2. SPHAGNACEAE Dumortier
|
|
|
- Magdalene Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2. SPHAGNACEAE Dumortier Cyrus B. McQueen Richard E. Andrus Plants with branches in fascicles, branches usually of spreading and pendent types but rarely spreading only. Protonemata thallose. Leaves usually of two distinctly different types; branch leaves that are normally inrolled and broadest ca. 1 /4 1 /3 the distance from the base, more or less tapered to a cucullate to involute apex; stem leaves more or less flat and usually broadest at the base; both leaf types of a network of hyaline, dead cells and green chlorophyllose cells; pores and reinforcing fibrils frequent in branch leaf hyaline cells and uncommon in stem leaf hyaline cells. Rhizoids lacking. Sporophytes consisting of a spherical capsule with pseudostomata on capsule surface, a very short seta, and a foot, exserted on a pseudopodium of gametophyte tissue. Spores released by explosive opening of operculum. The sphagnum mosses, or peat mosses, are unique not only morphologically but also ecologically. With their abundant clear cells they can retain up to 25 times their dry weight in water, and a uniquely strong acidifying power permits sphagnum to direct succession wherever conditions are suitable for them to flourish. Much of the earth s surface with a cool humid climate is dominated, thus, by sphagnum peatlands. Genus 1, species ca. 285 (89 species in the flora): nearly worldwide. 1. SPHAGNUM Linnaeus, Sp. Pl. 2: ; Gen. Pl. ed. 5, [Greek sphagnos, an unknown plant] Plants typically with upright stems, young branches arranged spirally around stem at growing apex into a capitulum, branches clustered into fascicles along stem, stem and branch leaves of alternating inflated, S-shaped to rhomboid hyaline cells and narrow linear chlorophyllous cells, hyaline cells typically fibrillose and porose on branch leaves. Protonema typically 1-stratose, gametophyte developing from lateral margin. Stems differentiated into a central cylinder of thin-walled parenchymatous cells, merging into a cylinder of thick-walled cortical cells surrounded by 0 4 layers of thin-walled inflated cells, superficial layer of cells usually aporose, but may be porose. Stem leaves may be less fibrillose or efibrillose and less porose or aporose 45
2 46 SPHAGNACEAE Sphagnum than the branch leaves, often septate, a distinct border of narrow linear chlorophyllous cells often along margins and at base, and with a greater width:length ratio than branch leaves in anisophyllous forms, partly differentiated in hemiisophyllous forms, and identical in isophyllous forms. Branches typically dimorphic as spreading and pendent branches, but some species lack branches or branches are not clearly differentiated, pendent branches typically more slender than spreading branches and with a tendency to adhere to and cover the stem. Branch fascicles typically with 2 spreading and 1 2 pendent branches, but there may be up to 12( 14) per fascicle. Branch stems typically green, with a superficial layer of inflated retort cells; these grouped or solitary, usually porose at the distal end with a conspicuous or inconspicuous neck. Branch leaves with 2 /5 phyllotaxy, of a 1-stratose network of alternating chlorophyllous and hyaline cells; hyaline cells usually S-shaped, rarely rhomboid, nearly always strengthened with conspicuous spiral fibrils, small to large, round to elliptic and sometimes ringed pores occur along commissures or rarely on cell lumen, convex surface typically with more pores per cell than concave surface; chlorophyllous cells may be enclosed on both surfaces, more broadly exposed on one surface or equally exposed on both surfaces as viewed in transverse section, adjacent cell walls typically smooth, but various types of cell wall projections may be clearly visible in transverse section. Sexual condition dioicous or monoicous; stalked globose antheridia borne at the tips of branches usually with swollen colored tips of branches near capitulum; long-necked archegonia borne on short branches singly surrounded by perichaetial leaves that are typically longer than branch leaves. Capsule spherical, brown to black, lacking an annulus or peristome with a operculum convex; spore sac amphithecial in origin, over-arching columella. Calyptra membranous. Spores tetrahedral, with prominent trilete mark, fine to coarse superficial surface, distal surface may have raised Y-mark, bifurcated Y-mark sculpture, or none. Species 285 (89 in the flora): worldwide except Antarctica, primarily in boreal regions but also in cool, moist montane and oceanic habitats such as nutrient-poor and acidic wetlands and mires. The concept of species in Sphagnum is controversial. We have followed P. Isoviita (1966) and K. I. Flatberg (1994) in the recognition of species. H. A. Crum (1984) and others (R. E. Daniels and A. Eddy 1985; A. L. Andrews 1958, 1959) have adopted more conservative taxonomic concepts for species in the Northern Hemisphere. Description of the spores above is from Cao T. and D. H. Vitt (1986); for additional discussion of the protonema see C. B. McQueen (1988). Microscopic features can be observed by using a concentrated aqueous or alcohol solution of Crystal Violet. A 50% solution of alcohol and Methylene Blue or Safranin Red can be used, but these usually do not stain features such as minute pores, fibrils, wall thinnings, and surface sculpture on the chlorophyllous cells. The number and kinds of branches should be determined, individual stem and branch leaves (from the middle of a spreading branch) should be examined from the distal 2 cm of the plant, and the superficial surface of stem cortical cells as well as cross sections of branch leaves and stems may need examination. SELECTED REFERENCES Crum, H. A Sphagnaceae. In: N. L. Britton et al., eds North American Flora vols. New York. Ser. 2, part 11. Crum, H. A Sphagnaceae. In: G. S. Mogensen, ed. Illustrated moss flora of arctic North America and Greenland. 2. Meddel. Grønland, Biosci. 18: Daniels, R. E. and A. Eddy Handbook of European Sphagna. Huntingdon. Flatberg, K. I The Norwegian Sphagna: A Field Colour Guide. Trondheim. Isoviita, P Studies on Sphagnum L. 1. Nomenclatural revision of the European taxa. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 3: McQueen, C. B Field Guide to the Peat Mosses of Boreal North America. London. Nyholm, E Illustrated Moss Flora of Fennoscandia II: Musci. Lund. Pp
3 Sphagnum SPHAGNACEAE Outer stem cortical cell walls reinforced with spiral fibrils a. Sphagnum sect. Sphagnum, p Outer stem cortical cell walls smooth. 2. Outer cortical cells of branches nearly all porose at distal end; branch leaves with denticulate margins and bordered with resorption furrow b. Sphagnum sect. Rigida, p Outer cortical cells of branches of two kinds, smaller aporose cells and larger retortshaped cells with pore at apical end; branch leaf margins usually entire. 3. Fascicles of 7 or more branches h. Sphagnum sect. Polyclada, p Fascicles of 6 or fewer branches. 4. Branch leaf hyaline cells efibrillose, but see 46. S. splendens in sect. Cuspidata e. Sphagnum sect. Isocladus, p Branch leaf hyaline cells fibrillose. 5. Branch and stem leaves isophyllous; branches in fascicles of 2 3, spreading and pendent branches similar, or plants may have single or no branches; hyaline cells of branch leaves usually with numerous pores along the commissures, giving a bead-like appearance; chlorophyllous cells of branch leaves in transverse section barrel-shaped, truncate-elliptic to trapezoidal, exposed equally on both surfaces or slightly broader on the convex surface g. Sphagnum sect. Subsecunda (in part), p Branch and stem leaves usually anisophyllous; 3 6 branches per fascicle, spreading branches clearly differentiated from pendent branches; hyaline cells of branch leaves with scattered pores along the commissures or free; chlorophyllous cells of branch leaves in transverse section triangular, truncate-trapezoidal to elliptical and may be more broadly exposed on either surface. 6. Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells triangular to trapezoidal, exposed much more broadly on concave or convex surface. 7. Chlorophyllous cells of branch leaves triangular to trapezoidal in transverse section, more broadly exposed on the convex surface; in plants with stellate capitula, the branches between the rays of the capitulum occur in pairs; stem leaves often hanging downward on the stem f. Sphagnum sect. Cuspidata, p Chlorophyllous cells of branch leaves triangular to trapezoidal in transverse section, more broadly exposed on the concave surface; in plants with stellate capitula, the branches between the rays of the capitulum single; stem leaves upright on the stem i. Sphagnum sect. Acutifolia, p Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells lenticular, truncate-elliptic to trapezoidal; exposed more or less equally on both surfaces or slightly more broadly on convex surface. 8. Stem leaves with apex broad and fimbriate; branch leaves often squarrose from an enlarged clasping base; interior surface of chlorophyllous cells often finely papillose.... 1d. Sphagnum sect. Squarrosa, p Stem leaves with apex obtuse and entire to erose; branch leaves straight, slightly subsecund, or slightly recurved; interior surface of chlorophyllous cells always smooth. 9. Branch leaves with broad truncate toothed apex, hyaline cells with pores in cell ends and angles c. Sphagnum sect. Insulosa, p Branch leaves with rounded, untoothed or weakly toothed apex, hyaline cells on convex surface with numerous pores along commissures or free.... 1g. Sphagnum sect. Subsecunda (in part), p. 78
4 48 SPHAGNACEAE Sphagnum 1a. SPHAGNUM Linnaeus sect. SPHAGNUM Plants typically large, with distinct capitulum; green, pale green, yellowish, red, tan, brown to dark brown. Stems green, brown or reddish, outer cortex of 3 4 layers of inflated, thin-walled cells, superficial cells with conspicuous to faint spiral fibrils, no or strong ornamention on interior wall, and 1 6 round to ovate pores per cell. Stem leaves typically as large as or larger than branch leaves, lingulate to ovate-lingulate with broad rounded apex, border fringed; hyaline cells rhomboid, efibrillose or fibrillose, sometimes ornamented, aporose, 0 2-septate, and often resorbed on exterior surface. Branches dimorphic, spreading branches tumid, pendent branches usually shorter and more slender. Branch fascicles with 2 3 spreading branches and 1 3 pendent branches. Branch stems green, surrounded by 1 layer of enlarged thin-walled cells, typically porose and fibrillose, in some species ornamented on interior wall; retort cells absent. Branch leaves ovate to broadly ovate, apex cucullate and roughened on convex surface; margin toothed; hyaline cells fibrillose; convex surface pores round to elliptic, usually with 1 at each corner of three adjacent hyaline cells; chlorophyllous cells lenticular to triangular, sometimes with wall ornamentation visible in transverse section; chlorophyllous cells enclosed, equally exposed, or more broadly exposed on concave surface, end walls thickened or unthickened. Sexual condition usually dioicous. Capsule 2 mm or more. Spores typically µm, distal surface sculpture may be present; proximal laesura usually more than 0.5 spore radius. Species 54 (12 in the flora): worldwide except Antarctica. 1. Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells in transverse section ± equilateral-triangular, often with conspicuous vertically oriented comb-fibrils on the hyaline cells where overlying chlorophyllous cells. 2. Branch cortical cells with funnel-like projections often extending halfway or more into the next cell; branches strongly clavate and blunt Sphagnum portoricense 2. Branch cortical cells with flat end walls or with weak funnel-like projections extending less than halfway into the next cell; branches not clavate or if clavate, with pointed ends. 3. Interior layer of stem cortical cells with distinct comb-lamellae; branch leaves with or without comb-lamellae; stem leaves without comb-lamellae Sphagnum affine 3. Interior layer of stem cortical cells without comb-lamellae or at least not visible with a light microscope; branch leaves with comb-lamellae; stem leaves with or without comb-lamellae. 4. Stem leaf hyaline cells with distinct comb-lamellae; branches clavate and pointed; branches leaves strongly imbricate Sphagnum austinii 4. Stem leaf hyaline cells without distinct comb-lamellae; branches not clavate; branch leaves more or less spreading. 5. Stem leaves short (ca mm); branch leaves broad (breadth:length ca ), branch leaf comb-lamellae usually distinct only in lower half of leaf; branch cortical comb-lamellae present; plants yellow to golden brown Sphagnum imbricatum 5. Stem leaves long (ca mm.); branch leaves narrow (breadth:length ca ), branch leaf comb-lamellae distinct throughout most of leaf; branch cortical cell comb-lamellae usually absent; plants dark brown Sphagnum steerei 1. Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells in transverse section narrowly triangular, trapezoidal, truncate-elliptic, elliptic or lenticular; comb-fibrils if present horizontally oriented. 6. Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells in transverse section short-elliptic, elliptic to lenticular, and enclosed on both surfaces.
5 Sphagnum SPHAGNACEAE Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells in transverse section short-elliptic and well enclosed; plants purplish red when pigmented Sphagnum magellanicum 7. Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells in transverse section narrowly elliptic and slightly enclosed on both surfaces; plants brown when pigmented. 8. Branch leaf chlorphyllous cells in transverse section without thickened ends walls; superficial stem cortical cells with reinforcing fibrils weak or absent; branch leaf hyaline cells where overlying chlorophyll cells often with combfibrils Sphagnum alaskense 8. Branch leaf chlorphyllous cells in transverse section with thickened end walls; superficial stem cortical cells with strong reinforcing fibrils; branch leaf hyaline cells where overlying chlorophyllous cells smooth Sphagnum centrale [6. Shifted to left margin. Ed.] 6. Branch leaf chlorophyllous cells in transverse section narrowly triangular, rectangular to truncate-elliptic, exposed equally on both surfaces or more broadly on the convex surface. 9. Branch leaf hyaline cells papillose where overlying chlorophyllous cells Sphagnum papillosum 9. Branch leaf hyaline cells epapillose where overlying chlorophyllous cells. 10. Superficial stem cortical cells with fibrils weak or lacking; chlorophyllous cells rectangular to truncate-elliptic, exposed equally on both surfaces Sphagnum perichaetiale 10. Superficial stem cortical cells with strong fibrils; chlorophyllous cells triangular, exposed more broadly on concave surface. 11. Branch leaf hyaline cells where overlying chlorophyllous cells often with irregular worm-like ridges, especially at the leaf base; pores on the convex surface numerous, small and round to elliptic Sphagnum henryense 11. Branch leaf hyaline cells smooth throughout; pores on the convex surface elliptic to flattened-elliptic, not numerous Sphagnum palustre 1. Sphagnum affine Renauld & Cardot, Rev. Bryol. 12: Sphagnum imbricatum subsp. affine (Renauld & Cardot) Flatberg; S. imbricatum var. affine (Renauld & Cardot) Warnstorf; S. imbricatum var. laeve Warnstorf Plants moderate-sized and lax to somewhat compact, ± stiffstemmed; moderate-sized to large, forming lawns or low, loose hummocks; green, yellow-brown to golden brown and often tinged with brown to purplish brown; capitulum ± flat in lax open-grown forms to ± rounded and compact in open-grown forms. Stems brown, superficial cortical layer with spiral reinforcing fibrils clearly visible, usually 2 or more pores per cell, comb-fibrils visible on interior wall. Stem leaves to mm; rarely hemiisophyllous; hyaline cells non-ornamented, nonseptate or sometimes septate. Branches ± tapering, leaves loosely imbricate to spreading and often squarrose in shade forms. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 2 3 pendent branches. Branch stems with cortical cell comb-lamellae weakly differentiated on interior wall, no or weak funnel-like projections on the interior end walls, pores in superficial wall mostly restricted to leaf attachments. Branch leaves ovate to ovate elliptical, mm; hyaline cells on convex surface with elliptic to more often round pores along the commissures, comb-lamellae can be present, but often absent or restricted to leaf bases; chlorophyllous cells broadly triangular in transverse section and well-enclosed on the convex surface; end wall not thickened. Sexual condition dioicous. Capsule with scattered pseudostomata. Spores µm; granulate on both surfaces; laesura on proximal surface less than 0.5 the spore radius. Capsules fairly common, mature early to late summer. Widespread and often ruderal, wide variety of minerotrophic wetlands, especially abundant in forested mires; low to moderate elevations; Nfld. and Labr. (Nfld.), N.S., P.E.I.; Ala., Ark., Conn., Del., D.C., Fla., Ga., Ill., Ind., Ky., La., Maine, Md., Mass., Miss., Mo., N.H., N.J., N.Y., N.C., Ohio., Okla., Pa., R.I., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Vt., Va., W.Va.; Europe. Sphagnum affine may occur elsewhere but the taxonomy is unclear (K. I. Flatberg 1984). Although species of sect. Sphagnum are notoriously difficult to tell apart in the field, S. affine is typically smaller than S. centrale, S. palustre, and S. papillosum, the other brown species of this section with which it may occur. It is also much more likely to have somewhat squarrose branch leaves, especially in shade forms.
Sphagnum SPHAGNACEAE 65
 SPHAGNACEAE 65 Wet carpets, lawns, and mud bottoms in poor to medium fens, in mire-wide and mire-edge habitats; low to high elevations; Alta., B.C., Man., Nfld. and Labr. (Nfld.), N.W.T., Ont., Que., Yukon;
SPHAGNACEAE 65 Wet carpets, lawns, and mud bottoms in poor to medium fens, in mire-wide and mire-edge habitats; low to high elevations; Alta., B.C., Man., Nfld. and Labr. (Nfld.), N.W.T., Ont., Que., Yukon;
Sphagnum. Sphagnum [unranked] Rigida Lindberg, Öfvers. Kongl. Vetensk.-Akad. Förh. 19:
![Sphagnum. Sphagnum [unranked] Rigida Lindberg, Öfvers. Kongl. Vetensk.-Akad. Förh. 19: Sphagnum. Sphagnum [unranked] Rigida Lindberg, Öfvers. Kongl. Vetensk.-Akad. Förh. 19:](/thumbs/94/118314765.jpg) SPHAGNACEAE 55 SPHAGNUM nonseptate, comb-lamellae usually absent, but sometimes weak. Branches short and blunt-tipped, leaves spreading. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 1 pendent branch. Branch stems
SPHAGNACEAE 55 SPHAGNUM nonseptate, comb-lamellae usually absent, but sometimes weak. Branches short and blunt-tipped, leaves spreading. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 1 pendent branch. Branch stems
70 SPHAGNACEAE. Sphagnum
 70 SPHAGNACEAE with leaves unranked to 5-ranked, leaves not much elongated at distal branch tip. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 2 3 pendent branches. Branch leaves ovate, 1.1 1.3 mm long, stiff,
70 SPHAGNACEAE with leaves unranked to 5-ranked, leaves not much elongated at distal branch tip. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 2 3 pendent branches. Branch leaves ovate, 1.1 1.3 mm long, stiff,
Sphagnum Structure and Terminology. By Sharon Pilkington on behalf of the Species Recovery Trust
 Sphagnum Structure and Terminology By Sharon Pilkington on behalf of the Species Recovery Trust Capitulum Branch Stem leaf Stem Branch leaf SPHAGNUM SHOOT Single fascicle Prominent terminal bud e.g. S.
Sphagnum Structure and Terminology By Sharon Pilkington on behalf of the Species Recovery Trust Capitulum Branch Stem leaf Stem Branch leaf SPHAGNUM SHOOT Single fascicle Prominent terminal bud e.g. S.
Overview. Revised through 30 June Initial Groups ("naked-eye" characters)
 Overview Revised through 30 June 2010 Initial Groups ("naked-eye" characters) Plants essentially leafless, consisting of strongly inclined, highly asymmetric capsules on a stout papillose seta; the "bug-on-a-stick"
Overview Revised through 30 June 2010 Initial Groups ("naked-eye" characters) Plants essentially leafless, consisting of strongly inclined, highly asymmetric capsules on a stout papillose seta; the "bug-on-a-stick"
3. ANDREAEACEAE Dumortier
 3. ANDREAEACEAE Dumortier Richard H. Zander Plants dark green to black, small to large, often in dense turf. Stems erect, irregularly branched, bearing rhizoids at base; central strand absent. Leaves erect
3. ANDREAEACEAE Dumortier Richard H. Zander Plants dark green to black, small to large, often in dense turf. Stems erect, irregularly branched, bearing rhizoids at base; central strand absent. Leaves erect
acknowledged for his unqualified support and commitment to this project as well as to
 Introduction Central America has one of the most diverse moss floras in the world. Its 871 species are found in an area three-fourths the size of Texas. Indeed, it has roughly the same number of mosses
Introduction Central America has one of the most diverse moss floras in the world. Its 871 species are found in an area three-fourths the size of Texas. Indeed, it has roughly the same number of mosses
Nonvascular Plants. Believed to have evolved from green-algae. Major adaptations in going from water to land. Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids
 Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
A New Locality of Fossombronia mylioides (Fossombroniaceae, Marchantiophyta)
 Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 42(1), pp. 19 23, February 22, 2016 A New Locality of Fossombronia mylioides (Fossombroniaceae, Marchantiophyta) Masanobu Higuchi Department of Botany, National Museum
Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 42(1), pp. 19 23, February 22, 2016 A New Locality of Fossombronia mylioides (Fossombroniaceae, Marchantiophyta) Masanobu Higuchi Department of Botany, National Museum
S. SANDHYA RANI, M. SOWGHANDIKA,
 S. SANDHYA RANI, M. SOWGHANDIKA, 76 Habitat: Rare, grows on red rocks over soil. Specimen examined: Coffee plantations in Galikonda (VSKP), MS 33959. India : Darjeeling, Sikkim, Khasi hills. World : East
S. SANDHYA RANI, M. SOWGHANDIKA, 76 Habitat: Rare, grows on red rocks over soil. Specimen examined: Coffee plantations in Galikonda (VSKP), MS 33959. India : Darjeeling, Sikkim, Khasi hills. World : East
CHAPTER 4-3 ADAPTIVE STRATEGIES: PHENOLOGY, A SPHAGNUM CASE STUDY
 Glime, J. M. 2017. Adaptive Strategies: Phenology, A Sphagnum Case Study. Chapt. 4-3. In: Glime, J. M. Bryophyte Ecology. Volume 4-3-1 1. Physiological Ecology. Ebook sponsored by Michigan Technological
Glime, J. M. 2017. Adaptive Strategies: Phenology, A Sphagnum Case Study. Chapt. 4-3. In: Glime, J. M. Bryophyte Ecology. Volume 4-3-1 1. Physiological Ecology. Ebook sponsored by Michigan Technological
-plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem. -spores with tough walls. -life history of alternation of generations
 Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
A handful of primary features are useful for distinguishing water primrose (Ludwigia) from other plants. Understand what to look for, such as leaf
 A handful of primary features are useful for distinguishing water primrose (Ludwigia) from other plants. Understand what to look for, such as leaf arrangement and number of petals. Pairing morphological
A handful of primary features are useful for distinguishing water primrose (Ludwigia) from other plants. Understand what to look for, such as leaf arrangement and number of petals. Pairing morphological
CHAPTER 2-5 BRYOPHYTA SPHAGNOPSIDA
 Glime, J. M. 2017. Bryophyta - Sphagnopsida. Chapt. 2-5. In: Glime, J. M. Bryophyte Ecology. Volume 1. Physiological Ecology. 2-5-1 Ebook sponsored by Michigan Technological University and the International
Glime, J. M. 2017. Bryophyta - Sphagnopsida. Chapt. 2-5. In: Glime, J. M. Bryophyte Ecology. Volume 1. Physiological Ecology. 2-5-1 Ebook sponsored by Michigan Technological University and the International
ARE PLAGIOTHECIUM CAVIFOLIUM, P. NEMORALE AND P. SUCCULENTUM INDEED VARIABLE SPECIES?
 Pak. J. Bot., 50(4): 1579-1589, 2018. ARE PLAGIOTHECIUM CAVIFOLIUM, P. NEMORALE AND P. SUCCULENTUM INDEED VARIABLE SPECIES? Department of Geobotany and Plant Ecology, Faculty of Biology and Environmental
Pak. J. Bot., 50(4): 1579-1589, 2018. ARE PLAGIOTHECIUM CAVIFOLIUM, P. NEMORALE AND P. SUCCULENTUM INDEED VARIABLE SPECIES? Department of Geobotany and Plant Ecology, Faculty of Biology and Environmental
SPECIES FACT SHEET. Taxonomic Note: None.
 SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Granite moss, Lantern moss Scientific Name: Andreaea nivalis Hook. Recent synonyms: Andreaea baileyi Holz. A. macounii Kindb. in Mac. Division: Bryophyta Class: Bryopsida
SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Granite moss, Lantern moss Scientific Name: Andreaea nivalis Hook. Recent synonyms: Andreaea baileyi Holz. A. macounii Kindb. in Mac. Division: Bryophyta Class: Bryopsida
10. TIMMIACEAE Schimper
 10. TIMMIACEAE Schimper Guy R. Brassard Plants acrocarpous, large. Stems stiff, erect, mostly unbranched, in cross-section with a cortical region of small, thick-walled cells, a parenchyma of larger, thin-walled
10. TIMMIACEAE Schimper Guy R. Brassard Plants acrocarpous, large. Stems stiff, erect, mostly unbranched, in cross-section with a cortical region of small, thick-walled cells, a parenchyma of larger, thin-walled
Plant Crib VERONICA. 1. Veronica serpyllifolia
 VERONICA 1. Veronica serpyllifolia Illustrations reproduced, with permission, from M. McC. Webster (1978). Flora of Moray, Nairn & East Inverness. Aberdeen. Subsp. humifusa (Dicks.) Syme Subsp. serpyllifolia
VERONICA 1. Veronica serpyllifolia Illustrations reproduced, with permission, from M. McC. Webster (1978). Flora of Moray, Nairn & East Inverness. Aberdeen. Subsp. humifusa (Dicks.) Syme Subsp. serpyllifolia
Introduction to Bryophyta
 Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
I. Lycopodiales: The Vegetative Features of the Sporophyte Phase
 Lab II. Lycopodiales: the Clubmosses I. Lycopodiales: The Vegetative Features of the Sporophyte Phase The clubmosses (traditionally classified as species of the genus Lycopodium) are low, evergreen plants
Lab II. Lycopodiales: the Clubmosses I. Lycopodiales: The Vegetative Features of the Sporophyte Phase The clubmosses (traditionally classified as species of the genus Lycopodium) are low, evergreen plants
ILLUSTRATED GLOSSARY TO THE FIELD GUIDES OF THE MOSSES & LIVERWORTS OF MINNESOTA. Joannes A. Janssens Minneapolis
 ILLUSTRATED GLOSSARY TO THE FIELD GUIDES OF THE MOSSES & LIVERWORTS OF MINNESOTA Joannes A. Janssens 2013 Minneapolis 2014 State of Minnesota, Department of Natural Resources Unless otherwise credited,
ILLUSTRATED GLOSSARY TO THE FIELD GUIDES OF THE MOSSES & LIVERWORTS OF MINNESOTA Joannes A. Janssens 2013 Minneapolis 2014 State of Minnesota, Department of Natural Resources Unless otherwise credited,
Equisetaceae Horsetails
 Equisetaceae Horsetails Another ancient family of plants, there is but a single extant genus. Annual or perennial, all have jointed hollow stems, marked by ridges. Coarse texture is further enhanced by
Equisetaceae Horsetails Another ancient family of plants, there is but a single extant genus. Annual or perennial, all have jointed hollow stems, marked by ridges. Coarse texture is further enhanced by
PHYTOTAXA ISSN (online edition)
 Phytotaxa 333 (1): 001 021 http://www.mapress.com/j/pt/ ISSN 1179-3155 (print edition) Copyright 2018 Magnolia Press Article PHYTOTAXA ISSN 1179-3163 (online edition) https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.333.1.1
Phytotaxa 333 (1): 001 021 http://www.mapress.com/j/pt/ ISSN 1179-3155 (print edition) Copyright 2018 Magnolia Press Article PHYTOTAXA ISSN 1179-3163 (online edition) https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.333.1.1
FIELD IDENTIFICATION CARDS FOR INVASIVE NON-NATIVE PLANT SPECIES KNOWN TO THREATEN ARIZONA WILDLANDS.
 FIELD IDENTIFICATION CARDS FOR INVASIVE NON-NATIVE PLANT SPECIES KNOWN TO THREATEN ARIZONA WILDLANDS. PACKET CONTAINS INFORMATION ON 74 INVASIVE NON-NATIVE PLANTS INCLUDING: morphologic descriptions photos
FIELD IDENTIFICATION CARDS FOR INVASIVE NON-NATIVE PLANT SPECIES KNOWN TO THREATEN ARIZONA WILDLANDS. PACKET CONTAINS INFORMATION ON 74 INVASIVE NON-NATIVE PLANTS INCLUDING: morphologic descriptions photos
COMMON CONIFERS OF THE PNW
 COMMON CONIFERS OF THE PNW The common conifers in the Pacific Northwest belong to the following genera: Abies, Calocedrus, Callitropsis, Juniperus, Larix, Picea, Pinus, Pseudotsuga, Taxus, Thuja, and Tsuga.
COMMON CONIFERS OF THE PNW The common conifers in the Pacific Northwest belong to the following genera: Abies, Calocedrus, Callitropsis, Juniperus, Larix, Picea, Pinus, Pseudotsuga, Taxus, Thuja, and Tsuga.
LENTIBULARIACEAE BLADDERWORT FAMILY
 LENTIBULARIACEAE BLADDERWORT FAMILY Barry Rice Center for Plant Diversity, Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, 1 Shields Avenue, Davis CA 95616 Perennial and annual herbs, carnivorous,
LENTIBULARIACEAE BLADDERWORT FAMILY Barry Rice Center for Plant Diversity, Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, 1 Shields Avenue, Davis CA 95616 Perennial and annual herbs, carnivorous,
and Engineering Laboratory Cold Regions Research ERDC/CRREL TN-08-2 A Guide to Alaskan Black Spruce Wetland Bryophytes
 ERDC/CRREL TN-08-2 A Guide to Alaskan Black Spruce Wetland Bryophytes Species Specific to Delineation for Interior and South Central Regions Rodney D. Seppelt, Gary A. Laursen, and Robert W. Lichvar June
ERDC/CRREL TN-08-2 A Guide to Alaskan Black Spruce Wetland Bryophytes Species Specific to Delineation for Interior and South Central Regions Rodney D. Seppelt, Gary A. Laursen, and Robert W. Lichvar June
Literature. Morphology. Morphology of the mycorrhizal system. Morphology of the unramified ends
 Literature references Müller WR, Rauscher T, Agerer R, Chevalier G (1996) Tuber aestivum Vitt. + Corylus avellana L.Descr Ectomyc 1: 167-172. Rauscher T, Müller WR, Chevalier G, Agerer R (1996) Tuber aestivum.
Literature references Müller WR, Rauscher T, Agerer R, Chevalier G (1996) Tuber aestivum Vitt. + Corylus avellana L.Descr Ectomyc 1: 167-172. Rauscher T, Müller WR, Chevalier G, Agerer R (1996) Tuber aestivum.
Part 1: Naming the cultivar
 REGISTRATION FORM FOR a CULTIVAR NAME of POPULUS L. Sub-Committee for Nomenclature and Registration FAO - International Poplar Commission (appointed in 1958 as the ICRA for the genus Populus) Addresses
REGISTRATION FORM FOR a CULTIVAR NAME of POPULUS L. Sub-Committee for Nomenclature and Registration FAO - International Poplar Commission (appointed in 1958 as the ICRA for the genus Populus) Addresses
SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Scientific Name: Technical Description: Distinctive characters: Similar species:
 SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Platyhypnidium moss Scientific Name: Platyhypnidium riparioides Recent synonym: Eurhynchium riparioides, Rhynchostegium riparioides Phylum: Bryophyta Class: Bryopsida Order:
SPECIES FACT SHEET Common Name: Platyhypnidium moss Scientific Name: Platyhypnidium riparioides Recent synonym: Eurhynchium riparioides, Rhynchostegium riparioides Phylum: Bryophyta Class: Bryopsida Order:
Fungi Coloring Worksheet
 Fungi Coloring Worksheet The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube formed
Fungi Coloring Worksheet The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube formed
Phaeocalicium populneum
 Phaeocalicium populneum markpowell222@btinternet.com After conducting a survey of the RHS garden at Wisley on 18 th August 2018, Fay Newbery kindly showed me the colony of P. populneum at Esher Common.
Phaeocalicium populneum markpowell222@btinternet.com After conducting a survey of the RHS garden at Wisley on 18 th August 2018, Fay Newbery kindly showed me the colony of P. populneum at Esher Common.
Common Name: GEORGIA QUILLWORT. Scientific Name: Isoetes georgiana Luebke. Other Commonly Used Names: none. Previously Used Scientific Names: none
 Common Name: GEORGIA QUILLWORT Scientific Name: Isoetes georgiana Luebke Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Isoetaceae (quillwort) Rarity Ranks: G2G3/S2S3 State
Common Name: GEORGIA QUILLWORT Scientific Name: Isoetes georgiana Luebke Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Isoetaceae (quillwort) Rarity Ranks: G2G3/S2S3 State
Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages ) Generation Description Haploid or Diploid? Gamete-producing plant Spore-producing plant
 Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555) What Is a Plant? (page 551) 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about plants. a. Plants are multicellular prokaryotes. b. Plants
Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555) What Is a Plant? (page 551) 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about plants. a. Plants are multicellular prokaryotes. b. Plants
Acrobotrys tritubus Riedel
 151 Acrobotrys tritubus Riedel Acrobotrys tritubus Riedel, 1957, p.80, pl.1, fig.5 DESCRIPTION Cephalis trilobate, with large subglobular [antecephalic] lobe, smaller globular [cephalic] lobe, and inflated-conical
151 Acrobotrys tritubus Riedel Acrobotrys tritubus Riedel, 1957, p.80, pl.1, fig.5 DESCRIPTION Cephalis trilobate, with large subglobular [antecephalic] lobe, smaller globular [cephalic] lobe, and inflated-conical
Other Commonly Used Names: wintergreen quillwort, evergreen quillwort
 Common Name: WINTER QUILLWORT Scientific Name: Isoetes hyemalis D.F. Brunton Other Commonly Used Names: wintergreen quillwort, evergreen quillwort Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Isoetaceae
Common Name: WINTER QUILLWORT Scientific Name: Isoetes hyemalis D.F. Brunton Other Commonly Used Names: wintergreen quillwort, evergreen quillwort Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Isoetaceae
Systematics of the Sphagnum recurvum Complex: Arielle K. Garrett. Department of Biology Duke University. Date: Approved: A. Jonathan Shaw, Supervisor
 Systematics of the Sphagnum recurvum Complex: Morphological Variation, Hybridization and the Delineation of Intermediate Taxa by K. Department of Biology Duke University Date: Approved: A. Jonathan Shaw,
Systematics of the Sphagnum recurvum Complex: Morphological Variation, Hybridization and the Delineation of Intermediate Taxa by K. Department of Biology Duke University Date: Approved: A. Jonathan Shaw,
Bryophytes: Liverworts, Hornworts and Mosses.
 Bryophytes: Liverworts, Hornworts and Mosses. Bryophytes Plant scien+sts recognize two kinds of land plants Bryophytes, or nonvascular plants Tracheophytes, or vascular plants. Distribu+on tropical rainforests,
Bryophytes: Liverworts, Hornworts and Mosses. Bryophytes Plant scien+sts recognize two kinds of land plants Bryophytes, or nonvascular plants Tracheophytes, or vascular plants. Distribu+on tropical rainforests,
8. POLYTRICHACEAE Schwägrichen
 8. POLYTRICHACEAE Schwägrichen Gary L. Smith Merrill Plants small, medium to large, densely to loosely caespitose or scattered among other bryophytes, rarely with individual plants scattered on a persistent
8. POLYTRICHACEAE Schwägrichen Gary L. Smith Merrill Plants small, medium to large, densely to loosely caespitose or scattered among other bryophytes, rarely with individual plants scattered on a persistent
Aquatic Bryophytes. What is a bryophyte? I. Big picture. II. Biology -Life Life Cycle -Major Groups -Adaptations. III. Aquatic Bryophyte Ecology
 Aquatic Bryophytes What is a bryophyte? -Life Life Cycle -Major Groups -Adaptations Heather Lintz Botany and Plant Pathology Oregon State University Bryophytes are here All land plants likely to have freshwater
Aquatic Bryophytes What is a bryophyte? -Life Life Cycle -Major Groups -Adaptations Heather Lintz Botany and Plant Pathology Oregon State University Bryophytes are here All land plants likely to have freshwater
Angiosperms: Dicotyledons
 Angiosperms: Dicotyledons This section contains anatomical descriptions of stem and twig xylem, as well as the bark and pith regions of 244 dicotyledonous species belonging to 61 families. Angiosperms:
Angiosperms: Dicotyledons This section contains anatomical descriptions of stem and twig xylem, as well as the bark and pith regions of 244 dicotyledonous species belonging to 61 families. Angiosperms:
PROTOCOL FOR DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY TESTS
 PROTOCOL FOR DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY TESTS Gaura L. GAURA UPOV Species Code: GAURA Adopted on 21/03/2012 Entry into force on 21/03/2012 1 I SUBJECT OF THE PROTOCOL The protocol describes
PROTOCOL FOR DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY TESTS Gaura L. GAURA UPOV Species Code: GAURA Adopted on 21/03/2012 Entry into force on 21/03/2012 1 I SUBJECT OF THE PROTOCOL The protocol describes
Type studies on Pycnolejeunea (Lejeuneaceae, Hepaticae), III. Two Asiatic species described by Hoffmann
 Ann. Bot. Fennici 33: 59 64 ISSN 0003-3847 Helsinki 6 May 1996 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 1996 Type studies on Pycnolejeunea (Lejeuneaceae, Hepaticae), III. Two Asiatic species described
Ann. Bot. Fennici 33: 59 64 ISSN 0003-3847 Helsinki 6 May 1996 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 1996 Type studies on Pycnolejeunea (Lejeuneaceae, Hepaticae), III. Two Asiatic species described
Plant Tissues and Organs. Topic 13 Plant Science Subtopics , ,
 Plant Tissues and Organs Topic 13 Plant Science Subtopics 13.1.2, 13.1.3, 13.1.4 Objectives: List and describe the major plant organs their structure and function List and describe the major types of plant
Plant Tissues and Organs Topic 13 Plant Science Subtopics 13.1.2, 13.1.3, 13.1.4 Objectives: List and describe the major plant organs their structure and function List and describe the major types of plant
SPORE-FORMS IN SPOROPHORES OF GANODERMA LUCIDUM (LEYSS.) KARST.
 SPORE-FORMS IN SPOROPHORES OF GANODERMA LUCIDUM (LEYSS.) KARST. BY SACHINDRANATH BANERJEE AND ANJALI SARKAR (Department of Botany, University o[ Calcutta) Received September 12, 1958 (Communicated by Dr.
SPORE-FORMS IN SPOROPHORES OF GANODERMA LUCIDUM (LEYSS.) KARST. BY SACHINDRANATH BANERJEE AND ANJALI SARKAR (Department of Botany, University o[ Calcutta) Received September 12, 1958 (Communicated by Dr.
 Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark the regions where active cell division and rapid division
Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark the regions where active cell division and rapid division
Symphysodontella madhusoodananii (Pterobryaceae, Moss) a new species from the Western Ghats of India
 PhytoKeys 18: 39 44 (2012) doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.18.3314 www.phytokeys.com Symphysodontella madhusoodananii (Pterobryaceae, Moss) a new species... 39 research article A peer-reviewed open-access journal
PhytoKeys 18: 39 44 (2012) doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.18.3314 www.phytokeys.com Symphysodontella madhusoodananii (Pterobryaceae, Moss) a new species... 39 research article A peer-reviewed open-access journal
ANATOMY OF PLANTS Introduction: The study of gross internal structure of plant organs by the technique of section cutting is called plant anatomy.
 ANATOMY OF PLANTS Introduction: The study of gross internal structure of plant organs by the technique of section cutting is called plant anatomy. (Pandey, 2002). Various plant organ viz. root, stem, leaves,
ANATOMY OF PLANTS Introduction: The study of gross internal structure of plant organs by the technique of section cutting is called plant anatomy. (Pandey, 2002). Various plant organ viz. root, stem, leaves,
The Shoot System: Primary Stem Structure - 1
 The Shoot System: Primary Stem Structure - 1 Shoot System The shoot system comprises the leaves and stems of plants. Leaves are located at nodes on the stem; the distance along the stem between nodes is
The Shoot System: Primary Stem Structure - 1 Shoot System The shoot system comprises the leaves and stems of plants. Leaves are located at nodes on the stem; the distance along the stem between nodes is
MARINE FUNGI IN giscayne BAY, FLORIDA 1
 MARINE FUNGI IN giscayne BAY, FLORIDA 1 SAMUEL P. MEYERS The Marine Laboratory, University of Miami ABSTRACT A recent collection in Biscayne Bay, Florida, of various marine fungal forms, several previously
MARINE FUNGI IN giscayne BAY, FLORIDA 1 SAMUEL P. MEYERS The Marine Laboratory, University of Miami ABSTRACT A recent collection in Biscayne Bay, Florida, of various marine fungal forms, several previously
Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue
 PLANT TISSUES Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue Undifferentiated plant cells that are continually dividing by mitosis Large thin walled cells No vacuole Dense cytoplasm Large nucleus Found at
PLANT TISSUES Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue Undifferentiated plant cells that are continually dividing by mitosis Large thin walled cells No vacuole Dense cytoplasm Large nucleus Found at
Chapter 20 Nonvascular Plants: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts
 Chapter 20 Nonvascular Plants: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts Major plant groups Topics Bryophyte adaptations synapomorphies Alternation of generation in Bryophytes Phylum Hepaticophyta Phylum Bryophyta
Chapter 20 Nonvascular Plants: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts Major plant groups Topics Bryophyte adaptations synapomorphies Alternation of generation in Bryophytes Phylum Hepaticophyta Phylum Bryophyta
A MEGASECOPTERON FROM UPPER CARBONIFEROUS BY F. M. CARPENTER. In I962 Professor F. Stockmans, of the Institut Royal des Sciences STRATA IN SPAIN
 A MEGASECOPTERON FROM UPPER CARBONIFEROUS STRATA IN SPAIN BY F. M. CARPENTER Harvard University In I962 Professor F. Stockmans, of the Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de. Belgique, kindly sent me
A MEGASECOPTERON FROM UPPER CARBONIFEROUS STRATA IN SPAIN BY F. M. CARPENTER Harvard University In I962 Professor F. Stockmans, of the Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de. Belgique, kindly sent me
Useful Terms. Bryophyte Habitats
 Common Mosses and Liverworts of the Chicago Region Kalman Strauss, Jerry Jenkins, Gary Merrill, Charles DeLavoi, Juan Larraín, Laura Briscoe & Matt von Konrat The Field Museum, The Northern Forest Atlas
Common Mosses and Liverworts of the Chicago Region Kalman Strauss, Jerry Jenkins, Gary Merrill, Charles DeLavoi, Juan Larraín, Laura Briscoe & Matt von Konrat The Field Museum, The Northern Forest Atlas
Global Patterns Gaston, K.J Nature 405. Benefit Diversity. Threats to Biodiversity
 Biodiversity Definitions the variability among living organisms from all sources, including, 'inter alia', terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems, and the ecological complexes of which they
Biodiversity Definitions the variability among living organisms from all sources, including, 'inter alia', terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems, and the ecological complexes of which they
Short guide to some common mycological terms
 Short guide to some common mycological terms Thomas Læssøe & Jens H. Petersen Macro-morphology English (latinised English) Bulb-like (= bulbous) used for swollen stem bases, can be rimmed (= marginate).
Short guide to some common mycological terms Thomas Læssøe & Jens H. Petersen Macro-morphology English (latinised English) Bulb-like (= bulbous) used for swollen stem bases, can be rimmed (= marginate).
Lecture 19. A Sieve Plate with large Sieve Pores. Secondary Phloem. Secondary phloem (cont d)
 Lecture 19 Secondary phloem (cont d) Secondary Phloem in Tilia americana (American Basswood) Secondary Phloem of Tilia Stained with Toluidine Blue & viewed with Crossed Polarizers. Secondary Phloem A Sieve
Lecture 19 Secondary phloem (cont d) Secondary Phloem in Tilia americana (American Basswood) Secondary Phloem of Tilia Stained with Toluidine Blue & viewed with Crossed Polarizers. Secondary Phloem A Sieve
1 Conducting Units: Tracheids and Vessels 1.1 Evolutionary Specialization
 1 Conducting Units: Tracheids and Vessels 1.1 Evolutionary Specialization The development of upright land plants depended on the development of a waterconducting system. Many of the earliest land plants,
1 Conducting Units: Tracheids and Vessels 1.1 Evolutionary Specialization The development of upright land plants depended on the development of a waterconducting system. Many of the earliest land plants,
Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology
 Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark
Class XI Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology Question 1: State the location and function of different types of meristem. Meristems are specialised regions of plant growth. The meristems mark
Microthyriales of Tierra del Fuego I: The Genus Parasterinella SPEGAZZINI
 Verlag Ferdinand Berger & Söhne Ges.m.b.H., Horn, Austria, download unter www.biologiezentrum. Sydowia, Annales Mycologici Ser. II. Vol. 38: 1-5 (1985) Verlag Ferdinand Berger & Söhne Gesellschaft m.b.h.,
Verlag Ferdinand Berger & Söhne Ges.m.b.H., Horn, Austria, download unter www.biologiezentrum. Sydowia, Annales Mycologici Ser. II. Vol. 38: 1-5 (1985) Verlag Ferdinand Berger & Söhne Gesellschaft m.b.h.,
An Overview of Peatland Bryophytes. Dale H. Vitt Department of Plant Biology Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL
 An Overview of Peatland Bryophytes Dale H. Vitt Department of Plant Biology Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL dvitt@siu.edu Outline Differences between mosses and liverworts Basic morphology
An Overview of Peatland Bryophytes Dale H. Vitt Department of Plant Biology Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL dvitt@siu.edu Outline Differences between mosses and liverworts Basic morphology
NOTES: CH 35 - Plant Structure & Growth
 NOTES: CH 35 - Plant Structure & Growth In their evolutionary journey, plants adapted to the problems of a terrestrial existence as they moved from water to land ANGIOSPERMS (flowering plants) -most diverse
NOTES: CH 35 - Plant Structure & Growth In their evolutionary journey, plants adapted to the problems of a terrestrial existence as they moved from water to land ANGIOSPERMS (flowering plants) -most diverse
Plant Structure. Lab Exercise 24. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise Plant Structure Objectives - Be able to identify plant organs and give their functions. - Learn distinguishing characteristics between monocot and dicot plants. - Understand the anatomy of
Lab Exercise Plant Structure Objectives - Be able to identify plant organs and give their functions. - Learn distinguishing characteristics between monocot and dicot plants. - Understand the anatomy of
Today: Plant Structure Exam II is on F March 31
 Next few lectures are on plant form and function Today: Plant Structure Exam II is on F March 31 Outline Plant structure I. Plant Cells structure & different types II. Types of meristems Apical meristems:
Next few lectures are on plant form and function Today: Plant Structure Exam II is on F March 31 Outline Plant structure I. Plant Cells structure & different types II. Types of meristems Apical meristems:
March, 1906.] Life Cycle 0/ a Homosporous Pteridophyte. 483 THE LIFE CYCLE OF A HOMOSPOROUS PTERIDOPHYTE. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER.
![March, 1906.] Life Cycle 0/ a Homosporous Pteridophyte. 483 THE LIFE CYCLE OF A HOMOSPOROUS PTERIDOPHYTE. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER. March, 1906.] Life Cycle 0/ a Homosporous Pteridophyte. 483 THE LIFE CYCLE OF A HOMOSPOROUS PTERIDOPHYTE. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER.](/thumbs/89/100118323.jpg) March, 1906.] Life Cycle 0/ a Homosporous Pteridophyte. 483 THE LIFE CYCLE OF A HOMOSPOROUS PTERIDOPHYTE. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER. The Homosporous Pteridophytes constitute the lowest subkingdom of vascular plants.
March, 1906.] Life Cycle 0/ a Homosporous Pteridophyte. 483 THE LIFE CYCLE OF A HOMOSPOROUS PTERIDOPHYTE. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER. The Homosporous Pteridophytes constitute the lowest subkingdom of vascular plants.
Name: Block: FUNGI WORKSHEET
 FUNGI WORKSHEET Name: Block: The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube
FUNGI WORKSHEET Name: Block: The basic structural features of fungi are not cells but hyphae. Hyphae are microscopic branching filaments filled with cytoplasm and nuclei. Each thread consists of a tube
Notes on American Musci
 Notes on American Musci BY P.A. Florschütz Botanical Museum and Herbarium, Utrecht (.Received June 2nd, 1953) Papillaria nigrescens (Hedw.) Jaeg. and P. appressa (Hornsch.) Jaeg. The variability of Papillaria
Notes on American Musci BY P.A. Florschütz Botanical Museum and Herbarium, Utrecht (.Received June 2nd, 1953) Papillaria nigrescens (Hedw.) Jaeg. and P. appressa (Hornsch.) Jaeg. The variability of Papillaria
The endemic West African GLYCYMERIDIDAE species. summary and presentation of two new species
 The endemic West African GLYCYMERIDIDAE species summary and presentation of two new species The family GLYCYMERIDIDAE in West Africa - limited to the genus Glycymeris; - a very difficult mind-breaking
The endemic West African GLYCYMERIDIDAE species summary and presentation of two new species The family GLYCYMERIDIDAE in West Africa - limited to the genus Glycymeris; - a very difficult mind-breaking
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants
 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Verwijsnummer rapporterende autoriteit: MDN 5 Reference number reporting authority: MDN 5
 Medinilla Gaudich. Variety description: NL/MDN/1 1. Reference number of reporting authority Reference number of requesting 2. authority 3. Breeder s reference Medin-8295 4. Applicant Corn.Bak, ASSENDELFT,
Medinilla Gaudich. Variety description: NL/MDN/1 1. Reference number of reporting authority Reference number of requesting 2. authority 3. Breeder s reference Medin-8295 4. Applicant Corn.Bak, ASSENDELFT,
APPLICATIONS UNDER EXAMINATION. MAGNOLIA (Magnolia) Proposed denomination: Cleopatra Application number: Application date: 2011/02/25
 (Magnolia) Proposed denomination: Cleopatra Application number: 11-7201 Application date: 2011/02/25 Applicant: Agent in Canada: BioFlora Inc., St. Thomas, Ontario Breeder: Description: PLANT: weak vigour,
(Magnolia) Proposed denomination: Cleopatra Application number: 11-7201 Application date: 2011/02/25 Applicant: Agent in Canada: BioFlora Inc., St. Thomas, Ontario Breeder: Description: PLANT: weak vigour,
The GLYCYMERIDIDAE of the NE Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea
 The GLYCYMERIDIDAE of the NE Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea 6 endemic species and 1 immigrant species: * NE Atlantic Ocean: G. glycymeris * Mediterranean Sea: Glycymeris bimaculata; G. inflata; G.
The GLYCYMERIDIDAE of the NE Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea 6 endemic species and 1 immigrant species: * NE Atlantic Ocean: G. glycymeris * Mediterranean Sea: Glycymeris bimaculata; G. inflata; G.
Leaf Identification Kit
 Introduction Leaf Identification Kit Catalog No. FB0490 Publication No. 10673 Leaves can be found in a wide variety of sizes, shapes and colors. Each species of tree produces its own variation of leaf.
Introduction Leaf Identification Kit Catalog No. FB0490 Publication No. 10673 Leaves can be found in a wide variety of sizes, shapes and colors. Each species of tree produces its own variation of leaf.
The Petiolar Structure of Christella dentata (Forssk.) Brownsey & Jermy (Thelypteridaceae, Pteridophyta)
 Ethnobotanical Leaflets 12: 96-102. 2008. The Petiolar Structure of Christella dentata (Forssk.) Brownsey & Jermy (Thelypteridaceae, Pteridophyta) KAMINI SRIVASTAVA, M.Sc, D.Phil Department of Botany,
Ethnobotanical Leaflets 12: 96-102. 2008. The Petiolar Structure of Christella dentata (Forssk.) Brownsey & Jermy (Thelypteridaceae, Pteridophyta) KAMINI SRIVASTAVA, M.Sc, D.Phil Department of Botany,
Although the changing position of the Sun throughout the day
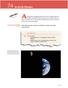 74 As Earth Rotates R E A D I N G Although the changing position of the throughout the day makes it look like the is moving, you now know that it is really Earth that moves. The rotation of Earth around
74 As Earth Rotates R E A D I N G Although the changing position of the throughout the day makes it look like the is moving, you now know that it is really Earth that moves. The rotation of Earth around
ON SOLIDAGO MACVAUGHII (ASTERACEAE: ASTEREAE), A RARE MEXICAN ENDEMIC OF THE TORTIFOLIAE GROUP OF SOLIDAGO. SUBSECT. TRIPLINERVIAE
 Semple, J.C. 2018. On Solidago macvaughii (Asteraceae: Astereae), a rare Mexican endemic in the Tortifoliae group of Solidago subsect. Triplinerviae. Phytoneuron 2018-35: 1 6. Published 30 May 2018. ISSN
Semple, J.C. 2018. On Solidago macvaughii (Asteraceae: Astereae), a rare Mexican endemic in the Tortifoliae group of Solidago subsect. Triplinerviae. Phytoneuron 2018-35: 1 6. Published 30 May 2018. ISSN
Mosquito Systematics Vol. 6(Z) June 1974
 Mosquito Systematics Vol. 6(Z) June 1974 93 Research on the Mosquitoes of Angola. VII - Redescription of the Larva of Aedes durbanensis durbanensis (Theo., 1903) and Description of Aedes durbanensis angozae
Mosquito Systematics Vol. 6(Z) June 1974 93 Research on the Mosquitoes of Angola. VII - Redescription of the Larva of Aedes durbanensis durbanensis (Theo., 1903) and Description of Aedes durbanensis angozae
Studies on the Bryophyte Flora of the Tien Shan Mountains. 2.* Encalyptaceae and Splachnaceae (Bryophyta)
 Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 41(1), pp. 9 13, February 20, 2015 Studies on the Bryophyte Flora of the Tien Shan Mountains. 2.* Encalyptaceae and Splachnaceae (Bryophyta) Masanobu Higuchi Department
Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 41(1), pp. 9 13, February 20, 2015 Studies on the Bryophyte Flora of the Tien Shan Mountains. 2.* Encalyptaceae and Splachnaceae (Bryophyta) Masanobu Higuchi Department
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF COCKROACH EGG CAPSULES. II. THE OOTHECA OF CARIBLATTA LUTEA LUTEA (ORTHOPTERA: BLATTIDAE) 1
 STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF COCKROACH EGG CAPSULES. II. THE OOTHECA OF CARIBLATTA LUTEA LUTEA (ORTHOPTERA: BLATTIDAE) 1 FRED A. LAWSON Department of Zoology and Entomology, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville
STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF COCKROACH EGG CAPSULES. II. THE OOTHECA OF CARIBLATTA LUTEA LUTEA (ORTHOPTERA: BLATTIDAE) 1 FRED A. LAWSON Department of Zoology and Entomology, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville
Banana t hri p s i n t he We s t I ndi e s
 Thrips are tiny (1-2 mm), slender insects with typical long fringes on the margins of their narrow wings. Adults may cause major damage by puncturing the fruit epidermis to suck out the contents. The fruit
Thrips are tiny (1-2 mm), slender insects with typical long fringes on the margins of their narrow wings. Adults may cause major damage by puncturing the fruit epidermis to suck out the contents. The fruit
Bryophyte Gametophytes. Bryophyte Gametophytes. A spore germinates into a gametophyte. composed of a protonema and gamete producing gametophore
 A spore germinates into a composed of a protonema and gamete producing gametophore Rhizoids Anchor s to substrate Lack of vascular :ssues Bryophyte Gametophytes Restricts the height of s Mature s produce
A spore germinates into a composed of a protonema and gamete producing gametophore Rhizoids Anchor s to substrate Lack of vascular :ssues Bryophyte Gametophytes Restricts the height of s Mature s produce
CHAPTER 2-4 BRYOPHYTA TAKAKIOPSIDA
 Glime, J. M. 2017. Bryophyta - Takakiopsida. Chapt. 2-4. In: Glime, J. M. Bryophyte Ecology. Volume 1. Physiological Ecology. 2-4-1 Ebook sponsored by Michigan Technological University and the International
Glime, J. M. 2017. Bryophyta - Takakiopsida. Chapt. 2-4. In: Glime, J. M. Bryophyte Ecology. Volume 1. Physiological Ecology. 2-4-1 Ebook sponsored by Michigan Technological University and the International
PTERIS REPTANS (PTERIDACEAE) - A NEW RECORD FOR INDIA
 FERN GAZ. 19(1):25-29. 2012 25 PTERIS REPTANS (PTERIDACEAE) - A NEW RECORD FOR INDIA V.K. SREENIVAS 1 & P.V. MADHUSOODANAN 2 1 Department of Botany, University of Calicut, Kerala, India - 673635 (Email:
FERN GAZ. 19(1):25-29. 2012 25 PTERIS REPTANS (PTERIDACEAE) - A NEW RECORD FOR INDIA V.K. SREENIVAS 1 & P.V. MADHUSOODANAN 2 1 Department of Botany, University of Calicut, Kerala, India - 673635 (Email:
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
The Japanese Fissidens neomagofukui (Bryophyta: Fissidentaceae) new to India from the Western Ghats
 The Japanese Fissidens neomagofukui (Bryophyta: Fissidentaceae) new to India from the Western Ghats Author(s): Albert Ebenezer Dulip Daniels, Ratheesh Sreebha and Kochumani Chinnapilla Kariyappa Source:
The Japanese Fissidens neomagofukui (Bryophyta: Fissidentaceae) new to India from the Western Ghats Author(s): Albert Ebenezer Dulip Daniels, Ratheesh Sreebha and Kochumani Chinnapilla Kariyappa Source:
Water Wise. Wendy Mee. Published by Utah State University Press. For additional information about this book
 Water Wise Wendy Mee Published by Utah State University Press Mee, Wendy. Water Wise: Native Plants for Intermountain Landscapes. Logan: Utah State University Press, 2003. Project MUSE., https://muse.jhu.edu/.
Water Wise Wendy Mee Published by Utah State University Press Mee, Wendy. Water Wise: Native Plants for Intermountain Landscapes. Logan: Utah State University Press, 2003. Project MUSE., https://muse.jhu.edu/.
SESSION 6: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS PART 1
 SESSION 6: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS PART 1 KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: - Anatomy of dicotyledonous plants Root and stem: distribution
SESSION 6: SUPPORT AND TRANSPORT SYSTEMS IN PLANTS PART 1 KEY CONCEPTS In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: - Anatomy of dicotyledonous plants Root and stem: distribution
THE ROOTS OF WILD RICE. ZIZANIA AQUATICA L.
 THE ROOTS OF WILD RICE. ZIZANIA AQUATICA L. E. L. STOVER, Eastern Illinois State Teachers College. This grass grows from Maine to Minnesota in aquatic habitats (2 and 5). It is common in marsh lands all
THE ROOTS OF WILD RICE. ZIZANIA AQUATICA L. E. L. STOVER, Eastern Illinois State Teachers College. This grass grows from Maine to Minnesota in aquatic habitats (2 and 5). It is common in marsh lands all
Note on an Amoeba-like Parasite from Clavellina.
 AN AMOEBA-LIKE PARASITE FROM CLAVEM/INA. 413 Note on an Amoeba-like Parasite from Clavellina. By.... Julian S. Huxley, Fellow of New College and Senior Demonstrator in the Department of Comparative Anatomy,
AN AMOEBA-LIKE PARASITE FROM CLAVEM/INA. 413 Note on an Amoeba-like Parasite from Clavellina. By.... Julian S. Huxley, Fellow of New College and Senior Demonstrator in the Department of Comparative Anatomy,
OF THE LEMNA FROND MORPHOLOGY
 MORPHOLOGY OF THE LEMNA FROND FREDERICK H. BLODGETT (WITH PLATE XIV AND ONE FIGURE) In the case of structure simplified by reduction, it is sometimes necessary to trace the development of the parts through
MORPHOLOGY OF THE LEMNA FROND FREDERICK H. BLODGETT (WITH PLATE XIV AND ONE FIGURE) In the case of structure simplified by reduction, it is sometimes necessary to trace the development of the parts through
Identification of Balsam poplars - 1
 Identification of Balsam poplars - 1 Poplars (Populus spp.) can be split into four groups: 1. Populus tremula (Aspen) 2. Populus alba (White Poplar) and its hybrid with P. tremula, P. x canescens (Grey
Identification of Balsam poplars - 1 Poplars (Populus spp.) can be split into four groups: 1. Populus tremula (Aspen) 2. Populus alba (White Poplar) and its hybrid with P. tremula, P. x canescens (Grey
Laboratory 8: Ginkgo, Cycads, and Gnetophytes
 IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 8: Ginkgo, Cycads, and Gnetophytes This is the third and final lab concerning the gymnosperms. Today we are looking at Ginkgo, the Cycads, and the Gnetophytes, the so-called
IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 8: Ginkgo, Cycads, and Gnetophytes This is the third and final lab concerning the gymnosperms. Today we are looking at Ginkgo, the Cycads, and the Gnetophytes, the so-called
Lecture 4 Root Put line under your answer! There is only one correct answer in the multiple choice questions
 Lecture 4 Root Put line under your answer! There is only one correct answer in the multiple choice questions 1. The perception of gravity by a root is thought to take place in a) root hairs b) the region
Lecture 4 Root Put line under your answer! There is only one correct answer in the multiple choice questions 1. The perception of gravity by a root is thought to take place in a) root hairs b) the region
Topic 14. The Root System. II. Anatomy of an Actively Growing Root Tip
 Topic 14. The Root System Introduction. This is the first of two lab topics that focus on the three plant organs (root, stem, leaf). In these labs we want you to recognize how tissues are organized in
Topic 14. The Root System Introduction. This is the first of two lab topics that focus on the three plant organs (root, stem, leaf). In these labs we want you to recognize how tissues are organized in
Morphological comparison and key to Juniperus deltoides and J. oxycedrus
 58 Morphological comparison and key to Juniperus deltoides and J. oxycedrus Robert P. Adams Baylor University, Biology Department, One Bear Place, #97388, Waco, TX 76798, USA, email Robert_Adams@baylor.edu
58 Morphological comparison and key to Juniperus deltoides and J. oxycedrus Robert P. Adams Baylor University, Biology Department, One Bear Place, #97388, Waco, TX 76798, USA, email Robert_Adams@baylor.edu
PROTOCOL FOR DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY TESTS
 PROTOCOL FOR DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY TESTS Aster L. ASTER UPOV Species Code: ASTER Adopted on 23/06/2011 Entry into force on 01/06/2011 1 I SUBJECT OF THE PROTOCOL The protocol describes
PROTOCOL FOR DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY TESTS Aster L. ASTER UPOV Species Code: ASTER Adopted on 23/06/2011 Entry into force on 01/06/2011 1 I SUBJECT OF THE PROTOCOL The protocol describes
POLARITY OF PEATMOSS (SPHAGNUM) EVOLUTION: WHO
 American Journal of Botany 90(12): 1777 1787. 2003. POLARITY OF PEATMOSS (SPHAGNUM) EVOLUTION: WHO SAYS BRYOPHYTES HAVE NO ROOTS? 1 A. JONATHAN SHAW, 2 CYMON J. COX, AND SANDRA B. BOLES Department of Biology,
American Journal of Botany 90(12): 1777 1787. 2003. POLARITY OF PEATMOSS (SPHAGNUM) EVOLUTION: WHO SAYS BRYOPHYTES HAVE NO ROOTS? 1 A. JONATHAN SHAW, 2 CYMON J. COX, AND SANDRA B. BOLES Department of Biology,
Key to Non-native and invasive aquatic plants in Rhode Island (Adapted from C. Barre Hellquist, Massachusetts College of Liberal Arts)
 Key to Non-native and invasive aquatic plants in Rhode Island (Adapted from C. Barre Hellquist, Massachusetts College of Liberal Arts) 1. Leaves arising from base of plant in flowering plants 2. Flowers
Key to Non-native and invasive aquatic plants in Rhode Island (Adapted from C. Barre Hellquist, Massachusetts College of Liberal Arts) 1. Leaves arising from base of plant in flowering plants 2. Flowers
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
 SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
