Kindergarten. Weather & Climate.
|
|
|
- Chester Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 Kindergarten Weather & Climate
3 Weather Describing Weather Temperature Wind Clouds Rain Snow Table of Contents Recording Weather Season I Sky observations Wind Speed and Direction Temperature Precipitation Analyzing Data Seasons Recording Weather Season II Click on the topic to go to that section 3
4 Teacher's Notes about Unit Weather is the combination of sunlight, wind, snow or rain, and temperature in a particular region at a particular time. People measure these conditions to describe and record the weather and to notice patterns over time. The students will first use terms and instruments to describe weather conditions. Then the students will record weather conditions for two different seasons. After the second season, students will compare recorded data. 4
5 Weather Return to Table of Contents 5
6 Weather Weather affects us all. On a sunny day we can go outside. If it is rainy we stay indoors. If we know what the weather is likely to be we can make better plans. 6
7 Meteorology Meteorology is the study of weather. During this unit you will be meteorologists. 7
8 Weather Weather changes from day to day. It changes from season to season. Weather is different in different parts of the world. 8
9 Weather Where do you live? Is it cold or warm there? Is it cloudy or bright and sunny? Is it windy or very calm? Is it snowing or drizzling? 9
10 Weather occurs in the air. Weather Weather changes when the temperature changes. When the temperature changes this causes wind. Weather is the combination of heat, wind, and moisture. 10
11 Weather Weather is constantly changing. The sun is a great weather changer. The heat from the sun can help create wind or warm the air so we have rain instead of snow. Teacher Notes Weather is important in our daily lives. 11
12 Weather Forecasters Meteorologists or Weather Forecasters keep track of information that helps them report and predict the weather. Some of the information they track is: temperatureof the weather direction and speed of the wind types of clouds how much moisture is in the air how much rain or snowfalls 12
13 Weather Stations Weather stations around the world report to one large weather bureau. The weather station tells sailors on ships, airplane pilots, farmers, and us about the weather. 13
14 Weather There are instruments that help forecast the weather. These include satellite photography, doppler radar, and weather balloons. Other instruments that help forecast the weather are thermometers, weather vanes, wind socks, anemometers, and rain gauges. We will learn how to use and construct some of these instruments. Teacher Notes anemometer rain gauge weathervane windsock thermomete r 14
15 Weather One instrument we cannot build is a weather satellite. A weather satellite goes around the earth. It has cameras that take pictures of clouds, land, ice in the sea, and hurricanes. This instrument can measure temperaturesall over the world. Click here to see how to make a Weather Satellite 15
16 1 Meteorology is the study of A plants B weather C animals Answer 16
17 2 Weather is the combination of heat, wind, and moisture. Which of these would be a great weather changer? A stars B moon C sun Answer 17
18 3 Meteorologists keep track of information to predict weather. Which information would not be necessary in predicting the weather? A temperature Answer B C phase of moon wind speed 18
19 4 Meteorologists need to use instruments to help them predict the weather. Yes No Answer 19
20 5 A weather satellite measures temperature A B just where we live all over the world Answer 20
21 Describing Weather Return to Table of Contents 21
22 Describing Weather Climate is the typical weather that occurs over a particular region of the Earth. We are going to study the weather that occurs where you live. 22
23 Temperature Return to Table of Contents 23
24 Describing Weather Temperature It takes heat to make the weather. Heat from the sun warms the land and the water. The land and water warms the air. Temperature how hot or cold is the air? The most common weather instrument is the thermometer. The thermometer is an instrument used for measuring temperature. 24
25 Describing Weather Temperature Look at the thermometer. When the temperature goes up (it gets warmer) the indicator rises. The indicator is the red line. When the temperature goes down (gets colder) the indicator moves down. 25
26 Describing Weather Temperature How do we react to warm and cold air? When it gets cold, we bring our arms and legs close to our bodies to stay warm. We shrink (get smaller). The thermometer does the same thing. When it gets colder outside the red line (indicator)shrinks. Teacher Notes When it is warm, we stand tall and stretch our arms to feel the warmth. The indicator on the thermometer also rises when the air is warmer. 26
27 Describing Weather Temperature Lab We are going to observe how the indicator moves. Materials two bowls ice warm water thermometer bowls ice warm water thermometer Teacher Notes 27
28 Describing Weather Temperature Lab Put ice in one of the bowls and warm water in the other. Place the thermometer in the "ice" bowl. Look at the red indicator. Now place the thermometer in the "warm water" bowl. Look at the red indicator. How did the indicator change? ice warm water 28
29 Describing Weather Temperature Lab ice Draw indicator line on thermometer to show how it moved. warm water Teacher Notes 29
30 Describing Weather Temperature Discovery Center Activity Set up the materials from previous page at discovery center. Let the children explore on their own. bowls ice warm water thermometer 30
31 Describing Weather Lab Build a Simple Thermometer scale A thermometer usually has a tube with red colored liquid inside it. As we have learned, the liquid moves up and down inside the tube. There is a scale on the tube that shows degrees. This scale helps us determine if it is warm or cool outside. We will build a thermometer to help us understand this concept. 31
32 Describing Weather Lab Build a Simple Thermometer Materials: Paper Square Cold Water Food Coloring black red blue Markers Glass Bottle 32
33 Lab Simple Thermometer 1. Pour cold water into the bottle until it is about 3/4 full. Add a few drops of food coloring. 2. Put a straw in the bottle so that it is in the water. Seal the top with clay. 3. Blow gently into the straw. The water will rise up. Stop when the water is halfway up the straw. 33
34 Lab Simple Thermometer 4. Cut two slits in the paper square. Slide it over the straw. Use black marker to mark the level of the water. Black shows a normal temperature. 5. Put the thermometer in a warm place. Leave for a while. Mark the new level with red marker. Red mark shows a warmer temperature. Teacher Notes 6. Put the thermometer in a refrigerator. Leave for a while. Mark the new level with the blue marker. Blue mark shows a cooler temperature. 34
35 Describing Weather Temperature We can use a color range on our thermometer to help us understand if the air is hot or cold. As the indicator moves up and down we can see if the air is hot, warm, cool, cold or bitter cold. Hot Red Warm Orange Cool Green Cold Blue Frigid Violet 35
36 Describing Weather Temperature Use this slide and activity sheet 3 to fill in color scale for temperature. hot warm cool Teacher Notes Color Range Code cold frigid 36
37 6 A thermometer measures temperature. Yes No Answer 37
38 7 When it gets warmer outside the indicator on the thermometer. A shrinks B rises Answer 38
39 8 Which thermometer shows the temperature on a cold day? A B C Answer 39
40 Wind Return to Table of Contents 40
41 Describing Weather Wind Wind is a smooth flowing movement of air. Air is always moving. Wind is air that is moving faster. As the earth spins winds pass over the surface of the world. 41
42 Describing Weather Wind Activity Stand up. Twirl around on your tiptoes. Air rushes past your face, arms, and fingers. Do you feel it? 42
43 Where does wind begin? Describing Weather Wind Wind begins where warm and cool air meet. When air is heated by the sun, it rises. Then cold air flows down to take the place of the air that rose. The sun heats the cold air and then it rises. Warm air expands, and cool air shrinks. As air warms and cools; rises and moves downward; sinks and stirs; this causes winds. Winds are an important part of our weather. 43
44 Describing Weather Wind Winds can blow leaves, turn windmills, make chimes ring, and dry clothes hanging outside. On a summer day you can feel a cool breeze coming in across the water. Teacher Notes We need the wind for some sports; like sailing a boat, wind surfing, and kite flying. 44
45 Describing Weather Wind Kite Activity Activity 1. Grab a kite. 2. Find large open area. 3. Run with kite behind you! 4. Let the kite catch the wind. 5. Up it goes! Keep running! Teacher Notes 45
46 Describing Weather Wind In the past kites where made in the shape of socks to help determine the strength and direction of the wind. Today we use windsocks at airports just like those old kites. We use kites as toys but we do have other instruments we can use to test the wind. 46
47 Describing Weather Wind Speed Device Anemometer Anemometer instrument used to determine how fast the wind is blowing. It is important to measure the speed of the wind. If we have winds that are high speed, this may cause damage. The moving air makes the cups on the anemometer whirl around. There is a scale on the anemometer to describe wind strength. 47
48 Describing Weather Wind Speed Device Anemometer Lab We can make our own anemometer. It will help us measure the wind's speed. As meteorologists we can report what we learn about the wind's speed. Materials Needed: Four (4) paper cups Paper plate Felt tip pen Pencil with eraser Pin Clay Stopwatch 48
49 Describing Weather Wind Speed Device Anemometer Lab 1.Take you paper plate and draw crossing lines on it. Where the lines cross is the center. 2. Put your cups on the plate so they all face the same direction. 3. Push the pin through the center into the eraser on the pencil. 4. Make sure the cups can turn easily. 5. Stick the pencil into the lump of modeling clay. Staple the cups in place at four points. Mark one cup with a thick stripe using felt pen. 49
50 Describing Weather Wind Speed Device Anemometer Lab Take your Anemometer outside. As the wind whips by it makes the cups turn in a circle. Their speed shows how fast the wind is blowing. Using a stopwatch, count the number of times the marked cup passes around in a minute. The more times it passes in a minute, the faster the wind is blowing. Teacher Notes 50
51 Wind Speed Lab Use your anemometer for one week to record wind speed. Do you see a pattern? Which day was the wind fastest? Was there a day when there was no wind recorded? How many turns in one minute? Recording Wind Speed Teacher Notes Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 51
52 Describing Weather Wind Direction Device Wind Vane Lab We use a wind vane to determine which way the wind is blowing. Winds move all around the planet, bringing warmer air to cooler areas and cooler air to warmer areas. Some winds blow in the same direction all year long. Others blow certain times of the day or when storms come. These winds do not always blow in the same direction. We can use a wind vane to help us figure out which way the wind is blowing. Let's make one! 52
53 Wind Vane Lab Wind vane or Weather vane Materialsspool straw paper arrow 1. W 1. Put a long nail/pin through a spool. 2. Slip a straw over the pin. The straw should be able to turn easily. 3. Glue a paper arrow to one end of the straw. 4. Add North, South, East, West symbols to the spool. 5. Put your wind vane outside. 6. Which way is the wind blowing? N E Teacher Notes 53
54 9 Wind is a flowing movement of air. Yes No Answer 54
55 10 Wind begins when. A B C warm and cool air meet warm and warm air meet cool and cold air meet Answer 55
56 11 Which instrument is used to determine how fast the wind is moving? A thermometer B wind vane Answer C anemometer 56
57 12 A wind vane can tells us which way the wind is blowing. True False Answer 57
58 Clouds Return to Table of Contents 58
59 Clouds Clouds form from water vapor. Water vapor is a gas. We can't see it but water vapor is rising into the sky around us. When the vapor gets high in the sky, it cools down. Little drops of water form around bits of dust. When enough droplets come together, we have a cloud. Teacher Notes 59
60 Clouds Water Vapor Lab Experiment We will create droplets from water vapor. Materials: tin can water (cold and warm) ice bowl 60
61 Clouds Water Vapor Lab Fill a tin can with water and ice. Set the can over a bowl of warm water. What do you see and feel? Water vapor in the air will form drops on the cold can. The drops will run down the side of the can. Teacher Notes 61
62 Clouds Some clouds are thin and some are thick. Because sunlight easily passes through thin clouds, they appear bright or white. The parts where light passes through will appear white, but the thick parts where light doesn't pass through will look gray or black. 62
63 Clouds Lab We will try to create our own cloud. jar cubes Materials: ice warm water paper black resealable plastic bag match 63
64 Clouds Lab 1. Tape the black paper to back of the jar. Fill the jar 1/4 full with warm water. 2. Fill the plastic bag with ice cubes and seal it shut. The bag should be able to cover top of jar. Make sure it does not fall into jar. 3. Teacher should light one match and then blow it out. Wait one or two seconds before you throw it into jar. 4. Quickly put the bag of ice on top of the jar. Watch as a cloud forms. 64
65 Clouds Lab Teacher Notes What happened? Some of the warm water rises and evaporates. The water vapor condenses when it hits the air cooled by the ice. 65
66 13 Some clouds appear white because sunlight can pass through them. Yes No Answer 66
67 14 In the sky little drops of water form around bits of dust. When enough droplets come together we have. Answer A lightening B a cloud C snow 67
68 Rain Return to Table of Contents 68
69 Rain What do you like to do on a rainy day? Do you stay inside or do you like to go outside and splash in the puddles? What is rain? Teacher Notes 69
70 Rain What is rain? Rain is made of drops of water. These drops are called raindrops. Raindrops can be big or small. Clouds are filled with water. Rain clouds have more water than they can hold. When a cloud has too much water it rains. 70
71 Rain When raindrops are small the rain is light. We call this a drizzle. When raindrops are larger the rain is heavy. We call this a shower. Meteorologists measure the amount of rain that falls during a storm. You can measure the rain by placing a container outside. This is called a rain gauge. 71
72 Rain Gauge Lab Rain often falls in small amounts. It is easiest to collect rain in a small container. Meteorologists measure and report rainfall in inches(or centimeters). They read the level of water markings on a rain gauge. Materials: empty bottle masking tape coffee can 1.Mark a piece of masking tape with 1/2" or 1 cm intervals. 2.Place the masking tape on the empty bottle. 3.When it rains, place the coffee can outside to collect the rain water. 4.After the rain stops, pour the rain water from the coffee can into the small jar and read the measurement. 72
73 Rain Gauge Lab Teacher Notes When it rains, place the coffee can outside. After the rain stops, pour the rain water into the jar and read the measurement. 73
74 Snow Return to Table of Contents 74
75 Snow When the air is cold enough, water vapor in the air freezes before it can form drops of water. The particles get heavy and start falling. If the air on the way down is warm, the snow melts and falls as rain. If the air is cold the snow doesn't melt as it falls. 75
76 We can use our rain gauge to measure snow. Snow Lab Snow 1. Let the can fill with snow. Then bring it inside and let the snow melt. 2. Check the can a little later. See how little water it takes to make all that snow. 3. Pour the water into rain gauge to measure. Teacher Notes 76
77 15 Rain is made of drops of water. When a cloud has water it rains. A too little B no Answer C too much 77
78 16 Which instrument measures the amount of rain that falls during a storm? Answer A B C 78
79 17 Light rain is a. A shower B drizzle Answer 79
80 Recording Daily Weather Return to Table of Contents 80
81 Recording Weather Season One This unit is set up with identical sections so the students can observe and record weather; and then compare/contrast two different seasons. Before you begin this section you may want to create a weather journal using document activity sheets and cover sheet #17. The children will record the data collected in their journals as you record on the slides. At the end of unit the students can use their journals to look for patterns and compare/contrast data between the two seasons. 81
82 Recording Weather You are going to establish a regular pattern of observing weather. You will see how the weather is the same or different each day. You will begin a daily routine of reporting outdoor conditions. You will then gather as a group to assemble the weather information gathered by individual members. As a group you will perceive changes occurring in a familiar location. You will look for patterns in the weather. 82
83 Recording Weather Meteorologists study the weather. Meteorologists study the following... Weather Condition Instrument Sky Conditions Cloud Cover Temperature Wind Direction Wind Speed Precipitation Method or Look up! Look up! Thermometer Weather vane Anemometer Rain Gauge 83
84 Weather Exploratory Lab Take the children outside for a "weather hunt". Tell the children about specific places to look to discover the state of the weather. (Look at the trees to find signs of the wind; look for clouds in the sky; where is the sun?; are the clouds moving?) Stand in a sunny spot. How does it feel? Stand in a sheltered spot. How does it feel? Other clues; Can you find ice or a puddle? Is anyone's hair moving? Does it feel different if the sun goes behind a cloud? Toss leaves into the air. What happens? Blow bubbles. Do they go up or down or otherwise. Look for shadows. What are people wearing? Teacher Notes 84
85 Weather Exploratory Lab Regroup inside lead discussion of what they saw and felt. Weather Observations Teacher Notes Students will draw "Weather Report" of something observed outside. 85
86 Recording Sky Observations Return to Table of Contents 86
87 Recording Weather Sky Observations Lab The first thing we will do is use our observation skills to record what we see in the sky. The first week we will compare morning sky observations with afternoon sky observations. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM Teacher Notes PM Weather Symbols sunny partly sunny cloudy rainy snowy 87
88 Recording Weather Sky Observations Lab We will now record our observations for a month. Record morning or afternoon observations. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Teacher Notes Week 5 Weather Symbols sunny partly sunny cloudy rainy snowy 88
89 Recording Wind Speed and Wind Direction Return to Table of Contents 89
90 Recording Weather Wind Speed Lab Use anemometer to measure daily wind speed. You can also use weather vane to determine wind direction. Wind Conditions 1. Wind or No Wind 2. Speed # of turns Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Teacher Notes 3. Direction N S E W Wind Symbols Windy No Wind 90
91 Recording Daily Temperature Return to Table of Contents 91
92 Recording Weather Daily Temperature Now that we have an established routine with sky and wind observations we will add daily temperature to our routine. Remember temperature is recorded by meteorologists so we know how hot or cold it is outside. hot or cold 92
93 Recording Weather Daily Temperature Lab Place a thermometer outside in the morning and then the afternoon. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM Temperature Indicator Hot Warm Cool Cold Frigid Teacher Notes 93
94 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Recording Weather Daily Temperature Lab Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Teacher Notes Hot Warm Cool Cold Frigid Temperature Indicator 94
95 Recording Precipitation Return to Table of Contents 95
96 Recording Weather Precipitation We will now add recording the amount of daily precipitation to our daily routine. It may not rain or snow everyday but a meteorologist would record his or her observation everyday. 96
97 Recording Weather Precipitation Lab Each morning, place rain can outside. Each afternoon, bring can inside and pour any contents into rain gauge. Record daily observations on chart. Morning Rain/Snow inches or cm Afternoon Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Teacher Notes 97
98 Analyzing Data Return to Table of Contents 98
99 Weather Journal Analyzing Data Weather Journal At the end of each week look over your data. Do you see any patterns in sky observations? Do you see any patterns in wind speed or wind direction? Teacher Notes Do you see any patterns for precipitation? 99
100 18 Were there more sunny days in the morning(am) or afternoon(pm)? Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM Answer A same B morning C afternoon 100
101 19 On what day was there no wind? Wind Conditions Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1. Wind or No Wind 2. Speed # of turns Answer 3. Direction N S E W E E S S A Monday B Tuesday C Friday 101
102 20 On what day was the wind blowing fastest? Wind Conditions 1. Wind or No Wind Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2. Speed # of turns Answer 3. Direction N S E W E E S S A Tuesday B Wednesday C Thursday 102
103 21 For this week was it cooler in the morning(am) or afternoon(pm)? AM Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday PM Answer A morning (AM) B afternoon (PM) 103
104 22 Which day had the least amount of rain? Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Rain/Snow inches or cm 4 cm 2 cm 4 cm 3 cm 5 cm Answer A Monday B Tuesday C Friday 104
105 Seasons Return to Table of Contents 105
106 Seasons Some places don't get the same amount of heat from the sun all the time. In the hot season they get a lot of heat. They get much less heat in the cold season. Summer During summer months there is a lot of heat from the sun. There can be very hot weather. Autumn During autumn months there is less heat than in summer but more than in the winter. So the weather is usually neither very hot nor very cold. Winter During winter there is only a little heat from the sun, so the weather is cold. Spring During spring months there is more heat from the sun than in winter, but it is not as hot as summer. The weather is pleasant and warm. 106
107 Seasons Use the next two slides to identify characteristics of the four seasons. Lead discussion as to why the pictures should be placed in winter, summer, spring, or fall. 107
108 108
109 109
110 Seasons What season is it? click During this season there is a lot of heat from the sun. There can be very hot weather. autumn click summer During this season there is less heat than in summer but more than in the winter. So the weather is usually neither very hot nor very cold. The leaves on trees change color. Teacher Notes 110
111 Seasons What season is it? During this season there is more heat from the sun than in winter, but it is not as hot as summer. The weather is pleasant and warm. The flowers start to grow. click spring Teacher Notes click winter During this season there is only a little heat from the sun, so the weather is cold. We might see snow. 111
112 23 During the season of summer the temperature is. A cold B cool Answer C hot 112
113 24 During winter there is little heat from the sun so the weather is. A warm B cold Answer C hot 113
114 25 Think about the weather in spring. Which would be an activity you could enjoy in the spring? A B jump rope swim in the ocean Answer C build a snowman 114
115 Recording Weather Season Two Return to Table of Contents 115
116 Recording Weather Season Two This unit is set up with identical recording weather sections as season one. The students can observe and record weather; and then compare/contrast two different seasons. It would be best to choose a month were the weather observations would be different from season one. Let each student record results in a weather journal, the same as season one. When you have completed observations for another month, analyze data for the month. Then compare and contrast the data collected for the two different seasons. 116
117 Recording Weather Sky Observations Lab The first thing we will do is use our observation skills to record what we see in the sky. The first week we will compare morning sky observations with afternoon sky observations. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM Weather Symbols sunny partly sunny cloudy rainy snowy 117
118 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Recording Weather Sky Observations Lab We will now record our observations for a month. Record morning or afternoon observations. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Weather Symbols sunny partly sunny cloudy rainy snowy 118
119 Recording Weather Wind Speed Lab Use anemometer to measure daily wind speed. You can also use weather vane to determine wind direction. Wind Conditions 1. Wind or No Wind Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2. Speed # of turns 3. Direction N S E W Wind Symbols Windy No Wind 119
120 Recording Weather Daily Temperature Lab Place thermometer outside in the morning and then again in the afternoon. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM Hot Warm Cool Cold Frigid Temperature Indicator Teacher Notes 120
121 Week 1 Week 2 Recording Weather Daily Temperature Lab Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Hot Warm Cool Cold Frigid Temperature Indicator 121
122 Recording Weather Precipitation Lab Each morning, place rain can outside. Each afternoon, bring can inside and pour any contents into rain gauge. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Rain/Snow inches cm 122
123 Comparing Seasons Weather Journal Use the data you have collected as meteorologists and compare and contrast data for the two seasons. In which season did you observe more sunny days? In which season did you observe less cloudy days? In which season was the wind speed faster? Did the wind blow in different directions? Teacher Notes In which season was there more precipitation? Was it rain or snow? 123
124 26 Were there more snowy days in the morning(am) or afternoon(pm)? AM Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday PM Answer A same B morning C afternoon 124
125 27 On what day was there no wind? Wind Conditions Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1. Wind or No Wind 2. Speed # of turns Answer 3. Direction N S E W E S E S A Monday B Tuesday C Friday 125
126 28 On what day was the wind speed 20? Wind Conditions 1. Wind or No Wind Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 2. Speed # of turns 3. Direction N S E W E E S S Answer A Tuesday B Wednesday C Thursday 126
127 29 For this week was it warmer in the morning(am) or afternoon(pm)? AM Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday PM Answer A morning (AM) B afternoon (PM) 127
128 30 Which day had the most rain? Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Rain/Snow inches or cm 4 cm 2 cm 4 cm 3 cm 5 cm Answer A Monday B Tuesday C Friday 128
129 Congratulations! You are now a meteorologist. Use your skills to observe the weather and recognize weather patterns. 129
ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION. A Collection of Learning Experiences WEATHER Weather Student Activity Book
 ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION A Collection of Learning Experiences WEATHER Weather Student Activity Book Name This learning experience activity book is yours to keep.
ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION A Collection of Learning Experiences WEATHER Weather Student Activity Book Name This learning experience activity book is yours to keep.
Earth Science: Second Quarter Grading Rubric Kindergarten
 Earth Science: Second Quarter Grading Rubric Kindergarten of their senses Observation skills are used to note characteristics of our environment on a daily basis. The weather may be sunny one day and cloudy
Earth Science: Second Quarter Grading Rubric Kindergarten of their senses Observation skills are used to note characteristics of our environment on a daily basis. The weather may be sunny one day and cloudy
The grade 5 English science unit, Weather, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 Among the diverse meteorological elements, this area focuses on humidity, dew, fog, clouds, rain, snow, wind and atmospheric pressure. Weather influences not only our daily outdoor activities, but also
Among the diverse meteorological elements, this area focuses on humidity, dew, fog, clouds, rain, snow, wind and atmospheric pressure. Weather influences not only our daily outdoor activities, but also
weather, cloudy, rainy, sunny, snowy, windy
 Halifax County Schools 1st Six Weeks Goal 2 Weather The learner will make observations and build an understanding of weather concepts. 2.01 Observe and report daily weather changes throughout the year.
Halifax County Schools 1st Six Weeks Goal 2 Weather The learner will make observations and build an understanding of weather concepts. 2.01 Observe and report daily weather changes throughout the year.
Weather Instruments WHAT IS WEATHER
 TOPIC TWO 1 WHAT IS WEATHER Weather is the combined short-term conditions found in the lower atmosphere. These conditions include precipitation, or rain and snow, as well as wind, pressure, storminess,
TOPIC TWO 1 WHAT IS WEATHER Weather is the combined short-term conditions found in the lower atmosphere. These conditions include precipitation, or rain and snow, as well as wind, pressure, storminess,
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
CHAPTER 16 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather?
Ebook Code: REAU4045. The Earth & Life Science Series. Weather. Science activities for 6 to 9 year olds
 Ebook Code: REAU4045 The Earth & Life Science Series Weather Science activities for 6 to 9 year olds Written by Judy Gabrovec. Ready-Ed Publications - 2005. Published by Ready-Ed Publications (2005) P.O.
Ebook Code: REAU4045 The Earth & Life Science Series Weather Science activities for 6 to 9 year olds Written by Judy Gabrovec. Ready-Ed Publications - 2005. Published by Ready-Ed Publications (2005) P.O.
4 Forecasting Weather
 CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
CHAPTER 2 4 Forecasting Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What instruments are used to forecast weather? How
WHAT IS WEATHER? many kinds of weather, such as hot, cold, sunny, rainy, snowy, and windy. Storms and winds can change the weather in a hurry.
 WHAT IS WEATHER? Weather tells us what the outside air is like. There are Why did the woman go outside with her purse open? She thought there was going to be some change in the weather! many kinds of weather,
WHAT IS WEATHER? Weather tells us what the outside air is like. There are Why did the woman go outside with her purse open? She thought there was going to be some change in the weather! many kinds of weather,
Climate versus Weather
 Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Climate versus Weather What is climate? Climate is the average weather usually taken over a 30-year time period for a particular region and time period. Climate is not the same as weather, but rather,
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts)
 Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Watching the Weather
 Watching the Weather Topic Observing the weather Key Question What is the weather like today? Focus Students will observe and record weather conditions over a long period of time. Guiding Documents NCTM
Watching the Weather Topic Observing the weather Key Question What is the weather like today? Focus Students will observe and record weather conditions over a long period of time. Guiding Documents NCTM
Introduction. Sunny Partly Cloudy Cloudy. Flurries Snow Ice. Showers Thunderstorms Rain. High Pressure Low Pressure FRONTS. Cold Warm Stationary
 Introduction Weather can change from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day, or season to season. Meteorologists are scientists who study Earth s atmosphere in order to predict these changes. Meteorologists
Introduction Weather can change from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day, or season to season. Meteorologists are scientists who study Earth s atmosphere in order to predict these changes. Meteorologists
Three things necessary for weather are Heat, Air, Moisture (HAM) Weather takes place in the Troposphere (The lower part of the atmosphere).
 Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
Grade 5 SCIENCE WEATHER WATCH Name: STUDY NOTES Weather - The condition of the atmosphere with respect to heat/cold, wetness/dryness, clearness/ cloudiness for a period of time. Weather changes over time
The sun and water cycle
 reflect The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time
reflect The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time
Air Is There. What can air do? balloon cotton ball feather flex straw foam ball piece of paper plastic bag
 What can air do? Air Is There balloon cotton ball feather flex straw foam ball piece of paper plastic bag Investigation 1: Exploring Air No. 1 Notebook Master Parachutes How does a parachute use air? Investigation
What can air do? Air Is There balloon cotton ball feather flex straw foam ball piece of paper plastic bag Investigation 1: Exploring Air No. 1 Notebook Master Parachutes How does a parachute use air? Investigation
primary PR48 teach with space NOSE UP HIGH IN THE SKY Observing and measuring weather conditions teacher guide & student worksheets
 primary PR48 teach with space NOSE UP HIGH IN THE SKY Observing and measuring weather conditions teacher guide & student worksheets Fast facts page 3 Summary of activities page 4 Introduction page 5 Activity
primary PR48 teach with space NOSE UP HIGH IN THE SKY Observing and measuring weather conditions teacher guide & student worksheets Fast facts page 3 Summary of activities page 4 Introduction page 5 Activity
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Objectives Understand what causes weather. Explore weather factors related to air. Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Explore weather
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Objectives Understand what causes weather. Explore weather factors related to air. Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Explore weather
Thank you for choosing AIMS!
 Thank you for choosing AIMS! Please use this free activity in your classroom, and watch your students begin to experience the "Aha!" moments of real learning. We like hearing from you. Like us and share
Thank you for choosing AIMS! Please use this free activity in your classroom, and watch your students begin to experience the "Aha!" moments of real learning. We like hearing from you. Like us and share
The Sun and Water Cycle
 The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time in the
The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time in the
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
SCIENCE FUN. Copyright by The Adventures of Scuba Jack, Inc., All rights reserved.
 SCIENCE FUN AIR Air is all around you. It is made up of many different gasses. The most important gas in air is oxygen. Animals and people need oxygen to live. When you breathe, you are breathing in air,
SCIENCE FUN AIR Air is all around you. It is made up of many different gasses. The most important gas in air is oxygen. Animals and people need oxygen to live. When you breathe, you are breathing in air,
Post-Show. Weather. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Weather After the Show We recently presented a Weather show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The following
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Weather After the Show We recently presented a Weather show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The following
Keep Your Own Weather Journal Every meteorologist needs to keep a good weather journal. Remember, good observations make good forecasts.
 Meteorologists study the weather by recording and analyzing data. You can become an amateur meteorologist by building your own weather station and keeping a record of your measurements. After a while,
Meteorologists study the weather by recording and analyzing data. You can become an amateur meteorologist by building your own weather station and keeping a record of your measurements. After a while,
Weather. science centers. created by: The Curriculum Corner.
 Weather science centers created by: The Curriculum Corner Weather Centers 1. Weather Flap Book 2. Future Meteorologist / Make a Forecast 3. Ready for the Weather 4. Make a Match 5. What s the Temperature?
Weather science centers created by: The Curriculum Corner Weather Centers 1. Weather Flap Book 2. Future Meteorologist / Make a Forecast 3. Ready for the Weather 4. Make a Match 5. What s the Temperature?
Rainy Days. Upper Primary. Weather
 Rainy Days Weather Rainy Days Teacher Notes Key Concepts Earth s weather changes from day to day and from season to season. National Science Education Content Standards (1996) Unifying Concepts and Processes
Rainy Days Weather Rainy Days Teacher Notes Key Concepts Earth s weather changes from day to day and from season to season. National Science Education Content Standards (1996) Unifying Concepts and Processes
Bridge Grade Two Winter 1/09 1. GRADE TWO WINTER NATURE WALK Using Thermometers
 Bridge Grade Two Winter 1/09 1 GRADE TWO WINTER NATURE WALK Using Thermometers OBJECTIVES: Use thermometers to measure temperature. Compare temperature of air and water inside and outside the school. Relate
Bridge Grade Two Winter 1/09 1 GRADE TWO WINTER NATURE WALK Using Thermometers OBJECTIVES: Use thermometers to measure temperature. Compare temperature of air and water inside and outside the school. Relate
Evaporation - Water evaporates (changes from a liquid to a gas) into water vapor due to heat from the Sun.
 Erin Kathryn 2016 Weather is the conditions of Earth s atmosphere at a certain time and place. For example, sunshine, rain, hurricanes, and storms are all examples of weather. Weather is different at different
Erin Kathryn 2016 Weather is the conditions of Earth s atmosphere at a certain time and place. For example, sunshine, rain, hurricanes, and storms are all examples of weather. Weather is different at different
How Are Weather Data Collected?
 1.2 Investigate 1.2 Build How Are Weather Data Collected? The details of the weather in the different regions of the United States show the wide range of events that can take place in the atmosphere. Meteorologists
1.2 Investigate 1.2 Build How Are Weather Data Collected? The details of the weather in the different regions of the United States show the wide range of events that can take place in the atmosphere. Meteorologists
Science (K) 2 nd Lesson. Aim: To learn about the four seasons of the year and the types of weather in each.
 Science (K) 2 nd Lesson Aim: To learn about the four seasons of the year and the types of weather in each. Objectives: Terms: seasons, spring, summer, fall, autumn and winter, deciduous, evergreen, weather,
Science (K) 2 nd Lesson Aim: To learn about the four seasons of the year and the types of weather in each. Objectives: Terms: seasons, spring, summer, fall, autumn and winter, deciduous, evergreen, weather,
Weather and climate. reflect. what do you think? look out!
 reflect You re going on vacation in a week and you have to start thinking about what clothes you re going to pack for your trip. You ve read the weather reports for your vacation spot, but you know that
reflect You re going on vacation in a week and you have to start thinking about what clothes you re going to pack for your trip. You ve read the weather reports for your vacation spot, but you know that
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Weather Maps. The Sun s radiation produces weather on Earth.
 Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Sunny days give way to rainy days. Storms appear, then fade away. Howling winds become gentle breezes. At one o clock on an autumn afternoon, an outdoor thermometer reads 20 C. An hour later, the temperature
Science and Technology sample unit: What Should I Wear? Booragul Public School
 Science and Technology sample unit: What Should I Wear? Early Stage 1 Term 3 Duration: 10 weeks Booragul Public School Unit context Students investigate ways daily and seasonal changes in our environment
Science and Technology sample unit: What Should I Wear? Early Stage 1 Term 3 Duration: 10 weeks Booragul Public School Unit context Students investigate ways daily and seasonal changes in our environment
learning outcomes To: know what air pressure is know that you can use a barometer to measure air pressure end product a barometer
 Q Strong air Weather 46 time 40 minutes (day 1), 5 minutes (day 2) & 15 minutes (day 3) learning outcomes To: know what air pressure is know that you can use a barometer to measure air pressure end product
Q Strong air Weather 46 time 40 minutes (day 1), 5 minutes (day 2) & 15 minutes (day 3) learning outcomes To: know what air pressure is know that you can use a barometer to measure air pressure end product
The Sun and Water Cycle
 Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
WEATHER AND CLIMATE (K.ES.NGSS)
 TM WEATHER AND CLIMATE (K.ES.NGSS) UNIT AT A GLANCE ACTIVITY 1 - Weather Watchers: Making Observations QUESTIONS: What do we need to know about the weather, and what do we need to find out? Preparation:
TM WEATHER AND CLIMATE (K.ES.NGSS) UNIT AT A GLANCE ACTIVITY 1 - Weather Watchers: Making Observations QUESTIONS: What do we need to know about the weather, and what do we need to find out? Preparation:
Weather Watching. DELTA SCIENCE READER Overview Before Reading Guide the Reading After Reading WEATHER WATCHING OVERVIEW
 Weather Watching T ABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment and
Weather Watching T ABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment and
1st Grade. Slide 1 / 90. Slide 2 / 90. Slide 3 / 90. The Sun, Moon, Earth and Stars. Table of Contents The Sun.
 Slide 1 / 90 Slide 2 / 90 1st Grade The Sun, Moon, Earth and Stars 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 90 Click on the topic to go to that section The Sun The Moon The Stars The Seasons
Slide 1 / 90 Slide 2 / 90 1st Grade The Sun, Moon, Earth and Stars 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 90 Click on the topic to go to that section The Sun The Moon The Stars The Seasons
Science in the Schoolyard Guide: FOSS Air and Weather
 Air and Weather Air and Weather > Investigation 1: Exploring Air > Part 3: Parachutes, page 17 Parachutes Repeat Part 3, taking students outside to fly the parachutes. Students will compare the flights
Air and Weather Air and Weather > Investigation 1: Exploring Air > Part 3: Parachutes, page 17 Parachutes Repeat Part 3, taking students outside to fly the parachutes. Students will compare the flights
Where does the rain go?
 Where does the go? Weather Q 26 time 45 minutes (day 1) & 5 minutes (days 2 to 4) & 20 minutes (day 5) learning outcomes To: know different forms of precipitation:, hail, and snow observe changes in the
Where does the go? Weather Q 26 time 45 minutes (day 1) & 5 minutes (days 2 to 4) & 20 minutes (day 5) learning outcomes To: know different forms of precipitation:, hail, and snow observe changes in the
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17. Weather and Climate
 Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Earth Science Chapter 16 and 17 Weather and Climate Prediction Old way Groundhog Color of the sky Modern way satellites instruments computers Goal Weather Factors Studied by meteorologists Several factors
Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12)
 Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Name Class Period Atmosphere, Weather & Climate Review for Unit Assessment (Can be taken on Study Island Due Mon., 11/26/12) 1. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes
Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6)
 Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6) Temperature is the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere. Air pressure is due to the weight of the air and is determined by several factors including
Earth/Space Systems and Cycles (SOL 4.6) Temperature is the measure of the amount of heat energy in the atmosphere. Air pressure is due to the weight of the air and is determined by several factors including
Weather and Climate. An Introduction
 Weather and Climate An Introduction Basic Plant Anatomy Leaves Absorbs sunlight to produce glucose for food Roots Supports the plant, absorbs water & minerals Flower Attracting pollinators to help with
Weather and Climate An Introduction Basic Plant Anatomy Leaves Absorbs sunlight to produce glucose for food Roots Supports the plant, absorbs water & minerals Flower Attracting pollinators to help with
Code Proposed Standards Code Current Standards ESS1A The Universe and Its Stars Describe the presence of the Sun, Moon, and stars in the sky over time
 Kindergarten Earth Science Code Proposed Standards Code Current Standards ESS1A The Universe and Its Stars Describe the presence of the Sun, Moon, and stars in the sky over time 6.1.A.K.a. Observe and
Kindergarten Earth Science Code Proposed Standards Code Current Standards ESS1A The Universe and Its Stars Describe the presence of the Sun, Moon, and stars in the sky over time 6.1.A.K.a. Observe and
Condensation is the process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid. Clouds form by this process.
 CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
CHAPTER 16 1 Water in the Air SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is weather? How does water in the air affect
2 nd Grade Science Fair Ideas
 2 nd Grade Science Fair Ideas Science Rocks! Suggested Science Fair Project Ideas Reporting Category 1 Matter & Energy (2 nd Grade) Physical Properties: shape, relative mass, relative temperature, texture,
2 nd Grade Science Fair Ideas Science Rocks! Suggested Science Fair Project Ideas Reporting Category 1 Matter & Energy (2 nd Grade) Physical Properties: shape, relative mass, relative temperature, texture,
Weather An Introduction to Weather
 Non-fiction: Weather An Introduction To Weather Weather An Introduction to Weather Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday What does the word weather mean to you? Everyone knows how to describe the weather.
Non-fiction: Weather An Introduction To Weather Weather An Introduction to Weather Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday What does the word weather mean to you? Everyone knows how to describe the weather.
Sample. Illustrate and explain how items in the matter bag were classified. Label the property of each group.
 Classifying Matter Matter and Energy Name: Which matter bag was your favorite? Date: STUDENT JOURNAL Illustrate and explain how items in the matter bag were classified. Label the property of each group.
Classifying Matter Matter and Energy Name: Which matter bag was your favorite? Date: STUDENT JOURNAL Illustrate and explain how items in the matter bag were classified. Label the property of each group.
Guided Notes Weather. Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models
 Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
Guided Notes Weather Part 1: Weather Factors Temperature Humidity Air Pressure Winds Station Models. 1. What is weather? Weather: short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area at a specific time
also known as barometric pressure; weight of the air above the surface of the earth; measured by a barometer air pressure, high
 Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Weather Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Meaning/Definition air mass * large bodies of air that have the similar properties throughout such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure; causes most of the weather
Energy in the Earth's Systems - How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth's systems? KINDERGARTEN
 Teacher Trail Guides We have created a set of Trail Guides for use by you and your students. The first section consists of the trail guides with teacher notes; the second section s Trail Guides omit the
Teacher Trail Guides We have created a set of Trail Guides for use by you and your students. The first section consists of the trail guides with teacher notes; the second section s Trail Guides omit the
Weather Predictor. NC Standards 5.E.1.1, 5.P.1.2 Page 28. Grade 5 Earth Science. Activity Description & Estimated Class Time.
 Weather Predictor NC Standards 5.E.1.1, 5.P.1.2 Page 28 Grade 5 Earth Science Throughout the guide, teaching tips are in red. Activity Description & Estimated Class Time In this 50-minute activity, students
Weather Predictor NC Standards 5.E.1.1, 5.P.1.2 Page 28 Grade 5 Earth Science Throughout the guide, teaching tips are in red. Activity Description & Estimated Class Time In this 50-minute activity, students
2. What causes these weather changes?
 Weather Table of Contents Essential Questions... 1 Vocabulary... 2 Weather Symbols... 5 Bringing the Rain to Kapiti Plain... 7 Weather Instruments... 8 Weather Forecasting... 13 Essential Questions 1.
Weather Table of Contents Essential Questions... 1 Vocabulary... 2 Weather Symbols... 5 Bringing the Rain to Kapiti Plain... 7 Weather Instruments... 8 Weather Forecasting... 13 Essential Questions 1.
WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER
 NAME DATE PARTNERS WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER You are lying in the grass enjoying a few relaxing hours in the summer sun. You have your favorite cold drink and magazine close at hand. You close your eyes
NAME DATE PARTNERS WONDERING ABOUT WEATHER You are lying in the grass enjoying a few relaxing hours in the summer sun. You have your favorite cold drink and magazine close at hand. You close your eyes
What Is It Like Outside?
 What Is It Like Outside? Focus: Students will describe daily changes in temperature and weather. Specific Curriculum Outcomes Students will be expected to: 1.0 pose questions that lead to exploration and
What Is It Like Outside? Focus: Students will describe daily changes in temperature and weather. Specific Curriculum Outcomes Students will be expected to: 1.0 pose questions that lead to exploration and
Unit 1: Weather. Real-World Math 2
 Unit 1: Weather Key Concepts Discuss temperatures below zero. Draw a number line to review negative numbers. Do some whole-class practice with sample questions. For example, If it was degrees when you
Unit 1: Weather Key Concepts Discuss temperatures below zero. Draw a number line to review negative numbers. Do some whole-class practice with sample questions. For example, If it was degrees when you
Weather Systems Study Guide:
 Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Weather Systems Study Guide: 1. Draw a diagram of Earth s water cycle and label each part. 2. Explain how the water cycle works. 3. What happens in the troposphere and stratosphere? Atmosphere Level What
Created by Mrs. Susan Dennison
 Created by Mrs. Susan Dennison 2015-2015 The atmosphere is a layer of invisible gas (air) that surrounds the Earth. It wraps around the planet like a blanket. All weather happens in the lower atmosphere.
Created by Mrs. Susan Dennison 2015-2015 The atmosphere is a layer of invisible gas (air) that surrounds the Earth. It wraps around the planet like a blanket. All weather happens in the lower atmosphere.
GRADE ONE EARTH SCIENCE: EXPLORING THE SUN AND MOON
 GRADE ONE EARTH SCIENCE: EXPLORING THE SUN AND MOON Standard 1.E.3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the patterns of the Sun and the Moon and the Sun s effect on Earth. 1.E.3A. Conceptual
GRADE ONE EARTH SCIENCE: EXPLORING THE SUN AND MOON Standard 1.E.3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the patterns of the Sun and the Moon and the Sun s effect on Earth. 1.E.3A. Conceptual
Meteorology Study Guide
 Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
3 Weather and Climate
 CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
bark the tough outer covering of the stems and roots of trees, shrubs, and other woody plants (IG)
 FOSS Trees and Weather Module Glossary NGSS Edition 2018 adopt to take on something as if it is yours (IG) air a mixture of gases that we breathe (IG) bark the tough outer covering of the stems and roots
FOSS Trees and Weather Module Glossary NGSS Edition 2018 adopt to take on something as if it is yours (IG) air a mixture of gases that we breathe (IG) bark the tough outer covering of the stems and roots
5) Water vapor is water in the state. a. solid b. liquid c. *gas
 1 NAME DATE January 15, 2004_ GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water cycle ( evaporation, condensation, precipitation.). 1) The sketch above shows: a. a life cycle. b. *the
1 NAME DATE January 15, 2004_ GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water cycle ( evaporation, condensation, precipitation.). 1) The sketch above shows: a. a life cycle. b. *the
Making Bubbles. Sung to the tune of I ve Been Working on the Railroad
 Making Bubbles Sung to the tune of I ve Been Working on the Railroad The bubble wand is something solid, With one end that is round. The bubble wand is big and yellow. It feels smooth is what I found.
Making Bubbles Sung to the tune of I ve Been Working on the Railroad The bubble wand is something solid, With one end that is round. The bubble wand is big and yellow. It feels smooth is what I found.
Background: What is Weather?
 Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Weather Maps Background: What is Weather? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere. The interaction of three important factors result in weather systems: air temperature, air pressure, and the
Weather Watchers Part II: Mini-Meteorologists
 Weather Watchers Part II: Mini-Meteorologists Key Words: anemometer, barometer, climate, clouds, hail, meteorologist, precipitation, rain, rain gauge, sleet, snow, weather, wind vane Goals: Desired Outcomes
Weather Watchers Part II: Mini-Meteorologists Key Words: anemometer, barometer, climate, clouds, hail, meteorologist, precipitation, rain, rain gauge, sleet, snow, weather, wind vane Goals: Desired Outcomes
Weather Walks. Summary Students will learn about weather by taking walks in various types conditions: sunny, rainy, windy and snowy.
 Weather Walks Summary Students will learn about weather by taking walks in various types conditions: sunny, rainy, windy and snowy. Main Core Tie Science Kindergarten Standard 2 Objective 3 Additional
Weather Walks Summary Students will learn about weather by taking walks in various types conditions: sunny, rainy, windy and snowy. Main Core Tie Science Kindergarten Standard 2 Objective 3 Additional
Grade K, Unit C, Physical. this chapter students discover: - different kinds of objects - some properties of matter
 Pearson Scott Foresman CORRELATION TO CONNECTICUT SCIENCE FRAMEWORK Grade K Core Themes, Content Standards and Expected Performances (User Note: In addition to the student text there are Leveled Readers
Pearson Scott Foresman CORRELATION TO CONNECTICUT SCIENCE FRAMEWORK Grade K Core Themes, Content Standards and Expected Performances (User Note: In addition to the student text there are Leveled Readers
above the land to be warmer, causing convection currents because of the difference in air pressure.
 Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Name Date Period Earth Science Unit Test Review Sheet Directions: Use my web site and/or your lab book to help to answer the following questions. 1. What type of weather does a low pressure system bring?
Extending Learning Beyond the Classroom
 Extending Learning Beyond the Classroom School is out, but learning continues! GRADE 1 Clayton County Public Schools Department of Curriculum, Instruction, & Assessment DR. EBONY T. LEE Director of Curriculum,
Extending Learning Beyond the Classroom School is out, but learning continues! GRADE 1 Clayton County Public Schools Department of Curriculum, Instruction, & Assessment DR. EBONY T. LEE Director of Curriculum,
3 Day Weather Game Plan
 Weather 8.10A- Recognize that the Sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents. 8.10B- Identify how global patterns of atmospheric
Weather 8.10A- Recognize that the Sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents. 8.10B- Identify how global patterns of atmospheric
Science Grade 01 Unit 01 Exemplar Lesson 02: Observing and Recording Weather
 Unit: 01 Lesson: 02 Suggested Duration: 5 days Grade 01 Unit 01 Exemplar Lesson 02: Observing and Recording Weather This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
Unit: 01 Lesson: 02 Suggested Duration: 5 days Grade 01 Unit 01 Exemplar Lesson 02: Observing and Recording Weather This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit.
2nd Grade. Earth's Water. Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111. Slide 3 / 111. Slide 4 / 111. Slide 5 (Answer) / 111. Slide 5 / 111. Role of Water on Earth
 Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111 2nd Grade Role of Water on Earth 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 111 Slide 4 / 111 Table of Contents: The Role of Water on Earth Earth's Water The Use of Maps Click on the
Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111 2nd Grade Role of Water on Earth 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 111 Slide 4 / 111 Table of Contents: The Role of Water on Earth Earth's Water The Use of Maps Click on the
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Hurricanes form over warm ocean water.
 KEY CONCEPT Low-pressure systems can become storms. BEFORE, you learned Moving air masses cause changes in weather A low-pressure system brings stormy weather NOW, you will learn How hurricanes develop
KEY CONCEPT Low-pressure systems can become storms. BEFORE, you learned Moving air masses cause changes in weather A low-pressure system brings stormy weather NOW, you will learn How hurricanes develop
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Elementary Science Department TERM 4 GRADE 4. Revision. 1. Weather ( ) 1. Is too little precipitation.
 EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Elementary Science Department TERM 4 GRADE 4 A. Match using letters: Revision 1. Weather ( ) 1. Is too little precipitation. 2. Humidity ( ) 2. Is the condition of
EGYPTIAN AMERICAN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Elementary Science Department TERM 4 GRADE 4 A. Match using letters: Revision 1. Weather ( ) 1. Is too little precipitation. 2. Humidity ( ) 2. Is the condition of
ASSESSMENT CHART FOR INVESTIGATIONS 1 AND 2 STUDENT NAME
 ASSESSMENT CHART FOR INVESTIGATIONS 1 AND 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. STUDENT NAME Weather Measurements (TO)
ASSESSMENT CHART FOR INVESTIGATIONS 1 AND 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. STUDENT NAME Weather Measurements (TO)
Maham Masood Sadiq. Ahmed Waqas Zubairi. Supervisor: Dr. Muhammad Sabieh Anwar
 EXPERIMENTS ON WEATHER CHANGE Maham Masood Sadiq Ahmed Waqas Zubairi Supervisor: Dr. Muhammad Sabieh Anwar EXPERIMENT-1 (INTENSITY OF SUN RAYS) 1. Balloon 2. Black Marker 3. Torch 1. Blow up a balloon
EXPERIMENTS ON WEATHER CHANGE Maham Masood Sadiq Ahmed Waqas Zubairi Supervisor: Dr. Muhammad Sabieh Anwar EXPERIMENT-1 (INTENSITY OF SUN RAYS) 1. Balloon 2. Black Marker 3. Torch 1. Blow up a balloon
Weather. Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of the air. Air temperature is measured using a thermometer.
 Weather Weather Weather describes the conditions in Earth's atmosphere at a given place at a given time. Temperature, precipitation, humidity, and cloud formation are aspects of weather, and they can be
Weather Weather Weather describes the conditions in Earth's atmosphere at a given place at a given time. Temperature, precipitation, humidity, and cloud formation are aspects of weather, and they can be
My Journal By: Copyright 2015 A Dab of Glue Will Do
 My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: Science Notebook Contract This is my Science Notebook for the 20 school year: I promise to take care of my notebook. use one page at a time.
My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: Science Notebook Contract This is my Science Notebook for the 20 school year: I promise to take care of my notebook. use one page at a time.
Probabilistic Decision-Making and Weather Assessment
 5 Student Packet Probabilistic Decision-Making and Weather Assessment Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents
5 Student Packet Probabilistic Decision-Making and Weather Assessment Use contents of this packet as you feel appropriate. You are free to copy and use any of the material in this lesson plan. Packet Contents
Hurricanes. Where's the Really Bad Weather 1. What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide
 Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
WEATHER. rain. thunder. The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning.
 WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
WEATHER rain thunder The explosive sound of air as it is heated by lightning. rainbow lightning hurricane They are intense storms with swirling winds up to 150 miles per hour. tornado cold front warm front
Weather and Seasons. Look out the window and think about the weather. What is it like? Circle all the words that describe the weather today.
 Weather and Seasons Lesson 1 Weather Look out the window and think about the weather. What is it like? Circle all the words that describe the weather today. 1. sunny cold rainy hot snowy windy warm cloudy
Weather and Seasons Lesson 1 Weather Look out the window and think about the weather. What is it like? Circle all the words that describe the weather today. 1. sunny cold rainy hot snowy windy warm cloudy
2 nd Grading Cycle Science and Technology How do engineers solve problems? What is the Design Process? TEKS 2D, 3A, 1C, 2B, 2E,
 SISD Year At A Glance Curriculum Calendar- Kindergarten 1 st Grading Cycle Doing Science How do we use our senses? How do we use science skills? How do we use science tools? 1A, 2C, 2D, 2E, 3C,4A, 4B,
SISD Year At A Glance Curriculum Calendar- Kindergarten 1 st Grading Cycle Doing Science How do we use our senses? How do we use science skills? How do we use science tools? 1A, 2C, 2D, 2E, 3C,4A, 4B,
latent heat/humidity
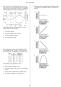 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables, the graph below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The graph shows variations in air temperature and relative
are moving around faster today than yesterday, today s temperature is higher.
 Taking Temperatures Summary: Students use a thermometer to investigate how shading, coloring, and other factors affect temperature. Objectives Students will be able to use a thermometer to measure and
Taking Temperatures Summary: Students use a thermometer to investigate how shading, coloring, and other factors affect temperature. Objectives Students will be able to use a thermometer to measure and
A Teaching Unit for Years 3 6 children
 A Teaching Unit for Years 3 6 children 1 SEREAD and ARGO: Concept Overview for Years 3-6 Teaching Programme This is the overview for the first part of the SEREAD programme link with ARGO. The overview
A Teaching Unit for Years 3 6 children 1 SEREAD and ARGO: Concept Overview for Years 3-6 Teaching Programme This is the overview for the first part of the SEREAD programme link with ARGO. The overview
Natural Disasters and Storms in Philadelphia. What is a storm? When cold, dry air meets warm, moist (wet) air, there is a storm.
 Natural Disasters and Storms in Philadelphia 1. What is a natural disaster? 2. Does Philadelphia have many natural disasters? o Nature (noun) everything in the world not made No. Philadelphia does not
Natural Disasters and Storms in Philadelphia 1. What is a natural disaster? 2. Does Philadelphia have many natural disasters? o Nature (noun) everything in the world not made No. Philadelphia does not
There are 100 boxes in the table below.
 Classwork #1 Earth s Water Name: There are 100 boxes in the table below. 1. Color 97 of them blue. This is how much of the water is in the ocean. 2. Color 2 and ½ of the boxes green. This is water in glaciers
Classwork #1 Earth s Water Name: There are 100 boxes in the table below. 1. Color 97 of them blue. This is how much of the water is in the ocean. 2. Color 2 and ½ of the boxes green. This is water in glaciers
Temperature Changes OBJECTIVES PREPARATION SCHEDULE MATERIALS. The students. For each student. For each team of two. For the class
 activity 3 Temperature Changes OBJECTIVES Students observe changes in air temperature and discover the role of the Sun in heating Earth. The students measure and record outdoor air temperature at three
activity 3 Temperature Changes OBJECTIVES Students observe changes in air temperature and discover the role of the Sun in heating Earth. The students measure and record outdoor air temperature at three
Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction
 Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction Key Concepts Adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling)
Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction Key Concepts Adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling)
Weather. A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket.
 Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
Weather I. The air around us A. atmosphere is a layer of gases that wrap around the Earth like a blanket. II. Weather Temperature Humidity Air pressure Wind 1. contains the air we breathe, protects us
What a Hurricane Needs to Develop
 Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
Weather Weather is the current atmospheric conditions, such as air temperature, wind speed, wind direction, cloud cover, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, etc. 8.10B: global patterns of atmospheric
K-ESS2-1. By: Natalie Rapson and Cassidy Smith
 K-ESS2-1 By: Natalie Rapson and Cassidy Smith Standard K-ESS2-1 Use and share observations of local weather conditions to describe patterns over time. Clarification Statement Examples of qualitative observations
K-ESS2-1 By: Natalie Rapson and Cassidy Smith Standard K-ESS2-1 Use and share observations of local weather conditions to describe patterns over time. Clarification Statement Examples of qualitative observations
Georgia Milestones 4TH GRADE PRE-TEST. Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA
 Georgia Milestones 4TH GRADE PRE-TEST Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA 1 1. What role do deer play in their environment? A. Consumer B. Decomposer
Georgia Milestones 4TH GRADE PRE-TEST Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA 1 1. What role do deer play in their environment? A. Consumer B. Decomposer
