Extending the use of surface-sensitive microwave channels in the ECMWF system
|
|
|
- Barbra Patrick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Extending the use of surface-sensitive microwave channels in the ECMWF system Enza Di Tomaso and Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park, Reading, RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Abstract This paper gives an overview on the use of microwave sounding observations for Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) at ECMWF with a focus on the assimilation of surface-sensitive radiances. The assimilation of AMSU-A and MHS radiances in the ECMWF system is currently limited over high orography, snow covered surfaces and sea ice due to large uncertainties in the estimated surface emission. We have investigated an enhancement of the use of MHS and AMSU-A surface-sensitive data, namely over sea ice surfaces. MHS observations are currently assimilated operationally only over surfaces with skin temperature TS 278 K and over low orography. The constraint on the skin temperature means that there is no humidity sounding coverage in most of the areas of the globe with latitudes larger than ± 6 degrees which include sea ice. The assimilation of humidity sounding observations from MHS has been extended in research experiments over sea ice and over sea at any skin temperature, with dynamically retrieved emissivities used over sea ice for both MHS and AMSU-A. As for the assimilation of microwave sounder data over land, the dynamic retrieval of emissivities improves the simulation of microwave sounding also over sea ice, compared to the static retrieval scheme currently used at ECMWF for sea ice surfaces. However, care must be taken within the dynamic retrieval scheme as emissivity spectra vary with the type of sea ice. Assimilation experiments were run in the summer season and the results are significantly positive for the forecast of the temperature, geopotential and winds in the Southern Hemisphere. INTRODUCTION ECMWF is currently assimilating microwave sounding data from six polar orbiting satellites (NOAA-15, NOAA-17, NOAA-18, NOAA-19, MetOp-A, and Aqua) for a total of five AMSU-A and three MHS. MHS observations from channel 3, 4 and 5 (the 3 channels in the 183 GHz water vapour band) are assimilated operationally only over surfaces with skin temperature TS 278 K and over low orography. The constraint on the skin temperature means that there is no humidity sounding coverage in most areas polewards of ± 6 degrees which include sea ice. The other two MHS channels (namely window channels) are used for emissivity retrieval over land (channel 1 at 89 GHz) and quality control purposes (channel 2 at 157 GHz). AMSU-A observations from channel 5 to 14 are assimilated operationally over low orography, sea and sea ice, but with channel 5 not active south of 6S. Other channels are either discarded or used for emissivity retrieval over land (channel 3 at 5.3 GHz), and quality control purposes over land (channel 4 at 52.8 GHz) and over sea (channel 3 at 5.3 GHz). Emissivities over sea ice for AMSU-A are calculated 1
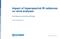
2 emissivity emissivity frequency (GHz).7 1 frequency (GHz) Figure 1: Emissivity spectra for two different types of sea ice, where the emissivities are dynamically retrieved from MHS observations at 89, 157 and GHz. with a static scheme based on a classification of the surface type and an appropriate parametric model per surface type (Kelly and Bauer ). As for the assimilation of microwave sounder data over land, the dynamic retrieval of emissivities provides a good basis to improve the use of microwave sounding over sea ice, as shown also in (Bouchard et al. 21). The dynamic retrieval of emissivities is based on re-arranging the radiative transfer equation for window channel observations and using the ECMWF model background field (Karbou et al. 5). Over land the assumption is made that the error introduced by using, for a given frequency, emissivities calculated at a different frequency, is small. As shown in Di Tomaso and Bormann (211), MHS departure statistics show that emissivities retrieved at 89 GHz can be used over land for the water vapour channels without introducing a relevant bias. Over sea ice the situation is more complex as the emissivity spectra vary greatly with the type of ice (Harlow 211). There are surfaces for which the emission at 89 GHz might be quite different than the one at 157 GHz or 183 GHz. Figure 1 shows an example of two emissivity spectra for different types of sea ice where the emissivities are dynamically retrieved from MHS observations at 89, 157 and GHz. These issues have been taken into account in the experiments described in the next section. ENHANCED ASSIMILATION OF MICROWAVE SOUNDING DATA OVER SEA AND SEA ICE Assimilation experiments We have run assimilation experiments with the active usage of additional MHS observations over sea and sea ice, and with dynamically retrieved emissivities used in the simulation of both AMSU-A and MHS radiances over sea ice. Experiments were run at a low resolution (T319) with cycle CY37R3 from June to September 211 with MHS channel 3, 4 and 5 active over sea with any skin temperature, and channel 3 and 4 active also over sea ice. The current constraint on the skin temperature has been left unchanged over land (i.e. MHS observations are assimilated only over surfaces with skin temperature TS 278 K to exclude snow-covered surfaces). The assimilation of MHS channel 5 over land is included in these experiments as in the control experiment (which was not yet implemented in cycle CY37R3). For MHS we have considered two cases: the use of emissivities retrieved from channel 2 observations (at 157 GHz) (experiment EXP1) and the use of emissivities retrieved from channel 1 observations (at 89 GHz) (experiment EXP2). Note that at high latitudes the surface contribution to the observed radiation is relevant also at 157 GHz. In both experiments the additional data over sea with TS < 278 K are simulated with FASTEM emissivities (Liu at al. 211) (as it is done for all the other MHS observations over sea). Emissivities for AMSU-A over sea ice are retrieved, in both experiments, from channel 3 observations (at 5.3 GHz), similarly to land observations. These two experiments are identical to the 2
3 N STATISTICS FOR RADIANCES FROM FROM METOP-A/MHS VS METOP-A/MHS NUMBER OF OBSERVATIONS PER GRID SQUARE (USED) DATA PERIOD = EXP = FNTA_VS_FNRK, CHANNEL = 4 Min: -24 Max: 27 Mean: 9.58 STATISTICS FOR RADIANCES FROM FROM METOP-A/MHS VS METOP-A/MHS NUMBER OF OBSERVATIONS PER GRID SQUARE (USED) DATA PERIOD = EXP = FNTA_VS_FNRK, CHANNEL = 5 Min: -24 Max: 163 Mean: W 12 W 9 W 6 W 3 W E 3 E 6 E 9 E 12 E 15 E 15 W 12 W 9 W 6 W 3 W E 3 E 6 E 9 E 12 E 15 E N 6 N N 6 N N 3 N 6 3 N 3 N N 15 N N S 3 S S 3 S S 6 S S 6 S W 12 W 9 W 6 W 3 W E 3 E 6 E 9 E 12 E 15 E 15 W 12 W 9 W 6 W 3 W E 3 E 6 E 9 E 12 E 15 E Figure 2: Count differences for MHS channel 4 (left), channel 5 (right) observations per grid box used in the atmospheric analysis between experiment EXP1 and the control experiment in June 211. control experiment (experiment CTL) except for the usage of observations over cold sea and sea ice. The emissivities at 89 GHz might differ considerably from the ones at 183 GHz over certain surfaces. Therefore emissivities retrieved over sea ice at 89 GHz need to be corrected before being used to simulate the water vapour channels. We have applied as correction term the one currently used in the Meteo France system based on the brightness temperature difference between MHS channel 2 and 1 (Bouchard et al. 21). The emissivities retrieved at 157 GHz are used without correction for the water vapour channels as these differences are in general smaller for emissivities retrieved at 157 GHz. We have also run an experiment (experiment EXP3) which uses over sea ice emissivities calculated with an old scheme (Kelly and Bauer ). As stated earlier, this static scheme is based on a classification of the surface type and an appropriate parametric model per surface type. Table 1 summarises the settings used for MHS in the assimilation experiments described above. In all the experiments sea ice is identified as a surface having land-sea mask less than.1 and surface skin temperature T S < K. Results Figure 2 shows the difference in counts between the observations actively assimilated in experiment EXP1 and the control for MHS channel 4 and 5 (the plot for channel 3 is quite similar to the one for channel 4). A considerable number of additional MHS observations is assimilated in particular below -5 degrees latitude, where there is no humidity sounding coverage in the control experiment (and similarly in the operational configuration). Many observations over sea ice are rejected in EXP3 due to very high departures between the observations and the first-guess, proving that the dynamic emissivities over sea ice are more accurate than the Experiment Experiment Emissivity estimation Emissivity correction Channel used for name ID over sea ice over sea ice QC over sea ice EXP1 fnta Retrieved from Channel 2 correction for Channel 1 Channel 1 EXP2 fnv8 Retrieved from Channel 1 correction for Channel 2-5 Channel 2 EXP3 fmqy static scheme NA Channel 2 Table 1: MHS settings for the assimilation experiments on the enhanced use of microwave sounders over sea and sea ice. 3
4 Counts CTL EXP1 EXP FG-departures [K] Counts CTL EXP1 EXP FG-departures [K] Counts 1 CTL EXP1 EXP FG-departures [K] Figure 3: Histograms of first-guess departures for MHS channel 3 (left), channel 4 (centre) and channel 5 (right) over sea ice in July 211 when emissivities are estimated by an old static scheme (CTL, red), are retrieved dynamically from observations at 157GHz (EXP1, green) or from observations at 89 GHz and with a correction for the variation of emissivities with frequency (EXP2, blue). static ones. As for the assimilation of microwave sounder data over land, using the dynamically retrieved emissivities over sea ice provides a better representation of model-estimated brightness temperatures than a static scheme. Figure 3 shows histograms of first-guess departures for MHS channel 3 (left), channel 4 (centre) and channel 5 (right) observations over sea ice when emissivities are estimated by the old static scheme (CTL, red), are retrieved dynamically from observations at 157 GHz (EXP1, green) or from observations at 89 GHz and with a correction for the variation of emissivities with frequency (EXP2, blue). Here all data have been considered, i.e. before any screening and quality control stage and before bias correction. Therefore, in the control experiment, emissivities over sea ice are estimated by the static scheme, though are not actively assimilated. The dynamic emissivities lead to improved simulations for the 183 GHz sounding channels (histograms for EXP1 and EXP2 are narrower and more centred around than for the control experiment). Similar is the case for histograms of first-guess departures for AMSU- A surface-sensitive channels over sea ice (not shown). Furthermore using the 157 GHz channel for MHS emissivity retrieval appears to perform best (the histogram for EXP1 is slightly narrower than for EXP2). Bias and standard deviation of first-guess departures for assimilated MHS channel 4 measurements over the Southern Hemisphere are slightly smaller (and a greater number of observations is assimilated) in experiment EXP1 than in experiment EXP2. Global maps of first-guess departure statistics show that this is the case particularly over sea ice (see Figure 4). This suggests that the emissivities calculated from 157 GHz, and used without a correction, might be more accurate than the ones calculated from 89 GHz, after a correction is applied to them. Forecast results are computed for different variables and regions for 92 days of assimilation experiments. The results in the Southern Hemisphere for EXP1 are very positive for the forecast of the temperature, geopotential and winds. The positive impact for forecast of the temperature appears statistically significant at 95% confidence level for all the forecast days at hpa and from day 2 to 6 at 85 hpa, when averaged over the Southern Hemisphere (see Figure 5 and Figure 6). Also experiment EXP2 shows a positive impact in the Southern Hemisphere for the forecast of all the relevant variables. Forecast scores show a considerable negative impact for relative humidity in the short range at the location of the additional data assimilated in both experiment EXP1 and experiment EXP2 (see Figure 7). As argued in Geer et al. (9), this is likely an apparent degradation in the forecast error of the relative humidity due to adding humidity observations in a data-poor area and verifying using the experiment own-analysis as proxy of the true state of the atmosphere. The degradation is in fact not observed for the other atmospheric parameters, or in verification of short-term forecasts against observations. Results on the forecast impact are very encouraging towards a more extensive exploitation of MHS observations over sea and sea ice and better simulation of AMSU-A observations over sea ice surfaces. 4
5 N STATISTICS FOR RADIANCES FROM FROM METOP-A/MHS VS METOP-A/MHS MEAN FIRST GUESS DEPARTURE (OBS-FG) (USED) DATA PERIOD = EXP = FNTA_VS_FNV8, CHANNEL = 4 Min: Max: Mean: W 12 W 9 W 6 W 3 W E 3 E 6 E 9 E 12 E 15 E 6 N 3 N 3 S 6 S 15 W 12 W 9 W 6 W 3 W E 3 E 6 E 9 E 12 E 15 E 6 N 3 N N 3 S 6 S Figure 4: Global difference of mean first-guess departures for MHS channel 4 on MetOp-A between experiment EXP1 (fnta) and experiment EXP2 (fnv8) in June 211. Normalised difference T: 9 to 2, 85 hpa Forecast day Normalised difference T: 9 to 2, hpa Forecast day Figure 5: Normalised differences in the root mean squared forecast error between the experiment EXP1 (fnta) and the control experiment (fnrk) for the Z forecast of the 85 hpa and hpa temperature. Verification is against the experiment own-analysis. Experiments have been run at a low resolution and will require some further testing at higher resolutions and over different seasons. CONCLUSIONS The use of dynamically retrieved emissivities over sea ice has allowed the assimilation of a considerable amount of humidity and temperature sounding observations in data sparse areas of the globe. Furthermore, removing the current skin temperature constraint on the assimilation of MHS measurements over sea has allowed a great number of additional observations to be used at high latitudes. We have tested different ways of retrieving the emissivities over sea ice for the simulation of the actively assimilated MHS and AMSU-A measurements. Dynamically retrieved emissivities over sea ice provides a better representation of model-estimated brightness temperatures, for both AMSU-A and MHS, than a static scheme currently implemented at ECMWF. In particular, retrieving emissivities at 157 GHz and using them (without any correction) for the water vapour channels allows the assimilation of MHS high peaking channels over sea ice with a clear improvement to the fit of MHS channel 3 and 4 observations both in the Northern and Southern Hemisphere. Results of assimilation experiments are encouraging towards a more extensive exploitation of MHS observations over sea and sea ice and a better usage of AMSU-A over sea ice surfaces. 5
6 .1 RMS forecast errors in T(fnta fnrk), 16 Jun 211 to 15 Sep 211, from 84 to 92 samples. Point confidence 99.8% to give multiple comparison adjusted confidence 95%. Verified against own analysis. T+12 T+24 T+48 T+96 T+144 T+192 T+72 T+12 T Normalised difference in RMS error Figure 6: Normalised differences in the root mean squared forecast error between the experiment EXP1 (fnta) and the control experiment (fnrk) for the Z forecast of temperature at different pressure levels. Verification is against the experiment own-analysis. RMS forecast errors in R(fnta fnrk), 16 Jun 211 to 15 Sep 211, from 84 to 92 samples. Point confidence 99.8% to give multiple comparison adjusted confidence 95%. Verified against own analysis. T+12 T+24 T+48 T+96 T+144 T+192 T+72 T+12 T Normalised difference in RMS error Figure 7: Normalised differences in the root mean squared forecast error between the experiment EXP1 (fnta) and the control experiment (fnrk) for the Z forecast of the relative humidity at different pressure levels. Verification is against the experiment own-analysis. 6
7 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Enza Di Tomaso is funded by the EUMETSAT Fellowship Programme. REFERENCES Bouchard, A., F. Rabier, V. Guidard, F. Karbou (21), Enhancements of Satellite Data Assimilation over Antarctica, Monthly Weather Review, 138(6), Di Tomaso, E., N. Bormann (211), Assimilation of ATOVS radiances at ECMWF, In Proceedings of of the 211 EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, Oslo, Norway. Geer, A. J., P. Bauer and P. Lopez (9), Direct 4D-Var assimilation of all-sky radiances. Assessment, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc.,, Part II: Harlow, R.C. (211), Sea Ice Emissivities and Effective Temperatures at MHS Frequencies: An Analysis of Airborne Microwave Data Measured During Two Arctic Campaigns, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 49(4), Karbou, F., E. Grard, F. Rabier (5), Microwave land emissivity and skin temperature for AMSU-A and -B assimilation over land. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 132, Kelly, G. and Bauer, P. (), The use of AMSU-A surface channels to obtain surface emissivity over land, snow and ice for numerical weather prediction, In Proceedings of 11th International TOVS Study Conference, Budapest, Hungary, Liu, Q., F.Weng and S.J. English (211), An Improved Fast Microwave Water Emissivity Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 49,
THE ASSIMILATION OF SURFACE-SENSITIVE MICROWAVE SOUNDER RADIANCES AT ECMWF
 THE ASSIMILATION OF SURFACE-SENSITIVE MICROWAVE SOUNDER RADIANCES AT ECMWF Enza Di Tomaso and Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park, Reading, RG2 9AX, United Kingdom
THE ASSIMILATION OF SURFACE-SENSITIVE MICROWAVE SOUNDER RADIANCES AT ECMWF Enza Di Tomaso and Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park, Reading, RG2 9AX, United Kingdom
OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENTS ON ATOVS ORBIT CONSTELLATIONS
 OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENTS ON ATOVS ORBIT CONSTELLATIONS Enza Di Tomaso and Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park, Reading, RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Abstract
OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENTS ON ATOVS ORBIT CONSTELLATIONS Enza Di Tomaso and Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park, Reading, RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Abstract
Towards a better use of AMSU over land at ECMWF
 Towards a better use of AMSU over land at ECMWF Blazej Krzeminski 1), Niels Bormann 1), Fatima Karbou 2) and Peter Bauer 1) 1) European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), Shinfield Park,
Towards a better use of AMSU over land at ECMWF Blazej Krzeminski 1), Niels Bormann 1), Fatima Karbou 2) and Peter Bauer 1) 1) European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), Shinfield Park,
ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS WITH DATA FROM THREE CONICALLY SCANNING MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS (SSMIS, AMSR-E, TMI) IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM
 ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS WITH DATA FROM THREE CONICALLY SCANNING MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS (SSMIS, AMSR-E, TMI) IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM Niels Bormann 1, Graeme Kelly 1, Peter Bauer 1, and Bill Bell 2 1 ECMWF,
ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS WITH DATA FROM THREE CONICALLY SCANNING MICROWAVE INSTRUMENTS (SSMIS, AMSR-E, TMI) IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM Niels Bormann 1, Graeme Kelly 1, Peter Bauer 1, and Bill Bell 2 1 ECMWF,
All-sky assimilation of MHS and HIRS sounder radiances
 All-sky assimilation of MHS and HIRS sounder radiances Alan Geer 1, Fabrizio Baordo 2, Niels Bormann 1, Stephen English 1 1 ECMWF 2 Now at Bureau of Meteorology, Australia All-sky assimilation at ECMWF
All-sky assimilation of MHS and HIRS sounder radiances Alan Geer 1, Fabrizio Baordo 2, Niels Bormann 1, Stephen English 1 1 ECMWF 2 Now at Bureau of Meteorology, Australia All-sky assimilation at ECMWF
An Evaluation of FY-3C MWHS-2 and its potential to improve forecast accuracy at ECMWF
 An Evaluation of FY-3C MWHS-2 and its potential to improve forecast accuracy at ECMWF Heather Lawrence, final-year EUMETSAT fellow, ECMWF Supervised by: Niels Bormann & Stephen English Slide 1 China s
An Evaluation of FY-3C MWHS-2 and its potential to improve forecast accuracy at ECMWF Heather Lawrence, final-year EUMETSAT fellow, ECMWF Supervised by: Niels Bormann & Stephen English Slide 1 China s
Cliquez pour modifier le style des sous-titres du masque
 Techniques for modelling land, snow and sea ice emission and scattering in support of data assimilation Fatima Karbou CNRM-GAME, Cliquez pour modifier le stylemétéo-france du titre & CNRS Saint Martin
Techniques for modelling land, snow and sea ice emission and scattering in support of data assimilation Fatima Karbou CNRM-GAME, Cliquez pour modifier le stylemétéo-france du titre & CNRS Saint Martin
Estimates of observation errors and their correlations in clear and cloudy regions for microwave imager radiances from NWP
 Estimates of observation errors and their correlations in clear and cloudy regions for microwave imager radiances from NWP Niels Bormann, Alan J. Geer and Peter Bauer ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2
Estimates of observation errors and their correlations in clear and cloudy regions for microwave imager radiances from NWP Niels Bormann, Alan J. Geer and Peter Bauer ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2
New screening of cold-air outbreak regions used in 4D-Var all-sky assimilation
 EUMETSAT/ECMWF Fellowship Programme Research Report No. 35 New screening of cold-air outbreak regions used in 4D-Var all-sky assimilation Katrin Lonitz and Alan Geer February 2015 Series: EUMETSAT/ECMWF
EUMETSAT/ECMWF Fellowship Programme Research Report No. 35 New screening of cold-air outbreak regions used in 4D-Var all-sky assimilation Katrin Lonitz and Alan Geer February 2015 Series: EUMETSAT/ECMWF
Bias correction of satellite data at Météo-France
 Bias correction of satellite data at Météo-France É. Gérard, F. Rabier, D. Lacroix, P. Moll, T. Montmerle, P. Poli CNRM/GMAP 42 Avenue Coriolis, 31057 Toulouse, France 1. Introduction Bias correction at
Bias correction of satellite data at Météo-France É. Gérard, F. Rabier, D. Lacroix, P. Moll, T. Montmerle, P. Poli CNRM/GMAP 42 Avenue Coriolis, 31057 Toulouse, France 1. Introduction Bias correction at
Assimilation of precipitation-related observations into global NWP models
 Assimilation of precipitation-related observations into global NWP models Alan Geer, Katrin Lonitz, Philippe Lopez, Fabrizio Baordo, Niels Bormann, Peter Lean, Stephen English Slide 1 H-SAF workshop 4
Assimilation of precipitation-related observations into global NWP models Alan Geer, Katrin Lonitz, Philippe Lopez, Fabrizio Baordo, Niels Bormann, Peter Lean, Stephen English Slide 1 H-SAF workshop 4
ASSIMILATION OF CLOUDY AMSU-A MICROWAVE RADIANCES IN 4D-VAR 1. Stephen English, Una O Keeffe and Martin Sharpe
 ASSIMILATION OF CLOUDY AMSU-A MICROWAVE RADIANCES IN 4D-VAR 1 Stephen English, Una O Keeffe and Martin Sharpe Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB Abstract The assimilation of cloud-affected satellite
ASSIMILATION OF CLOUDY AMSU-A MICROWAVE RADIANCES IN 4D-VAR 1 Stephen English, Una O Keeffe and Martin Sharpe Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB Abstract The assimilation of cloud-affected satellite
Evaluation and comparisons of FASTEM versions 2 to 5
 Evaluation and comparisons of FASTEM versions 2 to 5 Niels Bormann, Alan Geer and Stephen English European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts, ECMWF, Reading, United Kingdom, email: n.bormann@ecmwf.int
Evaluation and comparisons of FASTEM versions 2 to 5 Niels Bormann, Alan Geer and Stephen English European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts, ECMWF, Reading, United Kingdom, email: n.bormann@ecmwf.int
Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF
 Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF Peter Bauer, Alan Geer, Philippe Lopez, Deborah Salmond European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, UK Slide 1 17
Direct assimilation of all-sky microwave radiances at ECMWF Peter Bauer, Alan Geer, Philippe Lopez, Deborah Salmond European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, UK Slide 1 17
Assimilation of hyperspectral infrared sounder radiances in the French global numerical weather prediction ARPEGE model
 Assimilation of hyperspectral infrared sounder radiances in the French global numerical weather prediction ARPEGE model N. Fourrié, V. Guidard, M. Dahoui, T. Pangaud, P. Poli and F. Rabier CNRM-GAME, Météo-France
Assimilation of hyperspectral infrared sounder radiances in the French global numerical weather prediction ARPEGE model N. Fourrié, V. Guidard, M. Dahoui, T. Pangaud, P. Poli and F. Rabier CNRM-GAME, Météo-France
Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation at the Met Office
 Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation at the Met Office Ed Pavelin, Stephen English, Brett Candy, Fiona Hilton Outline Summary of satellite data used in the Met Office NWP system Processing and quality
Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation at the Met Office Ed Pavelin, Stephen English, Brett Candy, Fiona Hilton Outline Summary of satellite data used in the Met Office NWP system Processing and quality
Satellite Application Facility for Numerical Weather Prediction
 Satellite Application Facility for Numerical Weather Prediction Document Version 1.0 January 2007 Towards the assimilation of satellite microwave : feasibility studies using SSMI/S, AMSU-A and AMSU-B Fatima
Satellite Application Facility for Numerical Weather Prediction Document Version 1.0 January 2007 Towards the assimilation of satellite microwave : feasibility studies using SSMI/S, AMSU-A and AMSU-B Fatima
COMPARISON OF SIMULATED RADIANCE FIELDS USING RTTOV AND CRTM AT MICROWAVE FREQUENCIES IN KOPS FRAMEWORK
 COMPARISON OF SIMULATED RADIANCE FIELDS USING RTTOV AND CRTM AT MICROWAVE FREQUENCIES IN KOPS FRAMEWORK Ju-Hye Kim 1, Jeon-Ho Kang 1, Hyoung-Wook Chun 1, and Sihye Lee 1 (1) Korea Institute of Atmospheric
COMPARISON OF SIMULATED RADIANCE FIELDS USING RTTOV AND CRTM AT MICROWAVE FREQUENCIES IN KOPS FRAMEWORK Ju-Hye Kim 1, Jeon-Ho Kang 1, Hyoung-Wook Chun 1, and Sihye Lee 1 (1) Korea Institute of Atmospheric
The assimilation of AMSU and SSM/I brightness temperatures in clear skies at the Meteorological Service of Canada
 The assimilation of AMSU and SSM/I brightness temperatures in clear skies at the Meteorological Service of Canada Abstract David Anselmo and Godelieve Deblonde Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval,
The assimilation of AMSU and SSM/I brightness temperatures in clear skies at the Meteorological Service of Canada Abstract David Anselmo and Godelieve Deblonde Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval,
Modelling the surface emissivity to assimilate SSMI/S observations over Land
 Modelling the surface emissivity to assimilate SSMI/S observations over Land Fatima KARBOU and Jean-François MAHFOUF CNRM-GAME Météo-France & CNRS 1) SSMI/S observations SSMI/S = AMSU-A + AMSU-B + SSM/I
Modelling the surface emissivity to assimilate SSMI/S observations over Land Fatima KARBOU and Jean-François MAHFOUF CNRM-GAME Météo-France & CNRS 1) SSMI/S observations SSMI/S = AMSU-A + AMSU-B + SSM/I
Rosemary Munro*, Graeme Kelly, Michael Rohn* and Roger Saunders
 ASSIMILATION OF METEOSAT RADIANCE DATA WITHIN THE 4DVAR SYSTEM AT ECMWF Rosemary Munro*, Graeme Kelly, Michael Rohn* and Roger Saunders European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park,
ASSIMILATION OF METEOSAT RADIANCE DATA WITHIN THE 4DVAR SYSTEM AT ECMWF Rosemary Munro*, Graeme Kelly, Michael Rohn* and Roger Saunders European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts Shinfield Park,
Assimilating AMSU-A over Sea Ice in HIRLAM 3D-Var
 Abstract Assimilating AMSU-A over Sea Ice in HIRLAM 3D-Var Vibeke W. Thyness 1, Leif Toudal Pedersen 2, Harald Schyberg 1, Frank T. Tveter 1 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute (met.no) Box 43 Blindern,
Abstract Assimilating AMSU-A over Sea Ice in HIRLAM 3D-Var Vibeke W. Thyness 1, Leif Toudal Pedersen 2, Harald Schyberg 1, Frank T. Tveter 1 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute (met.no) Box 43 Blindern,
Élisabeth Gérard, Fatima Karbou, Florence Rabier, Jean-Philippe Lafore, Jean-Luc Redelsperger
 Land surface emissivity at microwave frequencies: operational implementation in the French global 4DVar system and impact of using surface sensitive channels on the African Monsoon during AMMA Élisabeth
Land surface emissivity at microwave frequencies: operational implementation in the French global 4DVar system and impact of using surface sensitive channels on the African Monsoon during AMMA Élisabeth
Satellite data assimilation for NWP: II
 Satellite data assimilation for NWP: II Jean-Noël Thépaut European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) with contributions from many ECMWF colleagues Slide 1 Special thanks to: Tony McNally,
Satellite data assimilation for NWP: II Jean-Noël Thépaut European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) with contributions from many ECMWF colleagues Slide 1 Special thanks to: Tony McNally,
Impact of hyperspectral IR radiances on wind analyses
 Impact of hyperspectral IR radiances on wind analyses Kirsti Salonen and Anthony McNally Kirsti.Salonen@ecmwf.int ECMWF November 30, 2017 Motivation The upcoming hyper-spectral IR instruments on geostationary
Impact of hyperspectral IR radiances on wind analyses Kirsti Salonen and Anthony McNally Kirsti.Salonen@ecmwf.int ECMWF November 30, 2017 Motivation The upcoming hyper-spectral IR instruments on geostationary
Toward a better modeling of surface emissivity to improve AMSU data assimilation over Antarctica GUEDJ Stephanie, KARBOU Fatima and RABIER Florence
 Toward a better modeling of surface emissivity to improve AMSU data assimilation over Antarctica GUEDJ Stephanie, KARBOU Fatima and RABIER Florence International TOVS Study Conference, Monterey, California
Toward a better modeling of surface emissivity to improve AMSU data assimilation over Antarctica GUEDJ Stephanie, KARBOU Fatima and RABIER Florence International TOVS Study Conference, Monterey, California
Assimilation of MIPAS limb radiances at ECMWF using 1d and 2d radiative transfer models
 Assimilation of MIPAS limb radiances at ECMWF using 1d and 2d radiative transfer models Niels Bormann, Sean Healy, Mats Hamrud, and Jean-Noël Thépaut European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts
Assimilation of MIPAS limb radiances at ECMWF using 1d and 2d radiative transfer models Niels Bormann, Sean Healy, Mats Hamrud, and Jean-Noël Thépaut European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts
Plans for the Assimilation of Cloud-Affected Infrared Soundings at the Met Office
 Plans for the Assimilation of Cloud-Affected Infrared Soundings at the Met Office Ed Pavelin and Stephen English Met Office, Exeter, UK Abstract A practical approach to the assimilation of cloud-affected
Plans for the Assimilation of Cloud-Affected Infrared Soundings at the Met Office Ed Pavelin and Stephen English Met Office, Exeter, UK Abstract A practical approach to the assimilation of cloud-affected
Exploitation of microwave sounder/imager data over land surfaces in the presence of clouds and precipitation. SAF-HYDROLOGY, Final Report
 Exploitation of microwave sounder/imager data over land surfaces in the presence of clouds and precipitation SAF-HYDROLOGY, Final Report By Fatima KARBOU 1, Peter BAUER 2, Alan GEER 2 and William BELL
Exploitation of microwave sounder/imager data over land surfaces in the presence of clouds and precipitation SAF-HYDROLOGY, Final Report By Fatima KARBOU 1, Peter BAUER 2, Alan GEER 2 and William BELL
Of Chessboards and Ghosts Signatures of micro-vibrations from IASI monitoring in NWP?
 Of Chessboards and Ghosts Signatures of micro-vibrations from IASI monitoring in NWP? Niels Bormann 1, James R.N. Cameron 2, and Anthony P. McNally 1 1 European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts
Of Chessboards and Ghosts Signatures of micro-vibrations from IASI monitoring in NWP? Niels Bormann 1, James R.N. Cameron 2, and Anthony P. McNally 1 1 European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts
F. Rabier, N. Saint-Ramond, V. Guidard, A. Doerenbecher, A. Vincensini Météo-France and CNRS
 Impact of observations in the Southern Polar Area during the Concordiasi field experiment F. Rabier, N. Saint-Ramond, V. Guidard, A. Doerenbecher, A. Vincensini Météo-France and CNRS C. Cardinali ECMWF
Impact of observations in the Southern Polar Area during the Concordiasi field experiment F. Rabier, N. Saint-Ramond, V. Guidard, A. Doerenbecher, A. Vincensini Météo-France and CNRS C. Cardinali ECMWF
Satellite data assimilation for Numerical Weather Prediction II
 Satellite data assimilation for Numerical Weather Prediction II Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) (with contributions from Tony McNally, Jean-Noël Thépaut, Slide
Satellite data assimilation for Numerical Weather Prediction II Niels Bormann European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) (with contributions from Tony McNally, Jean-Noël Thépaut, Slide
Treatment of Surface Emissivity in Microwave Satellite Data Assimilation
 Treatment of Surface Emissivity in Microwave Satellite Data Assimilation Fatima KARBOU (CNRM / GAME, Météo-France & CNRS) With contributions from: Peter BAUER (ECMWF) Niels BORMANN (ECMWF) John DERBER
Treatment of Surface Emissivity in Microwave Satellite Data Assimilation Fatima KARBOU (CNRM / GAME, Météo-France & CNRS) With contributions from: Peter BAUER (ECMWF) Niels BORMANN (ECMWF) John DERBER
The Use of ATOVS Microwave Data in the Grapes-3Dvar System
 The Use of ATOVS Microwave Data in the Grapes-3Dvar System Peiming Dong 1 Zhiquan Liu 2 Jishan Xue 1 Guofu Zhu 1 Shiyu Zhuang 1 Yan Liu 1 1 Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, China 2
The Use of ATOVS Microwave Data in the Grapes-3Dvar System Peiming Dong 1 Zhiquan Liu 2 Jishan Xue 1 Guofu Zhu 1 Shiyu Zhuang 1 Yan Liu 1 1 Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, China 2
Initial results from using ATMS and CrIS data at ECMWF
 Initial results from using ATMS and CrIS data at ECMWF Niels Bormann 1, William Bell 1, Anne Fouilloux 1, Tony McNally 1, Ioannis Mallas 1, Nigel Atkinson 2, Steve Swadley 3 Slide 1 1 ECMWF, 2 Met Office,
Initial results from using ATMS and CrIS data at ECMWF Niels Bormann 1, William Bell 1, Anne Fouilloux 1, Tony McNally 1, Ioannis Mallas 1, Nigel Atkinson 2, Steve Swadley 3 Slide 1 1 ECMWF, 2 Met Office,
Treatment of Surface Emissivity for Satellite Microwave Data Assimilation
 Treatment of Surface Emissivity for Satellite Microwave Data Assimilation Fatima Karbou CNRM / GAME, MÉTÉO-FRANCE & CNRS Toulouse, France fatima.karbou@meteo.fr SUMMARY Observations from satellite microwave
Treatment of Surface Emissivity for Satellite Microwave Data Assimilation Fatima Karbou CNRM / GAME, MÉTÉO-FRANCE & CNRS Toulouse, France fatima.karbou@meteo.fr SUMMARY Observations from satellite microwave
On the importance of land surface emissivity to assimilate low level humidity and temperature observations over land
 CNRM / GAME F. KARBOU 2nd Workshop on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Surface Properties Slide 1 On the importance of land surface emissivity to assimilate low level humidity and temperature observations
CNRM / GAME F. KARBOU 2nd Workshop on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Surface Properties Slide 1 On the importance of land surface emissivity to assimilate low level humidity and temperature observations
Evaluation of FY-3B data and an assessment of passband shifts in AMSU-A and MSU during the period
 Interim report of Visiting Scientist mission NWP_11_05 Document NWPSAF-EC-VS-023 Version 0.1 28 March 2012 Evaluation of FY-3B data and an assessment of passband Qifeng Lu 1 and William Bell 2 1. China
Interim report of Visiting Scientist mission NWP_11_05 Document NWPSAF-EC-VS-023 Version 0.1 28 March 2012 Evaluation of FY-3B data and an assessment of passband Qifeng Lu 1 and William Bell 2 1. China
Prospects for radar and lidar cloud assimilation
 Prospects for radar and lidar cloud assimilation Marta Janisková, ECMWF Thanks to: S. Di Michele, E. Martins, A. Beljaars, S. English, P. Lopez, P. Bauer ECMWF Seminar on the Use of Satellite Observations
Prospects for radar and lidar cloud assimilation Marta Janisková, ECMWF Thanks to: S. Di Michele, E. Martins, A. Beljaars, S. English, P. Lopez, P. Bauer ECMWF Seminar on the Use of Satellite Observations
Towards the assimilation of AIRS cloudy radiances
 Towards the assimilation of AIRS cloudy radiances N. FOURRIÉ 1, M. DAHOUI 1 * and F. RABIER 1 1 : National Center for Meteorological Research (CNRM, METEO FRANCE and CNRS) Numerical Weather Prediction
Towards the assimilation of AIRS cloudy radiances N. FOURRIÉ 1, M. DAHOUI 1 * and F. RABIER 1 1 : National Center for Meteorological Research (CNRM, METEO FRANCE and CNRS) Numerical Weather Prediction
An evaluation of radiative transfer modelling error in AMSU-A data
 An evaluation of radiative transfer modelling error in AMSU-A data Cristina Lupu, Alan Geer, Niels Bormann and Stephen English 20 th International TOVS Study Conference, Lake Geneva, USA 28 October 2015
An evaluation of radiative transfer modelling error in AMSU-A data Cristina Lupu, Alan Geer, Niels Bormann and Stephen English 20 th International TOVS Study Conference, Lake Geneva, USA 28 October 2015
Monitoring and Assimilation of IASI Radiances at ECMWF
 Monitoring and Assimilation of IASI Radiances at ECMWF Andrew Collard and Tony McNally ECMWF Slide 1 Overview Introduction Assimilation Configuration IASI First Guess Departures IASI Forecast Impacts The
Monitoring and Assimilation of IASI Radiances at ECMWF Andrew Collard and Tony McNally ECMWF Slide 1 Overview Introduction Assimilation Configuration IASI First Guess Departures IASI Forecast Impacts The
Use and impact of ATOVS in the DMI-HIRLAM regional weather model
 Use and impact of ATOVS in the DMI-HIRLAM regional weather model J. Grove-Rasmussen B. Amstrup and K.S. Mogensen E-mail: jgr@dmi.dk, bja@dmi.dk and ksm@dmi.dk Danish Meteorological Institute Lyngbyvej,
Use and impact of ATOVS in the DMI-HIRLAM regional weather model J. Grove-Rasmussen B. Amstrup and K.S. Mogensen E-mail: jgr@dmi.dk, bja@dmi.dk and ksm@dmi.dk Danish Meteorological Institute Lyngbyvej,
Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
Spatial and inter-channel observation error characteristics for AMSU-A and IASI and applications in the ECMWF system
 Spatial and inter-channel observation error characteristics for AMSU-A and IASI and applications in the system Niels Bormann, Andrew Collard, Peter Bauer Outline 1) Estimation of observation errors AMSU-A
Spatial and inter-channel observation error characteristics for AMSU-A and IASI and applications in the system Niels Bormann, Andrew Collard, Peter Bauer Outline 1) Estimation of observation errors AMSU-A
AMVs in the ECMWF system:
 AMVs in the ECMWF system: Highlights of the operational and research activities Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann Slide 1 Number of used AMVs Look back: how the use of AMVs has evolved NOAA-15,-16,-18,-19
AMVs in the ECMWF system: Highlights of the operational and research activities Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann Slide 1 Number of used AMVs Look back: how the use of AMVs has evolved NOAA-15,-16,-18,-19
AMVs in the ECMWF system:
 AMVs in the ECMWF system: Overview of the recent operational and research activities Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann Slide 1 AMV sample coverage: monitored GOES-15 GOES-13 MET-10 MET-7 MTSAT-2 NOAA-15
AMVs in the ECMWF system: Overview of the recent operational and research activities Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann Slide 1 AMV sample coverage: monitored GOES-15 GOES-13 MET-10 MET-7 MTSAT-2 NOAA-15
Bias correction of satellite data at the Met Office
 Bias correction of satellite data at the Met Office Nigel Atkinson, James Cameron, Brett Candy and Stephen English Met Office, Fitzroy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, United Kingdom 1. Introduction At the Met Office,
Bias correction of satellite data at the Met Office Nigel Atkinson, James Cameron, Brett Candy and Stephen English Met Office, Fitzroy Road, Exeter, EX1 3PB, United Kingdom 1. Introduction At the Met Office,
IMPACT OF IASI DATA ON FORECASTING POLAR LOWS
 IMPACT OF IASI DATA ON FORECASTING POLAR LOWS Roger Randriamampianina rwegian Meteorological Institute, Pb. 43 Blindern, N-0313 Oslo, rway rogerr@met.no Abstract The rwegian THORPEX-IPY aims to significantly
IMPACT OF IASI DATA ON FORECASTING POLAR LOWS Roger Randriamampianina rwegian Meteorological Institute, Pb. 43 Blindern, N-0313 Oslo, rway rogerr@met.no Abstract The rwegian THORPEX-IPY aims to significantly
The potential impact of ozone sensitive data from MTG-IRS
 The potential impact of ozone sensitive data from MTG-IRS R. Dragani, C. Lupu, C. Peubey, and T. McNally ECMWF rossana.dragani@ecmwf.int ECMWF May 24, 2017 The MTG IRS Long-Wave InfraRed band O 3 Can the
The potential impact of ozone sensitive data from MTG-IRS R. Dragani, C. Lupu, C. Peubey, and T. McNally ECMWF rossana.dragani@ecmwf.int ECMWF May 24, 2017 The MTG IRS Long-Wave InfraRed band O 3 Can the
All-sky assimilation of SSMIS humidity sounding channels over land within the ECMWF system
 EUMETSAT/ECMWF Fellowship Programme Research Report No. 38 All-sky assimilation of SSMIS humidity sounding channels over land within the ECMWF system Fabrizio Baordo and Alan J. Geer July 2015 To be submitted
EUMETSAT/ECMWF Fellowship Programme Research Report No. 38 All-sky assimilation of SSMIS humidity sounding channels over land within the ECMWF system Fabrizio Baordo and Alan J. Geer July 2015 To be submitted
Use of ATOVS raw radiances in the operational assimilation system at Météo-France
 Use of ATOVS raw radiances in the operational assimilation system at Météo-France Élisabeth Gérard, Florence Rabier, Delphine Lacroix Météo-France, Toulouse, France Zahra Sahlaoui Maroc-Météo, Casablanca,
Use of ATOVS raw radiances in the operational assimilation system at Météo-France Élisabeth Gérard, Florence Rabier, Delphine Lacroix Météo-France, Toulouse, France Zahra Sahlaoui Maroc-Météo, Casablanca,
AMVs in the operational ECMWF system
 AMVs in the operational ECMWF system Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann Slide 1 AMV sample coverage: monitored GOES-15 GOES-13 MET-10 MET-7 MTSAT-2 NOAA-15 NOAA-18 NOAA-19 FY-2D FY-2E AQUA TERRA METOP-A
AMVs in the operational ECMWF system Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann Slide 1 AMV sample coverage: monitored GOES-15 GOES-13 MET-10 MET-7 MTSAT-2 NOAA-15 NOAA-18 NOAA-19 FY-2D FY-2E AQUA TERRA METOP-A
Assimilation of IASI data at the Met Office. Fiona Hilton Nigel Atkinson ITSC-XVI, Angra dos Reis, Brazil 07/05/08
 Assimilation of IASI data at the Met Office Fiona Hilton Nigel Atkinson ITSC-XVI, Angra dos Reis, Brazil 07/05/08 Thanks to my other colleagues! Andrew Collard (ECMWF) Brett Candy, Steve English, James
Assimilation of IASI data at the Met Office Fiona Hilton Nigel Atkinson ITSC-XVI, Angra dos Reis, Brazil 07/05/08 Thanks to my other colleagues! Andrew Collard (ECMWF) Brett Candy, Steve English, James
ACCOUNTING FOR THE SITUATION-DEPENDENCE OF THE AMV OBSERVATION ERROR IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM
 ACCOUNTING FOR THE SITUATION-DEPENDENCE OF THE AMV OBSERVATION ERROR IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Abstract This article reports
ACCOUNTING FOR THE SITUATION-DEPENDENCE OF THE AMV OBSERVATION ERROR IN THE ECMWF SYSTEM Kirsti Salonen and Niels Bormann ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Abstract This article reports
UPDATES IN THE ASSIMILATION OF GEOSTATIONARY RADIANCES AT ECMWF
 UPDATES IN THE ASSIMILATION OF GEOSTATIONARY RADIANCES AT ECMWF Carole Peubey, Tony McNally, Jean-Noël Thépaut, Sakari Uppala and Dick Dee ECMWF, UK Abstract Currently, ECMWF assimilates clear sky radiances
UPDATES IN THE ASSIMILATION OF GEOSTATIONARY RADIANCES AT ECMWF Carole Peubey, Tony McNally, Jean-Noël Thépaut, Sakari Uppala and Dick Dee ECMWF, UK Abstract Currently, ECMWF assimilates clear sky radiances
Data assimilation of IASI radiances over land.
 Data assimilation of IASI radiances over land. PhD supervised by Nadia Fourrié, Florence Rabier and Vincent Guidard. 18th International TOVS Study Conference 21-27 March 2012, Toulouse Contents 1. IASI
Data assimilation of IASI radiances over land. PhD supervised by Nadia Fourrié, Florence Rabier and Vincent Guidard. 18th International TOVS Study Conference 21-27 March 2012, Toulouse Contents 1. IASI
Bias correction of satellite data at the Met Office
 Bias correction of satellite data at the Met Office Nigel Atkinson, James Cameron, Brett Candy and Steve English ECMWF/EUMETSAT NWP-SAF Workshop on Bias estimation and correction in data assimilation,
Bias correction of satellite data at the Met Office Nigel Atkinson, James Cameron, Brett Candy and Steve English ECMWF/EUMETSAT NWP-SAF Workshop on Bias estimation and correction in data assimilation,
Impact of observations in the Southern Polar Area during the Concordiasi field experiment
 Impact of observations in the Southern Polar Area during the Concordiasi field experiment F. Rabier, N. Saint-Ramond, V. Guidard, A. Doerenbecher, A. Vincensini Météo-France and CNRS C. Cardinali ECMWF
Impact of observations in the Southern Polar Area during the Concordiasi field experiment F. Rabier, N. Saint-Ramond, V. Guidard, A. Doerenbecher, A. Vincensini Météo-France and CNRS C. Cardinali ECMWF
Assimilation of Cloud-Affected Infrared Radiances at Environment-Canada
 Assimilation of Cloud-Affected Infrared Radiances at Environment-Canada ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop on Assimilating Satellite Observations of Clouds and Precipitation into NWP models ECMWF, Reading (UK) Sylvain
Assimilation of Cloud-Affected Infrared Radiances at Environment-Canada ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop on Assimilating Satellite Observations of Clouds and Precipitation into NWP models ECMWF, Reading (UK) Sylvain
Toward assimilation of CrIS and ATMS in the NCEP Global Model
 Toward assimilation of CrIS and ATMS in the NCEP Global Model Andrew Collard 1, John Derber 2, Russ Treadon 2, Nigel Atkinson 3, Jim Jung 4 and Kevin Garrett 5 1 IMSG at NOAA/NCEP/EMC 2 NOAA/NCEP/EMC 3
Toward assimilation of CrIS and ATMS in the NCEP Global Model Andrew Collard 1, John Derber 2, Russ Treadon 2, Nigel Atkinson 3, Jim Jung 4 and Kevin Garrett 5 1 IMSG at NOAA/NCEP/EMC 2 NOAA/NCEP/EMC 3
All-sky assimilation of microwave humidity sounders
 74 All-sky assimilation of microwave humidity sounders Alan J. Geer, Fabrizio Baordo, Niels Bormann and Stephen English Research Department November 24 Series: ECMWF Technical Memoranda A full list of
74 All-sky assimilation of microwave humidity sounders Alan J. Geer, Fabrizio Baordo, Niels Bormann and Stephen English Research Department November 24 Series: ECMWF Technical Memoranda A full list of
The assimilation of AMSU-A radiances in the NWP model ALADIN. The Czech Hydrometeorological Institute Patrik Benáček 2011
 The assimilation of AMSU-A radiances in the NWP model ALADIN The Czech Hydrometeorological Institute Patrik Benáček 2011 Outline Introduction Sensor AMSU-A Set-up of model ALADIN Set-up of experiments
The assimilation of AMSU-A radiances in the NWP model ALADIN The Czech Hydrometeorological Institute Patrik Benáček 2011 Outline Introduction Sensor AMSU-A Set-up of model ALADIN Set-up of experiments
MET report. The IASI moisture channel impact study in HARMONIE for August-September 2011
 MET report no. 19/2013 Numerical Weather Prediction The IASI moisture channel impact study in HARMONIE for August-September 2011 Trygve Aspelien, Roger Randriamampianina, Harald Schyberg, Frank Thomas
MET report no. 19/2013 Numerical Weather Prediction The IASI moisture channel impact study in HARMONIE for August-September 2011 Trygve Aspelien, Roger Randriamampianina, Harald Schyberg, Frank Thomas
All-sky observations: errors, biases, representativeness and gaussianity
 All-sky observations: errors, biases, representativeness and gaussianity Alan Geer, Peter Bauer, Philippe Lopez Thanks to: Bill Bell, Niels Bormann, Anne Foullioux, Jan Haseler, Tony McNally Slide 1 ECMWF-JCSDA
All-sky observations: errors, biases, representativeness and gaussianity Alan Geer, Peter Bauer, Philippe Lopez Thanks to: Bill Bell, Niels Bormann, Anne Foullioux, Jan Haseler, Tony McNally Slide 1 ECMWF-JCSDA
Improved assimilation of IASI land surface temperature data over continents in the convective scale AROME France model
 Improved assimilation of IASI land surface temperature data over continents in the convective scale AROME France model Niama Boukachaba, Vincent Guidard, Nadia Fourrié CNRM-GAME, Météo-France and CNRS,
Improved assimilation of IASI land surface temperature data over continents in the convective scale AROME France model Niama Boukachaba, Vincent Guidard, Nadia Fourrié CNRM-GAME, Météo-France and CNRS,
Effects of all-sky assimilation of GCOM-W1/AMSR2 radiances in the ECMWF system
 732 Effects of all-sky assimilation of GCOM-W1/AMSR2 radiances in the ECMWF system Masahiro Kazumori 1, Alan J. Geer, and Stephen J. English Research Department 1 Japan Meteorological Agency To be submitted
732 Effects of all-sky assimilation of GCOM-W1/AMSR2 radiances in the ECMWF system Masahiro Kazumori 1, Alan J. Geer, and Stephen J. English Research Department 1 Japan Meteorological Agency To be submitted
All-sky assimilation: better snow-scattering radiative transfer and addition of SSMIS humidity sounding channels
 706 All-sky assimilation: better snow-scattering radiative transfer and addition of SSMIS humidity sounding channels Alan J. Geer Research Department October 2013 Series: ECMWF Technical Memoranda A full
706 All-sky assimilation: better snow-scattering radiative transfer and addition of SSMIS humidity sounding channels Alan J. Geer Research Department October 2013 Series: ECMWF Technical Memoranda A full
METEOSAT cloud-cleared radiances for use in three/fourdimensional variational data assimilation
 METEOSAT cloud-cleared radiances for use in three/fourdimensional variational data assimilation G. A. Kelly, M. Tomassini and M. Matricardi European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading,
METEOSAT cloud-cleared radiances for use in three/fourdimensional variational data assimilation G. A. Kelly, M. Tomassini and M. Matricardi European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading,
OSSE to infer the impact of Arctic AMVs extracted from highly elliptical orbit imagery
 OSSE to infer the impact of Arctic AMVs extracted from highly elliptical orbit imagery L. Garand 1 Y. Rochon 1, S. Heilliette 1, J. Feng 1, A.P. Trishchenko 2 1 Environment Canada, 2 Canada Center for
OSSE to infer the impact of Arctic AMVs extracted from highly elliptical orbit imagery L. Garand 1 Y. Rochon 1, S. Heilliette 1, J. Feng 1, A.P. Trishchenko 2 1 Environment Canada, 2 Canada Center for
Assimilation of Cross-track Infrared Sounder radiances at ECMWF
 ssimilation of ross-track Infrared Sounder radiances at EMWF Reima Eresmaa, nthony P. McNally and Niels Bormann European entre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, United Kingdom Introduction
ssimilation of ross-track Infrared Sounder radiances at EMWF Reima Eresmaa, nthony P. McNally and Niels Bormann European entre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Reading, Berkshire, United Kingdom Introduction
The impact of assimilation of microwave radiance in HWRF on the forecast over the western Pacific Ocean
 The impact of assimilation of microwave radiance in HWRF on the forecast over the western Pacific Ocean Chun-Chieh Chao, 1 Chien-Ben Chou 2 and Huei-Ping Huang 3 1Meteorological Informatics Business Division,
The impact of assimilation of microwave radiance in HWRF on the forecast over the western Pacific Ocean Chun-Chieh Chao, 1 Chien-Ben Chou 2 and Huei-Ping Huang 3 1Meteorological Informatics Business Division,
Use of AMSU data in the Met Office UK Mesoscale Model
 Use of AMSU data in the Met Office UK Mesoscale Model 1. Introduction Brett Candy, Stephen English, Richard Renshaw & Bruce Macpherson The Met Office, Exeter, United Kingdom In common with other global
Use of AMSU data in the Met Office UK Mesoscale Model 1. Introduction Brett Candy, Stephen English, Richard Renshaw & Bruce Macpherson The Met Office, Exeter, United Kingdom In common with other global
Assessing the impact of different liquid water permittivity models on the fit between model and observations
 Assessing the impact of different liquid water permittivity models on the fit between model and observations Katrin Lonitz 1 and Alan J. Geer 1 1 European Centre for Medium-Weather Range Forecasts, Shinfield
Assessing the impact of different liquid water permittivity models on the fit between model and observations Katrin Lonitz 1 and Alan J. Geer 1 1 European Centre for Medium-Weather Range Forecasts, Shinfield
A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system
 A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system Li Bi James Jung John Le Marshall 16 April 2008 Outline WindSat overview and working
A two-season impact study of the Navy s WindSat surface wind retrievals in the NCEP global data assimilation system Li Bi James Jung John Le Marshall 16 April 2008 Outline WindSat overview and working
The assimilation of AIRS radiance over land at Météo -France
 The assimilation of AIRS radiance over land at Météo -France Abstract Hua Zhang *1,2,Florence Rabier 1, Malgorzata Szczech-Gajewska 3, Delphine Lacroix 1 1 Météo-France/CNRM/GMAP, Toulouse, France 2 Chinese
The assimilation of AIRS radiance over land at Météo -France Abstract Hua Zhang *1,2,Florence Rabier 1, Malgorzata Szczech-Gajewska 3, Delphine Lacroix 1 1 Météo-France/CNRM/GMAP, Toulouse, France 2 Chinese
Recent improvements in the all-sky assimilation of microwave radiances at the ECMWF
 Recent improvements in the all-sky assimilation of microwave radiances at the ECMWF Katrin Lonitz, Alan Geer and many more katrin.lonitz@ecmwf.int ECMWF January 30, 2018 clear sky assimilation all-sky
Recent improvements in the all-sky assimilation of microwave radiances at the ECMWF Katrin Lonitz, Alan Geer and many more katrin.lonitz@ecmwf.int ECMWF January 30, 2018 clear sky assimilation all-sky
Lambertian surface scattering at AMSU-B frequencies:
 Lambertian surface scattering at AMSU-B frequencies: An analysis of airborne microwave data measured over snowcovered surfaces Chawn Harlow, 2nd Workshop on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Land Surface
Lambertian surface scattering at AMSU-B frequencies: An analysis of airborne microwave data measured over snowcovered surfaces Chawn Harlow, 2nd Workshop on Remote Sensing and Modeling of Land Surface
Effect of Predictor Choice on the AIRS Bias Correction at the Met Office
 Effect of Predictor Choice on the AIRS Bias Correction at the Met Office Brett Harris Bureau of Meterorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia James Cameron, Andrew Collard and Roger Saunders, Met
Effect of Predictor Choice on the AIRS Bias Correction at the Met Office Brett Harris Bureau of Meterorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia James Cameron, Andrew Collard and Roger Saunders, Met
Assimilating AMSU-A temperature sounding channels in the presence of cloud and precipitation
 EUMETSAT/ECMWF Fellowship Programme Research Report No. 24 Assimilating AMSU-A temperature sounding channels in the presence of cloud and precipitation Alan J. Geer, Peter Bauer and Stephen J. English
EUMETSAT/ECMWF Fellowship Programme Research Report No. 24 Assimilating AMSU-A temperature sounding channels in the presence of cloud and precipitation Alan J. Geer, Peter Bauer and Stephen J. English
A New Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer Channel Selection and Assessment of Its Impact on Met Office NWP Forecasts
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 34, NOVEMBER 2017, 1265 1281 Original Paper A New Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer Channel Selection and Assessment of Its Impact on Met Office NWP Forecasts
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 34, NOVEMBER 2017, 1265 1281 Original Paper A New Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer Channel Selection and Assessment of Its Impact on Met Office NWP Forecasts
SSMIS 1D-VAR RETRIEVALS. Godelieve Deblonde
 SSMIS 1D-VAR RETRIEVALS Godelieve Deblonde Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval, Québec, Canada Summary Retrievals using synthetic background fields and observations for the SSMIS (Special Sensor Microwave
SSMIS 1D-VAR RETRIEVALS Godelieve Deblonde Meteorological Service of Canada, Dorval, Québec, Canada Summary Retrievals using synthetic background fields and observations for the SSMIS (Special Sensor Microwave
All-sky observations: errors, biases, and Gaussianity
 All-sky observations: errors, biases, and Gaussianity Alan Geer and Peter Bauer ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Alan.Geer@ecmwf.int ABSTRACT Microwave imager observations are sensitive
All-sky observations: errors, biases, and Gaussianity Alan Geer and Peter Bauer ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading RG2 9AX, United Kingdom Alan.Geer@ecmwf.int ABSTRACT Microwave imager observations are sensitive
Ninth Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems. Timeliness and Impact of Observations in the CMC Global NWP system
 Ninth Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems ECMWF, Reading, United Kingdom 10 14 November 2003 Timeliness and Impact of Observations in the CMC Global NWP system Réal Sarrazin, Yulia Zaitseva
Ninth Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems ECMWF, Reading, United Kingdom 10 14 November 2003 Timeliness and Impact of Observations in the CMC Global NWP system Réal Sarrazin, Yulia Zaitseva
Assimilating cloud and precipitation: benefits and uncertainties
 Assimilating cloud and precipitation: benefits and uncertainties Alan Geer Thanks to: Katrin Lonitz, Peter Lean, Richard Forbes, Cristina Lupu, Massimo Bonavita, Mats Hamrud, Philippe Chambon, Fabrizio
Assimilating cloud and precipitation: benefits and uncertainties Alan Geer Thanks to: Katrin Lonitz, Peter Lean, Richard Forbes, Cristina Lupu, Massimo Bonavita, Mats Hamrud, Philippe Chambon, Fabrizio
Data impact studies in the global NWP model at Meteo-France
 Data impact studies in the global NWP model at Meteo-France Patrick Moll, Fatima Karbou, Claudia Faccani, Nathalie Saint- Ramond, Florence Rabier Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques CNRS/GAME,
Data impact studies in the global NWP model at Meteo-France Patrick Moll, Fatima Karbou, Claudia Faccani, Nathalie Saint- Ramond, Florence Rabier Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques CNRS/GAME,
EXPERIMENTAL ASSIMILATION OF SPACE-BORNE CLOUD RADAR AND LIDAR OBSERVATIONS AT ECMWF
 EXPERIMENTAL ASSIMILATION OF SPACE-BORNE CLOUD RADAR AND LIDAR OBSERVATIONS AT ECMWF Marta Janisková, Sabatino Di Michele, Edouard Martins ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading, U.K. Abstract Space-borne active
EXPERIMENTAL ASSIMILATION OF SPACE-BORNE CLOUD RADAR AND LIDAR OBSERVATIONS AT ECMWF Marta Janisková, Sabatino Di Michele, Edouard Martins ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading, U.K. Abstract Space-borne active
Parameterization of the surface emissivity at microwaves to submillimeter waves
 Parameterization of the surface emissivity at microwaves to submillimeter waves Catherine Prigent, Filipe Aires, Observatoire de Paris and Estellus Lise Kilic, Die Wang, Observatoire de Paris with contributions
Parameterization of the surface emissivity at microwaves to submillimeter waves Catherine Prigent, Filipe Aires, Observatoire de Paris and Estellus Lise Kilic, Die Wang, Observatoire de Paris with contributions
Assimilation of the IASI data in the HARMONIE data assimilation system
 Assimilation of the IASI data in the HARMONIE data assimilation system Roger Randriamampianina Acknowledgement: Andrea Storto (met.no), Andrew Collard (ECMWF), Fiona Hilton (MetOffice) and Vincent Guidard
Assimilation of the IASI data in the HARMONIE data assimilation system Roger Randriamampianina Acknowledgement: Andrea Storto (met.no), Andrew Collard (ECMWF), Fiona Hilton (MetOffice) and Vincent Guidard
Assimilation of cloud and precipitation affected microwave radiances at ECMWF
 Assimilation of cloud and precipitation affected microwave radiances at ECMWF Abstract Alan Geer, Peter Bauer and Philippe Lopez European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Cloud and precipitation
Assimilation of cloud and precipitation affected microwave radiances at ECMWF Abstract Alan Geer, Peter Bauer and Philippe Lopez European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts Cloud and precipitation
International TOVS Study Conference-XV Proceedings
 Relative Information Content of the Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder, the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit and the Microwave Humidity Sounder Suite Motivation Thomas J. Kleespies National Oceanic
Relative Information Content of the Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder, the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit and the Microwave Humidity Sounder Suite Motivation Thomas J. Kleespies National Oceanic
The Use of Hyperspectral Infrared Radiances In Numerical Weather Prediction
 The Use of Hyperspectral Infrared Radiances In Numerical Weather Prediction J. Le Marshall 1, J. Jung 1, J. Derber 1, T. Zapotocny 2, W. L. Smith 3, D. Zhou 4, R. Treadon 1, S. Lord 1, M. Goldberg 1 and
The Use of Hyperspectral Infrared Radiances In Numerical Weather Prediction J. Le Marshall 1, J. Jung 1, J. Derber 1, T. Zapotocny 2, W. L. Smith 3, D. Zhou 4, R. Treadon 1, S. Lord 1, M. Goldberg 1 and
Does the ATOVS RARS Network Matter for Global NWP? Brett Candy, Nigel Atkinson & Stephen English
 Does the ATOVS RARS Network Matter for Global NWP? Brett Candy, Nigel Atkinson & Stephen English Met Office, Exeter, United Kingdom 1. Introduction Along with other global numerical weather prediction
Does the ATOVS RARS Network Matter for Global NWP? Brett Candy, Nigel Atkinson & Stephen English Met Office, Exeter, United Kingdom 1. Introduction Along with other global numerical weather prediction
Andrew Collard, ECMWF
 Assimilation of AIRS & IASI at ECMWF Andrew Collard, ECMWF Slide 1 Acknowledgements to Tony McNally, Richard Engelen & Rossana Dragani Overview Introduction Assimilation Configuration - Channel Selection
Assimilation of AIRS & IASI at ECMWF Andrew Collard, ECMWF Slide 1 Acknowledgements to Tony McNally, Richard Engelen & Rossana Dragani Overview Introduction Assimilation Configuration - Channel Selection
Application of PCA to IASI: An NWP Perspective. Andrew Collard, ECMWF. Acknowledgements to Tony McNally, Jean-Noel Thépaut
 Application of PCA to IASI: An NWP Perspective Andrew Collard, ECMWF Acknowledgements to Tony McNally, Jean-Noel Thépaut Overview Introduction Why use PCA/RR? Expected performance of PCA/RR for IASI Assimilation
Application of PCA to IASI: An NWP Perspective Andrew Collard, ECMWF Acknowledgements to Tony McNally, Jean-Noel Thépaut Overview Introduction Why use PCA/RR? Expected performance of PCA/RR for IASI Assimilation
Use and impact of satellite data in the NZLAM mesoscale model for the New Zealand region
 Use and impact of satellite data in the NZLAM mesoscale model for the New Zealand region V. Sherlock, P. Andrews, H. Oliver, A. Korpela and M. Uddstrom National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research,
Use and impact of satellite data in the NZLAM mesoscale model for the New Zealand region V. Sherlock, P. Andrews, H. Oliver, A. Korpela and M. Uddstrom National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research,
Feature-tracked 3D Winds from Satellite Sounders: Derivation and Impact in Global Models
 Feature-tracked 3D Winds from Satellite Sounders: Derivation and Impact in Global Models David Santek 1, A.-S. Daloz 1, S. Tushaus 1, M. Rogal 1, W. McCarty 2 1 Space Science and Engineering Center/University
Feature-tracked 3D Winds from Satellite Sounders: Derivation and Impact in Global Models David Santek 1, A.-S. Daloz 1, S. Tushaus 1, M. Rogal 1, W. McCarty 2 1 Space Science and Engineering Center/University
Operational Rain Assimilation at ECMWF
 Operational Rain Assimilation at ECMWF Peter Bauer Philippe Lopez, Angela Benedetti, Deborah Salmond, Sami Saarinen, Marine Bonazzola Presented by Arthur Hou Implementation* SSM/I TB s 1D+4D-Var Assimilation:
Operational Rain Assimilation at ECMWF Peter Bauer Philippe Lopez, Angela Benedetti, Deborah Salmond, Sami Saarinen, Marine Bonazzola Presented by Arthur Hou Implementation* SSM/I TB s 1D+4D-Var Assimilation:
Next generation of EUMETSAT microwave imagers and sounders: new opportunities for cloud and precipitation retrieval
 Next generation of EUMETSAT microwave imagers and sounders: new opportunities for cloud and precipitation retrieval Christophe Accadia, Sabatino Di Michele, Vinia Mattioli, Jörg Ackermann, Sreerekha Thonipparambil,
Next generation of EUMETSAT microwave imagers and sounders: new opportunities for cloud and precipitation retrieval Christophe Accadia, Sabatino Di Michele, Vinia Mattioli, Jörg Ackermann, Sreerekha Thonipparambil,
PCA assimilation techniques applied to MTG-IRS
 PCA assimilation techniques applied to MTG-IRS Marco Matricardi ECMWF Shinfield Park, Reading, UK WORKSHOP Assimilation of Hyper-spectral Geostationary Satellite Observation ECMWF Reading UK 22-25 May
PCA assimilation techniques applied to MTG-IRS Marco Matricardi ECMWF Shinfield Park, Reading, UK WORKSHOP Assimilation of Hyper-spectral Geostationary Satellite Observation ECMWF Reading UK 22-25 May
