Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades
|
|
|
- Reginald Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: /NGEO2277 Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades Masato Mori 1*, Masahiro Watanabe 1, Hideo Shiogama 2, Jun Inoue 3, & Masahide Kimoto 1 1: Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, the University of Tokyo, Chiba, Japan 2: Center for Global Environmental Research, National Institute for Environmental Studies, Ibaraki, Japan 3: National Institute of Polar Research, Tokyo, Japan Supplementary Information S1. Differences of ensemble-mean fields between AGCM and reanalysis data Despite similarity in the pattern of SAT anomalies between the reanalysis data and the AGCM ensemble simulation (Fig. 1a, 1b), there is a discernible difference in the associated circulation pattern over the Pacific Atlantic side (Fig. 1c, 1d). The major cause of this difference is that the composite field in reanalysis data contains considerable signals associated with the AO, which ought to be largely eliminated from the AGCM ensemble-mean field. In order to demonstrate this, an additional analysis was performed. Figure S5 shows the same composite as Figs. 1a and 1c, but the anomalies have been reconstructed only using EOF1 and EOF2 (Fig. 2a-b). A comparison between Fig. 1a, c, and Fig. S5a, b indicates that the composite fields in reanalysis can be reconstructed well from two EOFs. Furthermore, decomposition into each EOF (Fig. S5c-f) reveals that the AO has imprints over the North Atlantic and the polar region. This is in contrast to the ensemble-mean fields in the AGCM, which can be explained predominantly by the WACE (Fig. S6, compared with Fig. S5). These differences between the AGCM and the reanalysis are due to the small sample size in the composite of the reanalysis. NATURE GEOSCIENCE 1
2 S2. Relevance of the AO/NAO in the SIC-forced circulation response Several modeling studies have shown a negative AO/NAO-like response to Arctic sea-ice loss 2,13-16, It should be noted that the pattern of ensemble-mean circulation response to sea-ice loss in our simulation (Fig. 1d) is very similar to ensemble mean responses shown in previous numerical experiments prescribing realistic sea-ice reduction in their AGCMs. Specifically, the pattern of Z500 responses shown in ref. 22 (their Fig. 7b) and in ref. 16 (their Fig. 6e) are similar to our Fig. 1d, although they referred to those responses as a negative AO/NAO-like pattern. In this study, we showed that the atmospheric response to sea-ice loss is detectable more clearly when it is decomposed into a canonical AO/NAO (not AO/NAO-like ) and the WACE pattern. We believe that the results in previous modeling studies would also be clearer if their ensembles were decomposed in a similar way. S3. Temperature anomaly associated with the WACE pattern The mid-latitude cold SAT anomalies, spreading over central to eastern Asia, observed from the WACE pattern (Fig. 2b, Supplementary Figs. S3b, S4b, S7b, and S7d), are induced primarily by a northerly cold-air advection associated with the anticyclonic circulation anomaly centred around 60 E, 60 N (Fig. 2b). Over central Eurasia, this circulation anomaly shows equivalent barotropic and baroclinic structure to the west and east, respectively (Supplementary Fig. S8). By contrast, the WACE accompanies warm SAT anomalies over northern Europe and western Russia. The influence of the WACE on SAT anomalies is insignificant over North America in both the reanalysis and the AGCM simulation (Supplementary Fig. S7), which indicates that the contribution of the WACE to the warm Arctic cold continents pattern 7 is restricted to the Eurasian continent. In this study, the WACE is defined by EOF2 for SAT over the domain of 0 180, 20 N 90 N. When the EOF is computed over the entire Northern Hemisphere north of 20 N, EOF2 shows features similar to Fig. 2b. However, its fractional variance is reduced and the spatial pattern contains significant signals over North America, even though the WACE does not in reality exhibit a 2
3 correlation over that region (Supplementary Fig. S7). Therefore, the WACE could better be extracted using the EOF for SAT over the eastern hemisphere. S4. CMIP5 models analysed in this study We analysed monthly outputs of the CMIP5 historical and Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) 4.5 experiments 24 for the period from 22 coupled general circulation models: ACCESS1.0, BCC-CSM1.1, CanESM2, CCSM4, CNRM-CM5, CSIRO-Mk3.6.0, GFDL-CM3, GFDL-ESM2G, GFDL-ESM2M, GISS-E2-R, HadGEM2-CC, HadGEM2-ES, INM-CM4, IPSL-CM5A-LR, IPSL-CM5A-MR, MIROC-ESM, MIROC-ESM-CHEM, MIROC5, MPI-ESM-LR, MRI-CGCM3, NorESM1-M, and NorESM1-ME (see for more detail). These models were chosen based on the availability of SIC output. Before examining a future change in the frequency of cold winters, we checked dominant modes of SAT variability in CMIP5 climate model simulations in a similar manner to Figs. 2a and 2b. We found that the two leading EOFs for 22 CMIP5 simulations for represent the AO and WACE (Supplementary Fig. S9). Associated SIC anomalies reveal that the WACE is strongly coupled with the sea-ice change in BKS compared to the AO (Supplementary Fig. S9). The above results demonstrate that the dominant WACE response to BKS sea-ice loss shown in our ensemble simulations is not an artifact due to a single model and reinforce our conclusions. S5. Projection uncertainty The results of analysis of simulation performed by 22 CMIP5 models suggest that the frequent occurrence of cold winters in the past decade may be a temporary phenomenon in a transitional phase of eventual global warming (Supplementary Fig. S10). However, for a robust estimation of sea-ice loss impact in future, we need to pay attention to projection uncertainty originating from at least two sources. The first source is the large ambiguity in 3
4 SIC decrease in the BKS (99 percentile ranging from 66 to 6% during , Supplementary Fig. S10), which can excite WACE responses of varying magnitudes. The second source is most relevant to our findings, arising from an insufficient number of ensemble members. Indeed, the single-member ensemble of 22 CMIP5 models failed to reproduce the recently observed cooling over central Eurasia (Supplementary Fig. S11). Based on our estimate of signal detection (Fig. 3), each model should have at least four members for robust estimation of SAT response to future sea-ice retreat in the BKS. Such a large ensemble projection would contribute to obtaining more concrete conclusions on the possible change in cold winter frequency in Eurasia. 4
5 Supplementary Figures Figure S1 a-b, The 10-year mean SAT differences between and in DJF (the recent minus the previous decade) for GISTEMP (a) and ERA-Interim (b). Stippling indicates regions exceeding 95% statistical confidence. Grey shading in a indicates missing-data grids. c, Time series of SAT anomalies averaged over central Eurasia (60 E 120 E, 40 N 60 N, indicated by rectangular box in b) for GISTEMP (green curve; anomaly relative to mean) and ERA-Interim (black curve; anomaly relative to mean). The severely warm (red dots) and cold (blue dots) winters are defined by the SAT anomaly above and below one standard deviation (dashed lines) for in ERA-Interim.
6 Figure S2 a, Interannual change of SIC in September averaged over the Barents Kara Sea (30 E 90 E, 65 N 85 N; black rectangular region in b) with area weight, based on HadISST (for ). Blue and red marks indicate the bottom and top 10 years of the time series, which define low- and high-ice years, respectively. b-c, Composite-SIC differences between the low- and high-ice years (former minus latter) in SON (b) and DJF (c). d, The 10-year mean SIC differences between and (former minus latter) in DJF. 6
7 Figure S3 a-b, As in Fig. 2a-b, but for SAT computed from GISTEMP during the period. EOF1 (a) and EOF2 (b) account for 39 and 20% of the total variance, respectively. Grey shading indicates data missing grids. c-d, PC1 (c) and PC2 (d) of the leading two modes (indicated by blue curves). Grey curves indicate PCs obtained from ERA-Interim, shown in Fig. 2c-d. 7
8 Figure S4 a-b, As in Fig. 2a-b, but for the combined 200-member ensemble of LICE and HICE simulations. EOF1 (a) and EOF2 (b) account for 20 and 17% of the total variance, respectively. c-d, PDFs of the corresponding PC1 (c) and PC2 (d), calculated separately for LICE (blue curves) and HICE (red curves). 8
9 Figure S5 a-b, As in Figs. 1a and 1c, but anomalies, taken from ERA-Interim, have been reconstructed only using EOF1 and EOF2 of SAT shown in Figs. 2a-b. c-d, As in a-b, but anomalies have been reconstructed only using EOF1, e-f, As in a-b, but anomalies have been reconstructed only using EOF2. 9
10 Figure S6 a-b, As in Fig. S5, but for the AGCM ensemble simulation. The contour interval is 3 hpa in a, c, and e. Note that the contour interval and colour scales are different from that in Figs. 1b and 1d. 10
11 Figure S7 a-b, DJF-mean SAT anomalies regressed on PC1 (a) and PC2 (b) normalised by one standard deviation, associated with two leading EOFs to winter SAT anomalies over 0 180, 20 N 90 N, taken from ERA-Interim ( ). c-d, As in a-b, but for the combined 200-member ensemble of LICE and HICE simulations. Stippling indicates regions exceeding 95% statistical confidence. 11
12 Figure S8 Meridionally (40 N 60 N) averaged vertical structure of the temperature (colour) and geo-potential height (contours) anomalies. a-b, Difference of composite fields between low- and high-ice years (former minus latter), taken from ERA-Interim (a) and from the 100-member ensemble-mean of the AGCM experiments (b). The contour interval is 4 m in a and 1 m in b, with negative contours dotted. c-d, Anomalies regressed on PC1 (c) and PC2 (d) shown in Fig. 2c-d, taken from ERA-Interim. e-f, As in c-d, but for combined 200-member ensemble simulation. Note that polarity of AO is reversed in c and e (i.e. negative phase is shown). Contour interval is 3 m in c-f. Stippling indicates regions exceeding 95% statistical confidence. Grey shading indicates data missing grids. 12
13 Figure S9 a-b, DJF-mean SAT anomalies regressed on PC1 (a) and PC2 (b) normalised by one standard deviation, associated with two leading EOFs for DJF-mean SAT anomalies over 0 180, 20 N 90 N, taken from combined 22 CMIP5 historical and RCP4.5 simulations during the period (748 winters are analysed). SAT anomalies are defined by subtracting DJF climatology ( ) in each model. EOF1 and EOF2 account for 24 and 16% of the total variance, respectively. c-d, As in a-b, but for DJF-mean SIC anomalies regressed on PC1 (c) and PC2 (d). Stippling in a-b indicates regions exceeding 95% statistical confidence. 13
14 Figure S10 Long-term changes in DJF-mean values in CMIP5 historical and RCP4.5 simulations. a, SAT anomaly (curves) and frequency of severe winters (bar) over central Eurasia. The severe winters are defined by the averaged SAT anomaly below one standard deviation computed each model during b-c, Projection coefficients of SAT anomalies on EOF1 (b) and EOF2 (c) shown in Fig. 2a-b, respectively. Scale of the SAT anomaly associated with EOF1 and EOF2 over central Eurasia is shown at the right of each panel (note that the axis is reversed in c). d, SIC anomaly in the BKS. The black curves are derived from ERA-Interim in a-c and from HadISST in d. Thin and thick curves show individual models and the multi model ensemble (MME) mean, respectively. The anomalies are defined by deviations from the mean, for observations and for each model. 14
15 Figure S11 a, As in Fig. S1a, but for MME mean of the 22 CMIP5 models. b, Regional mean values over central Eurasia, indicated by the rectangular box in a (60 E 120 E, 40 N 60 N). Grey dots indicate individual models, red dot indicates MME mean, and the black dot indicates ERA-Interim. 15
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation S. Pfahl 1 *,P.A.O Gorman 2 and E. M. Fischer 1 Changes in extreme
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation S. Pfahl 1 *,P.A.O Gorman 2 and E. M. Fischer 1 Changes in extreme
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2517 Two distinct influences of Arctic warming on cold winters over North America and East Asia Jong-Seong Kug 1, Jee-Hoon Jeong 2*, Yeon-Soo Jang 1, Baek-Min
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2517 Two distinct influences of Arctic warming on cold winters over North America and East Asia Jong-Seong Kug 1, Jee-Hoon Jeong 2*, Yeon-Soo Jang 1, Baek-Min
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods and obtained
 Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
Supplementary Figure 1 Observed change in wind and vertical motion. Anomalies are regime differences between periods 1999 2013 and 1979 1998 obtained from ERA-interim. Vectors are horizontal wind at 850
The Implication of Ural Blocking on the East Asian Winter Climate in CMIP5 Models
 The Implication of Ural Blocking on the East Asian Winter Climate in CMIP5 Models Hoffman H. N. Cheung, Wen Zhou (hncheung-c@my.cityu.edu.hk) City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Institute Guy Carpenter
The Implication of Ural Blocking on the East Asian Winter Climate in CMIP5 Models Hoffman H. N. Cheung, Wen Zhou (hncheung-c@my.cityu.edu.hk) City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Institute Guy Carpenter
Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2820 Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss Kelly E. McCusker 1,2, John C. Fyfe 2 & Michael Sigmond 2 1 School
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2820 Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss Kelly E. McCusker 1,2, John C. Fyfe 2 & Michael Sigmond 2 1 School
Supplement of Insignificant effect of climate change on winter haze pollution in Beijing
 Supplement of Atmos. Chem. Phys., 18, 17489 17496, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-17489-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Supplement of Atmos. Chem. Phys., 18, 17489 17496, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-17489-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2988 Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol-cloud interactions Eui-Seok Chung and Brian
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2988 Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol-cloud interactions Eui-Seok Chung and Brian
More extreme precipitation in the world s dry and wet regions
 More extreme precipitation in the world s dry and wet regions Markus G. Donat, Andrew L. Lowry, Lisa V. Alexander, Paul A. O Gorman, Nicola Maher Supplementary Table S1: CMIP5 simulations used in this
More extreme precipitation in the world s dry and wet regions Markus G. Donat, Andrew L. Lowry, Lisa V. Alexander, Paul A. O Gorman, Nicola Maher Supplementary Table S1: CMIP5 simulations used in this
Contents of this file
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Future changes in tropical cyclone activity in high-resolution large-ensemble simulations Kohei Yoshida 1, Masato Sugi 1, Ryo Mizuta 1, Hiroyuki
Significant anthropogenic-induced changes. of climate classes since 1950
 Significant anthropogenic-induced changes of climate classes since 95 (Supplementary Information) Duo Chan and Qigang Wu * School of Atmospheric Science, Nanjing University, Hankou Road #22, Nanjing, Jiangsu,
Significant anthropogenic-induced changes of climate classes since 95 (Supplementary Information) Duo Chan and Qigang Wu * School of Atmospheric Science, Nanjing University, Hankou Road #22, Nanjing, Jiangsu,
Changes in the El Nino s spatial structure under global warming. Sang-Wook Yeh Hanyang University, Korea
 Changes in the El Nino s spatial structure under global warming Sang-Wook Yeh Hanyang University, Korea Changes in El Nino spatial structure Yeh et al. (2009) McPhaden et al. (2009) Why the spatial structure
Changes in the El Nino s spatial structure under global warming Sang-Wook Yeh Hanyang University, Korea Changes in El Nino spatial structure Yeh et al. (2009) McPhaden et al. (2009) Why the spatial structure
Low-level wind, moisture, and precipitation relationships near the South Pacific Convergence Zone in CMIP3/CMIP5 models
 Low-level wind, moisture, and precipitation relationships near the South Pacific Convergence Zone in CMIP3/CMIP5 models Matthew J. Niznik and Benjamin R. Lintner Rutgers University 25 April 2012 niznik@envsci.rutgers.edu
Low-level wind, moisture, and precipitation relationships near the South Pacific Convergence Zone in CMIP3/CMIP5 models Matthew J. Niznik and Benjamin R. Lintner Rutgers University 25 April 2012 niznik@envsci.rutgers.edu
Early benefits of mitigation in risk of regional climate extremes
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3259 Early benefits of mitigation in risk of regional climate extremes Andrew Ciavarella 1 *, Peter Stott 1,2 and Jason Lowe 1,3
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3259 Early benefits of mitigation in risk of regional climate extremes Andrew Ciavarella 1 *, Peter Stott 1,2 and Jason Lowe 1,3
Desert Amplification in a Warming Climate
 Supporting Tables and Figures Desert Amplification in a Warming Climate Liming Zhou Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, SUNY at Albany, Albany, NY 12222, USA List of supporting tables
Supporting Tables and Figures Desert Amplification in a Warming Climate Liming Zhou Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, SUNY at Albany, Albany, NY 12222, USA List of supporting tables
Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1530 Twenty-first-century projections of North Atlantic tropical storms from CMIP5 models SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. Annual tropical Atlantic SST anomalies (top
Global Warming Attenuates the. Tropical Atlantic-Pacific Teleconnection
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplementary Information for Global Warming Attenuates the Tropical Atlantic-Pacific Teleconnection Fan Jia 1, Lixin Wu 2*, Bolan
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplementary Information for Global Warming Attenuates the Tropical Atlantic-Pacific Teleconnection Fan Jia 1, Lixin Wu 2*, Bolan
Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3275 Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target Jianping Huang 1 *, Haipeng Yu 1,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3275 Drylands face potential threat under 2 C global warming target Jianping Huang 1 *, Haipeng Yu 1,
Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, 1 2 3 Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material Marie C. McGraw
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1002/, 1 2 3 Reconciling the Observed and Modeled Southern Hemisphere Circulation Response to Volcanic Eruptions Supplemental Material Marie C. McGraw
Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.18/NCLIMATE2 Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor, Axel Timmermann, Malte F. Stuecker, Matthew H. England,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.18/NCLIMATE2 Recent Walker circulation strengthening and Pacific cooling amplified by Atlantic warming Shayne McGregor, Axel Timmermann, Malte F. Stuecker, Matthew H. England,
Supplementary Figure 1 Current and future distribution of temperate drylands. (a b-f b-f
 Supplementary Figure 1 Current and future distribution of temperate drylands. (a) Five temperate dryland regions with their current extent for 1980-2010 (green): (b) South America; (c) North America; (d)
Supplementary Figure 1 Current and future distribution of temperate drylands. (a) Five temperate dryland regions with their current extent for 1980-2010 (green): (b) South America; (c) North America; (d)
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Copyright 2018 American Meteorological Society Permission to use figures, tables, and brief excerpts from this work in scientific and educational works is hereby granted provided
Supplemental Material Copyright 2018 American Meteorological Society Permission to use figures, tables, and brief excerpts from this work in scientific and educational works is hereby granted provided
The importance of ENSO phase during volcanic eruptions for detection and attribution
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for The importance of ENSO phase during volcanic eruptions for detection and attribution Flavio Lehner 1, Andrew P. Schurer 2, Gabriele C. Hegerl 2,
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for The importance of ENSO phase during volcanic eruptions for detection and attribution Flavio Lehner 1, Andrew P. Schurer 2, Gabriele C. Hegerl 2,
Recent anomalously cold Central Eurasian winters forced by Arctic sea ice retreat in an atmospheric model
 Recent anomalously cold Central Eurasian winters forced by Arctic sea ice retreat in an atmospheric model Vladimir A. Semenov A.M. Obukhov Institute of Atmospheric Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia and Helmholtz
Recent anomalously cold Central Eurasian winters forced by Arctic sea ice retreat in an atmospheric model Vladimir A. Semenov A.M. Obukhov Institute of Atmospheric Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia and Helmholtz
Supporting Information for Relation of the double-itcz bias to the atmospheric energy budget in climate models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Relation of the double-itcz bias to the atmospheric energy budget in climate models Ori Adam 1, Tapio Schneider 1,2, Florent Brient 1, and Tobias
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Relation of the double-itcz bias to the atmospheric energy budget in climate models Ori Adam 1, Tapio Schneider 1,2, Florent Brient 1, and Tobias
CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projection of storm track change under global warming
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd018578, 2012 CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projection of storm track change under global warming Edmund K. M. Chang, 1 Yanjuan Guo, 2 and Xiaoming
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd018578, 2012 CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projection of storm track change under global warming Edmund K. M. Chang, 1 Yanjuan Guo, 2 and Xiaoming
Supplementary Figure 1 A figure of changing surface air temperature and top-1m soil moisture: (A) Annual mean surface air temperature, and (B) top
 Supplementary Figure 1 A figure of changing surface air temperature and top-1m soil moisture: (A) Annual mean surface air temperature, and (B) top 1-m soil moisture averaged over California from CESM1.
Supplementary Figure 1 A figure of changing surface air temperature and top-1m soil moisture: (A) Annual mean surface air temperature, and (B) top 1-m soil moisture averaged over California from CESM1.
Fewer large waves projected for eastern Australia due to decreasing storminess
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 0.08/NCLIMATE Fewer large waves projected for eastern Australia due to decreasing storminess 6 7 8 9 0 6 7 8 9 0 Details of the wave observations The locations of the five
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 0.08/NCLIMATE Fewer large waves projected for eastern Australia due to decreasing storminess 6 7 8 9 0 6 7 8 9 0 Details of the wave observations The locations of the five
Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3136 Persistent shift of the Arctic polar vortex towards the Eurasian continent in recent decades Jiankai Zhang 1, Wenshou Tian 1 *, Martyn P. Chipperfield
AMIP-type horizontal resolution experiments with NorESM. Øyvind Seland, Trond Iversen, Ivar Seierstad
 AMWG meeting 10th-12th February 2014 AMIP-type horizontal resolution experiments with NorESM Øyvind Seland, Trond Iversen, Ivar Seierstad Motivation: For given a computer resource, ESMs need to balance
AMWG meeting 10th-12th February 2014 AMIP-type horizontal resolution experiments with NorESM Øyvind Seland, Trond Iversen, Ivar Seierstad Motivation: For given a computer resource, ESMs need to balance
BREA Final Results Forum Results from the Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis
 BREA Final Results Forum Results from the Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Gregory M. Flato (PI), W. Merryfield, W.S. Lee, M. Sigmond, B. Pal, C. Reader Project Title: FORECASTING OCEAN
BREA Final Results Forum Results from the Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Gregory M. Flato (PI), W. Merryfield, W.S. Lee, M. Sigmond, B. Pal, C. Reader Project Title: FORECASTING OCEAN
Arctic sea ice reduction and European cold winters in CMIP5 climate change experiments
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:1.129/212gl53338, 212 Arctic sea ice reduction and European cold winters in CMIP5 imate change experiments Shuting Yang 1 and Jens H. Christensen 1 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:1.129/212gl53338, 212 Arctic sea ice reduction and European cold winters in CMIP5 imate change experiments Shuting Yang 1 and Jens H. Christensen 1 Received
Future freshwater stress for island populations
 Future freshwater stress for island populations Kristopher B. Karnauskas, Jeffrey P. Donnelly and Kevin J. Anchukaitis Summary: Top left: Overview map of the four island stations located in the U.S. state
Future freshwater stress for island populations Kristopher B. Karnauskas, Jeffrey P. Donnelly and Kevin J. Anchukaitis Summary: Top left: Overview map of the four island stations located in the U.S. state
Future Projections of the Large Scale Meteorology Associated with California Heat Waves in CMIP5 Models
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supporting Information for Future Projections of the Large Scale Meteorology Associated with California Heat Waves in CMIP5 Models Erool Palipane 1 and Richard Grotjahn 1* 1 Department of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supporting Information for Future Projections of the Large Scale Meteorology Associated with California Heat Waves in CMIP5 Models Erool Palipane 1 and Richard Grotjahn 1* 1 Department of
Supplemental Material for
 Supplemental Material for Northern North Atlantic Sea Level in CMIP5 Climate Models: Evaluation of Mean State, Variability, and Trends against Altimetric Observations Kristin Richter, a Jan Even Øie Nilsen,
Supplemental Material for Northern North Atlantic Sea Level in CMIP5 Climate Models: Evaluation of Mean State, Variability, and Trends against Altimetric Observations Kristin Richter, a Jan Even Øie Nilsen,
Decreased monsoon precipitation in the Northern Hemisphere due to anthropogenic aerosols
 Decreased monsoon precipitation in the Northern Hemisphere due to anthropogenic aerosols Article Supplemental Material Polson, D., Bollasina, M., Hegerl, G. C. and Wilcox, L. J. (214) Decreased monsoon
Decreased monsoon precipitation in the Northern Hemisphere due to anthropogenic aerosols Article Supplemental Material Polson, D., Bollasina, M., Hegerl, G. C. and Wilcox, L. J. (214) Decreased monsoon
S16. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 2014 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT
 S6. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 204 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT Chris Funk, Shraddhanand Shukla, Andy Hoell, and Ben Livneh This document is a supplement
S6. ASSESSING THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF EAST AFRICAN AND WEST PACIFIC WARMING TO THE 204 BOREAL SPRING EAST AFRICAN DROUGHT Chris Funk, Shraddhanand Shukla, Andy Hoell, and Ben Livneh This document is a supplement
Winter Forecast for GPC Tokyo. Shotaro TANAKA Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
 Winter Forecast for 2013 2014 GPC Tokyo Shotaro TANAKA Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) NEACOF 5, October 29 November 1, 2013 1 Outline 1. Numerical prediction 2. Interannual
Winter Forecast for 2013 2014 GPC Tokyo Shotaro TANAKA Tokyo Climate Center (TCC) Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) NEACOF 5, October 29 November 1, 2013 1 Outline 1. Numerical prediction 2. Interannual
Supplementary Figure 1: Time series of 48 N AMOC maximum from six model historical simulations based on different models. For each model, the wavelet
 Supplementary Figure 1: Time series of 48 N AMOC maximum from six model historical simulations based on different models. For each model, the wavelet analysis of AMOC is also shown; bold contours mark
Supplementary Figure 1: Time series of 48 N AMOC maximum from six model historical simulations based on different models. For each model, the wavelet analysis of AMOC is also shown; bold contours mark
Paul W. Stackhouse, Jr., NASA Langley Research Center
 An Assessment of Actual and Potential Building Climate Zone Change and Variability From the Last 30 Years Through 2100 Using NASA s MERRA and CMIP5 Simulations Paul W. Stackhouse, Jr., NASA Langley Research
An Assessment of Actual and Potential Building Climate Zone Change and Variability From the Last 30 Years Through 2100 Using NASA s MERRA and CMIP5 Simulations Paul W. Stackhouse, Jr., NASA Langley Research
Beyond IPCC plots. Ben Sanderson
 Beyond IPCC plots Ben Sanderson What assumptions are we making? The Chain of Uncertainty: Heat waves Future Emissions Global Climate Sensitivity Regional Feedbacks Random variability Heat wave frequency
Beyond IPCC plots Ben Sanderson What assumptions are we making? The Chain of Uncertainty: Heat waves Future Emissions Global Climate Sensitivity Regional Feedbacks Random variability Heat wave frequency
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:.8/NCLIMATE76 Supplementary information for Changes in South Pacific rainfall bands in a warming climate Matthew J. Widlansky, Axel Timmermann,, Karl Stein, Shayne McGregor,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:.8/NCLIMATE76 Supplementary information for Changes in South Pacific rainfall bands in a warming climate Matthew J. Widlansky, Axel Timmermann,, Karl Stein, Shayne McGregor,
The final push to extreme El Ninõ
 The final push to extreme El Ninõ Why is ENSO asymmetry underestimated in climate model simulations? WonMoo Kim* and Wenju Cai CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research *Current Affiliation: CCCPR, Ewha Womans
The final push to extreme El Ninõ Why is ENSO asymmetry underestimated in climate model simulations? WonMoo Kim* and Wenju Cai CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research *Current Affiliation: CCCPR, Ewha Womans
The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models
 1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
Sensitivity of climate simulations to low-level cloud feedbacks
 Sensitivity of climate simulations to low-level cloud feedbacks C. Roberto Mechoso 1, Timothy Myers 1 and Mike DeFlorio 2 1 U. California, Los Angeles, USA 2 NASA/Caltech Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA
Sensitivity of climate simulations to low-level cloud feedbacks C. Roberto Mechoso 1, Timothy Myers 1 and Mike DeFlorio 2 1 U. California, Los Angeles, USA 2 NASA/Caltech Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA
Anthropogenic forcing dominates global mean sea-level rise since 1970
 Anthropogenic forcing dominates global mean sea-level rise since 1970 Aimée B. A. Slangen 1,2 *, John A. Church 1, Cecile Agosta 3, Xavier Fettweis 3, Ben Marzeion 4 and Kristin Richter 5 1 CSIRO Oceans
Anthropogenic forcing dominates global mean sea-level rise since 1970 Aimée B. A. Slangen 1,2 *, John A. Church 1, Cecile Agosta 3, Xavier Fettweis 3, Ben Marzeion 4 and Kristin Richter 5 1 CSIRO Oceans
CMIP5 Projection of Significant Reduction in Extratropical Cyclone Activity over North America
 15 DECEMBER 2013 C H A N G 9903 CMIP5 Projection of Significant Reduction in Extratropical Cyclone Activity over North America EDMUND K. M. CHANG School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, Stony Brook
15 DECEMBER 2013 C H A N G 9903 CMIP5 Projection of Significant Reduction in Extratropical Cyclone Activity over North America EDMUND K. M. CHANG School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, Stony Brook
The role of sea-ice in extended range prediction of atmosphere and ocean
 The role of sea-ice in extended range prediction of atmosphere and ocean Virginie Guemas with contributions from Matthieu Chevallier, Neven Fučkar, Agathe Germe, Torben Koenigk, Steffen Tietsche Workshop
The role of sea-ice in extended range prediction of atmosphere and ocean Virginie Guemas with contributions from Matthieu Chevallier, Neven Fučkar, Agathe Germe, Torben Koenigk, Steffen Tietsche Workshop
Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations
 Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations Erica K. Dolinar Xiquan Dong and Baike Xi University of North Dakota This talk is based on Dolinar
Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations Erica K. Dolinar Xiquan Dong and Baike Xi University of North Dakota This talk is based on Dolinar
Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability
 Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability Gerald A. Meehl 1, Julie M. Arblaster 1,2, Cecilia M. Bitz 3, Christine T.Y. Chung 4, and Haiyan
Antarctic sea-ice expansion between 2000 and 2014 driven by tropical Pacific decadal climate variability Gerald A. Meehl 1, Julie M. Arblaster 1,2, Cecilia M. Bitz 3, Christine T.Y. Chung 4, and Haiyan
Karonga Climate Profile: Full Technical Version
 Karonga Climate Profile: Full Technical Version Prepared by: University of Cape Town November 2017 For enquiries regarding this Climate Profile, please contact Lisa van Aardenne (lisa@csag.uct.ac.za) or
Karonga Climate Profile: Full Technical Version Prepared by: University of Cape Town November 2017 For enquiries regarding this Climate Profile, please contact Lisa van Aardenne (lisa@csag.uct.ac.za) or
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Projection Results from the CORDEX Africa Domain
 Projection Results from the CORDEX Africa Domain Patrick Samuelsson Rossby Centre, SMHI patrick.samuelsson@smhi.se Based on presentations by Grigory Nikulin and Erik Kjellström CORDEX domains over Arab
Projection Results from the CORDEX Africa Domain Patrick Samuelsson Rossby Centre, SMHI patrick.samuelsson@smhi.se Based on presentations by Grigory Nikulin and Erik Kjellström CORDEX domains over Arab
Effects of Arctic sea ice loss on Northern Hemisphere blocking highs
 Effects of Arctic sea ice loss on Northern Hemisphere blocking highs B. Ayarzagüena 1, J. Screen 1, E. Barnes 2 1 University of Exeter, UK 2 Colorado State University, USA Motivation Arctic amplification
Effects of Arctic sea ice loss on Northern Hemisphere blocking highs B. Ayarzagüena 1, J. Screen 1, E. Barnes 2 1 University of Exeter, UK 2 Colorado State University, USA Motivation Arctic amplification
Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming
 Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming Gerald A. Meehl 1, Haiyan Teng 1, and Julie M. Arblaster 1,2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 2. CAWCR,
Climate model simulations of the observed early-2000s hiatus of global warming Gerald A. Meehl 1, Haiyan Teng 1, and Julie M. Arblaster 1,2 1. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 2. CAWCR,
Contents of this file
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Predictability of the Recent Slowdown and Subsequent Recovery of Large-Scale Surface Warming using Statistical Methods Michael E. Mann 1, Byron A.
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Predictability of the Recent Slowdown and Subsequent Recovery of Large-Scale Surface Warming using Statistical Methods Michael E. Mann 1, Byron A.
Intensification of landfalling typhoons over the northwest Pacific since the late 1970s
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:.8/NGEO79 Intensifiation of landfalling typhoons over the northwest Paifi sine the late 97s Wei Mei and Shang-Ping Xie Supplementary Figures Lifetime peak intensity (m/s)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:.8/NGEO79 Intensifiation of landfalling typhoons over the northwest Paifi sine the late 97s Wei Mei and Shang-Ping Xie Supplementary Figures Lifetime peak intensity (m/s)
Supplementary Information for Impacts of a warming marginal sea on torrential rainfall organized under the Asian summer monsoon
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Information for Impacts of a warming marginal sea on torrential rainfall organized under the Asian summer monsoon 12 13 14 Atsuyoshi Manda 1, Hisashi Nakamura 2,4,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Information for Impacts of a warming marginal sea on torrential rainfall organized under the Asian summer monsoon 12 13 14 Atsuyoshi Manda 1, Hisashi Nakamura 2,4,
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
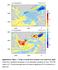 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Nonlinear atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss under different sea ice scenarios
 Nonlinear atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss under different sea ice scenarios Hans Chen, Fuqing Zhang and Richard Alley Advanced Data Assimilation and Predictability Techniques The Pennsylvania
Nonlinear atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss under different sea ice scenarios Hans Chen, Fuqing Zhang and Richard Alley Advanced Data Assimilation and Predictability Techniques The Pennsylvania
Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations
 Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations Spencer A. Hill Yi Ming, Isaac Held, Leo Donner, Ming Zhao Motivations Severe uncertainty in rainfall response
Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations Spencer A. Hill Yi Ming, Isaac Held, Leo Donner, Ming Zhao Motivations Severe uncertainty in rainfall response
Future change in the frequency and intensity of wintertime North Pacific blocking in CMIP5 models
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 37: 75 7 (7) Published online September in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI:./joc.7 Future change in the frequency and intensity
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 37: 75 7 (7) Published online September in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI:./joc.7 Future change in the frequency and intensity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
On the ability of CMIP3 and CMIP5 models in representing Caribbean current climate
 On the ability of CMIP3 and CMIP5 models in representing Caribbean current climate Sullyandro Oliveira Guimarães sullyandro@gmail.com Alexandre Araújo Costa Domingo Cassain Sales Universidade Estadual
On the ability of CMIP3 and CMIP5 models in representing Caribbean current climate Sullyandro Oliveira Guimarães sullyandro@gmail.com Alexandre Araújo Costa Domingo Cassain Sales Universidade Estadual
Decadal shifts of East Asian summer monsoon in a climate. model free of explicit GHGs and aerosols
 Decadal shifts of East Asian summer monsoon in a climate model free of explicit GHGs and aerosols Renping Lin, Jiang Zhu* and Fei Zheng International Center for Climate and Environment Sciences, Institute
Decadal shifts of East Asian summer monsoon in a climate model free of explicit GHGs and aerosols Renping Lin, Jiang Zhu* and Fei Zheng International Center for Climate and Environment Sciences, Institute
A revival of Indian summer monsoon rainfall since 2002
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3348 A revival of Indian summer monsoon rainfall since 2002 Qinjian Jin and Chien Wang* Center for Global
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3348 A revival of Indian summer monsoon rainfall since 2002 Qinjian Jin and Chien Wang* Center for Global
Two Types of California Central Valley Heat Waves
 Two Types of California Central Valley Heat Waves Virgin River junction with Orderville Canyon UT R. Grotjahn Richard Grotjahn and Yun-Young Lee University of California Davis Outline 1. Introduction Region
Two Types of California Central Valley Heat Waves Virgin River junction with Orderville Canyon UT R. Grotjahn Richard Grotjahn and Yun-Young Lee University of California Davis Outline 1. Introduction Region
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2571 Mechanisms of change in ENSO-induced tropical Pacific rainfall variability in a warming climate Ping Huang and Shang-Ping Xie Comparison with the results
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2571 Mechanisms of change in ENSO-induced tropical Pacific rainfall variability in a warming climate Ping Huang and Shang-Ping Xie Comparison with the results
The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl052006, 2012 The two types of ENSO in CMIP5 models Seon Tae Kim 1 and Jin-Yi Yu 1 Received 12 April 2012; revised 14 May 2012; accepted 15 May
Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future. warming scenarios
 Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future warming scenarios Liang Ning 1,2,3* and Raymond S. Bradley 2 1 Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment of Ministry
Snow occurrence changes over the central and eastern United States under future warming scenarios Liang Ning 1,2,3* and Raymond S. Bradley 2 1 Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment of Ministry
Operational Practices in South African Weather Service (SAWS)
 Operational Practices in South African Weather Service (SAWS) Abiodun Adeola, Hannes Rautenbach, Cobus Olivier 2018/06/12 1 Overview Seasonal Forecasting System at SAWS How to Interpret Seasonal Forecasts
Operational Practices in South African Weather Service (SAWS) Abiodun Adeola, Hannes Rautenbach, Cobus Olivier 2018/06/12 1 Overview Seasonal Forecasting System at SAWS How to Interpret Seasonal Forecasts
DOES EAST EURASIAN SNOW COVER TRIGGER THE NORTHERN ANNULAR MODE?
 DOES EAST EURASIAN SNOW COVER TRIGGER THE NORTHERN ANNULAR MODE? Eun-Jeong Cha and Masahide Kimoto Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo 1. Introduction A dominant mode of winter climate
DOES EAST EURASIAN SNOW COVER TRIGGER THE NORTHERN ANNULAR MODE? Eun-Jeong Cha and Masahide Kimoto Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo 1. Introduction A dominant mode of winter climate
Arctic Change and Possible Influence on Midlatitude Climate and Weather. Workshop Summary
 Arctic Change and Possible Influence on Midlatitude Climate and Weather Workshop Summary J. Cohen, X. Zhang, J. Francis, T. Jung, R. Kwok and J. Overland July 20, 2017 ARCTIC AMPLIFICATION Sea Ice Decline
Arctic Change and Possible Influence on Midlatitude Climate and Weather Workshop Summary J. Cohen, X. Zhang, J. Francis, T. Jung, R. Kwok and J. Overland July 20, 2017 ARCTIC AMPLIFICATION Sea Ice Decline
Enhanced warming of the subtropical mode water in the North Pacific and North Atlantic
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3371 Enhanced warming of the subtropical mode water in the North Pacific and North Atlantic Shusaku Sugimoto
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3371 Enhanced warming of the subtropical mode water in the North Pacific and North Atlantic Shusaku Sugimoto
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation
 Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
From short range forecasts to climate change projections of extreme events in the Baltic Sea region
 Great Baltic Sea flood, November 13, 1872 Farm houses in Niendorf (near Lübeck) being torn away. Privately owned, Fam. Muuß, Hotel Friedrichsruh. Sea level 3.50 m above normal. From short range forecasts
Great Baltic Sea flood, November 13, 1872 Farm houses in Niendorf (near Lübeck) being torn away. Privately owned, Fam. Muuß, Hotel Friedrichsruh. Sea level 3.50 m above normal. From short range forecasts
Extreme, transient Moisture Transport in the high-latitude North Atlantic sector and Impacts on Sea-ice concentration:
 AR conference, June 26, 2018 Extreme, transient Moisture Transport in the high-latitude North Atlantic sector and Impacts on Sea-ice concentration: associated Dynamics, including Weather Regimes & RWB
AR conference, June 26, 2018 Extreme, transient Moisture Transport in the high-latitude North Atlantic sector and Impacts on Sea-ice concentration: associated Dynamics, including Weather Regimes & RWB
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12310 We present here two additional Tables (Table SI-1, 2) and eight further Figures (Figures SI-1 to SI-8) to provide extra background information to the main figures of the paper.
doi:10.1038/nature12310 We present here two additional Tables (Table SI-1, 2) and eight further Figures (Figures SI-1 to SI-8) to provide extra background information to the main figures of the paper.
Correction to Evaluation of the simulation of the annual cycle of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice coverages by 11 major global climate models
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006jc003949, 2006 Correction to Evaluation of the simulation of the annual cycle of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice coverages by 11 major global climate
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006jc003949, 2006 Correction to Evaluation of the simulation of the annual cycle of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice coverages by 11 major global climate
The Response of ENSO Events to Higher CO 2 Forcing: Role of Nonlinearity De-Zheng Sun, Jiabing Shuai, and Shao Sun
 The Response of ENSO Events to Higher CO 2 Forcing: Role of Nonlinearity De-Zheng Sun, Jiabing Shuai, and Shao Sun CIRES, University of Colorado & Earth System Research Laboratory, NOAA http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/people/dezheng.sun/
The Response of ENSO Events to Higher CO 2 Forcing: Role of Nonlinearity De-Zheng Sun, Jiabing Shuai, and Shao Sun CIRES, University of Colorado & Earth System Research Laboratory, NOAA http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/people/dezheng.sun/
On-Line Supplementary Material IPCC WGII AR5 Chapter 30
 Tables Table SM30-1: Table SM30-2: Table SM30-3: Table SM30-4: Percentage area of the Ocean, average primary productivity (SEAWiFS: 4 Sep 1997 30 Nov 2010) and fisheries productivity of key ocean sub-regions
Tables Table SM30-1: Table SM30-2: Table SM30-3: Table SM30-4: Percentage area of the Ocean, average primary productivity (SEAWiFS: 4 Sep 1997 30 Nov 2010) and fisheries productivity of key ocean sub-regions
The East Asian winter monsoon: Re-amplification in the mid-2000s. WANG Lin* & CHEN Wen
 The East Asian winter monsoon: Re-amplification in the mid-2000s WANG Lin* & CHEN Wen Center for Monsoon System Research, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190,
The East Asian winter monsoon: Re-amplification in the mid-2000s WANG Lin* & CHEN Wen Center for Monsoon System Research, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190,
Response of the North Atlantic jet and its variability to increased greenhouse gasses in the CMIP5 models
 Response of the North Atlantic jet and its variability to increased greenhouse gasses in the CMIP5 models 1,3 Lorenzo Polvani 2 Dennis Hartman 3 1 Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory 2 Columbia University
Response of the North Atlantic jet and its variability to increased greenhouse gasses in the CMIP5 models 1,3 Lorenzo Polvani 2 Dennis Hartman 3 1 Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory 2 Columbia University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Intensification of Northern Hemisphere Subtropical Highs in a Warming Climate Wenhong Li, Laifang Li, Mingfang Ting, and Yimin Liu 1. Data and Methods The data used in this study consists of the atmospheric
Intensification of Northern Hemisphere Subtropical Highs in a Warming Climate Wenhong Li, Laifang Li, Mingfang Ting, and Yimin Liu 1. Data and Methods The data used in this study consists of the atmospheric
Anthropogenic forcing fingerprint on the tropical Pacific sea level trend pattern from the CMIP5 simulations of the XXI st century
 Anthropogenic forcing fingerprint on the tropical Pacific sea level trend pattern from the CMIP5 simulations of the XXI st century Benoît t Meyssignac 1, David Salas y Melia Anny Cazenave 1 1 LEGOS, CNRM/Météo
Anthropogenic forcing fingerprint on the tropical Pacific sea level trend pattern from the CMIP5 simulations of the XXI st century Benoît t Meyssignac 1, David Salas y Melia Anny Cazenave 1 1 LEGOS, CNRM/Météo
9.7 Climate Sensitivity and Climate Feedbacks
 Evaluation of Models Chapter precipitation projections was explained by the differences in global model boundary conditions, although much of the spread in projected summer precipitation was explained
Evaluation of Models Chapter precipitation projections was explained by the differences in global model boundary conditions, although much of the spread in projected summer precipitation was explained
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11784 Methods The ECHO-G model and simulations The ECHO-G model 29 consists of the 19-level ECHAM4 atmospheric model and 20-level HOPE-G ocean circulation model.
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude
 Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
Linkages between Arctic sea ice loss and midlatitude weather patterns Response of the wintertime atmospheric circulation to current and projected Arctic sea ice decline Gudrun Magnusdottir and Yannick
Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material The multivariate bias correction algorithm presented by Bürger et al. (2011) is based on a linear transformation that is specified in terms of the observed and climate model multivariate
Supplemental material The multivariate bias correction algorithm presented by Bürger et al. (2011) is based on a linear transformation that is specified in terms of the observed and climate model multivariate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO1799 Robust direct effect of carbon dioxide on tropical circulation and regional precipitation Sandrine Bony 1,, Gilles Bellon 2, Daniel Klocke 3, Steven Sherwood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO1799 Robust direct effect of carbon dioxide on tropical circulation and regional precipitation Sandrine Bony 1,, Gilles Bellon 2, Daniel Klocke 3, Steven Sherwood
EL NIÑO MODOKI IMPACTS ON AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL
 EL NIÑO MODOKI IMPACTS ON AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL Andréa S. Taschetto*, Alexander Sen Gupta, Caroline C. Ummenhofer and Matthew H. England Climate Change Research Centre (CCRC), University of New South Wales,
EL NIÑO MODOKI IMPACTS ON AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL Andréa S. Taschetto*, Alexander Sen Gupta, Caroline C. Ummenhofer and Matthew H. England Climate Change Research Centre (CCRC), University of New South Wales,
Geophysical Research Letters. Supporting Information for. Ozone-induced climate change propped up by the Southern Hemisphere oceanic front
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Ozone-induced climate change propped up by the Southern Hemisphere oceanic front Authors and affiliations Fumiaki Ogawa, Geophysical Institute, University
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Ozone-induced climate change propped up by the Southern Hemisphere oceanic front Authors and affiliations Fumiaki Ogawa, Geophysical Institute, University
Production and use of CORDEX projections a Swedish perspective on building climate services in practice
 Production and use of CORDEX projections a Swedish perspective on building climate services in practice Erik Kjellström 1, Lars Bärring 1, Grigory Nikulin 1, Carin Nilsson 2, Gustav Strandberg 1 1 Rossby
Production and use of CORDEX projections a Swedish perspective on building climate services in practice Erik Kjellström 1, Lars Bärring 1, Grigory Nikulin 1, Carin Nilsson 2, Gustav Strandberg 1 1 Rossby
Interannual Teleconnection between Ural-Siberian Blocking and the East Asian Winter Monsoon
 Interannual Teleconnection between Ural-Siberian Blocking and the East Asian Winter Monsoon Hoffman H. N. Cheung 1,2, Wen Zhou 1,2 (hoffmancheung@gmail.com) 1 City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Institute
Interannual Teleconnection between Ural-Siberian Blocking and the East Asian Winter Monsoon Hoffman H. N. Cheung 1,2, Wen Zhou 1,2 (hoffmancheung@gmail.com) 1 City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Institute
Maritime Continent seasonal climate biases in AMIP experiments of the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble
 Clim Dyn DOI 10.1007/s00382-017-3641-x Maritime Continent seasonal climate biases in AMIP experiments of the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble Ying Ying Toh 1,2 Andrew G. Turner 1,3 Stephanie J. Johnson 1,3,4
Clim Dyn DOI 10.1007/s00382-017-3641-x Maritime Continent seasonal climate biases in AMIP experiments of the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble Ying Ying Toh 1,2 Andrew G. Turner 1,3 Stephanie J. Johnson 1,3,4
Introduction to Climate Projections and Analysis
 Introduction to Climate Projections and Analysis Jack Katzfey, CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere 1 June 2016 The project is being implemented by the Asian Development Bank through the technical assistance (TA
Introduction to Climate Projections and Analysis Jack Katzfey, CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere 1 June 2016 The project is being implemented by the Asian Development Bank through the technical assistance (TA
On the Robustness of Emergent Constraints Used in Multimodel Climate Change Projections of Arctic Warming
 15 JANUARY 2013 B R A C E G I R D L E A N D S T E P H E N S O N 669 On the Robustness of Emergent Constraints Used in Multimodel Climate Change Projections of Arctic Warming THOMAS J. BRACEGIRDLE British
15 JANUARY 2013 B R A C E G I R D L E A N D S T E P H E N S O N 669 On the Robustness of Emergent Constraints Used in Multimodel Climate Change Projections of Arctic Warming THOMAS J. BRACEGIRDLE British
Research Article Detecting Warming Hiatus Periods in CMIP5 Climate Model Projections
 International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 6, Article ID 9657659, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/6/9657659 Research Article Detecting Warming Hiatus Periods in CMIP5 Climate Model Projections Tony W. Li
International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 6, Article ID 9657659, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/6/9657659 Research Article Detecting Warming Hiatus Periods in CMIP5 Climate Model Projections Tony W. Li
