NATURA MONTENEGRINA, Podgorica, 2013, 12(1):
|
|
|
- Lora Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATURA MONTENEGRINA, Podgorica, 2013, 12(1): ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER SEQUENTIAL PATH ANALYSIS OF SPINACH YIELD USING SEVERAL QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE TRAITS Naser SABAGHNIA 1 Hossein Ali ASADI-GHARNEH 2 & Mohsen JANMOHAMMADI 1 1 Dep. of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Maragheh, Maragheh, Iran. sabaghnia@maragheh.ac.ir 2 Department of Horticulture Science, Islamic Azad University, Khorasgan Branch, Isfahan, Iran. SYNOPSIS Key words: bootstrap analysis, conventional path analysis, multi-collinearity. Development of new spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) verities needs efficient tools to mange character relationships in a breeding program. This research uses correlation coefficients as well as sequential path analysis to determine the interrelationships among dry yield and several quantitative and qualitative related traits. Fiftyfour spinach landraces, which collected from different geographical regions of Iran, were grown to determine the important components of dry yield. Sequential path analysis identified the petiole diameter, petiole length and days to flowering as important first order traits that influenced dry yield. Leaf length, leaf width, leaf numbers in flowering and stem anthocyanin content were indentified as important second order traits that influenced dry yield. All direct effects were significant, as indicated by bootstrap analysis. The results suggest that petiole and leaf properties could be used as a selection criterion in selecting for increased yield in spinach. Such similar outcome could be used in the future to delineate predictive, more rigorous secetion strategies as well as to help define indicator traits for recommendations for spinach and other vegetable crops. INTRODUCTION Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) is one of the important salad vegetable crops providing remarkable amounts of vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium and iron. Its increasing consumption during the two past decades can be related to growing public awareness of the health benefits (Brandenberger et al., 2007). According to Goldman (2003) functional foods have health benefits as well as fulfill the human s nutritional needs and 205
2 Natura Montenegrina 12(1), 2013 spinach could be regarded as functional foods which is increasing antioxidant intake in diets (Brandenberger et al., 2004). Spinach as cool season crop is grown for fresh or processing market and is resistant to low temperatures and drought reduce yield and deteriorate the quality in spinach (Salk et al., 2008). Different spinach breeding programs aim to incorporate important traits into improved spinach cultivars including high yield, adaptation, resistances diseases, pests, and herbicides, and nutritional quality (Murphy & Morelock, 2000). Awareness from traits relationships with yield analysis is important in breeding programs that can enhance some yield components. Therefore, the study of the correlation among yield-related traits can help the plant breeders in selection for higher yields. Different statistical methods have been introduced in modeling yield characteristic, including simple correlation coefficient, linear regression model, path analysis, factor analysis and clustering procedure. Path analysis is a statistical method for partitioning the correlation coefficients into direct and indirect effects, so that the contribution of each characteristic to yield could be estimated (Sabaghnia et al., 2010). The coefficients of path analysis are standardized partial regression coefficients which are scaled in terms of standard deviations so that the direct and indirect effects related with different yield components. Most of path analysis investigations ignored the importance of the causal relationship and usually used a model, in which bidirectional causation among yield components is assumed (Mohammadi et al., 2003). Path analysis needs the determination of causal relationships among different characteristics, based on either a priori evidence or a postulated hypothesis. Yield components develop sequentially with later-developing characteristics under the control of earlier-developing. The analysis of the values of correlation coefficients of the different characteristics with yield helps in deciding their importance as selection criteria for yielding ability. This conventional path analysis might result in multi-collinearity for involved traits, particularly when correlations among traits were high. The multi-collinearity maybe causes difficulties in interpretation of the actual contribution of each trait. Feyzian et al. (2009) used a sequential path analysis for determining the relationships among yield and its components in rice by analyzing several predictor traits in first, second and third order paths. Recently sequential path analysis is used in different crops including maize (Mohammadi et al., 2003), potato (Asghari-Zakaria et al., 2007) and rapeseed (Sabaghnia et al., 2010). Although, there are several investigations about correlation and path coefficient analysis of several agronomic crops, but such detailed cause and effect relationships using sequential path analysis have not been examined in horticultural crops. The main objectives of this investigation were to analyze the correlation between yield and related traits in spinach by applying the sequential path 206
3 Sabaghnia et al.: SEQUENTIAL PATH ANALYSIS OF SPINACH YIELD USING... analysis and identify traits of genotypes which may prove useful in breeding higheryielding genotypes. MATERIALS AND METHODS For the purpose of this investigation, fifty-four native Iranian spinach germplasms were collected from different spinach producing areas of Iran. The landraces were evaluated in the field using a randomized complete block design (RCBD) layout with four replicates. The geographical characteristics of the 54 regions of the spinach landraces were given in Table 1. Field soil was calcareous, loamy structure, low organic matter, low salt content and had poor nitrogen and phosphorous. Fertilization was done by spreading 80 kg N ha -1 (half at sowing and half at seedling emergence) and sowing was performed at the rate of 50 kg seed ha -1. Weed control was performed twice when the weed density was high, in the pre-flowering and post-flowering stages. Each field plot contained six rows (3 m long with 25 cm space between rows) and 4.5 m 2 plot size. The harvested plot size was 2.5 m 2 (four 2.5 rows at the center of each plot). Several quantitative traits consist on leaf length (LL), leaf width (LW), petiole length (PL), petiole diameter (PD), leaf area (LA), leaf numbers in flowering (LN), days to flowering (DF), female plants percent (FP), fresh yield (FY) and dry yield (DY) were measured. Also, various qualitative traits consist on leaf texture (LT, 1=smooth, 2=slight crinkled, 3= crinkled), seed type (ST, 1=smooth, 2=prickly), stem anthocyanin (SA, 1=very low, 3=low, 5=intermediate, 7=high, 9=very high), petiole attitude (PA, 1=erect, 2=semi-spared, 3= spared), vegetative leaf shape (VL, 1=elliptic, 2=broad elliptic, 3=circular, 4=ovate, 5=broad ovate, 6=triangular), reproductive leaf shape (RL, 1=smooth, 2=Pointy); leaf edge (LE, 1=smooth, 2= Rippler); leaf color (LC, 1=yellowgreen, 2=grey-green, 3=blue-green); seed color (SC, 1=yellow-green, 2=grey-green, 3=blue-green) were measured. The datasets were first tested for normality by Anderson and Darling normality test using MINITAB version 16 (2010) software. The correlation coefficients were calculated for all the possible comparisons using the Pearson (quantitative traits) and Spearman (qualitative traits) correlation coefficients. The correlation coefficients were partitioned into direct and indirect effects using the conventional path coefficient analysis. Sequential stepwise regression was performed to organize the predictor traits into first, second and third order paths on the basis of their respective contributions to the total variation of dry yield and minimal collinearity by SPSS 16 (SPSS, 2008). The sequential path model consisted of predictor and response variables. The level of multi-collinearity in each component path was measured from two common 207
4 Natura Montenegrina 12(1), 2013 measures, namely the Tolerance value and its inverse, the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF). Tolerance value is the amount of variability of the selected independent variable not explained by other independent variables (1-R 2 ), where R 2 is the coefficient of determination for the prediction variable by the predictor variables). Variance inflation factor (VIF) indicates the extent of effects of other independent variables on the variance of the selected independent variable [VIF =1/(1/ R 2 )]. Thus, very small tolerance values (much below 0.1) or large variance inflation factor values (above 10) indicate high collinearity (Mohammadi et al., 2003). Partial coefficients of determination (analogous of linear regression) were calculated from the path coefficients for all predictor variables. To estimate the standard error path coefficients, bootstrap analysis was performed by S-PLUS version 8 (Springr-Verlag Inc., 2007) statistical package. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The results of ANOVA indicated highly significant differences among spinach landraces for all the measured traits under investigation (data are not shown). In order to determine in the most precise manner the interrelation of direct and indirect dry yield components, simple correlation coefficients were established and then path coefficient analysis was performed. The Pearson simple correlation coefficients among quantitative traits (Table 1) showed that there were significant positive correlations between leaf length (LL) and all of the measured traits except days to flowering (DF) and female plants percent (FP). Eftekhari et al. (2010) reported relatively similar results for association between LL and most of traits which are mentioned here, but they found negative significant correlation between LL and FP. The petiole length showed significant positive correlation with leaf area (LA), leaf numbers in flowering (LN), and dry yield (DY). Asadi & Hasandokht (2007) found similar results for interrelationships among DY, PL and PD. The leaf width had significant positive correlation with other traits except petiole diameter (PD) and female plants percent (FP). The petiole diameter indicated positive significant correlation with leaf area (LA), leaf numbers in flowering (LN), days to flowering (DF), and dry yield (DY). The leaf area (LA) had significant positive correlation with leaf numbers in flowering (LN), days to flowering (DF), and dry yield (DY). The leaf numbers in flowering (LN) indicated significant positive correlation with to flowering (DF), and dry yield (DY). It is clear that all quantitative traits except female plants percent (FP) had significant positive correlation with dry yield and so it is better to extract the direct and indirect of these traits on spinach dry yield via path analysis. The obtained results verified the investigations of Asadi & Hasandokht (2007) and 208
5 Sabaghnia et al.: SEQUENTIAL PATH ANALYSIS OF SPINACH YIELD USING... Eftekhari et al. (2010) on some Iranian spinach landraces and showed the importance of most spinach quantitative traits on dry yield. Table 1: Pearson s correlation coefficients between nine quantitative traits of 54 Iranian spinach landraces. LL LW PL PD LA LN DF FP LW 0.53** PL 0.50** 0.77** PD 0.64** 0.18 ns 0.25 ns LA 0.78** 0.87** 0.68** 0.46** LN 0.46** 0.53** 0.55** 0.41** 0.61** DF 0.10 ns 0.31 * 0.19 ns 0.28* 0.27* 0.33** FP 0.20 ns 0.09 ns 0.02 ns 0.06 ns 0.12 ns 0.00 ns 0.16 ns DY 0.49** 0.36** 0.40** 0.70** 0.48** 0.50** 0.57** ns Critical values of correlation P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 (df= 52) are 0.35 and 0.27, respectively. ** Significant at 1% level; * Significant at 5% level; ns Non-significant. Table 2: Spearman s correlation coefficients between eight qualitative traits of 54 Iranian spinach landraces. LT ST SA PA VL RL LE ST 0.10 ns SA ns ns PA ns ns 0.23 ns VL ns * 0.18 ns 0.27 ns RL ns ns 0.16 ns 0.17 ns 0.41 ** LE 0.19 ns 0.05 ns 0.05 ns 0.00 ns 0.31 * 0.20 ns LC 0.18 ns * 0.34 * 0.04 ns 0.23 ns 0.01 ns 0.31 * LT, Leaf texture; Seed type; SA, Stem anthocyanin; PA, Petiole attitude; VL, Vegetative leaf shape; RL, Reproductive leaf shape; LE, Leaf edge; LC, Leaf color; SC, Seed color. Critical values of correlation P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 (df= 52) are 0.35 and 0.27, respectively. ** Significant at 1% level; * Significant at 5% level; ns Non-significant. The Spearman s rank correlation coefficients between pairs of qualitative traits of spinach (Table 2) indicated that most of these traits were not correlated with each other. Only, vegetative leaf shape (VL) had significant positive correlation with reproductive leaf shape (RL) and leaf edge (LE). Also, leaf color showed significant positive correlation with content of stem anthocyanin (SA) and leaf edge (LE); and indicated significant negative correlation with seed type (SA). Our results are in good 209
6 Natura Montenegrina 12(1), 2013 agreement with the findings of Asadi & Hasandokht (2007) in investigation of some qualitative traits in Iranian spinach landraces. Therefore it seems that, the most of spinach qualitative traits are not good indicators for assessing yield performance quantity, but they maybe proper for increasing quality of spinach. Table 3: Direct effects of first-order predictor variables on the dry yield (DY) of 54 spinach landraces and two common measures of collinearity indices in path analysis. Direct effect Tolerance VIF LL LW PL PD LA LN DF FP LTT ST SA PA VL RL lee lc VIF: variance inflation factor. To determine the relative importance of the measured traits on spinach dry yield, the data were subjected to conventional path analysis which permits the separation of simple correlation coefficients with components of direct and indirect effects. The results pertaining to direct effects of components traits, where the traits were considered as first order variables with spinach dry yield as the response variable, are presented in Table 3. Also, the results of two measures of multicollinearity analysis (Tolerance and Variance Inflation Factor) for this path analysis are given in Table 3. According to the results of conventional path analysis and multicollinearity analysis, there are inconsistent patterns of relationships among the studied variables. Results of this analysis, where the all traits were considered as the first-order variables (Model I) with dry yield as the response variable, indicated high multicollinearity for some traits, 210
7 Sabaghnia et al.: SEQUENTIAL PATH ANALYSIS OF SPINACH YIELD USING... particularly for those showing high direct effects such as leaf width (LW) and leaf area (LA) and thus these traits were removed as the first-order variables from the analysis. Such similar strategy in evaluation of different traits correlations in path analysis was used by Feyzian et al. (2009) in rice, Mohammadi et al. (2003) in maize and Sabaghnia et al. (2010) in rapeseed. Estimation of direct effects by the second strategy (sequential path analysis), where the yield-related traits were considered as grouped into first, second, and thirdorder variables with dry yield (Model II), and analysis of multicollinearity indicated a better understanding of the interrelationships among various traits and their relative contribution to spinach dry yield (Table 4). Results of Tolerance and variance inflation factor (VIF) values for the predictor variables indicated the remarkable reduction of VIF values in Model I in comparison to Model II. It is clear that stepwise regression in the present study minimized the collinearity measures (Tolerance and VIF) of all variables, thereby facilitating detection of actual contributions of each predictor variables in different path components, with negligible confounding effects and interference. The advantage of sequential path procedure over conventional path analysis in minimizing collinearity problems and identifying actual contributions of each component in different path components are similar to those reported in the other investigations (Asghari- Zakaria et al., 2007; Sabaghnia et al., 2010; Ibrahim & Ramadan, 2013), indicating that it would be very effective to achieve a favorable results. Table 4: Measures of collinearity values (tolerance and variance inflation factor, VIF) for predictor variables in conventional path analysis (CPA, all predictor variables as first-order variables) and sequential path analysis (SPA, predictors grouped into first-, second-, and third-order variables). Variable Tolerance VIF Predictor Response CPA SPA CPA SPA DY PD DF PL PD LL SA DF LN PL LW
8 Natura Montenegrina 12(1), 2013 In most statistical analysis procedures, the plant breeder is usually interested in obtaining not only a point estimate of a statistic but also an estimate of the variation in this point estimate and a confidence interval for the true value of the parameter. Resampling techniques, such as the bootstrap, provide good estimates of the standard error, confidence intervals, and distributions for any statistics. To apply above procedures on path analysis, the mean direct effects estimated from a set of 1000 bootstrap samples were in close agreement with the observed direct effects of different measured traits (Table 5). The low standard error for all the direct effects and low bias also indicated the robustness of the sequential path analysis. The T-test of significance, using standard error values obtained through bootstrap resampling, indicated that all the direct effects were significant (data are not shown). The adjusted coefficient of determination (R 2 Adj. = 0.67) represents the influence of the petiole diameter (PD), days to flowering (DF), and petiole length (PL) traits as first-order variables involved in the research on total variability of dry yield (Table 5). Among these three traits, PD, DF and PL traits, PD had the greater direct effect (0.55) than two other traits on spinach dry yield (Table 6). Indirect effect to the DY was low and positive (0.11) via DF but indirect effect to the DY was very low and positive (0.05) via PL. The DF had the moderate direct effect (0.38) on spinach dry yield and indirect effect to the DY was low and positive (0.15) via PD but indirect effect to the DY was very low and positive (0.04) via PL (Table 6). The PL had the low direct effect (0.19) on dry yield and indirect effect to the DY was low and positive (0.14) via PD but indirect effect to the DY was very low and positive (0.07) via DF (Table 6). Table 5: Estimation of standard error values of path coefficients (direct effects) using bootstrap analysis. Variable Direct effect Adj. R 2 Bootstrap Predictor Predictor Mean Bias SE DY PD DF PL PD LL SA DF LN PL LW
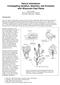
9 Sabaghnia et al.: SEQUENTIAL PATH ANALYSIS OF SPINACH YIELD USING... Table 6: Direct and indirect effects for the predictor variables in sequential path analysis (grouped into first, second and third order variables). DY PD DF PL PD DF PL PD LL SA LL SA According to this famous belief that a picture is worth a thousand words, large attempts have been performed to graphically present statistical outputs in plant breeding areas. The diagrams of sequential path analysis (Graph 1) provided a better understanding of the interrelationships among various traits and their relative contribution to spinach dry yield. Based on this diagram, when the second-order traits were used as predictors and first-order variables as response variables indicated that LL and SA positively influenced DY and accounted for more than 48% of observed variation (Graph 1). Also, LN positively influenced DF and accounted for more than 33% of observed variation while LW positively influenced PL and accounted for more than 60% of observed variation (Table 5). Yield component study indicated, petiole properties (length and diameter) were positively associated with dry yield and had the important direct effect on dry yield. Conventional path analysis and yield component studies provide the usual conflicting results. For future spinach breeding and selection of the most favorable genotypes, it is important to ascertain the variation available for plant structure and yield components in these landraces. Better understanding of how yield components influence the yield formation process can be obtained by applying path analysis to determine the direct and indirect effects of primary, secondary and tertiary traits on the yield formation process. The main advantage is that path analysis not only identifies the most important factor directly affecting a trait, but also indicates how factors affect the trait indirectly through other factors. Previous investigations have indicated that the path analysis provides more information on the interrelationships between the yield components and yield than do the correlation coefficients (Asghari-Zakaria et al., 2007; Sabaghnia et al., 2010). Path analysis helps determine whether yield component compensation is occurring. 213
10 Natura Montenegrina 12(1), 2013 Yield component compensation is when two or more yield components affecting yield or any other yield component act inversely in their effects. Our study demonstrates the utility of the sequential path analysis over conventional path analysis in discerning direct and indirect effects of different yieldrelated traits. Various characters consist on PD, DF, PL, LL, SA, LN and LW traits were identified as the first, second and third order variables (Graph 1). The role of petiole (length and diameter) regarding direct and indirect effects on spinach dry yield was important. These findings could be verified regarding the investigations of Asadi & Hasandokht (2007) and Eftekhari et al. (2010), who worked on different sets of Iranian spinach landraces. Also, the leaf properties (LL and LW) were identified as the other influencing factors on dry yield. Graph 1: Sequential path analysis diagram illustrating the interrelationships among various traits contributing to dry yield of spinach. In general, based on the findings of correlation and sequential path analyses in this research very close interrelationships were recorded among dry yield with some measured traits. On the other hand, the most important yield components which do not differ in different studies were leaf and petiole properties which could be used in conducted breeding research to increase yield. As a result, it may be recommended that genotypes having good manner of these mentioned traits should be criteria preferred specifically in both cultivation and selection in spinach. It can be concluded the great importance of above traits for selection in breeding programs which is meaning with the improvement of spinach yield under the native condition. 214
11 Sabaghnia et al.: SEQUENTIAL PATH ANALYSIS OF SPINACH YIELD USING... REFERENCES: ASADI, H. A. & HASANDOKHT, M. R. 2007: An evaluation of genetic diversity of Iranian spinach landraces. Iranian Journal of Horticulture Science, 38: ASGHARI ZAKARIA, R., FATHI, M. & HASAN PANAH, D. 2007: Sequential path analysis of yield components in potato. Potato Research, 49: BRANDENBERGER, L. P., WELLS, L. K. & HAIGH, M. M. 2004: Yield and quality characteristics of spring spinach grown in Oklahoma. HortTechnology, 14: BRANDENBERGER, L., CAVINS, T., PAYTON, M., WELLS, L. & JOHNSON, T. 2007: Yield and quality of spinach cultivars for greenhouse production in Oklahoma. HortTechnology, 17: EFTEKHARI, S. A. A., HASANDOKHT, M. R., FATAHI-MOGHADAM, M. R. & KASHI, A. A. K. 2010: Genetic diversity of some Iranian spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) landraces using morphological traits. Iranian Journal of Horticulture Science, 41: FEYZIAN, E., DEHGHANI, H., REZAI, A. M. & JALALI, M. 2009: Correlation and sequential path model for some yield-related traits in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Journal of Agriculture Science and Technology, 11: GOLDMAN I.L., Recognition of fruit and vegetables as healthful: Vitamins and phytonutrients. HortTechnology, 13: IBRAHIM, E. A. & RAMADAN A. Y. 2013: Correlation and path coefficient analyses in sweet melon (Cucumis melo Var. Aegyptiacus L.) under irrigated and drought conditions. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 16: MINITAB INC. 2010: MINITAB 16. MINITAB User s guide. - Minitab Inc, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. USA, 345 p. MOHAMMADI S. A., PRASANNA B. M., & SINGH N. N. 2003: Sequential path model for determining interrelationships among grain yield and related characters in maize. Crop Science, 43: MURPHY, J. B. & MORELOCK, T. E. 2000: Spinach breeding program yields lines containing high levels of carotenoid antioxidants. Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Series, 475: SABAGHNIA, N., DEHGHANI, H., ALIZADEH, B. & MOHGHADDAM, M. 2010: Interrelationships between seed yield and 20 related traits of 49 canola (Brassica napus L.) genotypes in nonstressed and waterstressed environments. Spanish Journal of Agriculture Research, 8: SALK A., ARIN L., DEVECI M. & POLAT S. 2008: Special Vegetable Production. - Onur Press, Tekirdag, 488 p. SPRINGR-VERLAG INC 2007: User s guide S-PLUS 8 for Windows. - Springr-Verlag Inc, Berlin, Germany. 215
12 Natura Montenegrina 12(1), 2013 SPSS INC., 2008: SPSS 16 for Windows, SPSS User s guide. - SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL. USA. ( Receive: 2 August
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein
 C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance for Yield, Yield Related Components of Brinjal [Solanum melongena (L.
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5404 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (5): 872-878 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5404 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (5): 872-878 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic
INVESTIGATING YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENT OF WINTER RAPESEED CULTIVARS AT BOJNORD-IRAN
 Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life Sciences ISSN: 2231 6345 (Online) INVESTIGATING YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENT OF WINTER RAPESEED CULTIVARS AT BOJNORD-IRAN Souri Khabazan, *Amir Behzad Bazrgar,
Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life Sciences ISSN: 2231 6345 (Online) INVESTIGATING YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENT OF WINTER RAPESEED CULTIVARS AT BOJNORD-IRAN Souri Khabazan, *Amir Behzad Bazrgar,
Investigation of Correlation and Board Sense Heritability in Tritipyrum Lines under Normal and Drought Stress Conditions
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 3 (): 07-, 03 ISSN 88-6769 IDOSI Publications, 03 DOI: 0.589/idosi.aejaes.03.3.0.333 Investigation of Correlation and Board Sense Heritability in Tritipyrum
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 3 (): 07-, 03 ISSN 88-6769 IDOSI Publications, 03 DOI: 0.589/idosi.aejaes.03.3.0.333 Investigation of Correlation and Board Sense Heritability in Tritipyrum
CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES
 SAARC J. Agri., 11(1): 45-52 (2013) CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES S. R. Singh, N. A. Ahmed, S. Lal, Asima Amin 1, Mudasir Amin 5 S. A.
SAARC J. Agri., 11(1): 45-52 (2013) CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES S. R. Singh, N. A. Ahmed, S. Lal, Asima Amin 1, Mudasir Amin 5 S. A.
Genetic Variability and Heritability Estimation in Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.) Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3018-3024 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.370
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3018-3024 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.370
The role of Pseudomonas fluorescens strains in growth and phosphate concentration of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
 829 The role of Pseudomonas fluorescens strains in growth and phosphate of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Mojtaba Yousefi Rad * and Nazila Heshmatpoure Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Saveh
829 The role of Pseudomonas fluorescens strains in growth and phosphate of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Mojtaba Yousefi Rad * and Nazila Heshmatpoure Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Saveh
Evaluation of Physio-Agronomic and Chemical Traits in Relation to The Productivity of Eggplant (Solanum Melongena L.)
 Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 16: 14-24 (2004) Evaluation of Physio-Agronomic and Chemical Traits in Relation to The Productivity of Eggplant (Solanum Melongena L.) T.K. Illangakoon, D.C Bandara
Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 16: 14-24 (2004) Evaluation of Physio-Agronomic and Chemical Traits in Relation to The Productivity of Eggplant (Solanum Melongena L.) T.K. Illangakoon, D.C Bandara
YIELD STABILITY OF PERFORMANCE IN MULTI-ENVIRONMENT TRIALS OF BARLEY (HORDEUM VULGAR L.) GENOTYPES
 ACTA UNIVERSITATIS AGRICULTURAE ET SILVICULTURAE MENDELIANAE BRUNENSIS Volume LXI 87 Number 3, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.11118/actaun201361030787 YIELD STABILITY OF PERFORMANCE IN MULTI-ENVIRONMENT TRIALS
ACTA UNIVERSITATIS AGRICULTURAE ET SILVICULTURAE MENDELIANAE BRUNENSIS Volume LXI 87 Number 3, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.11118/actaun201361030787 YIELD STABILITY OF PERFORMANCE IN MULTI-ENVIRONMENT TRIALS
TECHNICAL WORKING PARTY FOR AGRICULTURAL CROPS. Twenty-Ninth Session Uppsala, Sweden, June 27 to 30, 2000
 E TWA/29/17 ORIGINAL: English DATE: June 6, 2000 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA TECHNICAL WORKING PARTY FOR AGRICULTURAL CROPS Twenty-Ninth Session Uppsala, Sweden,
E TWA/29/17 ORIGINAL: English DATE: June 6, 2000 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA TECHNICAL WORKING PARTY FOR AGRICULTURAL CROPS Twenty-Ninth Session Uppsala, Sweden,
Extension Organization, Iran) 2 (Horticulture crops Research Department, Agricultural and Natural Resources Research and Education Center
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 5 Ver. VI (Sep. Oct. 2017), PP 01-11 www.iosrjournals.org Vegetative Growth, Yield and
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 5 Ver. VI (Sep. Oct. 2017), PP 01-11 www.iosrjournals.org Vegetative Growth, Yield and
Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem
 J. Indian Soc. Coastal Agric. Res. 34(): 50-54 (016) Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem T. ANURADHA* Agricultural Research Station, Machilipatnam
J. Indian Soc. Coastal Agric. Res. 34(): 50-54 (016) Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem T. ANURADHA* Agricultural Research Station, Machilipatnam
ADIOLUS GLADIOL. Jitendra Kumar*, Rakesh Kumar and Krishan Pal
 Agric. Sci. Digest., 31 (4) : 280-284, 2011 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.ar.arccjour ccjournals.com / indianjournals.com nals.com VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN GLADIOL ADIOLUS
Agric. Sci. Digest., 31 (4) : 280-284, 2011 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.ar.arccjour ccjournals.com / indianjournals.com nals.com VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN GLADIOL ADIOLUS
Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
Variability Studies in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv]
![Variability Studies in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv] Variability Studies in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv]](/thumbs/94/119241936.jpg) International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 955-960 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.115
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 955-960 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.115
Effects of high plant populations on the growth and yield of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus)
 Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1999), 132, 173 180. 1999 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 173 Effects of high plant populations on the growth and yield of winter oilseed
Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1999), 132, 173 180. 1999 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 173 Effects of high plant populations on the growth and yield of winter oilseed
Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis
 150 Journal of Root Crops, 2011, Vol. 37 No. 2, pp. 150-154 Indian Society for Root Crops ISSN 0378-2409 Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis Central
150 Journal of Root Crops, 2011, Vol. 37 No. 2, pp. 150-154 Indian Society for Root Crops ISSN 0378-2409 Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis Central
Study of Genetic Divergence in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on Agro-Morphic Traits
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3816-3821 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.448
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3816-3821 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.448
Genetic Parameters for Yield and Yield Components in F 1 Hybrids and Parents of Bell Pepper
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.308
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.308
BIPLOT ANALYSIS OF TRAIT RELATIONS OF SPINACH (Spinacia oleracea L.) LANDRACES
 UDC 575.630 DOI: 10.2298/GENSR1602675S Original scientific paper BIPLOT ANALYSIS OF TRAIT RELATIONS OF SPINACH (Spinacia oleracea L.) LANDRACES Naser SABAGHNIA 1*, Mehdi MOHEBODINI, Mohsen JANMOHAMMADI
UDC 575.630 DOI: 10.2298/GENSR1602675S Original scientific paper BIPLOT ANALYSIS OF TRAIT RELATIONS OF SPINACH (Spinacia oleracea L.) LANDRACES Naser SABAGHNIA 1*, Mehdi MOHEBODINI, Mohsen JANMOHAMMADI
Lassen Community College Course Outline
 Lassen Community College Course Outline AGR 20 Introduction to Plant Science 4.0 Units I. Catalog Description This course is an introduction to plant science including structure, growth processes, propagation,
Lassen Community College Course Outline AGR 20 Introduction to Plant Science 4.0 Units I. Catalog Description This course is an introduction to plant science including structure, growth processes, propagation,
Genetic Variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance in Garlic (Allium sativum L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Kumar et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (3): 849-853 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2594 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5
Available online at www.ijpab.com Kumar et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (3): 849-853 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2594 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5
Evaluation of drought stress effect in summer Safflower genotypes
 ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 Evaluation of drought stress effect in summer Safflower genotypes Behnam Tahmasebpour*, Omid Sofalian**, Hasan Dehghanian*** and Seyed Sajad Hoseini****
ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 Evaluation of drought stress effect in summer Safflower genotypes Behnam Tahmasebpour*, Omid Sofalian**, Hasan Dehghanian*** and Seyed Sajad Hoseini****
GENOTYPE-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION FOR FORAGE YIELD OF VETCH (VICIA SATIVA L.) IN MEDITERRANEAN ENVIRONMENTS. G. Pacucci and C.
 GENOTYPE-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION FOR FORAGE YIELD OF VETCH (VICIA SATIVA L.) IN MEDITERRANEAN ENVIRONMENTS ID # 12-16 G. Pacucci and C. Troccoli Department of Scienze delle Produzioni Vegetali, Università
GENOTYPE-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION FOR FORAGE YIELD OF VETCH (VICIA SATIVA L.) IN MEDITERRANEAN ENVIRONMENTS ID # 12-16 G. Pacucci and C. Troccoli Department of Scienze delle Produzioni Vegetali, Università
THE EFFECTS OF FOLIAR APPLICATION OF SALICYLIC ACID ON QUALITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE YIELD OF WHEAT UNDER SALINE CONDITIONS
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 2 (9), 366-370, 2011 Available online at http://www. irjabs.com 2011 THE EFFECTS OF FOLIAR APPLICATION OF SALICYLIC ACID ON QUALITATIVE
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 2 (9), 366-370, 2011 Available online at http://www. irjabs.com 2011 THE EFFECTS OF FOLIAR APPLICATION OF SALICYLIC ACID ON QUALITATIVE
COVARIANCE ANALYSIS. Rajender Parsad and V.K. Gupta I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi
 COVARIANCE ANALYSIS Rajender Parsad and V.K. Gupta I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi - 110 012 1. Introduction It is well known that in designed experiments the ability to detect existing differences
COVARIANCE ANALYSIS Rajender Parsad and V.K. Gupta I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi - 110 012 1. Introduction It is well known that in designed experiments the ability to detect existing differences
Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology
 Volume 1 Article 6 4-1-1974 Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G.
Volume 1 Article 6 4-1-1974 Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G.
Assessment of genetic variability for quantitative and qualitative traits in Rice Germplasm Accessions (Oryza sativa L.).
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [] 27: 76-83 27 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-88 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [] 27: 76-83 27 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-88 Journal
Correlation and path coefficient analysis in vegetable Amaranthus (Amaranthus tricolor L.)
 2018; 6(1): 14261431 ISSN: 2349 8528 EISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(1): 14261431 2018 IJCS Received: 13112017 Accepted: 14122017 Bhanupratap Jangde h. D. (Scholar), Science, Indira andhi Krishi Vishwavidyalaya,
2018; 6(1): 14261431 ISSN: 2349 8528 EISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(1): 14261431 2018 IJCS Received: 13112017 Accepted: 14122017 Bhanupratap Jangde h. D. (Scholar), Science, Indira andhi Krishi Vishwavidyalaya,
Study of Genetic Diversity in Some Newly Developed Rice Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants
 Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Pea Patch Pollination Game
 Pea Patch Pollination Game Classroom Activity: 5-8 Time: One 45-60-minute class period Overview: In this activity, students play a simulation game modeling changes in a plant population (a Pea Patch) caused
Pea Patch Pollination Game Classroom Activity: 5-8 Time: One 45-60-minute class period Overview: In this activity, students play a simulation game modeling changes in a plant population (a Pea Patch) caused
Correlation and Path Analysis Study in Dolichos Bean (Lablab purpureus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(9): 22282235 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 22282235 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(9): 22282235 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 22282235 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia
 Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
American Journal of Plant Biology. Performance of Brinjal (Solanum melongena) Genotypes through Genetic Variability Analysis
 Nishi NSB et al. American Journal of Plant Biology 2017, 3:22-30 Page 1 of 9 Research Article American Journal of Plant Biology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajplantbio/ Performance of Brinjal (Solanum
Nishi NSB et al. American Journal of Plant Biology 2017, 3:22-30 Page 1 of 9 Research Article American Journal of Plant Biology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajplantbio/ Performance of Brinjal (Solanum
Evaluation of genetic diversity of iranian turnip accessions (Brassica rapa L.) based on morphological characteristics
 International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR) ISSN: 2223-7054 (Print) 2225-3610 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 5, No. 1, p. 29-38, 2014 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Evaluation
International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR) ISSN: 2223-7054 (Print) 2225-3610 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 5, No. 1, p. 29-38, 2014 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Evaluation
Situation of corn in Myanmar
 Situation of corn in Myanmar Phyu Phwe New Plant Variety Protection Unit Department of Agricultural Research(DAR) (2. 8.2016) Introduction Maize - second mandate cereal in Myanmar after rice Mainly utilized
Situation of corn in Myanmar Phyu Phwe New Plant Variety Protection Unit Department of Agricultural Research(DAR) (2. 8.2016) Introduction Maize - second mandate cereal in Myanmar after rice Mainly utilized
Estimates of Variability for Growth and Yield Attributes in Taro (Colocasia esculenta var. Antiquorum (L.) Schott)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1282-1286 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.155
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1282-1286 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.155
Relation between air temperature and length of vegetation period of potato crops.
 Mazurczyk W., Lutomirska B. and Wierzbicka A. Plant Breeding and Acclimatization Institute (IHAR) Research Division at Jadwisin Relation between air temperature and length of vegetation period of potato
Mazurczyk W., Lutomirska B. and Wierzbicka A. Plant Breeding and Acclimatization Institute (IHAR) Research Division at Jadwisin Relation between air temperature and length of vegetation period of potato
SAMPLING IN FIELD EXPERIMENTS
 SAMPLING IN FIELD EXPERIMENTS Rajender Parsad I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi-0 0 rajender@iasri.res.in In field experiments, the plot size for experimentation is selected for achieving a prescribed
SAMPLING IN FIELD EXPERIMENTS Rajender Parsad I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi-0 0 rajender@iasri.res.in In field experiments, the plot size for experimentation is selected for achieving a prescribed
Character Association and Path Coefficient Analysis in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1966-1972 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.233
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1966-1972 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.233
GENETIC VARIABILITY WITHIN TWO ADAPTED POPULATIONS OF TALL WHEATGRASS (THYNOPYRUM PONTICUM) IN ARGENTINA.
 ID # 12-03 GENETIC VARIABILITY WITHIN TWO ADAPTED POPULATIONS OF TALL WHEATGRASS (THYNOPYRUM PONTICUM) IN ARGENTINA A. Andrés 1 and R. Guillen 2 1 INTA EEA Pergamino. CC 31 (2700) Pergamino, Buenos Aires.,
ID # 12-03 GENETIC VARIABILITY WITHIN TWO ADAPTED POPULATIONS OF TALL WHEATGRASS (THYNOPYRUM PONTICUM) IN ARGENTINA A. Andrés 1 and R. Guillen 2 1 INTA EEA Pergamino. CC 31 (2700) Pergamino, Buenos Aires.,
Effect of Growth Habit on Agronomic Characters in Faba Bean
 ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER 43 Effect of Growth Habit on Agronomic Characters in Faba Bean Salvador NADAL 1 * Alfonso CABELLO 2 Fernando FLORES 2 María Teresa MORENO 1 SUMMARY A change in growth habit in
ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER 43 Effect of Growth Habit on Agronomic Characters in Faba Bean Salvador NADAL 1 * Alfonso CABELLO 2 Fernando FLORES 2 María Teresa MORENO 1 SUMMARY A change in growth habit in
PER SE PERFORMANCE STUDIES ON BIDI TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum L.)
 J.Bio.Innov 4(6),pp:236-245,2015 ISSN 2277-8330 (Electronic) PER SE PERFORMANCE STUDIES ON BIDI TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Ramachandra, R.K, Nagappa 1 B.H and Amarananjundeswara 2, H. Assistant Professor
J.Bio.Innov 4(6),pp:236-245,2015 ISSN 2277-8330 (Electronic) PER SE PERFORMANCE STUDIES ON BIDI TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Ramachandra, R.K, Nagappa 1 B.H and Amarananjundeswara 2, H. Assistant Professor
Morphological Markers Related to Sex Expression in Papaya (Carica papaya L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Soni et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 526-531 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5132 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4):
Available online at www.ijpab.com Soni et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 526-531 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5132 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4):
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Processes Photosynthesis. Plant Growth & Development
 Plant Growth & Development Growth Processes Growth Requirements Types of Growth & Development Factors Growth Processes Photosynthesis Creating carbohydrates (stored energy) from CO 2 + water + sunlight
Plant Growth & Development Growth Processes Growth Requirements Types of Growth & Development Factors Growth Processes Photosynthesis Creating carbohydrates (stored energy) from CO 2 + water + sunlight
Variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance Analysis in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2687-2691 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.321
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2687-2691 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.321
7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg
 7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg. 305-311 Key Terms: natural selection, selective pressure, fitness, artificial selection, biotechnology, and monoculture. Natural Selection is the process
7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg. 305-311 Key Terms: natural selection, selective pressure, fitness, artificial selection, biotechnology, and monoculture. Natural Selection is the process
III Conduct of tests:
 Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link) I Subject: These test guidelines apply to all the varieties, hybrids and parental lines of Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link)
Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link) I Subject: These test guidelines apply to all the varieties, hybrids and parental lines of Barnyard millet (Echinocloa frumentaceae (Roxb.) Link)
Department of Agriculture, Zahedan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Zahedan, Iran. Corresponding author: Hamidreza Mobasser
 Journal of Novel Applied Sciences Available online at www.jnasci.org 2013 JNAS Journal-2013-2-10/456-460 ISSN 2322-5149 2013 JNAS Study of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungi symbiosis with maize
Journal of Novel Applied Sciences Available online at www.jnasci.org 2013 JNAS Journal-2013-2-10/456-460 ISSN 2322-5149 2013 JNAS Study of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungi symbiosis with maize
A recipe for the perfect salsa tomato
 The National Association of Plant Breeders in partnership with the Plant Breeding and Genomics Community of Practice presents A recipe for the perfect salsa tomato David Francis, The Ohio State University
The National Association of Plant Breeders in partnership with the Plant Breeding and Genomics Community of Practice presents A recipe for the perfect salsa tomato David Francis, The Ohio State University
Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013
 ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL Advancements in Life Sciences Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013 Open Access Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis
ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL Advancements in Life Sciences Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013 Open Access Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis
ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK
 ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK Conference on Biotechnological Developments 21 November
ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK Conference on Biotechnological Developments 21 November
Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet
 Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet SK Gupta 1 *, Ranjana Bhattacharjee 1,2, KN Rai 1 and M Suresh Kumar 1 1. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet SK Gupta 1 *, Ranjana Bhattacharjee 1,2, KN Rai 1 and M Suresh Kumar 1 1. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
Multiple linear regression S6
 Basic medical statistics for clinical and experimental research Multiple linear regression S6 Katarzyna Jóźwiak k.jozwiak@nki.nl November 15, 2017 1/42 Introduction Two main motivations for doing multiple
Basic medical statistics for clinical and experimental research Multiple linear regression S6 Katarzyna Jóźwiak k.jozwiak@nki.nl November 15, 2017 1/42 Introduction Two main motivations for doing multiple
G E INTERACTION USING JMP: AN OVERVIEW
 G E INTERACTION USING JMP: AN OVERVIEW Sukanta Dash I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi-110012 sukanta@iasri.res.in 1. Introduction Genotype Environment interaction (G E) is a common phenomenon in agricultural
G E INTERACTION USING JMP: AN OVERVIEW Sukanta Dash I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi-110012 sukanta@iasri.res.in 1. Introduction Genotype Environment interaction (G E) is a common phenomenon in agricultural
Hacking Hybrid Plants and Seeds Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University. Presentation Credit: Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University
 Hacking Hybrid Plants and Seeds Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University Hybrid: In biology, hybrid means something different when applied to animals versus plants A) hybrid animals progeny of two different species
Hacking Hybrid Plants and Seeds Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University Hybrid: In biology, hybrid means something different when applied to animals versus plants A) hybrid animals progeny of two different species
Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose
 Journal of Crop and Weed, 9(2):44-49(2013) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose VANLALRUATI, T. MANDAL AND S. PRADHAN Department of Floriculture and Landscaping, Faculty of Horticulture
Journal of Crop and Weed, 9(2):44-49(2013) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose VANLALRUATI, T. MANDAL AND S. PRADHAN Department of Floriculture and Landscaping, Faculty of Horticulture
GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.)
 Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT THE INFLUENCE OF: LIGHT, WATER & TEMPERATURE ON PLANT GROWTH ACORN Presents: Organic Greenhouse Growers Conference Profiting From Your Greenhouse Effect: The Essentials Of Season
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT THE INFLUENCE OF: LIGHT, WATER & TEMPERATURE ON PLANT GROWTH ACORN Presents: Organic Greenhouse Growers Conference Profiting From Your Greenhouse Effect: The Essentials Of Season
Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris var. altissima Döll
 PROTOCOL FOR TESTS ON DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris var. altissima Döll SUGARBEET COMPONENTS UPOV Code: BETAA_VUL Adopted on 21/03/2018 Entry into force on 01/02/2018
PROTOCOL FOR TESTS ON DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris var. altissima Döll SUGARBEET COMPONENTS UPOV Code: BETAA_VUL Adopted on 21/03/2018 Entry into force on 01/02/2018
Detailed Course Outline
 Detailed Course Outline Unit 1 Worlds of Opportunity Lesson 1.1 A World without Enough Plants 1. Many people work in a variety of agricultural enterprises to produce food, fiber, and fuel, which are essential
Detailed Course Outline Unit 1 Worlds of Opportunity Lesson 1.1 A World without Enough Plants 1. Many people work in a variety of agricultural enterprises to produce food, fiber, and fuel, which are essential
natural selection: theory that organisms with traits that are well suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully
 What do you know about evolution? Evolution is a population s change in inheritable traits over time. One of the most common examples of evolution is an ape walking and evolving into an animal that stands
What do you know about evolution? Evolution is a population s change in inheritable traits over time. One of the most common examples of evolution is an ape walking and evolving into an animal that stands
Let light motivate your flowers
 Let light motivate your flowers LightDec Horticulture Light recipes from LEDIG are the best in this market. Their recommendations increased my profits in year one by 23% LED Solutions from LEDIG LED Industrial
Let light motivate your flowers LightDec Horticulture Light recipes from LEDIG are the best in this market. Their recommendations increased my profits in year one by 23% LED Solutions from LEDIG LED Industrial
By the end of this lesson, you should be able to
 Allelopathy 1 Allelopathy By the end of this lesson, you should be able to define allelopathy explain the difference between allelopathy and competition identify the key interactions in allelopathy provide
Allelopathy 1 Allelopathy By the end of this lesson, you should be able to define allelopathy explain the difference between allelopathy and competition identify the key interactions in allelopathy provide
Variability and genetic divergence in paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) 1
 Journal of Spices and Aromatic Crops 71 Vol. 19 (1 & 2) : 71 75 (2010) Indian Society for Spices Variability and genetic divergence in paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) 1 S Surya Kumari, K Uma Jyothi, D Srihari,
Journal of Spices and Aromatic Crops 71 Vol. 19 (1 & 2) : 71 75 (2010) Indian Society for Spices Variability and genetic divergence in paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) 1 S Surya Kumari, K Uma Jyothi, D Srihari,
6 2 Insects and plants
 6 2 Insects and plants Insect DIY 1. Find plant habitat 2. Find plant 3. Accept plant 4. Eat survive, reproduce Plant characteristics Shape structure Mechanical defenses trichomes Chemical defenses sap,
6 2 Insects and plants Insect DIY 1. Find plant habitat 2. Find plant 3. Accept plant 4. Eat survive, reproduce Plant characteristics Shape structure Mechanical defenses trichomes Chemical defenses sap,
Genetic Analysis for Heterotic Traits in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Using Six Parameters Model
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
Managing segregating populations
 Managing segregating populations Aim of the module At the end of the module, we should be able to: Apply the general principles of managing segregating populations generated from parental crossing; Describe
Managing segregating populations Aim of the module At the end of the module, we should be able to: Apply the general principles of managing segregating populations generated from parental crossing; Describe
MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND PATHOGENIC CHARACTERISTICS OF MACROPHOMINA PHASEOLINA ISOLATES FROM SUGAR BEET
 MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND PATHOGENIC CHARACTERISTICS OF MACROPHOMINA PHASEOLINA ISOLATES FROM SUGAR BEET Stojšin, V., Budakov, D., Bagi, F., Đuragin, N., Marinkov, R. Department for Environmental and
MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND PATHOGENIC CHARACTERISTICS OF MACROPHOMINA PHASEOLINA ISOLATES FROM SUGAR BEET Stojšin, V., Budakov, D., Bagi, F., Đuragin, N., Marinkov, R. Department for Environmental and
Keywords: CGMS, combining ability, fertility restoration, heterosis, pigeonpea. Introduction
 Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Characterization of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Germplasm Through Various Agro-Morphological Traits
 Scientia Agriculturae www.pscipub.com/sa E-ISSN: 2310-953X / P-ISSN: 2311-0228 DOI: 10.15192/PSCP.SA.2015.9.2.8388 Sci. Agri. 9 (2), 2015: 83-88 PSCI Publications Characterization of Rice (Oryza Sativa
Scientia Agriculturae www.pscipub.com/sa E-ISSN: 2310-953X / P-ISSN: 2311-0228 DOI: 10.15192/PSCP.SA.2015.9.2.8388 Sci. Agri. 9 (2), 2015: 83-88 PSCI Publications Characterization of Rice (Oryza Sativa
The Effects of Harvesting Time on Herbage Yield, Essence and Thymol Yield in Kouhi thyme (Thymus kotschyanus Boiss. & Hohen.)
 The Effects of Harvesting Time on Herbage Yield, Essence and Thymol Yield in Kouhi thyme (Thymus kotschyanus Boiss. & Hohen.) Ahmad Reza Golparvar Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Khorasgan (Isfahan)
The Effects of Harvesting Time on Herbage Yield, Essence and Thymol Yield in Kouhi thyme (Thymus kotschyanus Boiss. & Hohen.) Ahmad Reza Golparvar Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Khorasgan (Isfahan)
Flower Species as a Supplemental Source of Pollen for Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) in Late Summer Cropping Systems
 Flower Species as a Supplemental Source of Pollen for Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) in Late Summer Cropping Systems Rhonda Simmons, Ramesh Sagili, and Bruce Martens Abstract Honey bee forager preference
Flower Species as a Supplemental Source of Pollen for Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) in Late Summer Cropping Systems Rhonda Simmons, Ramesh Sagili, and Bruce Martens Abstract Honey bee forager preference
SC705: Advanced Statistics Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Class notes: Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
 SC705: Advanced Statistics Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Class notes: Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) SEM is a family of statistical techniques which builds upon multiple regression,
SC705: Advanced Statistics Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Class notes: Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) SEM is a family of statistical techniques which builds upon multiple regression,
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN BIDI TOBACCO (NicotianatabacumL.)
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
Diallel Analysis in Taramira (Eruca sativa)
 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1): 2934, Jan 2011 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1) : 2011 29 Diallel Analysis in Taramira (Eruca sativa) K.C. Sharma, J.P. Kumhar, E.V.D. Sastry and M.L. Jakhar* Abstract
Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1): 2934, Jan 2011 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1) : 2011 29 Diallel Analysis in Taramira (Eruca sativa) K.C. Sharma, J.P. Kumhar, E.V.D. Sastry and M.L. Jakhar* Abstract
Growth Stages of Wheat: Identification and Understanding Improve Crop Management
 Growth Stages of Wheat: Identification and Understanding Improve Crop Management B y Travis D. Miller Understanding growth stages of wheat is important in matching management decisions and inputs with
Growth Stages of Wheat: Identification and Understanding Improve Crop Management B y Travis D. Miller Understanding growth stages of wheat is important in matching management decisions and inputs with
Estimates of Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance of oat (Avena sativa L.) genotypes for grain and fodder yield
 Agricultural Science Research Journals Vol. 3(2), pp. 56-61, February 2013 Available online at http://www.resjournals.com/arj ISSN-L:2026-6073 2013 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Agricultural Science Research Journals Vol. 3(2), pp. 56-61, February 2013 Available online at http://www.resjournals.com/arj ISSN-L:2026-6073 2013 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Some changes in germination and morphological traits of black seed under different soil types and common bean densities
 Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 3, No. 5, p. 31-35, 2013 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Some changes in germination
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 3, No. 5, p. 31-35, 2013 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Some changes in germination
Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet)
 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet) Singh, ramod K. 1*, Rai, N. 1, Lal, Hira 1, Bhardwaj, D.R.
Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet) Singh, ramod K. 1*, Rai, N. 1, Lal, Hira 1, Bhardwaj, D.R.
The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids
 The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids Hassan Kia Heirati 1*, Rasoul Onsinejad 2 and Fattaneh Yari 3 1 M.S. Student, Department
The Effect of Pollination Time and Gibberellic Acid (GA3) on the Production and Seed Germination of Phalaenopsis Orchids Hassan Kia Heirati 1*, Rasoul Onsinejad 2 and Fattaneh Yari 3 1 M.S. Student, Department
Effect of polyethylene glycol on the amount of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and total leaf of sugar beet genotypes
 Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 4, No. 1, p. 233-237, 2014 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of polyethylene
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 4, No. 1, p. 233-237, 2014 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of polyethylene
EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN CASTOR (RICINUS COMMUNIS L.) UNDER SEMI RABI CONDITION
 Indian J. Agric. Res.., 47 (4) : 368-372, 2013 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN
Indian J. Agric. Res.., 47 (4) : 368-372, 2013 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN
Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011
 Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011 Highly discriminating descriptors in this descriptor list are marked with an asterisk [ ]. Characterization should preferably be done during
Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011 Highly discriminating descriptors in this descriptor list are marked with an asterisk [ ]. Characterization should preferably be done during
Ethephon in Sugarcane Cultivation
 Ethephon in Sugarcane Cultivation by M. Edmond Lewis Sugar Industry Research Institute ABSTRACT Sugarcane remains an important commercial crop in Jamaica, and in spite of improved technology in production,
Ethephon in Sugarcane Cultivation by M. Edmond Lewis Sugar Industry Research Institute ABSTRACT Sugarcane remains an important commercial crop in Jamaica, and in spite of improved technology in production,
Genetics and Genetic Prediction in Plant Breeding
 Genetics and Genetic Prediction in Plant Breeding Which traits will be most responsive to selection? What stage will be best to select for specific characters? What environments are most suited to the
Genetics and Genetic Prediction in Plant Breeding Which traits will be most responsive to selection? What stage will be best to select for specific characters? What environments are most suited to the
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1
 Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Received: October Accepted: November. Abstract
 Using an Infrared Gas Analyzer for Evaluation of Photosynthetic Activity in Some Iranian Pistachio Cultivars H. R. Roosta*, A.R. Sajjadinia. Department of Horticultural Sciences, Vali-e-Asr University
Using an Infrared Gas Analyzer for Evaluation of Photosynthetic Activity in Some Iranian Pistachio Cultivars H. R. Roosta*, A.R. Sajjadinia. Department of Horticultural Sciences, Vali-e-Asr University
Studies on genetic divergence on cucumber (Cucumber sativum L.)
 RESEARCH PAPER Asian Journal of Bio Science, Volume 7 Issue 2 October, 2012 169-173 Received : 14.06.2012; Revised : 15.07.2012; Accepted : 20.07.2012 Studies on genetic divergence on cucumber (Cucumber
RESEARCH PAPER Asian Journal of Bio Science, Volume 7 Issue 2 October, 2012 169-173 Received : 14.06.2012; Revised : 15.07.2012; Accepted : 20.07.2012 Studies on genetic divergence on cucumber (Cucumber
PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE (140)
 PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE (140) DESCRIPTION Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in a wide range of scientific principles, such as genetics, disease, pests, and management practices. The scientific
PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE (140) DESCRIPTION Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in a wide range of scientific principles, such as genetics, disease, pests, and management practices. The scientific
IN SUNFLOWER (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS L.)
 Recent Research in Science and Technology 2009, 1(5): 202 206 ISSN: 2076-5061 www.recent-science.com GENETICS & GENOMICS USING LINE X TESTER ANALYSIS FOR EARLINESS AND PLANT HEIGHT TRAITS IN SUNFLOWER
Recent Research in Science and Technology 2009, 1(5): 202 206 ISSN: 2076-5061 www.recent-science.com GENETICS & GENOMICS USING LINE X TESTER ANALYSIS FOR EARLINESS AND PLANT HEIGHT TRAITS IN SUNFLOWER
Identifying Wheat Growth Stages
 AGR-224 Identifying Wheat Growth Stages Carrie A. Knott, Plant and Soil Sciences University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Service Identifying growth stages
AGR-224 Identifying Wheat Growth Stages Carrie A. Knott, Plant and Soil Sciences University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Service Identifying growth stages
Drought Tolerant Criterion of Wheat Genotypes Using Carbon Isotopes Discrimination Technique
 Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 5 (2015) 256-261 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2015. 01. 005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Drought Tolerant Criterion of Wheat Genotypes Using Carbon Isotopes Discrimination Technique
Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 5 (2015) 256-261 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2015. 01. 005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Drought Tolerant Criterion of Wheat Genotypes Using Carbon Isotopes Discrimination Technique
Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists
 Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists Gerry P. Quinn Monash University Michael J. Keough University of Melbourne CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xv I I Introduction 1 1.1
Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists Gerry P. Quinn Monash University Michael J. Keough University of Melbourne CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xv I I Introduction 1 1.1
HANDBOOK OF PRECISION AGRICULTURE PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 http://agrobiol.sggw.waw.pl/cbcs Communications in Biometry and Crop Science Vol. 2, No. 2, 2007, pp. 90 94 International Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture and Biology, Warsaw University of Life Sciences,
http://agrobiol.sggw.waw.pl/cbcs Communications in Biometry and Crop Science Vol. 2, No. 2, 2007, pp. 90 94 International Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture and Biology, Warsaw University of Life Sciences,
Click to edit Master title style Effect of seed and foliar treatments on vigor of soybean plants Jerseyville, IL
 Click to edit Master title style Effect of seed and treatments on vigor of soybean plants Jerseyville, IL Click to edit Master text styles Plant vigor 8.0 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 Second level UTC
Click to edit Master title style Effect of seed and treatments on vigor of soybean plants Jerseyville, IL Click to edit Master text styles Plant vigor 8.0 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 Second level UTC
SELECTING NEW Brachiaria FOR BRAZILIAN PASTURES. 2 CNPq fellow. Abstract
 ID # 13 14 SELECTING NEW Brachiaria FOR BRAZILIAN PASTURES C.B. do Valle 1,2, V.P.B. Euclides 1,2, M.C.M. Macedo 1,2, J R. Valério 1,2 and S. Calixto 1 1 Embrapa Gado de Corte, Caixa Postal 154, 79002-970
ID # 13 14 SELECTING NEW Brachiaria FOR BRAZILIAN PASTURES C.B. do Valle 1,2, V.P.B. Euclides 1,2, M.C.M. Macedo 1,2, J R. Valério 1,2 and S. Calixto 1 1 Embrapa Gado de Corte, Caixa Postal 154, 79002-970
Komala, N. T*, Gurumurthy, R and Surendra, P
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Morphological Characterization of Advanced Lines of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Derived from Swarna x Ranbir Basmati at Seedling Stage Komala, N. T*, Gurumurthy, R and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Morphological Characterization of Advanced Lines of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Derived from Swarna x Ranbir Basmati at Seedling Stage Komala, N. T*, Gurumurthy, R and
Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011
 Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011 Draft Descriptor List Carum spp. Highly discriminating descriptors in this descriptor list are marked with an asterisk [ ]. Characterization
Working Group on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants November 2011 Draft Descriptor List Carum spp. Highly discriminating descriptors in this descriptor list are marked with an asterisk [ ]. Characterization
