PLGA Nanoparticles of Anti Tubercular Drug: Drug Loading and Release Studies of a Water In-Soluble Drug
|
|
|
- Barbra Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : Vol.2, No.3, pp , July-Sept 21 PLGA Nanoparticles of Anti Tubercular Drug: Drug Loading and Release Studies of a Water In-Soluble Drug Akansha Tripathi*, Ranjana Gupta, Shubhini A. Saraf Faculty of Pharmacy, BBDNITM, Sector-I, Dr. Akhilesh Das Nagar, Faizabad Road, Lucknow, (UP), India *Corres.author: ranjanagunja2@gmail.com Abstract: Poly lactic-co-glycolic-acid (PLGA) nanoparticles are often produced using the single emulsion solvent evaporation method. In most cases poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) is used as stabilizer of the emulsion. The rationale of this study was to develop PLGA nanoparticles loaded with rifampicin, intended to be intravenously administered and able to improve the therapeutic index of the drug. The influence of the concentration of PVA and the polymers was tested on particle size of prepared particles. PLGA-based rifampicin nanoparticles were prepared by single and double evaporation method, solvent diffusion and ionic interaction method. The incorporation efficiency of Rifampicin was higher with the single emulsion evaporation method in the nanosize range particles. The processing parameters involved in the method were optimized, including drug / polymer ratio, concentration of surfactant, phase ratio (organic phase/ aqueous phase) and sonication time to obtain small nanoparticles with maximum drug entrapment. The release behaviour of rifampicin exhibited a biphasic pattern characterized by an initial burst (11.26 % in 1 days) release followed by a slower and continuous release (more than 3 days). Therefore, Rifampicin loaded PLGA-nanoparticles may be considered as an effective antitubercular drug delivery system for therapy. Key Words: Rifampicin, Poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolide) (PLGA), Poly vinyl Alcohol (PVA), Antitubercular drugs (ATDs). Introduction Drugs do not deliver themselves 1. For a molecule to reach the target site from the site of administration in sufficient concentration, and to maintain therapeutic levels for a sufficient period of time, a delivery system is needed. The delivery system is as important as the therapeutic moiety itself. Controlled and novel drug delivery, which was only a dream or at bests a possibility, is now a reality. During last decade and half, pharmaceutical and other scientist have carried out extensive and intensive investigation in the field of drug research 2. Among those, nanoparticulte drug delivery systems from biodegradable and biocompatible polymer are interesting option for controlled drug delivery and drug targeting. Poly (lactide-co- glycolide) has gained attention for preparation of wide variety of delivery systems containing several drugs due to their biodegradable and biocompatible properties and low toxicity. Because of their biodegradability and biocompatibility, Polylactic acid and its copolymers with glycolic acid (PLGA) are widely employed for the preparation of sustained release preparations 3 and PLGA microparticles have successfully employed as Antitubercular drug (ATD) carrier 4-7. With injectable PLGA microparticle a sustained drug release has been observed for 6-7 weeks in mice 4-5. The formulation was subsequently explored as an ATD-carrier in order to avoid the discomfort associated with subcutaneous injection. However, oral PLGA microparticle suffered from several drawbacks such as low drug encapsulation, high polymer composition, sustained drug release for 3-4 days 6 and a partial therapeutic benefit 7. It is possible to circumvent these drawbacks by developing PLGA nanoparticles (PLGA-NP) encapsulated three front line antitubercular drugs, i.e. rifampicin (RIF), isoniazid (INH) and pyrazinamide (PZA) which resulted in a reduced dosing frequency in a murine TB model 8. The administration routes of PLGA nano / micro particle may vary from parenteral,
2 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) 2117 oral, dermatological, pulmonary and nasal to ocular 9. Recently, diclofenac sodium-loaded PLGA nanoparticles were developed for ocular use and found good biocompatibility with eye 1. Sparfloxcin loaded PLGA (5:5) nanoparticles were also studied extensively in various pharmacological aspects for their application in treatment of conjunctivitis and proved to have good stability and ocular tolerance 11. Tuberculosis (TB), a ubiquitous, high contagious chronic granulomatous bacterial infection caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis that infects over 8 million people worldwide and is responsible for 2 million deaths annually 12. Although an effective therapeutic regimen is available, patient noncompliance (because of the need to take antitubercular drugs (ATDs) daily or several times a week) results in treatment failure as well as the emergence of drug resistance. The study also reveals that fabrication of a polymeric once-daily oral multiparticulate fixed dose combination of the principal antitubercular drugs, which attains segregated delivery of rifampicin and isoniazid for improved rifampicin bioavailability, could be a step in the right direction in addressing issues of treatment failure due to patient noncompliance 13. Patient compliance can be improved by the use of ATD formulations, which reduce the dosing frequency of the drugs. Thus the purpose of the present study was to prepare Rifampicin loaded PLGA nanoparticles for sustained action. Materials and Methods Materials Rifampicin was obtained from M/s LI TAKA Drugs Ltd. Pune, India, as a gift sample. Poly (lactide-coglycolide) (5:5) was obtained from Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Germany as a gift sample. All other ingredients used were of analytical grade. Method Rifampicin loaded nanoparticles were prepared through single emulsion evaporation method mg of PLGA and 4mg of rifampicin were dissolved in 2ml of dichloromethane. This solution was added drop wise to an aqueous 2ml PVA (3%, w/v) solution under sonication for 2 min (in pulsed manner, 4% intensity) using a probe sonicator (Lapsonic P, Sartorious Biotech GmbH, Germany) over an ice bath. The solvent was evaporated at room temperature (28 C) for 12h, under magnetic stirring. Rifampicin loaded nanoparticles were isolated by 3 min centrifugation at 35, rpm. After centrifugation, the supernatant was recovered and assayed for unentrapped drug and sediment was washed using the same amount of distilled water as of the supernatant and again centrifuged at 35, rpm for 2 min. The washing process was repeated 3 times. All the washings were collected and assayed for unentrapped drug. Optimization of Drug/Polymer ratio with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size For optimization of Drug/polymer ratio the nanoparticles were prepared with 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4 1and 1:5 w/w ratio of drug and PLGA and other parameters were kept constant. The average particle size was determined using Laser Particle Size Analyzer (Malvern UK) (Table 1). Optimization of surfactant concentration with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size In order to optimize the concentration of aqueous PVA solution, the nanoparticles were prepared by using PVA concentration of.5 to 3.5% and other parameters were kept constant. The Average particle size was determined using Laser Particle Size Analyzer (Malvern UK) (Table 2). Optimization of Phase Ratio (Organic/ Aqueous Phase) with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size Phase ratio was optimized in regard to average particle size and %drug entrapment and other parameters were kept constant. For optimization the nanoparticles were prepared with 1:1 to 1:2 (v/v) ratio of organic phase to aqueous phase and determined their particle size and % drug entrapment (Table 3). Optimization of Sonication time with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size Nanoparticle formulation with optimized drug/ polymer ratio, surfactant concentration and phase ratio was selected (NP IV F-3). Nanoparticles were again prepared by same procedure however; with a varying sonication time 4, 8, 12, 16, 2 and 24 minutes. Average particle size and drug entrapment were determined and recorded (Table 4). Nanoparticle Characterization Size and shape morphology of nanoparticles The morphology of Rifampicin loaded PLGA nanoparticles were analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (Hitachi High Technology, Pleasanton, CA). Samples were prepared from dilutions in distilled water of particle suspensions and dropped onto stubs. After air drying, particle were coated with a thin layer of gold and then examined by scanning electron microscopy. (Figure: 1). Average particle size and polydispersity index of nanoparticles were measured by Laser Particle size analyzer after suitable dilution. Data of size and polydispersity were discussed earlier
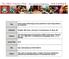
3 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) 2118 (Table no. 1-4). Particle size density was also measured by Zetasizer (Malvern, UK). Zeta Potential Study The surface charge of nanoparticles was determined by the eletrophoretic mobility of nanoparticles in a U type tube at 25 C, using a zetasizer (Malvern, UK). The zeta potential was found to be Drug Loading, Encapsulation Efficiency, Drug Content and Process Yield The loading efficiency of drug in PLGA nanoparticles was determined as described below. Nanoparticles were separated from the aqueous medium by ultracentrifugation at 35, rpm for 3 min. The amount of drug present in the nanoparticles was determined as the difference between the total amount of drug used to prepare the nanoparticles and the amount of drug present in the aqueous medium. In vitro release studies 1 mg of PLGA/Rifampicin nanoparticles were redispersed in 2. ml of ph 7.4 PBS and kept in an incubator at 37 C (without agitation). The supernatant obtained after centrifugation (35, rpm, 3 min) of the suspension was collected daily for 3 days to determine the release of drug. The buffer solution was changed with fresh one every day and the rifampicin concentration in the dispersing medium was spectrophotometrically (UV17 Shimadzu, Japan) measured at 475 nm. Results were expressed as concentration of rifampicin released in the buffer daily. The release study was carried out with n = 3 for 3 days (Table 6). Drug content (% w/w) = (Mass of the total drug Mass of free drug) 1 Mass of nanoparticles Drug entrapment (%, w/w) = (Mass of the total drug Mass of free drug) 1 Mass of total drug Drug loading (%, w/ w) = (Mass of the total drug Mass of free drug) 1 Mass of total polymer Process Yield (%) = (Mass of nanoparticles) 1 Total mass of drug + polymer Table 1: Optimization of Drug/Polymer ratio with regard to per cent drug entrapment average particle size Formulation Code NP I NP II NP III NP IV* NP V Drug/ Polymer Ratio (w/w) 1:1 1:2 1:3 1:4 1:5 Entrapment Avg Particle Size(nm) Polydispersity Index Table 2: Optimization of surfactant concentration with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size Formulation Average Particle Code Entrapment Size(nm) NP IV A NP IV B NP IV C NP IV D NP IV E NP IV F* NP IV G Concentration of aq. PVA solution (% w/v) Polydispersity Index
4 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) 2119 Table 3: Optimization of Phase Ratio (Organic/ Aqueous Phase) with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size Formulation Code NP IV F- 1 NP IV F- 2 NP IV F- 3* NP IV F- 4 NP IV F- 5 Table 4: Optimization of Sonication time with regard to per cent drug entrapment and average particle size Formulation Code Sonication Time (min) Entrapment Avg Particle Size(nm) Polydispersity Index NP- T1 NP-T2 NP-T3 NP-T4 NP-T5* NP-T6 Phase Ratio 1:1 1:5 1:1 1:15 1: Table 5: Characterization parameters of rifampicin nanoparticles Characterization parameters Drug content (%, w/ w) Drug Entrapment (%, w/w) Drug Loading (%, w/w) Process Yield (%) Entrapment Table 6: In vitro release study of rifampicin nanoparticles Avg Particle Size(nm) Result (Mean ± S.D., n=3) 26.69± ± ± ±2.67 Polydispersity Index Time (days) Release* % Cumulative Drug Release* ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±1.9 31± ± ± ± ± ±1.294
5 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) 212 Fig 1 - SEM image of Rifampicin nanoparticles Fig 2: Effect of drug / polymer ratio w/w on % drug entrapment and average particle size Entarpment :1 1:2 1:3 1:4 1:5 D rug/ Polymer R atio w/w % D rug Entrapment Average Particle Size(nm) A verage particle Size (nm) Fig 3: Effect of surfactant concentration on %drug entrapment and average particle size Entrapment Conc. of PVA solution (% w/v) Average Particle Size (nm) Entrapment Average Particle Size(nm)
6 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) 2121 Fig 4: Effect of Phase ratio on % drug entrapment and average particle size 8 8 Entrapmen Average Particle Size (nm) 1:1 1:5 1:1 1:15 1:2 Phase Ratio Entrapment Average Particle Size(nm) Fig 5: Effect of sonication time on average particle size and % drug entrapment Entrapment Sonication Time (min) Average Particle size (nm) Entrapment Average Particle Size(nm) Fig 6: % Cumulative release of drug in 3 days
7 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) 2122 Result and Discussion Preparation and optimization of nanoparticles On the basis of particle size, single emulsion evaporation techniques were optimized in single and double evaporation method, solvent diffusion and ionic interaction technique. Microemulsions are clear, thermodynamically stable, optically isotropic systems, obtained spontaneously by mixing surfactant, cosurfactant. The nanoparticles size is affected by the composition of the micro emulsion system, particularly by the surfactant and co-surfactant used, as well as by the experimental parameter. The nanoparticles size is affected processing parameters such as drug /polymer ratio, concentration of surfactant, phase ratio (organic phase/ aqueous phase) and sonication time. A drastic decrease in particle size and increase in percent drug entrapment was observed by increasing drug /polymer ratio. The size of nanoparticles decreased from 92nm to 43nm and per cent drug entrapment increased from 38.5% to 71.6% as on increasing drug/ polymer ratio from 1:1 to 1:4 w/w. There was no significant increase in particle size and percent drug entrapment as polymer concentration was increased. The results indicate the optimal drug/ polymer ratio to be 1:4 w/w for maximal nanoparticles formulation (Table 1, Fig. 2). Although a satisfactory yield was obtained at PLGA concentrations lower than 1:4 w/w, the value decreased with the increase in the PLGA concentration. This was probably caused by the increasing viscosity and hence resulting poor dispersibility of PLGA solution into the aqueous phase. The concentration of surfactant was optimized in order to obtain small nanoparticles with maximum percent drug entrapment. At concentration 3% w/v of PVA a minimum average particle size 38nm and maximum per cent drug entrapment 72.5% were recorded (Table 2). The mean nanoparticles size was found to decrease with increasing PVA concentration. The polydispersity index also decreased with increasing PVA concentration. It can be concluded that with increasing PVA concentration more PVA molecules overlap the surface of the droplets, providing increased protection of the latter against coalescence and resulting in smaller emulsion droplets. There was no significant difference in particle size and percent drug entrapment with PVA concentration 3.5% (w/v). Therefore 3% (w/v) PVA was recorded as optimized surfactant concentration (Fig. 3). The phase ratio (organic/ aqueous phase) was optimized in order to obtain nanoparticles selectively. At phase ratio 1:1 (v/v) of organic phase to aqueous phase a minimum average particle size 373nm and maximum per cent drug entrapment 74.8 % were recorded (Table 3). Upon increasing the phase ratio from 1:1 to 1:2 (v/v) an increase in average particle size 56nm was recorded, where as the per cent drug entrapment decreased considerably to 63.7% (Fig 4). It may be due to formation of some aggregates in the formulation. Sonication time was also optimized in order to achieve stable formulation with minimum average particle size and maximum per cent drug entrapment. Emulsification is carried out under high-shear stress to reduce the size of the emulsion droplets (directly related to the final size of nanoparticles). A stable nanoparticulte formulation was achieved after sonicating the formulation for 2 minutes in a pulsed manner with minimum average particle size and maximum percent drug entrapment, i.e. 36nm and 75.8% respectively (Table 4). A further increase in sonication time (24 minutes) resulted in an increase in particle size (39nm) and decrease in per cent drug entrapment (75.1%) (Fig 5) This may be due to the agglomeration of particles due to generation of surface charge. Nanoparticles were prepared by single emulsion evaporation method using optimized drug/ polymer ratio (1:4 w/w), PVA concentration (3% w/v), phase ratio (1:1 v/v) with sonication time 2 minutes (pulsating, 4% intensity). Size and shape morphology of nanoparticles Shape and surface morphology of prepared nanoparticles were evaluated by SEM. The study revealed that most of the nanoparticles were fairly spherical in shape. The surface of the particles showed a characteristic smoothness (Fig 1). The polydispersity index is a measure of the distribution of nanoparticles. Laser particle size analyzer yields the diameter of the bulk population (average) and a polydispersity index gives the distribution range from. to.5. Polydispersity index greater than.5 indicate the aggregation of particles. With increase in PVA concentration and sonication time, particle size and polydispersity index decrease. Therefore 3% (w/v) PVA concentration with sonication time 2 minutes (in apused manner) was used. Zeta Potential Study In general, particle aggregation is less likely to occur for charged particles (high zeta potential) due to electric repulsion. Lower zeta potential facilitates aggregation. The zeta potential of nanoparticles was found to be 11.6, which would not allow aggregation. Drug Loading, Encapsulation Efficiency, Drug Content and Process Yield Percent drug entrapment was found to be 75.8±2.16 %. Per cent drug entrapment increases with increase in surfactant concentration. This may be due to the stability of emulsion droplets. Drug content, drug loading and process yield was found to be
8 Akansha Tripathi et al /Int.J. PharmTech Res.21,2(3) ±.14% (w/w), 18.95±1.65% (w/w) and 56.8±2.67% (w/w) respectively and recorded in Table 5. In vitro release Studies The in-vitro release profile was biphasic with an initial burst release (7.266%) in 1 days attributed to surface associated drug, followed by a slower release phase as the entrapped drug slowly diffused out into the release medium (Figure 6) and 75.49% drug was released after 3 days. A low burst release of the drug was observed due to washing of prepared PLGA nanoparticles. There was a sustained release of drug at a constant rate. The concentration of drug was above MIC (invitro) even after 3 days. The adsorbed molecules on the surface of particles are rapidly desorbed when in contact with the dissolution medium. The diffusion of the drug, the erosion and swelling of polymer matrix and the degradation of polymer are the main mechanism for the drug release. Since degradation of PLGA is slow, the release of rifampicin from nanoparticles would mainly depend on the drug diffusion, in the time of experimental studies. Conclusion Conclusion drawn from the present study is that the nanoparticles may be a suitable device for administration of rifampicin. The encapsulation method was suitable for the preparation of nanoparticles because the system has nanometric size and regular shape. The development of a system whereby drugs could be administered in a single dose, that maintain active levels of the drug for a prolonged period would be the ideal system. Such a system has been developed in this study in the form of PLGA nanoparticles. The technology would improve patient compliance, the lack of which is the major reason for the development of multi-drug resistant strains of mycobacterium. Further studies, such as confocal microscopy and study of accumulation of drugs in infected macrophages can be done and is suggested as future scope of this work. References 1. Davis S.S. and Illum L., Int, J. Pharm., 1998, 176, Bala I., Hariharan S. and Kumar R., Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug. Carrier System, 24, 21, 5, Anderson J.M. and Shive M.S., Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres, Adv. Drug. Delivery Rev., 1997, 28, Dutt M., Khuller G.K., Chemothearpy of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice with a combination of isoniazid entrapped in poly (DLlactide-co-glycolide) microparticle. J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 21, 4, Dutt M., Khuller G.K., Therapeutics efficacy of poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide)-encapsulated antitubercular druds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection induced in mice, Antimicrob. agent and Chemother., 21, 45, Ain Q., Sharma S., Khuller G.K., Role of poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide) in development of a sustained oral drug delivery system for antitubercular drugs(s), Int. J. Pharm., 22, 239, Ain Q., Sharma S., Khuller G.K., Chemotherapeutic potential of orally administered microparticles containing isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide against experimental tuberculosis, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 23, 47, Pandey R., Zahoor A., Sharma S., Khuller G.K., Nanoparticle- encapsulated antitubercular drugs as a potential oral drug delivery system against experimental murine tuberculosis, Tuberculosis (Ed-inb), 23, 83, Vandervoort J. and Ludwig A., Biocompatible stabilizers in the preparation of PLGA nanoparticles: a factorial design study, Int. J. Pharm., 22, 238, Agnihotri S.M. and Vavia P.R. Diclofenac-loaded biopolymeric nanosuspension for ophthalmic application, Nanomedicine: NBM, 29, 5, Gupta H., Aqil M., Khar R.K., Ali A., Bhatnagar A., Mittal G., Sparfloxacin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for sustained ocular drug delivery, Nanomedicine : NBM, 21, 6, Pandey R., Zahoor A., Sharma S., Khuller G.K., Tuberculosis, 23, 83, Pillay V., Toit L.S., Danckwerts M.P., Tuberculosis chemotherapy: current drug delivery approaches, Respiratory Research, 26, 7, Govender J., Stolnik S., Garnett M.C., Illum L., Davis S.S., J. Control Rel., 1999, 57, *****
8. FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES
 8. FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES Preparation of capsule of modified solubility to protect the drug from degradation To protect the drug from degradation
8. FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES Preparation of capsule of modified solubility to protect the drug from degradation To protect the drug from degradation
Preparation And Characterization Of Simvastatin Nanosuspension By Homogenization Method
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.5, No.1, pp 193-197, Jan-Mar 2013 Preparation And Characterization Of Simvastatin Nanosuspension By Homogenization Method
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.5, No.1, pp 193-197, Jan-Mar 2013 Preparation And Characterization Of Simvastatin Nanosuspension By Homogenization Method
NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION USING COUNTER ION INDUCED GELIFICATION TECHNIQUE: IN VITRO CHLORAMPHENICOL RELEASE
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 3, Issue 3, 2011 Research Article NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION USING COUNTER ION INDUCED GELIFICATION TECHNIQUE: IN VITRO
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 3, Issue 3, 2011 Research Article NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION USING COUNTER ION INDUCED GELIFICATION TECHNIQUE: IN VITRO
Preparation and characterization of antidiabetic drug loaded polymeric nanoparticles
 Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2015, 7(12):398-404 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) ISSN 09-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX Preparation and
Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2015, 7(12):398-404 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) ISSN 09-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX Preparation and
NANO 243/CENG 207 Course Use Only
 L12: Drug Loading & Quantification May 15, 2018 1. Drug loading techniques 1.1 Physical approaches Nanprecipitation Single emulsion Double emulsion Encapsulation Remote loading 1.2 Chemical approaches
L12: Drug Loading & Quantification May 15, 2018 1. Drug loading techniques 1.1 Physical approaches Nanprecipitation Single emulsion Double emulsion Encapsulation Remote loading 1.2 Chemical approaches
Model based design of controlled release drug delivery systems
 Model based design of controlled release drug delivery systems Aditya Pareek, Praduman Arora, Venkataramana Runkana Copyright 2012 Tata Consultancy Services Limited 1 Why we need controlled drug delivery?
Model based design of controlled release drug delivery systems Aditya Pareek, Praduman Arora, Venkataramana Runkana Copyright 2012 Tata Consultancy Services Limited 1 Why we need controlled drug delivery?
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
SURFACE-MODIFIED BIODEGRADABLE NANOPARTICLES FOR TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY
 SURFACE-MODIFIED BIODEGRADABLE NANOPARTICLES FOR TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SEDYAKINA Nataliya E. 1, GORSHKOVA Marina Y. 2, MAKSIMENKO Olga O. 1, GELPERINA Svetlana E. 1 1 Nanosystem LTD., Moscow, Russian
SURFACE-MODIFIED BIODEGRADABLE NANOPARTICLES FOR TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SEDYAKINA Nataliya E. 1, GORSHKOVA Marina Y. 2, MAKSIMENKO Olga O. 1, GELPERINA Svetlana E. 1 1 Nanosystem LTD., Moscow, Russian
Preparation of PLGA nanoparticles using TPGS in the spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion method
 Journal of Experimental Nanoscience ISSN: 1745-8080 (Print) 1745-8099 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tjen20 Preparation of PLGA nanoparticles using TPGS in the spontaneous emulsification
Journal of Experimental Nanoscience ISSN: 1745-8080 (Print) 1745-8099 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tjen20 Preparation of PLGA nanoparticles using TPGS in the spontaneous emulsification
Continuous Microfluidic Synthesis of PLGA Nanoparticles by Micromixing
 Continuous Microfluidic Synthesis of PLGA Nanoparticles by Micromixing Dolomite s Nanoparticle Generation System Application Note Page Summary 2 Polymer Nanoparticles 3 Mechanism Micromixing Solvent Diffusion
Continuous Microfluidic Synthesis of PLGA Nanoparticles by Micromixing Dolomite s Nanoparticle Generation System Application Note Page Summary 2 Polymer Nanoparticles 3 Mechanism Micromixing Solvent Diffusion
D'Addio, SM; Chan, JG; Kwok, P; Prud'homme, R; Chan, HK
 Title Spray freeze dried large porous particles for nano drug delivery by inhalation Author(s) D'Addio, SM; Chan, JG; Kwok, P; Prud'homme, R; Chan, HK Citation The 2012 Respiratory Drug Delivery (RDD)
Title Spray freeze dried large porous particles for nano drug delivery by inhalation Author(s) D'Addio, SM; Chan, JG; Kwok, P; Prud'homme, R; Chan, HK Citation The 2012 Respiratory Drug Delivery (RDD)
Dicyclomine-loaded Eudragit -based Microsponge with Potential for Colonic Delivery: Preparation and Characterization
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical esearch, February 2010; 9 (1): 67-72 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001 Nigeria. All rights reserved. esearch Article
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical esearch, February 2010; 9 (1): 67-72 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001 Nigeria. All rights reserved. esearch Article
Continuous Microfluidic Synthesis of PLGA Microparticles by Droplet Method
 Microfluidic Synthesis PLGA Microparticles by Droplet Method - App. Note Continuous Microfluidic Synthesis of PLGA Microparticles by Droplet Method Dolomite s API encapsulation system for PLGA 20 µm to
Microfluidic Synthesis PLGA Microparticles by Droplet Method - App. Note Continuous Microfluidic Synthesis of PLGA Microparticles by Droplet Method Dolomite s API encapsulation system for PLGA 20 µm to
DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC AND THEIR COMBINATIONS AS DISPERSION CARRIERS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.1, pp 480-484, Jan-Mar 2010 DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.1, pp 480-484, Jan-Mar 2010 DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC
Formulation of 5-fluorouracil Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles By Emulsion Droplet Coalescence Method For Cancer Therapy
 Available Online at www.ijpba.info. International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(3):926-931 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 0976 3333 Formulation of 5-fluorouracil Loaded Chitosan
Available Online at www.ijpba.info. International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(3):926-931 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 0976 3333 Formulation of 5-fluorouracil Loaded Chitosan
Jacek Balcerzak, Maria Mucha
 ANALYSIS OF MODEL DRUG RELEASE KINETICS FROM COMPLEX MATRICES OF POLYLACTIDE-CHITOSAN Jacek Balcerzak, Maria Mucha Technical University of Lodz, Faculty of Process and Environmental Engineering Wolczanska
ANALYSIS OF MODEL DRUG RELEASE KINETICS FROM COMPLEX MATRICES OF POLYLACTIDE-CHITOSAN Jacek Balcerzak, Maria Mucha Technical University of Lodz, Faculty of Process and Environmental Engineering Wolczanska
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TOLBUTAMIDE MICROCAPSULES NAGESWARA RAO. G, RAMA KRISHNA. A Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TOLBUTAMIDE MICROCAPSULES NAGESWARA RAO. G, RAMA KRISHNA. A Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry,
RESEARCH ARTICAL PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SELF EMULSIFYING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF TELMISARTAN
 Available Online at www.pharmacia.ipsgwalior.org ISSN. No. 2229-4309 (Online), Vol. 3, Issue 1, July 2016 Pharmacia: An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences RESEARCH ARTICAL PREPARATION AND
Available Online at www.pharmacia.ipsgwalior.org ISSN. No. 2229-4309 (Online), Vol. 3, Issue 1, July 2016 Pharmacia: An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences RESEARCH ARTICAL PREPARATION AND
Formulation and Characterization of Repaglinide Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type II
 ISSN: 2250 2688 CODEN: CRPSBZ (USA) Formulation and Characterization of Repaglinide Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type II Nidhi Gautam and Ashwani Mishra Received: 31/11/2018
ISSN: 2250 2688 CODEN: CRPSBZ (USA) Formulation and Characterization of Repaglinide Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type II Nidhi Gautam and Ashwani Mishra Received: 31/11/2018
PRODUCTION OF PEG SUBMICRON PARTICLES BY THE SOLUTION ENHANCED DISPERSION WITH ENHANCED MASS TRANSFER BY ULTRASOUND IN SUPERCRITICAL CO 2 (SEDS-EM)
 PRODUCTION OF PEG SUBMICRON PARTICLES BY THE SOLUTION ENHANCED DISPERSION WITH ENHANCED MASS TRANSFER BY ULTRASOUND IN SUPERCRITICAL CO 2 (SEDS-EM) Heyang Jin, Sining Li, Daode Hu and Yaping Zhao* Email
PRODUCTION OF PEG SUBMICRON PARTICLES BY THE SOLUTION ENHANCED DISPERSION WITH ENHANCED MASS TRANSFER BY ULTRASOUND IN SUPERCRITICAL CO 2 (SEDS-EM) Heyang Jin, Sining Li, Daode Hu and Yaping Zhao* Email
The microparticle system has become an indispensable part of the controlled drug delivery fields for the past few decades since it can
 Microencapsulation Microencapsulation is a process or technique by which thin coatings can be applied reproducibly to small particles of solids, droplets of liquids, or dispersions, thus, forming microcapsules.
Microencapsulation Microencapsulation is a process or technique by which thin coatings can be applied reproducibly to small particles of solids, droplets of liquids, or dispersions, thus, forming microcapsules.
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION ENHANCEMENT OF BICALUTAMIDE SOLID BY DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION ENHANCEMENT OF BICALUTAMIDE SOLID BY DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Katare M. Kumar 1*, Jain A. Pal 2 and Kohli S 3 1. Shri Ram Institute of Technology (Pharmacy),
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION ENHANCEMENT OF BICALUTAMIDE SOLID BY DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Katare M. Kumar 1*, Jain A. Pal 2 and Kohli S 3 1. Shri Ram Institute of Technology (Pharmacy),
Nanocapsules are submicroscopic colloidal drug delivery system and are composed of an oily or an aqueous core surrounded
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preparation and characterization of diltiazem nanocapsules: Influence of various polymers G Ashwini Kumar, Amit Bhat, Shoba Rani 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Bharat Institute of Technology
RESEARCH ARTICLE Preparation and characterization of diltiazem nanocapsules: Influence of various polymers G Ashwini Kumar, Amit Bhat, Shoba Rani 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Bharat Institute of Technology
International Journal of Drug Discovery and Medical Research
 International Journal of Drug Discovery and Medical Research URL: www. ijddmr.org Email : editor@ijddmr.com, VOL. 1; 2;2012 ISSN 2278 4799 FORMULATION & EVALUATION OF METHOTREXATE LOADED NANOPARTICLE Jaimin
International Journal of Drug Discovery and Medical Research URL: www. ijddmr.org Email : editor@ijddmr.com, VOL. 1; 2;2012 ISSN 2278 4799 FORMULATION & EVALUATION OF METHOTREXATE LOADED NANOPARTICLE Jaimin
Formulation and Ocular Bioavailability of Certain Drugs from Ophthalmic Preparations
 Formulation and Ocular Bioavailability of Certain Drugs from Ophthalmic Preparations Thesis presented by Ghada Saad Ahmed El-Moursy B. Pharm. Mansoura University (2007) Submitted in Partial Fulfillment
Formulation and Ocular Bioavailability of Certain Drugs from Ophthalmic Preparations Thesis presented by Ghada Saad Ahmed El-Moursy B. Pharm. Mansoura University (2007) Submitted in Partial Fulfillment
Preparation of Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles via Supercritical Carbon-dioxide Extraction Of Emulsions.
 Preparation of Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles via Supercritical Carbon-dioxide Extraction Of Emulsions. Adejumoke Lara Ajiboye* a, Vivek Trivedi a, *, and John Mitchell a a University of Greenwich, Central
Preparation of Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles via Supercritical Carbon-dioxide Extraction Of Emulsions. Adejumoke Lara Ajiboye* a, Vivek Trivedi a, *, and John Mitchell a a University of Greenwich, Central
Biodegradable hollow fibres containing drug-loaded nanoparticles as controlled release systems
 Polymer International Polym Int 51:1464 1472 (2002) DOI: 10.1002/pi.1086 Biodegradable hollow fibres containing drug-loaded nanoparticles as controlled release systems Giovanni Polacco,* Maria Grazia Cascone,
Polymer International Polym Int 51:1464 1472 (2002) DOI: 10.1002/pi.1086 Biodegradable hollow fibres containing drug-loaded nanoparticles as controlled release systems Giovanni Polacco,* Maria Grazia Cascone,
Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials with multiple cavities
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Electronic Supplementary Infomaton Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Electronic Supplementary Infomaton Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials
6.0 Preparation and Evaluation of Tenofovir nanoparticles
 6.1 Introduction Nanoparticle technology has evolved over the years in pharmaceutical drug delivery. This technology has been used to targeting drug to different sites of the body as per requirements of
6.1 Introduction Nanoparticle technology has evolved over the years in pharmaceutical drug delivery. This technology has been used to targeting drug to different sites of the body as per requirements of
EXPERIMENTAL CONTRIBUTIONS IN THE SYNTHESIS OF PLGA NANOPARTICLES WITH EXCELLENT PROPERTIES FOR DRUG DELIVERY: INVESTIGATION OF KEY PARAMETERS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, Vol. 79, Iss. 2, 2017 ISSN 1454-2331 EXPERIMENTAL CONTRIBUTIONS IN THE SYNTHESIS OF PLGA NANOPARTICLES WITH EXCELLENT PROPERTIES FOR DRUG DELIVERY: INVESTIGATION OF KEY PARAMETERS
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B, Vol. 79, Iss. 2, 2017 ISSN 1454-2331 EXPERIMENTAL CONTRIBUTIONS IN THE SYNTHESIS OF PLGA NANOPARTICLES WITH EXCELLENT PROPERTIES FOR DRUG DELIVERY: INVESTIGATION OF KEY PARAMETERS
ELECTROSPRAY: NOVEL FABRICATION METHOD FOR BIODEGRADABLE POLYMERIC NANOPARTICLES FOR FURTHER APPLICATIONS IN DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 ELECTROSPRAY: NOVEL FABRICATION METHOD FOR BIODEGRADABLE POLYMERIC NANOPARTICLES FOR FURTHER APPLICATIONS IN DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ali Zarrabi a, Manouchehr Vossoughi b a Institute for Nanscience & Nanotechnology,
ELECTROSPRAY: NOVEL FABRICATION METHOD FOR BIODEGRADABLE POLYMERIC NANOPARTICLES FOR FURTHER APPLICATIONS IN DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ali Zarrabi a, Manouchehr Vossoughi b a Institute for Nanscience & Nanotechnology,
Preparation and characterization of genipin-cross-linked chitosan microparticles by water-in-oil emulsion solvent diffusion method
 Vol.2, No.10, 101-105 (10) http://dx.doi.org/10.423/ns.10.210131 Natural Science Preparation and characterization of genipin-cross-linked chitosan microparticles by water-in-oil emulsion solvent diffusion
Vol.2, No.10, 101-105 (10) http://dx.doi.org/10.423/ns.10.210131 Natural Science Preparation and characterization of genipin-cross-linked chitosan microparticles by water-in-oil emulsion solvent diffusion
Supplementary Information. Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro
 Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
Chiotsan Nanoparticles Loaded with Thiocolchicoside
 Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2012, 4(4):1619-1625 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) Chiotsan Nanoparticles Loaded with Thiocolchicoside
Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2012, 4(4):1619-1625 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) Chiotsan Nanoparticles Loaded with Thiocolchicoside
Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers
 Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers Arlin Jose Amali, a Shashi Singh, b Nandini Rangaraj,
Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers Arlin Jose Amali, a Shashi Singh, b Nandini Rangaraj,
In Vivo-In Vitro Evaluation of Solid Dispersion Containing Ibuprofen
 American Journal of Advanced Drug Delivery www.ajadd.co.uk In Vivo-In Vitro Evaluation of Solid Dispersion Containing Ibuprofen Original Article Sachin K. Gawai*, Subhash V. Deshmane, R. N. Purohit, Kailash
American Journal of Advanced Drug Delivery www.ajadd.co.uk In Vivo-In Vitro Evaluation of Solid Dispersion Containing Ibuprofen Original Article Sachin K. Gawai*, Subhash V. Deshmane, R. N. Purohit, Kailash
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fully acid-degradable biocompatible polyacetal microparticles for drug delivery Sergey E. Paramonov, Eric M. Bachelder, Tristan T. Beaudette, Stephany M. Standley, Cameron C. Lee,
Supporting Information Fully acid-degradable biocompatible polyacetal microparticles for drug delivery Sergey E. Paramonov, Eric M. Bachelder, Tristan T. Beaudette, Stephany M. Standley, Cameron C. Lee,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and characterization of clarithromycin based nanoparticulate drug delivery system
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and characterization of clarithromycin based nanoparticulate drug delivery system Rajkumari Thagele*, Ashwani Mishra and A.K.Pathak Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and characterization of clarithromycin based nanoparticulate drug delivery system Rajkumari Thagele*, Ashwani Mishra and A.K.Pathak Department
2 Preparation of hollow spheres, microcapsules and microballoons by surfactant free emulsion templating
 2 Preparation of hollow spheres, microcapsules and microballoons by surfactant free emulsion templating We report on the synthesis of new types of monodisperse, micrometer-sized hollow particles obtained
2 Preparation of hollow spheres, microcapsules and microballoons by surfactant free emulsion templating We report on the synthesis of new types of monodisperse, micrometer-sized hollow particles obtained
Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics. Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi
 Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Gold Nanoparticle Conjugated PLGA-PEG-SA-PEG-PLGA Multiblock Copolymer Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, In-vivo Release of Rifampicin
 Gold Nanoparticle Conjugated PLGA-PEG-SA-PEG-PLGA Multiblock Copolymer Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, In-vivo Release of Rifampicin Mani Gajendiran, a Sheik Mohammed Jainuddin Yousuf, b Vellaichamy
Gold Nanoparticle Conjugated PLGA-PEG-SA-PEG-PLGA Multiblock Copolymer Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, In-vivo Release of Rifampicin Mani Gajendiran, a Sheik Mohammed Jainuddin Yousuf, b Vellaichamy
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Near-infrared Light Triggerable Deformation-free Polysaccharide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Near-infrared Light Triggerable Deformation-free Polysaccharide
Modelling of drug release from ensembles of aspirin microcapsules of certain particle size distribution
 Eichie & Okor, 23 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, June 23; 2 (1): 137-145 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria. All rights reserved. Available
Eichie & Okor, 23 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, June 23; 2 (1): 137-145 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria. All rights reserved. Available
Different Biodegradable Silica Structures In Drug Delivery. Mika Jokinen
 Different Biodegradable Silica Structures In Drug Delivery Mika Jokinen & Different Morphologies of Biodegradable Silica - Several levels of morphology ; different forms & structures - monoliths, fibers,
Different Biodegradable Silica Structures In Drug Delivery Mika Jokinen & Different Morphologies of Biodegradable Silica - Several levels of morphology ; different forms & structures - monoliths, fibers,
Continuous Synthesis of Monodisperse PLGA Particles using Droplets
 Continuous Synthesis of Monodisperse PLGA Particles using Droplets Droplet system for controlled and reproducible encapsulation of API in uniform polymer beads Version 1.2 21/04/2017 Pavel Abdulkin and
Continuous Synthesis of Monodisperse PLGA Particles using Droplets Droplet system for controlled and reproducible encapsulation of API in uniform polymer beads Version 1.2 21/04/2017 Pavel Abdulkin and
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Preparation, optimization and characterization of PLGA nanoparticle R. S. Dangi 1 *and S. Shakya 2 1, Central India Institute of Pharmacy, Indore, (M.P.)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Preparation, optimization and characterization of PLGA nanoparticle R. S. Dangi 1 *and S. Shakya 2 1, Central India Institute of Pharmacy, Indore, (M.P.)
A study on the effects of different surfactants on morphology and drug release of Repaglinide Microspheres
 August - September 2017; 6(5): 2786-2792 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy & Life Science An International Open access peer reviewed journal ISSN (P): 2393-932X, ISSN (E): 2278-0238
August - September 2017; 6(5): 2786-2792 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy & Life Science An International Open access peer reviewed journal ISSN (P): 2393-932X, ISSN (E): 2278-0238
CHARACTERISATION OF NANOPARTICLE THROUGH SEM, FTIR, XRD & DSC
 Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur From the SelectedWorks of Ajit Behera 2011 CHARACTERISATION OF NANOPARTICLE THROUGH SEM, FTIR, XRD & DSC Ajit Behera, Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur From the SelectedWorks of Ajit Behera 2011 CHARACTERISATION OF NANOPARTICLE THROUGH SEM, FTIR, XRD & DSC Ajit Behera, Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Copper nanoparticulates in guar-gum: a recyclable catalytic system for the Huisgen[3+2]-Cycloaddition of Azides and Alkynes without additives under ambient conditions Ajeet Kumar,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Copper nanoparticulates in guar-gum: a recyclable catalytic system for the Huisgen[3+2]-Cycloaddition of Azides and Alkynes without additives under ambient conditions Ajeet Kumar,
EFFECT OF PROCESS AND FORMULATION PARAMETERS ON PREDNISOLONE LOADED PLGA SUSTAINED RELEASE NANOPARTICLES: QUALITY BY DESIGN APPROACH
 Page5111 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 014 ISSN NO: 31-6876 EFFECT OF PROCESS AND FORMULATION PARAMETERS ON PREDNISOLONE LOADED PLGA SUSTAINED RELEASE NANOPARTICLES: QUALITY BY DESIGN
Page5111 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 014 ISSN NO: 31-6876 EFFECT OF PROCESS AND FORMULATION PARAMETERS ON PREDNISOLONE LOADED PLGA SUSTAINED RELEASE NANOPARTICLES: QUALITY BY DESIGN
IJPRD, 2013; Vol 5(03): May-2013 ( ) International Standard Serial Number
 IJPRD, 2013; Vol 5(03): May-2013 (039 045) International Standard Serial Number 0974 9446 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IJPRD, 2013; Vol 5(03): May-2013 (039 045) International Standard Serial Number 0974 9446 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
295 J App Pharm 03(03): (2011) Nayak et al., 2011 COMPARATIVE STABILITY STUDY OF METRONIDAZOLE IN AQUEOUS AND NON AQUEOUS VEHICLE
 295 J App Pharm 03(03): 295-300 (2011) Nayak et al., 2011 Research Article COMPARATIVE STABILITY STUDY OF METRONIDAZOLE IN AQUEOUS AND NON AQUEOUS VEHICLE Satish Nayak, D. C. Goupale*, Atul Dubey and Vipin
295 J App Pharm 03(03): 295-300 (2011) Nayak et al., 2011 Research Article COMPARATIVE STABILITY STUDY OF METRONIDAZOLE IN AQUEOUS AND NON AQUEOUS VEHICLE Satish Nayak, D. C. Goupale*, Atul Dubey and Vipin
Microencapsulation of fish liver oil by complex coacervation method with gelatin-arabic gum
 Microencapsulation of fish liver oil by complex coacervation method with gelatin-arabic gum Abstract Hiep X. Nguyen 1, Chien N. Nguyen 1,* 1 Department of Pharmaceutial Industry, Hanoi University of Pharmacy,
Microencapsulation of fish liver oil by complex coacervation method with gelatin-arabic gum Abstract Hiep X. Nguyen 1, Chien N. Nguyen 1,* 1 Department of Pharmaceutial Industry, Hanoi University of Pharmacy,
PLGA nanoparticles containing praziquantel: effect of formulation variables on size distribution
 International Journal of Pharmaceutics 290 (2005) 137 144 PLGA nanoparticles containing praziquantel: effect of formulation variables on size distribution Rubiana M. Mainardes, Raul C. Evangelista Programa
International Journal of Pharmaceutics 290 (2005) 137 144 PLGA nanoparticles containing praziquantel: effect of formulation variables on size distribution Rubiana M. Mainardes, Raul C. Evangelista Programa
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Encapsulation. Battelle Technology. Introduction
 Encapsulation Introduction The encapsulation methods reported in the literature 1-7 for the production of microcapsules are generally achieved using one of the following techniques: 1. Phase separation
Encapsulation Introduction The encapsulation methods reported in the literature 1-7 for the production of microcapsules are generally achieved using one of the following techniques: 1. Phase separation
CEINT/NIST PROTOCOL REPORTING GUIDELINES FOR THE PREPARATION OF AQUEOUS NANOPARTICLE DISPERSIONS FROM DRY MATERIALS. Ver. 2.0
 CEINT/NIST PROTOCOL REPORTING GUIDELINES FOR THE PREPARATION OF AQUEOUS NANOPARTICLE DISPERSIONS FROM DRY MATERIALS Ver. 2.0 July 8, 2010 Protocol Contributors: J. S. Taurozzi 1, V. A. Hackley 1, M. R.
CEINT/NIST PROTOCOL REPORTING GUIDELINES FOR THE PREPARATION OF AQUEOUS NANOPARTICLE DISPERSIONS FROM DRY MATERIALS Ver. 2.0 July 8, 2010 Protocol Contributors: J. S. Taurozzi 1, V. A. Hackley 1, M. R.
often display a deep green color due to where the SPR occurs (i.e., the wavelength of light that interacts with this specific morphology).
 Synthesis-Dependent Catalytic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Nanoscience is the study of materials that have dimensions, intuitively, on the nanoscale, typically between 1 100 nm. This field has received
Synthesis-Dependent Catalytic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Nanoscience is the study of materials that have dimensions, intuitively, on the nanoscale, typically between 1 100 nm. This field has received
Preparation and Characterization of Nisoldipine Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method
 Preparation and Characterization of Nisoldipine Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method Nepolean.R 1, Narayanan.N 2 Subramaniyan.N 3, Venkateswaran.K 3 and Vinoth.J 3 1 Thanthai Roever College of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Characterization of Nisoldipine Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method Nepolean.R 1, Narayanan.N 2 Subramaniyan.N 3, Venkateswaran.K 3 and Vinoth.J 3 1 Thanthai Roever College of Pharmacy,
NRT 16: Hetero-structured Polymer Nanoparticles for Toner Materials
 NRT-16, Quarterly report, Mar2009-May2009, Page 1 of 9 NRT 16: Hetero-structured Polymer Nanoparticles for Toner Materials Aasheesh Srivastava and Galen D. Stucky Background and Motivation: The commercial
NRT-16, Quarterly report, Mar2009-May2009, Page 1 of 9 NRT 16: Hetero-structured Polymer Nanoparticles for Toner Materials Aasheesh Srivastava and Galen D. Stucky Background and Motivation: The commercial
SUPERCRITICAL ANTI SOLVENT PRECIPITATION OF CAROTENOIDS FROM AN EMULSION. F. Mattea, A.Martín, C. Azpeleta, A. Serna, M.J. Cocero
 SUPERCRITICAL ANTI SOLVENT PRECIPITATION OF CAROTENOIDS FROM AN EMULSION F. Mattea, A.Martín, C. Azpeleta, A. Serna, M.J. Cocero High Pressure Process Research Group, Department of Chemical Engineering
SUPERCRITICAL ANTI SOLVENT PRECIPITATION OF CAROTENOIDS FROM AN EMULSION F. Mattea, A.Martín, C. Azpeleta, A. Serna, M.J. Cocero High Pressure Process Research Group, Department of Chemical Engineering
Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water. (a) A typical photograph of fullerence (C60), C60S nanoparticles,
Supplementary Figure 1. Fullerence has poor solubility in water while the C60S and LC60S nanoparticles can be stably dispersed in water. (a) A typical photograph of fullerence (C60), C60S nanoparticles,
Development and characterization of Irinotecan loaded colloidal drug delivery system
 Development and characterization of Irinotecan loaded colloidal drug delivery system Prakash Goudanavar 1*, Shiva Kumar 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sri Adichunchanagiri College of Pharmacy, B.G. Nagar-571448,
Development and characterization of Irinotecan loaded colloidal drug delivery system Prakash Goudanavar 1*, Shiva Kumar 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sri Adichunchanagiri College of Pharmacy, B.G. Nagar-571448,
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic supplementary information Surface plasmon resonance enhanced upconversion luminescence in aqueous media for TNT selective detection Nina Tu and Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource
Electronic supplementary information Surface plasmon resonance enhanced upconversion luminescence in aqueous media for TNT selective detection Nina Tu and Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource
Preparation of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by modified spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion method
 International Journal of Pharmaceutics 187 (1999) 143 152 www.elsevier.com/locate/promis Preparation of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by modified spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion
International Journal of Pharmaceutics 187 (1999) 143 152 www.elsevier.com/locate/promis Preparation of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by modified spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion
Dissolution study and method validation of alprazolam by high performance liquid chromatography method in pharmaceutical dosage form
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-252 Dissolution study and method validation of alprazolam by high performance liquid chromatography method in pharmaceutical dosage form Abstract Rele Rajan
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-252 Dissolution study and method validation of alprazolam by high performance liquid chromatography method in pharmaceutical dosage form Abstract Rele Rajan
PHRC 4110 Pharmaceutics I
 CO01: Use interpretive tools for proper data handling CO01.01: Describe basic mathematics and statistic to interpret pharmaceutical data CO01.02: Work with exponents, powers, roots, logarithms, and antilogarithms
CO01: Use interpretive tools for proper data handling CO01.01: Describe basic mathematics and statistic to interpret pharmaceutical data CO01.02: Work with exponents, powers, roots, logarithms, and antilogarithms
Bound polymer layer in nanocomposites
 Supplementary Information Bound polymer layer in nanocomposites Nicolas Jouault, Joseph F. Moll, Dong Meng,Kendra Windsor, Stacy Ramcharan, Clare Kearney, Sanat K. Kumar * Department of Chemical Engineering,
Supplementary Information Bound polymer layer in nanocomposites Nicolas Jouault, Joseph F. Moll, Dong Meng,Kendra Windsor, Stacy Ramcharan, Clare Kearney, Sanat K. Kumar * Department of Chemical Engineering,
Research Article. Dissolution Study of Oxolamine Citrate by UV Spectrophotometric Method in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):108-112 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Dissolution Study of Oxolamine Citrate by UV Spectrophotometric
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):108-112 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Dissolution Study of Oxolamine Citrate by UV Spectrophotometric
Controlled Release Theory
 Controlled Release Theory Last time: tailoring the structure of degradable polymers Fundamental concepts in controlled release Today: Theory of degradable polymer-based controlled release Reading: Charlier
Controlled Release Theory Last time: tailoring the structure of degradable polymers Fundamental concepts in controlled release Today: Theory of degradable polymer-based controlled release Reading: Charlier
Supporting Information. Golf ball-shaped PLGA microparticles with internal pores fabricated by simple O/W emulsion
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information Golf ball-shaped PLGA microparticles with internal pores fabricated by simple O/W emulsion Mi Ri Kim, a Seungwoo Lee, b Jung-Ki
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information Golf ball-shaped PLGA microparticles with internal pores fabricated by simple O/W emulsion Mi Ri Kim, a Seungwoo Lee, b Jung-Ki
Formulation and Characterization of Asenapine Maleate Nanoparticles
 Research Article Formulation and Characterization of Asenapine Maleate Nanoparticles Appanna Chowdary K*, Navya Lakshmi Raju Suravarapu, Swathi Meddala St. Ann s College of Pharmacy, Andhra University,
Research Article Formulation and Characterization of Asenapine Maleate Nanoparticles Appanna Chowdary K*, Navya Lakshmi Raju Suravarapu, Swathi Meddala St. Ann s College of Pharmacy, Andhra University,
King Saud University College of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics. Biopharmaceutics PHT 414. Laboratory Assignments 2010 G 1431 H
 King Saud University College of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Biopharmaceutics PHT 414 Laboratory Assignments 20 G 1431 H Department of Pharmaceutics Biopharmaceutics PHT -414 Laboratory Assignments
King Saud University College of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Biopharmaceutics PHT 414 Laboratory Assignments 20 G 1431 H Department of Pharmaceutics Biopharmaceutics PHT -414 Laboratory Assignments
Development of NIR Bioimaging Systems
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series 16 (28) 1223 doi:1.188/1742-6596/16/1/1223 Development of NIR Bioimaging Systems Kohei SOGA 1, Takashi TSUJI 1, Fumio TASHIRO 1, Joe CHIBA 1 Motoi OISHI 2, Keitaro
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 16 (28) 1223 doi:1.188/1742-6596/16/1/1223 Development of NIR Bioimaging Systems Kohei SOGA 1, Takashi TSUJI 1, Fumio TASHIRO 1, Joe CHIBA 1 Motoi OISHI 2, Keitaro
ph-triggered aggregation of responsive polymer-stabilized colloids and the reversible formation of porous scaffolds
 Supporting Information: ph-triggered aggregation of responsive polymer-stabilized colloids and the reversible formation of porous scaffolds Robert T. Woodward, Christopher Hight, Ufuk Yildiz, Nicolas Schaeffer,
Supporting Information: ph-triggered aggregation of responsive polymer-stabilized colloids and the reversible formation of porous scaffolds Robert T. Woodward, Christopher Hight, Ufuk Yildiz, Nicolas Schaeffer,
Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering for Particle Size Determination
 www.horiba.com/us/particle Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering for Particle Size Determination 2016 HORIBA, Ltd. All rights reserved. 1 Sizing Techniques 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10
www.horiba.com/us/particle Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering for Particle Size Determination 2016 HORIBA, Ltd. All rights reserved. 1 Sizing Techniques 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10
Research Article DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FORMULATIONS OF THEOPHYLLINE USING NATURAL POLYMERS
 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2013, Vol. 2, No.6, pp 721-725 ISSN: 2278-0238 Research Article
International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2013, Vol. 2, No.6, pp 721-725 ISSN: 2278-0238 Research Article
Seeing the Nano-scale: Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis HVM MNT Expo 2006 Oxford. Jeremy Warren CEO, NanoSight Ltd
 Seeing the Nano-scale: Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis HVM MNT Expo Oxford Jeremy Warren CEO, NanoSight Ltd 1 NanoSight Particle Characterisation at Nano-scale: Electron Microscopy PCS (Photon Correlation
Seeing the Nano-scale: Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis HVM MNT Expo Oxford Jeremy Warren CEO, NanoSight Ltd 1 NanoSight Particle Characterisation at Nano-scale: Electron Microscopy PCS (Photon Correlation
Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 19, No. 5 (2007), 3455-3460 Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl V.K. CHATAP, D.K. SHARMA*, ANIL MIDDHA, R.D. GUPTA, VIPIN SAINI, MAHENDRA SHIRADKAR
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 19, No. 5 (2007), 3455-3460 Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl V.K. CHATAP, D.K. SHARMA*, ANIL MIDDHA, R.D. GUPTA, VIPIN SAINI, MAHENDRA SHIRADKAR
Physicochemical Characterization of Acyclovir Topical Semisolid Dosage Forms Towards TCS Validation Flavian Ștefan Rădulescu, Dalia Simona Miron
 Physicochemical Characterization of Acyclovir Topical Semisolid Dosage Forms Towards TCS Validation Flavian Ștefan Rădulescu, Dalia Simona Miron University of Medicine and Pharmacy Carol Davila, Bucharest,
Physicochemical Characterization of Acyclovir Topical Semisolid Dosage Forms Towards TCS Validation Flavian Ștefan Rădulescu, Dalia Simona Miron University of Medicine and Pharmacy Carol Davila, Bucharest,
Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Víctor Sebastian, M. Pilar Calatayud, Gerardo F. Goya
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Víctor Sebastian, M. Pilar Calatayud, Gerardo F. Goya
Preparation and characterization of PLGA particles for subcutaneous controlled drug release by membrane emulsification
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 61 (2008) 199 207 Preparation and characterization of PLGA particles for subcutaneous controlled drug release by membrane
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 61 (2008) 199 207 Preparation and characterization of PLGA particles for subcutaneous controlled drug release by membrane
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Polymer-coated spherical mesoporous silica for ph-controlled delivery of insulin Sae Rom Choi a,, Dong-jin Jang b,, Sanghyun Kim a, Sunhyung An c, Jinwoo Lee c, Euichaul
Electronic Supplementary Information Polymer-coated spherical mesoporous silica for ph-controlled delivery of insulin Sae Rom Choi a,, Dong-jin Jang b,, Sanghyun Kim a, Sunhyung An c, Jinwoo Lee c, Euichaul
Zetasizer Nano ZSP: A Perfect Tool For Life Science Applications
 Zetasizer Nano ZSP: A Perfect Tool For Life Science Applications Dr Mike Kaszuba Technical Support Manager E-mail: michael.kaszuba@malvern.com Contents Zetasizer Nano ZSP Software Enhancements Protein
Zetasizer Nano ZSP: A Perfect Tool For Life Science Applications Dr Mike Kaszuba Technical Support Manager E-mail: michael.kaszuba@malvern.com Contents Zetasizer Nano ZSP Software Enhancements Protein
Using the Zetasizer Nano to optimize formulation stability
 Using the Zetasizer Nano to optimize formulation stability PARTICLE SIZE ZETA POTENTIAL The top five ways you can use the Zetasizer Nano to help improve the stability of your formulation. Formulation development
Using the Zetasizer Nano to optimize formulation stability PARTICLE SIZE ZETA POTENTIAL The top five ways you can use the Zetasizer Nano to help improve the stability of your formulation. Formulation development
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences V1(2)2010
 P. S.GOUDANAVAR *, R.S.BAGALI, CHANDRASHEKHARA.S AND S. M.PATIL K.L.E s College of Pharmacy, Nipani, Karnataka, India * Corresponding Author p.goudanavar@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT Sustained release oral
P. S.GOUDANAVAR *, R.S.BAGALI, CHANDRASHEKHARA.S AND S. M.PATIL K.L.E s College of Pharmacy, Nipani, Karnataka, India * Corresponding Author p.goudanavar@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT Sustained release oral
Preparation and characterization of PLGA. PLGA particles for subcutaneous controlled drug release by membrane emulsification.
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Preparation and characterization of PLGA particles for subcutaneous controlled drug release by membrane emulsification This item was submitted to Loughborough
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Preparation and characterization of PLGA particles for subcutaneous controlled drug release by membrane emulsification This item was submitted to Loughborough
Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization OF Ethylcellulose Microspheres
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol. 3, No., pp 775-783, April-June 011 Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization OF Ethylcellulose Microspheres
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol. 3, No., pp 775-783, April-June 011 Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization OF Ethylcellulose Microspheres
Droplet based microfluidic fabrication of designer microparticles for encapsulation applications
 Droplet based microfluidic fabrication of designer microparticles for encapsulation applications Tiantian Kong, Jun Wu, Michael To, Kelvin Wai Kwok Yeung, Ho Cheung Shum et al. Citation: Biomicrofluidics
Droplet based microfluidic fabrication of designer microparticles for encapsulation applications Tiantian Kong, Jun Wu, Michael To, Kelvin Wai Kwok Yeung, Ho Cheung Shum et al. Citation: Biomicrofluidics
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dual nanocomposite multihollow polymer microspheres prepared by suspension polymerization based on a multiple Pickering emulsion Quanxing Gao, Chaoyang Wang,* Hongxia Liu, Xinxing
Supporting Information Dual nanocomposite multihollow polymer microspheres prepared by suspension polymerization based on a multiple Pickering emulsion Quanxing Gao, Chaoyang Wang,* Hongxia Liu, Xinxing
International Journal of Pharmacy
 International Journal of Pharmacy Journal Homepage: http://www.pharmascholars.com Original Article CODEN: IJPNL6 Formulation and Evaluation of Sildenafil Citrate Nanosuspension M. Sreenivasulu Reddy, A.
International Journal of Pharmacy Journal Homepage: http://www.pharmascholars.com Original Article CODEN: IJPNL6 Formulation and Evaluation of Sildenafil Citrate Nanosuspension M. Sreenivasulu Reddy, A.
Particle Size Analysis with Differential Centrifugal Sedimentation. Marc Steinmetz Sales & Support Manager CPS Instruments Europe
 Particle Size Analysis with Differential Centrifugal Sedimentation Marc Steinmetz Sales & Support Manager CPS Instruments Europe What is important to you from a particle sizing technique? Many people talk
Particle Size Analysis with Differential Centrifugal Sedimentation Marc Steinmetz Sales & Support Manager CPS Instruments Europe What is important to you from a particle sizing technique? Many people talk
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A HPLC METHOD FOR IN-VIVO STUDY OF DICLOFENAC POTASSIUM
 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 2 (Research Article) Received on 28 September, 2012; received in revised form, 24 November, 2012; accepted, 23 January, 2013 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A HPLC METHOD FOR
IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 2 (Research Article) Received on 28 September, 2012; received in revised form, 24 November, 2012; accepted, 23 January, 2013 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A HPLC METHOD FOR
SOLID DISPERSION OF POORLY WATER SOLUBLE DRUGS EARLY PROMISES SUBSEQUENT ELECTROSPUN AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSIONS OF POORLY WATER
 PROBLEMS AND RECENT BREAKTHROUGHS SOLID DISPERSION OF POORLY PDF ELECTROSPUN AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSIONS OF POORLY WATER EVALUATION OF AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSION PROPERTIES USING 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 solid
PROBLEMS AND RECENT BREAKTHROUGHS SOLID DISPERSION OF POORLY PDF ELECTROSPUN AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSIONS OF POORLY WATER EVALUATION OF AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSION PROPERTIES USING 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 solid
Magnetic Nano Particles for In-Vitro Diagnostics
 Magnetic Nano Particles for In-Vitro Diagnostics has utilized its many years of experience in creating a Magnetic Nano Particles Developer Kit for in-vitro biomedical applications. The kit offers a unique
Magnetic Nano Particles for In-Vitro Diagnostics has utilized its many years of experience in creating a Magnetic Nano Particles Developer Kit for in-vitro biomedical applications. The kit offers a unique
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications
 Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Sci Pharm
 Sci Pharm www.scipharm.at Conference article Open Access Curcumin-Loaded PLA Nanoparticles: Formulation and Physical Evaluation Heni RACHMAWATI * 1, Yulia L. YANDA 1, Annisa RAHMA 1, Nobuyuki MASE 2 1
Sci Pharm www.scipharm.at Conference article Open Access Curcumin-Loaded PLA Nanoparticles: Formulation and Physical Evaluation Heni RACHMAWATI * 1, Yulia L. YANDA 1, Annisa RAHMA 1, Nobuyuki MASE 2 1
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND CHEMICAL SCIENCES
 Research Article An In-Vitro Evaluation for the Effect of Β-Cyclodextrin and PVP-K 3 on Drug Release Pattern of Sertraline Hydrochloride Deepa Warrier 1, Aanna Zagade 1, Amir Shaikh 2*, Yogesh Pawar 2
Research Article An In-Vitro Evaluation for the Effect of Β-Cyclodextrin and PVP-K 3 on Drug Release Pattern of Sertraline Hydrochloride Deepa Warrier 1, Aanna Zagade 1, Amir Shaikh 2*, Yogesh Pawar 2
