D. Associate Professor School of Environmental Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Metal Ions Produce Acid Aqueous Environments
Environmental Chemistry Spring 2005 Chapter 5 Ji Yang, Ph.D. Associate Professor School of Environmental Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Metal Ions Produce Acid Aqueous Environments
Supporting material. Figures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Study on Coal Methane Adsorption Behavior Under Variation Temperature and Pressure-Taking Xia-Yu-Kou Coal for Example
 International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(4): 60-66 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180604.13 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online) Study
International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(4): 60-66 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180604.13 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online) Study
Chemical Alterations Occurring During Biomass Charring and their Impact on Char Recalcitrance
 Chemical Alterations ccurring During Biomass Charring and their Impact on Char Recalcitrance Heike Knicker Instituto de Recursos Naturales y Agrobiología, CSIC, Sevilla, Spain Impact of fire on soil organic
Chemical Alterations ccurring During Biomass Charring and their Impact on Char Recalcitrance Heike Knicker Instituto de Recursos Naturales y Agrobiología, CSIC, Sevilla, Spain Impact of fire on soil organic
Advanced TRS - ZEOLITE IN A COLLOIDAL SUSPENSION
 Advanced TRS - ZEOLITE IN A COLLOIDAL SUSPENSION The need for this product is summarized in the following graphic Since this data was collected the numbers of deaths have gone up yearly. 25 MARCH 2014
Advanced TRS - ZEOLITE IN A COLLOIDAL SUSPENSION The need for this product is summarized in the following graphic Since this data was collected the numbers of deaths have gone up yearly. 25 MARCH 2014
Water Extractable Organic Carbon in Fresh and Treated Biochars
 Water Extractable Organic Carbon in Fresh and Treated Biochars Yun Lin a, Paul Munroe a, Stephen Joseph a, Rita Henderson b, Artur. Ziolkowski c a School of Materials Science and Engineering, The University
Water Extractable Organic Carbon in Fresh and Treated Biochars Yun Lin a, Paul Munroe a, Stephen Joseph a, Rita Henderson b, Artur. Ziolkowski c a School of Materials Science and Engineering, The University
Highly doped and exposed Cu(I)-N active sites within graphene towards. efficient oxygen reduction for zinc-air battery
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science.
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science.
Influence of dissolved organic matters prepared from organisms in aquatic ecosystem on mercury adsorption in sediment
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(5):1654-1658 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Influence of dissolved organic matters prepared
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(5):1654-1658 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Influence of dissolved organic matters prepared
Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Penn State Harrisburg. Robert Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE University of Alabama
 Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE University of Alabama Site Stormwater Characteristics and Permit Limits Analytes on Permit 90 th percentile
Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE University of Alabama Site Stormwater Characteristics and Permit Limits Analytes on Permit 90 th percentile
Priority Pollutants in Untreated and Treated Discharges from Coal Mines
 Priority Pollutants in Untreated and Treated Discharges from Coal Mines Charles A. Cravotta III Research Hydrologist USGS Pennsylvania Water Science Center New Cumberland, PA Presented March, 28, 2012,
Priority Pollutants in Untreated and Treated Discharges from Coal Mines Charles A. Cravotta III Research Hydrologist USGS Pennsylvania Water Science Center New Cumberland, PA Presented March, 28, 2012,
An Experimental I nvestigation o f Manufacturing Activated Carbon Prototype Setup R. Pravinkumar 1 J.Yasin 2
 An Experimental I nvestigation o f Manufacturing Activated Carbon Prototype Setup R. Pravinkumar 1 J.Yasin 2 PG Scholars, Department of Manufacturing Engineering, Government college of Technology, Coimbatore,
An Experimental I nvestigation o f Manufacturing Activated Carbon Prototype Setup R. Pravinkumar 1 J.Yasin 2 PG Scholars, Department of Manufacturing Engineering, Government college of Technology, Coimbatore,
General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported. Bicomponent Metal Monoxides as Alternative High- Performance Li-Ion Anodes to Binary Spinel Oxides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
CAUSTIC MAGNESIA IN ENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS
 CAUSTIC MAGNESIA IN ENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS T. Zampetakis, D. Karatzovalis Grecian Magnesite SA, Research Center, 570.06 Vassilika, Thessaloniki ABSTRACT Caustic magnesia (MgO) and its derivatives are
CAUSTIC MAGNESIA IN ENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS T. Zampetakis, D. Karatzovalis Grecian Magnesite SA, Research Center, 570.06 Vassilika, Thessaloniki ABSTRACT Caustic magnesia (MgO) and its derivatives are
6. Reaction Chemistry
 6. Reaction Chemistry 6.1 Chemical Elements 6.2 Chemical Bonding 6.3 Chemical Reactions 6.4 Thermodynamics 6.5 Properties of Water 6.6 Important Biomolecules 6.1 Chemical Elements It is common for elements
6. Reaction Chemistry 6.1 Chemical Elements 6.2 Chemical Bonding 6.3 Chemical Reactions 6.4 Thermodynamics 6.5 Properties of Water 6.6 Important Biomolecules 6.1 Chemical Elements It is common for elements
Removal of sulfamethazine and sulfathiazole from water using modified bamboo biochar
 Removal of sulfamethazine and sulfathiazole from water using modified bamboo biochar Md. Boshir Ahmed (PhD, 2 nd Year) Principle Supervisor: Professor John L. Zhou Cosupervisor: Professor Huu Hao Ngo University
Removal of sulfamethazine and sulfathiazole from water using modified bamboo biochar Md. Boshir Ahmed (PhD, 2 nd Year) Principle Supervisor: Professor John L. Zhou Cosupervisor: Professor Huu Hao Ngo University
The make-up of a natural solution.
 The make-up of a natural solution http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c220/ The make-up of a natural solution I Particulate or solids II- Colloidal material III Truly dissolved a) non-associated (free) b) associated
The make-up of a natural solution http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c220/ The make-up of a natural solution I Particulate or solids II- Colloidal material III Truly dissolved a) non-associated (free) b) associated
Structure Properties and Uses Mark Scheme 1
 Structure Properties and Uses Mark Scheme Level IGCSE Subject Chemistry (4402) Exam Board AQA Unit C2 Topic Structure Properties and Uses Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 54 minutes Score: / 54 Percentage:
Structure Properties and Uses Mark Scheme Level IGCSE Subject Chemistry (4402) Exam Board AQA Unit C2 Topic Structure Properties and Uses Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 54 minutes Score: / 54 Percentage:
Mineralogical and geochemical features of human body ash residue of spatially-localized technogenic system (Norilsk city)
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Mineralogical and geochemical features of human body ash residue of spatially-localized technogenic system (Norilsk city) To cite
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Mineralogical and geochemical features of human body ash residue of spatially-localized technogenic system (Norilsk city) To cite
Microorganisms. Dissolved inorganics. Native vs. Introduced; Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Millions to billions per ml or g Complex consortia
 1 Microorganisms Native vs. Introduced; Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Millions to billions per ml or g Complex consortia Species makeup: f(t, O 2, ph, nutrients, etc.) Indicators & pathogens Dissolved inorganics
1 Microorganisms Native vs. Introduced; Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Millions to billions per ml or g Complex consortia Species makeup: f(t, O 2, ph, nutrients, etc.) Indicators & pathogens Dissolved inorganics
Potential Impacts of Tailings and Tailings Cover. Fertilization on Arsenic Mobility in Surface and. Ground Waters
 Potential Impacts of Tailings and Tailings Cover Fertilization on Arsenic Mobility in Surface and Ground Waters Sierra Rayne * and Kaya Forest Water Treatment Technology Program, Thompson Rivers University,
Potential Impacts of Tailings and Tailings Cover Fertilization on Arsenic Mobility in Surface and Ground Waters Sierra Rayne * and Kaya Forest Water Treatment Technology Program, Thompson Rivers University,
HEAVY METAL AVAILABILITY IN SOIL IN THE PRESENCE OF ANIONIC SURFACTANTS
 Comm. Appl. Biol. Sci, Ghent University, 7/, 8 57 HEAVY METAL AVAILABILITY IN SOIL IN THE PRESENCE OF ANIONIC SURFACTANTS INTRODUCTION M.C. HERNANDEZ-SORIANO, F. DEGRYSE, E. SMOLDERS Division of Soil and
Comm. Appl. Biol. Sci, Ghent University, 7/, 8 57 HEAVY METAL AVAILABILITY IN SOIL IN THE PRESENCE OF ANIONIC SURFACTANTS INTRODUCTION M.C. HERNANDEZ-SORIANO, F. DEGRYSE, E. SMOLDERS Division of Soil and
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry
 Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Unit 2: Basic Chemistry I. Matter and Energy A. Matter anything that occupies space and has mass (weight) B. Energy the ability to do work 1. Chemical 2. Electrical 3. Mechanical 4. Radiant C. Composition
Molecular Dynamic Simulation on the Absorbing Process of Isolating and Coating of α-olefin Drag Reducing Polymer
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 23, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 27, 2010 ARTICLE Molecular Dynamic Simulation on the Absorbing Process of Isolating and Coating of α-olefin Drag Reducing Polymer Bing Li
CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 23, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 27, 2010 ARTICLE Molecular Dynamic Simulation on the Absorbing Process of Isolating and Coating of α-olefin Drag Reducing Polymer Bing Li
Environmental Aspects of Oil Shale Development: A Review
 Environmental Aspects of Oil Shale Development: A Review Tom Wildeman, Ron Klusman, & Jim Ranville Dept. of Chemistry & Geochemistry Colorado School of Mines Background During the last oil shale development
Environmental Aspects of Oil Shale Development: A Review Tom Wildeman, Ron Klusman, & Jim Ranville Dept. of Chemistry & Geochemistry Colorado School of Mines Background During the last oil shale development
Chapter 6. Weathering, Erosion, and Soil
 Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Chapter 02 The Chemical Basis of Life I: Atoms, Molecules, and Water
 Chapter 02 The Chemical Basis of Life I: Atoms, Molecules, and Water Multiple Choice Questions 1. The atomic number of an atom is A. the number of protons in the atom. B. the number of neutrons in the
Chapter 02 The Chemical Basis of Life I: Atoms, Molecules, and Water Multiple Choice Questions 1. The atomic number of an atom is A. the number of protons in the atom. B. the number of neutrons in the
SOIL and WATER CHEMISTRY
 SOIL and WATER CHEMISTRY An Integrative Approach MICHAEL E. ESSINGTON CRC PRESS Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C. Table of Contents Chapter 1 The Soil Chemical Environment: An Overview 1 1.1
SOIL and WATER CHEMISTRY An Integrative Approach MICHAEL E. ESSINGTON CRC PRESS Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C. Table of Contents Chapter 1 The Soil Chemical Environment: An Overview 1 1.1
Atoms, the basic building block of matter, are composed of three basic particles. Nucleus: Proton (+) Neutron (-) Outside the nucleus: Electron (-)
 Atoms, the basic building block of matter, are composed of three basic particles Nucleus: Proton (+) Neutron (-) Outside the nucleus: Electron (-) Atomic number = # protons Atomic mass number = # protons
Atoms, the basic building block of matter, are composed of three basic particles Nucleus: Proton (+) Neutron (-) Outside the nucleus: Electron (-) Atomic number = # protons Atomic mass number = # protons
A photo-catalytic reactor for degrading volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in paper mill environment
 Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts. 2018, 3(2) 78-83 ORIGINAL PAPER DOI: 10.21967/jbb.v3i2.113 A photo-catalytic reactor for degrading volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in paper mill environment Jun
Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts. 2018, 3(2) 78-83 ORIGINAL PAPER DOI: 10.21967/jbb.v3i2.113 A photo-catalytic reactor for degrading volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in paper mill environment Jun
Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Robert E. Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE
 Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Robert E. Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE Current PA Guidance Many guidance documents apply expected pollutant removals based on literature. However, typically presented
Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Robert E. Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE Current PA Guidance Many guidance documents apply expected pollutant removals based on literature. However, typically presented
Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water
 Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water Biochemistry & Medicine Biochemistry can be defined as the science concerned with the chemical basis of life. Biochemistry can be described as the science concerned with the chemical
Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water Biochemistry & Medicine Biochemistry can be defined as the science concerned with the chemical basis of life. Biochemistry can be described as the science concerned with the chemical
Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with. Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang Yang, Pu-Can Guo, Han-Qing Yu*
 Supporting Information for Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn 1.8 Fe 1.2 O 4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang
Supporting Information for Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn 1.8 Fe 1.2 O 4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang
Modification of Pineapple Leaf Cellulose with Citric Acid for Fe 2+ Adsorption
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.4, pp 674-680, 2017 Modification of Pineapple Leaf Cellulose with Citric Acid for Fe 2+
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.4, pp 674-680, 2017 Modification of Pineapple Leaf Cellulose with Citric Acid for Fe 2+
Matter: Elements and Compounds
 Matter: Elements and Compounds Matter is defined as anything that takes up space and has mass. Matter exists in many diverse forms, each with its own characteristics. Rock, metals, and glass are just few
Matter: Elements and Compounds Matter is defined as anything that takes up space and has mass. Matter exists in many diverse forms, each with its own characteristics. Rock, metals, and glass are just few
Types of Chemical Reactions
 Types of Chemical Reactions 1) Combination (Synthesis) Reaction 2) Decomposition 3) Single Replacement 4) Double Replacement 5) Combustion 6) Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Combination (Synthesis) Reactions
Types of Chemical Reactions 1) Combination (Synthesis) Reaction 2) Decomposition 3) Single Replacement 4) Double Replacement 5) Combustion 6) Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Combination (Synthesis) Reactions
Lecture 7. Environmental Organic Chemistry
 Lecture 7 Environmental Organic Chemistry 1. Organic Chemistry Intro 2. dissolved and particulate organic carbon, Humic substances 3. DOC/POC distribution 4. Reactivity of simple organic molecules 5. Organic
Lecture 7 Environmental Organic Chemistry 1. Organic Chemistry Intro 2. dissolved and particulate organic carbon, Humic substances 3. DOC/POC distribution 4. Reactivity of simple organic molecules 5. Organic
Supporting Information. Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for. Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen Batteries
 Supporting Information Hierarchical Mesoporous/Macroporous Perovskite La 0.5 Sr 0.5 CoO 3-x Nanotubes: a Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen
Supporting Information Hierarchical Mesoporous/Macroporous Perovskite La 0.5 Sr 0.5 CoO 3-x Nanotubes: a Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen
Environmental Chemistry Spring 2005 Chapter 3
 Environmental Chemistry Spring 2005 Chapter 3 Ji Yang, Ph.D. Associate Professor School of Environmental Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Aqueous Chemistry The complexity of the chemistry
Environmental Chemistry Spring 2005 Chapter 3 Ji Yang, Ph.D. Associate Professor School of Environmental Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Aqueous Chemistry The complexity of the chemistry
AQA C1 Atomic Structure
 AQA C1 Atomic Structure What s in an atom? Elements in the periodic have different sizes of atoms. The size of the atoms depends on the number of protons, electrons and neutrons they have. Each element
AQA C1 Atomic Structure What s in an atom? Elements in the periodic have different sizes of atoms. The size of the atoms depends on the number of protons, electrons and neutrons they have. Each element
Removal of Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solution by Activated Biocharfibers. Maria A. Andreou and Ioannis Pashalidis
 Removal of Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solution by Activated Biocharfibers Maria A. Andreou and Ioannis Pashalidis Department of Chemistry, University of Cyprus, P.O. Box 20537, 1678 Nicosia, Cyprus Corresponding
Removal of Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solution by Activated Biocharfibers Maria A. Andreou and Ioannis Pashalidis Department of Chemistry, University of Cyprus, P.O. Box 20537, 1678 Nicosia, Cyprus Corresponding
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 10.1 to 10.4.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 10.1 to 10.4 Forms of Carbon Hydrogen (The Groupless Element) Hydrogen has three isotopes:
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 10.1 to 10.4 Forms of Carbon Hydrogen (The Groupless Element) Hydrogen has three isotopes:
Alleviating Soil Acidity through Organic Matter Management. Malcolm E. Sumner, University of Georgia Marcos A Pavan IAPAR
 Alleviating Soil Acidity through Organic Matter Management Malcolm E. Sumner, University of Georgia Marcos A Pavan IAPAR Introduction Most work on topsoil acidity amelioration Mechanical lime incorporation
Alleviating Soil Acidity through Organic Matter Management Malcolm E. Sumner, University of Georgia Marcos A Pavan IAPAR Introduction Most work on topsoil acidity amelioration Mechanical lime incorporation
SCHOOL YEAR CH- 13 IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE : 11 TEST A
 SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 13 IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE : 11 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. A solute
SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 13 IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE : 11 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. A solute
Advanced Chemistry Final Review
 Advanced Chemistry Final Review 1. What are the products of complete combustion of hydrocarbons? Hydrocarbons are compounds made of carbon and oxygen. When they burn (combine with oxygen) they form carbon
Advanced Chemistry Final Review 1. What are the products of complete combustion of hydrocarbons? Hydrocarbons are compounds made of carbon and oxygen. When they burn (combine with oxygen) they form carbon
Bonding Mrs. Pugliese. Name March 02, 2011
 Bonding Mrs. Pugliese Name March 02, 2011 1. Atoms of which element have the greatest tendency to gain electrons? 1. bromine 3. fluorine 2. chlorine 4. iodine 2. Which polyatomic ion contains the greatest
Bonding Mrs. Pugliese Name March 02, 2011 1. Atoms of which element have the greatest tendency to gain electrons? 1. bromine 3. fluorine 2. chlorine 4. iodine 2. Which polyatomic ion contains the greatest
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Enhanced Adsorption of Cu(II) Ions on the Chitosan Microspheres Functionalized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Enhanced Adsorption of Cu(II) Ions on the Chitosan Microspheres Functionalized
The Study of Natural Nano-Composite Filter for Industrial Wastewater Treatment
 The Study of Natural Nano-Composite Filter for Industrial Wastewater Treatment Chin-Ya Kuo, Hsiao-Han Liu * Department of Biological Science & Technology, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung 824, Taiwan, ROC
The Study of Natural Nano-Composite Filter for Industrial Wastewater Treatment Chin-Ya Kuo, Hsiao-Han Liu * Department of Biological Science & Technology, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung 824, Taiwan, ROC
Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils. Fig. 5.14
 Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils Fig. 5.14 OBJECTIVES Recognize that weathering breaks down minerals and rocks and occurs as a result of both mechanical and chemical processes. Explain the processes that
Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils Fig. 5.14 OBJECTIVES Recognize that weathering breaks down minerals and rocks and occurs as a result of both mechanical and chemical processes. Explain the processes that
Kenji Narimura, *Katsutoshi Inoue, Keisuke Ohto, Hiroyuki Harada, Hidetaka Kawakita
 544 J. ION EXCHANGE Article Adsorption and Separation of Hexavalent Chromium by Using Adsorption Gel Prepared from Grape Residue Kenji Narimura, *Katsutoshi Inoue, Keisuke Ohto, Hiroyuki Harada, Hidetaka
544 J. ION EXCHANGE Article Adsorption and Separation of Hexavalent Chromium by Using Adsorption Gel Prepared from Grape Residue Kenji Narimura, *Katsutoshi Inoue, Keisuke Ohto, Hiroyuki Harada, Hidetaka
New Specification 2018 Recurring Exam Questions. How Science Works. C1 - Particles. Atom with the same atomic number and different mass number
 How Science Works Why is it important that scientist publish their results? Results can be checked Further evidence can be collected How do scientists publish their work? Scientific conference Scientific
How Science Works Why is it important that scientist publish their results? Results can be checked Further evidence can be collected How do scientists publish their work? Scientific conference Scientific
Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Weathering and Soil
 Chapter 6 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Weathering and Soil Tarbuck and Lutgens Weathering Weathering involves the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock
Chapter 6 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Weathering and Soil Tarbuck and Lutgens Weathering Weathering involves the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock
Screening of Synthesis Conditions of Polymers and the Effects on Viscosity Reduction Performance
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Screening of Synthesis Conditions of Polymers and the Effects on Viscosity Reduction Performance To cite this article: Lijun Zhu
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Screening of Synthesis Conditions of Polymers and the Effects on Viscosity Reduction Performance To cite this article: Lijun Zhu
CHEM 316/318. Molecule(s) of the day
 Molecule(s) of the day Creative minds have been known to survive any sort of bad training. - Anna Freud Your theory is crazy, but it's not crazy enough to be true. Niels Bohr Never express yourself more
Molecule(s) of the day Creative minds have been known to survive any sort of bad training. - Anna Freud Your theory is crazy, but it's not crazy enough to be true. Niels Bohr Never express yourself more
Chapter 6. Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
 Chapter 6 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry Chapter 6 Table of Contents (6.1) (6.2) (6.3) (6.4) (6.5) (6.6) (6.7) (6.8) Water, the common solvent The nature of aqueous solutions: Strong
Chapter 6 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry Chapter 6 Table of Contents (6.1) (6.2) (6.3) (6.4) (6.5) (6.6) (6.7) (6.8) Water, the common solvent The nature of aqueous solutions: Strong
STUDY ON THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE REDUCTION CAPACITY OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBER
 STUDY ON THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE REDUCTION CAPACITY OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBER Chen Shuixia, Zeng Hanmin Materials Science Institute, Zhongshan University, Guangzhou 51275, China Key Laboratory for Polymeric
STUDY ON THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE REDUCTION CAPACITY OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBER Chen Shuixia, Zeng Hanmin Materials Science Institute, Zhongshan University, Guangzhou 51275, China Key Laboratory for Polymeric
About me (why am I giving this talk) Dr. Bruce A. Snyder
 Ecology About me (why am I giving this talk) Dr. Bruce A. Snyder basnyder@ksu.edu PhD: Ecology (University of Georgia) MS: Environmental Science & Policy BS: Biology; Environmental Science (University
Ecology About me (why am I giving this talk) Dr. Bruce A. Snyder basnyder@ksu.edu PhD: Ecology (University of Georgia) MS: Environmental Science & Policy BS: Biology; Environmental Science (University
Lab: Types of Chemical Reactions Safety is very important when combining chemicals
 Safety is very important when combining chemicals Students: Please read the following information given below, and then come to class on your lab day with the following already prepared in your notebooks:
Safety is very important when combining chemicals Students: Please read the following information given below, and then come to class on your lab day with the following already prepared in your notebooks:
Cation Exchange Capacity, CEC
 Cation Exchange Capacity, CEC The basic building blocks of clay minerals are: silicon atoms surrounded by four oxygen atoms (tetrahedra), and aluminium atoms surrounded by six hydroxide groups (dioctahedra),
Cation Exchange Capacity, CEC The basic building blocks of clay minerals are: silicon atoms surrounded by four oxygen atoms (tetrahedra), and aluminium atoms surrounded by six hydroxide groups (dioctahedra),
Study on mechanism of mercury oxidation by fly ash from coal combustion
 Articles Engineering Thermophysics January 2010 Vol.55 No.2: 163 167 doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0567-7 SPECIAL TOPICS: Study on mechanism of mercury oxidation by fly ash from coal combustion ZHAO YongChun
Articles Engineering Thermophysics January 2010 Vol.55 No.2: 163 167 doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0567-7 SPECIAL TOPICS: Study on mechanism of mercury oxidation by fly ash from coal combustion ZHAO YongChun
Basic Principles of Chemistry Lecture Notes #11 Types of Chemical Reactions
 Basic Principles of Chemistry Lecture Notes #11 Types of Chemical Reactions Types of Chemical Reactions Part 1 Precipitation Reactions In a precipitation reaction, a solid substance is formed in a solution
Basic Principles of Chemistry Lecture Notes #11 Types of Chemical Reactions Types of Chemical Reactions Part 1 Precipitation Reactions In a precipitation reaction, a solid substance is formed in a solution
Let s Review Bonding. Chapter 3 Water and Life 7/19/2016 WATER AND SOLUTIONS. Properties of Water
 Let s Review Bonding Chapter 3 Water and Life Covalent Ionic Hydrogen Van der Waals Interactions Between nonmetals Between metal and non-metal All important to life H bonds to other electronegative atoms
Let s Review Bonding Chapter 3 Water and Life Covalent Ionic Hydrogen Van der Waals Interactions Between nonmetals Between metal and non-metal All important to life H bonds to other electronegative atoms
BIOSORPTION OF HEAVY METALS BY PSEUDOMONAS BACTERIA
 BIOSORPTION OF HEAVY METALS BY PSEUDOMONAS BACTERIA ABBAS ALI A 1, MOHAMED SIHABUDEEN M 2 AND ZAHIR HUSSAIN A 3 1 Professor, M.I.E.T Engineering College, Tiruchirappalli. 2 Associate Professor and Head,
BIOSORPTION OF HEAVY METALS BY PSEUDOMONAS BACTERIA ABBAS ALI A 1, MOHAMED SIHABUDEEN M 2 AND ZAHIR HUSSAIN A 3 1 Professor, M.I.E.T Engineering College, Tiruchirappalli. 2 Associate Professor and Head,
