Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields
|
|
|
- Lesley Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields Victor G Bezchastnov victor@tcpciuni-heidelbergde Theoretische Chemie Physikalisch-Chemisches Institut Universität Heidelberg INF 229, D Heidelberg, Germany Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p1/21
2 Ion Cyclotron Frequency Ω = QB/M Acomplexioninastationaryanduniformmagneticfieldcanexhibita varietyofcyclotronfrequenciesasaresultofthecouplingofcmtothe internal structure The effects of the coupling are important when Ω is not negligible compared to the binding energy ε for the infinitely heavy ion Negative( magnetically induced) ions: laboratory field strengths VG Bezchastnov, P Schmelcher and LS Cederbaum, Phys Rev A, 2007, 75, Positiveions(He + ):astrophysicallystrongfields GG Pavlov and VG Bezchastnov, Ap J Lett, 2005, 635, L61 Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p2/21
3 Landau Levels, Cyclotron Transition Energies and Oscillator Strengths Landau levels E N = E N=0 + N Ω N = 0, 1, 2, Selection rules N N ± 1 N x ± iy N ± 1 Absorption N N + 1: Transitionenergies Ω N = E N+1 E N = Ω Oscillatorstrengths F N = (Q 2 /M)(2N + 1) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p3/21
4 Atomic Ions: Quantum States with CM Motion Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p4/21
5 Atomic Ions: Hamiltonian and Integrals of Motion H = 1 2M ( P cm Q 2 B R cm) 2 + H rel + W H rel = 1 2M 0 W = α M α 1 = 1 Q M [ (p i + 1 ) ] 2 2 α 1 B r i i [ B ( ) 2 1 M ( P cm Q )] 2 B R cm i i r i,, α 2 = 1 Q M 2, α = 1 + Q M ( p i 1 2 α 2 B r i ) 2 + V, K = P cm + Q 2 B R cm K 2 = B(2N 0 + 1) N 0 = 0, 1, 2, L = P cm R cm + J = N 0 + L i p i r i L z = (Q/ Q )L L = 0, ±1, ±2, Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p5/21
6 Perturbation Analysis Incorporating the integrals of motion: E = E sj s = 0, 1,, J = σs, σs + 1,, σ = Q/ Q NocouplingtoCM(W = 0): Energies E sj = ε s + Ω(J σs), Ω = B/M Ioncyclotronabsorption sj s, J + 1 Transitionenergies Ω J = Ω Oscillatorstrengths F J = (Q 2 /M)(2J + s + 1) Including coupling: Energies E sj = E s, s + Ω eff (J σs), Ω eff = B/M eff E s, s > ε s, Ω eff < Ω Ioncyclotronabsorption sj s, J + 1 Transitionenergies ω J = (M/M eff ) Ω Oscillatorstrengths f J = (M/M eff ) 3 F J Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p6/21
7 Field-Induced Formation of Bound Anions BoundstatesoftheHamiltonian H rel formtheinfinitemanifold JE Avron, IW Herbst and B Simon, Commun Math Phys, 1981, 79, 529 Electron affinities binding energies of neutrals Exchange effects are not important z B r L extra electron guiding center A neutral atom is a static attractive center r c V (r) = α/(2r 4 ) The excess electron is confined in the plane transverse to the magnetic field l z isanintegralofmotion Bindingofanextraelectroncanbetreatedas a1dproblem,forthemotionoftheguiding centerr c alongthemagneticfield neutral atom Theelectroncanbeattachedwithdifferent l z = infinitemanifoldof bound states Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p7/21
8 Magnetically Induced Anions: Static and Beyond Bindingenergiesfor H rel :analyticalestimates l z = s, s = 0, 1, 2, I s = V s(z)dz < 0 = ε s = µi 2 s/2 Asaresult: ε 0 = 031 α 2 B 2, s = 0, ε s = α 2 B 3 δ 2 s, s = 1, 2,, δ 1 = 1, δ s = [1 (15/s)]δ s 1, s = 2, 3, ImpactofthecouplingtoCM(M Xe = , α Xe = 2729) ( ) ε 0 α 2 Ω = 237 M Xe 103 α Xe M ( ) ε 1 α 2 Ω = 039 M Xe α Xe M ( B 100 T B 100 T, ) 2 Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p8/21
9 Moving Anions: Quantum States Including coupling: E sj = E s, s + Ω eff (J + s) Ω eff = B/M eff s = 1, B = 100T atom ε s,mhz Ω,MHz Xe Mg Hg s = 0, B = 10T atom ε s,mhz Ω,MHz Ar Be Xe s=1, B=100 T: s=0,b=10t: Mg Hg Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p9/21
10 Moving Anions: Cyclotron Transitions Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p10/21
11 Cs at B = 100T Ω = 115MHz ε 1 = 9960MHz ε 2 = 623MHz ε 3 = 156MHz Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p11/21
12 He + (Z = 2)at B = T(γ = 2000) Strong field regime: γ = B/ T 1 Tightly-bound states: ε 0 Z 2 Ry [ ln(γ/z 2 ) ] 2 Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p12/21
13 He + (Z = 2)at B = G(γ = 2000) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p13/21
14 He + (Z = 2)at B = G(γ = 2000) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p14/21
15 He + (Z = 2)at B = G(γ = 2000) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p15/21
16 He + (Z = 2)at B = G(γ = 2000) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p16/21
17 He + (Z = 2)at B = G(γ = 2000) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p17/21
18 He + (Z = 2)at B = G(γ = 10000) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p18/21
19 He + atmagnetar-scalefields X-ray-dim isolated neutron stars sjν-states ν = 0 tightly-bound ν = 1, 2, H-like Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p19/21
20 He + atmagnetar-scalefields Broadabsorptionfeaturesat03-05keV Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p20/21
21 Conclusions Bound-ion cyclotron transitions are an interesting area of research For negative magnetically induced ions they directly relate to detecting that these ions do exist Forpositive(egHe + )ionsatsuperstrongmagneticfieldstheycanbe relevant for interpretation of the radiation from isolated neutron stars (eg magnetars) Magnetic Binding and Cyclotron Transitions of the Ions: Applications to Laboratory and Astrophysically Strong Magnetic Fields p21/21
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 2000
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 2000 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 2000](/thumbs/72/67399550.jpg) Bound states of negatively charged ions induced by a magnetic field arxiv:physics/0006016v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 000 Victor G. Bezchastnov, Peter Schmelcher, and Lorenz S. Cederbaum Theoretische Chemie,
Bound states of negatively charged ions induced by a magnetic field arxiv:physics/0006016v1 [physics.atom-ph] 7 Jun 000 Victor G. Bezchastnov, Peter Schmelcher, and Lorenz S. Cederbaum Theoretische Chemie,
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 16 Dec 1997
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 16 Dec 1997 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 16 Dec 1997](/thumbs/75/71639258.jpg) Positronium in crossed electric and magnetic fields: the existence of a long-lived ground state J. Shertzer College of the Holy Cross, Worcester MA 01610 arxiv:physics/9712028v1 [physics.atom-ph] 16 Dec
Positronium in crossed electric and magnetic fields: the existence of a long-lived ground state J. Shertzer College of the Holy Cross, Worcester MA 01610 arxiv:physics/9712028v1 [physics.atom-ph] 16 Dec
Summation of Periodic Trends
 Summation of Periodic Trends Factors Affecting Atomic Orbital Energies The Effect of Nuclear Charge (Z effective ) Higher nuclear charge lowers orbital energy (stabilizes the system) by increasing nucleus-electron
Summation of Periodic Trends Factors Affecting Atomic Orbital Energies The Effect of Nuclear Charge (Z effective ) Higher nuclear charge lowers orbital energy (stabilizes the system) by increasing nucleus-electron
Summation of Periodic Trends Factors Affecting Atomic Orbital Energies
 Summation of Periodic Trends Factors Affecting Atomic Orbital Energies The Effect of Nuclear Charge (Z effective ) Higher nuclear charge lowers orbital energy (stabilizes the system) by increasing nucleus-electron
Summation of Periodic Trends Factors Affecting Atomic Orbital Energies The Effect of Nuclear Charge (Z effective ) Higher nuclear charge lowers orbital energy (stabilizes the system) by increasing nucleus-electron
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
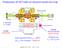 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Central density. Consider nuclear charge density. Frois & Papanicolas, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 37, 133 (1987) QMPT 540
 Central density Consider nuclear charge density Frois & Papanicolas, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 37, 133 (1987) Central density (A/Z* charge density) about the same for nuclei heavier than 16 O, corresponding
Central density Consider nuclear charge density Frois & Papanicolas, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 37, 133 (1987) Central density (A/Z* charge density) about the same for nuclei heavier than 16 O, corresponding
Bound states of two particles confined to parallel two-dimensional layers and interacting via dipole-dipole or dipole-charge laws
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 8 15 FEBRUARY 1997-II Bound states of two particles confined to parallel two-dimensional layers and interacting via dipole-dipole or dipole-charge laws V. I. Yudson
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 8 15 FEBRUARY 1997-II Bound states of two particles confined to parallel two-dimensional layers and interacting via dipole-dipole or dipole-charge laws V. I. Yudson
Exploring ICD and Dynamic Interference by Free Electron Lasers
 Exploring ICD and Dynamic Interference by Free Electron Lasers Lorenz Cederbaum Theoretische Chemie Physikalisch-Chemisches Institut Universität Heidelberg Exploring Intermolecular Coulombic Decay by Free
Exploring ICD and Dynamic Interference by Free Electron Lasers Lorenz Cederbaum Theoretische Chemie Physikalisch-Chemisches Institut Universität Heidelberg Exploring Intermolecular Coulombic Decay by Free
Radiative transitions of the helium atom in highly magnetized neutron star atmospheres
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 383, 6 7 (008) doi:0./j.365-966.007.58.x Radiative transitions of the helium atom in highly magnetized neutron star atmospheres Z. Medin, D. Lai and A. Y. Potekhin, Centre for
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 383, 6 7 (008) doi:0./j.365-966.007.58.x Radiative transitions of the helium atom in highly magnetized neutron star atmospheres Z. Medin, D. Lai and A. Y. Potekhin, Centre for
Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540
 Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540 Questions about organization Second quantization Questions about last class? Comments? Similar strategy N-particles Consider Two-body operators in Fock
Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540 Questions about organization Second quantization Questions about last class? Comments? Similar strategy N-particles Consider Two-body operators in Fock
Neda Sadooghi Sharif University of Technology (SUT) and Institute for Theoretical Physics and Mathematics (IPM) Tehran-Iran
 Modified Coulomb potential of QED in a strong magnetic field Neda Sadooghi Sharif University of Technology (SUT) and Institute for Theoretical Physics and Mathematics (IPM) Tehran-Iran Modified Coulomb
Modified Coulomb potential of QED in a strong magnetic field Neda Sadooghi Sharif University of Technology (SUT) and Institute for Theoretical Physics and Mathematics (IPM) Tehran-Iran Modified Coulomb
Particle Behavior of Light 1. Calculate the energy of a photon, mole of photons 2. Find binding energy of an electron (know KE) 3. What is a quanta?
 Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation 1. What is spectroscopy, a continuous spectrum, a line spectrum, differences and similarities 2. Relationship of wavelength to frequency, relationship of E to λ
Magnetized neutron star atmospheres: beyond the cold plasma approximation
 Magnetized neutron star atmospheres: beyond the cold plasma approximation IAAT, University of Tübingen, Germany Kazan Federal University, Russia E-mail: suleimanov@astro.uni-tuebingen.de George Pavlov
Magnetized neutron star atmospheres: beyond the cold plasma approximation IAAT, University of Tübingen, Germany Kazan Federal University, Russia E-mail: suleimanov@astro.uni-tuebingen.de George Pavlov
Ionization and dissociation equilibrium in strongly-magnetized helium atmosphere ABSTRACT
 Ionization and dissociation equilibrium in strongly-magnetized helium atmosphere Kaya Mori 1,2 and Jeremy S. Heyl 3 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0610253v1 9 Oct 2006 Recent observations and theoretical investigations
Ionization and dissociation equilibrium in strongly-magnetized helium atmosphere Kaya Mori 1,2 and Jeremy S. Heyl 3 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0610253v1 9 Oct 2006 Recent observations and theoretical investigations
International Nuclear Physics Conference Adelaide, Australia September 13, 2016
 International Nuclear Physics Conference Adelaide, Australia September 13, 2016 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-07NA27344. Lawrence
International Nuclear Physics Conference Adelaide, Australia September 13, 2016 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by under contract DE-AC52-07NA27344. Lawrence
On the Interaction of Elementary Particles
 H. Yukawa, PTP, 17, 48 1935 On the Interaction of Elementary Particles H. Yukawa (Received 1935) At the present stage of the quantum theory little is known about the nature of interaction of elementary
H. Yukawa, PTP, 17, 48 1935 On the Interaction of Elementary Particles H. Yukawa (Received 1935) At the present stage of the quantum theory little is known about the nature of interaction of elementary
2008 Brooks/Cole 2. Frequency (Hz)
 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter Oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Magnetic field Electric field Chapter 7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Traveling wave moves through space
Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter Oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Magnetic field Electric field Chapter 7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Traveling wave moves through space
Optical Properties of Lattice Vibrations
 Optical Properties of Lattice Vibrations For a collection of classical charged Simple Harmonic Oscillators, the dielectric function is given by: Where N i is the number of oscillators with frequency ω
Optical Properties of Lattice Vibrations For a collection of classical charged Simple Harmonic Oscillators, the dielectric function is given by: Where N i is the number of oscillators with frequency ω
The Structure of the Atom Review
 The Structure of the Atom Review Atoms are composed of PROTONS + positively charged mass = 1.6726 x 10 27 kg NEUTRONS neutral mass = 1.6750 x 10 27 kg ELECTRONS negatively charged mass = 9.1096 x 10 31
The Structure of the Atom Review Atoms are composed of PROTONS + positively charged mass = 1.6726 x 10 27 kg NEUTRONS neutral mass = 1.6750 x 10 27 kg ELECTRONS negatively charged mass = 9.1096 x 10 31
From neutrons to atoms (in 2D) and back
 From neutrons to atoms (in 2D) and back Alex Gezerlis Exploring nuclear physics with ultracold atoms workshop ECT*, Trento, Italy June 18, 2018 Outline Motivation Credit: Dany Page 2D cold gases Static
From neutrons to atoms (in 2D) and back Alex Gezerlis Exploring nuclear physics with ultracold atoms workshop ECT*, Trento, Italy June 18, 2018 Outline Motivation Credit: Dany Page 2D cold gases Static
Manifestations of Low-Mass Dark Bosons
 Manifestations of Low-Mass Dark Bosons Yevgeny Stadnik Humboldt Fellow Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany Collaborators (Theory): Victor Flambaum (UNSW) Collaborators (Experiment): CASPEr collaboration
Manifestations of Low-Mass Dark Bosons Yevgeny Stadnik Humboldt Fellow Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany Collaborators (Theory): Victor Flambaum (UNSW) Collaborators (Experiment): CASPEr collaboration
INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS
 DAMOP 2010 May 29, 2010 DEVELOPMENT OF A CONFIGURATION-INTERACTION INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA MIKHAIL KOZLOV PNPI, RUSSIA DANSHA JIANG UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
DAMOP 2010 May 29, 2010 DEVELOPMENT OF A CONFIGURATION-INTERACTION INTERACTION PLUS ALL-ORDER METHOD FOR ATOMIC CALCULATIONS MARIANNA SAFRONOVA MIKHAIL KOZLOV PNPI, RUSSIA DANSHA JIANG UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Graduate Accelerator Physics. G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Old Dominion University Lecture 1
 Graduate Accelerator Physics G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Old Dominion University Lecture 1 Course Outline Course Content Introduction to Accelerators and Short Historical Overview Basic Units and Definitions
Graduate Accelerator Physics G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Old Dominion University Lecture 1 Course Outline Course Content Introduction to Accelerators and Short Historical Overview Basic Units and Definitions
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Sep 2000
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Sep 2000 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Sep 2000](/thumbs/71/65830011.jpg) The beryllium atom and beryllium positive ion in strong magnetic fields arxiv:physics/0009004v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Sep 2000 M. V. Ivanov and P. Schmelcher Theoretische Chemie, Physikalisch Chemisches
The beryllium atom and beryllium positive ion in strong magnetic fields arxiv:physics/0009004v1 [physics.atom-ph] 1 Sep 2000 M. V. Ivanov and P. Schmelcher Theoretische Chemie, Physikalisch Chemisches
Many electron effects in semiconductor quantum dots
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 26, No. 1, January 2003, pp. 63 67. Indian Academy of Sciences. Many electron effects in semiconductor quantum dots K PANDEY*, MANOJ K HABOLA, V ANJAN and VIJAY A SINGH Physics
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 26, No. 1, January 2003, pp. 63 67. Indian Academy of Sciences. Many electron effects in semiconductor quantum dots K PANDEY*, MANOJ K HABOLA, V ANJAN and VIJAY A SINGH Physics
and S is in the state ( )
 Physics 517 Homework Set #8 Autumn 2016 Due in class 12/9/16 1. Consider a spin 1/2 particle S that interacts with a measuring apparatus that is another spin 1/2 particle, A. The state vector of the system
Physics 517 Homework Set #8 Autumn 2016 Due in class 12/9/16 1. Consider a spin 1/2 particle S that interacts with a measuring apparatus that is another spin 1/2 particle, A. The state vector of the system
Classical calculation of radiative lifetimes of atomic hydrogen in a homogeneous magnetic field
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 72, 033405 2005 Classical calculation of radiative lifetimes of atomic hydrogen in a homogeneous magnetic field M. W. Horbatsch, E. A. Hessels, and M. Horbatsch Department of Physics
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 72, 033405 2005 Classical calculation of radiative lifetimes of atomic hydrogen in a homogeneous magnetic field M. W. Horbatsch, E. A. Hessels, and M. Horbatsch Department of Physics
1. Nuclear Size. A typical atom radius is a few!10 "10 m (Angstroms). The nuclear radius is a few!10 "15 m (Fermi).
 1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
FACTS WHY? C. Alpha Decay Probability 1. Energetics: Q α positive for all A>140 nuclei
 C. Alpha Decay Probability 1. Energetics: Q α positive for all A>140 nuclei 2. Range of Measured Half-Lives (~10 44 ) 10 16 y > t 1/2 > 10 21 s 3. Why α? a. Proton & Neutron Emission: Q p, Q n are negative
C. Alpha Decay Probability 1. Energetics: Q α positive for all A>140 nuclei 2. Range of Measured Half-Lives (~10 44 ) 10 16 y > t 1/2 > 10 21 s 3. Why α? a. Proton & Neutron Emission: Q p, Q n are negative
Chem 325 NMR Intro. The Electromagnetic Spectrum. Physical properties, chemical properties, formulas Shedding real light on molecular structure:
 Physical properties, chemical properties, formulas Shedding real light on molecular structure: Wavelength Frequency ν Wavelength λ Frequency ν Velocity c = 2.998 10 8 m s -1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Physical properties, chemical properties, formulas Shedding real light on molecular structure: Wavelength Frequency ν Wavelength λ Frequency ν Velocity c = 2.998 10 8 m s -1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe
 Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe A. Yoshimi RIKEN K. Asahi, S. Emori, M. Tsukui, RIKEN, Tokyo Institute of Technology Nuclear
Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe A. Yoshimi RIKEN K. Asahi, S. Emori, M. Tsukui, RIKEN, Tokyo Institute of Technology Nuclear
Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions
 Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions W. Scheid 1,A.Pálffy 2,Z.Harman 2, C. Kozhuharov 3, and C. Brandau 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik der Justus-Liebig-Universität
Nuclear Effects in Electron Capture into Highly Charged Heavy Ions W. Scheid 1,A.Pálffy 2,Z.Harman 2, C. Kozhuharov 3, and C. Brandau 3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik der Justus-Liebig-Universität
Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1. Waves in plasmas. T. Johnson
 2017-02-14 Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasmas as a coupled system Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas
2017-02-14 Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasmas as a coupled system Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas
Chapter 7. Generally, the electronic structure of atoms correlates w. the prop. of the elements
 Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements I) Development of the P.T. Generally, the electronic structure of atoms correlates w. the prop. of the elements - reflected by the arrangement of the elements
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements I) Development of the P.T. Generally, the electronic structure of atoms correlates w. the prop. of the elements - reflected by the arrangement of the elements
- Potentials. - Liénard-Wiechart Potentials. - Larmor s Formula. - Dipole Approximation. - Beginning of Cyclotron & Synchrotron
 - Potentials - Liénard-Wiechart Potentials - Larmor s Formula - Dipole Approximation - Beginning of Cyclotron & Synchrotron Maxwell s equations in a vacuum become A basic feature of these eqns is the existence
- Potentials - Liénard-Wiechart Potentials - Larmor s Formula - Dipole Approximation - Beginning of Cyclotron & Synchrotron Maxwell s equations in a vacuum become A basic feature of these eqns is the existence
2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1. Waves in plasmas. T. Johnson
 2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasma physics Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas Transverse waves
2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasma physics Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas Transverse waves
So far, we considered quantum static, as all our potentials did not depend on time. Therefore, our time dependence was trivial and always the same:
 Lecture 20 Page 1 Lecture #20 L20.P1 Time-dependent perturbation theory So far, we considered quantum static, as all our potentials did not depend on time. Therefore, our time dependence was trivial and
Lecture 20 Page 1 Lecture #20 L20.P1 Time-dependent perturbation theory So far, we considered quantum static, as all our potentials did not depend on time. Therefore, our time dependence was trivial and
Modified Anti-de-Sitter Metric, Light-Front Quantized QCD, and Conformal Quantum Mechanics
 GEOMETRY AND PHYSICS II Institut Henri Poincaré, Nov. 8 &9, 013 Modified Anti-de-Sitter Metric, Light-Front Quantized QCD, and Conformal Quantum Mechanics H.G.Dosch Institut für Theoretische Physik der
GEOMETRY AND PHYSICS II Institut Henri Poincaré, Nov. 8 &9, 013 Modified Anti-de-Sitter Metric, Light-Front Quantized QCD, and Conformal Quantum Mechanics H.G.Dosch Institut für Theoretische Physik der
Energy and momentum losses in the process of neutrino scattering on plasma electrons with the presence of a magnetic field.
 Energy and momentum losses in the process of neutrino scattering on plasma electrons with the presence of a magnetic field. Nickolay V. Mikheev and Elena N. Narynskaya Division of Theoretical Physics,
Energy and momentum losses in the process of neutrino scattering on plasma electrons with the presence of a magnetic field. Nickolay V. Mikheev and Elena N. Narynskaya Division of Theoretical Physics,
Waves in plasma. Denis Gialis
 Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
CHEM 1411 STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-3 (CHAPTERS 7, 8)
 CHEM 1411 STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-3 (CHAPTERS 7, 8) 1. In the following diagram of a wave A) (a) is amplitude and (b) is wavelength D) (a) is amplitude and (b) is frequency B) (a) is frequency and (b) is
CHEM 1411 STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-3 (CHAPTERS 7, 8) 1. In the following diagram of a wave A) (a) is amplitude and (b) is wavelength D) (a) is amplitude and (b) is frequency B) (a) is frequency and (b) is
Relativistic corrections of energy terms
 Lectures 2-3 Hydrogen atom. Relativistic corrections of energy terms: relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and spin-orbit term. Fine structure. Lamb shift. Hyperfine structure. Energy levels of the
Lectures 2-3 Hydrogen atom. Relativistic corrections of energy terms: relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and spin-orbit term. Fine structure. Lamb shift. Hyperfine structure. Energy levels of the
The hydrogen molecule in magnetic fields: The ground states of the Σ manifold of the parallel configuration
 The hydrogen molecule in magnetic fields: The ground states of the Σ manifold of the parallel configuration T.Detmer, P. Schmelcher, F. K. Diakonos and L. S. Cederbaum Theoretische Chemie, Physikalisch
The hydrogen molecule in magnetic fields: The ground states of the Σ manifold of the parallel configuration T.Detmer, P. Schmelcher, F. K. Diakonos and L. S. Cederbaum Theoretische Chemie, Physikalisch
EXPLODING BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATES AND COLLAPSING NEUTRON STARS DRIVEN BY CRITICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS
 EXPLODING BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATES AND COLLAPSING NEUTRON STARS DRIVEN BY CRITICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS H. PÉREZ ROJAS, A. PÉREZ MARTíNEZ Instituto de Cibernética, Matemática y Física, 10400 La Habana, Cuba
EXPLODING BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATES AND COLLAPSING NEUTRON STARS DRIVEN BY CRITICAL MAGNETIC FIELDS H. PÉREZ ROJAS, A. PÉREZ MARTíNEZ Instituto de Cibernética, Matemática y Física, 10400 La Habana, Cuba
Constraining Astrophysical Reaction Rates with Transfer Reactions at Low and Intermediate Energies
 Constraining Astrophysical Reaction Rates with Transfer Reactions at Low and Intermediate Energies Christoph Langer (JINA/NSCL) INT Workshop: Reactions and Structure of Exotic Nuclei March 2015 1 Understanding
Constraining Astrophysical Reaction Rates with Transfer Reactions at Low and Intermediate Energies Christoph Langer (JINA/NSCL) INT Workshop: Reactions and Structure of Exotic Nuclei March 2015 1 Understanding
Ion traps, atomic masses and astrophysics. Outline. Positive ray parabolas. British beginnings
 Ion traps, atomic masses and astrophysics Kumar S. Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Manitoba Outline Some history Atomic masses Ion traps rp-process nucleosysnthesis Physics Day Slide
Ion traps, atomic masses and astrophysics Kumar S. Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Manitoba Outline Some history Atomic masses Ion traps rp-process nucleosysnthesis Physics Day Slide
Modern Atomic Theory. Chapter Rutherford s Atom Electromagnetic Radiation. Rutherford showed: Questions left unanswered:
 Copyright 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Modern Atomic Theory Chapter 10 All rights reserved. 1 10.1 Rutherford s Atom Rutherford showed: Atomic nucleus is composed of protons (positive) and neutrons
Copyright 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Modern Atomic Theory Chapter 10 All rights reserved. 1 10.1 Rutherford s Atom Rutherford showed: Atomic nucleus is composed of protons (positive) and neutrons
Variational wave function for a two-electron quantum dot
 Physica B 255 (1998) 145 149 Variational wave function for a two-electron quantum dot A. Harju *, V.A. Sverdlov, B. Barbiellini, R.M. Nieminen Laboratory of Physics, Helsinki University of Technology,
Physica B 255 (1998) 145 149 Variational wave function for a two-electron quantum dot A. Harju *, V.A. Sverdlov, B. Barbiellini, R.M. Nieminen Laboratory of Physics, Helsinki University of Technology,
Chapter VI: Beta decay
 Chapter VI: Beta decay 1 Summary 1. General principles 2. Energy release in decay 3. Fermi theory of decay 4. Selections rules 5. Electron capture decay 6. Other decays 2 General principles (1) The decay
Chapter VI: Beta decay 1 Summary 1. General principles 2. Energy release in decay 3. Fermi theory of decay 4. Selections rules 5. Electron capture decay 6. Other decays 2 General principles (1) The decay
Fundamental Forces. Range Carrier Observed? Strength. Gravity Infinite Graviton No. Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983)
 Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Nuclear Spectroscopy I
 Nuclear Spectroscopy I Augusto O. Macchiavelli Nuclear Science Division Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Many thanks to Rod Clark, I.Y. Lee, and Dirk Weisshaar Work supported under contract number
Nuclear Spectroscopy I Augusto O. Macchiavelli Nuclear Science Division Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Many thanks to Rod Clark, I.Y. Lee, and Dirk Weisshaar Work supported under contract number
Basic science. Atomic structure. Electrons. The Rutherford-Bohr model of an atom. Electron shells. Types of Electrons. Describing an Atom
 Basic science A knowledge of basic physics is essential to understanding how radiation originates and behaves. This chapter works through what an atom is; what keeps it stable vs. radioactive and unstable;
Basic science A knowledge of basic physics is essential to understanding how radiation originates and behaves. This chapter works through what an atom is; what keeps it stable vs. radioactive and unstable;
Broadband ESR from 500 MHz to 40 GHz using superconducting coplanar waveguides
 Broadband ESR from 500 MHz to 40 GHz using superconducting coplanar waveguides Martin Dressel 1. Physikalisches Institut, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Outline 1. Introduction ESR resonators 2. Strip
Broadband ESR from 500 MHz to 40 GHz using superconducting coplanar waveguides Martin Dressel 1. Physikalisches Institut, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Outline 1. Introduction ESR resonators 2. Strip
Chapter 1. I- Fill the following table. Element symbol and the mass no. n p n n n e. number. II - Choose the correct answer for the following: Ca-40
 Chapter 1 I- Fill the following table. Element symbol and the mass no. Ca-40 Ca 2+ -40 O-17 O 2- -16 C-12 C-13 Atomic number n p n n n e II - Choose the correct answer for the following: 1. Consider the
Chapter 1 I- Fill the following table. Element symbol and the mass no. Ca-40 Ca 2+ -40 O-17 O 2- -16 C-12 C-13 Atomic number n p n n n e II - Choose the correct answer for the following: 1. Consider the
Introduction to the physics of highly charged ions. Lecture 7: Direct and resonant photoionization of HCI
 Introduction to the physics of highly charged ions Lecture 7: Direct and resonant photoionization of HCI Zoltán Harman harman@mpi-hd.mpg.de Universität Heidelberg, 02.12.2013 So far: radiative decay and
Introduction to the physics of highly charged ions Lecture 7: Direct and resonant photoionization of HCI Zoltán Harman harman@mpi-hd.mpg.de Universität Heidelberg, 02.12.2013 So far: radiative decay and
Cold Polar Molecules and their Applications for Quantum Information H.P. Büchler
 Cold Polar Molecules and their Applications for Quantum Information H.P. Büchler Theoretische Physik III, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Outline Introduction to polar molecules - quantum melting transition
Cold Polar Molecules and their Applications for Quantum Information H.P. Büchler Theoretische Physik III, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Outline Introduction to polar molecules - quantum melting transition
Assignment 5. Ian Rittersdorf Nuclear Engineering & Radiological Sciences
 Assignment 5 Ian Rittersdorf Nuclear Engineering & Radiological Sciences ianrit@umich.edu March 19, 2007 1 All mass values taken from Krane unless otherwise noted. P5.1, 20% Krane, Problem 9.3, p. 332.
Assignment 5 Ian Rittersdorf Nuclear Engineering & Radiological Sciences ianrit@umich.edu March 19, 2007 1 All mass values taken from Krane unless otherwise noted. P5.1, 20% Krane, Problem 9.3, p. 332.
Atomic Theory and Atomic structure. Part A. d) Distance of electrons from the nucleus
 Grade Subject Topic : AP : Science : Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure Atomic Theory and Atomic structure Part A (1) The Principal quantum number represents a) Shape of an orbital b) Number of electrons
Grade Subject Topic : AP : Science : Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure Atomic Theory and Atomic structure Part A (1) The Principal quantum number represents a) Shape of an orbital b) Number of electrons
1. Why photons? 2. Photons in a vacuum
 1 Photons 1. Why photons? Ask class: most of our information about the universe comes from photons. What are the reasons for this? Let s compare them with other possible messengers, specifically massive
1 Photons 1. Why photons? Ask class: most of our information about the universe comes from photons. What are the reasons for this? Let s compare them with other possible messengers, specifically massive
The Periodic Table. Periodic Properties. Can you explain this graph? Valence Electrons. Valence Electrons. Paramagnetism
 Periodic Properties Atomic & Ionic Radius Energy Electron Affinity We want to understand the variations in these properties in terms of electron configurations. The Periodic Table Elements in a column
Periodic Properties Atomic & Ionic Radius Energy Electron Affinity We want to understand the variations in these properties in terms of electron configurations. The Periodic Table Elements in a column
Chapter 6 Part 3; Many-electron atoms
 Chapter 6 Part 3; Many-electron atoms Read: BLB 6.7 6.9 HW: BLB 6:59,63,64,67,71b-d,74,75,90,97; Packet 6:10 14 Know: s & atoms with many electrons Spin quantum number m s o Pauli exclusion principle o
Chapter 6 Part 3; Many-electron atoms Read: BLB 6.7 6.9 HW: BLB 6:59,63,64,67,71b-d,74,75,90,97; Packet 6:10 14 Know: s & atoms with many electrons Spin quantum number m s o Pauli exclusion principle o
Fundamental MRI Principles Module 2 N. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. X-ray. MRI Hydrogen Protons. Page 1. Electrons
 Fundamental MRI Principles Module 2 N S 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons positively charged neutrons no significant charge electrons negatively charged Protons
Fundamental MRI Principles Module 2 N S 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons positively charged neutrons no significant charge electrons negatively charged Protons
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford s α -particle scattering experiement? (i) Most of the space in the atom is empty. (ii) The
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford s α -particle scattering experiement? (i) Most of the space in the atom is empty. (ii) The
Chapter 8. Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity 10/17/ Development of the Periodic Table
 Chapter 8 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity 8-1 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity 8.1 Development of the Periodic Table 8.2 Characteristics of Many-Electron Atoms 8.3 The Quantum-Mechanical
Chapter 8 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity 8-1 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity 8.1 Development of the Periodic Table 8.2 Characteristics of Many-Electron Atoms 8.3 The Quantum-Mechanical
X-ray Energy Spectroscopy (XES).
 X-ray Energy Spectroscopy (XES). X-ray fluorescence as an analytical tool for element analysis is based on 3 fundamental parameters: A. Specificity: In determining an x-ray emission energy E certainty
X-ray Energy Spectroscopy (XES). X-ray fluorescence as an analytical tool for element analysis is based on 3 fundamental parameters: A. Specificity: In determining an x-ray emission energy E certainty
Periodic Table Trends. Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity
 Periodic Table Trends Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity 1. Atomic Radius Atomic Radius - distance from nucleus to outermost atom Measured by dividing the distance between 2
Periodic Table Trends Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity 1. Atomic Radius Atomic Radius - distance from nucleus to outermost atom Measured by dividing the distance between 2
CHM2045 S13: Exam # MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHM2045 S13: Exam #1 2013.02.01 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What value of l is represented by a d orbital? A) 2 B) 1 C) 0 D)
CHM2045 S13: Exam #1 2013.02.01 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What value of l is represented by a d orbital? A) 2 B) 1 C) 0 D)
The IC electrons are mono-energetic. Their kinetic energy is equal to the energy of the transition minus the binding energy of the electron.
 1 Lecture 3 Nuclear Decay modes, Nuclear Sizes, shapes, and the Liquid drop model Introduction to Decay modes (continued) Gamma Decay Electromagnetic radiation corresponding to transition of nucleus from
1 Lecture 3 Nuclear Decay modes, Nuclear Sizes, shapes, and the Liquid drop model Introduction to Decay modes (continued) Gamma Decay Electromagnetic radiation corresponding to transition of nucleus from
Charged mobile complexes in magnetic fields: a novel selection rule for magnetooptical transitions
 JETP LETTERS VOLUE 70, NUBER 8 25 OCT. 1999 Charged mobile complexes in magnetic fields: a novel selection rule for magnetooptical transitions A. B. Dyubenko Institut für Theoretische Physik, J. W. Goethe-Universität,
JETP LETTERS VOLUE 70, NUBER 8 25 OCT. 1999 Charged mobile complexes in magnetic fields: a novel selection rule for magnetooptical transitions A. B. Dyubenko Institut für Theoretische Physik, J. W. Goethe-Universität,
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics
 Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
Physics of heavy multiply-charged ions: Studies on the borderile of atomic and nuclear physics Andrey Surzhykov Technische Universität Braunschweig Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) Lecture 1
COLLECTIVE SPIN STATES IN THE ELECTRON GAS IN DIFFERENT DIMENSIONS AND GEOMETRIES*)
 COLLECTIVE SPIN STATES IN THE ELECTRON GAS IN DIFFERENT DIMENSIONS AND GEOMETRIES*) ENRICO LIPPARINI, LEONARDO COLLETTI, GIUSI ORLANDINI Dipartimento di Fisica, Universita di Trento, I-38100 Povo, Trento,
COLLECTIVE SPIN STATES IN THE ELECTRON GAS IN DIFFERENT DIMENSIONS AND GEOMETRIES*) ENRICO LIPPARINI, LEONARDO COLLETTI, GIUSI ORLANDINI Dipartimento di Fisica, Universita di Trento, I-38100 Povo, Trento,
Nuclear Decays. Alpha Decay
 Nuclear Decays The first evidence of radioactivity was a photographic plate, wrapped in black paper and placed under a piece of uranium salt by Henri Becquerel on February 26, 1896. Like many events in
Nuclear Decays The first evidence of radioactivity was a photographic plate, wrapped in black paper and placed under a piece of uranium salt by Henri Becquerel on February 26, 1896. Like many events in
Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs
 Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs JDL Decay of large scale magnetic fields We have seen that some upper main sequence stars host magnetic fields of global scale and dipolar topology
Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs JDL Decay of large scale magnetic fields We have seen that some upper main sequence stars host magnetic fields of global scale and dipolar topology
PHYS 5012 Radiation Physics and Dosimetry
 PHYS 5012 Radiation Physics and Dosimetry Tuesday 12 March 2013 What are the dominant photon interactions? (cont.) Compton scattering, photoelectric absorption and pair production are the three main energy
PHYS 5012 Radiation Physics and Dosimetry Tuesday 12 March 2013 What are the dominant photon interactions? (cont.) Compton scattering, photoelectric absorption and pair production are the three main energy
Astrophysical Radiation Processes
 PHY3145 Topics in Theoretical Physics Astrophysical Radiation Processes 3: Relativistic effects I Dr. J. Hatchell, Physics 407, J.Hatchell@exeter.ac.uk Course structure 1. Radiation basics. Radiative transfer.
PHY3145 Topics in Theoretical Physics Astrophysical Radiation Processes 3: Relativistic effects I Dr. J. Hatchell, Physics 407, J.Hatchell@exeter.ac.uk Course structure 1. Radiation basics. Radiative transfer.
Quantum theory predicts that an atom s electrons are found in: To account that orbitals hold two electrons, we need:
 Quantum theory predicts that an atom s electrons are found in: To account that orbitals hold two electrons, we need: Shells (principle quantum number, n) Subshells (angular momentum, l) Orbitals (magnetic
Quantum theory predicts that an atom s electrons are found in: To account that orbitals hold two electrons, we need: Shells (principle quantum number, n) Subshells (angular momentum, l) Orbitals (magnetic
Molecules in strong magnetic fields
 Molecules in strong magnetic fields Trygve Helgaker, Kai Lange, Alessandro Soncini, and Erik Tellgren Centre for Theoretical and Computational Chemistry Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, Norway
Molecules in strong magnetic fields Trygve Helgaker, Kai Lange, Alessandro Soncini, and Erik Tellgren Centre for Theoretical and Computational Chemistry Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, Norway
SOLID STATE PHYSICS. Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons. J. R. Hook H. E. Hall. Department of Physics, University of Manchester
 SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
I. The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table. Electronic Configuration and Periodicity. Announcements Newland Law of Octaves
 Announcements EM radiation --Exam 3 Oct 3...Includes chapters 7/8/9/10 The excluded items include: 1. Classical distinction between energy and matter (p. 217) 2. Numerical problems involving the Rydberg
Announcements EM radiation --Exam 3 Oct 3...Includes chapters 7/8/9/10 The excluded items include: 1. Classical distinction between energy and matter (p. 217) 2. Numerical problems involving the Rydberg
Physics 607 Exam 2. ( ) = 1, Γ( z +1) = zγ( z) x n e x2 dx = 1. e x2
 Physics 607 Exam Please be well-organized, and show all significant steps clearly in all problems. You are graded on your work, so please do not just write down answers with no explanation! Do all your
Physics 607 Exam Please be well-organized, and show all significant steps clearly in all problems. You are graded on your work, so please do not just write down answers with no explanation! Do all your
The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol λ.
 CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity 1 The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol
CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity 1 The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol
Karlsruhe Nuclide Chart
 Karlsruhe uclide Chart The ew Edition in 2015 s. Sóti 1, J. Magill 2 1 European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Transuranium Elements, Postfach 2340, 76125 Karlsruhe, Germany https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/
Karlsruhe uclide Chart The ew Edition in 2015 s. Sóti 1, J. Magill 2 1 European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Transuranium Elements, Postfach 2340, 76125 Karlsruhe, Germany https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/
Application and extension of a fast parallel code for calculating atomic data in neutron star magnetic fields
 Application and extension of a fast parallel code for calculating atomic data in neutron star magnetic fields Diploma Thesis by Akin Yildirim 22.1.29 First Supervisor: Second Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Günter
Application and extension of a fast parallel code for calculating atomic data in neutron star magnetic fields Diploma Thesis by Akin Yildirim 22.1.29 First Supervisor: Second Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Günter
Monopole polarization of C 60 fullerene shell
 Monopole polarization of C 6 fullerene shell M. Ya. Amusia 1, and A. S. Baltenkov 3 1 Racah Institute of Physics, the Hebrew University, Jerusalem, 9194 Israel Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute, St. Petersburg,
Monopole polarization of C 6 fullerene shell M. Ya. Amusia 1, and A. S. Baltenkov 3 1 Racah Institute of Physics, the Hebrew University, Jerusalem, 9194 Israel Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute, St. Petersburg,
Penning Traps. Contents. Plasma Physics Penning Traps AJW August 16, Introduction. Clasical picture. Radiation Damping.
 Penning Traps Contents Introduction Clasical picture Radiation Damping Number density B and E fields used to increase time that an electron remains within a discharge: Penning, 936. Can now trap a particle
Penning Traps Contents Introduction Clasical picture Radiation Damping Number density B and E fields used to increase time that an electron remains within a discharge: Penning, 936. Can now trap a particle
Chem 130 Key for First Exam
 Name Chem 130 Key for First Exam On the following pages you will find questions that cover various topics ranging from nomenclature to periodic properties, and from electromagnetic radiation to the quantum
Name Chem 130 Key for First Exam On the following pages you will find questions that cover various topics ranging from nomenclature to periodic properties, and from electromagnetic radiation to the quantum
s or Hz J atom J mol or -274 kj mol CHAPTER 4. Practice Exercises ΔE atom = ΔE mol =
 CHAPTER 4 Practice Exercises 4.1 10 1 2.1410 s or Hz 4.3 ΔE atom = ΔE mol = 4.5610 J atom 19 1 2.7410 J mol or -274 kj mol 5 1-1 4.5 excitation energy = 471 kj mol 1 + 275 kj mol 1 = 746 kj mol 1 Hg 4.7
CHAPTER 4 Practice Exercises 4.1 10 1 2.1410 s or Hz 4.3 ΔE atom = ΔE mol = 4.5610 J atom 19 1 2.7410 J mol or -274 kj mol 5 1-1 4.5 excitation energy = 471 kj mol 1 + 275 kj mol 1 = 746 kj mol 1 Hg 4.7
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions
 New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
New theoretical insights on the physics of compound nuclei from laser-nucleus reactions Adriana Pálffy Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Laser-Driven Radiation Sources for Nuclear
Proton decay and neutrino astrophysics with the future LENA detector
 Proton decay and neutrino astrophysics with the future LENA detector Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia tmarroda@ph.tum.de Institut E15 Physik-Department Technische Universität München Paris, 11.09.08 Outline
Proton decay and neutrino astrophysics with the future LENA detector Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia tmarroda@ph.tum.de Institut E15 Physik-Department Technische Universität München Paris, 11.09.08 Outline
Spectral shape of two-photon decay from 2S state in He-like tin
 Spectral shape of two-photon decay from 2S state in He-like tin Team Ajay Kumar GSI, Darmstadt a.kumar@gsi.de S. Trotsenko,2, D. Banas 3, H. Beyer, H. Bräuning,A. Gumberidze, S. Hagmann,2, S. Hess,2, P.
Spectral shape of two-photon decay from 2S state in He-like tin Team Ajay Kumar GSI, Darmstadt a.kumar@gsi.de S. Trotsenko,2, D. Banas 3, H. Beyer, H. Bräuning,A. Gumberidze, S. Hagmann,2, S. Hess,2, P.
Magnetic resonance in Dense Atomic Hydrogen Gas
 Magnetic resonance in Dense Atomic Hydrogen Gas S. Vasiliev University of Turku, Finland Turku Magnetic resonance in Dense Atomic Hydrogen Gas Sergey Vasiliev University of Turku H group at Turku: Janne
Magnetic resonance in Dense Atomic Hydrogen Gas S. Vasiliev University of Turku, Finland Turku Magnetic resonance in Dense Atomic Hydrogen Gas Sergey Vasiliev University of Turku H group at Turku: Janne
EXCITONS, PLASMONS, AND EXCITONIC COMPLEXES UNDER STRONG CONFINEMENT IN QUASI-1D SEMICONDUCTORS. Theory and Perspectives
 EXCITONS, PLASMONS, AND EXCITONIC COMPLEXES UNDER STRONG CONFINEMENT IN QUASI-1D SEMICONDUCTORS. Theory and Perspectives Igor Bondarev Math & Physics Department North Carolina Central University Durham,
EXCITONS, PLASMONS, AND EXCITONIC COMPLEXES UNDER STRONG CONFINEMENT IN QUASI-1D SEMICONDUCTORS. Theory and Perspectives Igor Bondarev Math & Physics Department North Carolina Central University Durham,
Homework Hint. Last Time
 Homework Hint Problem 3.3 Geometric series: ωs τ ħ e s= 0 =? a n ar = For 0< r < 1 n= 0 1 r ωs τ ħ e s= 0 1 = 1 e ħω τ Last Time Boltzmann factor Partition Function Heat Capacity The magic of the partition
Homework Hint Problem 3.3 Geometric series: ωs τ ħ e s= 0 =? a n ar = For 0< r < 1 n= 0 1 r ωs τ ħ e s= 0 1 = 1 e ħω τ Last Time Boltzmann factor Partition Function Heat Capacity The magic of the partition
Properties of Light and Atomic Structure. Chapter 7. So Where are the Electrons? Electronic Structure of Atoms. The Wave Nature of Light!
 Properties of Light and Atomic Structure Chapter 7 So Where are the Electrons? We know where the protons and neutrons are Nuclear structure of atoms (Chapter 2) The interaction of light and matter helps
Properties of Light and Atomic Structure Chapter 7 So Where are the Electrons? We know where the protons and neutrons are Nuclear structure of atoms (Chapter 2) The interaction of light and matter helps
Nuclear spin maser and experimental search for 129 Xe atomic EDM
 Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-012-0751-z Nuclear spin maser and experimental search for 129 Xe atomic EDM T. Inoue T. Furukawa A. Yoshimi Y. Ichikawa M. Chikamori Y. Ohtomo M. Tsuchiya N. Yoshida
Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-012-0751-z Nuclear spin maser and experimental search for 129 Xe atomic EDM T. Inoue T. Furukawa A. Yoshimi Y. Ichikawa M. Chikamori Y. Ohtomo M. Tsuchiya N. Yoshida
Two-stage Rydberg charge exchange in a strong magnetic field
 Two-stage Rydberg charge exchange in a strong magnetic field M. L. Wall, C. S. Norton, and F. Robicheaux Department of Physics, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama 36849-5311, USA Received 21 June 2005;
Two-stage Rydberg charge exchange in a strong magnetic field M. L. Wall, C. S. Norton, and F. Robicheaux Department of Physics, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama 36849-5311, USA Received 21 June 2005;
Project Paper May 13, A Selection of Dark Matter Candidates
 A688R Holly Sheets Project Paper May 13, 2008 A Selection of Dark Matter Candidates Dark matter was first introduced as a solution to the unexpected shape of our galactic rotation curve; instead of showing
A688R Holly Sheets Project Paper May 13, 2008 A Selection of Dark Matter Candidates Dark matter was first introduced as a solution to the unexpected shape of our galactic rotation curve; instead of showing
Back to basics : Maxwell equations & propagation equations
 The step index planar waveguide Back to basics : Maxwell equations & propagation equations Maxwell equations Propagation medium : Notations : linear Real fields : isotropic Real inductions : non conducting
The step index planar waveguide Back to basics : Maxwell equations & propagation equations Maxwell equations Propagation medium : Notations : linear Real fields : isotropic Real inductions : non conducting
What did you learn in the last lecture?
 What did you learn in the last lecture? Charge density distribution of a nucleus from electron scattering SLAC: 21 GeV e s ; λ ~ 0.1 fm (to first order assume that this is also the matter distribution
What did you learn in the last lecture? Charge density distribution of a nucleus from electron scattering SLAC: 21 GeV e s ; λ ~ 0.1 fm (to first order assume that this is also the matter distribution
10.4 Continuous Wave NMR Instrumentation
 10.4 Continuous Wave NMR Instrumentation coherent detection bulk magnetization the rotating frame, and effective magnetic field generating a rotating frame, and precession in the laboratory frame spin-lattice
10.4 Continuous Wave NMR Instrumentation coherent detection bulk magnetization the rotating frame, and effective magnetic field generating a rotating frame, and precession in the laboratory frame spin-lattice
