10. EXTREME CALIFORNIA RAINS DURING WINTER 2015/16: A CHANGE IN EL NIÑO TELECONNECTION?
|
|
|
- Rosa Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10. EXTREME CALIFORNIA RAINS DURING WINTER 2015/16: A CHANGE IN EL NIÑO TELECONNECTION? Xiao-Wei Quan, Martin Hoerling, Lesley Smith, Judith Perlwitz, Tao Zhang, Andrew Hoell, Klaus Wolter, and Jon Eischeid Failure of heavy rain in Southern California during the 2016 strong El Niño compared to flooding rains during the 1983 strong El Niño does not constitute a climate change effect. Introduction. This is a story of two extreme events one that was expected but failed to occur and the other that actually did occur but was not anticipated. The one that failed was extreme wetness over Southern California (SCAL) during winter 2015/16, which was predicted by seasonal forecasts. The extreme event that did occur was dryness whose considerable magnitude exacerbated one of the worst droughts on record over SCAL. Ranked among the three strongest historical El Niño events, the 2015/16 event fueled apprehensions for flooding rains over California. Analogs were drawn from abundant winter rain during the strong El Niño events of 1982/83 and 1997/98. NOAA s winter outlook indicated a greater than 60% probability that rain totals over SCAL would be in the upper tercile of the historical distribution ( /products/archives/long_lead/llarc.ind.php). December 2015 February 2016 precipitation over SCAL was 112 mm, which ranked in the lower tercile of the historical distribution of winter precipitation since 1895 (Fig. 10.1). While not unusual from a historical perspective (Fig. ES10.1a), this dryness was an extreme event when taking account of precipitation likelihoods during strong El Niño conditions (e.g., Hoell et al. 2016). We pose the attribution question whether a transformation of El Niño teleconnections has occurred due to climate change, the effect of which may have made such an extreme dry outcome during 2015/16 more likely than during 1982/83 and 1997/98. Such a transformation could arise from changes in atmospheric circulation that mediates AFFILIATIONS: Quan, Smith, Perlwitz, Zhang, Wolter, and Eischeid University of Colorado, Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, and NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory, Boulder, Colorado; Hoerling and Hoell NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory, Boulder, Colorado DOI: /BAMS-D A supplement to this article is available online ( /BAMS-D ) trajectories of tropically forced waves (e.g., Diaz et al. 2001; Meehl and Teng 2007), or from shifts in the intensity and longitude of equatorial Pacific rainfall during El Niño events (e.g., Kug et al. 2009; Wang et al. 2015; Zhou et al. 2014). In this study, we explore whether SCAL rainfall sensitivity to a strong El Niño occurring in 2016 has changed compared to a comparably strong El Niño in Datasets and methods. Observed monthly precipitation for is from the GPCC gridded 1 resolution analysis (Schneider et al. 2013). Monthly atmospheric circulation for is from the NCEP/ NCAR Reanalysis (Kalnay et al. 1996). Monthly sea surface temperature (SST) and sea ice concentration (SIC) data are based on Hurrell et al. (2008). Two ensemble suites of climate simulations are analyzed. The first is a 40-member historical transient simulation of the NCAR Community Earth System Model version 1 (CESM1; Kay et al. 2015). These All-Forcings simulations span , and use RCP8.5 for The second is a 20-member ensemble of atmospheric model simulations (AMIP) generated from the atmospheric component of CESM1, named Community Atmospheric Model version 5 (CAM5; Neale et al. 2012). In these AMIPstyle experiments spanning , observed time evolving lower boundary conditions (SSTs and SIC) are prescribed globally, while time varying external radiative forcings identical to those used in CESM1 are also specified. The atmospheric model uses horizontal resolution of and 30 vertical levels for all simulations. While the historical AMIP ensemble size is 20-members, the ensemble size was increased to 50 members for the strong El Niño cases of 1982/83 and 2015/16. A parallel set of 50-member AMIP-style runs were conducted for these two strong El Niño events in which SST forcing over an El Niño-core region (15 N 15 S, 175 E South America) only was specified, while AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY JANUARY 2018 S49
2 Fig Rows: Dec Feb (DJF) total precipitation anomalies (mm) in observation (top), CAM5 AMIP (middle), and CESM1 (bottom) simulations. Shadings indicate difference between DJF of 2015/16 (left column), 1982/83 (middle column) and climatological mean. Differences between the two strong El Niño winters are shown in right-side panels. Percentage values in each panel indicate departure of area mean of DJF total relative to observed and simulated climatology of area mean, respectively. Red region denotes SCAL domain used for area averaging. climatological SSTs were specified over the remaining world oceans. These experiments address how differences in the flavor of El Niño alone affected SCAL precipitation in 2016 versus Further, we address how SSTs over the rest-of-the-world affected SCAL precipitation by first calculating differences between the globally forced runs and the El Niño core-region runs, and then comparing these residual estimates for 2016 and To test the effect of climate change on the response to strong El Niño, we construct composites of strong El Niño events occurring around 1983 and 2016 by subsampling the 40-member CESM1 ensemble. Hurrell et al. (2013) demonstrate that the CESM1 realistically simulates the magnitude of the observed rise in global surface temperature during recent decades. Using a 15-year period centered in 1983 or 2016, we select all December February warm events that exceed 1.5 times the standard deviation of the model s Niño3.4 SST variability ( reference). This yields strong El Niño composites having about members for each period. Our results are robust to S50 JANUARY 2018
3 an alternate method in which El Niño occurrences are calculated relative to each 15-year climatology rather than from the single climatology. Results. a. Observations. Across all regions of California, less precipitation fell during winter (December February) 2016 compared to 1983 (Fig. 10.1, top row). For SCAL (Fig. 10.1, red outline), 2016 precipitation was 35% below the mean, compared to 48% above the mean in Owing to the positive skew of SCAL climatological winter rainfall, the 2016 total was only 22% below the climatological median. It was thus not particularly extreme when assessed in an unconditional framework. However, winter rainfall statistics derived from the CAM5 AMIP simulations indicate that the observed dryness was an extreme event when conditioned upon the particular global boundary forcing of strong El Niño (Fig. ES10.1b). The immediate cause for the Fig As in Fig. 10.1, but for the 200-hPa geopotential height anomalies drastic distinction in SCAL (gpm). Contour interval is 15 m for left and middle columns, and 10 m for rainfall between 2016 and 1983 right column. High and low anomaly centers are denoted by H and L, reis the difference in North Pacific spectively. Colored shadings indicate SST anomalies ( C). atmospheric circulations. Both winters exhibit features of the well-known canonithe magnitude of the CAM5 wet signal was dical El Niño teleconnection pattern (e.g., Horel and minished in 2016 when compared to 1983, however. Wallace 1981). A key distinction, however, is that Note especially that the simulated difference in enthe North Pacific 200-hPa negative height anomaly semble mean California precipitation between these is weaker and shifted farther north into the Gulf of two winters is remarkably similar to the difference in Alaska during 2016 (Fig. 10.2, top row). The circula- observations. Also, comparison of the model probtion difference between those two winters (Fig. 10.2, ability density function (PDF) of SCAL precipitation top right) consists of an anticyclonic anomaly across in 2016 versus 1983 (Fig. ES10.1b) indicates increased the central North Pacific which reduced the frequency likelihood for dryness in 2016; the two distributions of storms over SCAL during are significantly different at the 5% level according to a Kolmogorov Smirnov test. Nonetheless, the b. Atmospheric model simulations. The ensemble mean magnitude of observed dryness was a low probability of CAM5 experiments indicates a SST-forced wet within both ensembles. signal over SCAL in 2016 (Fig. 10.1, middle row), The dynamical basis for this weaker SCAL wet sigconsistent with aforementioned forecast guidance. nal in CAM5 is a weakened and northward displaced The dryness in 2016 was therefore unlikely due to North Pacific low pressure in the model s circulation boundary forcing. pattern during 2016 (Fig. 10.2, middle row). The AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY JANUARY 2018 S51
4 model, whose El Niño driven upper tropospheric wave train agrees well with observations (Fig. 10.2, top and middle rows), indicates that upper tropospheric heights are higher across the entire Pacific basin in 2016 compared to Importantly for SCAL rainfall, differences between the height patterns of the two events consist of an anomalous anticyclonic circulation across the mid-pacific basin which steers storms northward in 2016 relative to Results from the El Niño core-region experiments confirm that distinct El Niño flavors (e.g., stronger far east Pacific SST warmth in 1983 but stronger central Pacific SST warmth in 2016) did not cause the Pacific North American differences in the fully forced CAM5 simulations. Rather, the principal climate sensitivity distinguishing these two strong El Niño winters arises from the rest-of-the-world boundary conditions. In 2016 relative to 1983, these drive widespread increases in Pacific basin heights whose main feature is an anticyclonic circulation across the mid-pacific basin (Fig. ES10.2, bottom right). c. Coupled model simulations. To understand the AMIP results in the context of climate change, we compare CESM1 strong El Niño impacts on western U.S. precipitation for 2016 and 1983 (Fig. 10.1, bottom row). No statistically significant difference in their El Niño-related composite rainfall occurs over SCAL, even though El Niño events circa 2016 are immersed in a warmer ocean. Consistent with a warmer ocean, CESM1 indicates that climate change increases upper level heights across the entire Pacific basin (Fig. 10.2, bottom row). Importantly, however, these height increases are relatively uniform across the Pacific; there is thus no meaningful shift in the model s El Niño-related teleconnection and hence little change in the SCAL winter precipitation. The PDF of CESM1 SCAL winter precipitation for El Niño events circa 2016 versus 1983 are statistically indistinguishable according to a Kolmogorov Smirnov test (Fig. ES10.1c). Conclusion. Based on transient coupled climate simulations, no transformation of El Niño teleconnections has occurred since 1983 that would materially alter the remote sensitivity of Southern California precipitation to strong El Niño forcing. Both composites of strong El Niño in CESM1 experiments circa 1983 versus 2016 show wet signals over SCAL, with no significant difference in the probability distributions for either extreme wet or extreme dry winters. We conclude that the failure of heavy rains in SCAL during the strong El Niño of 2016, compared to the flooding rains of 1983, does not constitute a climate change effect. Our analysis of atmospheric simulations does indicate, however, that the actual global boundary forcing in 2016 (especially the rest-of-the-world boundary forcing outside of the El Niño core-region) was significantly less favorable for wet SCAL in 2016 than in Additional experiments are required to better understand the nature of these rest-of-world boundary conditions that operated in More research is especially needed to reconcile those conditions with plausible modes of internal natural variability (Berg and Hall 2015; Kumar and Chen 2016). ACKNOWLEDGMENTS. The authors thank three anonymous reviewers for thoughtful comments that help to improve the paper. REFERENCES Berg, N., and A. Hall, 2015: Increased interannual precipitation extremes over California under climate change. J. Climate, 28, , doi: /jcli-d Diaz, H., M. Hoerling, and J. Eischeid, 2001: ENSO variability, teleconnections, and climate change. Int. J. Climatol., 21, , doi: /joc.631. Hoell, A., and Coauthors, 2016: Does El Niño intensity matter for California precipitation? Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, , doi: /2015gl Horel, J. D., and J. M. Wallace, 1981: Planetary-scale atmospheric phenomena associated with the Southern Oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 109, Hurrell, J., J. Hack, D. Shea, J. Caron, and J. Rosinski, 2008: A new sea surface temperature and sea ice boundary dataset for the Community Atmosphere Model. J. Climate, 21, , doi: /2008jcli , and Coauthors, 2013: The Community Earth System Model: A framework for collaborative research. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 94, , doi: /BAMS-D Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, S52 JANUARY 2018
5 Kay, J. E., and Coauthors, 2015: The Community Earth System Model (CESM) Large Ensemble project: A community resource for studying climate change in the presence of internal climate variability. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 96, , doi: /BAMS-D Kug, J.-S., S.-Il An, Y.-G. Ham, and I.-S. Kang, 2009: Changes in El Niño and La Niña teleconnection over North Pacific-America in the global warming simulations. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 100, , doi: /s Kumar, A., and M. Chen, 2016: What is the variability in US west coast winter precipitation during strong El Niño events? Climate Dyn., First online, doi: /s Meehl, G., and H. Teng, 2007: Multi-model changes in El Niño teleconnections over North America in a future warmer climate. Climate Dyn., 29, , doi: /s Neale, R. B., and Coauthors, 2012: Description of the NCAR Community Atmospheric Model (CAM5.0). NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN- 486+STR, 289 pp. [Available online at www. cesm.ucar.edu/models/cesm1.0/cam/docs /description/cam5_desc.pdf.] Schneider, U., and Coauthors, 2013: GPCC s new land surface precipitation climatology based on quality-controlled in situ data and its role in quantifying the global water cycle. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 115, 15 40, doi: /s x. Wang, S.-Y., W.-R Huang, H.-H. Hsu, and R. Gilles, 2015: Role of the strengthened El Niño teleconnection in the May 2015 floods over the Southern Great Plains. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, , doi: /2015gl Zhou, Z.-Q., S.-P. Xie, X.-T. Zheng, Q. Liu, and H. Wang, 2014: Global warming-induced changes in El Niño teleconnections over the North Pacific and North America. J. Climate, 27, , doi: /JCLI-D AMERICAN METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY JANUARY 2018 S53
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
20. EXTREME RAINFALL (R20MM, RX5DAY) IN YANGTZE HUAI, CHINA, IN JUNE JULY 2016: THE ROLE OF ENSO AND ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE
 20. EXTREME RAINFALL (R20MM, RX5DAY) IN YANGTZE HUAI, CHINA, IN JUNE JULY 2016: THE ROLE OF ENSO AND ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE Qiaohong Sun and Chiyuan Miao Both the 2015/16 strong El Niño and anthropogenic
20. EXTREME RAINFALL (R20MM, RX5DAY) IN YANGTZE HUAI, CHINA, IN JUNE JULY 2016: THE ROLE OF ENSO AND ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE Qiaohong Sun and Chiyuan Miao Both the 2015/16 strong El Niño and anthropogenic
11. WAS THE JANUARY 2016 MID-ATLANTIC SNOWSTORM JONAS SYMPTOMATIC OF CLIMATE CHANGE?
 11. WAS THE JANUARY 2016 MID-ATLANTIC SNOWSTORM JONAS SYMPTOMATIC OF CLIMATE CHANGE? Klaus Wolter, Martin Hoerling, Jon K. Eischeid, and Dave Allured Model simulations indicate that anthropogenic climate
11. WAS THE JANUARY 2016 MID-ATLANTIC SNOWSTORM JONAS SYMPTOMATIC OF CLIMATE CHANGE? Klaus Wolter, Martin Hoerling, Jon K. Eischeid, and Dave Allured Model simulations indicate that anthropogenic climate
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific subtropical high
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 91 97 East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model ZENG Xian-Feng 1, 2, LI Bo 1, 2, FENG Lei
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 91 97 East China Summer Rainfall during ENSO Decaying Years Simulated by a Regional Climate Model ZENG Xian-Feng 1, 2, LI Bo 1, 2, FENG Lei
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
The Changing Impact of El Niño on US Winter Temperatures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 The Changing Impact of El Niño on US Winter Temperatures Jin-Yi Yu *1, Yuhao Zou
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 The Changing Impact of El Niño on US Winter Temperatures Jin-Yi Yu *1, Yuhao Zou
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
El Niño Seasonal Weather Impacts from the OLR Event Perspective
 Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin NOAA s National Weather Service 41 st NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Orono, ME, 3-6 October 2016 2015-16 El Niño Seasonal Weather
Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin NOAA s National Weather Service 41 st NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Orono, ME, 3-6 October 2016 2015-16 El Niño Seasonal Weather
A Multidecadal Variation in Summer Season Diurnal Rainfall in the Central United States*
 174 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 16 A Multidecadal Variation in Summer Season Diurnal Rainfall in the Central United States* QI HU Climate and Bio-Atmospheric Sciences Group, School of Natural Resource Sciences,
174 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 16 A Multidecadal Variation in Summer Season Diurnal Rainfall in the Central United States* QI HU Climate and Bio-Atmospheric Sciences Group, School of Natural Resource Sciences,
Nonlinear atmospheric teleconnections
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Nonlinear atmospheric teleconnections William W. Hsieh, 1 Aiming Wu, 1 and Amir Shabbar 2 Neural network models are used to reveal the nonlinear
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Nonlinear atmospheric teleconnections William W. Hsieh, 1 Aiming Wu, 1 and Amir Shabbar 2 Neural network models are used to reveal the nonlinear
10.5 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC VARIABILITY ASSOCIATED WITH GROWING SEASON DROUGHTS AND PLUVIALS ON THE CANADIAN PRAIRIES
 10.5 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC VARIABILITY ASSOCIATED WITH GROWING SEASON DROUGHTS AND PLUVIALS ON THE CANADIAN PRAIRIES Amir Shabbar*, Barrie Bonsal and Kit Szeto Environment Canada, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
10.5 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC VARIABILITY ASSOCIATED WITH GROWING SEASON DROUGHTS AND PLUVIALS ON THE CANADIAN PRAIRIES Amir Shabbar*, Barrie Bonsal and Kit Szeto Environment Canada, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Possible Roles of Atlantic Circulations on the Weakening Indian Monsoon Rainfall ENSO Relationship
 2376 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Possible Roles of Atlantic Circulations on the Weakening Indian Monsoon Rainfall ENSO Relationship C.-P. CHANG, PATRICK HARR, AND JIANHUA JU Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
2376 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE Possible Roles of Atlantic Circulations on the Weakening Indian Monsoon Rainfall ENSO Relationship C.-P. CHANG, PATRICK HARR, AND JIANHUA JU Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate
The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051977, 2012 The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle Harry van Loon 1,2 and Gerald A. Meehl 1 Received 9 April 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051977, 2012 The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle Harry van Loon 1,2 and Gerald A. Meehl 1 Received 9 April 2012;
The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models
 1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
The Climate System and Climate Models. Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado
 The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
22. DO CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF YANGTZE RIVER EXTREME RAINFALL?
 22. DO CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF YANGTZE RIVER EXTREME RAINFALL? Xing Yuan, Shanshan Wang, and Zeng-Zhen Hu Anthropogenic climate change has increased the risk of 216 Yangtze River
22. DO CLIMATE CHANGE AND EL NIÑO INCREASE LIKELIHOOD OF YANGTZE RIVER EXTREME RAINFALL? Xing Yuan, Shanshan Wang, and Zeng-Zhen Hu Anthropogenic climate change has increased the risk of 216 Yangtze River
ANTHROPOGENIC CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE INTENSITY OF THE 2017 UNITED STATES NORTHERN GREAT PLAINS DROUGHT
 ANTHROPOGENIC CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE INTENSITY OF THE 2017 UNITED STATES NORTHERN GREAT PLAINS DROUGHT Andrew Hoell, Judith Perlwitz, Candida Dewes, Klaus Wolter, Imtiaz Rangwala, Xiao-Wei Quan, and Jon
ANTHROPOGENIC CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE INTENSITY OF THE 2017 UNITED STATES NORTHERN GREAT PLAINS DROUGHT Andrew Hoell, Judith Perlwitz, Candida Dewes, Klaus Wolter, Imtiaz Rangwala, Xiao-Wei Quan, and Jon
ATTRIBUTION OF THE 2017 NORTHERN HIGH PLAINS DROUGHT
 ATTRIBUTION OF THE 2017 NORTHERN HIGH PLAINS DROUGHT Hailan Wang, Siegfried D. Schubert, Randal D. Koster, and Yehui Chang The 2017 northern High Plains precipitation deficits were largely the result of
ATTRIBUTION OF THE 2017 NORTHERN HIGH PLAINS DROUGHT Hailan Wang, Siegfried D. Schubert, Randal D. Koster, and Yehui Chang The 2017 northern High Plains precipitation deficits were largely the result of
The increase of snowfall in Northeast China after the mid 1980s
 Article Atmospheric Science doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5508-1 The increase of snowfall in Northeast China after the mid 1980s WANG HuiJun 1,2* & HE ShengPing 1,2,3 1 Nansen-Zhu International Research Center,
Article Atmospheric Science doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5508-1 The increase of snowfall in Northeast China after the mid 1980s WANG HuiJun 1,2* & HE ShengPing 1,2,3 1 Nansen-Zhu International Research Center,
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA
 27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
The Texas drought. Kingtse Mo Climate Prediction Center NWS/NCEP/NOAA
 The 2011-2012 Texas drought Kingtse Mo Climate Prediction Center NWS/NCEP/NOAA 1 outline Evolution of the 2011-2012 Texas drought Climatology and historical perspective The 2011 drought Onset Feedback
The 2011-2012 Texas drought Kingtse Mo Climate Prediction Center NWS/NCEP/NOAA 1 outline Evolution of the 2011-2012 Texas drought Climatology and historical perspective The 2011 drought Onset Feedback
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
On the Relationship between Western Maritime Continent Monsoon Rainfall and ENSO during Northern Winter
 1FEBRUARY 2004 CHANG ET AL. 665 On the Relationship between Western Maritime Continent Monsoon Rainfall and ENSO during Northern Winter C.-P. CHANG Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School,
1FEBRUARY 2004 CHANG ET AL. 665 On the Relationship between Western Maritime Continent Monsoon Rainfall and ENSO during Northern Winter C.-P. CHANG Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School,
Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015?
 24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015? Pandora Hope, Guomin Wang, Eun-Pa Lim, Harry H. Hendon, and Julie M. Arblaster Using a seasonal forecasting framework for attribution,
24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015? Pandora Hope, Guomin Wang, Eun-Pa Lim, Harry H. Hendon, and Julie M. Arblaster Using a seasonal forecasting framework for attribution,
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
Reprint 675. Variations of Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South China Sea. Y.K. Leung, M.C. Wu & W.L. Chang
 Reprint 675 Variations of Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South China Sea Y.K. Leung, M.C. Wu & W.L. Chang ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee Annual Review 25 Variations in Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South
Reprint 675 Variations of Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South China Sea Y.K. Leung, M.C. Wu & W.L. Chang ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee Annual Review 25 Variations in Tropical Cyclone Activity in the South
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
Weather Outlook for Spring and Summer in Central TX. Aaron Treadway Meteorologist National Weather Service Austin/San Antonio
 Weather Outlook for Spring and Summer in Central TX Aaron Treadway Meteorologist National Weather Service Austin/San Antonio Outline A Look Back At 2014 Spring 2015 So Far El Niño Update Climate Prediction
Weather Outlook for Spring and Summer in Central TX Aaron Treadway Meteorologist National Weather Service Austin/San Antonio Outline A Look Back At 2014 Spring 2015 So Far El Niño Update Climate Prediction
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Supplementary Material for. Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability
 1 2 Supplementary Material for Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability 3 4 Jie He 1, Clara Deser 2 & Brian J. Soden 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. Princeton University, and NOAA/Geophysical
1 2 Supplementary Material for Atmospheric and Oceanic Origins of Tropical Precipitation Variability 3 4 Jie He 1, Clara Deser 2 & Brian J. Soden 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1. Princeton University, and NOAA/Geophysical
The role of teleconnections in extreme (high and low) precipitation events: The case of the Mediterranean region
 European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2013 Vienna, Austria, 7 12 April 2013 Session HS7.5/NP8.4: Hydroclimatic Stochastics The role of teleconnections in extreme (high and low) events: The case of
European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2013 Vienna, Austria, 7 12 April 2013 Session HS7.5/NP8.4: Hydroclimatic Stochastics The role of teleconnections in extreme (high and low) events: The case of
Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings. with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM
 Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM Masakazu Taguchi* and Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of
Change in Occurrence Frequency of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings with ENSO-like SST Forcing as Simulated WACCM Masakazu Taguchi* and Dennis L. Hartmann Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of
18. ATTRIBUTION OF EXTREME RAINFALL IN SOUTHEAST CHINA DURING MAY 2015
 18. ATTRIBUTION OF EXTREME RAINFALL IN SOUTHEAST CHINA DURING MAY 2015 Claire Burke, Peter Stott, Ying Sun, and Andrew Ciavarella Anthropogenic climate change increased the probability that a short-duration,
18. ATTRIBUTION OF EXTREME RAINFALL IN SOUTHEAST CHINA DURING MAY 2015 Claire Burke, Peter Stott, Ying Sun, and Andrew Ciavarella Anthropogenic climate change increased the probability that a short-duration,
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
A strong bout of natural cooling in 2008
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041188, 2009 A strong bout of natural cooling in 2008 Judith Perlwitz, 1,2 Martin Hoerling, 2 Jon Eischeid, 1,2 Taiyi
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041188, 2009 A strong bout of natural cooling in 2008 Judith Perlwitz, 1,2 Martin Hoerling, 2 Jon Eischeid, 1,2 Taiyi
Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s
 Article Progress of Projects Supported by NSFC Atmospheric Science doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5285-x Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s WANG HuiJun 1,2* & HE
Article Progress of Projects Supported by NSFC Atmospheric Science doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5285-x Weakening relationship between East Asian winter monsoon and ENSO after mid-1970s WANG HuiJun 1,2* & HE
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Last updated: August 2009
 North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
North Pacific Climate Overview N. Bond (UW/JISAO), J. Overland (NOAA/PMEL) Contact: Nicholas.Bond@noaa.gov Last updated: August 2009 Summary. The North Pacific atmosphere-ocean system from fall 2008 through
Spring Heavy Rain Events in Taiwan during Warm Episodes and the Associated Large-Scale Conditions
 VOLUME 131 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW JULY 2003 Spring Heavy Rain Events in Taiwan during Warm Episodes and the Associated Large-Scale Conditions GEORGE TAI-JEN CHEN, ZHIHONG JIANG,* AND MING-CHIN WU Department
VOLUME 131 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW JULY 2003 Spring Heavy Rain Events in Taiwan during Warm Episodes and the Associated Large-Scale Conditions GEORGE TAI-JEN CHEN, ZHIHONG JIANG,* AND MING-CHIN WU Department
Interannual Variability of the South Atlantic High and rainfall in Southeastern South America during summer months
 Interannual Variability of the South Atlantic High and rainfall in Southeastern South America during summer months Inés Camilloni 1, 2, Moira Doyle 1 and Vicente Barros 1, 3 1 Dto. Ciencias de la Atmósfera
Interannual Variability of the South Atlantic High and rainfall in Southeastern South America during summer months Inés Camilloni 1, 2, Moira Doyle 1 and Vicente Barros 1, 3 1 Dto. Ciencias de la Atmósfera
Supplementary Material for: Coordinated Global and Regional Climate Modelling
 1 Supplementary Material for: Coordinated Global and Regional Climate Modelling 2 a. CanRCM4 NARCCAP Analysis 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 As CanRCM4 is a new regional model
1 Supplementary Material for: Coordinated Global and Regional Climate Modelling 2 a. CanRCM4 NARCCAP Analysis 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 As CanRCM4 is a new regional model
19. RECORD-BREAKING HEAT IN NORTHWEST CHINA IN JULY 2015: ANALYSIS OF THE SEVERITY AND UNDERLYING CAUSES
 19. RECORD-BREAKING HEAT IN NORTHWEST CHINA IN JULY 2015: ANALYSIS OF THE SEVERITY AND UNDERLYING CAUSES Chiyuan Miao, Qiaohong Sun, Dongxian Kong, and Qingyun Duan The record-breaking heat over northwest
19. RECORD-BREAKING HEAT IN NORTHWEST CHINA IN JULY 2015: ANALYSIS OF THE SEVERITY AND UNDERLYING CAUSES Chiyuan Miao, Qiaohong Sun, Dongxian Kong, and Qingyun Duan The record-breaking heat over northwest
Evaluation of the Twentieth Century Reanalysis Dataset in Describing East Asian Winter Monsoon Variability
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 6, 2013, 1645 1652 Evaluation of the Twentieth Century Reanalysis Dataset in Describing East Asian Winter Monsoon Variability ZHANG Ziyin 1,2 ( ), GUO Wenli
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 6, 2013, 1645 1652 Evaluation of the Twentieth Century Reanalysis Dataset in Describing East Asian Winter Monsoon Variability ZHANG Ziyin 1,2 ( ), GUO Wenli
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview
 The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
The 2009 Hurricane Season Overview Jae-Kyung Schemm Gerry Bell Climate Prediction Center NOAA/ NWS/ NCEP 1 Overview outline 1. Current status for the Atlantic, Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific basins
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113, D20118, doi: /2008jd009926, 2008
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd009926, 2008 Model assessment of the observed relationship between El Niño and the northern East Asian summer monsoon using the Community Climate
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd009926, 2008 Model assessment of the observed relationship between El Niño and the northern East Asian summer monsoon using the Community Climate
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College December 5, 2017 Summary: November was relatively cool and wet from central California throughout most of
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College December 5, 2017 Summary: November was relatively cool and wet from central California throughout most of
The Role of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature in Forcing East African Rainfall Anomalies during December January 1997/98
 DECEMBER 1999 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 3497 The Role of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature in Forcing East African Rainfall Anomalies during December January 1997/98 M. LATIF AND D. DOMMENGET Max-Planck-Institut
DECEMBER 1999 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 3497 The Role of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature in Forcing East African Rainfall Anomalies during December January 1997/98 M. LATIF AND D. DOMMENGET Max-Planck-Institut
The Influence of Intraseasonal Variations on Medium- to Extended-Range Weather Forecasts over South America
 486 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW The Influence of Intraseasonal Variations on Medium- to Extended-Range Weather Forecasts over South America CHARLES JONES Institute for Computational Earth System Science (ICESS),
486 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW The Influence of Intraseasonal Variations on Medium- to Extended-Range Weather Forecasts over South America CHARLES JONES Institute for Computational Earth System Science (ICESS),
Relative importance of the tropics, internal variability, and Arctic amplification on midlatitude climate and weather
 Relative importance of the tropics, internal variability, and Arctic amplification on midlatitude climate and weather Arun Kumar Climate Prediction Center College Park, Maryland, USA Workshop on Arctic
Relative importance of the tropics, internal variability, and Arctic amplification on midlatitude climate and weather Arun Kumar Climate Prediction Center College Park, Maryland, USA Workshop on Arctic
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. El Niño Southern Oscillation and North Atlantic Oscillation Control of Climate in Puerto Rico
 2713 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE El Niño Southern Oscillation and North Atlantic Oscillation Control of Climate in Puerto Rico BJÖRN A. MALMGREN Department of Earth Sciences, University of Göteborg, Goteborg,
2713 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE El Niño Southern Oscillation and North Atlantic Oscillation Control of Climate in Puerto Rico BJÖRN A. MALMGREN Department of Earth Sciences, University of Göteborg, Goteborg,
August Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2012
 August Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2012 Issued: 6 th August 2012 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK
August Forecast Update for Atlantic Hurricane Activity in 2012 Issued: 6 th August 2012 by Professor Mark Saunders and Dr Adam Lea Dept. of Space and Climate Physics, UCL (University College London), UK
The Correlation Between Fall and Winter Temperature Anomalies in the Midwest during ENSO Events
 The Correlation Between Fall and Winter Temperature Anomalies in the Midwest during ENSO Events Morgan E. Brown Iowa State University Mentors: Ray Arritt and Alan Czarnetzki ABSTRACT According to the National
The Correlation Between Fall and Winter Temperature Anomalies in the Midwest during ENSO Events Morgan E. Brown Iowa State University Mentors: Ray Arritt and Alan Czarnetzki ABSTRACT According to the National
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
9. THE 2015 EXTREME DROUGHT IN WESTERN CANADA
 9. THE 2015 EXTREME DROUGHT IN WESTERN CANADA Kit Szeto, Xuebin Zhang, Robert Edward White, and Julian Brimelow Analysis results indicate that the 2015 extreme drought in western Canada was likely an outcome
9. THE 2015 EXTREME DROUGHT IN WESTERN CANADA Kit Szeto, Xuebin Zhang, Robert Edward White, and Julian Brimelow Analysis results indicate that the 2015 extreme drought in western Canada was likely an outcome
The Enhanced Drying Effect of Central-Pacific El Niño on US Winter
 1 2 3 The Enhanced Drying Effect of Central-Pacific El Niño on US Winter 4 5 6 Jin-Yi Yu * and Yuhao Zou 7 8 9 Department of Earth System Science University of California, Irvine, CA 10 11 12 13 14 15
1 2 3 The Enhanced Drying Effect of Central-Pacific El Niño on US Winter 4 5 6 Jin-Yi Yu * and Yuhao Zou 7 8 9 Department of Earth System Science University of California, Irvine, CA 10 11 12 13 14 15
Climate Prediction Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction
 NOAA s Climate Prediction Center Monthly and Seasonal Forecast Operations Wassila M. Thiaw Climate Prediction Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction Acknowlegement: Mathew Rosencrans, Arun
NOAA s Climate Prediction Center Monthly and Seasonal Forecast Operations Wassila M. Thiaw Climate Prediction Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction Acknowlegement: Mathew Rosencrans, Arun
A Diagnosis of Rainfall over South America during the 1997/98 El Niño Event. Part I: Validation of NCEP NCAR Reanalysis Rainfall Data
 502 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 15 A Diagnosis of Rainfall over South America during the 1997/98 El Niño Event. Part I: Validation of NCEP NCAR Reanalysis Rainfall Data V. BRAHMANANDA RAO, CLÓVIS E. SANTO,
502 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 15 A Diagnosis of Rainfall over South America during the 1997/98 El Niño Event. Part I: Validation of NCEP NCAR Reanalysis Rainfall Data V. BRAHMANANDA RAO, CLÓVIS E. SANTO,
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry
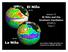 lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
IAP Dynamical Seasonal Prediction System and its applications
 WCRP Workshop on Seasonal Prediction 4-7 June 2007, Barcelona, Spain IAP Dynamical Seasonal Prediction System and its applications Zhaohui LIN Zhou Guangqing Chen Hong Qin Zhengkun Zeng Qingcun Institute
WCRP Workshop on Seasonal Prediction 4-7 June 2007, Barcelona, Spain IAP Dynamical Seasonal Prediction System and its applications Zhaohui LIN Zhou Guangqing Chen Hong Qin Zhengkun Zeng Qingcun Institute
Impacts of Recent El Niño Modoki on Extreme Climate Conditions In East Asia and the United States during Boreal Summer
 Impacts of Recent El Niño Modoki on Extreme Climate Conditions In East Asia and the United States during Boreal Summer Hengyi Weng 1, Karumuri Ashok 1, Swadhin Behera 1, Suryachandra A. Rao 1 and Toshio
Impacts of Recent El Niño Modoki on Extreme Climate Conditions In East Asia and the United States during Boreal Summer Hengyi Weng 1, Karumuri Ashok 1, Swadhin Behera 1, Suryachandra A. Rao 1 and Toshio
ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO and
 Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Summer 2018 Southern Company Temperature/Precipitation Forecast
 Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Inter ENSO variability and its influence over the South American monsoon system
 Inter ENSO variability and its influence over the South American monsoon system A. R. M. Drumond, T. Ambrizzi To cite this version: A. R. M. Drumond, T. Ambrizzi. Inter ENSO variability and its influence
Inter ENSO variability and its influence over the South American monsoon system A. R. M. Drumond, T. Ambrizzi To cite this version: A. R. M. Drumond, T. Ambrizzi. Inter ENSO variability and its influence
Impacts of Two Types of El Niño on Atmospheric Circulation in the Southern Hemisphere
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 6, 2013, 1732 1742 Impacts of Two Types of El Niño on Atmospheric Circulation in the Southern Hemisphere SUN Dan 1,2 ( ), XUE Feng 1 ( ), and ZHOU Tianjun
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 30, NO. 6, 2013, 1732 1742 Impacts of Two Types of El Niño on Atmospheric Circulation in the Southern Hemisphere SUN Dan 1,2 ( ), XUE Feng 1 ( ), and ZHOU Tianjun
Contribution of sea ice loss to Arctic amplification
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045022, 2010 Contribution of sea ice loss to Arctic amplification Arun Kumar, 1 Judith Perlwitz, 2 Jon Eischeid, 2 Xiaowei Quan, 2 Taiyi Xu, 2
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045022, 2010 Contribution of sea ice loss to Arctic amplification Arun Kumar, 1 Judith Perlwitz, 2 Jon Eischeid, 2 Xiaowei Quan, 2 Taiyi Xu, 2
Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains
 Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Large-Scale Circulation Features Typical of Wintertime Extensive and Persistent Low Temperature Events in China
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 4, 235 241 Large-Scale Circulation Features Typical of Wintertime Extensive and Persistent Low Temperature Events in China BUEH Cholaw 1, 2, FU
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 4, 235 241 Large-Scale Circulation Features Typical of Wintertime Extensive and Persistent Low Temperature Events in China BUEH Cholaw 1, 2, FU
COMPOSITE ANALYSIS OF EL NINO SOUTHERN OSCILLATION EVENTS ON ANTARCTICA
 COMPOSITE ANALYSIS OF EL NINO SOUTHERN OSCILLATION EVENTS ON ANTARCTICA Lee Welhouse 2*, Matthew Lazzara 2,3, Matt Hitchman 1 Linda Keller 1, Greg Tripoli 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Department
COMPOSITE ANALYSIS OF EL NINO SOUTHERN OSCILLATION EVENTS ON ANTARCTICA Lee Welhouse 2*, Matthew Lazzara 2,3, Matt Hitchman 1 Linda Keller 1, Greg Tripoli 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Department
The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 2, 87 92 The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model WEI Chao 1,2 and DUAN Wan-Suo 1 1
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 2, 87 92 The Spring Predictability Barrier Phenomenon of ENSO Predictions Generated with the FGOALS-g Model WEI Chao 1,2 and DUAN Wan-Suo 1 1
Why Has the Land Memory Changed?
 3236 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Why Has the Land Memory Changed? QI HU ANDSONG FENG Climate and Bio-Atmospheric Sciences Group, School of Natural Resource Sciences, University of Nebraska at Lincoln,
3236 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Why Has the Land Memory Changed? QI HU ANDSONG FENG Climate and Bio-Atmospheric Sciences Group, School of Natural Resource Sciences, University of Nebraska at Lincoln,
Winter Steve Todd Meteorologist In Charge National Weather Service Portland, OR
 Winter 07-08 Steve Todd Meteorologist In Charge National Weather Service Portland, OR Overview Winter Weather Outlook How to stay informed Winter Outlook LaNina conditions are present across the tropical
Winter 07-08 Steve Todd Meteorologist In Charge National Weather Service Portland, OR Overview Winter Weather Outlook How to stay informed Winter Outlook LaNina conditions are present across the tropical
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
Amajor concern about global warming is the
 High-Frequency Variability in Hurricane Power Dissipation and Its Relationship to Global Temperature BY JAMES B. ELSNER, ANASTASIOS A. TSONIS, AND THOMAS H. JAGGER Results from a statistical analysis are
High-Frequency Variability in Hurricane Power Dissipation and Its Relationship to Global Temperature BY JAMES B. ELSNER, ANASTASIOS A. TSONIS, AND THOMAS H. JAGGER Results from a statistical analysis are
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Delayed Response of the Extratropical Northern Atmosphere to ENSO: A Revisit *
 Delayed Response of the Extratropical Northern Atmosphere to ENSO: A Revisit * Ruping Mo Pacific Storm Prediction Centre, Environment Canada, Vancouver, BC, Canada Corresponding author s address: Ruping
Delayed Response of the Extratropical Northern Atmosphere to ENSO: A Revisit * Ruping Mo Pacific Storm Prediction Centre, Environment Canada, Vancouver, BC, Canada Corresponding author s address: Ruping
An observational study of the impact of the North Pacific SST on the atmosphere
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18611, doi:10.1029/2006gl026082, 2006 An observational study of the impact of the North Pacific SST on the atmosphere Qinyu Liu, 1 Na
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L18611, doi:10.1029/2006gl026082, 2006 An observational study of the impact of the North Pacific SST on the atmosphere Qinyu Liu, 1 Na
Global Climate Patterns and Their Impacts on North American Weather
 Global Climate Patterns and Their Impacts on North American Weather By Julie Malmberg and Jessica Lowrey, Western Water Assessment Introduction This article provides a broad overview of various climate
Global Climate Patterns and Their Impacts on North American Weather By Julie Malmberg and Jessica Lowrey, Western Water Assessment Introduction This article provides a broad overview of various climate
Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS)
 Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS) Christopher L. Castro and Roger A. Pielke, Sr. Department of
Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS) Christopher L. Castro and Roger A. Pielke, Sr. Department of
East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L15706, doi:10.1029/2005gl023010, 2005 East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon Toru Terao Faculty
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L15706, doi:10.1029/2005gl023010, 2005 East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon Toru Terao Faculty
NIWA Outlook: October - December 2015
 October December 2015 Issued: 1 October 2015 Hold mouse over links and press ctrl + left click to jump to the information you require: Overview Regional predictions for the next three months: Northland,
October December 2015 Issued: 1 October 2015 Hold mouse over links and press ctrl + left click to jump to the information you require: Overview Regional predictions for the next three months: Northland,
The impact of El Niño-Southern Oscillation on the Canadian climate
 Advances in Geosciences, 6, 149 153, 2006 SRef-ID: 1680-7359/adgeo/2006-6-149 European Geosciences Union 2006 Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences
Advances in Geosciences, 6, 149 153, 2006 SRef-ID: 1680-7359/adgeo/2006-6-149 European Geosciences Union 2006 Author(s). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences
Influence of South China Sea SST and the ENSO on Winter Rainfall over South China CHAN 2,3
 Influence of South China Sea SST and the ENSO on Winter Rainfall over South China ZHOU Lian-Tong ( 周连童 ) *1,2, Chi-Yung TAM 2,3, Wen ZHOU( 周文 ) 2,3, and Johnny C. L. CHAN 2,3 1 Center for Monsoon System
Influence of South China Sea SST and the ENSO on Winter Rainfall over South China ZHOU Lian-Tong ( 周连童 ) *1,2, Chi-Yung TAM 2,3, Wen ZHOU( 周文 ) 2,3, and Johnny C. L. CHAN 2,3 1 Center for Monsoon System
The 2005 North Atlantic Hurricane Season A Climate Perspective
 The 2005 North Atlantic Hurricane Season A Climate Perspective Gerald Bell 1, Eric Blake 2, Chris Landsea 2, Kingtse Mo 1, Richard Pasch 2, Muthuvel Chelliah 1, Stanley Goldenberg 3 1 Climate Prediction
The 2005 North Atlantic Hurricane Season A Climate Perspective Gerald Bell 1, Eric Blake 2, Chris Landsea 2, Kingtse Mo 1, Richard Pasch 2, Muthuvel Chelliah 1, Stanley Goldenberg 3 1 Climate Prediction
Instability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon-ENSO Relationship in a coupled global atmosphere-ocean GCM
 Instability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon-ENSO Relationship in a coupled global atmosphere-ocean GCM JIANG Dabang 1 WANG Huijun 1 DRANGE Helge 2 LANG Xianmei 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
Instability of the East Asian Summer Monsoon-ENSO Relationship in a coupled global atmosphere-ocean GCM JIANG Dabang 1 WANG Huijun 1 DRANGE Helge 2 LANG Xianmei 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND
 THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND Aphantree Yuttaphan 1, Sombat Chuenchooklin 2 and Somchai Baimoung 3 ABSTRACT The upper part of Thailand
THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND Aphantree Yuttaphan 1, Sombat Chuenchooklin 2 and Somchai Baimoung 3 ABSTRACT The upper part of Thailand
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific
 Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming
 Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming Gerald A. Meehl 1, Haiyan Teng 1, and Julie M. Arblaster 1,2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 2. CAWCR,
Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming Gerald A. Meehl 1, Haiyan Teng 1, and Julie M. Arblaster 1,2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 2. CAWCR,
