Enrichment Lesson 1: Making a Bee line
|
|
|
- Preston Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Focus Areas: Animal Lifestyles; Science, Physical Education Focus Skills: understanding patterns, conducting an experiment, role playing, cooperating to achieve a goal Objectives To recognize that cooperative behavior is involved in successful social interactions To understand that bees are capable of communicating with one another Essential Question How do bees cooperate to find food? Essential Understanding Forager bees use a pattern of movement combined with touch and smell to communicate the location of nectar to other worker bees responsible for providing food to the hive and ultimately humans too. Background INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT Although bees have five compound eyes, they do not see as we do. Simply put, their sight is rather like a photographic negative because they perceive ultra violet light that we do not. In addition, they spend much of their lives in the dark hive. Therefore, when gathering information bees rely heavily on their senses of touch and smell, centered in their antennae. Pheromones, or scents, are used to identify hive members, give alarm warnings, control hive behavior, and even prevent development of new queens! In addition, smell aids in the all important task of locating food sources. When a successful forager bee returns to the hive, she carries on her body the scent of the pollen from her find. Upon arrival back at the
2 hive, she goes directly to the platform at the hive s mouth where other forager bees gather around her, touching her with their antennae and thus picking up the scent of the food source. Scent tells the bees what the forager has found, but not where it is! Bees combine pheromone clues with a unique series of movements called dances to tell fellow foragers where to find the nectar she discovered. Using the vertical side of the entrance platform, the returning forager begins one of two basic patterns. If the food source is within 100 yards of the hive, she moves in a circle, first one way and then the other while shaking her abdomen and fluttering her wings. The pace of her movements indicates the quality and quantity of her find. This dance sends forager bees out from the hive in all directions seeking the nectar, which is nearby. If the discovery is farther afield than one hundred yards, a waggle dance is needed to add the vital information, distance and direction. Instead of a circle, the returning bee begins her gyrations with a half circle followed by a straight run up the vertical wall of the dance platform. The angle of this run is based on the sun s position at the moment the dance begins and indicates the exact direction from the hive the departing bees should fly. Each straight run is followed by a half circle in the opposite direction so the pattern resembles a figure eight. The length of the dance indicates distance from the hive with approximately 330 feet being added for every 75 milliseconds danced. The vigor of the dance and accompanying buzz indicates quality and quantity. Not all the bees attend the dance for its duration. Depending on age and foraging experience, bees determine the message of the dancer and take off on their search and find mission. This insures not all the foragers will end up harvesting nectar from only the one source found by the dancer. Other sources found along the way in the direction indicated by the first straight run will be found by bees leaving the dance early, thus insuring maximum harvesting of nectar! Finally, two other dances may be used in connection with supplying food. When more foragers are needed in the field, worker bees otherwise occupied are approached head on by a forager who shakes her abdomen side-to-side indicating they re needed on the dance floor. Page 2 Enrichment Lesson 1:
3 As many as 20 bees per minute are recruited in this way. Similarly, when returning foragers have more nectar than they can process into honey, non-foragers are approached and told to report to pollen processing duty. This dance involves a quiver of the entire body while rocking forward and backward. For such tiny-brained invertebrates, honey bees show remarkable communication skills! Vocabulary a b c d e f abdomen the third and largest segment of an adult insect s body circle dance the pattern of circular movements performed by a forager bee to indicate a nearby pollen source to others of her kind forager bees female worker bees who are responsible for providing nectar to the hive hive the place, natural or man-made, where bees live nectar a sweet liquid secreted by plants and used by bees in the production of honey pheromones a scent produced by bees affecting the hive s activities and behavior pollen a powdery substance produced by flowers and used by bees in the production of food waggle dance a series of movements resembling figure eights used to indicate direction and distance to nectar sources at some distance from the hive Making a Bee line Page 3
4 Logistics Time: 40 minutes (Follow Up may be done in a separate session; two 20 minute sessions) 12 Group Size: 10 to Space: a large open area (a playground or gymnasium) is preferred Materials large paper, silk, or plastic flowers, one per group of 5 to 6 children snack bags with 5 to 8 pieces of honey comb cereal covered opaque containers (film canisters work well), 2 per group cotton balls (8 per group) peppermint, lemon, banana, and vanilla extract, cinnamon, vinegar, (as needed, one scent per group) Video The Magic School Bus: In A Beehive * (if not shown previously) * single copy provided Preparation To Do: 1. Gather the materials listed above. 2. a. Dip eight of the cotton balls in one of the scents. b. Place two cotton balls in one container and the remaining six in the second container. c. Cap both containers tightly. d. Tape the two containers together lightly to prevent mix-ups. 3. Repeat container preparation (2a through 2d) using a different scent each time until enough sets are ready to accommodate each group. Page 4 Enrichment Lesson 1:
5 Activity Introduction 1. Ask if anyone knows what bee food humans also like. (honey) 2. Explain that bees make honey from nectar found in plants. 3. a. If previous lessons have been done, review what a social insect is and remind the group that only some bees are responsible for finding food for the hive. b. If previous lessons have not been done, take this opportunity to show the video, The Magic School Bus: In A Beehive and explain that social insects work together to provide for basic needs. Every insect has a special job to help the group. 4. Ask the group to pretend they are a bee who has found a huge field of flowers and ask how they would let other members of their food finding team know about their discovery. (accept suggestions) 5. Eliminate those suggestions not possible for bees (example: draw a map) and focus on tell the others. 6. Tell the group that they are going to become forager bees and discover how bees really tell other members of their hive about what they have found. Involvement 1. Demonstrate the bee dances with the group. a. Have the group form a circle and circle left one full turn; then right while wiggling and flapping their arms bent at the elbows with hands under armpits. b. Explain that this circle dance says that there are flowers within 100 yards of the hive. c. Tell the group to go faster and explain speed tells the bees how many flowers are in this location. The faster the dance the more nectar there is! 2. Call Halt and have the group sit. 3. Debrief the group by discussing what they know about the Making a Bee line Page 5
6 location of the flowers. (They are close and, in general, how many there are.) 4. Ask what the bees will do now. (Fly off in all directions to find the flowers) 5. Ask what else the bees may need to know if the nectar is miles away from their hive. (in which direction to fly) 6, Tell the group they are going to learn another dance, the WAGGLE, which allows bees to show the direction of the flowers from the hive. a. Tell the group to stand and circle to the right while wiggling. When they have moved half way around the circle, call Halt. b. Tell them to move by taking 3 steps in a straight line toward the center. c. Resume the dance to the left for a half turn and take 3 more steps directly toward the center. d. Call Halt and have the group sit. 7. Ask what was different about this dance. (They only circled halfway around and then went in a straight line.) 8. Repeat this dance, but instead of moving toward the center, move away from the center in a straight line. 9. Have group sit: a. Explain the straight line part of the dance shows the direction, N, S, E, or W in which the bees should fly to find the flowers. The dancer bee moves in the direction her teammates should fly. b. Draw the pattern of the dance where the group can see it, and call attention to the resemblance it has to a figure Call on a volunteer to perform this waggle dance while the group watches. 11. With the group in a circle sing and move to BEE lines TUNE: I Have Something in My Pocket. When I find some yummy nectar whether near or far away I let my bee buds know it in a very special way! I wiggle and I circle, beat my wings with all my might. Then I run straight as an arrow so they ll get direction right! Page 6 Enrichment Lesson 1:
7 When I dance a simple circle, the nectar is close by But when I dance in figure eights they may have miles to fly I wiggle and I circle, beat my wings with all my might. Then I run straight as an arrow so they ll get direction right! Follow Up Making a Bee line 1. Divide the group into food finding teams of 5 or 6 members. (This may be done most easily by having each child draw a color coded construction paper piece numbered 1 through 5.) a. Explain that each color represents a team of forager bees and that they will be looking for nectar. b. Show them the flowers and tell them nectar is in flowers; different flavors in different flowers. c. Ask how they would tell a rose from a lilac if they were blind folded. (touch and smell) 2. Show the group the covered containers and tell them that bees use smell to find exactly the right flowers described by the bee dance. To do this, they touch the dancer while she is dancing with their antennae and pick up the smell of the flowers the bee is telling them about. Tell them that they will watch a dance and smell the nectar and then try to find the flower described. 3. Each team s members choose a number 1 through 5 to determine the finder bee on each team. (#1) a. Give this child a flower and the two containers holding the cotton balls. b. Tell these forager bees to hide their flower with one container (cap on) somewhere in the designated area. The flowers should be partially visible and at least 40 steps away from every other team s flowers. c. Remind them they have to remember exactly where the flower is because they will have to give directions to their team mates by running in a line toward it during the waggle dance. 4. Ask all but the finder bees to sit in a circle with their eyes shut and covered with their hands while the flowers are hidden. a. Explain to the remaining members that when their finder bee returns, they will: Page 7
8 i. Smell the scent of their flower. ii. Watch the dance to learn the direction they must go to find it. b. Remind them that they must match the flower to the smell, finding any flower is not enough. c. When they find a flower; i. They should smell the cotton ball in the container. i. If the smell matches the smell the finder bee gave them, they remove a cotton ball and return to their circle. ii. If it is a different smell, they recap the container and keep looking. 5. When all the flowers are hidden, ask the teams to form a circle around their finder bee. These circles should allow space for the WAGGLE DANCE and have space between them. 6. The finder bee uncaps the second container and allows the team members to smell the cotton balls. She/he then does the WAGGLE DANCE indicating the direction of the flower from the circle by making a straight run of several steps toward it between circling right and circling left. 7. When the team members think they know where to find their flower, they may leave the circle to find it. The finder keeps repeating the dance until all team members have left to search. 8. As team members return, they check their smell with the canister of the finder bee. If it matches, they sit with the finder. If it doesn t they must go to other finder bees until they find the scent that matches the one they picked up. 9. When all bees have returned and are sitting with a group, distribute the honeycomb snacks. 10. Check to see how many teams have all their members, and how many teams have only their members. Record the results where the group can see them using hatch marks. Explain that finding other flowers happens to real bees too and that a bee who finds a flower with different NECTAR would return to the hive and do their own dance! Page 8 Enrichment Lesson 1: Making a Bee line
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Learning about bees - Maths Questions
 Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Bee Behavior. Summary of an article by. Stephen Taber III from Beekeeping in the United States
 Bee Behavior Summary of an article by Stephen Taber III from Beekeeping in the United States Bees Sense Organs: Vision Each compound eye is spherical in shape and comprised of some 6,300 cone-shaped facets
Bee Behavior Summary of an article by Stephen Taber III from Beekeeping in the United States Bees Sense Organs: Vision Each compound eye is spherical in shape and comprised of some 6,300 cone-shaped facets
 Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Funding for the duplication of this publication is provided by the St. Lucie County Board of County Commissioners.
 This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
The Bee, Part I: Dance of the Bees Gioietta Kuo
 January 9, 2018 Busy Bees by Sharon Sperry Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 The Bee, Part I: Dance of the Bees Gioietta Kuo Bees are not ordinary wildlife. They have a special relationship with human society. For
January 9, 2018 Busy Bees by Sharon Sperry Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 The Bee, Part I: Dance of the Bees Gioietta Kuo Bees are not ordinary wildlife. They have a special relationship with human society. For
28 3 Insects Slide 1 of 44
 1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY. Essential Question: MATERIALS. Chart Paper Markers Journals, Paper, or Digital Notebooks
 BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Major Emphasis: Major Curriculum Area: Related Curriculum Areas: Program Indicator: Student Outcomes:
 Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People
 Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
a British scientist who left his fortune to the United States Congress had trouble getting the Smithsonian project off the ground.
 ReadWorks.org Teacher Guide & Answers a British scientist who left his fortune to the United States Congress had trouble getting the Smithsonian project off the ground. The Smithsonian Institution is the
ReadWorks.org Teacher Guide & Answers a British scientist who left his fortune to the United States Congress had trouble getting the Smithsonian project off the ground. The Smithsonian Institution is the
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation
 Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who
 Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
Bee Communica,on A Hive Mind
 Bee Communica,on A Hive Mind Hive Mind Hive Mind One for all and all for one Kill self to protect the hive Fatal S,ng WHY? Kin Selec)on: So closely related The hive occupants: One queen a fer,le female
Bee Communica,on A Hive Mind Hive Mind Hive Mind One for all and all for one Kill self to protect the hive Fatal S,ng WHY? Kin Selec)on: So closely related The hive occupants: One queen a fer,le female
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE. 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & EarthsBirthday.org
 BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
Bees. Garden Classroom. 90 minutes. Grade 6 4/10. ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard Project Berkeley, CA. Bees Safety Pollinators Honey
 LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
Practical 5 SOCIAL BEHAVIOUR OF HONEY BEES
 Practical 5 SOCIAL BEHAVIOUR OF HONEY BEES Aim: To understand communication system of a honey bee colony. Introduction Among different insect orders, only 8 have been recognized by insect taxonomists which
Practical 5 SOCIAL BEHAVIOUR OF HONEY BEES Aim: To understand communication system of a honey bee colony. Introduction Among different insect orders, only 8 have been recognized by insect taxonomists which
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
TIME: 45 minutes. LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st SUMMARY:
 LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st TIME: 45 minutes SUMMARY: Students will make observations about the weather and sky, listen to a story about weather and discuss it. Students will go outside and
LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st TIME: 45 minutes SUMMARY: Students will make observations about the weather and sky, listen to a story about weather and discuss it. Students will go outside and
Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination
 Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination Grade Level: 2nd Grade Objective: The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand the important role that humans and animals play in
Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination Grade Level: 2nd Grade Objective: The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand the important role that humans and animals play in
Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors.
 Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Ball of yarn Laminated photographs or drawings of ecosystem parts (see later pages)
 This lesson has been adapted by Nature s Classroom Institute to help students comprehend the interdependencies of various ecosystems as well as their role within the larger environment. Through this activity
This lesson has been adapted by Nature s Classroom Institute to help students comprehend the interdependencies of various ecosystems as well as their role within the larger environment. Through this activity
Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year
 Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year Written by Khalil Hamdan Apeldoorn The Netherlands A honeybee gathering nectar from a flower. Photo source: forestwander.com Bee collecting pollen. Photo source:
Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year Written by Khalil Hamdan Apeldoorn The Netherlands A honeybee gathering nectar from a flower. Photo source: forestwander.com Bee collecting pollen. Photo source:
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life
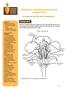 Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
The Basics: Grade Level 5 th - 8th. Subject Areas Life sciences. Duration 95 minutes. Number of Docents Needed 2. Wetland Stewards Program Lesson 8 1
 Grade Level 5 th - 8th The Basics: POLLINATORS AND WILDFLOWERS Summary Students will understand that plants depend on pollinators to reproduce and maintain their populations. They learn about wetland plant
Grade Level 5 th - 8th The Basics: POLLINATORS AND WILDFLOWERS Summary Students will understand that plants depend on pollinators to reproduce and maintain their populations. They learn about wetland plant
INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS. Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit
 INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit ONTARIO TEACHER-FOCUSED TOOLKIT INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Instructions to Teachers This unit is a Science and Technology lesson
INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit ONTARIO TEACHER-FOCUSED TOOLKIT INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Instructions to Teachers This unit is a Science and Technology lesson
Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers
 Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers The video for this transcript can be found on the Questacon website at: http://canberra.questacon.edu.au/sciencetime/ Transcription from video: Hi,
Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers The video for this transcript can be found on the Questacon website at: http://canberra.questacon.edu.au/sciencetime/ Transcription from video: Hi,
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
BEES AND FORESTS. Activity 1 After the clip. 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place?
 BEES AND FORESTS Activity 1 After the clip 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place? 2. Julian Wolfhagen is the president of which association
BEES AND FORESTS Activity 1 After the clip 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place? 2. Julian Wolfhagen is the president of which association
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee?
 o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Pheromones by Ellen Miller November 2015
 Pheromones by Ellen Miller November 2015 Greek word pherein to carry Greek word hormone to stimulate A released chemical that triggers a social response in members of the same species The chemical is transmitted
Pheromones by Ellen Miller November 2015 Greek word pherein to carry Greek word hormone to stimulate A released chemical that triggers a social response in members of the same species The chemical is transmitted
2nd Grade. Slide 1 / 106. Slide 2 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Plants. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
Blank paper & clip boards or nature journals Pencils Bug jars/bug boxes & Insect ID sheets/field guides
 LESSON: Catch and Release Insects GRADE: 5 th TIME: 45 min. SUMMARY: A field leader uses introduce students to the definition of insects and different insect groups. Afterwards, students work in groups
LESSON: Catch and Release Insects GRADE: 5 th TIME: 45 min. SUMMARY: A field leader uses introduce students to the definition of insects and different insect groups. Afterwards, students work in groups
Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research
 Overview Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research Public Participation in Scientific Research (PPSR) is a concept adopted by
Overview Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research Public Participation in Scientific Research (PPSR) is a concept adopted by
Observing Daphnia. Student Resources 1.4 Observing Daphnia, Pages 1 and Counting Daphnia Populations Inquiry Focus Observe
 Observing Daphnia Observing Daphnia, Page 1 30 minutes Pairs Observe the daphnia in your cup. List two ways you can tell the adults from the babies: 1 Babies are smaller. 2 Babies are brownish. How do
Observing Daphnia Observing Daphnia, Page 1 30 minutes Pairs Observe the daphnia in your cup. List two ways you can tell the adults from the babies: 1 Babies are smaller. 2 Babies are brownish. How do
Insect Investigations
 Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Cal and Tramp Camp. His dog Tramp ran up to him. Cal and Tramp set up. camp. They put up a tent in back of Cal s house. Cal and
 Cal and Tramp Camp Cal and Tramp Camp Cal said, Let s camp. His dog Tramp ran up to him. Cal and Tramp set up camp. They put up a tent in back of Cal s house. Cal and Tramp got in the tent. Then they heard,
Cal and Tramp Camp Cal and Tramp Camp Cal said, Let s camp. His dog Tramp ran up to him. Cal and Tramp set up camp. They put up a tent in back of Cal s house. Cal and Tramp got in the tent. Then they heard,
2nd Grade. Plants.
 1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
Elementary Science: Pollination
 Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
7 LITTLE GREEN MARTIANS
 7 LITTLE GREEN MARTIANS Many People thought the first probes to land on the surface of Mars- Viking I and Viking II- would discover little green Martian men or some other form of extraterrestrial, so there
7 LITTLE GREEN MARTIANS Many People thought the first probes to land on the surface of Mars- Viking I and Viking II- would discover little green Martian men or some other form of extraterrestrial, so there
DISAPPEARING SUN? TOTAL ECLIPSE OF THE SUN
 1 Lesson Title: DISAPPEARING SUN? TOTAL ECLIPSE OF THE SUN By Krista Bridenthal K. Bridenthal: 40 minutes (portions adapted from Project FIRST: How Can the Little Moon Hide the Giant Sun) Summary: Students
1 Lesson Title: DISAPPEARING SUN? TOTAL ECLIPSE OF THE SUN By Krista Bridenthal K. Bridenthal: 40 minutes (portions adapted from Project FIRST: How Can the Little Moon Hide the Giant Sun) Summary: Students
Amy Ant. Formica Mica Grant. Dr. Sheila Grant (Mica s mom)
 Dr. Sheila Grant (Mica s mom) Formica Mica Grant Amy Ant By Elisabeth Schlegel, Jessica Louton, Natasha Mehdiabadi, and Ted Schultz Illustrated by Katherine Arisumi At the Smithsonian Institution s National
Dr. Sheila Grant (Mica s mom) Formica Mica Grant Amy Ant By Elisabeth Schlegel, Jessica Louton, Natasha Mehdiabadi, and Ted Schultz Illustrated by Katherine Arisumi At the Smithsonian Institution s National
Where is the shadow?
 Where is the shadow? Light H 29 time 70 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that light travels in a straight line; obstacles placed in the way of the light cause it to change direction know how a shadow
Where is the shadow? Light H 29 time 70 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that light travels in a straight line; obstacles placed in the way of the light cause it to change direction know how a shadow
Next Generation Science Standards
 Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Creative Dance Lesson Plan Integrating. Math: Telling Time (A.M. vs. P.M.)
 Creative Dance Lesson Plan Integrating Math: Telling Time (A.M. vs. P.M.) Grade: 2nd Length: 45 minutes Written by: Erika Cravath Student Learning Outcome: The students will demonstrate an understanding
Creative Dance Lesson Plan Integrating Math: Telling Time (A.M. vs. P.M.) Grade: 2nd Length: 45 minutes Written by: Erika Cravath Student Learning Outcome: The students will demonstrate an understanding
(Sessions I and II)* BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN FOR PERSONAL USE
 activities 19&20 What Do Plants Need? (Sessions I and II)* BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 1 Quarter 2 Activities 19 & 20 SC.A.1.1.1 The student knows that objects can be described,
activities 19&20 What Do Plants Need? (Sessions I and II)* BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 1 Quarter 2 Activities 19 & 20 SC.A.1.1.1 The student knows that objects can be described,
THAT KEEP ESCAPING THE CASE OF THE CENTIGURPS THAT KEEP ESCAPING. 10s THAT KEEP ESCAPING THAT KEEP ESCAPING. THE CASE OF The CENTIGURPS
 4 5 Tape this flap under the other marker to connect the two. Tape the other marker to the backside of this marker. Create a Centigurps Counter from 0-100. Cut out the Centigurps Counter halves to the
4 5 Tape this flap under the other marker to connect the two. Tape the other marker to the backside of this marker. Create a Centigurps Counter from 0-100. Cut out the Centigurps Counter halves to the
Gravity - What Goes Up, Must Come Down
 Gravity - What Goes Up, Must Come Down Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb3/downloads/literacy4.pdf Jump up in the air and you will fall
Gravity - What Goes Up, Must Come Down Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb3/downloads/literacy4.pdf Jump up in the air and you will fall
Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams
 Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Termighty Fun & Games
 Termighty Fun & Games Social Insects L G S N K I N G O C S I R A L I R R I U N S E C N T S E L I F O Q O V R E A O N D C K D W E O U O U R S I K E E O R T O C M E G E N T E F T T L O S F Y H E E R A D
Termighty Fun & Games Social Insects L G S N K I N G O C S I R A L I R R I U N S E C N T S E L I F O Q O V R E A O N D C K D W E O U O U R S I K E E O R T O C M E G E N T E F T T L O S F Y H E E R A D
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1
 Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
Honey Bee. Bite-size Science
 Bite-size Science Trying new things can be hard. When you play a new sport, you have to learn and remember a whole new set of rules. When you try new food, you may end up not liking it (and you may even
Bite-size Science Trying new things can be hard. When you play a new sport, you have to learn and remember a whole new set of rules. When you try new food, you may end up not liking it (and you may even
3.6 Equations and Fractions
 .6 Equations and Fractions EQUATIONS INVOLVING THE MULTIPLICATION OF FRACTIONS In Section 1.5 you learned how to solve equations involving multiplication. Let s take a look at an example as a reminder.
.6 Equations and Fractions EQUATIONS INVOLVING THE MULTIPLICATION OF FRACTIONS In Section 1.5 you learned how to solve equations involving multiplication. Let s take a look at an example as a reminder.
Peter Dutton. 28 August Halesworth& District
 Peter Dutton 28 August 2014 Halesworth& District Bees Hymenoptera - 150,000+ species Sawflies, Wasps, Bees, Ants, Bees - 20,000+ species Most solitary, a few social Honey Bee - The only one which produces
Peter Dutton 28 August 2014 Halesworth& District Bees Hymenoptera - 150,000+ species Sawflies, Wasps, Bees, Ants, Bees - 20,000+ species Most solitary, a few social Honey Bee - The only one which produces
Page 1 of 5. New: evidence, measure, nutrients, light, soil, transport, volume, water, warmth, insect, pollen, pollinate, nectar.
 National Curriculum Objectives: (Statutory requirements) a) Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering : roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers b) Explore the requirements of for
National Curriculum Objectives: (Statutory requirements) a) Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering : roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers b) Explore the requirements of for
BASIC BEE BIOLOGY. Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist
 BASIC BEE BIOLOGY Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist THE HONEY BEE COLONY Regardless of the race of bees, the colony will have three castes: One Queen (female) Workers (female), numbers depend upon season Drones
BASIC BEE BIOLOGY Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist THE HONEY BEE COLONY Regardless of the race of bees, the colony will have three castes: One Queen (female) Workers (female), numbers depend upon season Drones
This is a one-week excerpt from the Starfall Kindergarten Mathematics Teacher s Guide. If you have questions or comments, please contact us.
 UNIT WEEK This is a one-week excerpt from the Starfall Kindergarten Mathematics Teacher s Guide. If you have questions or comments, please contact us. Email: helpdesk@starfall.com Phone: -888-857-8990
UNIT WEEK This is a one-week excerpt from the Starfall Kindergarten Mathematics Teacher s Guide. If you have questions or comments, please contact us. Email: helpdesk@starfall.com Phone: -888-857-8990
Food Chain Role Play
 Food Chain Role Play This simulation shows students how plants use energy from the sun to create carbohydrates during photosynthesis. Then students act out the flow of energy from one organism to another
Food Chain Role Play This simulation shows students how plants use energy from the sun to create carbohydrates during photosynthesis. Then students act out the flow of energy from one organism to another
1-ESS1 Earth s Place in the Universe 1-ESS1-2 Make observations at different times of year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year.
 LESSON: Sunlight GRADE: 1 OBJECTIVES: 1-ESS1 Earth s Place in the Universe 1-ESS1-2 Make observations at different times of year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year. MATERIALS & RESOURCES:
LESSON: Sunlight GRADE: 1 OBJECTIVES: 1-ESS1 Earth s Place in the Universe 1-ESS1-2 Make observations at different times of year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year. MATERIALS & RESOURCES:
Click Teacher Guide: May/June 2018
 Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
3PK. February 16-17, Matt s Friends Bring Him to Jesus. Luke 5: We can ask Jesus to help us!
 3PK February 16-17, 2012 Matt s Friends Bring Him to Jesus Luke 5:17-26 We can ask Jesus to help us! SCHEDULE for all sites: First 10 minutes of the service hour: Relationship-building time (kids get to
3PK February 16-17, 2012 Matt s Friends Bring Him to Jesus Luke 5:17-26 We can ask Jesus to help us! SCHEDULE for all sites: First 10 minutes of the service hour: Relationship-building time (kids get to
Listening. The Air. Did you know? Did you know?
 Listening 1. Find a place to sit. 2. Close your eyes and listen carefully to all the sounds you can hear. Cup your hands around your ears and turn your head to help you listen in particular directions.
Listening 1. Find a place to sit. 2. Close your eyes and listen carefully to all the sounds you can hear. Cup your hands around your ears and turn your head to help you listen in particular directions.
learning outcomes end product a model showing a solar eclipse
 Solar eclipse Looking at the stars * 53 time 50 minutes learning outcomes To: know that during a solar eclipse the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth know that a solar eclipse does not take place
Solar eclipse Looking at the stars * 53 time 50 minutes learning outcomes To: know that during a solar eclipse the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth know that a solar eclipse does not take place
Recording Seasonal Change
 Phenology Grade 2 Subjects: ELA, Science Recording Seasonal Change Overview The class works together to record seasonal changes over the course of the school year. In addition, each child selects a tree,
Phenology Grade 2 Subjects: ELA, Science Recording Seasonal Change Overview The class works together to record seasonal changes over the course of the school year. In addition, each child selects a tree,
Energy Transformations IDS 101
 Energy Transformations IDS 101 It is difficult to design experiments that reveal what something is. As a result, scientists often define things in terms of what something does, what something did, or what
Energy Transformations IDS 101 It is difficult to design experiments that reveal what something is. As a result, scientists often define things in terms of what something does, what something did, or what
Living in the Milky Way
 Living in the Milky Way Looking at the universe * 55 time 70 minutes Tip. You can see the Milky Way with the naked eye. You can see it best in January when the Moon is new. Encourage the children to look
Living in the Milky Way Looking at the universe * 55 time 70 minutes Tip. You can see the Milky Way with the naked eye. You can see it best in January when the Moon is new. Encourage the children to look
The Importance of Bees
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5
![V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5 V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5](/thumbs/77/75709676.jpg) 126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
2 nd. Science Notebook Insects & Plants. Investigation 2: Brassica Seeds. Name:
 2 nd Science Notebook Insects & Plants Investigation 2: Brassica Seeds Name: 1 Alignment with New York State Science Standards & Performance Indicators Standard 1: Mathematical Analysis M1.1 Use mathematical
2 nd Science Notebook Insects & Plants Investigation 2: Brassica Seeds Name: 1 Alignment with New York State Science Standards & Performance Indicators Standard 1: Mathematical Analysis M1.1 Use mathematical
FISKE KINDERGARTEN SPRING NATURE WALK Plants, Animals, and Seasonal Changes
 1 FISKE KINDERGARTEN SPRING NATURE WALK Plants, Animals, and Seasonal Changes OBJECTIVES: Using touch, smell, sight, and sound, observe, describe and compare seasonal changes in the weather and the schoolyard
1 FISKE KINDERGARTEN SPRING NATURE WALK Plants, Animals, and Seasonal Changes OBJECTIVES: Using touch, smell, sight, and sound, observe, describe and compare seasonal changes in the weather and the schoolyard
SCIENCE FUN. Copyright by The Adventures of Scuba Jack, Inc., All rights reserved.
 SCIENCE FUN AIR Air is all around you. It is made up of many different gasses. The most important gas in air is oxygen. Animals and people need oxygen to live. When you breathe, you are breathing in air,
SCIENCE FUN AIR Air is all around you. It is made up of many different gasses. The most important gas in air is oxygen. Animals and people need oxygen to live. When you breathe, you are breathing in air,
Appearances Can Be Deceiving!
 Appearances Can Be Deceiving! Overview: Students explore the relationship between angular width, actual size, and distance by using their finger, thumb and fist as a unit of angular measurement in this
Appearances Can Be Deceiving! Overview: Students explore the relationship between angular width, actual size, and distance by using their finger, thumb and fist as a unit of angular measurement in this
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit
 Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit p.1 = Part 1 p.2 = Part 2 p.3 = Part 3 The schedule for this unit is almost COMPLETELY dependent on what the living organisms are doing and where
Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit p.1 = Part 1 p.2 = Part 2 p.3 = Part 3 The schedule for this unit is almost COMPLETELY dependent on what the living organisms are doing and where
Feel like an astronaut!
 V Feel like an astronaut! People in space time 55 minutes Tip Carry out this activity in the gym. learning outcomes To: find out how an astronaut washes see how an astronaut eats breakfast know that an
V Feel like an astronaut! People in space time 55 minutes Tip Carry out this activity in the gym. learning outcomes To: find out how an astronaut washes see how an astronaut eats breakfast know that an
Orbital Paths. the Solar System
 Purpose To compare the lengths of the terrestrial planets orbital paths and revolution times. Process Skills Measure, form a hypothesis, predict, observe, collect data, interpret data, communicate, draw
Purpose To compare the lengths of the terrestrial planets orbital paths and revolution times. Process Skills Measure, form a hypothesis, predict, observe, collect data, interpret data, communicate, draw
The Shape, Center and Spread of a Normal Distribution - Basic
 The Shape, Center and Spread of a Normal Distribution - Basic Brenda Meery, (BrendaM) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version
The Shape, Center and Spread of a Normal Distribution - Basic Brenda Meery, (BrendaM) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version
Don t Duck Look Up Educator s Guide
 Don t Duck Look Up Educator s Guide Synopsis: This show presents the benefits of observing one s surroundings. Dudley is a duckling who lives on a farm. Dudley discovers many exciting features of the day
Don t Duck Look Up Educator s Guide Synopsis: This show presents the benefits of observing one s surroundings. Dudley is a duckling who lives on a farm. Dudley discovers many exciting features of the day
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Honey, It's Electric: Bees Sense Charge On Flowers
 Honey, It's Electric: Bees Sense Charge On Flowers Flowers are nature's ad men. They'll do anything to attract the attention of the pollinators that help them reproduce. That means spending precious energy
Honey, It's Electric: Bees Sense Charge On Flowers Flowers are nature's ad men. They'll do anything to attract the attention of the pollinators that help them reproduce. That means spending precious energy
ED 357/358 - FIELD EXPERIENCE - LD & EI LESSON DESIGN & DELIVERY LESSON PLAN #4
 ED 357/358 - FIELD EXPERIENCE - LD & EI LESSON DESIGN & DELIVERY LESSON PLAN #4 Your Name: Sarah Lidgard School: Bentheim Elementary School Lesson: Telling Time Length: approx. 50 minutes Cooperating Teacher:
ED 357/358 - FIELD EXPERIENCE - LD & EI LESSON DESIGN & DELIVERY LESSON PLAN #4 Your Name: Sarah Lidgard School: Bentheim Elementary School Lesson: Telling Time Length: approx. 50 minutes Cooperating Teacher:
POP ROCKET TRASH TO TREASURE
 POP ROCKET TRASH TO TREASURE Connie Stammen, 2nd-grade teacher North Star Elementary North Star, OH Lesson Summary for Grades 2 5 Students design a paper rocket propelled by an effervescent antacid tablet
POP ROCKET TRASH TO TREASURE Connie Stammen, 2nd-grade teacher North Star Elementary North Star, OH Lesson Summary for Grades 2 5 Students design a paper rocket propelled by an effervescent antacid tablet
There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000
 There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000 different species of Bee in Texas There are only 7-9 species
There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000 different species of Bee in Texas There are only 7-9 species
The complete lesson plan for this topic is included below.
 Home Connection Parent Information: Magnets provide a simple way to explore force with children. The power of a magnet is somewhat like magic to them and requires exploration to understand. When forces
Home Connection Parent Information: Magnets provide a simple way to explore force with children. The power of a magnet is somewhat like magic to them and requires exploration to understand. When forces
Kids Garden Teacher s Guide: Grade 3
 Kids Garden Teacher s Guide: Grade 3 California Content Standards Grade 2 Science: 2a, 6a, 6c, 6d, 6e What s Going On? The Kids Garden gives children the opportunity to explore the natural community of
Kids Garden Teacher s Guide: Grade 3 California Content Standards Grade 2 Science: 2a, 6a, 6c, 6d, 6e What s Going On? The Kids Garden gives children the opportunity to explore the natural community of
SAMPLE PAGE. Flowers Express Lapbook. Any Age. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN. SC.E The student understands the arrangement of planets in our Solar System.
 activity 12 Earth Orbits the Sun BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 2 Activity 12 SC.E.1.2.4 The student knows that the planets differ in size, characteristics, and composition
activity 12 Earth Orbits the Sun BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 2 Activity 12 SC.E.1.2.4 The student knows that the planets differ in size, characteristics, and composition
3rd Grade Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Pollinator Adaptations
 Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
*Add to Science Notebook Name 1
 *Add to Science Notebook Name 1 Arthropods, Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 Characteristics of Arthropods *Arthropods are the largest group of animals. *Arthropods have jointed and include,,, and. *Arthropod appendages
*Add to Science Notebook Name 1 Arthropods, Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 Characteristics of Arthropods *Arthropods are the largest group of animals. *Arthropods have jointed and include,,, and. *Arthropod appendages
Section 1: The Science of Energy¹
 SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
Old Testament. Part Two. Created for use with young, unchurched learners Adaptable for all ages including adults
 Old Testament Part Two Created for use with young, unchurched learners Adaptable for all ages including adults Mission Arlington Mission Metroplex Curriculum Lesson 66 Page 1 M ISSION ARLINGTON MISSION
Old Testament Part Two Created for use with young, unchurched learners Adaptable for all ages including adults Mission Arlington Mission Metroplex Curriculum Lesson 66 Page 1 M ISSION ARLINGTON MISSION
Pumpkins, Pumpkins. Bonus Activities for October Gee Whiz Education, LLC 1
 Bonus Activities for October 2017 TM 2017 Gee Whiz Education, LLC 1 www.geewhizeducation.com Enjoy the following activities with your children as desired. In most cases, you can substitute jack-o-lanterns
Bonus Activities for October 2017 TM 2017 Gee Whiz Education, LLC 1 www.geewhizeducation.com Enjoy the following activities with your children as desired. In most cases, you can substitute jack-o-lanterns
Up In the Air Lesson 15-1 Representing Situations with Inequalities
 Up In the Air Lesson 15-1 Learning Targets: Write inequalities to represent constraints or conditions within problems. Use substitution to determine whether a given number makes an inequality true. Graph
Up In the Air Lesson 15-1 Learning Targets: Write inequalities to represent constraints or conditions within problems. Use substitution to determine whether a given number makes an inequality true. Graph
Chapter 1, Lesson 3: The Ups and Downs of Thermometers
 Chapter 1, Lesson 3: The Ups and Downs of Thermometers Key Concepts The way a thermometer works is an example of heating and cooling a liquid. When heated, the molecules of the liquid in the thermometer
Chapter 1, Lesson 3: The Ups and Downs of Thermometers Key Concepts The way a thermometer works is an example of heating and cooling a liquid. When heated, the molecules of the liquid in the thermometer
Creepy, Crawly Critters
 Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
Physic 602 Conservation of Momentum. (Read objectives on screen.)
 Physic 602 Conservation of Momentum (Read objectives on screen.) Good. You re back. We re just about ready to start this lab on conservation of momentum during collisions and explosions. In the lab, we
Physic 602 Conservation of Momentum (Read objectives on screen.) Good. You re back. We re just about ready to start this lab on conservation of momentum during collisions and explosions. In the lab, we
Name Date Block LESSON CLUSTER 6: Expansion and Contraction
 LESSON CLUSTER 6: Expansion and Contraction Did you know that when you say that something is hot or cold, you are actually saying something about the molecules of that substance? Words like hot and cold
LESSON CLUSTER 6: Expansion and Contraction Did you know that when you say that something is hot or cold, you are actually saying something about the molecules of that substance? Words like hot and cold
